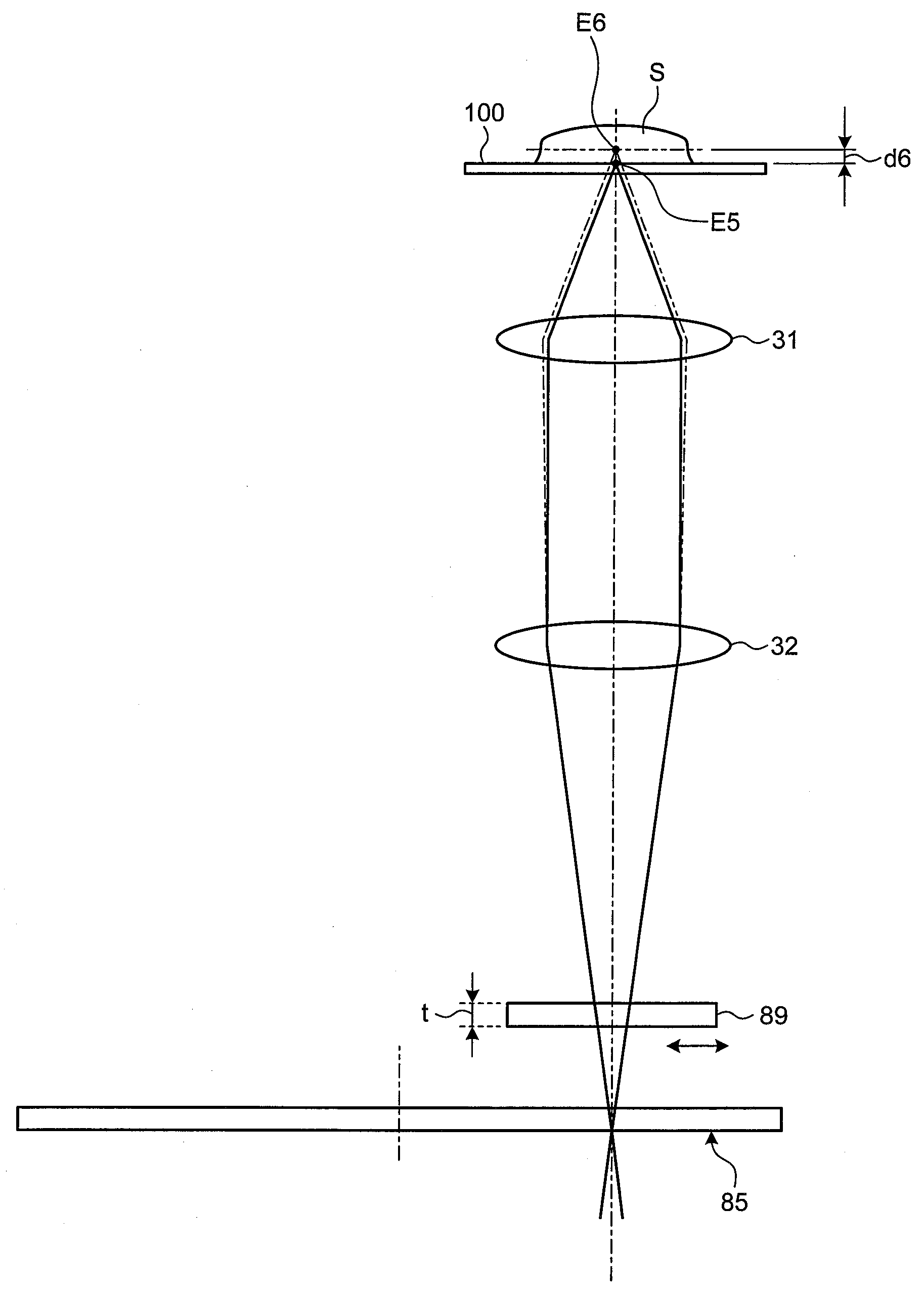
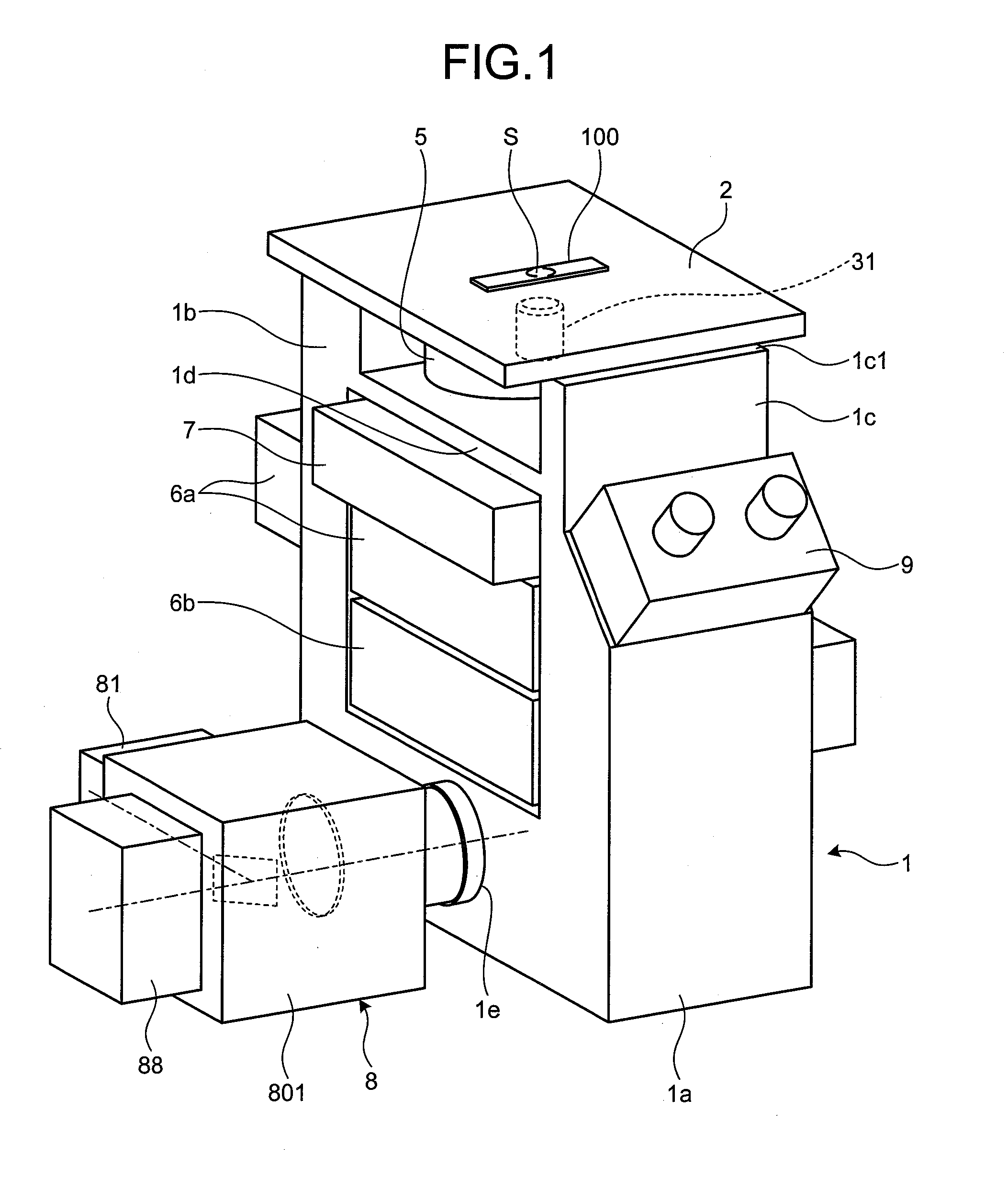
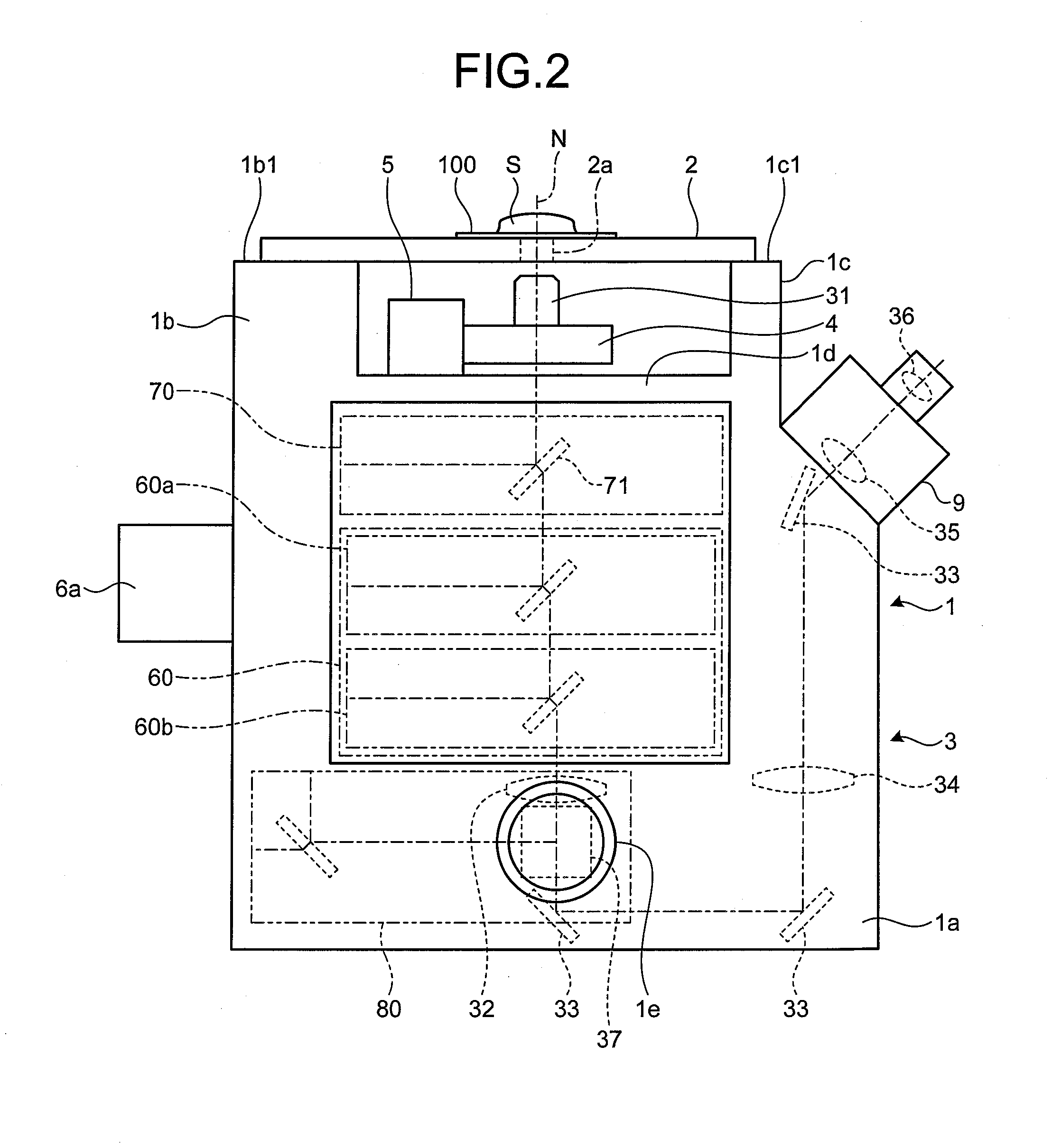
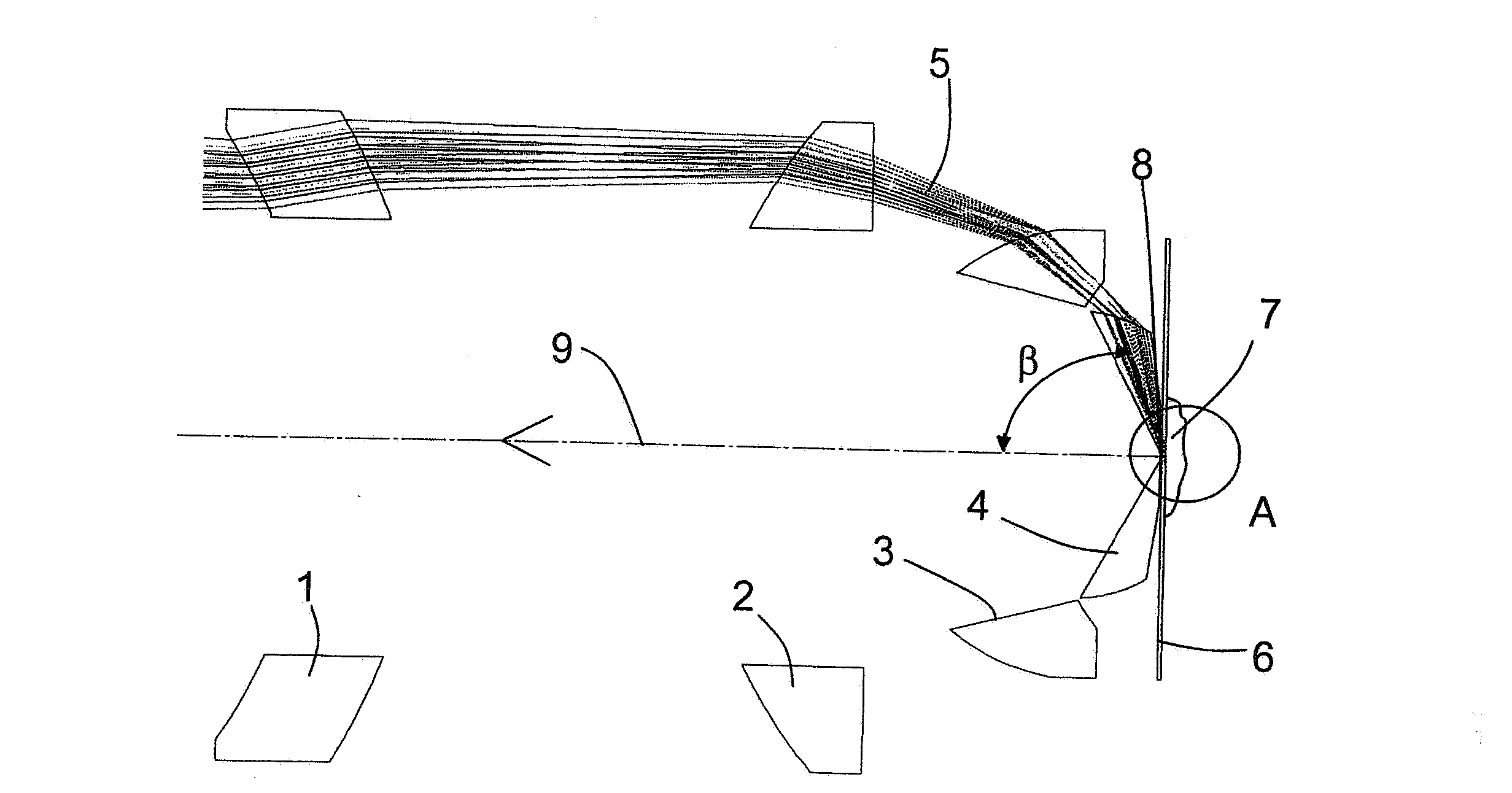
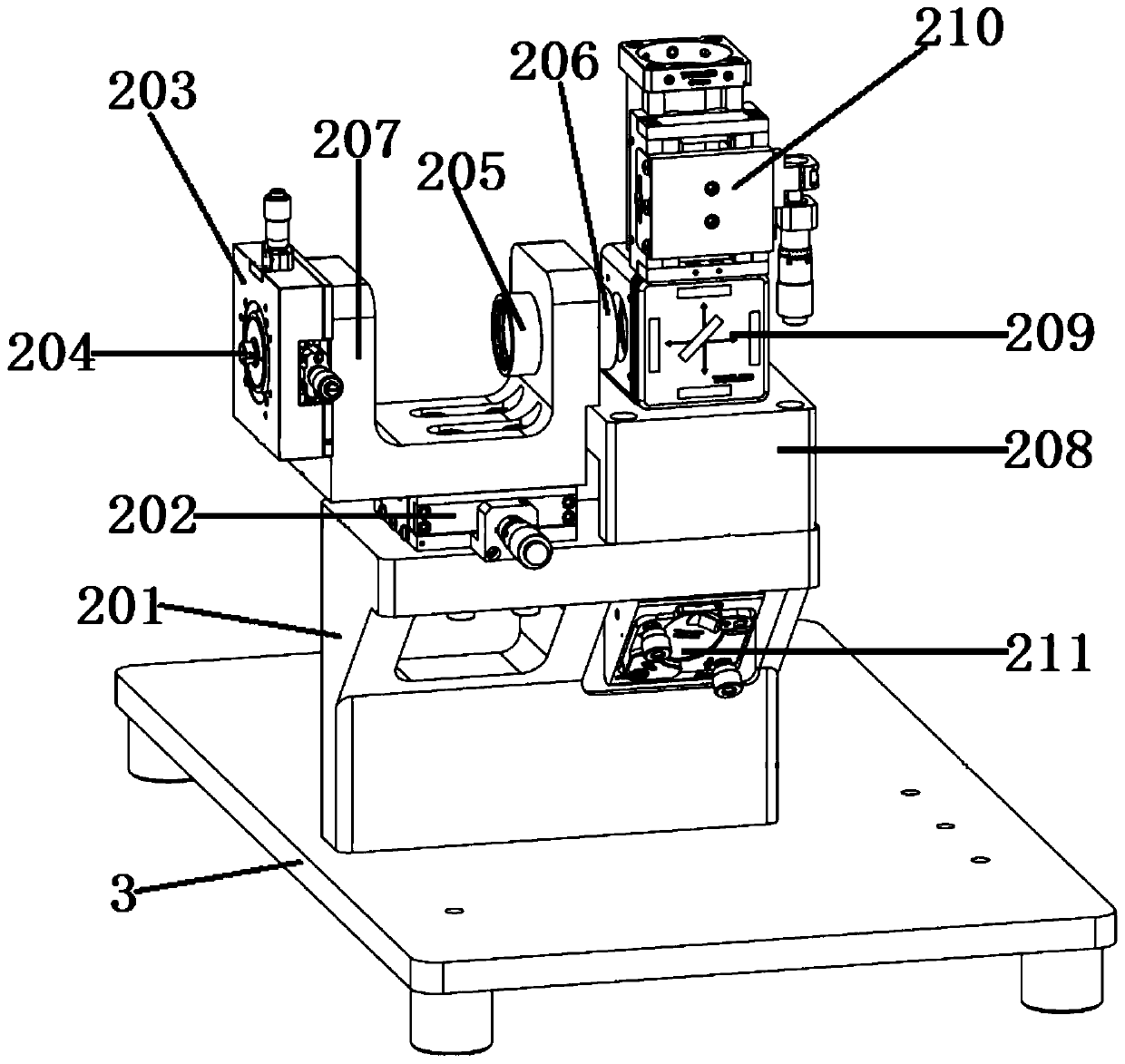
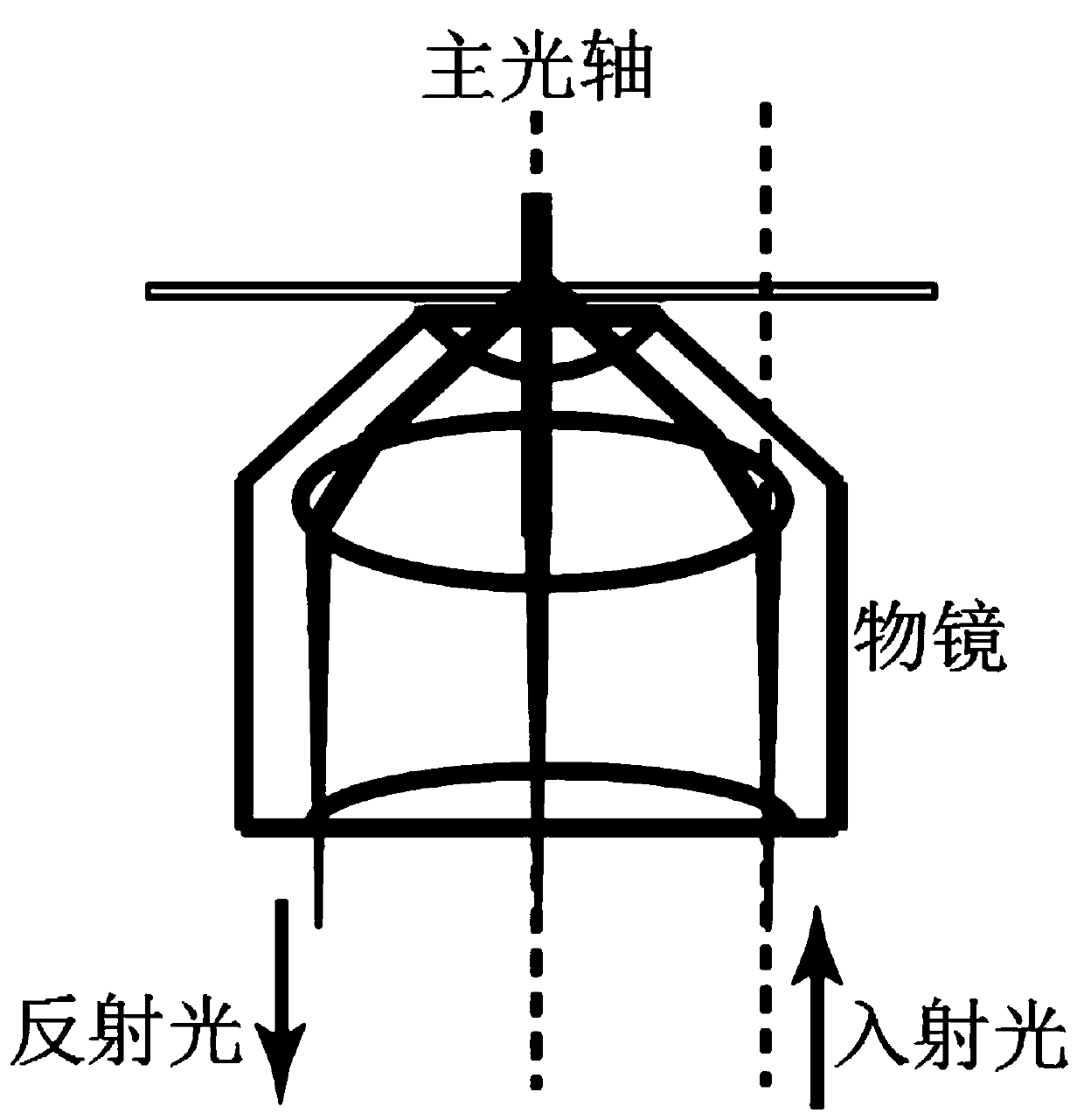
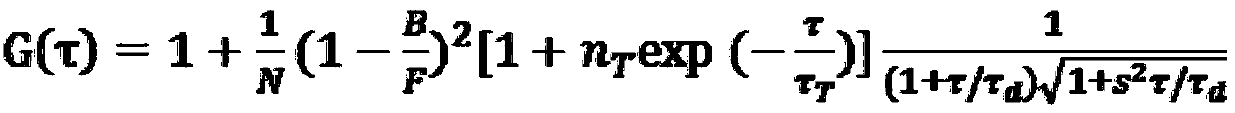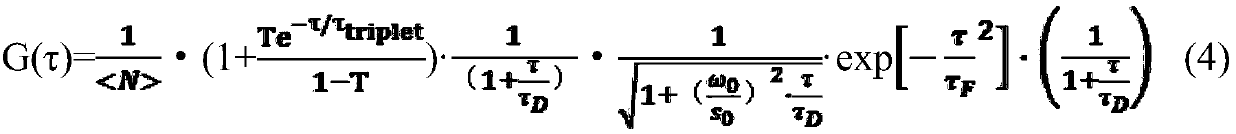Patents
Literature
35 results about "Total internal reflection fluorescence microscope" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
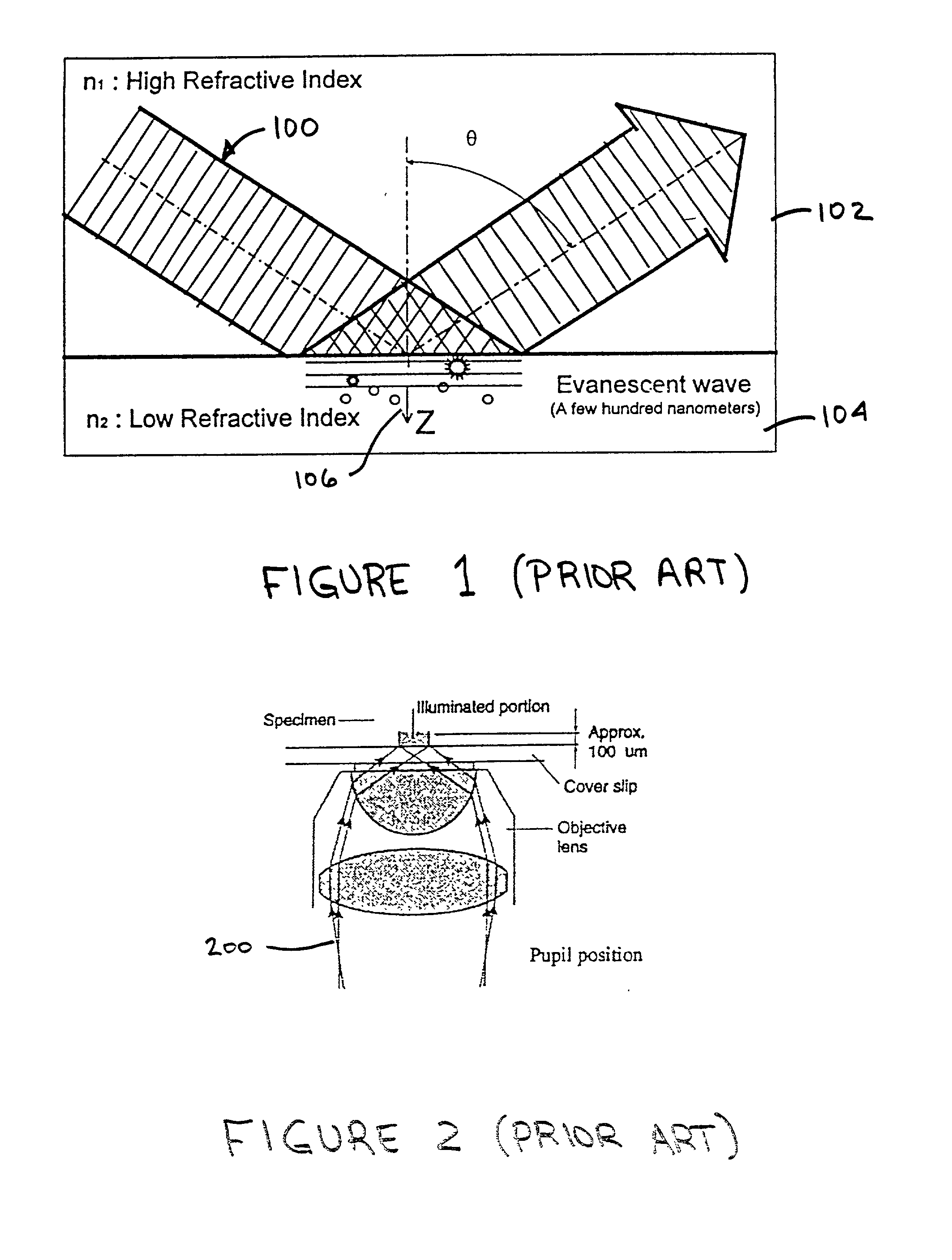
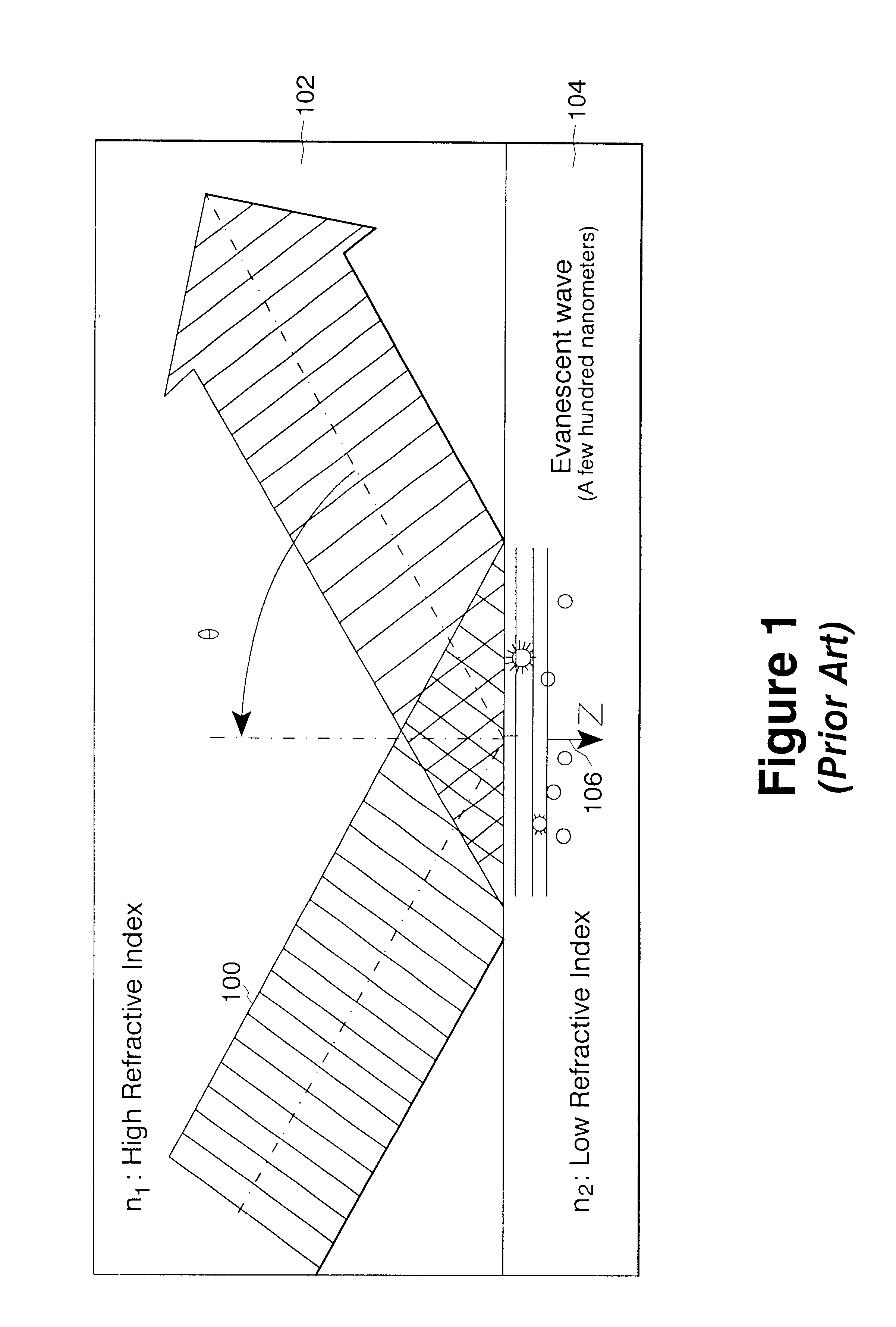
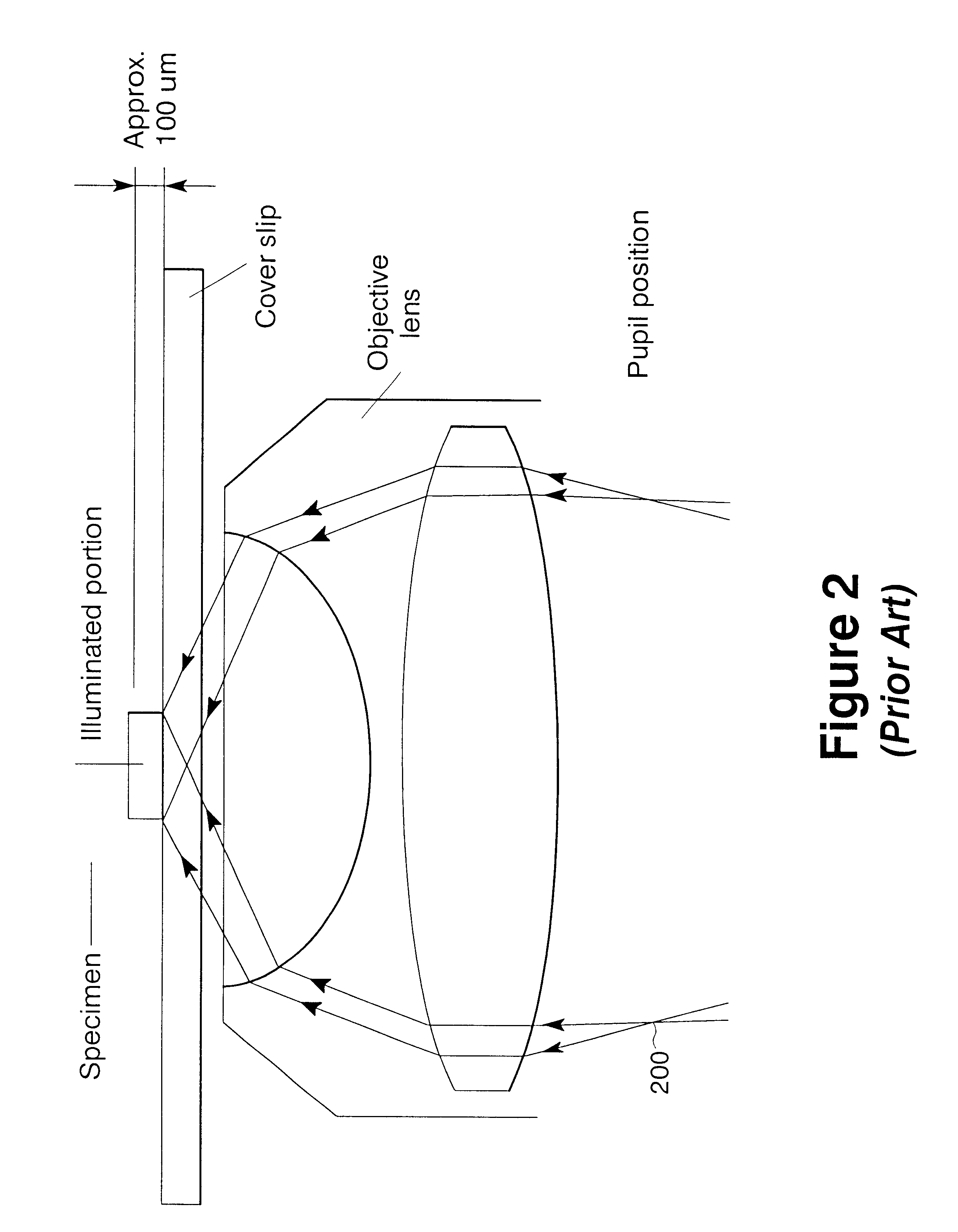
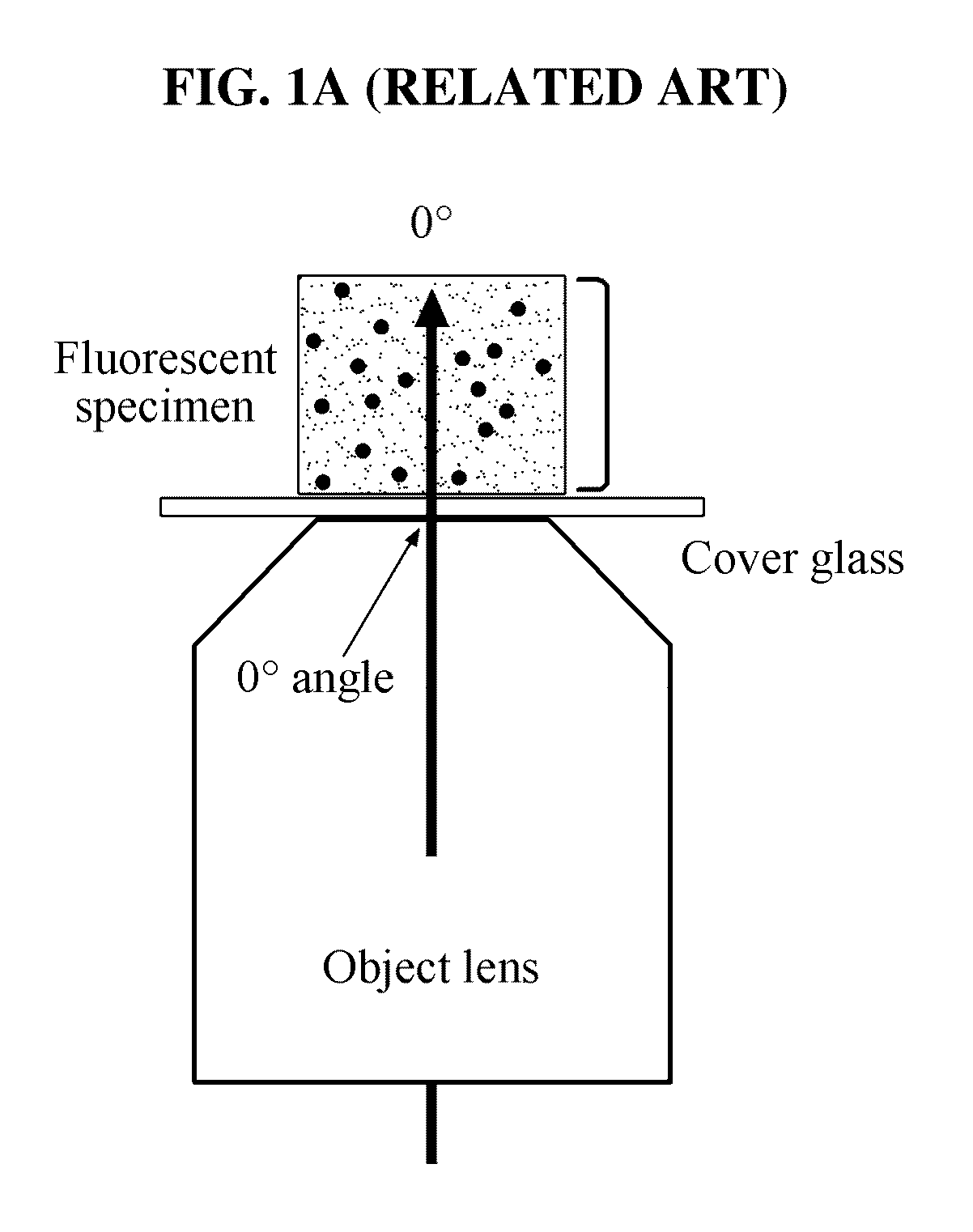
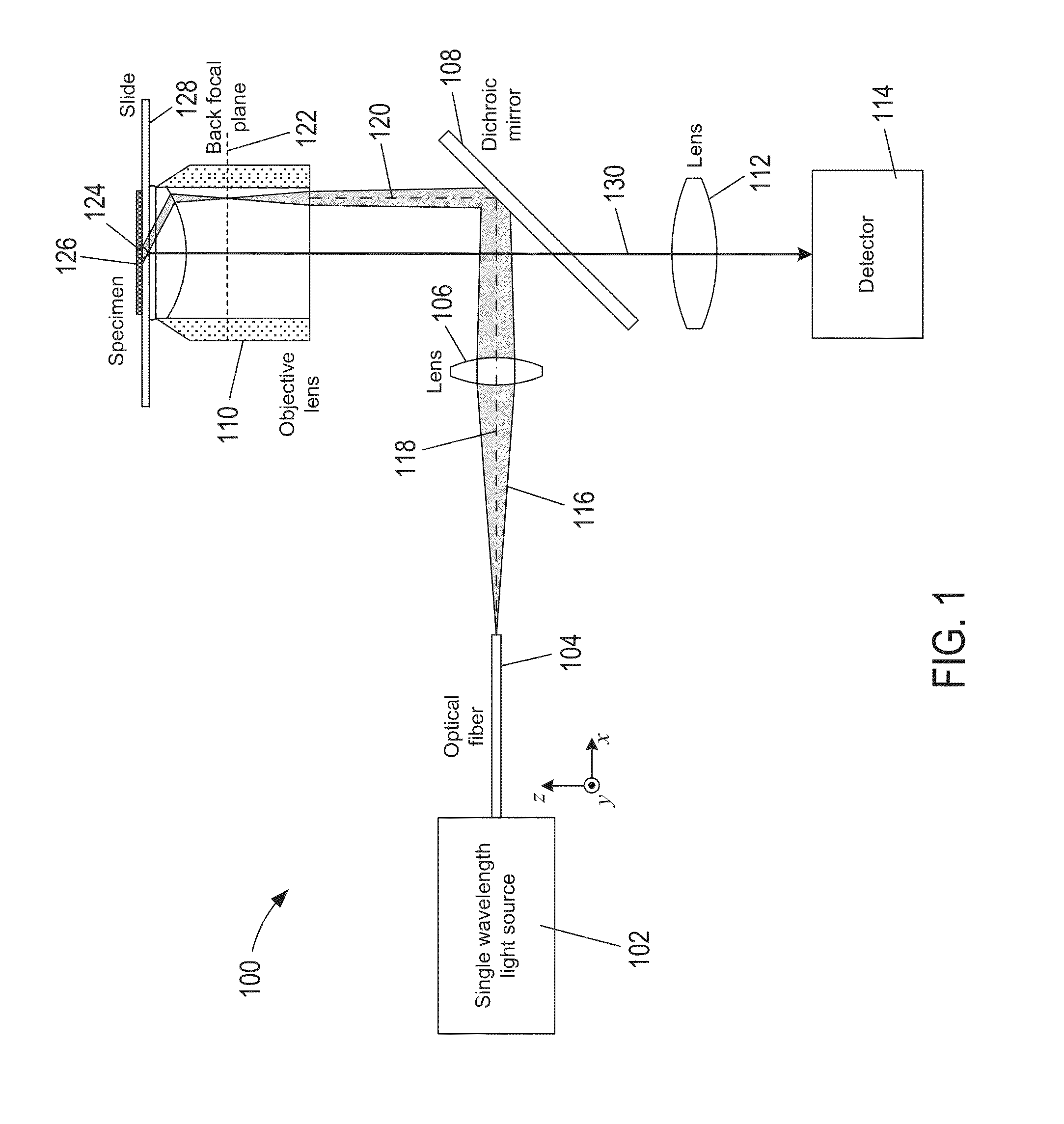
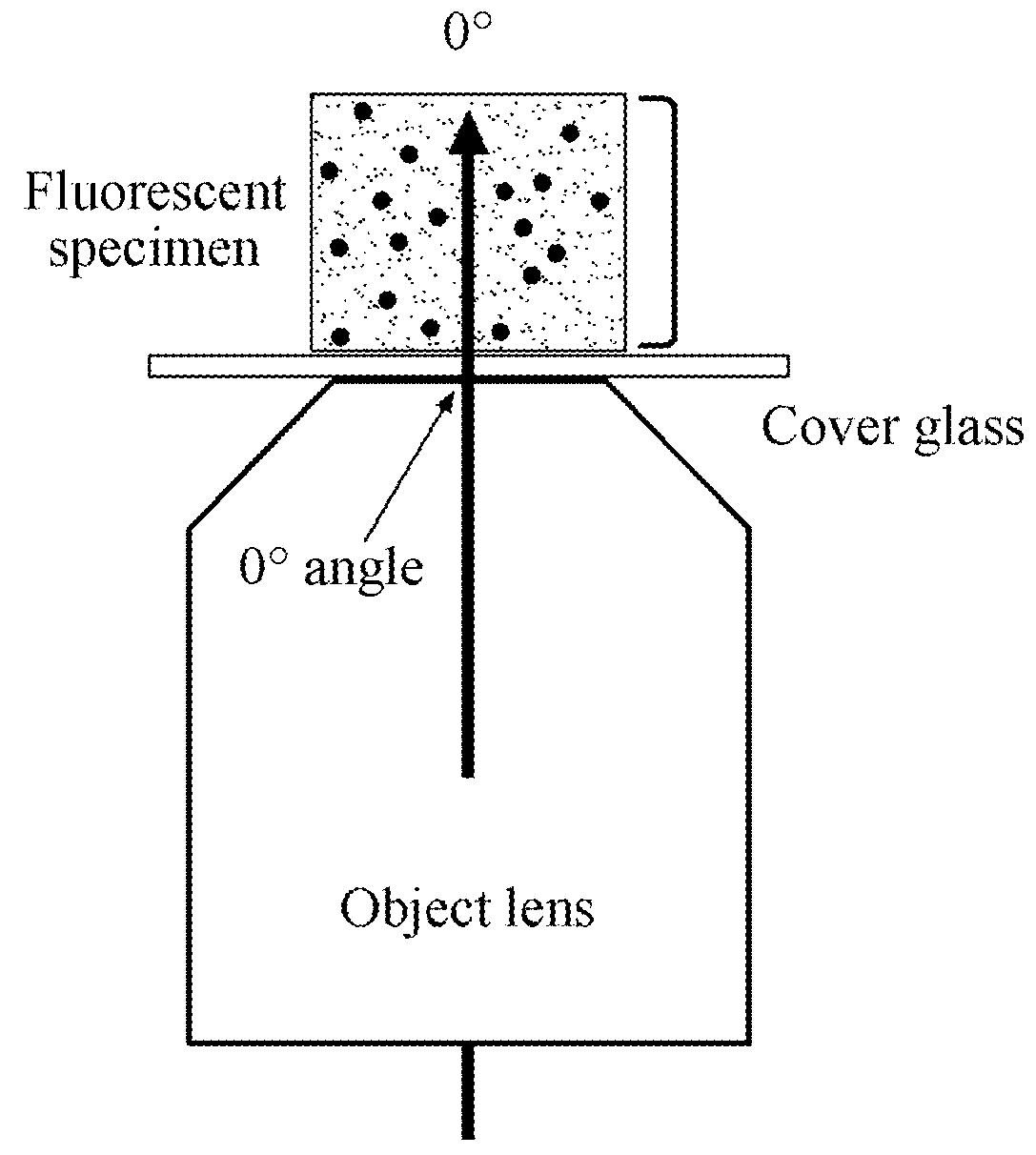
A total internal reflection fluorescence microscope (TIRFM) is a type of microscope with which a thin region of a specimen, usually less than 200 nanometers can be observed.
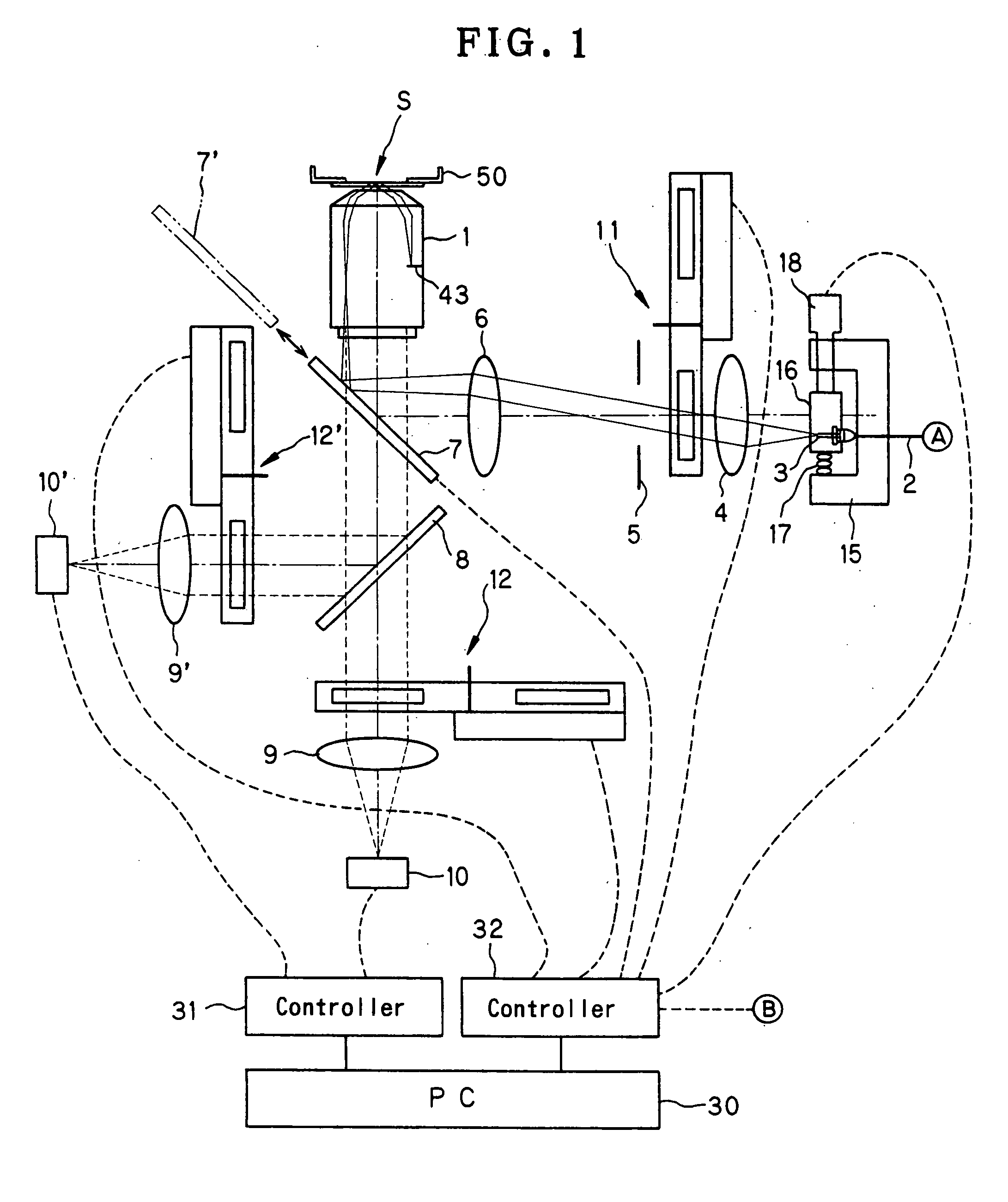
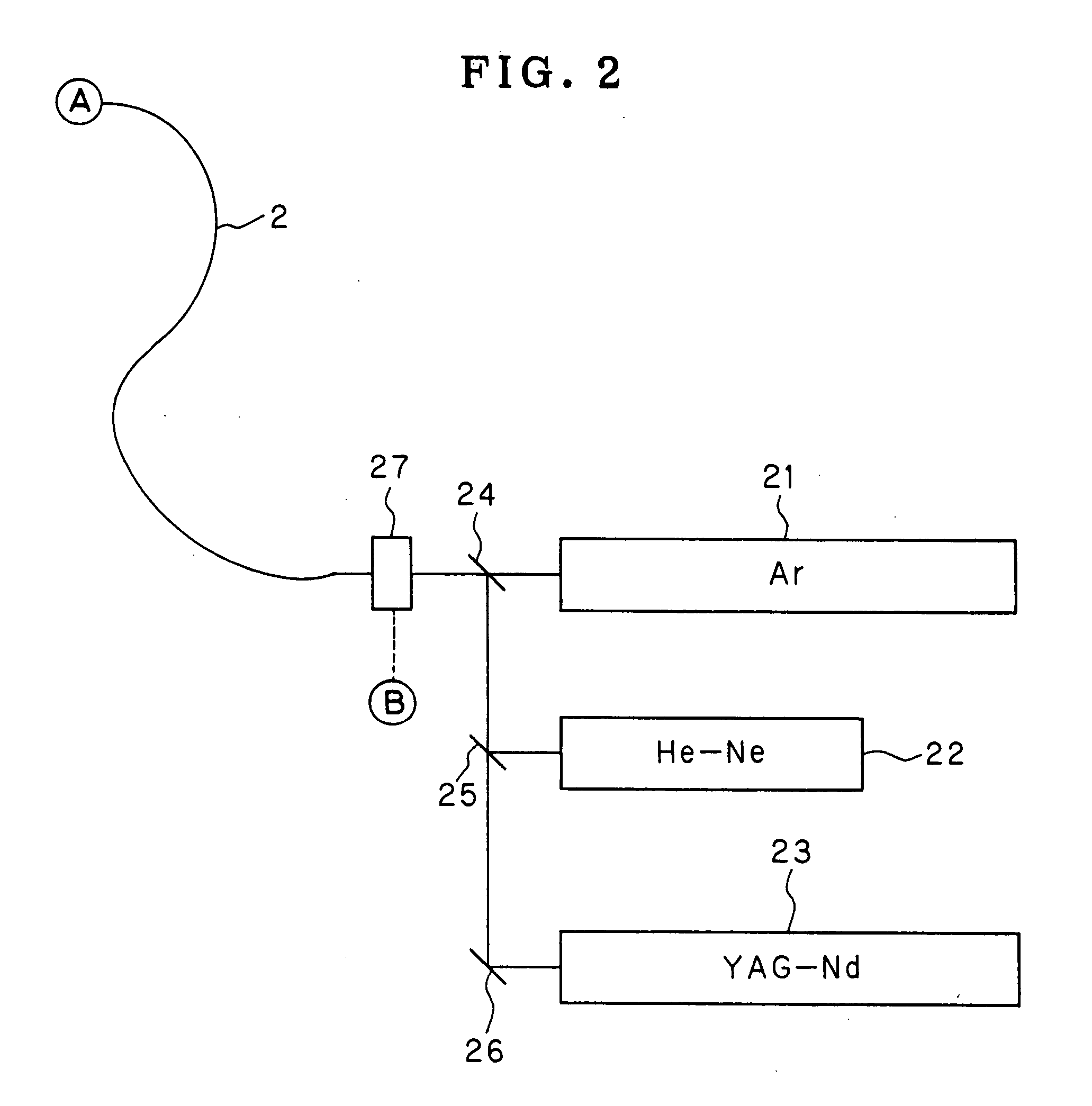
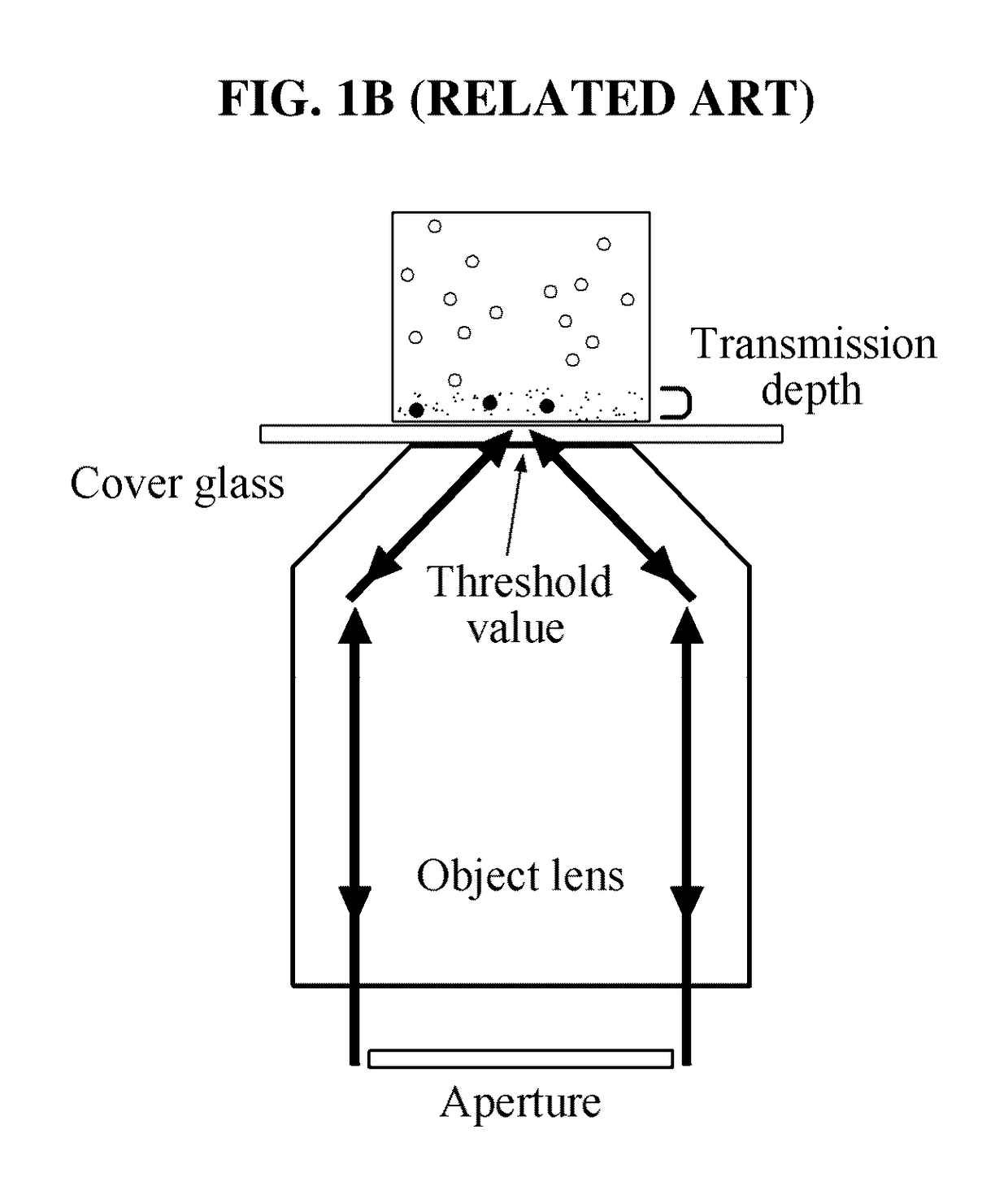
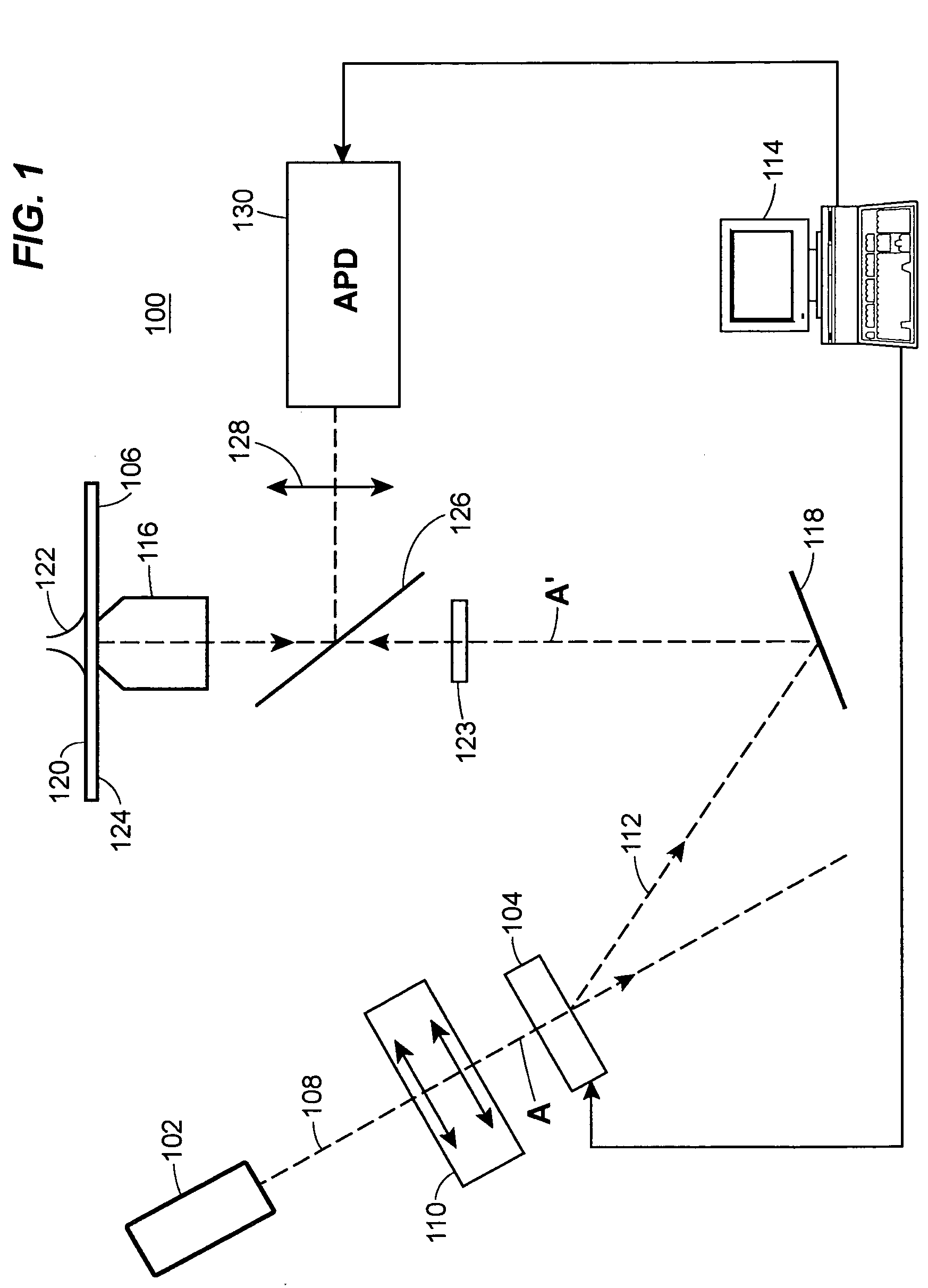
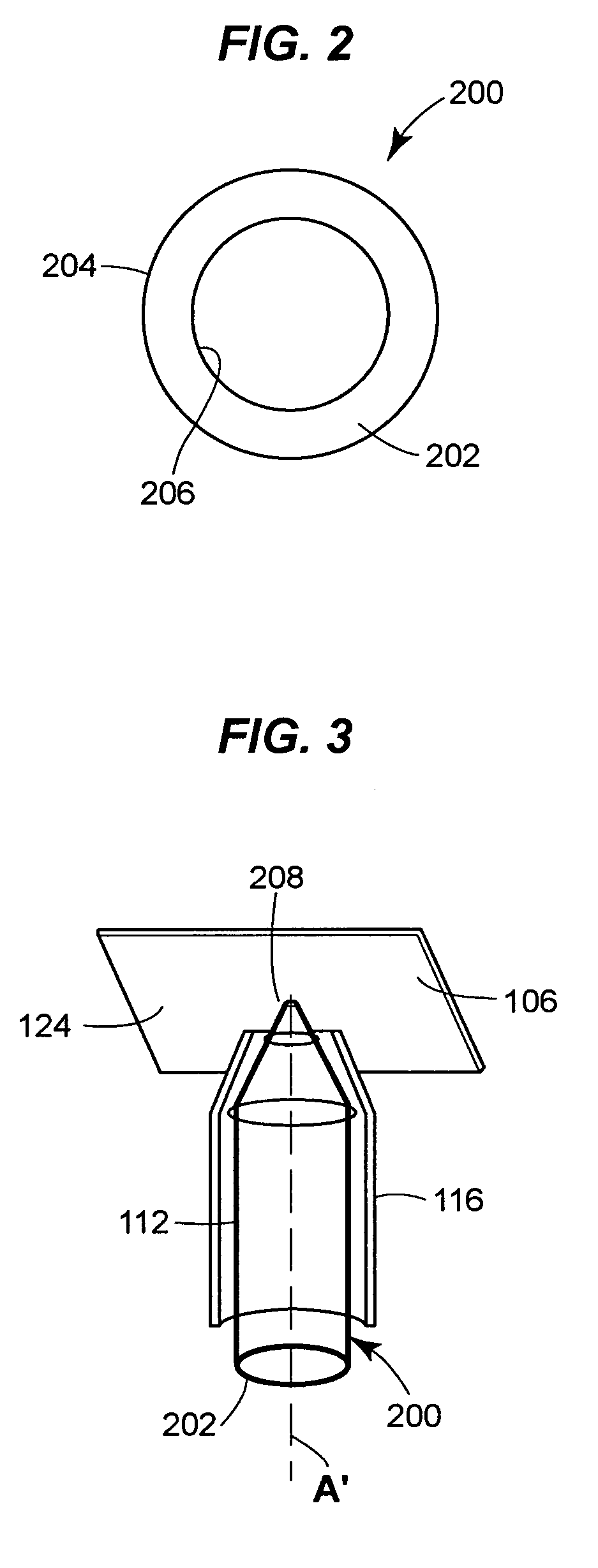
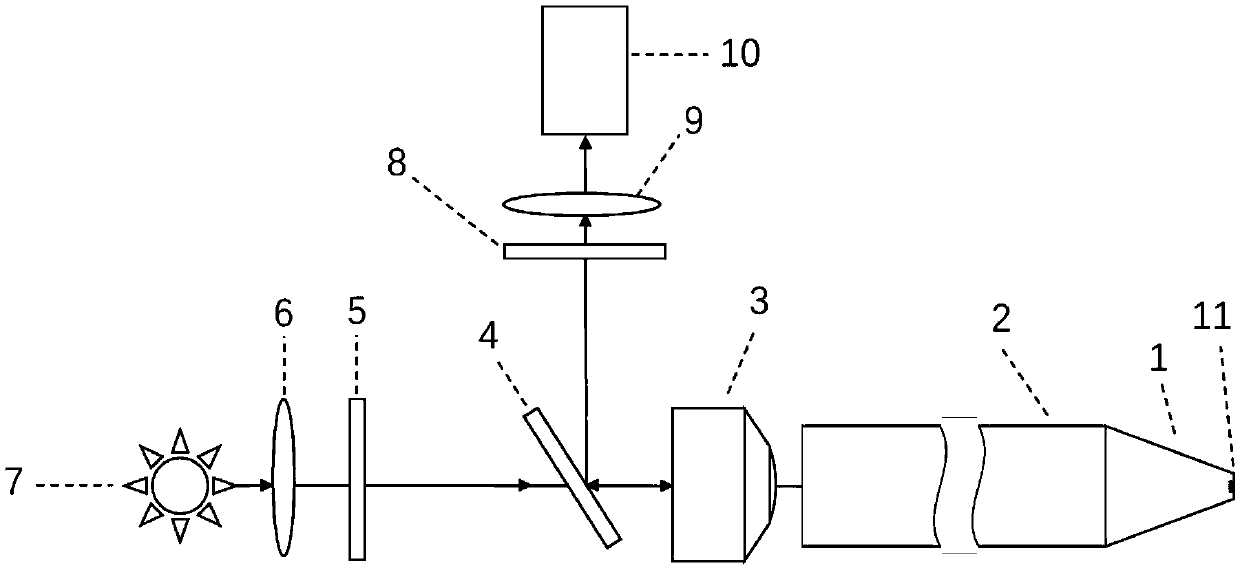
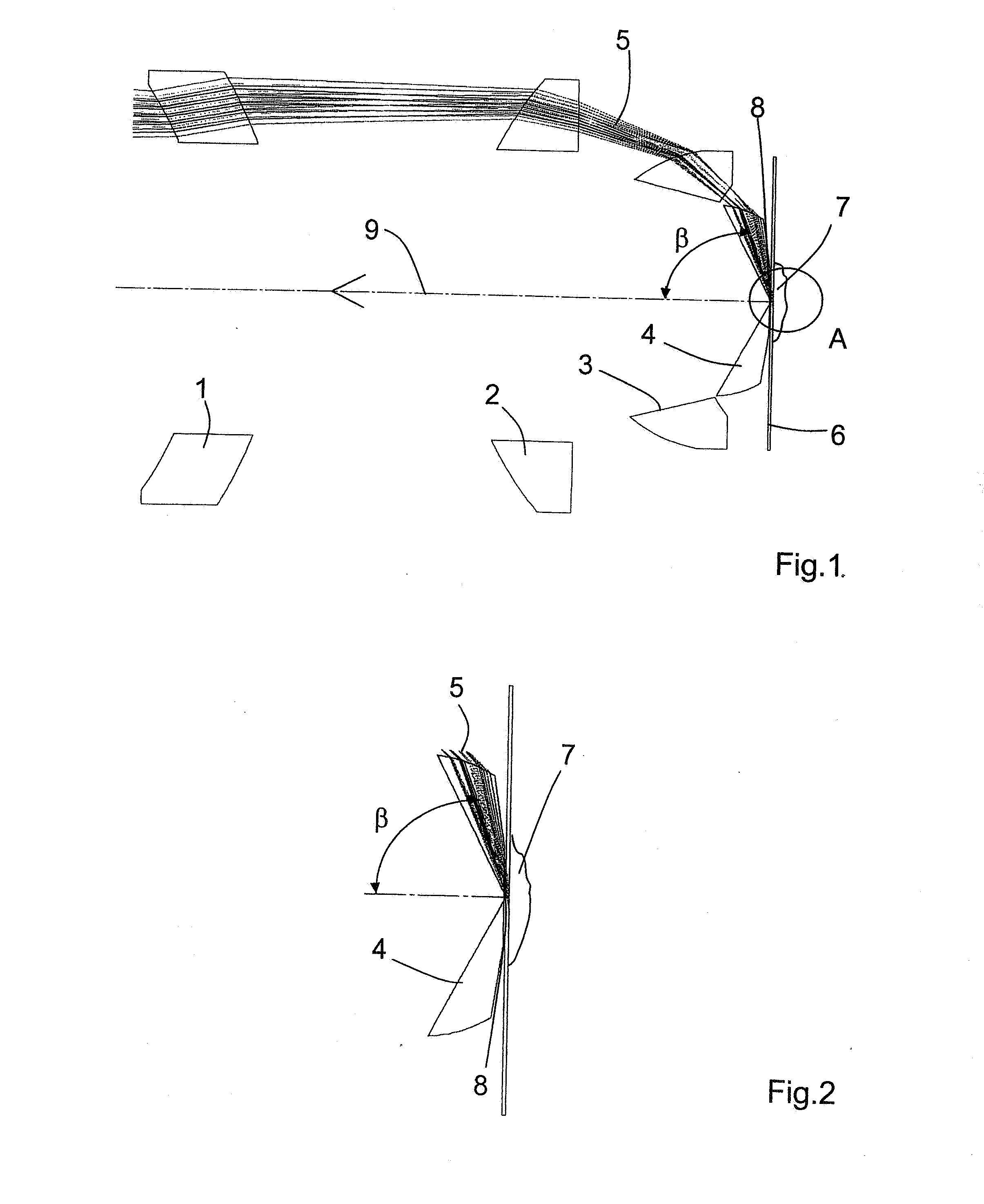
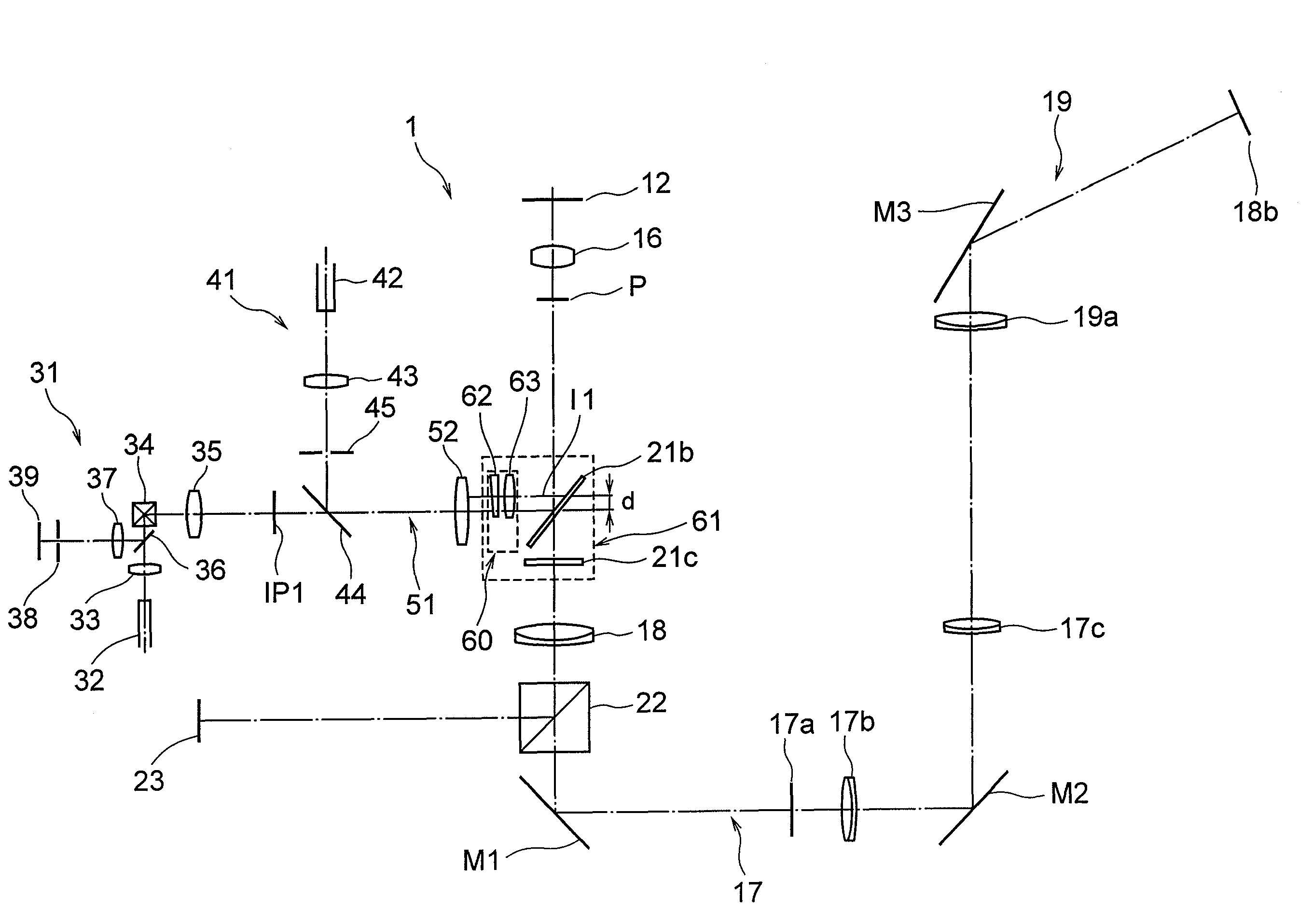
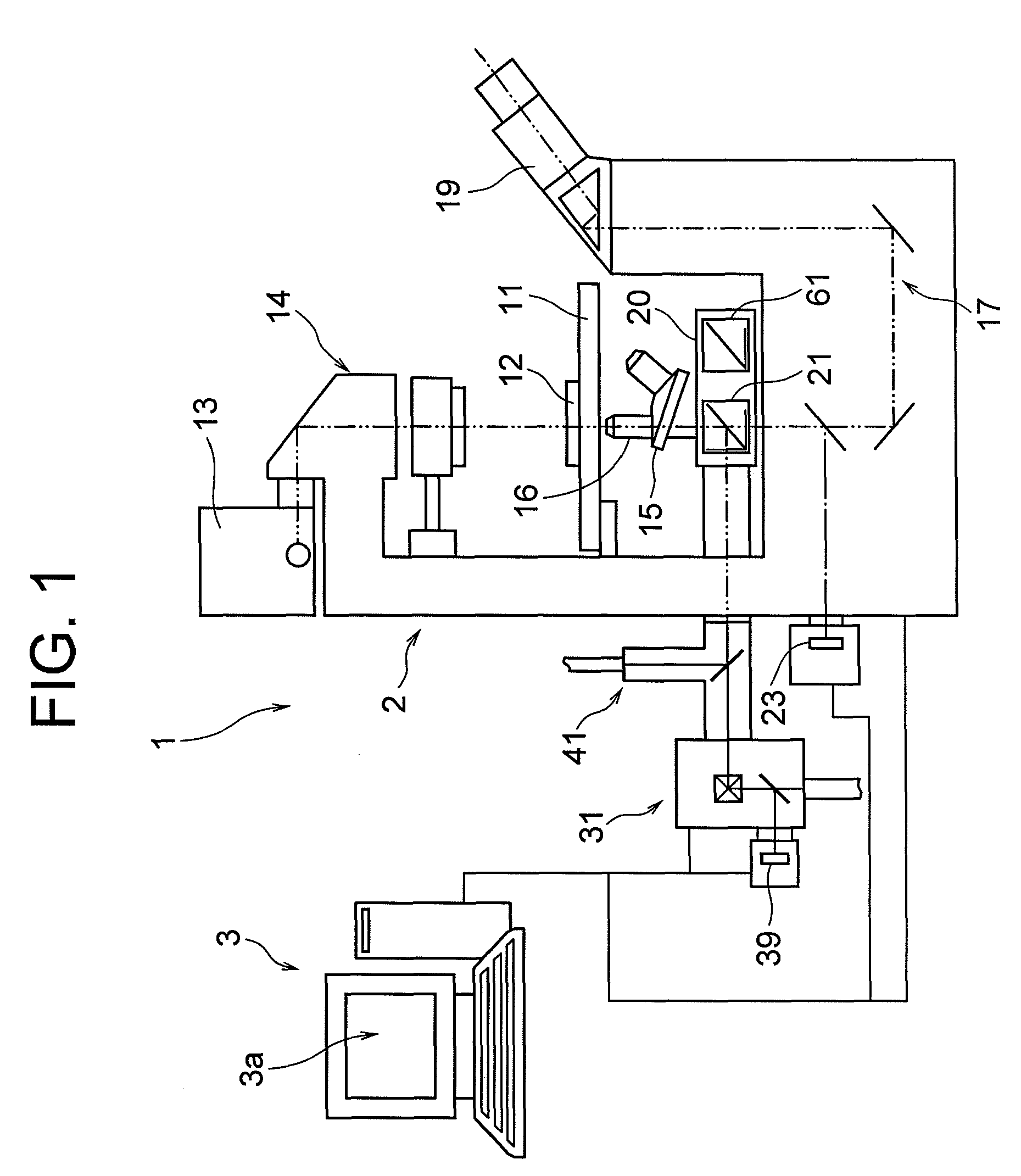
Total internal reflection fluorescence microscope having a conventional white-light source
InactiveUS20020097489A1PhotometryLuminescent dosimetersTotal internal reflectionTotal internal reflection fluorescence microscope
A microscope for use in total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy (TIRFM) is provided. The microscope includes a first white-light source for directing light along a first optical path; an annular slit member disposed in the first optical path, the annular slit member having an annular slit for blocking all but an annulus of light corresponding to the annular slit; and an objective lens for directing the annulus of light to a specimen such that TIRFM of the specimen is achieved. Also provided are various ways for converting the microscope to and from a TIRFM microscope and a conventional microscope.
Owner:OLYMPUS OPTICAL CO LTD
Total internal reflection fluorescence microscope having a conventional white-light source
InactiveUS6597499B2PhotometryLuminescent dosimetersTotal internal reflectionTotal internal reflection fluorescence microscope
A microscope for use in total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy (TIRFM) is provided. The microscope includes a first white-light source for directing light along a first optical path; an annular slit member disposed in the first optical path, the annular slit member having an annular slit for blocking all but an annulus of light corresponding to the annular slit; and an objective lens for directing the annulus of light to a specimen such that TIRFM of the specimen is achieved. Also provided are various ways for converting the microscope to and from a TIRFM microscope and a conventional microscope.
Owner:OLYMPUS OPTICAL CO LTD
Confocal and annular total internal reflection dual-mode microscope system based on scanning galvanometer
PendingCN108956561AEasy to operateLow costFluorescence/phosphorescenceTotal internal reflectionDual mode
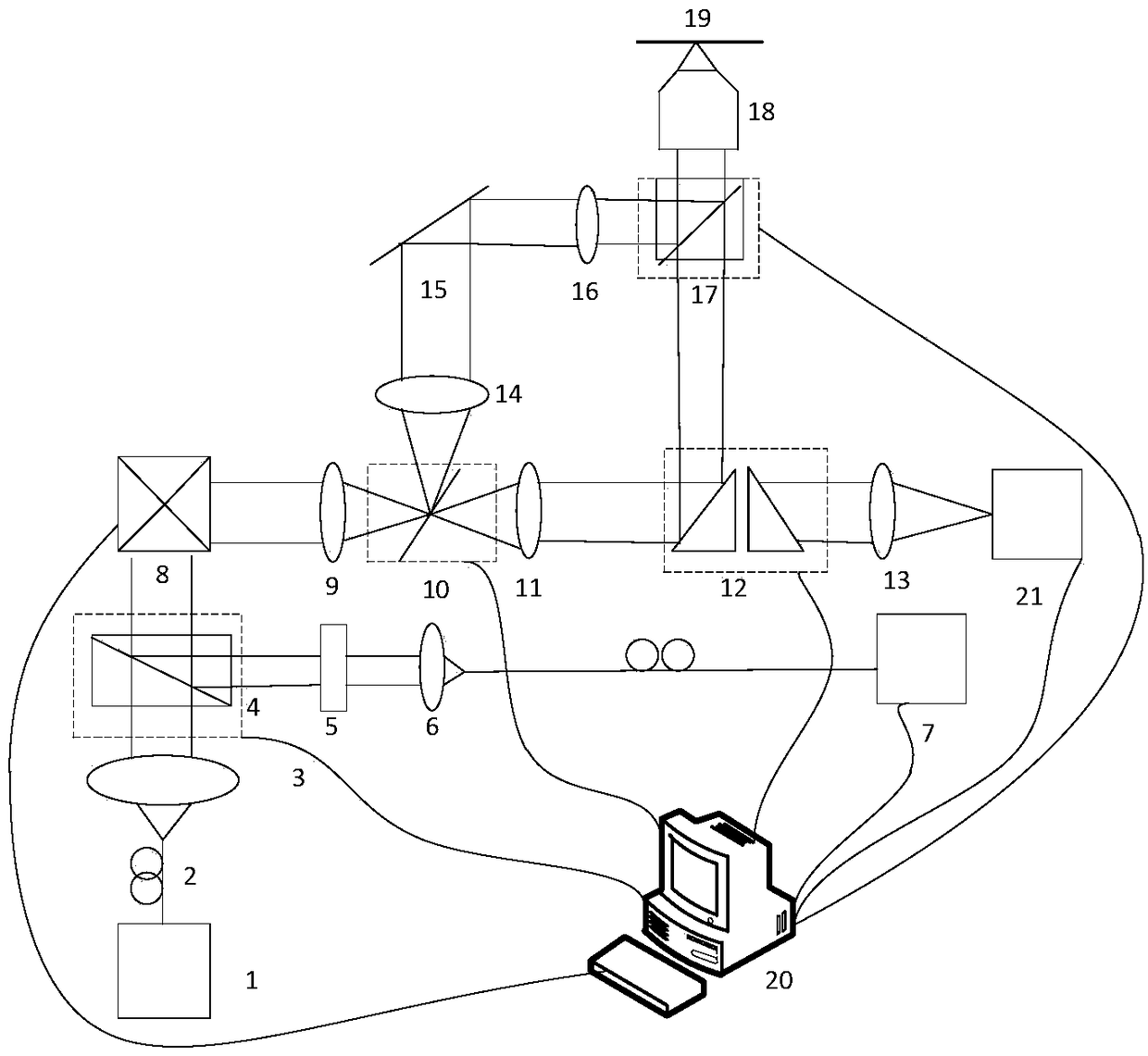
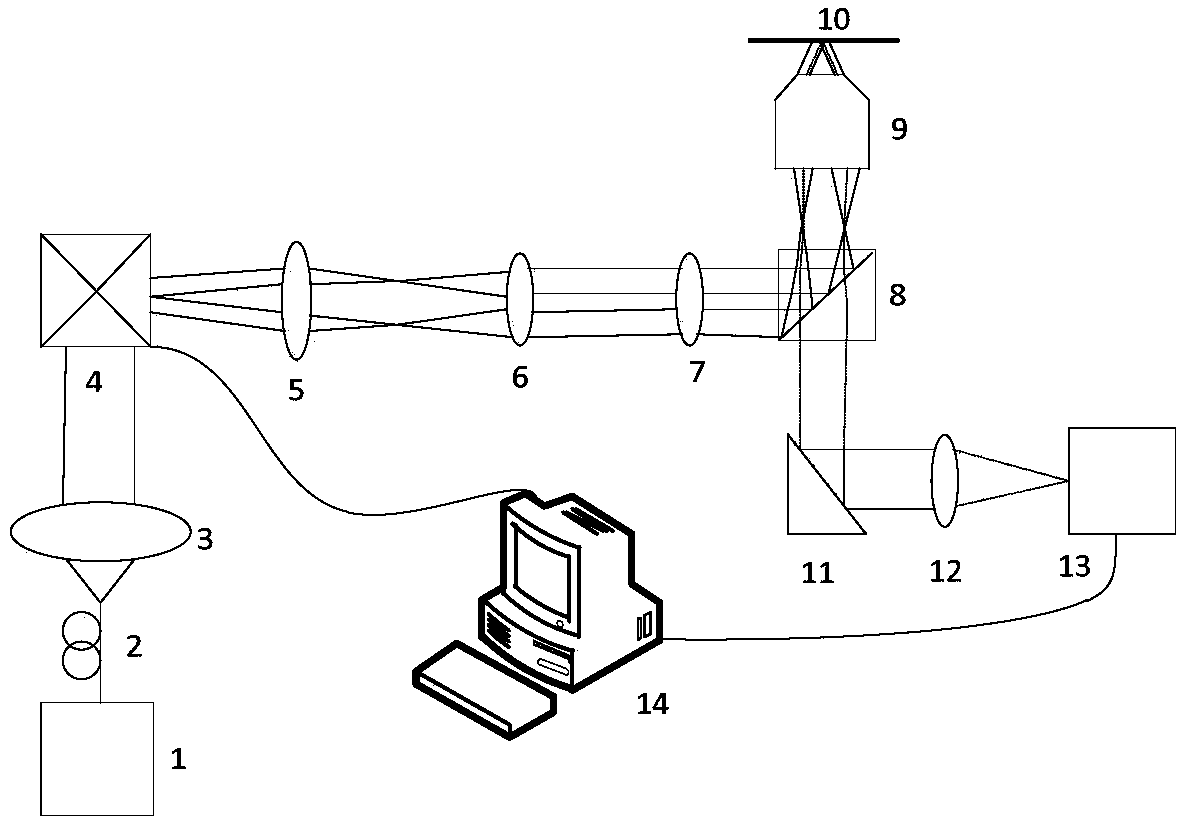
The invention discloses a confocal and annular total internal reflection dual-mode microscope system based on a scanning galvanometer, the confocal and annular total internal reflection dual-mode microscope system includes a light source and a movable first dichroic mirror, the first dichroic mirror is arranged on an optical path, and is used for transmitting excitation light and reflecting fluorescence; a first fluorescence detector is arranged on the reflective optical path of the first dichroic mirror; a two-dimensional scanning galvanometer, a mobile first mirror and a rotatable second mirror are arranged on the transmission optical path of the first dichroic mirror in turn; a mobile second dichroic mirror and a sample table on the reflective optical paths of the first mirror and the second mirror are arranged; a second fluorescent detector on the reflective optical path of the second mirror is also arranged; and a processing controller for controlling and processing is also arranged; the confocal and annular total internal reflection dual-mode microscope system has a laser scanning confocal microscope mode and an annular total internal reflection fluorescence microscope mode,the use efficiency of the system is improved, and the structure of the system is simplified.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Systems for chromatic aberration correction in total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy
