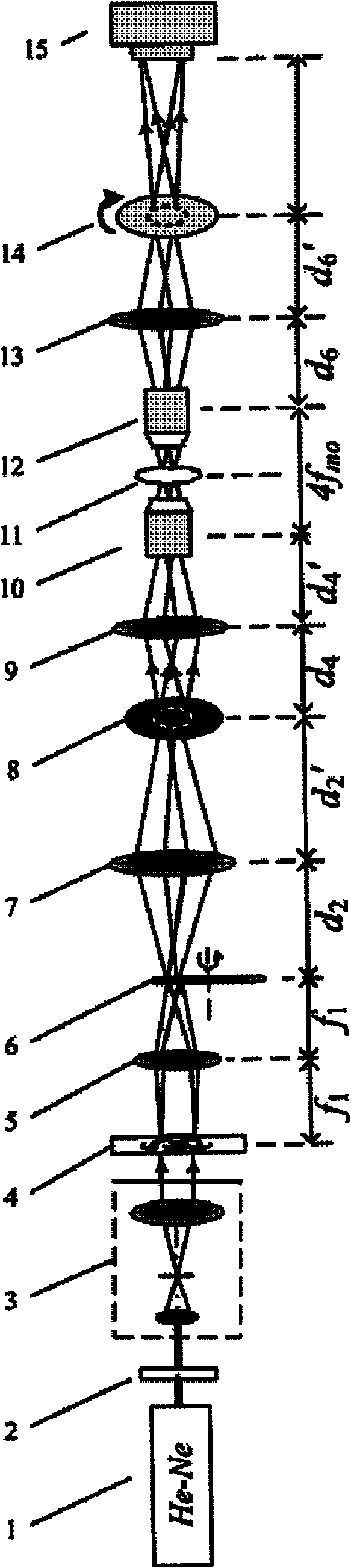
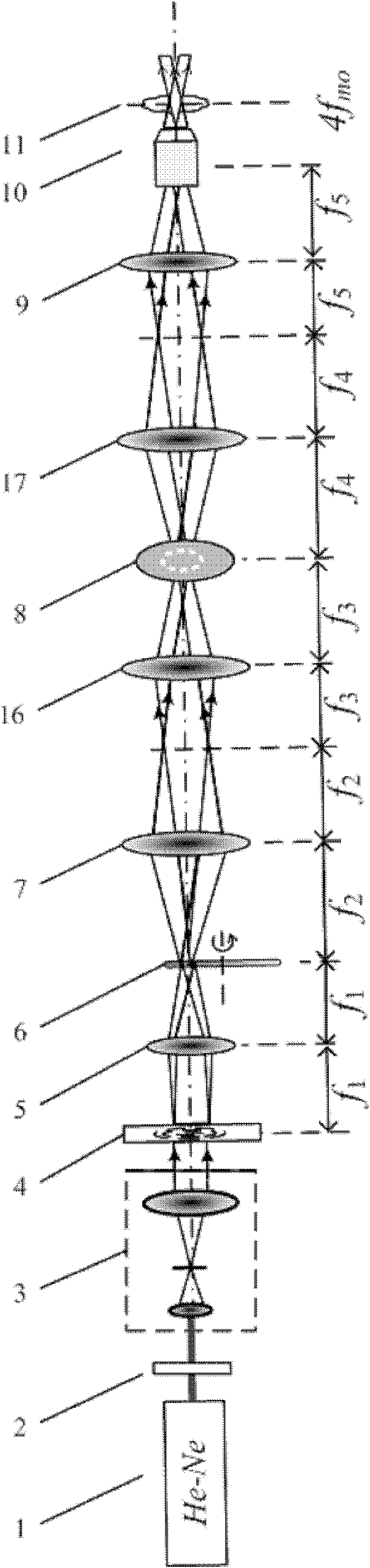
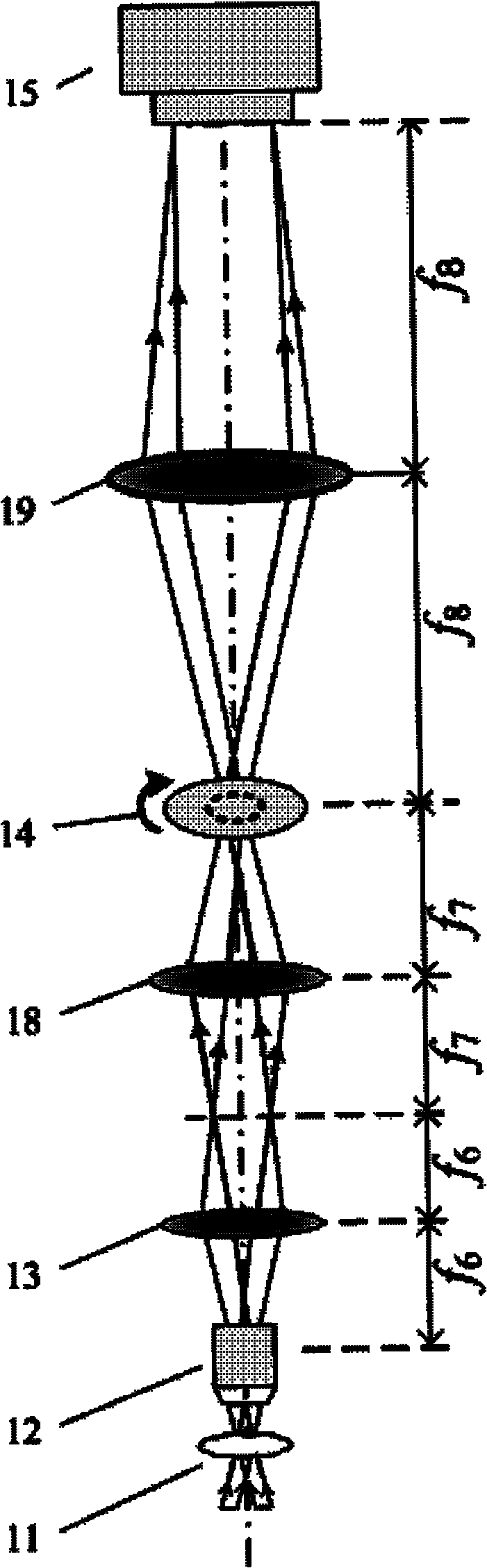
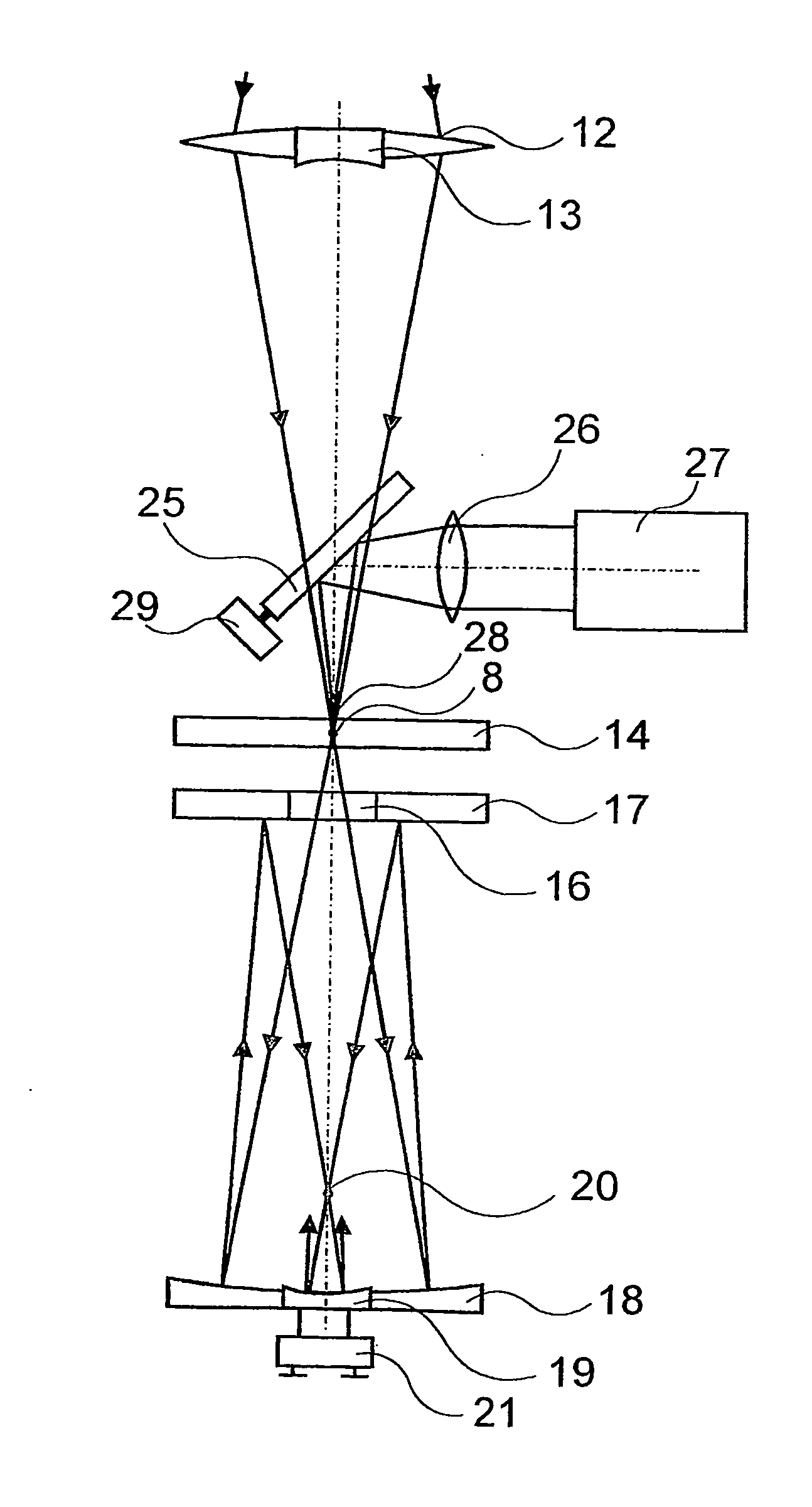
Patents
Literature
223 results about "Axicon" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
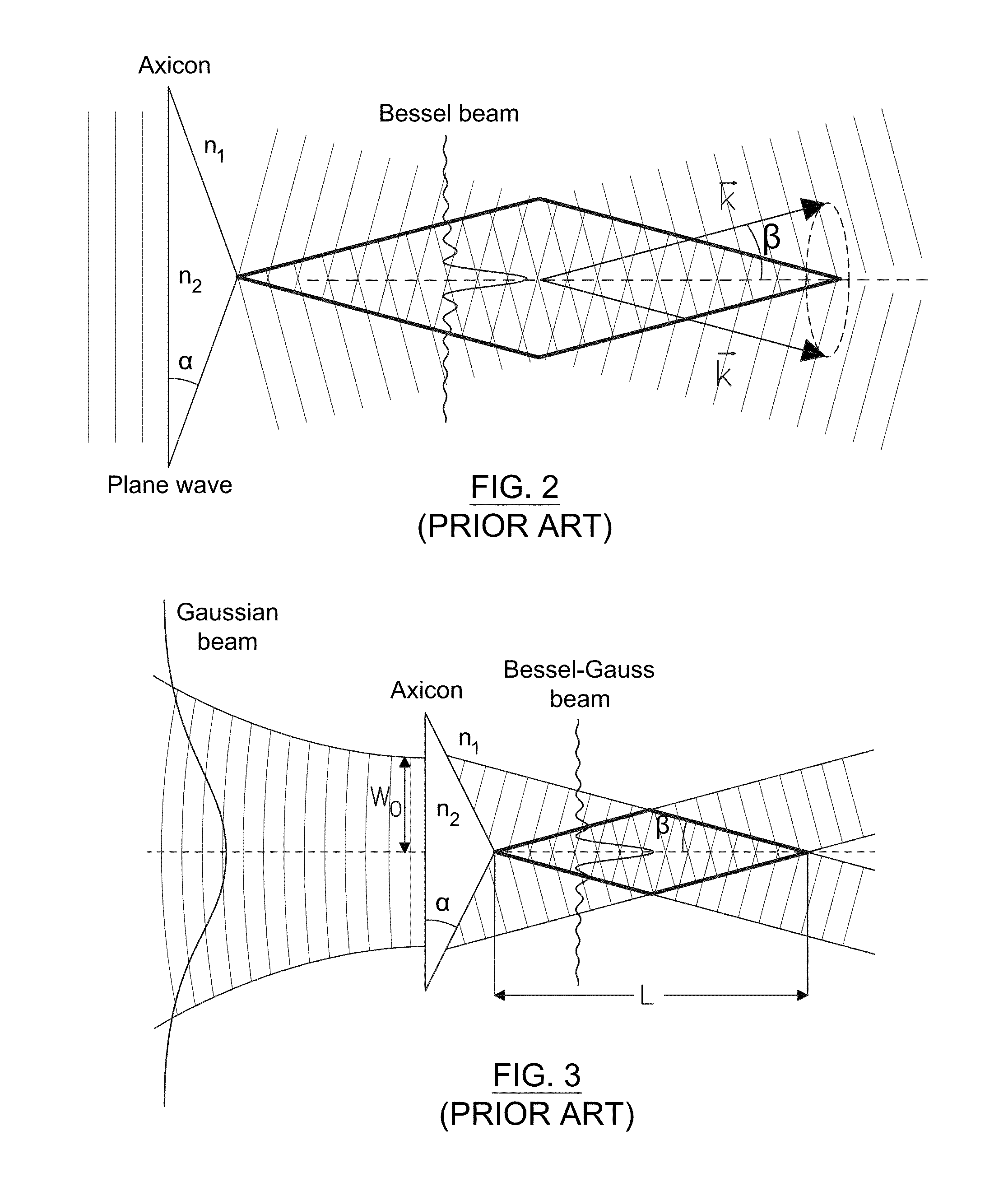
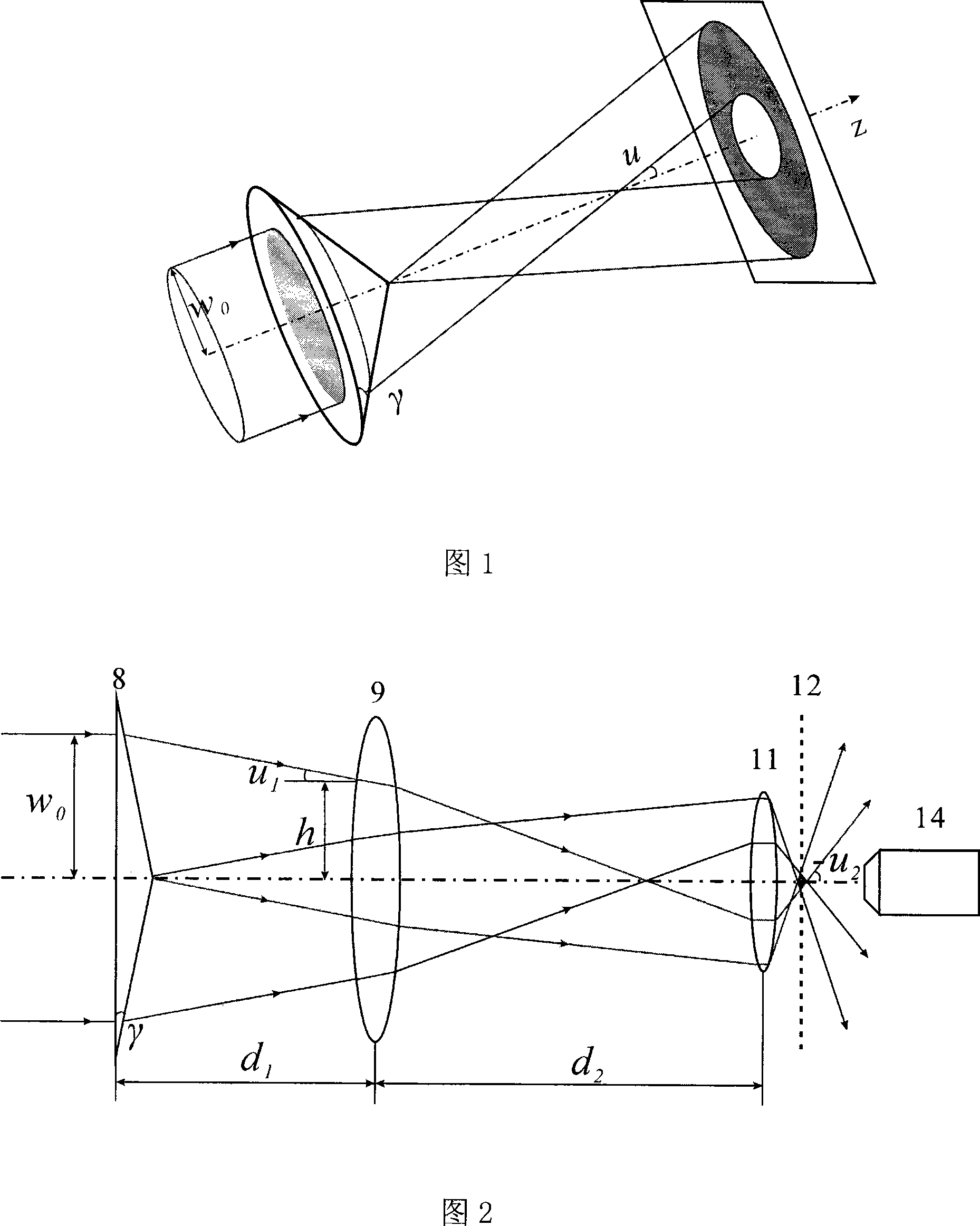
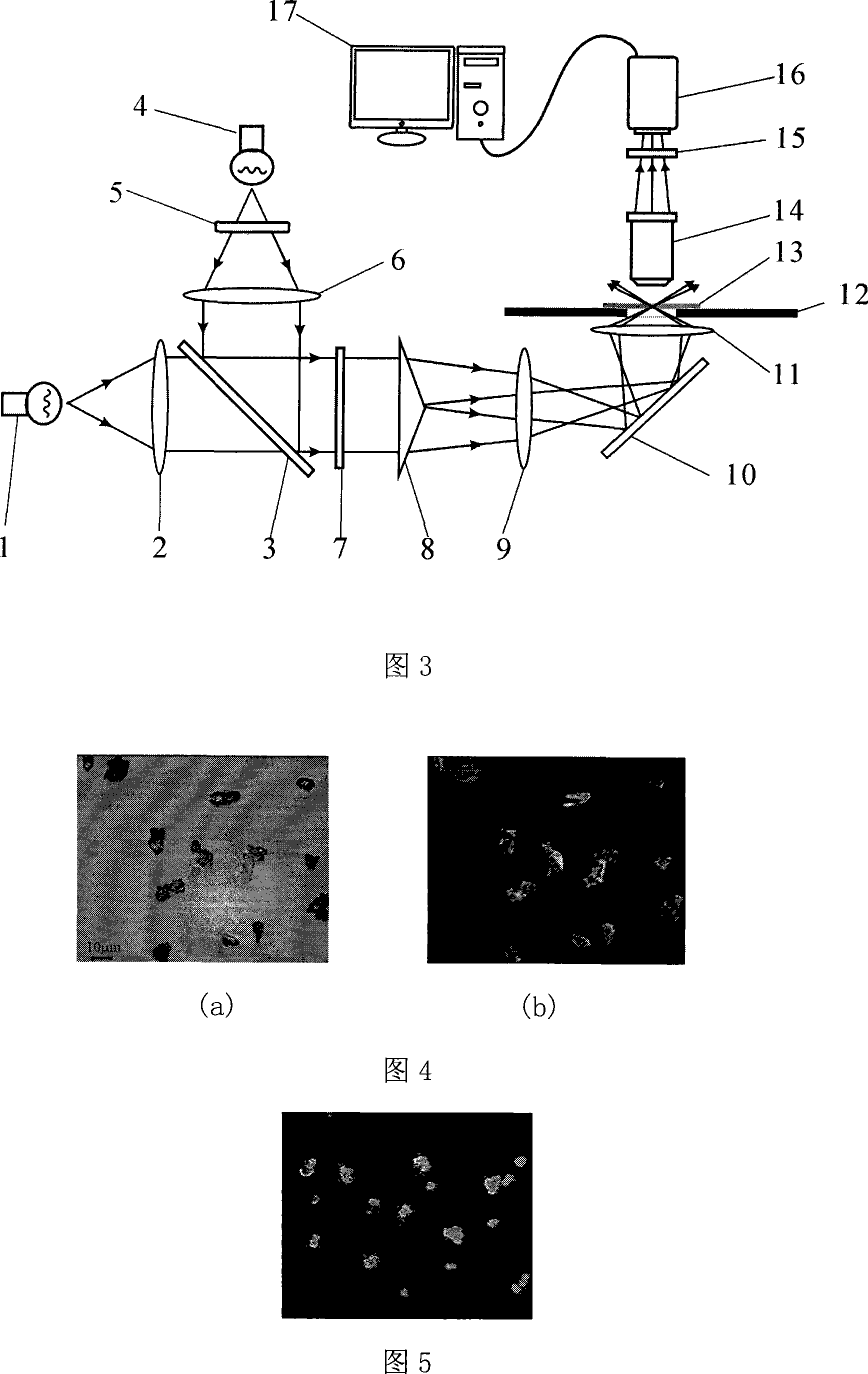
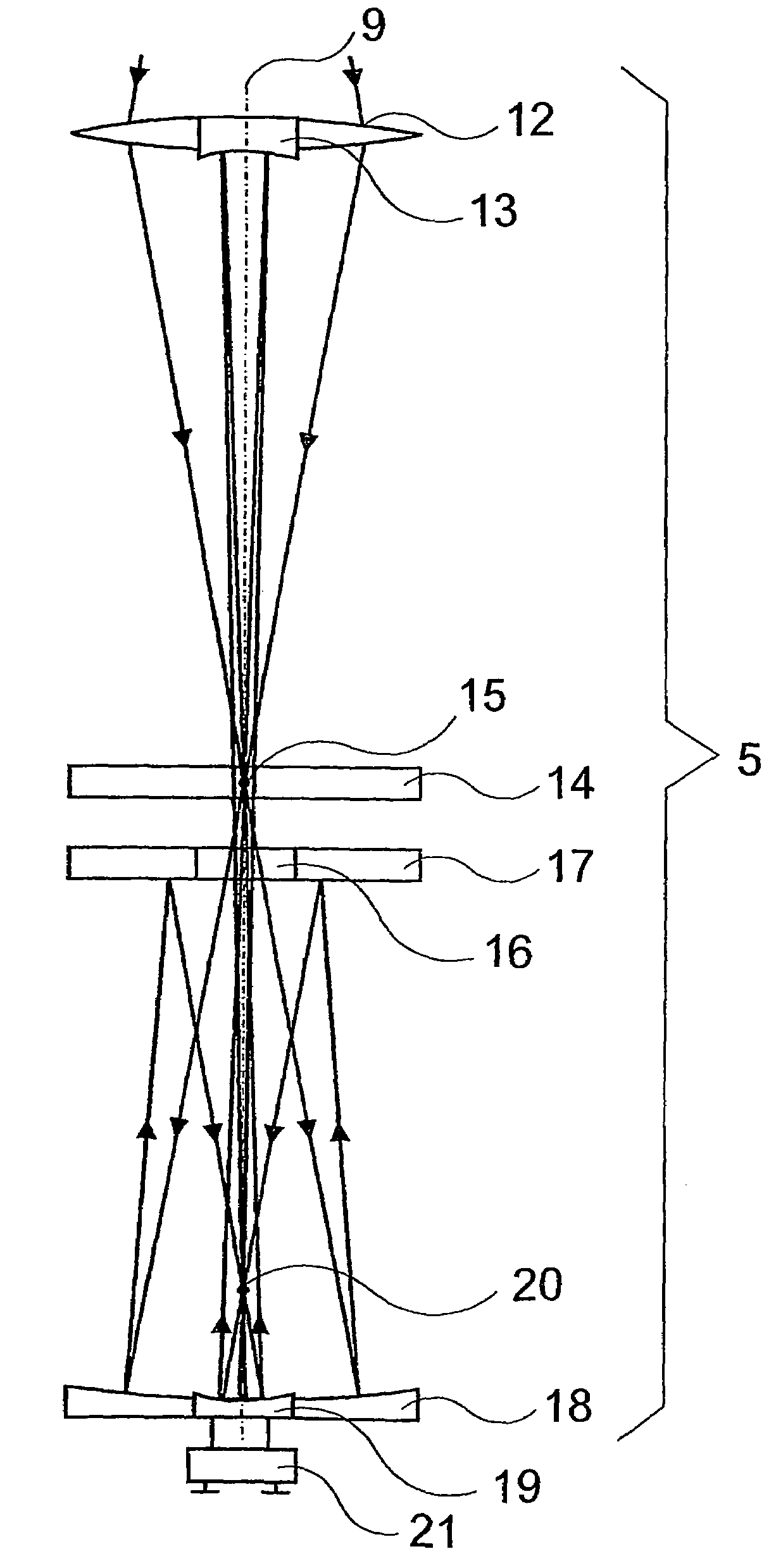
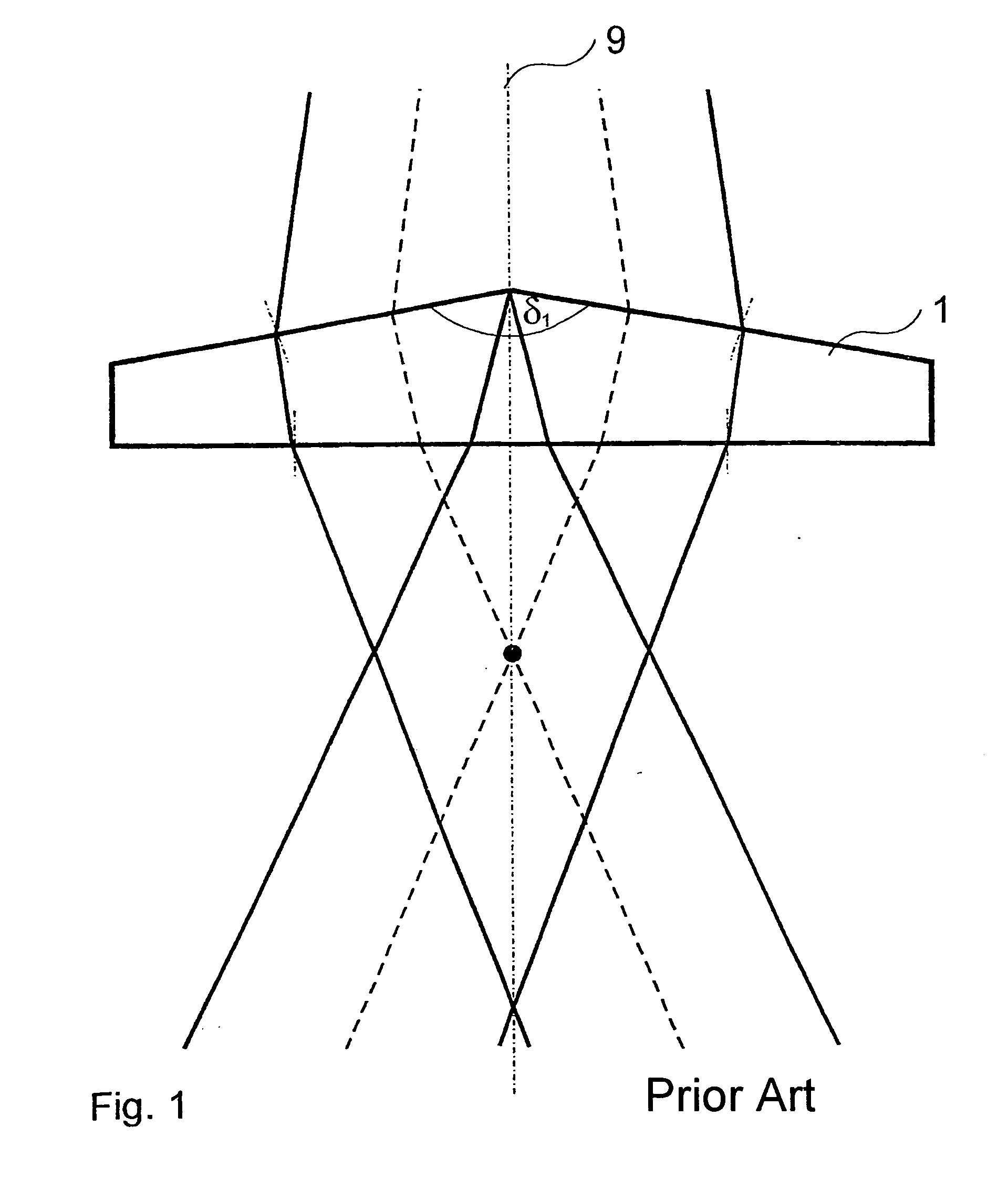
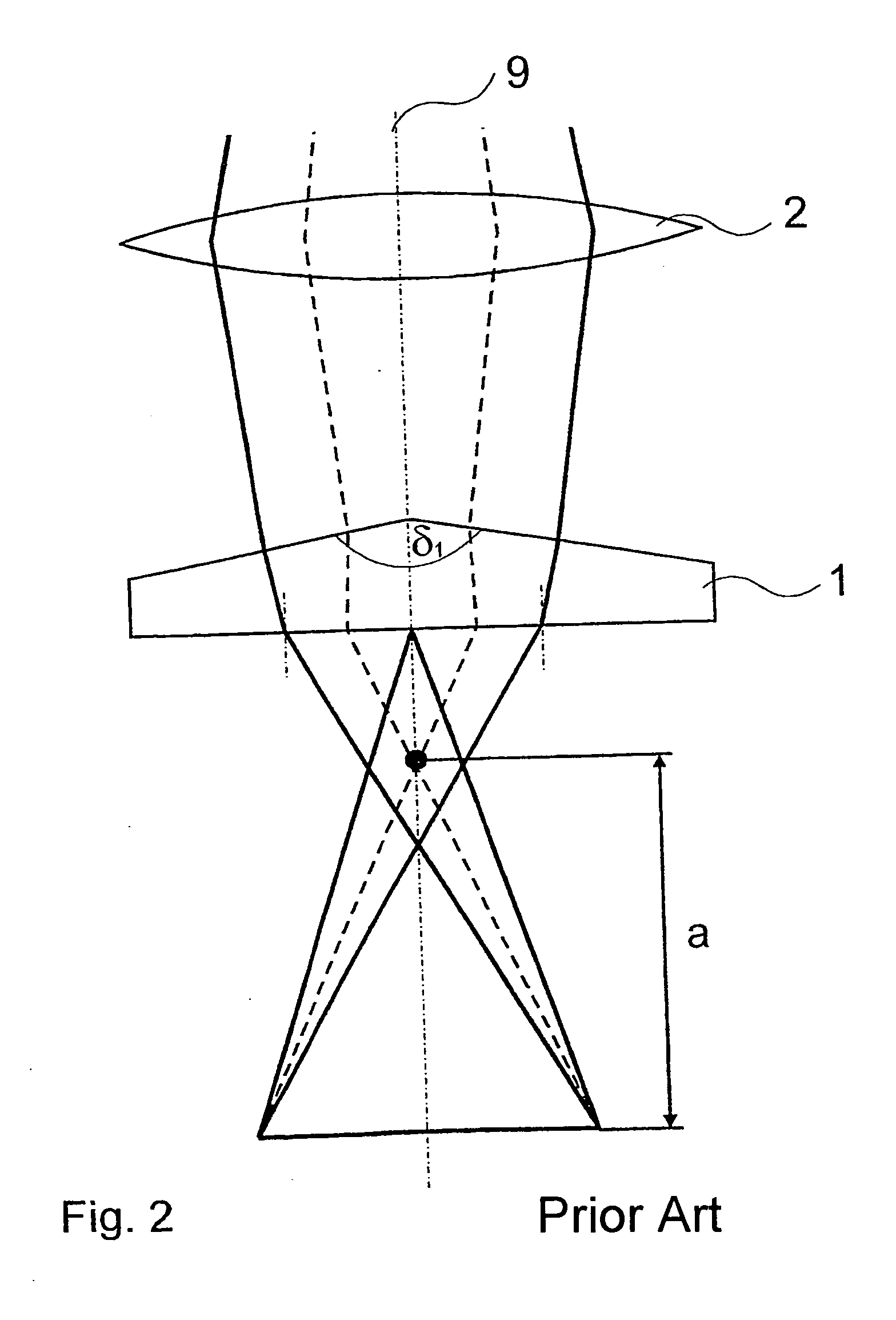
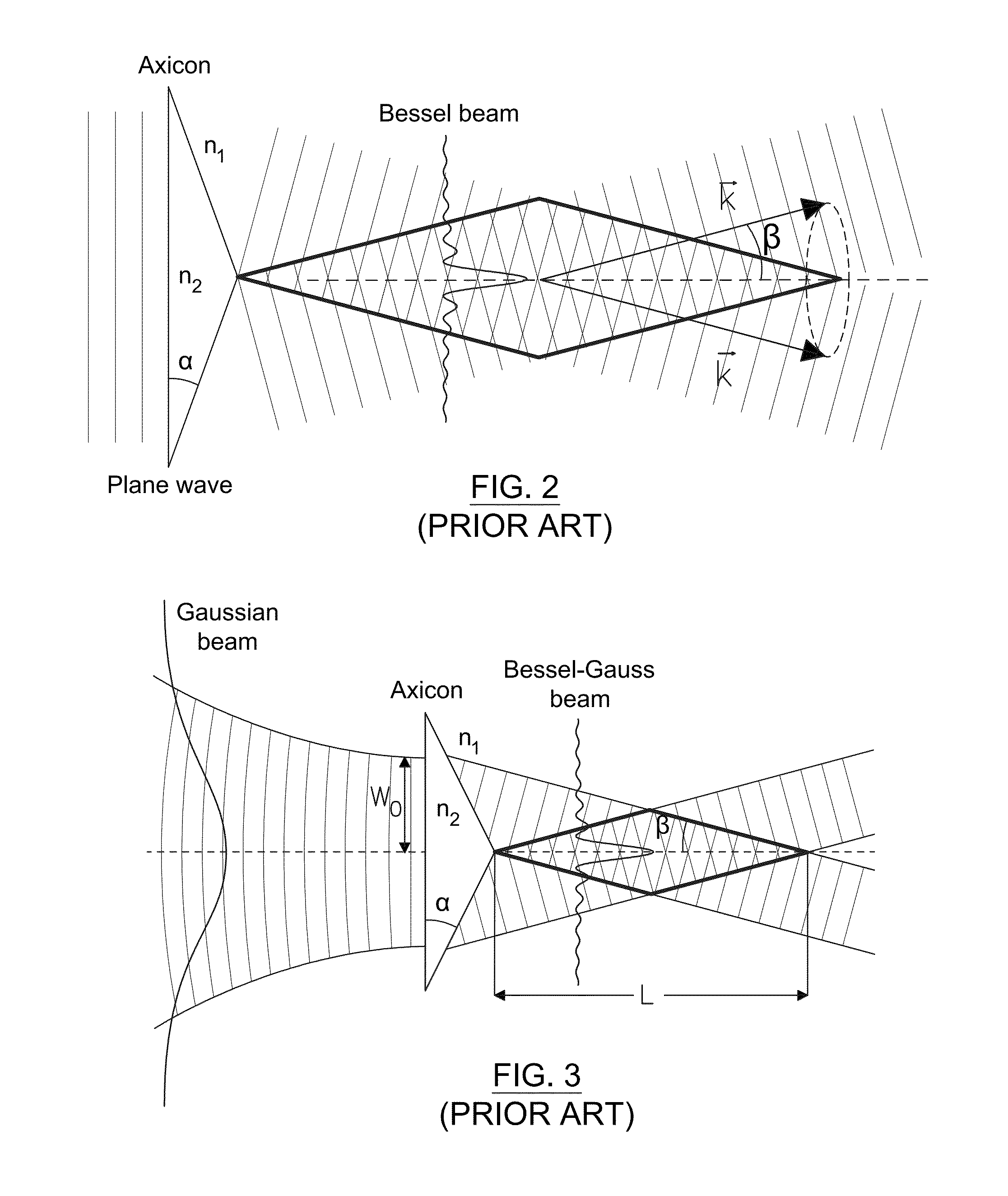
An axicon is a specialized type of lens which has a conical surface. An axicon transforms a laser beam into a ring shaped distribution. They can be convex or concave and be made of any optical material. The combination with other axicons or lenses allows a wide variety of beam patterns to be generated. It can be used to turn a Gaussian beam into a non-diffractive Bessel-like beam. Axicons were first proposed in 1954 by John McLeod.
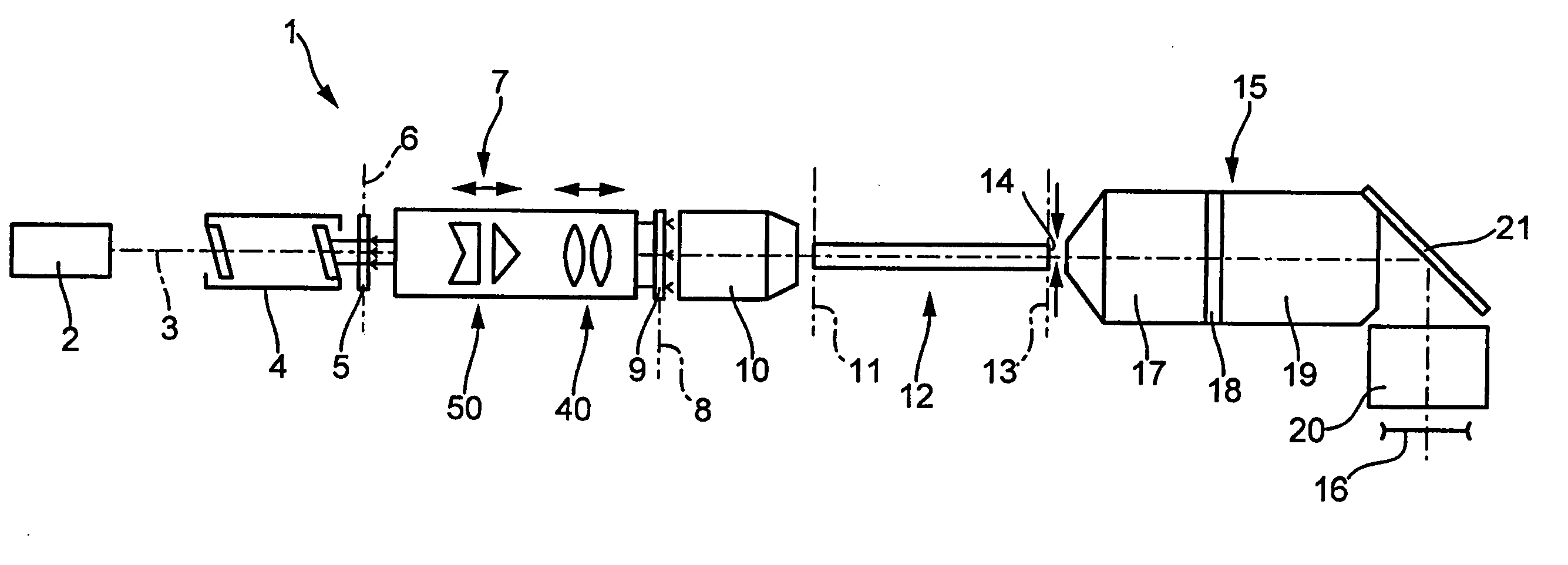
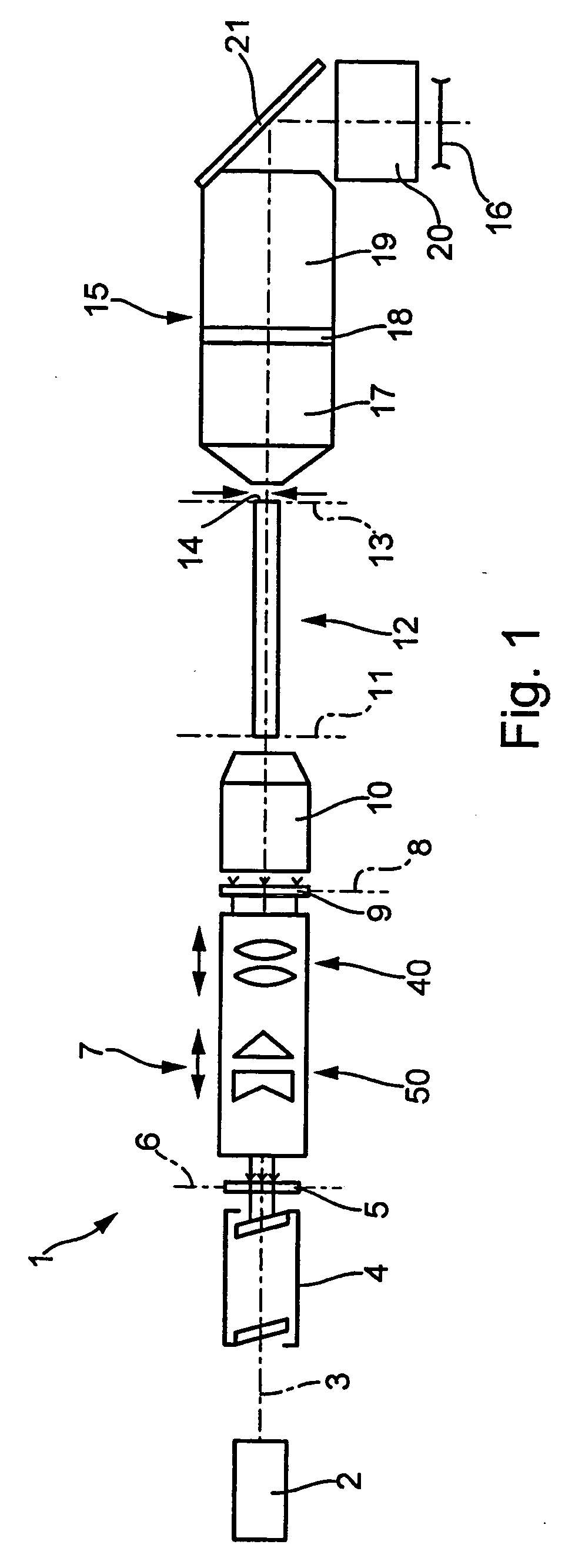
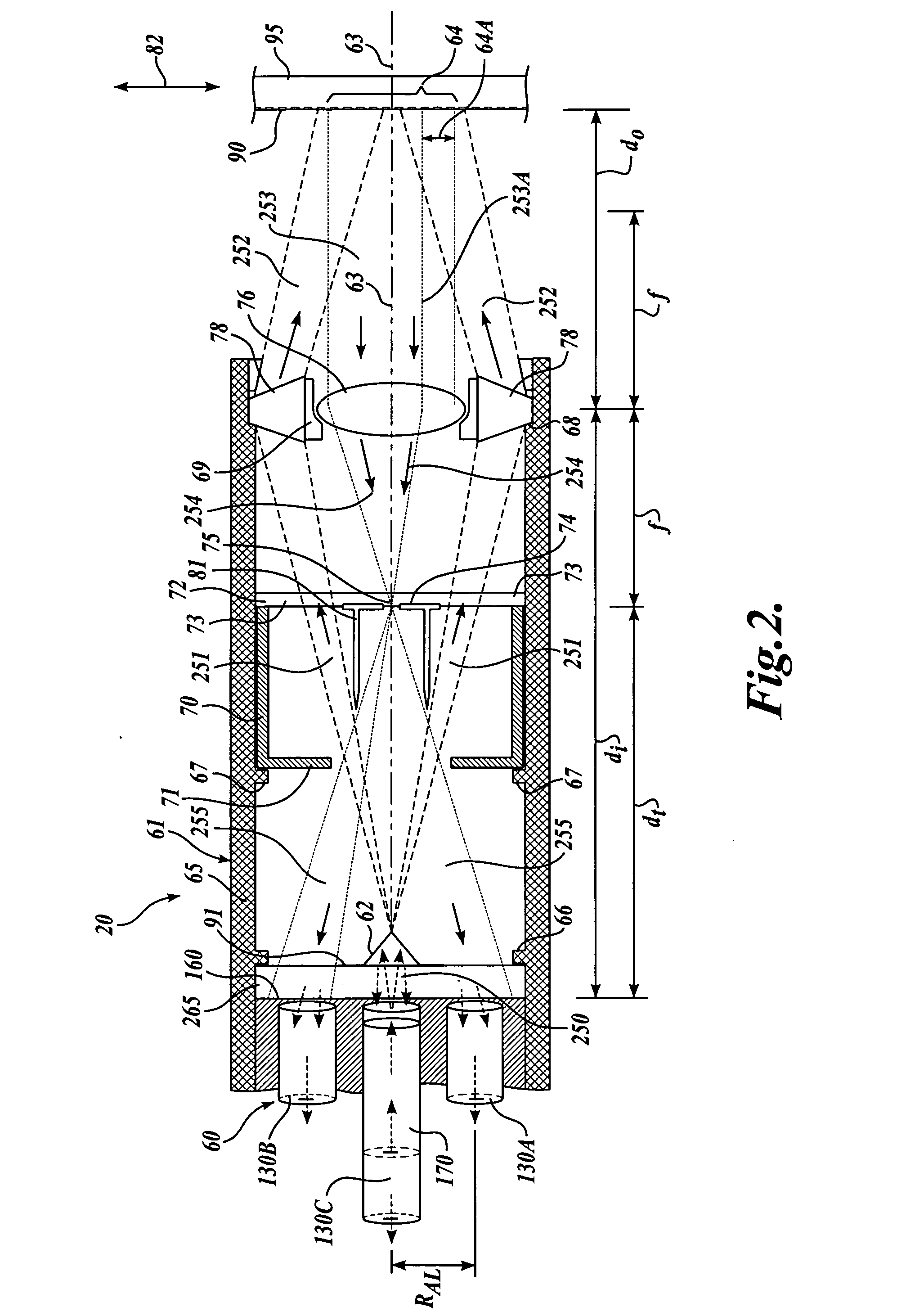
Optical beam transformation system and illumination system comprising an optical beam transformation system
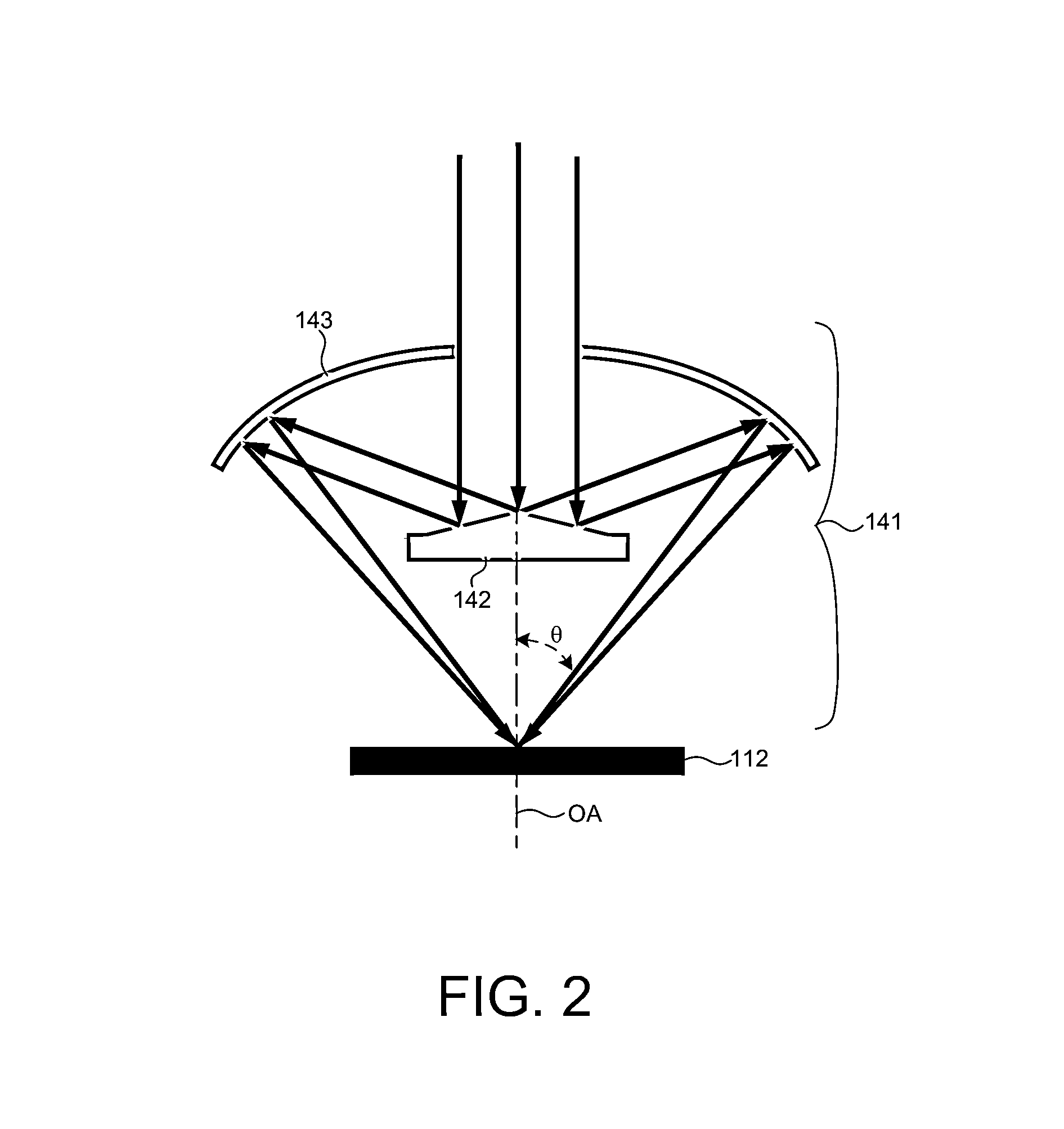
ActiveUS20060146384A1Reduction in polarization-varying effectPhotomechanical apparatusPhotographic printingOptical axisSelective reflection
