Patents
Literature
57 results about "Clostridia" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The Clostridia are a highly polyphyletic class of Firmicutes, including Clostridium and other similar genera. They are distinguished from the Bacilli by lacking aerobic respiration. They are obligate anaerobes and oxygen is toxic to them. Species of the class Clostridia are often but not always Gram-positive (see Halanaerobium hydrogenoformans) and have the ability to form spores. Studies show they are not a monophyletic group, and their relationships are not entirely certain. Currently, most are placed in a single order called Clostridiales, but this is not a natural group and is likely to be redefined in the future.
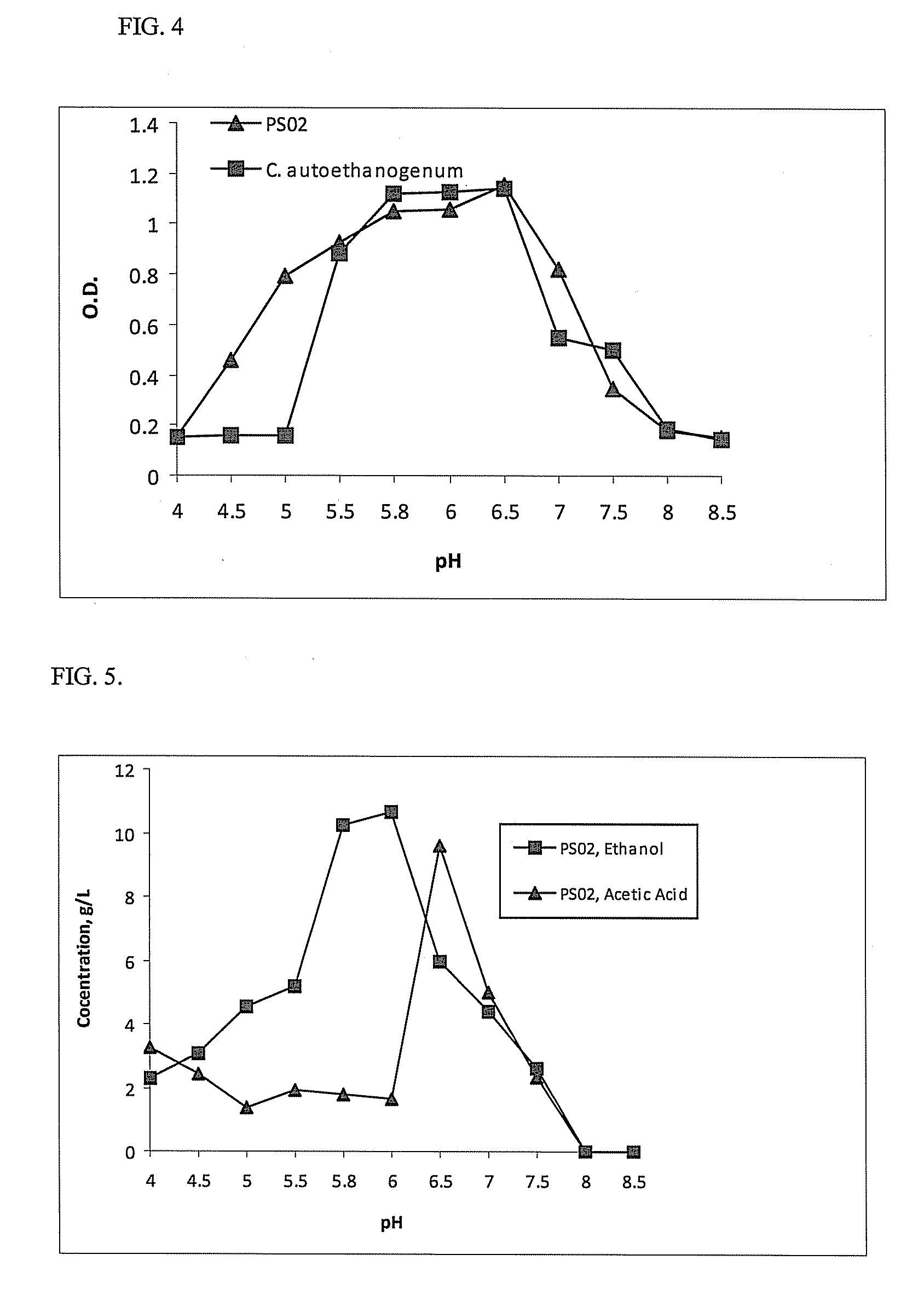
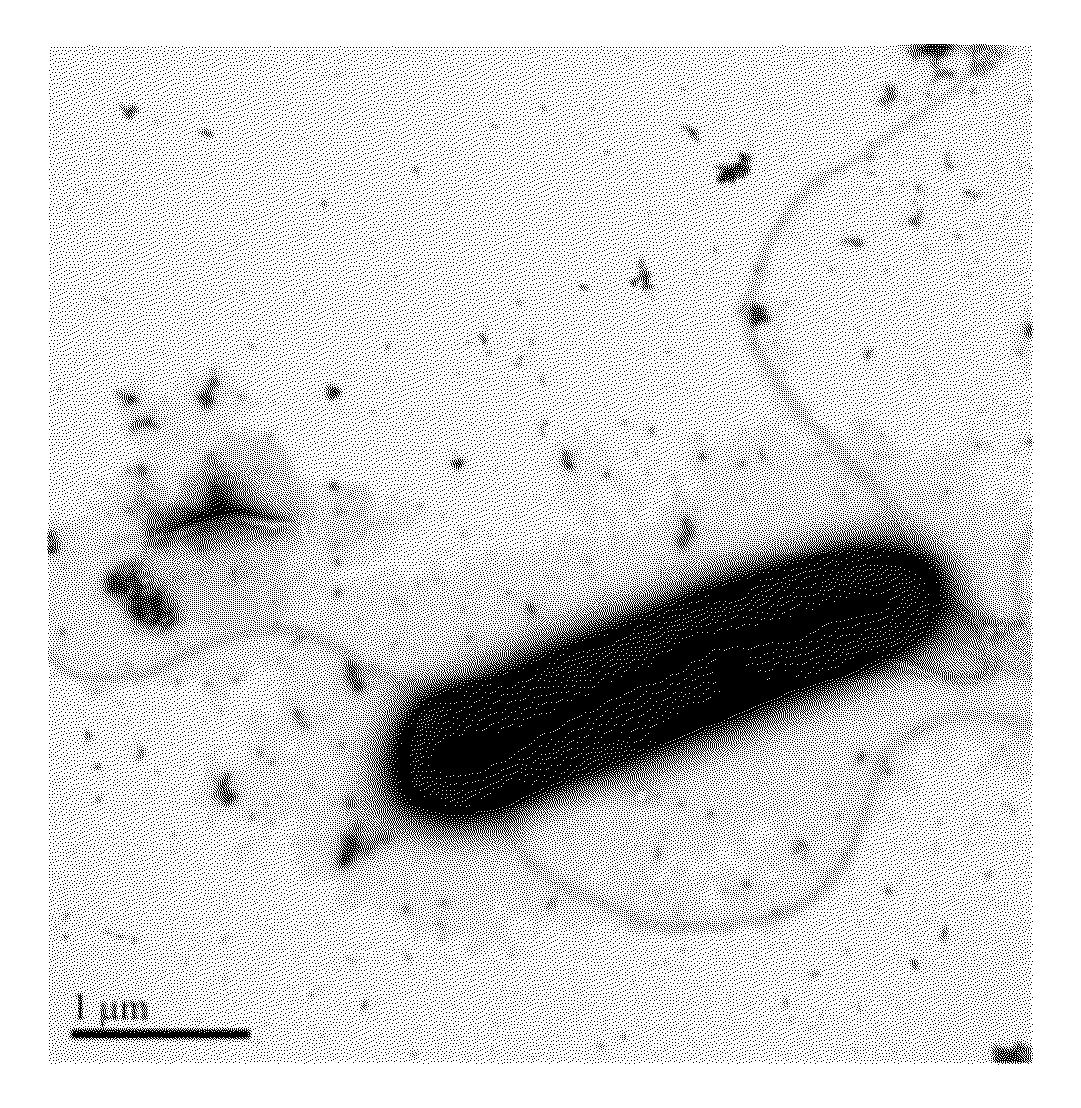
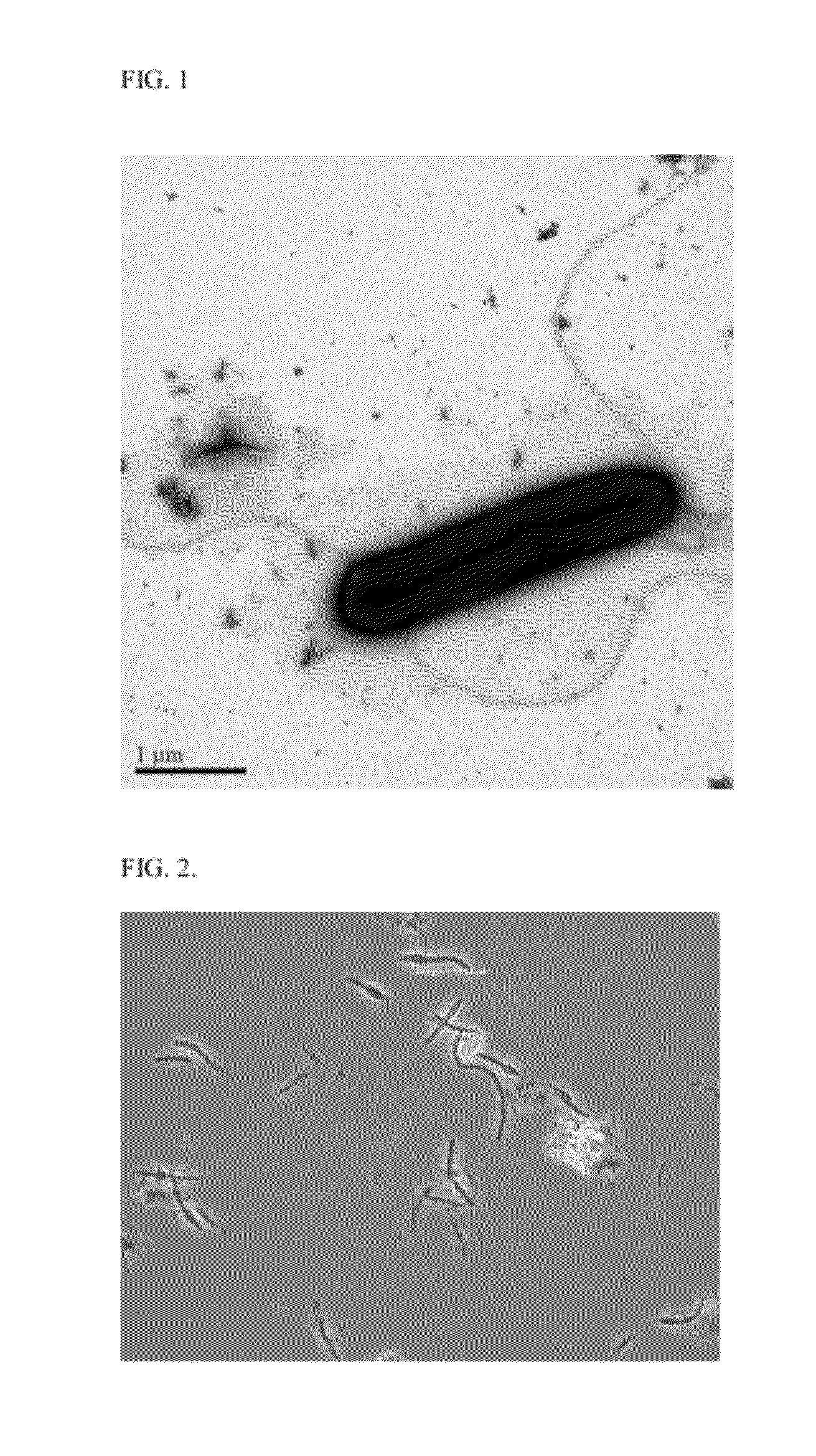
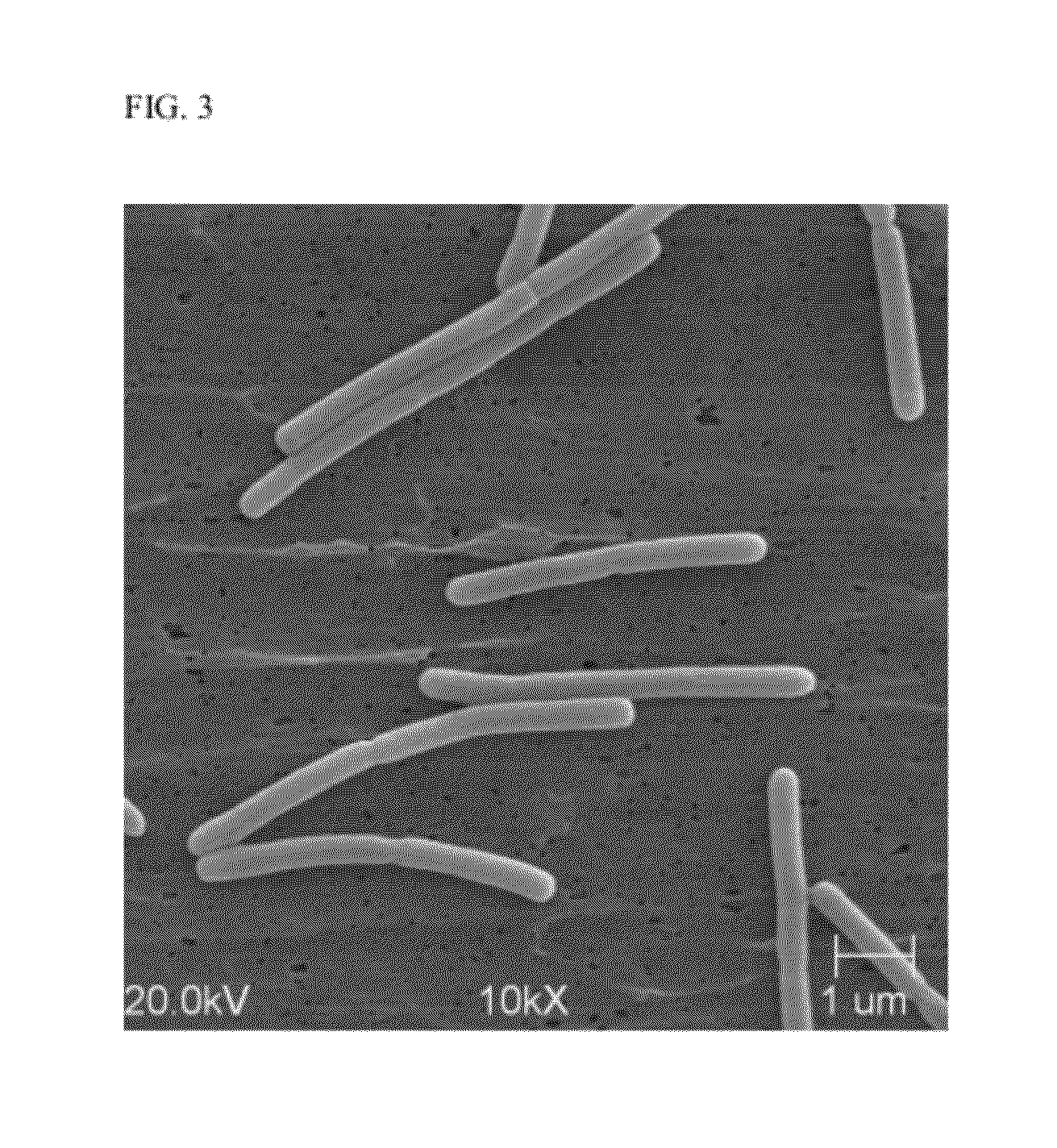
Novel Ethanologenic Clostridium species, Clostridium coskatii
A novel clostridia bacterial species (Clostridium coskatii ATCC No. PTA-10522, “PS02”) is provided. Under anaerobic conditions C. coskatii can convert CO and / or H2 and / or CO2 to ethanol or acetate. Thus, this novel bacterium is capable of transforming waste gases (e.g. syngas and refinery wastes) into useful products.
Owner:SYNATA BIO INC
Probiotic recolonisation therapy
The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions suitable for the treatment of chronic diseases associated with the presence of abnormal or an abnormal distribution of microflora in the gastrointestinal tract of a mammalian host, which compositions comprise viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic Clostridia. The compositions further comprise one or more additional viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic microorganisms selected from the group consisting of Bacteroides, Eubacteria, Fusobacteria, Propionibacteria, Lactobacilli, anaerobic cocci, Ruminococcus, E. Coli, Gemmiger, Desulfamonas, Peptostreptococcus, and fungi. The present invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions suitable for the treatment of the same chronic diseases comprising viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic Escherichia coli, at least one strain of viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathoenic Bacteroides and at least one strain of viable non-pathogenic or attenuated pathogenic microorganism.
