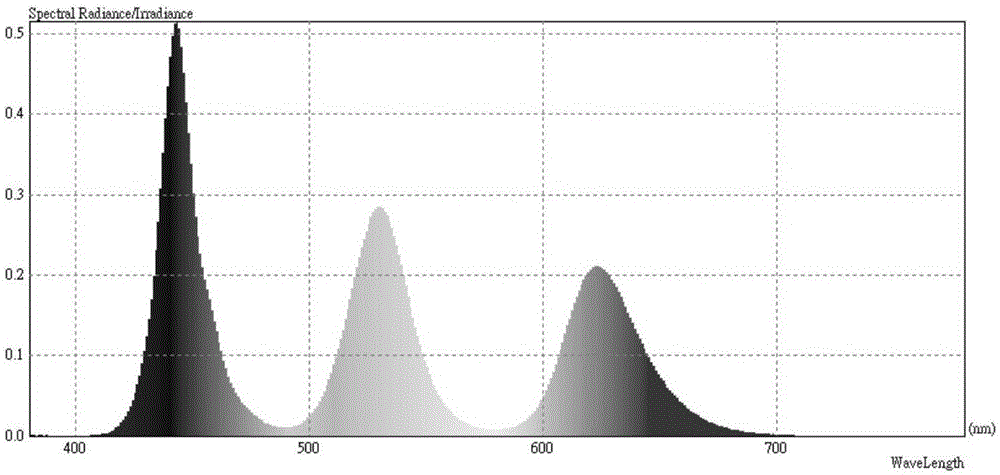
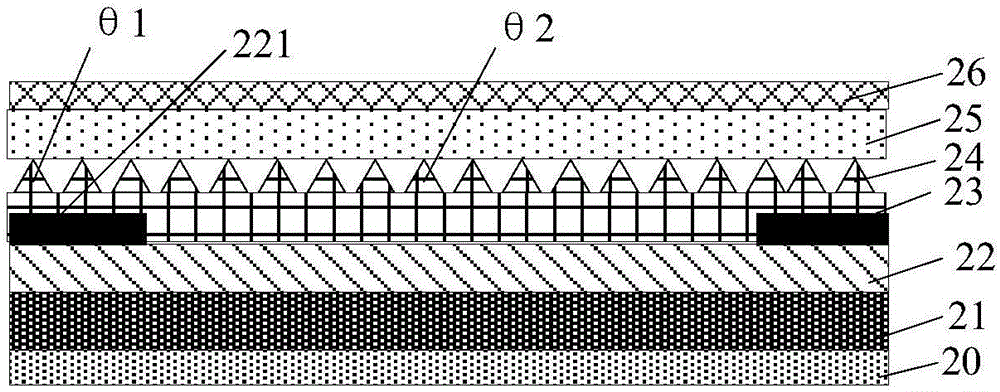
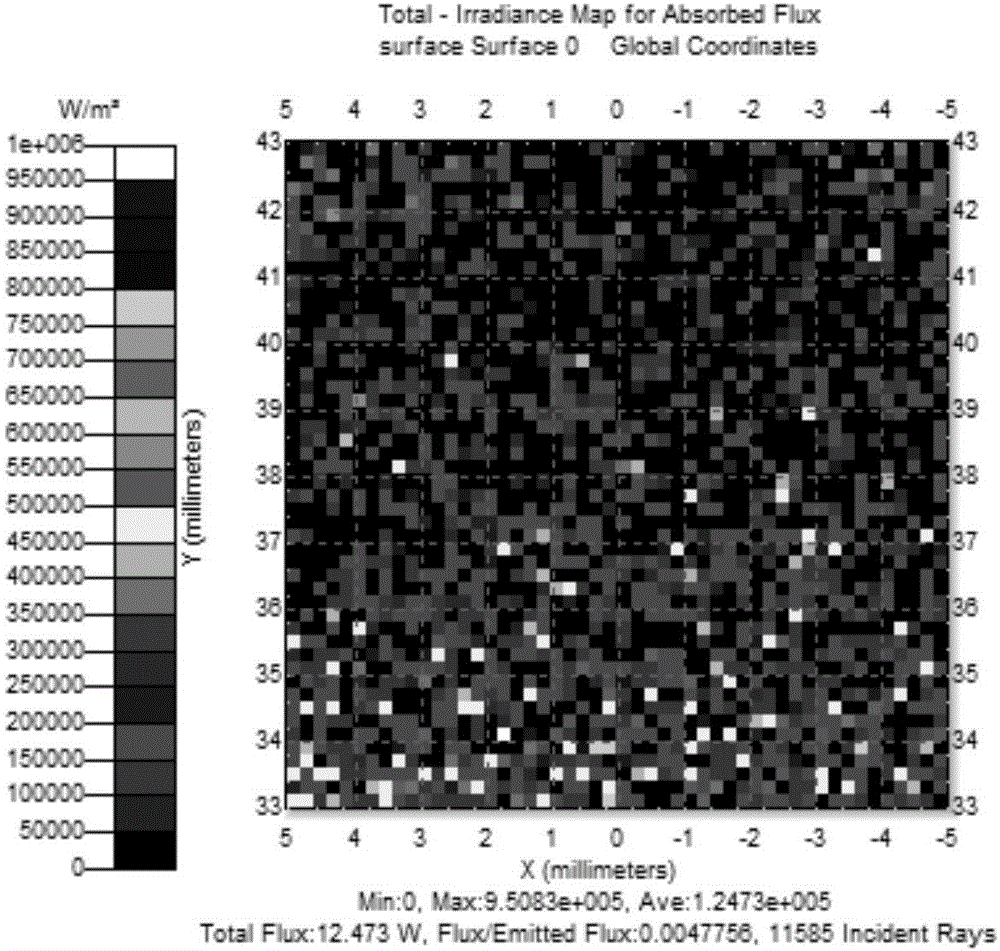
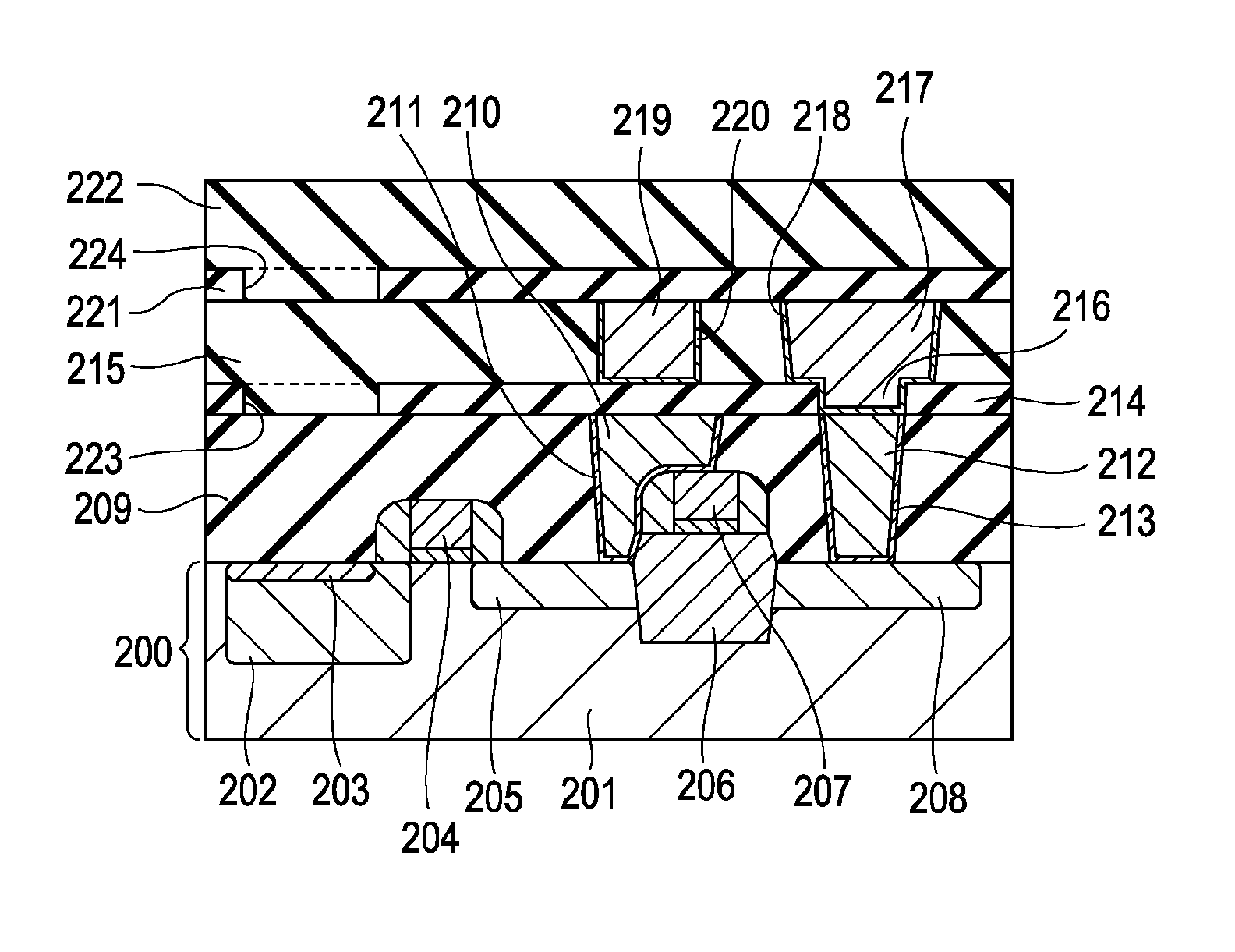
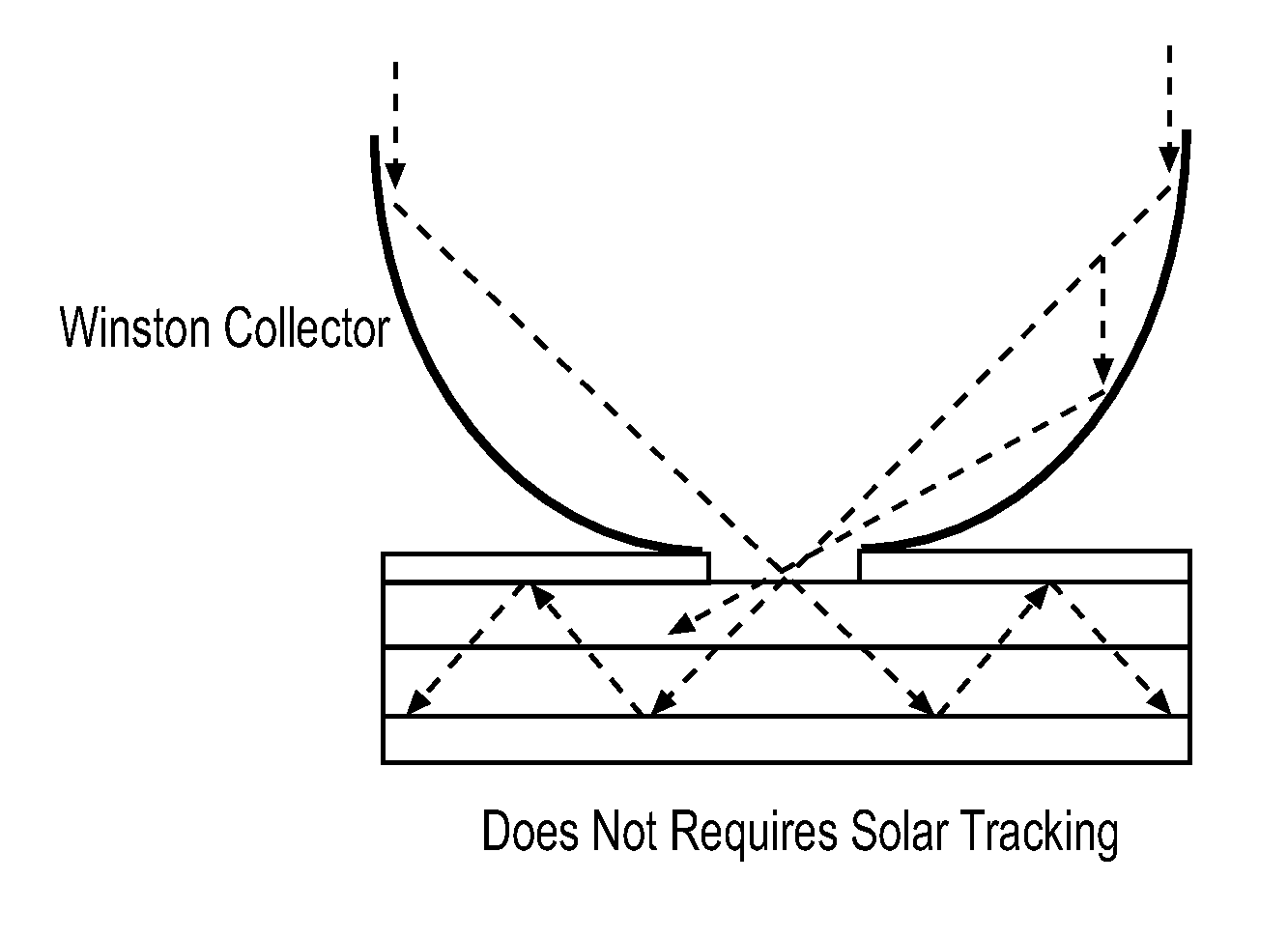
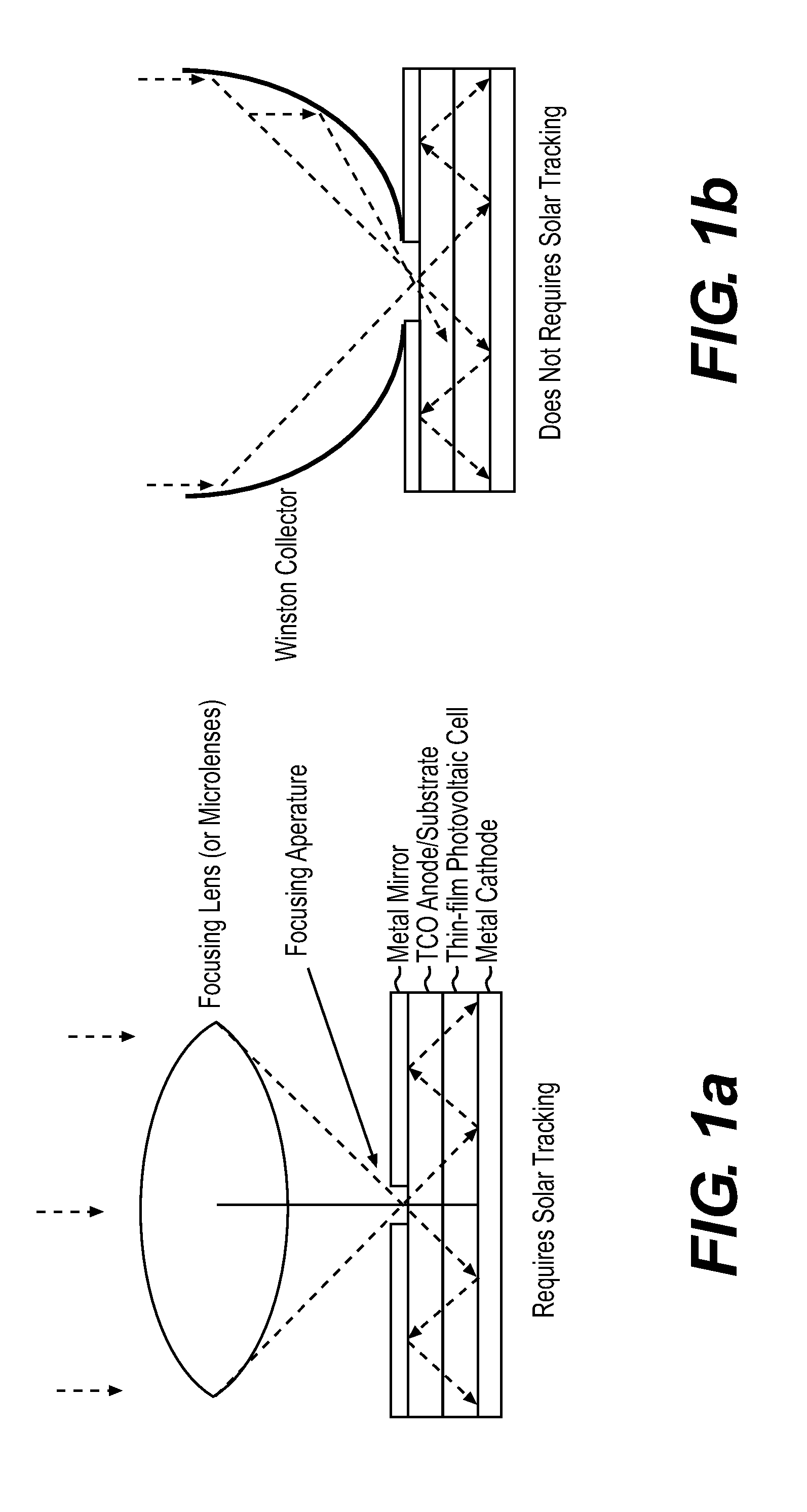
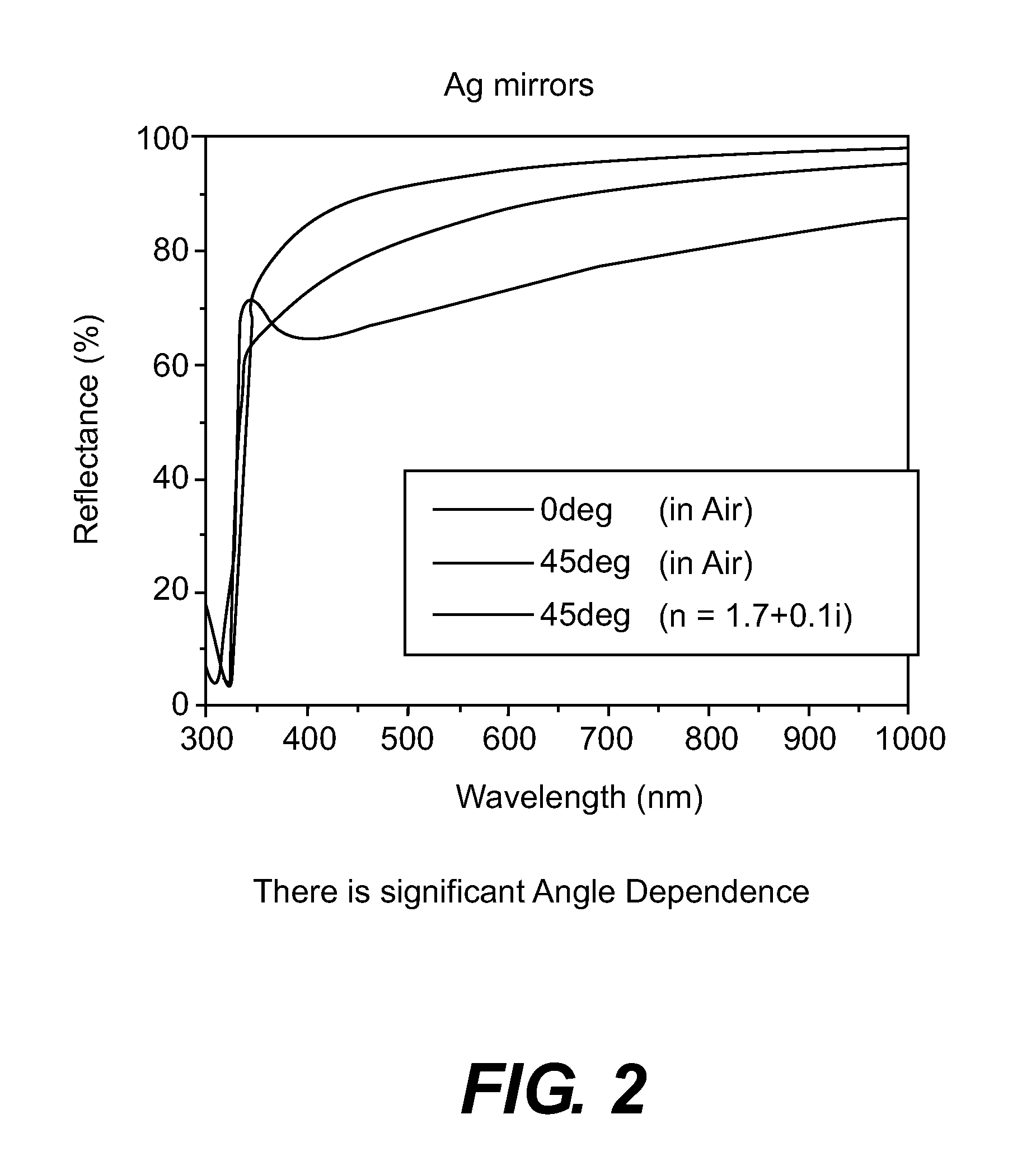
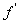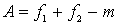Patents
Literature
95results about How to "Improve light collection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
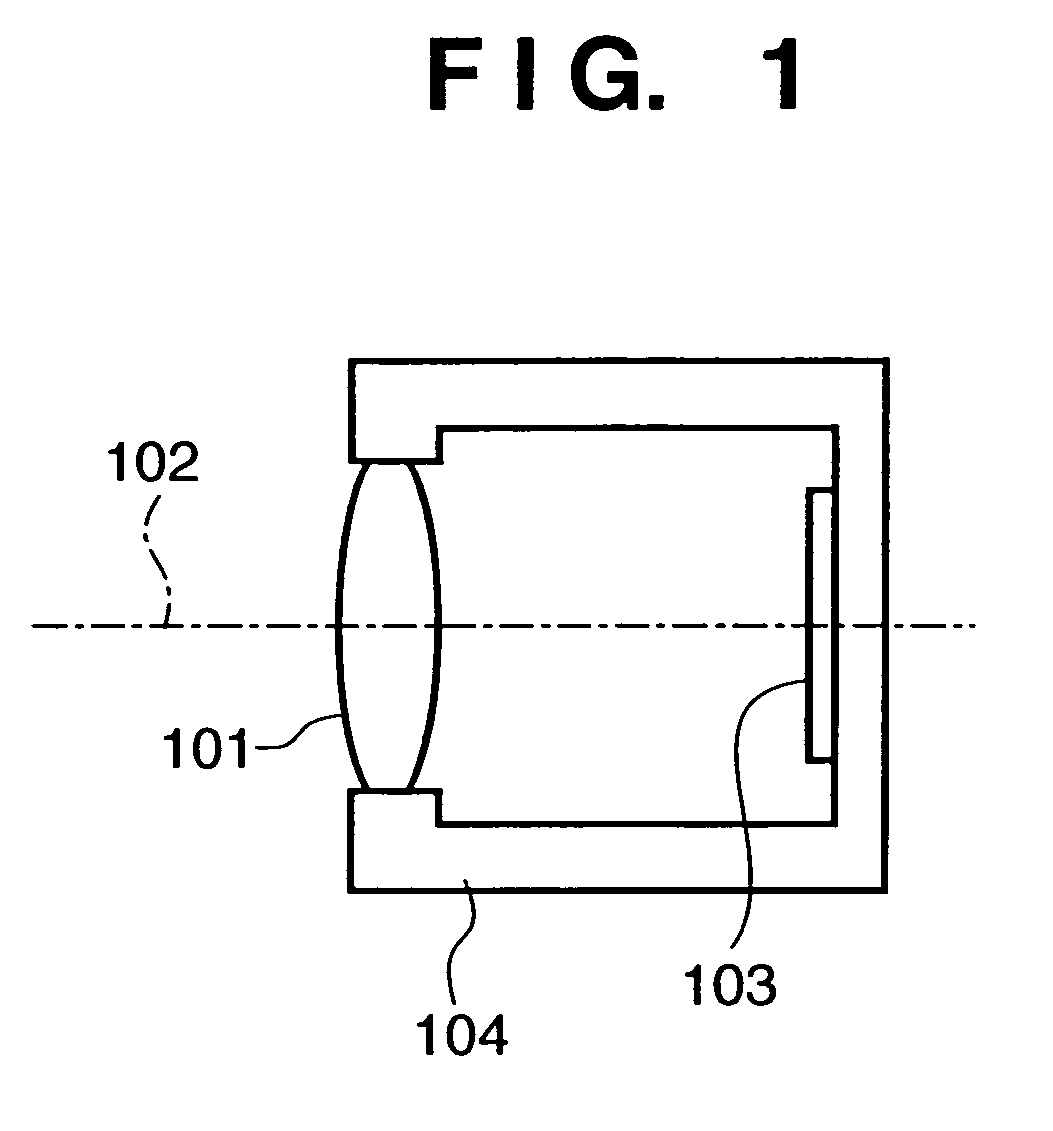
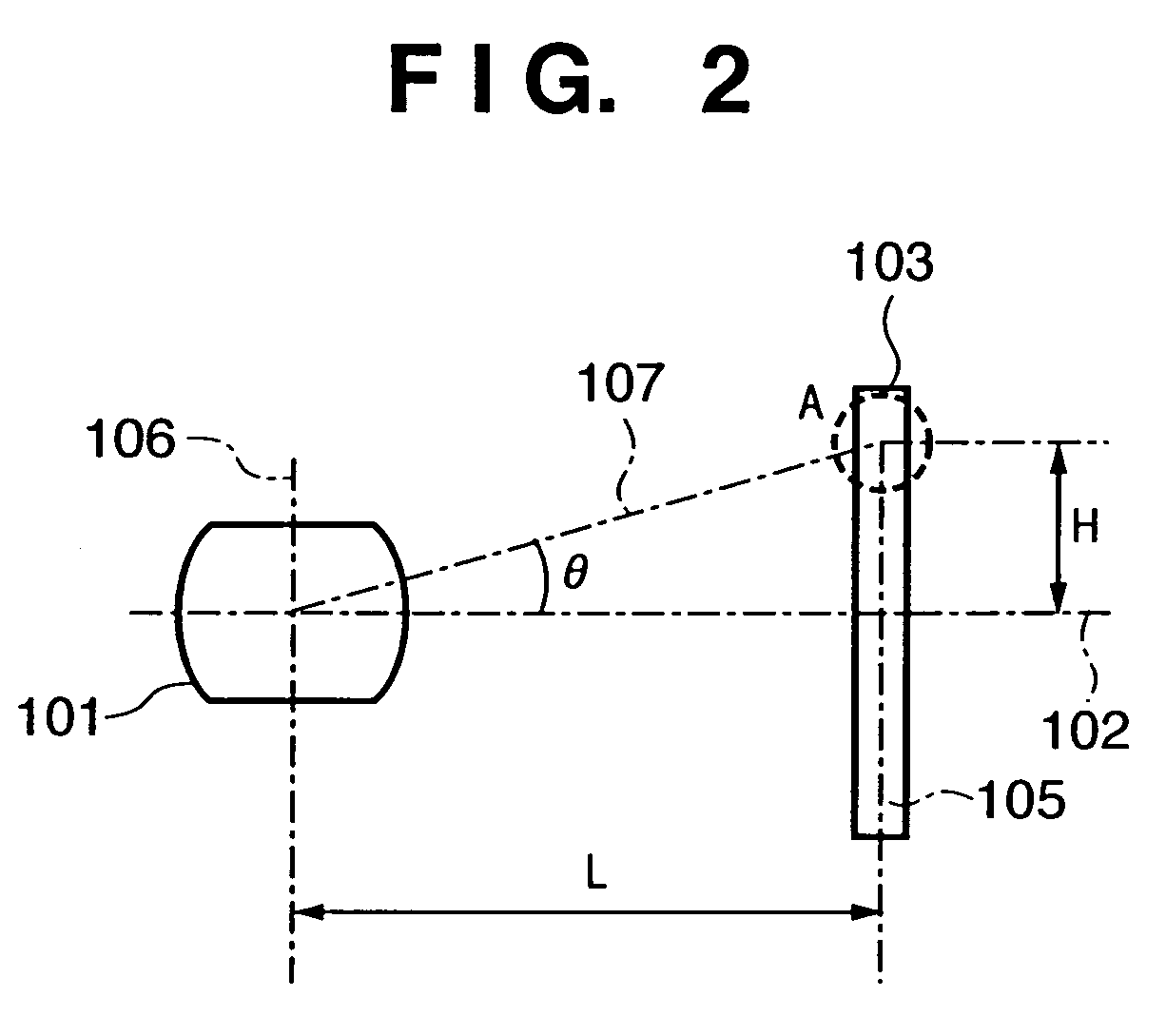
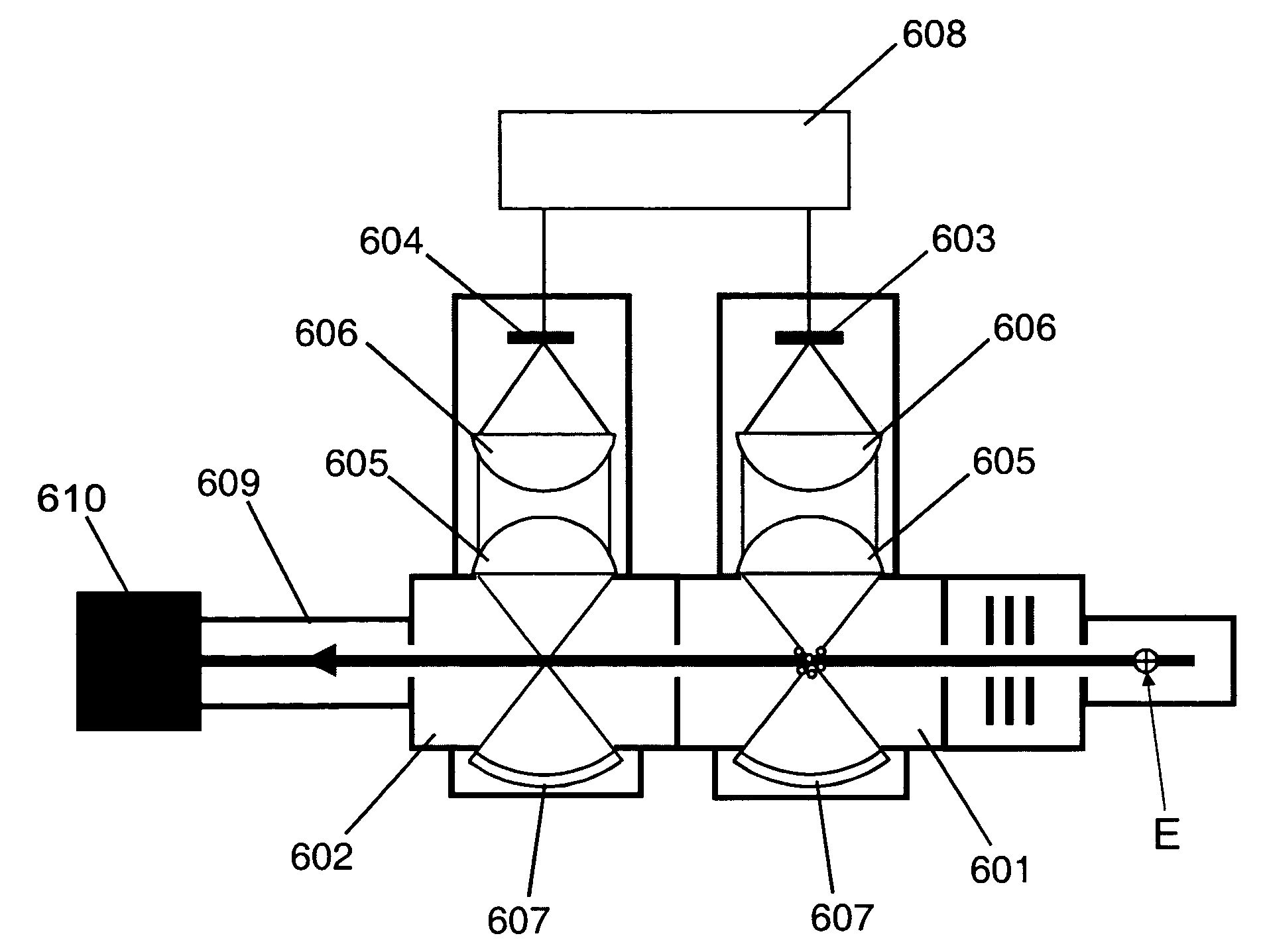
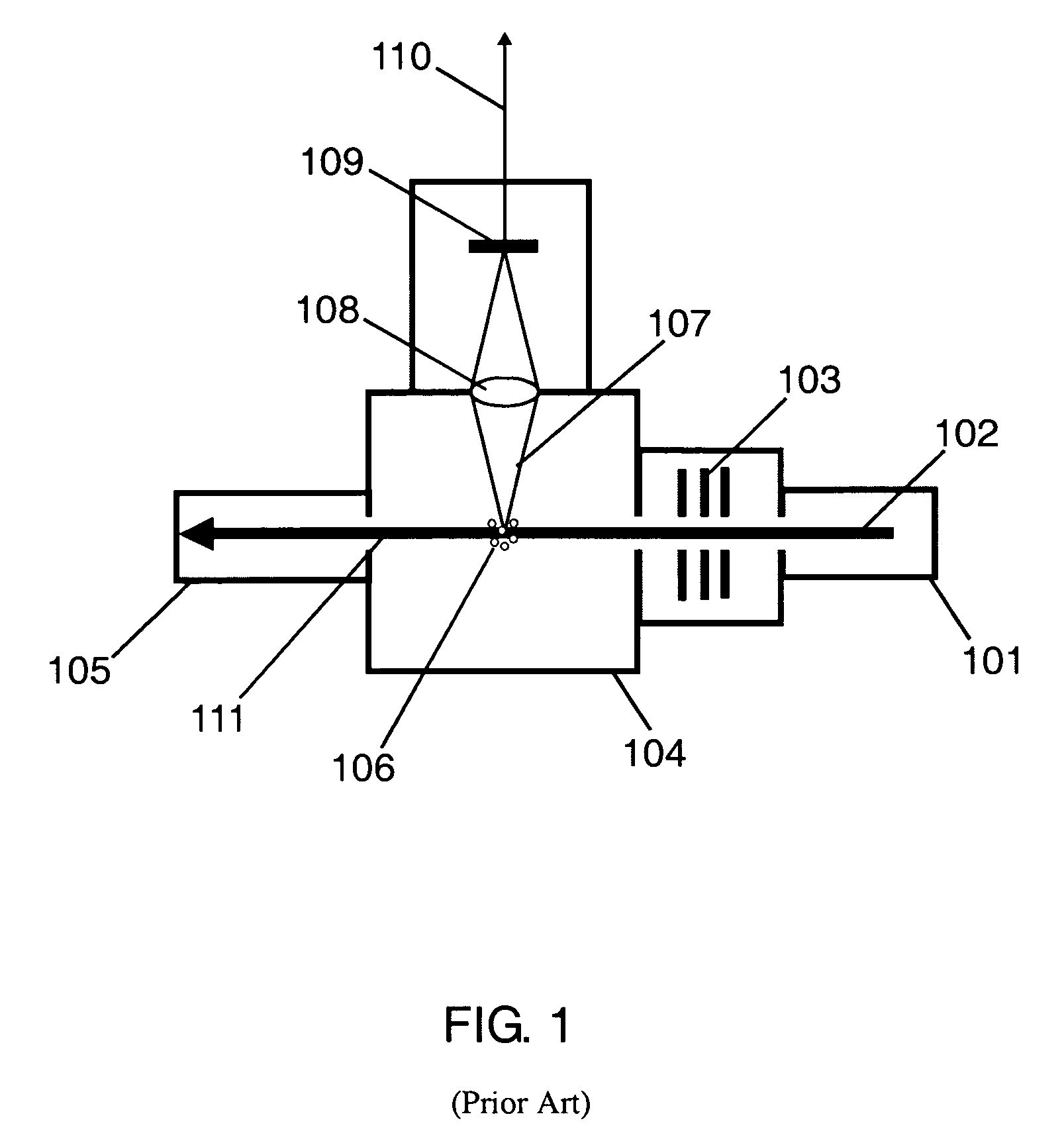
Solid-state image sensing element and its design support method, and image sensing device
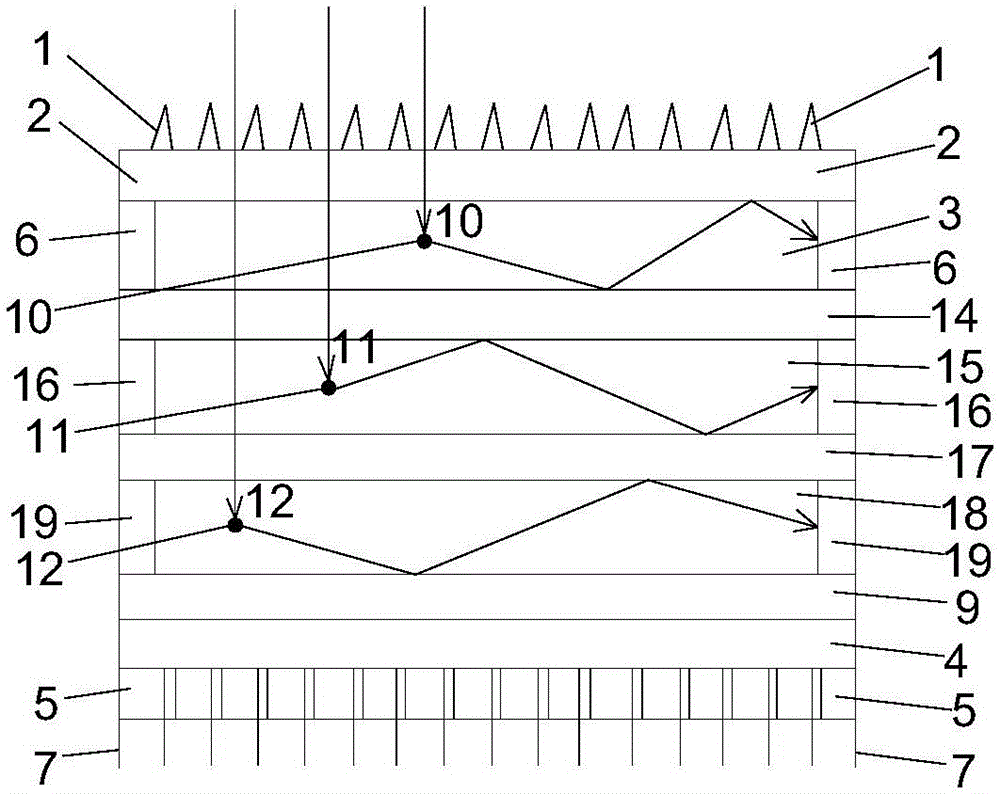
ActiveUS20050236553A1Increase freedomImprove light collection efficiencyTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesExit pupilLight guide
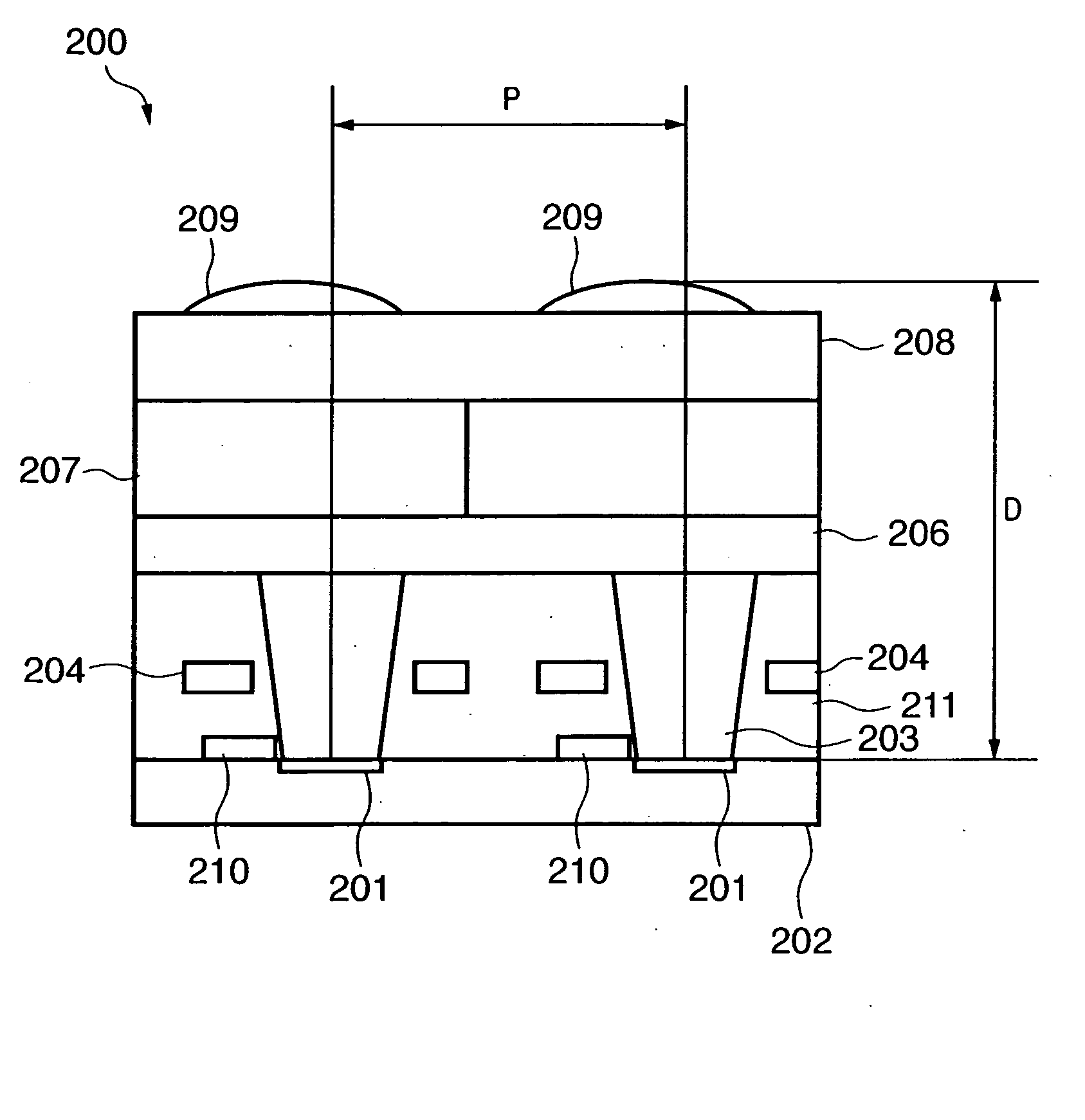
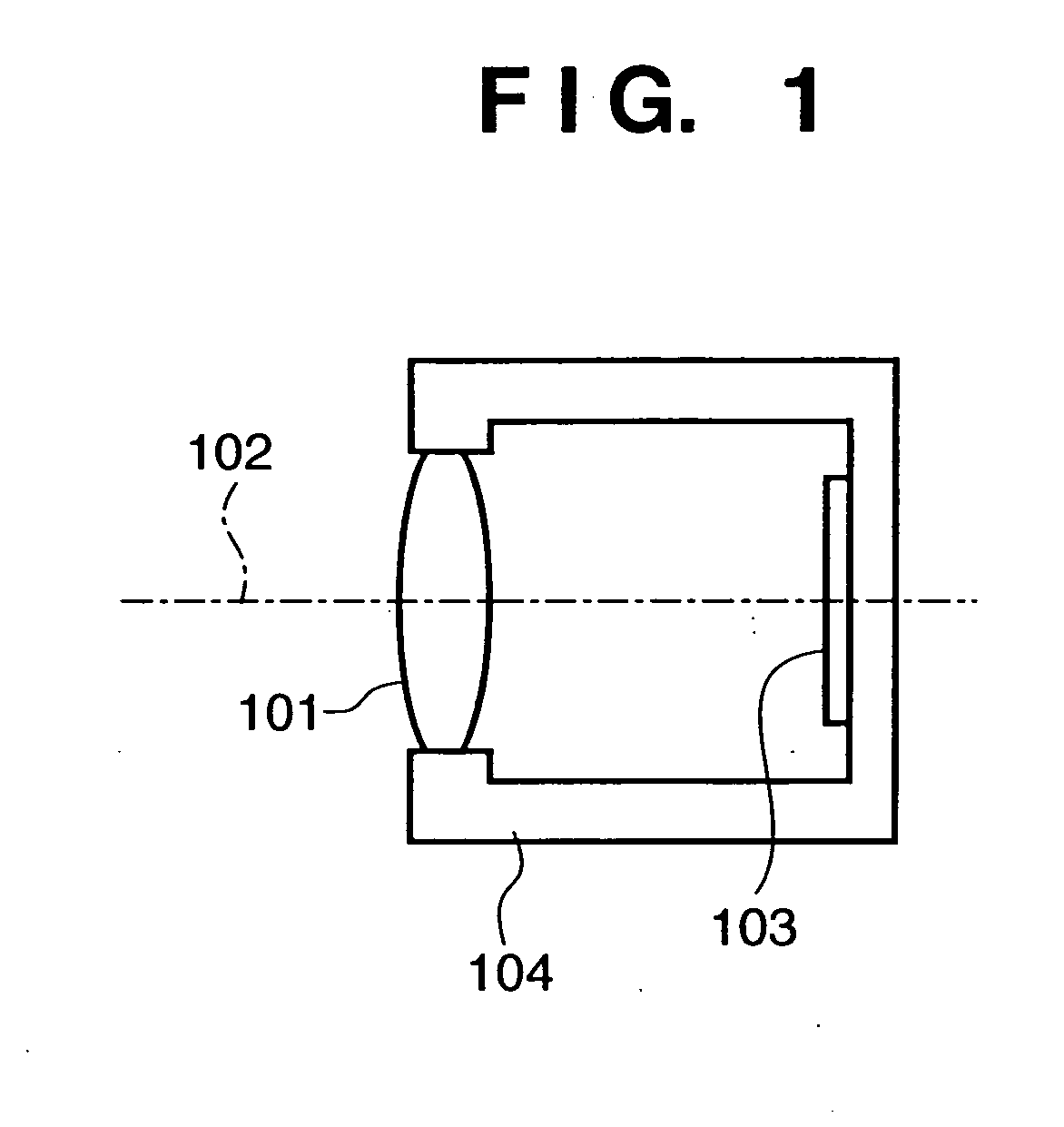
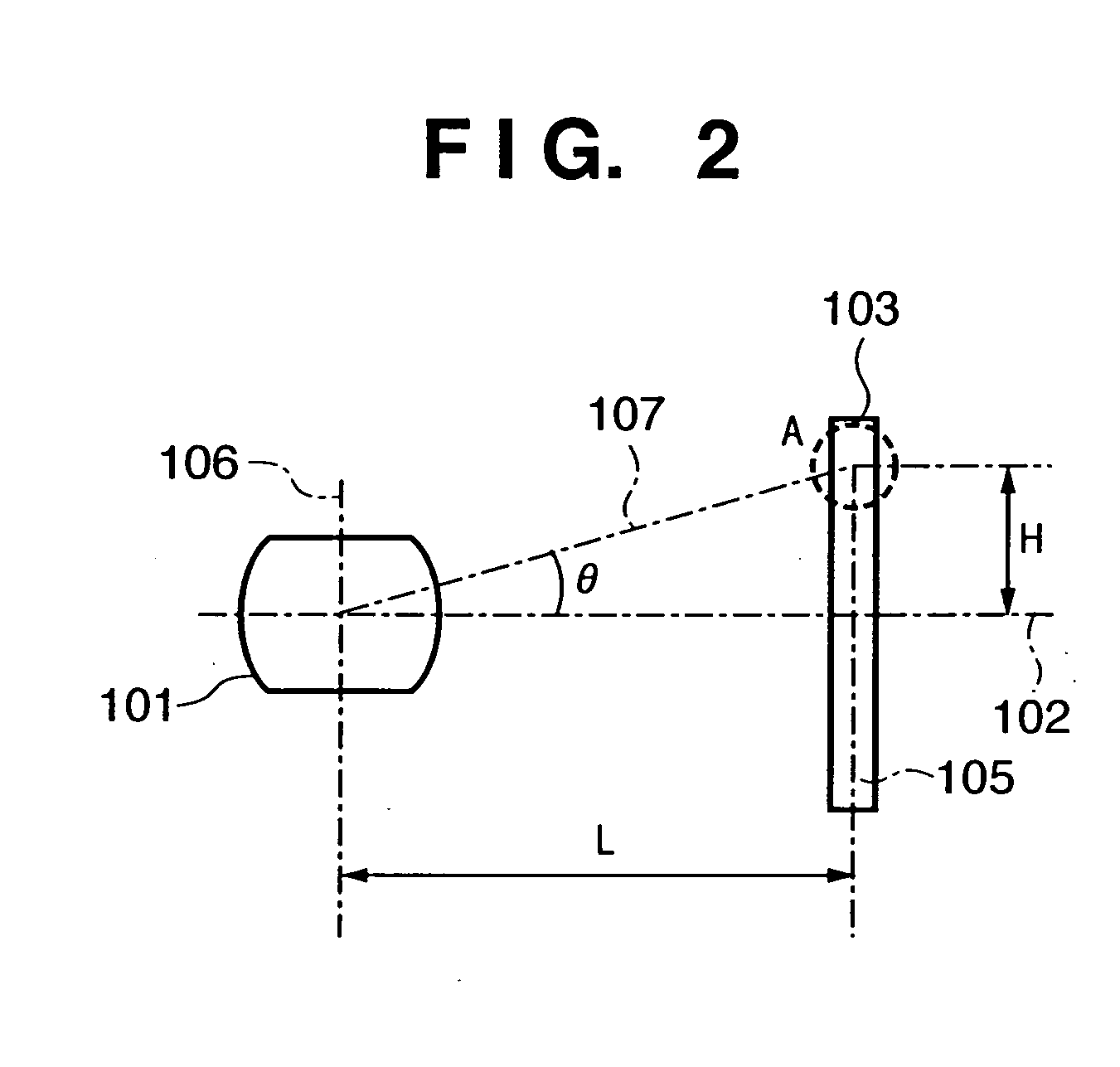
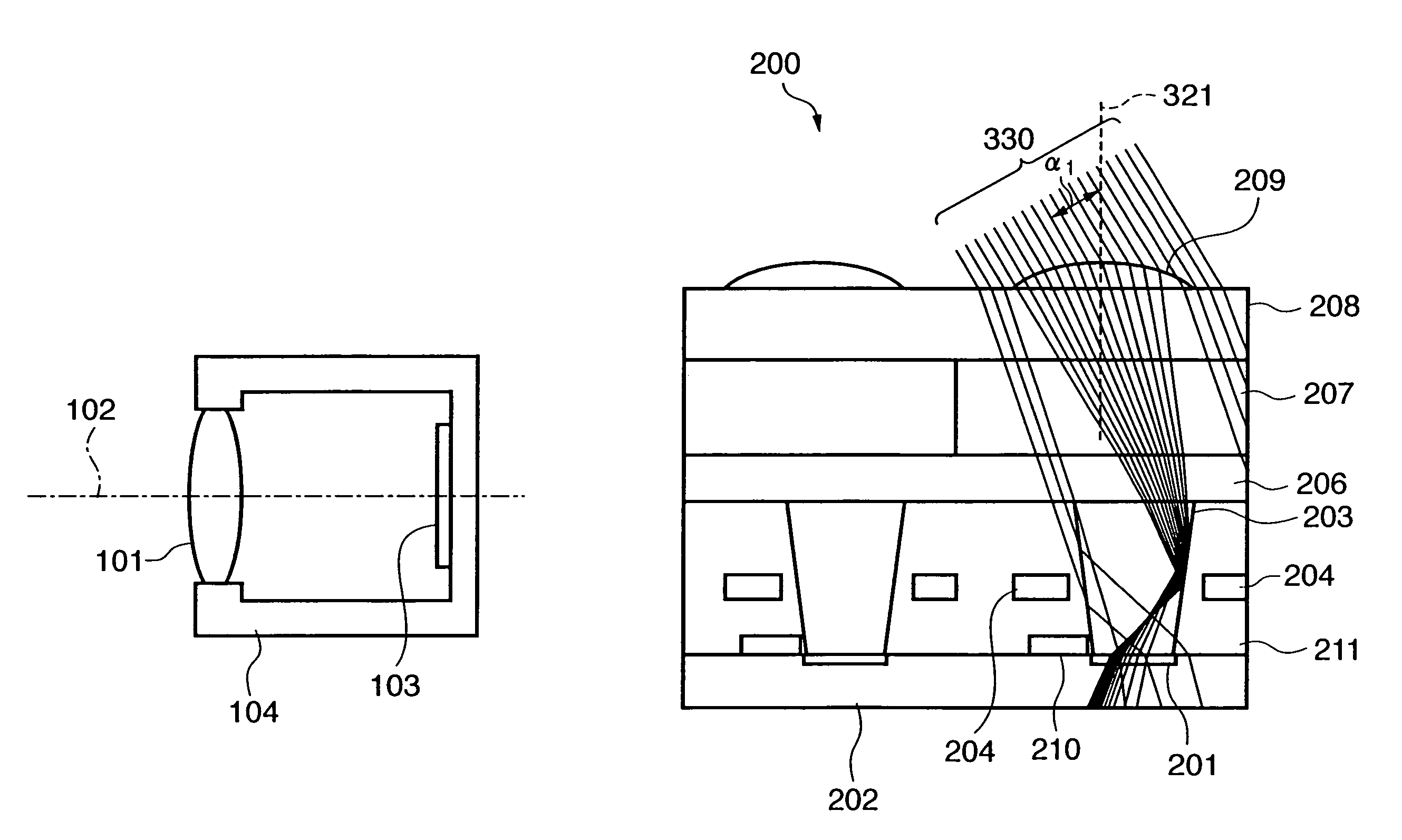
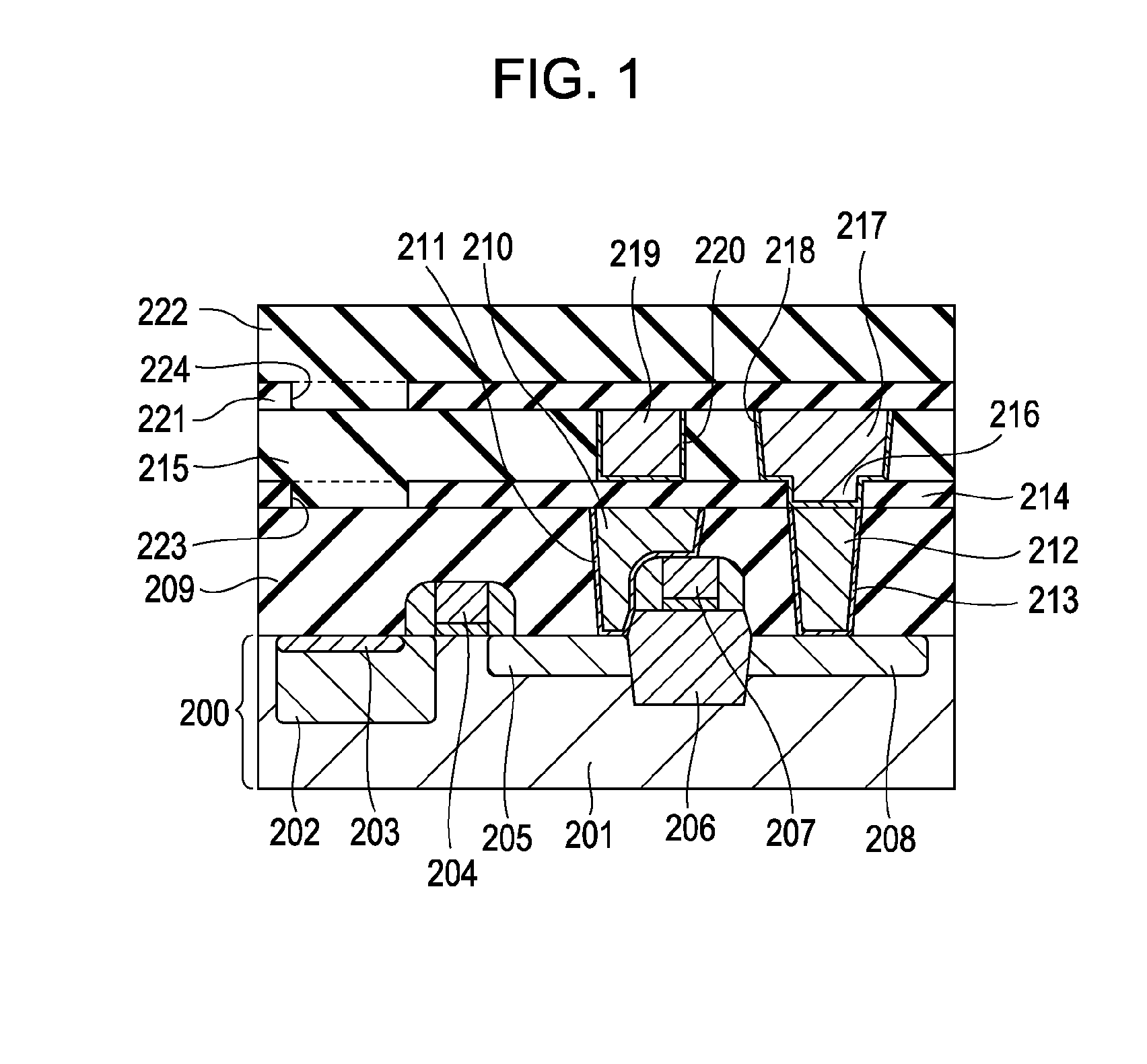
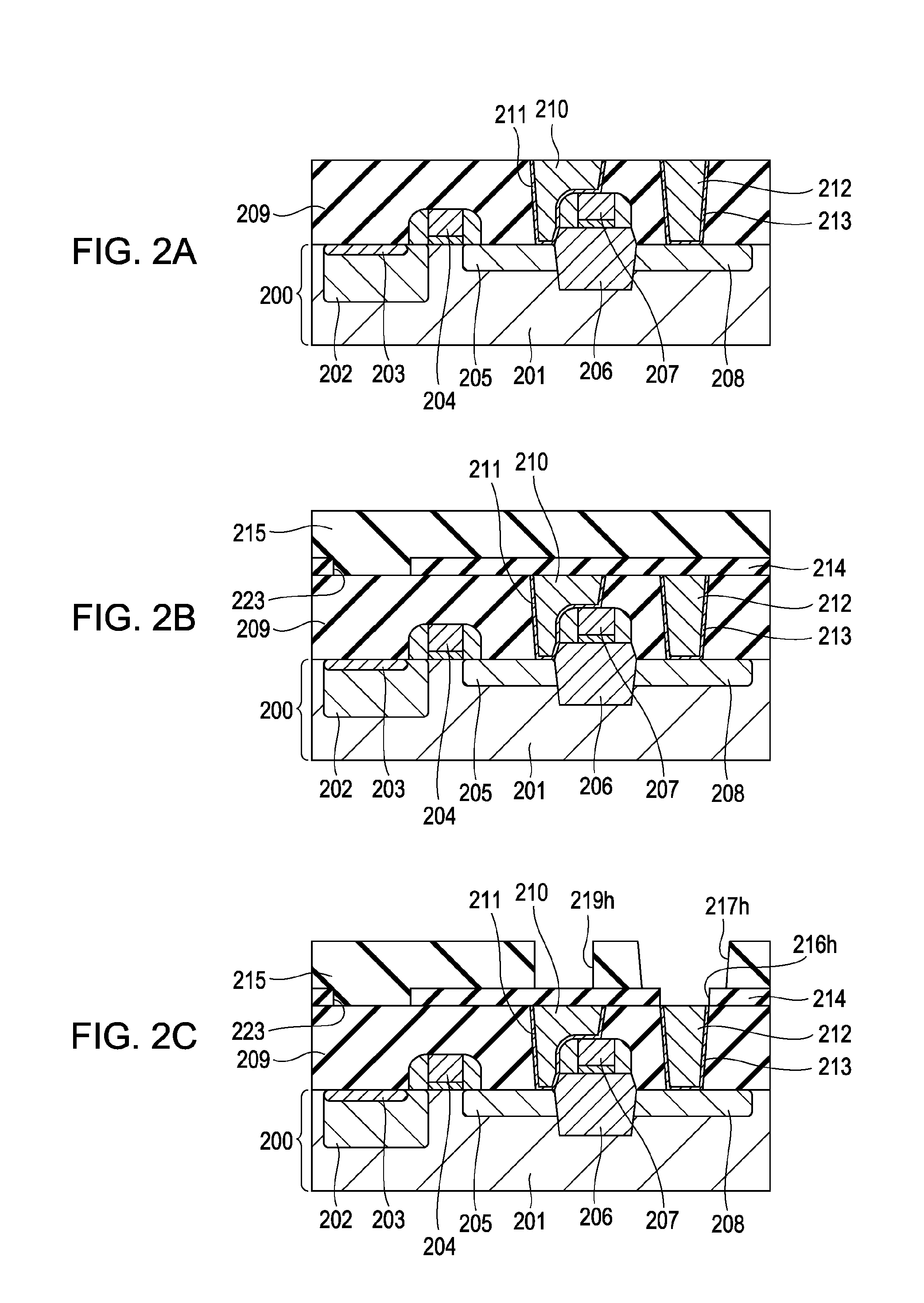
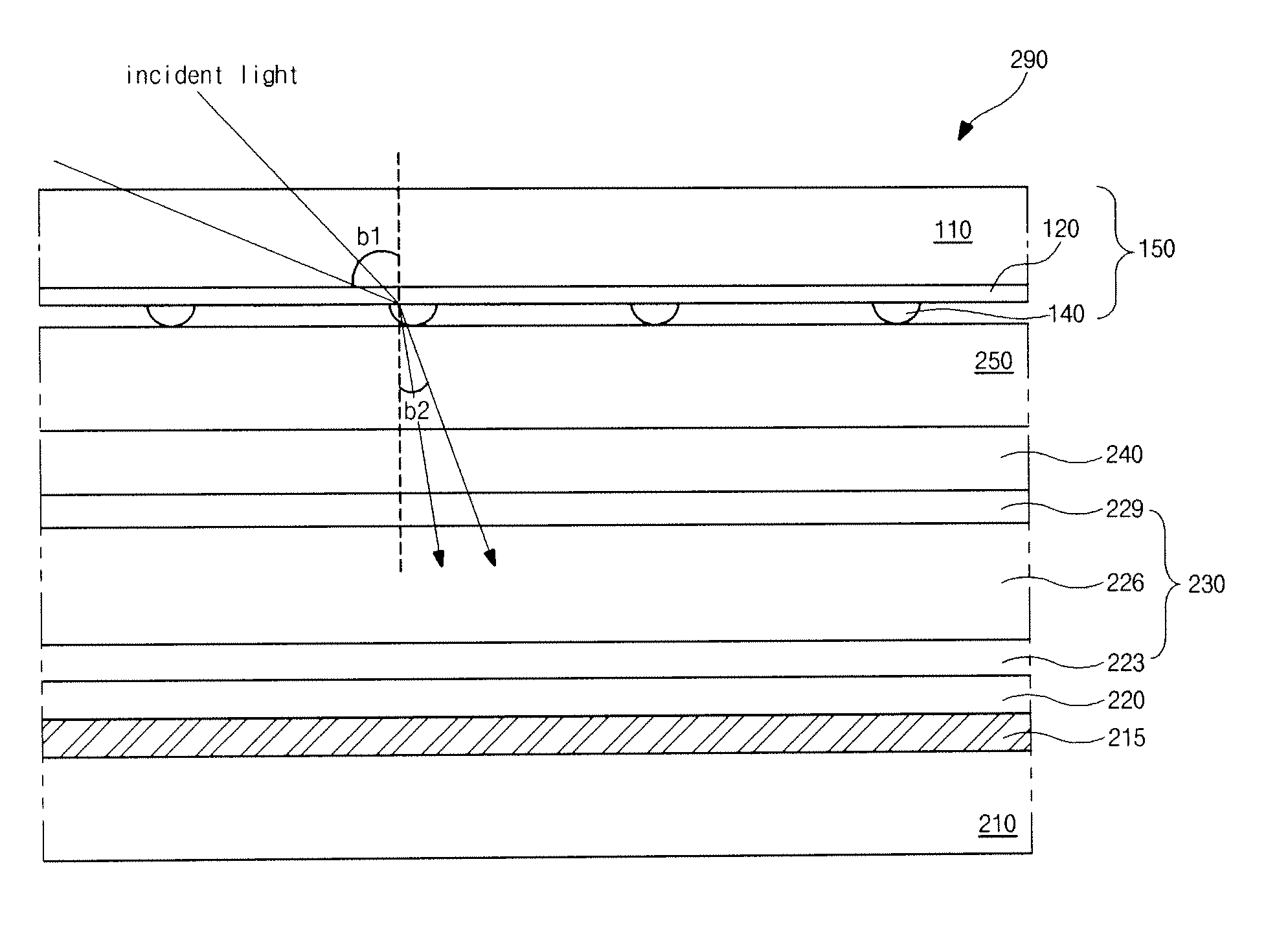
