Patents
Literature
14246 results about "Micrometer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A micrometer sometimes known as a micrometer screw gauge, is a device incorporating a calibrated screw widely used for accurate measurement of components in mechanical engineering and machining as well as most mechanical trades, along with other metrological instruments such as dial, vernier, and digital calipers. Micrometers are usually, but not always, in the form of calipers (opposing ends joined by a frame). The spindle is a very accurately machined screw and the object to be measured is placed between the spindle and the anvil. The spindle is moved by turning the ratchet knob or thimble until the object to be measured is lightly touched by both the spindle and the anvil.
Systems and methods of forming particles
InactiveUS20070054119A1Synthetic resin layered productsChemical/physical/physico-chemical microreactorsChemical reactionMicrometer
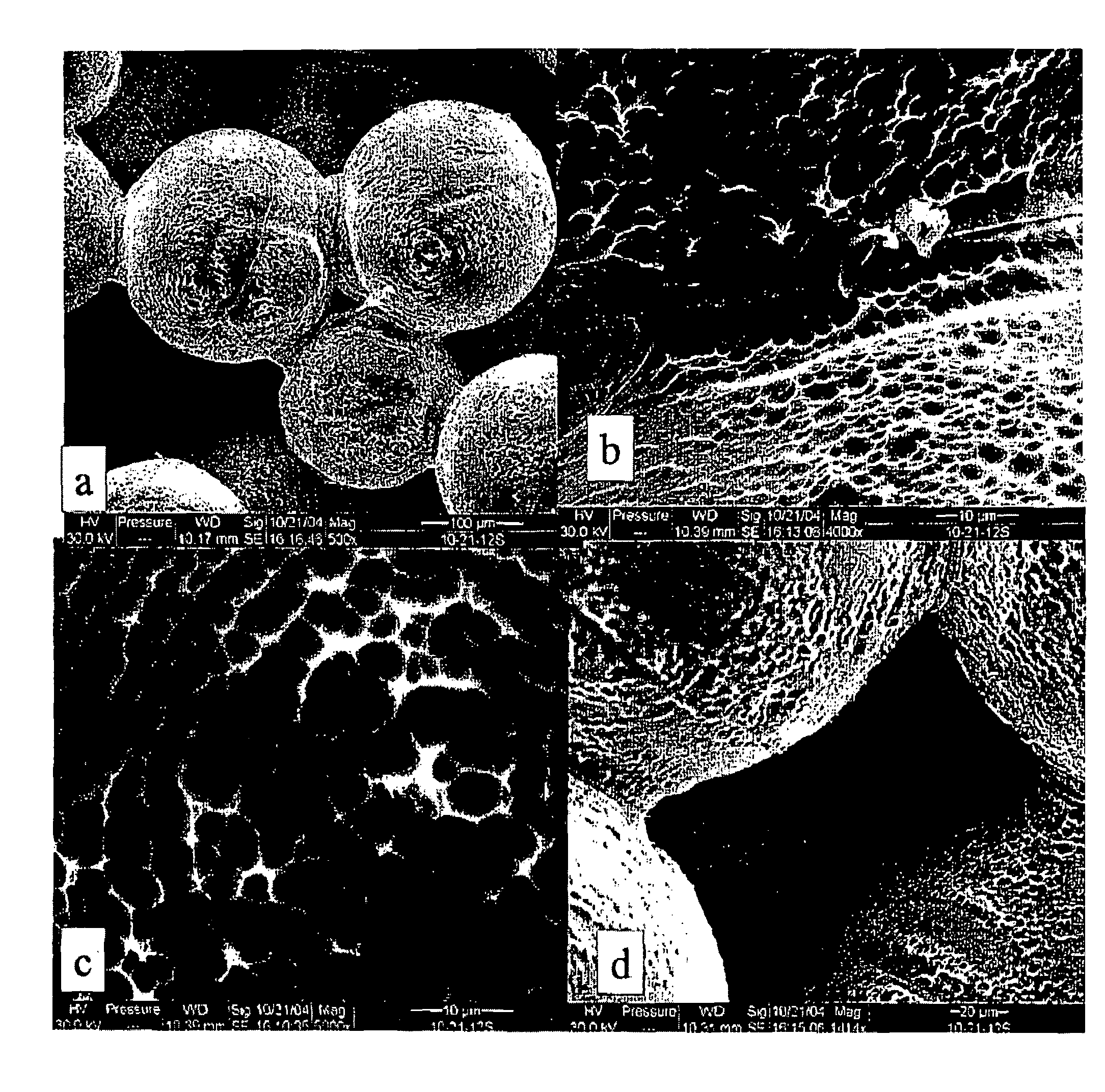
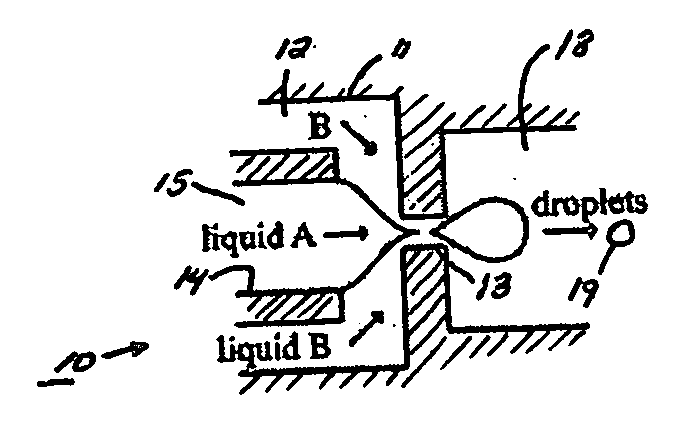
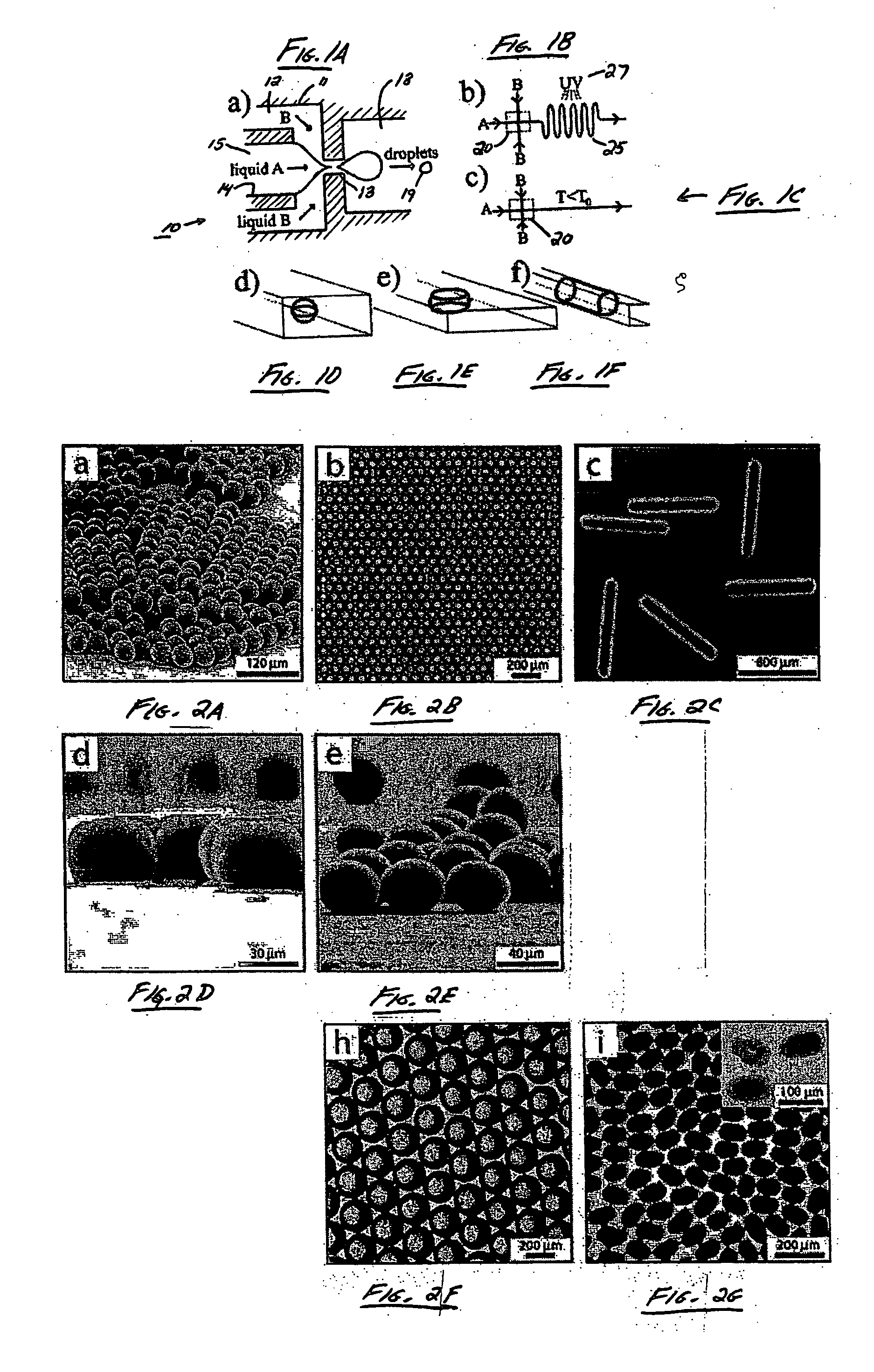
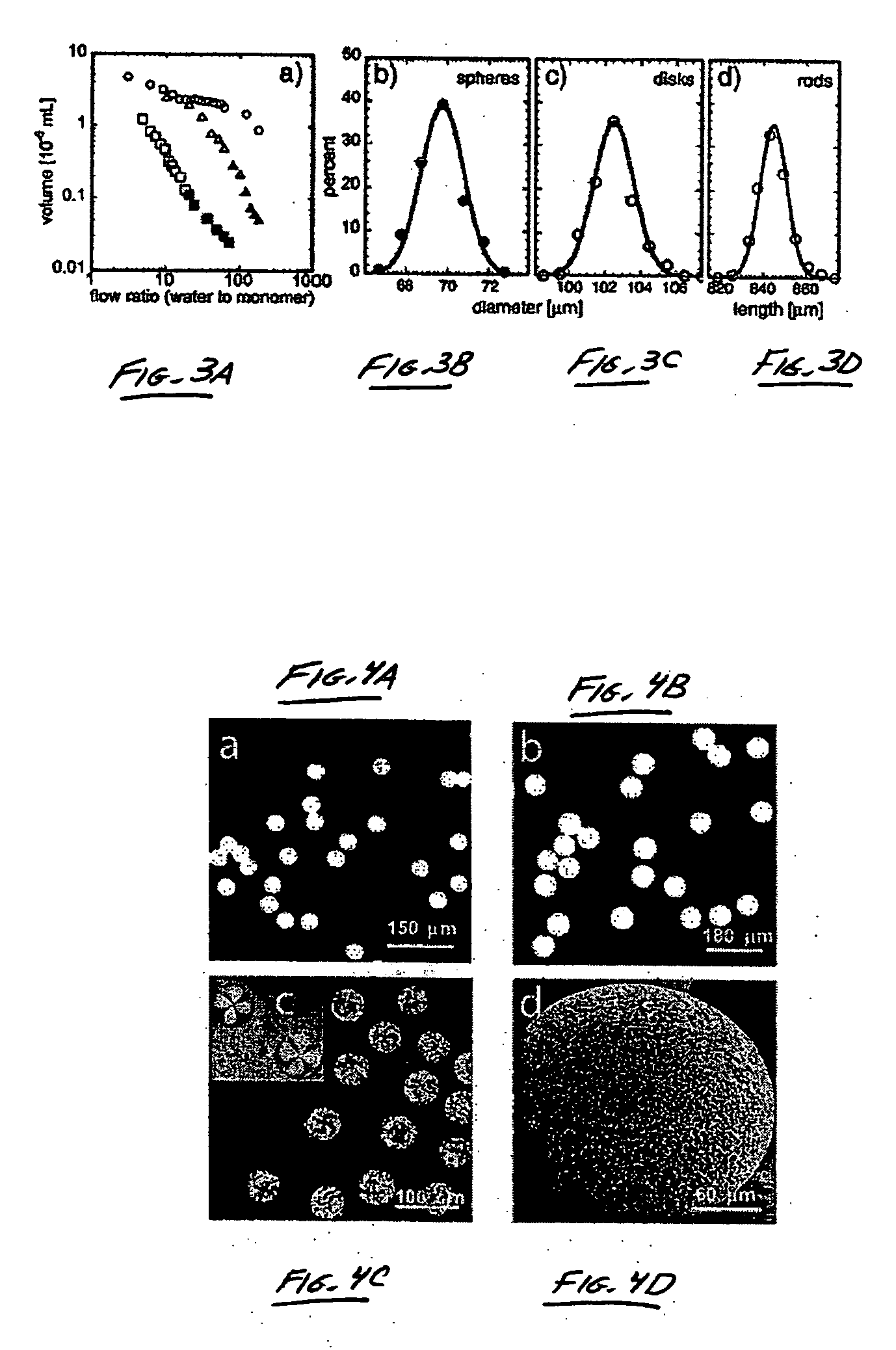
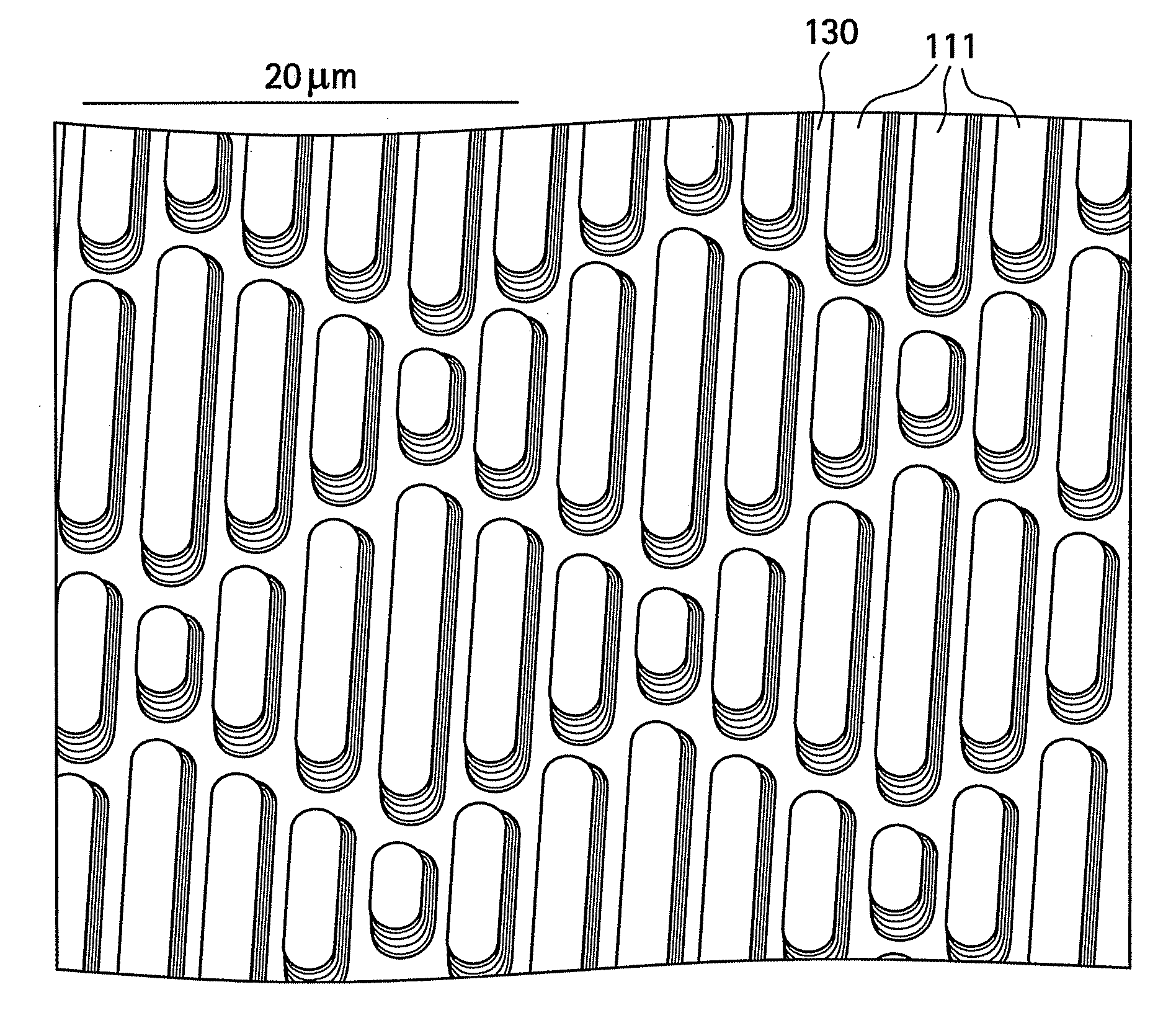
The present invention generally relates to systems and methods of forming particles and, in certain aspects, to systems and methods of forming particles that are substantially monodisperse. Microfluidic systems and techniques for forming such particles are provided, for instance, particles may be formed using gellation, solidification, and / or chemical reactions such as cross-linking, polymerization, and / or interfacial polymerization reactions. In one aspect, the present invention is directed to a plurality of particles having an average dimension of less than about 500 micrometers and a distribution of dimensions such that no more than about 5% of the particles have a dimension greater than about 10% of the average dimension, which can be made via microfluidic systems. In one set of embodiments, at least some of the particles may comprise a metal, and in certain embodiments, at least some of the particles may comprise a magnetizable material. In another set of embodiments, at least some of the particles may be porous. In some embodiments, the invention includes non-spherical particles. Non-spherical particles may be formed, for example, by urging a fluidic droplet into a channel having a smallest dimension that is smaller than the diameter of a perfect mathematical sphere having a volume of the droplet, and solidifying the droplet, and / or by exposing at least a portion of a plurality of particles to an agent able to remove at least a portion of the particles.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Surface topographies for non-toxic bioadhesion control
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Lighting device and lighting method
ActiveUS20080084685A1Improve efficiencyHigh color rendering indexDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsPhosphorMicrometer
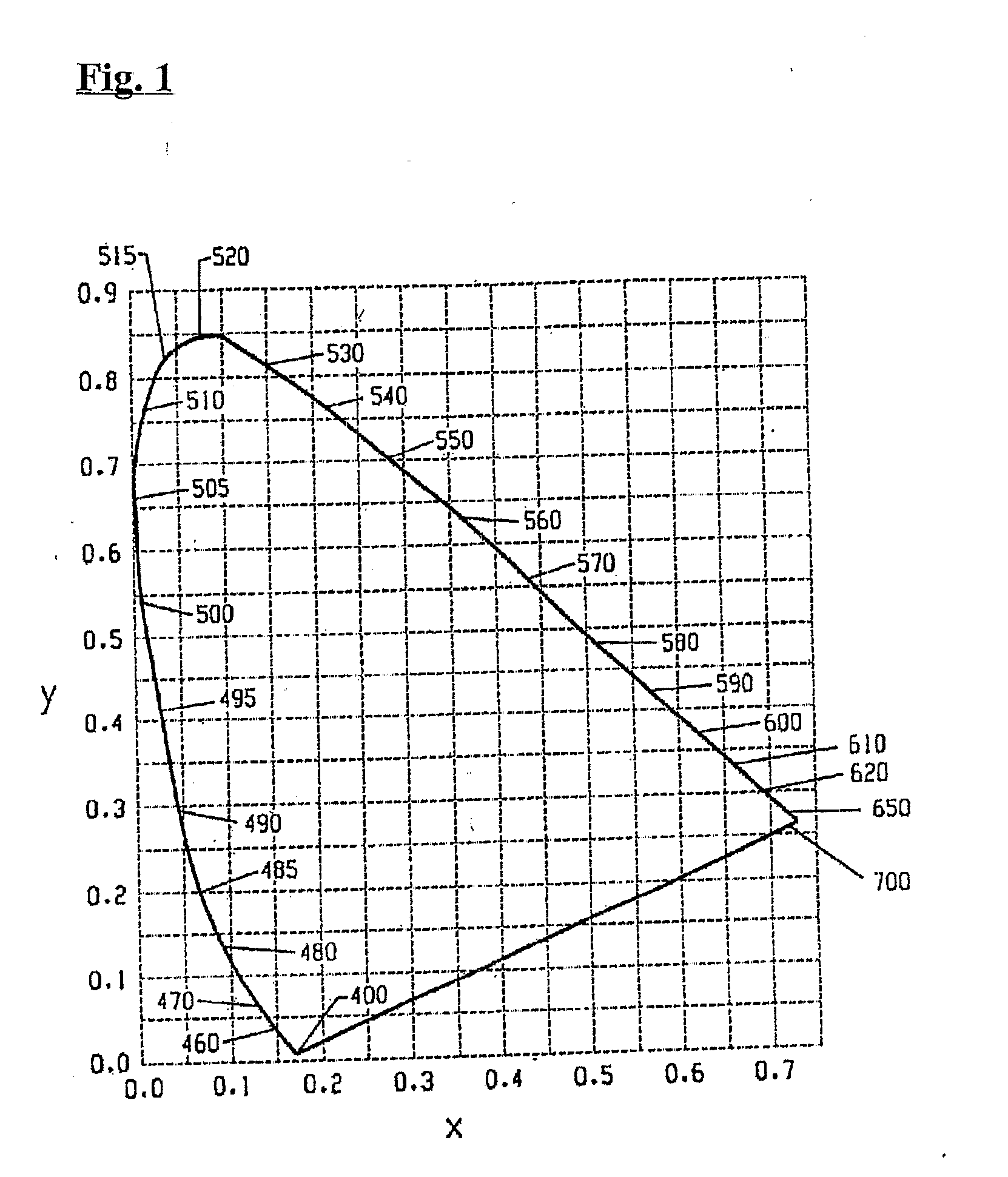
A lighting device comprising at least one solid state light emitter and at least one lumiphor. If each solid state light emitter is illuminated and each lumiphor is excited, a mixture of light emitted has x, y color coordinates within an area defined by the coordinates 0.32, 0.40; 0.36, 0,48; 0.43, 0.45; 0.42, 0.42; and 0.36, 0.38. The lumiphor(s) comprises phosphor particles, in the range of from 3 to 7 micrometers (or 5-15, 10-20, or 15-25 micrometers), or having a mean particle size of 5, 10, 15, 20 micrometers. Also, a lighting device comprising at least one emitter and at least one lumiphor in which the lumiphor comprises phosphor particles having sizes as mentioned above, where the lighting device has an efficacy of at least 60 (or 70, or 80) lumens per watt.