Owner:FINCH THERAPEUTICS HLDG LLC
Human-derived bacteria that induce proliferation or accumulation of regulatory t cells
InactiveCN104160014APromote proliferationPromote accumulationBacteriaAntipyreticBacteroidesRegulatory T cell
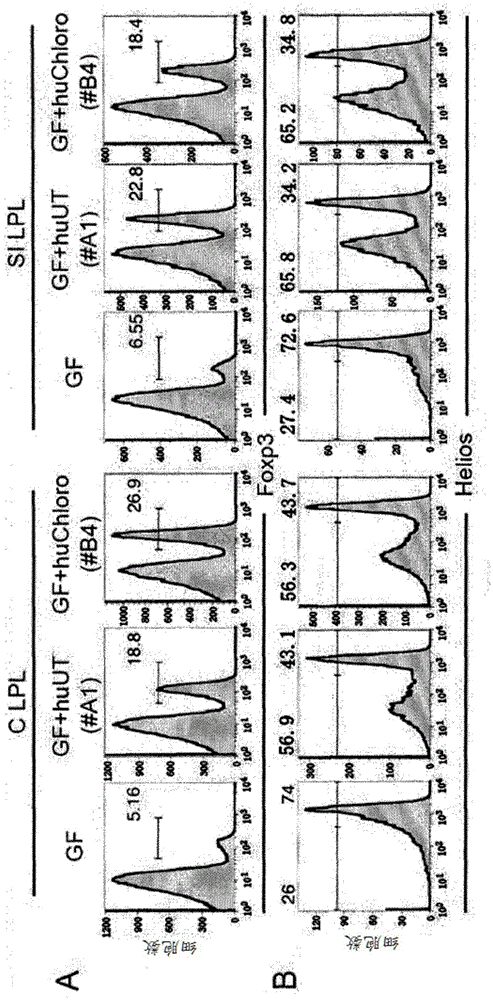
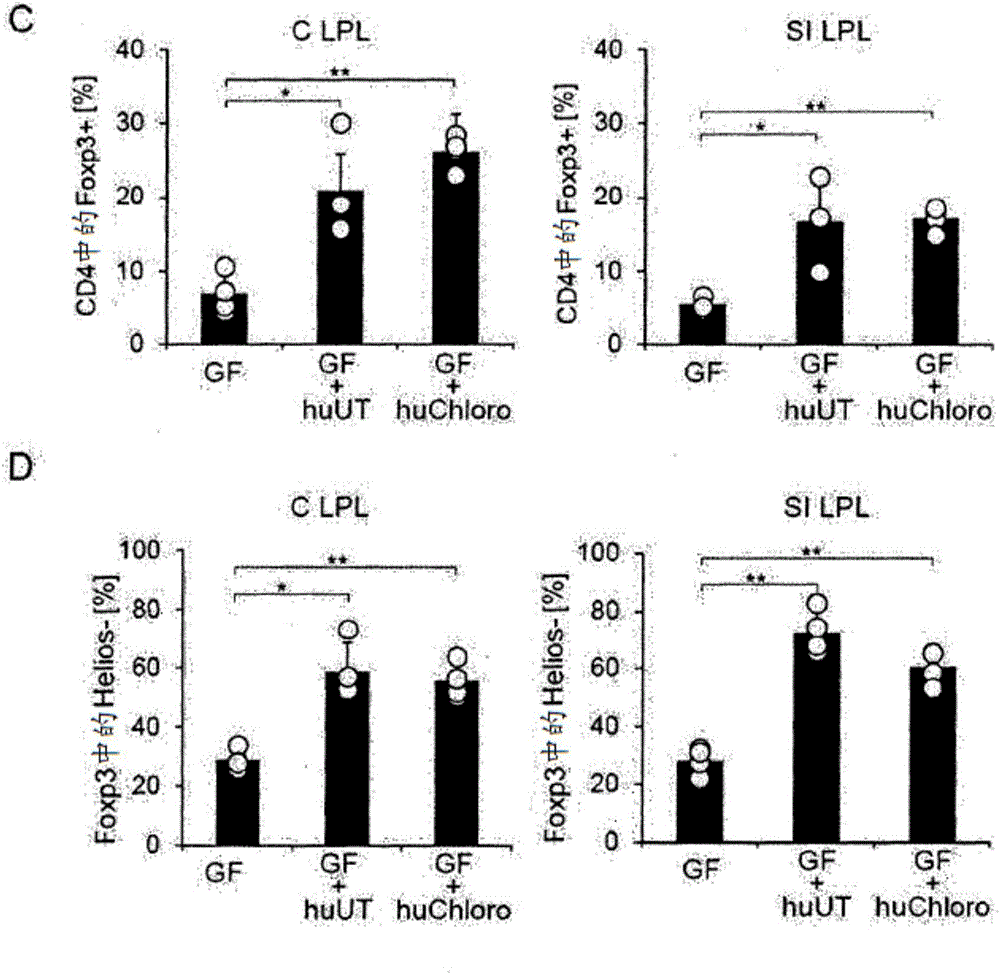
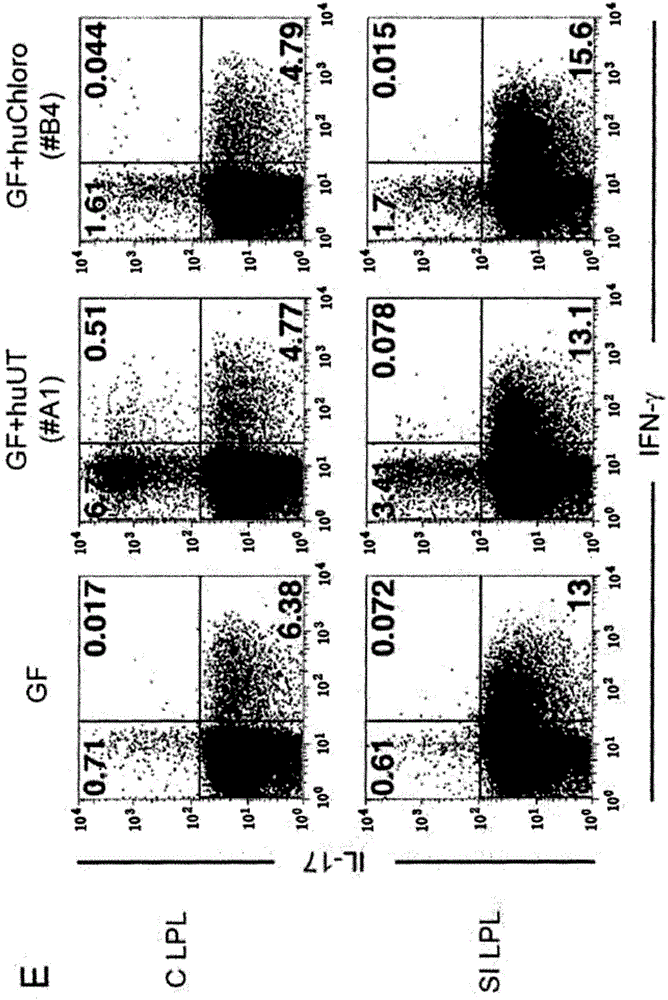
Species of human-derived bacteria belonging to the Clostridia class have been shown to induce accumulation of regulatory T cells (Treg cells) in the colon and suppress immune functions. Pharmaceutical compositions containing these bacteria can be used to prevent and treat immune-mediated diseases such as autoimmune diseases.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO +1
Treatment of holocrine gland dysfunction with clostridia neurotoxins
InactiveUS7288259B2Reduce the numberReduced activityBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteriaClostridiaPhysiology
Owner:SANDERS +1
Treatment of holocrine gland dysfunction with clostridia neurotoxins
InactiveUS20050220820A1Reduce the numberReduced activityBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteriaClostridiaPhysiology
Owner:SANDERS +1
Methods and compositions for treating eye disorders
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
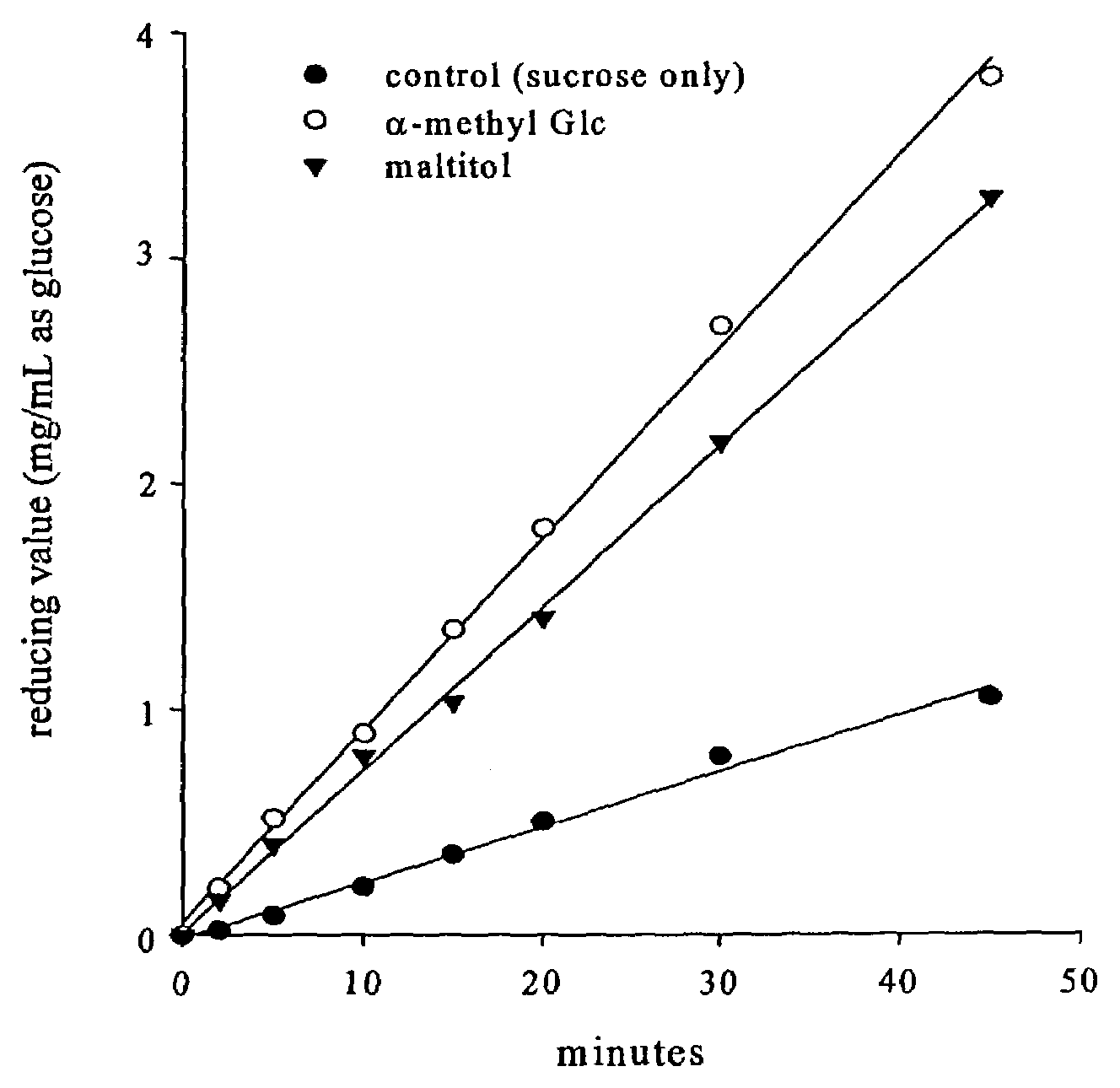
Prebiotic oligosaccharides via alternansucrase acceptor reactions
InactiveUS7182954B1Promote growthEffective controlBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsBacteroidesEscherichia coli
Oligosaccharides produced by an alternansucrase enzyme catalyzed reaction of sucrose with an acceptor oligosaccharide are effective as prebiotics for controlling enteric bacterial pathogens. Populations of enteropathogenic bacteria may be substantially reduced or inhibited by treatment of an animal with a composition comprising one or more of these oligosaccharides in an amount effective to promote the growth of beneficial bacteria. The method is particularly effective for the control of Salmonella species, enteropathogenic Escherichia coli, and Clostridia perfringens.
Owner:SOUTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY +1
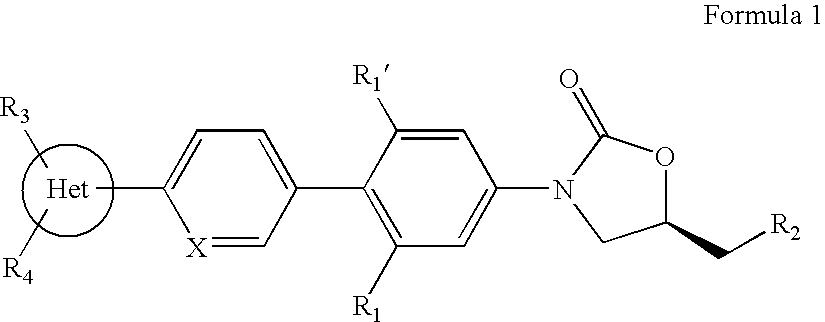
Cyclopropyl group substituted oxazolidinone antibiotics and derivatives thereof
This invention relates to new oxazolidinones having a cyclopropyl moiety, which are effective against aerobic and anerobic pathogens such as multi-resistant staphylococci, streptococci and enterococci, Bacteroides spp., Clostridia spp. species, as well as acid-fast organisms such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis and other mycobacterial species. The compounds are represented by structural formula I: its enantiomer, diastereomer, or pharmaceutically acceptable salt or ester thereof.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
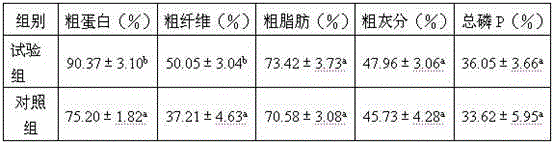
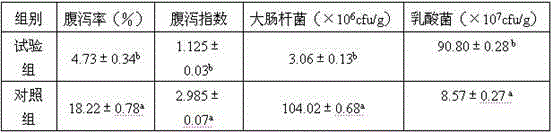
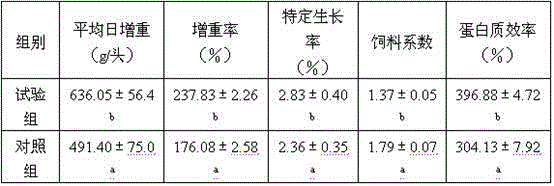
Composite bacillus preparation containing three strains, preparation method of composite bacillus preparation and application of composite bacillus preparation to ecological breeding
InactiveCN104480052APromote Microecological BalancePromote digestion and absorptionBacteriaAnimal feeding stuffEcological environmentBacillus megaterium
