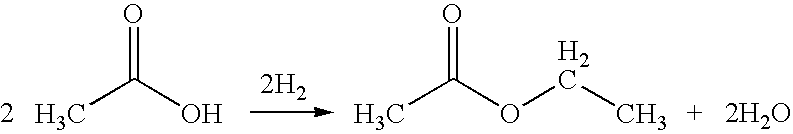
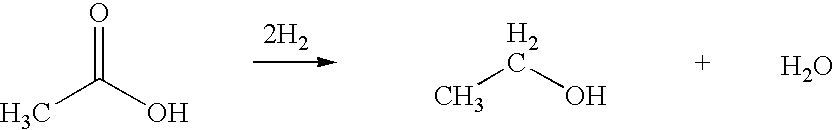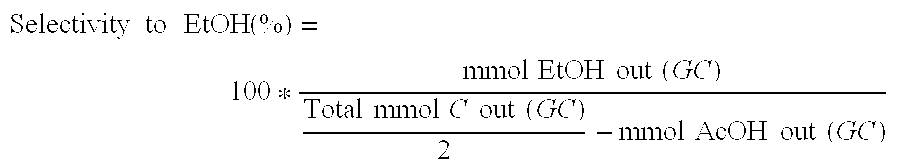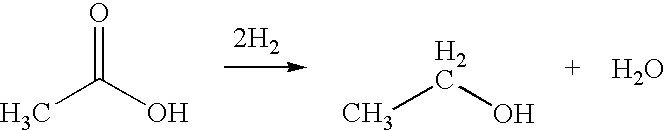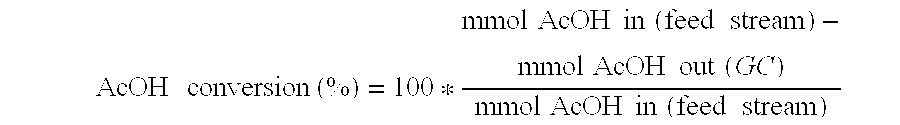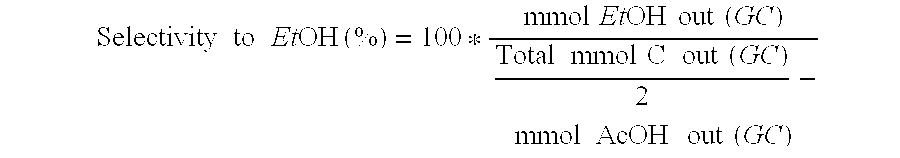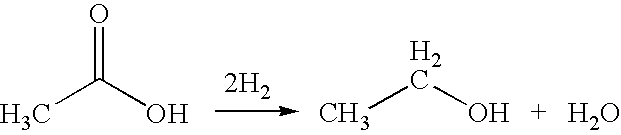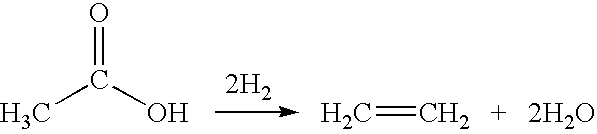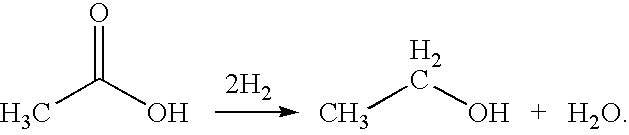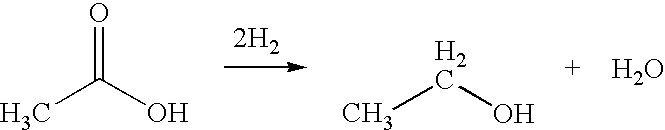Patents
Literature
48260 results about "Acetic acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Acetic acid is used to treat an outer ear infection (external otitis).
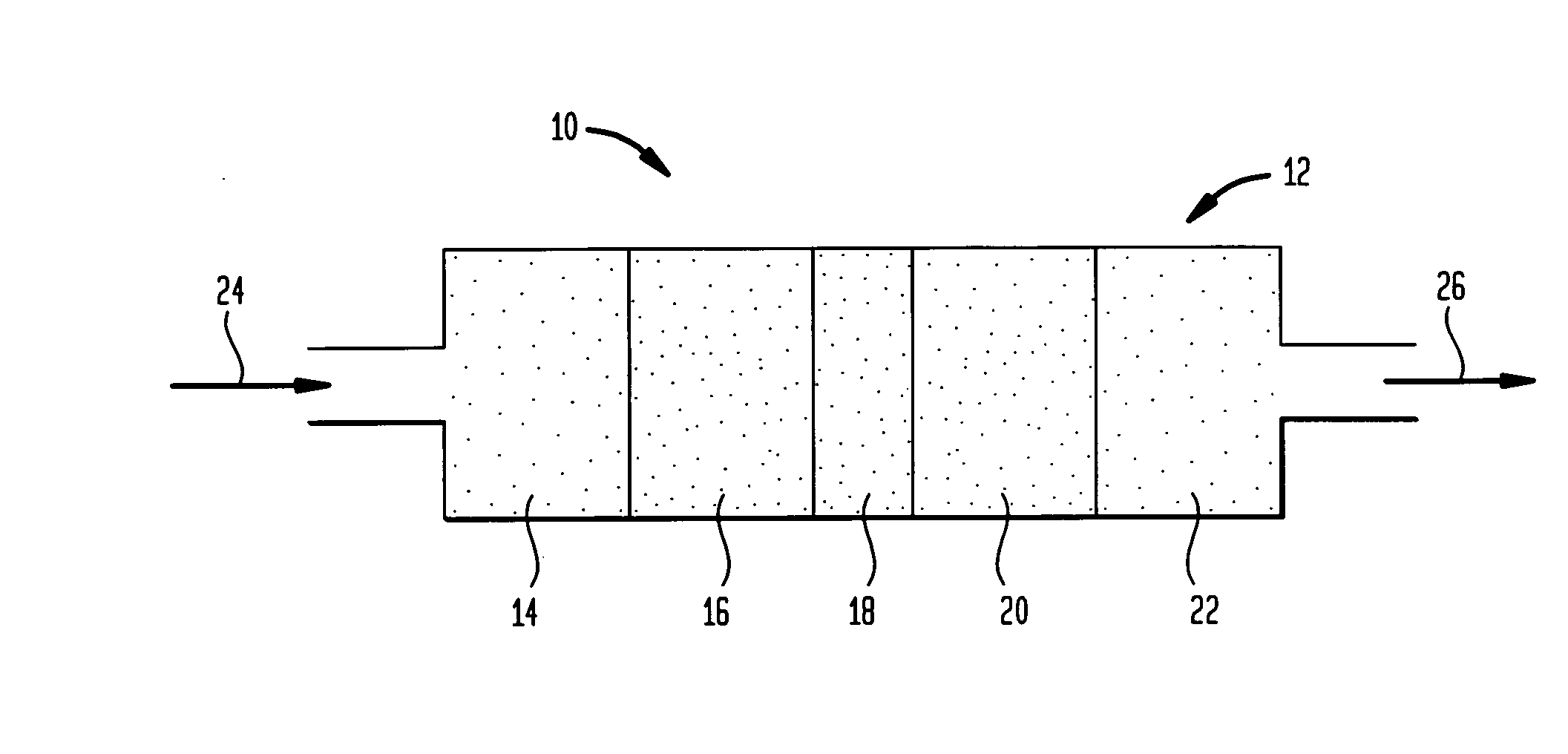
Low energy carbonylation process
InactiveUS6657078B2Weaken energyHigh purityOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsPropanoic acidIodide
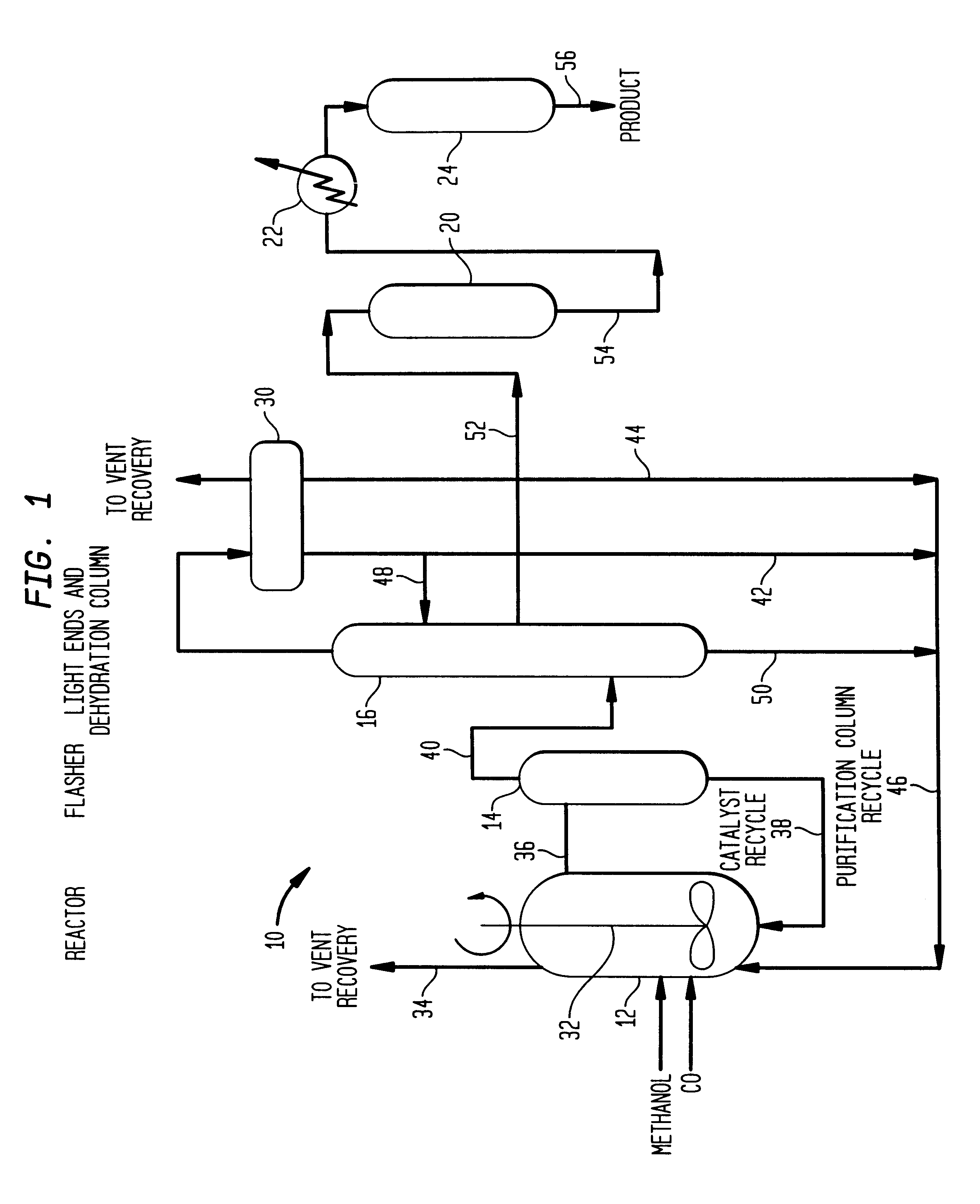
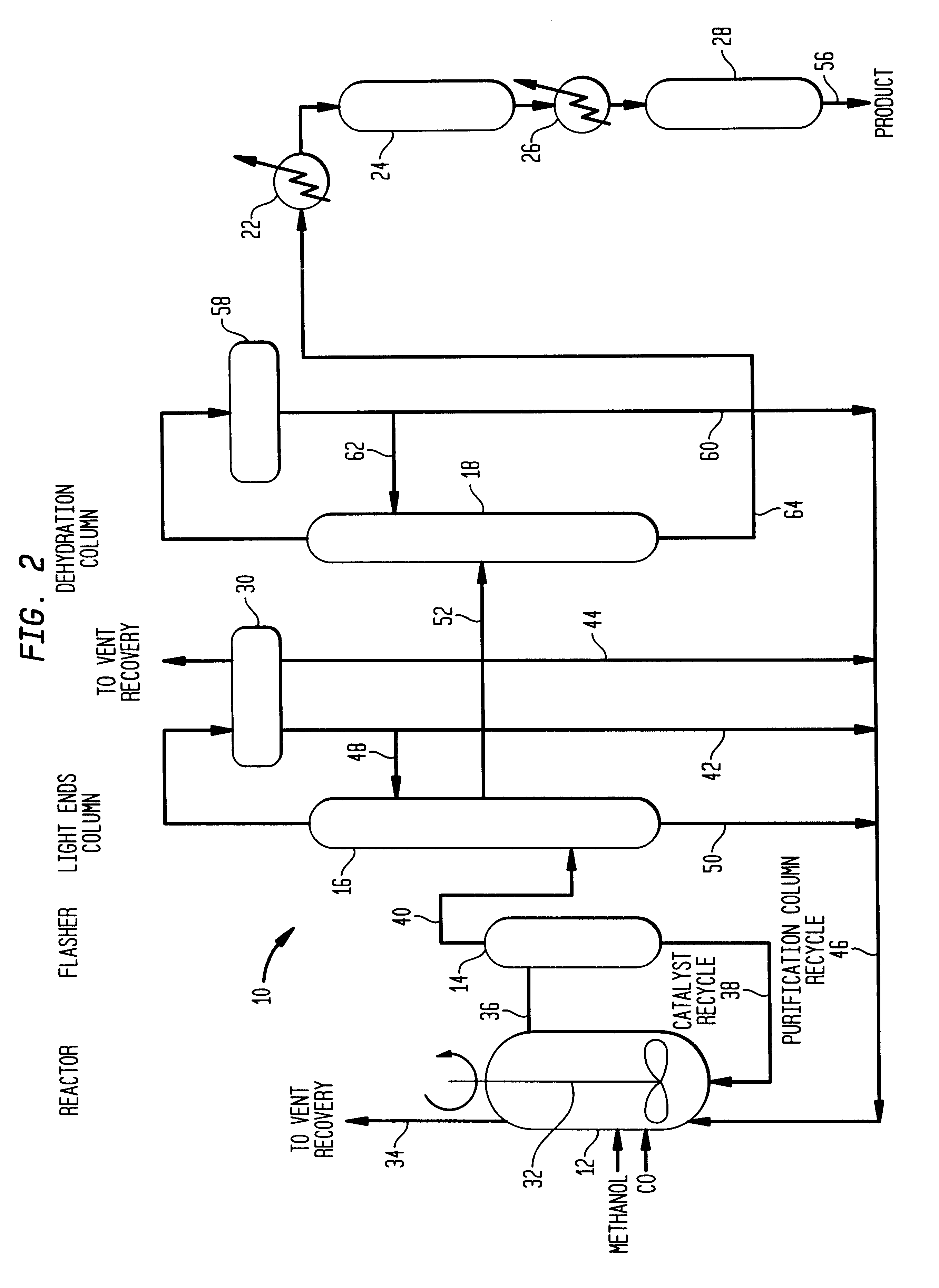
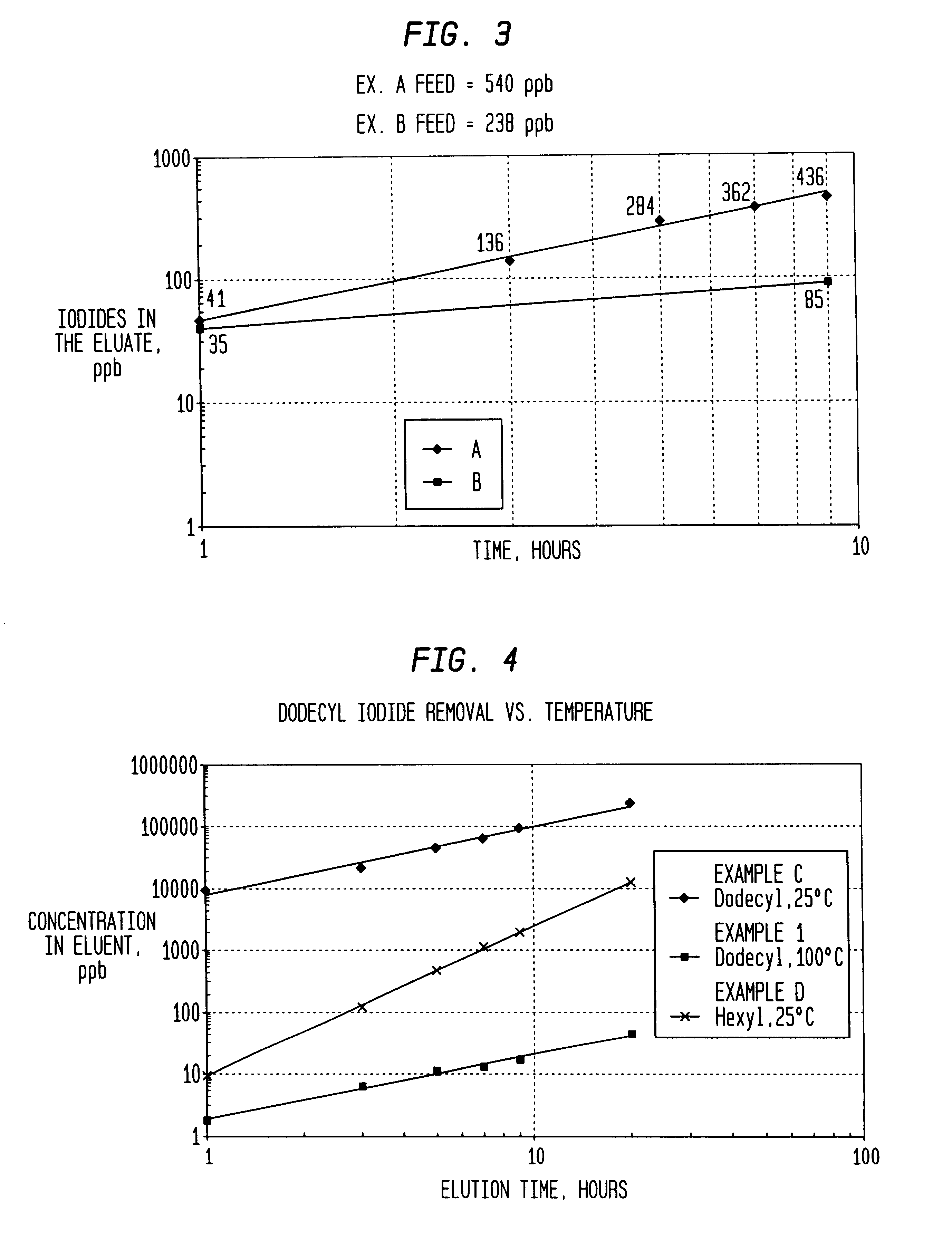
A low energy process for producing acetic acid by the carbonylation of methanol is disclosed. The process involves a rhodium-catalyzed system operated at less than about 14% water utilizing up to 2 distillation columns. The process is preferably controlled such that the product stream has a low level of propionic acid impurity and the level of aldehyde impurities is minimized by way of aldehyde removal or minimizing aldehyde generation. The level of iodides is controlled by contacting the product, at elevated temperatures, with ion exchange resins. In preferred embodiments, at least one silver or mercury exchanged macroreticular strong acid ion exchange resin is used to purify the product. The high temperature treatment provides the added benefit of controlling the Color Value (Pt-Co units) of the product stream.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Ethanol production from acetic acid utilizing a cobalt catalyst
InactiveUS7608744B1High selectivityHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationOxygen compounds preparation by reductionAcetic acidPlatinum
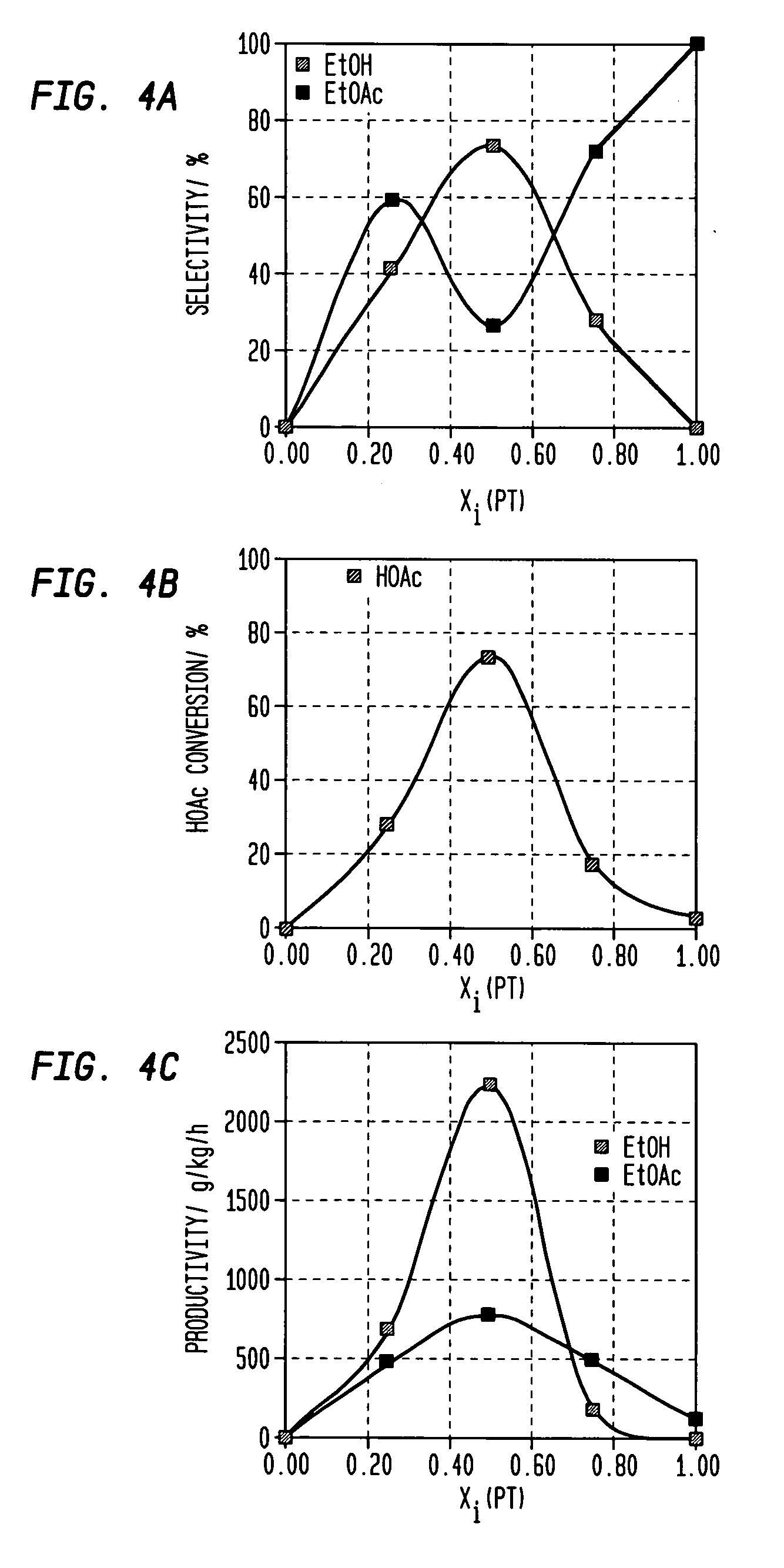