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
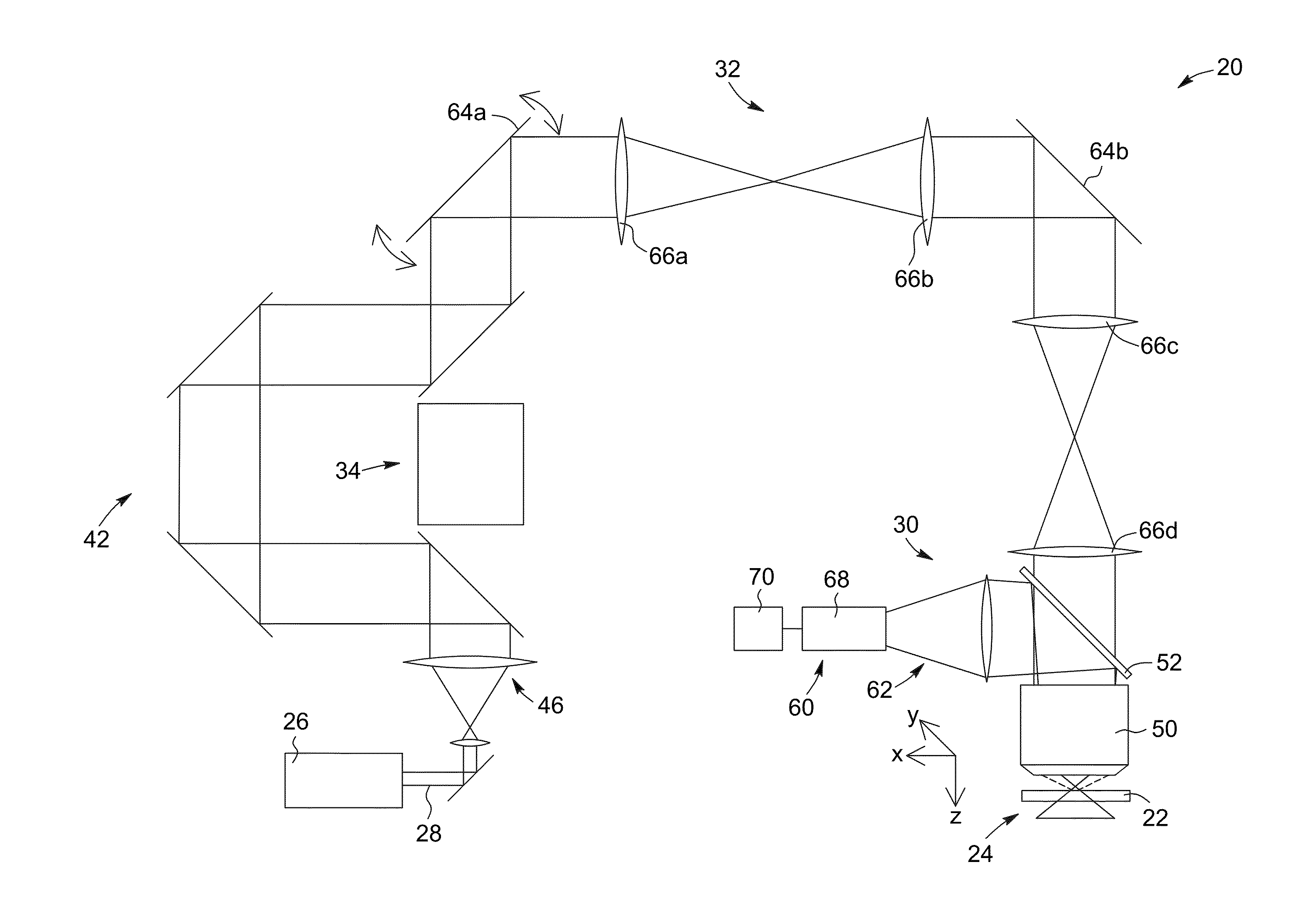
Systems, methods and computer-accessible medium which provide microscopic images of at least one anatomical structure at a particular resolution
ActiveUS20110218403A1Facilitate the μOCT CTFFacilitate a depth-of-field extensionSurgeryDiagnostics using spectroscopyAnatomical structuresMicroscopic image
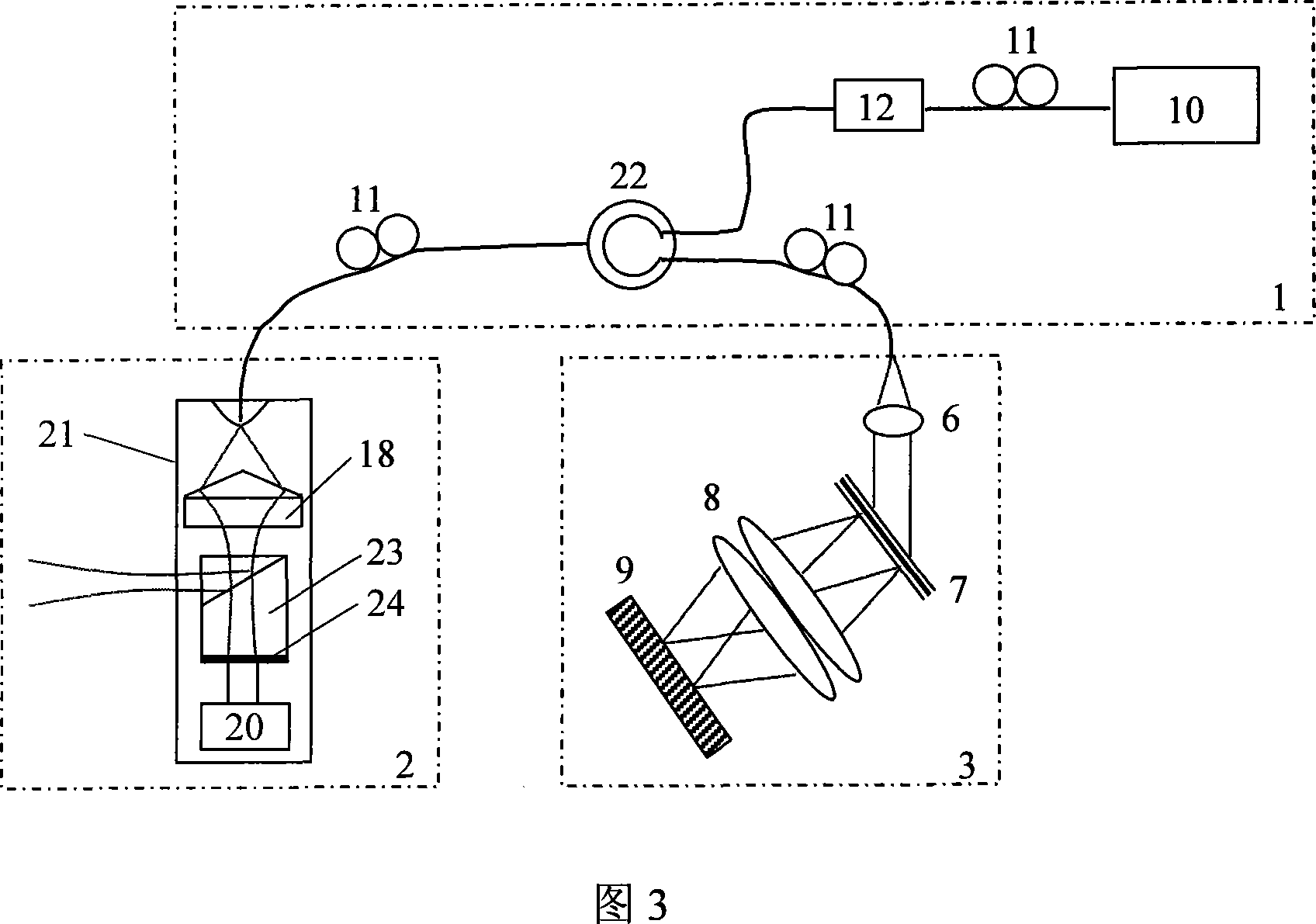
Exemplary embodiments of probes, apparatus, systems and methods can be provided which provide at least one electro-magnetic radiation to at least one sample. For example, a plurality of axicon lenses can be provided which are configured to provide the electro-magnetic radiation(s) having at least partially annulus shape. In addition or alternatively, at least one optical arrangement can be provided which is configured to forward at least one radiation to the sample therethrough having at least partially circularly-symmetric pattern. For example, at least one first portion of the radiation transmitted through a circular section of the pattern can have an optical path-length that is different from an optical path-length of at least one second portion of the radiation transmitted through at least one other section of the pattern.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Small Spot Size Spectroscopic Ellipsometer
