Patents
Literature
6171 results about "Facula" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A facula /ˈfækjʊlə/ (plural: faculae /ˈfækjʊliː/), Latin for "little torch", is literally a "bright spot". The term has several common technical uses. It is used in planetary nomenclature for naming certain surface features of planets and moons, and is also a type of surface phenomenon on the Sun. In addition, a bright region in the projected field of a light source is sometimes referred to as a facula, and photographers often use the term to describe bright, typically circular features in photographs that correspond to light sources or bright reflections in a defocused image.
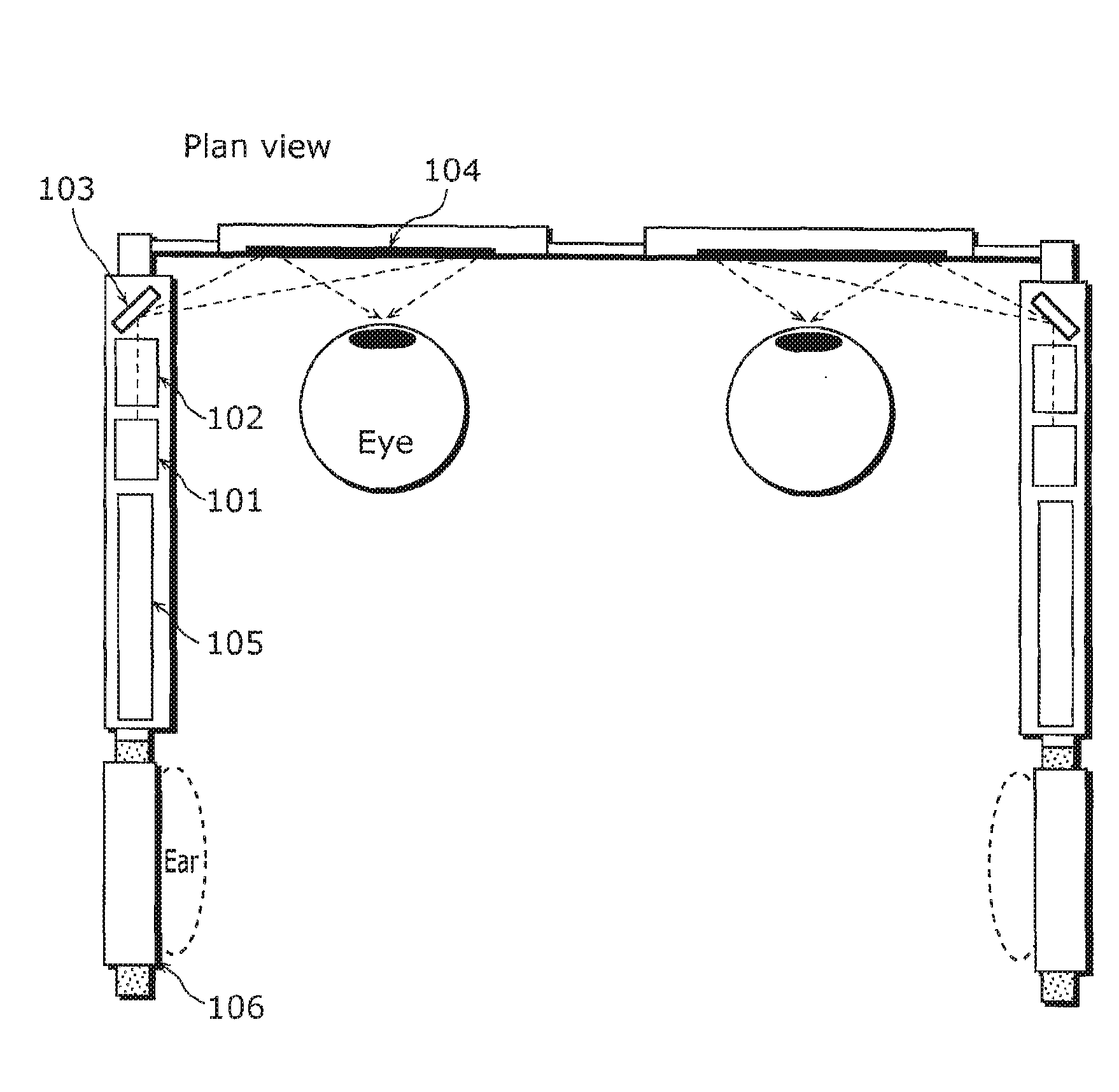
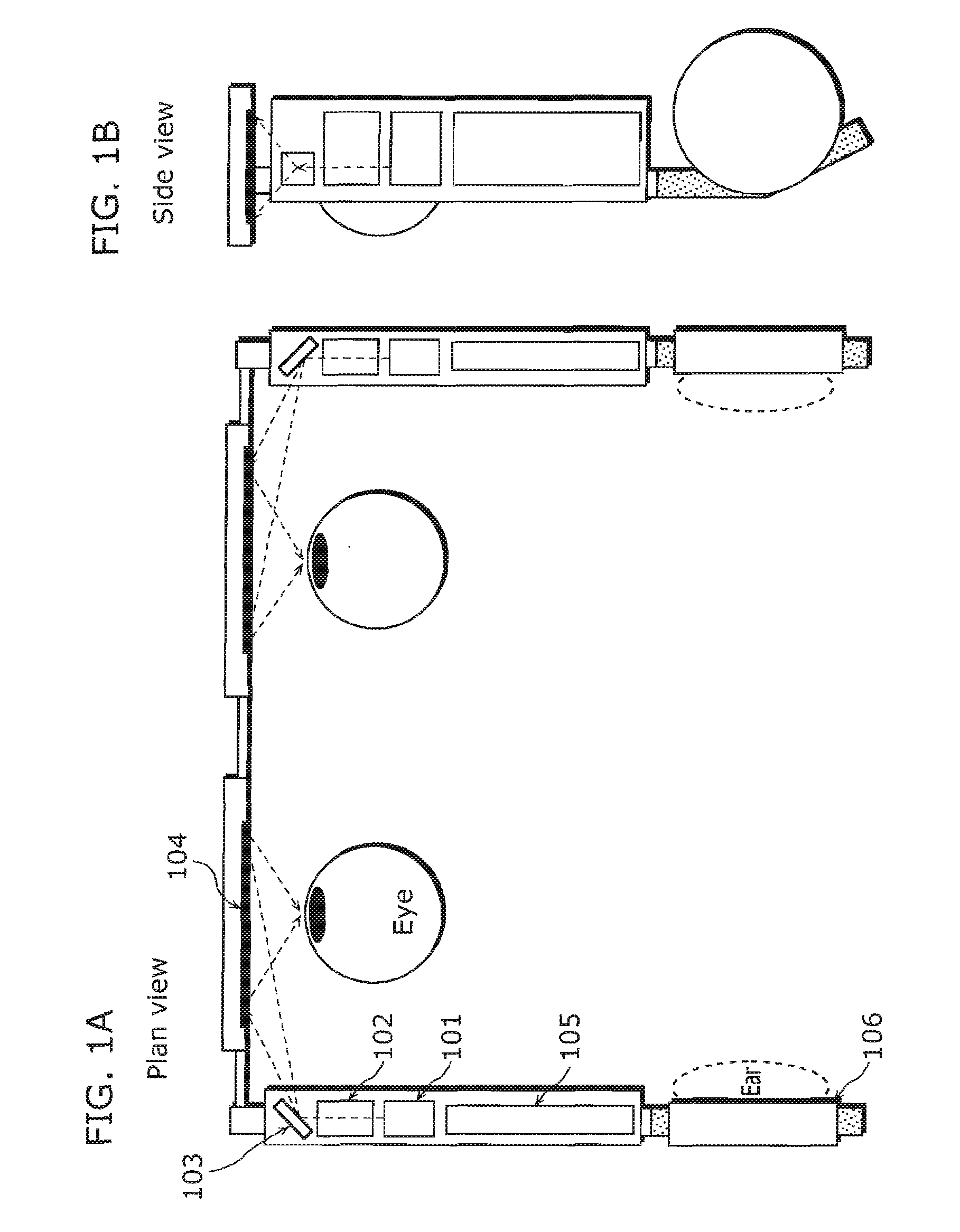
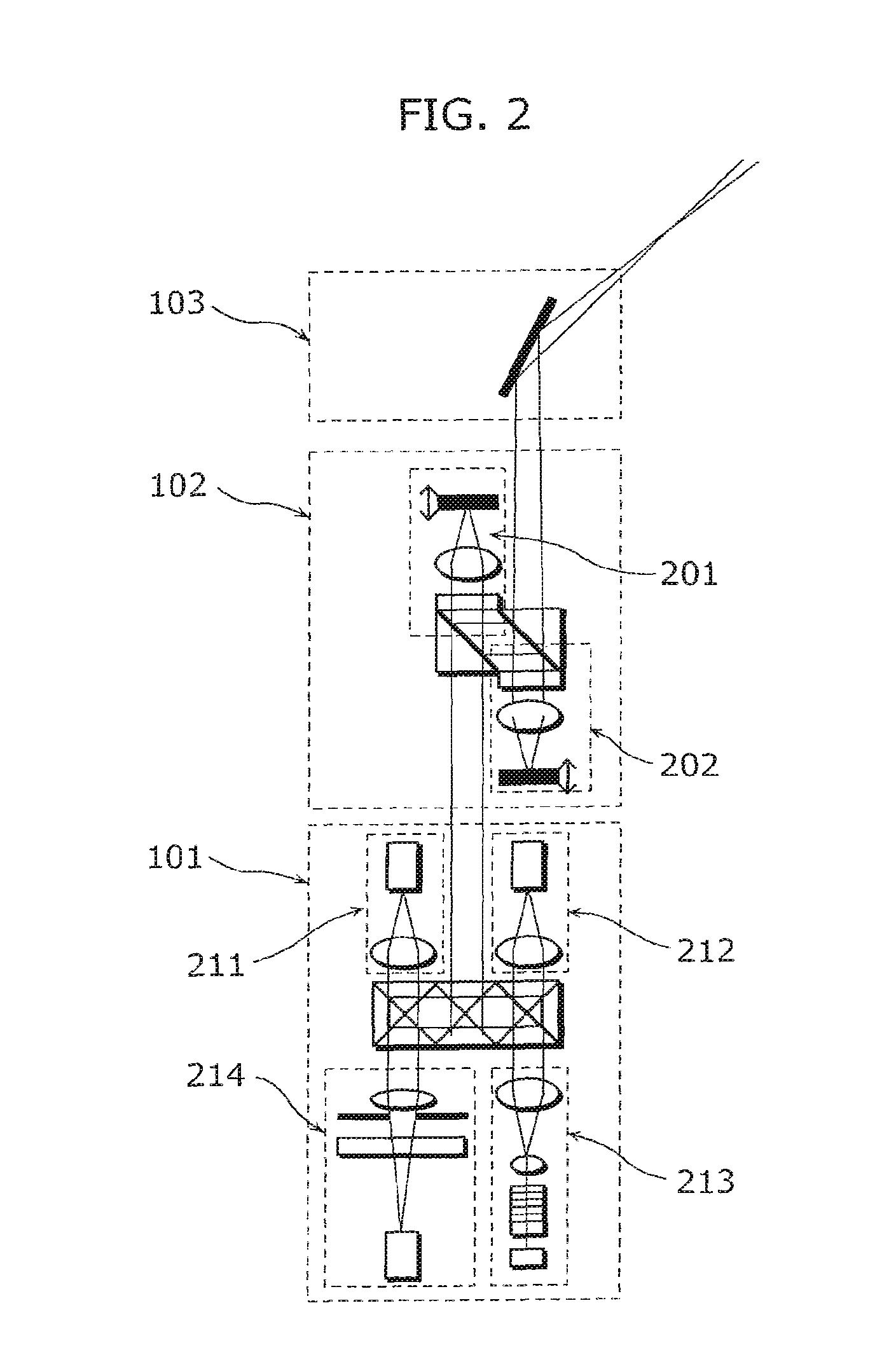
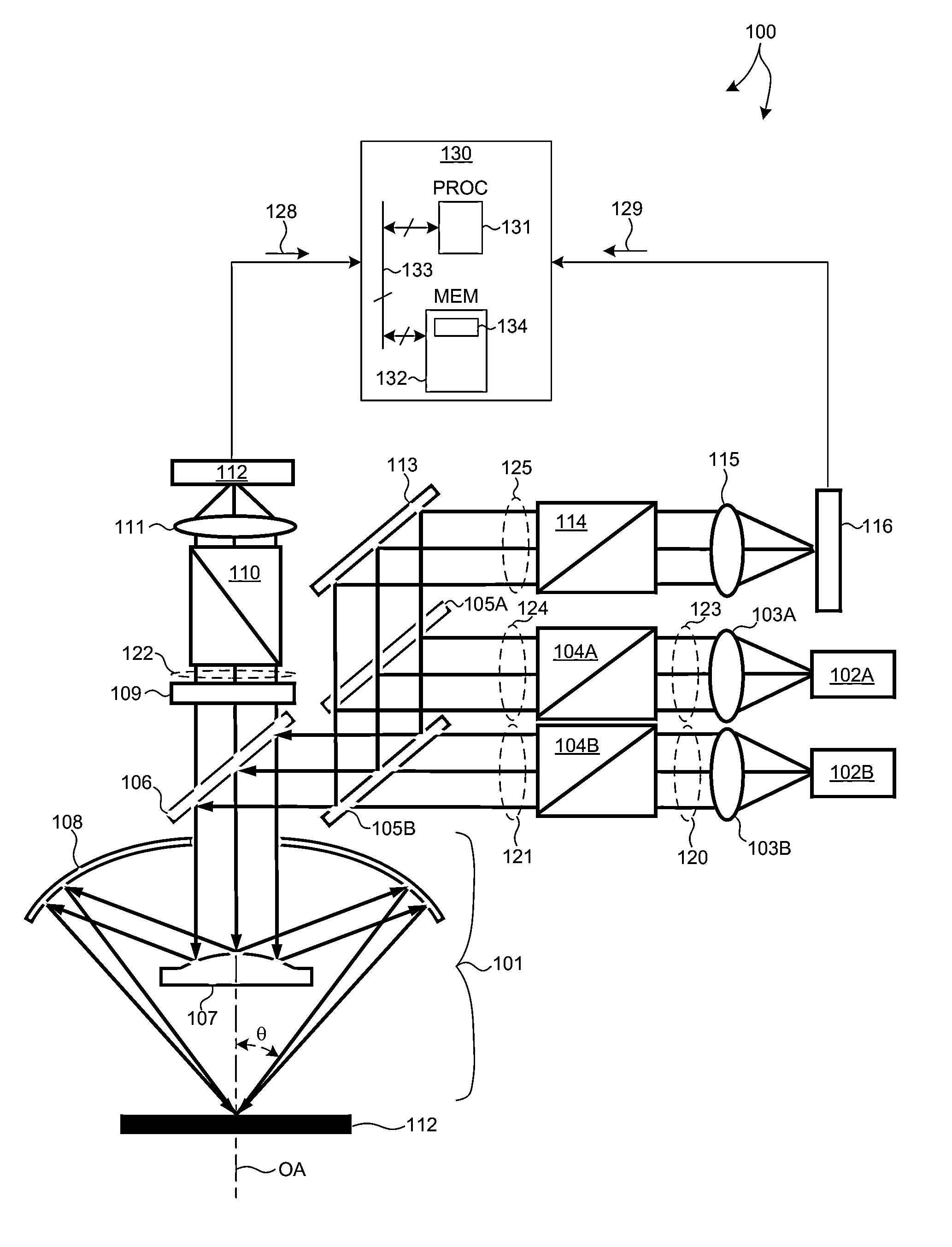
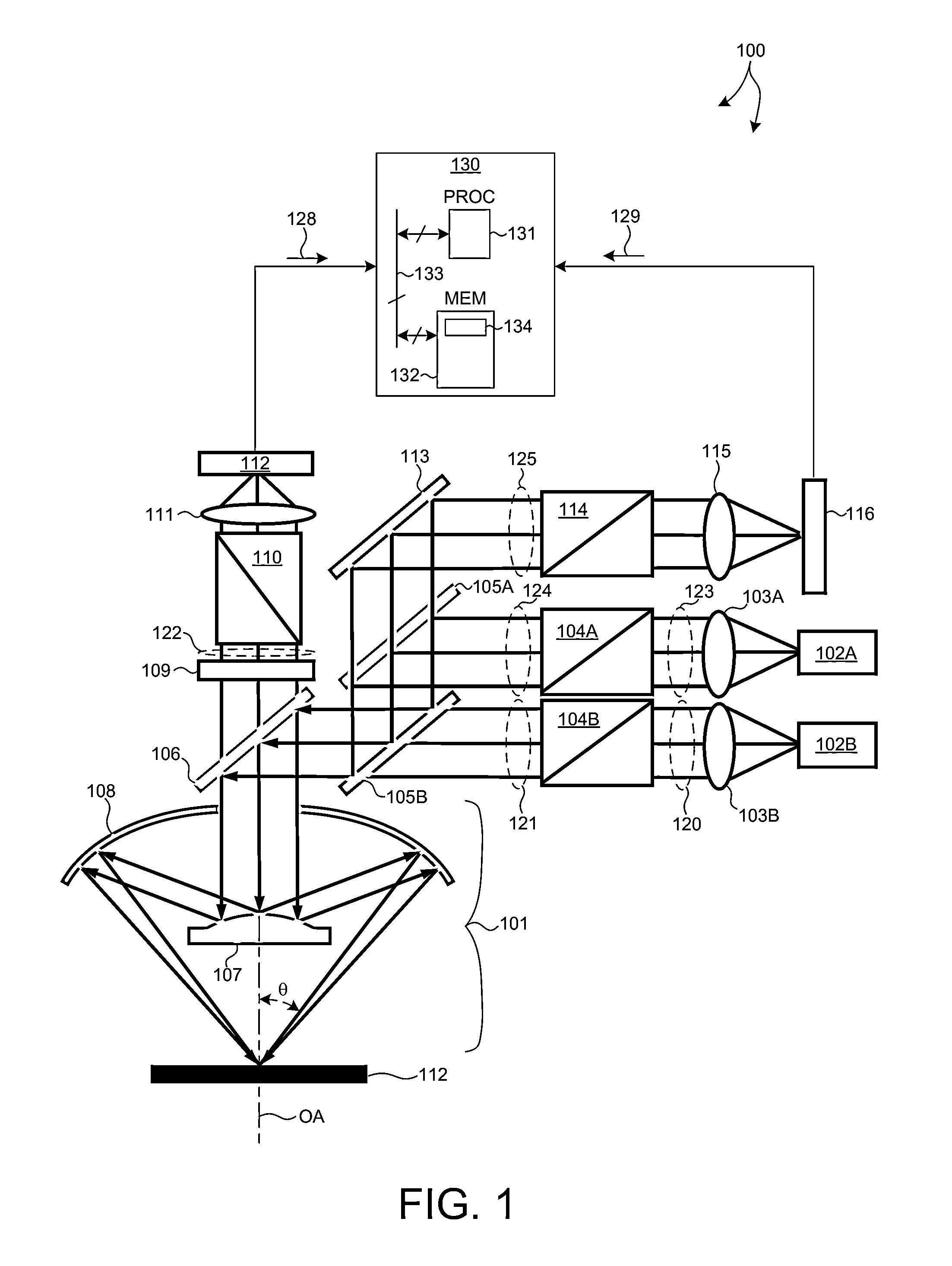
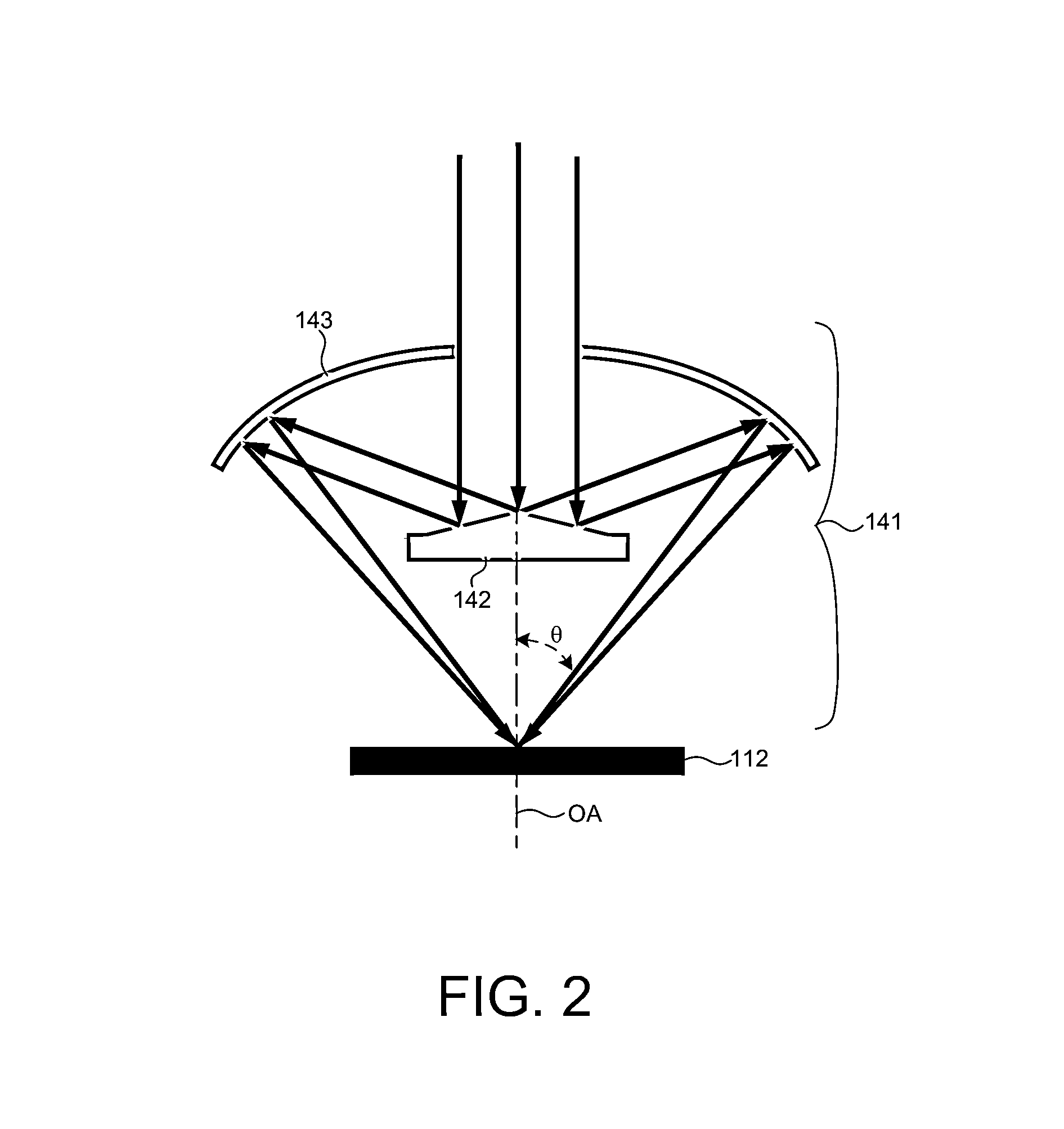
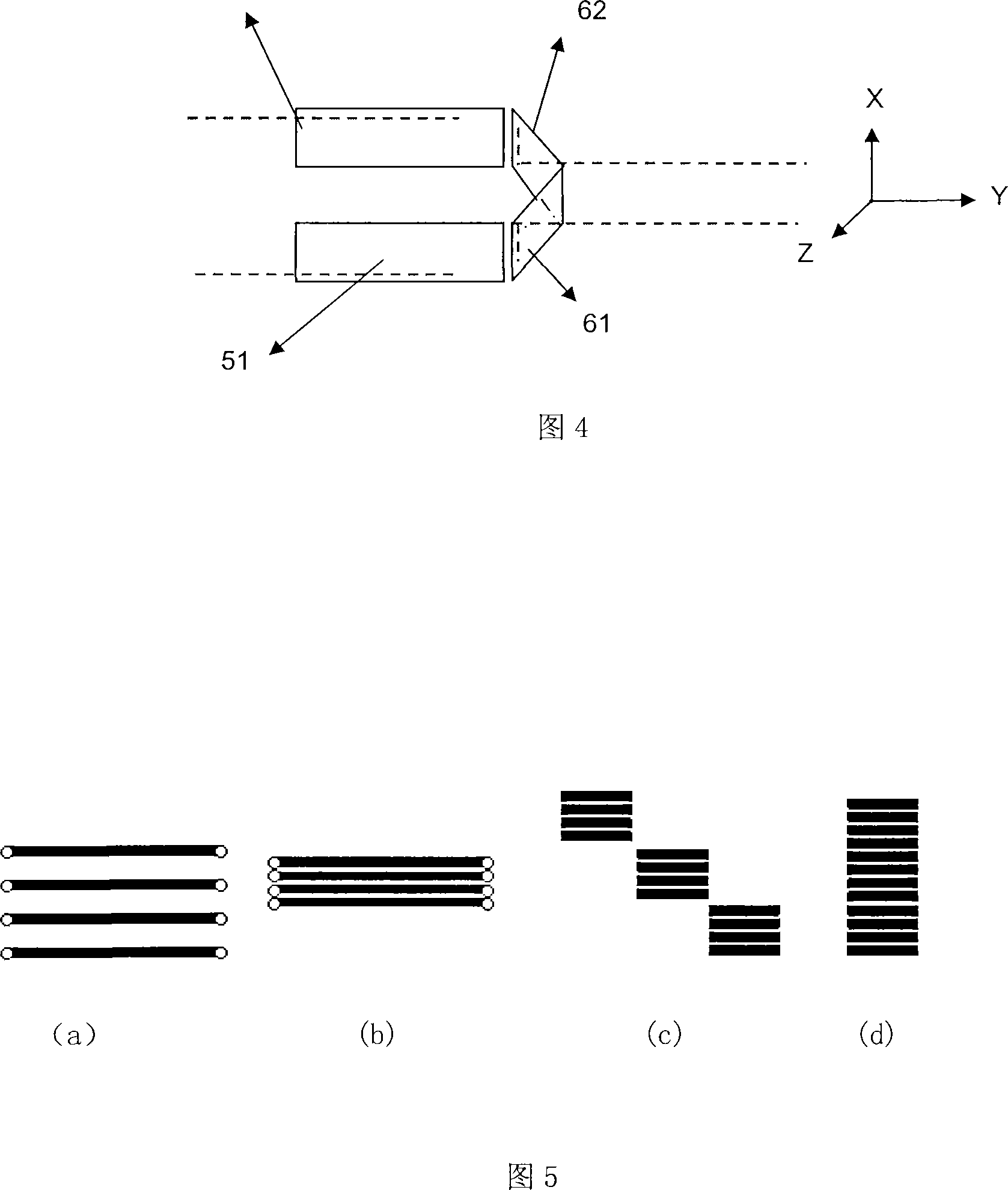
Beam scanning-type display device, method, program and integrated circuit
InactiveUS20100060551A1Change in shapeReduce image qualityTelevision system detailsProjectorsPhysicsHead worn display
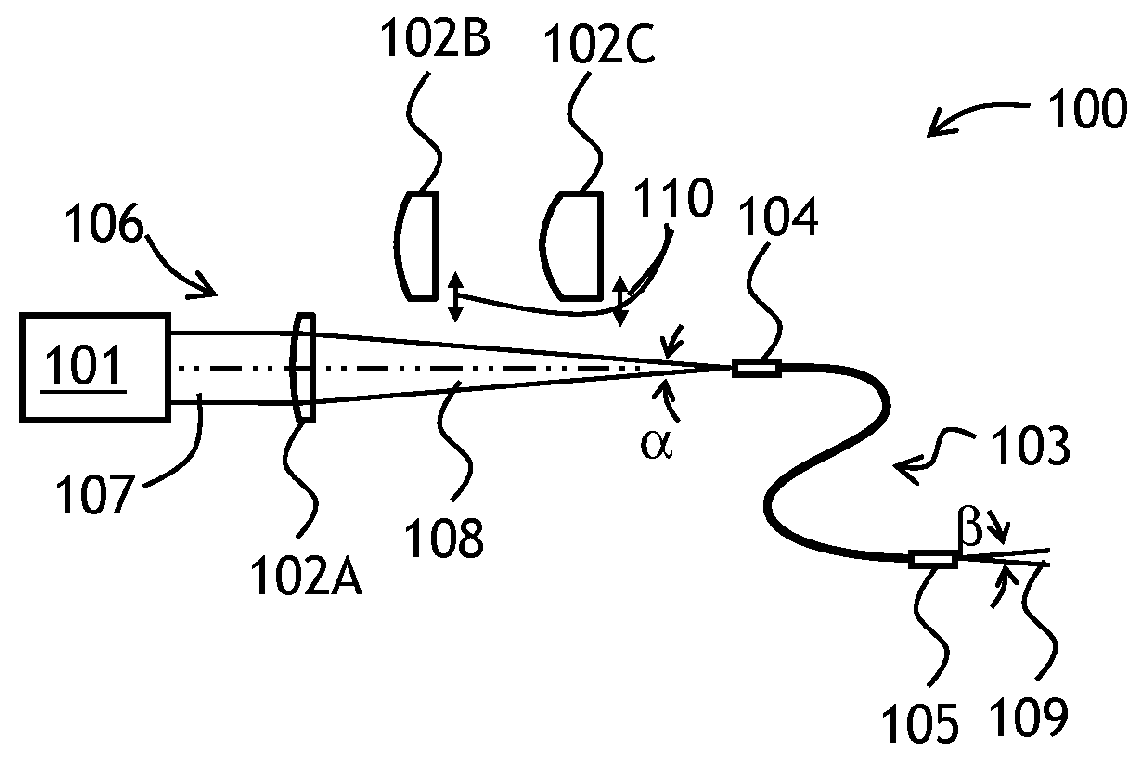
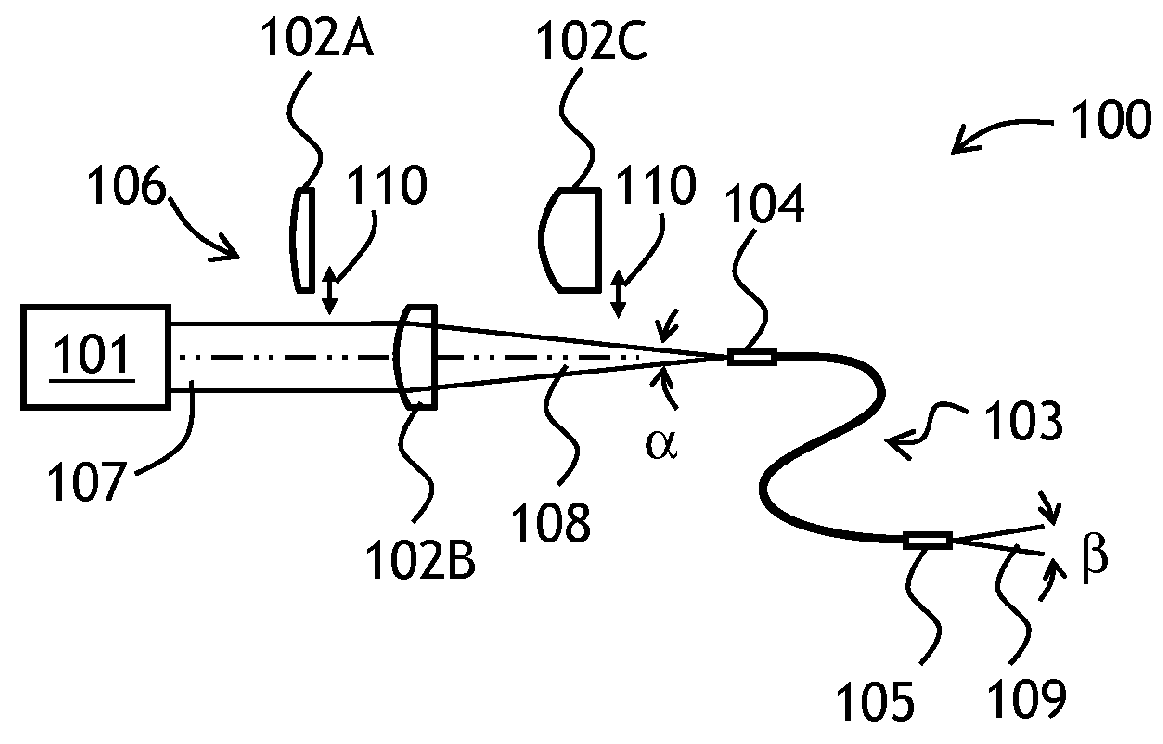
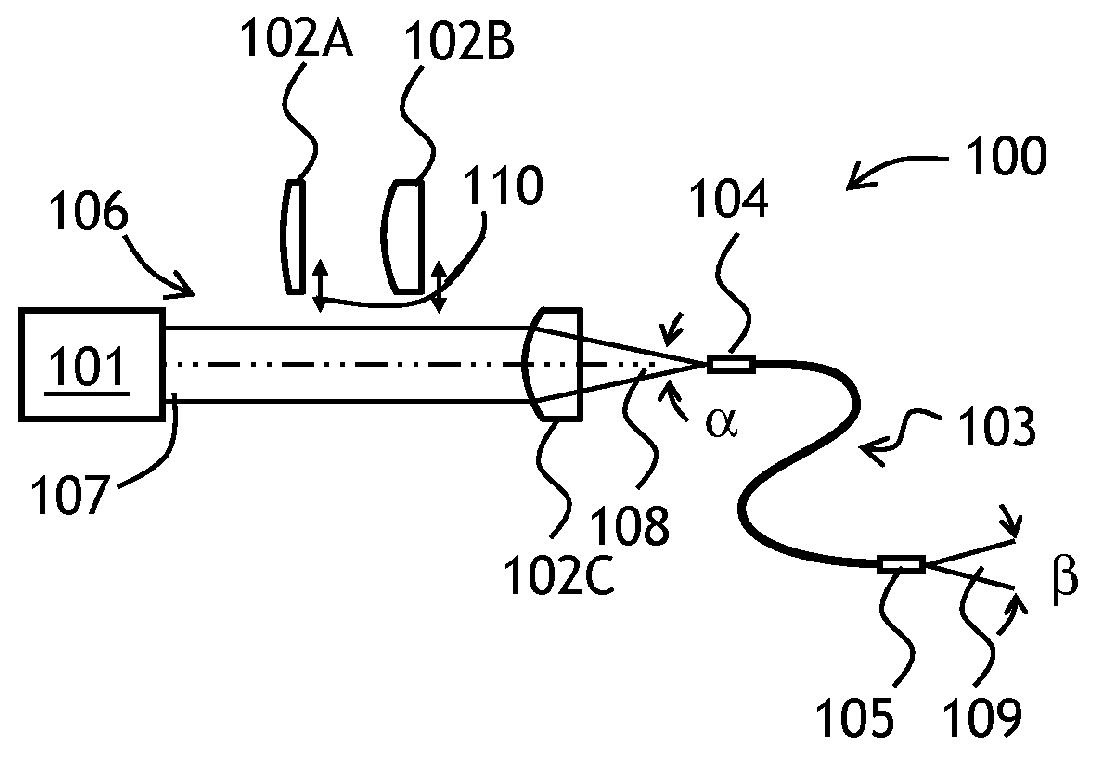
A beam scanning-type display device used as a head-mounted display (HMD) or a head-up display (HUD) includes a light source (101) which emits a beam, a scanning unit (103) which performs scanning using the beam emitted from the light source (101), a deflecting unit (104) which deflects the beam used for the scanning by the scanning unit (103) in the direction toward an eye of a user, and a wavefront shape changing unit (102) which changes the wavefront shape of the beam from the light source (101) so that the beam spot size falls within the predetermined allowable range, and emits the beam to the wavefront shape changing unit (102).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Laparoscopic Laser Device and Method
InactiveUS20070185474A1Reduce heatProtect from preventable damageLaser detailsEndoscopesMedicineVaporization
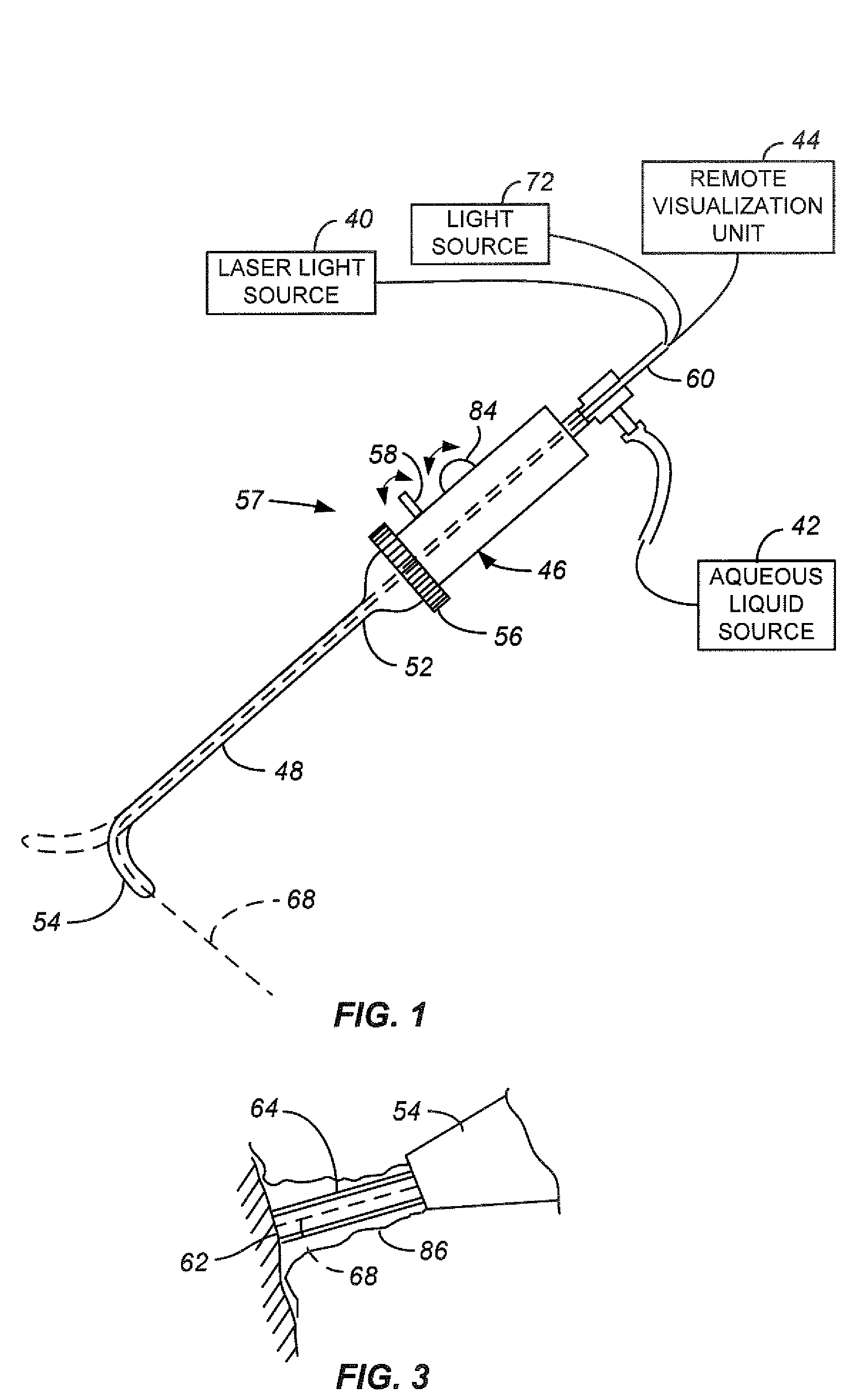
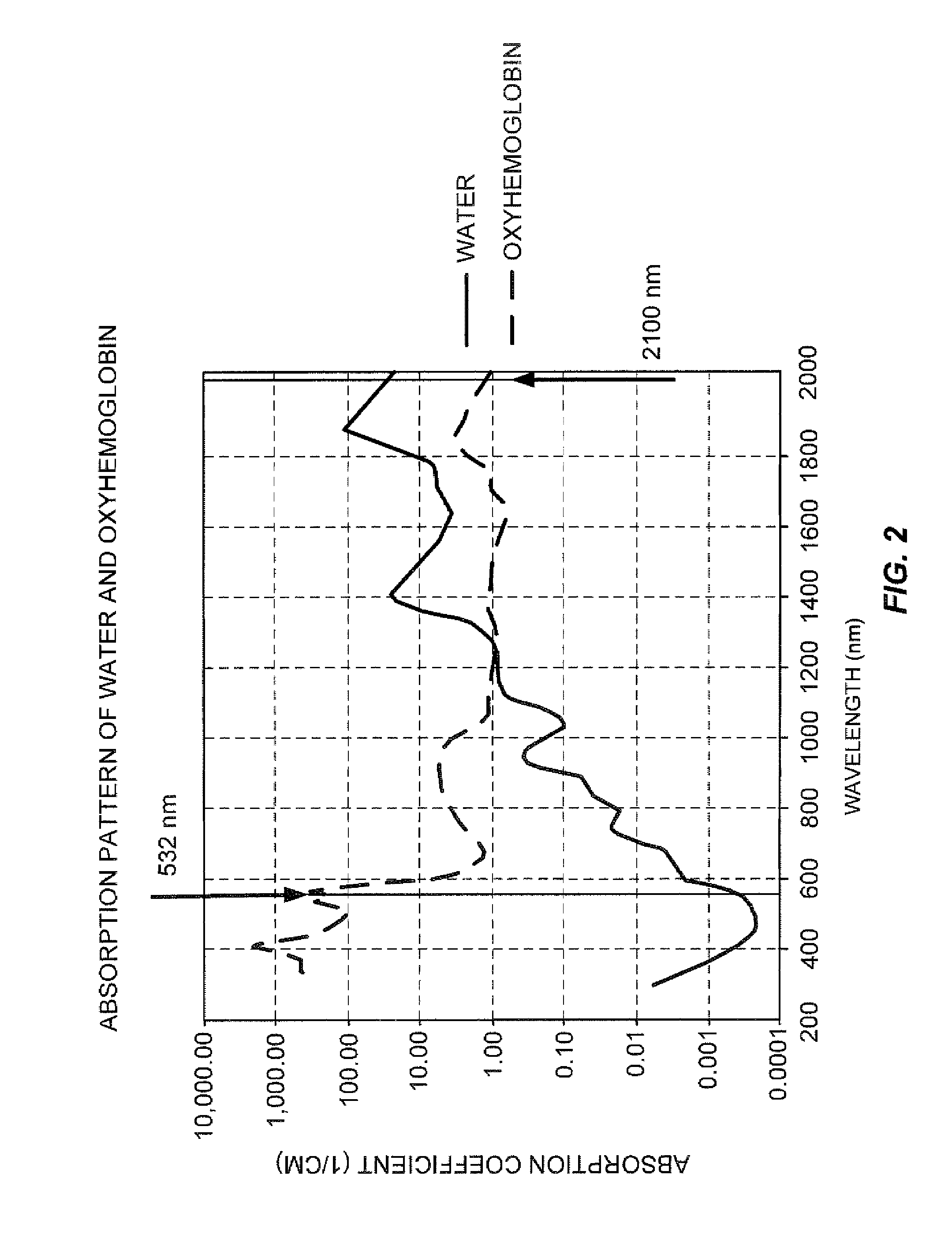