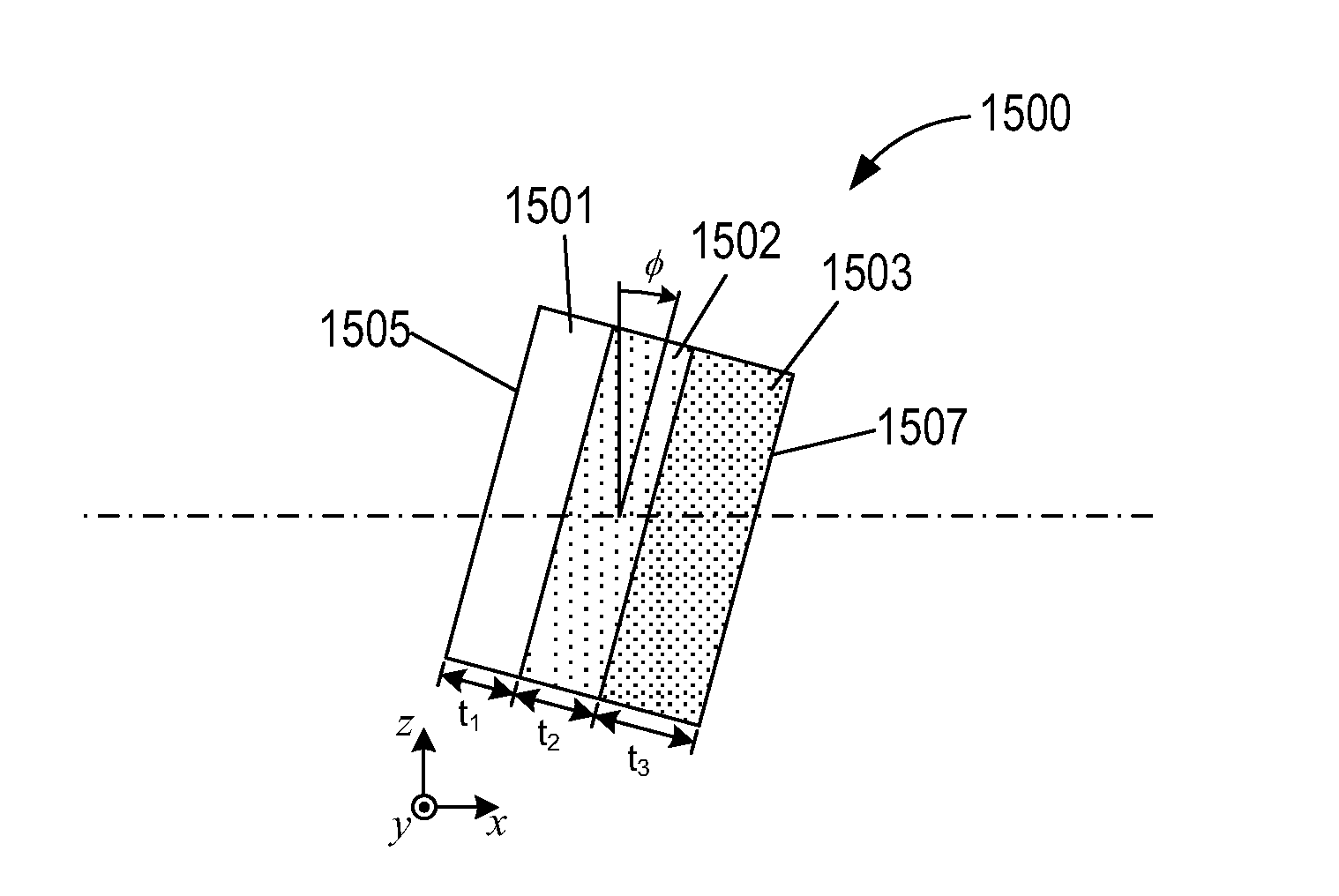
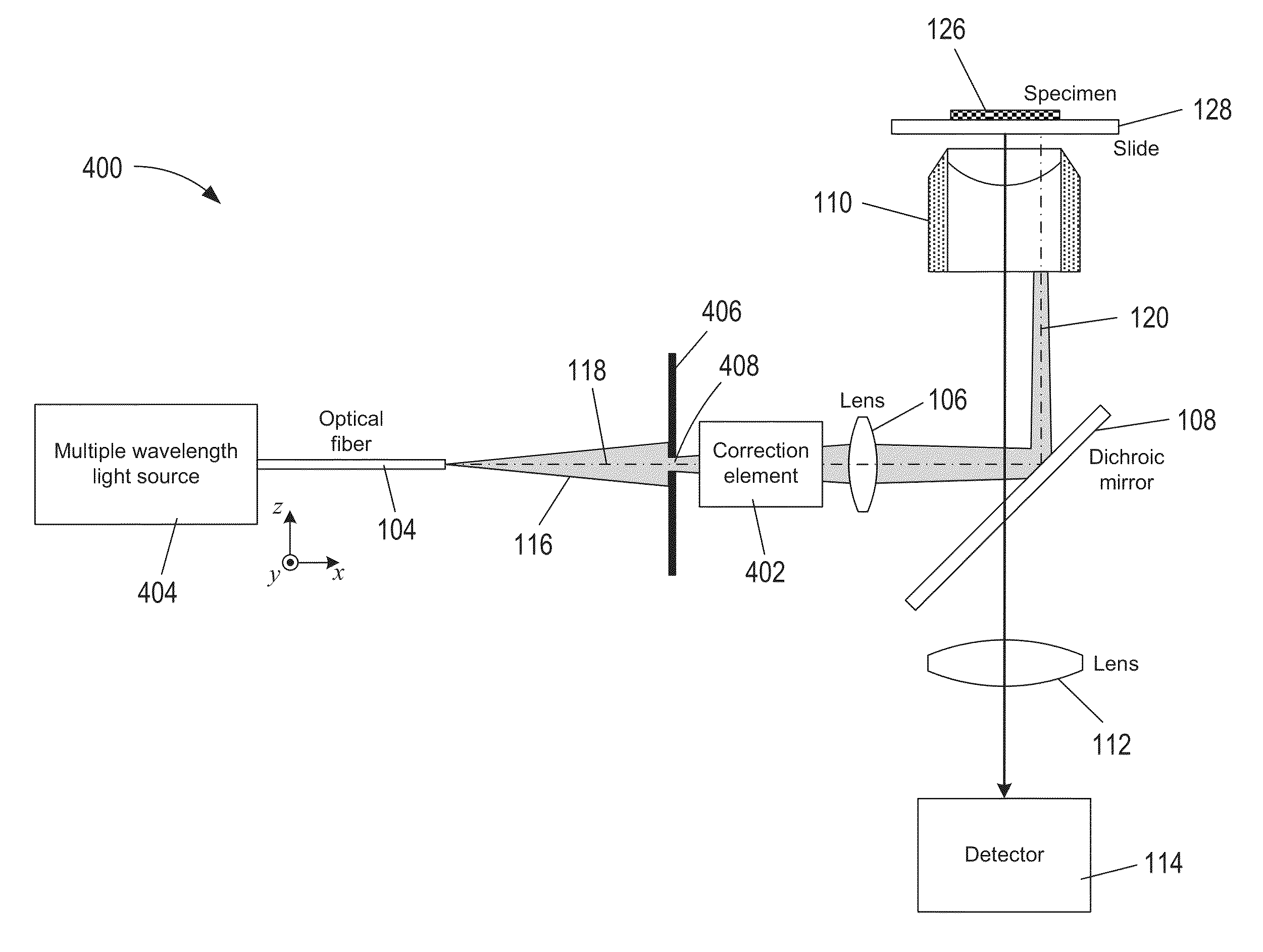
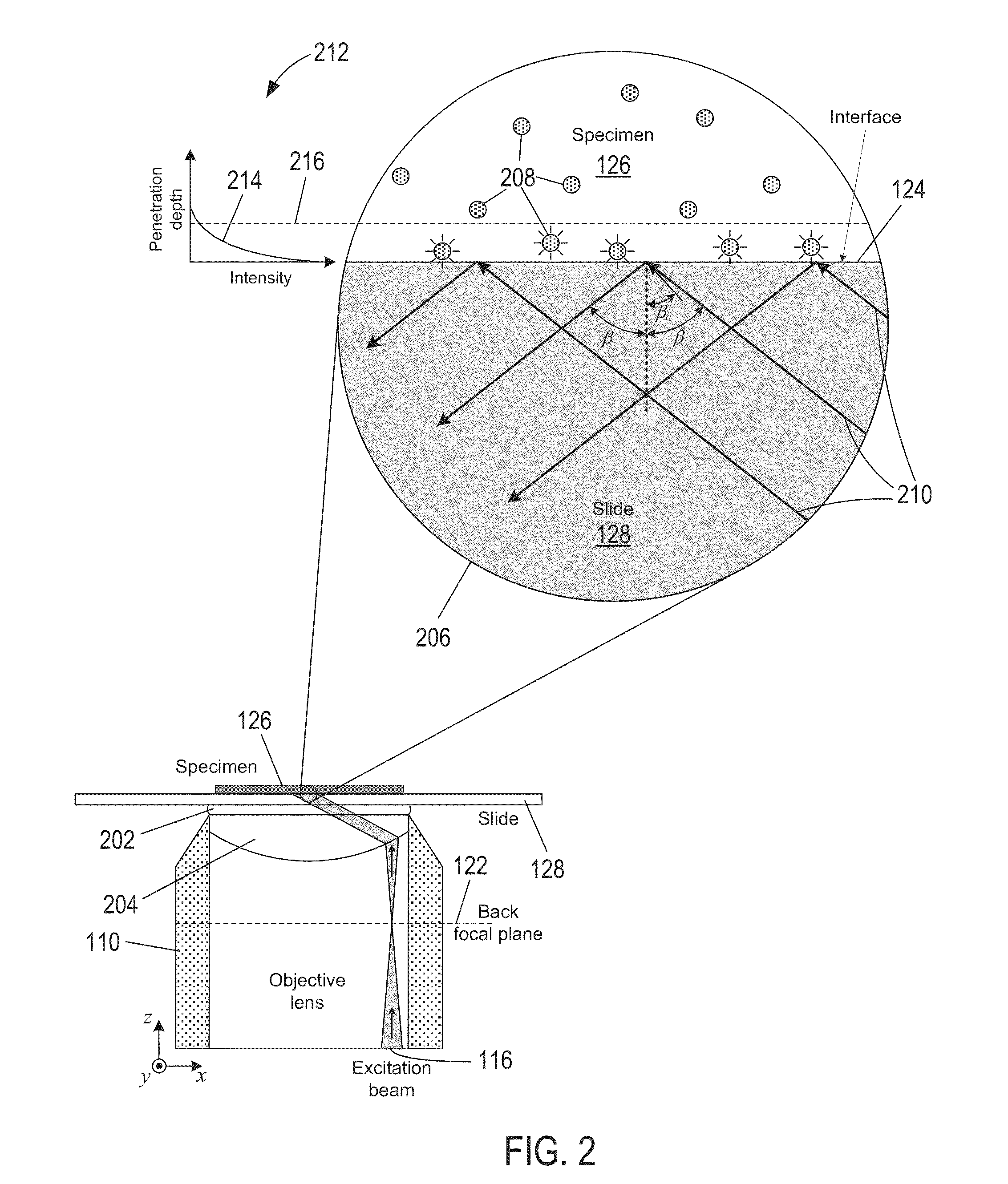
Correction elements that can be incorporated in objective-based TIRF microscopy instruments to correct for chromatic aberrations are described. A correction element can be placed between a multiple wavelength excitation beam source and the microscope objective lens. In one aspect, the thickness of the correction element is defined to compensate for different axial positions of the focal points associated with each excitation wavelengths traveling along the outer edge of lenses comprising a microscope objective lens. In another aspect, the correction element can be angled and / or configured so that the different wavelengths of multiple wavelength excitation light are shifted to adjust the angle of incidence for each wavelength at the specimen / substrate interface.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
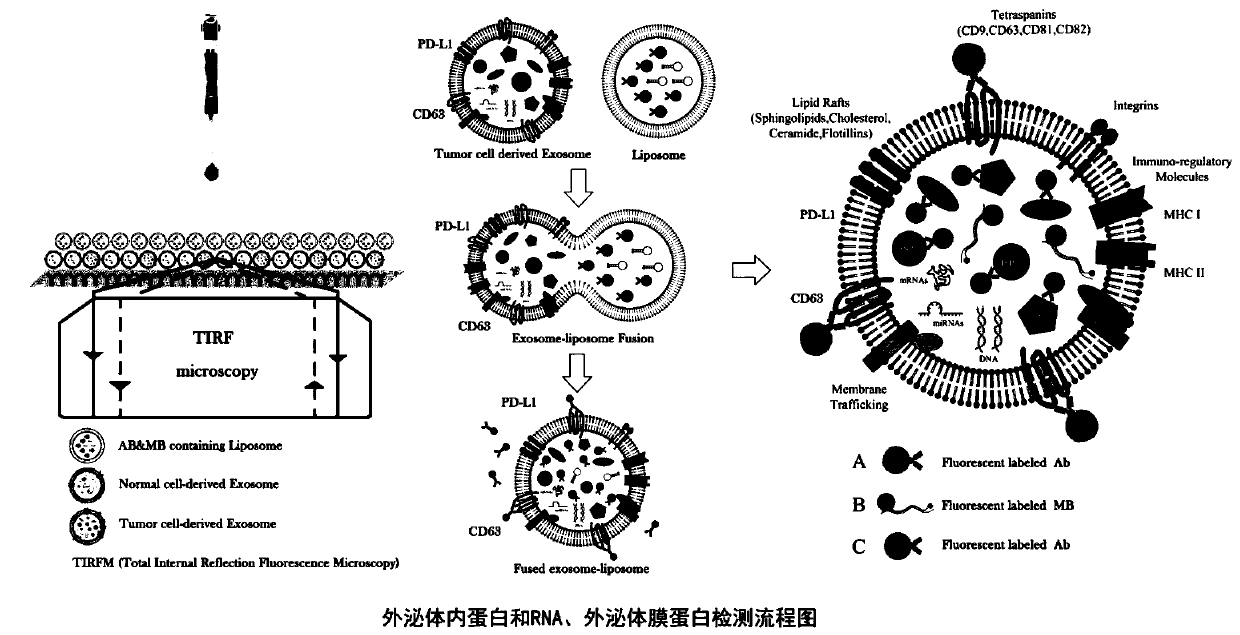
Method for simultaneously detecting protein, RNA and exosome membrane protein in exosome
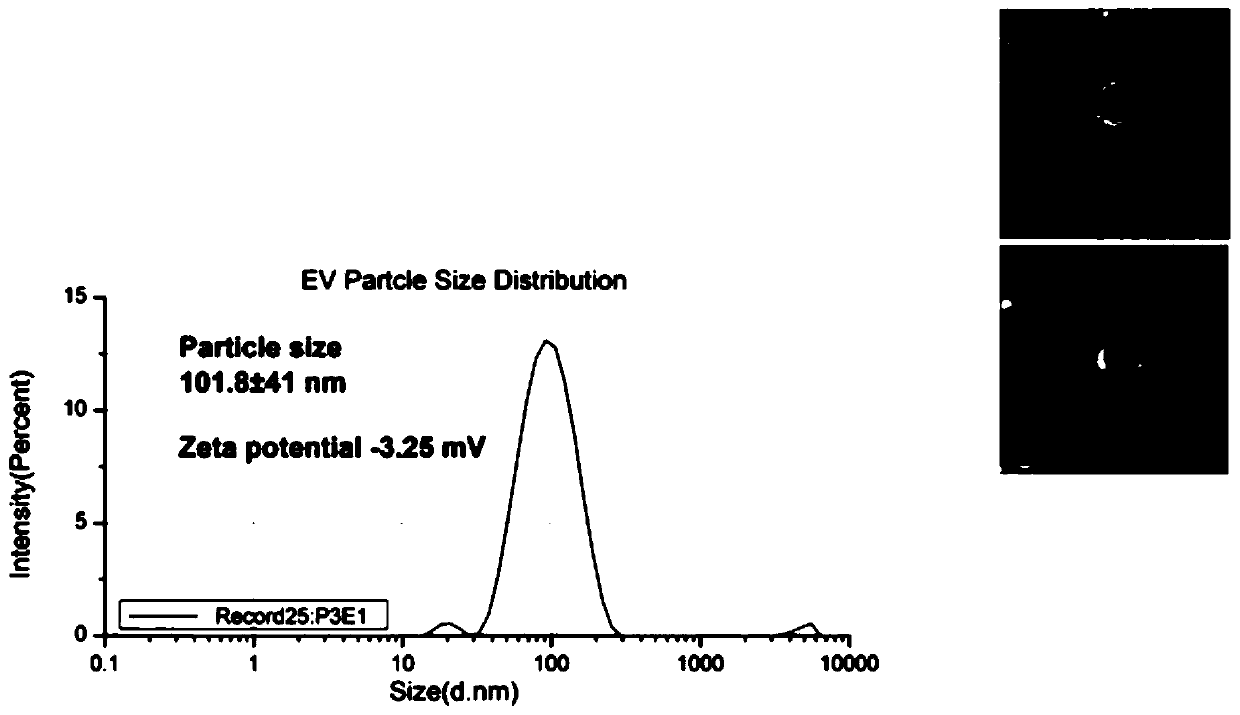
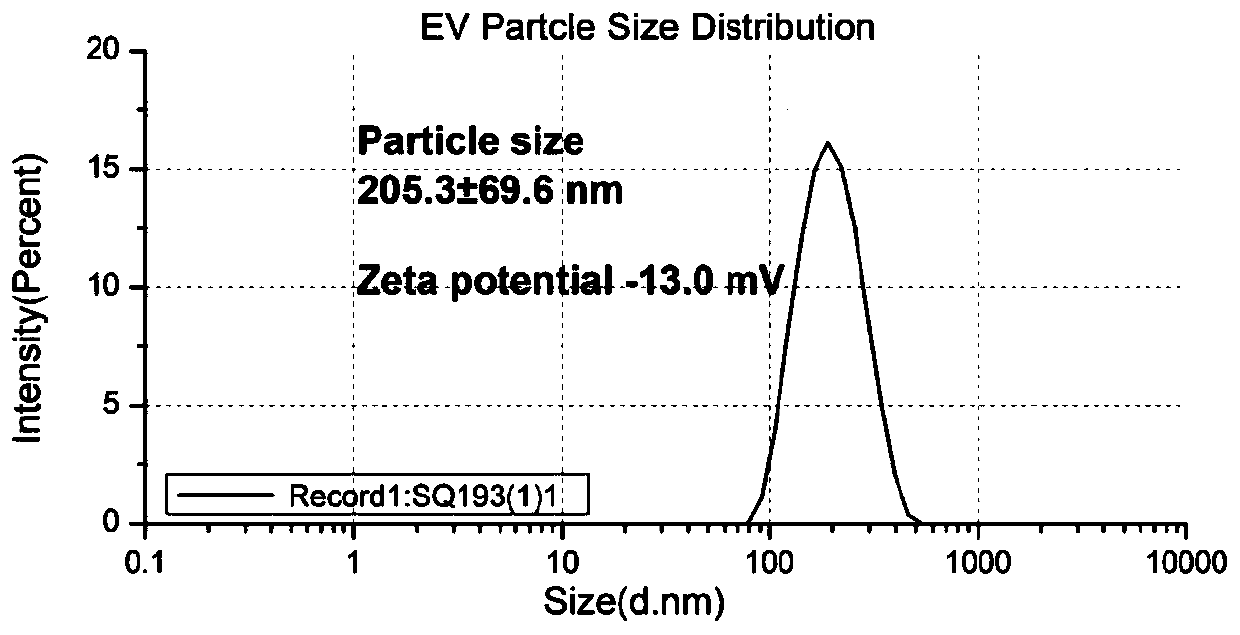
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously detecting protein, RNA and exosome membrane protein in exosome, and belongs to the technical field of exosome detection. The method comprises the following steps: capturing exosome in a sample; detecting the corresponding membrane protein; preparing nano particles; fusing the nanoparticles with the exosome; photographing and imaging by a total internal reflection fluorescence microscope, and analyzing and processing data. Verification is carried out in the aspects of exosome characterization detection, cell supernatant exosome membrane protein and mRNA expression comparison experiments, human plasma exosome specificity detection, human plasma exosome membrane protein comparison experiments and detection of various human plasma exosome intracellular proteins, RNA and membrane proteins. Compared with an existing recognized exosome detection technology, a comparison experiment shows that the same marker detection result of the technologyfor simultaneously detecting the same sample is consistent with that of the recognized technology, and the technology can be used for simultaneously detecting protein, RNA and exosome membrane protein in the exosome and judging the sample difference.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIXIANG CO LTD
Microscope switchable between observation modes
A high-performance microscope allows total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy, fluorescence microscopy and interference reflection microscopy (or reflection contrast microscopy) to be selectively performed by using the same objective. The microscope has an objective optical system and an image-forming optical system for imaging light from a sample passing through the objective optical system onto an image pickup device. An optical member is provided in a viewing optical path extending from the objective optical system to the image-forming optical system. The optical member reflects illuminating light from an illuminating optical system so that the illuminating light enters the objective optical system, and allows the light from the sample passing through the objective optical system to pass through the image-forming optical system. The illuminating optical system is provided therein with a mechanism for adjusting an illuminating light collecting position on a pupil plane of the objective optical system in a direction perpendicular to an optical axis. The viewing optical path is provided therein with a wavelength selecting device for selecting an observation wavelength according to the illuminating light collecting position on the pupil plane of the objective optical system.
Owner:KAWANO YOSHIHIRO
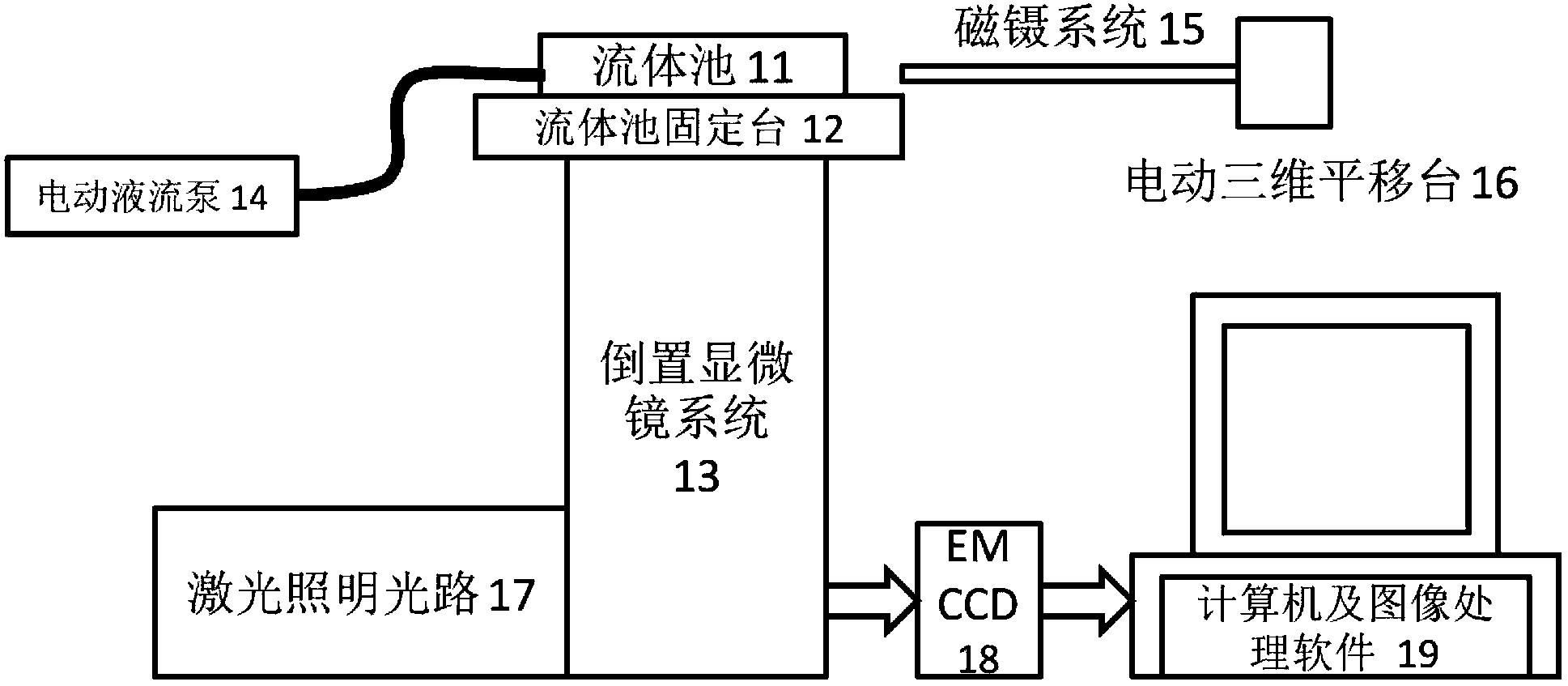
Single molecule fluorescence apparatus and application method thereof
InactiveCN103424386AAchieve Controlled StretchHigh precision observationFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescence microscopeHandling system