ActiveUS20130321810A1High measurement sensitivityIncrease the number ofPolarisation-affecting propertiesPhotomechanical apparatusAngle of incidenceMetrology
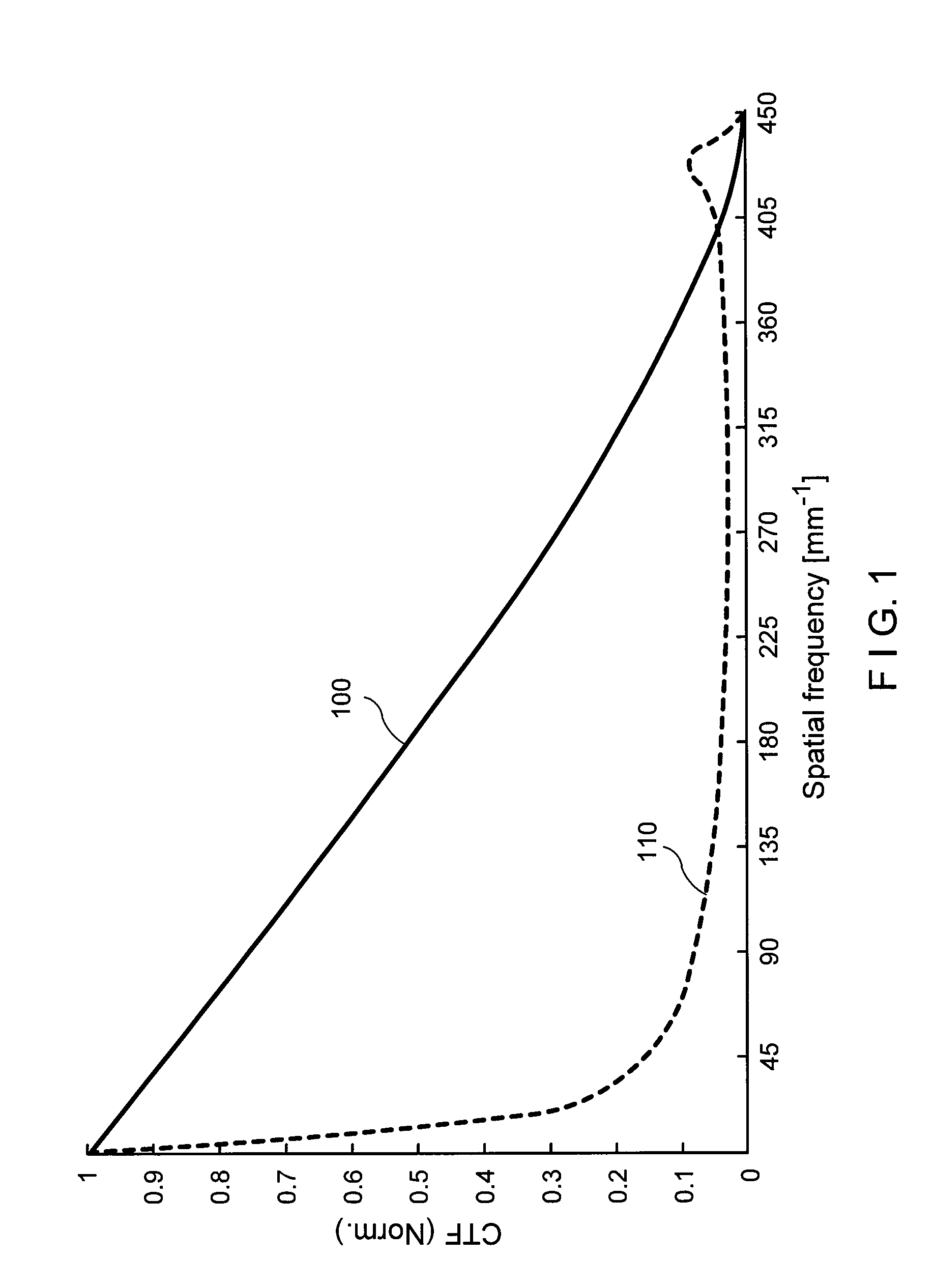
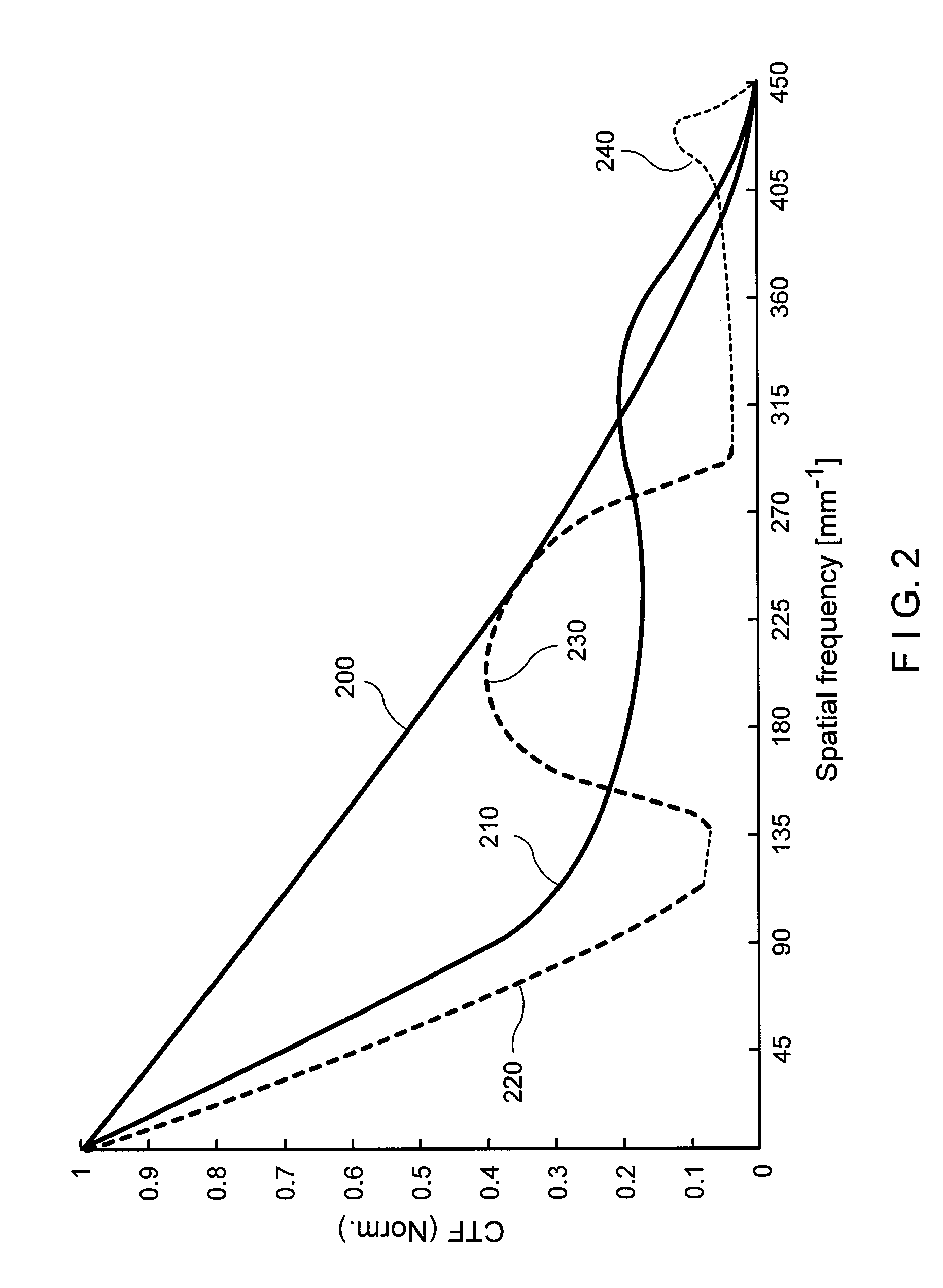
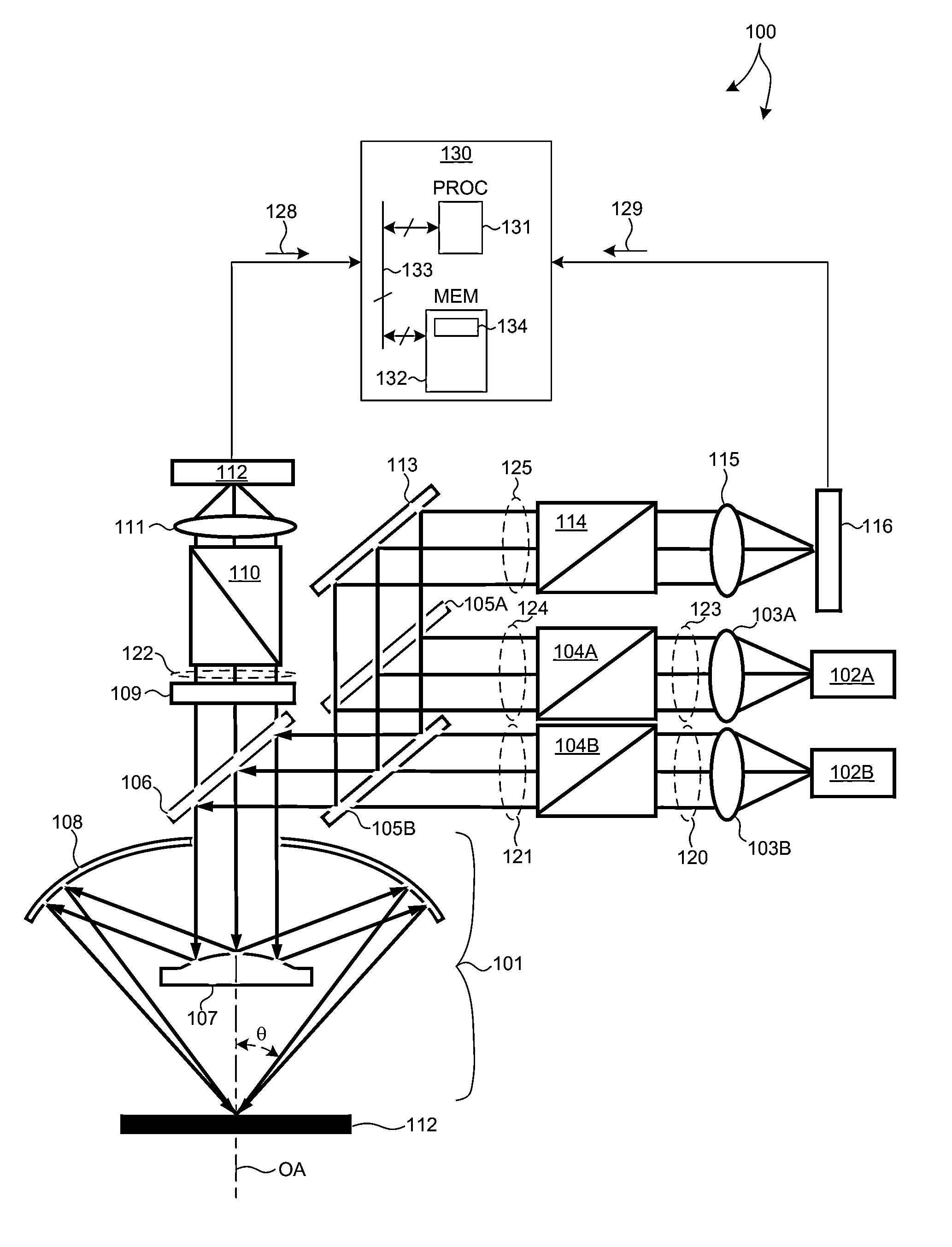
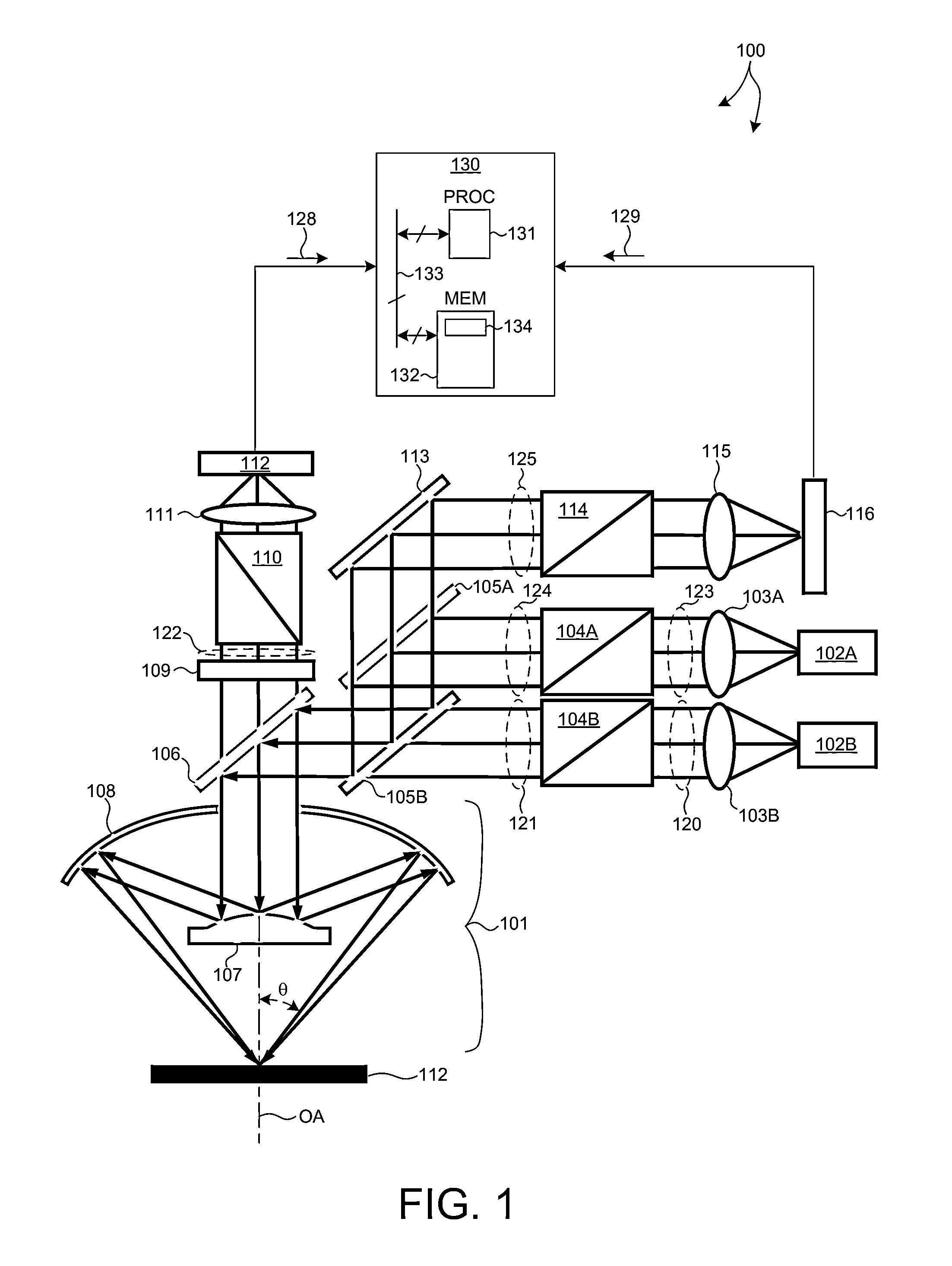
Methods and systems for small angle CD metrology with a small spot size are introduced to increase measurement sensitivity while maintaining adequate throughput necessary for modern semiconductor manufacture. A small angle CD metrology system includes a small angle spectroscopic ellipsometry (SE) subsystem combined with a small angle spectroscopic reflectometry system, both operated at small angles of incidence. The small angle SE subsystem is configured to operate in a complete Mueller Matrix mode to further improve measurement sensitivity. The small angle CD metrology system includes an objective having all reflective surfaces in the light path. In some embodiments, the all-reflective objective is a Schwartzschild objective having an axicon mirror element to further reduce measurement spot size. In some embodiments, the small angle CD metrology system includes a dynamic aperture subsystem to isolate specific ranges of angles of incidence and azimuth for improved measurement sensitivity.