A process for the selective production of ethanol by vapor phase reaction of acetic acid over a hydrogenating catalyst composition to form ethanol is disclosed and claimed. In an embodiment of this invention reaction of acetic acid and hydrogen over either cobalt and palladium supported on graphite or cobalt and platinum supported on silica selectively produces ethanol in a vapor phase at a temperature of about 250° C.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
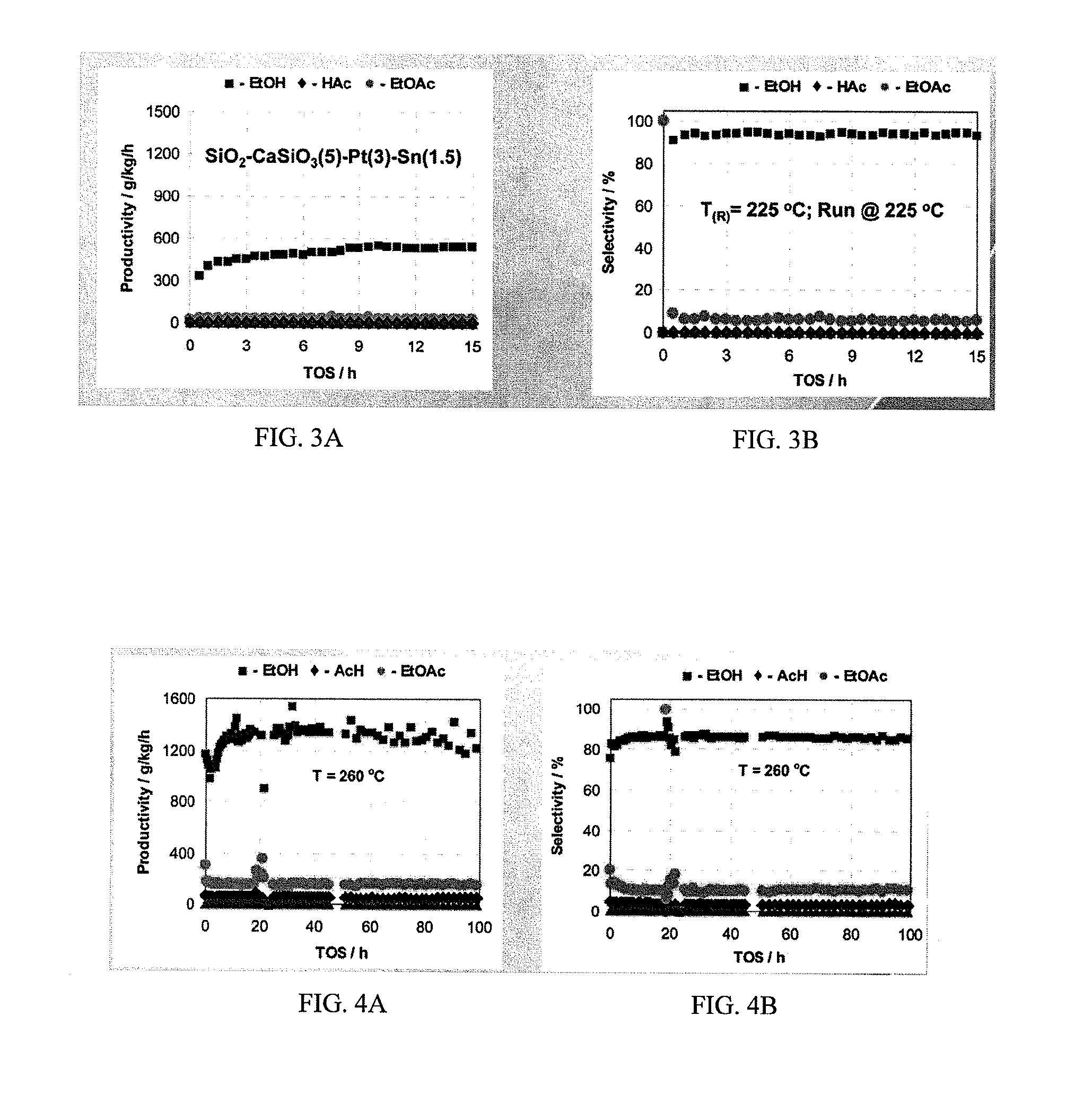
Direct and selective production of ethanol from acetic acid utilizing a platinum/tin catalyst
InactiveUS7863489B2High selectivityHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationOxygen compounds preparation by reductionCalcium silicateAcetic acid
A process for the selective production of ethanol by vapor phase reaction of acetic acid over a hydrogenating catalyst composition to form ethanol is disclosed and claimed. In an embodiment of this invention reaction of acetic acid and hydrogen over a platinum and tin supported on silica, graphite, calcium silicate or silica-alumina selectively produces ethanol in a vapor phase at a temperature of about 250° C.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Process for producing ethanol
InactiveUS6927048B2High carbon yieldHigh protein concentrationOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationAcetic acidHydrogenation reaction
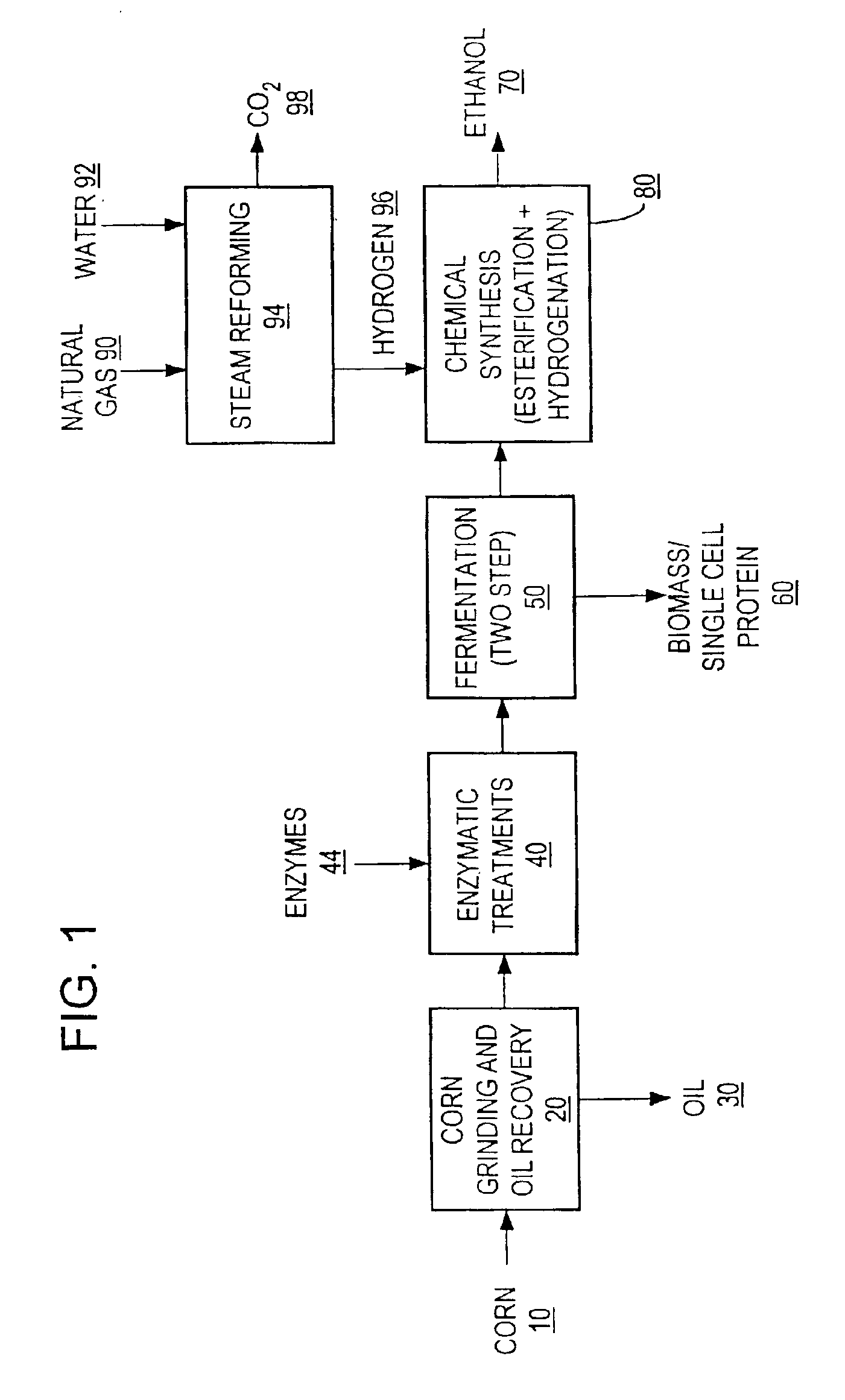
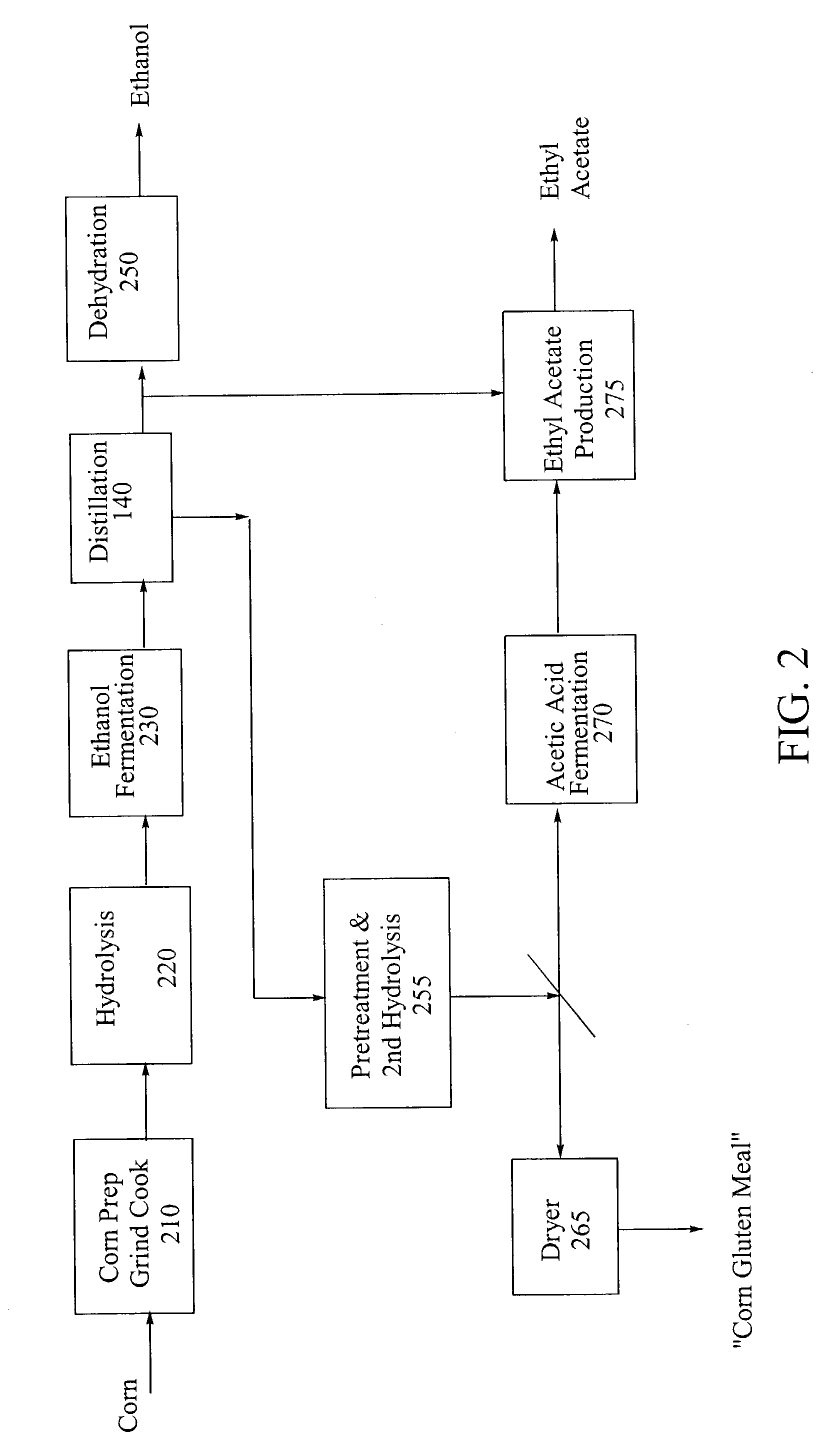
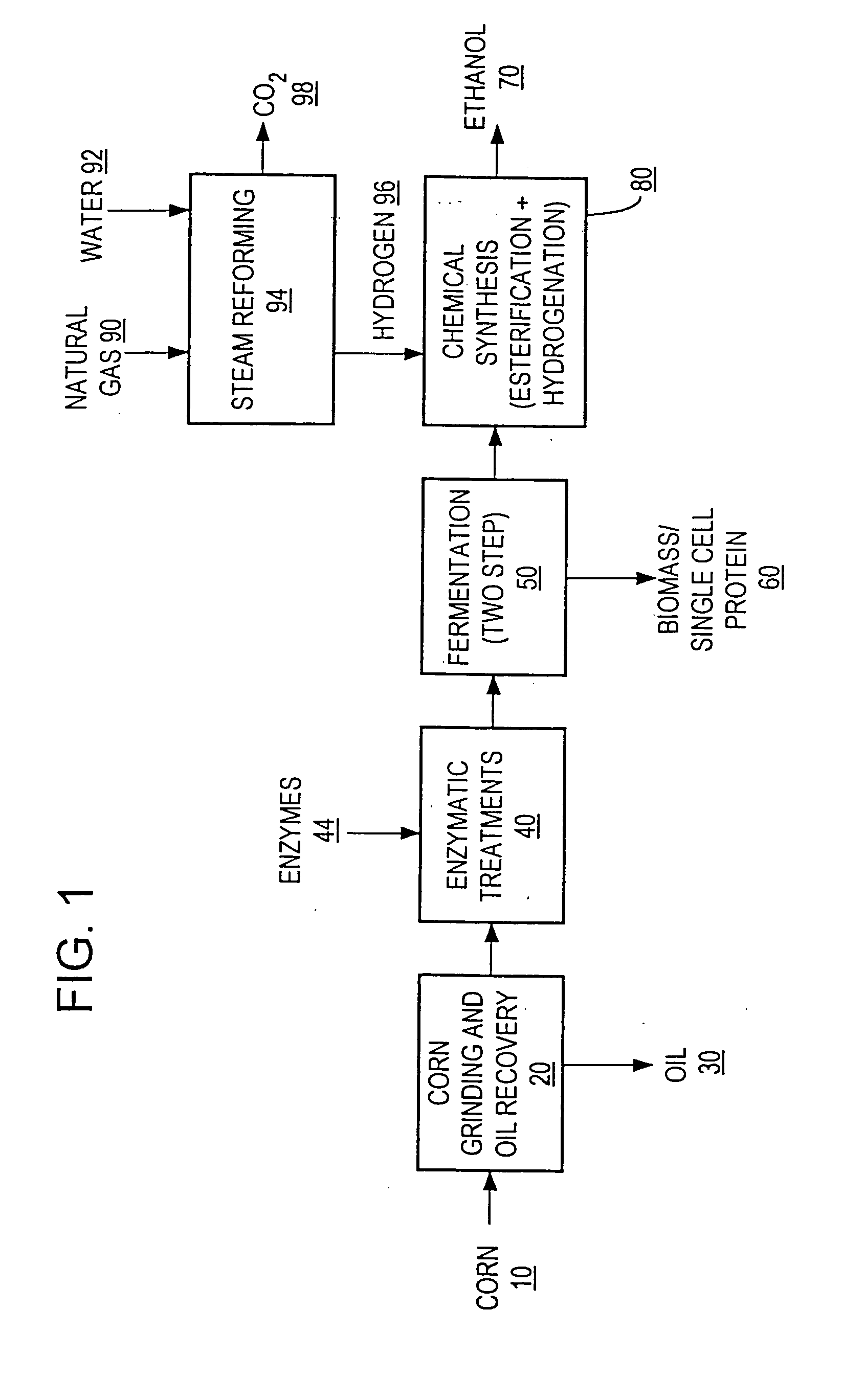
A process for producing ethanol including a combination of biochemical and synthetic conversions results in high yield ethanol production with concurrent production of high value coproducts. An acetic acid intermediate is produced from carbohydrates, such as corn, using enzymatic milling and fermentation steps, followed by conversion of the acetic acid into ethanol using esterification and hydrogenation reactions. Coproducts can include corn oil, and high protein animal feed containing the biomass produced in the fermentation.