A solid-state image sensing element has a photoelectric conversion element which converts incoming light into an electrical signal in accordance with an amount of the light, a microlens which is arranged on an incident surface, a light guide which is arranged between the photoelectric conversion element and the microlens, and an insulating interlayer which is arranged around the light guide. The solid-state image sensing element located at a distance (H) satisfies: H·DL·P<a·NHNL for 0<a<1where L is the distance from an exit pupil of an image sensing optical system of an image sensing device, which mounts an image sensor formed by two-dimensionally arranging a plurality of the solid-state image sensing elements, H is the distance from a center of the image sensor to a position of the solid-state image sensing element on the image sensor, D is the height from the photoelectric conversion element to an apex of the microlens, P is the spacing between the plurality of solid-state image sensing elements, NH is the refractive index of the light guide, and NL is the refractive index of the insulating interlayer.
Owner:CANON KK
Solid-state image sensing element and its design support method, and image sensing device
ActiveUS7119319B2Increase freedomHigh light collecting efficiencyTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesExit pupilLight guide
A solid-state image sensing element has a photoelectric conversion element which converts incoming light into an electrical signal in accordance with an amount of the light, a microlens which is arranged on an incident surface, a light guide which is arranged between the photoelectric conversion element and the microlens, and an insulating interlayer which is arranged around the light guide. The solid-state image sensing element located at a distance (H) satisfies:H·DL·P<a·NHNLfor0<a<1where L is the distance from an exit pupil of an image sensing optical system of an image sensing device, which mounts an image sensor formed by two-dimensionally arranging a plurality of the solid-state image sensing elements, H is the distance from a center of the image sensor to a position of the solid-state image sensing element on the image sensor, D is the height from the photoelectric conversion element to an apex of the microlens, P is the spacing between the plurality of solid-state image sensing elements, NH is the refractive index of the light guide, and NL is the refractive index of the insulating interlayer.