Owner:KLA CORP
Method and apparatus for manufacturing microstructure and device manufactured thereby
InactiveUS20070177116A1Improve throughputGood reproducibilityProjectorsPhotomechanical apparatusLight beamTelecentric lens
A method for manufacturing a microstructure, includes: dividing an incident laser beam into a plurality of diffracted beams by means of a diffractive optical element; concentrating said divided plurality of diffracted beams into mutually parallel diffracted beams by means of a telecentric lens; causing each of said mutually parallel diffracted beams to enter perpendicularly to the plane into a collection of axicons comprised of a plurality of axicons arranged into an array in such a manner that the center of each diffracted beam and the center of each axicon coincide, thereby forming a plurality of arrayed Bessel beams; and irradiating said plurality of arrayed Bessel beams onto a machined body.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Noncontact laser microsurgical method
InactiveUS6210399B1Reduce astigmatismAlleviate corneal refractive errorLaser surgeryDiagnosticsGonioplastyEpikeratoplasty
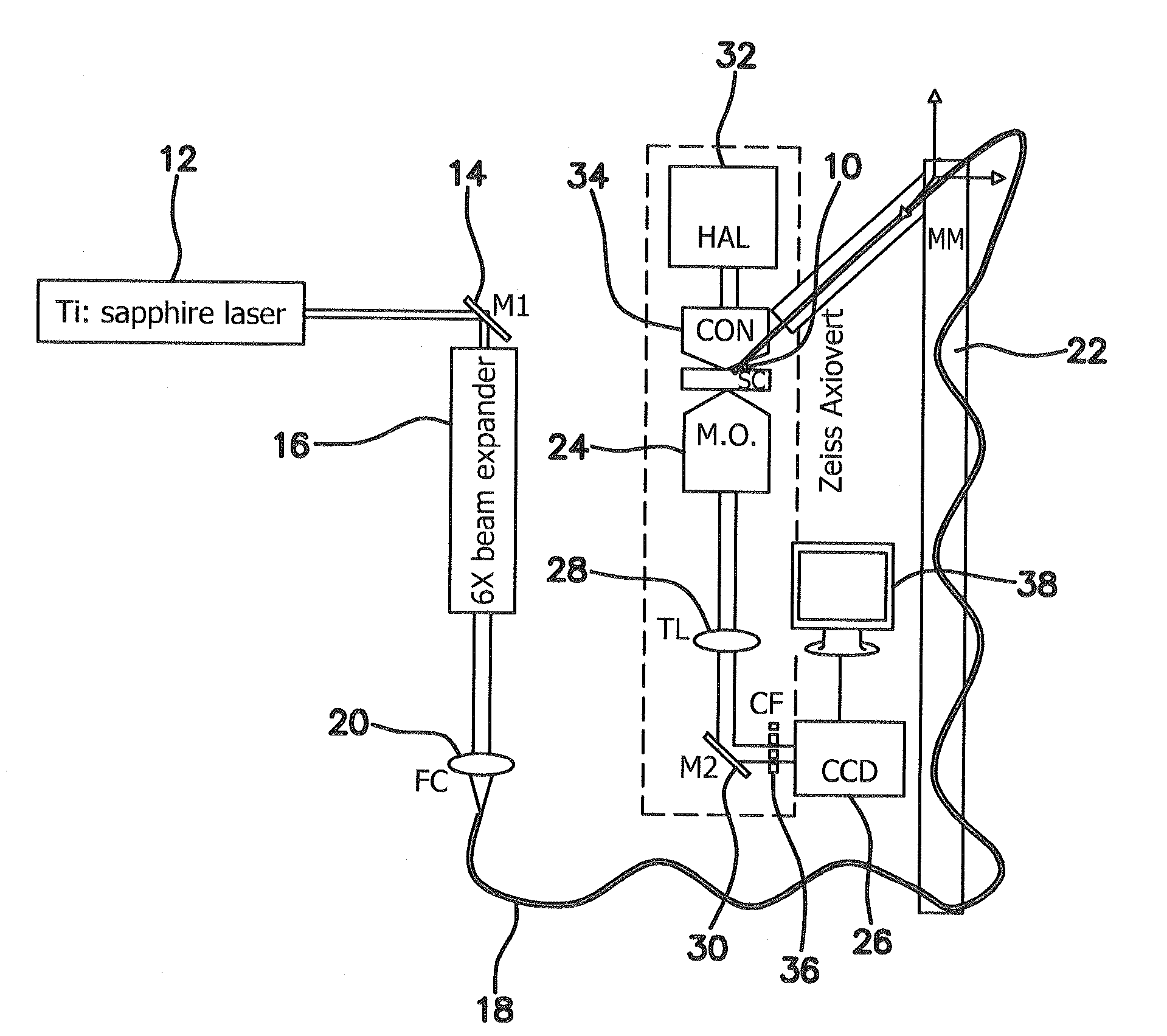
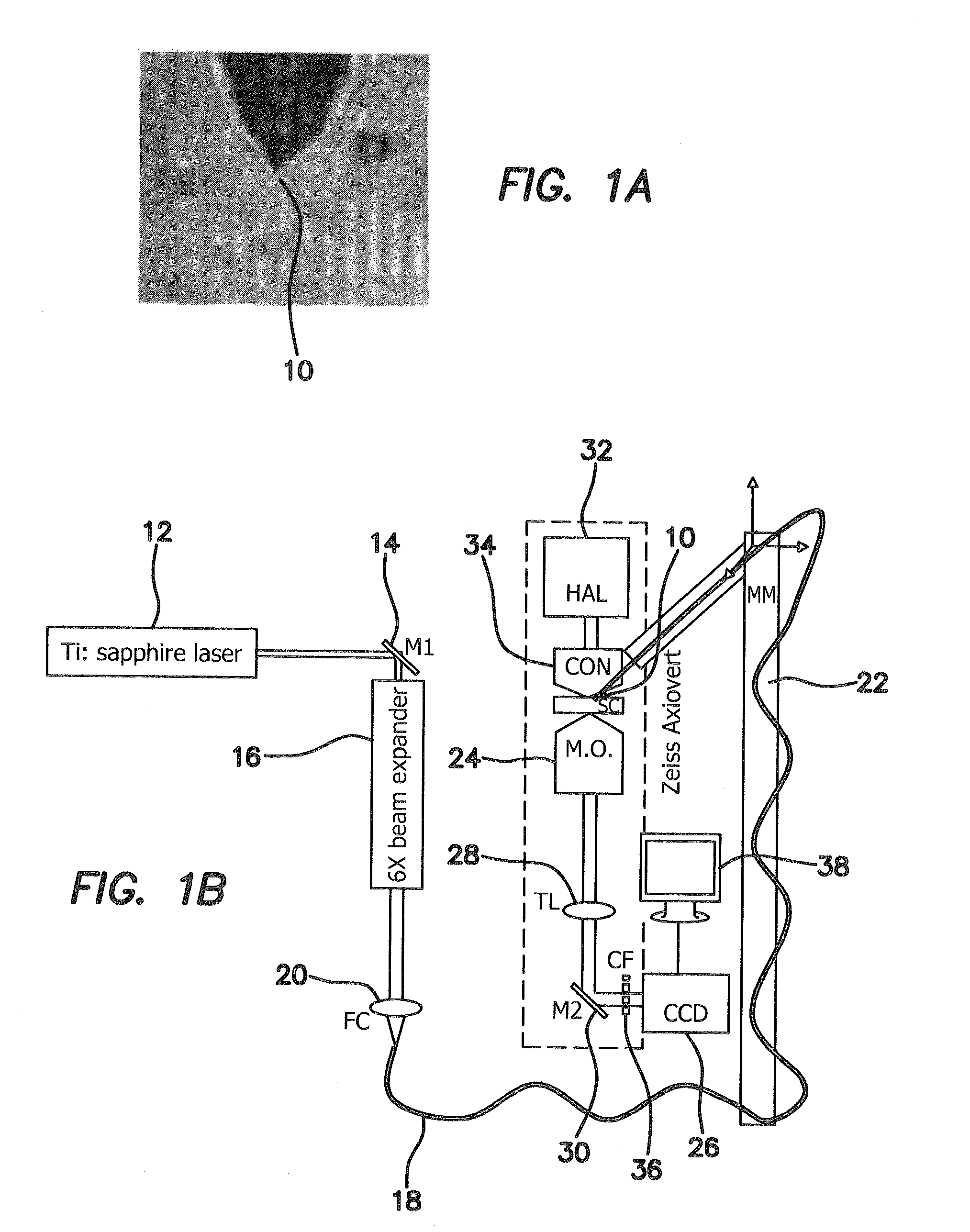
A noncontact laser microsurgical apparatus and method for marking a cornea of a patient's or donor's eye in transplanting surgery or keratoplasty, and in incising or excising the corneal tissue in keratotomy, and for tissue welding and for thermokeratoplasty. The noncontact laser microsurgical apparatus comprises a laser source and a projection optical system for converting laser beams emitted from the laser source into coaxially distributed beam spots on the cornea. The apparatus further includes a multiple-facet prismatic axicon lens system movably mounted for varying the distribution of the beam spots on the cornea. In a further embodiment of the method of the present invention, an adjustable mask pattern is inserted in the optical path of the laser source to selectively block certain portions of the laser beams to thereby impinge only selected areas of the cornea.
Owner:UNIV OF MIAMI
Method and system for obtaining an extended-depth-of-field volumetric image using laser scanning imaging
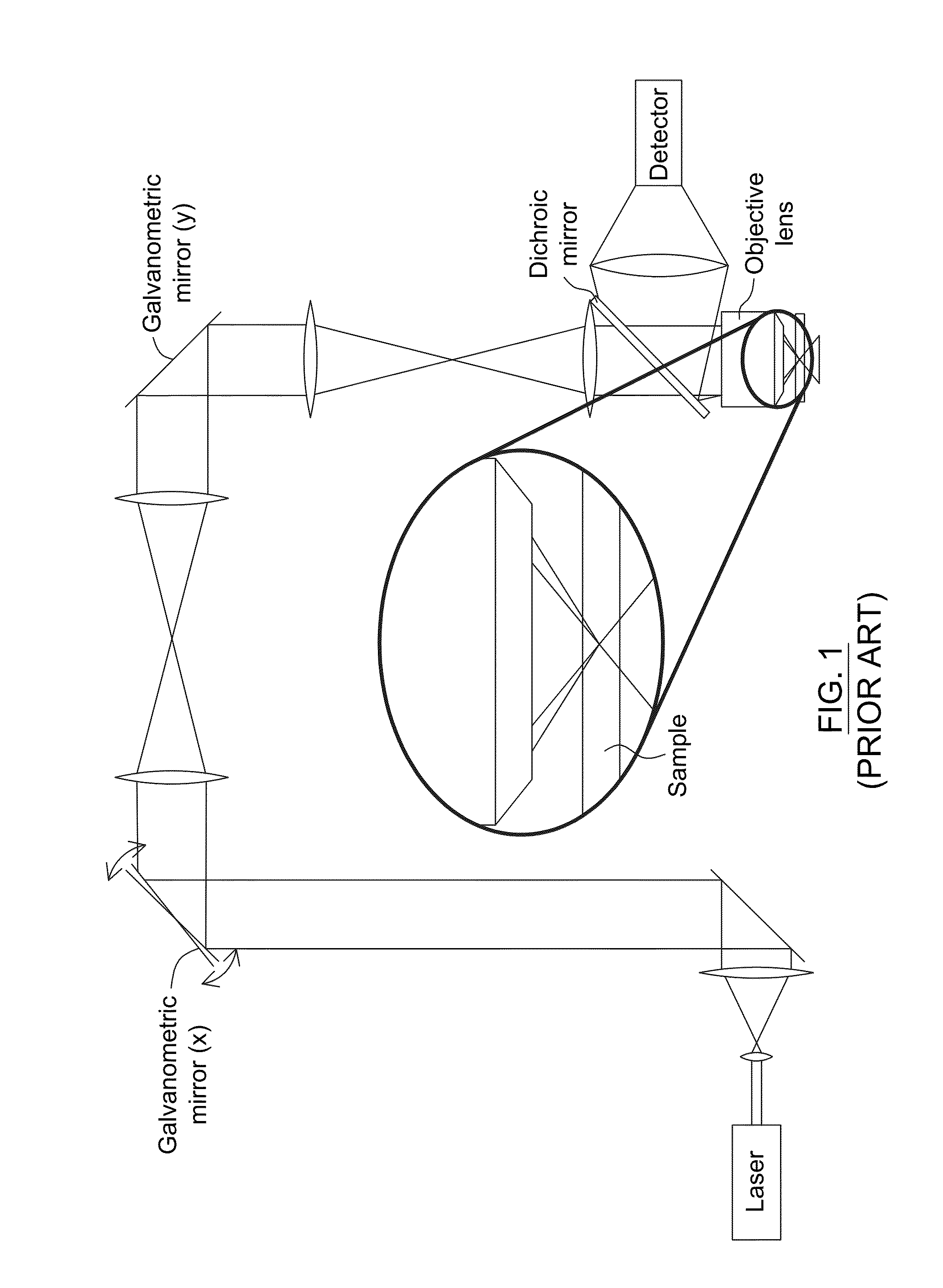
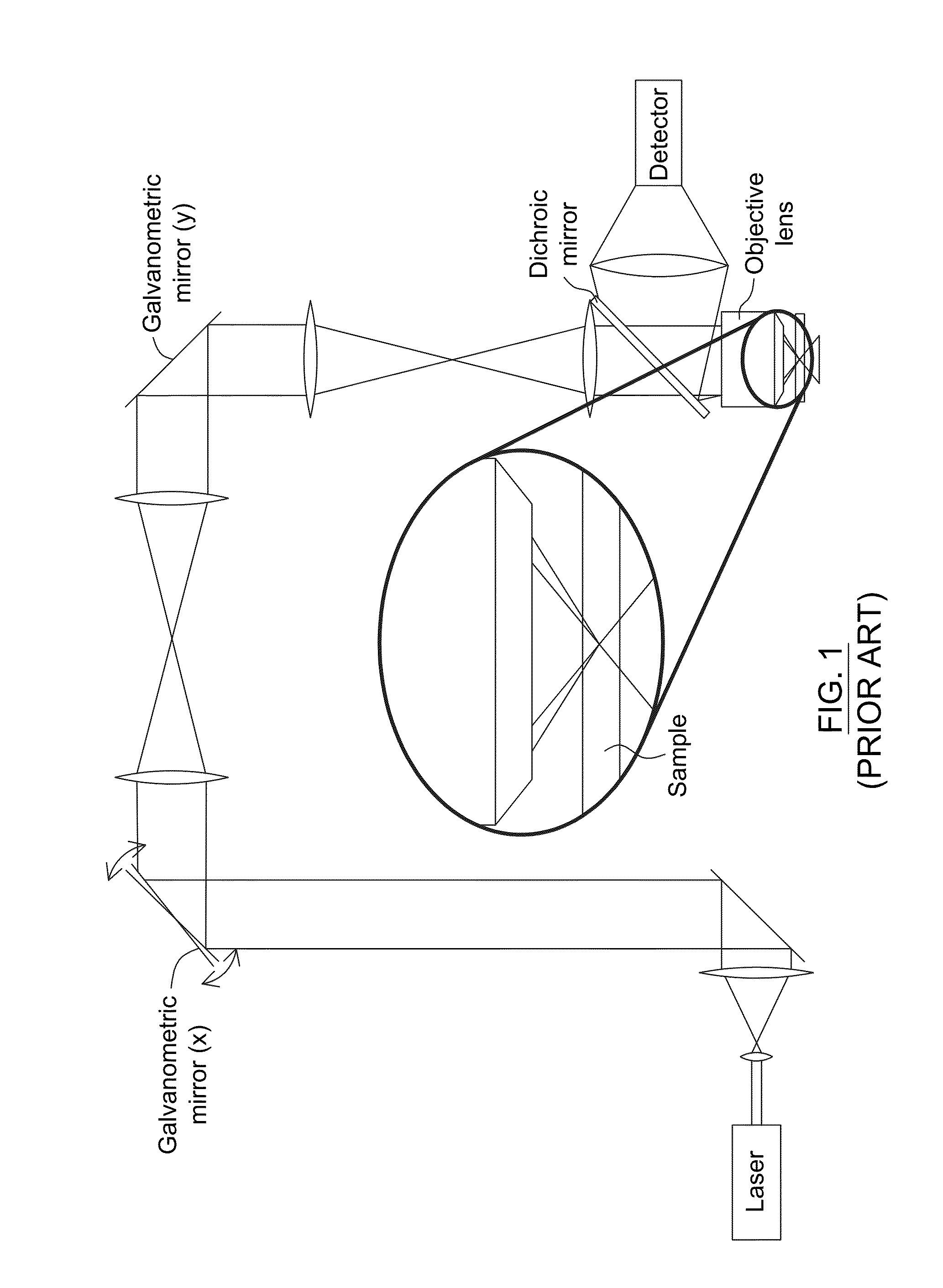
A laser scanning imaging system and method for obtaining an extended-depth-of-field image of a volume of a sample are provided. The system includes a laser module generating an input laser beam, a beam shaping module including an axicon and a Fourier-transform lens, and an imaging module including an objective lens and a detecting assembly. The axicon, Fourier-transform lens and objective lens are formed and disposed to successively convert the input laser beam into an intermediate non-diffracting beam, an intermediate annular beam, and an excitation non-diffracting beam. The excitation beam is projected onto the sample and has a depth of field and transverse resolution together defining a three-dimensional excitation region. The detecting assembly collects electromagnetic radiation from the excitation region to obtain one pixel of the extended-depth-of-field image. The system further includes a two-dimensional scanning module for scanning the excitation beam over the sample and build, pixel-by-pixel, the extended-depth-of-field image.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
Endoscopic imaging system in bulk optics biopsy spectral coverage OCT
InactiveCN101032390ASolve the problem that dynamic focus cannot be used to ensure lateral resolutionQuality of reliefEndoscopesDiagnostic recording/measuringBeam splitterPrism
The present invention discloses one kind of spectral-domain optical coherent tomography endoscopic image system for in vivo optical biopsy, and the system includes one fiber optical interferometer, one imaging probe, one detection unit, one image acquiring card and one computer. The detection unit has grating spectrograph for high imaging speed, and the imaging probe has axial axicon lens and inside rotating right angle prism or circularly symmetric beam splitter combined to ensure high transverse resolution in the whole depth range, so as to realize circularly scanning endoscopic imaging. The present invention proposes two embodiments of circularly scanning probe and their corresponding system structures. The present invention may be applied in the optical endoscopic biopsy and analytic study of oral cavity, respiratory tract, gastrointestinal tract, etc.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
High efficiency collector for laser plasma EUV source
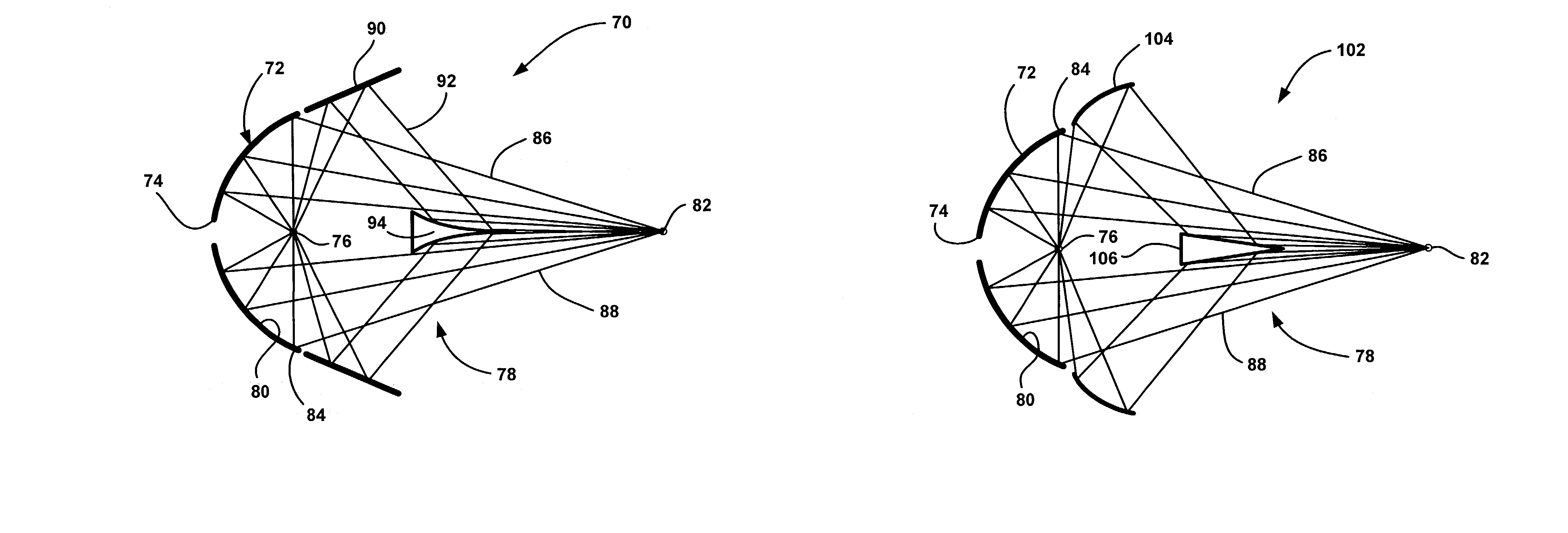
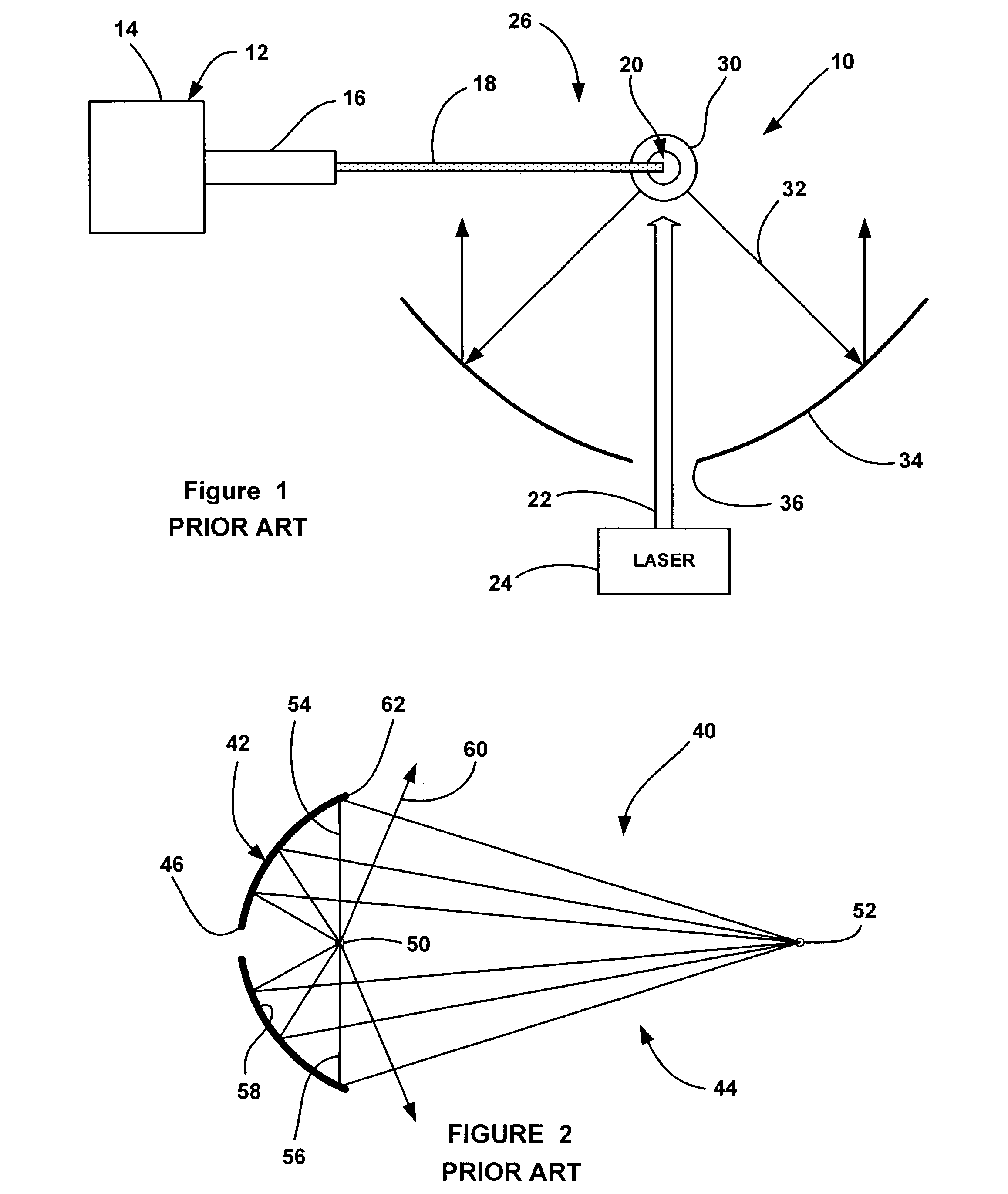
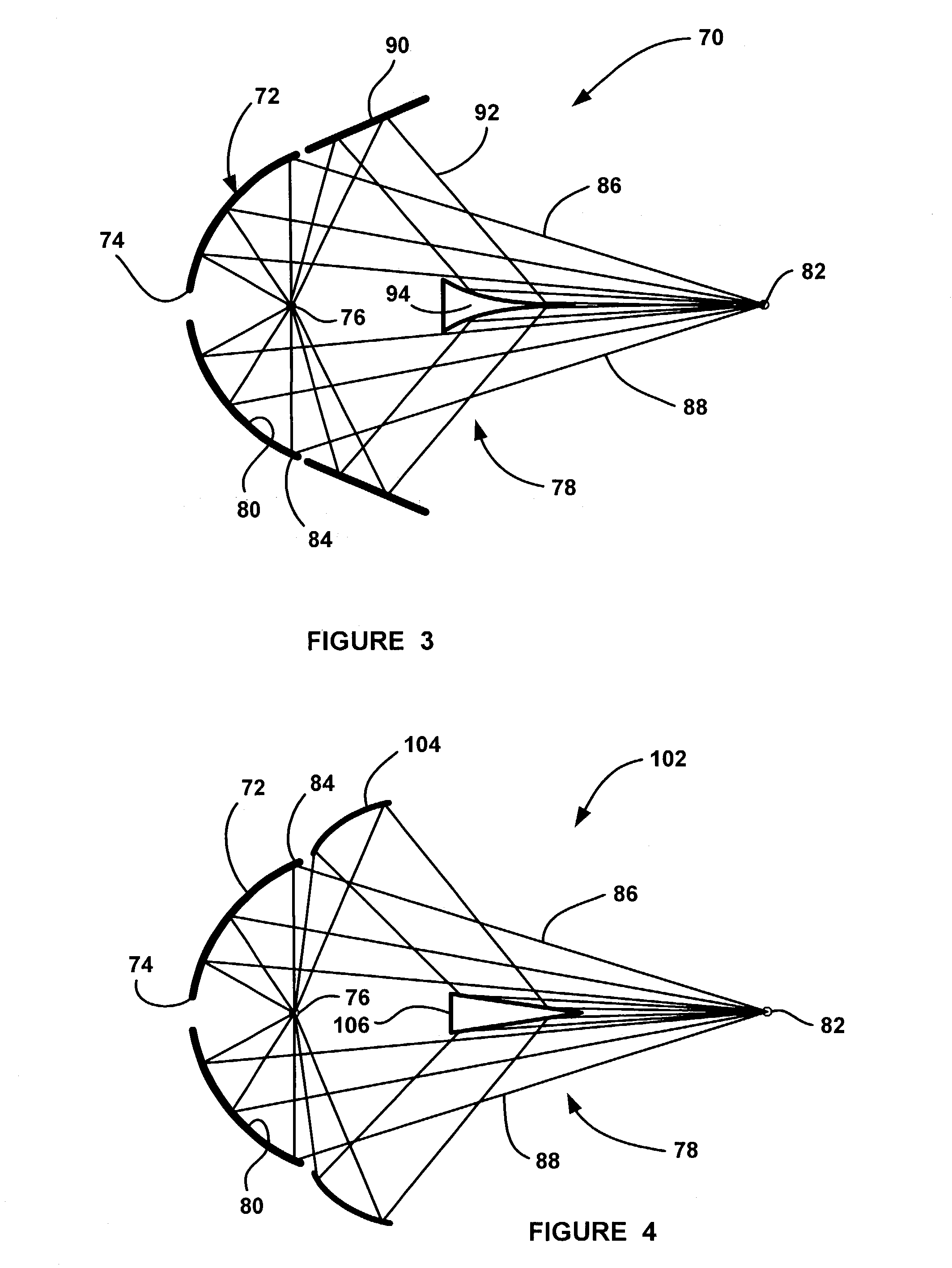
Collector optics (70) for an EUV radiation source (10) for collecting EUV radiation (78). The collector optics (70) includes an elliptical dish reflector (72) where light generated at a focal point (76) of the reflector (72) is collected by the reflector (72) and is directed to a collection location (82). A frustal annular reflector (90) is positioned around an outer edge (84) of the dish reflector (72) to collect more of the EUV radiation (78) that may otherwise be lost. The radiation (78) reflected by the annular reflector (90) is directed to a center axicon reflector (94) positioned between the focal point (76) of the dish reflector (72) and the collection location (82) to redirect the radiation (78) reflected by the annular reflector (90) to be within a predetermined collection angle.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMAN CORP
Laser processing method and device
InactiveCN105081586AImprove machining accuracyAchieve laser processingLaser beam welding apparatusComputer control systemLaser processing
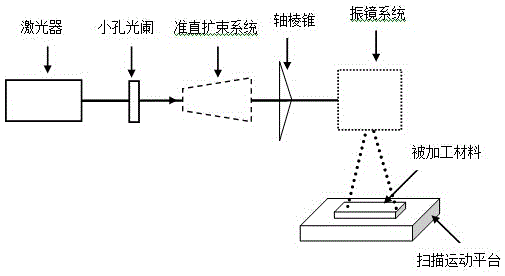
The invention discloses a laser processing method. The method includes the following steps that a laser device is started through a computer control system, so that the laser device emits laser beams; the light beams pass a small-hole diaphragm, so that the functions of mode selection and radius control over the laser beams are achieved; the laser beams passing the small-hole diaphragm are collimated and expanded through a lens set; the collimated and expanded laser beams are converted into Bessel beams through an axicon optical element; and the Bessel beams are emitted to the surface of a processed material through a galvanometer system. The invention further discloses a laser processing device. The position of a focus does not need to be determined during processing, and the laser processing method has the characteristics of being large in depth-diameter ratio, high in precision and the like. The implementation method is simple, an optical path is easy to adjust, and the laser processing method and device have good application prospects in the laser processing field.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY +1
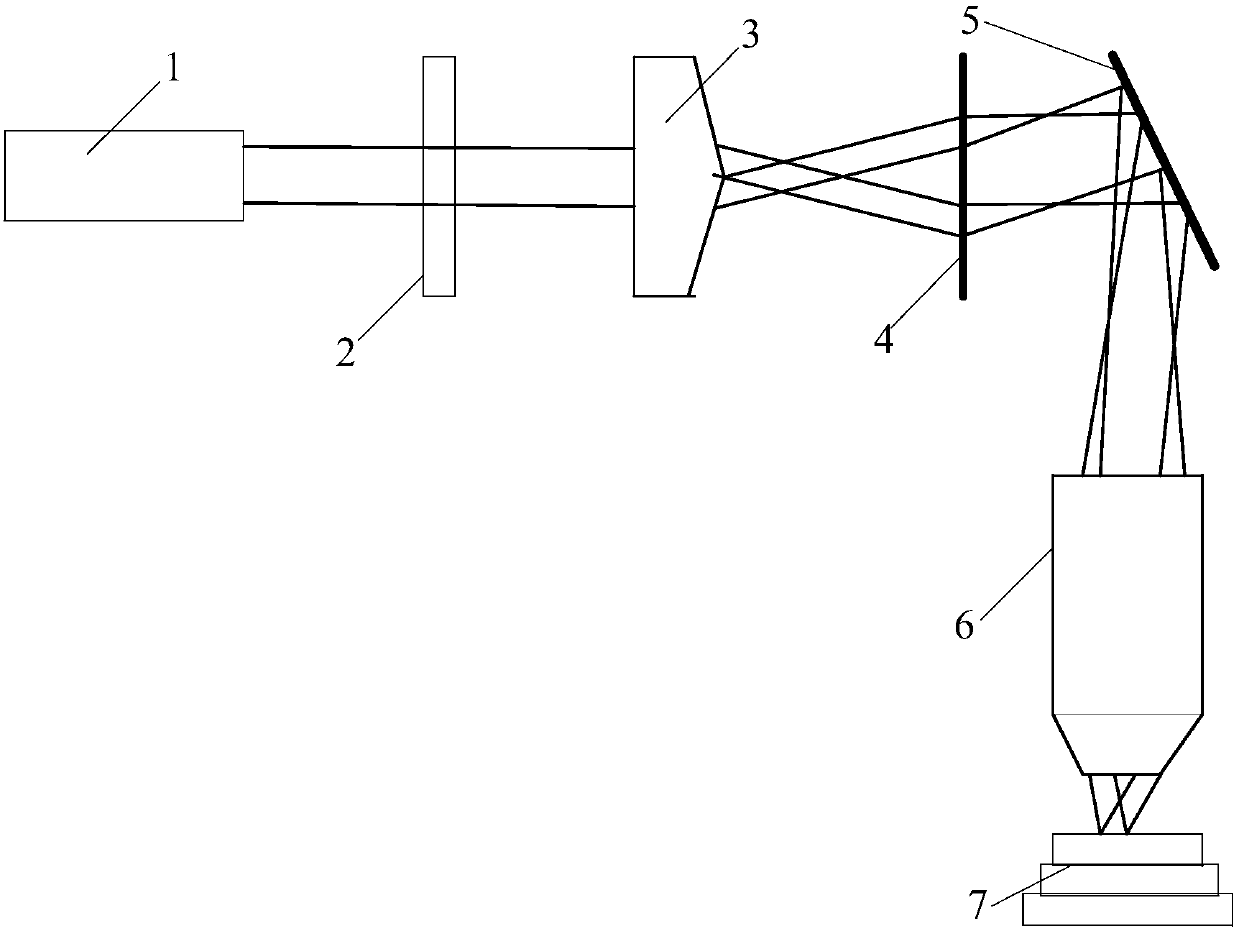
Combination measuring instrument of optical fiber Mach-Zehnder and Michelson interferometer array
InactiveCN101329184ASolving Multiplexing ProblemsRealize inquiryCoupling light guidesConverting sensor output opticallyMeasuring instrumentMultiple sensor