Owner:ZEACHEM
Ethylene production from acetic acid utilizing dual reaction zone process
A process for selective formation of ethylene from acetic acid includes contacting a feed stream containing acetic acid and hydrogen at an elevated temperature with a first catalytic composition including a suitable hydrogenating catalyst in a first reaction zone to form an intermediate mixture including ethanol and ethyl acetate; and subsequently reacting the intermediate mixture over a suitable dehydrating and / or cracking catalyst in a second reaction zone to form ethylene. Selectivities of ethylene of over 80% are achieved.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Process for catalytically producing ethylene directly from acetic acid in a single reaction zone
InactiveUS20100030001A1High selectivityHigh yieldHydrocarbonsBulk chemical productionAcetic acidHydrogen
A process for the selective production of ethylene by vapor phase reaction of acetic acid over a hydrogenating catalyst composition to form ethylene in a single reaction zone is disclosed and claimed. In an embodiment of this invention reaction of acetic acid and hydrogen over either a copper supported on iron oxide, copper-aluminum catalyst, cobalt supported on H-ZSM-5, ruthenium-cobalt supported on silica or cobalt supported on carbon selectively produces ethylene in a vapor phase at a temperature in the range of about 250° C. to 350° C.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Antibody formulations
The present application describes antibody formulations, including monoclonal antibodies formulated in histidine-acetate buffer, as well as a formulation comprising an antibody that binds to domain II of HER2 (for example, Pertuzumab), and a formulation comprising an antibody that binds to DR5 (for example, Apomab).
Owner:GENENTECH INC
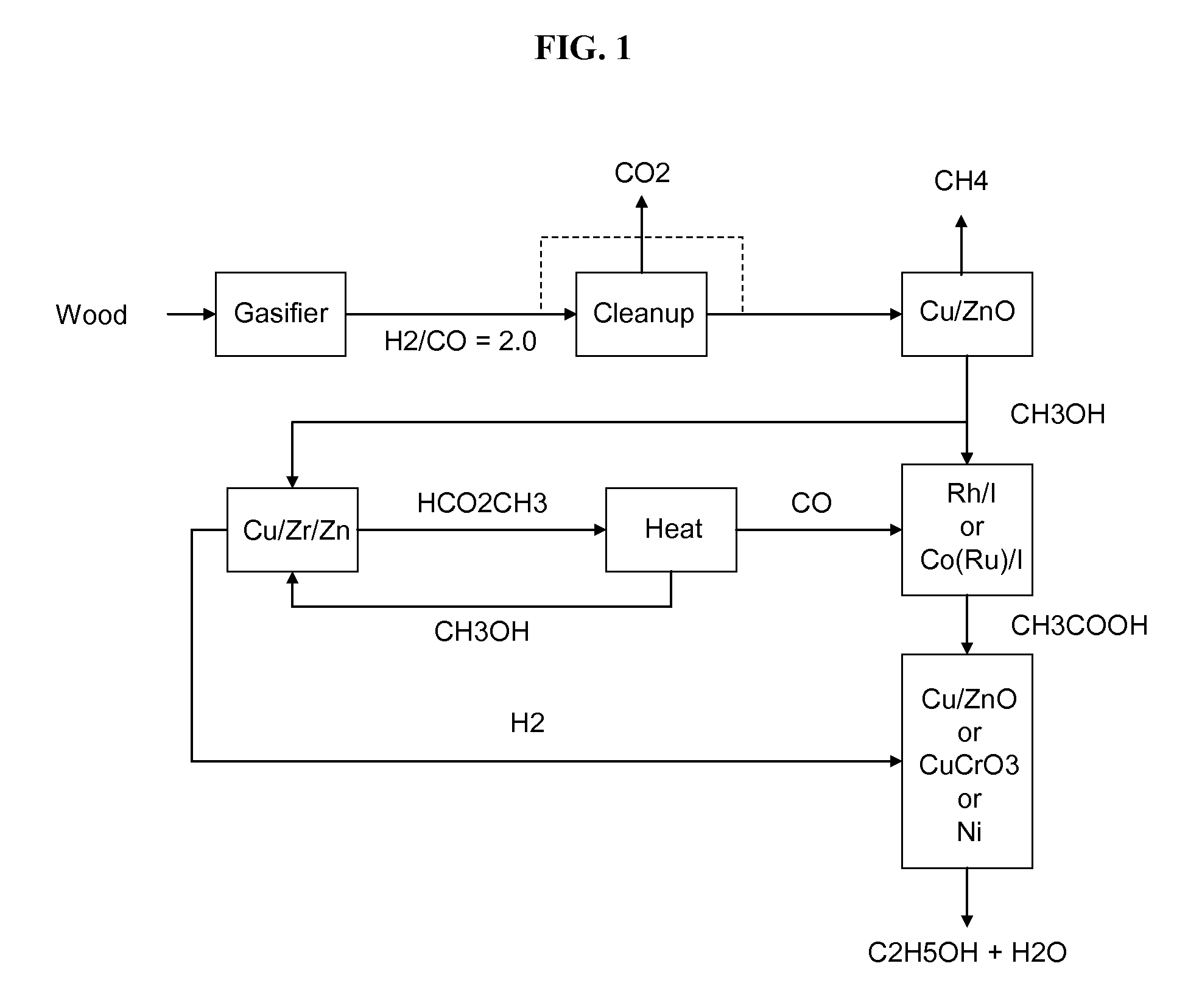
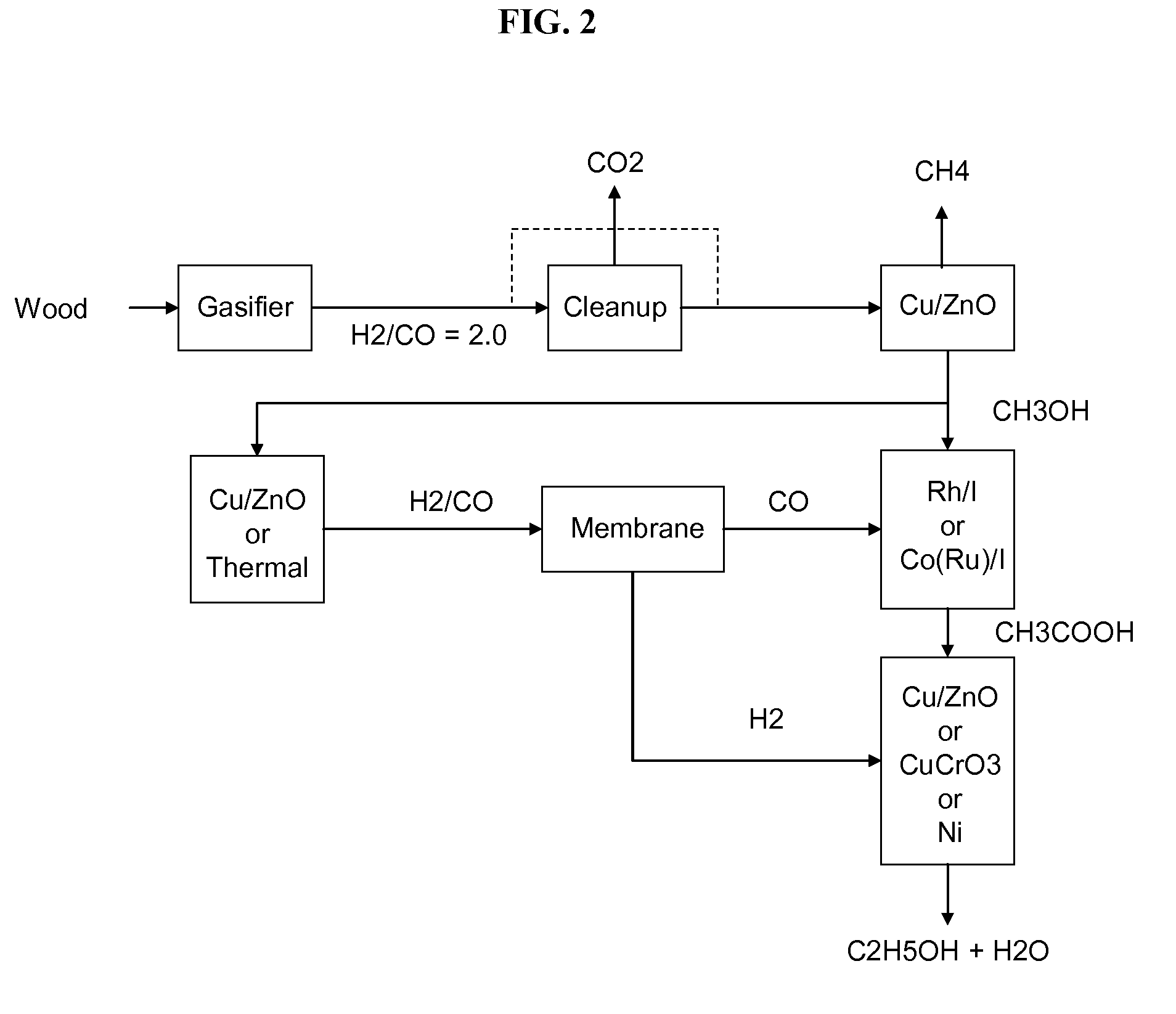
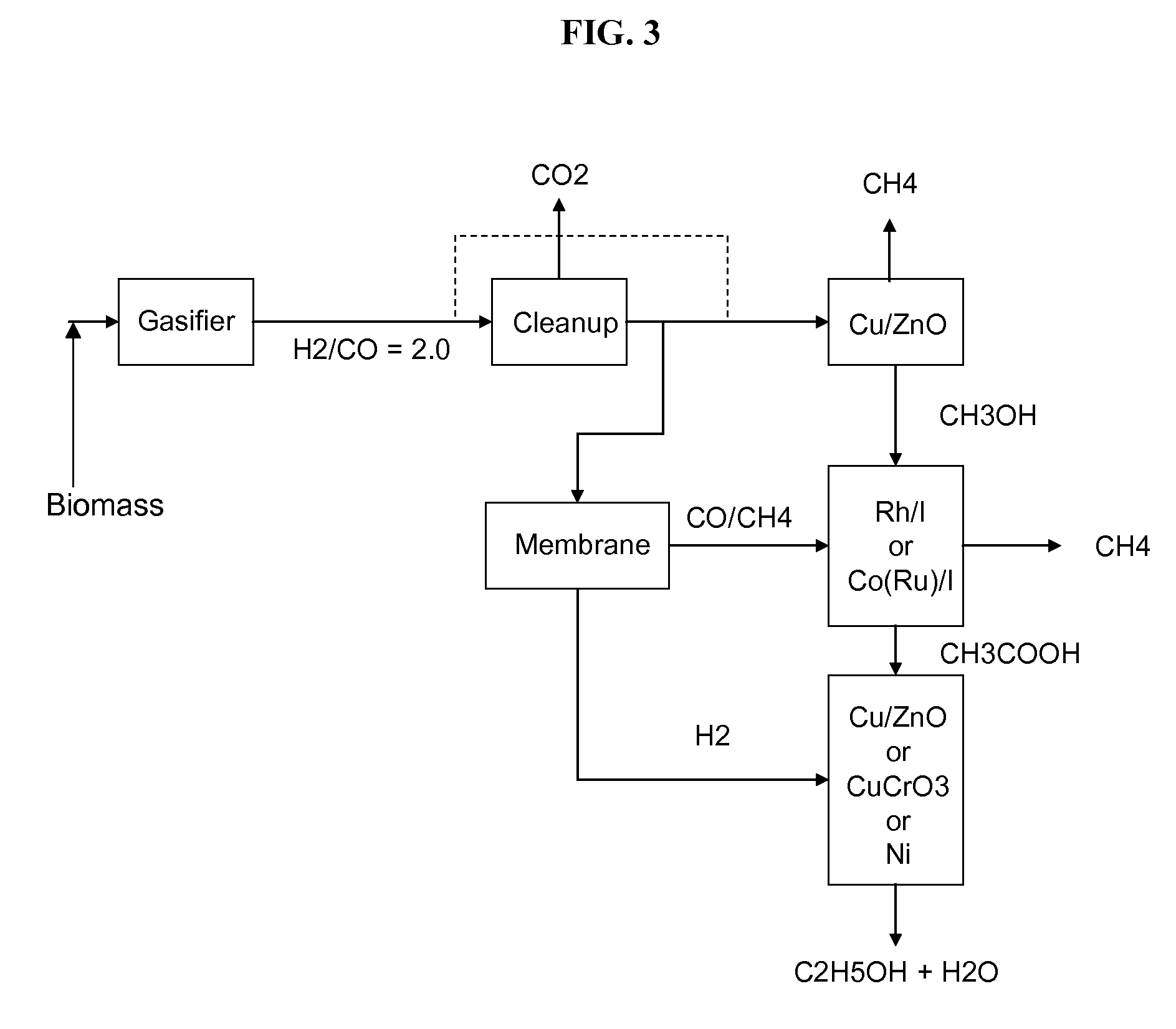
Methods and apparatus for selectively producing ethanol from synthesis gas
The invention provides methods and apparatus for selectively producing ethanol from syngas. As disclosed herein, syngas derived from cellulosic biomass (or other sources) can be catalytically converted into methanol, which in turn can be catalytically converted into acetic acid or acetates. Finally, the acetic acid or acetates can be reduced to ethanol according to several variations. In some embodiments, yields of ethanol from biomass can exceed 100 gallons per dry ton of biomass.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Damage resistant glass article for use as a cover plate in electronic devices
InactiveUS20090197048A1Minimizing transportEasy to disassembleFilm/foil adhesivesSynthetic resin layered productsAnti-reflective coatingChemical Linkage
An alkali aluminosilicate glass article, said alkali aluminosilicate glass having a surface compressive stress of at least about 200 MPa, a surface compressive layer having a depth of at least about 30 μm, a thickness of at least about 0.3 mm and an amphiphobic fluorine-based surface layer chemically bonded to the surface of the glass. In one embodiment the glass has an anti-reflective coating applied to one surface of the glass between the chemically strengthened surface of the glass and the amphiphobic coating. In another embodiment the surface of the chemically strengthened glass is acid treated using a selected acid (e.g., HCL, H2SO4, HClO4, acetic acid and other acids as described) prior to placement of the amphiphobic coating or the anti-reflective coating.