Owner:CANON KK
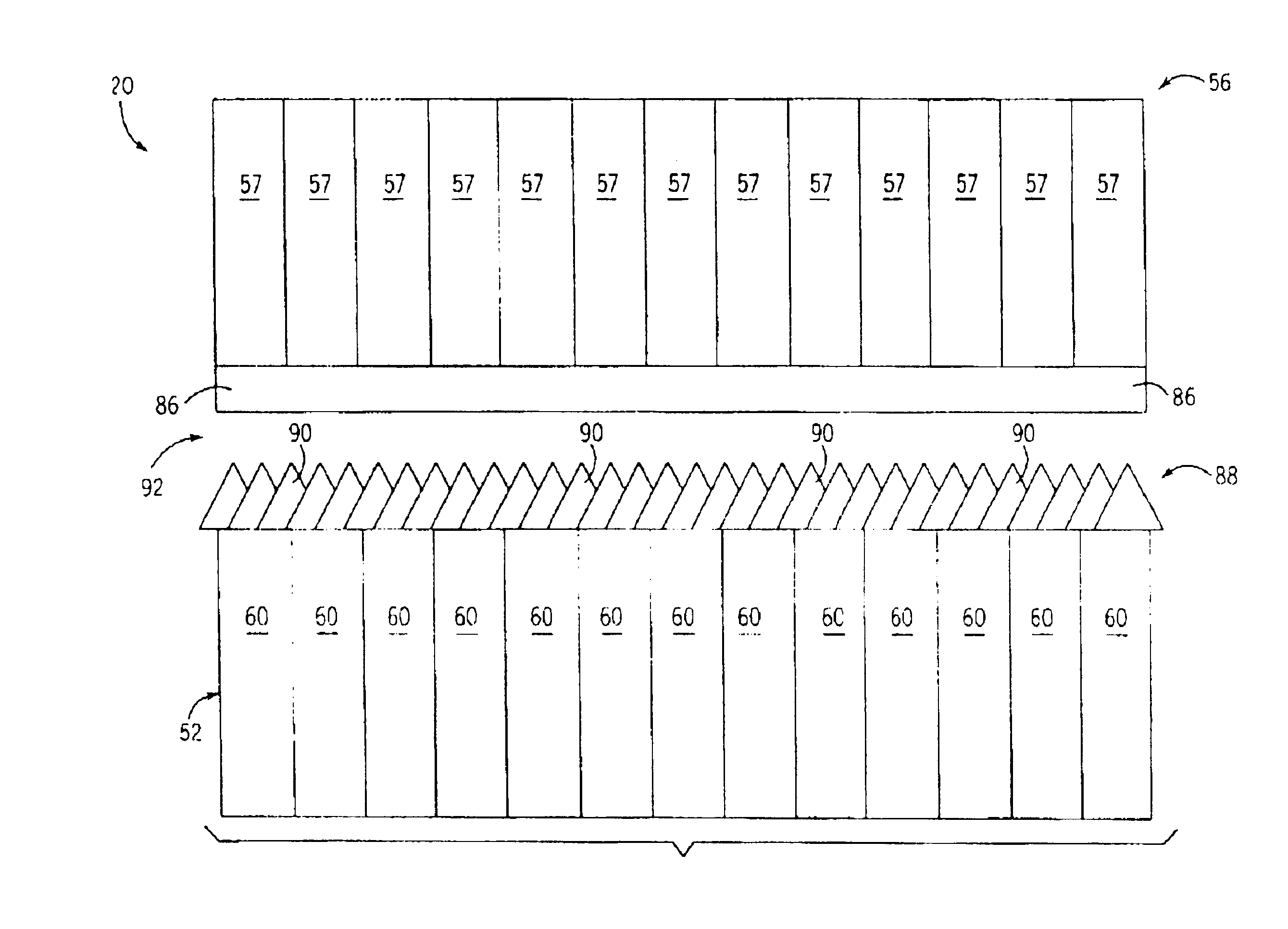
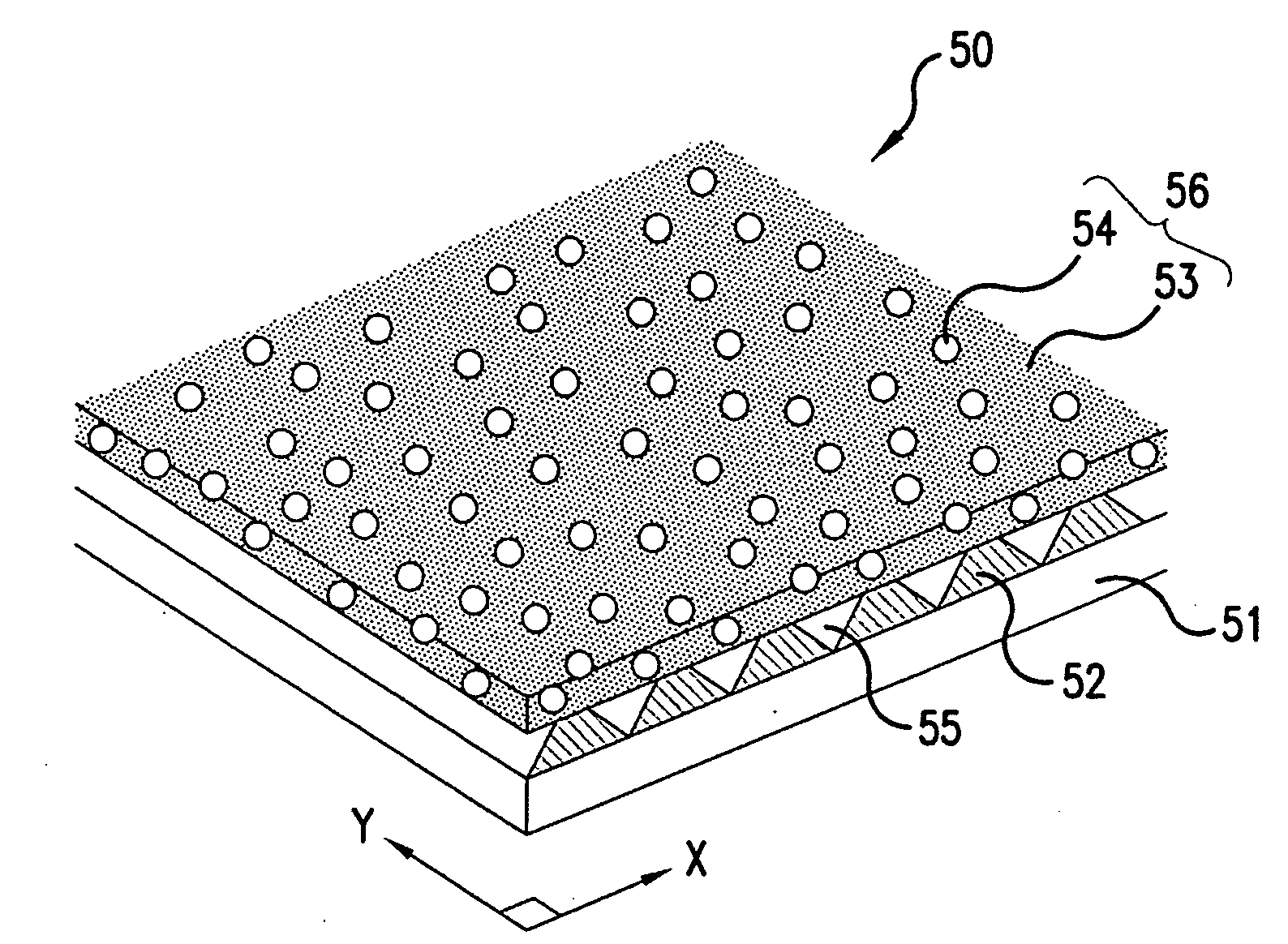
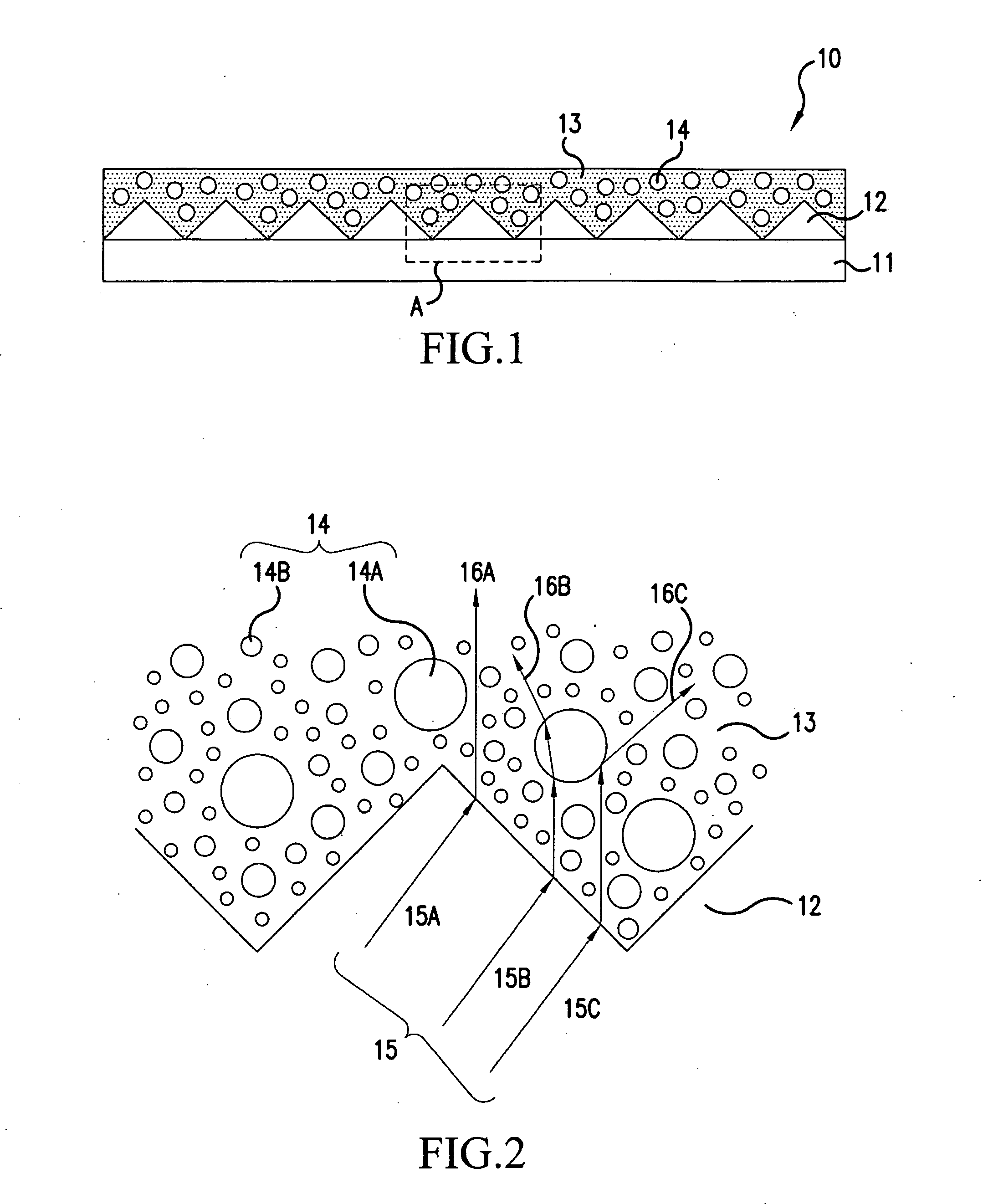
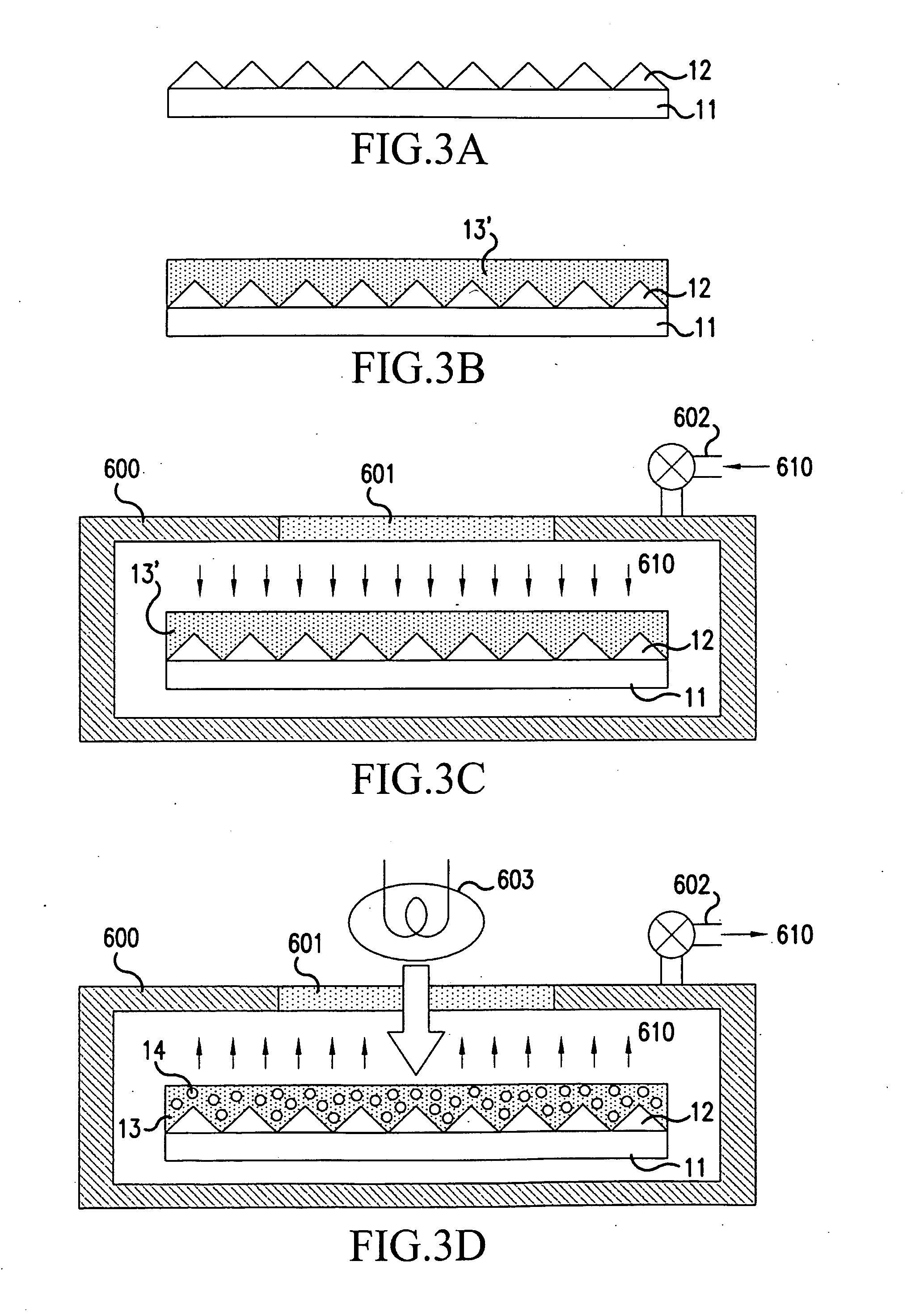
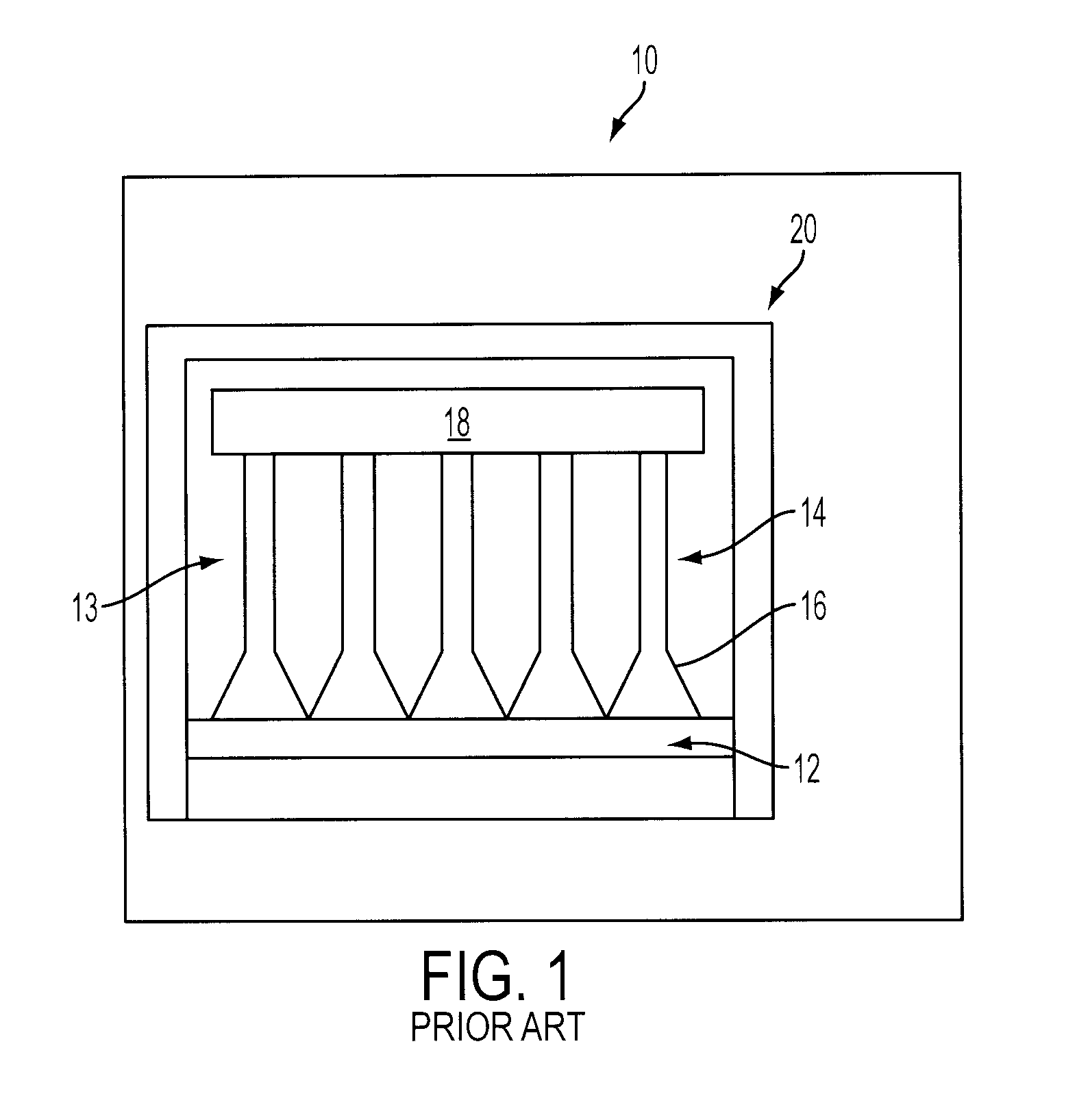
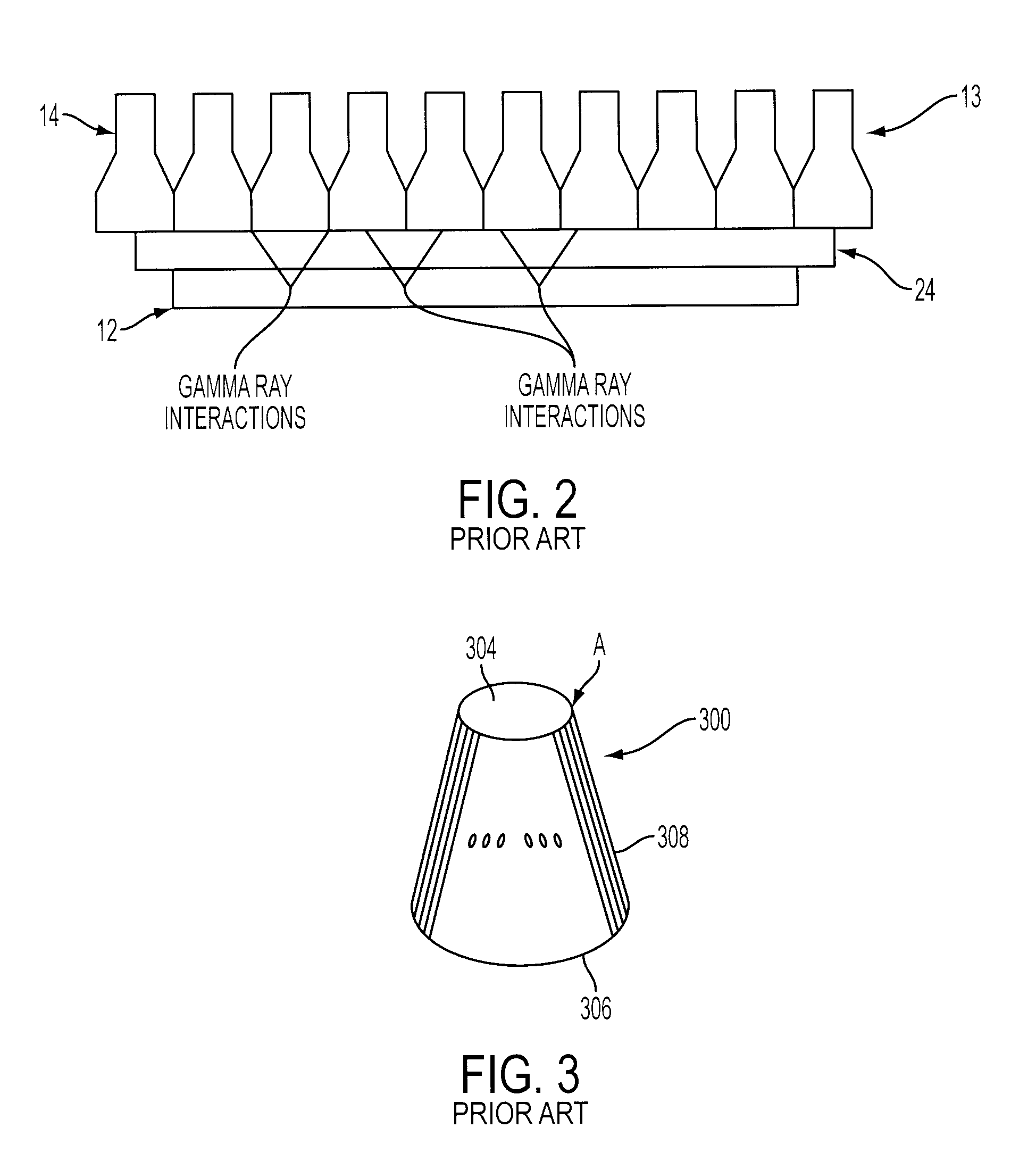
CT detector with integrated air gap
InactiveUS6907101B2Enhanced light absorptionImprove light collectionTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesScintillatorPhotodiode
The present invention is directed to an improved CT detector scintillator to photodiode optical coupling. The CT detector utilizes a controlled air gap between the photodiode array and the scintillator array together with an anti-reflective layer on the scintillator array. To improve the absorption of light at the photodiode array, the photodiode array includes a textured light reception surface. By incorporating a textured layer with the photodiode array, the light collection efficiency of the photodiodes is improved. The textured layer may extend along an x- and / or z-axis and the texturing may be in different forms. For example, the textured layer may include a series of pyramidally-shaped protrusions.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
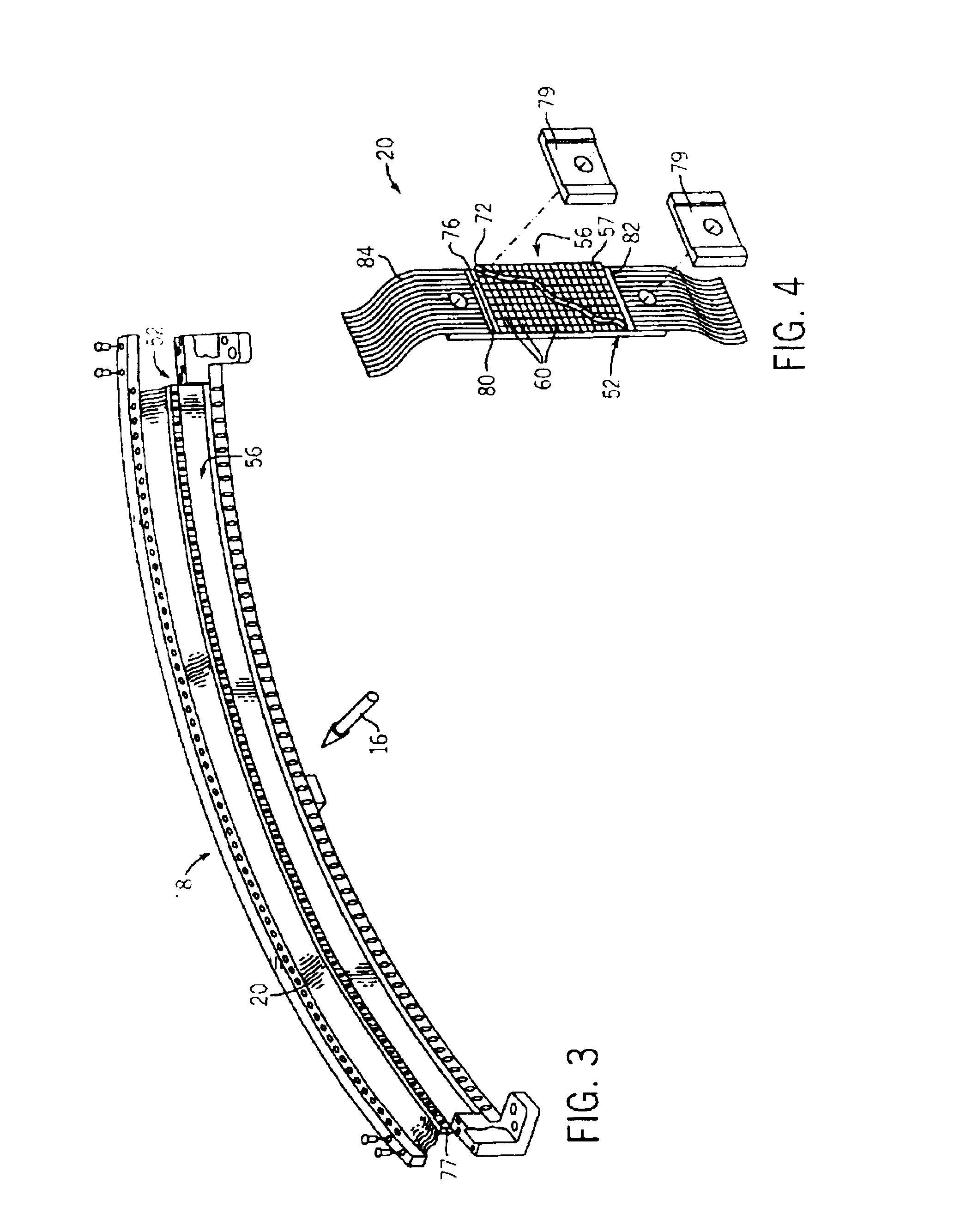
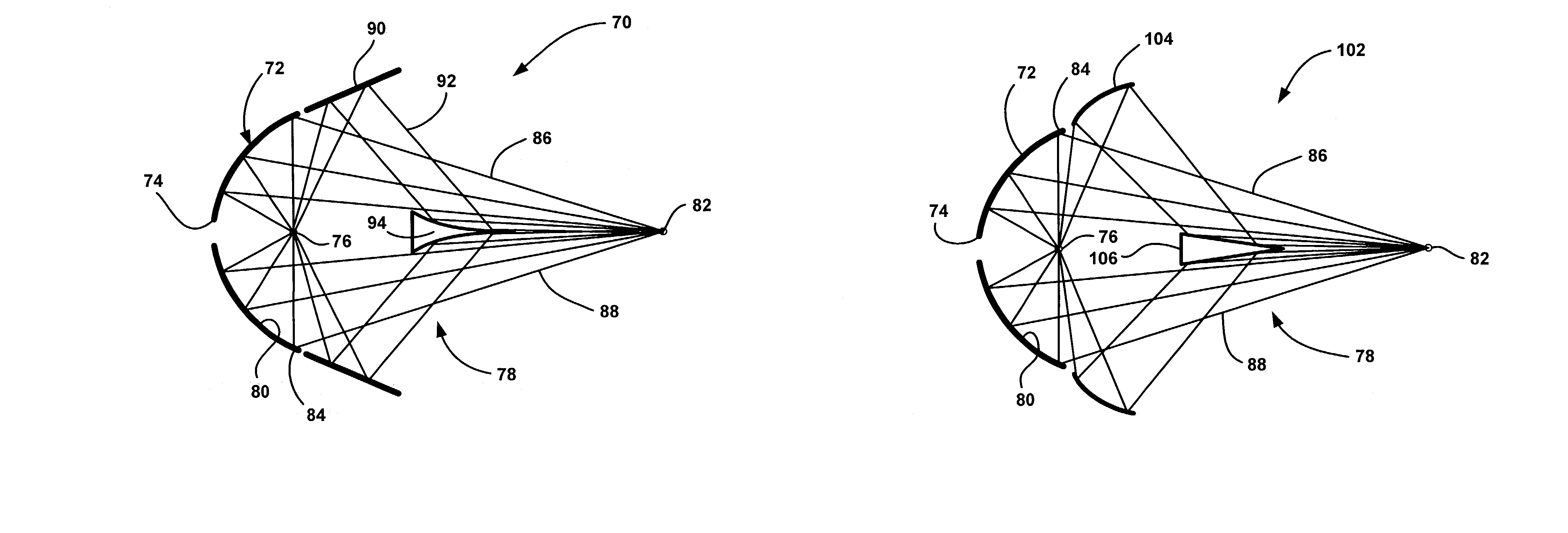
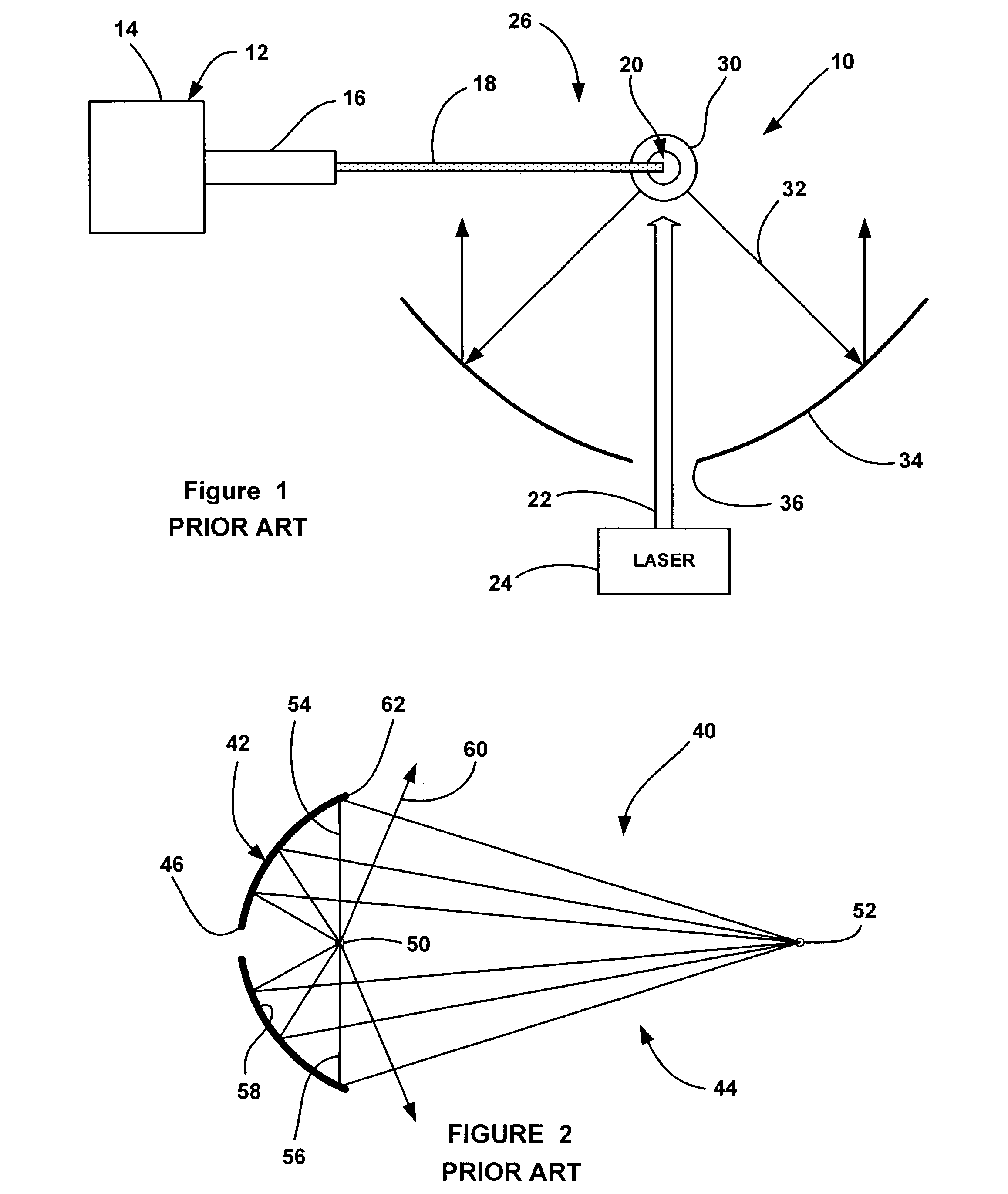
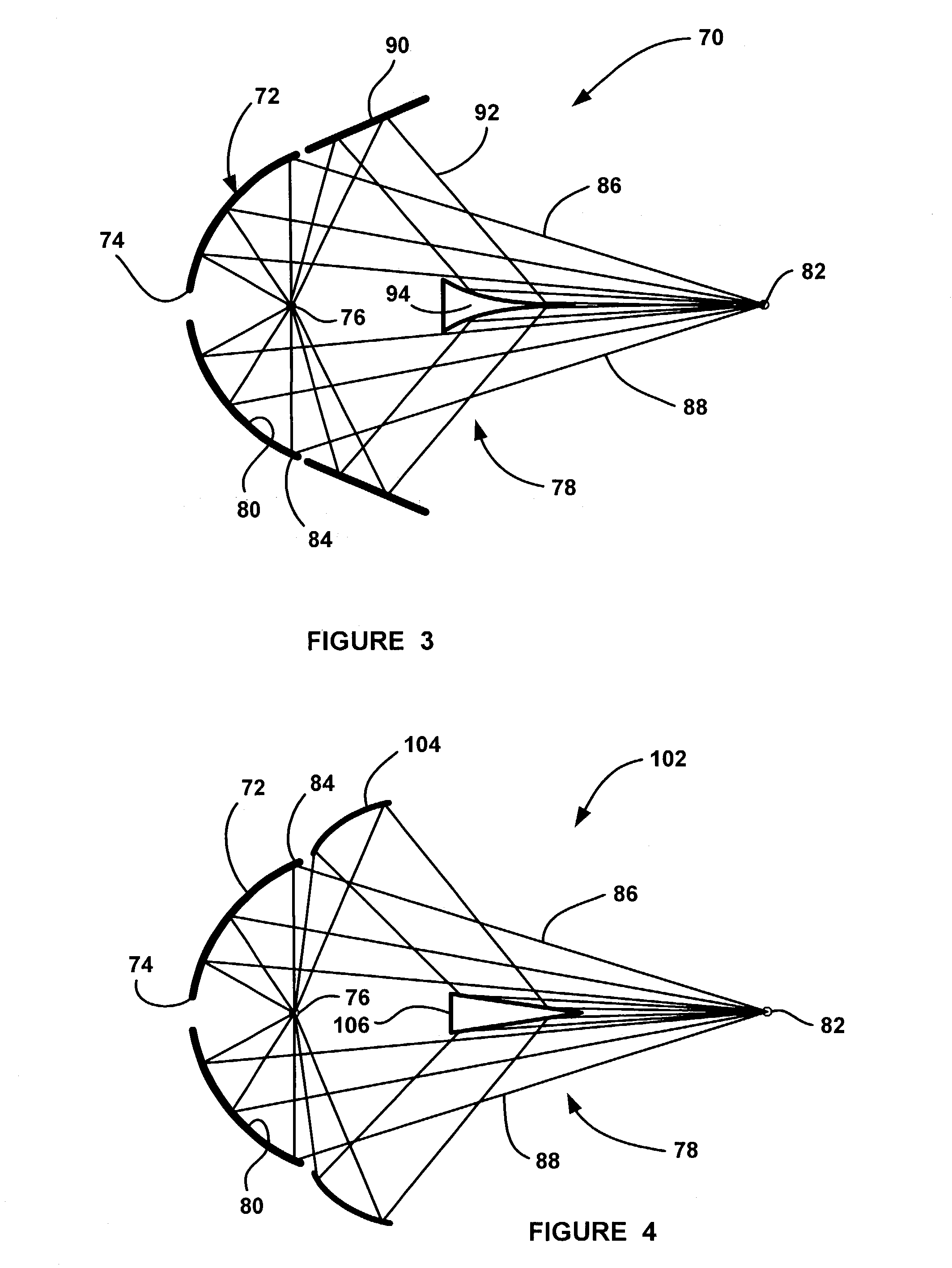
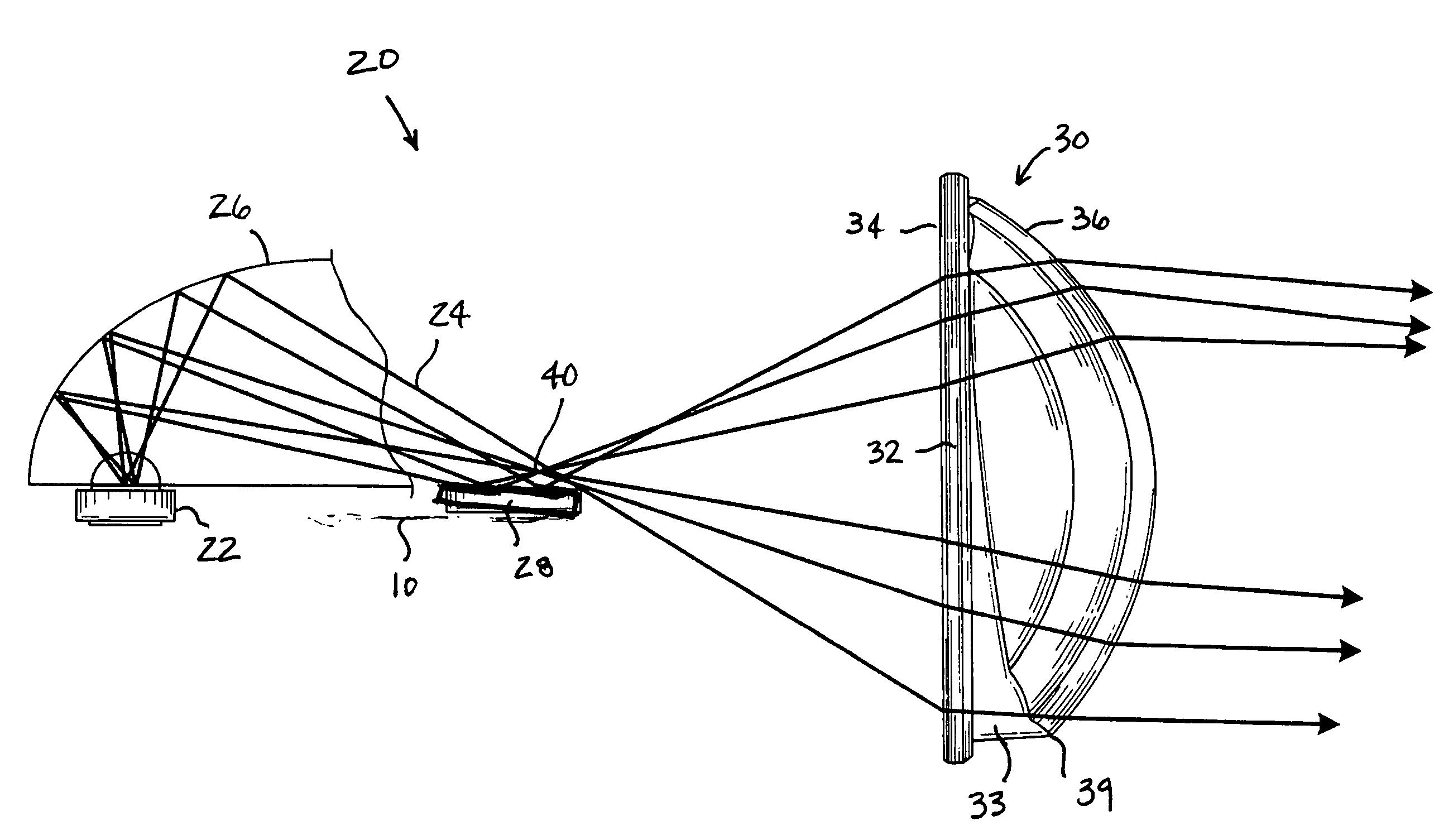
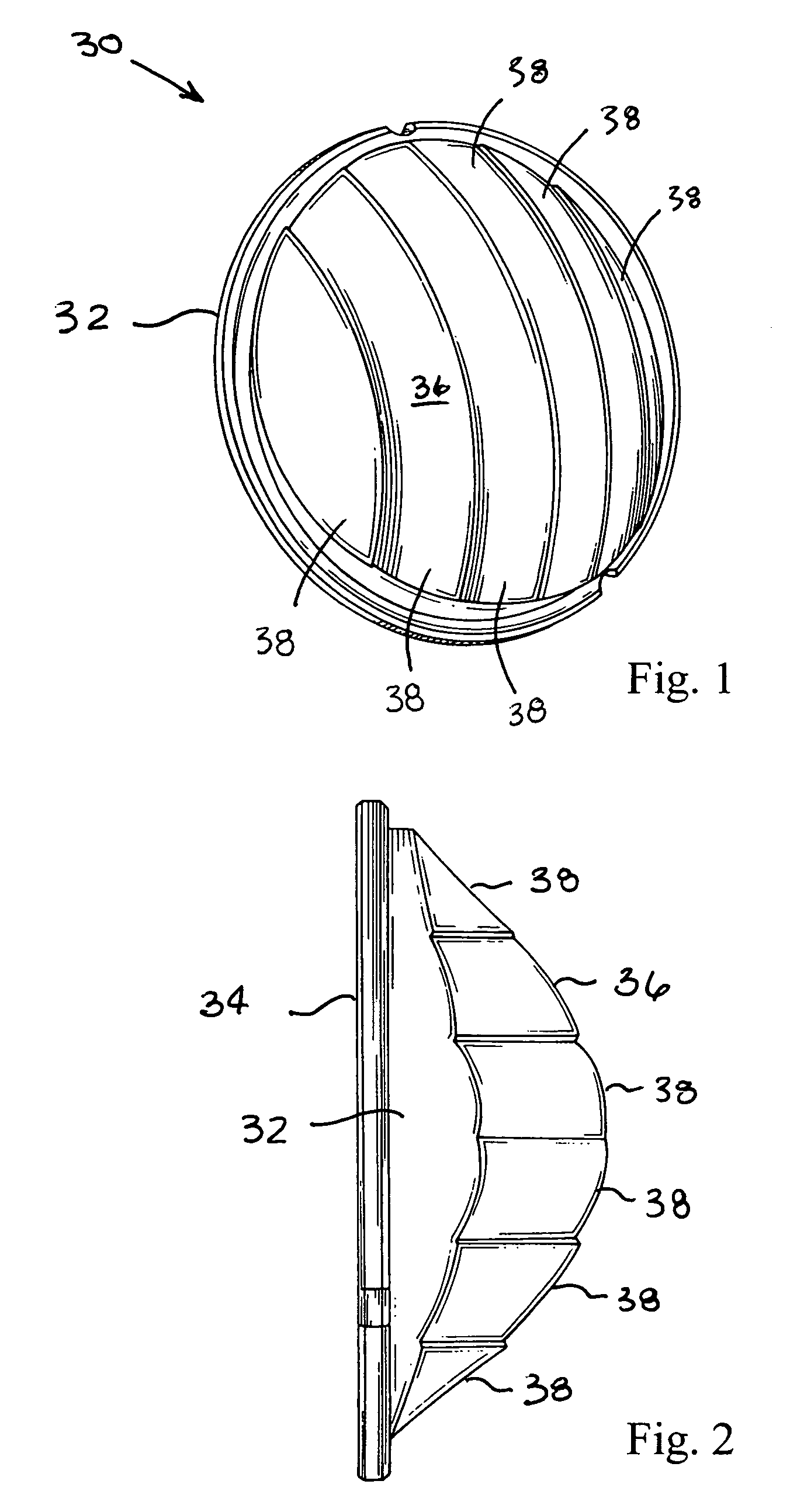
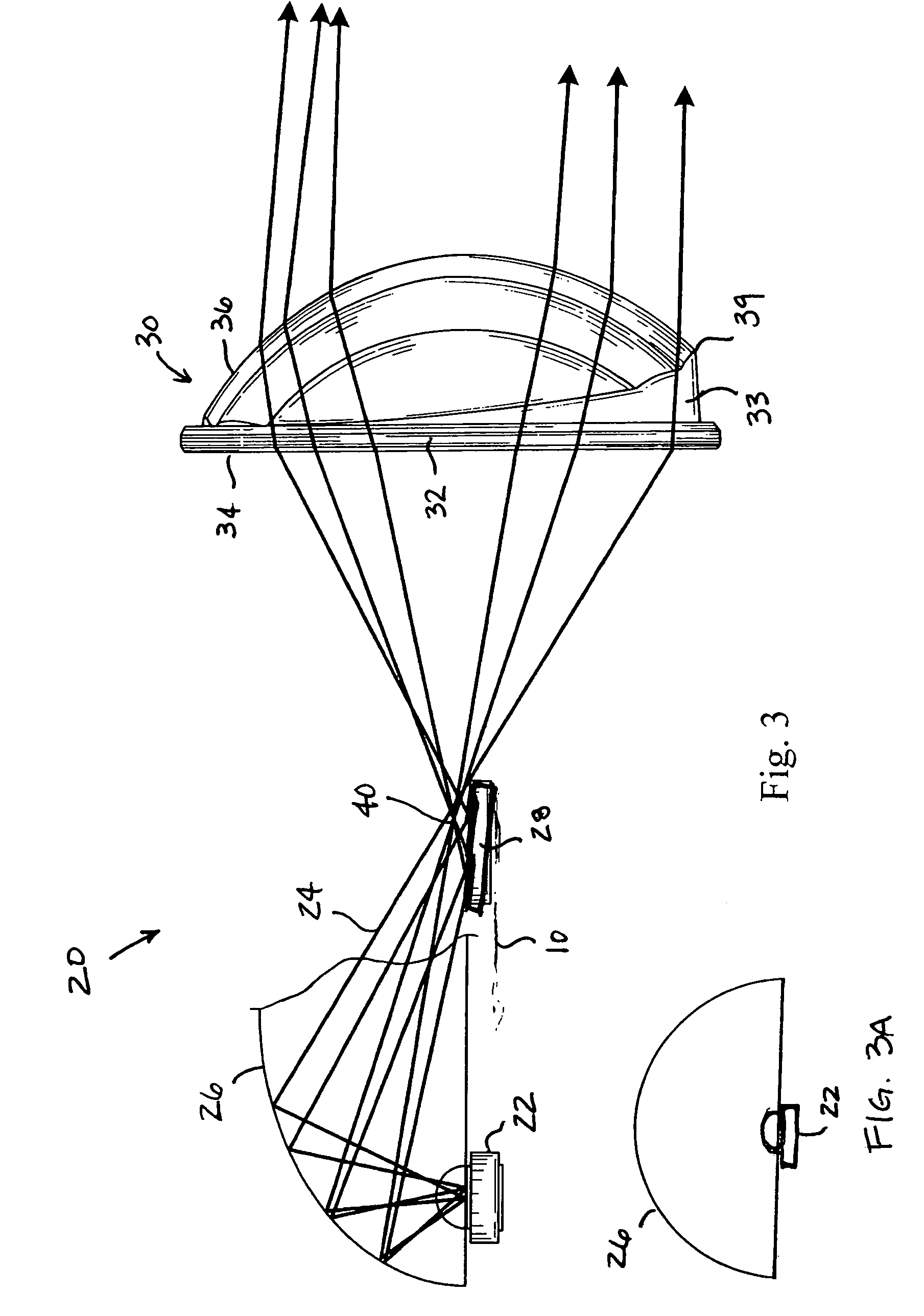
High efficiency collector for laser plasma EUV source