The invention discloses a single molecule fluorescence apparatus and an application method thereof. The single molecule fluorescence apparatus comprises a lens-type full internal reference fluorescence microscope system, an image acquisition and processing system, a controllable magnetic tweezer system and a fluid pool system. The fluid pool system comprises a fluid pool fixed station, a fluid pool and an electric liquid flow pump; one side of the fluid pool fixed station is fixed on a sample stage of an inverted microscope of the full internal reference fluorescence microscope system, and the other side of the fluid pool fixed station is fixed with the fluid pool. The electric liquid flow pump and the fluid pool are connected; and the bottom of the fluid pool is equipped with more than one column of DNA fixed points. Columns of DNA fixed points are arranged in the fluid pool, so controllable fixing of a large amount of DNA can be realized. Through the transverse magnetic tweezer system, controllable drawing on a large amount of DNA molecules can be realized; and high precision observation on protein fluorescence signals can be realized without dyeing on DNA molecules.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
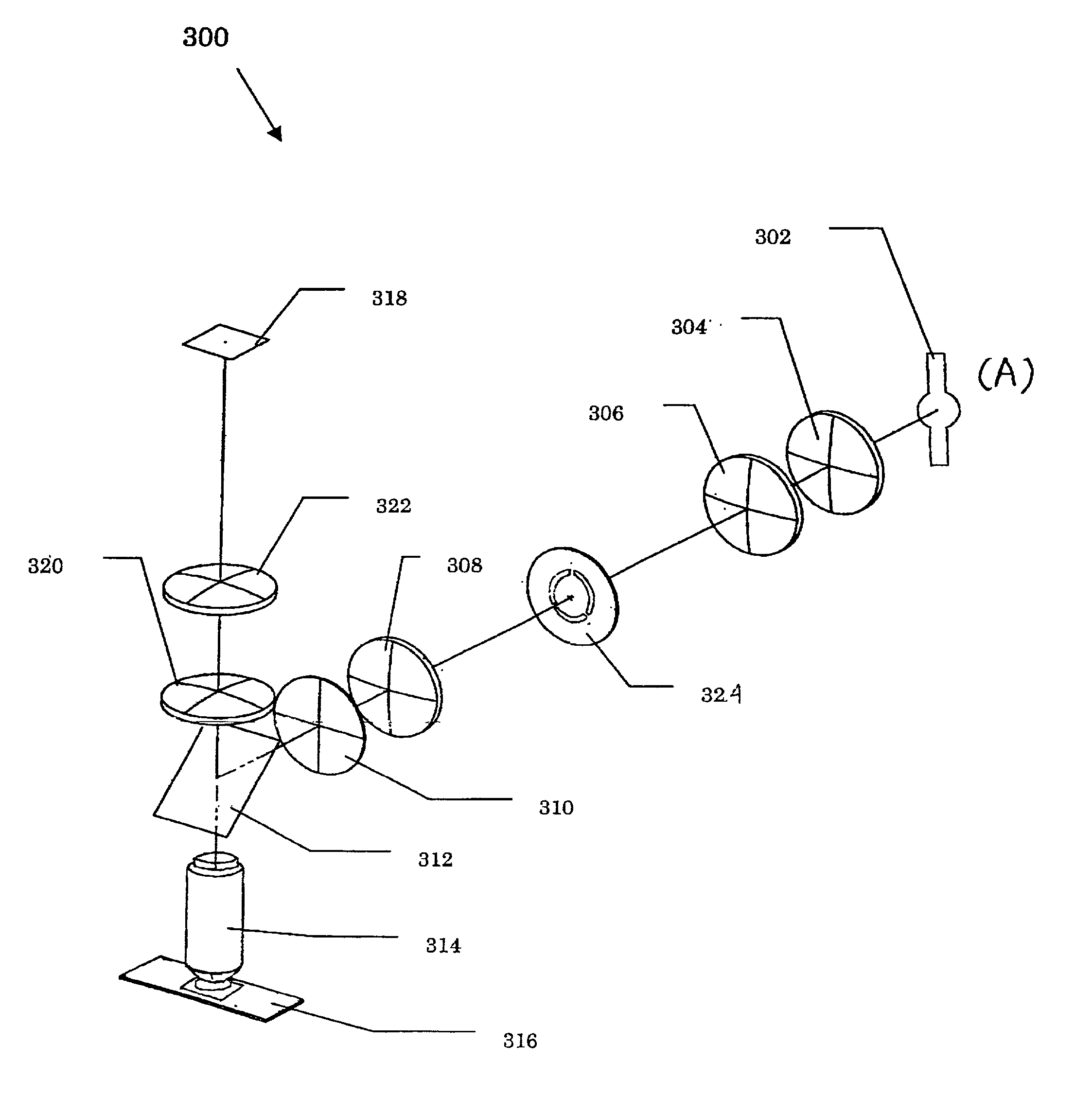
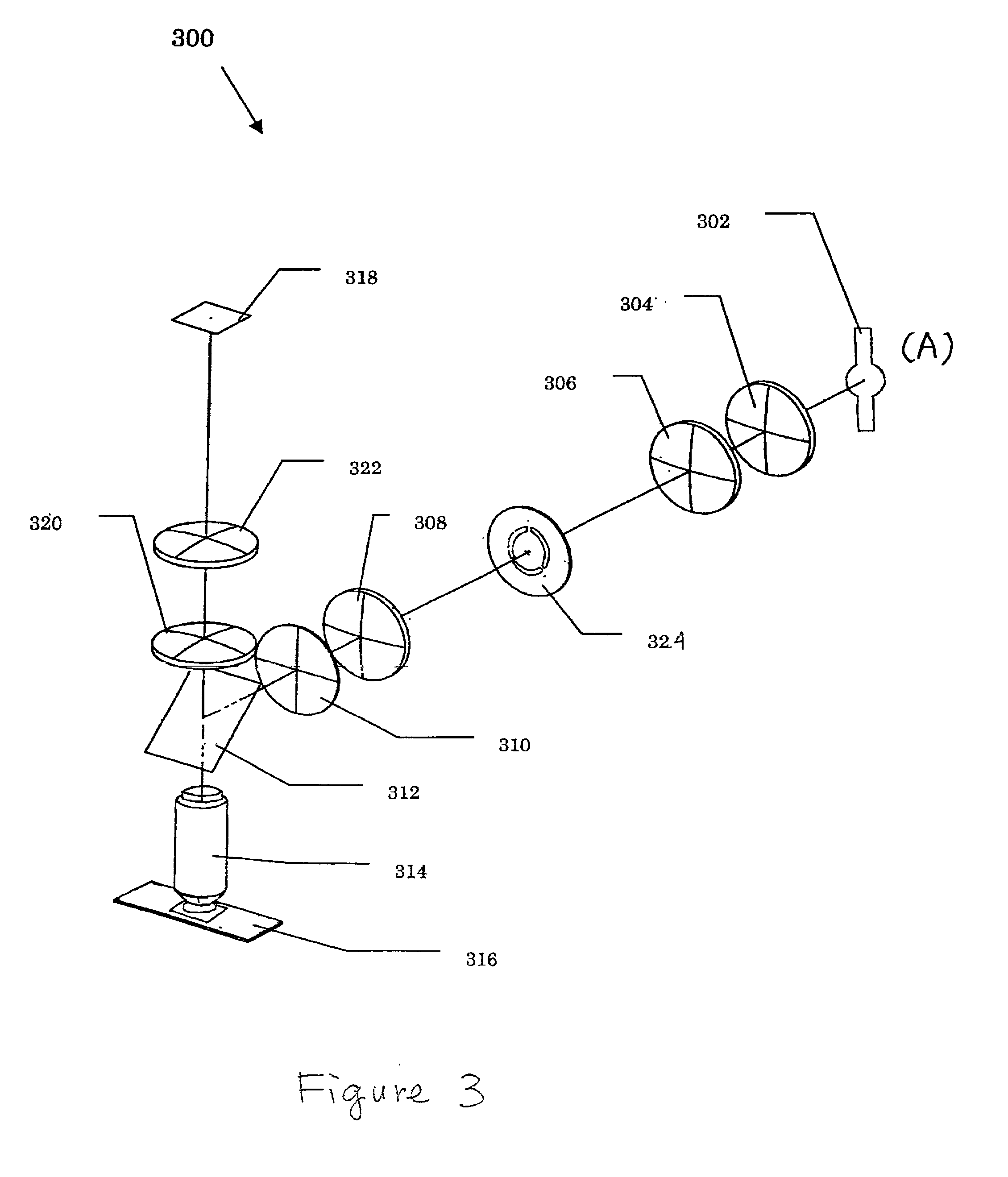
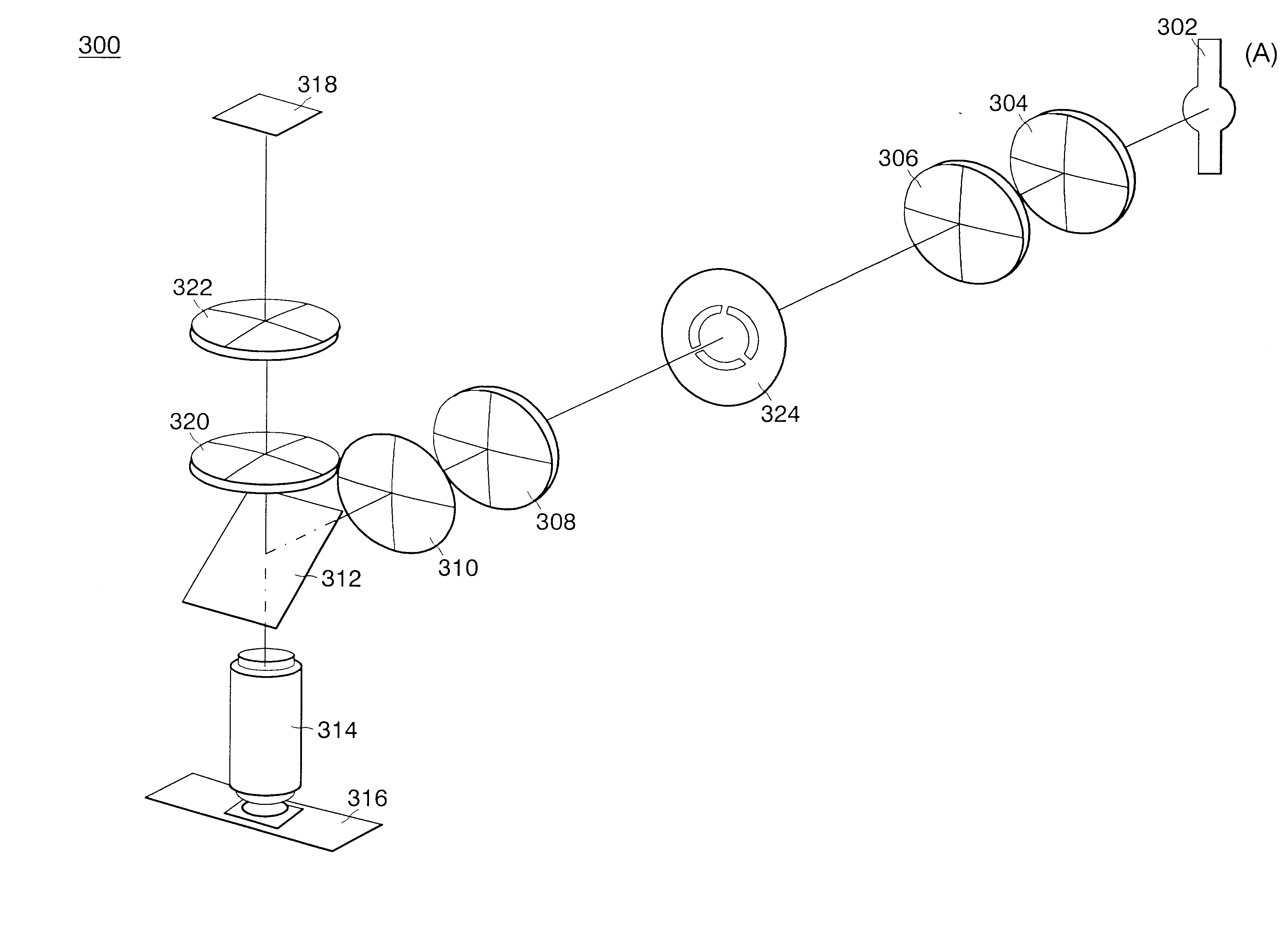
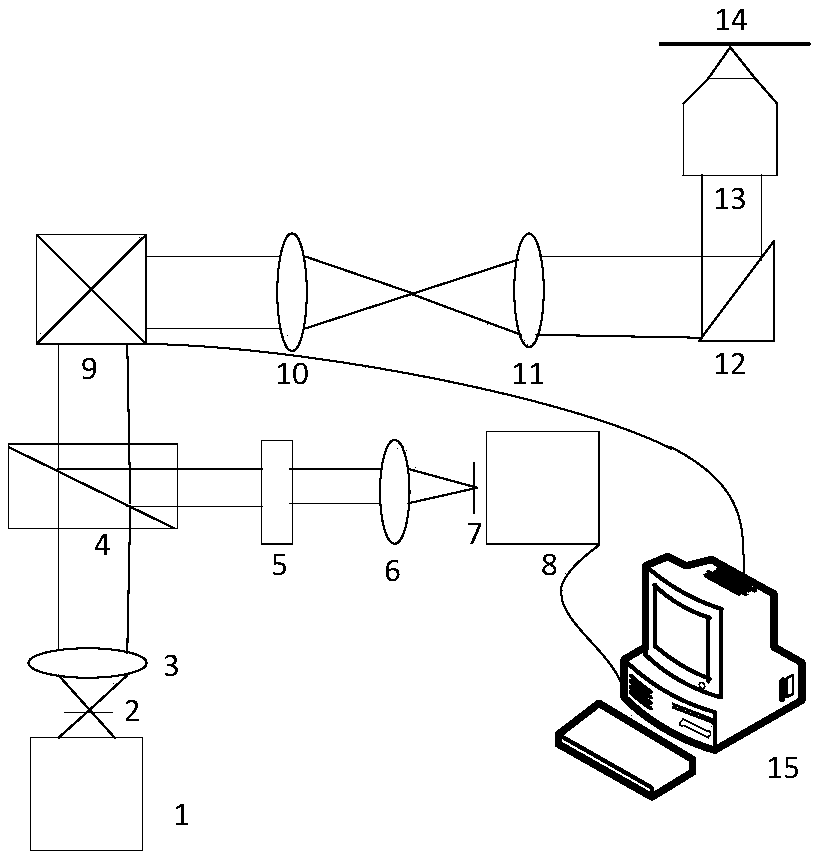
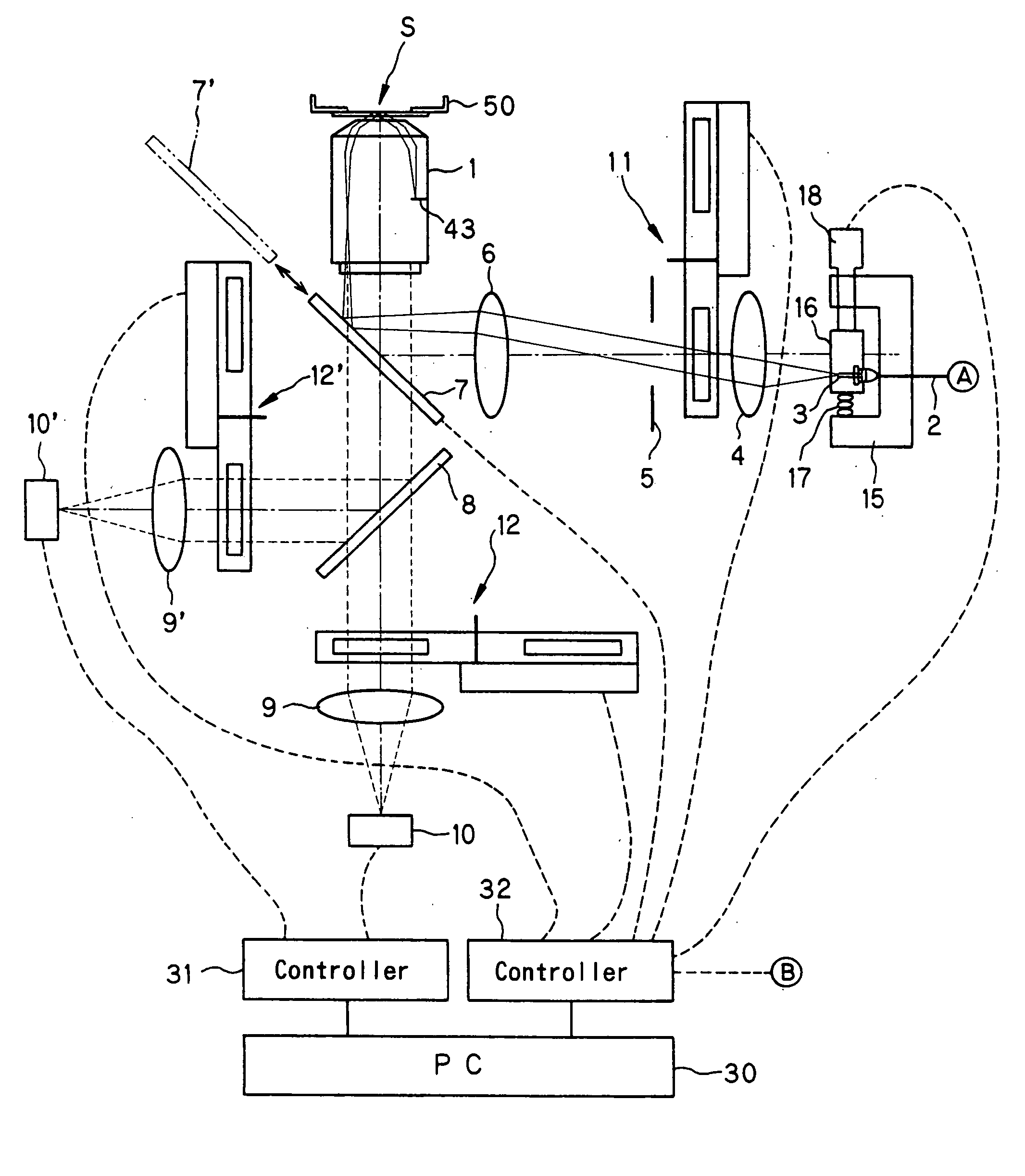
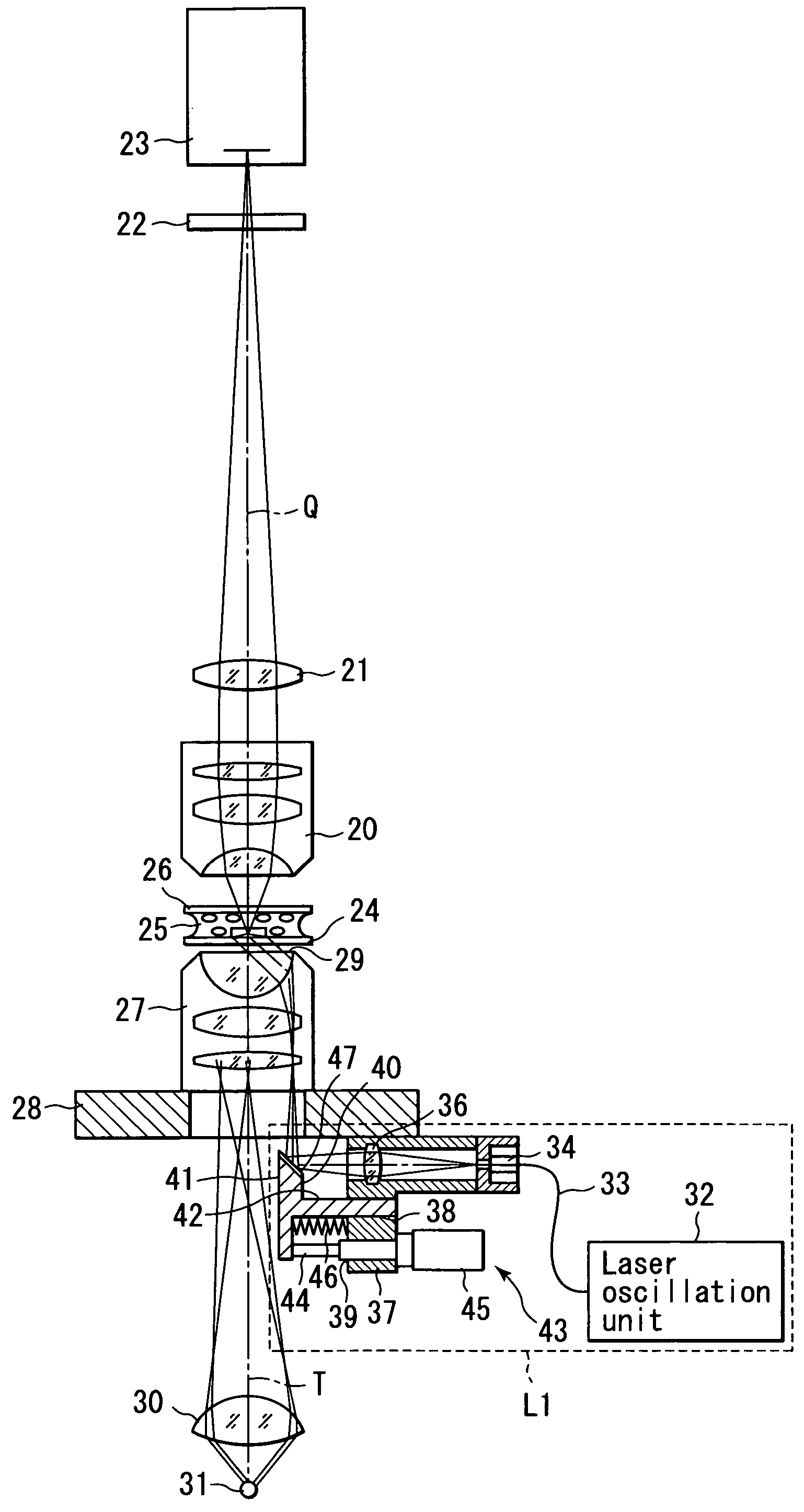
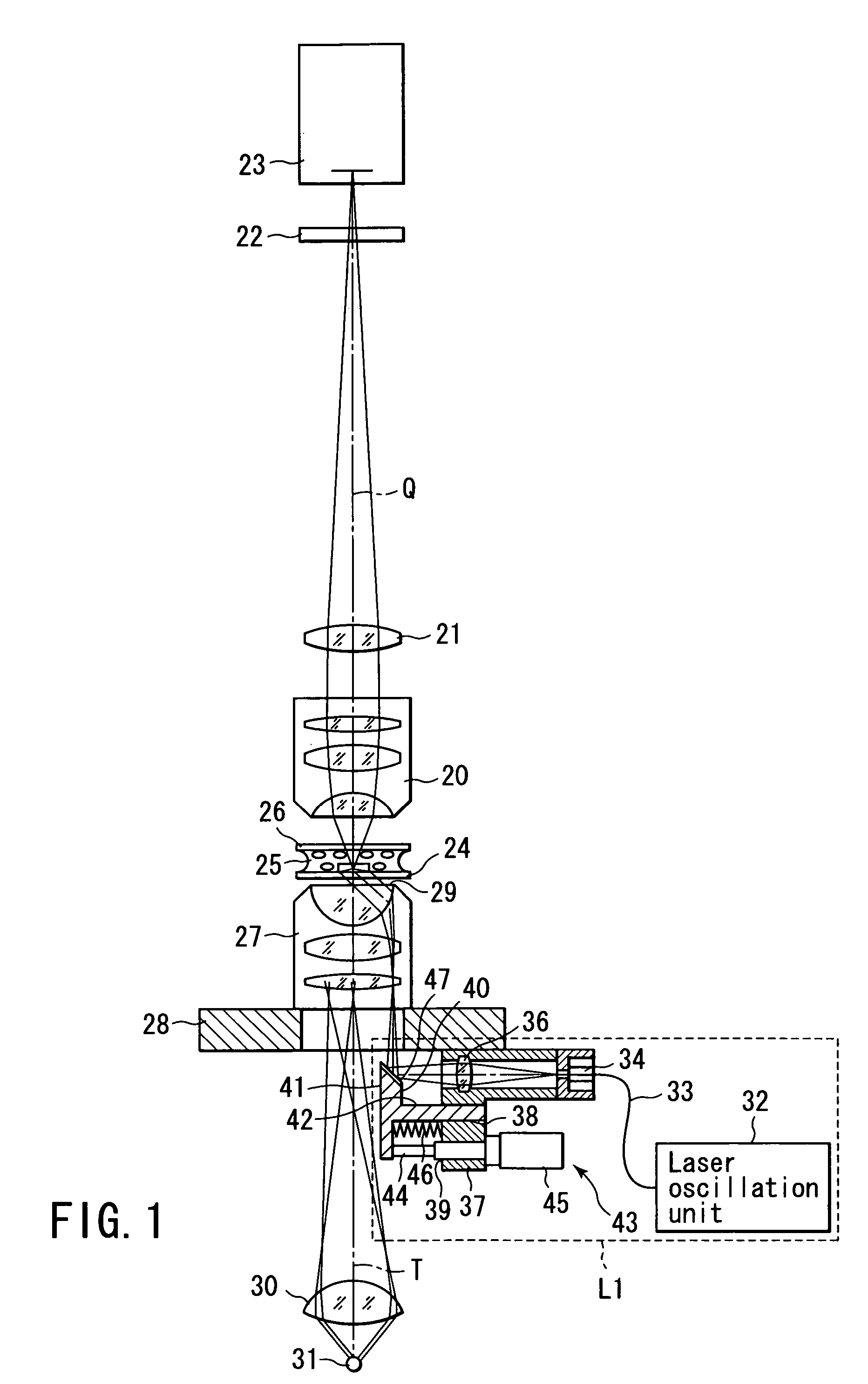
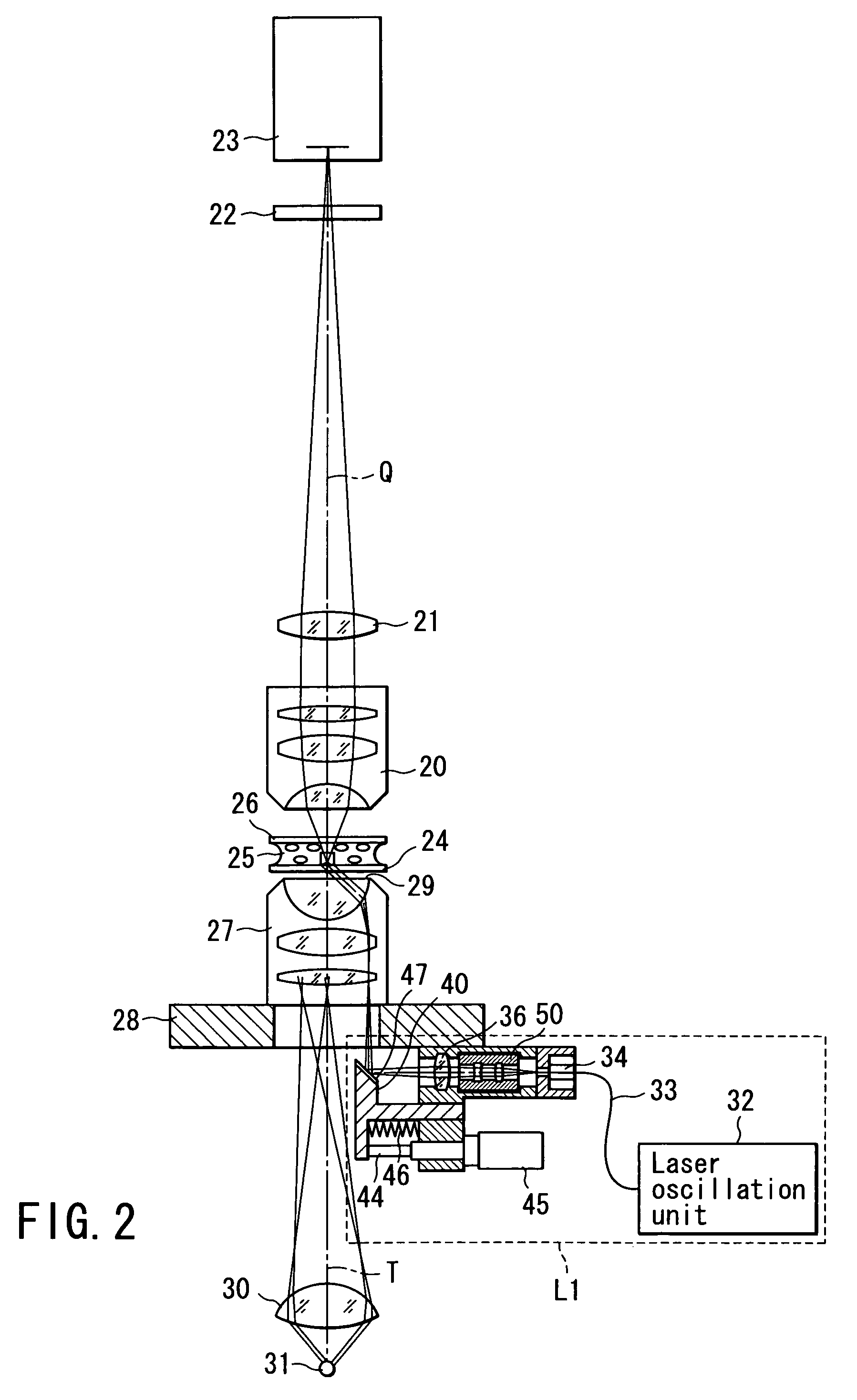
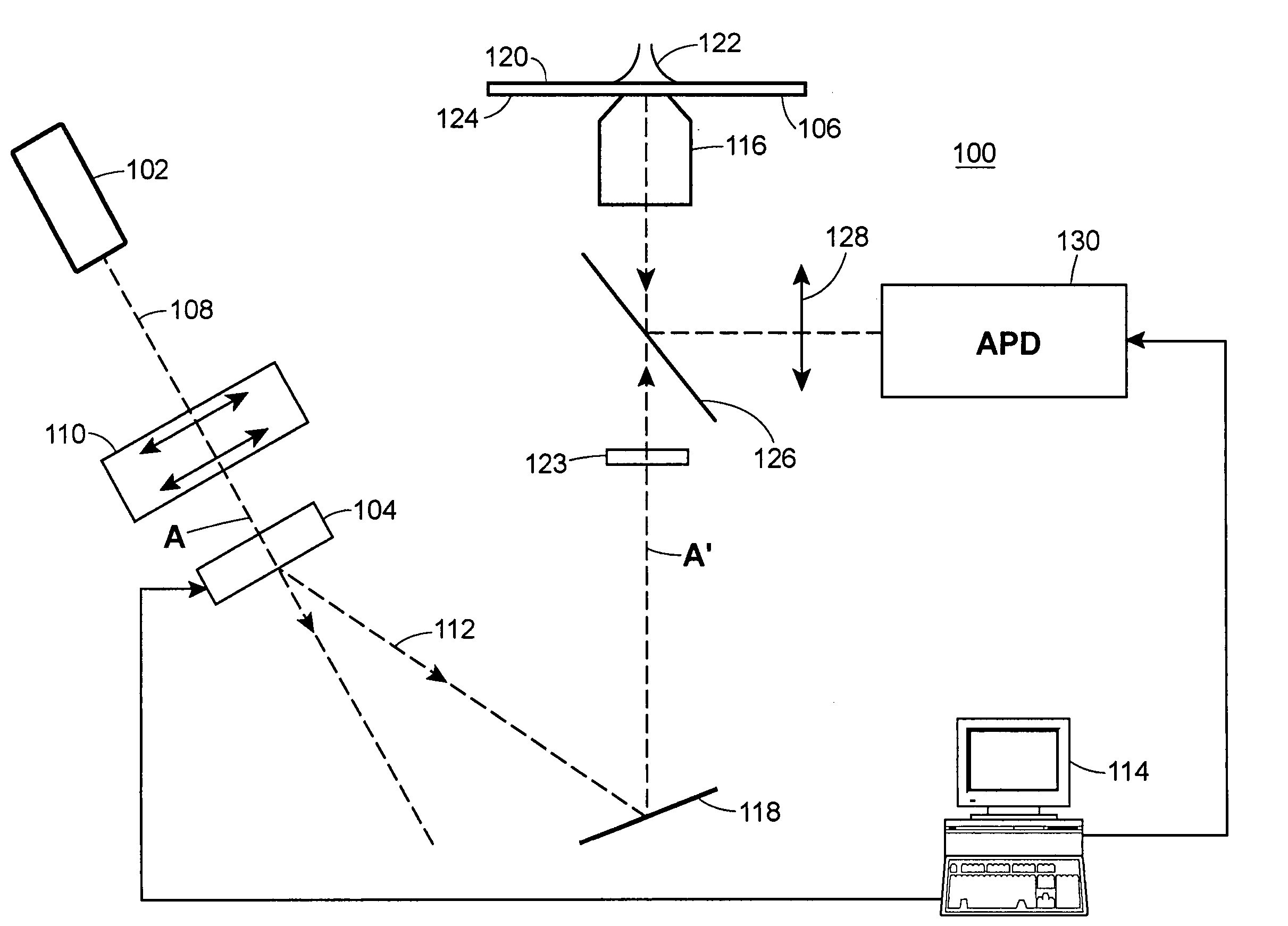
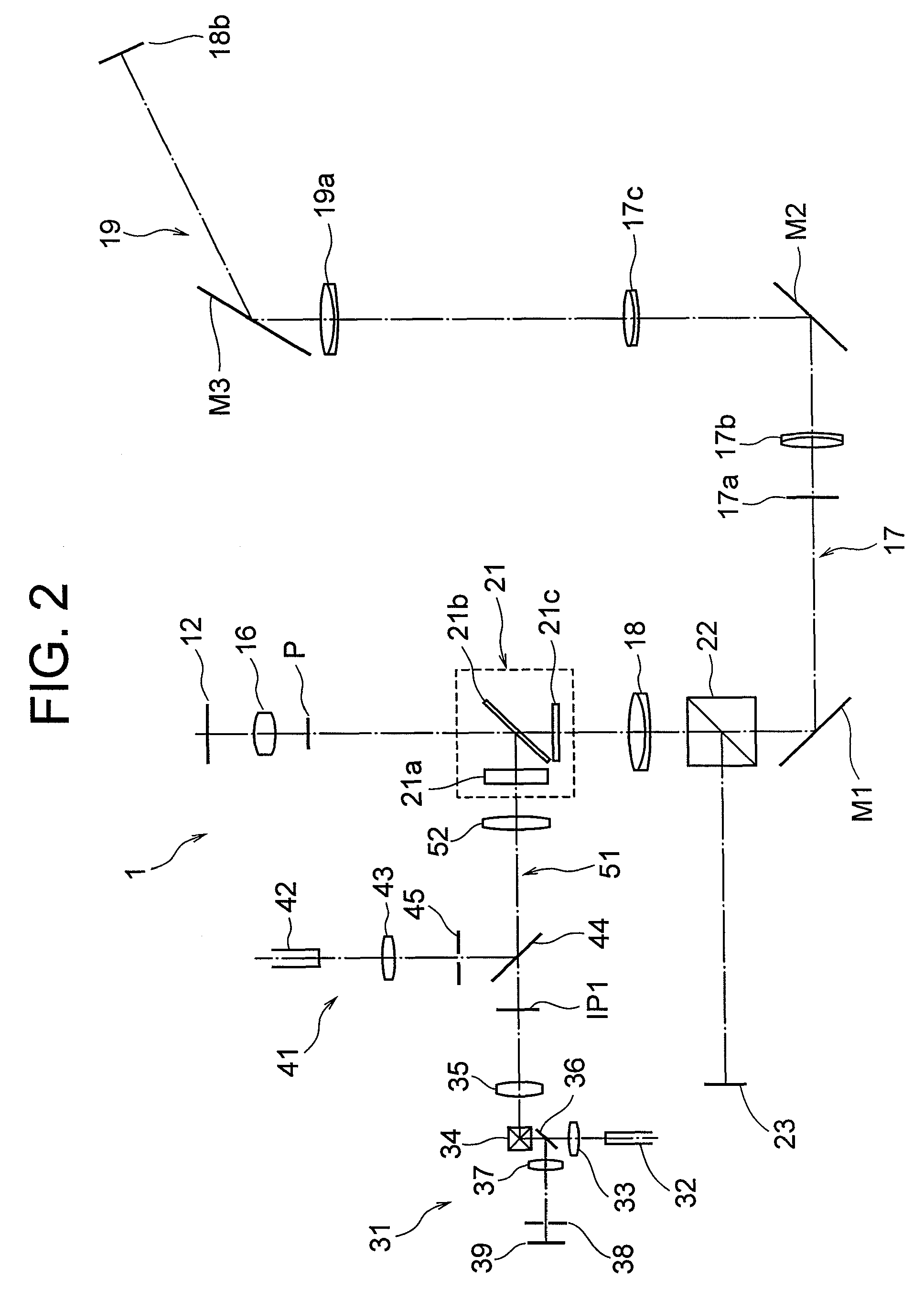
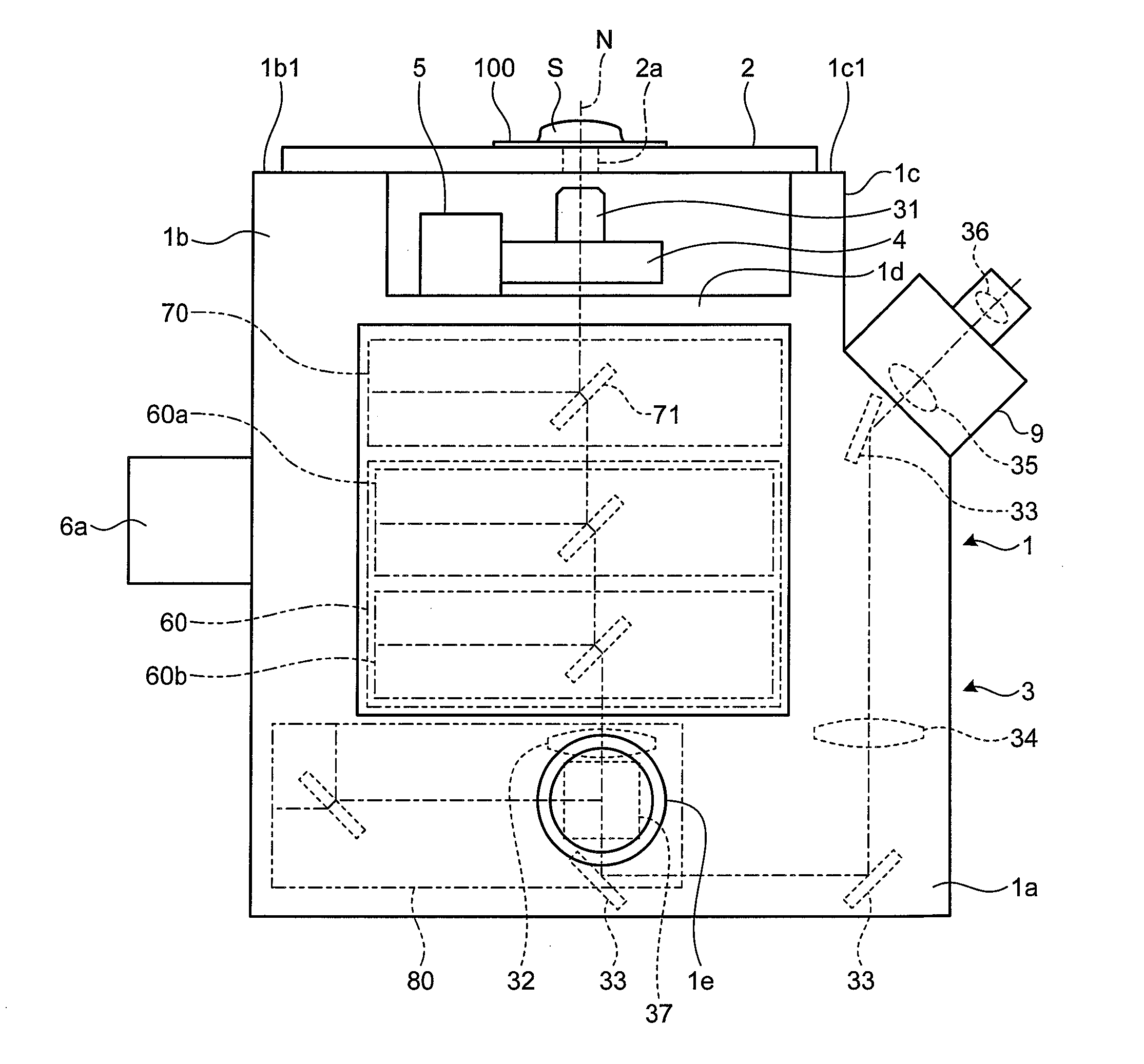
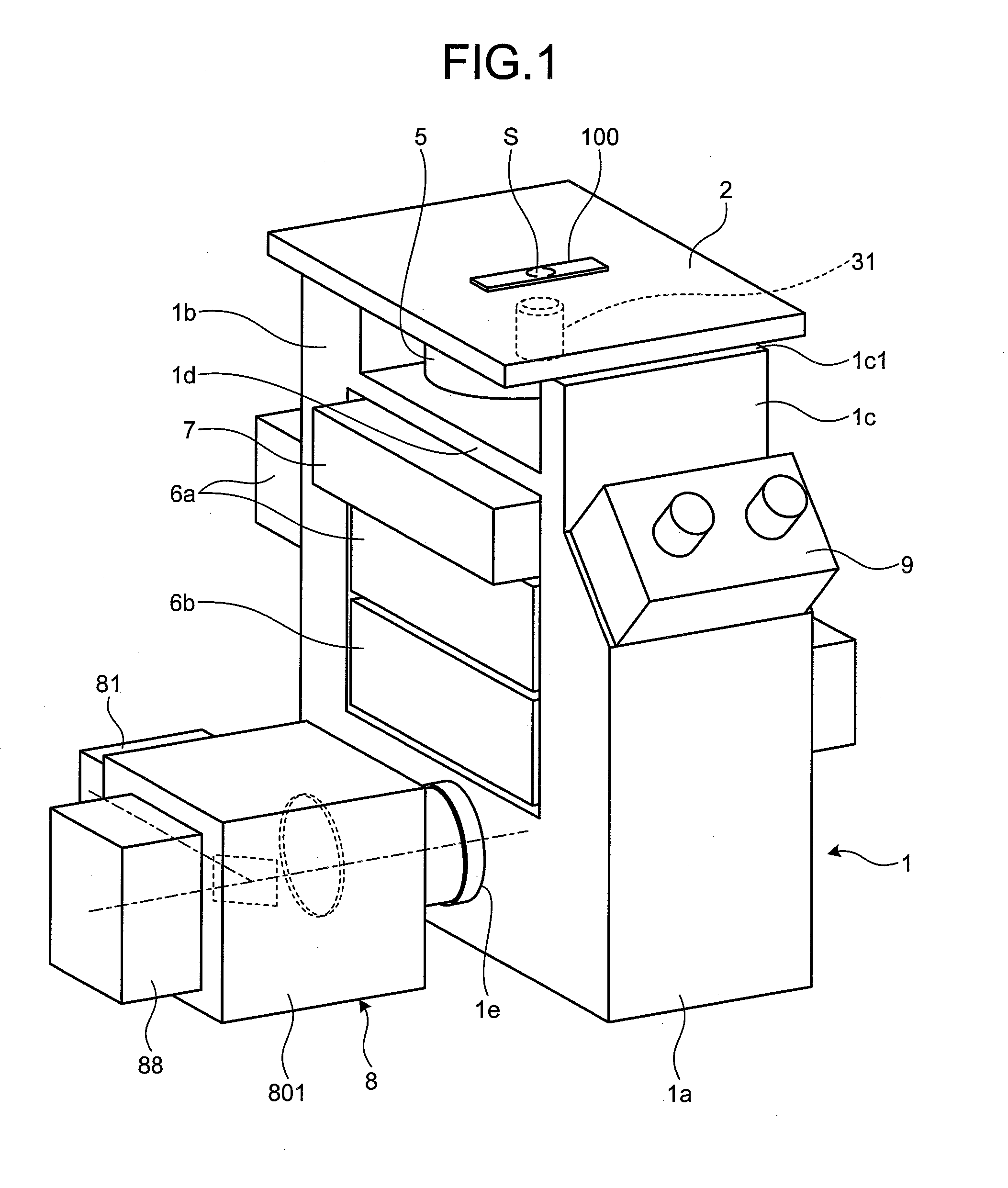
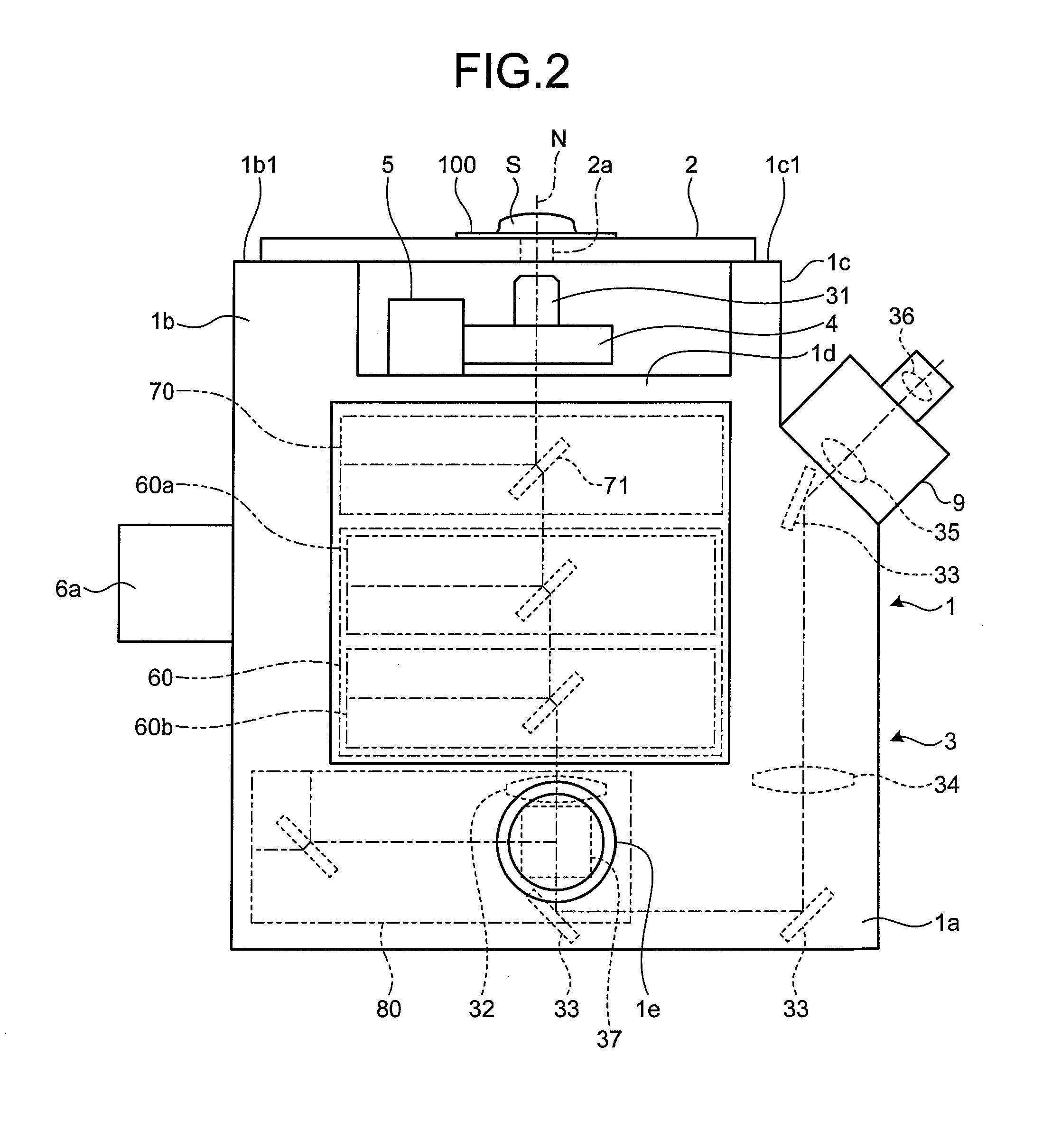
Total internal reflection fluorescence microscope
InactiveUS7385758B2Radiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationOptoelectronicsTotal internal reflection fluorescence microscope
A condenser lens is disposed in a position facing an objective lens via a specimen, a reflection mirror is movably disposed in the vicinity of an outermost part of a transmitted illuminative light path on the side of a transmitted illuminative light source from the condenser lens, and a laser beam output from a laser oscillation unit is reflected by the reflection mirror and is incident upon the condenser lens.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
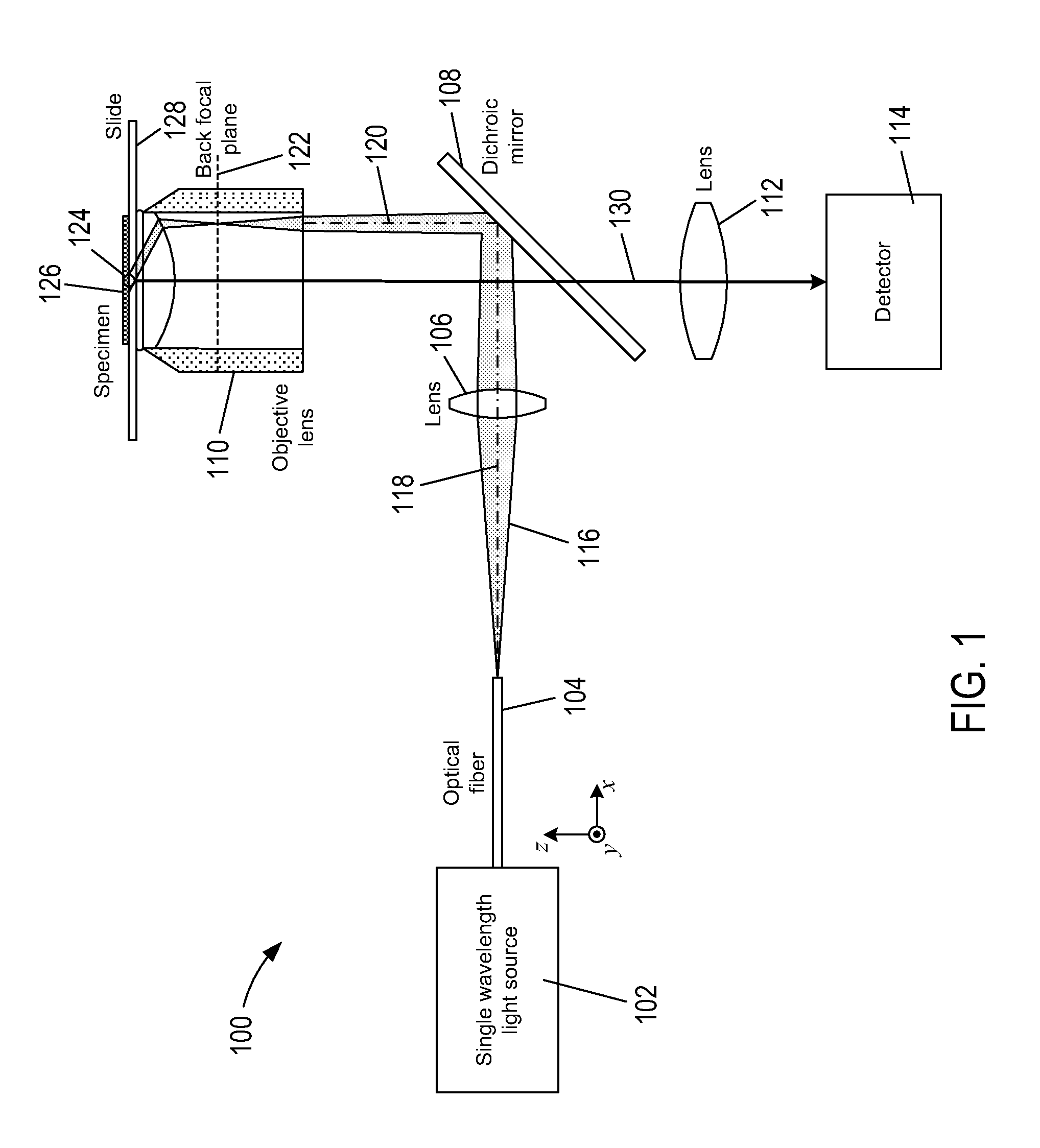
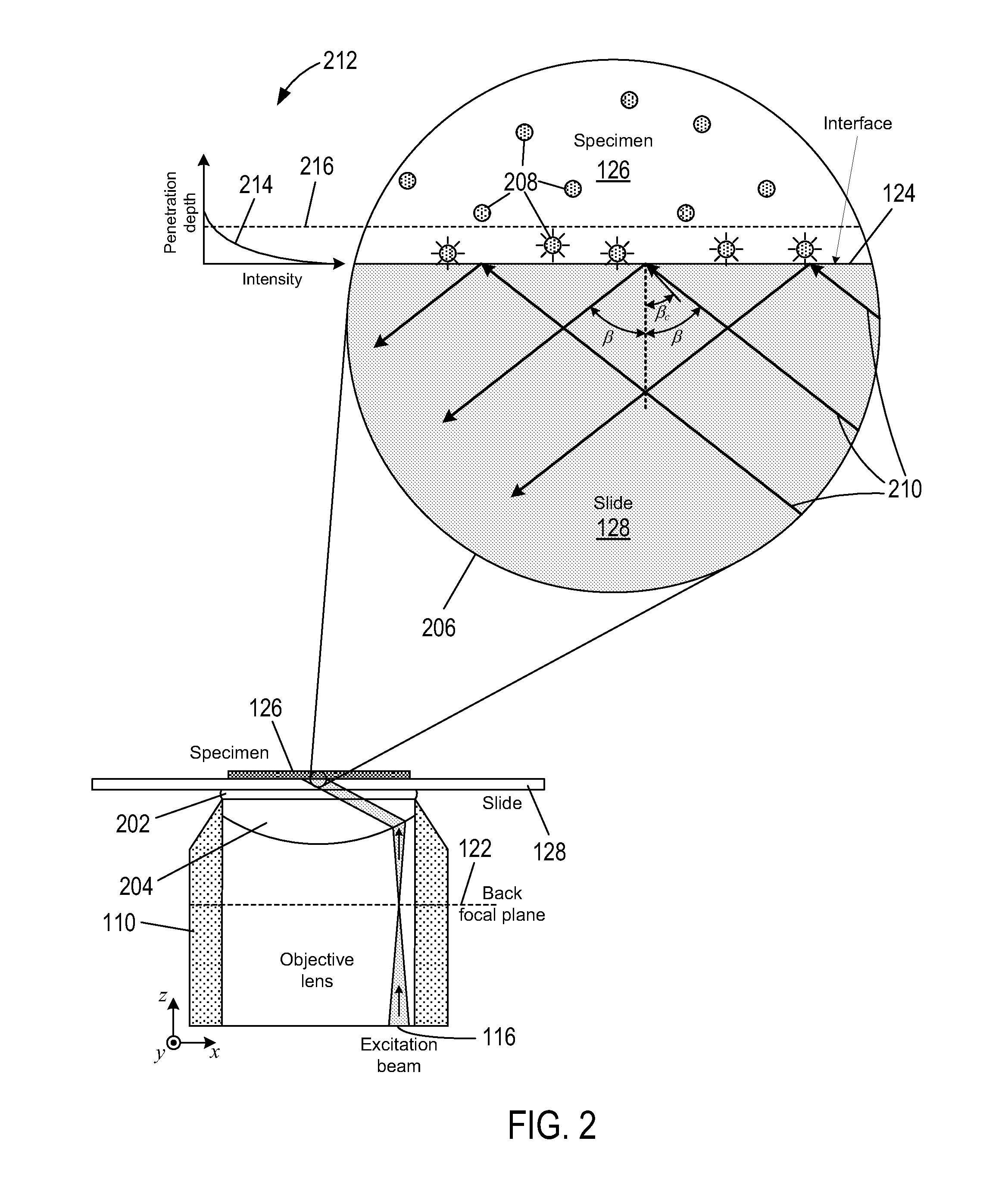
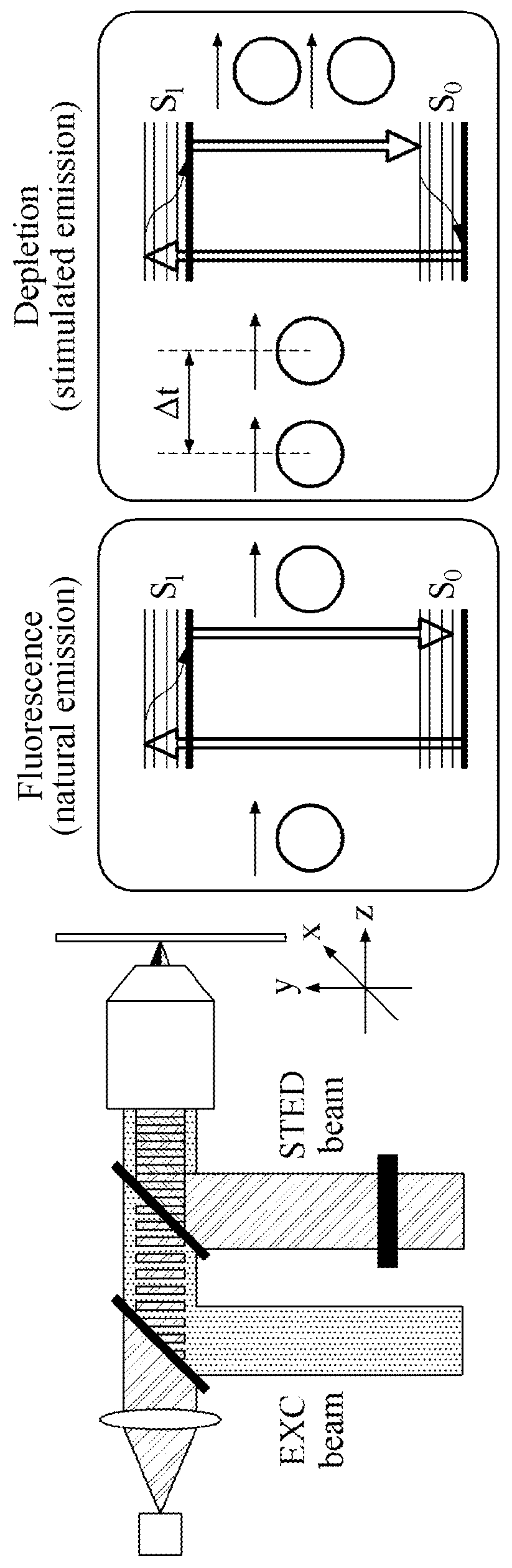
Total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy (TIRFM)
ActiveUS20170153436A1Improve light collectionSmall thicknessMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesOptoelectronicsTotal internal reflection fluorescence microscope
Disclosed is a fluorescence microscope for imaging a specimen a fluorescent substance, the fluorescence microscope including an excitation light source configured to emit an excitation light that excites a fluorescent substance to emit fluorescence; a de-excitation light source configured to emit a de-excitation light that de-excites the fluorescent substance excited by the excitation light emitted from the excitation light source; an optical body configured to overlap a light emitted from the excitation light source and a light emitted from the de-excitation light source, and to discharge the overlapped light toward the specimen; and a solid immersion lens to which the light discharged from the optical body is incident, and configured to refract the light discharged from the optical body toward the specimen. A total reflection of the light incident to the solid immersion lens occurs on a bottom of the solid immersion lens.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV
Total internal reflection fluorescence apparatus
InactiveUS7330255B2Radiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationTotal internal reflectionHigh numerical aperture
Techniques are provided for illuminating a sample by using total internal reflection (TIR) from a diffraction limited focused annular illumination beam. The illumination forms an affected region and an overlapping confocal region that may have dimensions the below 1 μm. An adjustable diffractive optical element, for example, may create a second order Bessel profile laser beam that is focused on a sample using a high-numerical aperture objective under TIR. An evanescent field excites fluorescent biological material in the confocal region, and fluorescence from the material is analyzed in fluorescence correlation spectroscopy system.