Owner:CORNING INC
Direct and selective production of ethanol from acetic acid utilizing a platinum/tin catalyst
InactiveUS20100029995A1High selectivityHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationOxygen compounds preparation by reductionCalcium silicatePlatinum
A process for the selective production of ethanol by vapor phase reaction of acetic acid over a hydrogenating catalyst composition to form ethanol is disclosed and claimed. In an embodiment of this invention reaction of acetic acid and hydrogen over a platinum and tin supported on silica, graphite, calcium silicate or silica-alumina selectively produces ethanol in a vapor phase at a temperature of about 250° C.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
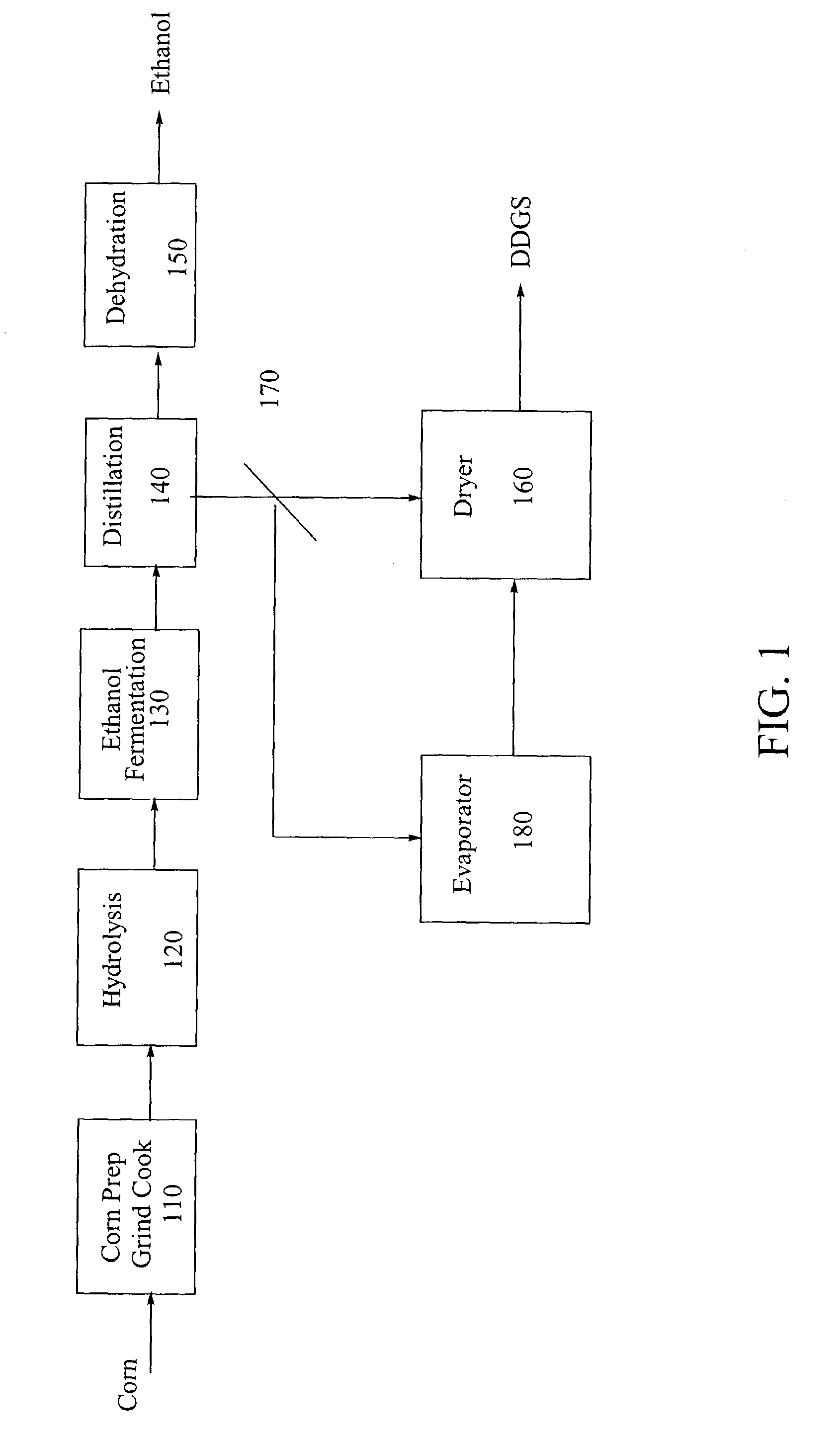
Process for producing ethanol from corn dry milling
InactiveUS7074603B2Fermented solutions distillation/rectificationOrganic compound preparationAcetic acidHydrogenation reaction
A process for producing ethanol by the conversion of carbohydrates from a corn dry milling process in which the bottoms fraction from distillation of ethanol in a conventional yeast fermentation is used in a process including a combination of biochemical and synthetic conversions. The process results in high yield ethanol production with concurrent production of high value coproducts. An acetic acid intermediate is produced from bottoms fraction, followed by conversion of the acetic acid into ethanol using esterification and hydrogenation reactions. Coproducts of the process include a high protein content solids fraction produced in the fermentation.
Owner:ZEACHEM
Tunable catalyst gas phase hydrogenation of carboxylic acids
InactiveUS20100121114A1High selectivityExcessive loss of activityOrganic compound preparationHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsPlatinumAcetic acid
A process for selective formation of ethanol from acetic acid includes contacting a feed stream containing acetic acid and hydrogen at an elevated temperature with catalyst comprising platinum and tin on a high surface area silica promoted with calcium metasilicate. Selectivities to ethanol of over 85% are achieved at 280° C. with catalyst life in the hundreds of hours.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
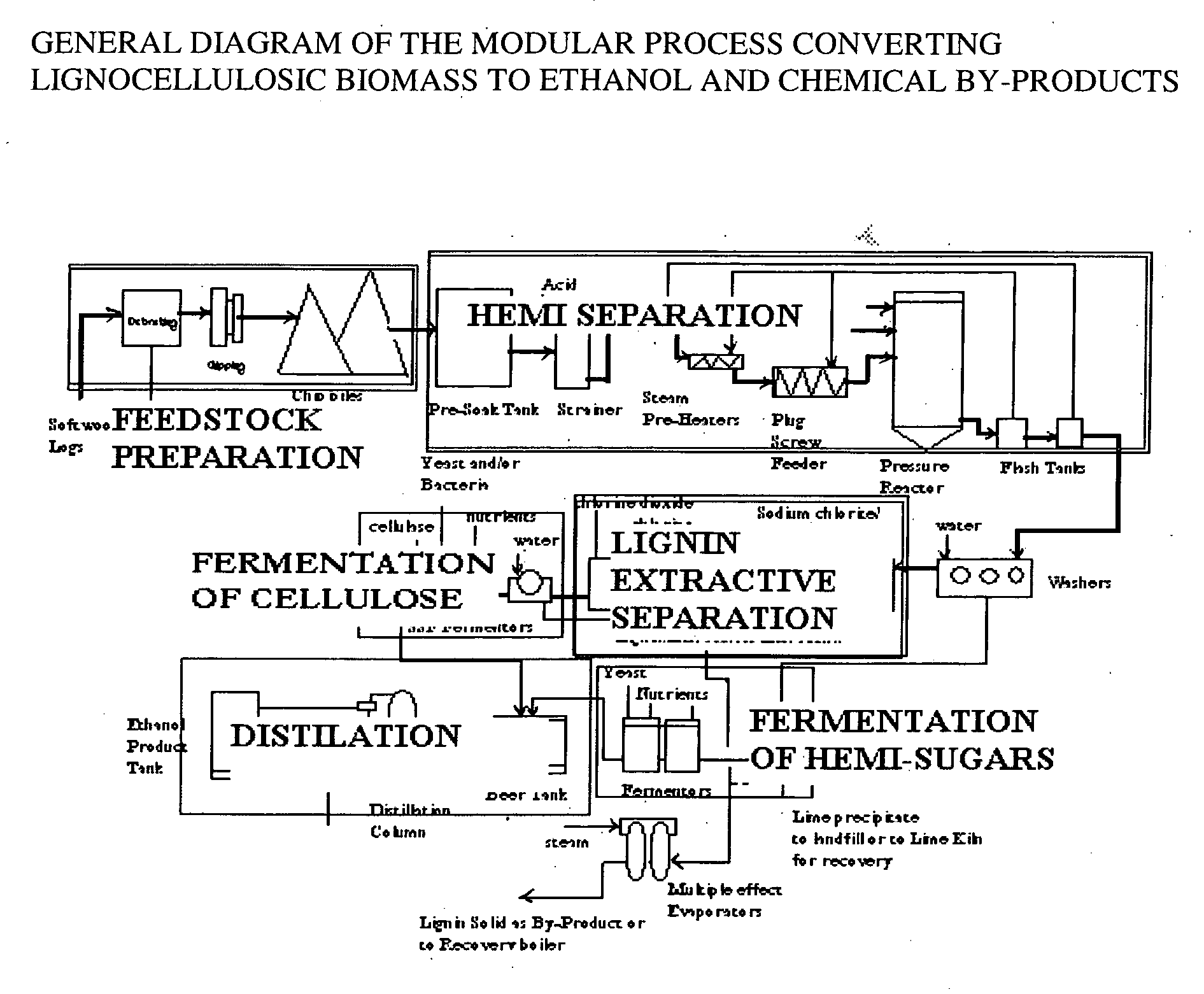
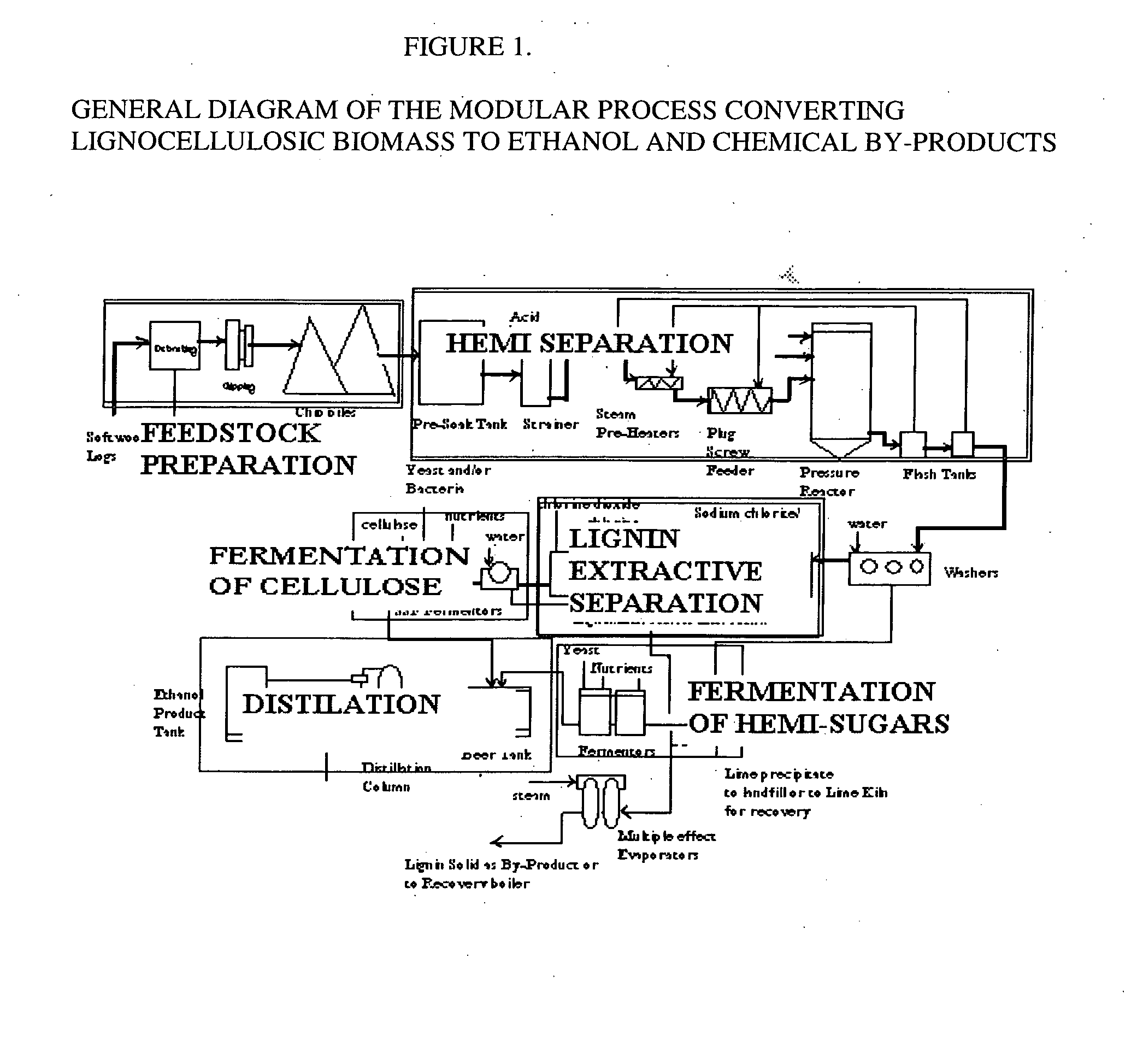
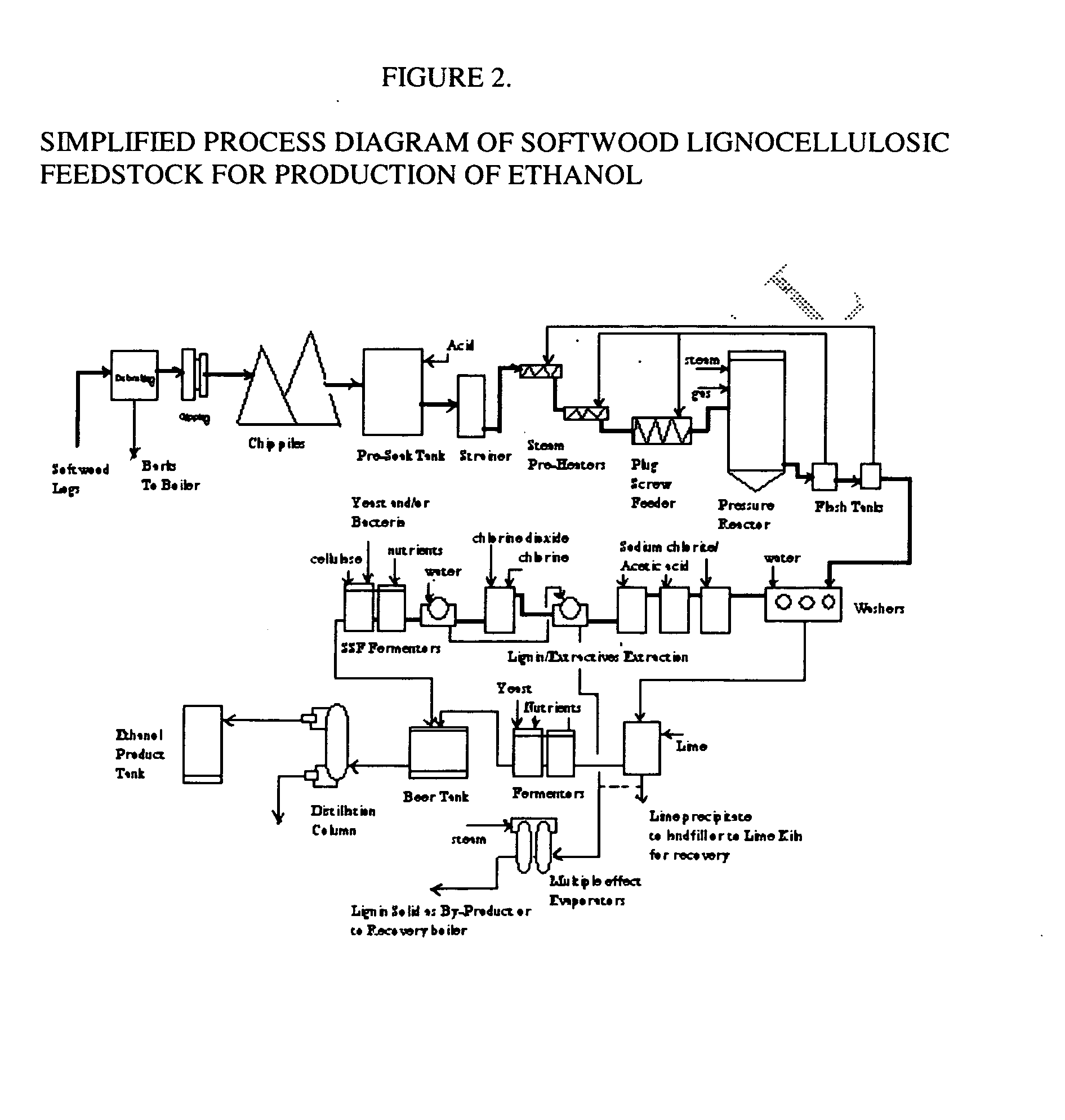
Integrated process for separation of lignocellulosic components to fermentable sugars for production of ethanol and chemicals
InactiveUS20080057555A1Robust and cost-effectiveImprove responseChemical industryBiofuelsChemical treatmentButanediol
A continuous and modular process converts lignocellulosic materials for the production of ethanol principally and / or chemicals such as methanol, butanediol, propanediol, hydrocarbon fuel, etc. Renewable lignocellulosic biomass such as but not all inclusive hardwoods (gum, beech, oak, sweet gum, poplar, eucalyptus, etc.), soft woods (pines, firs, spruce, etc.), corn stovers, straws, grasses, recycled papers, waste products from pulp and paper mills, etc can be used as feedstock. The process is designed to be modular and the feed entry point can be selected to adapt to different biomass feedstock. Lignocellulosic biomass such as hardwood and softwood are subjected to chemical / pressure treatment stages using potent and selective chemicals such as sodium chlorite / acetic acid (anhydrous) and chlorine / chlorine dioxide to separate the main components—lignin, cellulose (glucose) and hemicelluloses (xylose, arabinose, galactose)—into three process streams. The separated carbohydrates are further subjected to washing, cleaning, neutralization, and / or mild hydrolysis and subsequently fermented to produce ethanol. Residual lignin and extractives remained with the cellulose are removed by chemical treatment steps to enhance the fermentations of cellulose. Pre-hydrolysate after neutralization to neutralize and remove toxic components such as acetic acid, furfural, phenolics, etc. containing (xylose, arabinose, galactose) and hexoses (glucose) can be either separately or together with the purified cellulosic fraction fermented to produce ethanol. Approximately 100 gallons of ethanol, suitable to be used as a fuel, can be produced from one dried ton of wood. Significant amount of lignin are separated as a by-product and can be converted to hydrocarbon fuel, surfactant, drilling aid, or can be incinerated for generation of power and steam.