The invention provides a composite bacillus preparation containing three strains, a preparation method of the composite bacillus preparation and application of the composite bacillus preparation to ecological breeding, and belongs to the technical field of microorganism and feed additives. Bacillus coagulans, butyric acid clostridia and bacillus megaterium are used as fermentative strains respectively, and large-scale, low-cost and high-density fermentation production of spores is conducted through step-by-step magnification; three live bacterium preparations are prepared by mixing bacterial sludge with the spores and dry starch; the three live bacterium preparations are matched according to the equal weight ratio, the composite bacillus preparation is obtained, and the concentration of the spores reaches more than 1*108-109 cfu / g; the composite bacillus preparation serves as a microorganism and feed additive to be added to farmed animal feed according to the mass ratio ranging from 0.02% to 0.5%. The composite bacillus preparation is simple and stable in process, low in cost, high in spore content and environment tolerance, easy to store and high in survival rate; the purposes of composition and synergism are achieved through the collaborative supplementary effects of different bacilli in the aspect of micro-ecology adjustment, growth of farmed animals is promoted, the feed utilization rate and feed rewards are increased, diarrhea is prevented and reduced, and the breeding ecological environment is improved.
Owner:江苏省苏微微生物研究有限公司 +3
Treatment of fine wrinkles with clostridia neurotoxins
InactiveUS20080081049A1Reduce the numberReduced activityCosmetic preparationsBacterial antigen ingredientsClostridial toxinWrinkle skin
Methods of using clostridial toxins and other biological agents to thin skin and control fine wrinkles in humans are provided. In preferred embodiments the methods provide beneficial effects in humans.
Owner:SANDERS
Cyclopropyl group substituted oxazolidinone antibiotics and derivatives thereof
This invention relates to new oxazolidinones having a cyclopropyl moiety, which are effective against aerobic and anerobic pathogens such as multi-resistant staphylococci, streptococci and enterococci, Bacteroides spp., Clostridia spp. species, as well as acid-fast organisms such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis and other mycobacterial species.The compounds are represented by structural formula I:its enantiomer, diastereomer, or pharmaceutically acceptable salt or ester thereof.
Owner:KYORIN PHARMA CO LTD +1
Clay product and uses thereof
ActiveUS20140099373A1Reduce the impactImproving gastro intestinal healthBiocidePowder deliveryClostridiaCoccidia
The present invention relates to a combination of an anti-toxin, The present invention relates to a combination of an anti-toxin, an immunomodulator and a component that provides energy to mucosal cells, which may be useful for decreasing effects of Clostridia sp. or coccidia sp based diseases or other enteric diseases or by generally improving gastro intestinal health or function
Owner:OIL DRI OF AMERICA
Novel oxazolidinone derivatives
ActiveUS20090192197A1Improve solubilityLow toxicityAntibacterial agentsBiocidePhosphateAntibacterial activity
Owner:DONG A ST CO LTD +1
Method for quickly culturing anaerobic hydrogen-producing granular sludge
InactiveCN101767873AResolution timeSolve the easy loss of sludgeTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesActivated sludgeFermentation
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Treatment of mammalian reaction of ige interactions
ActiveUS20060008462A1Relieve symptomsDecrease coughing and wheezingPowder deliverySpray deliveryAntigenClostridia
A method is disclosed for blocking or reducing physiological reaction in a mammal to the interaction of IgE antibodies present in said mammal upon contact with the corresponding antigen, by the administration to said mammal of a therapeutically effective amount of a neurotoxin (CnT) derived from Clostridia sp.