Laser radiation delivered to a treatment area causes vaporization of a substantially greater volume of tissue than the volume of residual coagulated tissue. The laser radiation may have a wavelength of about 300 nm to about 700 nm, may be used with a smoke suppressing irrigant, may have an average irradiance greater than about 5 kilowatts / cm2, and may have a spot size of at least 0.05 mm2. A laparoscopic laser device, for use with an insufflated bodily cavity, may include an elongate body adapted for insertion into an insufflated bodily cavity. A laser energy delivery element, at the distal end of the elongate body, may be coupleable to a source of tissue-vaporization-capable laser energy and capable of delivering laser energy along a laser energy path extending away from the laser energy delivery element. A smoke-suppressing liquid pathway, extending along the elongate body to an exit opening at the distal end, may be coupleable to a source of a smoke-suppressing liquid. The smoke-suppressing liquid is directed generally along the laser energy path. A remote visualization device may be used to view along the laser energy path.
Owner:AMS RES CORP
Method and apparatus for dicing of thin and ultra thin semiconductor wafer using ultrafast pulse laser
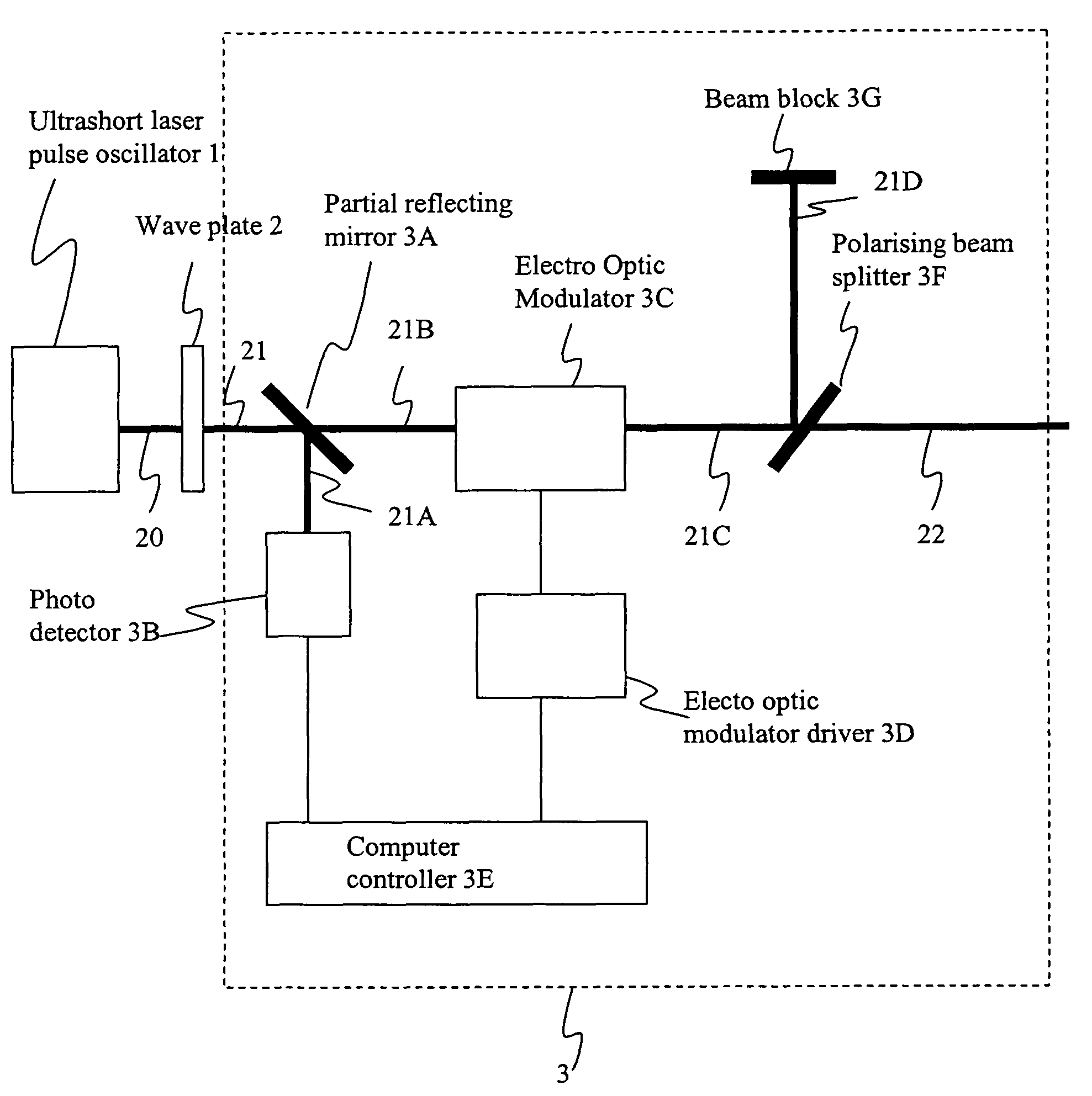
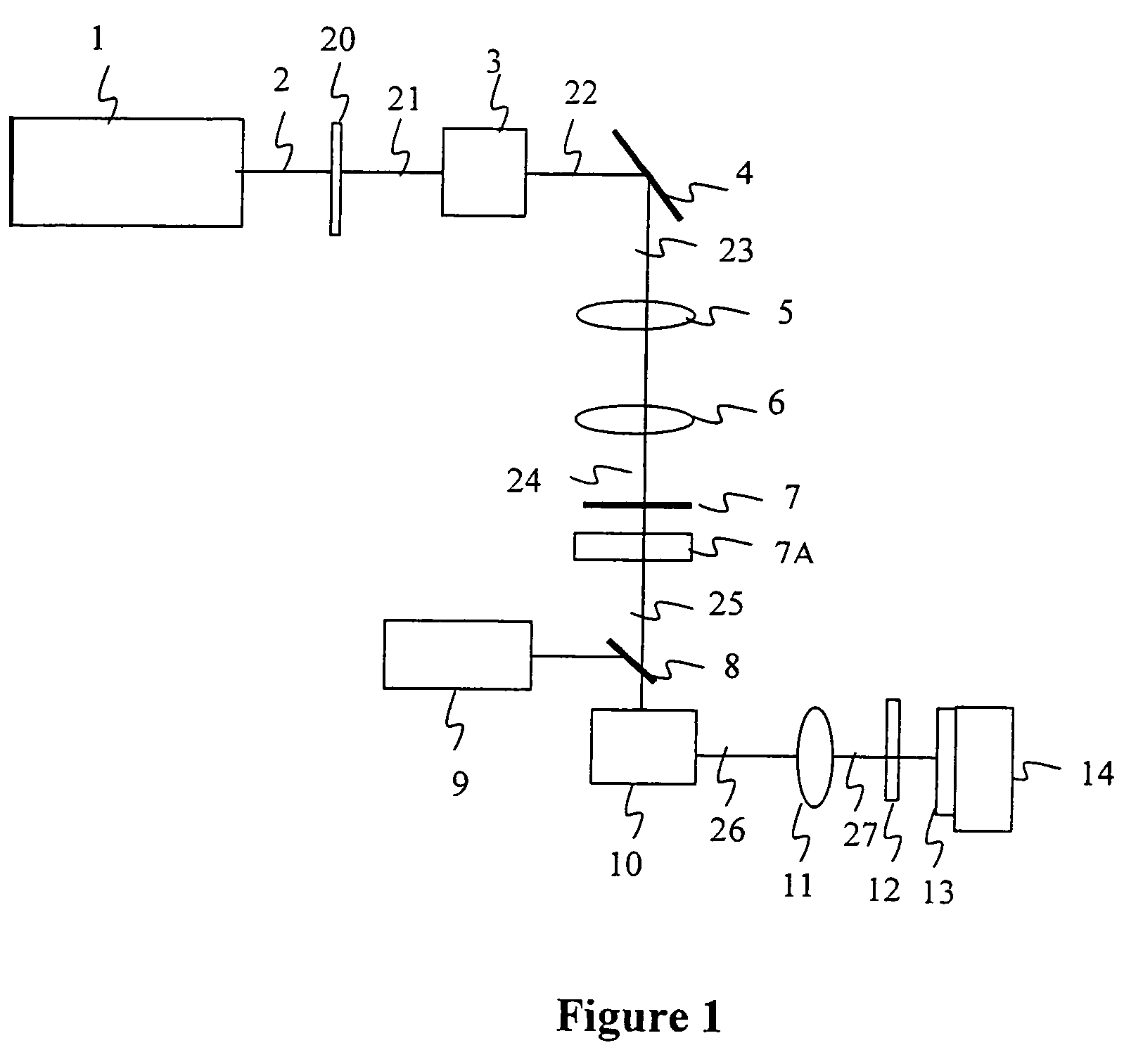
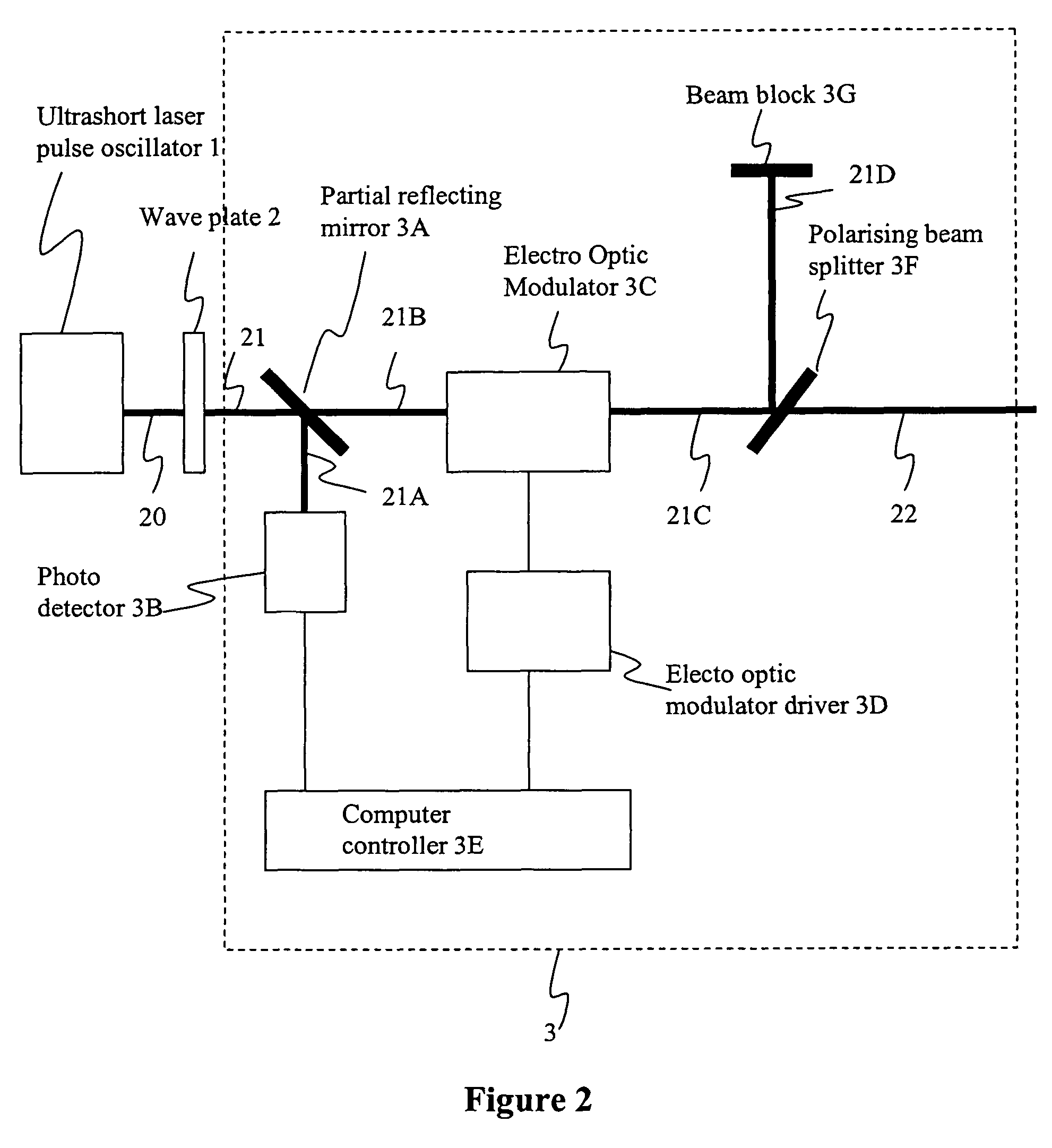
InactiveUS20050274702A1Improve inner wall qualityImprove surface qualityWelding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusPicosecond laserFacula
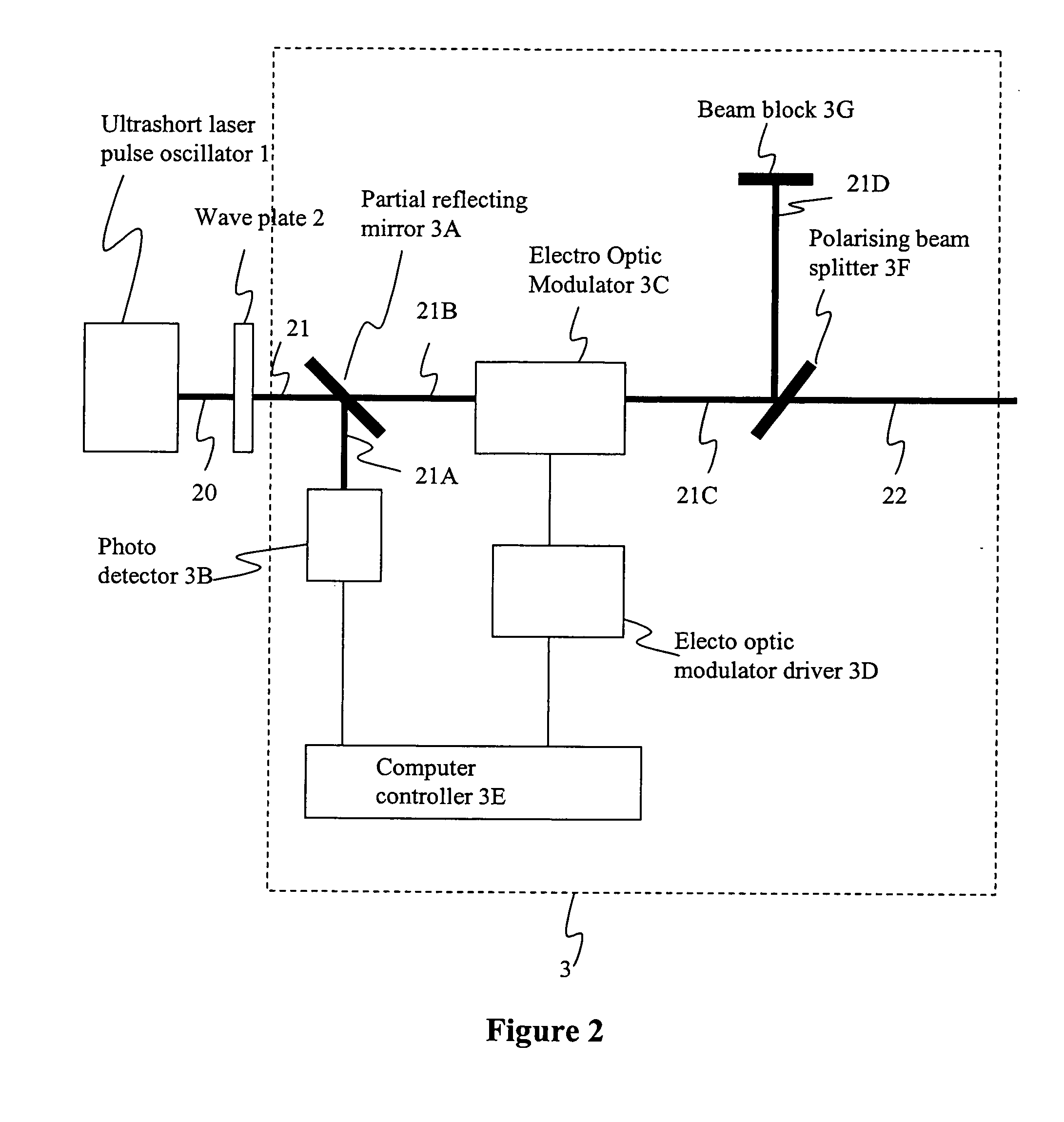
The present invention relates to the apparatus, system and method for dicing of semiconductor wafers using an ultrafast laser pulse of femtosecond and picosecond pulse widths directly from the ultrafast laser oscillator without an amplifier. Thin and ultrathin simiconductor wafers below 250 micrometer thickness, are diced using diode pumped, solid state mode locked ultrafast laser pulses from oscillator without amplification. The invention disclosed has means to avoid / reduce the cumulative heating effect and to avoid machine quality degrading in multi shot ablation. Also the disclosed invention provides means to change the polarization state of the laser beam to reduce the focused spot size, and improve the machining efficiency and quality. The disclosed invention provides a cost effective and stable system for high volume manufacturing applications. An ultrafast laser oscillator can be a called as femtosecond laser oscillator or a picosecond laser oscillator depending on the pulse width of the laser beam generated.