Owner:NGUYEN XUAN NGHINH
Soluble deverting agents
Methods and compositions for stimulating single and multiple intervals in subterranean wells by diverting well treatment fluids into a particular direction or into multiple intervals using water soluble coated diverting agents are described. The water soluble coating of the diverting material is preferably a collagen, poly(alkylene) oxide, poly(lactic acid), polyvinylacetate, polyvinylalcohol, polyvinylacetate / polyvinylalcohol polymer or a mixture thereof applied as a coating on any number of proppants. The method allows for the diverting of the flow of fluids in a downhole formation during a well treatment, such as during a fracturing process. Following completion of a treatment such as a hydraulic stimulation, the soluble diverting agent can be dissolved and removed by the water component of the well production.
Owner:FAIRMOUNT SANTROL
Removal of permanganate reducing compounds from methanol carbonylation process stream
ActiveUS7223886B2Reduce solubilitySimple methodOrganic compound preparationPreparation by carbon monoxide or formate reactionAcetic acidIodide
An improvement of the methanol carbonylation process for manufacturing acetic acid is disclosed. Specifically disclosed is a method for reducing the formation of alkyl iodides and C3-8 carboxylic acids by removing permanganate reducing compounds (“PRC's”) from the light phase of the condensed light ends overhead stream, including (a) distilling the light phase to yield a PRC enriched overhead stream; and (b) extracting the third overhead stream with water in at least two consecutive stages and separating therefrom one or more aqueous streams containing PRC's.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
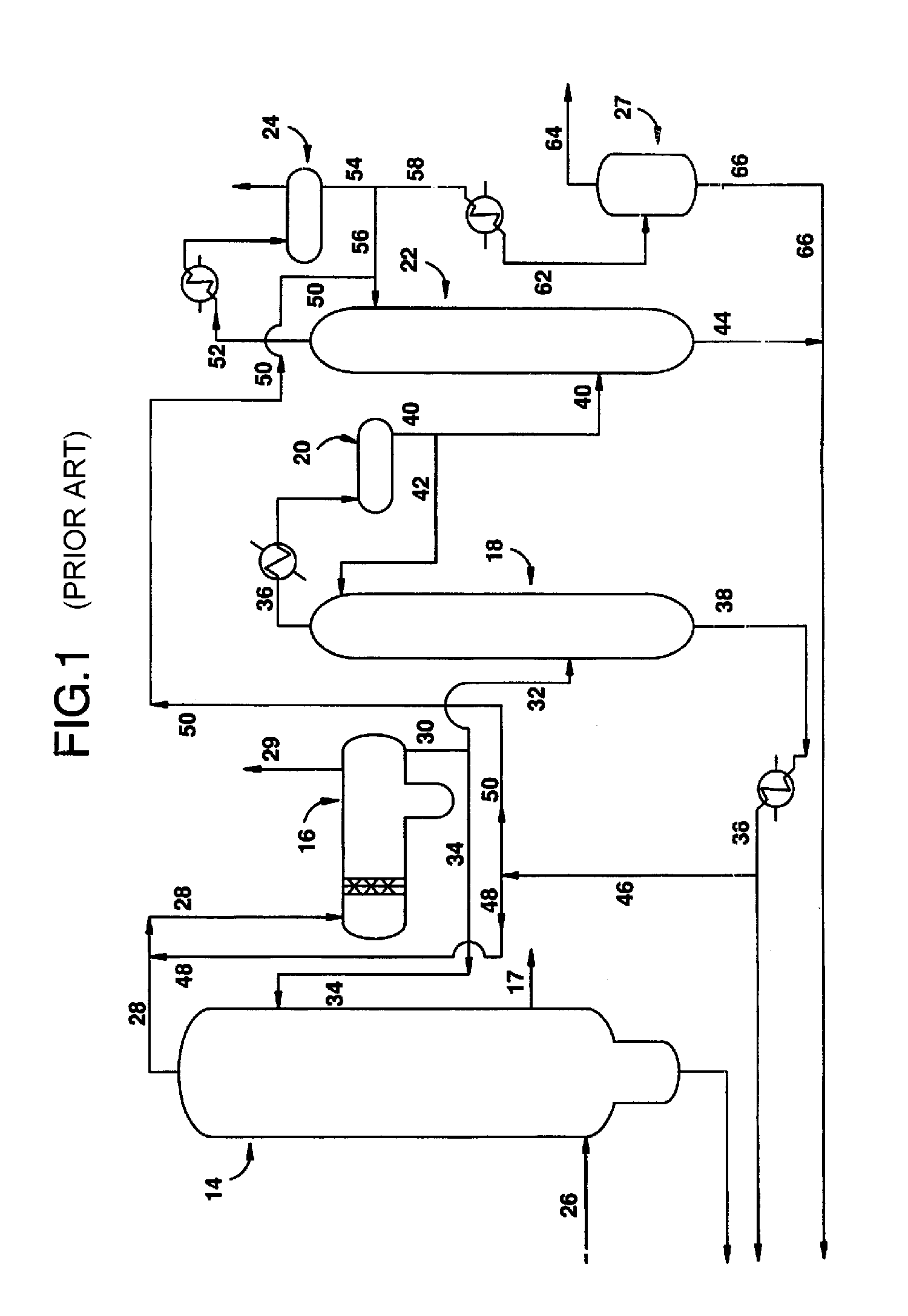
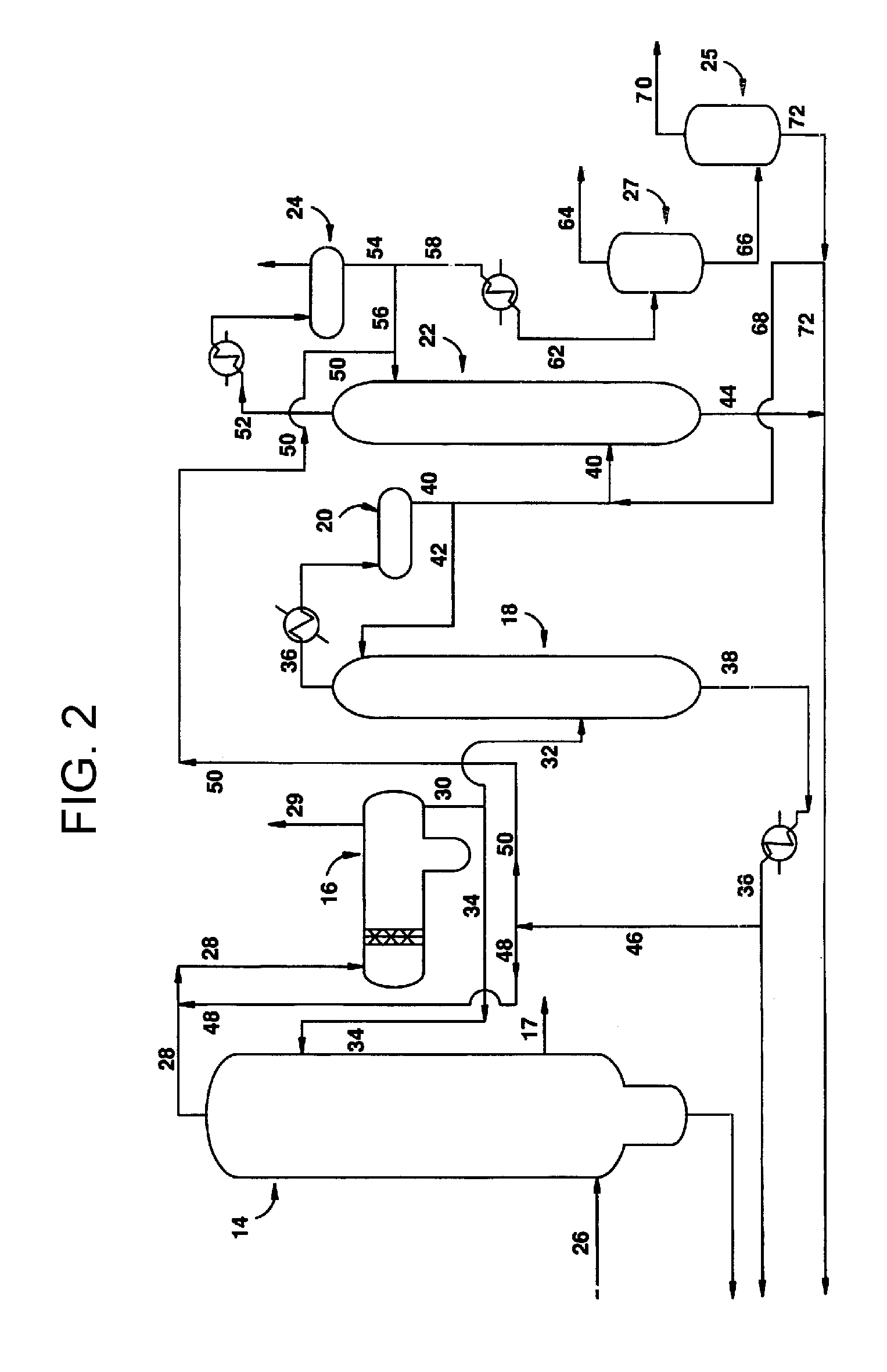
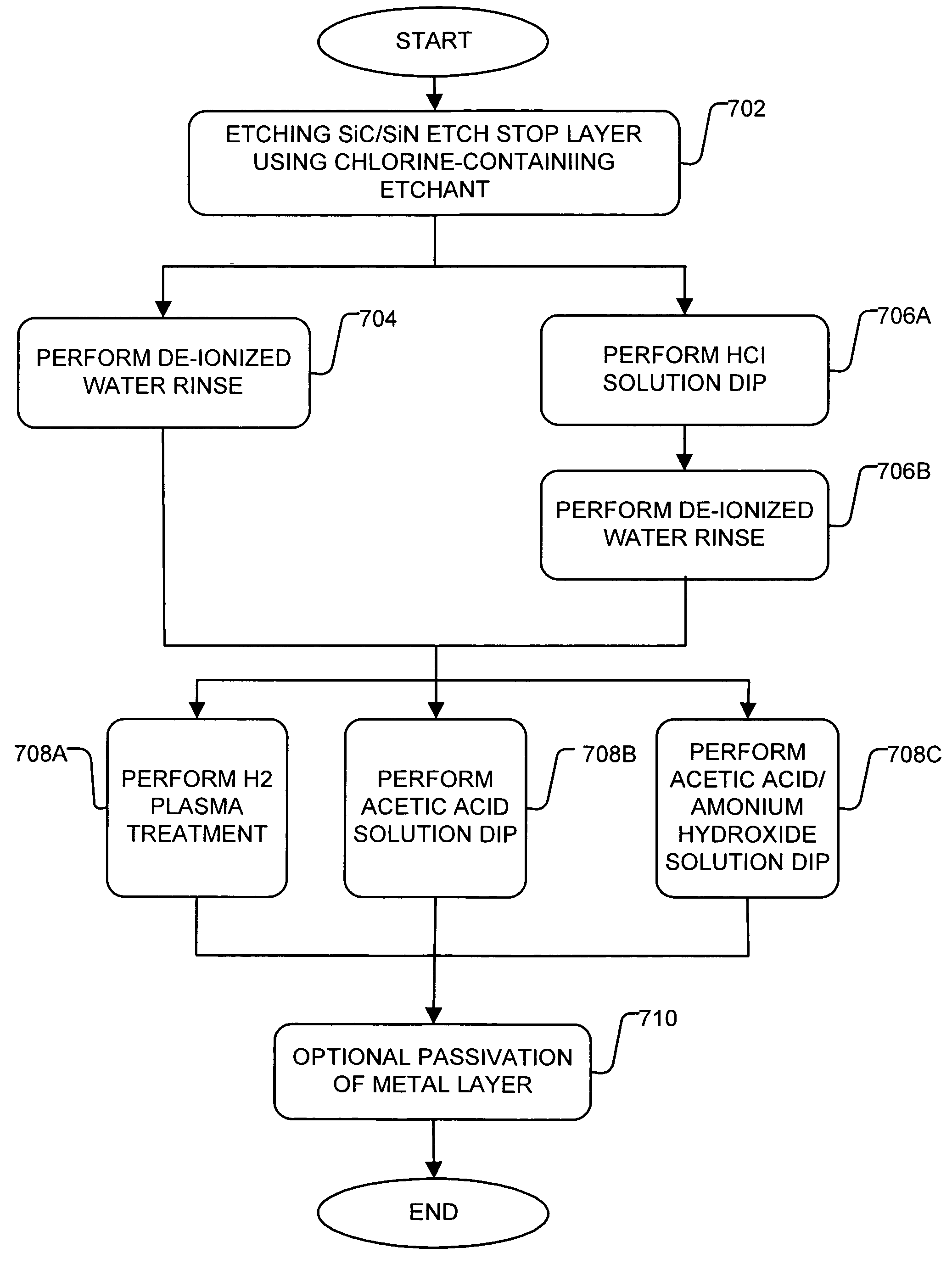
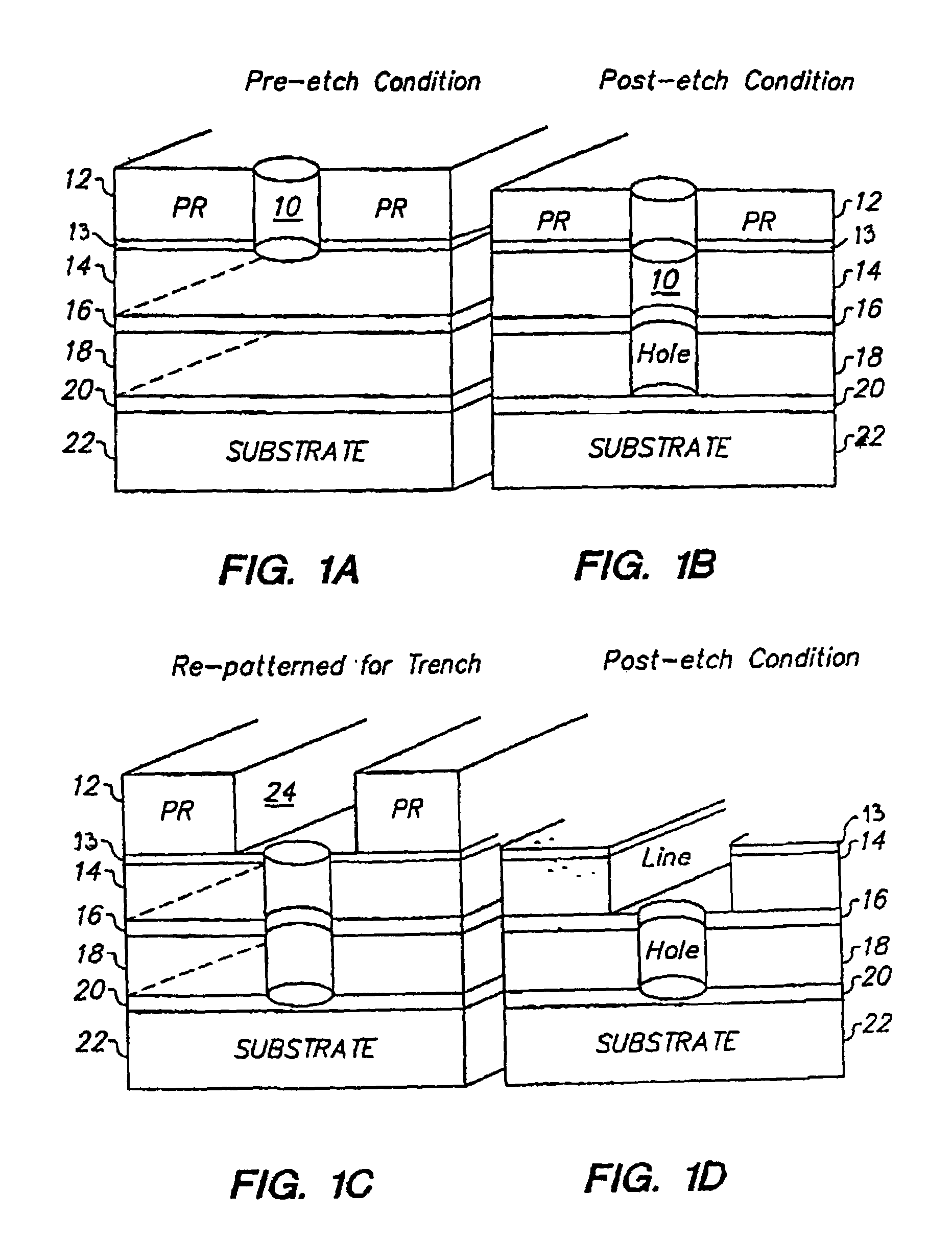
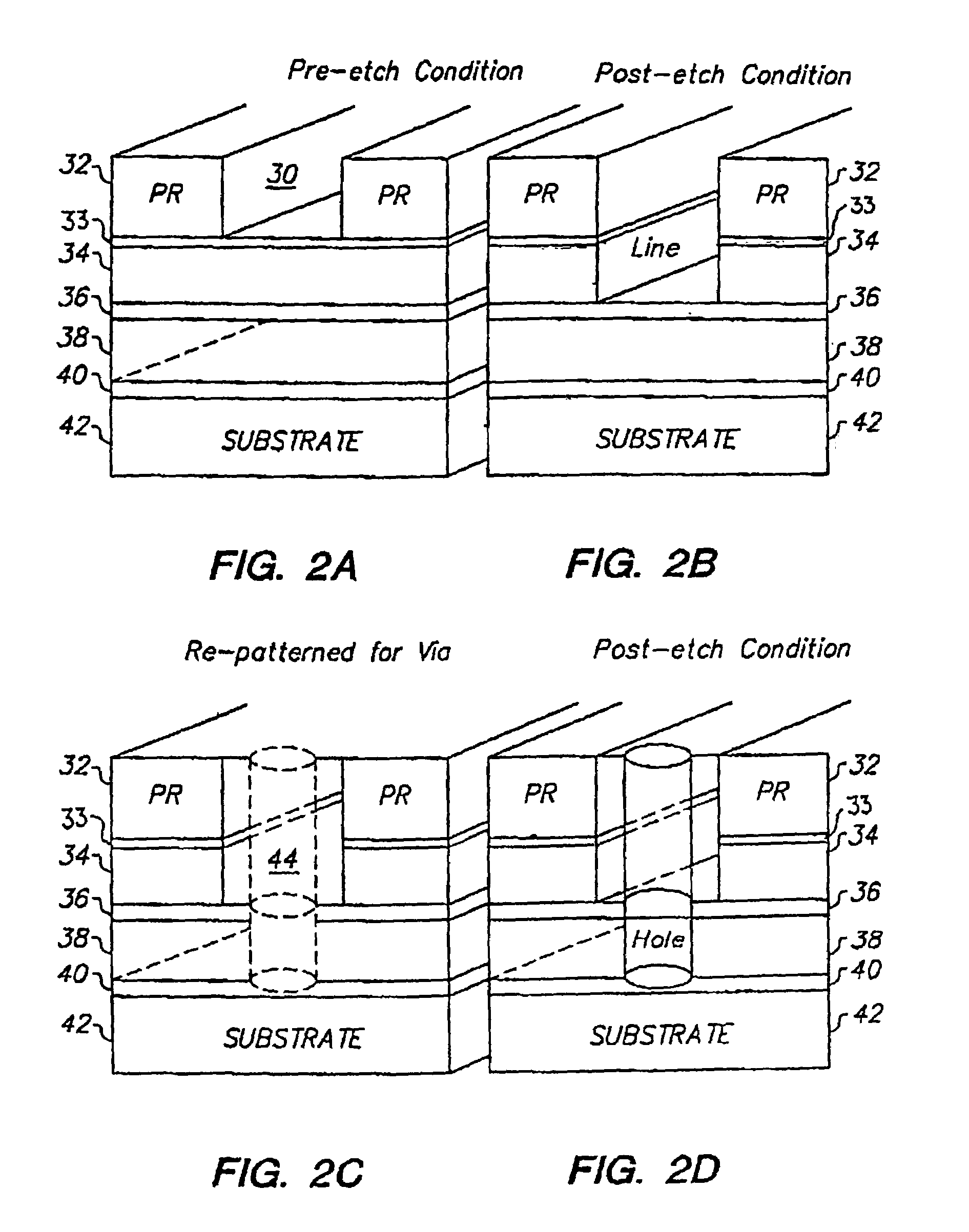
Treatment for corrosion in substrate processing
InactiveUS7084070B1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrostatic cleaningAcetic acidAmmonium hydroxide
A method for processing substrate to form a semiconductor device is disclosed. The substrate includes an etch stop layer disposed above a metal layer. The method includes etching through the etch stop layer down to the copper metal layer, using a plasma etch process that utilizes a chlorine-containing etchant source gas, thereby forming etch stop layer openings in the etch