Owner:SANDERS
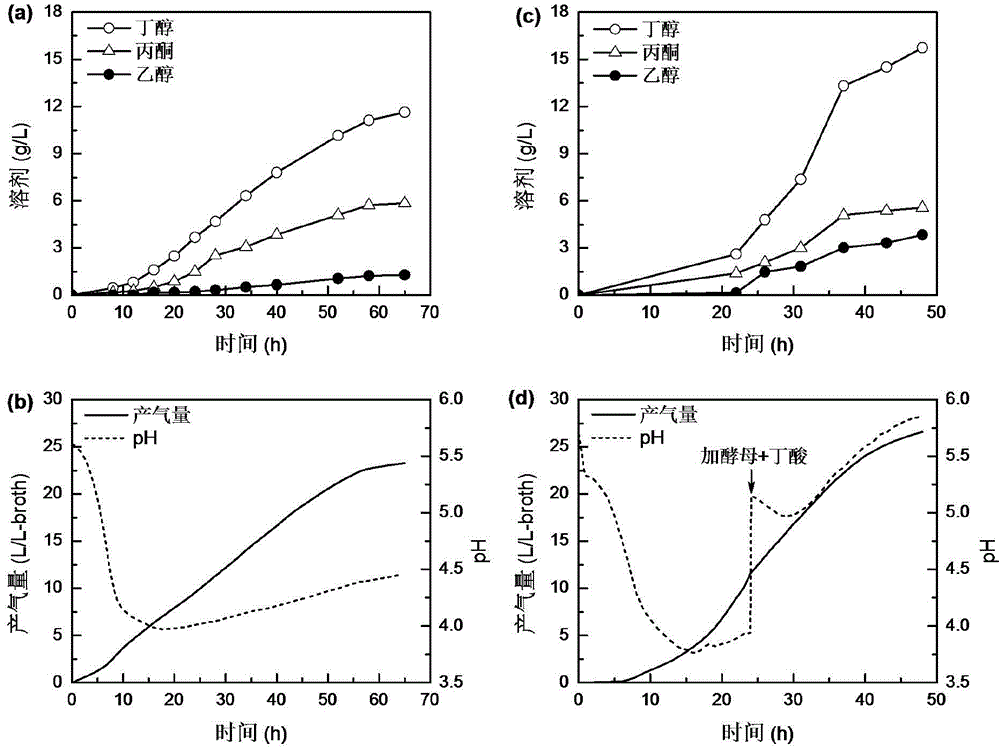
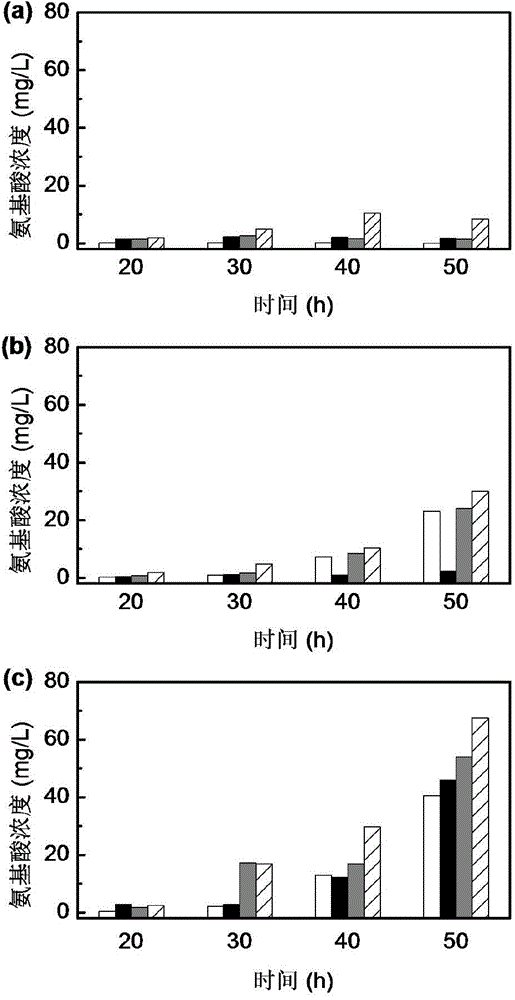
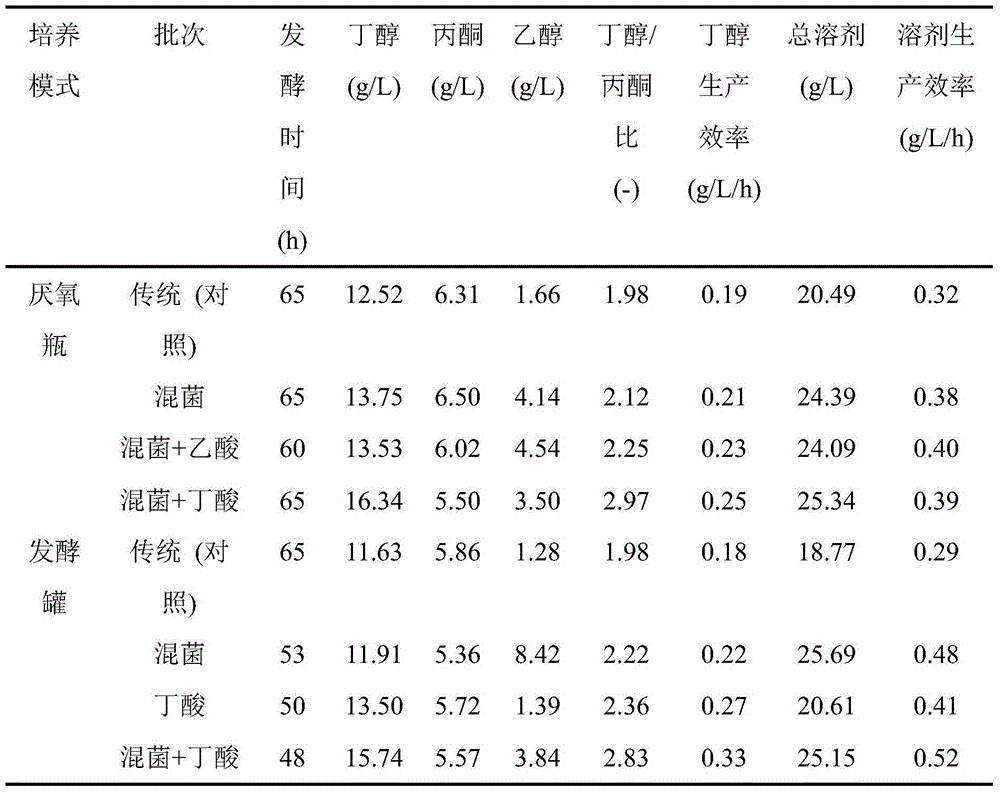
Method for increasing butanol-acetone ratio and butanol yield of clostridia ABE fermentation
ActiveCN104372033AImprove performanceEfficient removalBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesBatch fermentationSolvent
The invention discloses a method for increasing the butanol-acetone ratio and the butanol yield of clostridia ABE fermentation, and belongs to the technical field of biology. According to the method, corn flour is taken as a fermentation raw material, and a clostridium-saccharomyces cerevisiae mixed culture system is formed by appropriately adding an active saccharomyces cerevisiae and a