Owner:IDEAL IND LIGHTING LLC
Chemically synthesized and assembled electronics devices
InactiveUS6459095B1Simple and inexpensive implementationMaterial nanotechnologyElectronic circuit testingCrossbar switchChemical synthesis
A route to the fabrication of electronic devices is provided, in which the devices consist of two crossed wires sandwiching an electrically addressable molecular species. The approach is extremely simple and inexpensive to implement, and scales from wire dimensions of several micrometers down to nanometer-scale dimensions. The device of the present invention can be used to produce crossbar switch arrays, logic devices, memory devices, and communication and signal routing devices. The present invention enables construction of molecular electronic devices on a length scale than can range from micrometers to nanometers via a straightforward and inexpensive chemical assembly procedure. The device is either partially or completely chemically assembled, and the key to the scaling is that the location of the devices on the substrate are defined once the devices have been assembled, not prior to assembly.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD CO +1
Electret filter media
InactiveUS6119691AReduce filtration efficiencyImprove filtering effectSynthetic fibresBreathing filtersMicrometerFilter media
An electret filter media, and mask, that is made of a nonwoven web of thermoplastic microfibers. The thermoplastic microfibers are of substantially the same composition, are nonconductive, and have an effective fiber diameter less than about 15 micrometers. The nonwoven web also has sufficient unpolarized trapped charge to exhibit an initial filtration quality factor of at least 0.31 when measured under the DOP Penetration and Pressure Drop Test.
Owner:3M CO
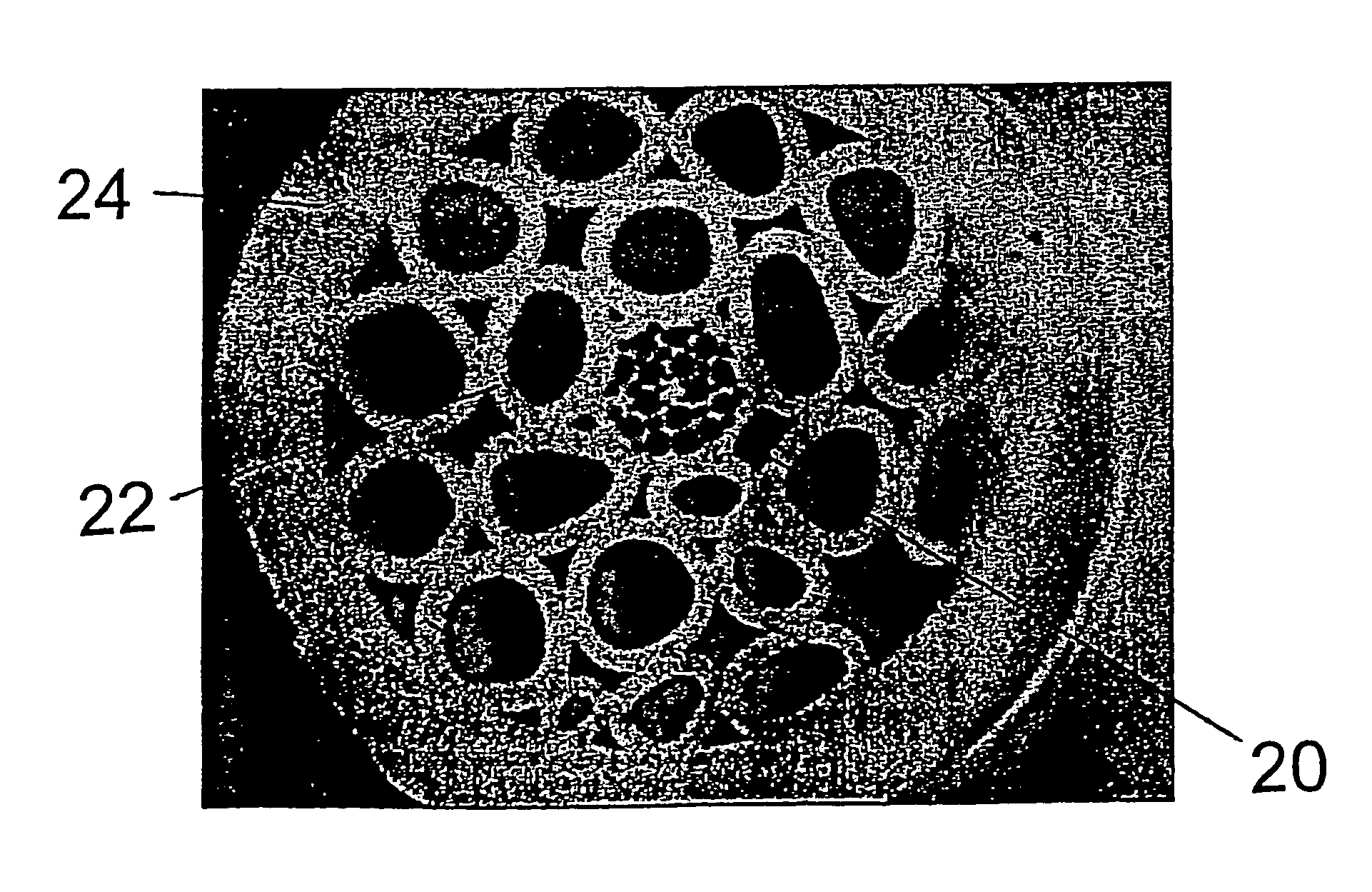
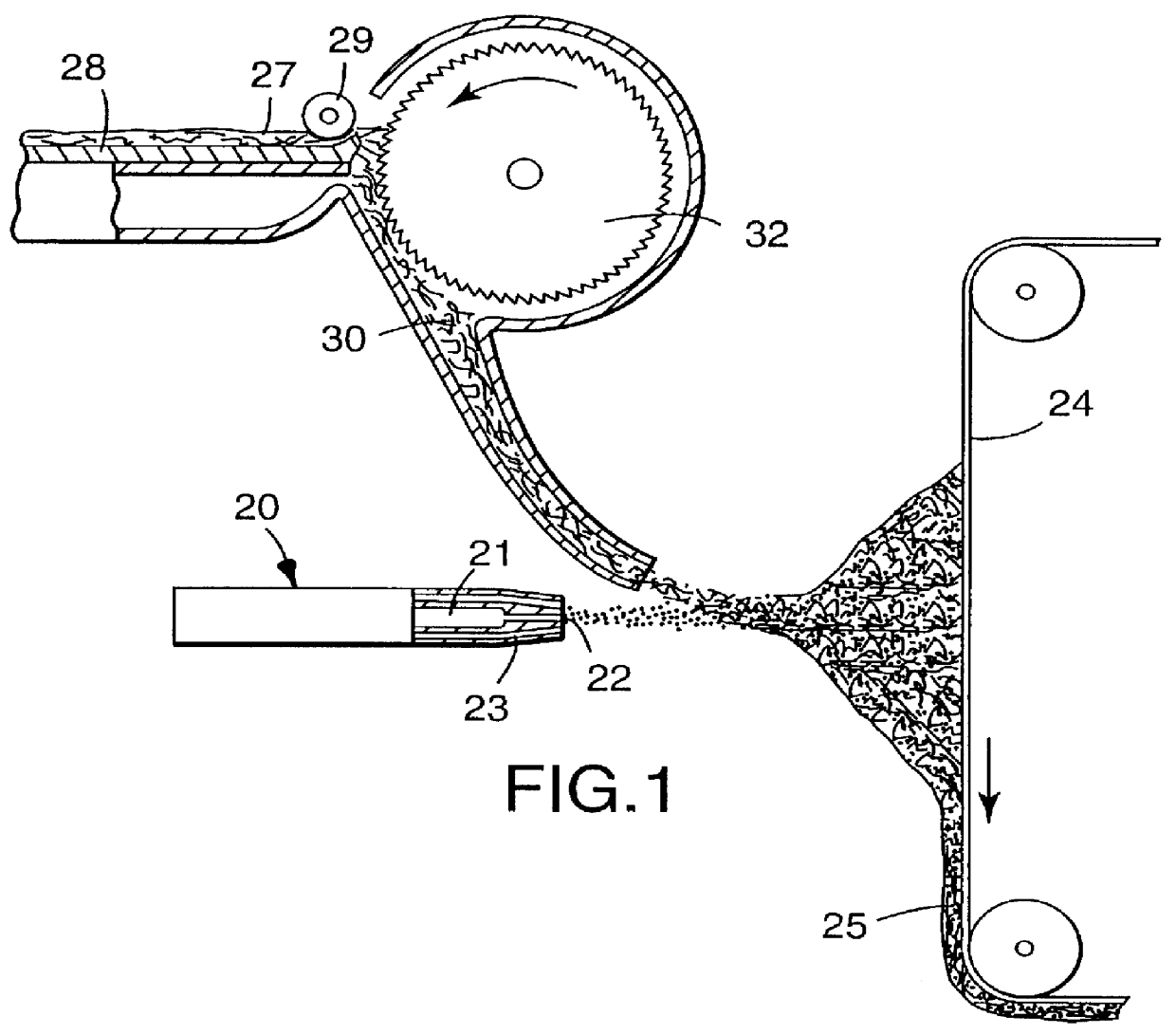
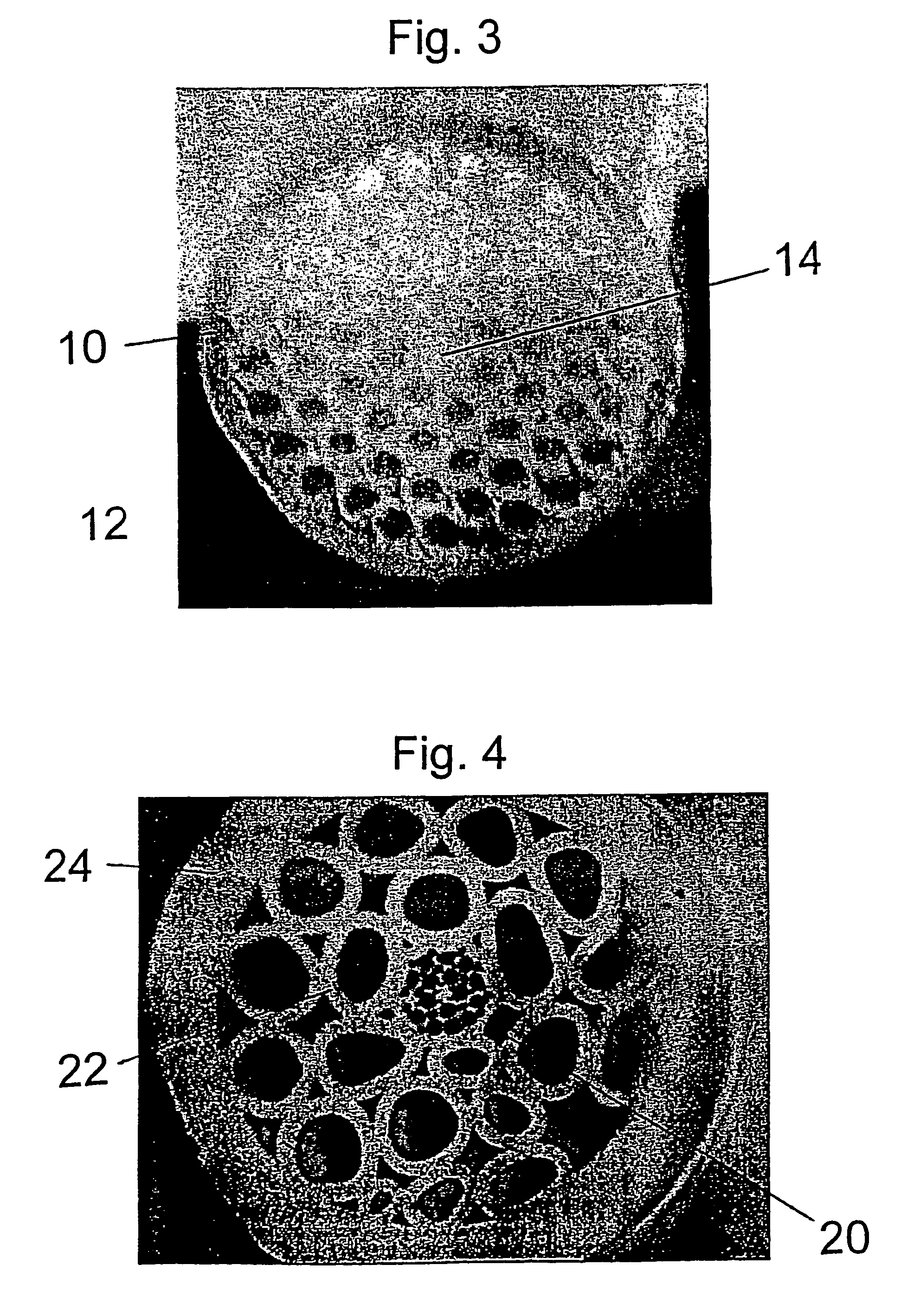
Holey optical fibres
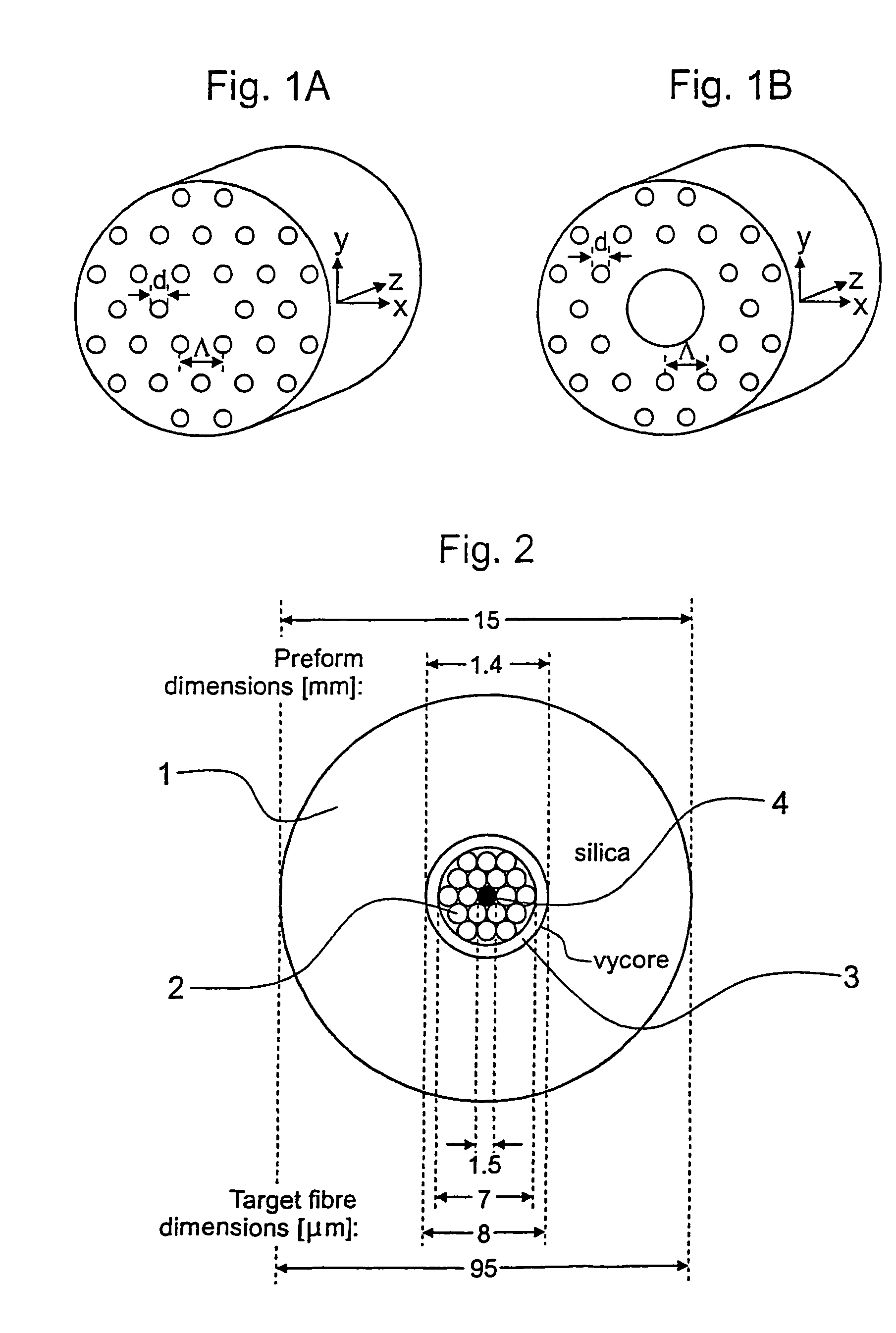