Owner:LASERFACTURING
Headlight, taillight and streetlight detection
ActiveUS7566851B2Photometry using reference valueVehicle headlampsLane departure warning systemEgo motion estimation
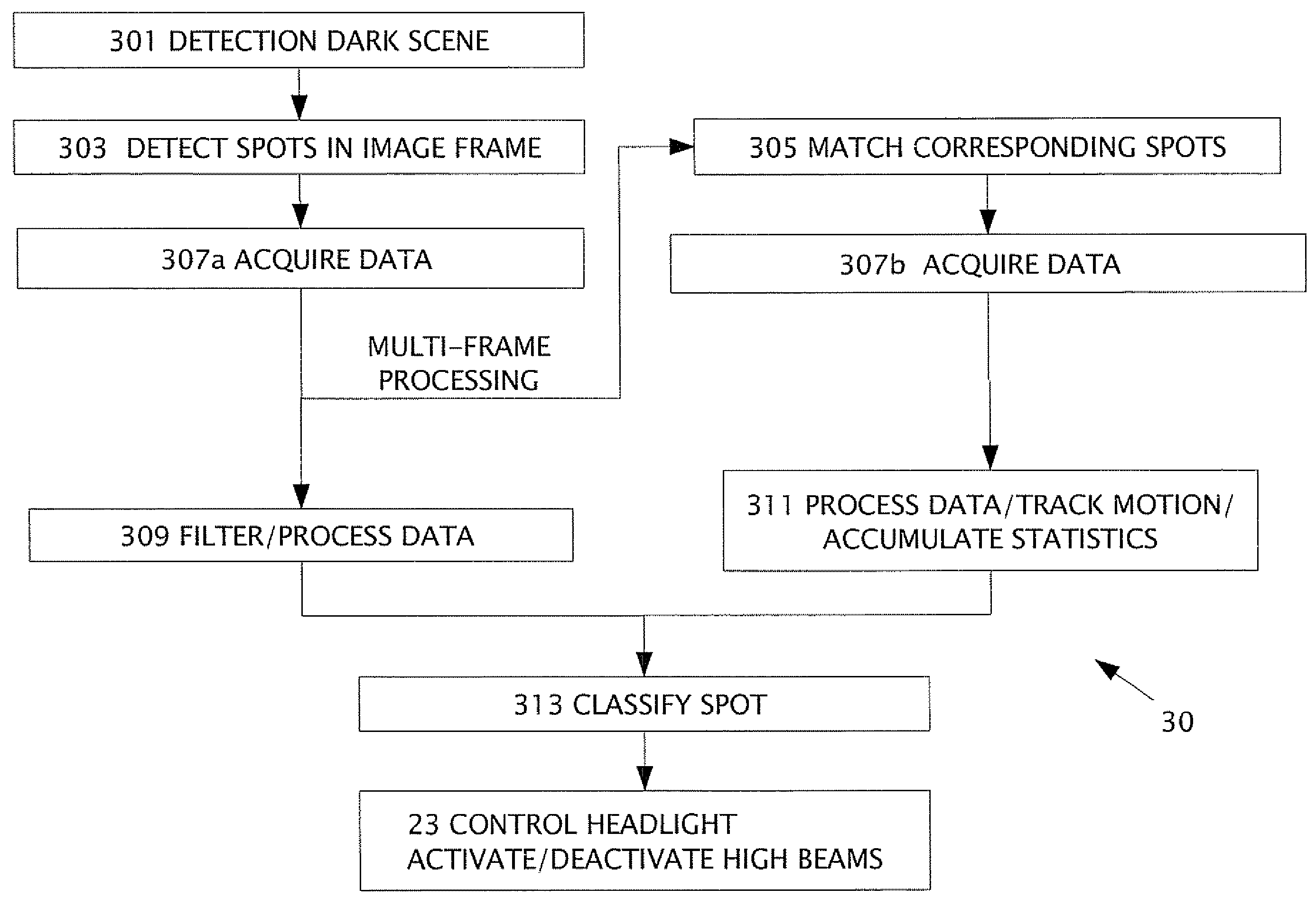
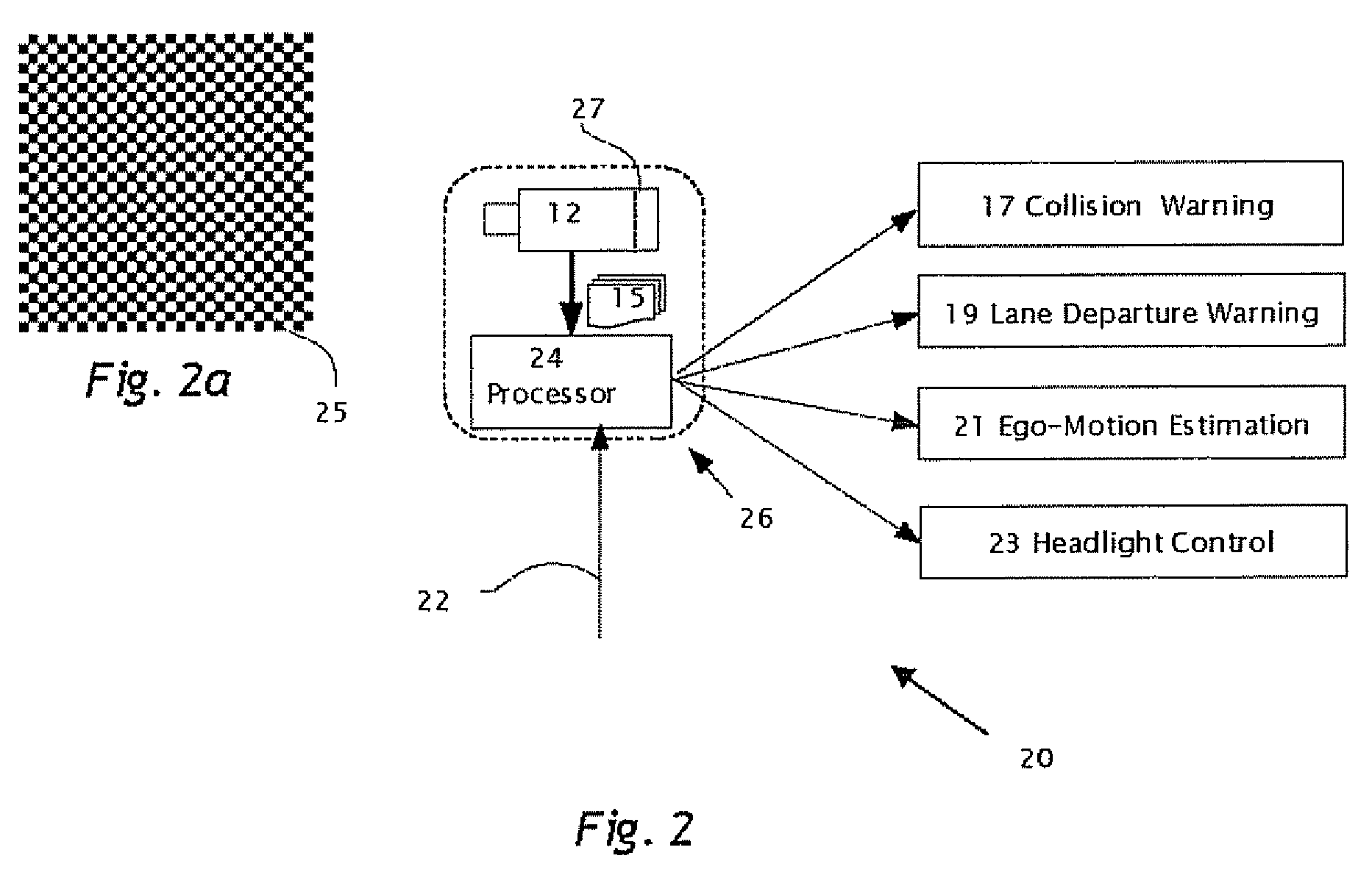
A method in a computerized system including an image sensor mounted in a moving vehicle. The image sensor captures image frames consecutively in real time. In one of the image flames, a spot is detected of measurable brightness; the spot is matched in subsequent image frames. The image frames are available for sharing between the computerized system and another vehicle control system. The spot and the corresponding spot are images of the same object. The object is typically one or more of headlights from an oncoming vehicle, taillights of a leading vehicle, streetlights, street signs and / or traffic signs. Data is acquired from the spot and from the corresponding spot. By processing the data, the object (or spot) is classified. producing an object classification. The vehicle control system controls preferably headlights of the moving vehicle based on the object classification. The other vehicle control system using the image frames is one or more of: lane departure warning system, collision warning system and / or ego-motion estimation system.
Owner:MOBILEYE VISION TECH LTD
Method and apparatus of treating tissue
InactiveUS20060020260A1Reduce laser powerSurgical instrument detailsLight therapyEnergy absorptionFacula
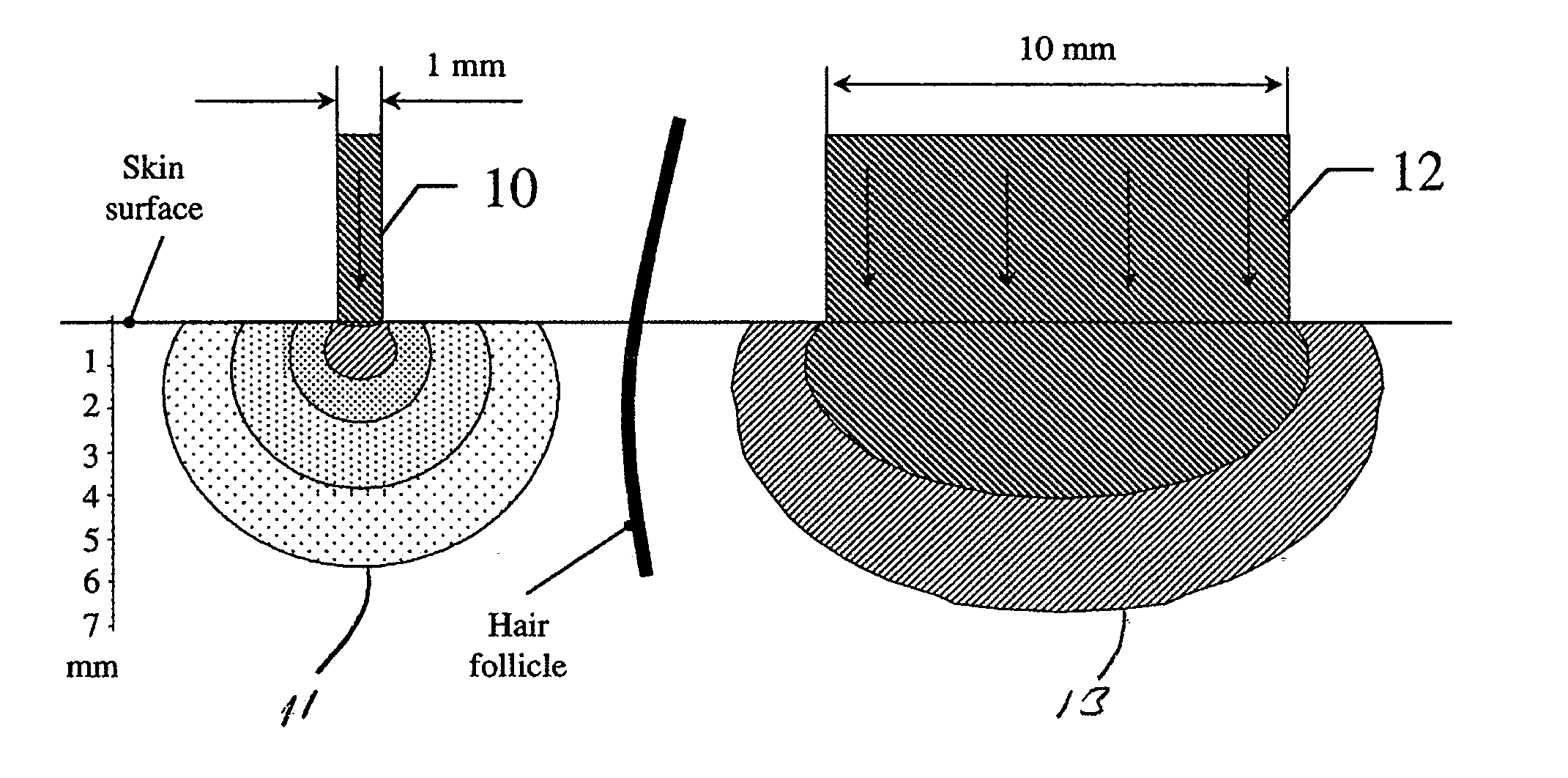
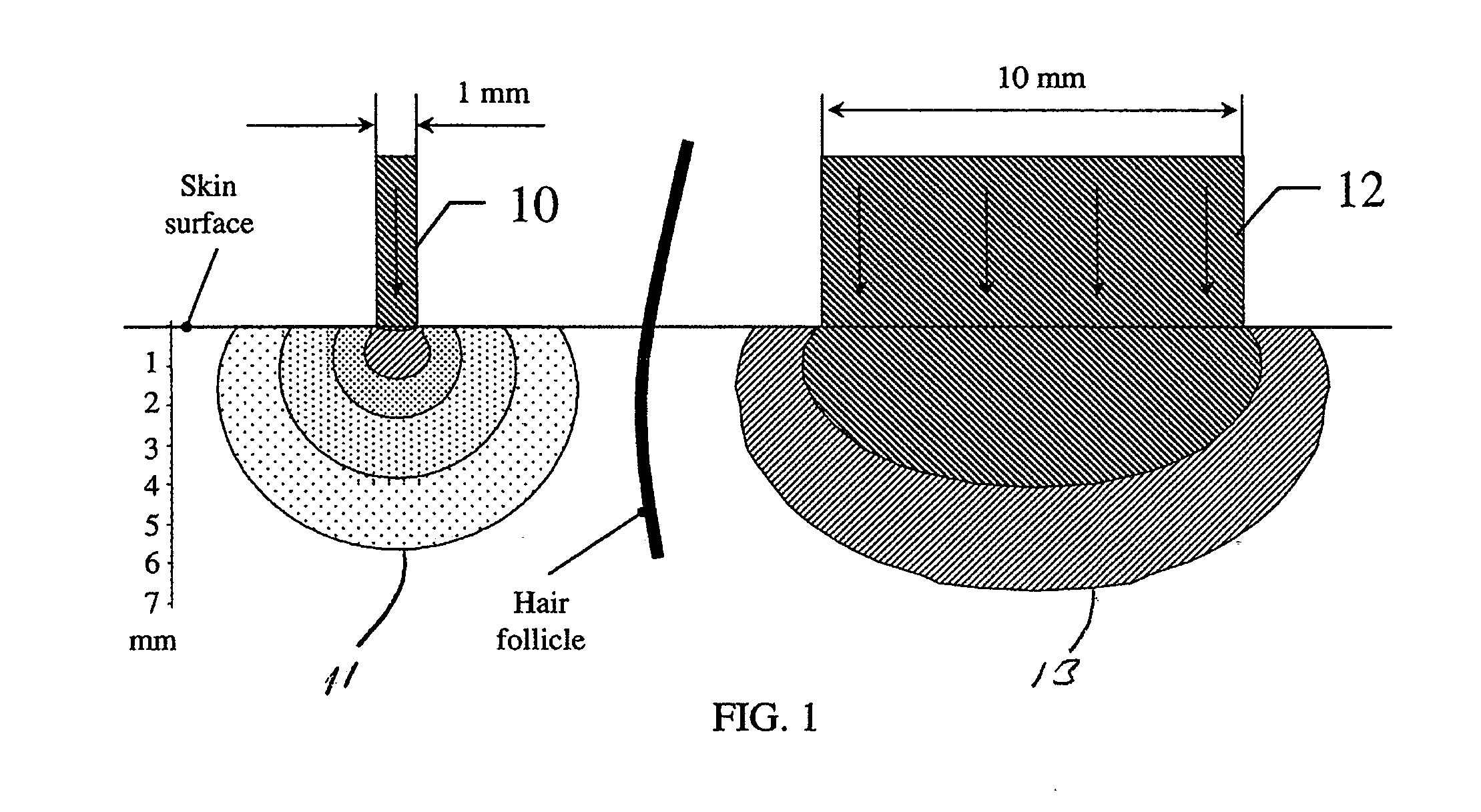
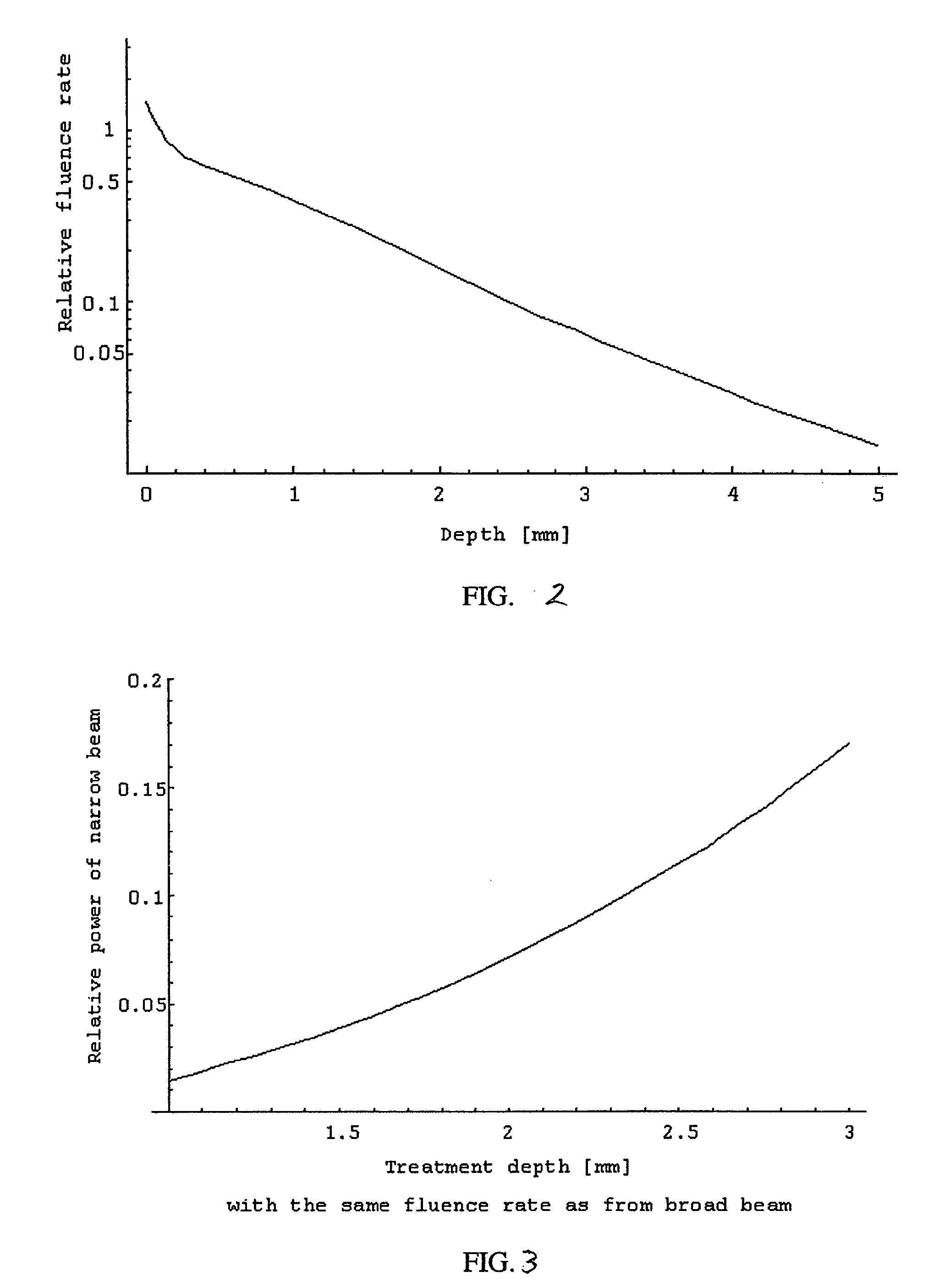
A method for the treatment of skin including the steps of determining the skin depth for energy absorption necessary for treatment; and generating a spot size for energy impinging on the skin to provide a desired amount of energy to the desired depth for treatment. In one embodiment the selected spot size has a small diameter. In another embodiment the spot diameter is narrower than the spacing between adjacent hairs on the skin. In another aspect the invention relates to an apparatus for the treatment of skin including a source of energy; and a means for selecting a spot size for energy from the source impinging on the skin to provide a desired amount of energy to a desired depth for treatment. In another embodiment the apparatus includes an interlock to prevent the laser from producing light unless the source is positioned to irradiate only the skin.