butyric acid solution at the solvent production stage of the clostridia. The saccharomyces cerevisiae is capable of secreting various amino acids under a strict anaerobic condition and in a severe saccharomyces cerevisiae growth environment, wherein aromatic amino acids and aspartic amino acids all advantageous for butanol synthesis are greatly accumulated. On the basis, the small amount of added butyric acid is further capable of weakening the metabolism intensity of the closed loop of butyric acid. Under the dual combined action, the butanol-acetone ratio and the final butanol concentration of the ABE fermentation can be greatly improved under the premise of unchanged or slightly improved total solvent production intensity. The two indexes, namely butanol-acetone ratio and butanol concentration of the method are at the highest level in the related study reports of the batch fermentation production of butanol by use of wild clostridia and have important guiding significance for the ABE fermentation.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Treatment of mammalian reaction of IgE interactions
Owner:SANDERS
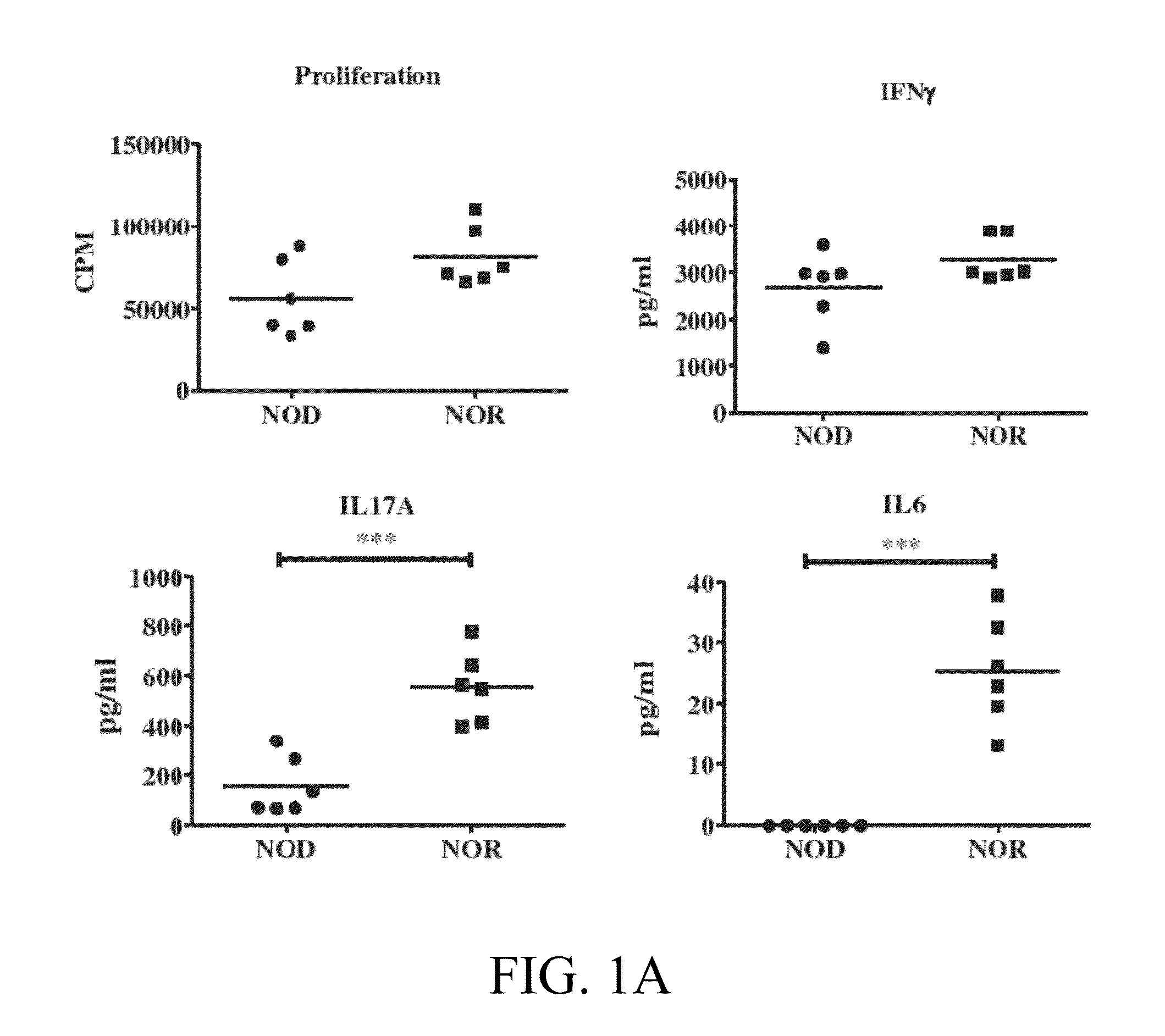
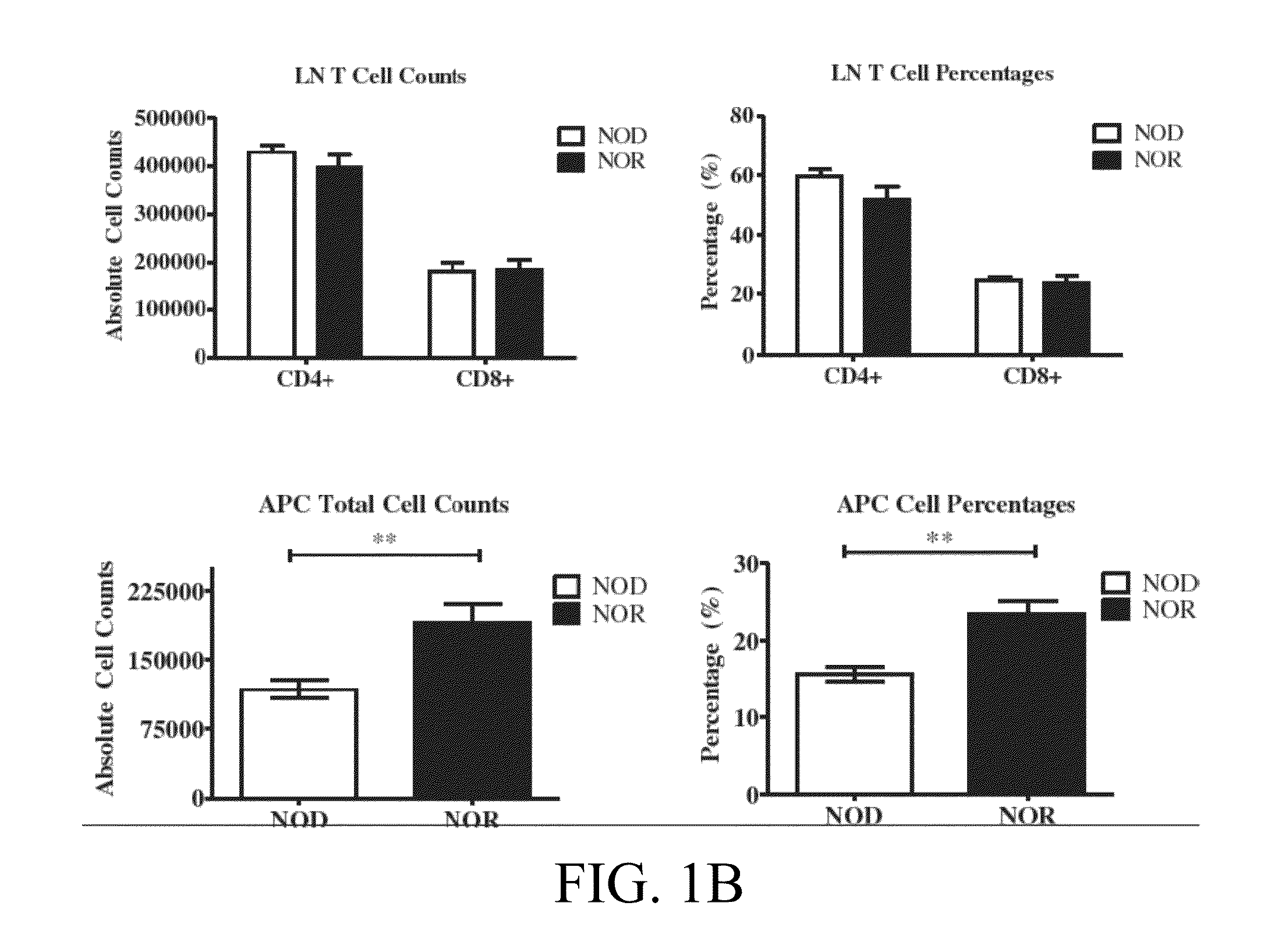
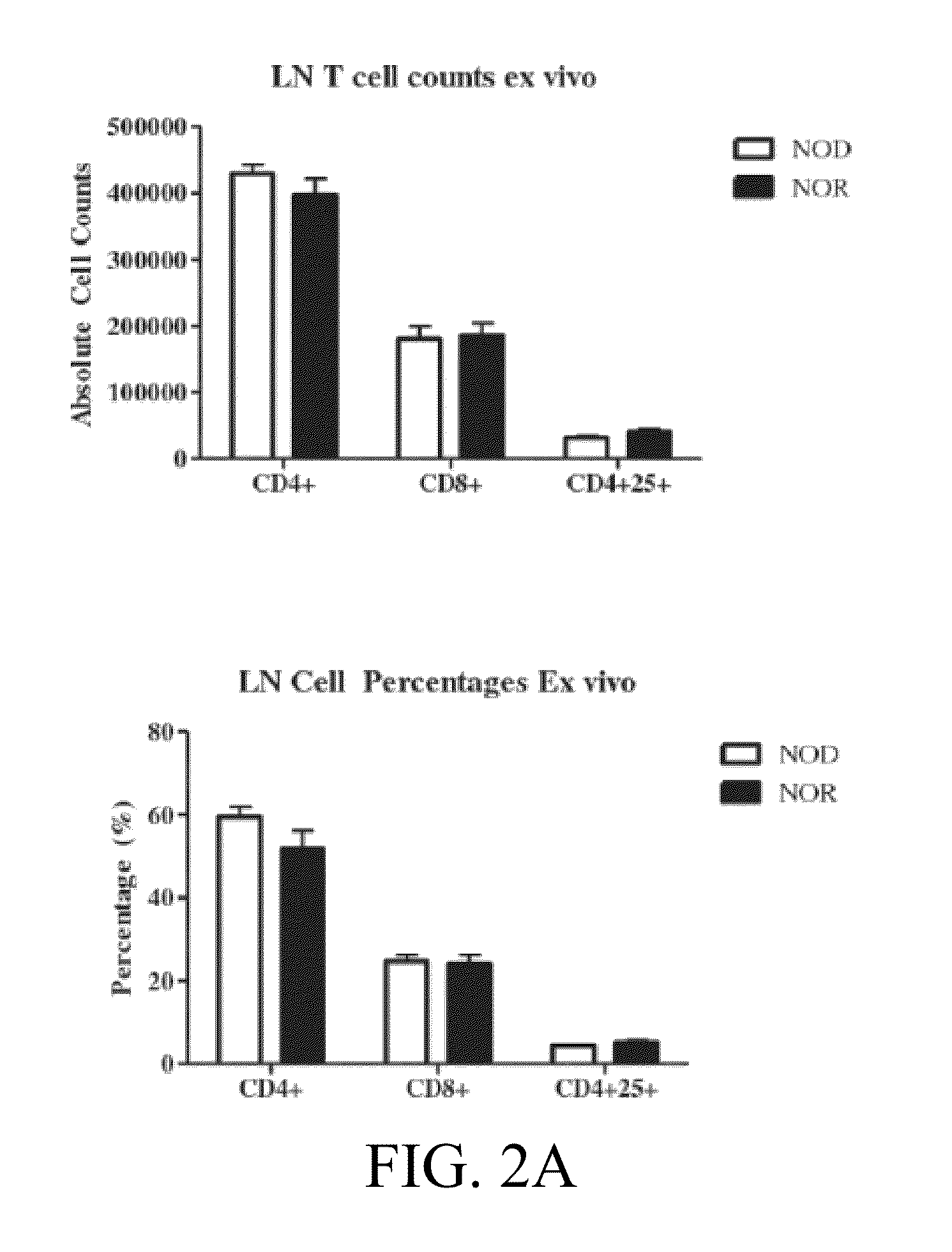
Novel type 1 diabetes vaccines, and methods of use
InactiveUS20140271718A1Prevent and delay onset of and reduce progressionSlow onsetBacterial antigen ingredientsMetabolism disorderClostridiaDendritic cell