An optical fiber structure having a holey fiber arranged in a holey outer support structure made up of holey tubes encased in a thin walled outer jacket. The holey fiber may have a solid core surrounded by a holey cladding having a plurality of rings of holes. With the invention it is possible to produce robust, coated and jacketed fibers with microstructured core features of micrometer size relatively easily using existing fiber fabrication technology. This improvement is a result of the outer holey structure which reduces the thermal mass of the supporting structure and makes it possible to reliably and controllably retain small hole features during the fiber fabrication process.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHAMPTON
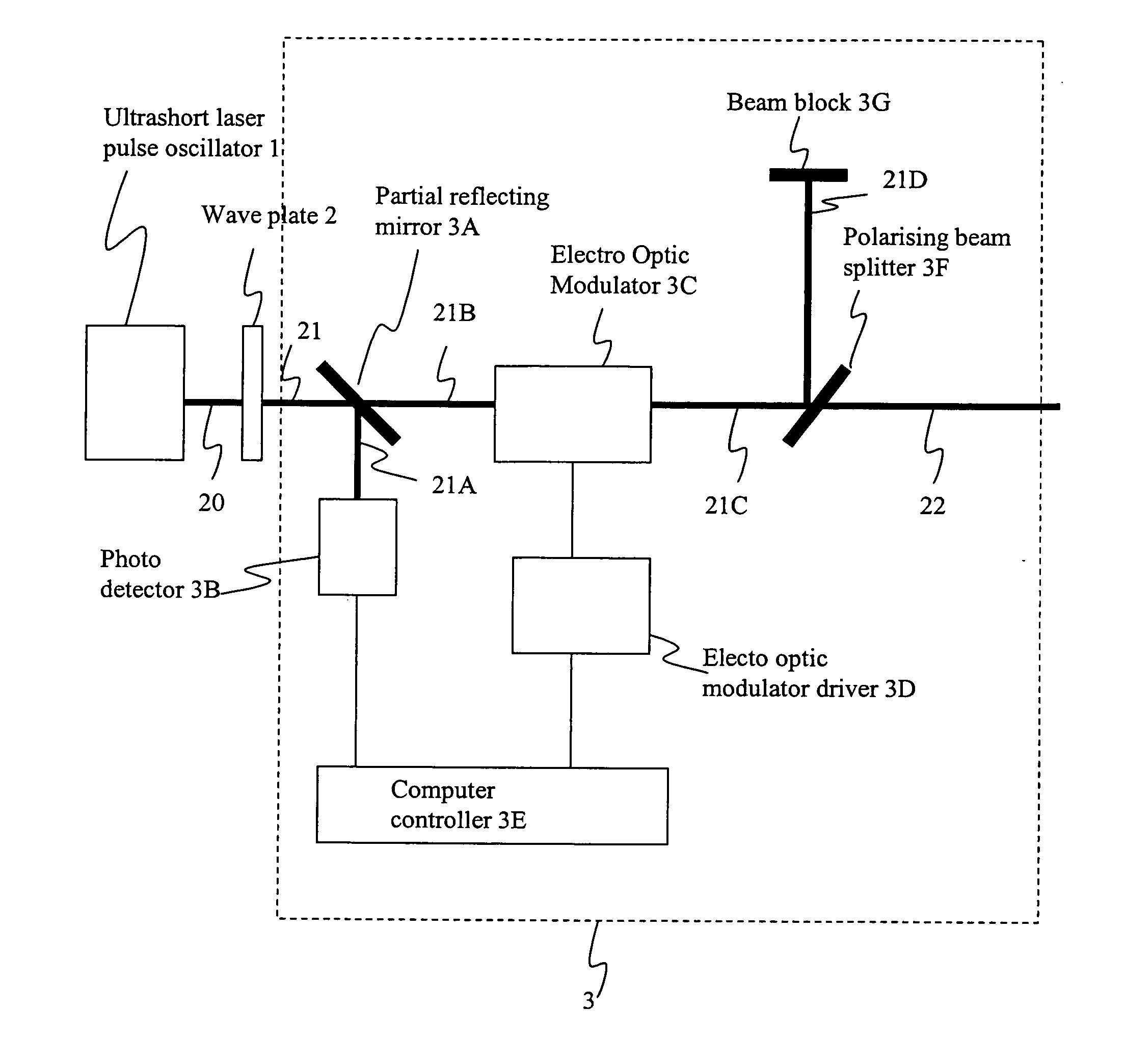
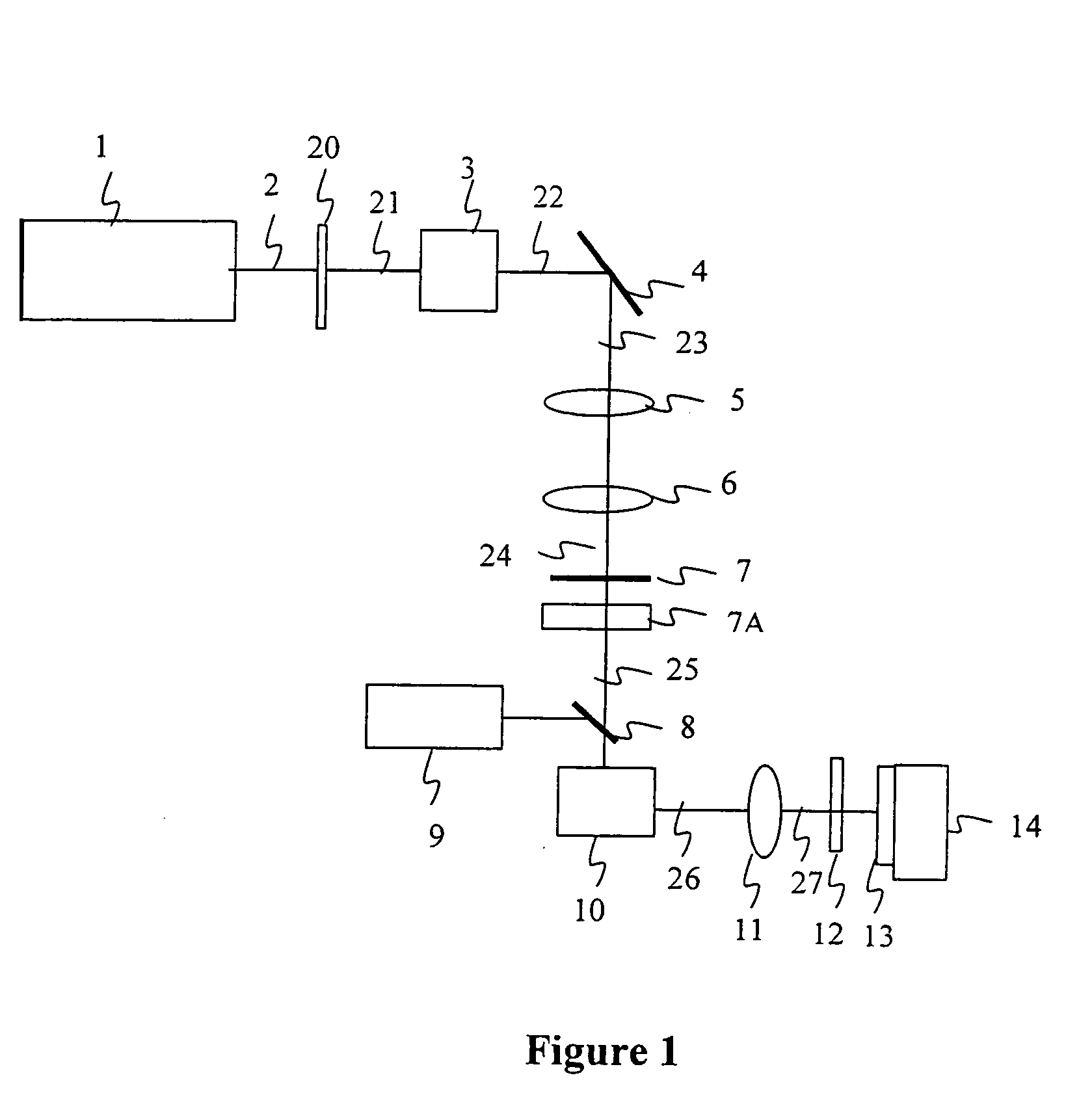
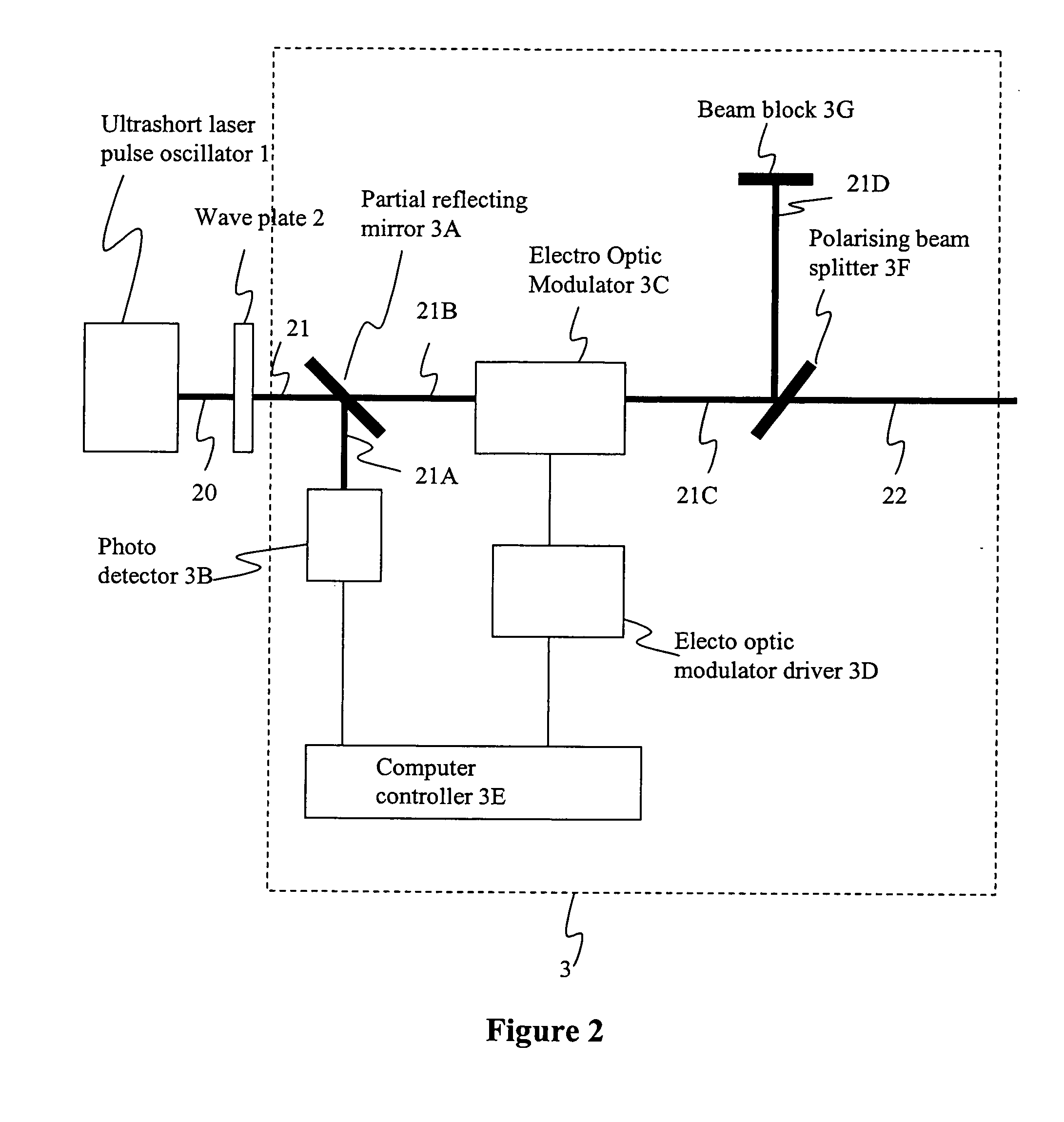
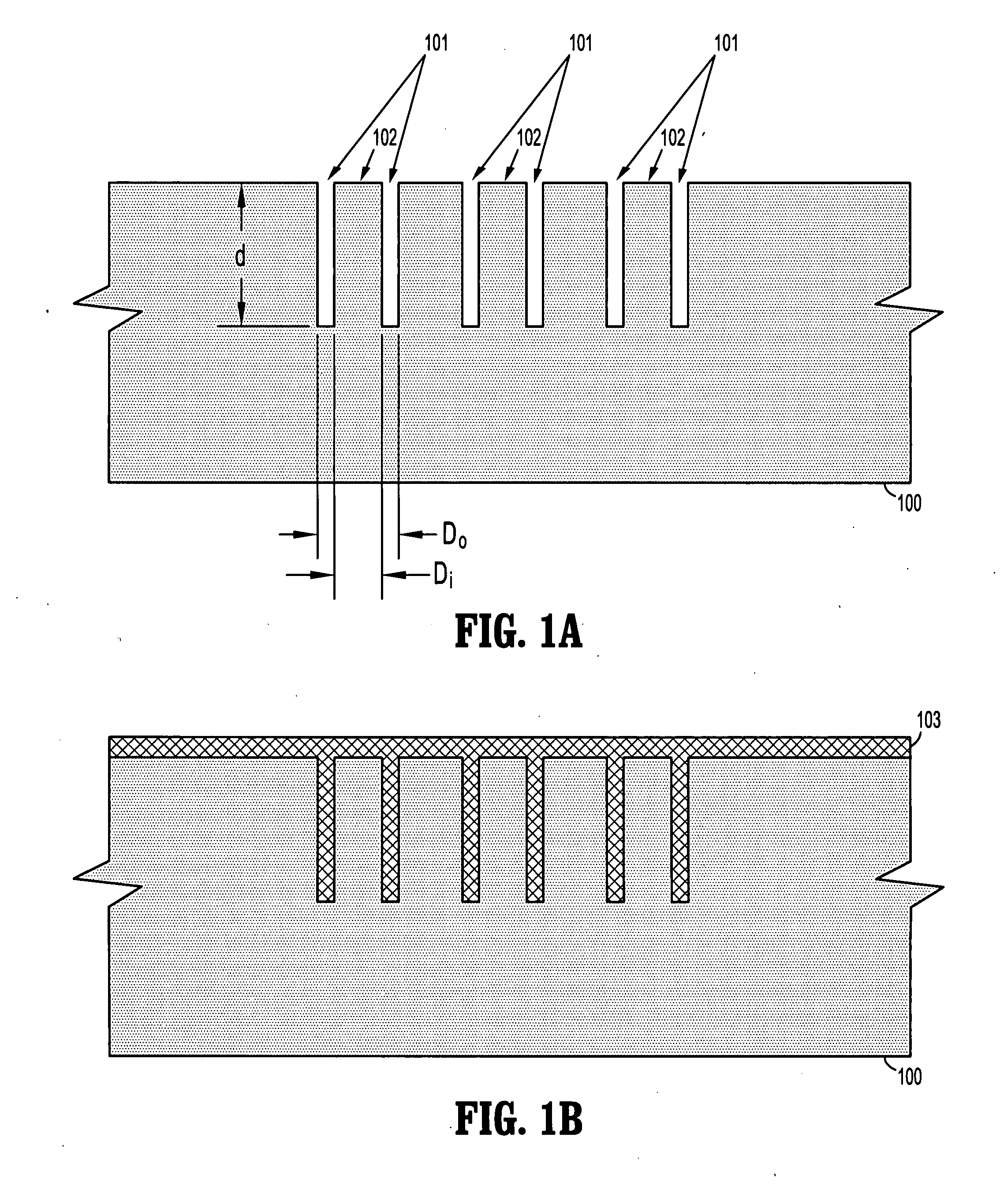
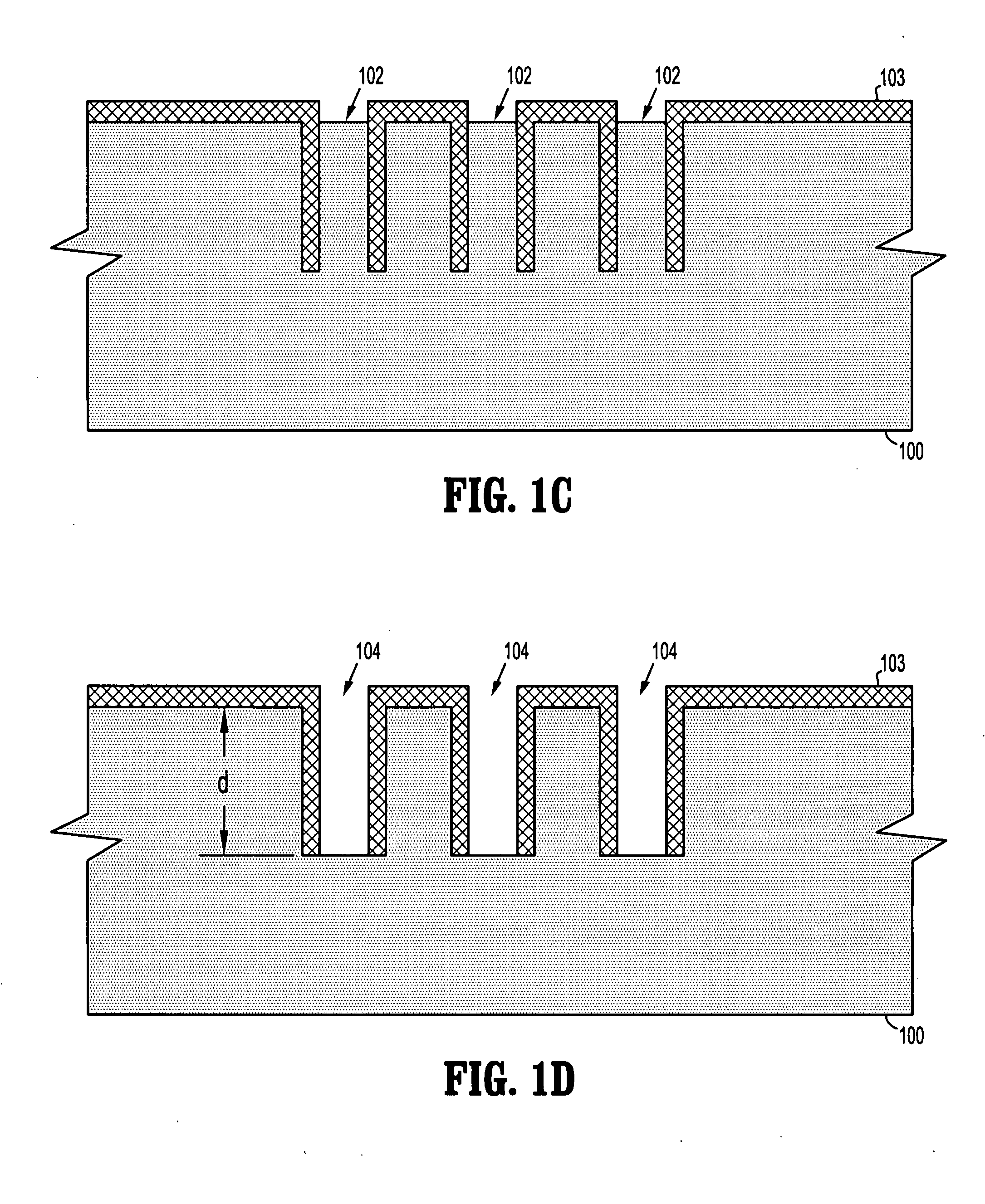
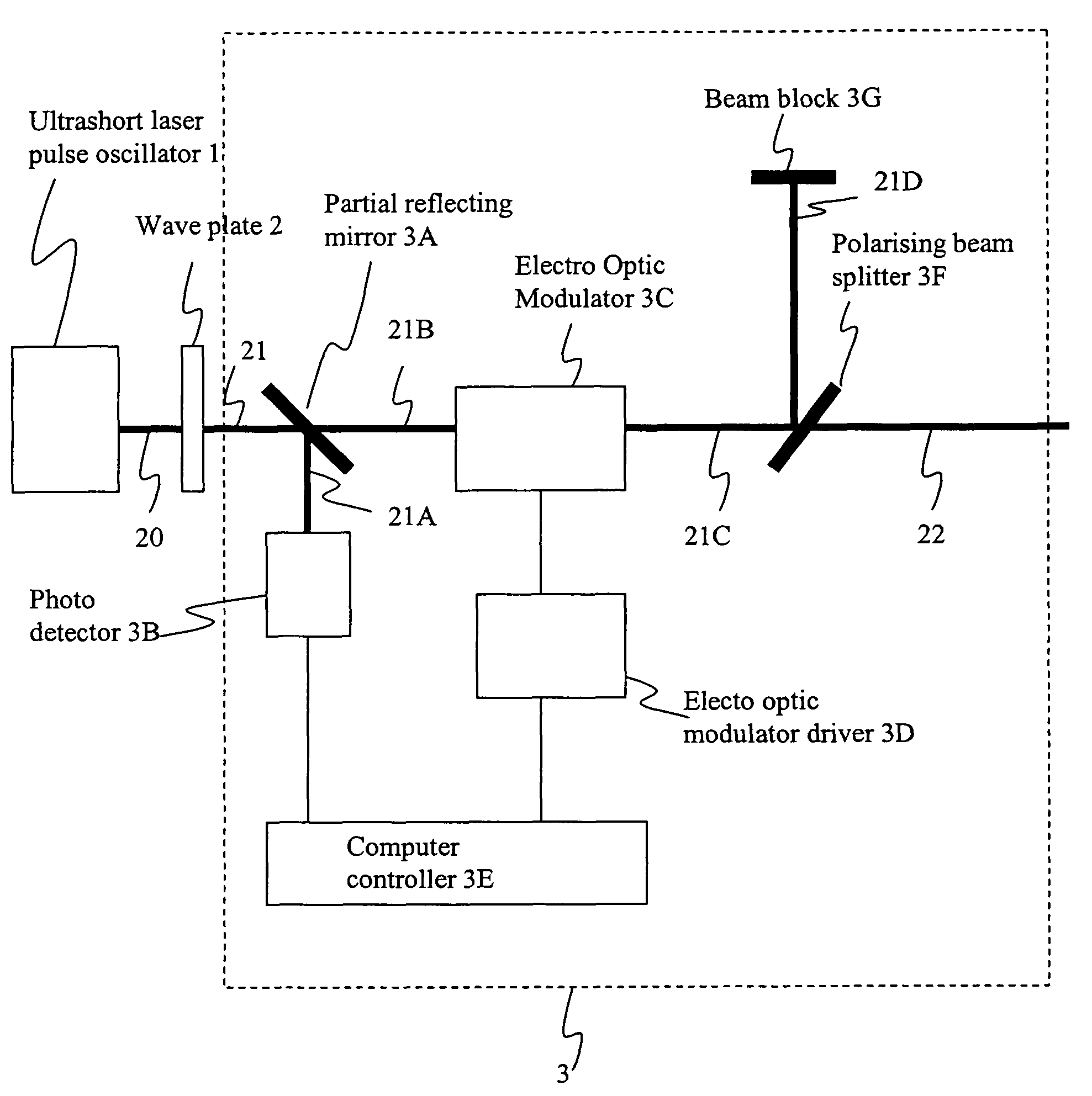
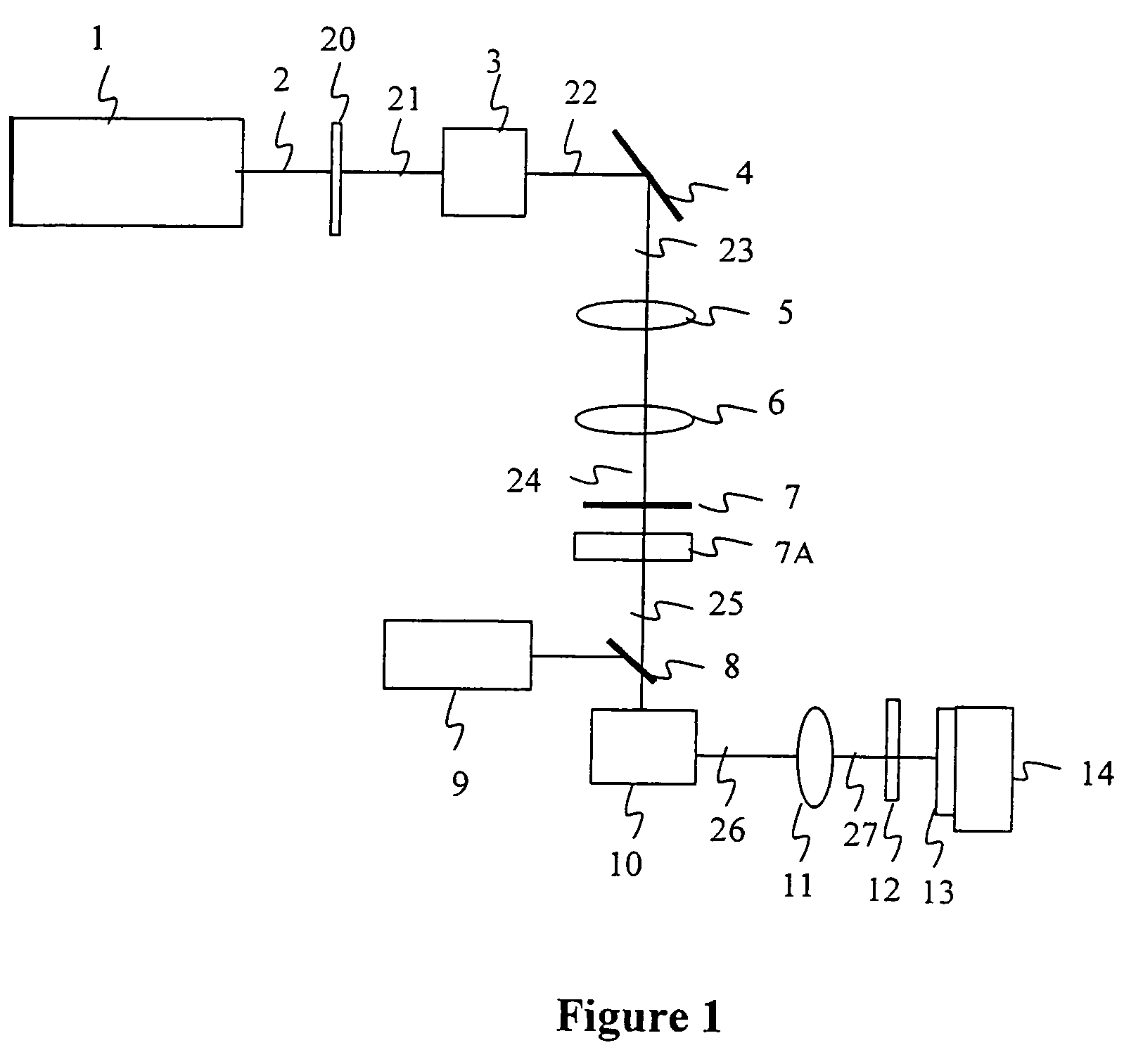
Method and apparatus for dicing of thin and ultra thin semiconductor wafer using ultrafast pulse laser
InactiveUS20050274702A1Improve inner wall qualityImprove surface qualityWelding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusPicosecond laserFacula
The present invention relates to the apparatus, system and method for dicing of semiconductor wafers using an ultrafast laser pulse of femtosecond and picosecond pulse widths directly from the ultrafast laser oscillator without an amplifier. Thin and ultrathin simiconductor wafers below 250 micrometer thickness, are diced using diode pumped, solid state mode locked ultrafast laser pulses from oscillator without amplification. The invention disclosed has means to avoid / reduce the cumulative heating effect and to avoid machine quality degrading in multi shot ablation. Also the disclosed invention provides means to change the polarization state of the laser beam to reduce the focused spot size, and improve the machining efficiency and quality. The disclosed invention provides a cost effective and stable system for high volume manufacturing applications. An ultrafast laser oscillator can be a called as femtosecond laser oscillator or a picosecond laser oscillator depending on the pulse width of the laser beam generated.