Owner:CHICAGO UNIV OF
Fluorescence-related spectrum measurement system
InactiveCN109520982AReduce cost of measurementReduce usageFluorescence/phosphorescenceMeasurement costFluorescence microscope
The invention belongs to the technical field of spectrum detection systems and in particular relates to a fluorescence-related spectrum measurement system. Exciting light is limited within a flying volume by utilizing a tapered optical fiber, and meanwhile, a fluorescence signal is collected by utilizing an optical fiber, so that time-related photo counting is performed, and furthermore, a fluorescence-related spectrum is acquired. By using the method, a fluorescence confocal microscope, a total internal reflection fluorescence microscope or a two-photon fluorescence microscope is prevented from being used, so that the measurement cost of a fluorescence-related spectrum is reduced; meanwhile, the optical fiber can be penetrated into a solution, a reactor, a microfluidic chip, a cell or a body, so that space imitation of imaging equipment is eliminated; and the fluorescence-related spectrum measurement system can be widely applied to the aspects such as reaction dynamic research, livingcell analysis, biological detection, disease diagnosis and drug screening in the fields of life sciences, physics and chemicals.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Inverted microscope system
ActiveUS20140293407A1Material analysis by optical meansMicroscopesTotal internal reflectionReflection illumination
An inverted microscope system includes an objective lens holding unit that holds an objective lens configured to collect at least observation light from a specimen, a tube lens configured to form an image using the observation light collected by the objective lens, a total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy optical system provided between the objective lens and the tube lens and configured to observe the observation light from the specimen using a total reflection illumination, and a disk scanning confocal optical system including a rotary disk on which a confocal opening is formed, the confocal opening being placed at a position substantially conjugate to a focus position of the objective lens. A relative distance between the focus position of the objective lens and the substantially conjugate position is changeable along an optical path of the observation light.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
Method for detecting lateral limitation area of living plant cytomembrane protein
InactiveCN104894210AThe laterally restricted area is simpleThe method of laterally restricted area is simpleMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionRange of motionCell membrane
The invention discloses a method for detecting the lateral limitation area of a living plant cytomembrane protein. The method comprises the following steps of (1) enabling a plant to express a fusion protein, so as to obtain a transgenic plant material which performs monochrome fluorescently labeling on the to-be-detected protein; (2) observing the transgenic plant material by using a variable-angle total internal reflection fluorescence microscope, so as to obtain a time sequence image; (3) recognizing and tracing a phosphor dot in a time series sequential image by using a single particle tracer technique, so as to obtain the trace of the phosphor dot along with the time and further calculate the mean square displacement of the phosphor dot along with the time; (4) fitting the mean square displacement of the phosphor dot along with the time by using Origin software, so as to obtain the corresponding constant, and calculating the moving range of the phosphor dot. The method for calculating the lateral limitation area of the living plant cytomembrane protein is simple, has good repeatability, can calculate the individual information of the protein and can calculate the population mean information.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Illumination optics for an optical observation device
InactiveUS20080049313A1Increase the range of variationLarge fieldMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesTotal internal reflectionLight beam