stop layer. The etch stop layer includes at least one of a SiN and SiC material. Thereafter, the method includes performing a wet treatment on the substrate using a solution that contains acetic acid (CH3COOH) or acetic acid / ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH) to remove at least some of the copper oxides. Alternatively, the copper oxides may be removed using a H2 plasma. BTA passivation may be optionally performed on the substrate.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
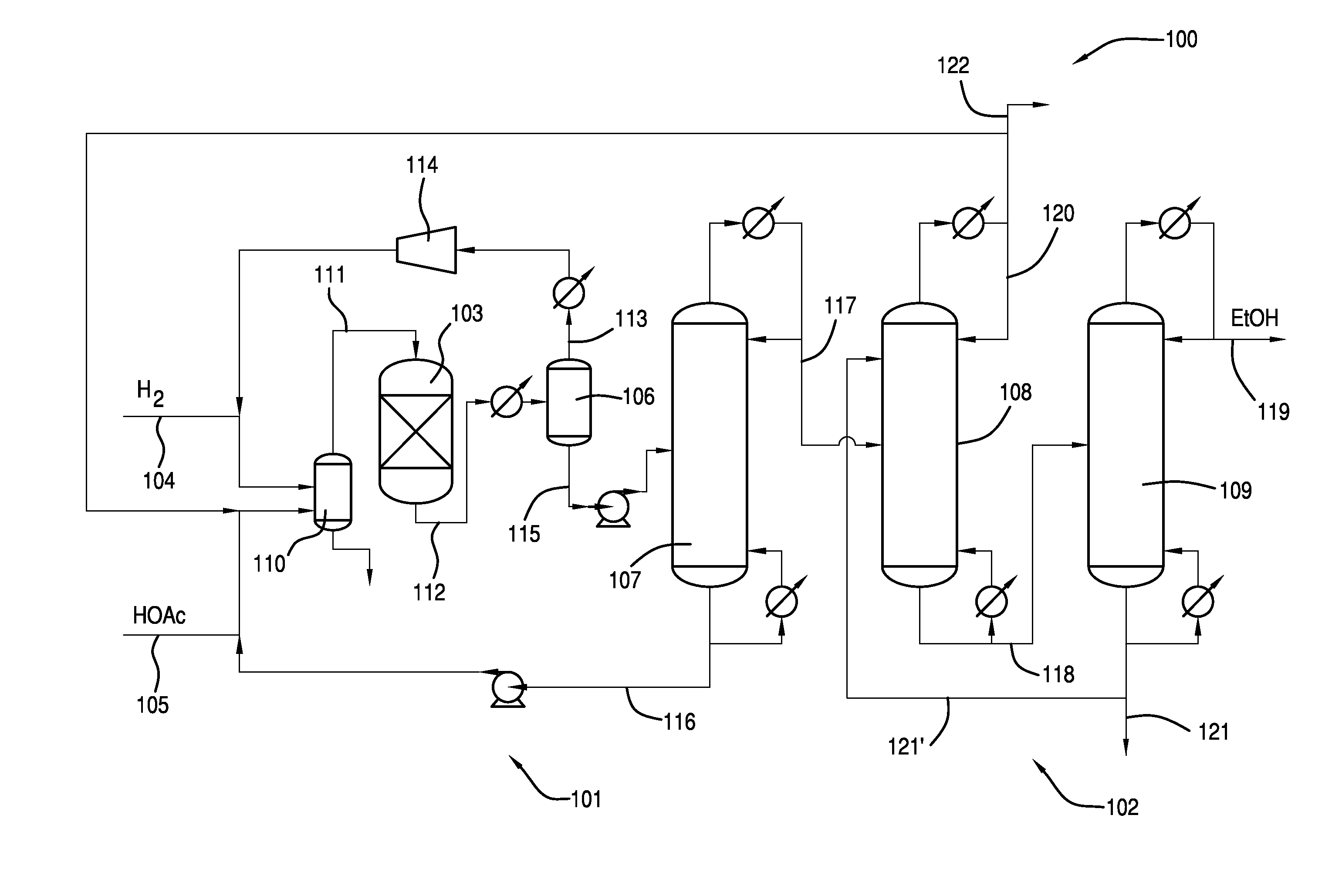
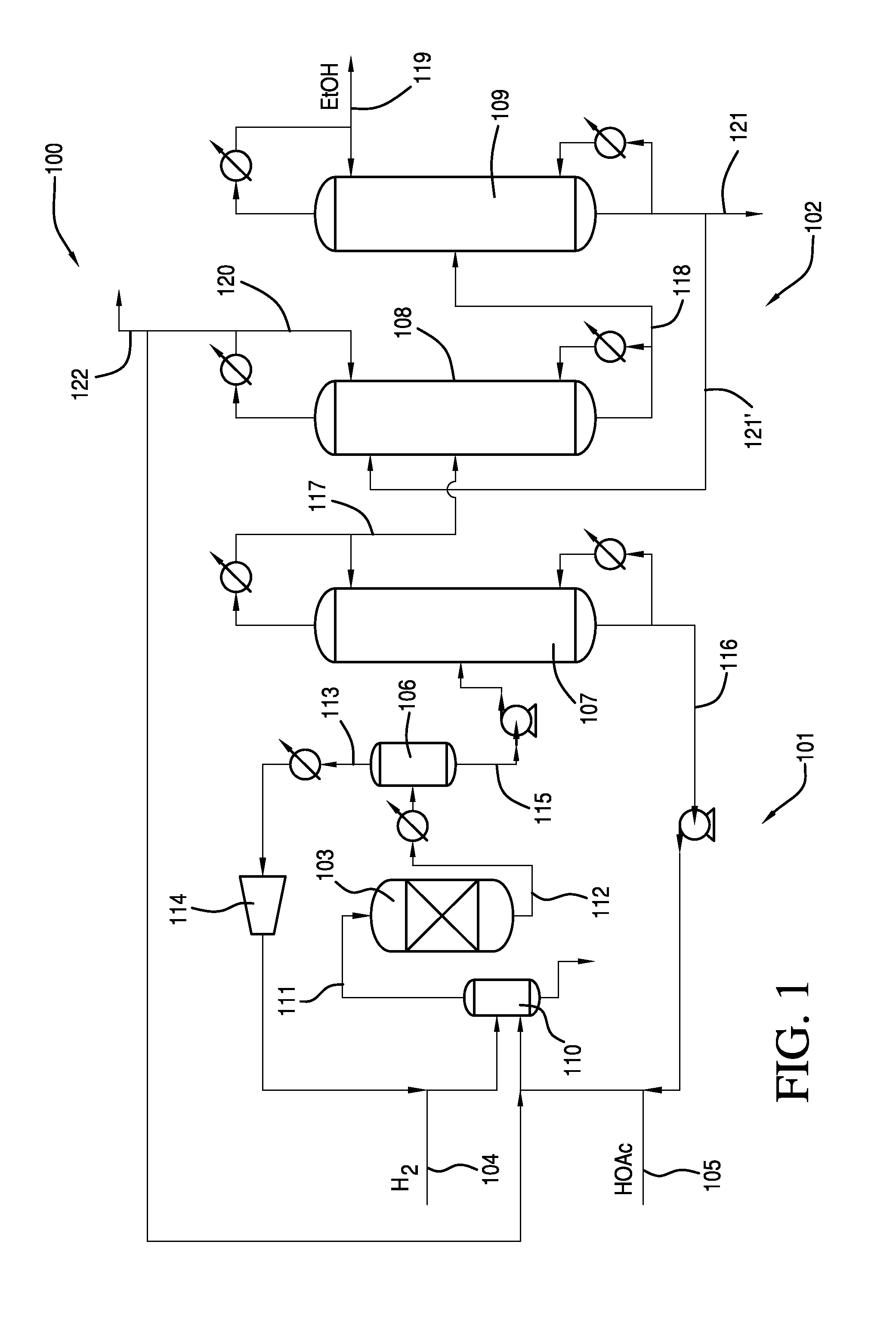
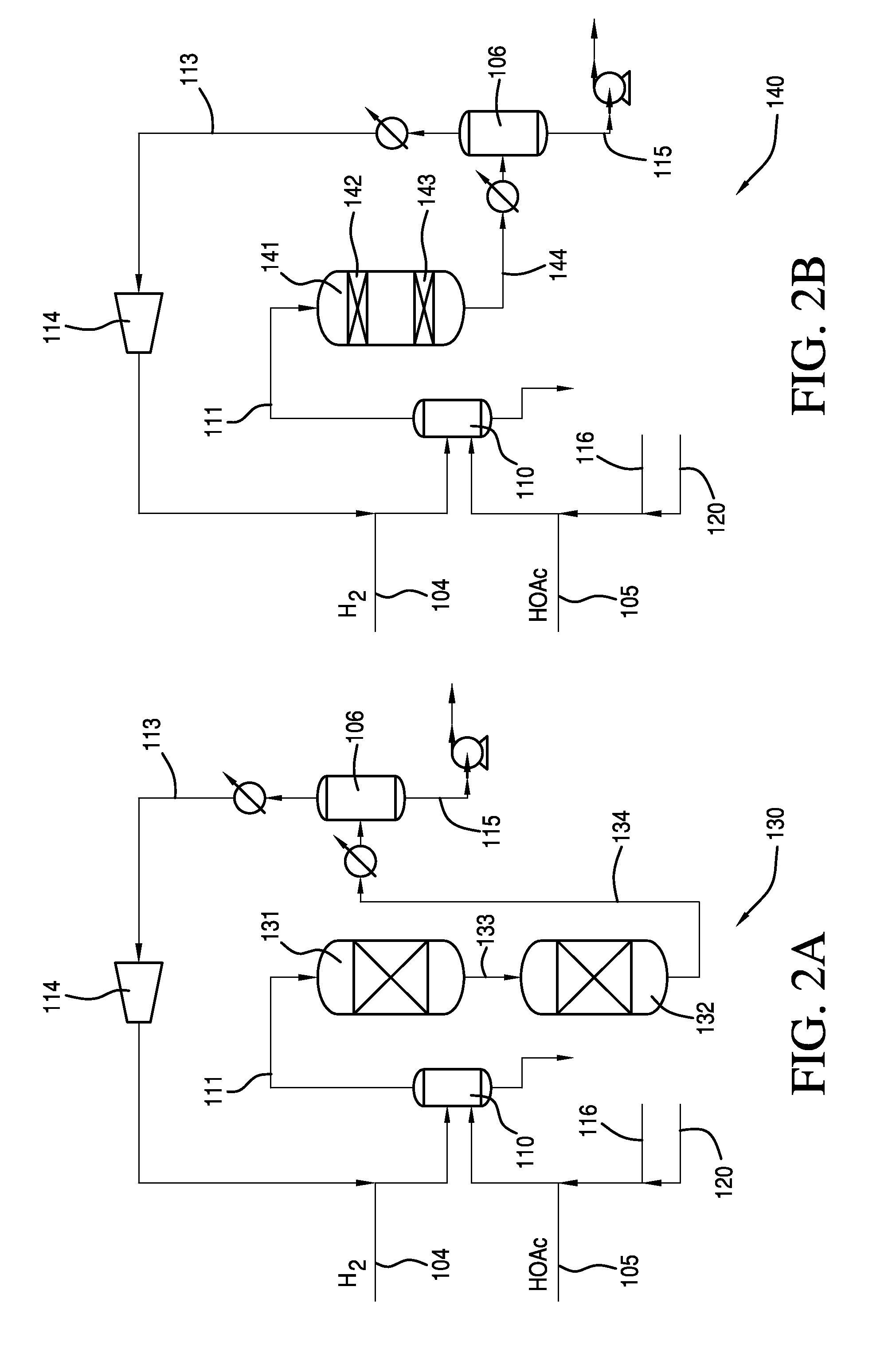
Process for Making Ethanol From Acetic Acid Using Acidic Catalysts
InactiveUS20110082322A1Organic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationAcetic acidMetal
A process for selective formation of ethanol from acetic acid by hydrogenating acetic acid in the presence of a catalyst comprises a first metal on an acidic support. The acidic support may comprise an acidic support material or may comprise an support having an acidic support modifier. The catalyst may be used alone to produced ethanol via hydrogenation or in combination with another catalyst. In addition, the crude ethanol product is separated to obtain ethanol.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
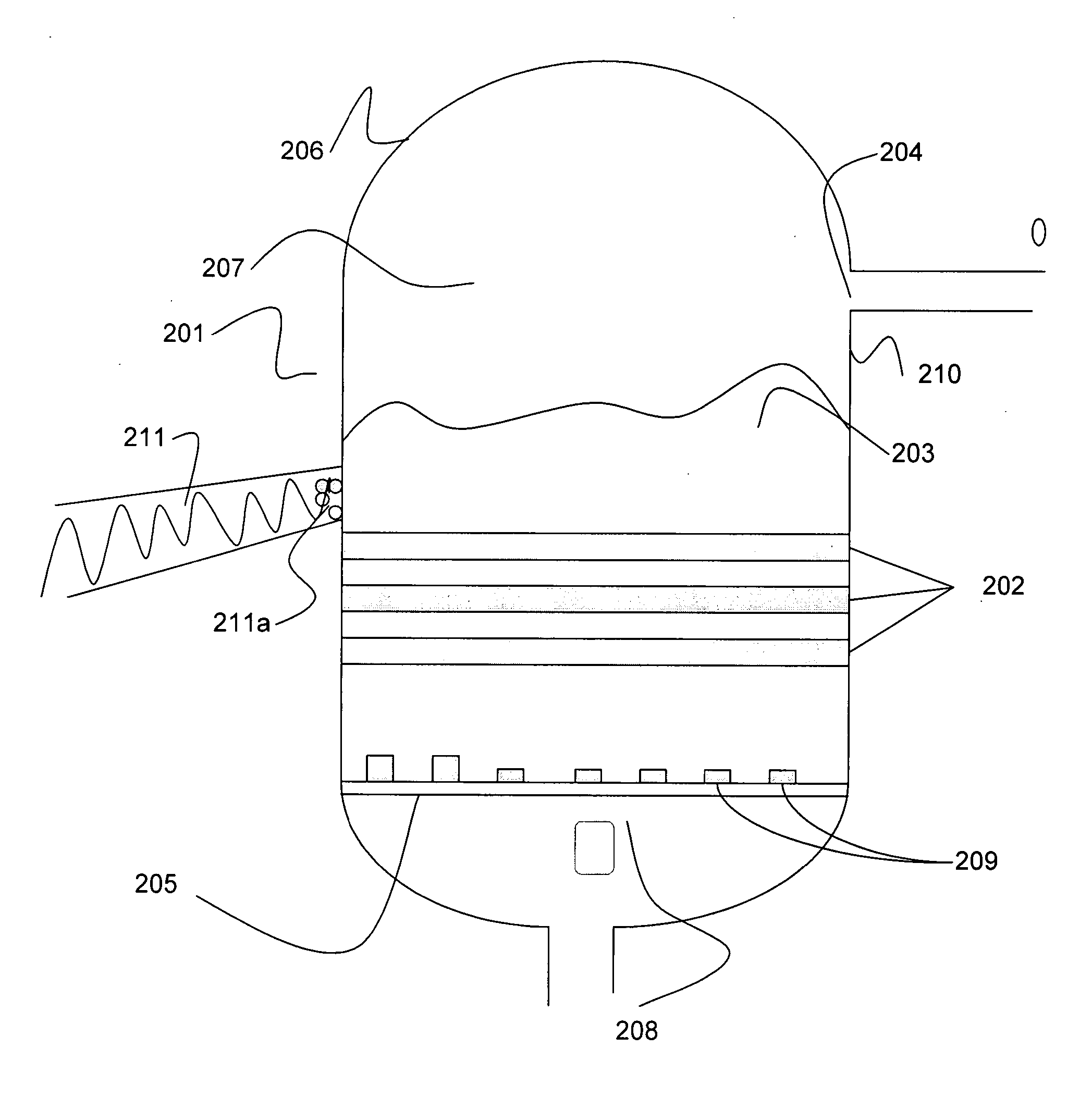
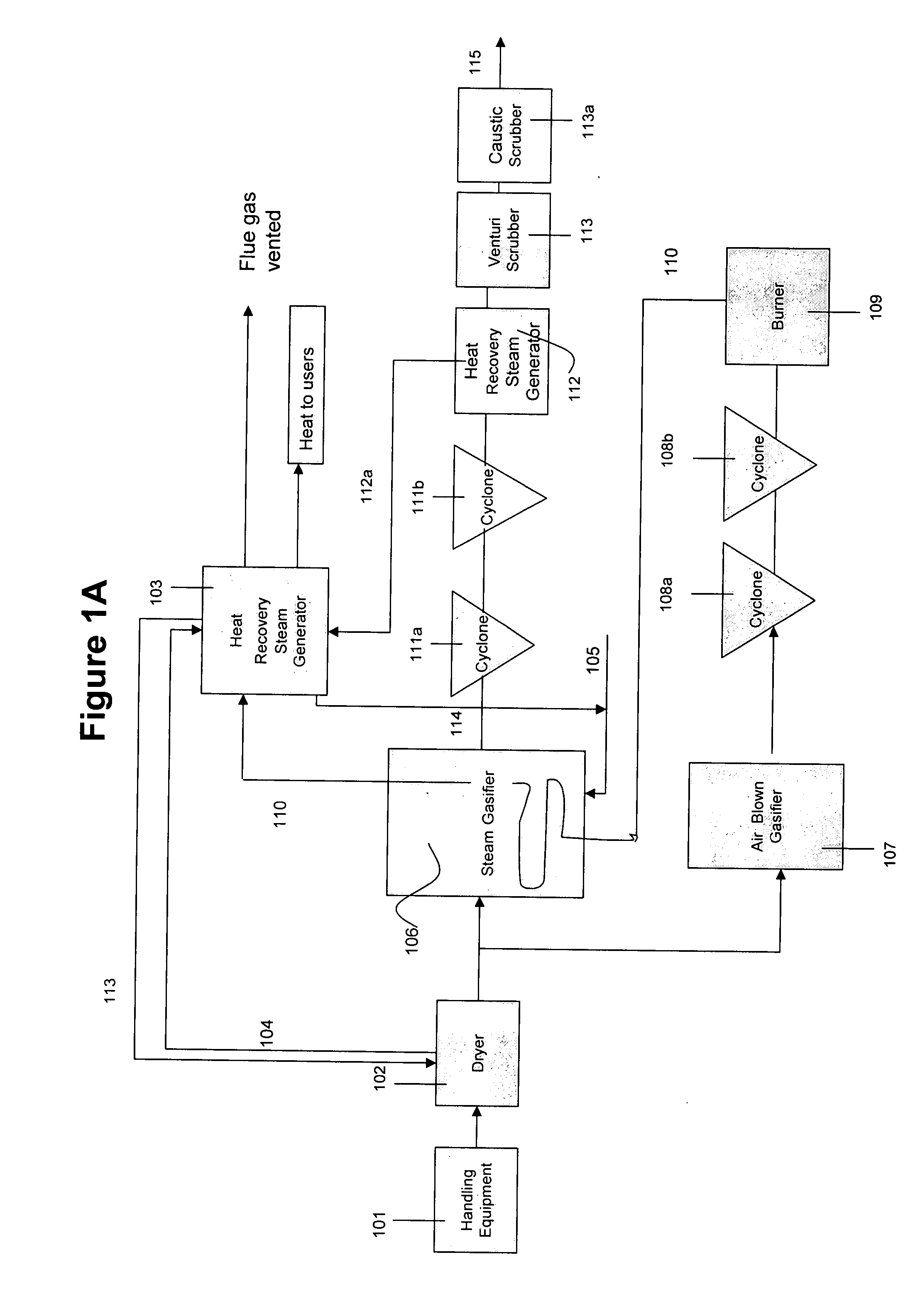
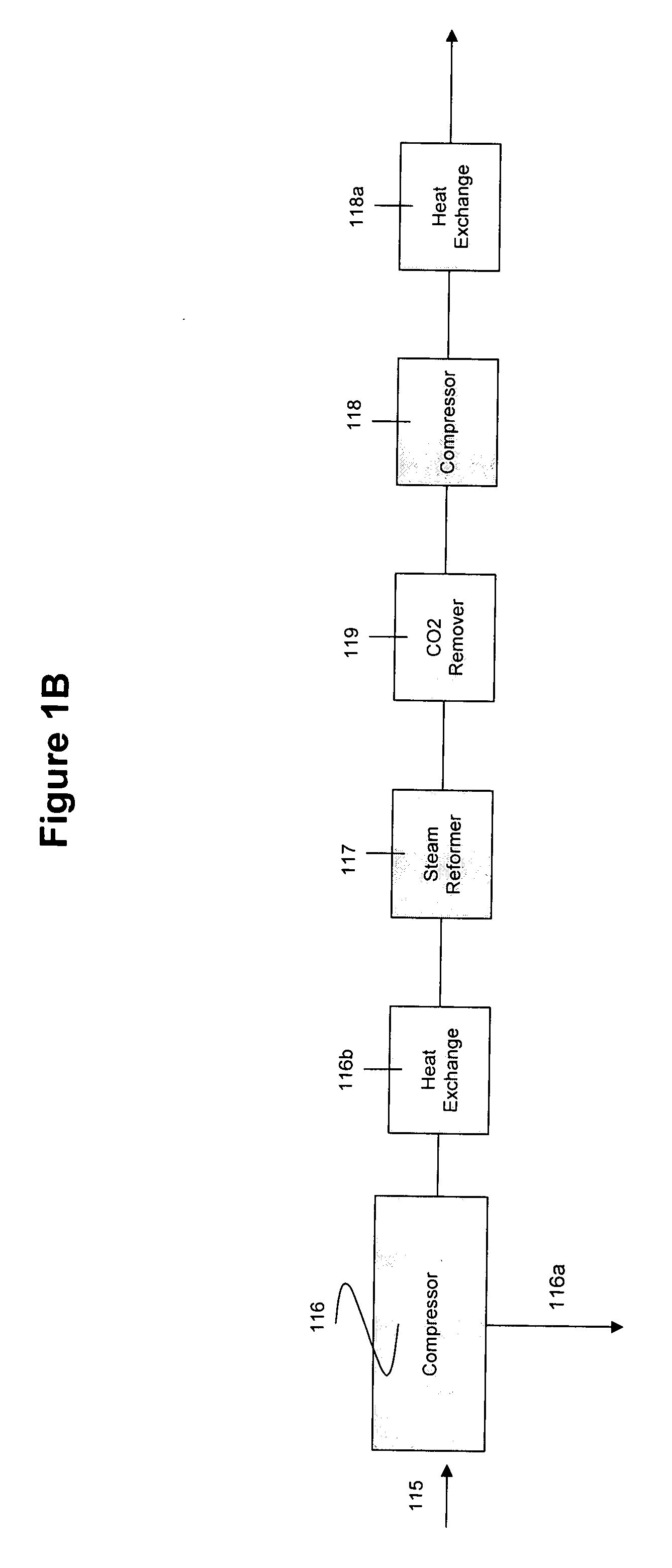
System and method for converting biomass to ethanol via syngas
A method and apparatus for synthesizing ethanol using synthetic routes via synthesis gas are disclosed. A method and apparatus for gasifying biomass, such as biomass, in a steam gasifier that employs a fluidized bed and heating using hot flue gases from the combustion of synthesis gas is described. Methods and apparatus for converting synthesis gas into ethanol are also disclosed, using stepwise catalytic reactions to convert the carbon monoxide and hydrogen into ethanol using catalysts including iridium acetate.
Owner:WOODLAND BIOFUELS
Process for producing ethanol
InactiveUS20060019360A1High carbon yieldHigh protein concentrationOrganic compound preparationChemical industryAcetic acidHydrogenation reaction
A process for producing ethanol including a combination of biochemical and synthetic conversions results in high yield ethanol production with concurrent production of high value coproducts. An acetic acid intermediate is produced from carbohydrates, such as corn, using enzymatic milling and fermentation steps, followed by conversion of the acetic acid into ethanol using esterification and hydrogenation reactions. Coproducts can include corn oil, and high protein animal feed containing the biomass produced in the fermentation.
