Method for detecting single biological marker by using total internal reflection fluorescent microscope
A biomarker and fluorescence microscope technology, applied in the field of biological detection, can solve the problems of unsure of the treatment method, missing the best treatment opportunity, and exacerbation of the disease in sick animals, and achieves convenient and easy detection steps, short detection time, and low background low noise effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
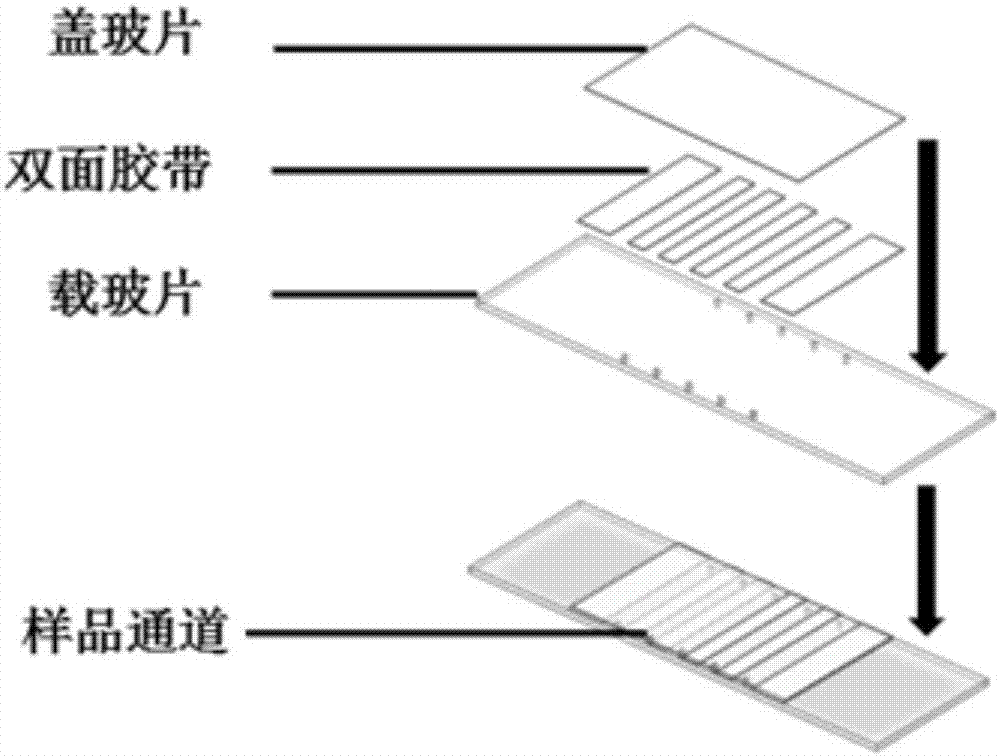
[0048] Embodiment 1 is made to be used for the sample small dish of sample addition
[0049] 1. Use an ordinary drill to drill 10 holes with a diameter of 0.8mm on a glass slide with a thickness of 1mm. This hole is very suitable for adding samples with a 200ul yellow tip;
[0050] 2. Rinse the slides repeatedly with deionized water;
[0051] 3. Ultrasonic cleaning of slides and coverslips with an acetone / alcohol solution with a volume ratio of 1:1 for 20 minutes;
[0052] 4. Rinse three times with deionized water;
[0053] 5. Ultrasonic cleaning with 1mol / L potassium hydroxide solution for 20 minutes;
[0054] 6. Rinse three times with deionized water;
[0055] 7. Dry the slides and coverslips in an oven;
[0056] 8. Place the slide and cover slip in a mixture containing 250ml of methanol, 10ml of anhydrous acetic acid, and 2ml of aminosilane coupling agent, sonicate for 1min, then let it stand for 20min to react;
[0057] 9. Place the slide and cover slip in methanol fo...