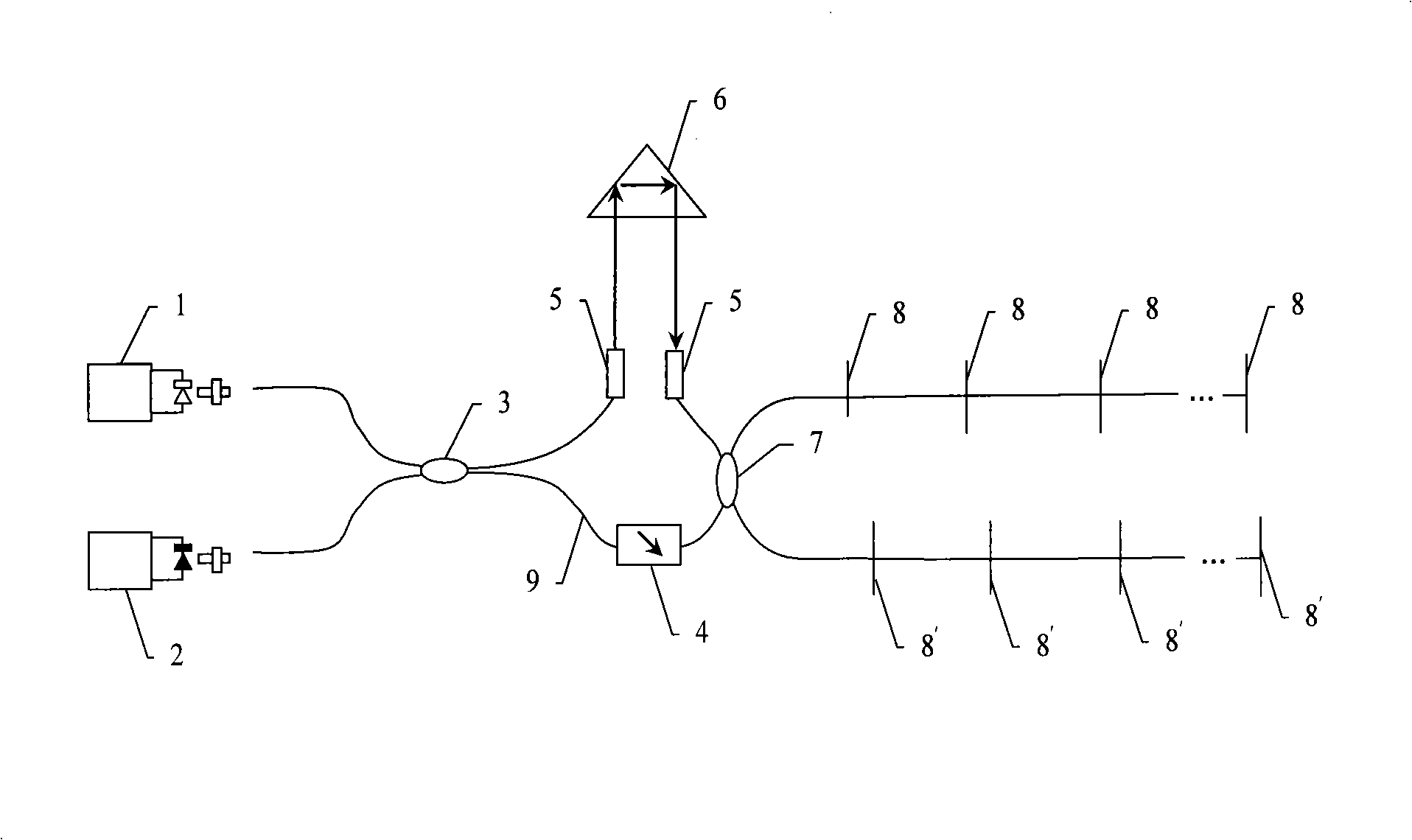
The invention provides a measuring instrument with an optical fiber Mach-Zehnder interferometer and optical fiber Michdson interferometer arrays, which comprises a broad-band light source 1, a photoelectric detector 2, a 3dB optical fiber 2 multiplied by 2 coupler 3, the optical fiber Mach-Zehnder interferometer, a transposed 3dB optical fiber 2 multiplied by 2 coupler 7, optical fiber Michdson interferometers arrays 8 and 8', and a single-mode connecting optical fiber 9, wherein, the optical fiber Mach-Zehnder interferometer consists of an attenuator 4, a self-focusing lens 5, an axicon lens 6 with total reflection angle, and the connecting optical fiber 9. The measuring instrument with the optical fiber Mach-Zehnder interferometer and the optical fiber Michdson interferometer arrays utilizes a technique that measures strain and temperature at the same time, realizes the temperature compensation technique and the array arrangement of optical fiber sensors, realizes absolute measurement under the situation that the multiple sensors are not interfered by each other, lowers the cost of single-point measurement and ensures real-time measurement; furthermore, the measuring instrument has simple techniques and easy implementation, and as standard optical fiber communication elements are adopted as the optical fiber materials and devices, the measuring instrument has low cost, easy acquisition of the optical fiber materials and devices and easy popularization.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Lithographic apparatus and device manufacturing method
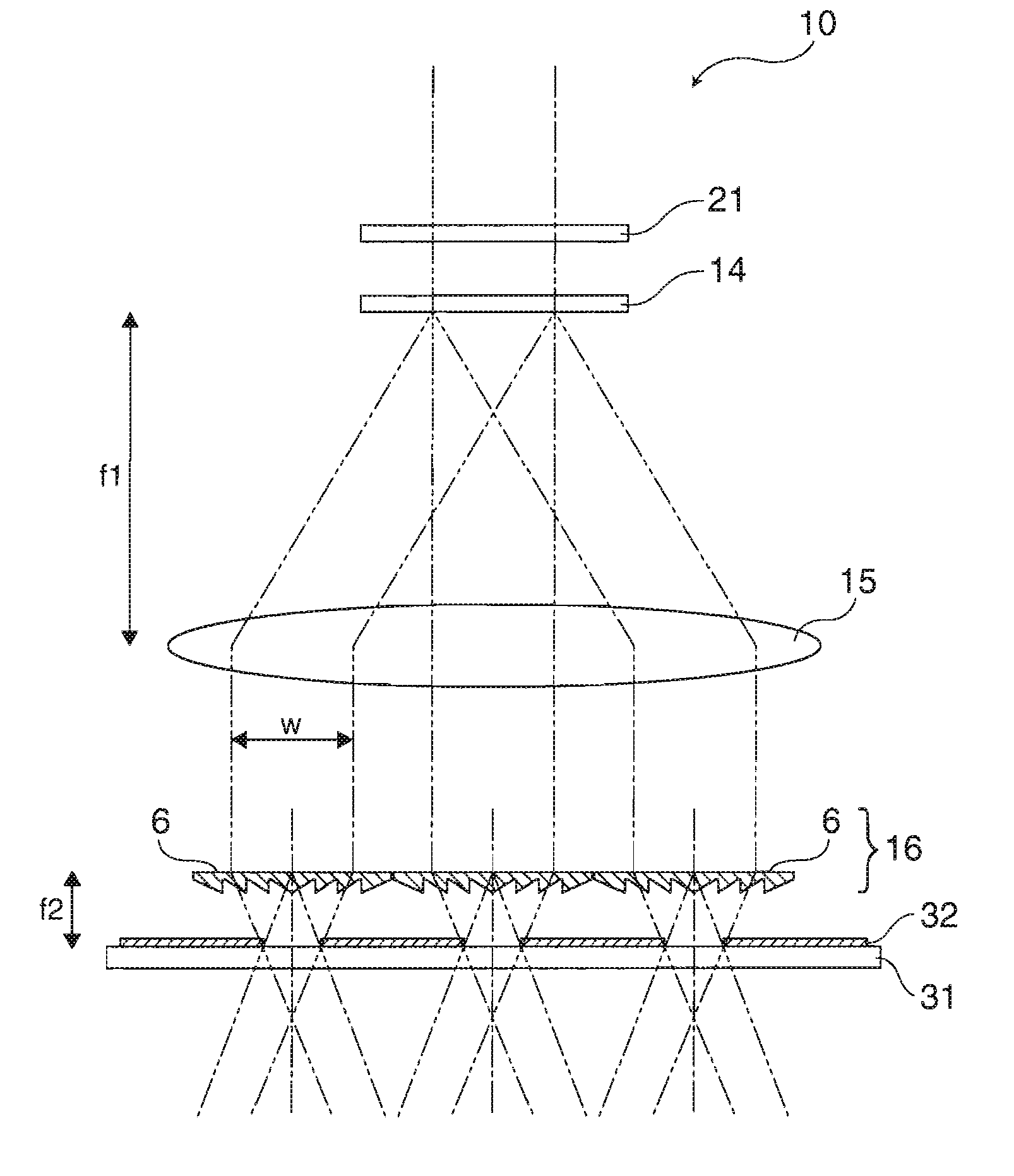
ActiveUS7148952B2Improve homogeneitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusIntegratorLight beam
The present invention provides a lithographic apparatus comprising an illumination system for providing a projection beam of radiation. The illumination system comprises at least one movable optical element (7), such that a projection beam of radiation (4) can be shifted around a central position. This ensures that inhomogeneities in the intensity distribution in the projection beam (4) will be smeared out, which in turn provides an improved homogeneity of the exposure of a surface to be illuminated by the system, such as a wafer or other substrate. The optical element (7) may comprise a motor movable mirror, prism, filter, lens, axicon, diffuser, diffractive optical array, optical integrator, etc. The invention further provides a device manufacturing method, using a lithographic apparatus according to the invention, wherein the optical element is moved, in order to provide an optimum homogeneity for the projection beam of radiation.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Lithographic apparatus and device manufacturing method
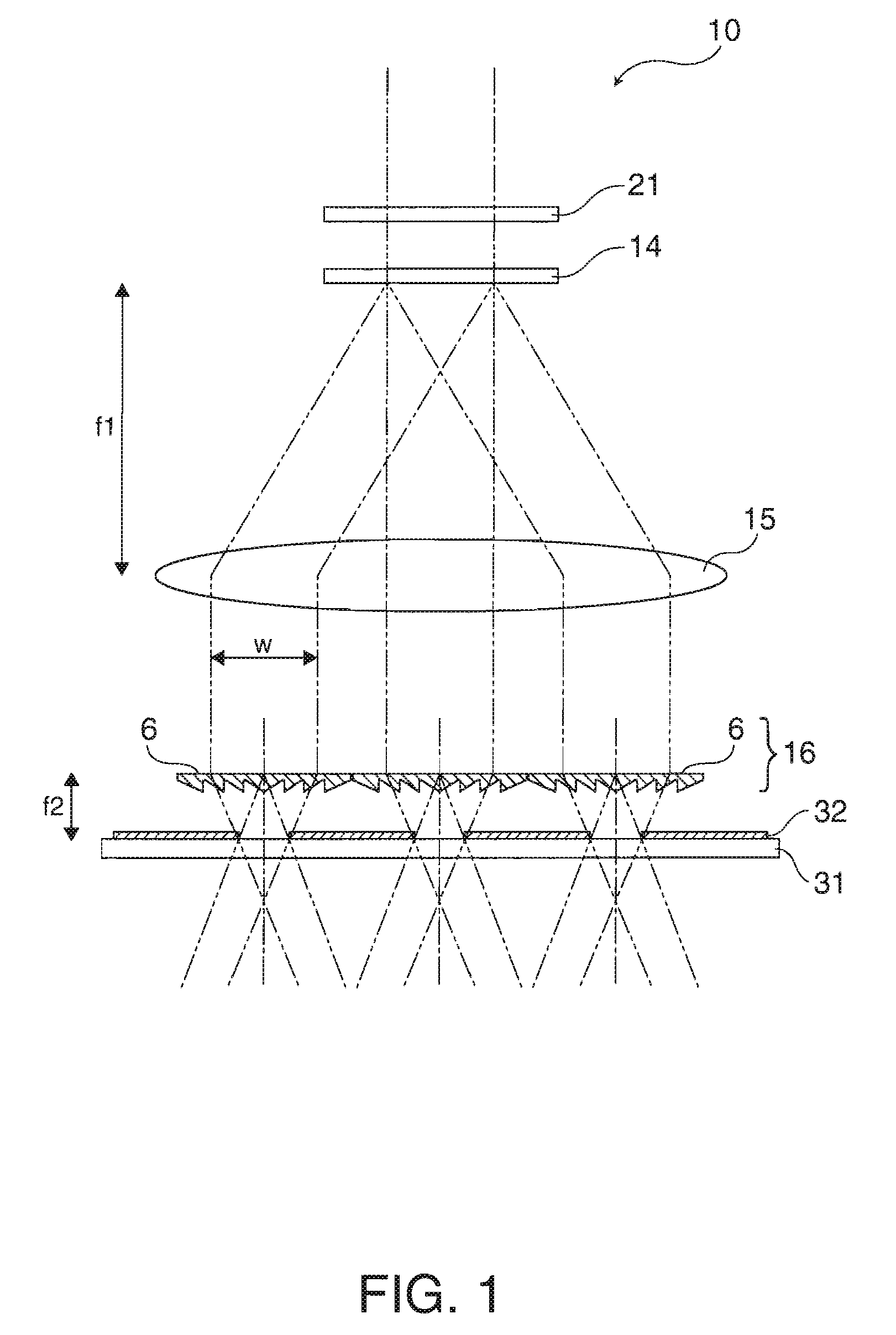
ActiveUS20050146702A1Minimal cross-sectional areaLow costSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusIntegratorLight beam
The present invention provides a lithographic apparatus comprising an illumination system for providing a projection beam of radiation. The illumination system comprises at least one movable optical element (7), such that a projection beam of radiation (4) can be shifted around a central position. This ensures that inhomogeneities in the intensity distribution in the projection beam (4) will be smeared out, which in turn provides an improved homogeneity of the exposure of a surface to be illuminated by the system, such as a wafer or other substrate. The optical element (7) may comprise a motor movable mirror, prism, filter, lens, axicon, diffuser, diffractive optical array, optical integrator, etc. The invention further provides a device manufacturing method, using a lithographic apparatus according to the invention, wherein the optical element is moved, in order to provide an optimum homogeneity for the projection beam of radiation.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
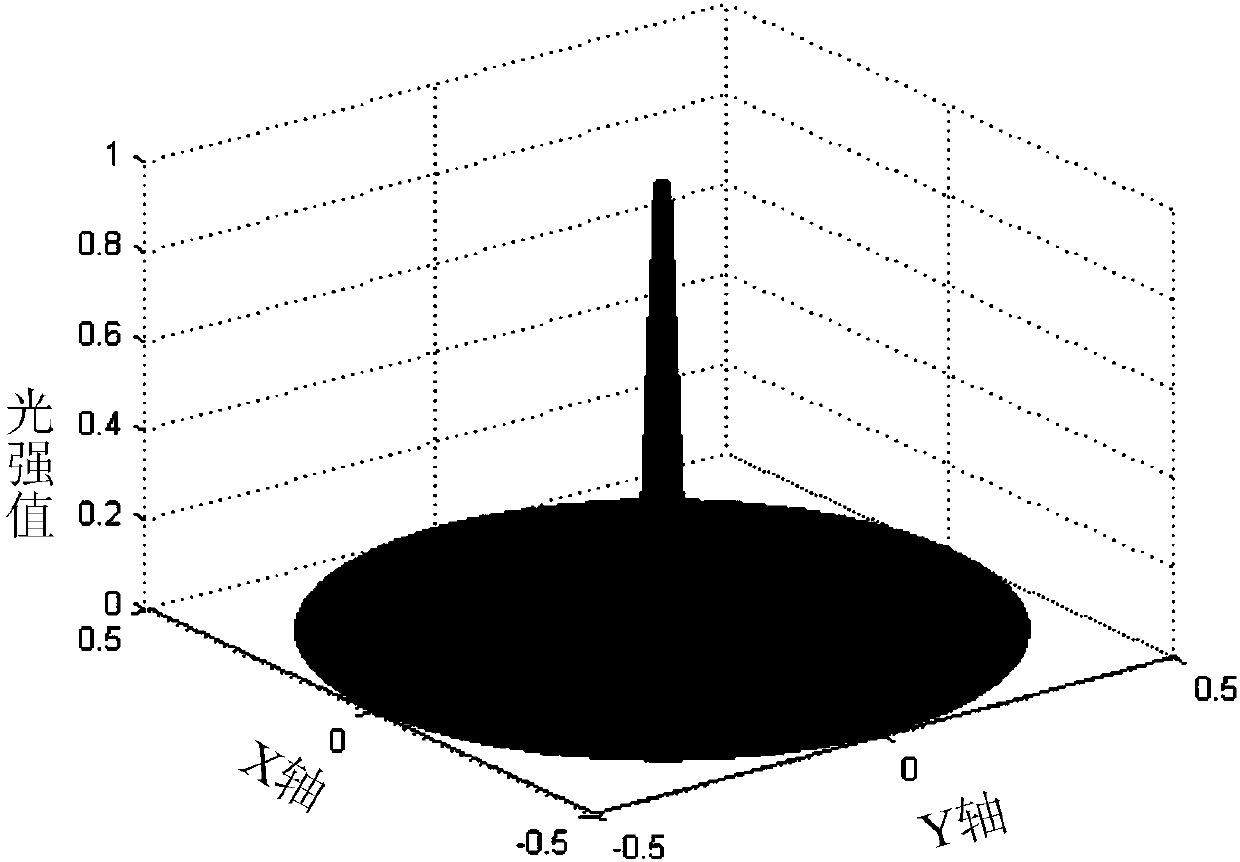
Optical system generating screw type Bessel beams and generating method
ActiveCN103792663ASimple secondary processing designPromote conversionOptical elementsGratingDiffraction order
The invention discloses an optical system generating screw type Bessel beams and a generating method. The optical system is composed of a He-Ne laser device, a polarizer, a first beam expander, a binary amplitude grating, a second beam expander, an aperture diaphragm, a liquid crystal spatial light modulator, an axicon and a CCD camera. Gauss beams emitted from the He-Ne laser device are converted into 0-degree linearly polarized light after passing through the polarizer with a 0-degree polarizing direction, beam expanding is carried out on the 0-degree linearly polarized light through the first beam expander, the 0-degree linearly polarized light is vertically emitted into the binary amplitude grating, generated diffracted light passes through the second beam expander, the diffraction angles of all diffraction orders of the diffracted light are enlarged, single-ring Laguerre-Guss beams are obtained through the aperture diaphragm and are sent to the liquid crystal spatial light modulator, the Bessel beams which are off an axis and are transmitted around the axis in a screw mode are generated by passing through the axicon, and the Bessel beams are irradiated to the CCD camera to obtain light distribution. The optical system generating the screw type Bessel beams and the generating method achieve generation of the Bessel beams which are off the optical axis and are transmitted around the optical axis in the screw mode.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF SPATIAL MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH
Method and device for accomplishing dark-field photomicrography and fluorescent photomicrography by axicon lens
The invention relates to a method and a device for achieving dark-field microscopy and fluorescent microscopy by using cone mirror. The method comprises the following steps of: first generating a parallel illumination light beam or a fluorescence-induced light beam; diverging the parallel illumination light beam by the cone mirror to form a hollow beam; transmitting the hollow beam to sequentially pass through a lens I and a lens II to make the divergence angle of the emergent light from the lens II larger than an aperture angle of a microscopic objective lens; and disposing a sample at the center of the hollow beam and observing the sample by the microscopic objective lens, wherein a CCD camera can be arranged in front of the microscopic objective lens. The inventive system has high transmissivity, can conveniently achieve switching between bright-field microscopy and dark-field microscopy and can simultaneously achieve dark-field microscopy and fluorescent microscopy functions, thus solving the technical problems of prior dark-field microscopy with low illumination light transmissivity and the technical problems of prior fluorescent microscopy which needs different filters for different fluorescent dyes and is incompatible to dark-field microscopy.