Owner:SHASER
Optical system and apparatus for laser heat treatment and method for producing semiconductor devices by using the same
InactiveUS6437284B1High crystallinityReduced lattice defectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetal working apparatusLight beamOptoelectronics
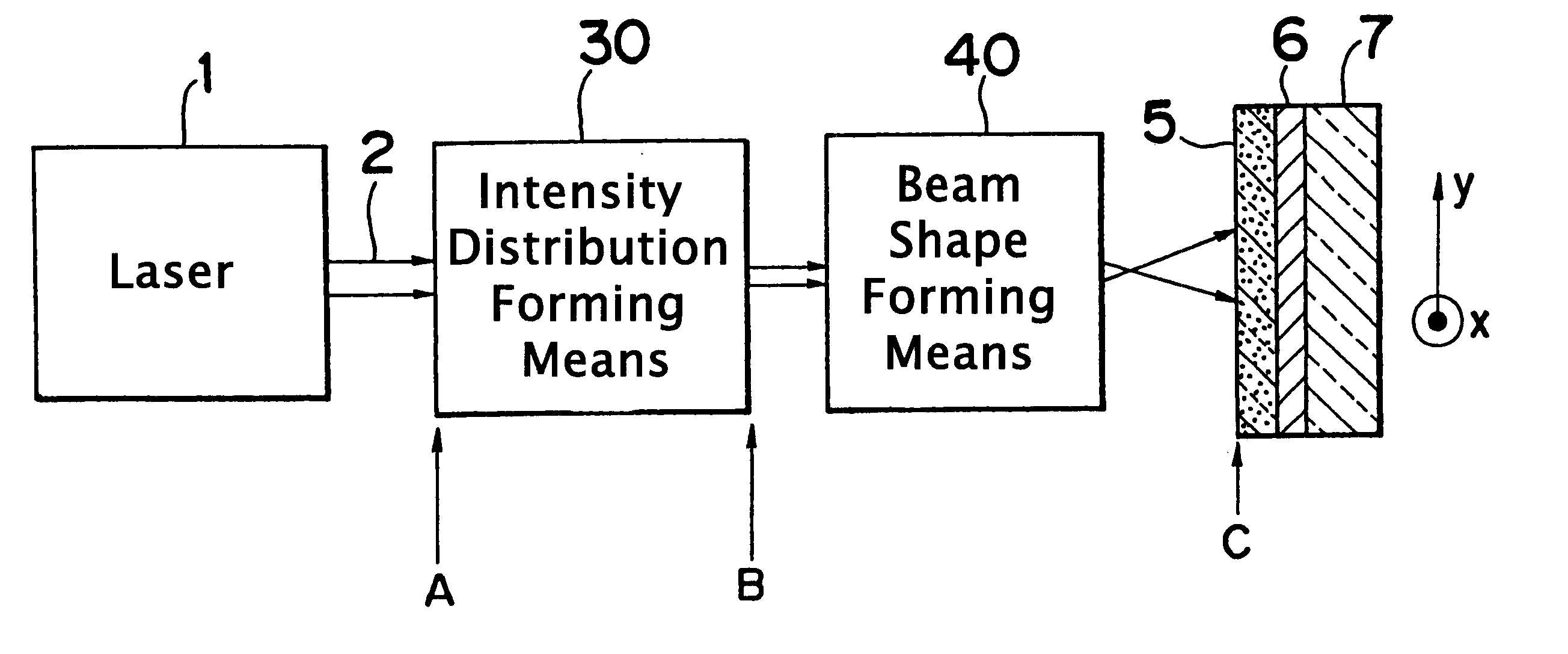
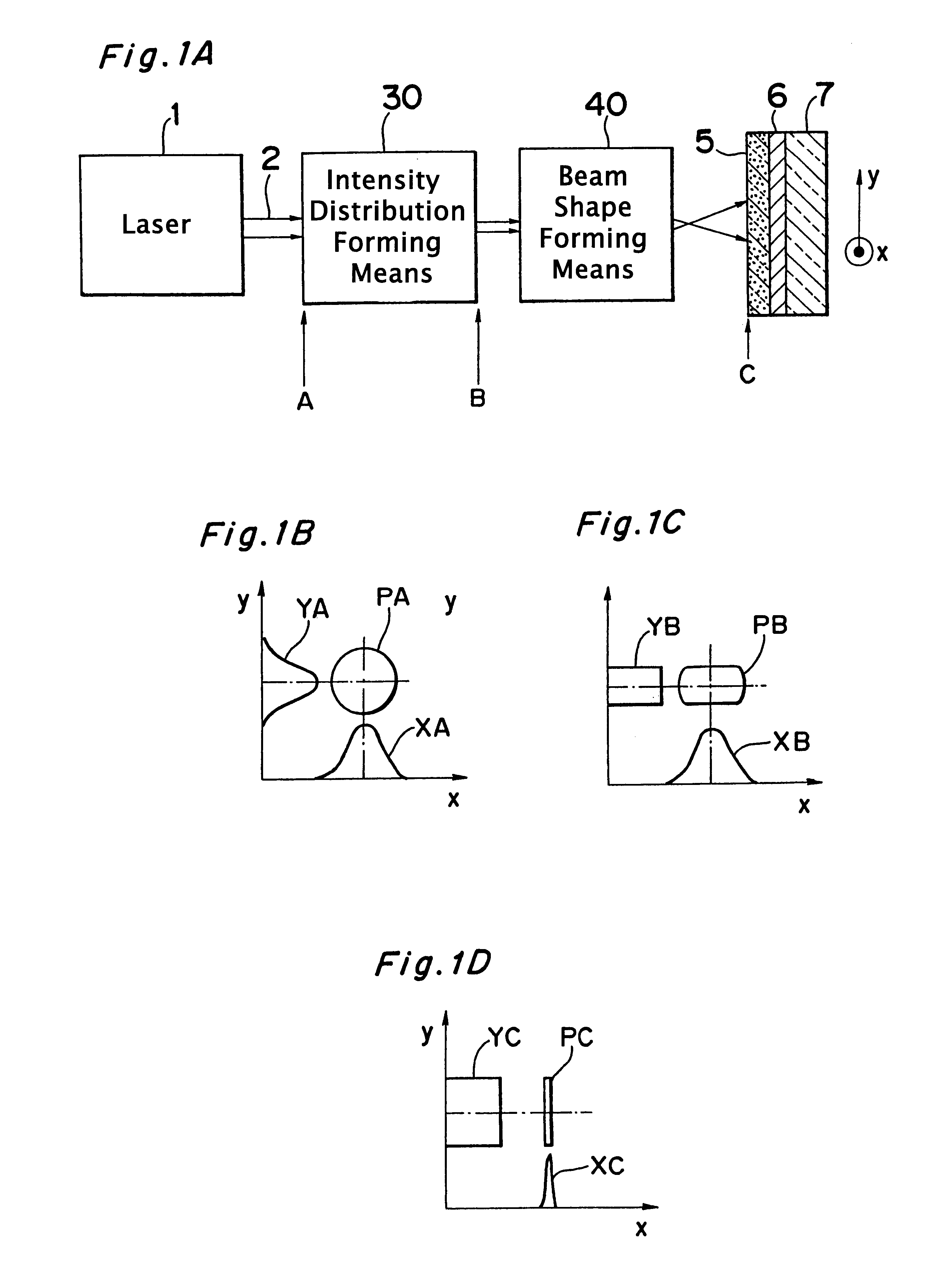
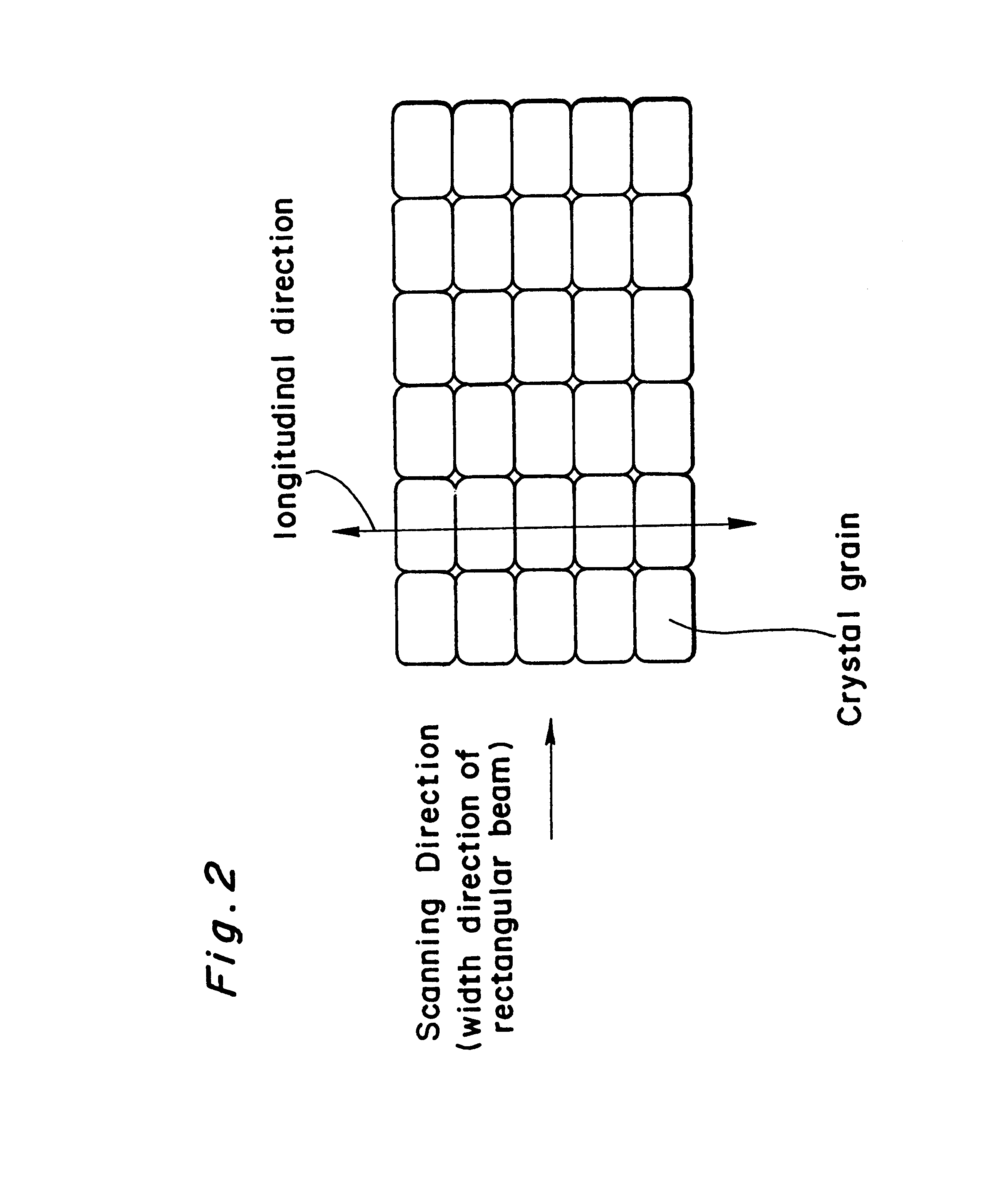
An optical system that controls laser beam spot profile for forming a high performance thin film by a laser heat treatment process is provided. In the optical system that irradiates a rectangular laser beam on a film formed on a substrate, intensity distribution forming, apparatus makes the intensity distribution uniform in the longitudinal direction while maintaining the properties of the laser beam 2 such as directivity in the direction of shorter side, making it possible to concentrate the light to a limit permitted by the nature of the laser beam and achieve the maximum intensity gradient on the film disposed on the substrate. Thus a steep temperature distribution can be generated on the film disposed on the substrate and, as a result, high performance thin film can be formed.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
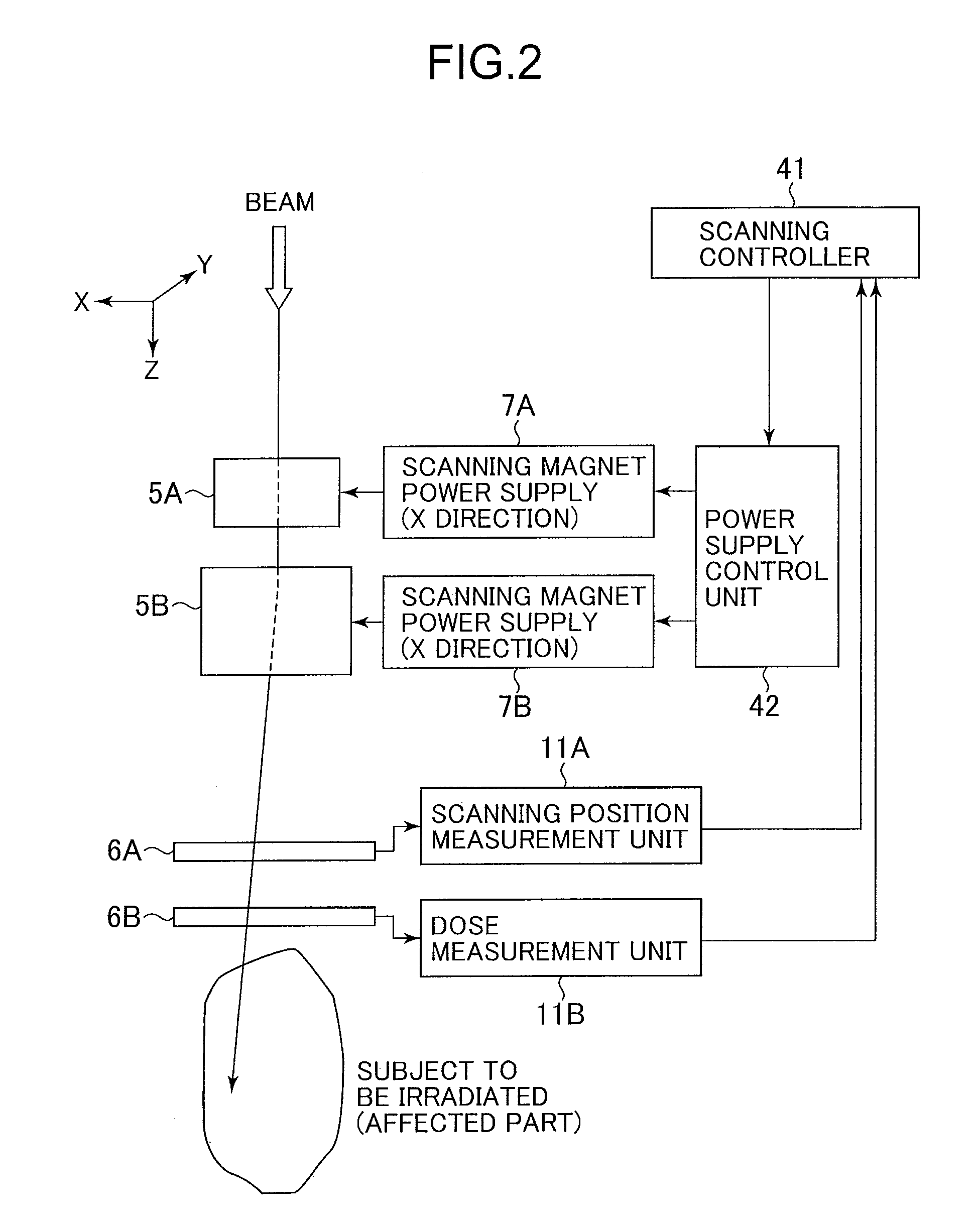
Charged particle irradiation system and method for controlling the same
ActiveUS20110073778A1Improve performanceEasy to operateChemical conversion by chemical reactionX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyLight beamSynchrotron
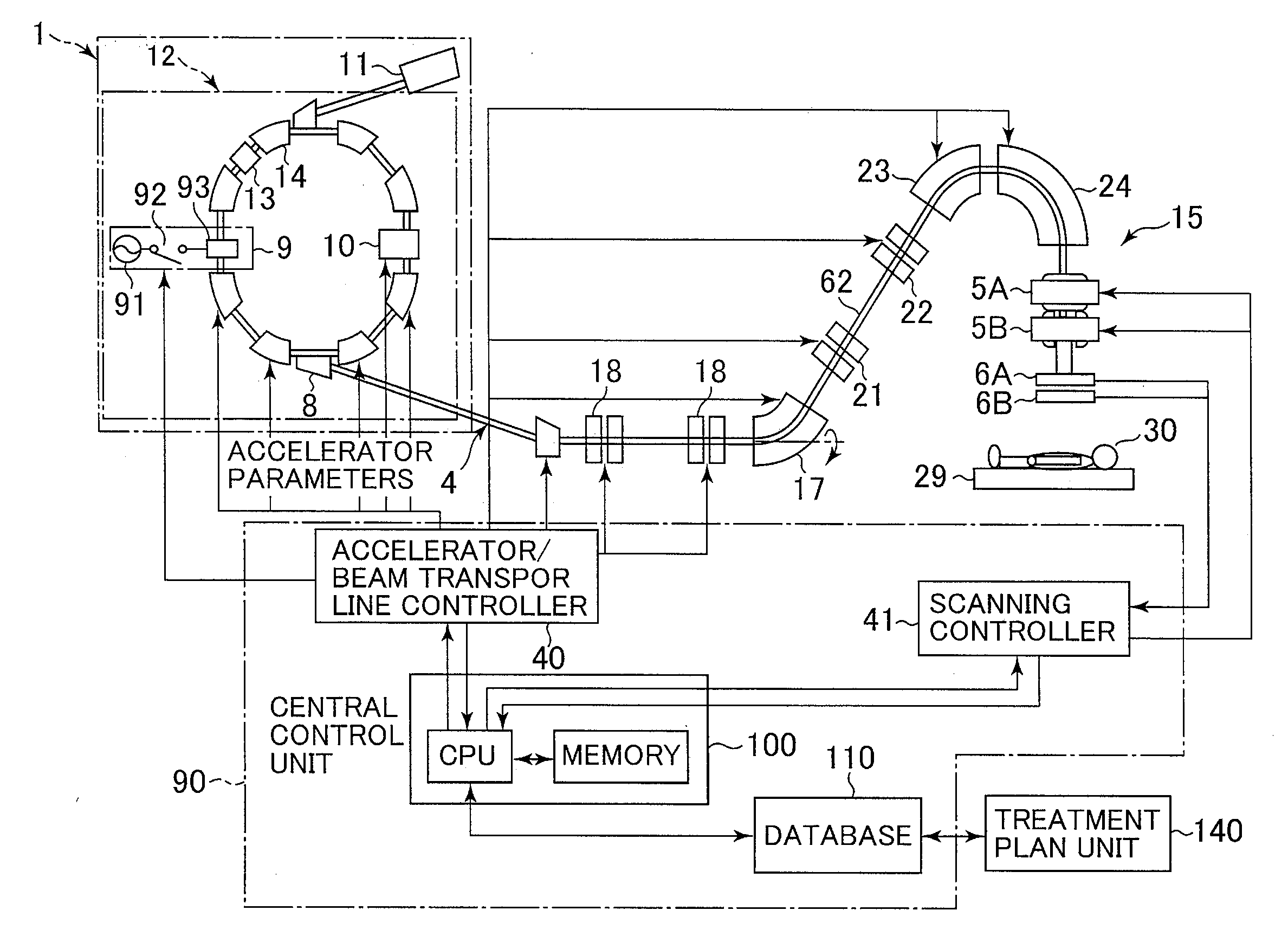
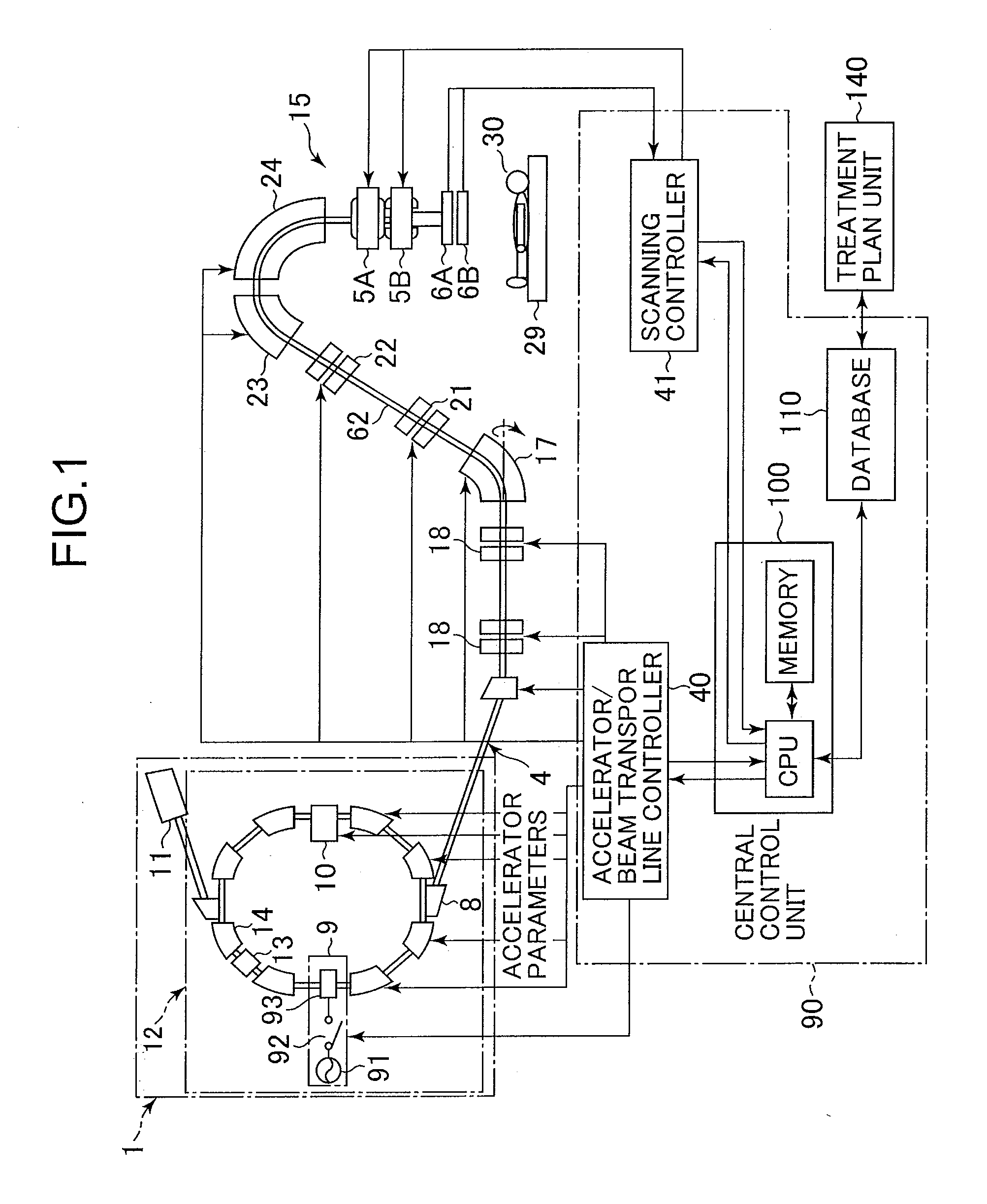
A beam extraction process (interruption and restart) is appropriately performed when a failure occurs during irradiation of a spot group. A charged particle irradiation system includes a synchrotron 12 and a scanning irradiation unit 15 that scans an ion beam extracted from the synchrotron over a subject. The extraction of the ion beam from the synchrotron is stopped on the basis of a beam extraction stop command. Scanning magnets 5A and 5B are controlled to change a point (spot) to be irradiated with the ion beam, while the extraction of the ion beam is stopped. The extraction of the ion beam from the synchrotron is restarted after the change of the spot to be irradiated. When a relatively minor failure in which continuous irradiation would be possible occurs during irradiation of a certain spot with the beam, the extraction of the beam is not immediately stopped.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Image-type intubation-aiding device
InactiveUS20060004258A1Rapid positioningIncrease spot ratioTracheal tubesBronchoscopesDisplay deviceEndotracheal tube
An image-type intubation-aiding device comprises a small-size image sensor and a light source module both placed into an endotracheal tube to help doctors with quick intubation. Light from light emission devices in the light source module passes through a transparent housing and is reflected by a target and then focused. The optical signal is converted into a digital or analog electric signal by the image sensor for displaying on a display device after processing. Doctors can thus be helped to quickly find the position of trachea, keep an appropriate distance from a patient for reducing the possibility of infection, and lower the medical treatment cost. Disposable products are available to avoid the problem of infection. The intubation-aiding device can be used as an electronic surgical image examination instrument for penetration into a body. Moreover, a light source with tunable wavelengths can be used to increase the spot ratio of nidus.