The invention is directed to illumination optics for an optical device for observing a sample, particularly for TIRF microscopy (Total Internal Reflection Fluorescence Microscopy), wherein the sample is positioned on the side of a carrier glass remote of the illumination optics and the illumination light exiting from the illumination optics is shaped into an illumination beam bundle which encloses an angle not equal to 90° with the normal to the surface of the carrier glass. According to the invention, the illumination optics of the type mentioned above comprise at least two optically active elements which influence the shape and direction of the illumination beam bundle and which are arranged outside of the detection beam path that guides light coming from the sample to a detector. The optically active elements are preferably constructed as annular lenses and are arranged concentrically around the detection beam path.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MIKROLMAGING
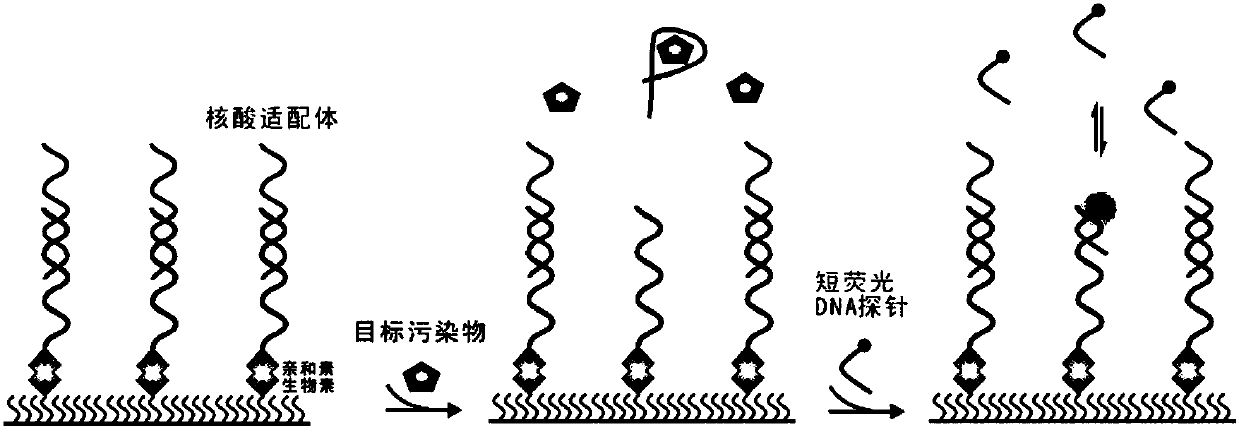
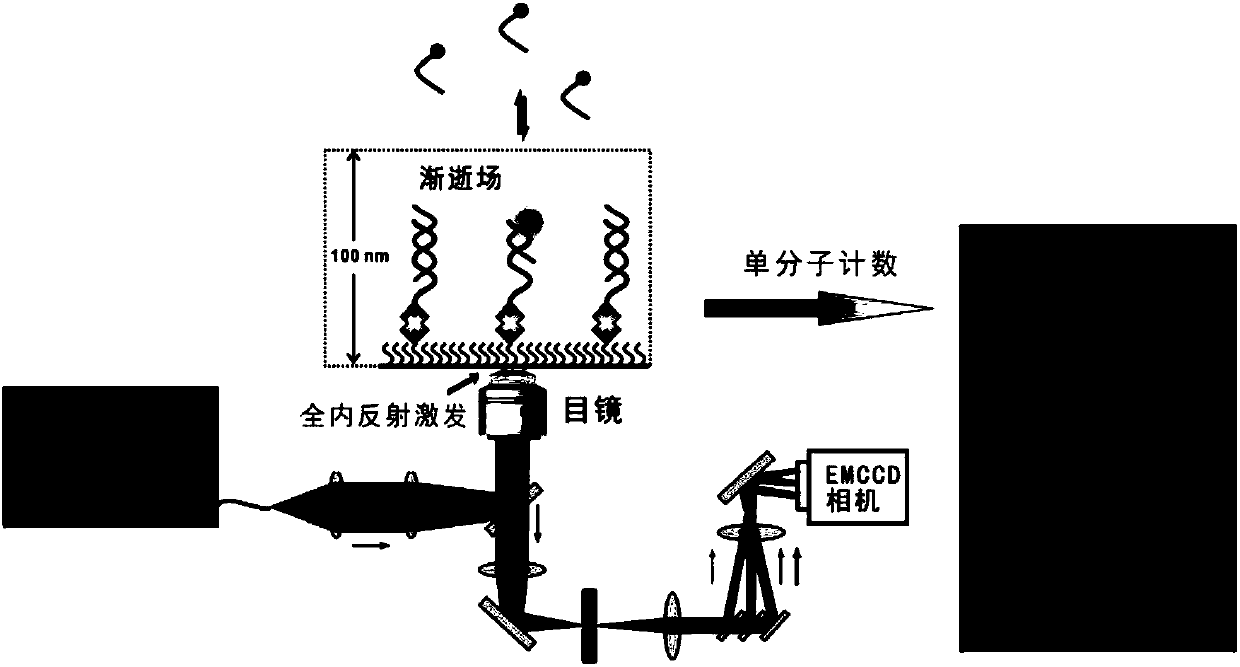
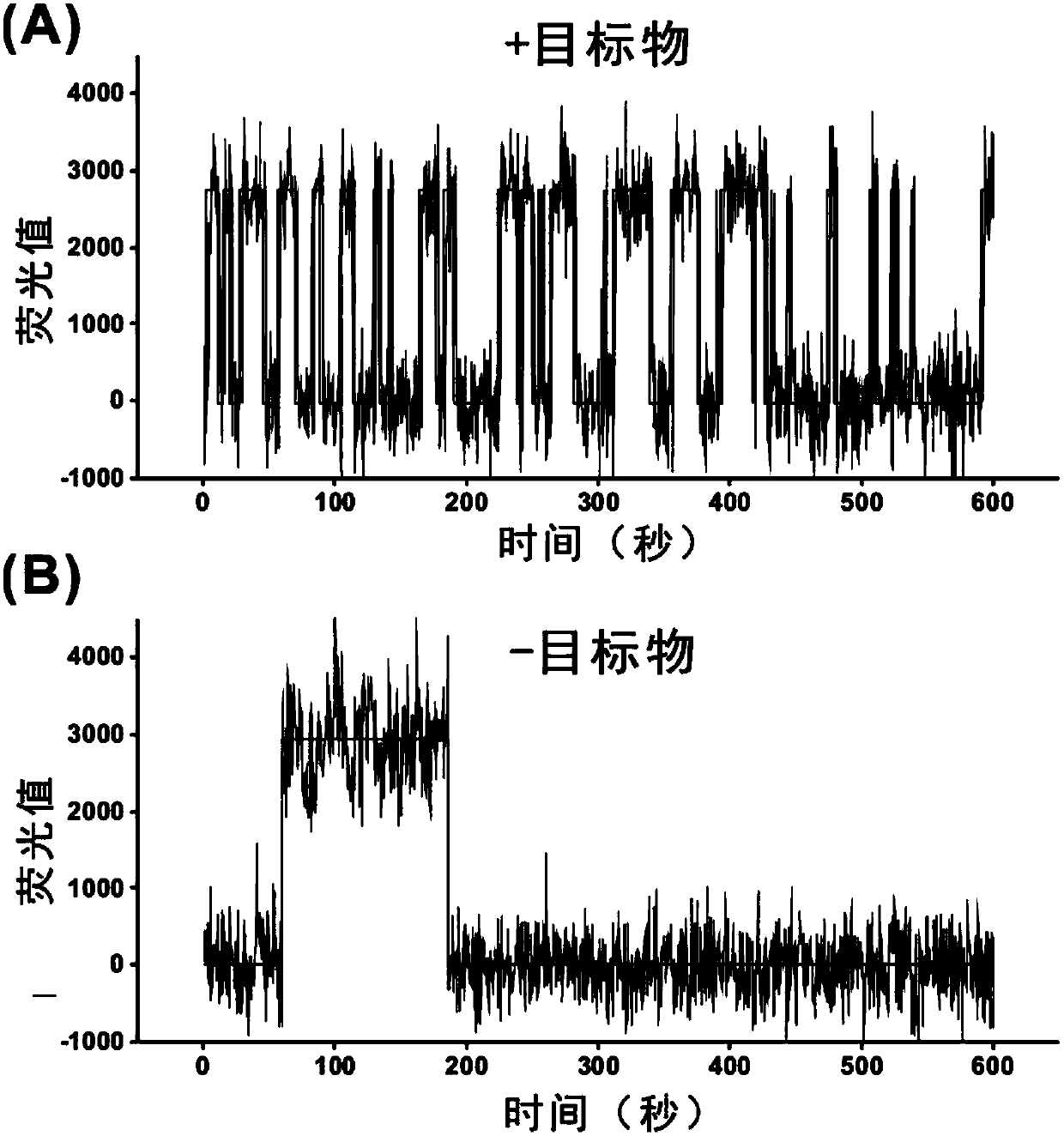
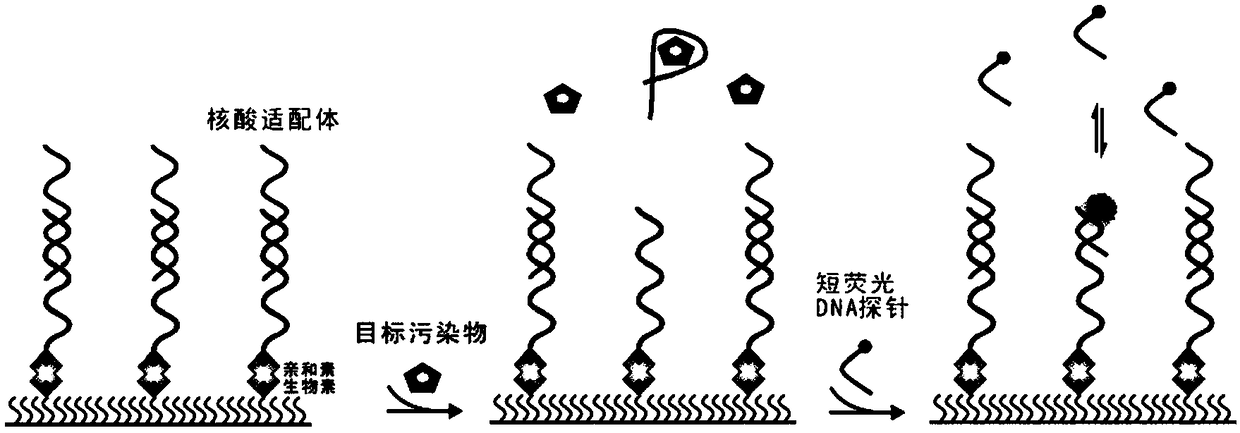
Detection method of trace amount of target based on monomolecular fluorescent sensing
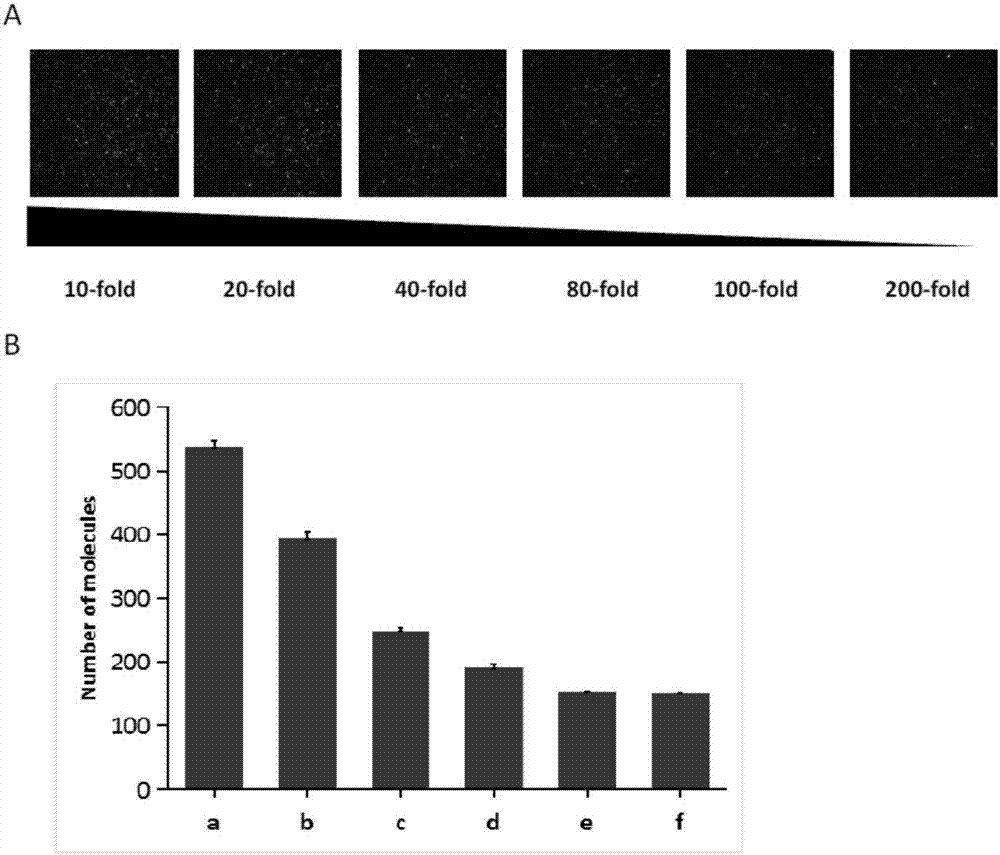
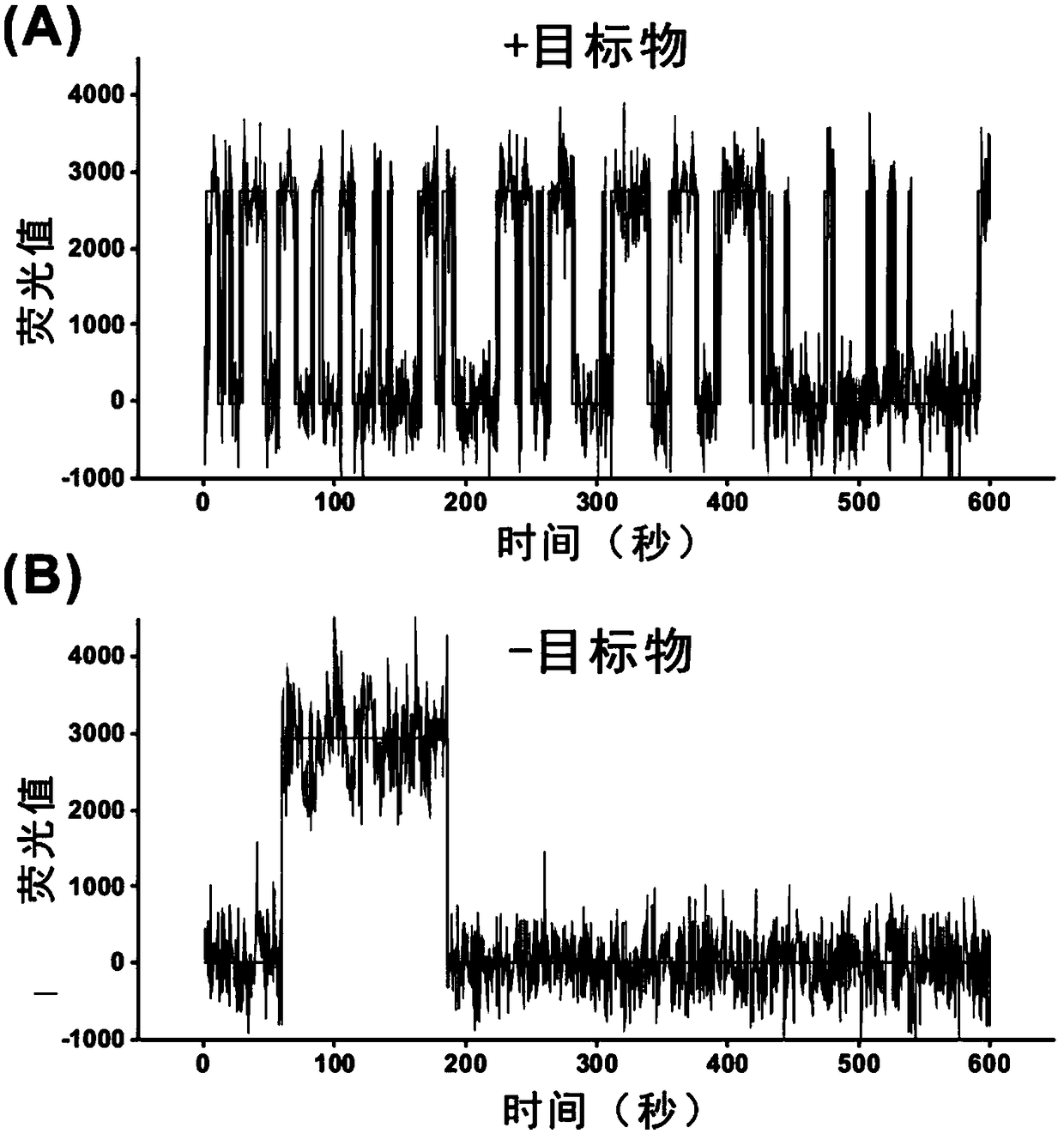
ActiveCN107858403AHigh sensitivityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementTrace AmountsTotal internal reflection fluorescence microscope
The invention discloses a detection method of a trace amount of a target based on monomolecular fluorescent sensing. The detection method comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing a standard solution containing a target object; (2) fixing an auxiliary probe on a slide, adding an aptamer, and hybridizing the auxiliary probe with the aptamer; (3) adding the standard solution to the slide, andbinding the target object with the aptamer to separate the target object from the auxiliary probe; (4) adding a signal probe to the slide, and carrying out transient hybridization on the signal probeand the released auxiliary probe; (5) placing the slide on an object stage of a total internal reflection fluorescence microscope for detection, recording single-molecule fluorescence points with thenumber of times of change of the fluorescence state being more than 15 times, taking the single-molecule fluorescence points as an ordinate and taking the concentration of the target object in the standard solution as an abscissa to make a standard curve; and (6) repeating the steps (3) to (5) for a sample to be detected, recording single-molecule fluorescence points with the number of times of change of the fluorescence state being more than 15 times, and obtaining the concentration of the target object in the sample to be detected according to the standard curve.
Owner:INST OF QUALITY STANDARD & TESTING TECH FOR AGRO PROD OF CAAS +1
Systems for chromatic aberration correction in total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Method for observing distribution and dynamic states of proteins on stomatal guard cell membrane at single-molecule level
ActiveCN108195801AAvoid damageHigh resolutionFluorescence/phosphorescenceCell membraneMolecular level
The invention provides a method for observing the distribution and dynamic states of proteins on a stomatal guard cell membrane at a single-molecule level, belonging to the field of biotechnology. Themethod comprises the following steps: A, acquiring a transgenic material in which a target gene is fluorescently labeled; B, acquiring the real-time images of proteins on a guard cell membrane by using a total internal reflection fluorescence microscope; C, processing the time series images by using the Image J software; D, carrying out single-particle tracing analysis on target proteins via Matlab R2014a so as to determine the dynamic state of each individual protein polymer; E, calculating the dwell time of the proteins on the cell membrane; and F, subjecting the dwell time parameters of the target proteins to Gaussian Fitting so as to determine the dwell time and changes of the target proteins. The method has the advantages of capacity of improving the signal-to-noise ratio of imagingand realizing high-resolution observation, fast imaging speed, in-vivo visibility and high repeatability. The method has practical application value in the research of the functions of plant genes.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Microscope apparatus with fluorescence cube for total-internal-reflection fluorescence microscopy