Collector optics (70) for an EUV radiation source (10) for collecting EUV radiation (78). The collector optics (70) includes an elliptical dish reflector (72) where light generated at a focal point (76) of the reflector (72) is collected by the reflector (72) and is directed to a collection location (82). A frustal annular reflector (90) is positioned around an outer edge (84) of the dish reflector (72) to collect more of the EUV radiation (78) that may otherwise be lost. The radiation (78) reflected by the annular reflector (90) is directed to a center axicon reflector (94) positioned between the focal point (76) of the dish reflector (72) and the collection location (82) to redirect the radiation (78) reflected by the annular reflector (90) to be within a predetermined collection angle.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMAN CORP
Optical adjusting member, and illumination device and liquid crystal display device including the same
InactiveUS20080303777A1Suppressing damages at the top edgeConvenient lightingStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsOptical transparencyLiquid-crystal display
An optical adjusting member according to the invention includes a base member, a plurality of lenses, and a light diffusion layer. The base member has optical transparency. The plurality of lenses are formed on the base member. The light diffusion layer is formed on the plurality of lenses, and at least top edge parts of the lenses are buried in the light diffusion layer. In the optical adjusting member according to the invention, at least the top edge parts of the plurality of lenses are buried in the light diffusion layer and therefore the lenses are less susceptible to damages. The optical adjusting member according to the invention has a light collecting function by the lenses and a diffusion function by the light diffusion layer.