Owner:BEIJING LUSTER LIGHTTECH
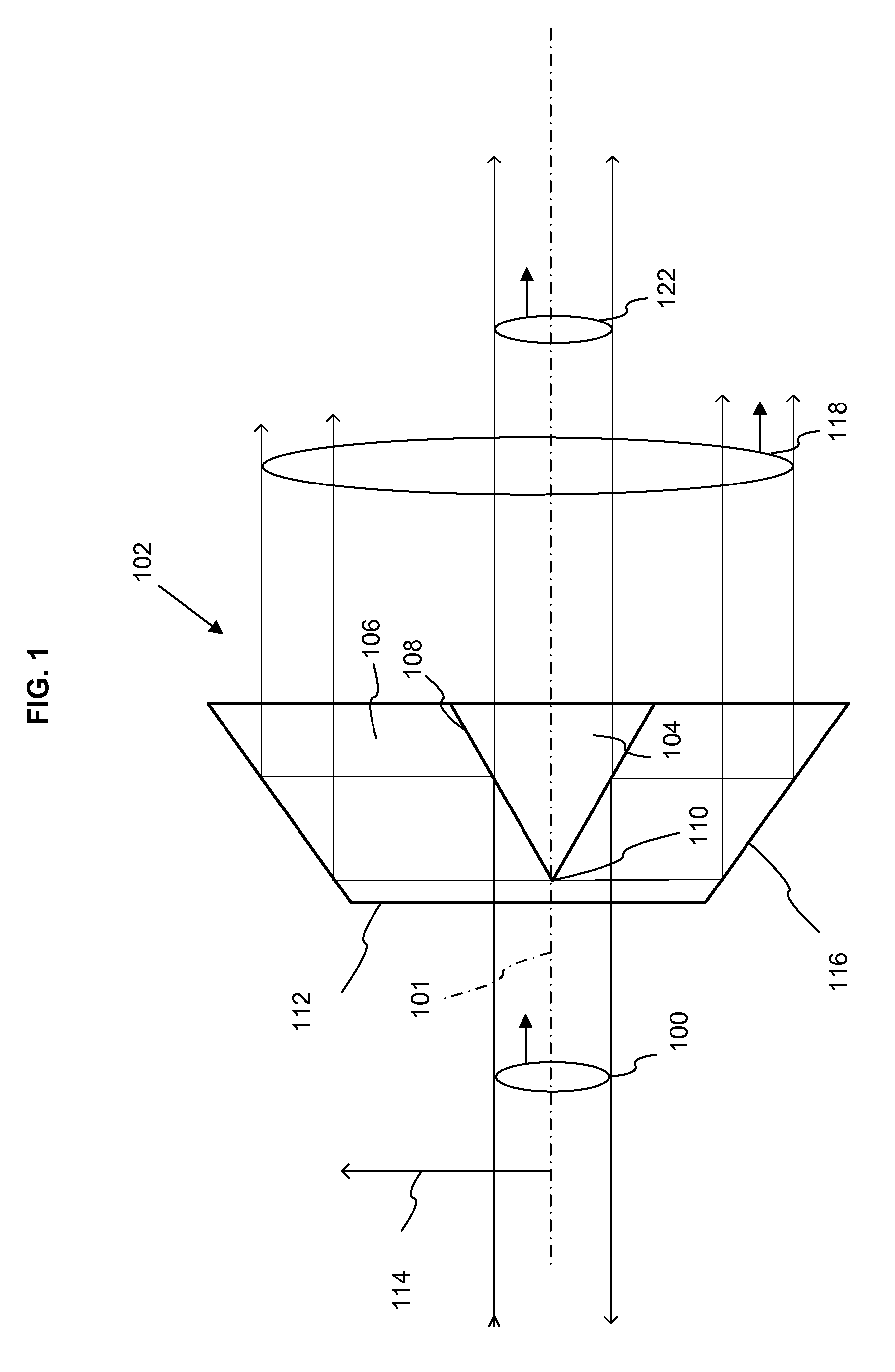
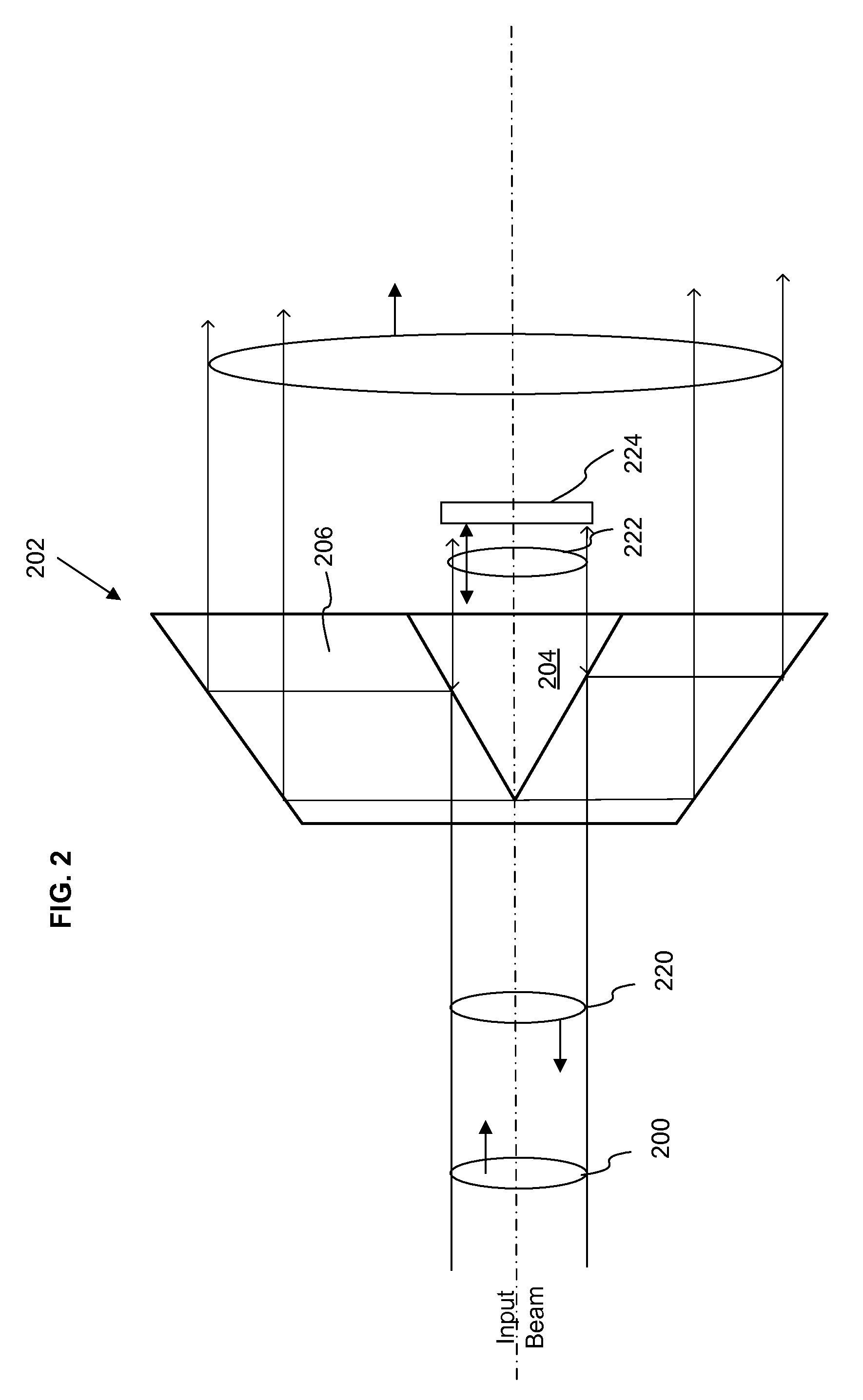
Beam formation unit comprising two axicon lenses, and device comprising one such beam formation unit for introducing radiation energy into a workpiece consisting of a weakly-absorbent material
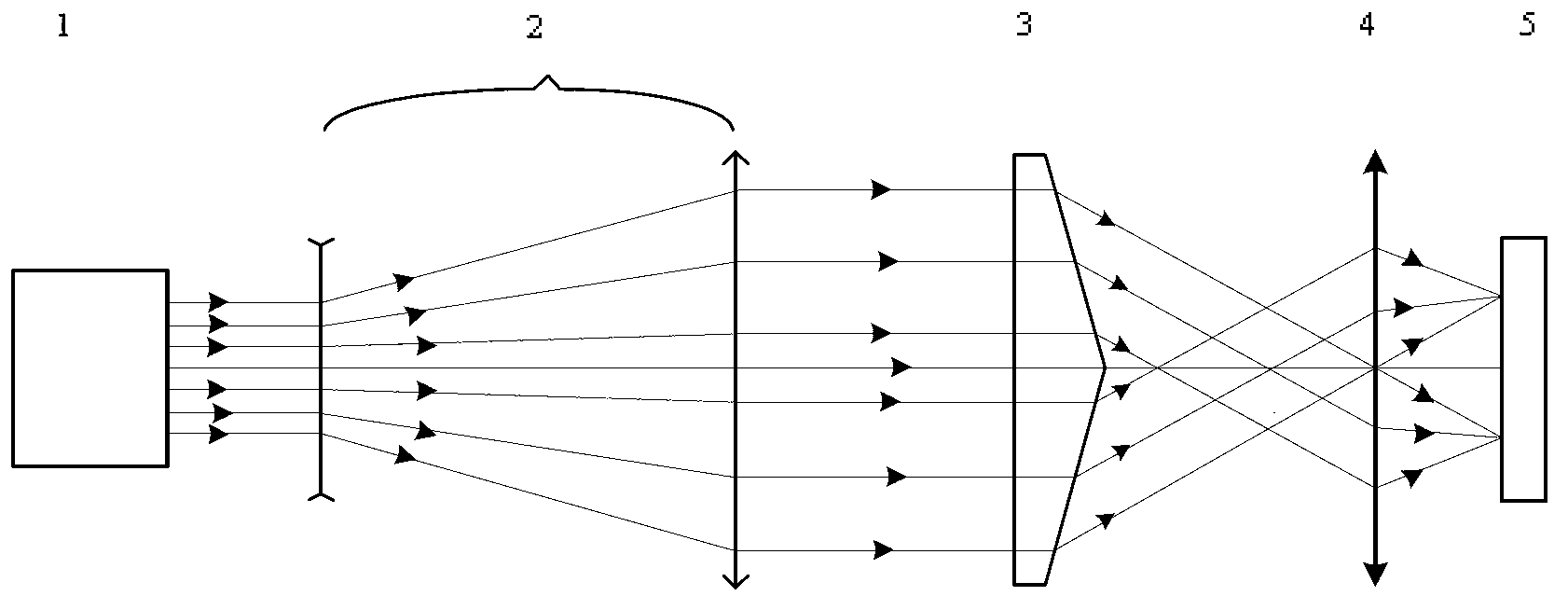
InactiveUS7102118B2Absorption in material is highMade useLaser detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsLight beamAbsorbent material
The invention is directed to a beam-shaping unit for generating a beam bundle which is focused in a punctiform manner, propagates in a ring shape, and has a radiationless central area, comprising a focusing lens, a first axicon and a second axicon, and to an arrangement with a beam-shaping unit of this kind for introducing radiation energy into a workpiece comprising weakly absorbent material which is arranged between a first resonator mirror and a second resonator mirror. The first resonator mirror which is arranged in front of the workpiece in the radiating direction is located in the radiationless central area. The radiation energy can be absorbed to the maximum extent by repeatedly passing through the same interaction volume in the workpiece.
Owner:JENOPTIK AUTOMATISIERUNGSTECHN
Miniature imaging encoder readhead using fiber optic receiver channels
InactiveUS20050047728A1Increase speedImprove accuracyUsing optical meansCoupling light guidesFiberImaging lens
A fiber optic readhead arrangement for imaging a scale onto a set of optical fiber receiver channels is disclosed. The readhead arrangement includes an imaging lens and may include an aperture positioned at a focal point of the imaging lens in a telecentric arrangement. An axicon lens may be utilized to direct source light away from the imaging lens and into a ring-shaped annular source lens which surrounds the imaging lens. A source lens may concentrate source light on the scale in an area where it will be imaged back through the imaging lens to the readhead. In one embodiment, multiple source fibers may be provided around the perimeter of the fiber optic readhead arrangement. In another embodiment, the receiver fibers may also function as source fibers. In various exemplary embodiments, high levels of displacement signal interpolation may be achieved to provide high resolution measurement.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Microporous array processing device and microporous array processing method
InactiveCN109570781AReduced impact strengthQuality improvementMicrostructural devicesLaser beam welding apparatusRotary stageLight beam
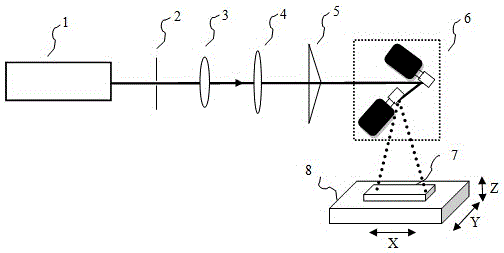
The invention discloses a microporous array processing device and a microporous array processing method. The microporous array processing method comprises the following steps of S1, converting a laserbeam into Bessel spots by means of an axicon principle, and focusing the spots to the surface of a to-be-processed component; S2, adjusting the axicon according to a microporous array needed by the to-be-processed component to obtain quantity and distribution of the needed spots; and S3, processing the spots to the to-be-processed component by means of laser pulse to form the microporous array. The microporous array processing device comprises a laser light source, a light source adjusting assembly, the axicon and a moving table successively arranged along the direction of propagation of light, wherein the axicon is mounted on a five-axis precision rotary table and is driven by the five-axis precision rotary table to adjust the angle the axicon and an incident beam. The microporous arrayprocessing device and the microporous array processing method process multiple micropores at single time, so that the work efficiency is improved. The heat effect is relatively long, the action of pulse laser is small, and the quality of a processed material is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS EQUIP (GRP) CO LTD
Device for measuring four-freedom-degree kinematic errors of guide rail through non-diffraction light
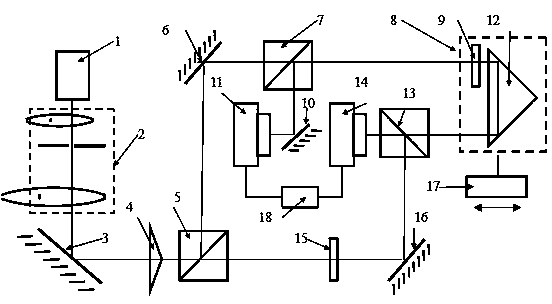
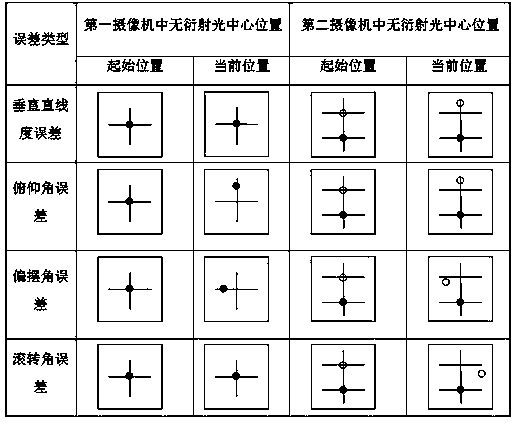
The invention discloses a device for measuring four-freedom-degree kinematic errors of a guide rail through non-diffraction light. The device comprises a laser device, a beam expansion collimating mirror, an axicon, a beam splitter prism, a reflecting mirror, a beam splitter, a rectangular prism and video cameras. A kinematic unit composed of the beam splitter and the rectangular prism is fixed to a working platform. Non-diffraction light beams reflected by the beam splitter are received by the first video camera, the non-diffraction light beams transmitted by the beam splitter and reference non-diffraction light beams are received by the second video camera, and by analyzing the change of the positions of center light of non-diffraction light in the two video cameras is analyzed, then the kinematic errors of the perpendicular straightness, the deflection angle, the pitch angle and the roll angle of the guide rail are recognized and measured. The device is simple in structure, large in measurement range, high in accuracy and stability, and good in overall performance, has the multi-freedom-degree measurement function and is a device for measuring multi-freedom-degree errors.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Design method of annular vortex array mask plate with controllable vortex number
InactiveCN106933027AOriginals for photomechanical treatmentNeutron particle radiation pressure manipulationComplex amplitudeComputational simulation
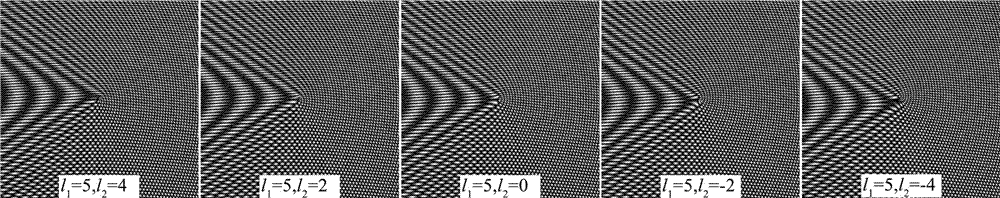
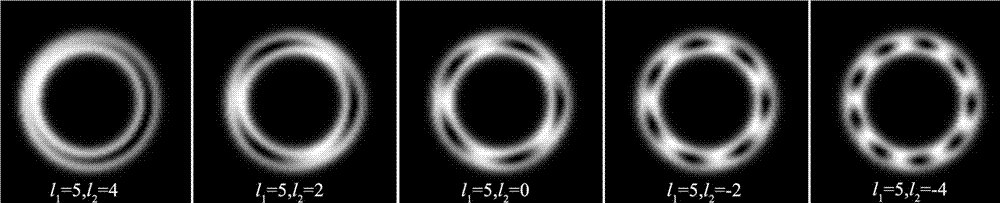
The invention relates to a design method of an annular vortex array mask plate with controllable vortex number. By means of computer generated hologram principle, light beam complex amplitude computational simulation is carried out to superimpose two perfect vortex beam mask plates with different radii, so that an annular vortex array can be generated in a far field. Cone angles of two axicon lens are adjusted to control the light ring superposition degree of concentric perfect vortexes, thus achieving generation of an annular vortex array. The annular vortex array can achieve arbitrary control of the dark nuclear number of the ring, thus having very important application prospects in particle manipulation technology.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
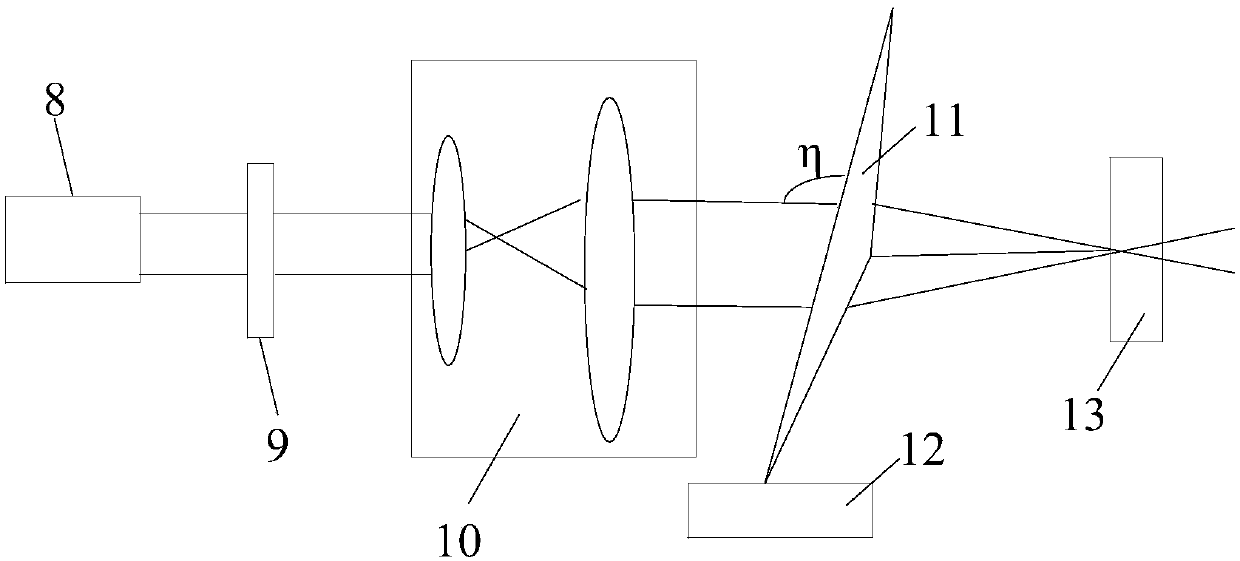
Micro laser beam precise finishing optical device
InactiveCN101508060AOvercoming demandsOvercoming matching couplingLaser beam welding apparatusOptical elementsSpray nozzleLight beam