A microscope apparatus has an illumination optical system illuminating a sample with laser light from laser light sources. A fluorescence detection optical system detects fluorescence from the sample. Fluorescence cubes are interchangeably provided in an optical path of the illumination optical system and lead the laser light to the sample. An objective lens is also provided. At least one of the fluorescence cubes includes an optical member that makes a principal ray of the laser light substantially parallel to an optical axis of the illumination optical system and concentrates the laser light on a given position that is on a pupil position of the objective lens and separated from the optical axis, thereby providing a microscope apparatus capable of changing from a confocal microscope to a total-internal-reflection fluorescence microscope by exchanging a fluorescence cube used in the fluorescence microscope.
Owner:NIKON CORP
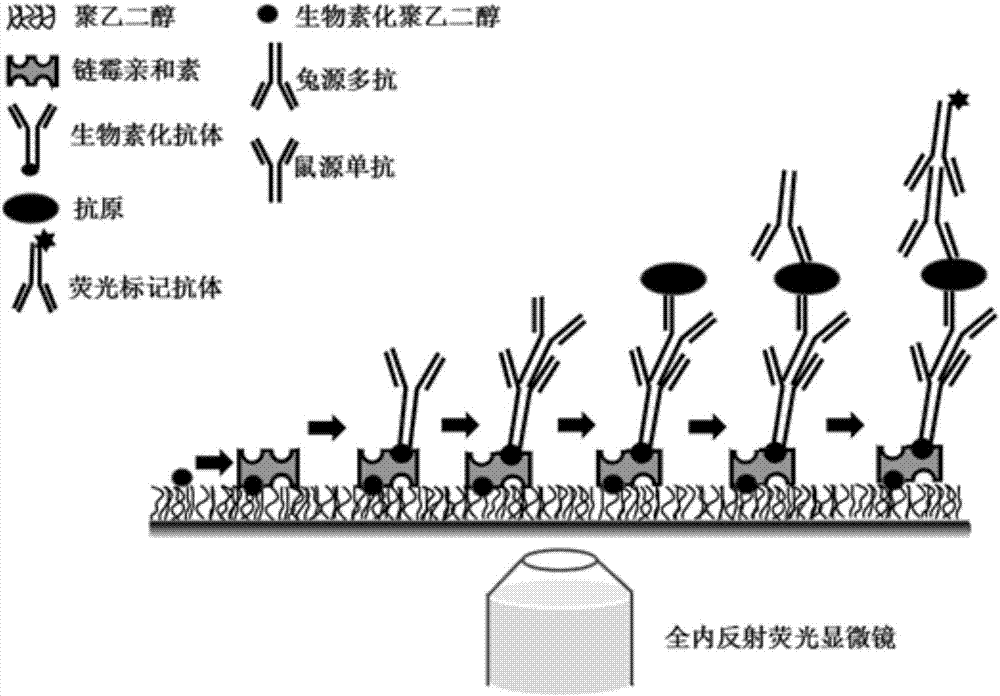
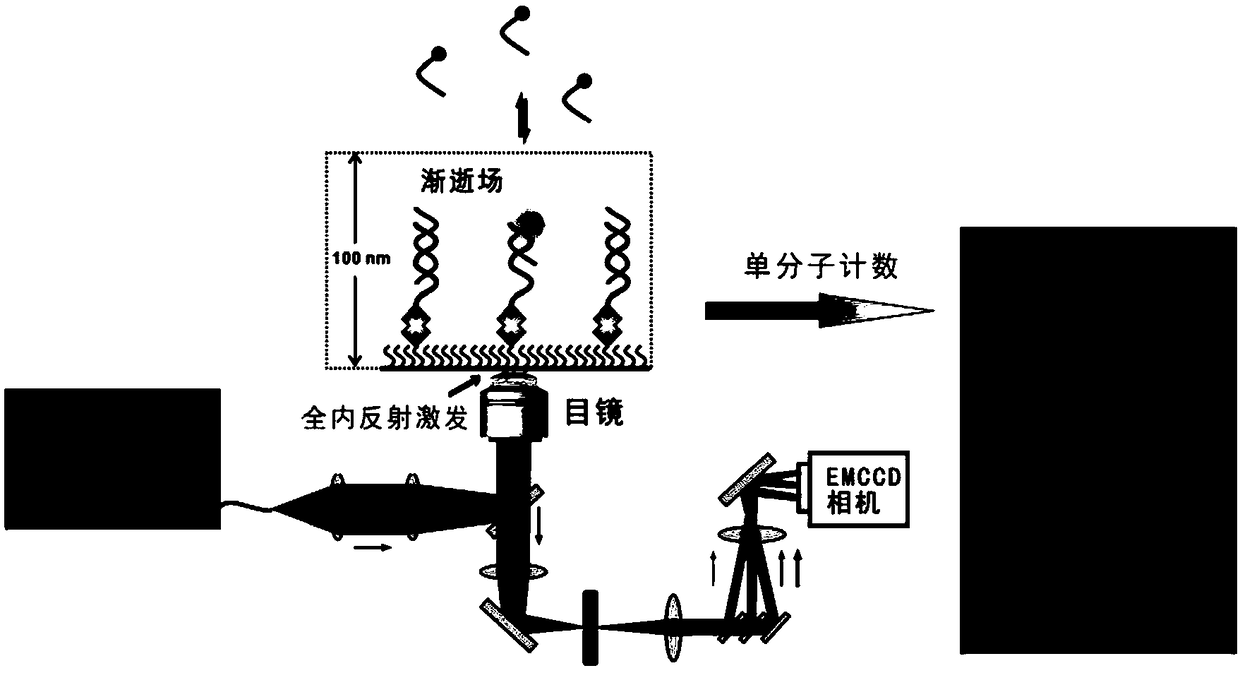
Method for detecting single biological marker by using total internal reflection fluorescent microscope
InactiveCN107101981AReduce background noiseImprove signal-to-noise ratioFluorescence/phosphorescenceAntigenTotal internal reflection
The invention discloses a method for detecting a biological marker by using a total internal reflection fluorescent microscope. The method comprises the following steps of utilizing biotin-avidin connection, and antigen and antibody reaction or nucleic acid molecule and probe reaction, using a total internal reflection fluorescent exciting type to excite a detection molecule of a fluorescent marker which is fixed in the 100nm range of the carrier surface, and collecting a fluorescent molecule signal by the fluorescent microscope, so as to obtain the number of to-be-detected biology markers. The method has the advantages that because the free fluorescent molecules in the solution are not excited, the background noise of the collected fluorescent signal is lower, and the signal to noise ratio is very high; the fluorescent signal of the single molecule can be distinguished, so that the detection sensitivity is high; the detection method can be used for detecting various types of biological markers, and an important meaning is realized for the finding of pathogen in diseases and the preventing and controlling of diseases.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Synchronous monitoring method for chemical signals and electric signals of neural cell network
ActiveCN110702650ARealize synchronized measurementsSimultaneous measurement result realizationFluorescence/phosphorescenceMaterial electrochemical variablesNeural cellSignal-to-noise ratio
The invention discloses a synchronous monitoring method for chemical signals and electric signals of a neural cell network. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, culturing a neural cellnetwork on a pretreated microelectrode array in situ; then dyeing neuron vesicles, and adding a buffer solution; observing the neural cell network by adopting a total internal reflection fluorescencemicroscope, and connecting a shooting camera and a controller of the microelectrode array with a pulse signal generator; and performing external stimulation on the neural cell network, starting the pulse signal generator, and synchronously collecting fluorescence signals and electric signals by the shooting camera and the controller of the microelectrode array respectively. The synchronous monitoring method is low in background signal and high in signal-to-noise ratio, has space-time resolution responsiveness, and can meet the monitoring requirements of the neural cell network; the method isstable in signal and high in sensitivity, can achieve imaging measurement for various neural cells and networks, and can achieve high-throughput analysis.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Total internal reflection fluorescence microscope (TIRFM)
ActiveUS9964749B2Improve light collectionSmall thicknessMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesTotal internal reflectionFluorescence microscope