Owner:LASERFACTURING
Acoustic-optical therapeutical devices and methods
InactiveUS20050137656A1Effective and specific body therapyUltrasound therapyElectrotherapyMicrometerMedicine
Acoustic-optical therapy devices and methods for therapeutical purposes are disclosed in this invention. The devices provide a combination of ultrasound energy and optical pulsed energy exposed to human and animal body at frequencies of ultrasound and optical pulses within the range of 1 Hz to 1 GHz and at wavelengths from 0.2 micrometer to 20 micrometers. Both ultrasound energy and pulsed light radiation are delivered in effective combinations to maximize the therapy. Because of different interaction nature of ultrasound and light with body, the new invented devices will provide much more effective and specific body treatment.
Owner:UNITED LAB & MFG
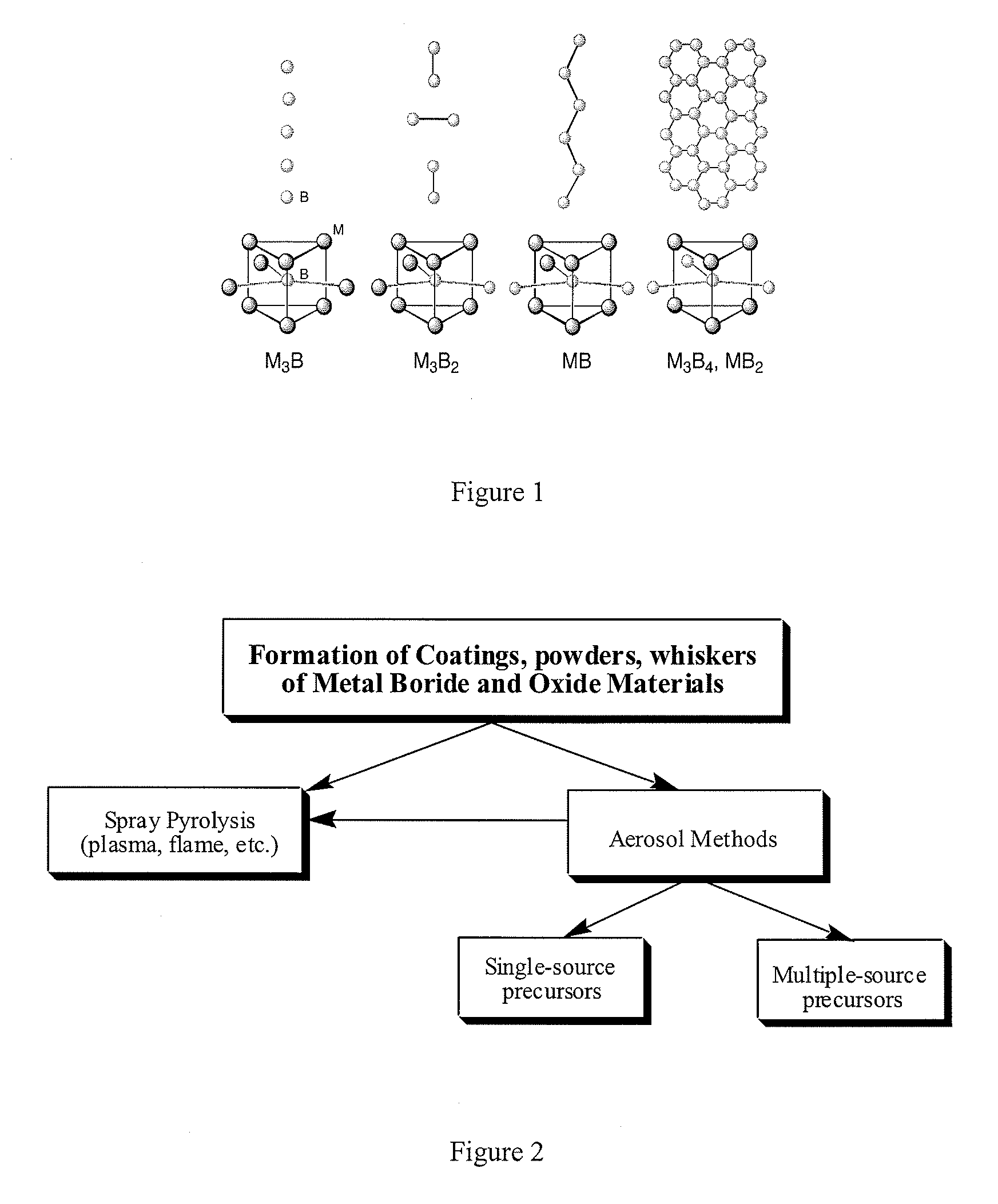
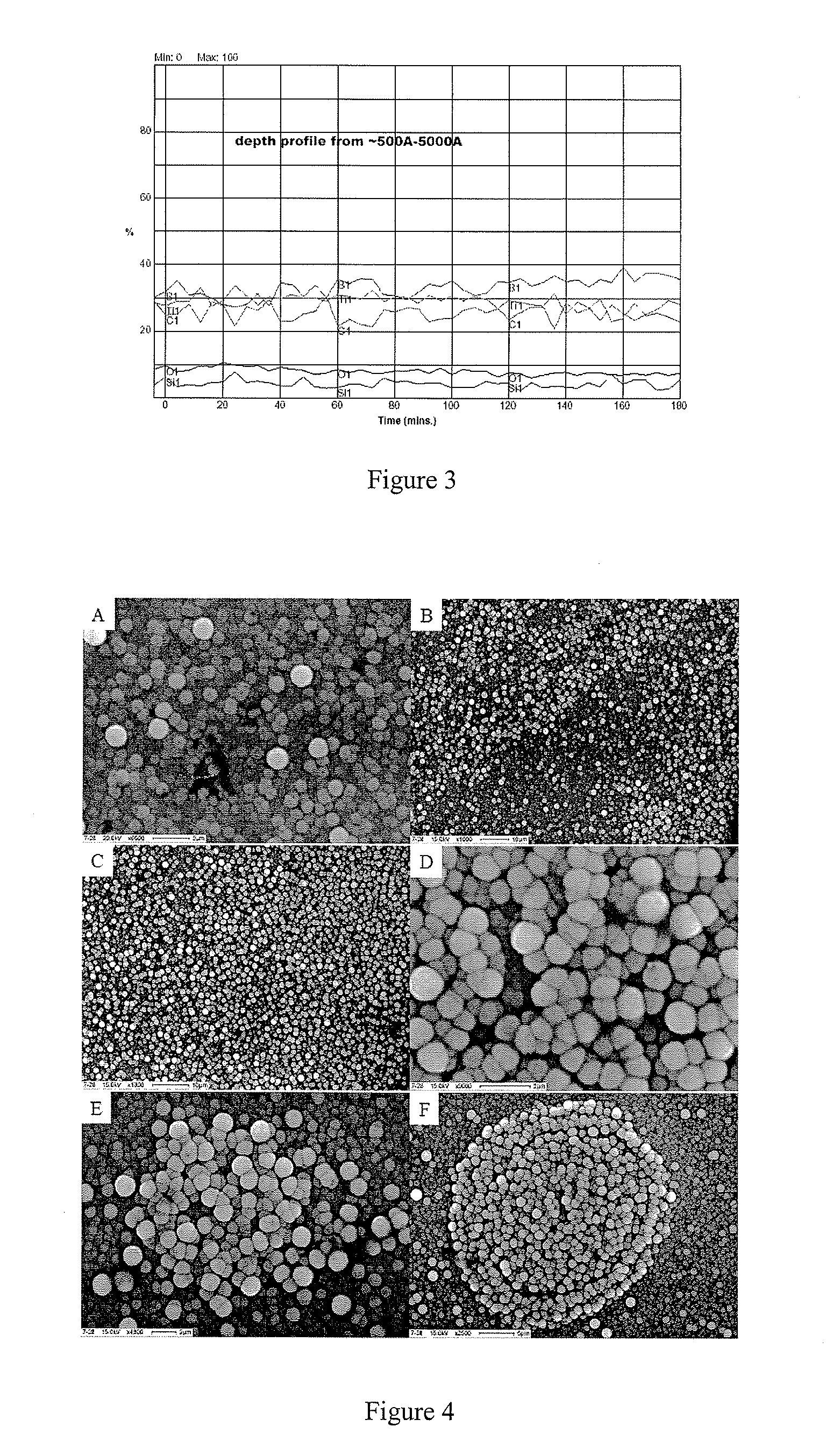
Systems and Methods of the Formation of Solid State Metal Boride and Oxide Coatings
InactiveUS20080003425A1Easy to implementMolten spray coatingLayered productsCelsius DegreeMicrometer
A system and method for the formation of novel small particles, thin films, and coatings of solid state metal boride material. The metal boride materials may be formed using aerosol methods and / or spray pyrolysis to form a generally uniform, thin film coating of boride compound spheres. Boride solutions or compounds are sprayed via a gas nebulizer in a reactor containing a substrate and heated to approximately 900° Celsius. The boride compounds form uniform, spherical particles of approximately one micrometer in diameter. The boride compounds are extremely strong, non-reactive, dense, and, when prepared as films or coating, adhere very well to substrates, such as metals.
Owner:SYRACUSE UNIVERSITY
Strontium feldspar aluminum titanate for high temperature applications
InactiveUS6620751B1Improve stabilityReduce bloatInternal combustion piston enginesDispersed particle filtrationMicrometerRoom temperature
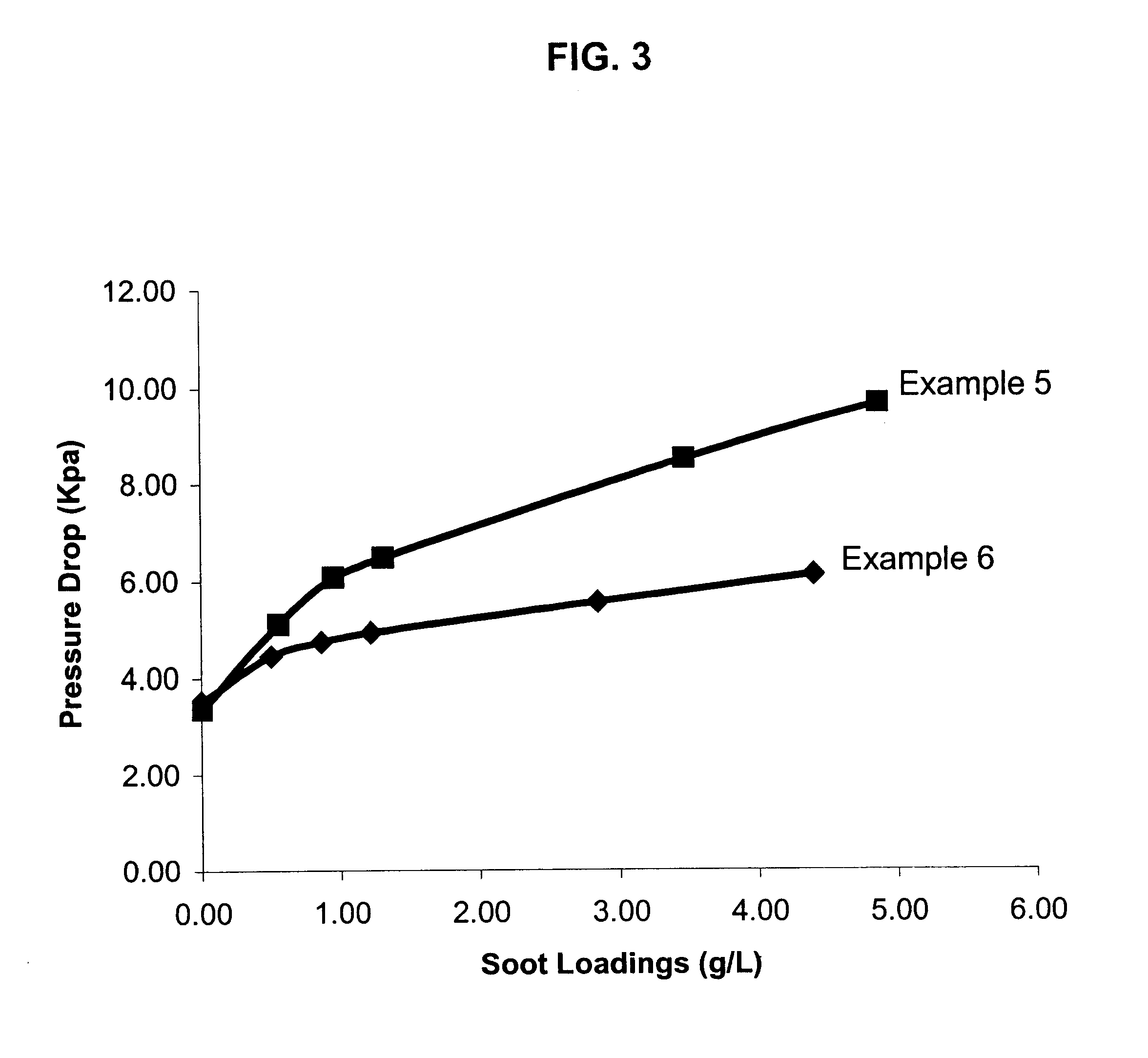
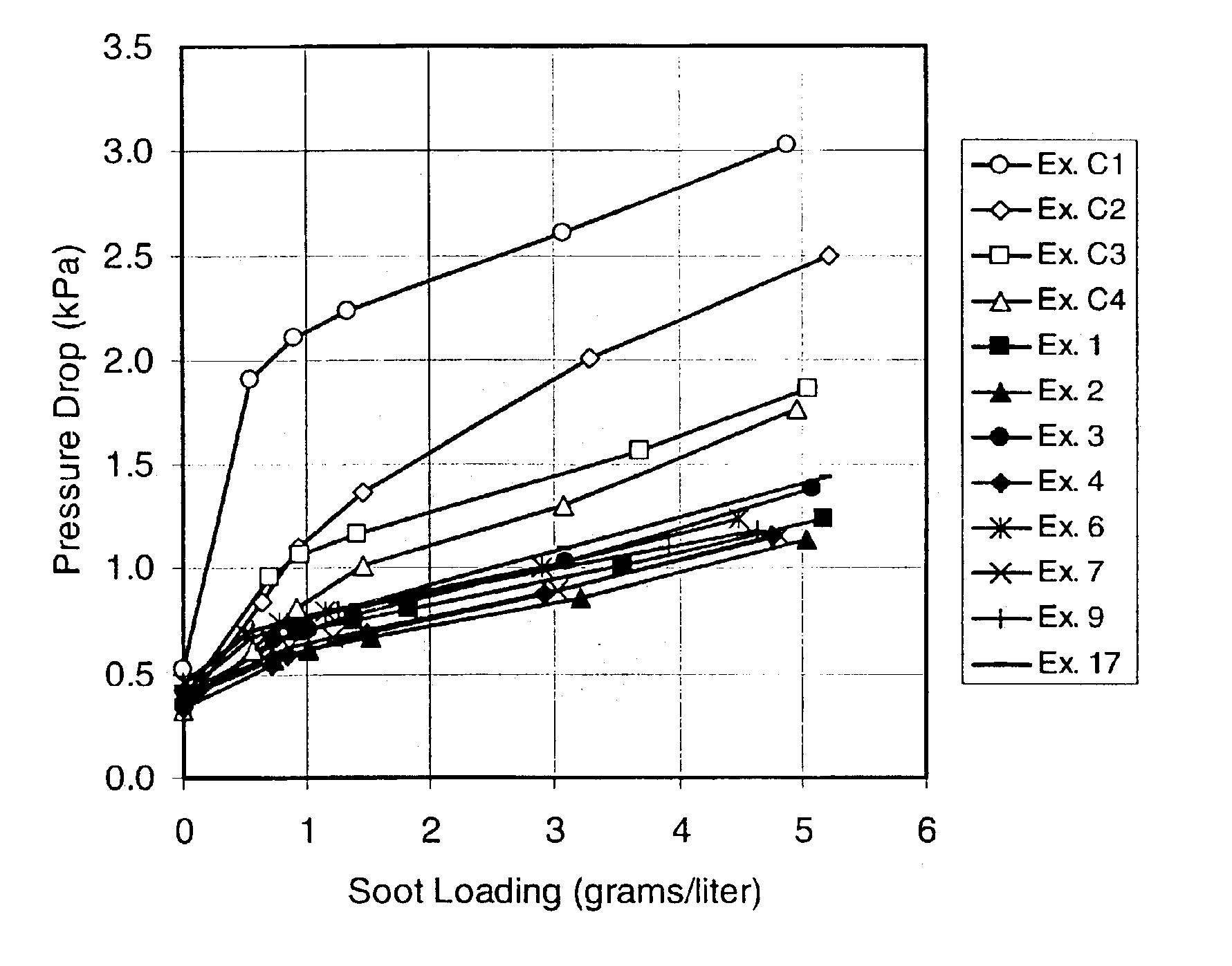
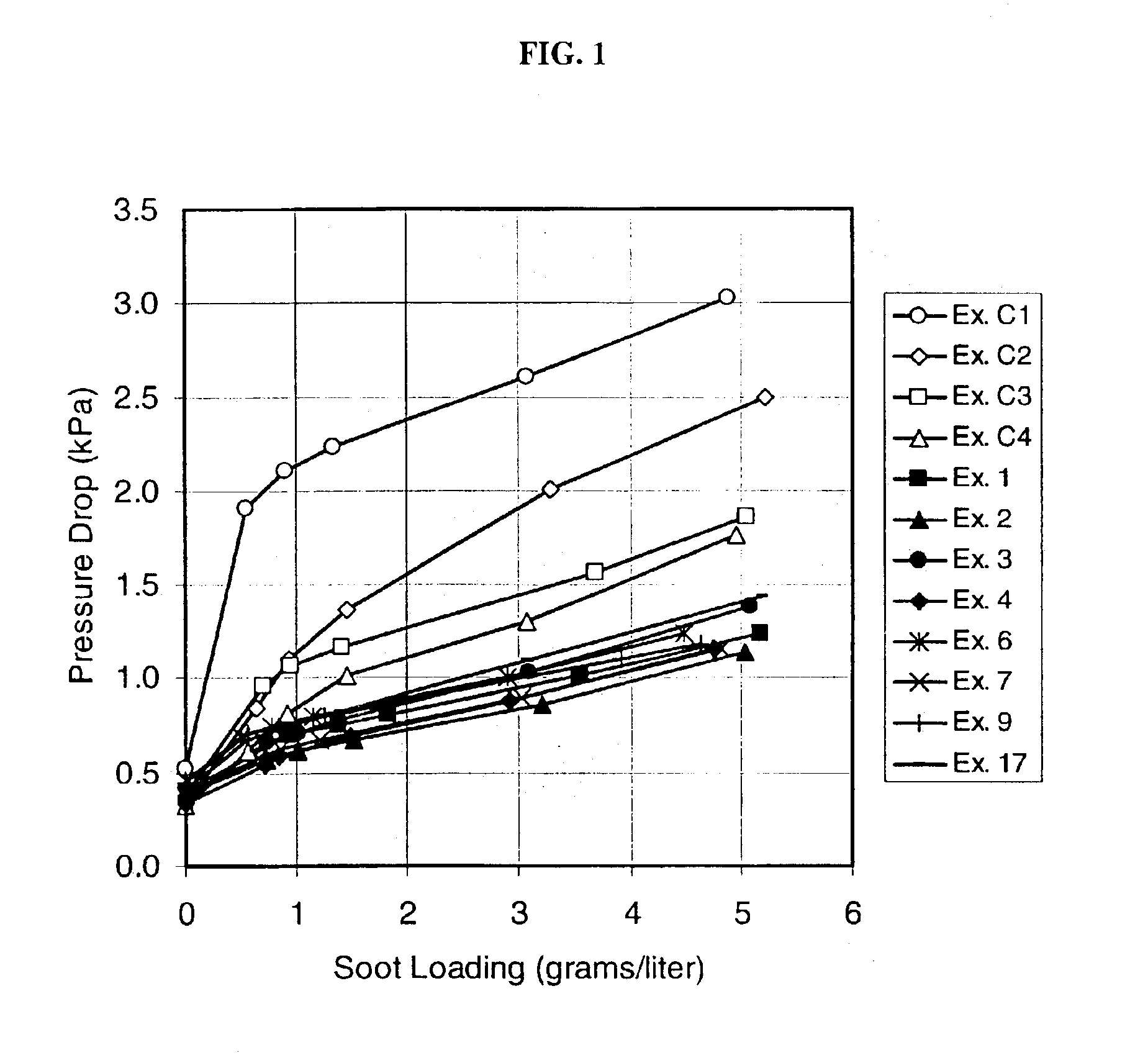
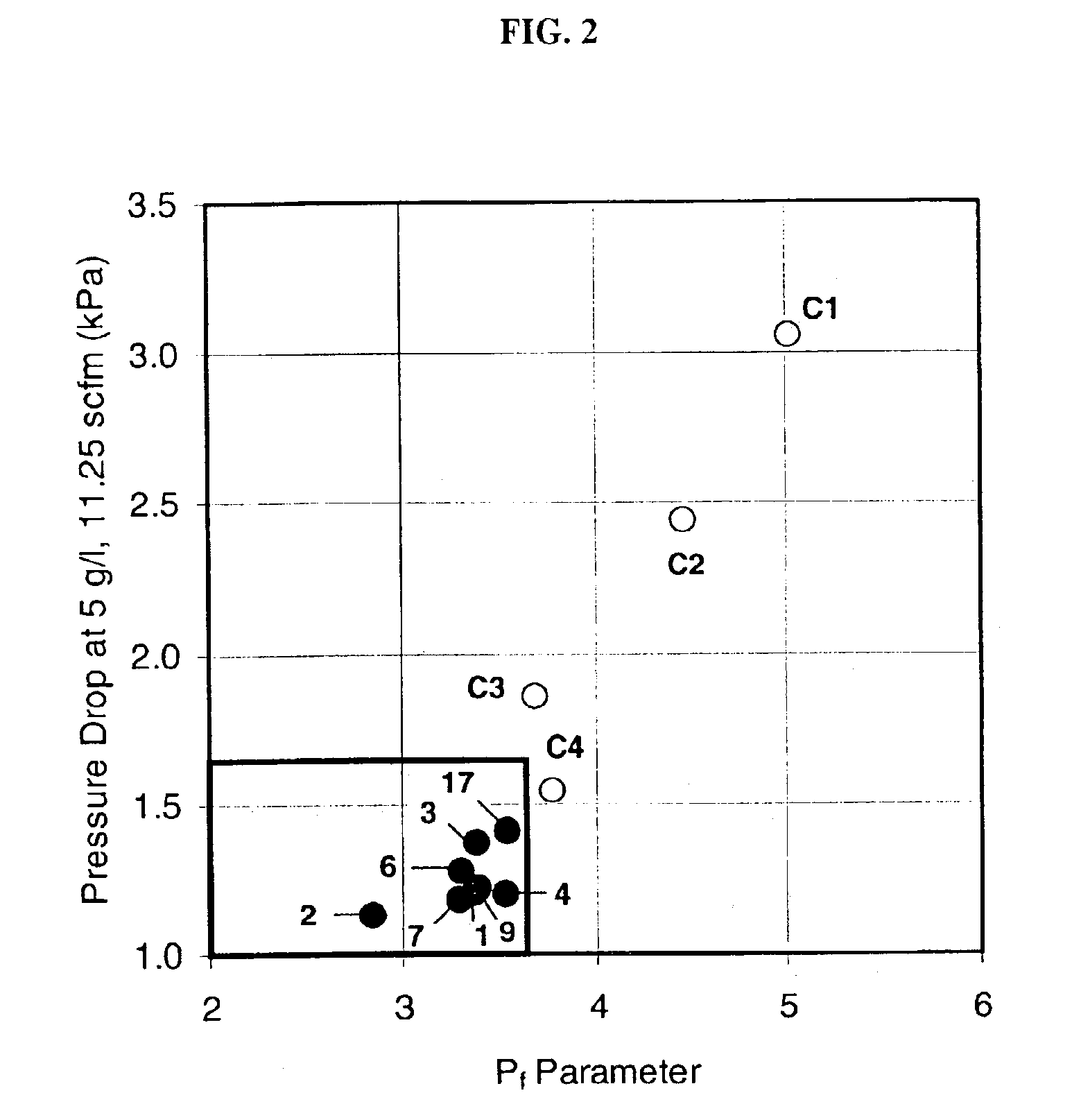
A structure for use in high temperature applications and including a porous ceramic material consisting essentially of about 50-90 percent by weight iron or magnesium stabilized aluminum titanate (AlTiO5) and about 10-50 percent by weight strontium feldspar (SrO.Al2O3.2SiO2), and having a coefficient of thermal expansion over a temperature range from room temperature to 1000° C. of about -10x10-7 / ° C. to +15x10-7 / ° C., a heat capacity at 500° C. greater than 3.2 J / cm3K, a porosity of about 15-50 percent by volume, preferably 40-50 percent by volume, and a median pore size of about 5-50 micrometers, preferably 8-15 micrometers. The structure is especially useful as a diesel exhaust particulate filter.
Owner:CORNING INC
Optical element with nanoparticles
InactiveUS7046439B2Effective lightingBrighter backlit displaysDiffusing elementsProjectorsMicrometerNanoparticle
Owner:SKC HI TECH & MARKETING CO LTD CO REGISTRATION NO 161511 0225312