The invention discloses a micro-laser beam precision machining optical device, and relates to a precision machining device. The invention provides the micro-laser beam precision machining optical device for laser precision machining, which is provided with visible light coaxial positioning indication and can conveniently realize direct coupling of diffraction-free beams and nozzle micropores. The micro-laser beam precision machining optical device is provided with a laser, a visible light source, a flat mirror, a beam expanding collimator, an axicon, an optical window, a pressure fluid chamber and nozzle micropores, wherein the flat mirror is positioned in front of the laser and the visible light source; laser beams emitted by the laser are coupled with beams of the visible light source through the flat mirror; the beam expanding collimator is positioned in front of the flat mirror; the axicon is positioned in front of the beam expanding collimator; the pressure fluid chamber is positioned in front of the axicon; the optical window is arranged on the top of the pressure fluid chamber; the bottom of the pressure fluid chamber is provided with the nozzle micropores; and the beams coupled through the flat mirror are coaxial with the beam expanding collimator, the axicon, the optical window and the nozzle micropores.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
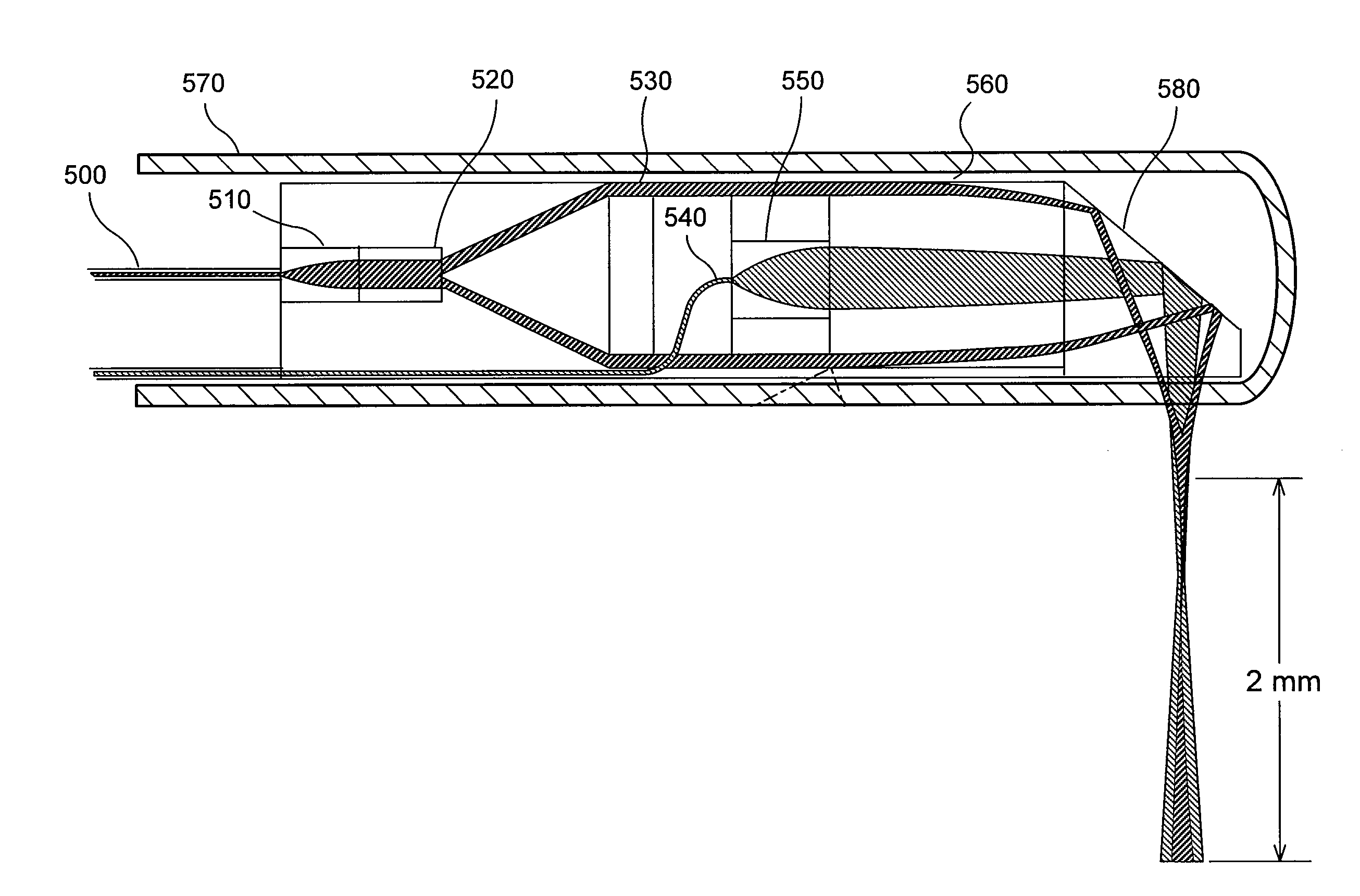
Apparatus and method for micromanipulation of microscale objects using laser light delivered through a single optical fiber and axicon lens
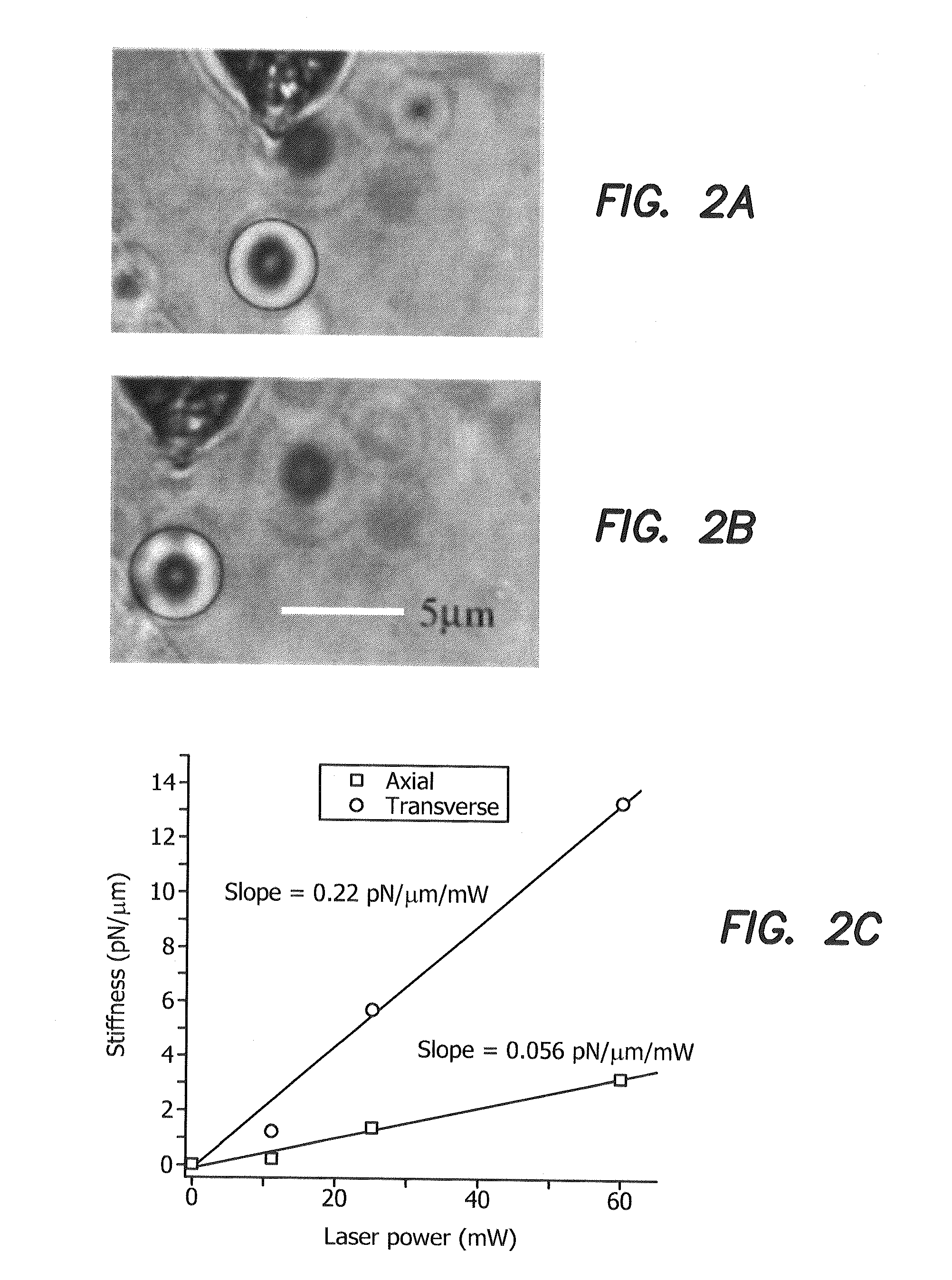
ActiveUS20100120113A1Improve throughputReduce throughputLaser detailsElectrotherapyLight beamLaser light
A single optical fiber having a distal end is optically coupled to the laser and distilling terminated with an axicon lens optically coupled to the single optical fiber to form a microscopic distal tip to provide a spatially shaped elongated laser focused spot for microprocessing and / or microdissection of a microscale object. A pulsed or continuous laser beam or superposition of pulsed and continuous laser beams is generated, controllably spatially shaped, selectively oriented, selectively moved via movement of a single optical fiber terminated with the axicon lens, and the oriented, spatially shaped laser beam applied via the single optical fiber terminated with the axicon lens to a living or nonliving microscopic object for manipulation, micro-dissection, alteration / ablation, and excitation of the living or nonliving microscopic object.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Cone angle measuring device and method for axicons
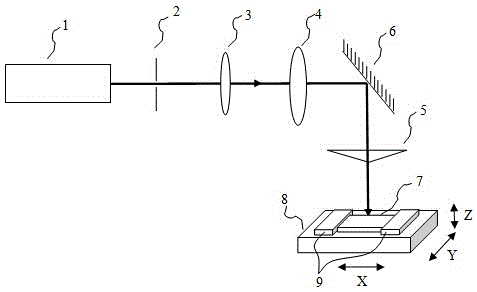
ActiveCN103292743ARealize cone angle measurementSimple structureUsing optical meansBeam expanderLight beam
Disclosed are a cone angle measuring device and method for axicons. The cone angle measuring device comprises a laser, a bean expander set, a focusing lens and an image sensor, wherein the beam expander set, the focusing lens and the image sensor are sequentially arranged along exit beams of the laser, and an insert hole for an axicon to be detected is arranged between the beam expander set and the focusing lens. The cone angle measuring device has the advantages of simple structure, easy measurement of any cone angles of the axicon and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
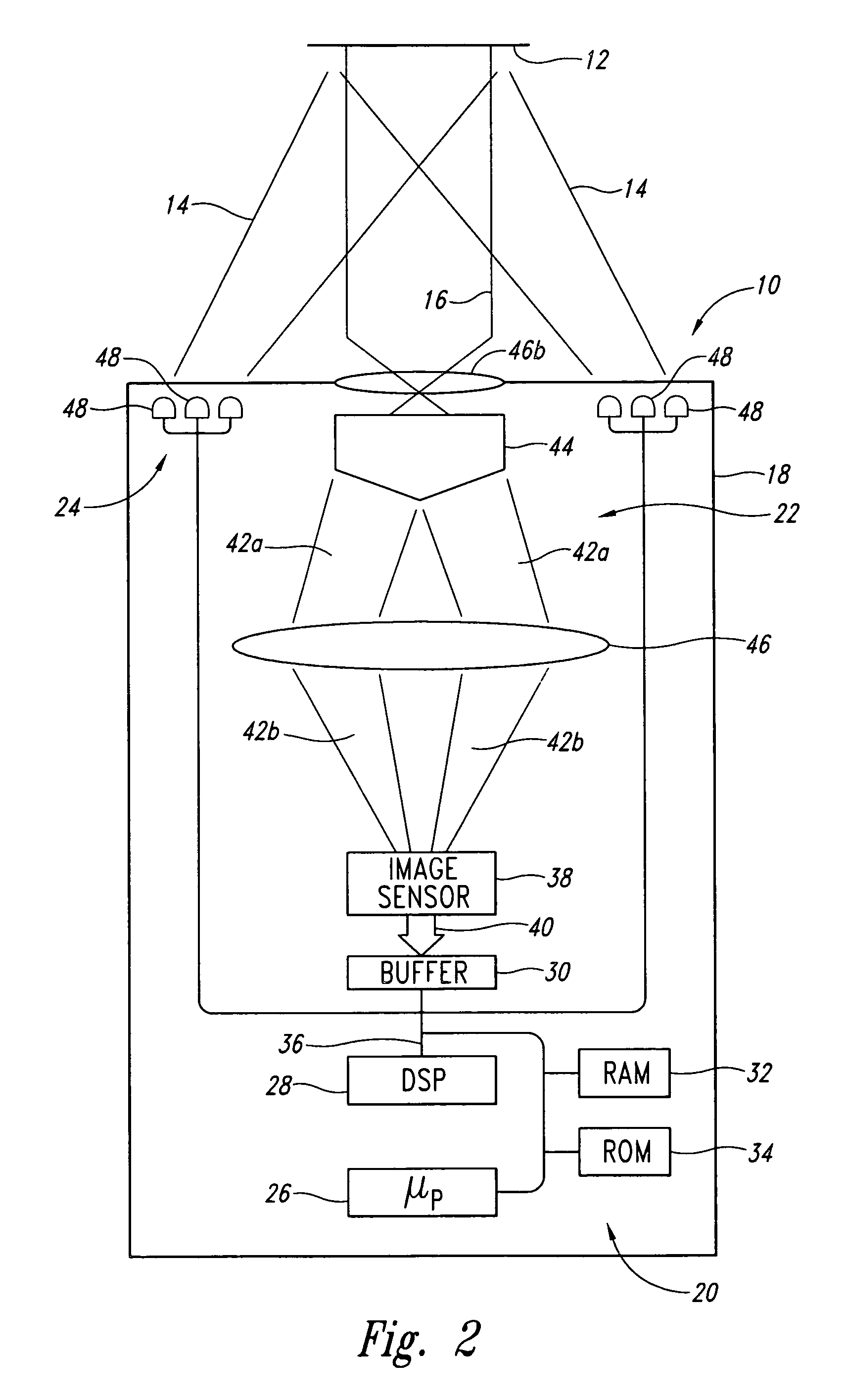
Optoelectronic reader and method for reading machine-readable symbols
InactiveUS20070063043A1Visual representatino by photographic printingSensing by electromagnetic radiationBarcodeAxicon
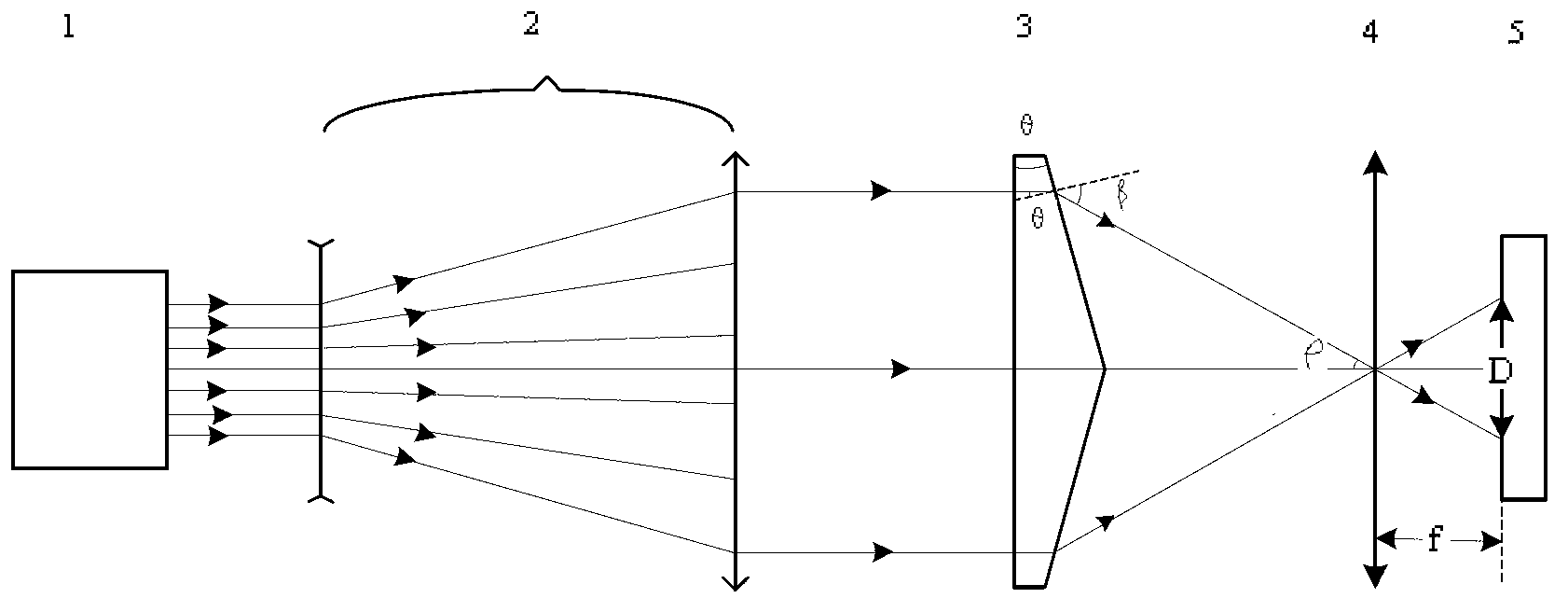
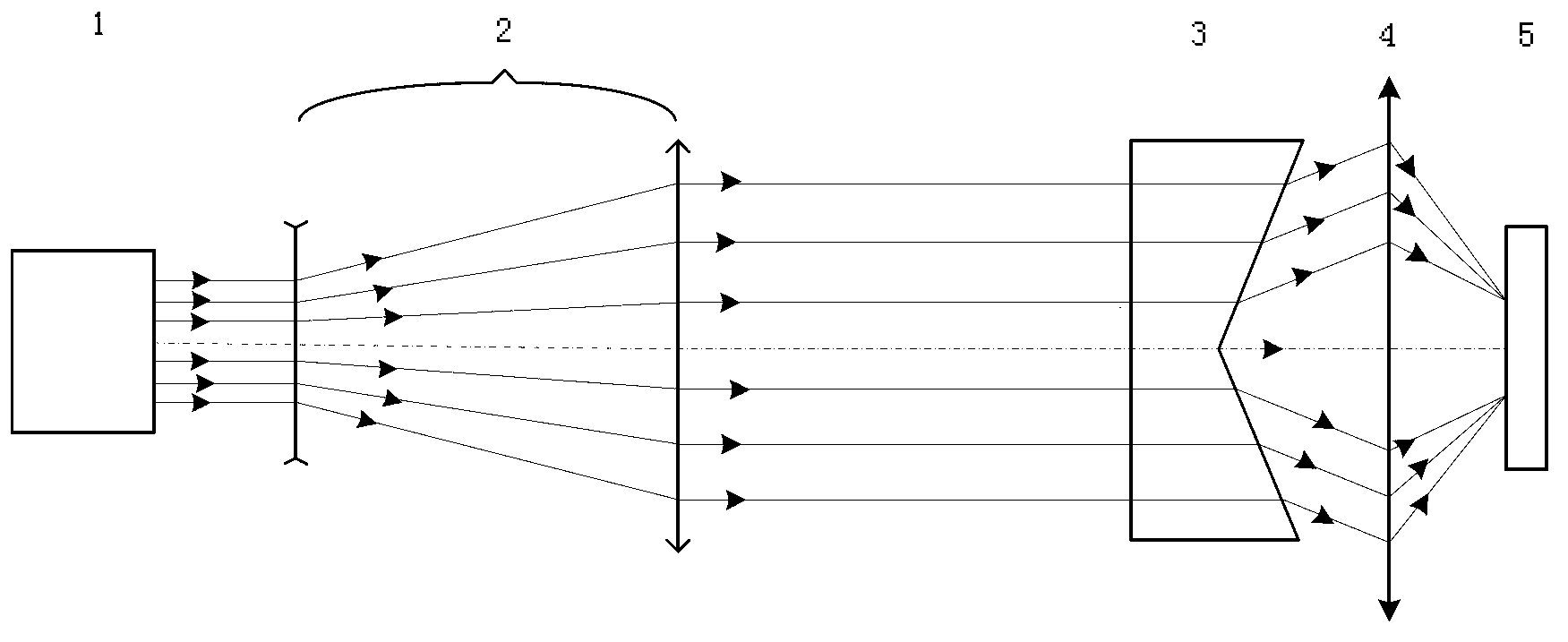
An optoelectronic reader for reading machine-readable symbols such as barcode symbols employs an optical assembly to focus a non-Gaussian image on an image sensor. The optical assembly may include a substantially diffraction free optical element, such as an annular slit aperture or a conical lens element, for example a conical refracting surface or axicon lens element.
Owner:INTERMEC IP
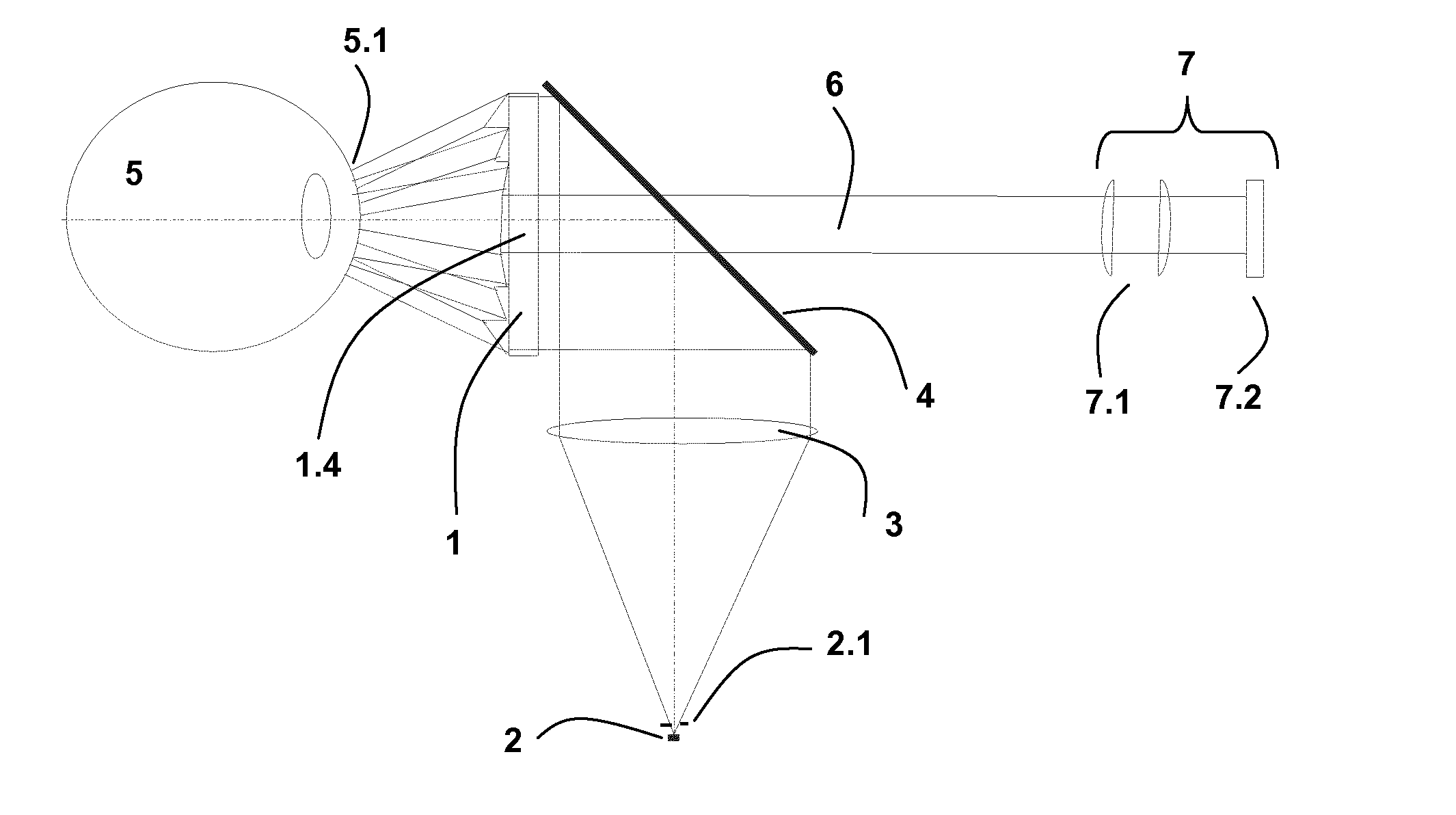
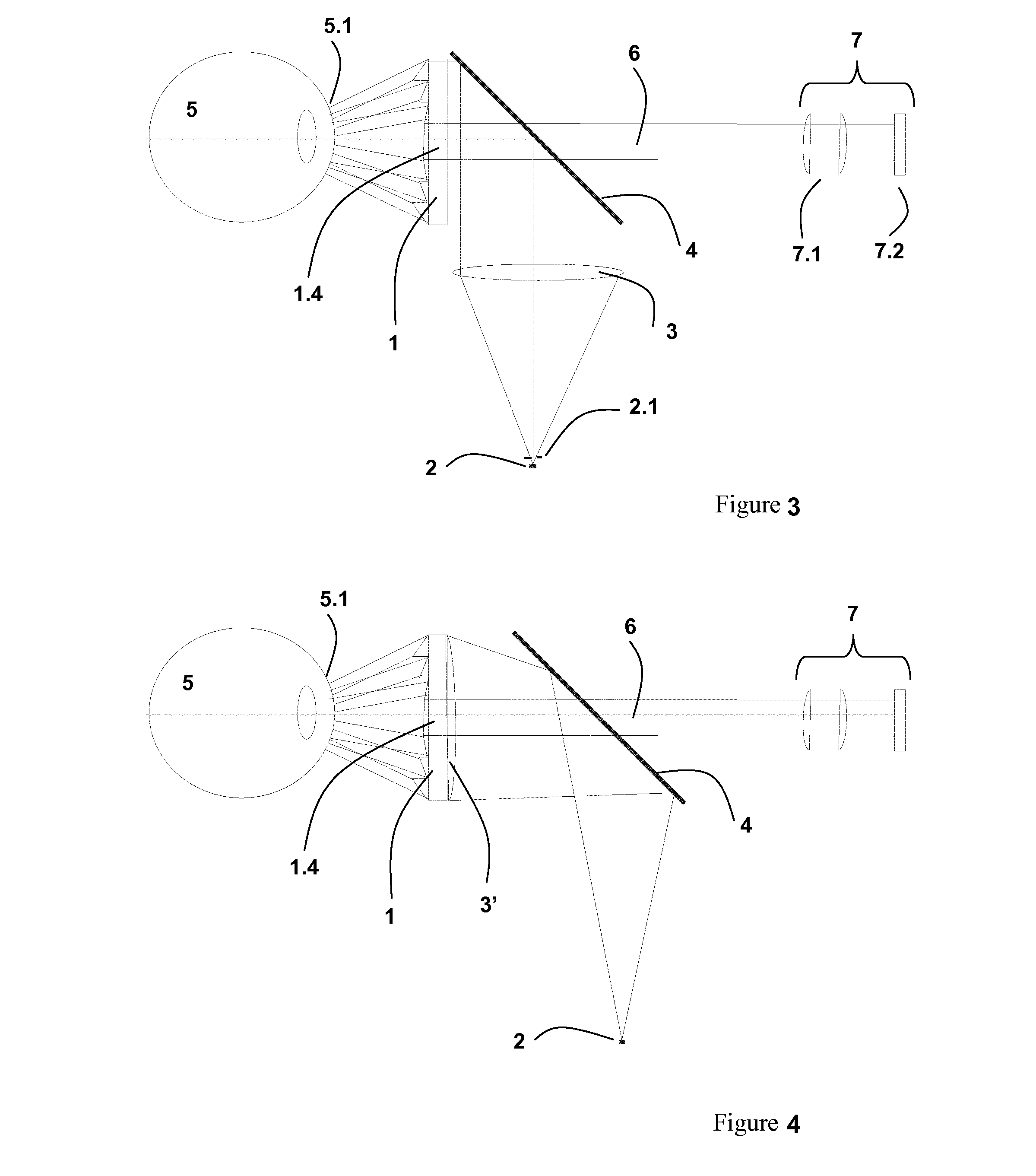
System for determining the topography of the cornea of an eye
ActiveUS20140078468A1High light efficiencyMore cost-effectivelyEye diagnosticsUsing optical meansImage detectionRing pattern
A system for determining the surface shape of the cornea of an eye by analyzing the reflection of a spatially distributed ring pattern. The system includes an element for generating a ring pattern, an illuminating unit, an image capturing unit, and a control and analyzing unit. The element for generating rings is a fresneled axicon with annular structures of different radii. Furthermore, an optical element for illuminating the entire surface of the fresneled axicon with plane waves and an optical element for separating the illuminating and detecting beam path are arranged between the illuminating unit and the fresneled axicon. Furthermore, the image capturing unit consisting of an imaging system and an image sensor is designed for a telecentric distance-independent image detection.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Phase shift interference microscopic device and method based on Zernike phase contrast imaging
ActiveCN102221327AOvercome limitationsExcellent anti-vibration performanceMicroscopesUsing optical meansCcd cameraCharge couple device
The invention relates to a phase shift interference microscopic device and method based on Zernike phase contrast imaging. The device comprises an illuminating unit, a microscopic amplifying unit and a phase contrast imaging unit which are arranged in sequence along the incident direction of light; the illuminating unit comprises a beam expanding system, a multi-beam illumination generating unit and a beam contraction collimating unit which are arranged in sequence along the light path direction; the beam expanding system comprises a laser, a light intensity controller and a beam expanding unit which are arranged in sequence along the light path direction; the multi-beam illumination generating unit comprises an axicon lens, a first lens, a rotary scatterer, a second lens and an amplitude mask plate which are arranged in sequence along a light path; a tested sample is arranged on a focal surface between a first objective lens and a second objective lens; and the tested sample and a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) camera meet an objective image relation. Due to the adoption of the device and the method, the vignetting effect of the conventional Zernike phase contrast imaging is avoided, quantitative measurement of a phase object is realized, and the light path has the advantages of low coherent noise, high vibration resistance, high transverse resolution and the like.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Beam formation unit comprising two axicon lenses, and device comprising one such beam formation unit for introducing radiation energy into a workpiece consisting of a weakly-absorbent material
InactiveUS20060091283A1Absorption in material is highMade useLaser detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsLight beamAbsorbent material
The invention is directed to a beam-shaping unit for generating a beam bundle which is focused in a punctiform manner, propagates in a ring shape, and has a radiationless central area, comprising a focusing lens, a first axicon and a second axicon, and to an arrangement with a beam-shaping unit of this kind for introducing radiation energy into a workpiece comprising weakly absorbent material which is arranged between a first resonator mirror and a second resonator mirror. The first resonator mirror which is arranged in front of the workpiece in the radiating direction is located in the radiationless central area. The radiation energy can be absorbed to the maximum extent by repeatedly passing through the same interaction volume in the workpiece.