Disclosed is a fluorescence microscope for imaging a specimen containing a fluorescent substance, the fluorescence microscope including an excitation light source configured to emit an excitation light that excites a fluorescent substance to emit fluorescence; a de-excitation light source configured to emit a de-excitation light that de-excites the fluorescent substance excited by the excitation light emitted from the excitation light source; an optical body configured to overlap a light emitted from the excitation light source and a light emitted from the de-excitation light source, and to discharge the overlapped light toward the specimen; and a solid immersion lens to which the light discharged from the optical body is incident, and configured to refract the light discharged from the optical body toward the specimen. A total internal reflection of the light incident to the solid immersion lens occurs on a bottom of the solid immersion lens.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV
A method for detecting trace target substances based on single-molecule fluorescence sensing
ActiveCN107858403BHigh sensitivityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical physicsPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a detection method of a trace amount of a target based on monomolecular fluorescent sensing. The detection method comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing a standard solution containing a target object; (2) fixing an auxiliary probe on a slide, adding an aptamer, and hybridizing the auxiliary probe with the aptamer; (3) adding the standard solution to the slide, andbinding the target object with the aptamer to separate the target object from the auxiliary probe; (4) adding a signal probe to the slide, and carrying out transient hybridization on the signal probeand the released auxiliary probe; (5) placing the slide on an object stage of a total internal reflection fluorescence microscope for detection, recording single-molecule fluorescence points with thenumber of times of change of the fluorescence state being more than 15 times, taking the single-molecule fluorescence points as an ordinate and taking the concentration of the target object in the standard solution as an abscissa to make a standard curve; and (6) repeating the steps (3) to (5) for a sample to be detected, recording single-molecule fluorescence points with the number of times of change of the fluorescence state being more than 15 times, and obtaining the concentration of the target object in the sample to be detected according to the standard curve.
Owner:INST OF QUALITY STANDARD & TESTING TECH FOR AGRO PROD OF CAAS +1
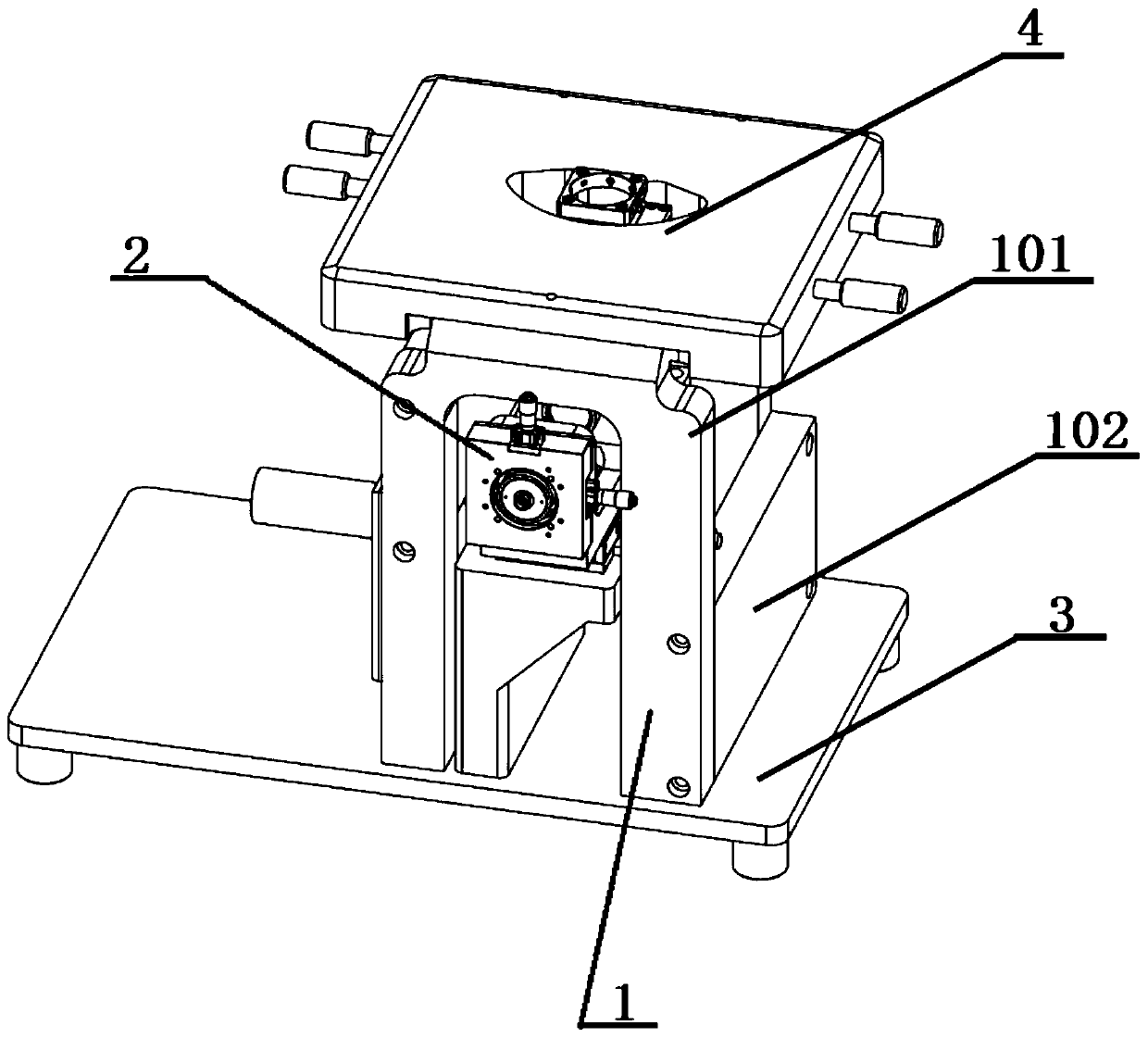
Total internal reflection fluorescence microscope capable of being used with atomic force microscope
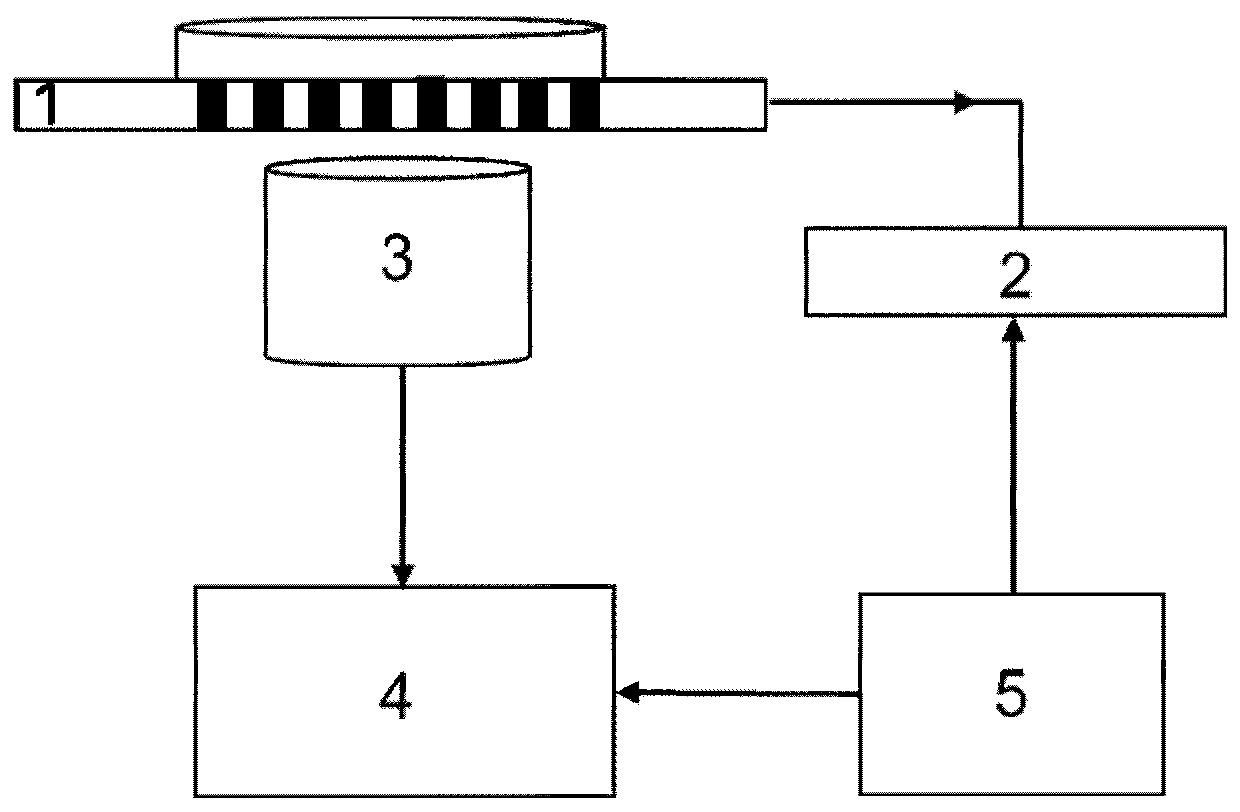
ActiveCN106896241AAchieve focusImprove compatibilityScanning probe techniquesAtomic force microscopyFluorescence microscope
The invention discloses a total internal reflection fluorescence microscope capable of being used with an atomic force microscope and belongs to the field of optical microscopes. The fluorescence microscope comprises a support assembly, an imaging assembly, a base, a sample objective table of the atomic force microscope. The size of the support assembly can be adjusted according to the size of the sample objective table. In the imaging assembly, a bearing body is arranged on the base, a one-dimensional translation seat is arranged on the bearing body, a second connection seat is fixed on the bearing body, a lens cone lens is arranged in an inner cavity and a reflection mirror is arranged on the bearing body and under the lens cone lens. A lower base plate of a first connection seat of a U-type structure is fixed on the one-dimensional translation seat. A two-dimensional translation seat is fixed on the outer end of a left side arm of the first connection seat. A fiber coupler is arranged in the two-dimensional translation seat in a two-dimensional moving manner. The end part of a first lens and the end part of a second lens are arranged on two ends of a second through hole of the right side arm of the first connection seat. A dichroscope assembly is arranged on the second connection seat. An objective lens is fixed on the dichroscope. The objective lens is arranged in an objective lens installation seat in a height-adjustable manner.