Owner:MEDICAL INTUBATION TECH CORP
Method and apparatus for dicing of thin and ultra thin semiconductor wafer using ultrafast pulse laser
InactiveUS7804043B2Minimize heating effectImprove machine qualityWelding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusPicosecond laserBeam polarization
The present invention relates to the apparatus, system and method for dicing of semiconductor wafers using an ultrafast laser pulse of femtosecond and picosecond pulse widths directly from the ultrafast laser oscillator without an amplifier. Thin and ultrathin semiconductor wafers below 250 micrometer thickness, are diced using diode pumped, solid state mode locked ultrafast laser pulses from oscillator without amplification. The invention disclosed has means to avoid / reduce the cumulative heating effect and to avoid machine quality degrading in multi shot ablation. Also the disclosed invention provides means to change the polarization state of the laser beam to reduce the focused spot size, and improve the machining efficiency and quality. The disclosed invention provides a cost effective and stable system for high volume manufacturing applications. An ultrafast laser oscillator can be a called as femtosecond laser oscillator or a picosecond laser oscillator depending on the pulse width of the laser beam generated.
Owner:LASERFACTURING
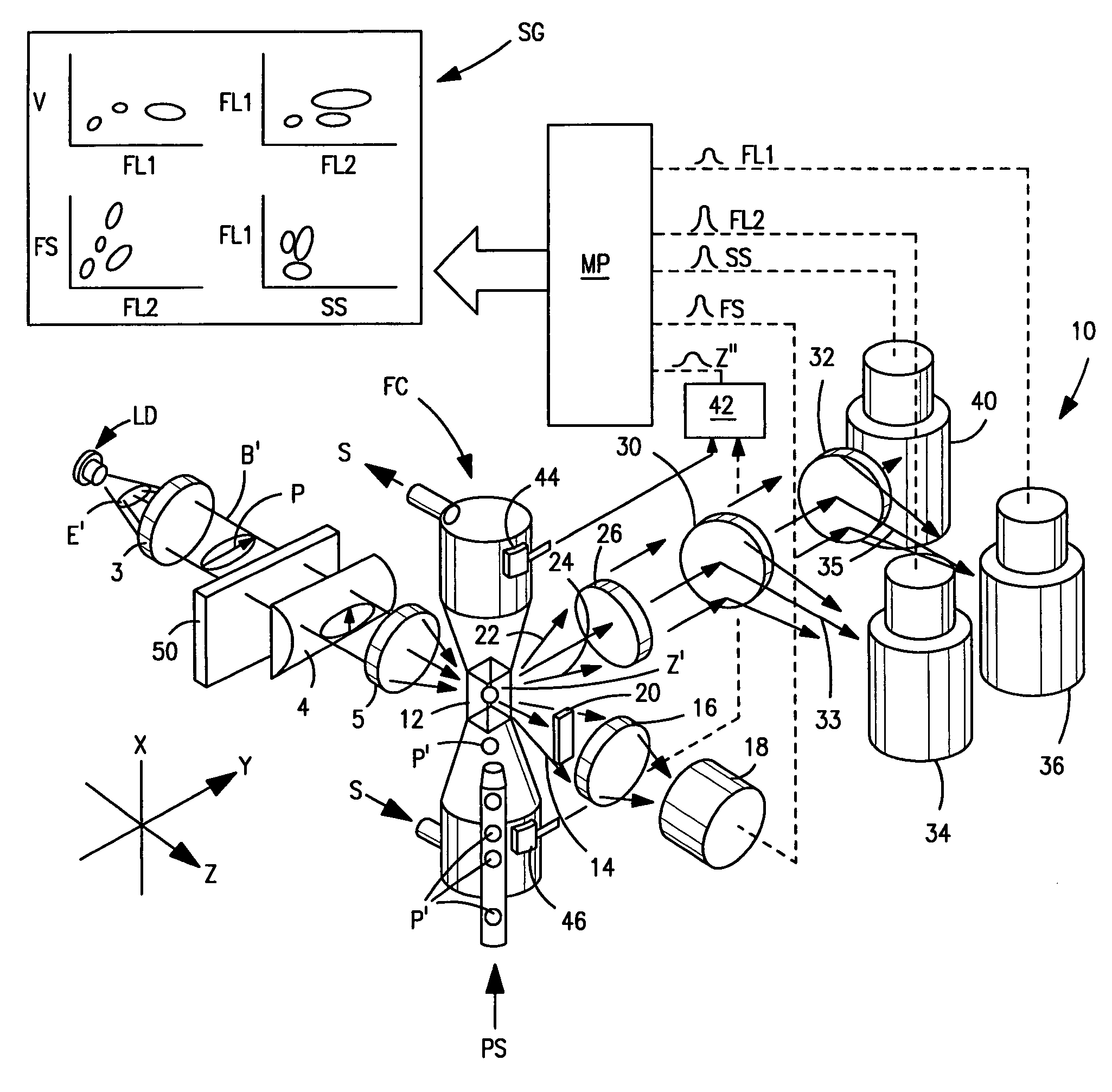
Flow cytometer for differentiating small particles in suspension
A flow cytometer includes an optical flow cell through which particles to be characterized on the basis of at least their respective side-scatter characteristics are caused to flow seriatim. A plane-polarized laser beam produced by a laser diode is used to irradiate the particles as they pass through a focused elliptical spot having its minor axis oriented parallel to the particle flow path. Initially, the plane of polarization of the laser beam extends perpendicular to the path of particles through the flow cell. A half-wave plate or the like is positioned in the laser beam path to rotate the plane of polarization of the laser beam so that it is aligned with the path of particles before it irradiated particles moving along such path.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Simultaneous multi-spot inspection and imaging
InactiveUS7130039B2High detection sensitivityImprove performanceAnalysis by electrical excitationOptically investigating flaws/contaminationDetector arrayAnnular aperture
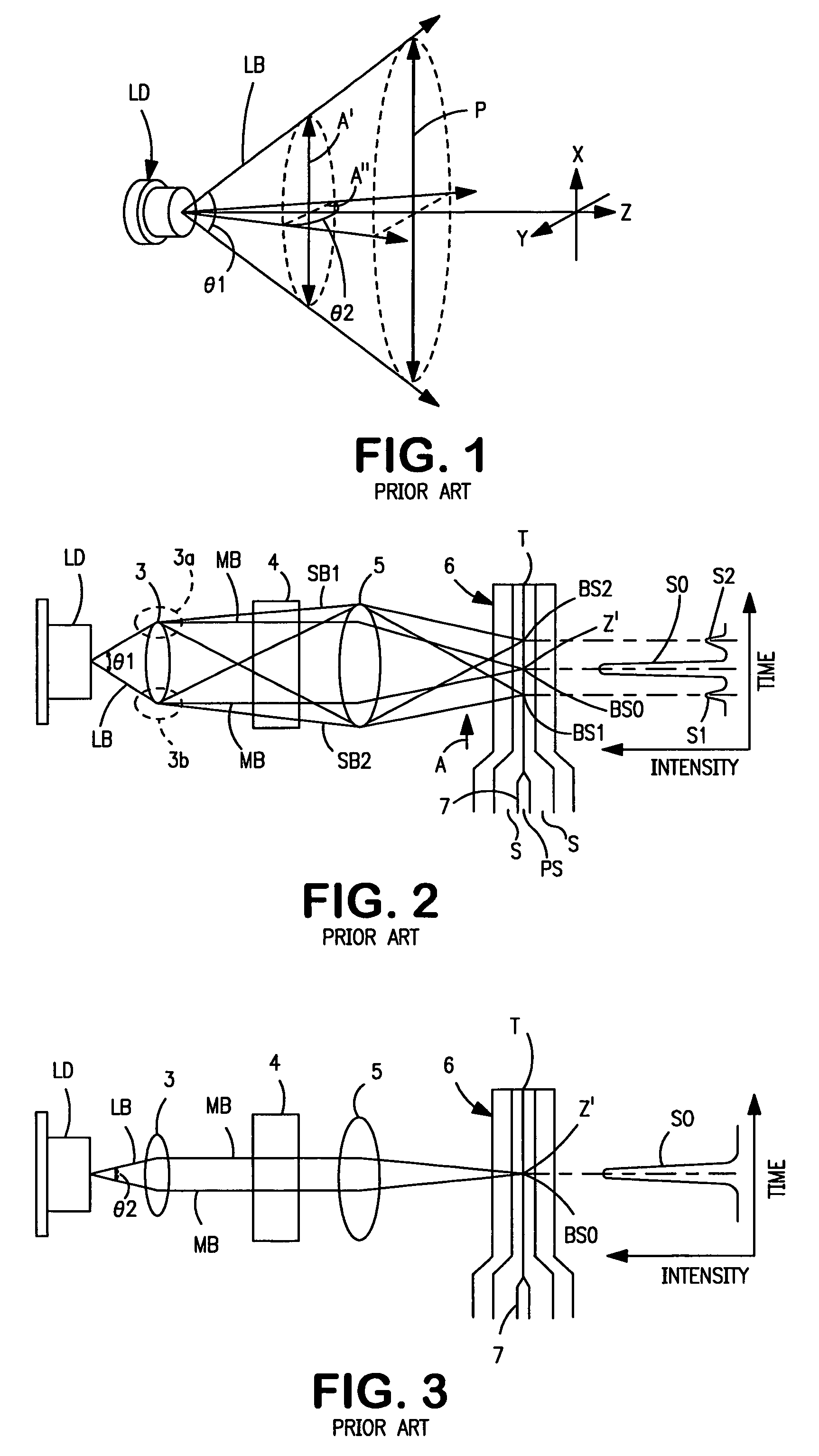
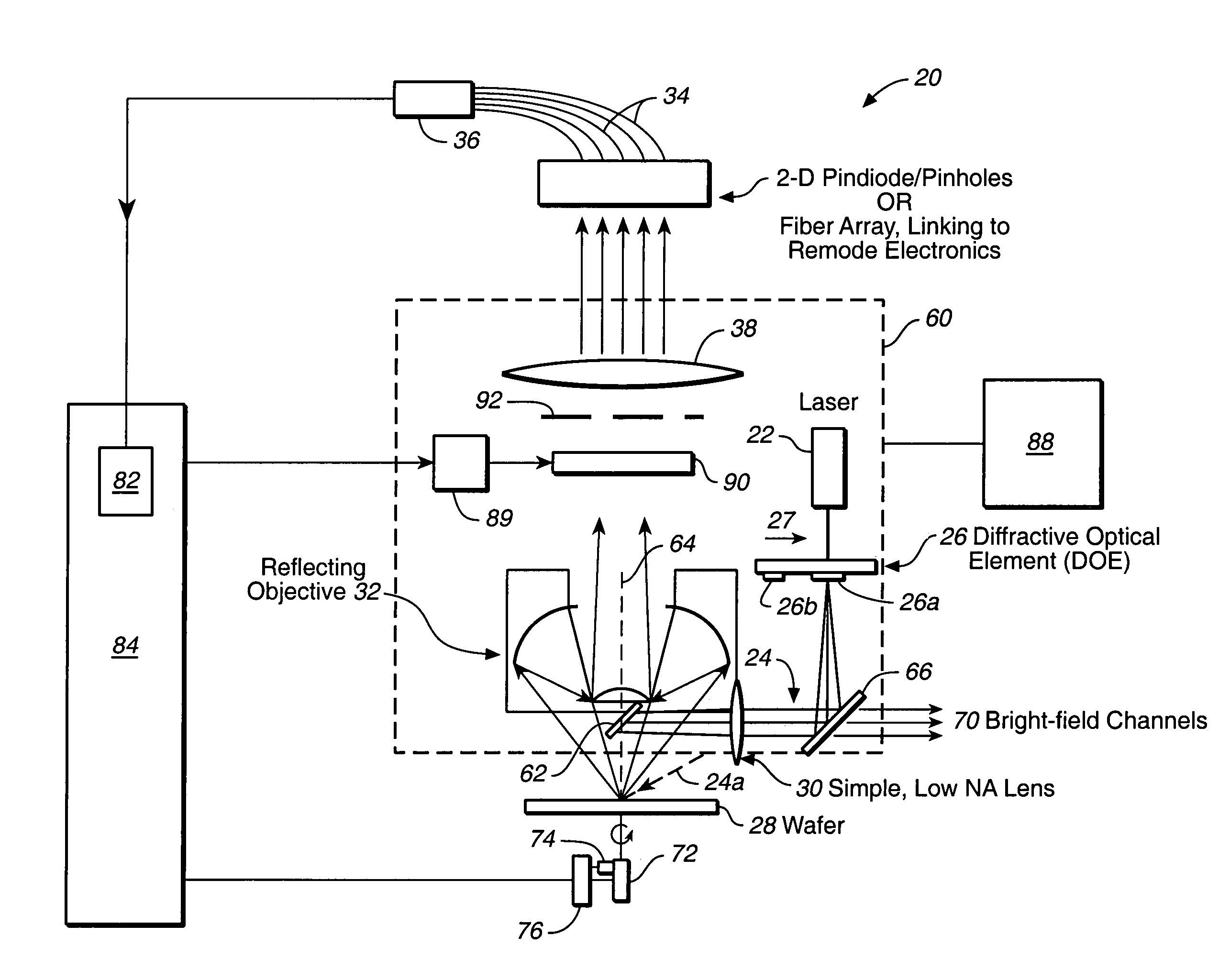
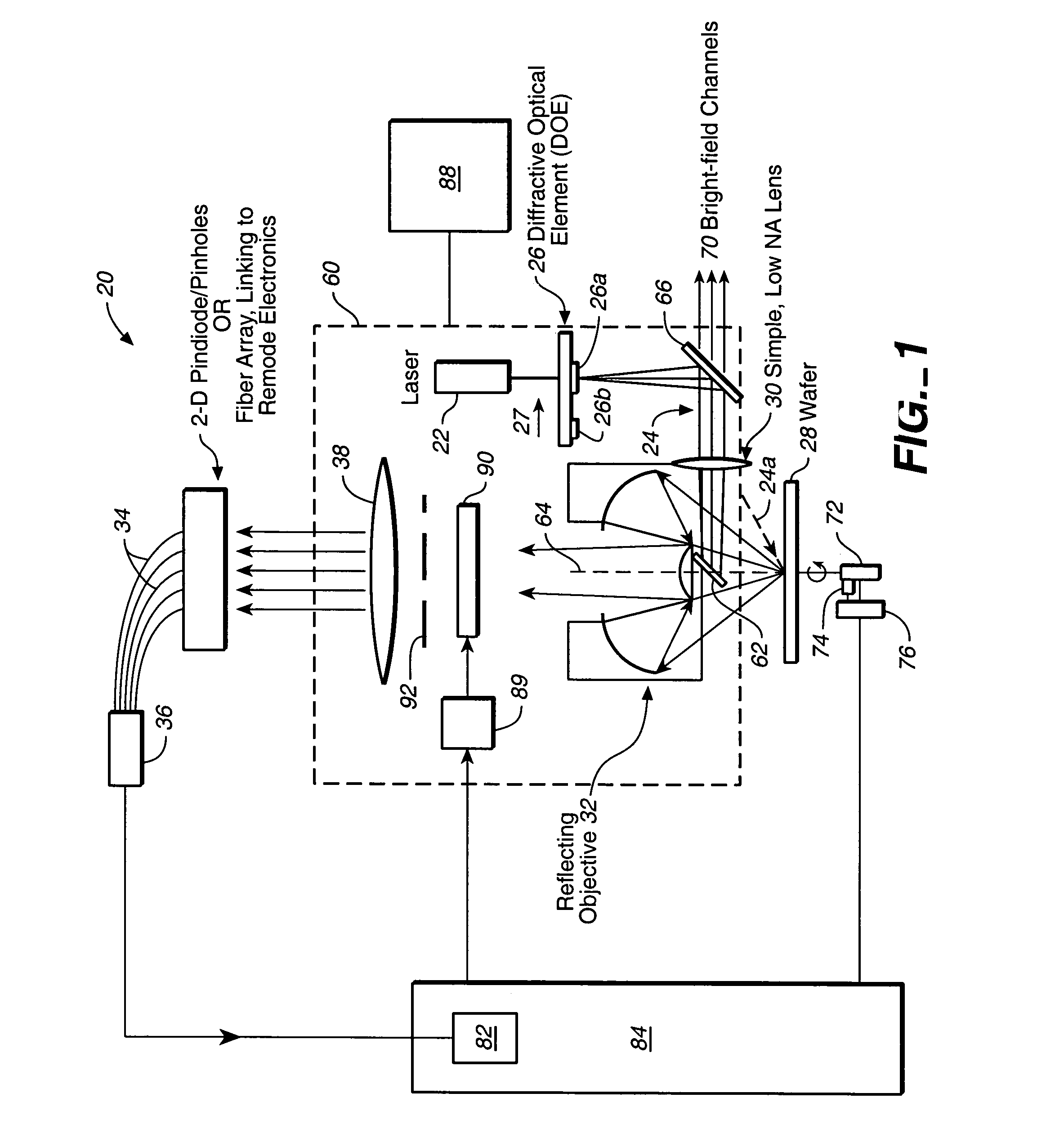
A compact and versatile multi-spot inspection imaging system employs an objective for focusing an array of radiation beams to a surface and a second reflective or refractive objective having a large numerical aperture for collecting scattered radiation from the array of illuminated spots. The scattered radiation from each illuminated spot is focused to a corresponding optical fiber channel so that information about a scattering may be conveyed to a corresponding detector in a remote detector array for processing. For patterned surface inspection, a cross-shaped filter is rotated along with the surface to reduce the effects of diffraction by Manhattan geometry. A spatial filter in the shape of an annular aperture may also be employed to reduce scattering from patterns such as arrays on the surface. In another embodiment, different portions of the same objective may be used for focusing the illumination beams onto the surface and for collecting the scattered radiation from the illuminated spots simultaneously. In another embodiment, a one-dimensional array of illumination beams are directed at an oblique angle to the surface to illuminate a line of illuminated spots at an angle to the plane of incidence. Radiation scattered from the spots are collected along directions perpendicular to the line of spots or in a double dark field configuration.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Laser flare measuring device and measuring method thereof
InactiveCN101458067AAccurate measurementImprove dynamic rangePhotometry using wholly visual meansUsing optical meansMeasurement deviceExposure control
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Varying beam parameter product of a laser beam
An optical delivery waveguide for a material laser processing system includes a small lens at an output end of the delivery waveguide, transforming laser beam divergence inside the waveguide into a spot size after the lens. By varying the input convergence angle and / or launch angle of the laser beam launched into the waveguide, the output spot size can be continuously varied, thus enabling a continuous and real-time laser spot size adjustment on the workpiece, without having to replace the delivery waveguide or a process head. A divergence of the laser beam can also be adjusted dynamically and in concert with the spot size.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Microarray dispensing with real-time verification and inspection
InactiveUS7025933B2Improve spotImprove accuracySequential/parallel process reactionsElement comparisonAnalysis dataReal time validation
A microarrayer for spotting solution onto a receiving surface in an automated microarray dispensing device. Elements of the present invention include: at least one dispense head for spotting the receiving surface, at least one light source capable of illuminating the receiving surface, at least one camera operating in conjunction with the at least one light source. The at least one camera is capable of acquiring and transmitting surface image data to a computer. The computer is programmed to receive the surface image data and analyze it. The computer will then generate post analysis data based on the analysis of the surface image data. The post analysis data is available for improving the spotting of the solution onto the receiving surface. In a preferred embodiment, the surface image data includes information relating to receiving surface alignment, information relating to spot quality, and receiving surface identification information. In a preferred embodiment, the analysis of the information relating to receiving surface alignment enables the computer to make automatic adjustments to the relative positions of the at least one dispense head and the receiving surface to increase the accuracy of the spotting. In a preferred embodiment, the analysis of the information relating to spot quality identifies a spot as pass or fail. An operator is then able to rework the spot. In a preferred embodiment, the analysis of the receiving surface identification information enables the computer to track each receiving surface. In a preferred embodiment the receiving surface is a plurality of slides.
Owner:AGENA BIOSCI
Method and apparatus for light modulation and exposure at high exposure levels with high resolution
InactiveUS6204875B1Overcomes intensity calibration and efficiency problemUniform intensity distributionInking apparatusAdditive manufacturing apparatusRelative motionExposure level
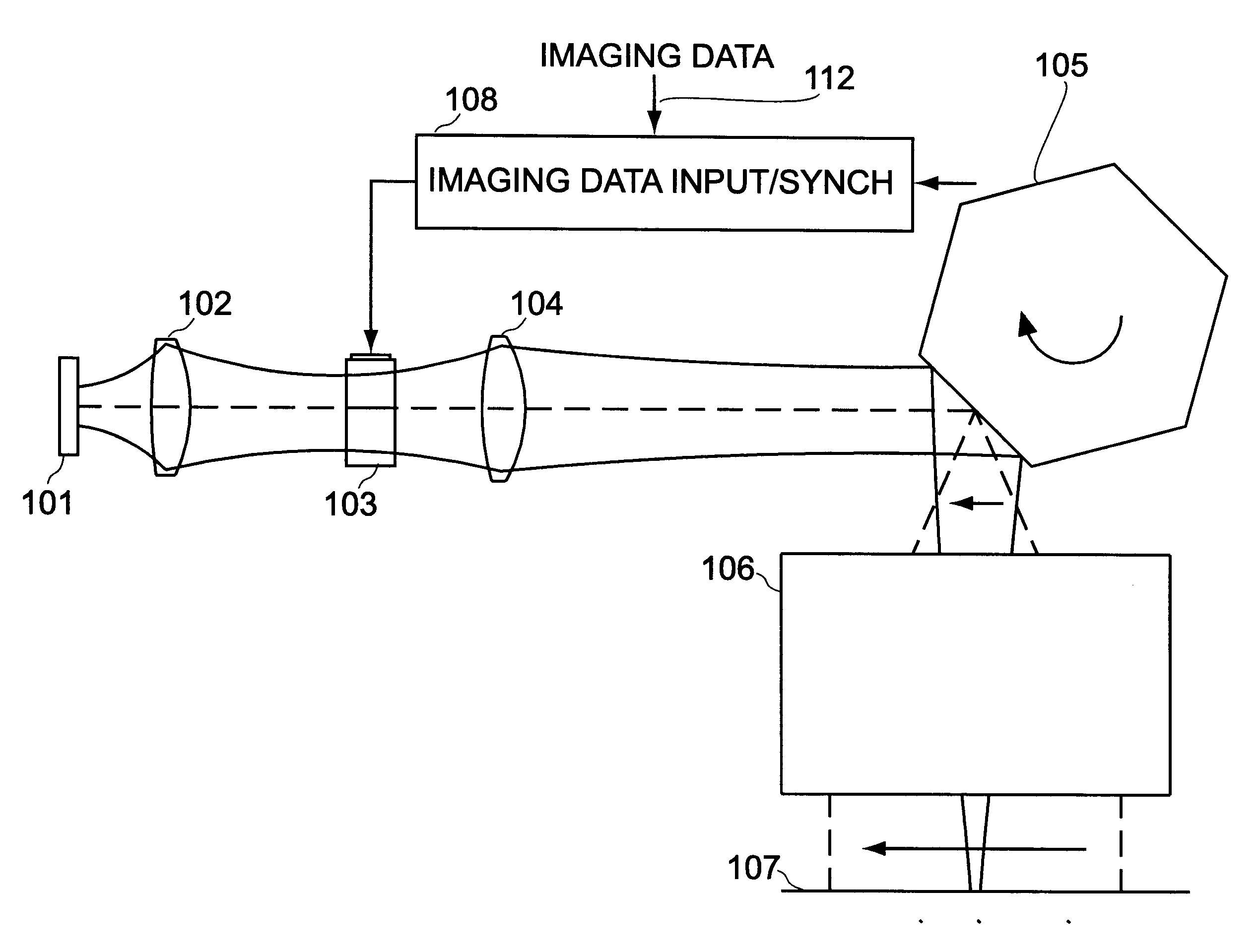
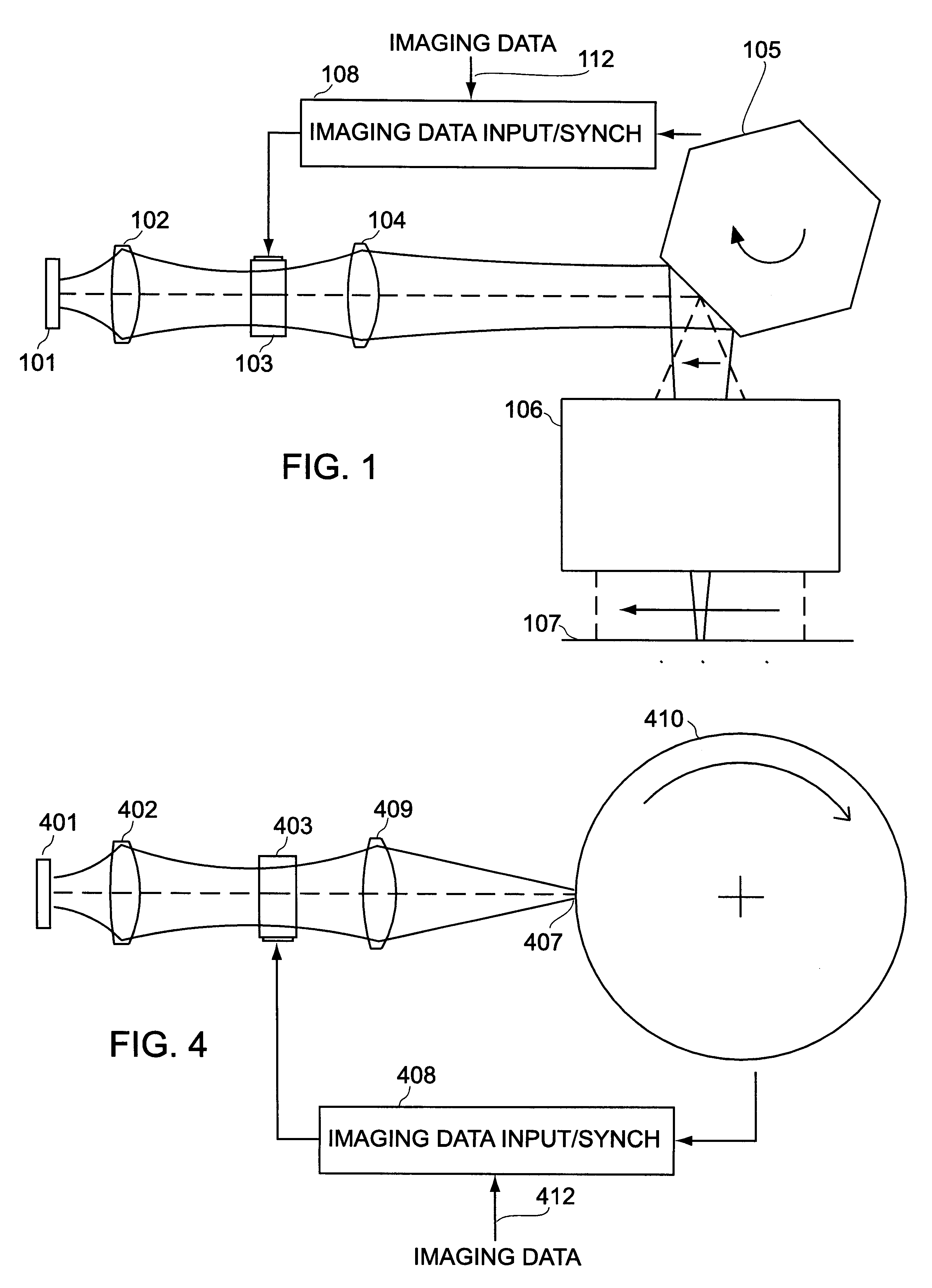
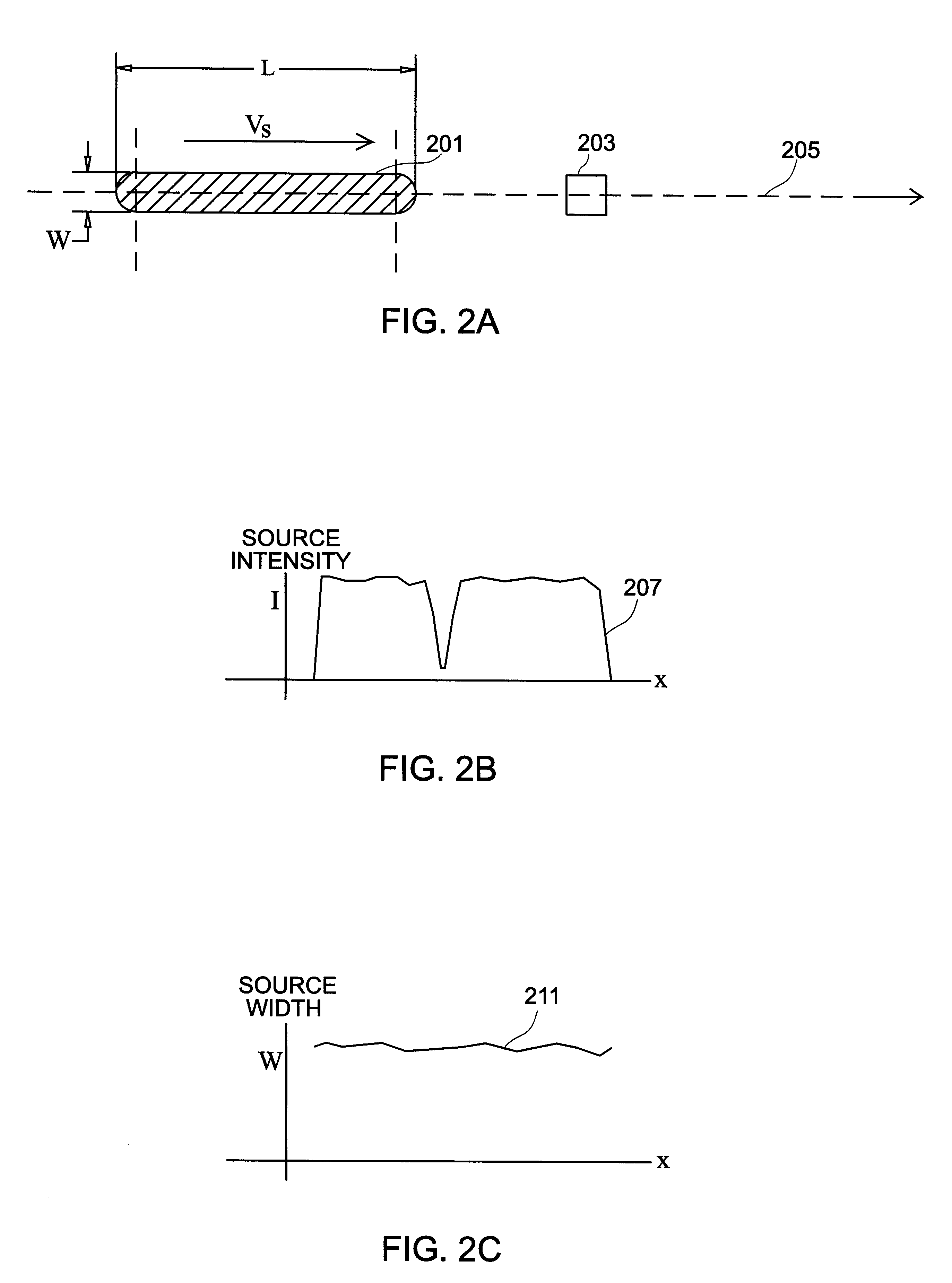
A method and system for exposing a light sensitive material using device for forming a row of spots of light onto the light sensitive material located on a focal plane, device for modulating each of the spots according to imaging data so that at any point of time, the row of spots forms a data pattern according to the imaging data, device for generating relative motion between the imaging mechanism and the light sensitive material on the focal plane, the direction of motion substantially parallel to the direction of the row of spots on the light sensitive material; and data synchronizing device for shifting the imaging data into the modulating device at a rate determined by the speed of relative motion to maintain the image of any data pattern substantially stationary on the light sensitive material.