Owner:JENOPTIK AUTOMATISIERUNGSTECHN
Retina dark field optical coherence tomographic imager for continuous adjustable ring lighting
ActiveCN103815867ASolve the problem of unsatisfactory imaging effectIncrease contrastOthalmoscopesBeam splittingData acquisition
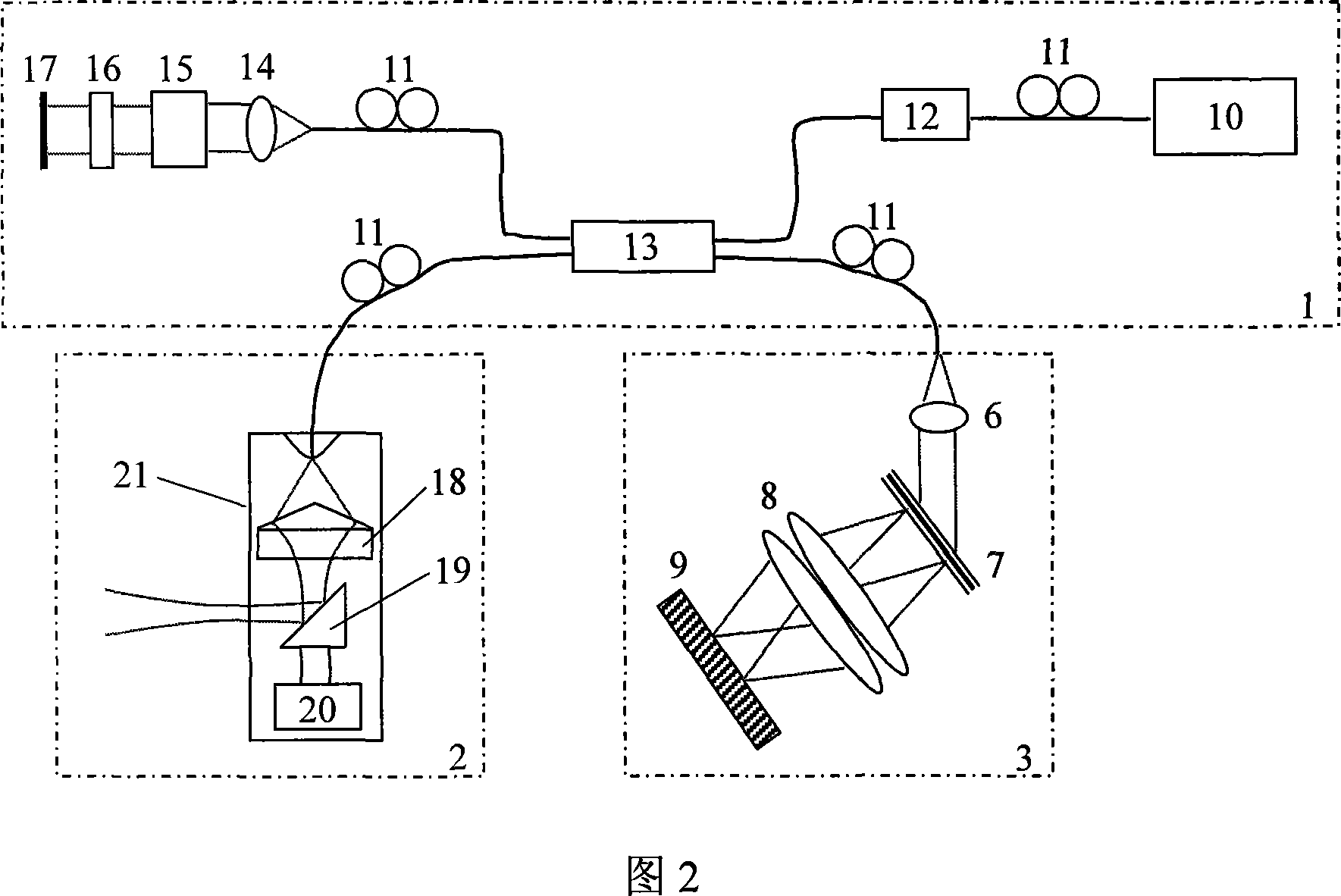
A retina dark field optical coherence tomographic imager for continuous adjustable ring lighting comprises a swept source, a first optical fiber coupler, a second optical fiber coupler, a first lens, a second lens, a third lens, a fourth lens, a fifth lens, a sixth lens, a first variable diaphragm, a second variable diaphragm, a first axicon, a second axicon, a first translation table, a second translation table, a beam splitting sheet, a vertical scanner, a horizontal scanner, a dispersion compensation sheet, a first polarization controller, a second polarization controller, a balance detector, a first single mode fiber, a second single mode fiber, a third single mode fiber, a fourth single mode fiber, a fifth single mode fiber, a sixth single mode fiber, a seventh single mode fiber, a function generation card, a data collection card, a computer and the like. The imager achieves longitudinal high-resolution tomography of the retina based on a frequency sweeping OCT technology, a ring lighting beam with the size and thickness continuously adjustable is formed through a pair of axicons with cone vertexes oppositely arranged so that dark field lighting is achieved, one variable diaphragm is used for filtering lighting light signals and backward reflected light signals of the lighting light signals, and only dark field light signals from the retina are detected. The retina dark field optical coherence tomographic imager has the advantages that ring lighting is continuously adjustable, and images have the high resolution, the high contrast ratio and the strong stereoscopic impression.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Polarizing device and laser unit
ActiveUS20100142049A1Reduce manufacturing costSimple processPolarising elementsOptical devices for laserLight beamOptoelectronics
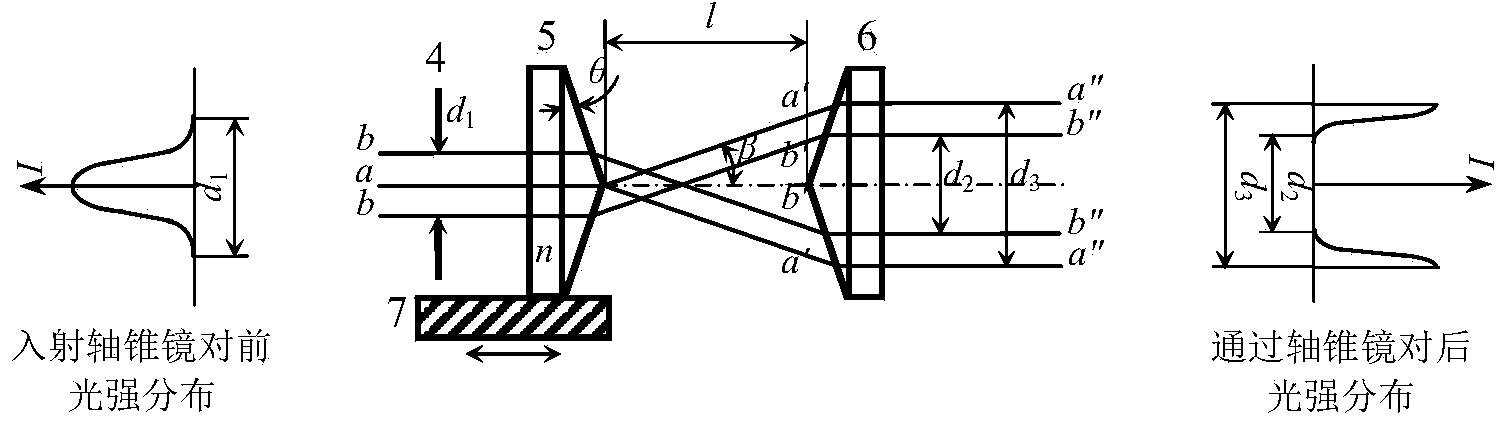
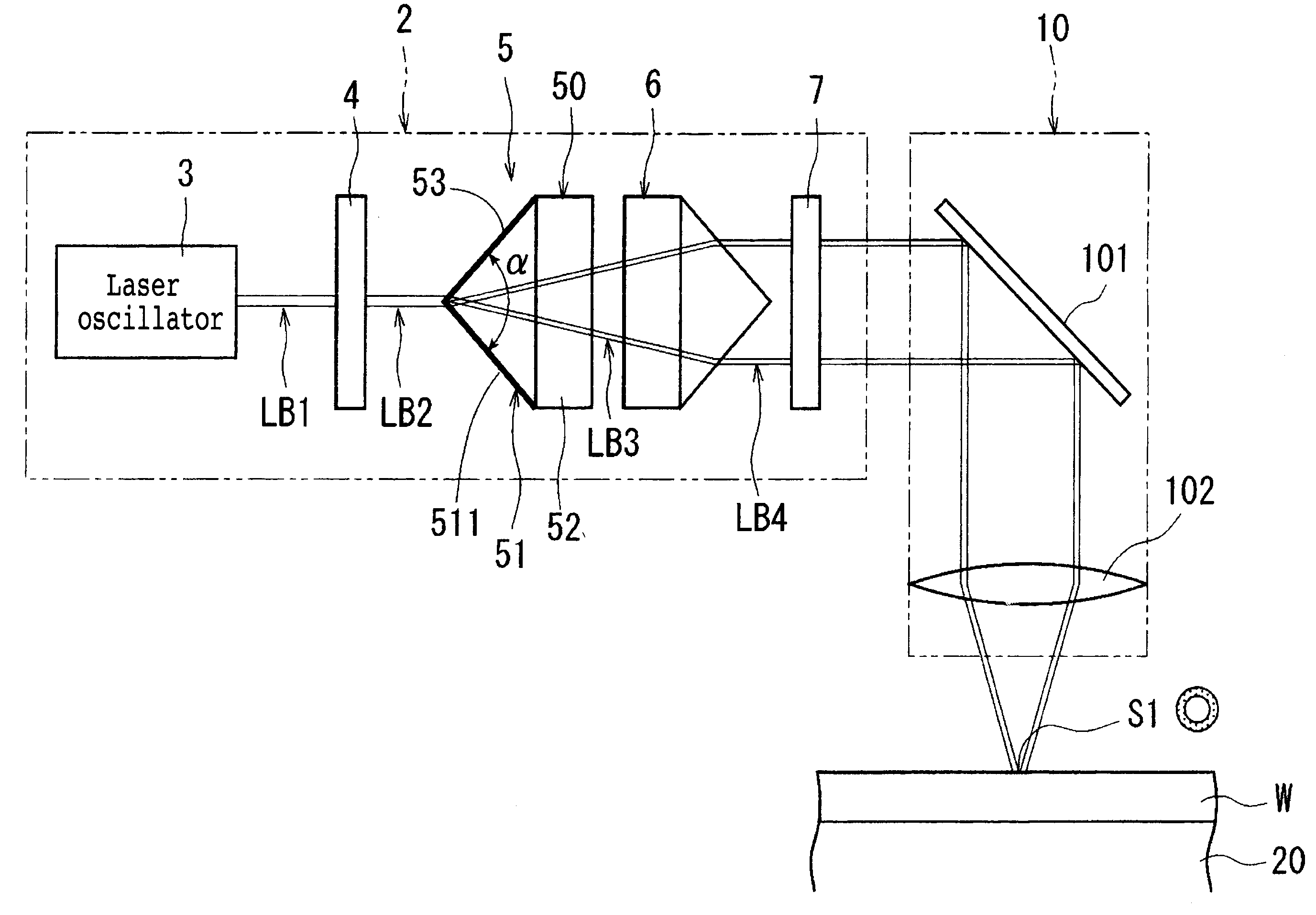
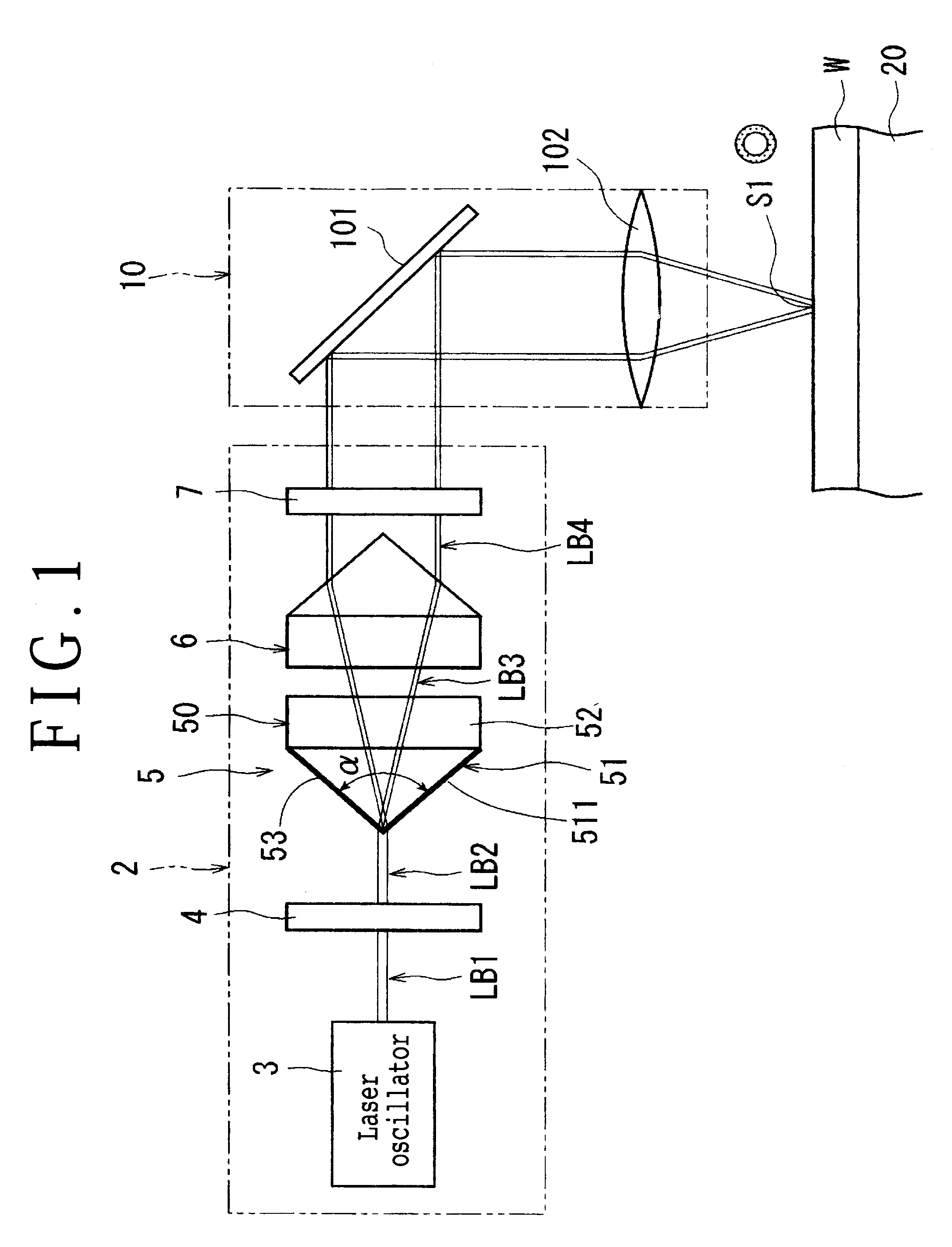
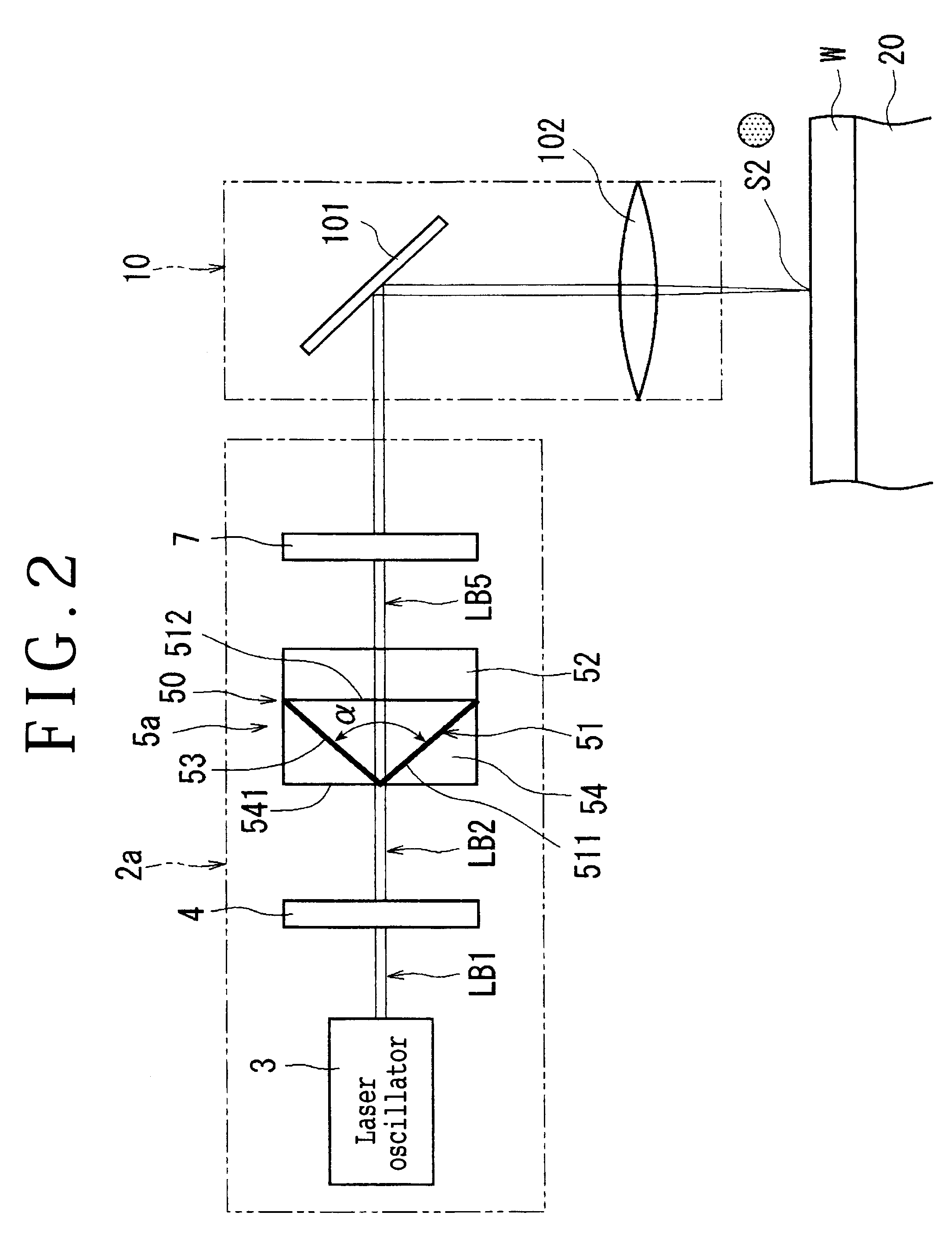
A polarizing device for converting a circularly polarized light beam into a radial polarized light beam, wherein the circularly polarized light beam is obtained by passing a linearly polarized light beam oscillated from a laser oscillator through a quarter-wave plate. The polarizing device includes an axicon lens having a conical surface and a dielectric film formed on the conical surface of the axicon lens.
Owner:DISCO CORP
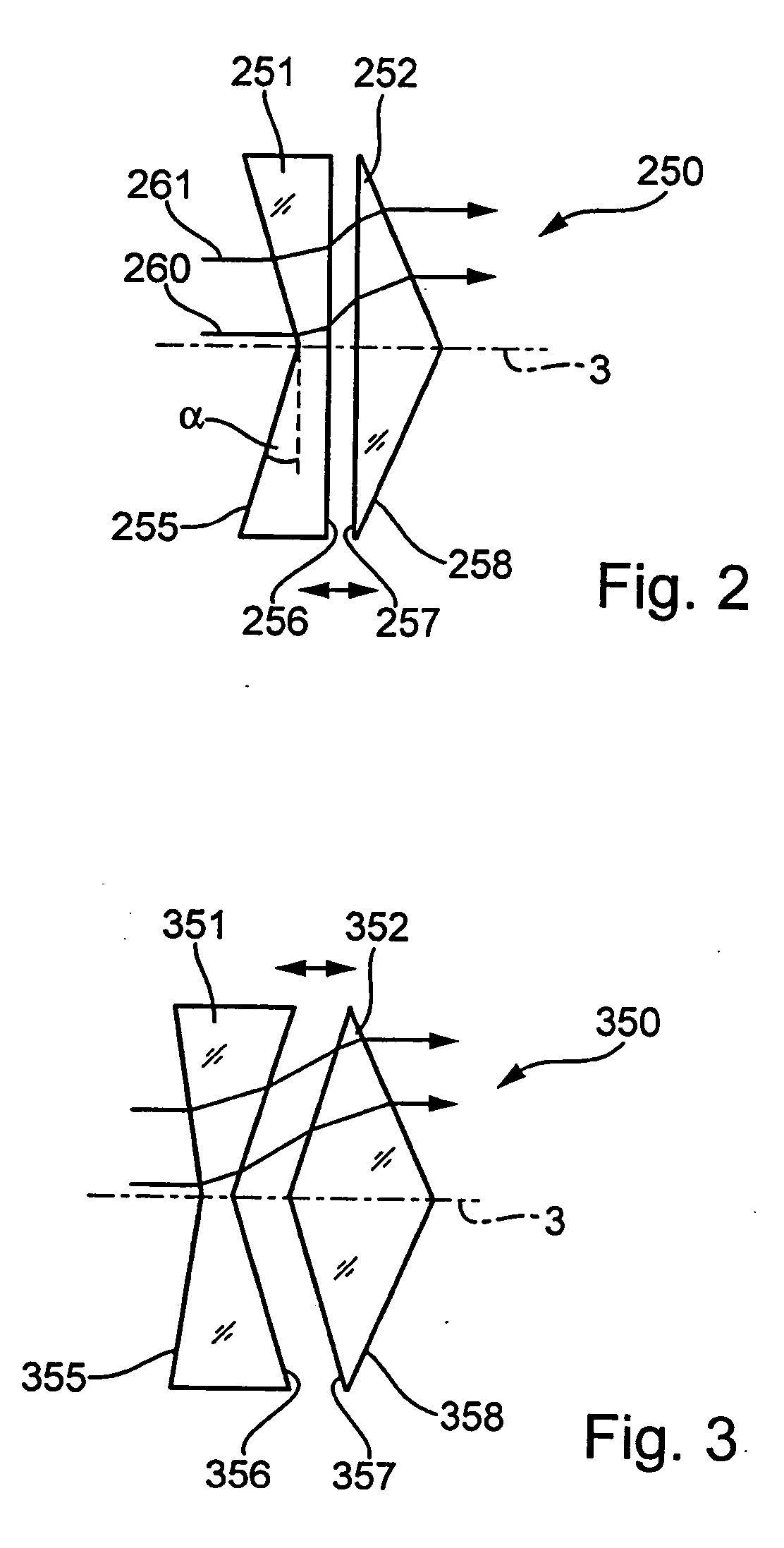
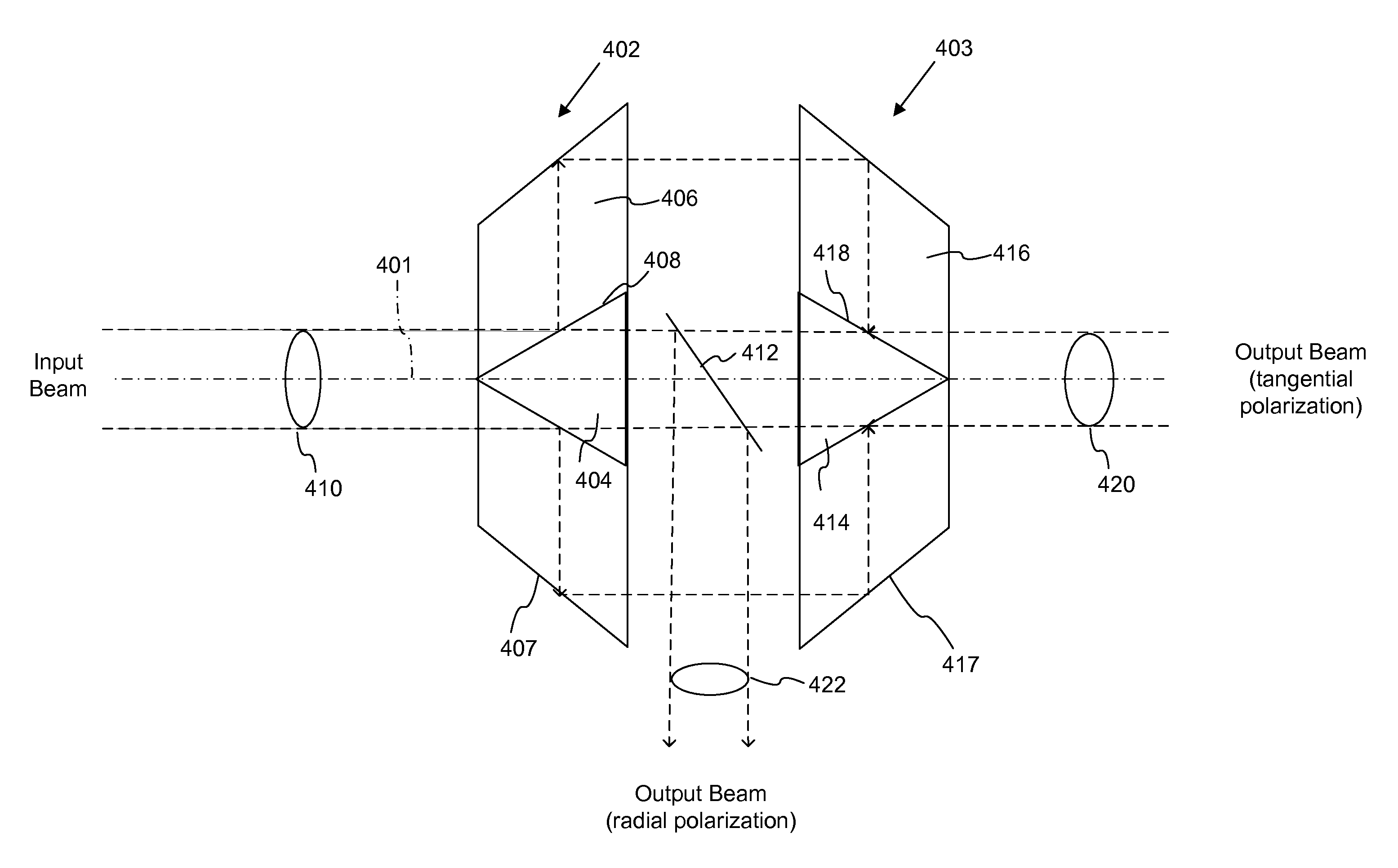
Azicon beam polarization devices
ActiveUS20120320458A1Reduce the cross-sectional areaPhotomechanical apparatusPolarising elementsBeam splitterLight beam
Polarizers and polarizing beam splitter include one or more pairs of axicons that are configured to separate an input beam into a radially polarized component and a tangentially (or azimuthally) polarized component. A second axicon pair can be provided to recombine the tangentially polarized component so as to provide a more uniform beam intensity. The radially polarized component can be reflected or otherwise directed so that one or both the radial and tangential components are available for use.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Method and system for obtaining an extended-depth-of-field volumetric image using laser scanning imaging
A laser scanning imaging system and method for obtaining an extended-depth-of-field image of a volume of a sample are provided. The system includes a laser module generating an input laser beam, a beam shaping module including an axicon and a Fourier-transform lens, and an imaging module including an objective lens and a detecting assembly. The axicon, Fourier-transform lens and objective lens are formed and disposed to successively convert the input laser beam into an intermediate non-diffracting beam, an intermediate annular beam, and an excitation non-diffracting beam. The excitation beam is projected onto the sample and has a depth of field and transverse resolution together defining a three-dimensional excitation region. The detecting assembly collects electromagnetic radiation from the excitation region to obtain one pixel of the extended-depth-of-field image. The system further includes a two-dimensional scanning module for scanning the excitation beam over the sample and build, pixel-by-pixel, the extended-depth-of-field image.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com