Owner:IPE BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
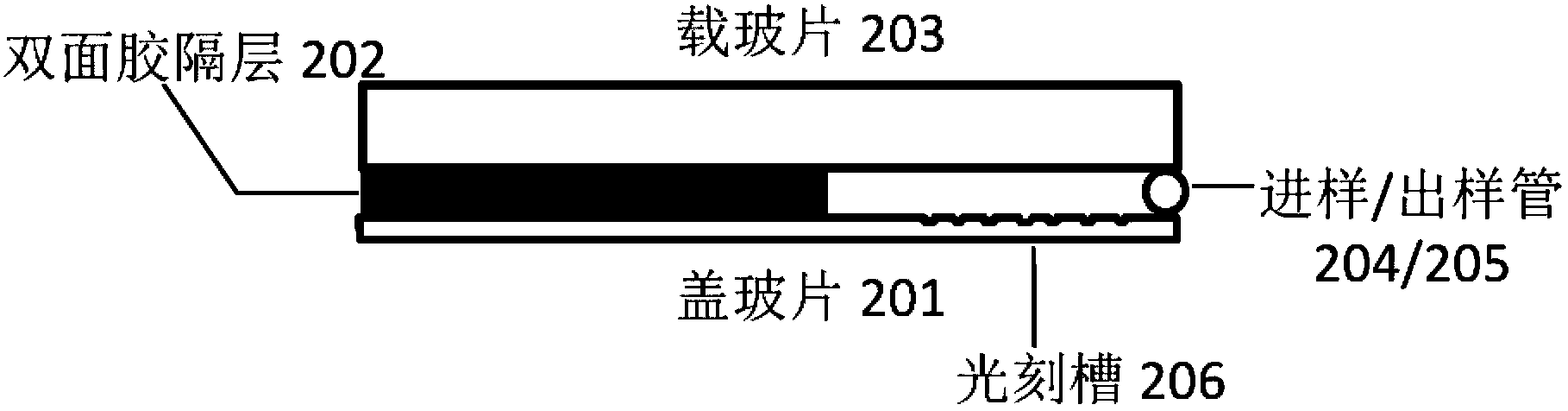
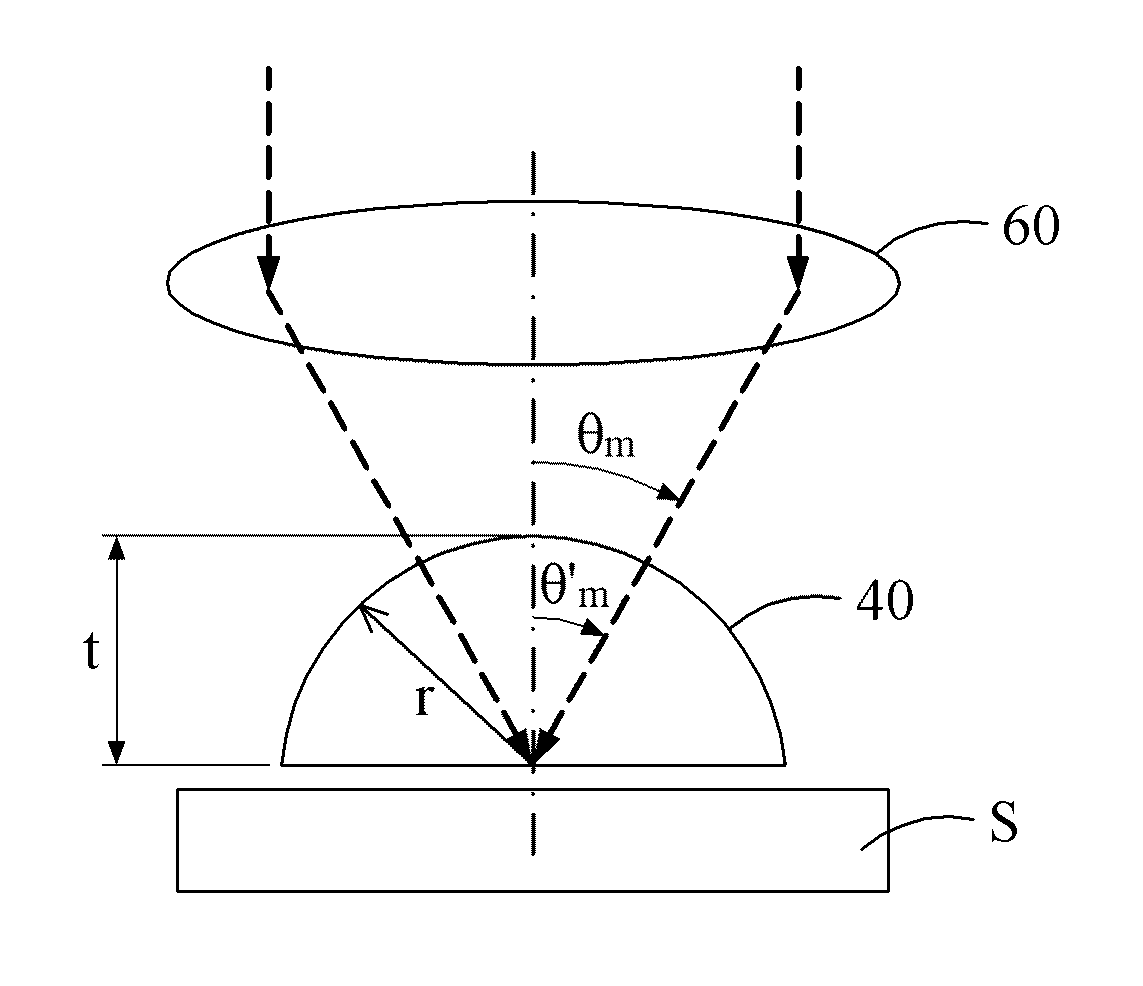
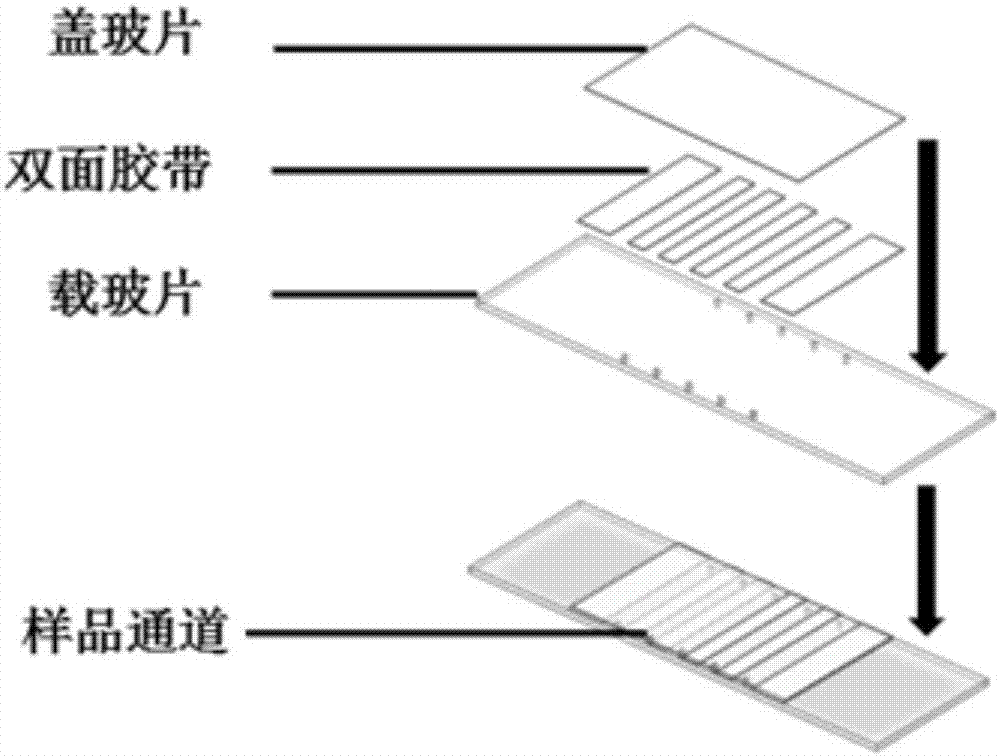
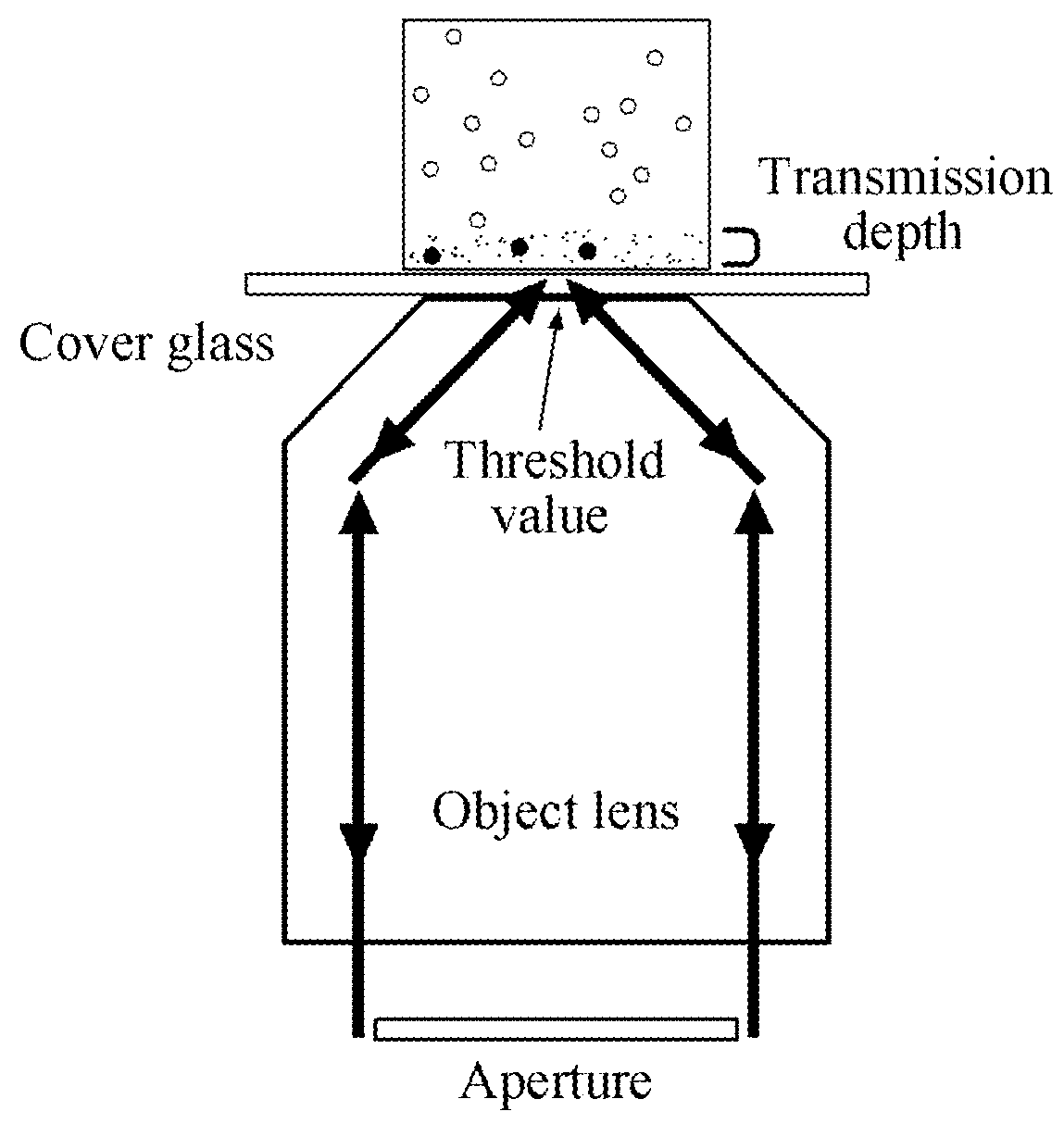
Novel calibration device and calibration method for total internal reflection fluorescence microscope penetration depth
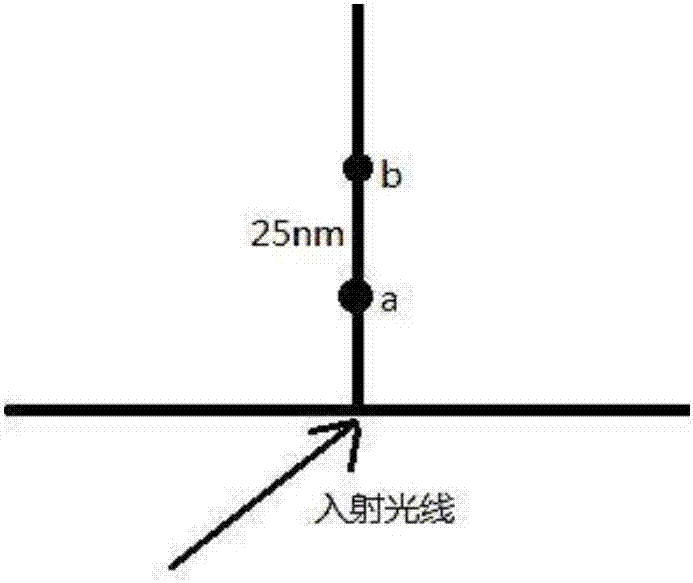
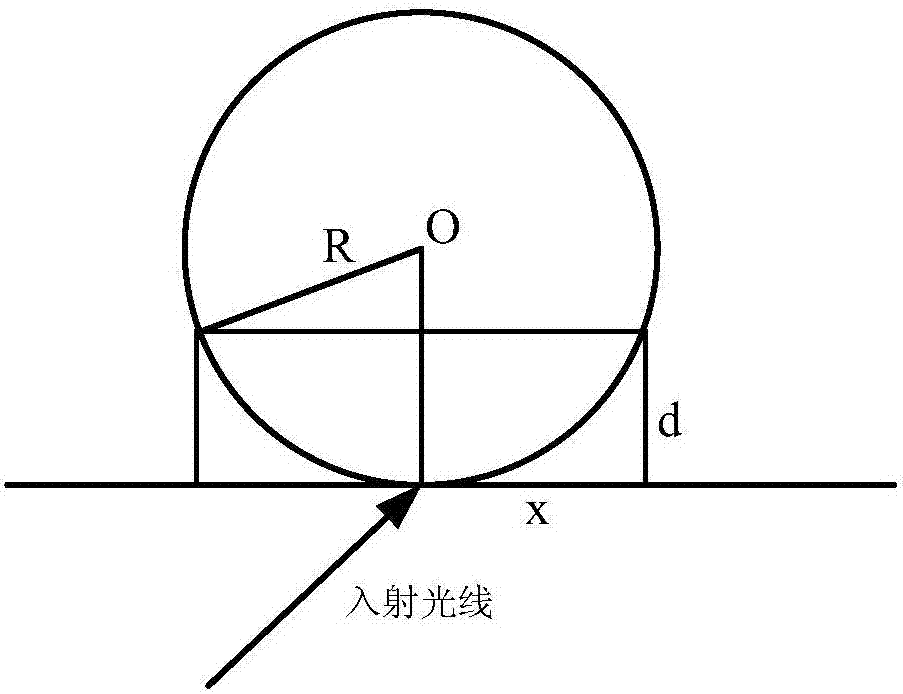
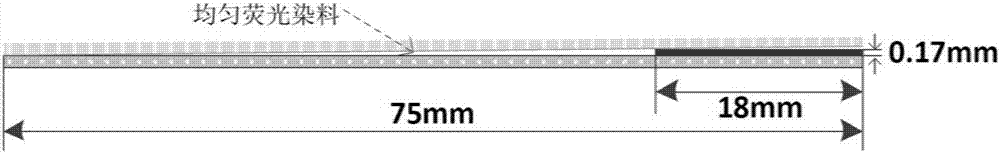
InactiveCN107014788ACalibration is effectively determinedSimple and fast operationMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicroscope slideGlass chip
The invention discloses a calibration device for the total internal reflection fluorescence microscope penetration depth. The device comprises a glass slide, square cover glass and a glass sheet, wherein the square cover glass covers the upper surface of the glass slide; the right sides of the square cover glass and the glass slide are aligned; the glass sheet is arranged on the glass slide; the left side edges of the glass sheet and the glass slide are in contact and are aligned; the lower surface of the glass sheet is supported by the direction cover glass; the lower surface of the glass sheet is uniformly coated with fluorescent dye. The invention also discloses a method for calibrating the total internal reflection fluorescence microscope penetration depth by using the calibration device. The device has the advantages that the structure is simple; the cost is low; the operation is convenient and flexible.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Detection method of target nucleic acid and application thereof
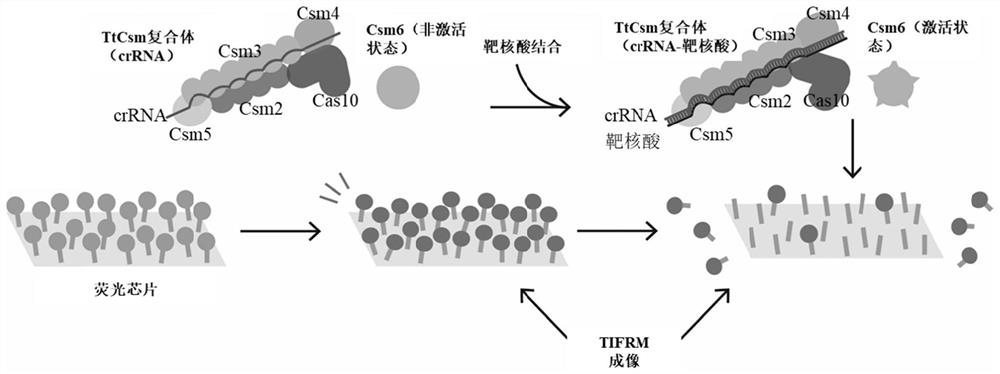
PendingCN114150087ALess quantityReduce background light noiseMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesNucleic acid detectionSingle strand
The invention discloses a target nucleic acid detection method and application thereof. In the first aspect, the invention provides a method for detecting target nucleic acid with a non-disease diagnosis purpose, and the method comprises the following steps: providing a substrate on which an RNA chain marked with a fluorescent reporter group is fixed; carrying out contact reaction on the Csm complex, Csm6 protein, a nucleic acid sample and a substrate, and washing the substrate after the reaction is finished; and respectively collecting fluorescence signals of the substrate before and after the reaction by using a total internal reflection fluorescence microscope, and obtaining the concentration of the target nucleic acid in the nucleic acid sample according to the fluorescence intensity change. The Csm complex recognizes the target nucleic acid to generate cA4, and further activates the activity of the non-specific cleavage single-stranded RNA of the Csm6 protein, so that the RNA chain anchored on the substrate is cleaved, the fluorescent reporter gene is dissociated along with the cleavage, and the amount of the fluorescent reporter group on the substrate is reduced. The high signal-to-noise ratio of the TIRFM is utilized to obtain obvious signals, and the accuracy and sensitivity of detection are improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Inverted microscope system
ActiveUS9372330B2MicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceTotal internal reflectionReflection illumination
An inverted microscope system includes an objective lens holding unit that holds an objective lens configured to collect at least observation light from a specimen, a tube lens configured to form an image using the observation light collected by the objective lens, a total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy optical system provided between the objective lens and the tube lens and configured to observe the observation light from the specimen using a total reflection illumination, and a disk scanning confocal optical system including a rotary disk on which a confocal opening is formed, the confocal opening being placed at a position substantially conjugate to a focus position of the objective lens. A relative distance between the focus position of the objective lens and the substantially conjugate position is changeable along an optical path of the observation light.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
A Total Internal Reflection Fluorescence Microscope Combined with Atomic Force Microscope
ActiveCN106896241BAchieve focusImprove compatibilityScanning probe techniquesAtomic force microscopyFluorescence microscope
The invention discloses a total internal reflection fluorescence microscope capable of being used with an atomic force microscope and belongs to the field of optical microscopes. The fluorescence microscope comprises a support assembly, an imaging assembly, a base, a sample objective table of the atomic force microscope. The size of the support assembly can be adjusted according to the size of the sample objective table. In the imaging assembly, a bearing body is arranged on the base, a one-dimensional translation seat is arranged on the bearing body, a second connection seat is fixed on the bearing body, a lens cone lens is arranged in an inner cavity and a reflection mirror is arranged on the bearing body and under the lens cone lens. A lower base plate of a first connection seat of a U-type structure is fixed on the one-dimensional translation seat. A two-dimensional translation seat is fixed on the outer end of a left side arm of the first connection seat. A fiber coupler is arranged in the two-dimensional translation seat in a two-dimensional moving manner. The end part of a first lens and the end part of a second lens are arranged on two ends of a second through hole of the right side arm of the first connection seat. A dichroscope assembly is arranged on the second connection seat. An objective lens is fixed on the dichroscope. The objective lens is arranged in an objective lens installation seat in a height-adjustable manner.
Owner:IPE BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
A method for synchronously monitoring chemical signals and electrical signals of nerve cell network
ActiveCN110702650BRealize synchronized measurementsSimultaneous measurement result realizationFluorescence/phosphorescenceMaterial electrochemical variablesTemporal resolutionEngineering
Owner:NANJING UNIV
A method for detecting the laterally restricted area of membrane proteins in living plants
InactiveCN104894210BThe laterally restricted area is simpleThe method of laterally restricted area is simpleMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionFusion Protein ExpressionPresent method
The invention discloses a method for detecting the laterally limited area of a living plant cell membrane protein. The method comprises: (1) expressing a fusion protein in a plant to obtain a transgenic plant material with single-color fluorescent labeling for the protein to be tested; (2) observing the transgenic plant material with a variable-angle total internal reflection fluorescence microscope, Obtain time series images; (3) use single particle tracking technology to identify and track fluorescent points in time series images, obtain the trajectory of fluorescent points over time, and then calculate the average square displacement of fluorescent points over time; (4) use The Origin software fits the average square displacement of the fluorescent point over time, obtains the corresponding constant, and calculates the moving range of the fluorescent point. The method for calculating the laterally restricted area of membrane proteins in living cells is simple and repeatable, and individual information of proteins and group average information can also be calculated.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Biological detection method for small ubiquitin-like modification
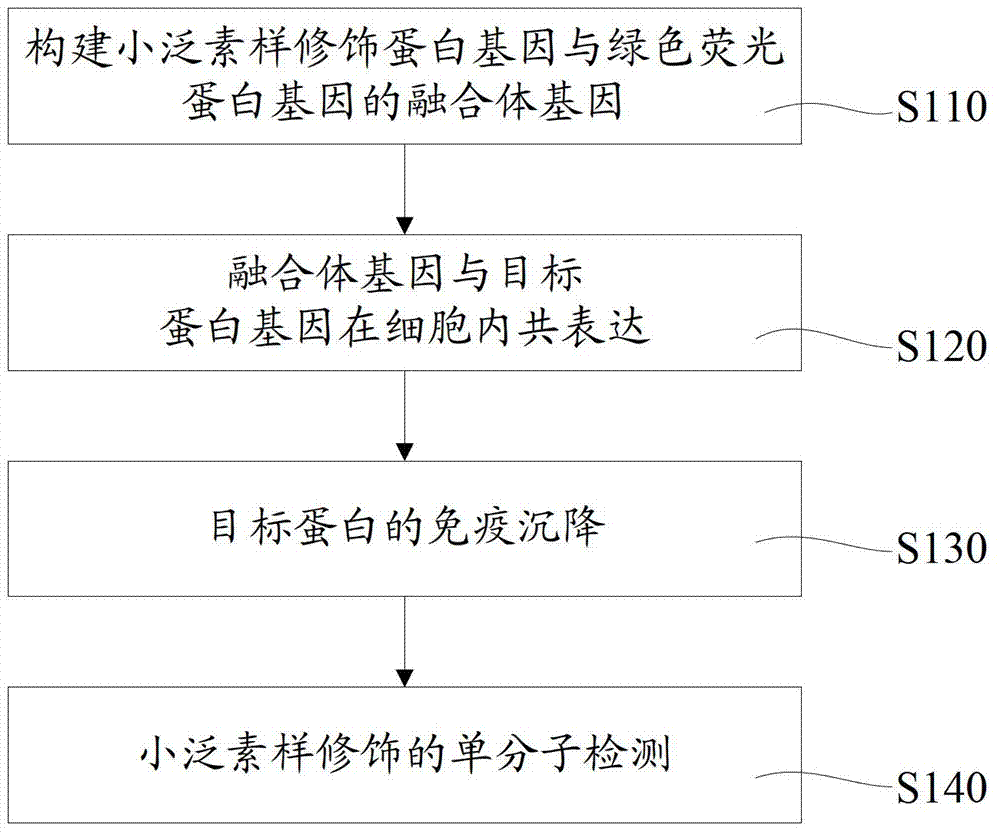
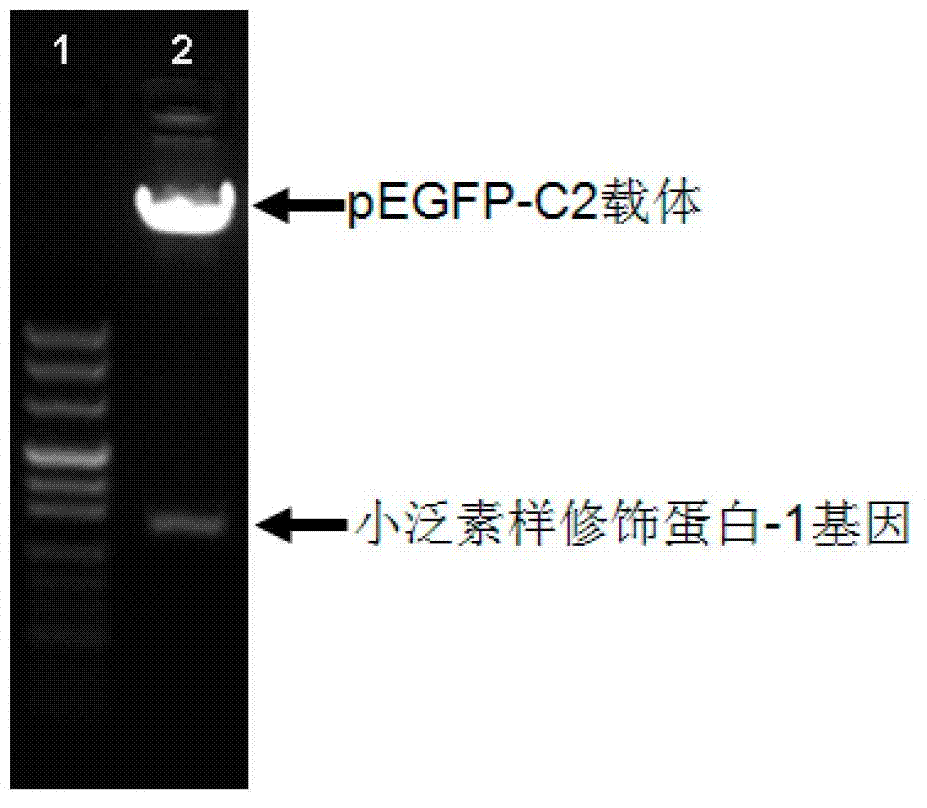
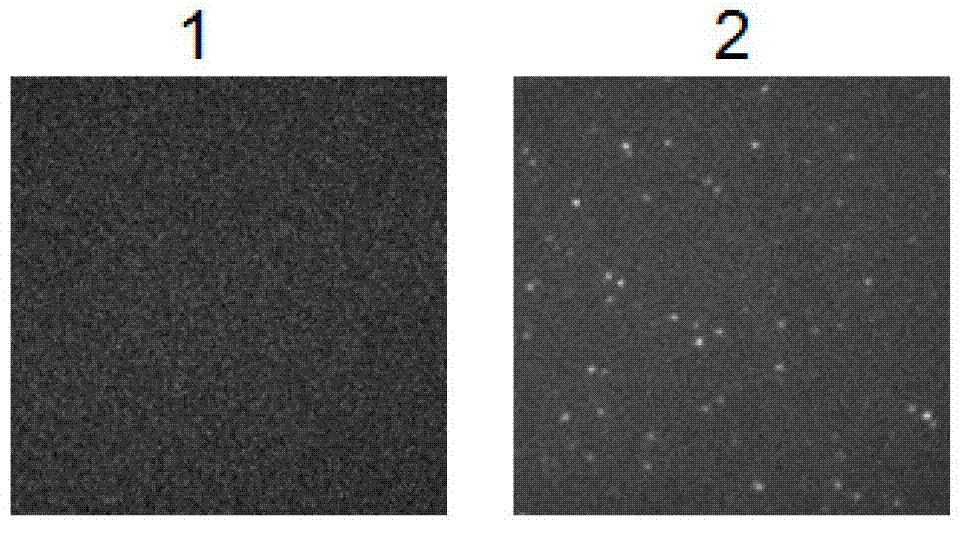
ActiveCN103630691BReduce experimental stepsShorten experiment timeBiological testingProtein targetTotal internal reflection
The invention relates to a biological detection method for small ubiquitin-like modification. Whether small ubiquitin-like modification occurs is detected by steps of constructing a gene fusion of a small ubiquitin-like modifier and a green fluorescent protein, performing compression of the gene fusion and a target protein in a cell, collecting the target protein through an immunosedimentation method and finally subjecting the target protein to molecule detection. According to the method, the target protein is eluted and observed after the target protein is collected by immunosedimentation, thus reducing experiment steps and shortening the experiment time. In addition, a total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy only excite fluorescence molecules in a 100 nm range on a cover glass, has high sensitivity and can detect the small ubiquitin-like modification in a single-molecule level. Accordingly, the method has characteristics of being rapid and sensitive.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com