Owner:HITACHT MAXELL LTD
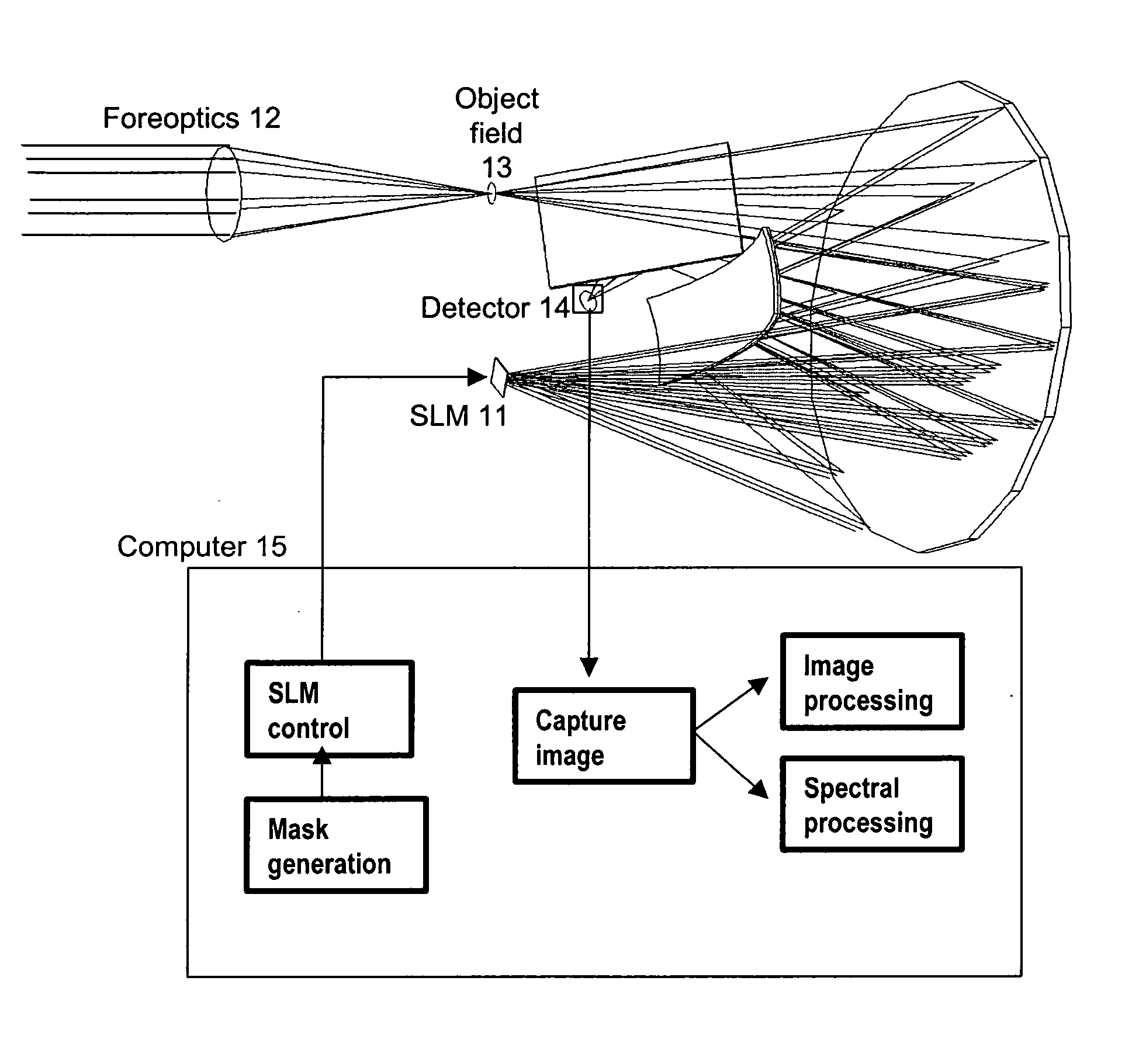
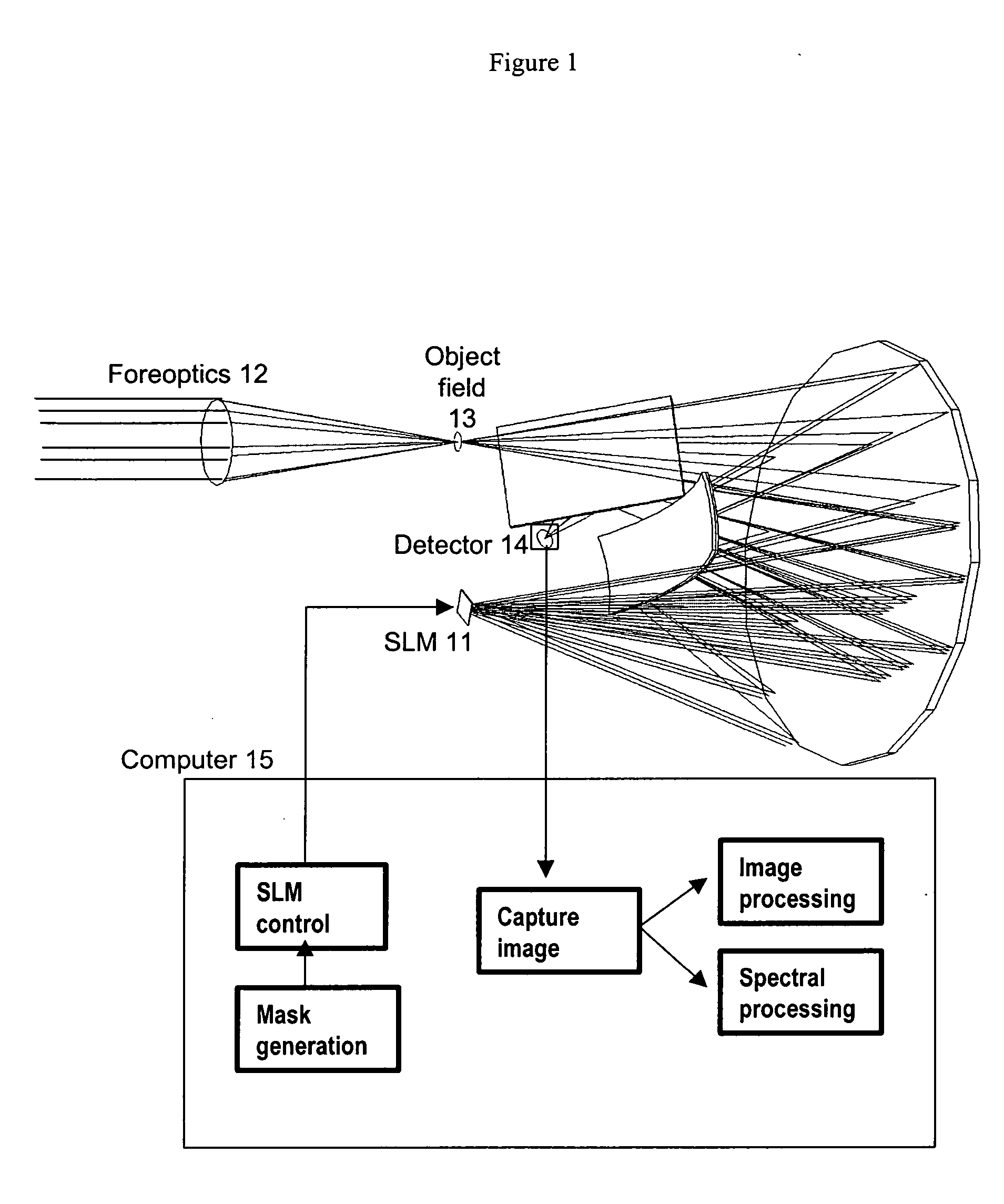
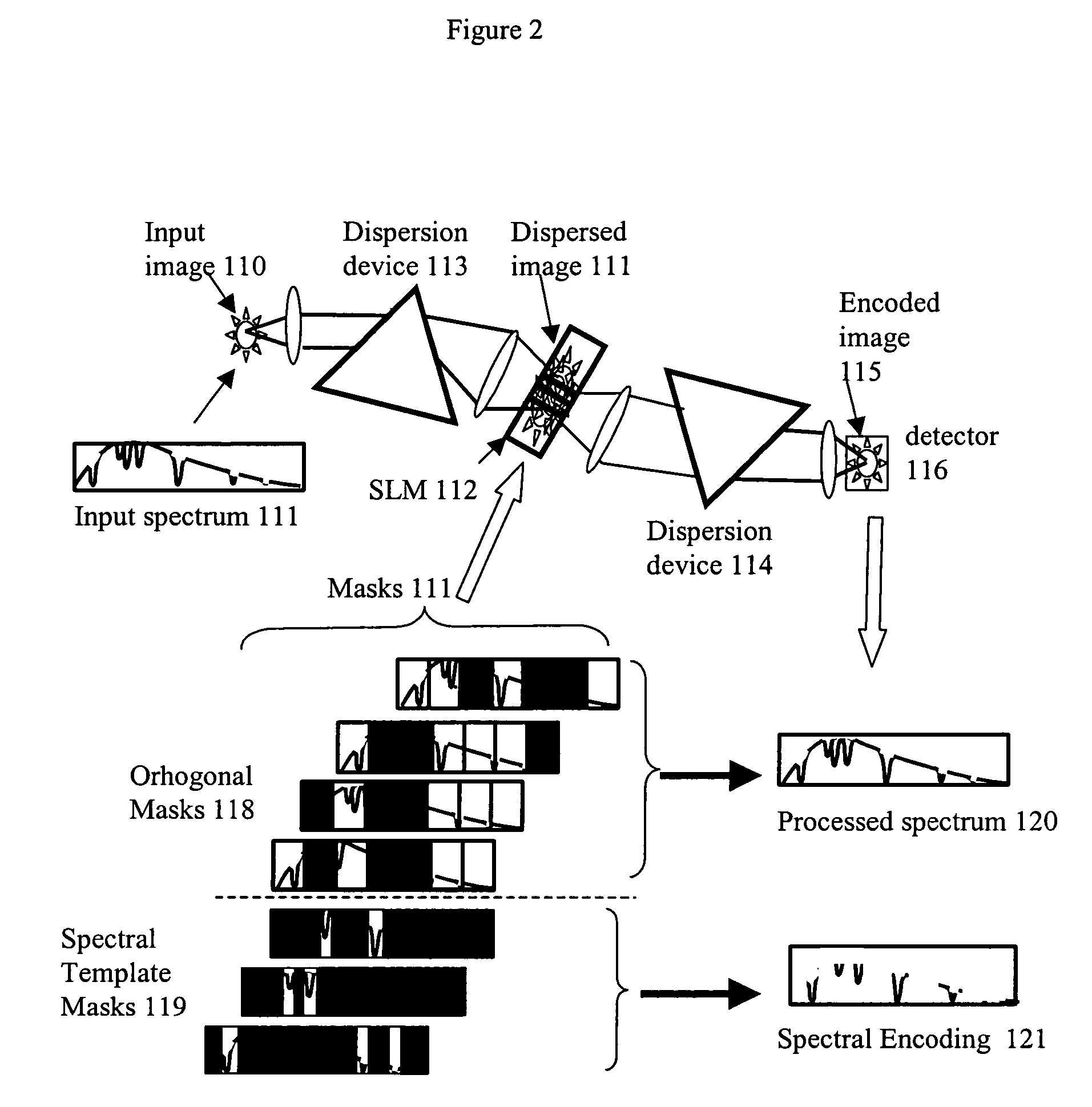
Spectral encoder
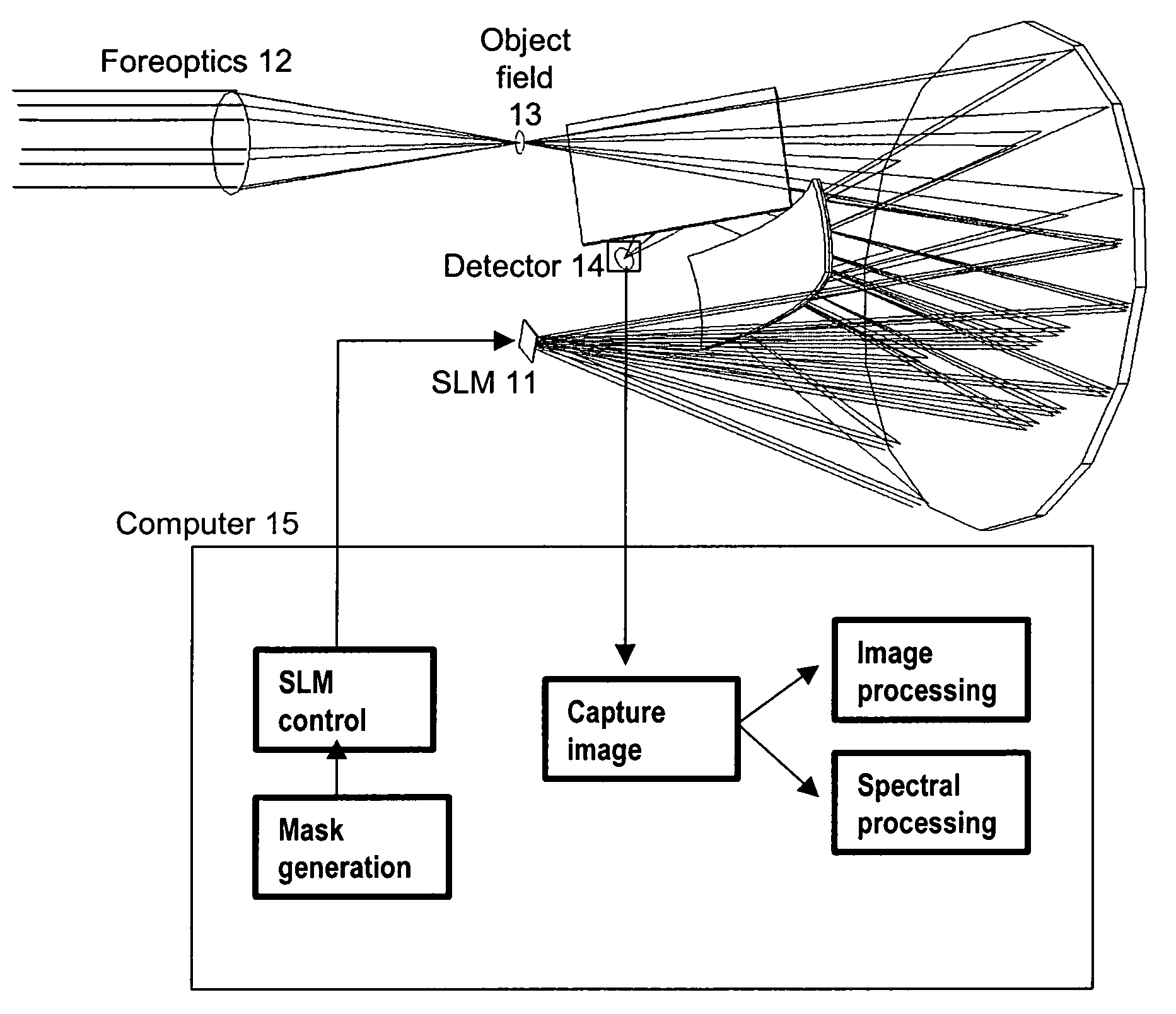
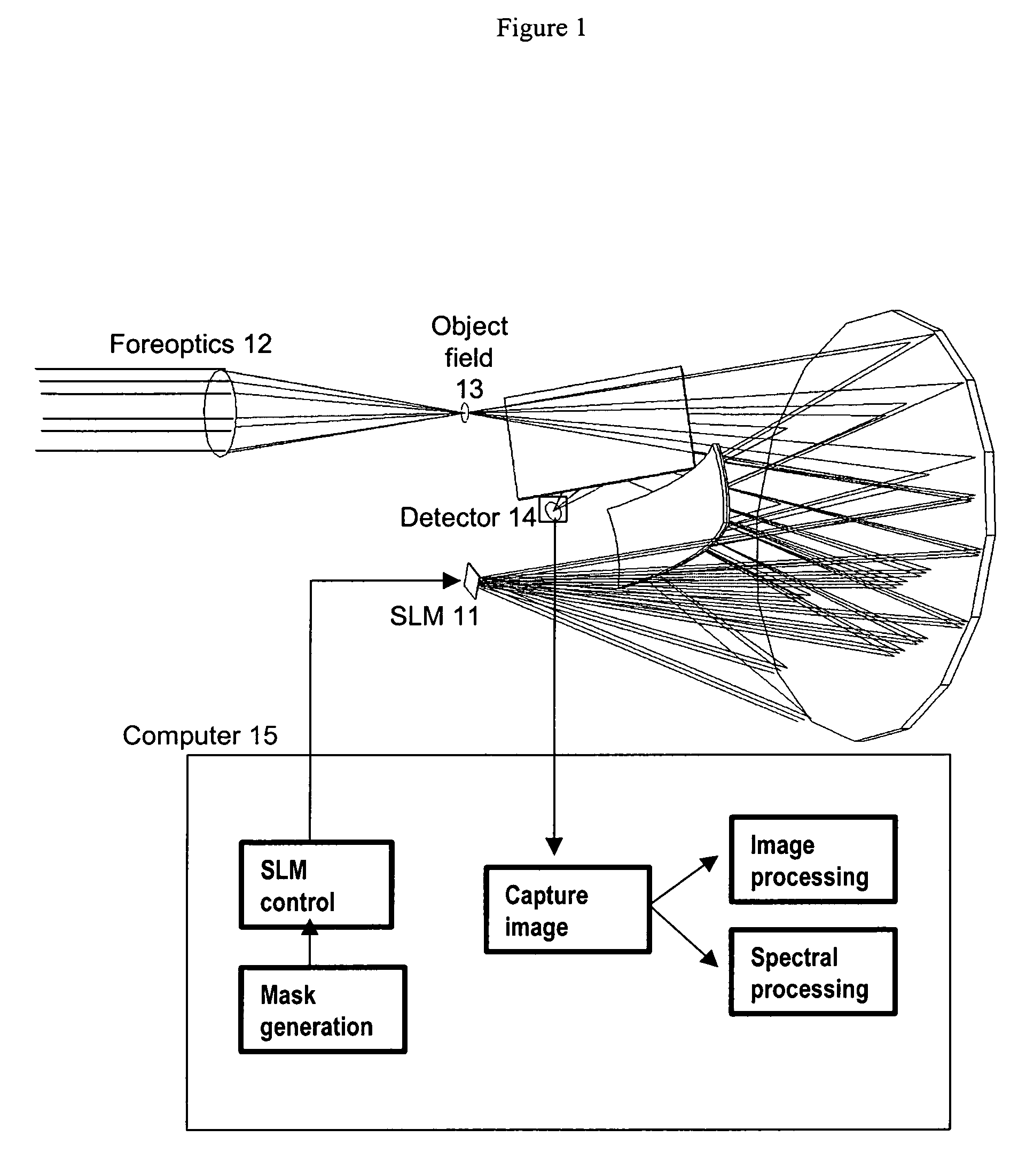
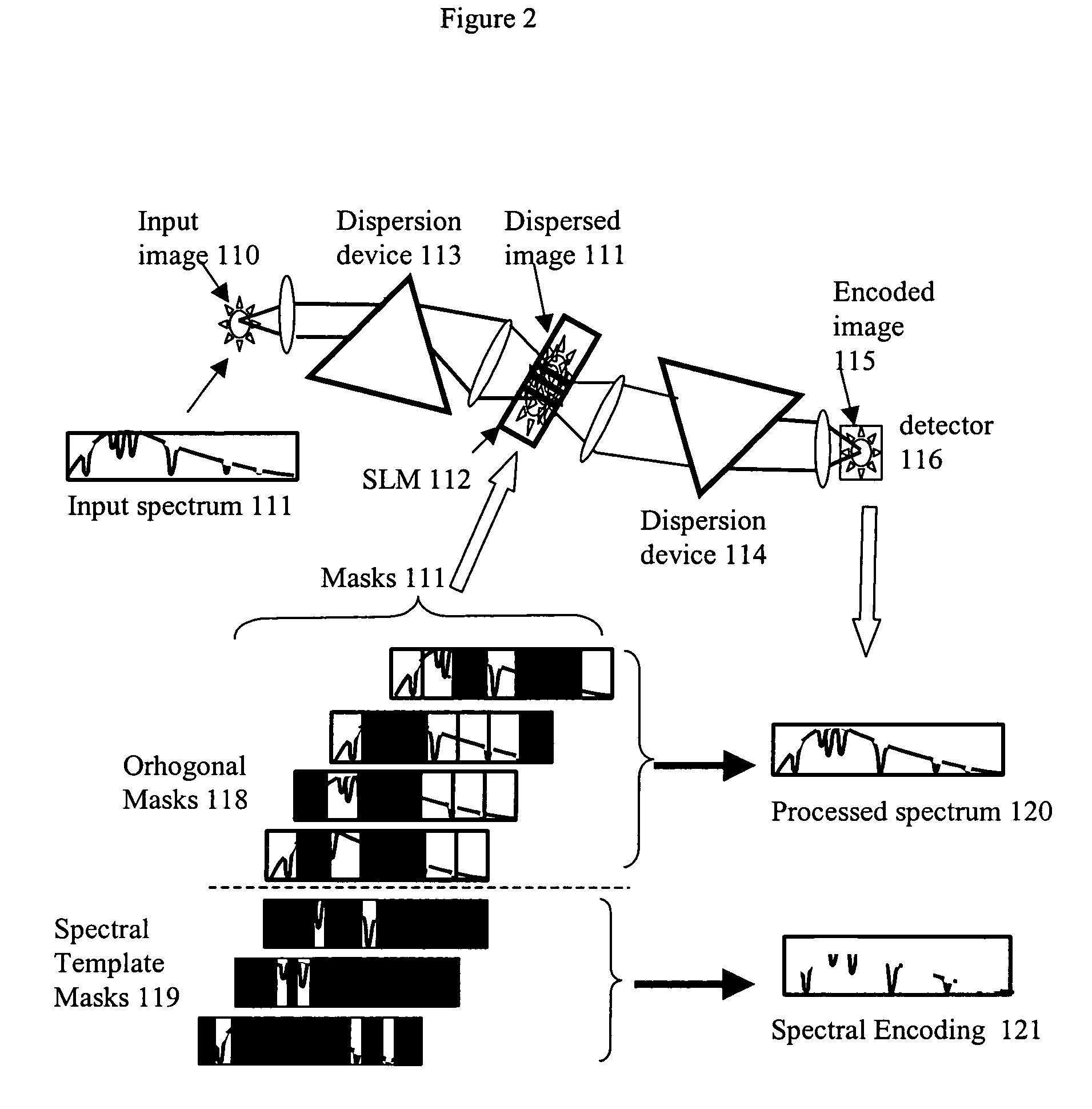
ActiveUS20070296969A1Reduce aberrationHigh quality two-dimensional imageRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationSpatial light modulatorSpectrograph
A spectral encoder for producing spectrally selected images of a radiation field containing multiple spectral components. An imaging spectrograph defines a first optical path that produces from the input radiation field a spectrally dispersed image comprising multiple spectral components displaced along a dispersion direction. Spectral pass bands are encoded on the dispersed image by a programmable spatial light modulator using one or more spatial masks. The imaging spectrograph further defines a second optical path that reverses the spectral dispersion of the first path and produces a spectrally-encoded polychromatic output image containing only those spectral components encoded by the spatial mask. The first and second optical paths share a common dispersing element. A detector records at least one spatial region of the spectrally encoded output image.
Owner:GOLDSTEIN NEIL +6
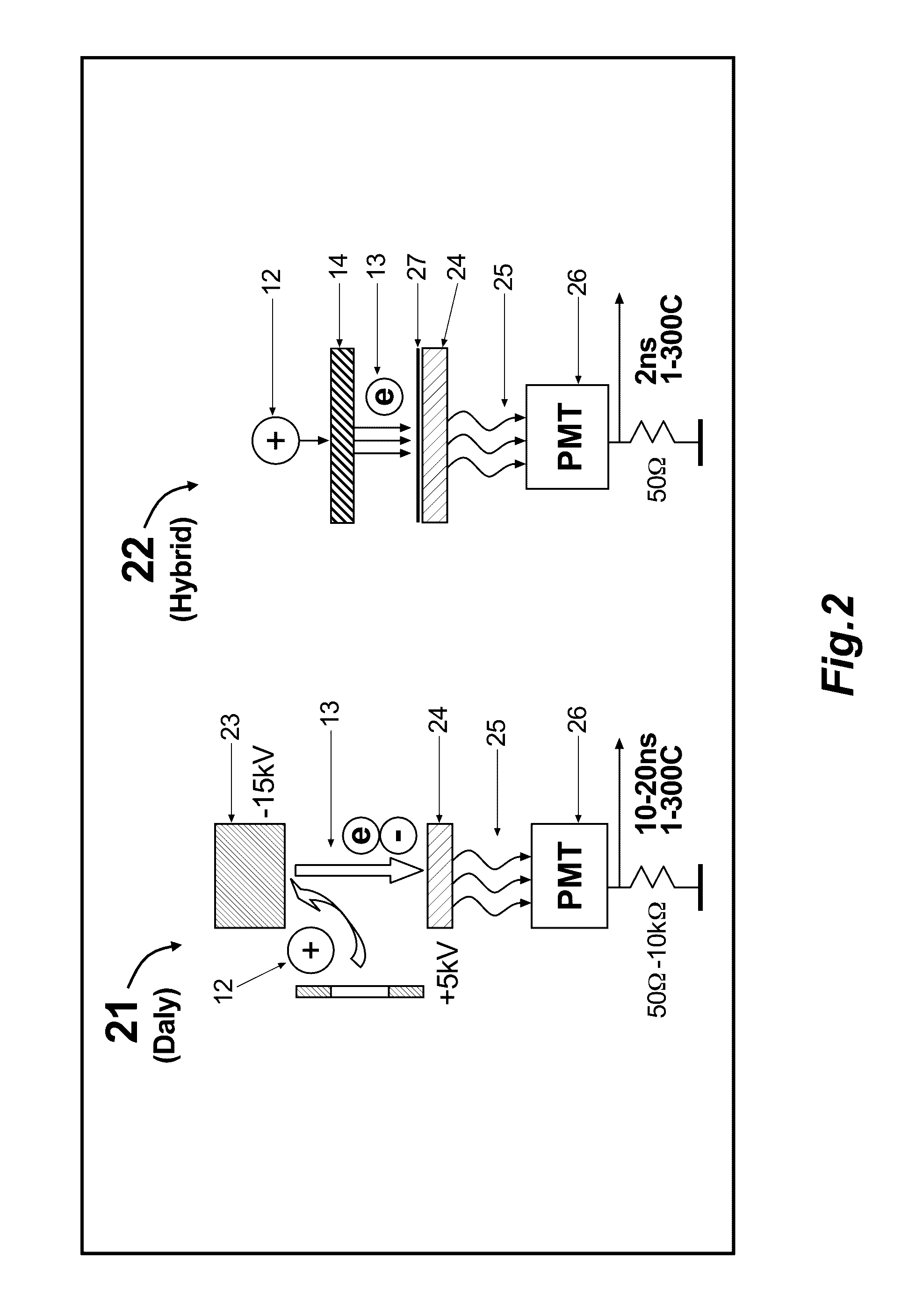
Right Angle Time-of-Flight Detector With An Extended Life Time
ActiveUS20170025265A1Improve detection efficiencyExtended service lifeTime-of-flight spectrometersSpectrometer detectorsSecondary electronsLife time
There is proposed a right angle time-of-flight detector (41, 117, 124, 143, 144, 145) comprising a conductive converter (46) for emitting and accelerating secondary electrons, a magnetic field formed by at least one magnet (47) for deflecting the secondary electrons at a right angle and a sealed photo-multiplier (26). The detector is expected to provide an extended resource and dynamic range and may be fit into tight assemblies, such as MR-TOF MS.
Owner:LECO CORPORATION
Automated chemiluminescence analyzer
InactiveUS6716391B1Improve light collectionMaximum sensitivityChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceLuminescent dosimetersChemical reactorEngineering
An automated chemiluminescence analyzer. A multiport selection valve has a common aspiration port for carrier solvent, sample, and reagent. A bi-directional pump is connected to the selection valve. A chemiluminescence cell is positioned between the selection valve and a T-block. One end of the cell is connected to the common port of the selection valve, and the other end is connected to the T-block. The T-block has a port connected to the pump, another port which communicates with the detector, and a third port connected to the other end of the cell. This unique arrangement enables the chemiluminescence cell to function as a chemical reactor, thus eliminating any delay between initiation and detection of emitted radiation, so that very rapid reactions can be viewed and high sensitivity attained.
Owner:GLOBAL FIA
LED projector headlamps using single or multi-faceted lenses
InactiveUS7563008B2Easy to controlReduce package sizeVehicle headlampsPoint-like light sourceMobile vehicleBeam pattern
A condenser lens and a headlamp assembly employing the condenser lens improves control over the beam spread characteristics, while at the same time reduces the package size of the headlamp assembly. The condenser lens is provided for a projector-type headlamp assembly having a light source emitting light which is projected longitudinally downstream in front of a motor vehicle. The condenser lens generally includes a main body of light transmitting material. The main body defines a first surface receiving light from the light source and a second surface emitting the light. The second surface has at least one facet structured to spread the light and provide a predetermined beam pattern.
Owner:VARROC LIGHTING SYST SRO
Light guide having a tapered geometrical configuration for improving light collection in a radiation detector
InactiveUS20080073542A1Improve light collectionImprove image qualityMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementPhotodetectorLight pipe
A radiation detector having a light guide with a plurality of light pipes is provided designed to improve light collection for reading out a larger scintillator array surface area than a photodetector assembly surface area. The light guide has a trapezoidal geometrical configuration and is symmetrical with respect to at least one axis thereof.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Light assembly for automotive lighting applications
InactiveUS20070121331A1Reduce light scatterEfficient collectionPoint-like light sourceLight guidesLight pipeEffect light
An automotive light assembly produces numerous beam patterns meeting automotive requirements through the reduction of light scatter and collection and redirection in efficiencies. A light source projects light laterally, which is collected by a light conducting body having a hub and a plurality of fingers extending from the hub. By using a plurality of small individual fingers, large and bulky light pipes are eliminated and the light collection and redirection efficiency is improved.
Owner:VARROC LIGHTING SYST SRO
Advanced SNM Detector
InactiveUS20110101230A1High detectabilityDecrease in background radiationMeasurement with semiconductor devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansOptoelectronicsRadiation
A detector for detecting SNM and or RDD radiation. The detector comprising: a plurality of elongated organic scintillator segments arranged in a side by side array; and at least one pair of light sensors optically coupled to ends of each of the scintillator segments such that they receive light from scintillations produced in the scintillator and generate electrical signals responsive thereto.
Owner:INBAR DAN
Light scattering detector
InactiveUS7268881B2High sensitivityEffective guidanceComponent separationWithdrawing sample devicesAngle of incidenceCurrent mode
The invention concerns high sensitivity light scattering detection and its application to evaporative light scattering detection in liquid chromatography. The exemplary embodiment includes a detection cell to accept particles suspended in a gas stream and permit a polarized light beam to pass through a trajectory of the particles and gas stream. A sample light detector is disposed to detect light scattered in the detection cell. A light trap accepts the polarized beam after it passes through the detection cell. The light trap includes an elongated housing through which the polarized beam passes, and light absorptive material within the elongated housing. An absorptive filter is aligned such that the angle of incidence of the light beam upon the filter approximates Brewster's angle and the electric field vector of the beam is aligned with the plane of incidence between the beam and the filter. Other embodiments of the invention provide increased light collection. Embodiments of the invention include temperature-controlled entrance and exit ports that control particle trajectory. Embodiments of the invention include a reference cell disposed between a detection cell and a light trap, and the reference cell includes lensing and a spherical mirror to direct light toward a reference light detector. The reference light detector provides a reference signal that may be used with noise cancellation circuitry, operating in either voltage or current mode, to reduce light source noise in the sample signal.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Low crosstalk integrated imaging three-dimensional display method based on microlens array group