Owner:BARCO GRAPHICS
Laser processing
InactiveUS6878899B2Limit temperature riseAvoid damageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLaser processingLength wave
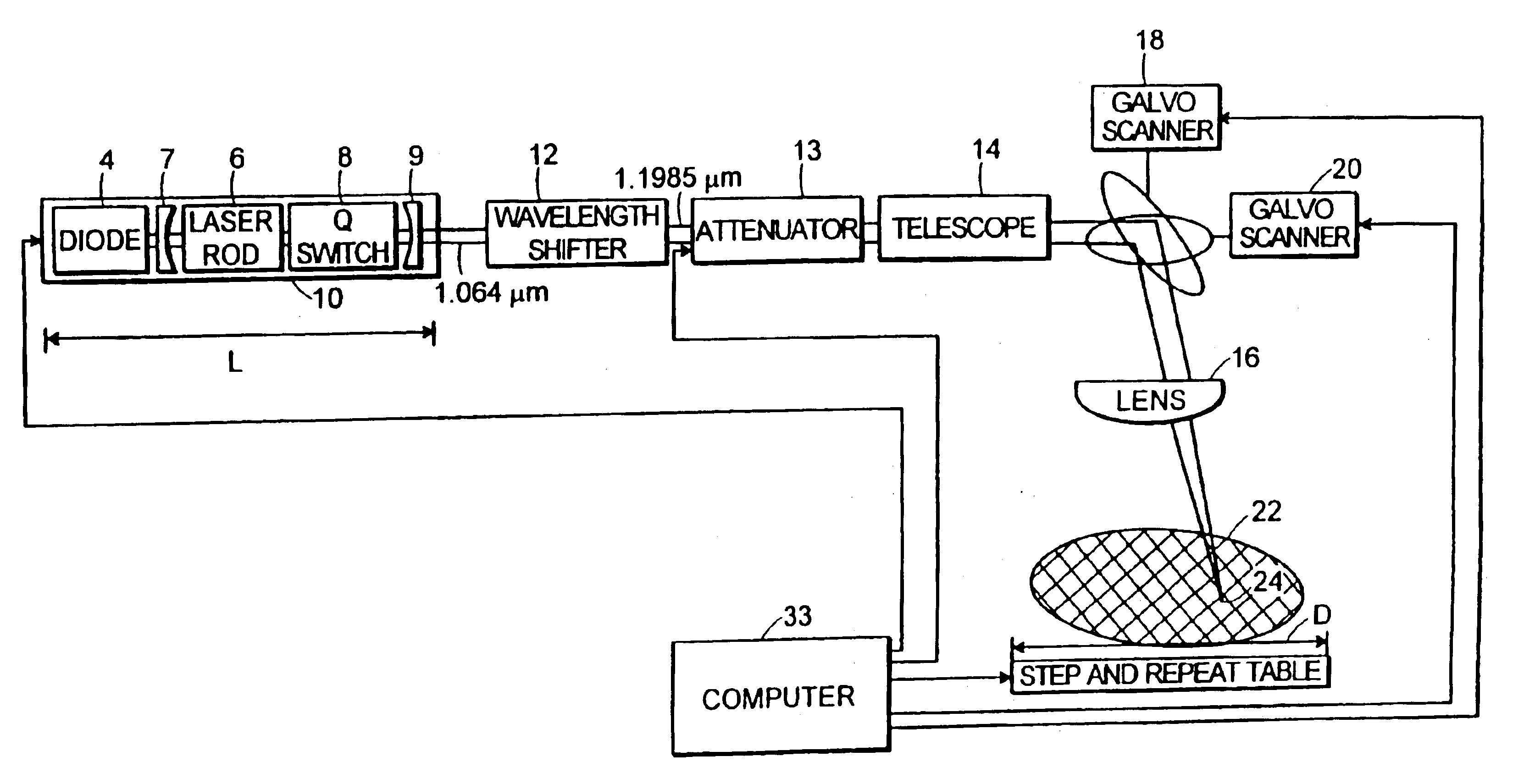
A controlled, switched laser system for vaporizing a target structure on a substrate includes a diode-pumped, solid-state laser for producing a laser output, a controllable switch for controlling the on / off state and power level of the laser, and a wavelength shifter. The wavelength shifter shifts the wavelength of the laser output from a conventional wavelength to a wavelength beyond the absorption edge of the substrate but shorter than 1.2 μm in order to obtain a decrease in absorption of the laser output by the substrate due to the shift in the wavelength of the laser output. The wavelength shifter is removably insertable into the switched laser system so as to enable the switched laser system to operate at the conventional wavelength and at the wavelength beyond the absorption edge of the substrate. Heating of the substrate and hence damage to the substrate is limited due to the wavelength being beyond the absorption edge of the substrate. Good depth of focus of the laser beam output is maintained relative to spot size of the laser beam output due to the wavelength being less than about 1.2 μm.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Galvanometer system correction device and correction method thereof
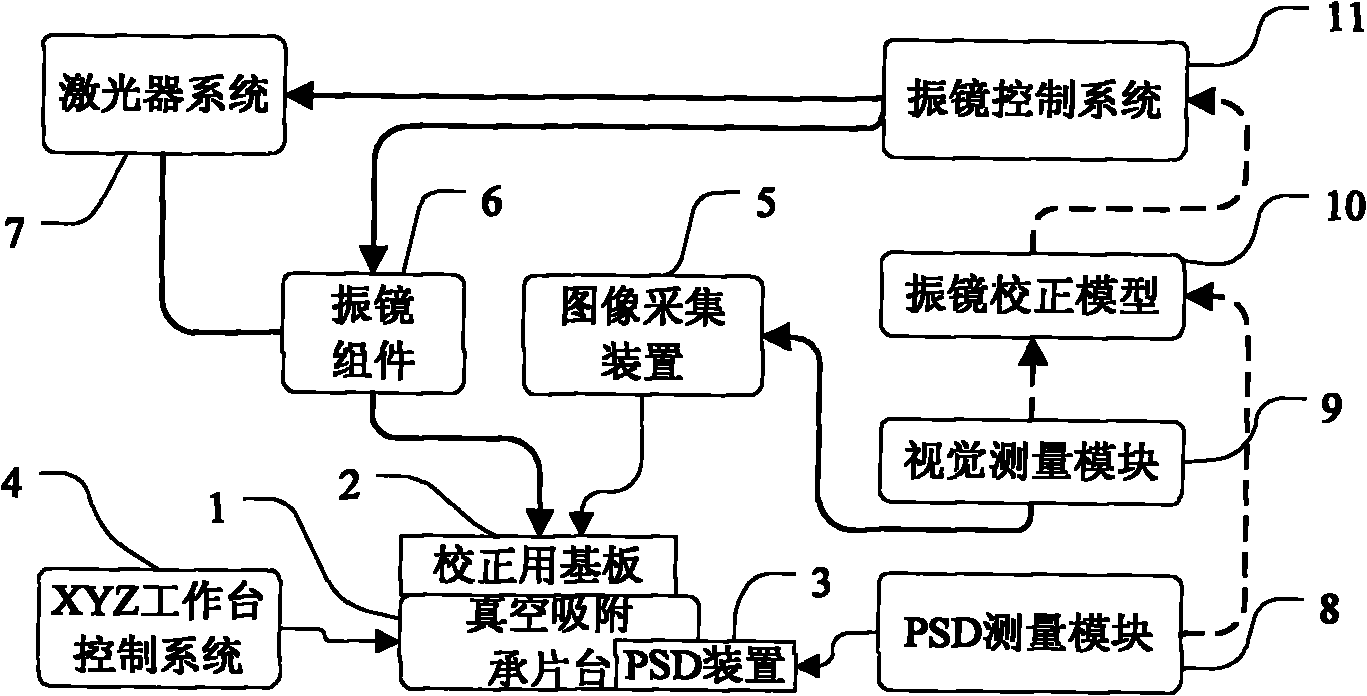
InactiveCN101804521AGood dynamic tracking abilitySolve the problem of calibration inefficiencyLaser beam welding apparatusGalvanometerCorrection method
The invention provides a galvanometer system correction device and a correction method thereof, and relates to the technical field of precision laser processing equipment. A honeycomb panel is arranged in the middle of the outer frame of a bearing platform, a base plate for corrective is absorbed on the honeycomb panel, and the vacuum chamber of the honeycomb panel is connected with a dust collector; a PSD sensor for measuring the actual output light spot center position of the laser of a galvanometer system is arranged on the vacuum absorption bearing platform; a CCD image acquisition device is arranged above the base plate for correcting, and then is provided with a light intensity regulating module and an image acquisition board card; and a visual measurement algorithm module is arranged. The invention can effectively inhibit the precision drift of the galvanometer system, improve the efficiency of the galvanometer system when in correction model updating and in real-time correction calculation operation, improve the automatic degree of equipment, reduce the labor intensity of an operator, greatly improve the processing precision of equipment, product quality and production efficiency, has simple structure and unique principle and method, and is particularly suitable for precision laser processing equipment to use.
Owner:THE 45TH RES INST OF CETC
Method and device for laser welding
ActiveUS20050150876A1Improve welding qualityShorten production timeLaser detailsSpecial data processing applicationsClassical mechanicsManipulator
A plurality of stretches of laser weld are executed on a structure to be welded by means of a device for focusing and orientation of the laser beam, which is associated to a component element of a manipulator robot. The focusing head is kept in the proximity of, but not closely adjacent to, the different areas to be welded and can consequently follow a simplified path, whilst the device for orientation of the laser beam aims the latter on the different areas of the structure to be welded, so that the speed of travel of the laser beam spot along the longitudinal direction of the weld stretch is independent from the speed of travel of the robot end element.
Owner:COMAU SPA
Laser radiation source
InactiveUS6888853B1High densityHigh energyInking apparatusLaser using scattering effectsFine structureOptoelectronics
A system and method for selectively process material on a processing surface of a printing form to create a fine structure or pattern for images or text. At least one fiber laser comprising a pump source and a laser fiber is provided. A laser gun is mounted adjacent the printing form and has at least a focusing optics. The fiber laser outputs a laser beam which is diffraction-limited to permit the focusing optics to focus the laser beam onto the processing surface of the printing form as a spot having a spot size sufficiently small to process the processing surface to create the fine structure or pattern images or text.
Owner:HELL GRAVURE SYST
Super-resolution fluorescence microscopy method and device based on tangential polarization
InactiveCN101907766ALow powerReduce bleachingMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicroscopic imageImage resolution
The invention discloses a super-resolution fluorescence microscopy method based on tangential polarization, comprising the following steps: carrying out 0-2pi vortex phase coding focus on tangential polarization exciting light, and obtaining an exciting spot below a diffraction limit on a fluorescence sample; adjusting tangential polarization STED laser and the phase coding tangential polarization exciting light to realize confluence and co-axis, focusing on the fluorescence sample to form a circle bread-shaped focusing spot the central point of which coincides with the central point of the exciting spot; adjusting the operating power of the STED laser to cause the area of a luminous point in the exciting spot to reach the super-resolution ratio; and collecting fluorescence emitted from the luminous point and carrying out detection processing to obtain a microimage with the super-resolution ratio. The invention also discloses a device for realizing the super-resolution fluorescence microscopy method based on tangential polarization. In the invention, on the premise of ensuring the super-resolution ratio, the working power of the STED is reduced greatly, thereby lowering bleaching of the sample and avoiding damage for the sample.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
LED road lamp and its lens
InactiveCN101105272AReduce lossesTake advantage ofMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceIlluminanceLed array
The invention relates to a lens for LED street lamp. A concave pit is provided in the middle of a first side face of the lens and allowing LED to be arranged therein, and the pit wall of the concave pit forms an incident face; an arcing bulge in the middle of a second side face of the lens forms an emergent face with the shape of pillow; and a totally reflecting face is circumferentially provided around the concave pit on the first side face of the lens. The invention also relates to a LED street lamp, which comprises a frame, and a lighting module arranged on the frame, wherein the lighting module comprises a thermal radiator, a substrate with a LED array, a PCB board with a through-hole array and a lens cap with a lens array. The substrate is provided on the undersurface of the thermal radiator, PCB board is provided on the outer surface of the substrate and connected with each LCD electrode, the lens cap is provided at the outer side of the PCB board, LEDs pass through the through-holes on the PCB board to be accommodated in the concave pit corresponding to the lens, and the lens array is formed by arranging and combining a plurality of above mentioned lenses. The invention can control the distribution of light to form rectangular light spot. The light in the effective illuminated zone is very uniform and there is no parasitic light outside the zone.
Owner:SHENZHEN BANG BELL ELECTRONICS
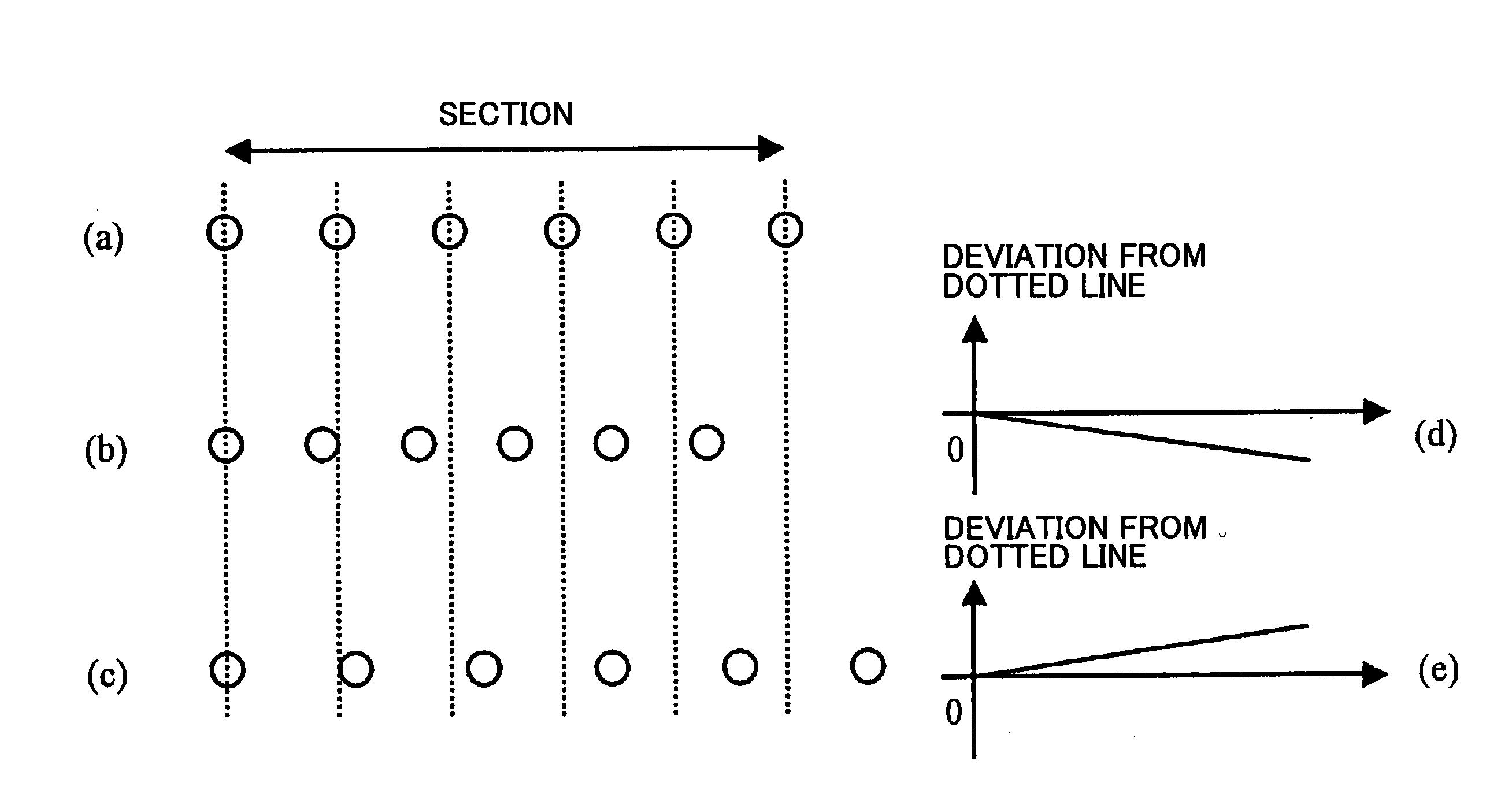
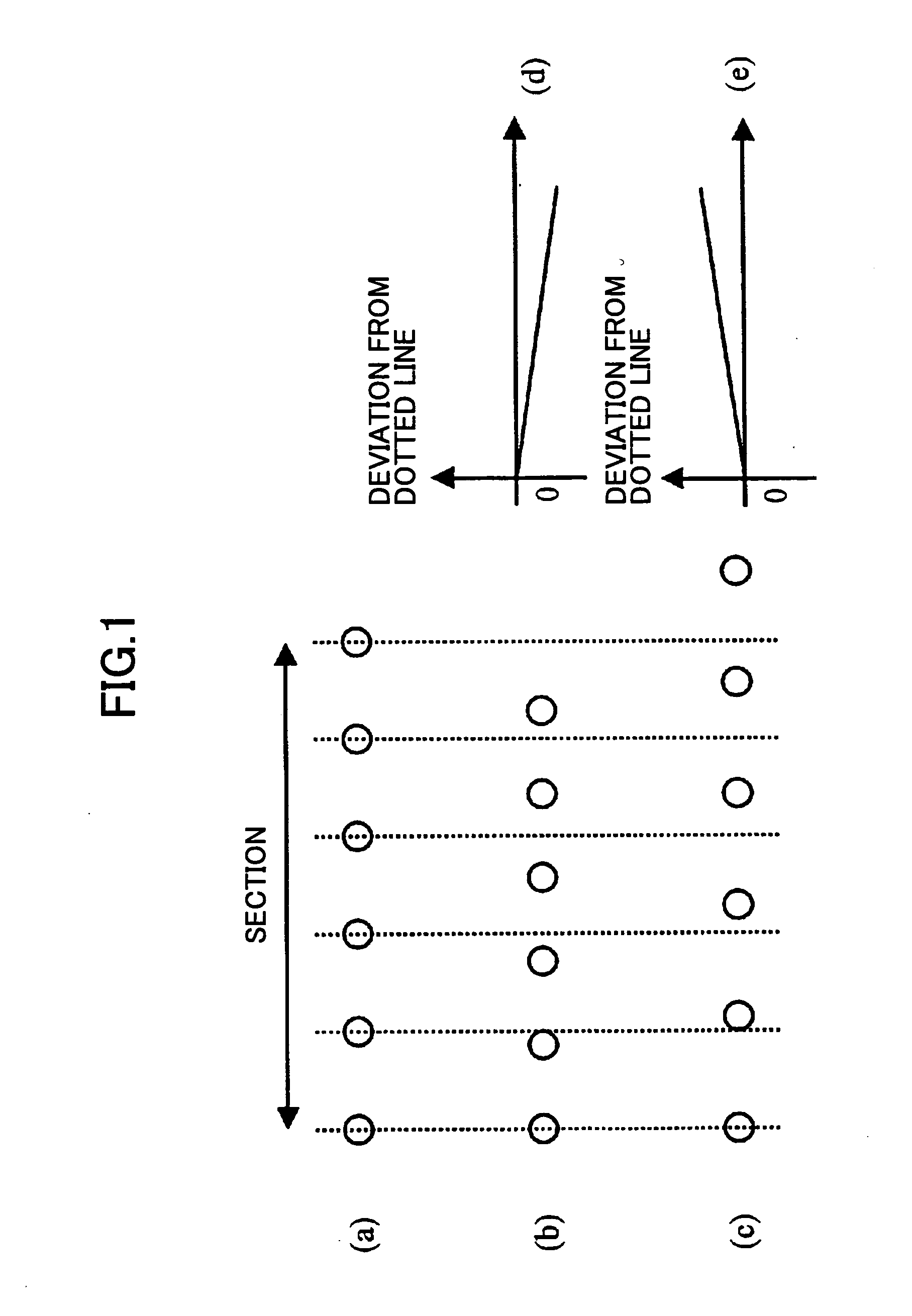
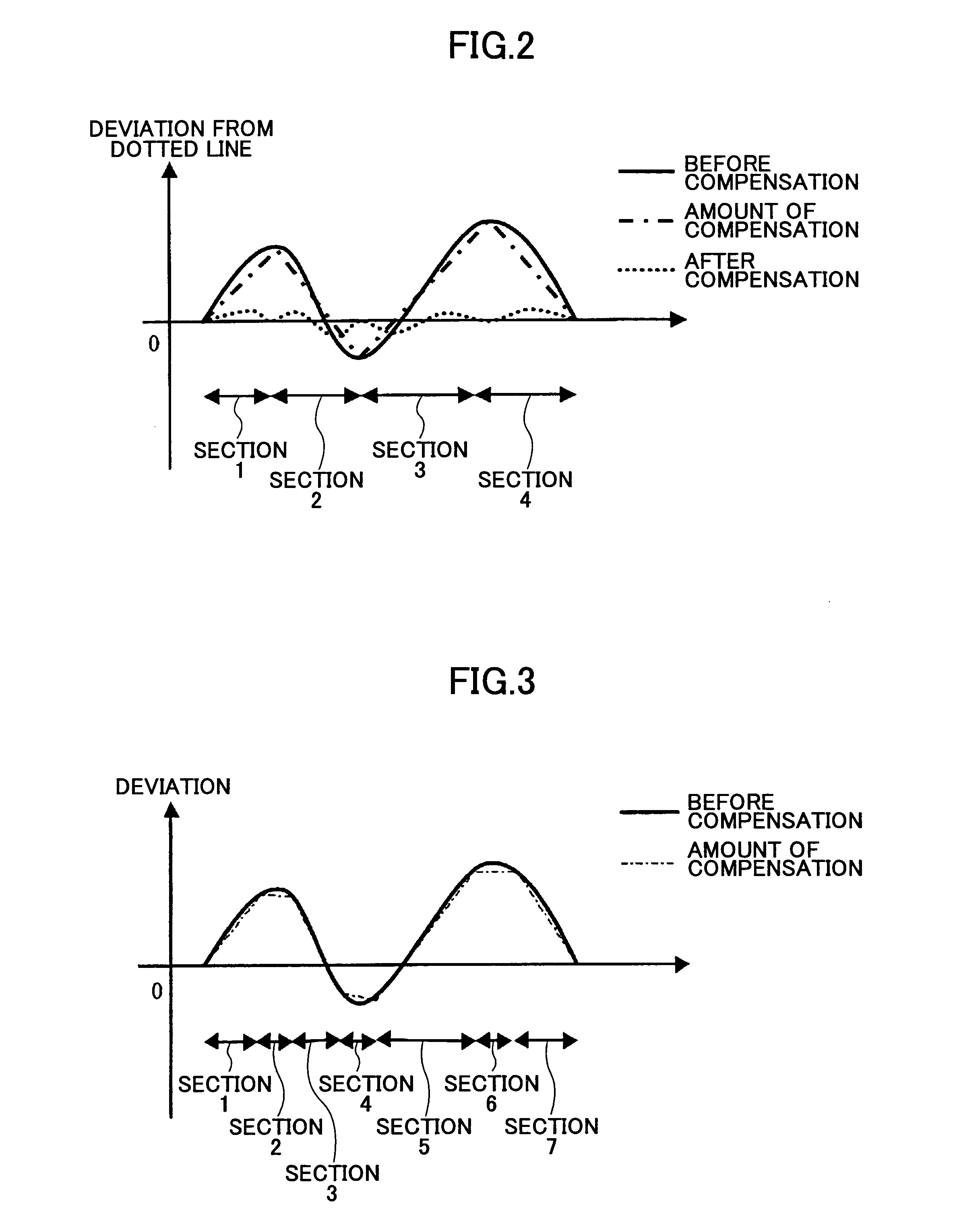
Beam-spot position compensation method, optical scanning device, and multi-color image forming device
InactiveUS20050190420A1Good image qualityFew color deviationOptical elementsOptoelectronicsLight source
In a beam-spot position compensation method for use in an optical scanning device which scans a surface of a photosensitive medium by a light beam emitted by a light source, a plurality of sections are defined by dividing a scanning region on the scanned surface. An emission timing of the light beam for every section is adjusted so that a spacing between beam-spot positions corresponding to pixels of start and end of each section is changed by a predetermined amount. The sparseness or denseness of beam-spot position spacings of the plurality of sections in the whole scanning region is compensated.