Embodiment 2
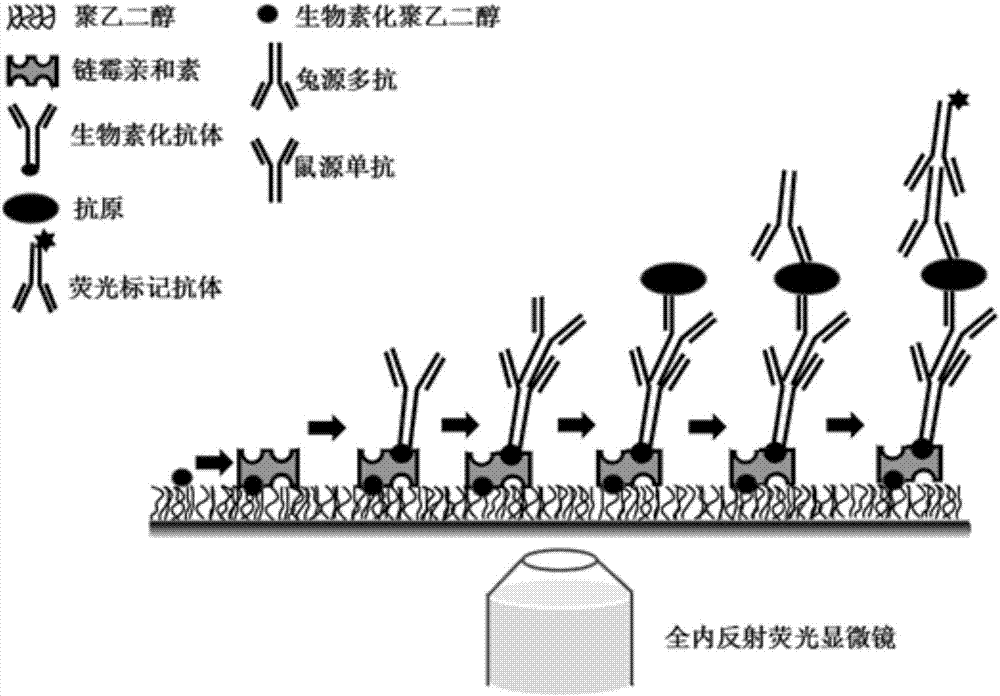
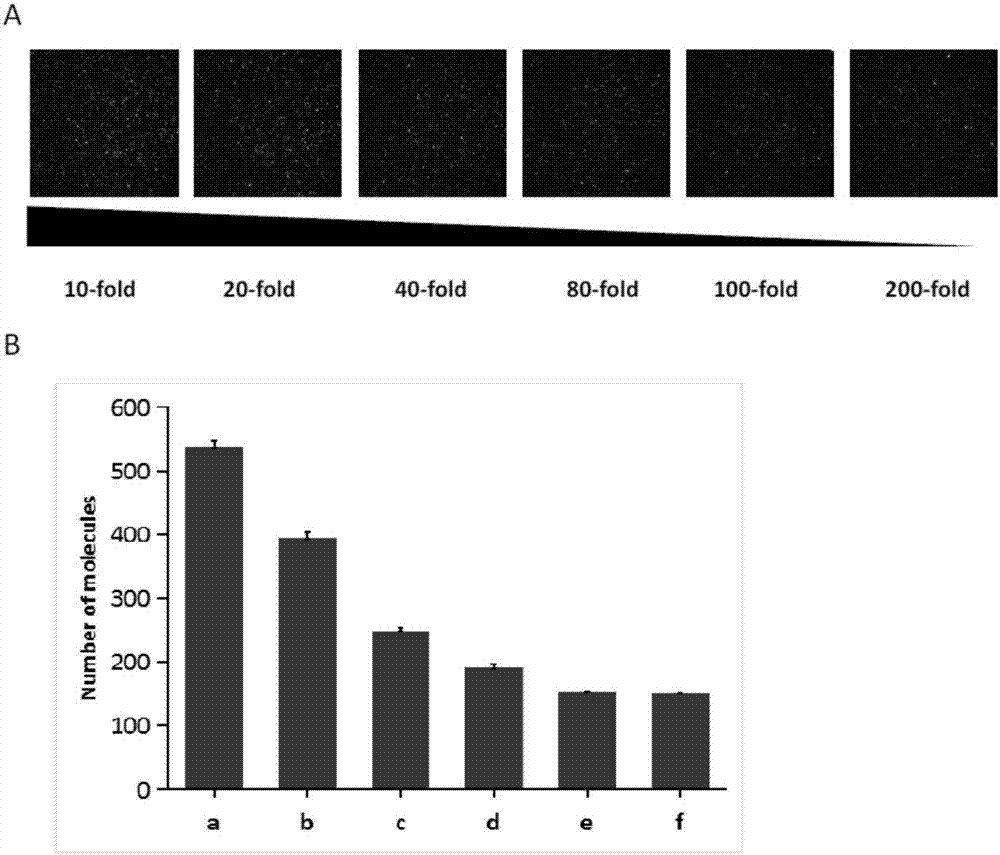
[0065] Example 2 Step-by-step loading of antibodies and antigens to be detected Immobilize pathogenic molecules, and use a fluorescent inverted microscope based on total internal reflection to obtain the number of pathogenic molecules
[0066] 1. Take 10ul of 0.2mg / mL streptavidin dissolved in T50 (10mmol / L Tris-HCl, (pH 8.0) and 50mmol / L NaCl) solution and add it to the sampling channel of the sample dish, and incubate at room temperature for 5min; There will be a connection between biotin and avidin;
[0067] 2. Take 20ul of T50 solution and add it to the sampling channel to wash away unbound streptavidin;
[0068] 3. Add 10ul of 40nM biotin-labeled goat anti-mouse secondary antibody to the loading channel, and incubate at room temperature for 15 minutes; the connection between biotin and avidin will occur, and the secondary antibody will be immobilized on the surface of the channel;
[0069] 4. Add 20ul of T50-BSA (0.1mg / ml bovine serum albumin (BSA) dissolved in T50 solut...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| refractive index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com