Owner:ZEACHEM
Process for producing ethanol from corn dry milling
InactiveUS20060127999A1Speed up the conversion processFermented solutions distillation/rectificationOrganic compound preparationAcetic acidDistillation
A process for producing ethanol by the conversion of carbohydrates from a corn dry milling process in which the bottoms fraction from distillation of ethanol in a conventional yeast fermentation is used in a process including a combination of biochemical and synthetic conversions. The process results in high yield ethanol production with concurrent production of high value coproducts. An acetic acid intermediate is produced from bottoms fraction, followed by conversion of the acetic acid into ethanol using esterification and hydrogenation reactions. Coproducts of the process include a high protein content solids fraction produced in the fermentation.
Owner:ZEACHEM
Isolation and characterization of novel clostridial species
InactiveUS7704723B2High yieldReadily availableBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSyngasAcetic acid
A novel clostridia bacterial species (Clostridium ragsdalei, ATCC BAA-622, “P11”) is provided. P11 is capable of synthesizing, from waste gases, products which are useful as biofuel. In particular, P11 can convert CO to ethanol. Thus, this novel bacterium transforms waste gases (e.g. syngas and refinery wastes) into useful products. P11 also catalyzes the production of acetate.
Owner:BOARD OF REGENTS FOR OKLAHOMA STATE UNIVERSITY +1
Method and apparatus for sustainable energy and materials
A process for the production of hydrogen from anaerobically decomposed organic materials by applying an electric potential to the anaerobically decomposed organic materials, including landfill materials and sewage, to form hydrogen, and for decreasing the time required to treat these anaerobically decomposed organic materials. The organic materials decompose to volatile acids such as acetic acid, which may be hydrolyzed by electric current to form hydrogen. The process may be continuously run in sewage digestion tanks with the continuous feed of sewage, at landfill sites, or at any site having a supply of anaerobically decomposed or decomposable organic materials.