Conductive adhesive agent with ultrafine particles
ActiveUS7262511B2Improve working efficiencyUniform and good thermal conductivity propertySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsConductive materialMicrometerFluid viscosity
The present invention provides a conductive adhesive agent capable of being diluted with a solvent to give good coating workability and allowing formation of a conductive joint excellent in both thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity by inhibiting a gas generated when a binder resin is heat-cured after attachment of a part. The conductive adhesive agent according to the present invention is a conductive adhesive agent wherein, based on 100 parts by weight of silver powder having an average particle diameter of micrometers, which is used for a conductive medium, e.g. as a main component, 1 to 10 parts by weight of silver fine particles having an average particle diameter of nanometers is used in combination therewith and 5 to 15 parts by weight of thermosetting resin as a binder resin component and 10 parts or less by weight of solvent for adjustment of a fluid viscosity are blended therein as essential components, and by selection of such a blending ratio, generation of a gas component during heating and curing of the thermosetting resin to prevent formation of voids, and at the same time, fabrication of a conductive joint excellent in thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity is achieved.
Owner:HARIMA CHEM INC +1
Cordierite ceramic body and method
InactiveUS6864198B2Lower overall pressure dropHigh filtration efficiencyDispersed particle filtrationTransportation and packagingPorosityFiltration
Owner:CORNING INC
Method and arrangement for high-resolution microscope imaging or cutting in laser endoscopy
ActiveUS20080081950A1Accurate imagingPrecise microcuttingEndoscopesCatheterMicroscopic imageFlexible endoscope
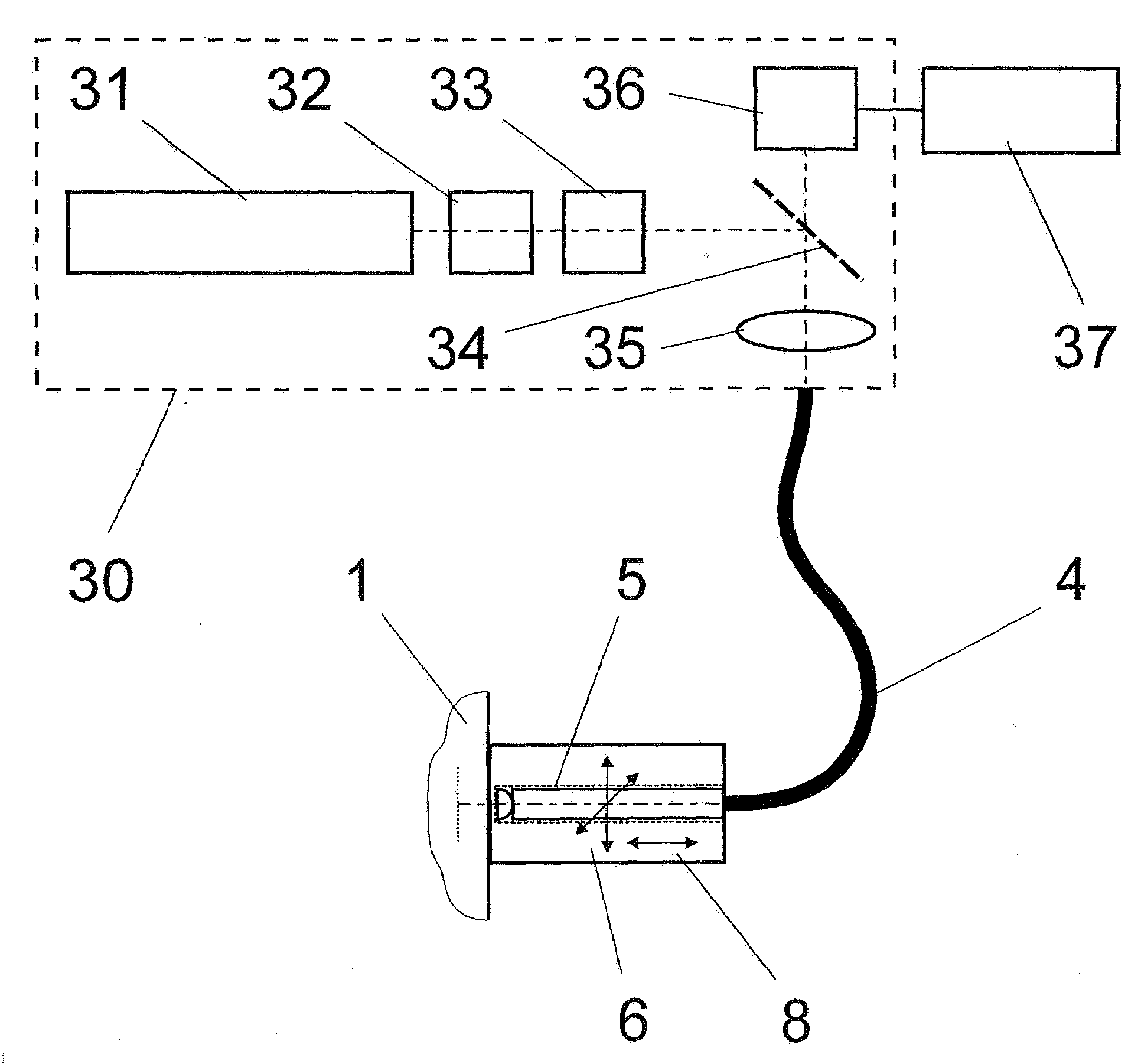
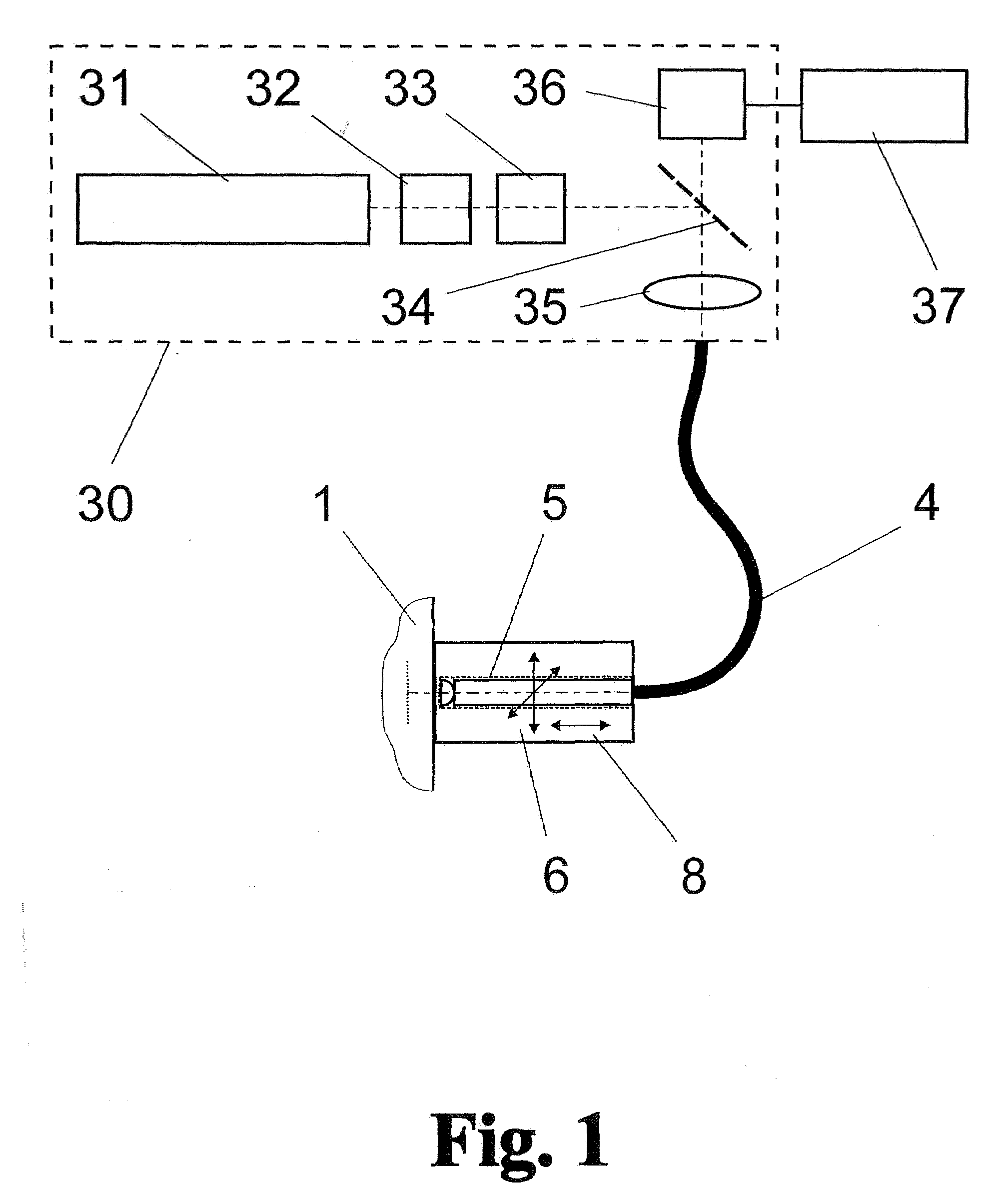
The invention is directed to a method and an arrangement for high-resolution microscopic imaging in laser endoscopy based on laser-induced object reaction radiation and for performing microscopic cuts in biological tissue. In using multiphoton processes for endoscopic applications in biological materials with an accuracy of under one millimeter, radiation of a pulsed femtosecond laser is focused into an object by means of a transmission focusing optics unit comprising a transmission system and miniature focusing optics having a high numerical aperture greater than 0.55 to trigger a local object reaction radiation in the micrometer to nanometer range, and the distal end of the transmission focusing optics unit is moved in at least two dimensions for highly spatially resolved scanning of the object and for transmitting object reaction radiation which is scanned in a locally progressive manner to an image-generating system with a photon detector. In an other embodiment the femtosecond laser radiation is energy enhanced is applied to the same transmission focusing optics unit to perform microendoscopic surgery in biological tissue.