Owner:RICOH KK
Method for processing blind hole by laser
InactiveCN101610643AAvoid Scanning RequirementsRemove distortionConductive material mechanical removalLaser beam welding apparatusUv laserLaser processing
The invention discloses a method for processing a blind hole by laser. The method combines fixed point UV laser impulse and UV laser spiral line or concentric circle scanning and is used for one-step blind hole processing or multi-step blind hole processing on multilayer circuit board. The method divides the UV laser blind hole drilling process into two parts, namely a part with an area near the circle center of the blind hole not more than UV laser spot diameter and a part with an area more than the UV laser spot diameter. Fixed point UV laser impulse is adopted to drill the blind hole, so as to remove material in the region with an area near the circle center not more than UV laser spot diameter; then UV laser spiral line or centric circle scanning method is adopted to move outside, so as to remove the material in the region with an area near the circle center more than UV laser spot diameter until meeting set blind hole size; and one-step blind hole or multi-step blind hole processing is drilled by UV laser through two steps or more steps. The method can ensure processing quality consistency of each blind hole, can greatly reduce bottom unevenness of the blind hole, and also can improve margin quality of blind hole processing.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
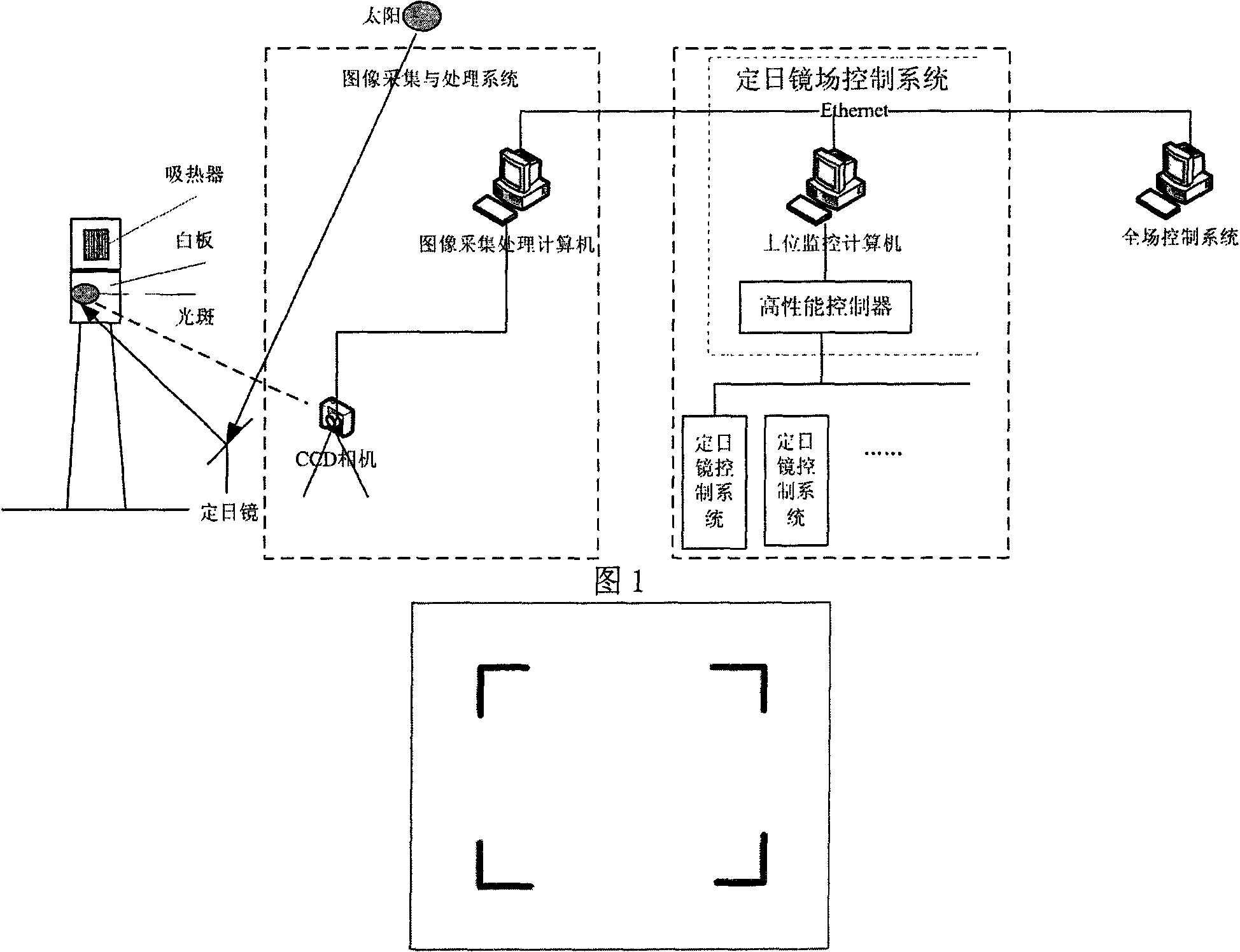
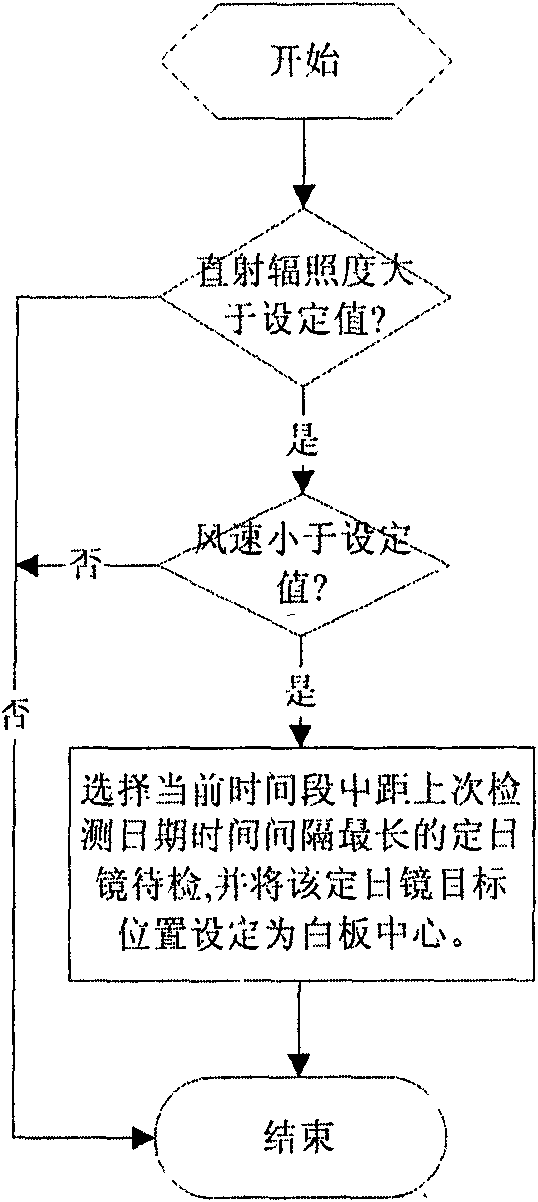
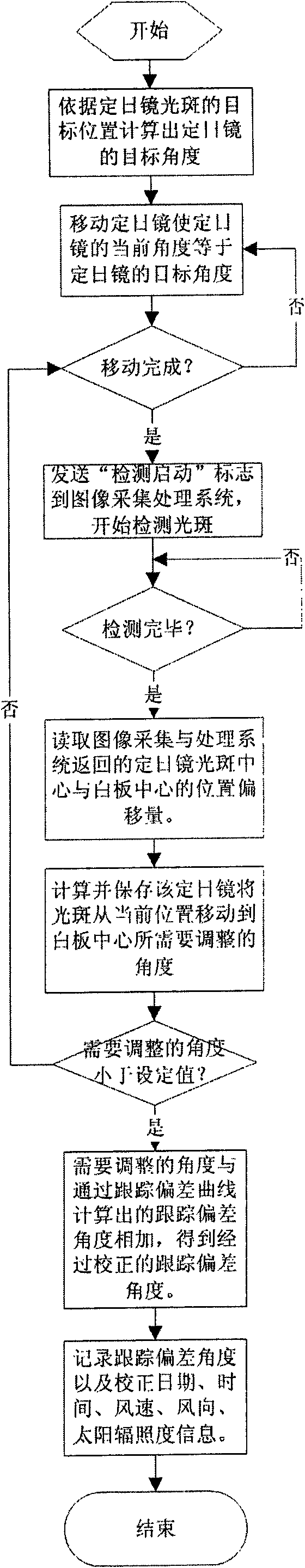
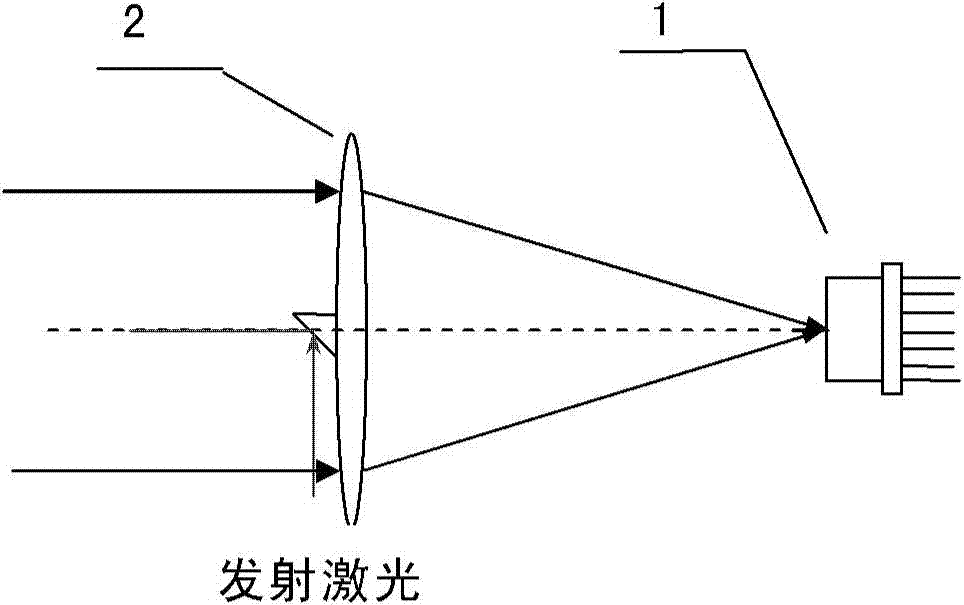
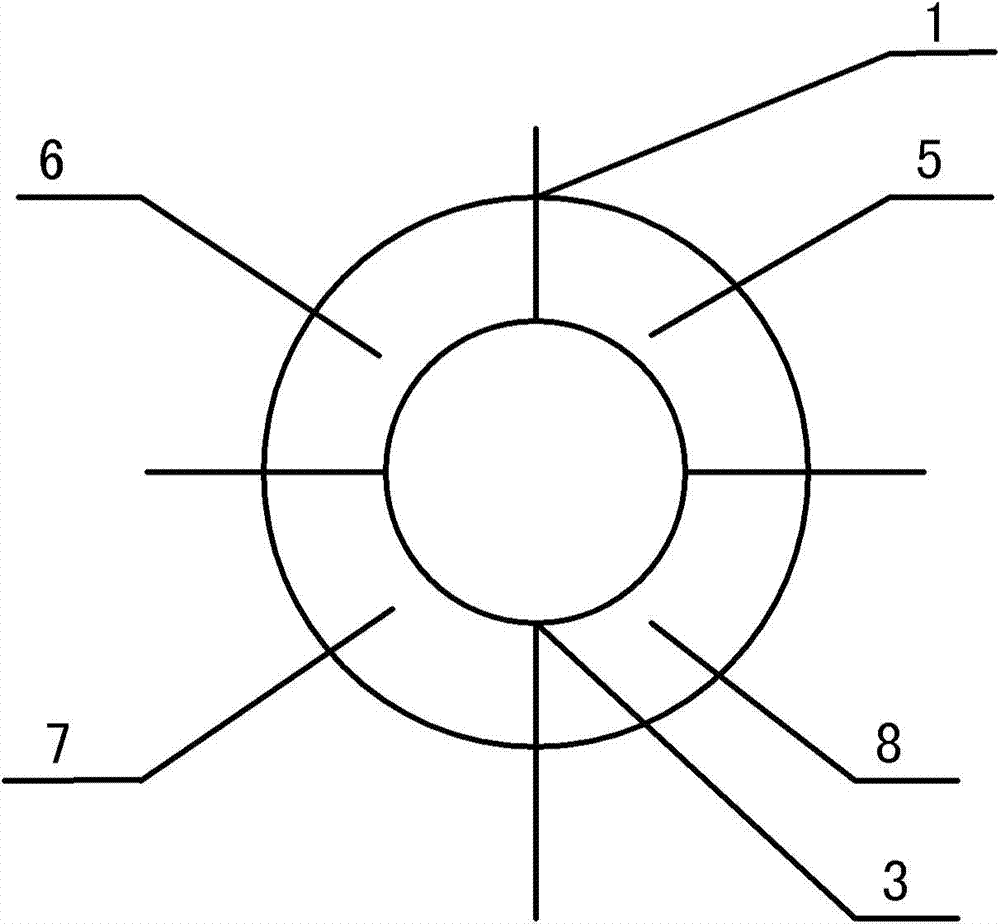
Heliostat tracking error correction method
The invention discloses a heliostat tracking error correction method. Based on the characteristics that a heliostat tracking deviation angle has small variation in a short time and the tracking deviation angles at the same moment in the adjacent days have small variation, an image collecting and processing system is adopted to detect and obtain the tracking deviation angles of a certain heliostat at multiple moments in the whole day, or the tracking deviation angles obtained by the heliostat at multiple moments in one day or previous days are taken as the intraday tracking deviation angle; an intraday tracking deviation curve of the heliostat is obtained by the interpolation; according to the tracking deviation curve, the current angle of the heliostat is corrected to ensure that the facula of the heliostat can basically accurately be projected to a target position. The invention obtains the tracking deviation angles at multiple moments by detection of heliostat tracking error many days a year or many times a day; the everyday corresponding tracking deviation curve of each heliostat can be found by one-year or multiple-year tracking deviation angle data analysis treatment and curve fitting; and thus, the facula of the heliostat can be projected to the target position more accurately.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Measuring device and method for target line-of-sight angel offset and distance
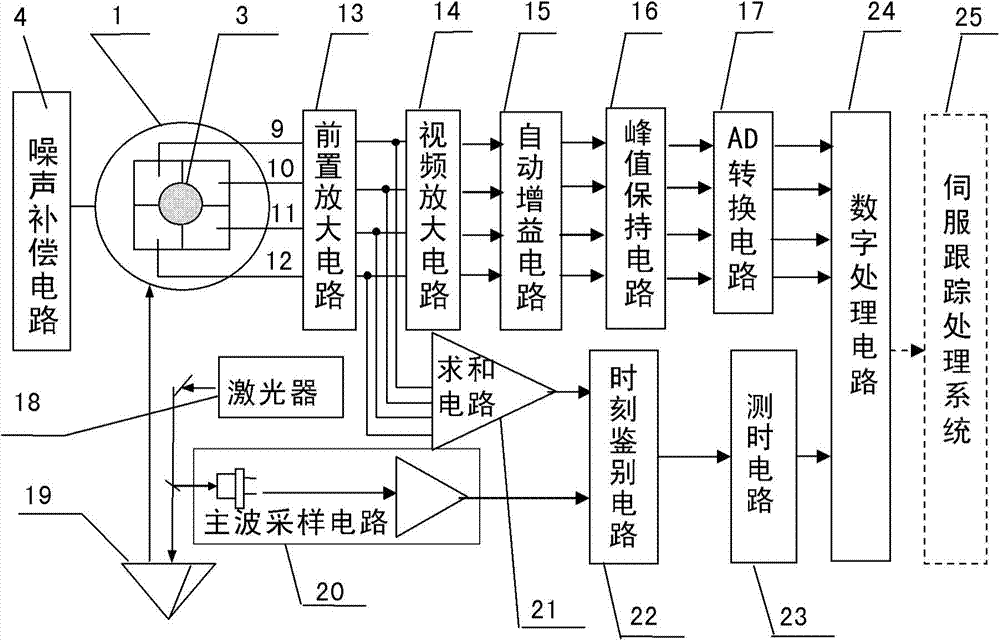
ActiveCN103499819AHigh sensitivityEnsuring Gain StabilityElectromagnetic wave reradiationMeasurement devicePhotodetector
The invention provides a measuring device and method for the target line-of-sight angel offset and distance. The device is composed of a four-quadrant avalanche photodetector, a receiving and sending optical unit, a noise compensation circuit, a four-circuit front amplification circuit, a video amplification circuit, an automatic gain amplification circuit, a peak keeping circuit, an AD conversion circuit, a laser, a dominant wave sampling circuit, a summing circuit, a time identifying circuit, a time test circuit and a digital processing circuit, wherein the receiving and sending optical unit enables narrow pulse laser rays emitted by the laser to be converged on the photoelectric detector to form echo light spots after target reflection, photovoltaic conversion of the four-quadrant avalanche photodetector, front amplification, video amplification and automatic gain amplification are conducted, narrow-pulse peak keeping is conducted, transmission of the AD conversion circuit is conducted, and the digital processing circuit extracts the digital line-of-sight angel offset; summing is conducted on the four-circuit front amplification circuit, the dominant wave sampling circuit is combined, the time identifying circuit determines laser emitting and echo coming and returning time, the time is transmitted to the time identifying circuit to be measured, and the digital processing circuit decodes the corresponding distance.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Scanning microscopy, fluorescence detection, and laser beam positioning
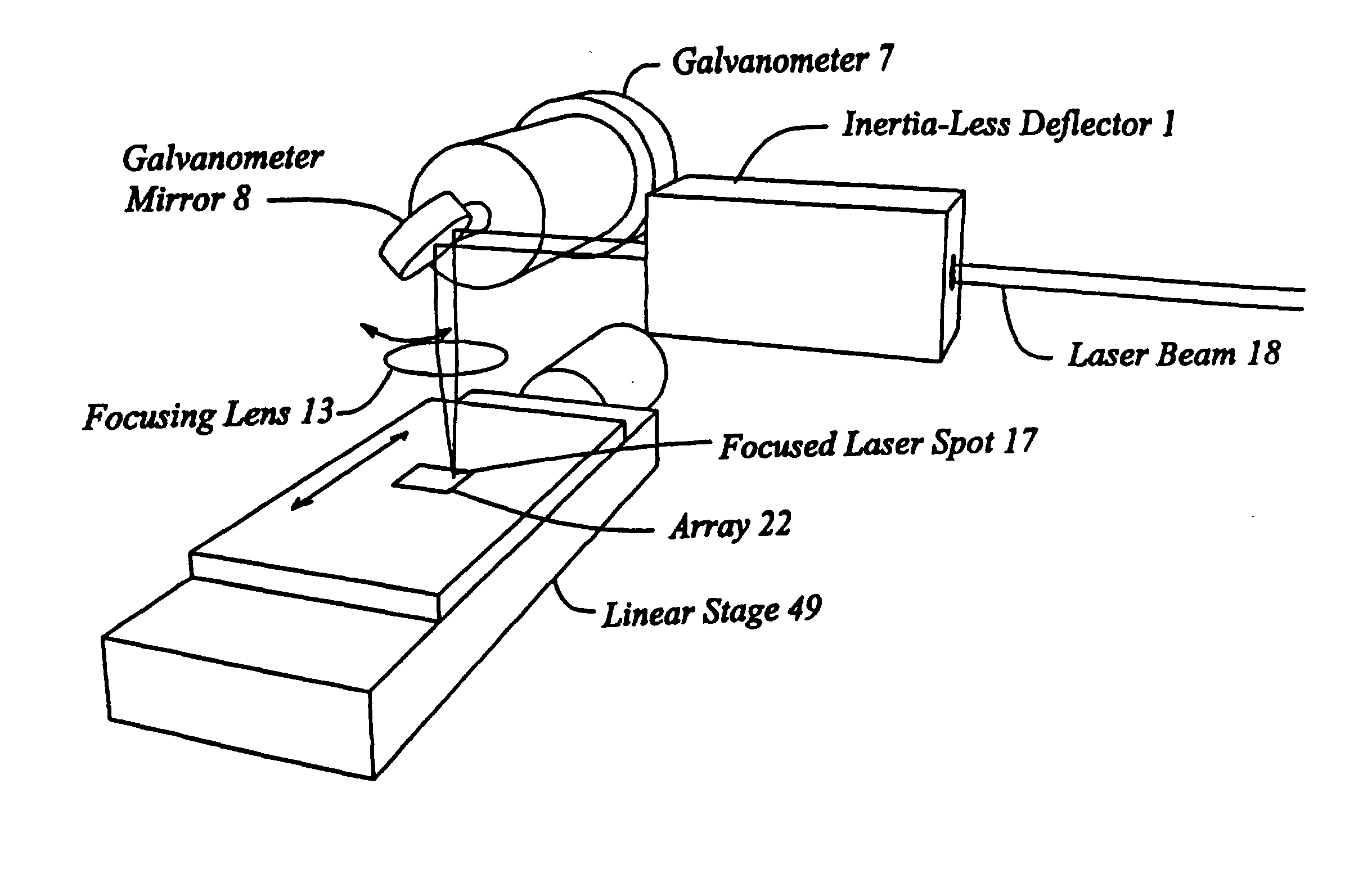
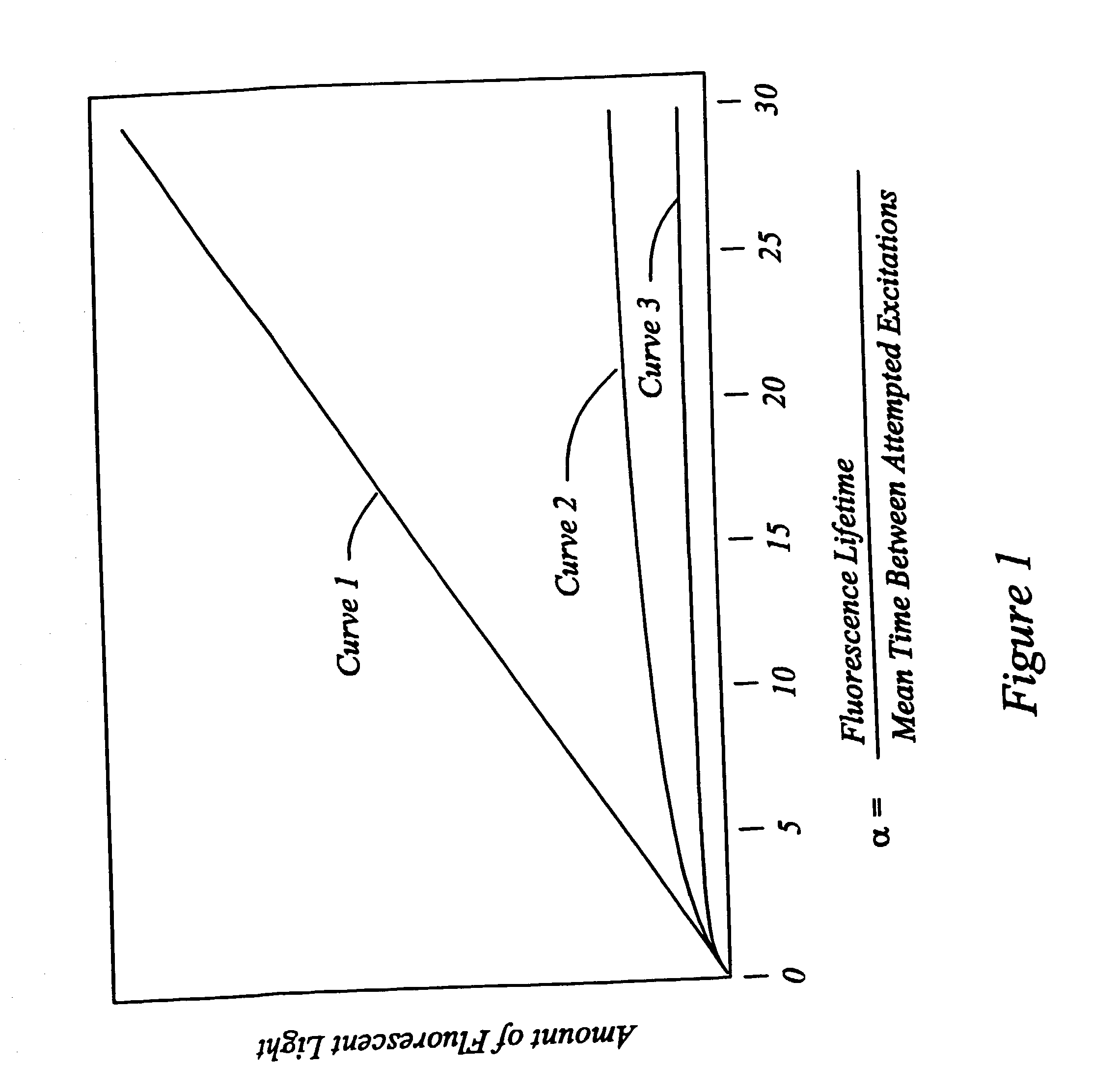
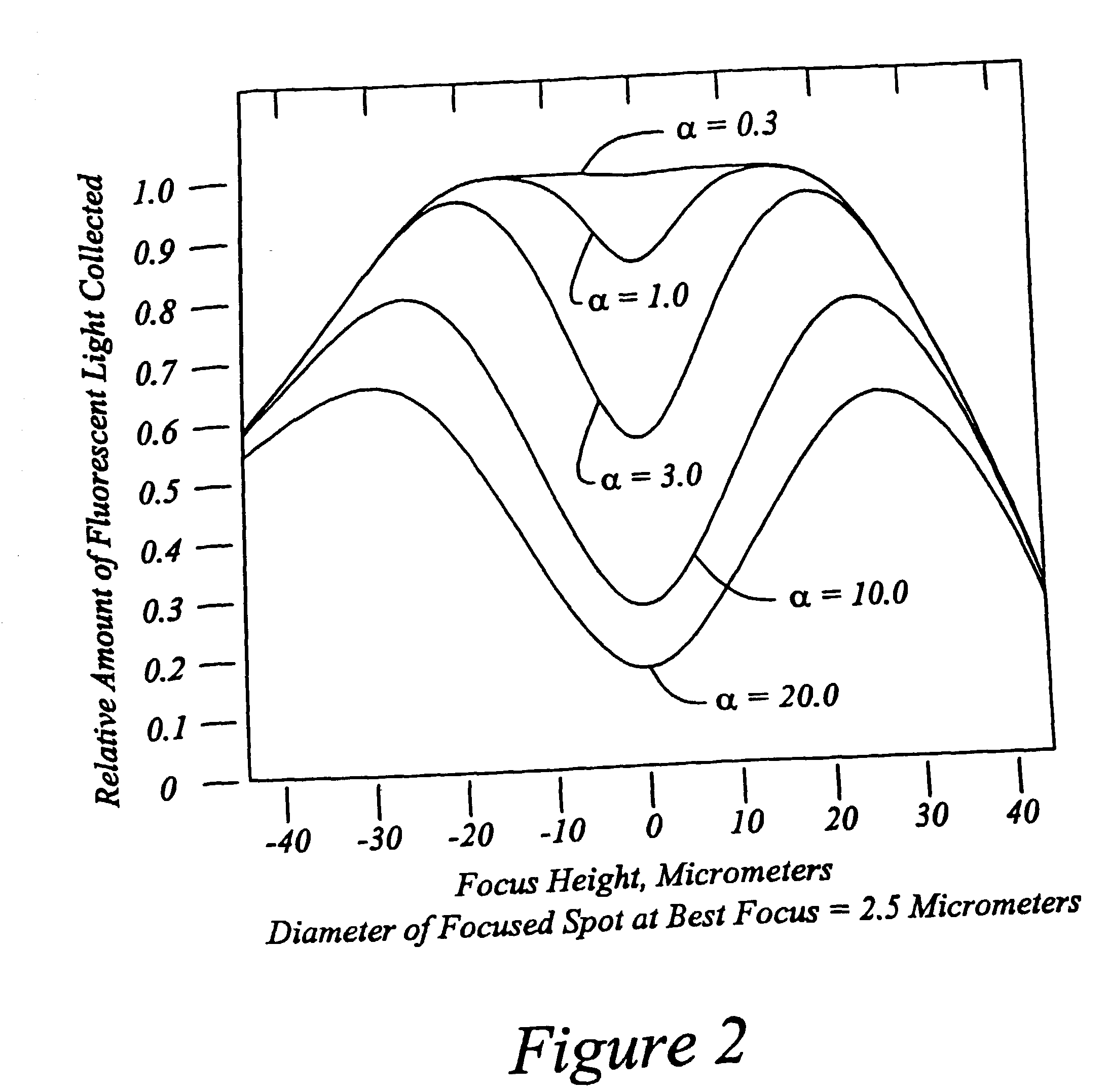
InactiveUS20030156323A1Diameter of to varyEnsure high efficiency and accuracyMirrorsMaterial analysis by optical meansWide areaGrating
High speed, wide area microscopic scanning or laser positioning is accomplished with an inertia-less deflector (for example an acousto-optic or electro-optic deflector) combined with a high speed wide area microscopic scanning mechanism or laser positioner mechanism that has inertia, the motion of the inertia-less deflector specially controlled to enable a focused spot to stabilize, for example to stop and dwell or be quickly aimed. It leads to improved data acquisition from extremely small objects and higher speed operation. In the case of fluorescence reading of micro-array elements, dwelling of fluorophore-exciting radiation in a spot that is relatively large enables obtaining the most fluorescent photons per array element, per unit time, a winning criterion for reducing fluorophore saturation effects. The same inertia-less deflector performs stop and dwell scanning, edge detection and raster scans. Automated mechanism for changing laser spot size enables selection of spot size optimal for the action being performed.