InactiveCN104007556AImprove light collectionExpand the observable rangeOptical elementsLight energyEngineering
The invention provides a low crosstalk integrated imaging three-dimensional display method based on a microlens array group. The method involves the double micro lens arrays in a group and a display screen which is to display an element image. The display screen is placed within the one-time focal length in front of the first microlens array, and the second microlens array is placed into the rear position of the first lens array. Due to the fact that the distance between the display screen and the lens arrays is shortened, more light enters the correspondingly correct lens element, the light energy utilization ratio is improved, meanwhile, the light which enters the adjacent lens to form crosstalk is reduced, crosstalk information sources are reduced, crosstalk of integrated images is reduced, and the field angle is enlarged. The second microlens array plays a role in integration, and integrates the magnified element image to be displayed. The element image in the display screen, and the lens elements in the two microlens arrays are in the one-to-one corresponding relation, and the centers are aligned.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Fluorescent waveguide light-harvesting type photovoltaic-photothermal combined power generation device
InactiveCN106788213ALower working temperatureImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyPV power plantsGenerators/motorsMicro nanoWaveguide
The invention relates to a fluorescent waveguide light-harvesting type photovoltaic-photothermal combined power generation device. The device comprises a laser type fluorescent waveguide light-harvesting type photovoltaic-photothermal combined power generation device and a solar-energy type fluorescent waveguide light-harvesting type photovoltaic-photothermal combined power generation device; both the two types of the fluorescent waveguide light-harvesting type photovoltaic-photothermal combined power generation devices comprise micro-nano light trap layers, light transmitting heat conduction layers and fluorescent waveguide light-harvesting type photovoltaic-photothermal combined power generation layers; each fluorescent waveguide light-harvesting type photovoltaic-photothermal combined power generation layer comprises a fluorescent waveguide light-harvesting device, a heat conduction layer, a thermoelectric temperature difference power generation device, a photovoltaic power generation device and a radiator; the two types of the devices are capable of producing a photovoltaic power generation effect and a photothermal power generation effect respectively under irradiation of laser, or sunlight, or solar concentrating light, and are capable of outputting externally electricity generated through photovoltaic-photothermal combined power generation. The fluorescent waveguide light-harvesting type photovoltaic-photothermal combined power generation device is capable of being widely applied in the fields of aerospace vehicles, unmanned aerial vehicles, unmanned ships and warships, unmanned vehicles, robots, engineering equipment and the like.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Spectral encoder
ActiveUS7324196B2Improve image qualityReduce aberrationRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationSpatial light modulatorSpectrograph
A spectral encoder for producing spectrally selected images of a radiation field containing multiple spectral components. An imaging spectrograph defines a first optical path that produces from the input radiation field a spectrally dispersed image comprising multiple spectral components displaced along a dispersion direction. Spectral pass bands are encoded on the dispersed image by a programmable spatial light modulator using one or more spatial masks. The imaging spectrograph further defines a second optical path that reverses the spectral dispersion of the first path and produces a spectrally-encoded polychromatic output image containing only those spectral components encoded by the spatial mask. The first and second optical paths share a common dispersing element. A detector records at least one spatial region of the spectrally encoded output image.
Owner:GOLDSTEIN NEIL +6
LED back light module and LED display equipment
ActiveCN106405938AImprove the problem of blue aroundImprove light collectionNon-linear opticsLED displayLight guide
The invention discloses an LED back light module. The module comprises sequentially a light guide plate, a quantum dot color enhancement film, a first bright enhancement film and a second bright enhancement film. The peripheral area of the quantum dot color enhancement film is filmed with light absorbing media. The second bright enhancement film comprises a plurality of lens structure. The lens structure includes a first lens structure located on the peripheral area of the second bright enhancement film and a second lens structure located at the center of the second bright enhancement film. The peripheral area encloses the central area. The light collection performance of the first lens structure exceeds the light collection performance of the second lens structure. Through the high light collection performance of the peripheral area of the second bright enhancement film, the module can enhance the emergent light brightness in the peripheral area, thus modify the problem of relatively low brightness in the peripheral area in comparison with the brightness of the central area of the LED display equipment, enhance the display uniformity of the LED display equipment. An LED display device is also disclosed.
Owner:XIAMEN TIANMA MICRO ELECTRONICS +1
Photoelectric conversion device and method for making the same
InactiveUS20100079636A1Reduced flexibilityIncrease thickness can be suppressedTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPhotoelectric conversionEngineering
A photoelectric conversion device includes a semiconductor substrate, a first insulating film on the semiconductor substrate, a second insulating film on the first insulating film, a third insulating film on the second insulating film, and a wiring disposed in the third insulating film, the wiring being a wiring layer closest to the semiconductor substrate. A first plug of a shared contact structure and a second plug are disposed in the first insulating film. A third plug and a first wiring that constitute a dual damascene structure are disposed in the second and third insulating films. The first insulating film is used as an etching stopper film during etching of the second insulating film and the second insulating film is used as an etching stopper film during etching of the third insulating film.