Owner:JENLAB
Implants with textured surface and methods for producing the same
ActiveUS7368065B2High retention rateConvenient coatingImpression capsDecorative surface effectsMicrometerChloride
Compositions and methods are provided for preparing a metal substrate having a uniform textured surface with a plurality of indentations with a diameter in the nanometer and micrometer range. The textured surface is produced by exposing the substrate to an etching fluid comprising a hydrohalic acid and a mixture of a hydrohalic acid and an oxyacid, a chloride containing compound, and an oxidant. The etching solution can be used at ambient temperature. This textured surface enhances adherence of coatings or cells onto the textured surface, improves the retention of proteins on the surface, and encourages bone in-growth.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Compositions produced using an in situ heat treatment process
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
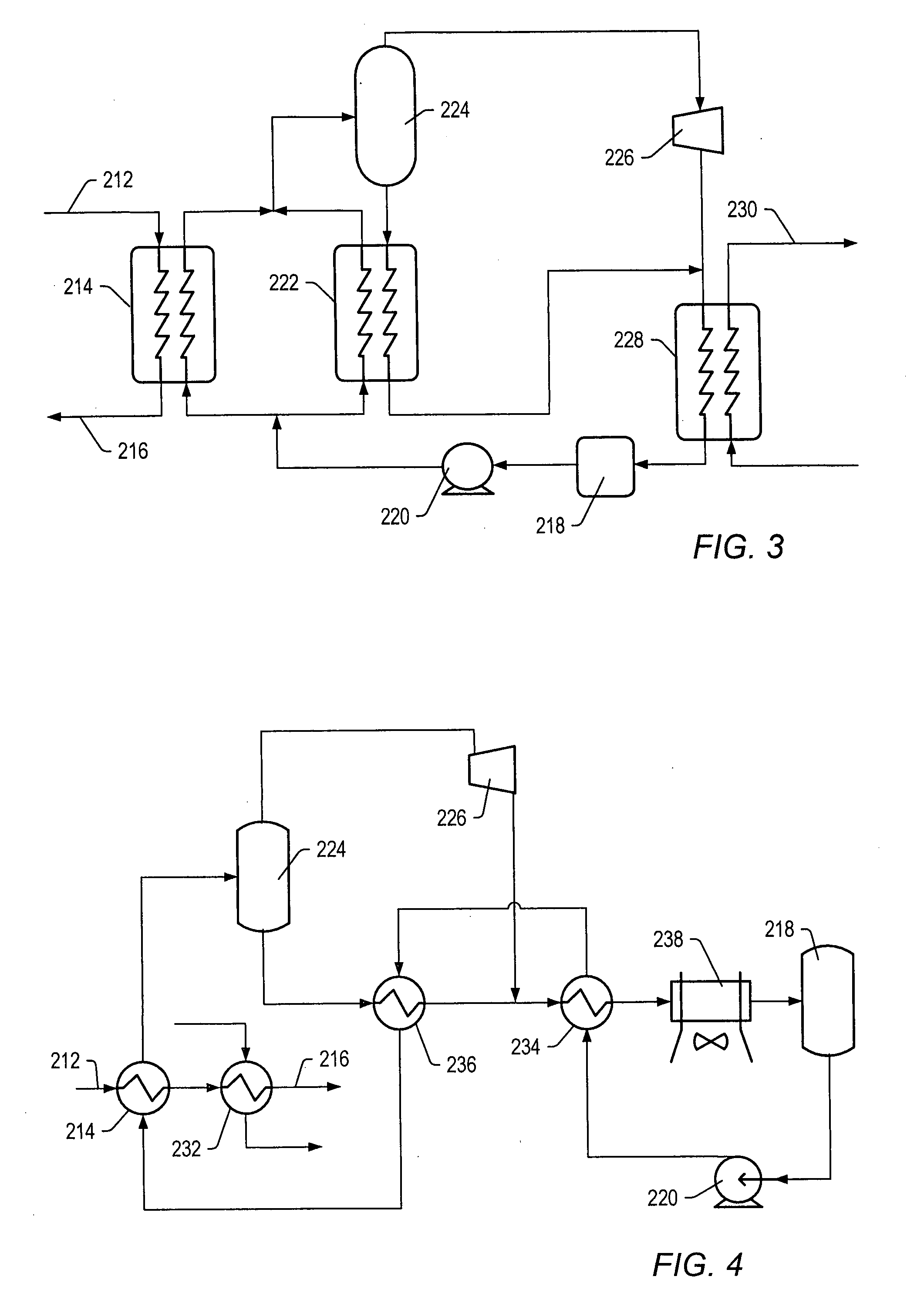
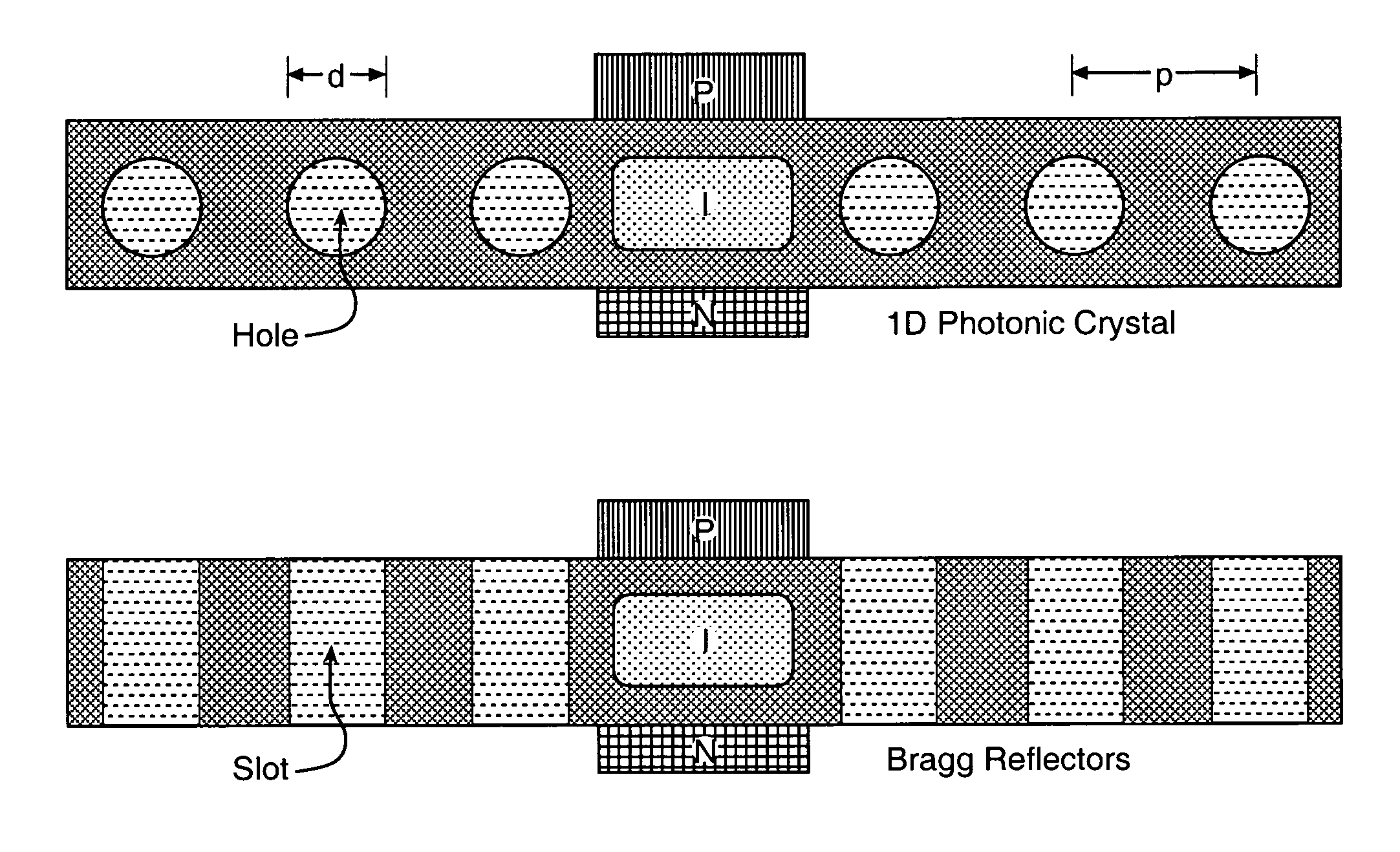
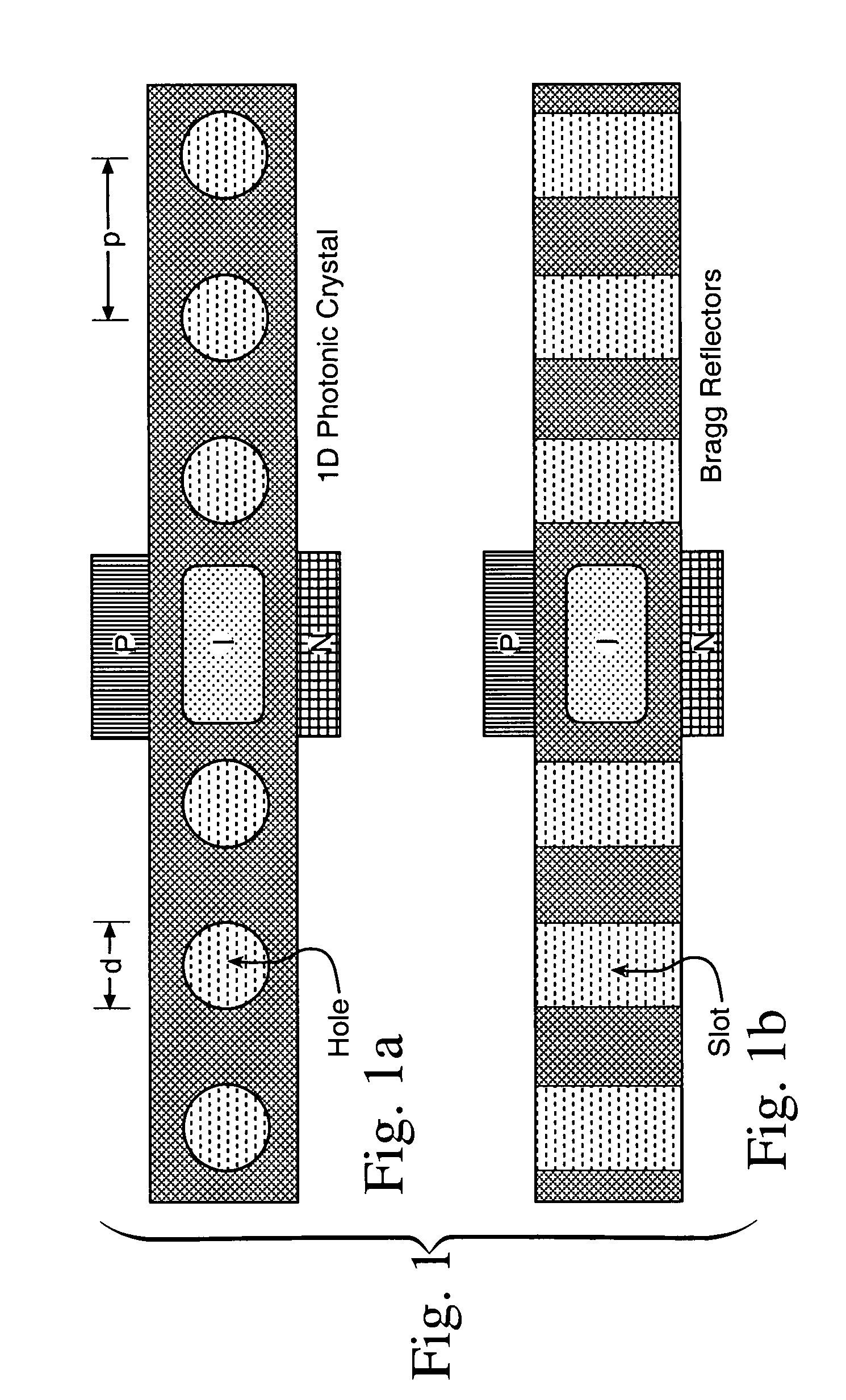
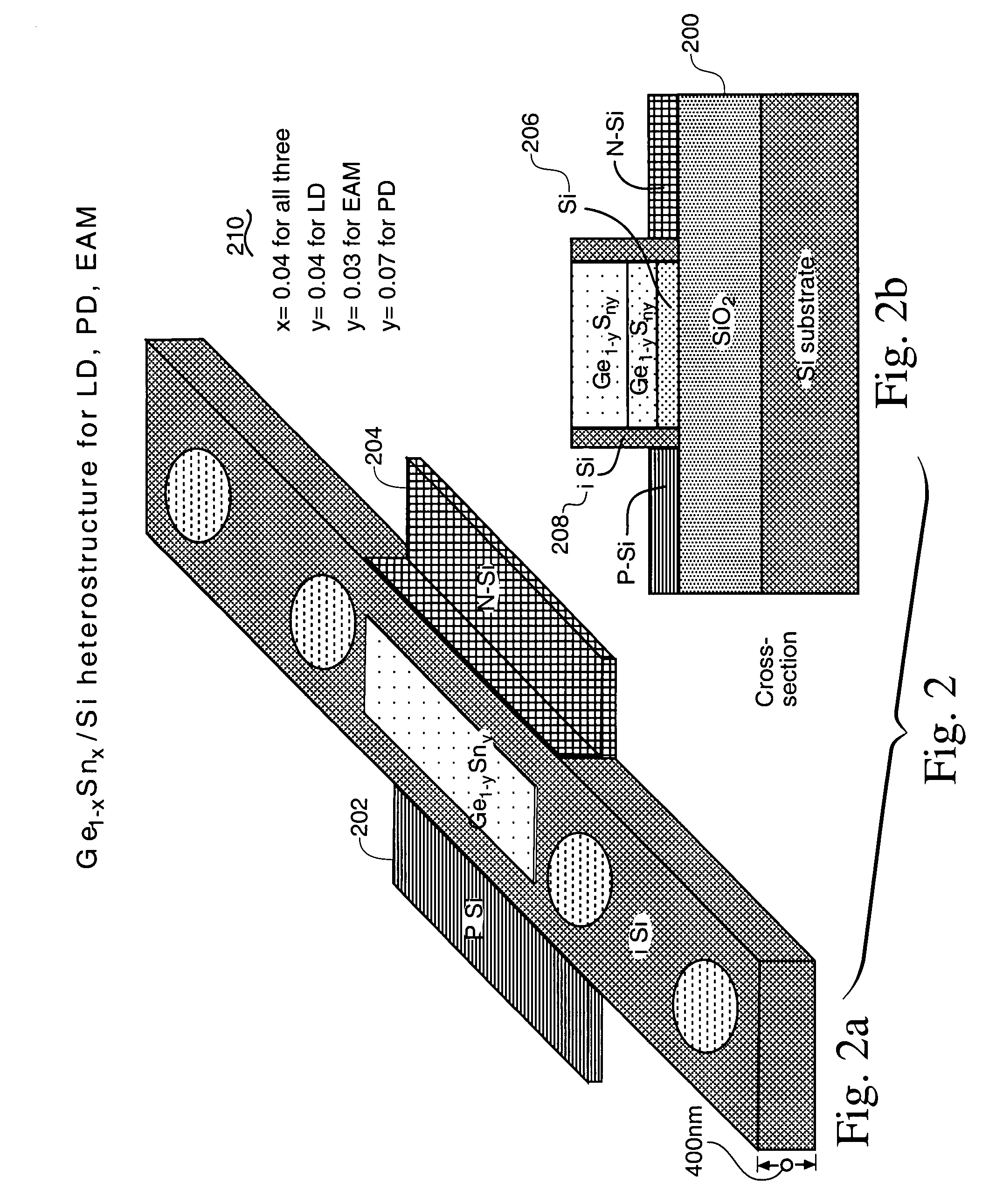
Semiconductor photonic nano communication link apparatus
InactiveUS7603016B1Eliminate needNanoopticsSemiconductor lasersElectro-absorption modulatorPhotonics
A CMOS compatible ten-gigabit-per-second region nano-waveguide included photonic communication link apparatus of low energy use per transmitted bit. An embodiment of the link includes an electrically pumped laser, an electro absorption modulator and a photodetector for the 1.5 to 2.0 micrometer infrared spectral region; omission of the separate electro absorption modulator is additionally disclosed. Each of these three nano-scale elements preferably includes active semiconductor crystal material situated in a preferably Silicon resonator within a nano-strip waveguide. The resonator is defined by dispersed resonator mirrors having tapered separation distance one dimensional photonic crystal lattice apertures of oxide holes or slots. Each of the three devices may be a semiconductor heterodiode pumped or controlled by laterally disposed wings enclosing the resonator to form a lateral PIN heterodiode for current injection or high E-field generation depending on bias and composition conditions selected.
Owner:US SEC THE AIR FORCE THE
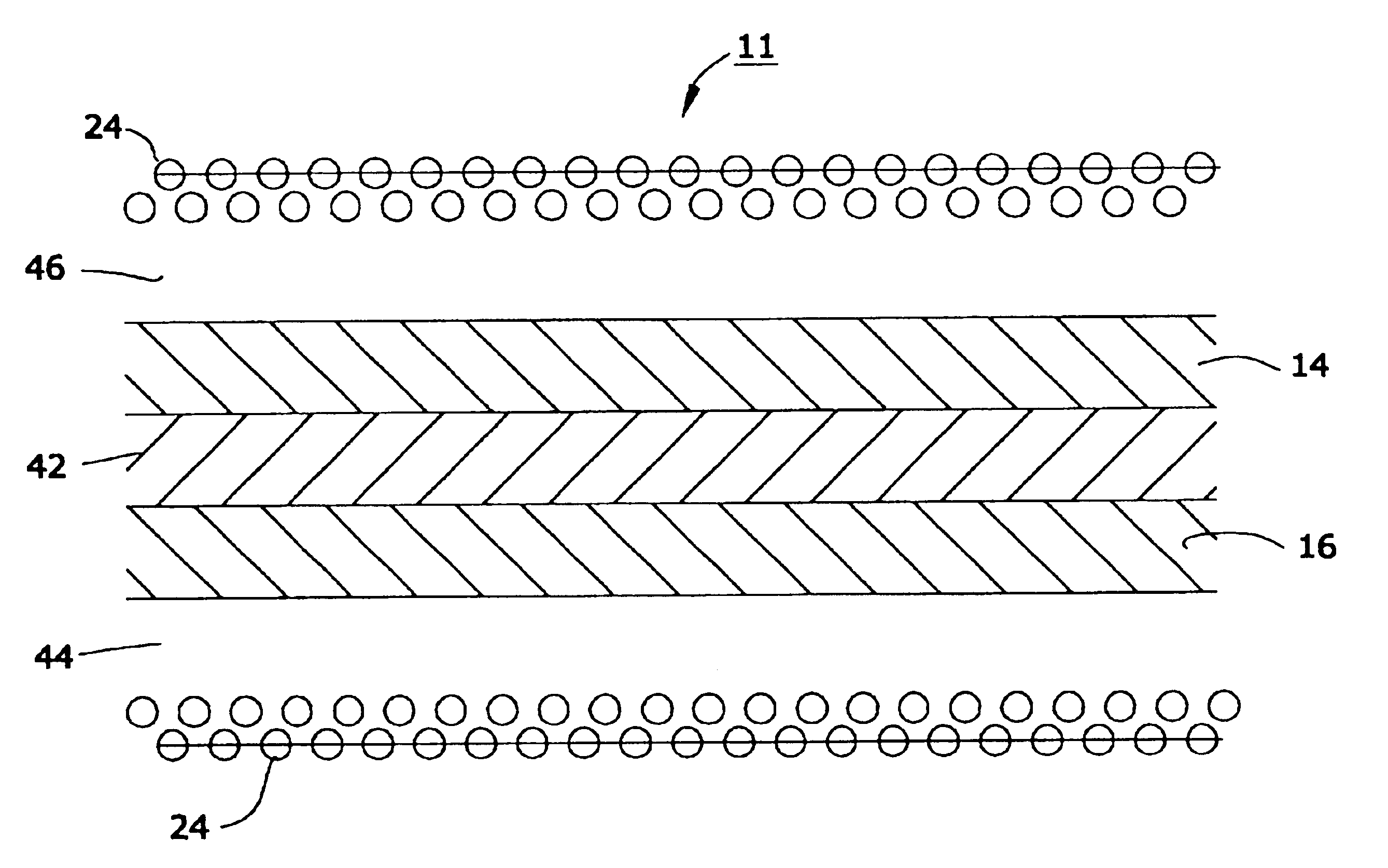
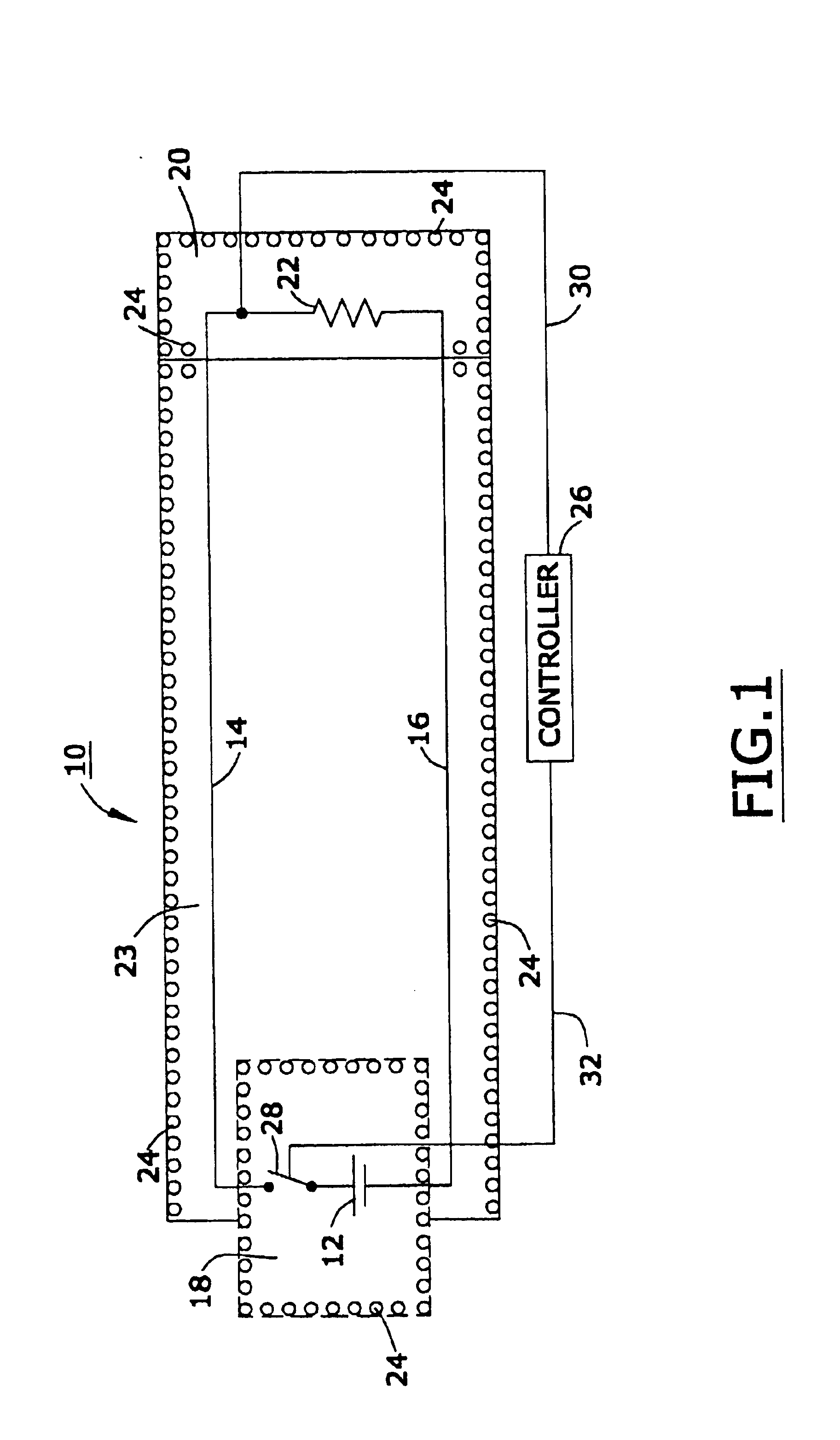
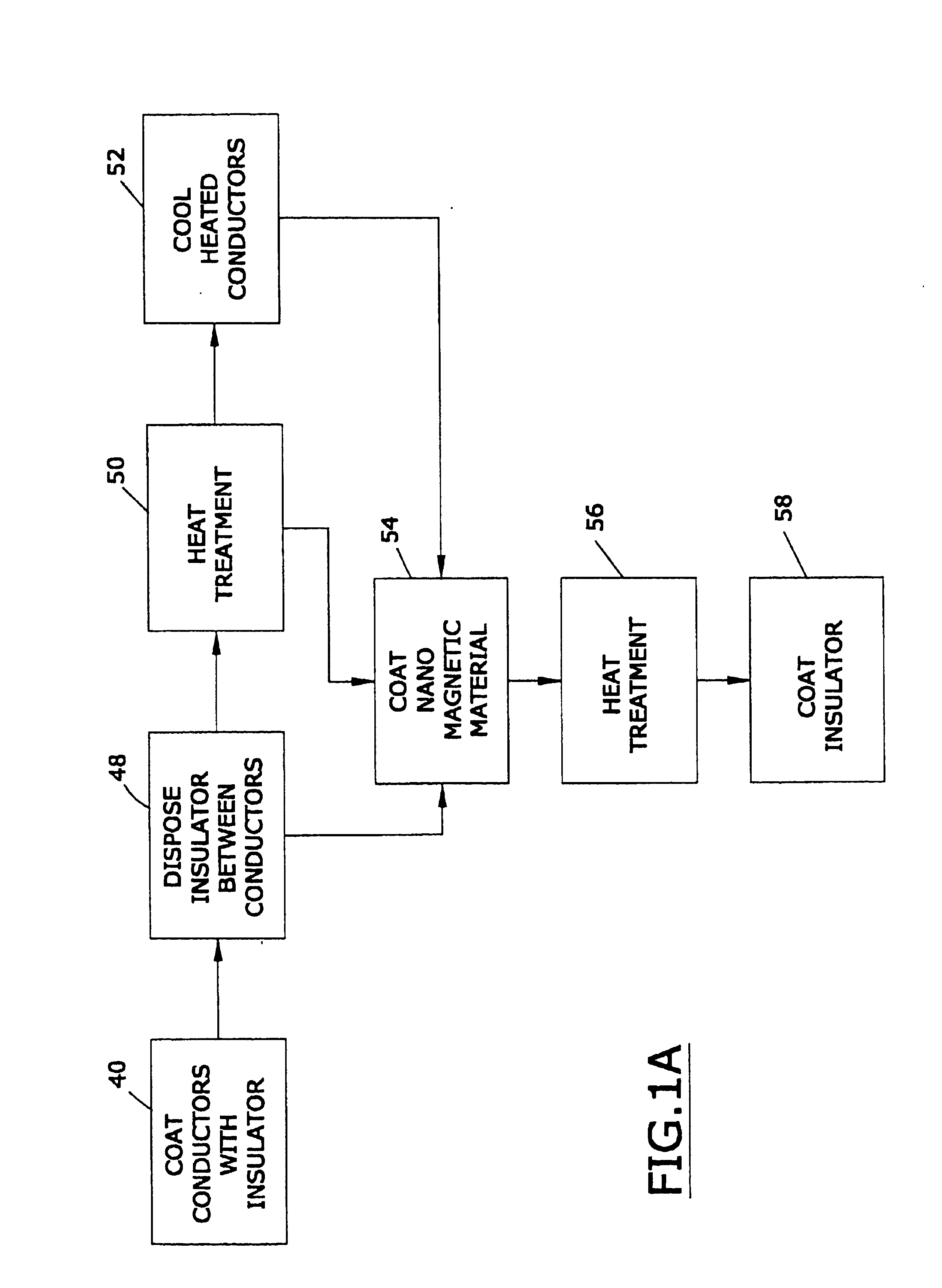
Magnetically shielded conductor
A magnetically shielded conductor assembly with a conductor device and a film of nanomagnetic material located above the conductor device. The conductor device has a resistivity of from about 1 to about 2,000 micro ohm-centimeters. The film of nanomagnetic material has a thickness of from about 100 nanometers to about 10 micrometers and a magnetic shielding factor of at least about 0.5. The nanomagnetic material has a mass density of at least about 0.01 grams per cubic centimeter, a saturation magnetization of from about 1 to about 36,000 Gauss, a coercive force of from about 0.01 to about 5,000 Oersteds, a relative magnetic permeability of from about 1 to about 500,000, and an average particle size of less than about 100 nanometers.