Owner:MCALISTER TECH LLC +1
Method for preparing lithium cobaltate by directly using invalid lithium ion battery
InactiveCN102030375AReduce dispersionHigh purityCell electrodesCobalt compoundsElectrical batteryPotassium hydroxide
The invention provides a method for preparing lithium cobaltate by directly using an invalid lithium ion battery. The method comprises the following steps: crushing the invalid lithium ion battery or scraps generated when a lithium cobaltate battery is produced by a mechanical crusher at normal temperature; adding water and one or more of acetic acid, sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid or nitric acid to produce mixed aqueous solution of the battery scraps and acid; filling the mixed aqueous solution into a hermetic pressure reactor, and controlling the temperature in the reactor to be between 50 and 150 DEG C; introducing or adding one leaching additive of sulfur dioxide or hydrogen, or adding hydrazine hydrate; stirring and leaching, cooling, and filtering; adding one precipitator of sodium carbonate, potassium carbonate and ammonium carbonate, or adding composite precipitator consisting of one of the sodium carbonate, the potassium carbonate and the ammonium carbonate and one of sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide to obtain mixture of lithium carbonate, cobalt carbonate and cobalt hydroxide; drying and calcining at high temperature to produce a lithium cobaltate product. The method is particularly suitable for the treatment scale of medium-sized and small enterprises, and is an effective method for directly materializing cobalt secondary resources.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
Processes for making ethanol from acetic acid
InactiveUS20100197985A1High selectivityPreparation by oxo-reaction and reductionEthylene productionCeriumCobalt
A process for selective formation of ethanol from acetic acid by hydrogenating acetic acid in the presence of first metal, a silicaceous support, and at least one support modifier. Preferably, the first metal is selected from the group consisting of copper, iron, cobalt, nickel, ruthenium, rhodium, palladium, osmium, iridium, platinum, titanium, zinc, chromium, rhenium, molybdenum, and tungsten. In addition the catalyst may comprise a second metal preferably selected from the group consisting of copper, molybdenum, tin, chromium, iron, cobalt, vanadium, tungsten, palladium, platinum, lanthanum, cerium, manganese, ruthenium, rhenium, gold, and nickel.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Materials and methods for the efficient production of acetate and other products
InactiveUS20040152159A1Increase productionIncrease acetate productionBacteriaHydrolasesGenes mutationAcetic acid
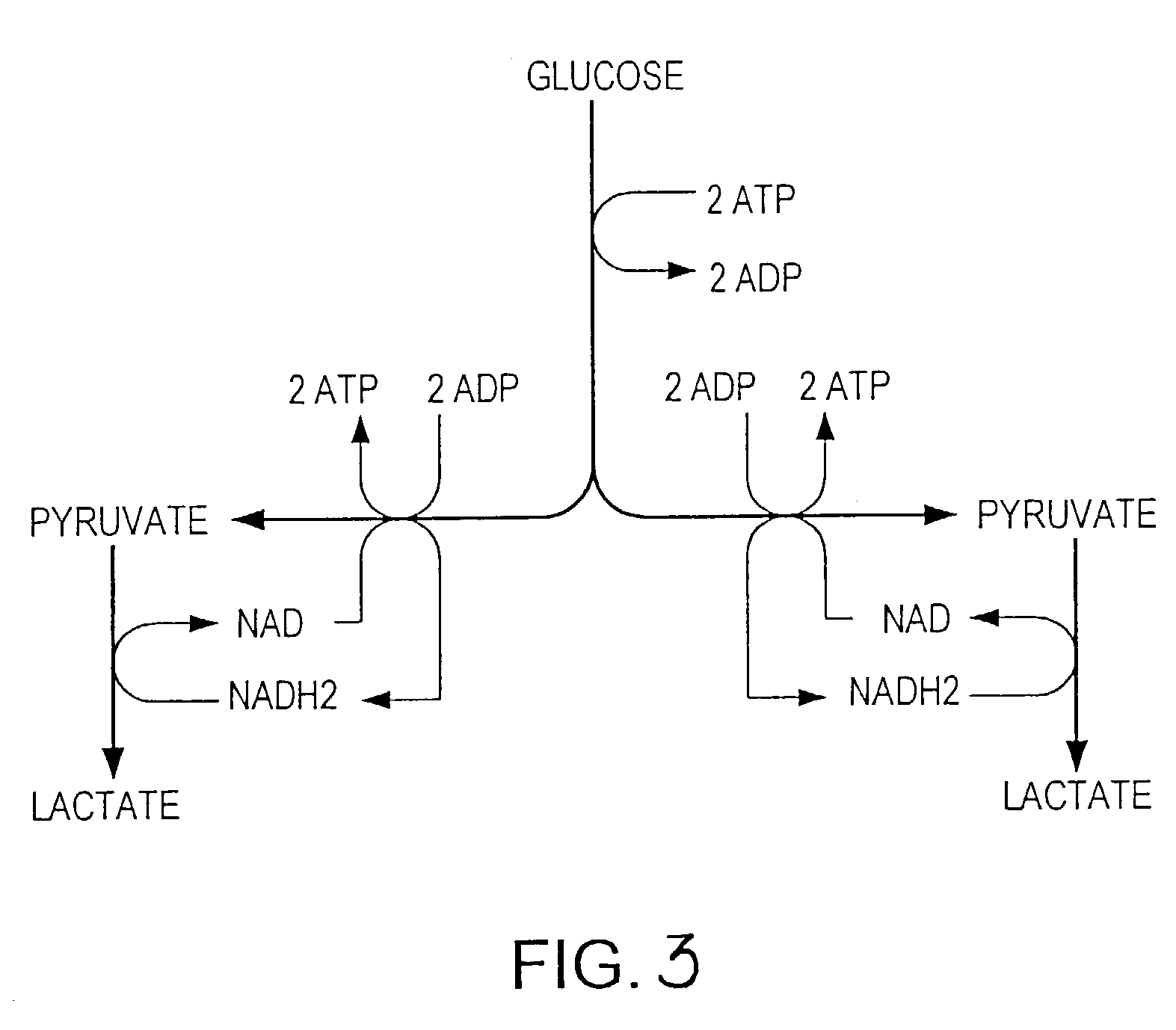
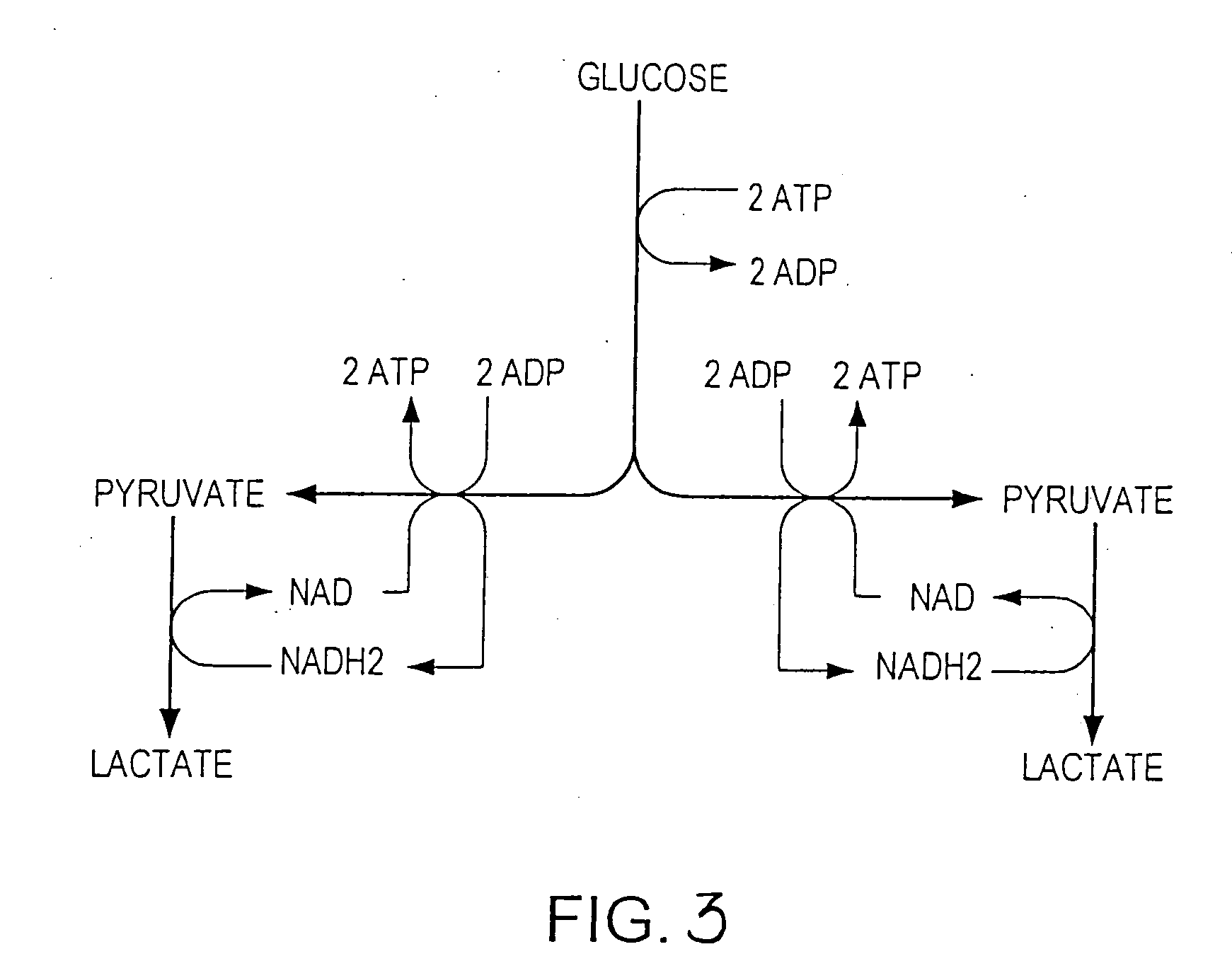
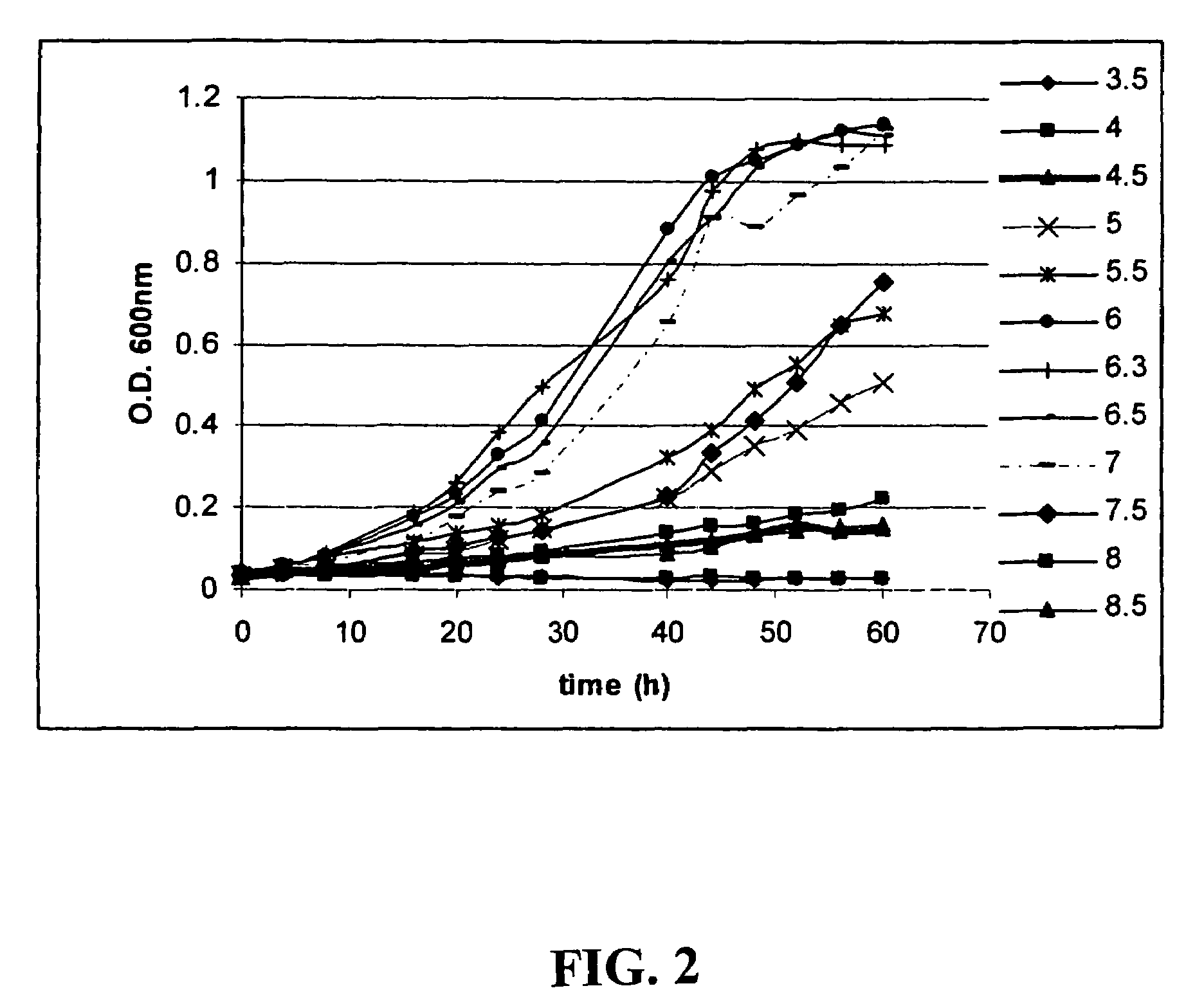
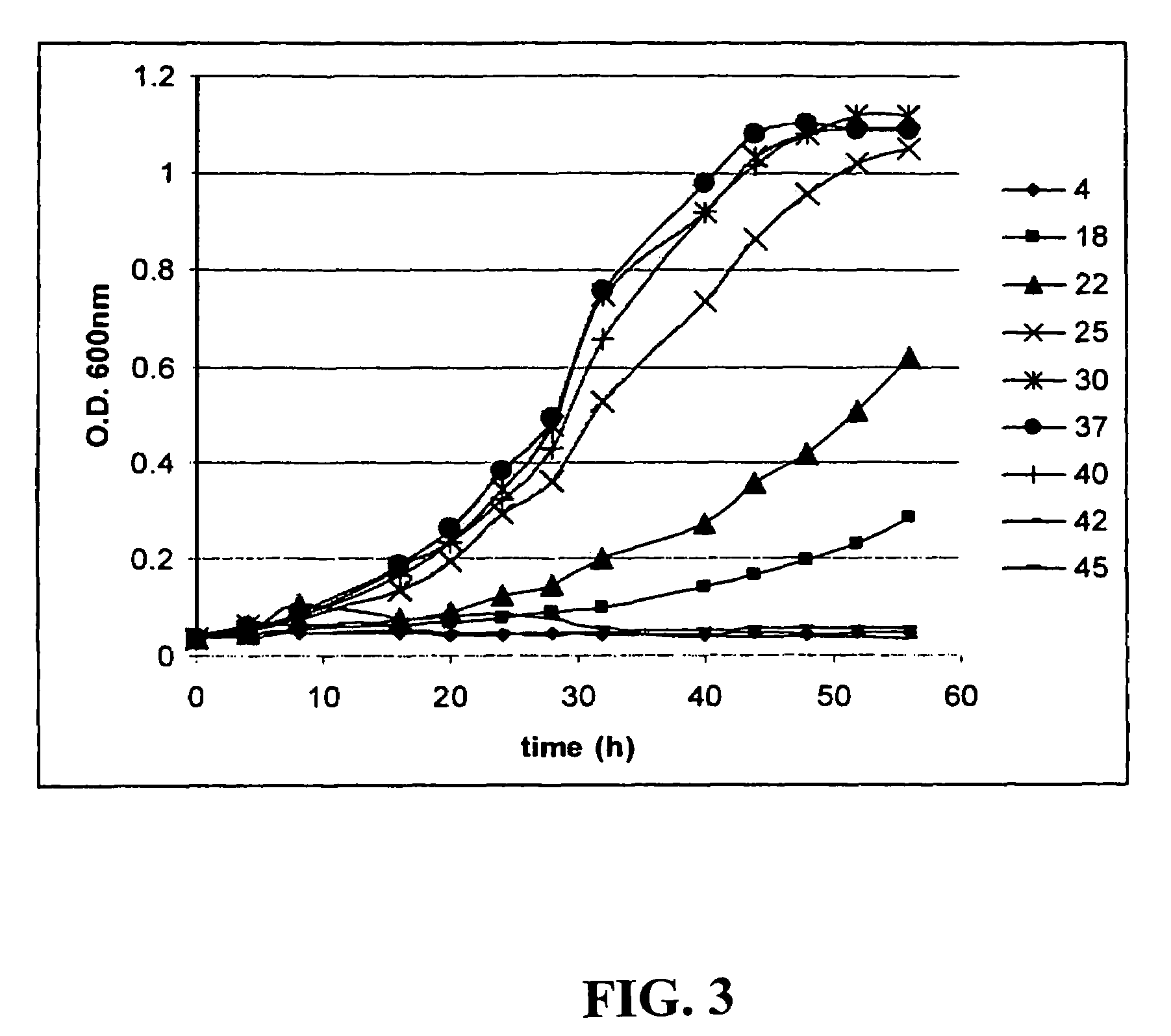
The subject invention provides materials and methods wherein unique and advantageous combinations of gene mutations are used to direct carbon flow from sugars to a single product. The techniques of the subject invention can be used to obtain products from native pathways as well as from recombinant pathways. In preferred embodiments, the subject invention provides new materials and methods for the efficient production of acetate and pyruvic acid.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Cementing compositions and methods of cementing in a subterranean formation using an additive for preventing the segregation of lightweight beads.
Cementing compositions and methods of cementing in a subterranean formation are provided. The cement composition includes a hydraulic cement, lightweight beads, and a desegregating agent for inhibiting segregation of the beads. The lightweight beads may be, for example, cenospheres, glass spheres, and ceramic spheres. The desegregating agent comprises a particulate substrate such as precipitated silica. It also comprises a polar molecule producing chemical disposed on the particulate substrate. Preferably, the polar molecule producing chemical is absorbed on the particulate substrate. The polar molecule producing chemical comprises at least one of a polar molecule producing acid such as glacial acetic acid, a salt of such an acid, and an acid anhydride. The method of cementing includes forming a pumpable slurry using the cement composition, pumping the slurry into a subterranean formation, and allowing the slurry to set.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Isolation and characterization of novel clostridial species
InactiveUS20080057554A1High yieldReadily availableBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBacteroidesAcetic acid
A novel clostridia bacterial species (Clostridium ragsdalei, ATCC BAA-622, “P11”) is provided. P11 is capable of synthesizing, from waste gases, products which are useful as biofuel. In particular, P11 can convert CO to ethanol. Thus, this novel bacterium transforms waste gases (e.g. syngas and refinery wastes) into useful products. P11 also catalyzes the production of acetate.
Owner:BOARD OF REGENTS FOR OKLAHOMA STATE UNIVERSITY +1
Use of a composition made of mineral nutrients and optionally acetogenic and/or butyrogenic bacteria in order to avoid or reduce the formation of gas in the large intestine of a mammal and the resulting abdominal problems
InactiveUS20100247489A1Raise countSufficient supplyHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideAcetic acidMammal
The present invention relates to a composition comprising one or more minerals selected from the group consisting of selenium, molybdenum or tungsten, which is carried out galenically or chemically in a way that the mineral or minerals are released completely or in part, just before, during or shortly after arrival at the large intestine, and their use in the manufacture of a medicament for administering to a mammal for the prevention or reduction of gas formation in the colon thus conditioned abdominal complaints, particularly bloatings, meteorism or abdominal cramps. Furthermore, the invention relates to a procedure for the isolation of acetogenic and butyrogenic bacterial strains that are suitable for therapeutic purposes outlined above.
Owner:SAUR BROSCH ROLAND
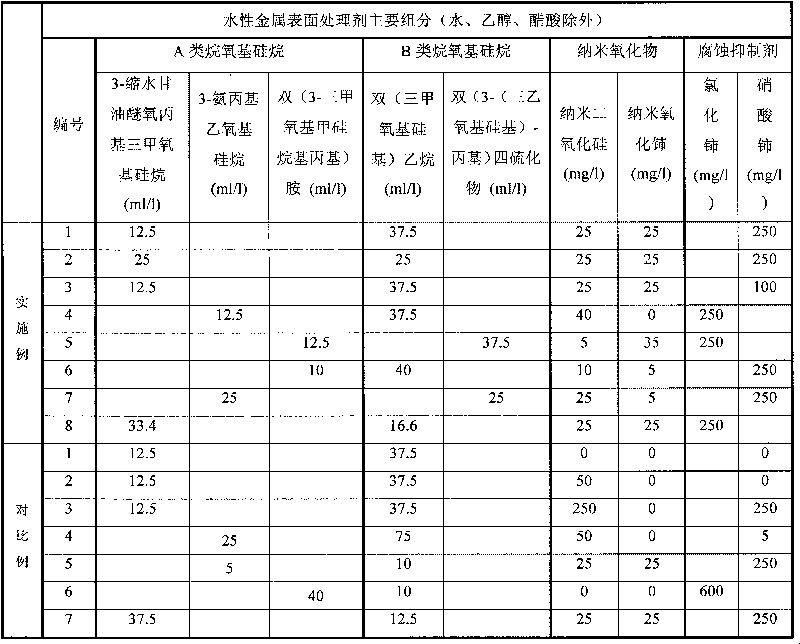
Environment-friendly nano water-based silane treatment agent capable of improving anti-corrosion performance of metal surface
ActiveCN101717930ASimple processApplicable industrial scaleMetallic material coating processesWater basedEpoxy
The invention discloses an environment-friendly nano water-based silane treatment agent capable of improving anti-corrosion performance of metal surface. The treatment agent is water-based silane solution which consists of at least one alkoxy silane containing epoxy or at least one alkoxy silane containing amino, at least one disilyl silane, nano-silicon dioxide, rare earth salt type corrosion inhibitor or rare earth salt type and rare earth nano oxide, water, or acetic acid and a small amount of ethanol. The metal material is coated by using the silane solution for impregnation, brushing, spraying or spin-coating, a siloxane layer is formed on the metal surface, then the long-acting corrosion resistance is formed by curing for 3 hours at the temperature of 100 DEG C, and a nano organic silane film which has close bonding force with a coating is formed. Nanoparticles can not only improve the corrosion resistance and enhance the mechanical strength of the silane film in a coating layer, but also realize the synergistic corrosion resistance with the corrosion inhibitor. The technology has the advantages of simple process, greenness, environmental protection and strong practicality.
Owner:HAISO TECH
Aripiprazole oral solution
The present invention provides for a pharmaceutical solution suitable for oral administration comprising aripiprazole, a pharmaceutically suitable solvent system, one or more taste-enhancing / masking agents and one or more agents selected from the group consisting of lactic acid, acetic acid, tartaric acid and citric acid, wherein said solution has a pH from 2.5 to 4.5.
Owner:OTSUKA PHARM CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com