Owner:CANON KK
Solar cell including microlens and method of fabricating the same
ActiveUS20110259407A1Simply and accurately formedFabrication timeOptical articlesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBoiling pointElectrical battery
Disclosed is a method of fabricating a microlens. The method includes forming a self assembly monolayer having a strong hydrophobicity on a substrate; forming a plurality of ink droplets on the self assembly monolayer by jetting a transparent ink using an inkjet apparatus, the transparent ink including a first solvent having a first boiling point, a second solvent having a second boiling point lower than the first boiling point and a silicon oxide (SiOx) solid material dispersed in the first and second solvents; and drying the plurality of ink droplets.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Light scattering detector
InactiveUS20070296971A1High sensitivityEffective guidanceComponent separationWithdrawing sample devicesAngle of incidenceCurrent mode
The invention concerns high sensitivity light scattering detection and its application to evaporative light scattering detection in liquid chromatography. The exemplary embodiment includes a detection cell to accept particles suspended in a gas stream and permit a polarized light beam to pass through a trajectory of the particles and gas stream. A sample light detector is disposed to detect light scattered in the detection cell. A light trap accepts the polarized beam after it passes through the detection cell. The light trap includes an elongated housing through which the polarized beam passes, and light absorptive material within the elongated housing. An absorptive filter is aligned such that the angle of incidence of the light beam upon the filter approximates Brewster's angle and the electric field vector of the beam is aligned with the plane of incidence between the beam and the filter. Other embodiments of the invention provide increased light collection. Embodiments of the invention include temperature-controlled entrance and exit ports that control particle trajectory. Embodiments of the invention include a reference cell disposed between a detection cell and a light trap, and the reference cell includes lensing and a spherical mirror to direct light toward a reference light detector. The reference light detector provides a reference signal that may be used with noise cancellation circuitry, operating in either voltage or current mode, to reduce light source noise in the sample signal.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Light trapping architecture for photovoltaic and photodector applications
ActiveUS20120261558A1Improve light collectionImprove efficiencySolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotovoltaic detectorsEngineering
There is disclosed photovoltaic device structures which trap admitted light and recycle it through the contained photosensitive materials to maximize photoabsorption. For example, there is disclosed a photosensitive optoelectronic device comprising: a first reflective layer comprising a thermoplastic resin; a second reflective layer substantially parallel to the first reflective layer; a first transparent electrode layer on at least one of the first and second reflective layer; and a photosensitive region adjacent to the first electrode, wherein the first transparent electrode layer is substantially parallel to the first reflective layer and adjacent to the photosensitive region, and wherein the device has an exterior face transverse to the planes of the reflective layers where the exterior face has an aperture for admission of incident radiation to the interior of the device.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Photodetector focal plane array systems and methods
ActiveUS9362324B1Improve characteristicImprove efficiencySolid-state devicesPretreated surfacesPhotodetectorPhotovoltaic detectors
A photodetector focal plane array system, comprising: a substrate comprising a plurality of photosensitive regions; and a microcomponent disposed adjacent to each of the plurality of photosensitive regions operable for receiving incident radiation and directing a photonic nanojet into the associated photosensitive region. Optionally, each of the microcomponents comprises one of a microsphere and a microcylinder. Each of the microcomponents has a diameter of between between ˜λ and ˜100λ, where λ is the wavelength of the incident radiation. Each of the microcomponents is manufactured from a dielectric or semiconductor material. Each of the microcomponents has an index of refraction of between ˜1.4 and ˜3.5. Optionally, high-index components can be embedded in a lower index material. The microcomponents form an array of microcomponents disposed adjacent to the substrate.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL +1
Light emitting device
InactiveUS20070069219A1Short current pathReduce thermal resistanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesElectrical connectionThermal resistance
A light emitting device is proposed, which emits light while connected to the power. The light emitting device includes a light emitting element having at least two electrodes disposed at the side of the light output surface thereof; and a base member having a recess and lead portions corresponding to the electrodes, the light emitting element being mounted on the base member and received in the recess, wherein the light output surface faces toward opening of the recess that becomes smaller while approaching the light output surface, and the electrodes are respectively in electrical connection with the lead portions that extend from the connection positions to outer edge of the base member for power connection. The light emitting device of the present invention has advantages of short current path, low series thermal resistance and low cost. In addition, the depth of the recess can further be increased to improve light collecting efficiency.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy (TIRFM)
ActiveUS20170153436A1Improve light collectionSmall thicknessMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesOptoelectronicsTotal internal reflection fluorescence microscope
Disclosed is a fluorescence microscope for imaging a specimen a fluorescent substance, the fluorescence microscope including an excitation light source configured to emit an excitation light that excites a fluorescent substance to emit fluorescence; a de-excitation light source configured to emit a de-excitation light that de-excites the fluorescent substance excited by the excitation light emitted from the excitation light source; an optical body configured to overlap a light emitted from the excitation light source and a light emitted from the de-excitation light source, and to discharge the overlapped light toward the specimen; and a solid immersion lens to which the light discharged from the optical body is incident, and configured to refract the light discharged from the optical body toward the specimen. A total reflection of the light incident to the solid immersion lens occurs on a bottom of the solid immersion lens.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV
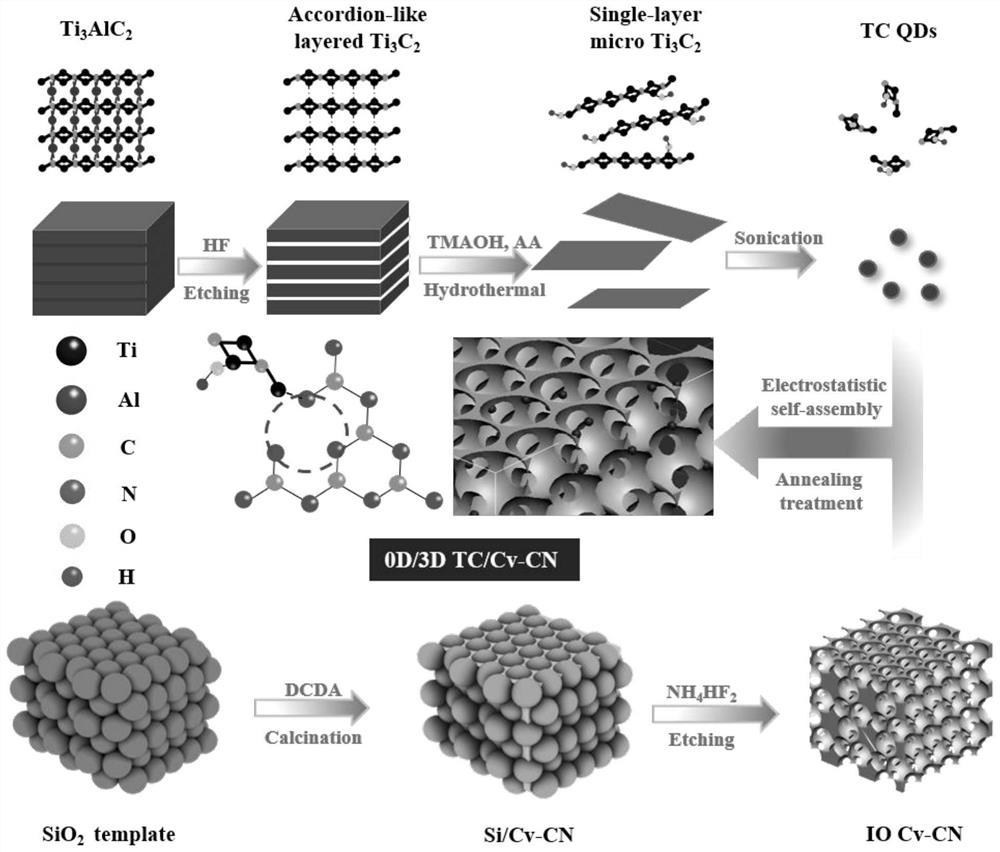
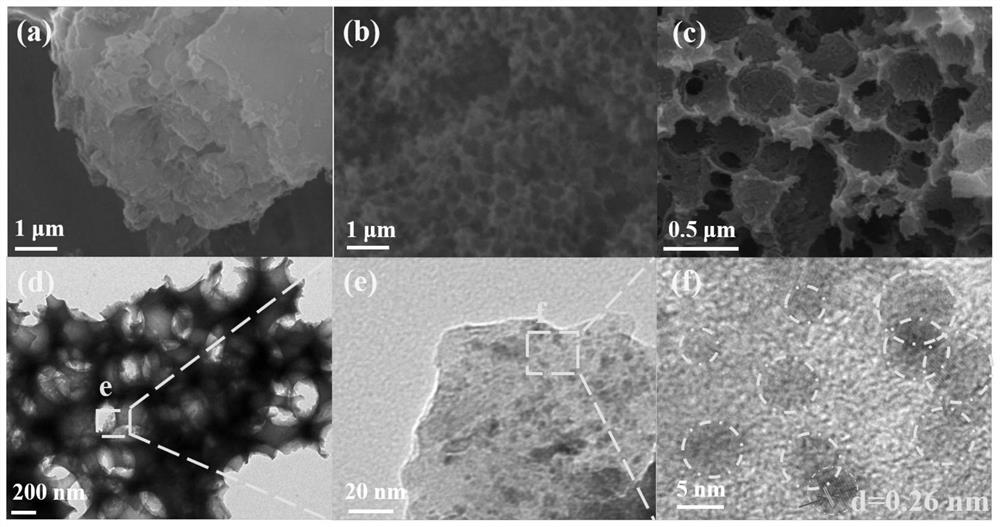
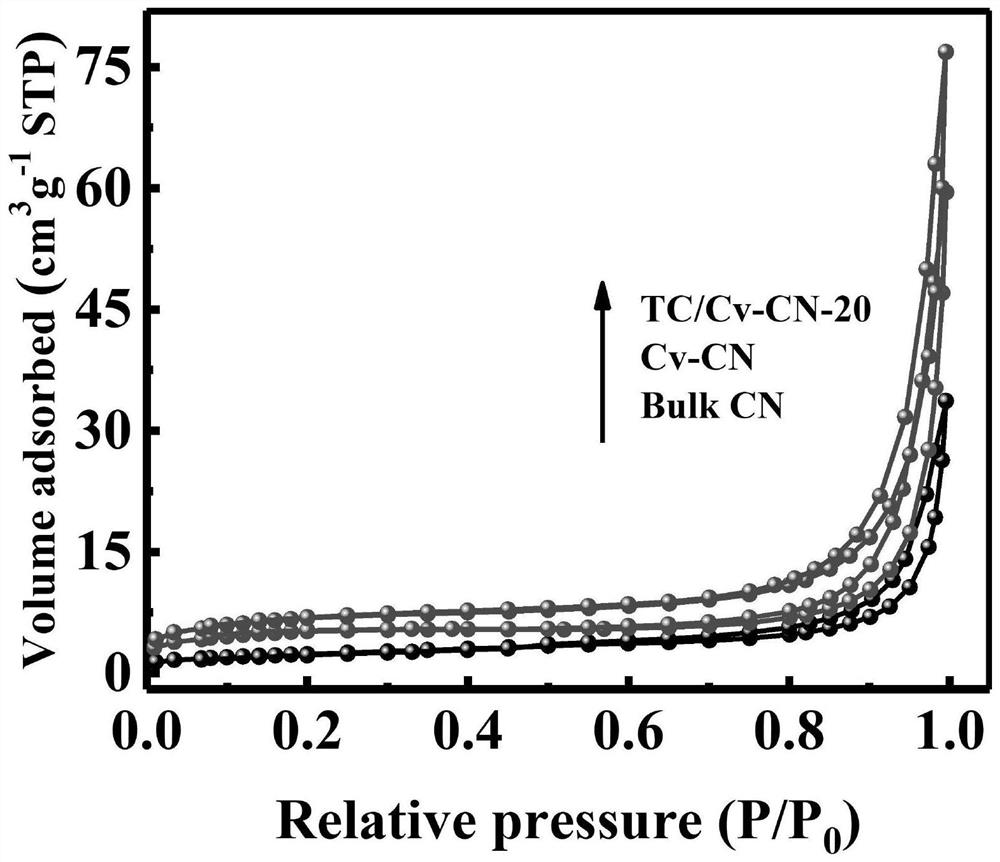
Catalyst loading inverse opal carbon nitride with carbon defect with titanium carbide quantum dots and preparation method of catalyst
InactiveCN112076774AHigh specific surface areaImprove separation efficiencyHydrogen peroxideCatalyst activation/preparationPhotonic crystalPtru catalyst
The invention provides a catalyst loading inverse opal carbon nitride with carbon defect with titanium carbide quantum dots and a preparation method of the catalyst. The catalyst can be well applied to photocatalytic production of H2O2. Firstly, an ordered macroporous structure (inverse opal structure) is synthesized by taking three-dimensional ordered SiO2 spheres as a hard template through a hard template method. Carbon nitride precursor dicyandiamide is poured into a photonic crystal obtained by regular arrangement of SiO2 spheres through high-temperature calcination in Ar gas, and NH4HF2 etching is used for removing the template, thereby obtaining the inverse opal carbon nitride with carbon defects. The carbon defect is introduced while the carbon nitride forms an inverse opal structure, so that the specific surface area and the carrier separation efficiency of the carbon nitride are increased. By applying the catalyst to photocatalytic production of H2O2, the invention finds thatthe catalyst can efficiently produce H2O2 in response to visible light and has better catalytic activity than pure carbon nitride or inverse opal carbon nitride with only the carbon defect.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Devices with Semiconductor Hyperbolic Metamaterials
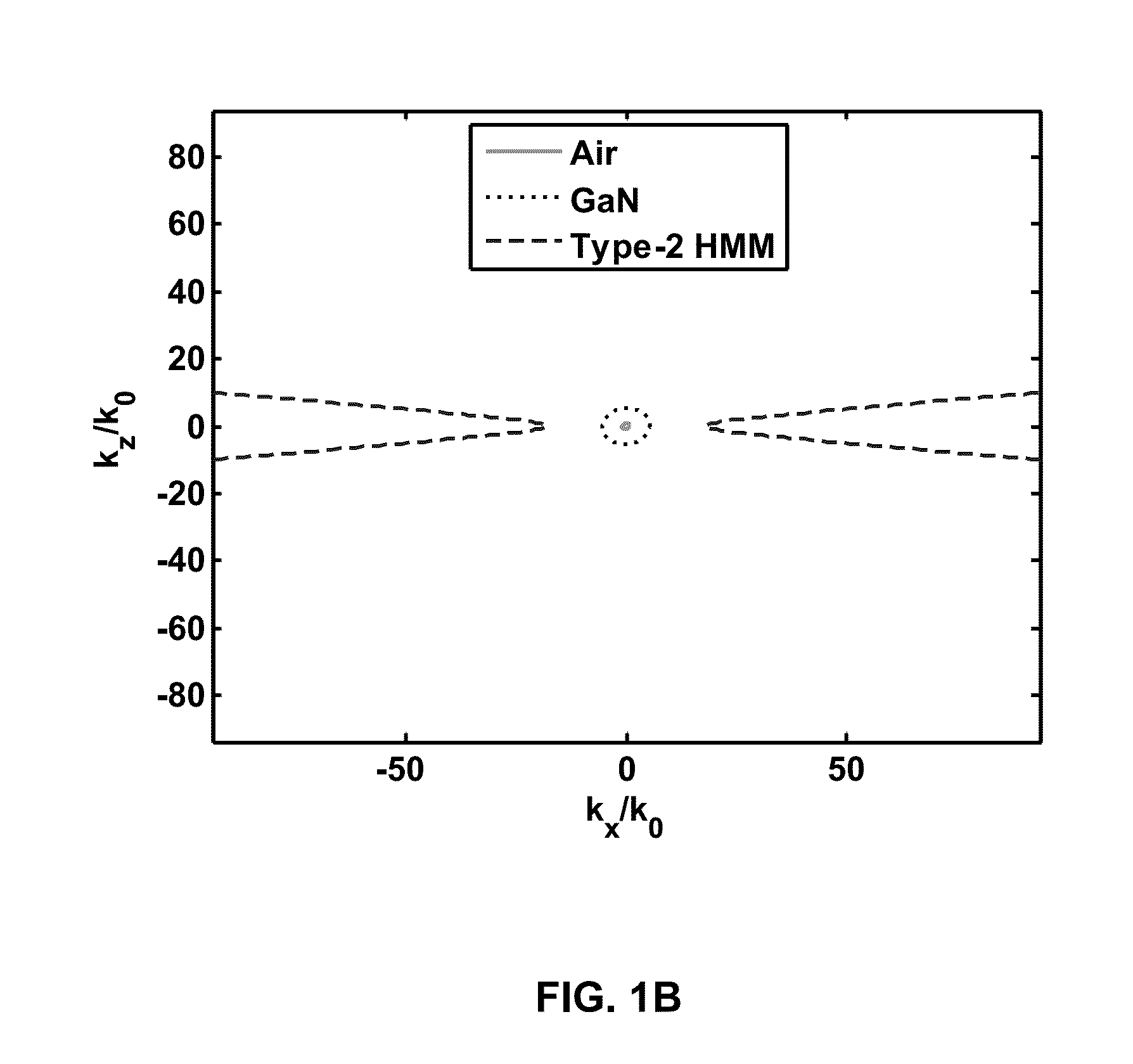
ActiveUS20160274301A1Improve cooling effectImprove responseCoupling light guidesSemiconductor lasersIn planePermittivity
A hyperbolic metamaterial assembly comprising alternating one or more first layers and one or more second layers forming a hyperbolic metamaterial, the one or more first layers comprising an intrinsic or non-degenerate extrinsic semiconductor and the one or more second layers comprising a two-dimensional electron or hole gas, wherein one of in-plane or out-of-plane permittivity of the hyperbolic metamaterial assembly is negative and the other is positive.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Solar energy converter using a solar cell in a shallow liquid-gel layer
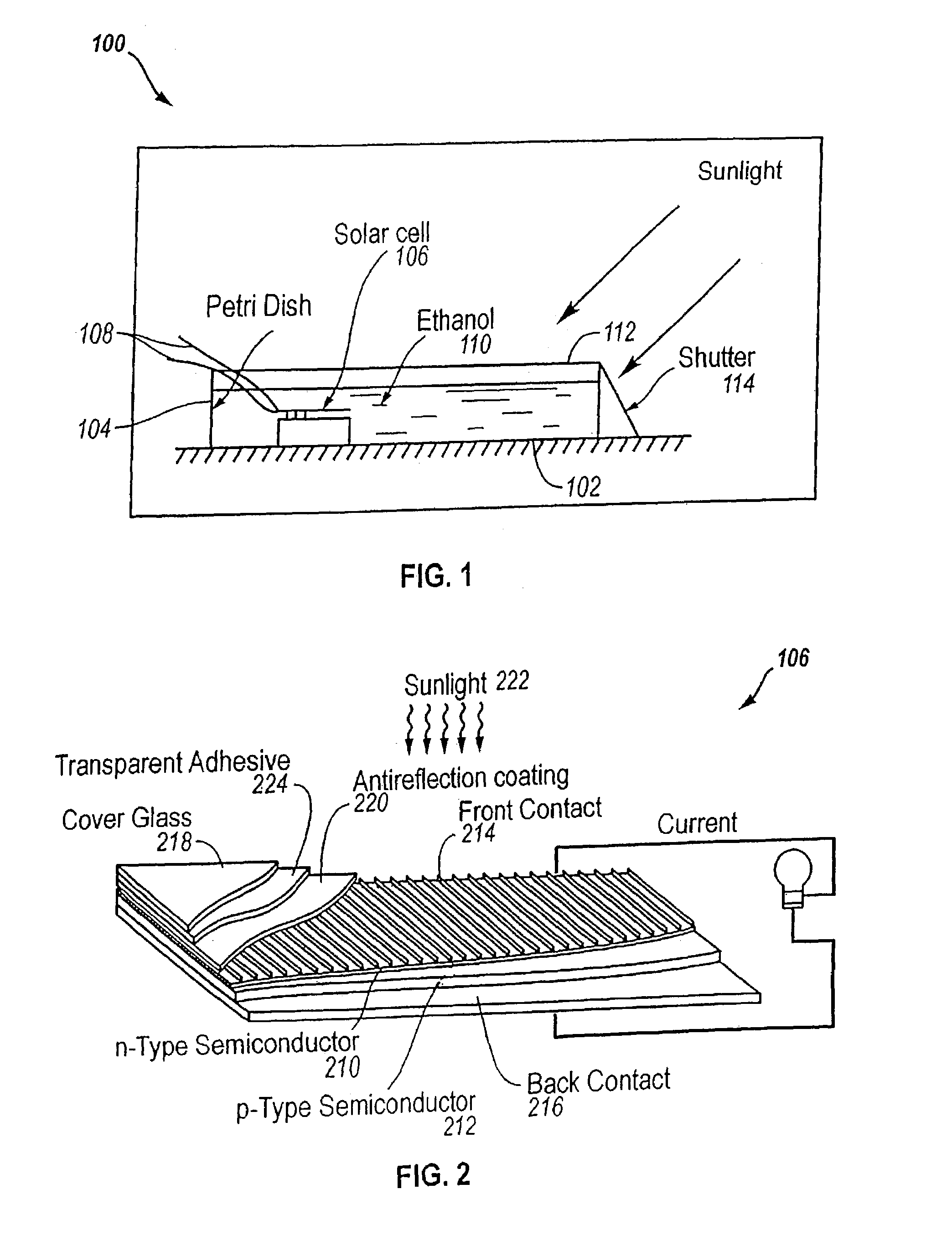
InactiveUS7244888B1Operation efficiency can be improvedImprove light collectionPV power plantsPhotovoltaic energy generationFluid gelThin layer
A solar energy converter comprises a thin panel enclosure, at least one solar cell contained within the enclosure, and a thin layer of gel contained within the thin panel enclosure and enclosing the at least one solar cell. The thin panel enclosure has a two-dimensional flat base, short side walls, and a transparent lid separated from the flat base by the short side walls, the short side walls enclosing an interior cavity having a depth substantially smaller than either of the two-dimensional base dimensions. The at least one solar cell has a front surface and a back surface. The thin layer of gel wets both the front surface and back surface of the at least one solar cell and holds the at least one solar cell separate from the base and lid.
Owner:TANAKA KUNIHIDE
Large-view-field miniature imaging system
The invention provides a large-view-field miniature imaging system, and belongs to the technical field of optical imaging. The imaging system comprises a curved surface imaging camera lens, an optical fiber taper and an imaging sensor. The curved surface imaging camera lens is formed by combining a plurality of spherical lenses or a plurality of semispherical lenses or is formed by combining the spherical lenses and the semispherical lenses. All the lenses share one sphere center. The image surface of the curved surface imaging camera lens is a spherical surface. One end of the optical fiber taper is a curved surface image surface, namely, a concave spherical surface coinciding with the image surface of the curved surface imaging camera lens. The other end of the optical fiber taper is a plane image surface, namely, a plane directly connected with the imaging sensor. The surface of the concave spherical surface is of a rough structure or a stair-shaped circular ring structure, and at the concave spherical surface end of the optical fiber taper, the included angle between each optical fiber forming the optical fiber taper and the image surface of the curved surface imaging camera lens ranges from 70 degrees to 90 degrees. The large-view-field miniature imaging system has the advantages of being large in view field, high in resolution, high in illumination, small in size, low in machining cost, and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV 5D TECH
Production method for nano focusing X ray lens combination
InactiveCN101221829AImprove light gathering abilityIncrease light collecting apertureHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionPhotoresistAluminium
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Solar-power enhancing module and sun tracking system thereof
InactiveUS20140311549A1Improve light collectionInstallation cost savingPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energySun trackingEngineering
Owner:WANG YUN MIN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com