Owner:BIOPHAN TECH
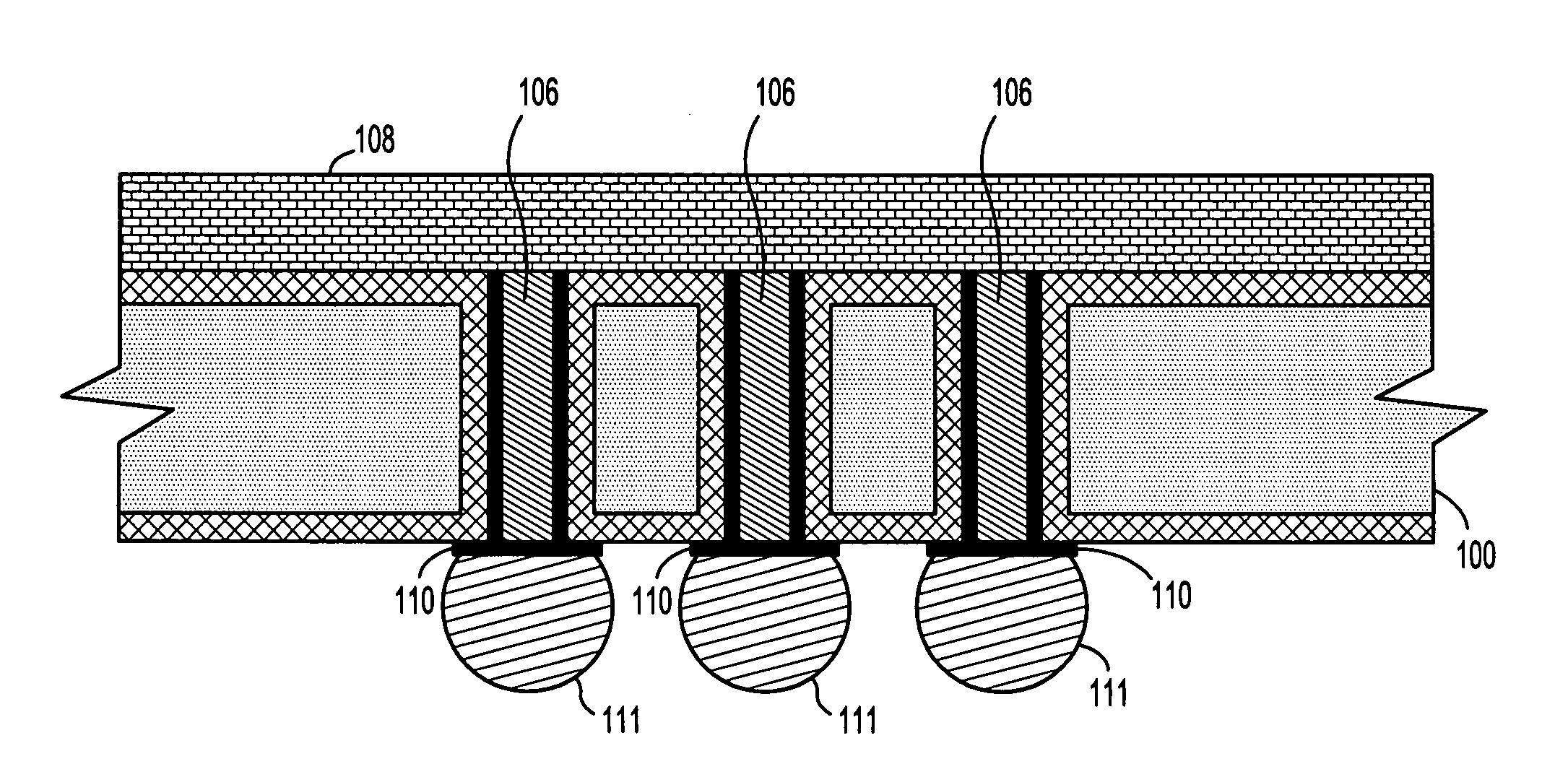
Methods for fabricating silicon carriers with conductive through-vias with low stress and low defect density
InactiveUS20080164573A1High-density packagingReduce stressSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorMicrometer
Methods are provided for fabricating silicon carriers with conductive through-vias that allow high-yield manufacture of silicon carrier with, low defect density. In particular, methods are provided which enable fabrication of silicon, carries with via diameters such as 1 to 10 microns in diameter for a vertical thickness of less than 10 micrometers to greater than 300 micrometers, which are capable robust to thermal-mechanical stresses during production to significantly minimize the thermal mechanical movement at the via sidewall interface between the silicon, insulator, liner and conductor materials.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Method and apparatus for dicing of thin and ultra thin semiconductor wafer using ultrafast pulse laser
InactiveUS7804043B2Minimize heating effectImprove machine qualityWelding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusPicosecond laserBeam polarization
The present invention relates to the apparatus, system and method for dicing of semiconductor wafers using an ultrafast laser pulse of femtosecond and picosecond pulse widths directly from the ultrafast laser oscillator without an amplifier. Thin and ultrathin semiconductor wafers below 250 micrometer thickness, are diced using diode pumped, solid state mode locked ultrafast laser pulses from oscillator without amplification. The invention disclosed has means to avoid / reduce the cumulative heating effect and to avoid machine quality degrading in multi shot ablation. Also the disclosed invention provides means to change the polarization state of the laser beam to reduce the focused spot size, and improve the machining efficiency and quality. The disclosed invention provides a cost effective and stable system for high volume manufacturing applications. An ultrafast laser oscillator can be a called as femtosecond laser oscillator or a picosecond laser oscillator depending on the pulse width of the laser beam generated.
Owner:LASERFACTURING
Piston ring
InactiveUS6325385B1Good sliding propertiesRelieve pressurePiston ringsBraking action transmissionCarbon filmDiamond-like carbon
Owner:TEIKOKU PISTON RING CO LTD
Compositions for abrasive articles
ActiveUS20050060947A1Attenuation consistentImprove cutting lifePigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesSurface finishMicrometer
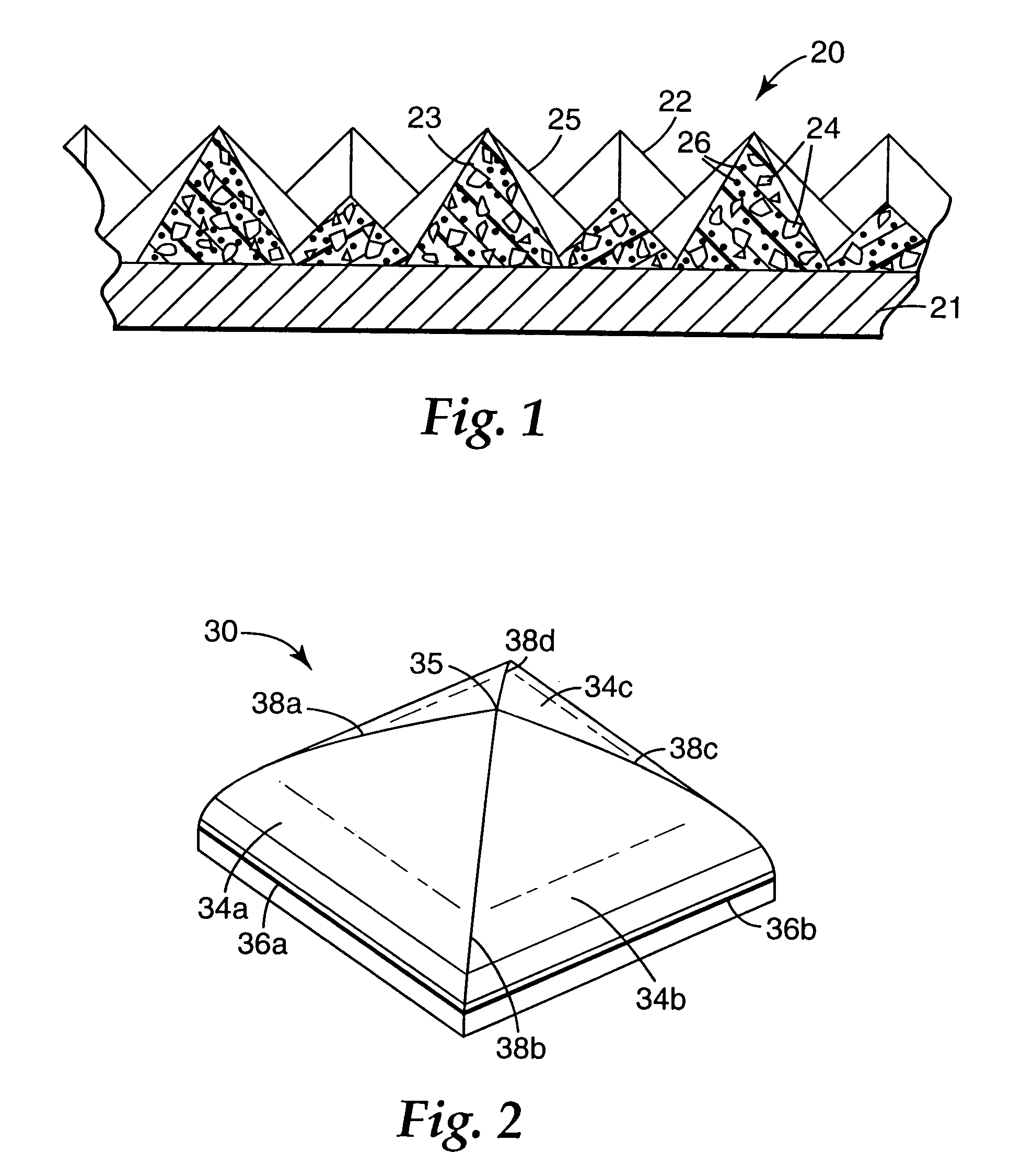
A structured abrasive article, methods of making an abrasive article, and methods of using an abrasive article. The abrasive composites forming the abrasive article have a height of at least 500 micrometers, and the abrasive particles in the composites have an average particle size of at least 40 micrometers, in some embodiments, at least about 85 micrometers. The large topography composites, together with the large ceramic abrasive particles, provides an abrasive article that has a more consistent cut, a longer cutting life, and a more consistent surface finish than conventional make / coat abrasive articles with the same size and type of abrasive particles. Additionally, the large topography composites, together with the large ceramic abrasive particles, provide an abrasive article that has a more consistent cut, a longer cutting life, and a more consistent surface finish than structured abrasive articles having a smaller topography, even with the same abrasive particles.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Magnetic recording medium
ActiveUS20180182422A1Excellent electromagnetic conversion propertyReduced track widthMaterials with ironRecord information storageMicrometerMagnetic layer
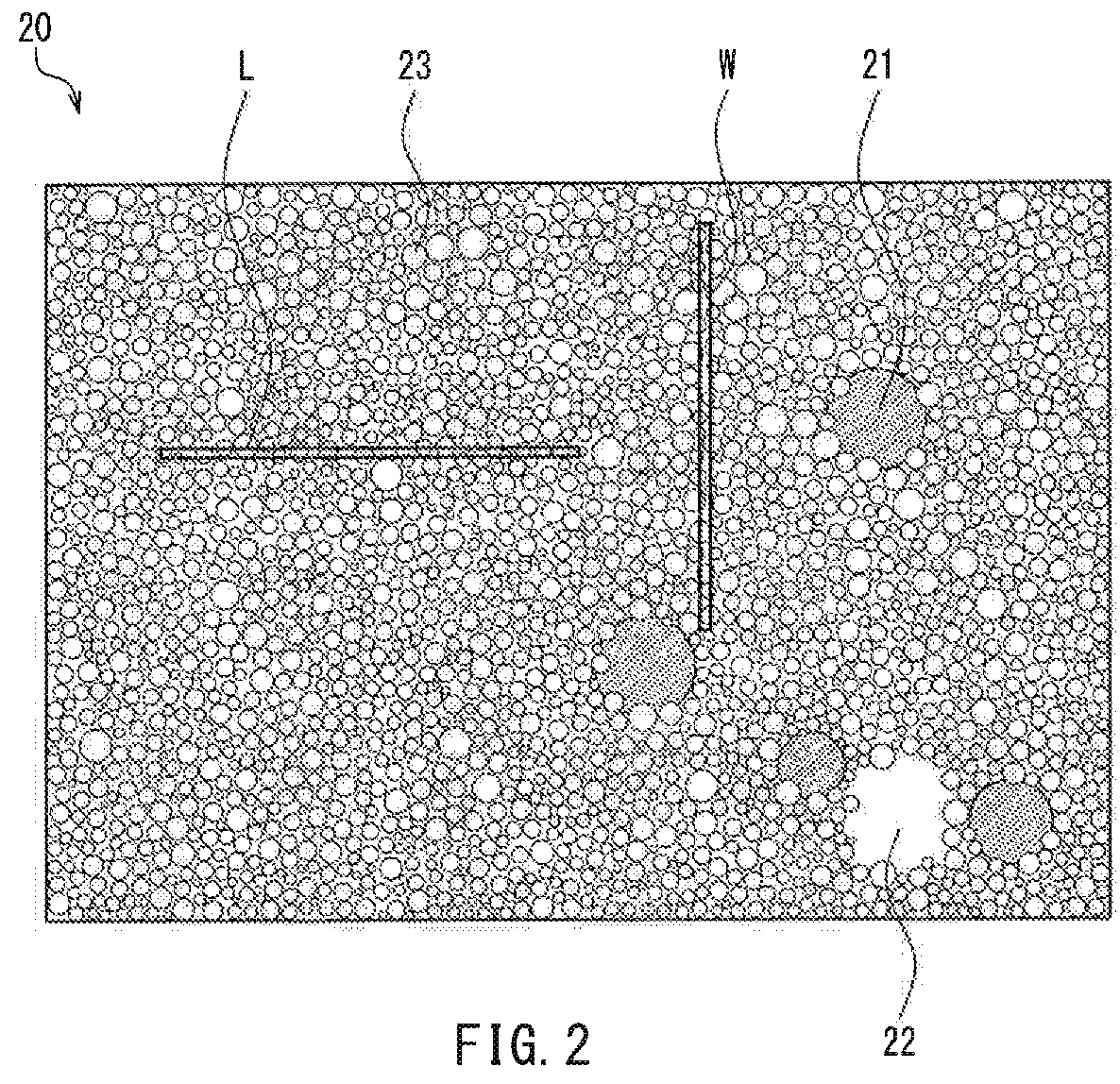
In a magnetic recording medium according to the present invention, if a straight line W having a length of 500 nm and a width of 15 nm is displayed parallel to a width direction of the magnetic layer and a straight line L having a length of 500 nm and a width of 15 nm is displayed parallel to a longitudinal direction of the magnetic layer, the number of magnetic particles that intersect the straight line W is N1, and the number of magnetic particles that intersect the straight line L is N2, then, a relationship of N1 / 0.5>60 and N2 / 0.5>60 is established where N1 / 0.5 is the number of magnetic particles per micrometer obtained by dividing N1 by 0.5 μm and N2 / 0.5 is the number of magnetic particles per micrometer obtained by dividing N2 by 0.5 μm.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
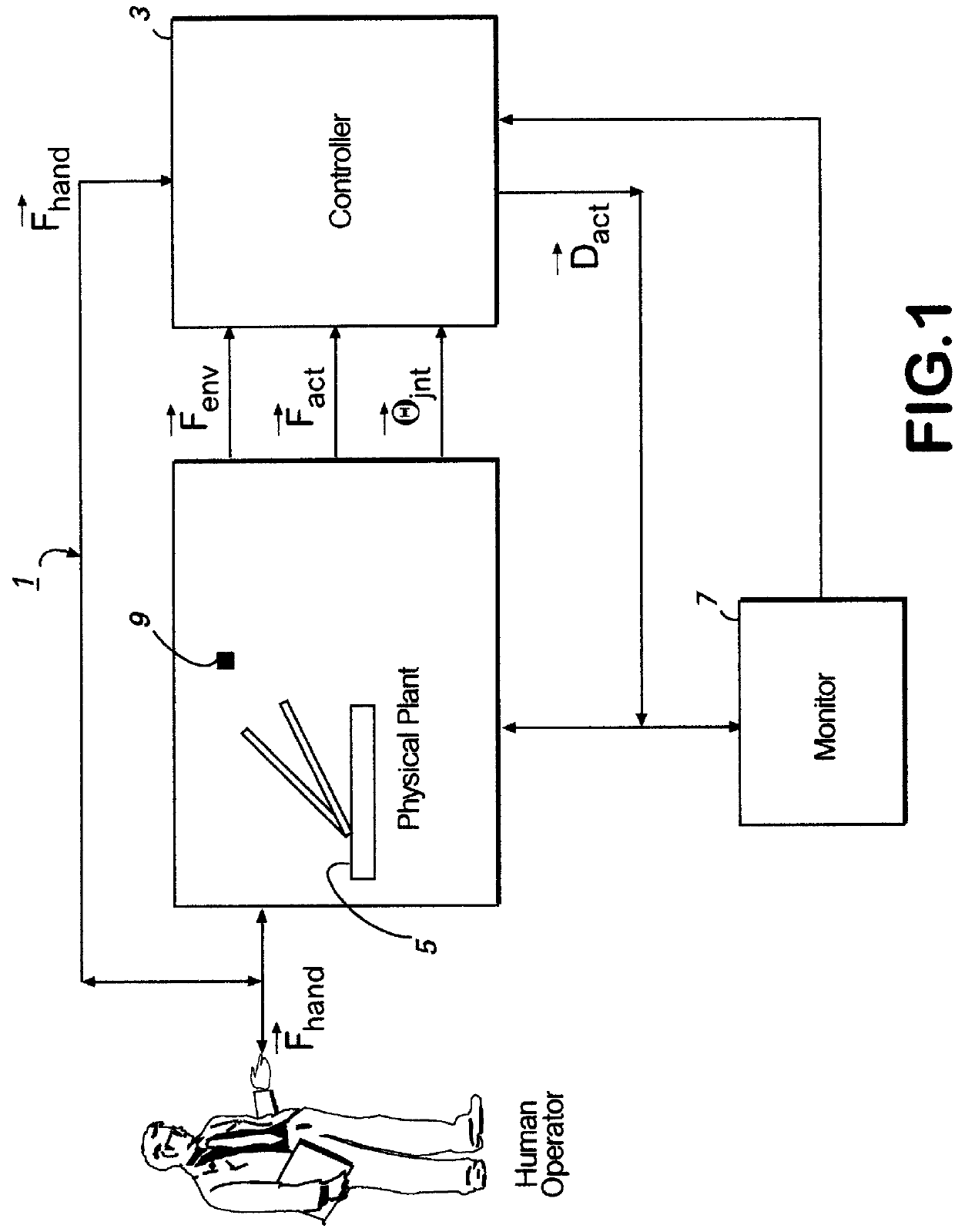
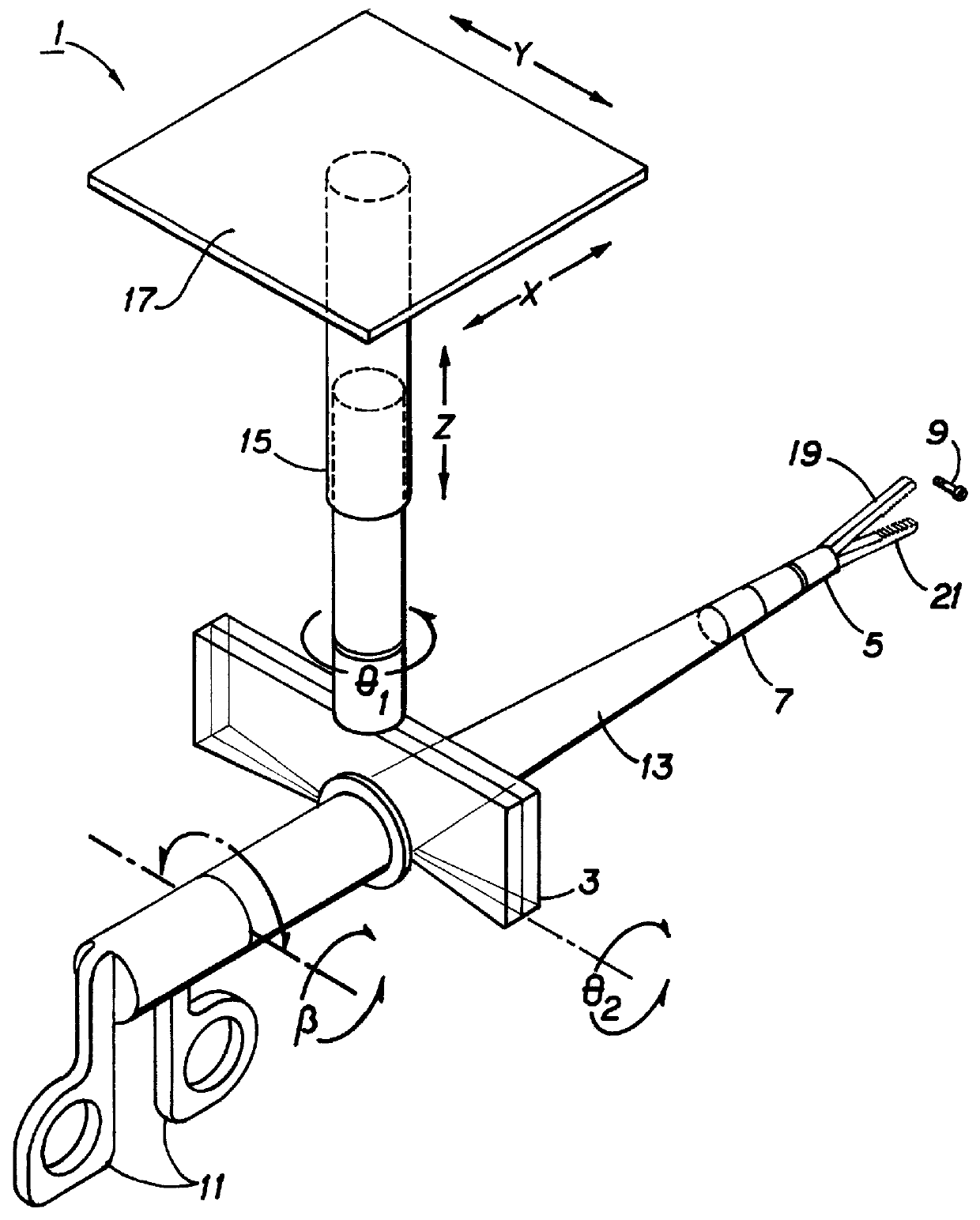
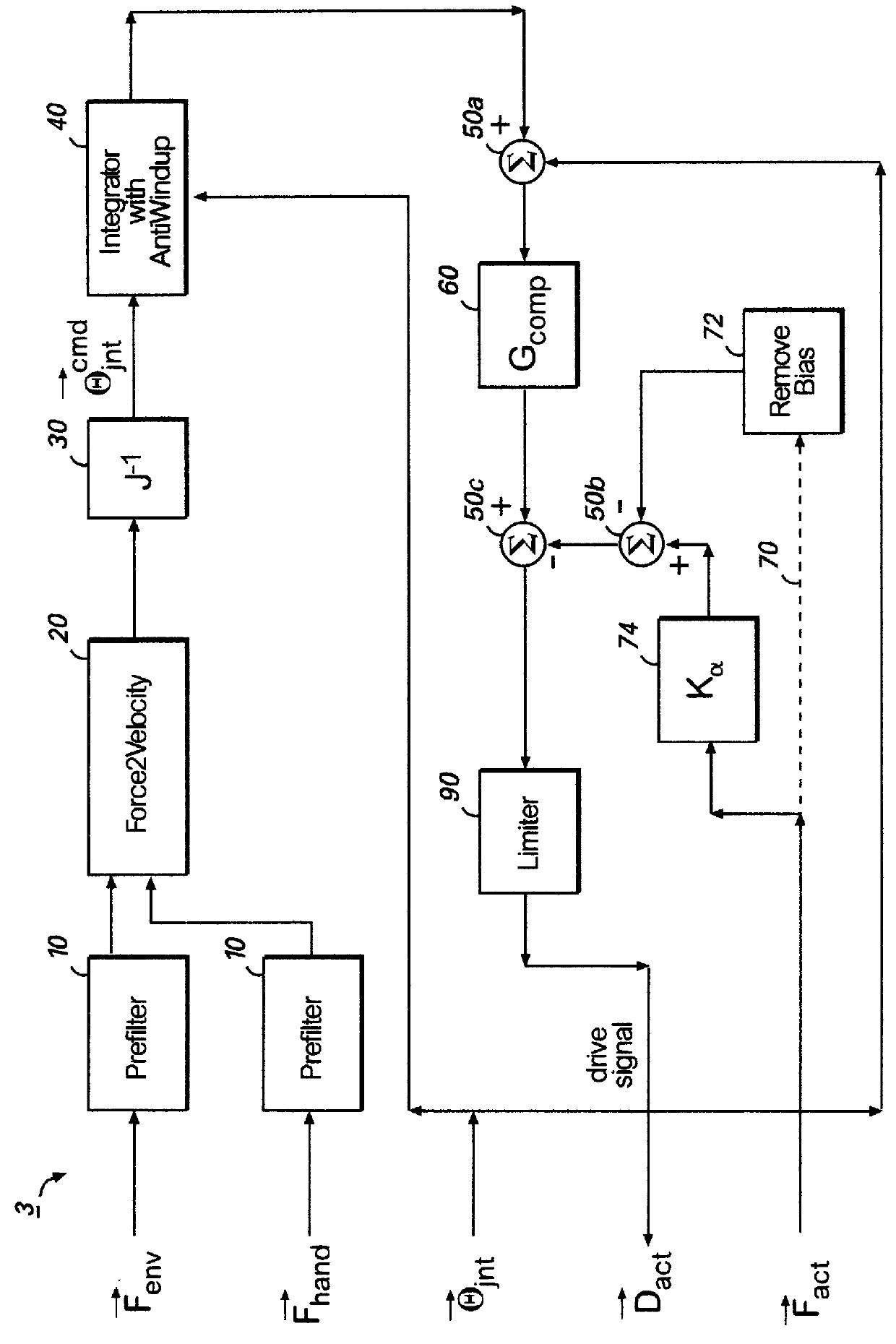
Apparatus and methods for a human de-amplifier system
InactiveUS6084371AProgramme-controlled manipulatorMicromanipulatorOperational systemAudio power amplifier
A human de-amplifier system for interfacing a human operator and a physical object through a physical plant, wherein the physical object has dimensions in the range of 1 micrometer to 1 mm. The human de-amplifier system uses an inner-feedback loop to increases the equivalent damping of the operating system to stabilize the system when it contacts with the environment and reduces the impact of the environment variation by utilizing a high feedback gain, determined by a root locus sketch. Because the stability of the human de-amplifier system of the present invention is greatly enhanced over that of the prior art, the de-amplifier system is able to manipulate the physical object has dimensions in the range of 1 micrometer to 1 mm with high stability and accuracy. The system also has a monitoring device to monitor the motion of the physical object under manipulation.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN ENERGY SYST INC