Owner:OVERBECK JAMES W
Small Spot Size Spectroscopic Ellipsometer
ActiveUS20130321810A1High measurement sensitivityIncrease the number ofPolarisation-affecting propertiesPhotomechanical apparatusAngle of incidenceMetrology
Methods and systems for small angle CD metrology with a small spot size are introduced to increase measurement sensitivity while maintaining adequate throughput necessary for modern semiconductor manufacture. A small angle CD metrology system includes a small angle spectroscopic ellipsometry (SE) subsystem combined with a small angle spectroscopic reflectometry system, both operated at small angles of incidence. The small angle SE subsystem is configured to operate in a complete Mueller Matrix mode to further improve measurement sensitivity. The small angle CD metrology system includes an objective having all reflective surfaces in the light path. In some embodiments, the all-reflective objective is a Schwartzschild objective having an axicon mirror element to further reduce measurement spot size. In some embodiments, the small angle CD metrology system includes a dynamic aperture subsystem to isolate specific ranges of angles of incidence and azimuth for improved measurement sensitivity.
Owner:KLA CORP
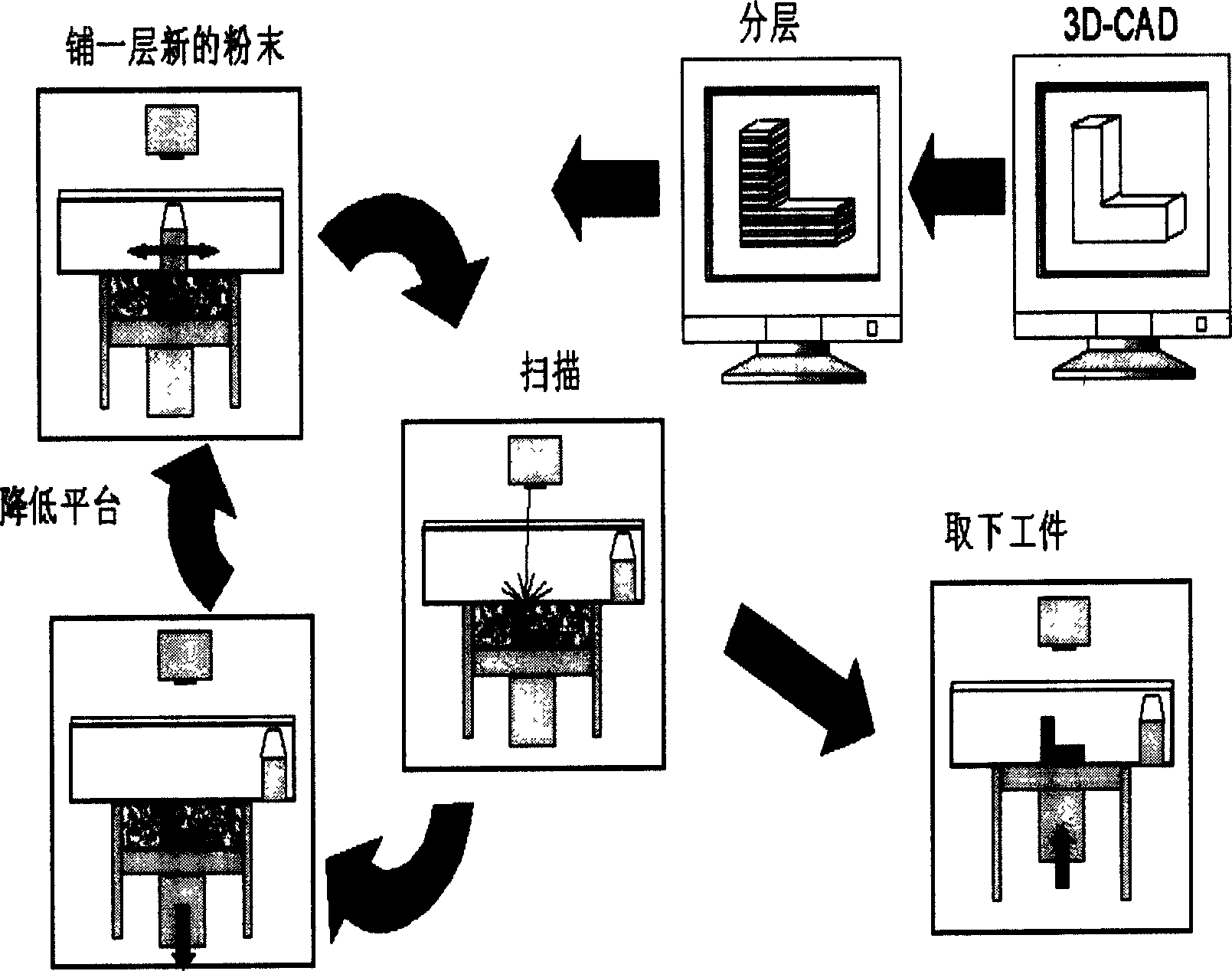
Selected zone laser melting and rapid forming method for metal parts and apparatus thereof
The invention relates to laser melting rapid forming method in the metal parts precinct and its installation. The method includes that setting CAD geometric model, doing stratification variance and laying powder layer by layer to the CAD geometric mode, adopting laser with high power density and high light speed factor of merit to form focusing facula with the diameter which is from thirty millimeter to fifty millimeter by focusing of beams system, melting the metal or alloy powder layer by layer, piling to a metallurgy unite, and forming to a compact solid mass. The installation is made up of semiconductor pumping YAG laser or fiber laser, focusing of beams system, shaped part jar, and powder jar. The semiconductor pumping YAG laser or fiber laser is light path connected to the focusing of beams system, and focalized and scanned at the shaped part jar. The shaped part jar is connected to the powder jar by powder laying roller. The powder laying roller is connected to the driving motor. And the driving motor is connected to the computer. The advantages of the invention are that the beam mode is good; mechanical features of the processed metal parts is well; the dimensional precision and the surface finish are high; and its range of application is wide.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Surface array semiconductor laser light beam shaping device
InactiveCN101144909AEasy to manufactureSimple structureLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersDivergence angleLight beam
The present invention relates to a beam reshaping device for a plane array semiconductor laser. The device includes a fast axis collimating lens, a slow axis collimating lens, a ladder lens, a first parallelepiped prism unit, and a second parallelepiped prism unit. The beam emitted by the plane array semiconductor laser passes through the fast axis collimating lens and the slow axis collimating lens, and lowers the divergence angle of the fast axis and the divergence angle of the slow axis. The irradiance interspace between bars can be eliminated by the ladder lens and can be compressed in the direction of the fast axis. Finally, part of beam can be moved parallel along the fast axis direction by the first parallelepiped prism unit and the second parallelepiped prism unit, and then be moved along the slow axis direction. Through the above process, the beam is realigned, and the purpose that the quality of the fast axis beam and the quality of the slow axis beam tend to be coincident is reached. The realigned beam can get high-power high-brightness facula after being focused. The optical apparatus used in the present invention is easy to be produced and convenient to be adjusted with simple structure.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
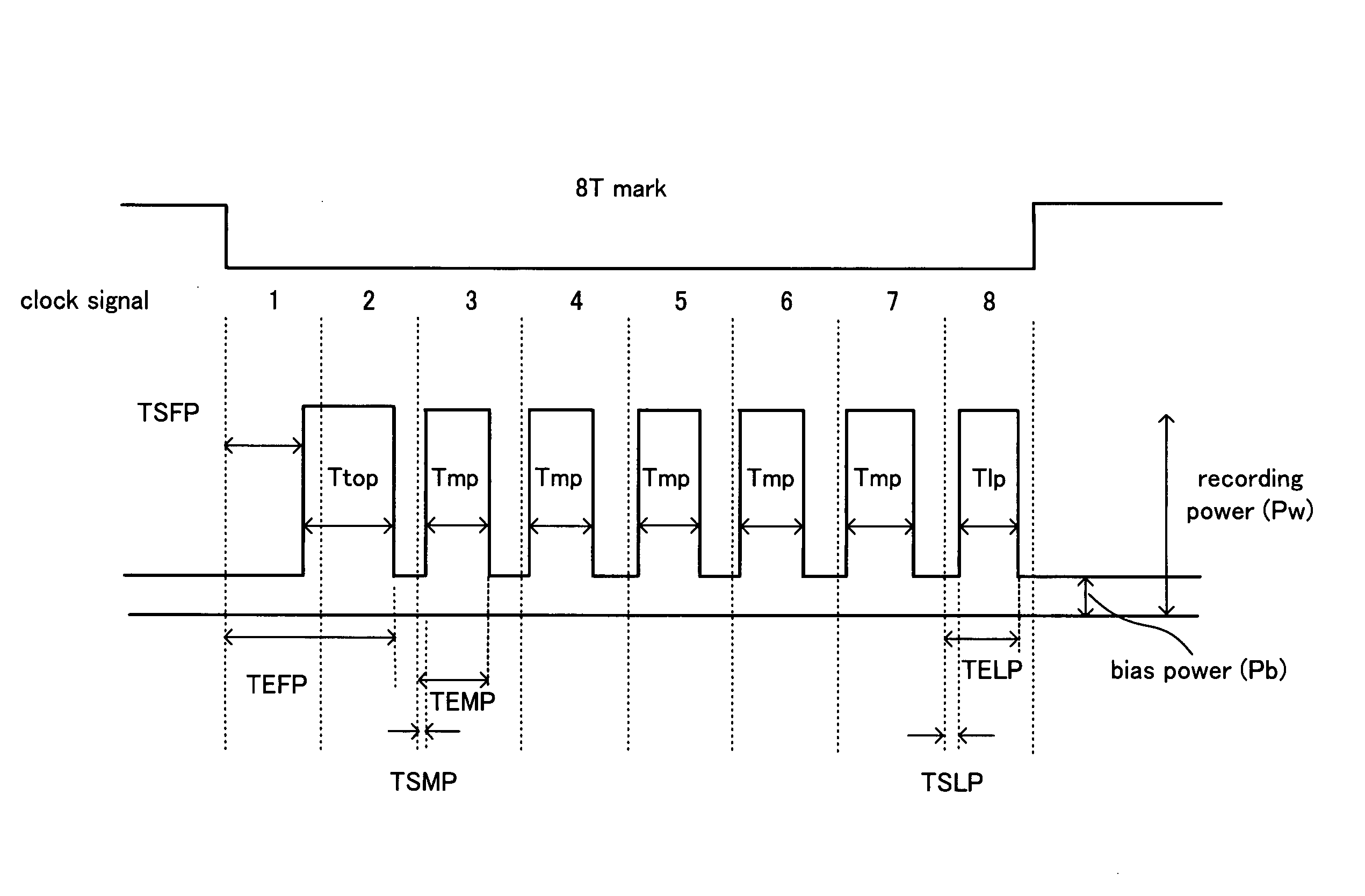
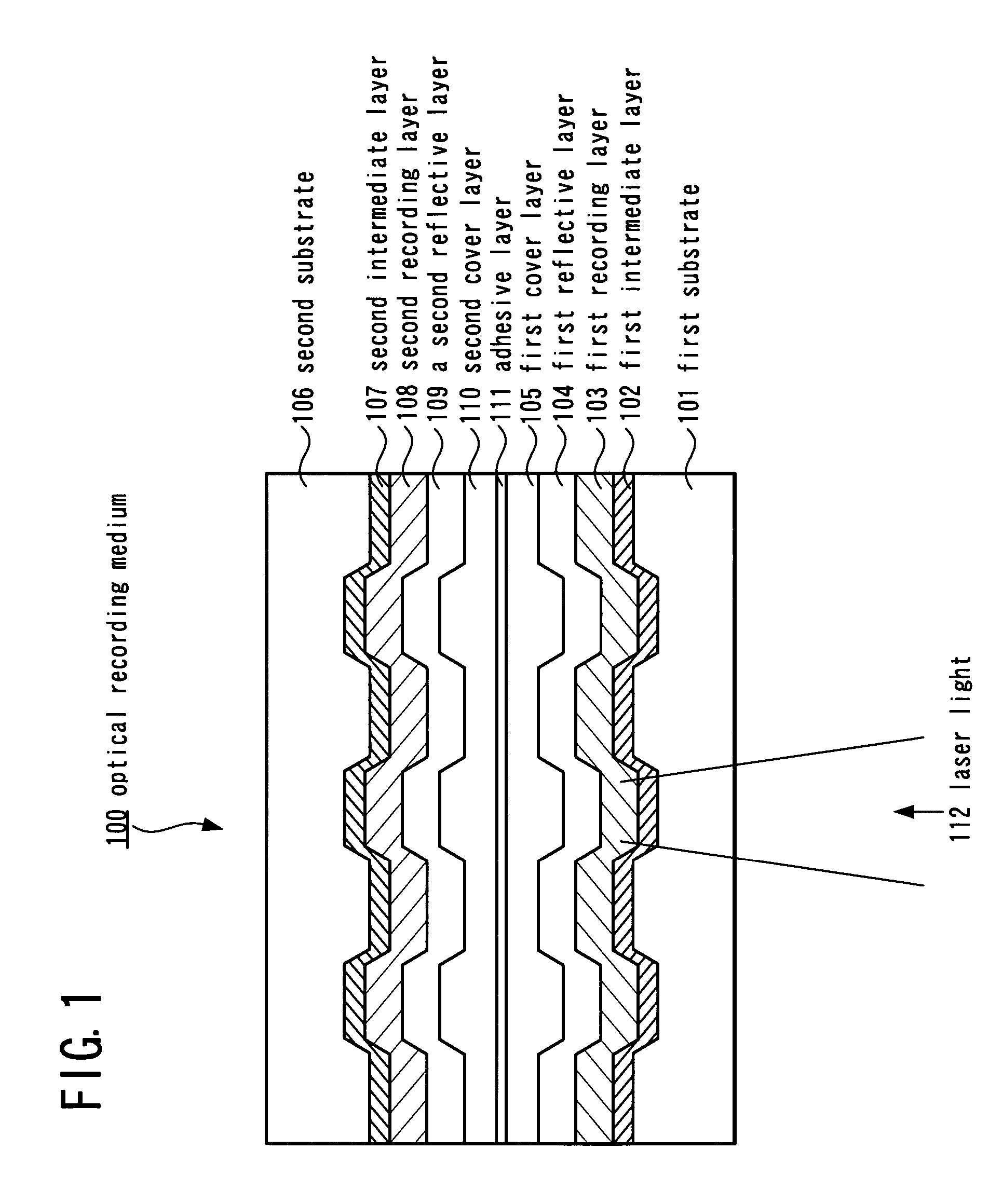
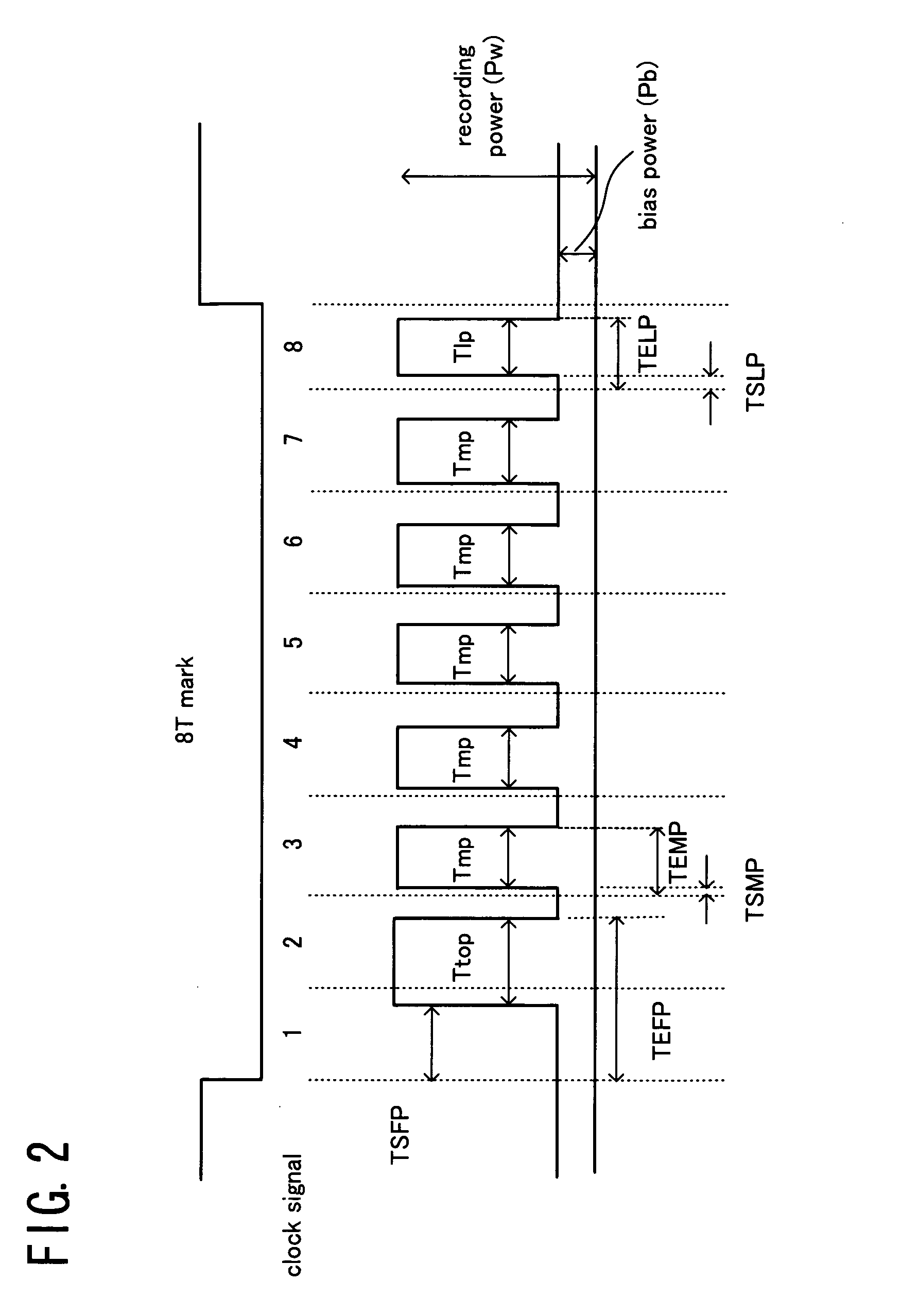
Information recording method and information recording medium
InactiveUS20050063274A1Enhanced informationRecording strategiesTelevision system detailsHigh densityEngineering
An information recording method allows optical information having a recording mark length smaller than a spot diameter of laser light to be recorded on an optical recording medium having a recording layer, at high density by laser light pulse application. The information recording method has: a power calibration step of determining a recording power for recording a signal having a predetermined signal length in the recording layer using the laser light; and a complementing step of complementing, based on the recording power determined in the power calibration step, a recording power for recording a signal having a signal length equal to or less than ½ of the spot diameter of the laser light in the recording layer using the laser light. In the information recording method, for example, an extremely small mark, such as a 2T signal, can be precisely formed.
Owner:VERBATIM CORPORATION +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com