Protective acoustic cover assembly
A protective acoustic cover assembly including a metal foil with perforations, and a treatment on one or more surfaces of said metal foil. The treatment is a hydrophobic or oleophobic treatment, or both. The protective acoustic cover assembly has an average specific acoustic resistance of less than about 11 Rayls MKS from 250-300 Hz, an average specific acoustic reactance magnitude of less than about 1 Rayls MKS from 250-300 Hz, and an instantaneous water entry pressure value of greater than about 11 cm. The perforations of the metal foil preferably have an average maximum pore size of less than about 150 micrometers. The protective acoustic cover assembly further includes an adhesive mounting system, and the preferred metal foil is nickel.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS20070020490A1Excellent electromagnetic characteristic and error rate and durabilityImproved electromagnetic characteristic and error rate and durabilityBase layers for recording layersRecord information storageHigh densityMicrometer
Provided is a magnetic recording medium for high-density recording, that has excellent electromagnetic characteristics, error rates, and durability. The magnetic recording medium comprises a magnetic layer comprising a ferromagnetic powder, a binder and an abrasive on a nonmagnetic support and is employed for recording a magnetic signal on the medium and reproducing the recorded signal with a reproduction head. The abrasive has a Vickers hardness ranging from 18 to 80 GPa and a mean particle diameter ranging from 10 to 100 nm. The magnetic layer comprises the abrasive in a quantity of 5 to 60 weight parts per 100 weight parts of the ferromagnetic powder and has a thickness ranging from 10 to 100 nm. The number of abrasive present on the surface of the magnetic layer ranges from 0.01 to 1 per {(minimum bit length of the recorded signal)×(read track width of the reproduction head)} micrometer2.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Electrical discharge catheter system for extracting emboli in endovascular interventions
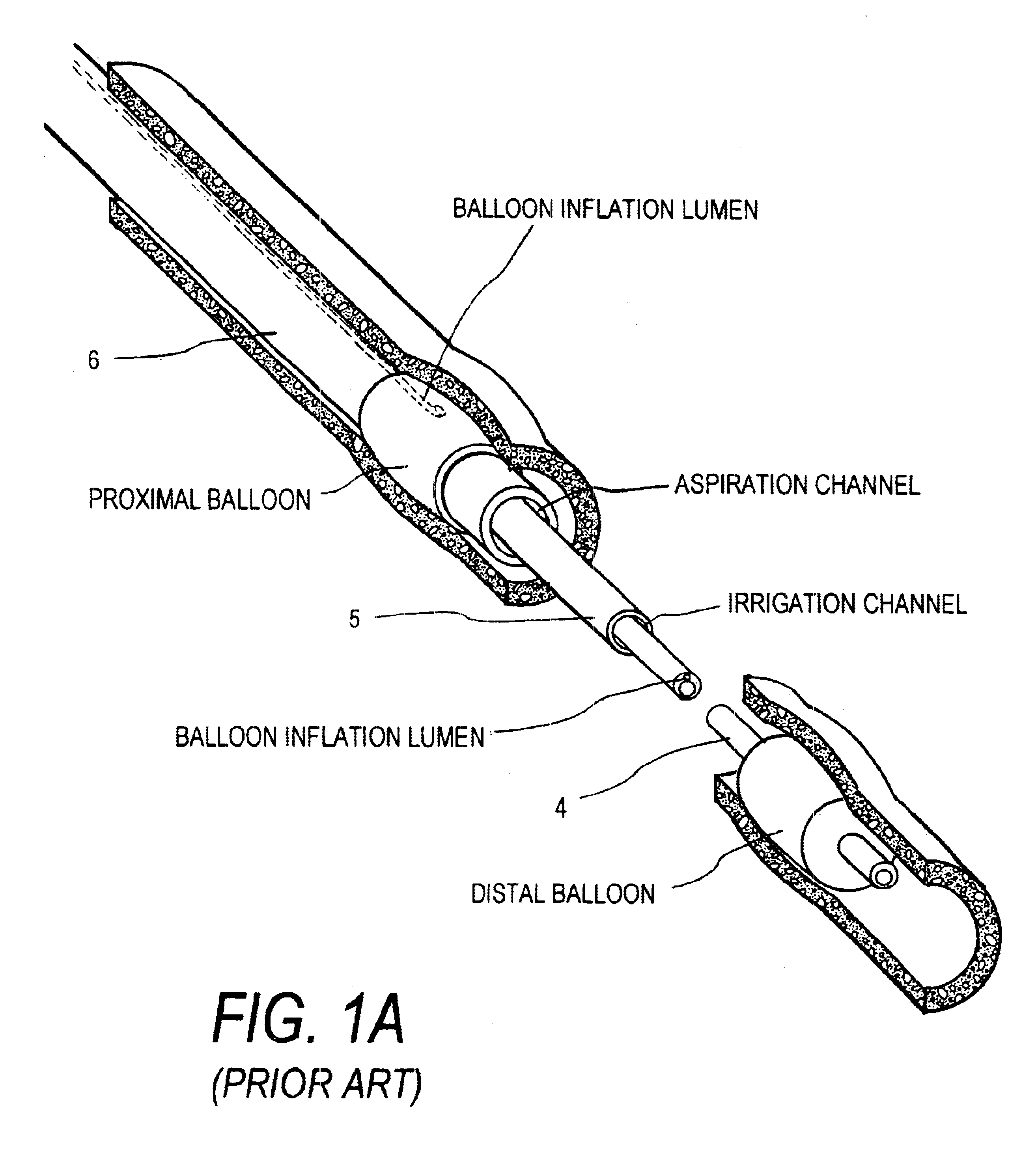
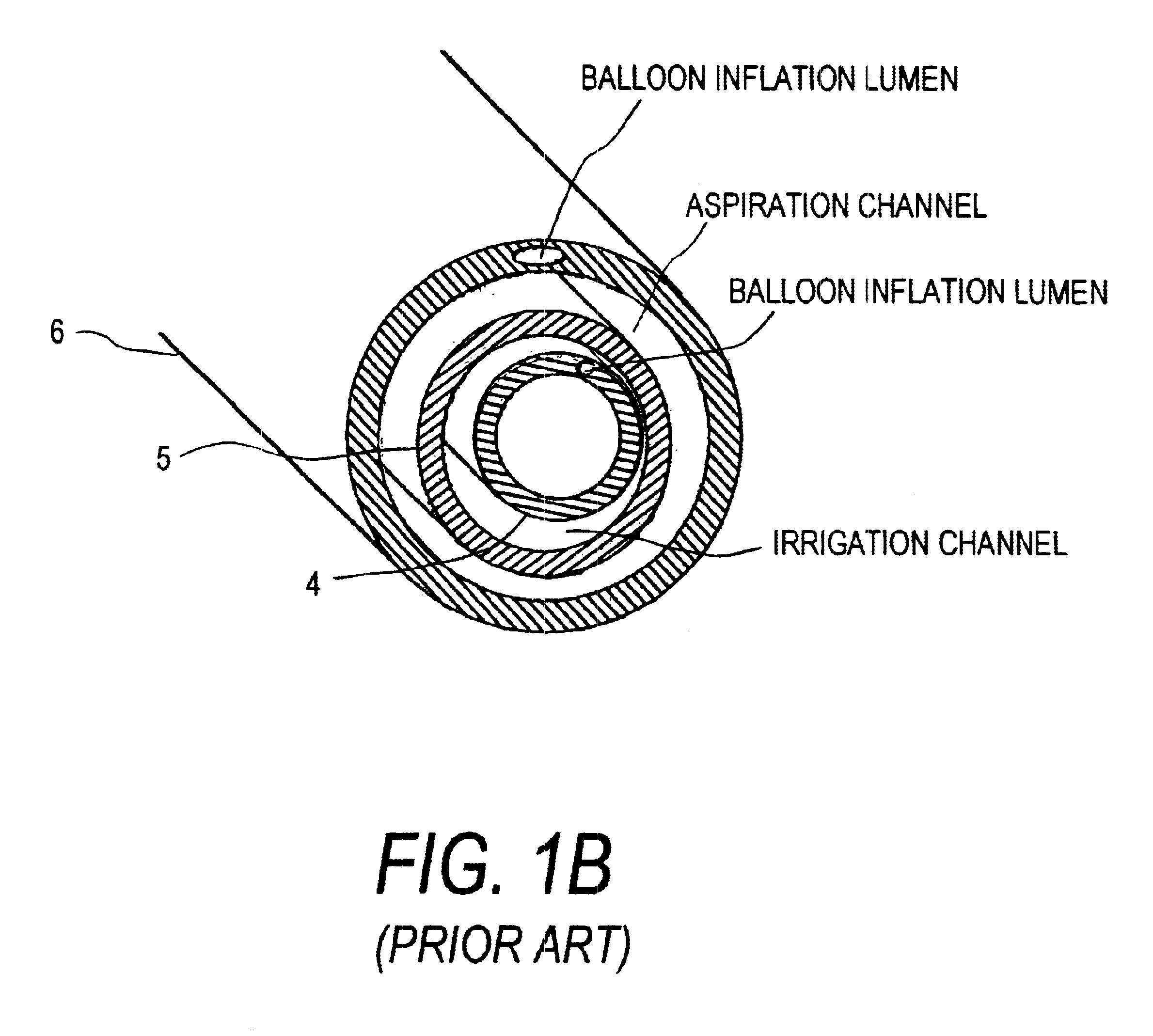
InactiveUS6679879B2Surgical instrument detailsFluid jet surgical cuttersMicrometerEndovascular interventions
A catheter system for removing occlusive materials from a targeted endoluminal site, such as a vascular graft. The catheter system utilizes an electrical source and a controller to deliver sequences of very small electrical discharges between paired electrodes in a fluid-jet arrangement (i) to cause high fluid flow velocities in the catheter's fluid extraction pathway based on Bernoulli's Law of Pressure Differential, (ii) to create a selected level of turbulent fluid flows within the targeted site to remove occlusive material from the vessel walls and to thereafter suction fluids and entrained embolic particles into the extraction pathway, and (iii) to emulsify any embolic particles having a cross-sectional dimension larger than a couple of hundred micrometers to allows passage of the embolic particles through the elongate catheter to the catheter handle.
Owner:SHADDUCK JOHN H
Perforated film clothing
InactiveUS8815057B2Improve stabilityHigh strengthLayered productsMachine wet endMicrometerEngineering
A fabric for a papermaking machine is configured as a belt, the two side edges of which are configured in each case as closed lines. Furthermore, the belt is formed in one layer from a solid material and has pores which form passages between the two surfaces of the belt. The belt has regions with a width of approximately 400 micrometers (μm) or less. These regions extend in the longitudinal direction over the entire circumference of the belt, transversely with respect to the side edges, and include no pores formed therein.
Owner:VOITH PATENT GMBH
Plasma treatment of porous materials
InactiveUS6878419B2Improve wettabilityEfficient processingSemi-permeable membranesLayered productsCapacitanceMicrometer
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS20060187589A1High reproductive outputHigh outputRecord information storageManufacture of flux-sensitive headsMetallurgyMicrometer
Provided is a magnetic recording medium capable of achieving high reproduction output in a short wavelength region. The magnetic recording medium comprises a nonmagnetic layer comprising a nonmagnetic powder and a binder and a magnetic layer comprising a ferromagnetic powder and a binder in this order on a nonmagnetic support. The magnetic layer has a squareness ranging from 0.6 to 1.0 in a perpendicular direction, and the magnetic recording medium is employed for recording a magnetic signal on the medium in a longitudinal direction at a linear recording density of equal to or greater than 300 Kbpi using a recording head with a gap length of equal to or less than 0.3 micrometer, and reproducing the magnetic signal using a magnetoresistive head with a shield spacing of equal to or less than 0.2 micrometer.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com