The subject invention provides compositions for alleviating type 1 diabetes (T1D). In preferred embodiments, the compositions comprise an effective amount of one or more antigen presenting cells (APCs) that have been pulsed with one or more bacterial isolates and / or compounds from the isolates. The bacteria used to pulse the APCs are, preferably, those that confer upon the APCs the ability to inhibit the generation of diabetes-promoting T cells. In specific embodiments, these bacteria may be, for example, Eubacteria or Clostridia. In a preferred embodiment, the APCs are dendritic cells (DCs).
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
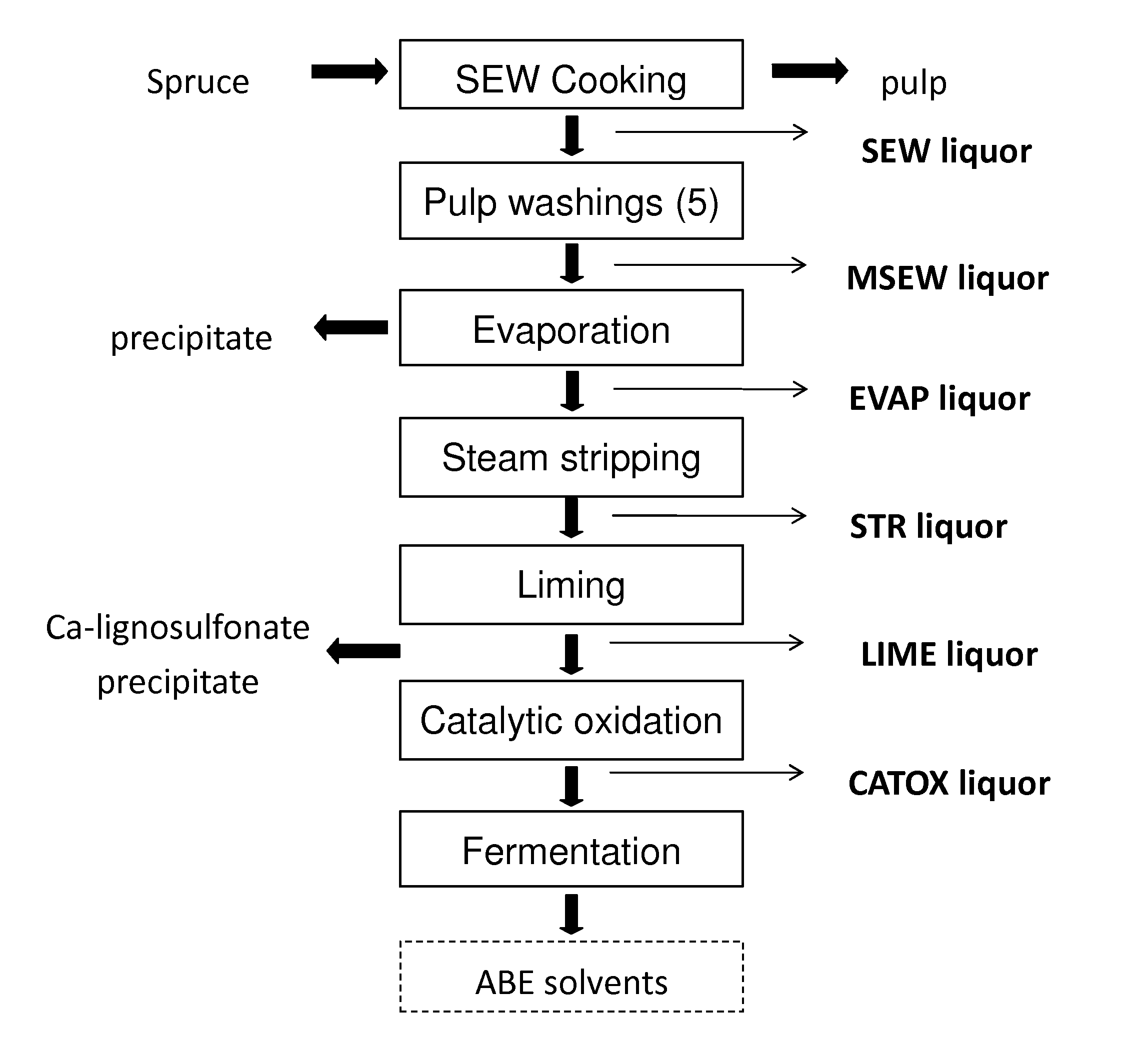
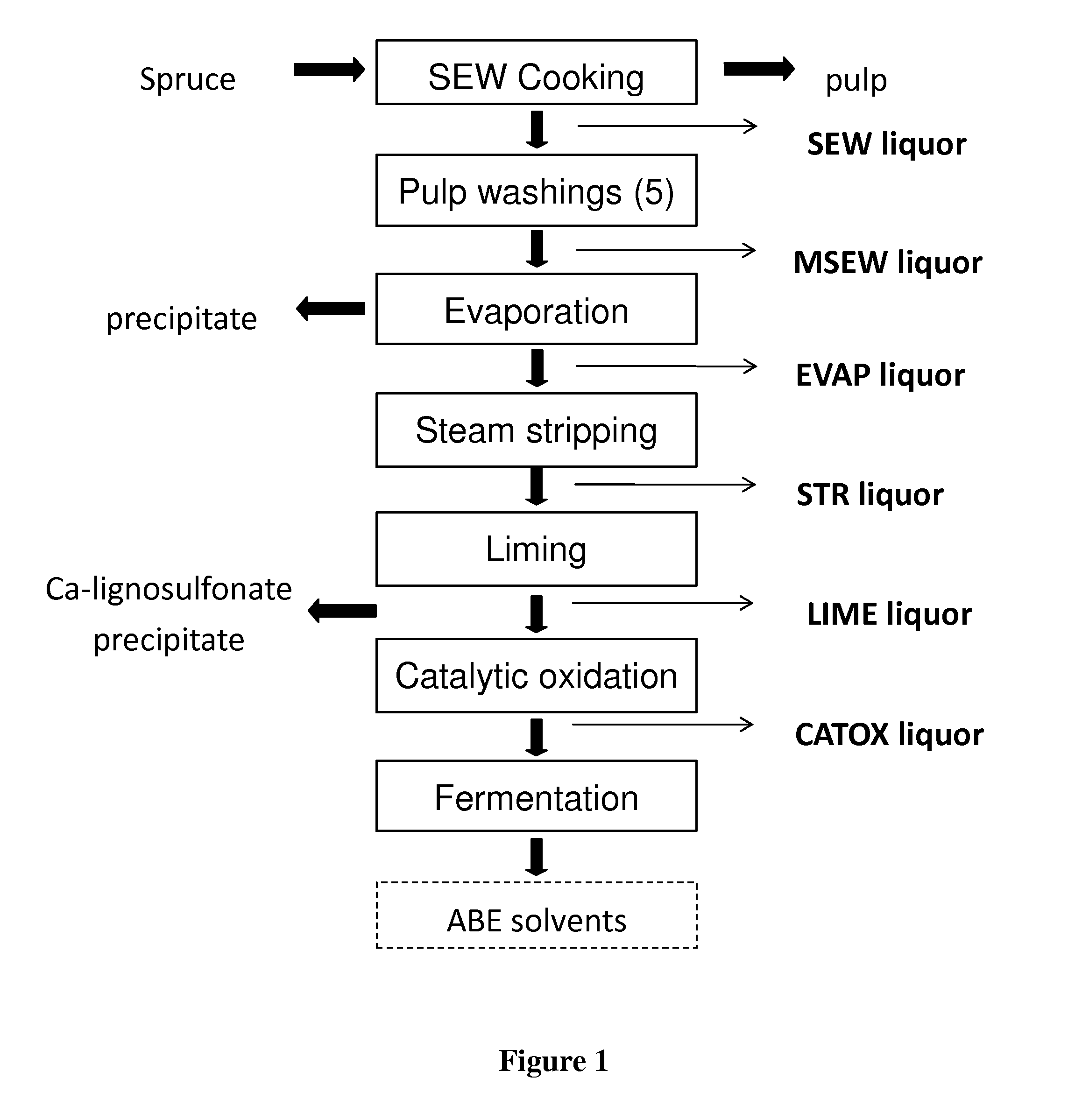
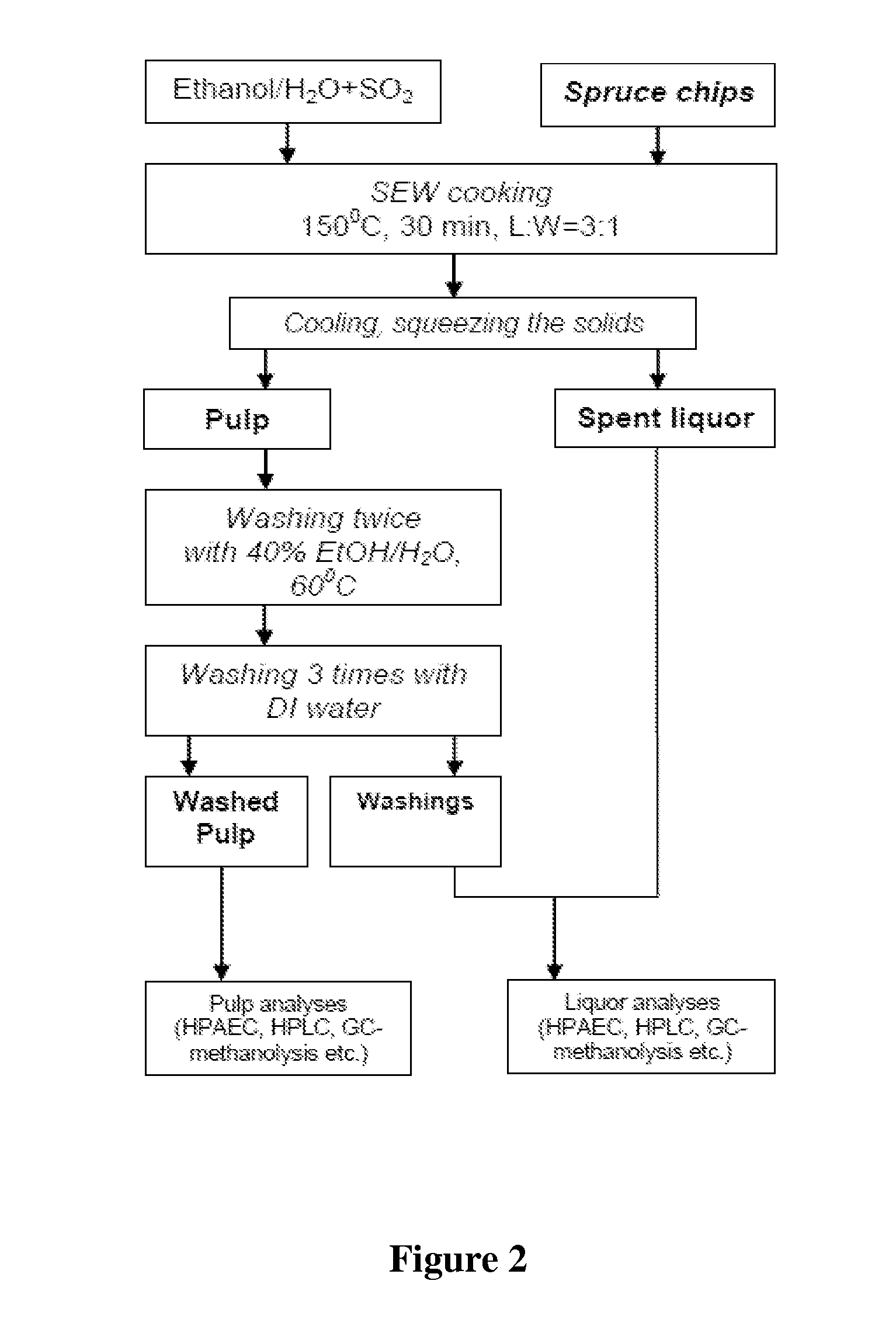
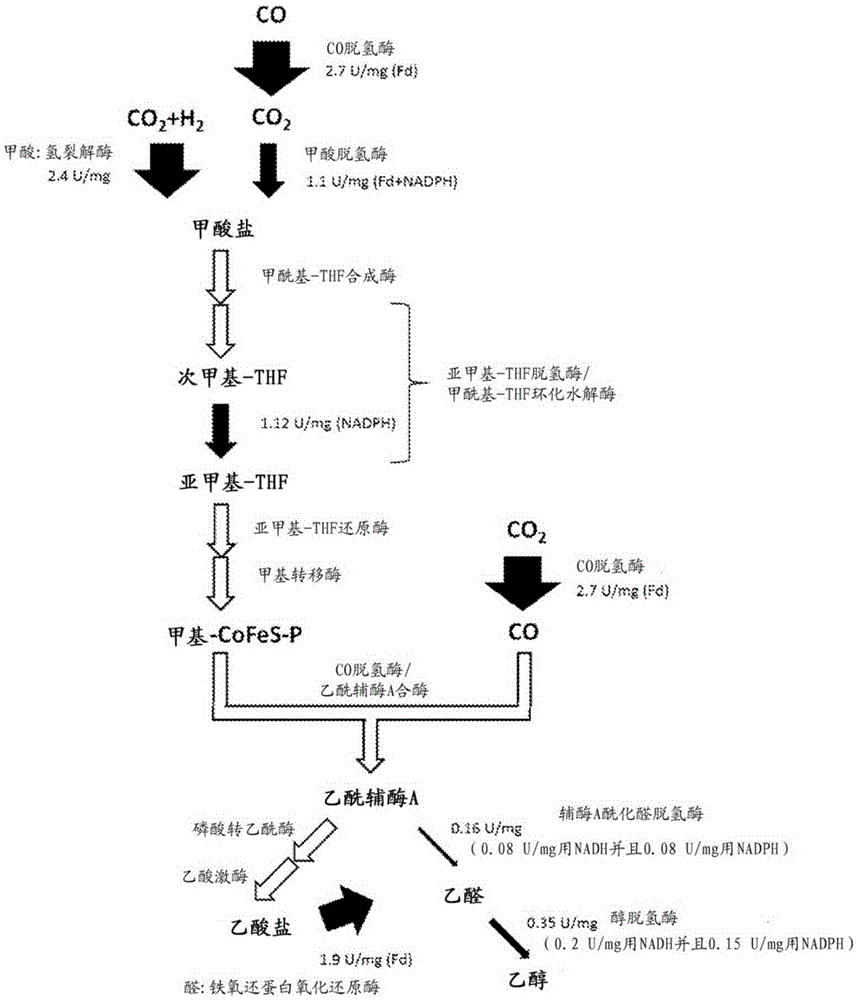
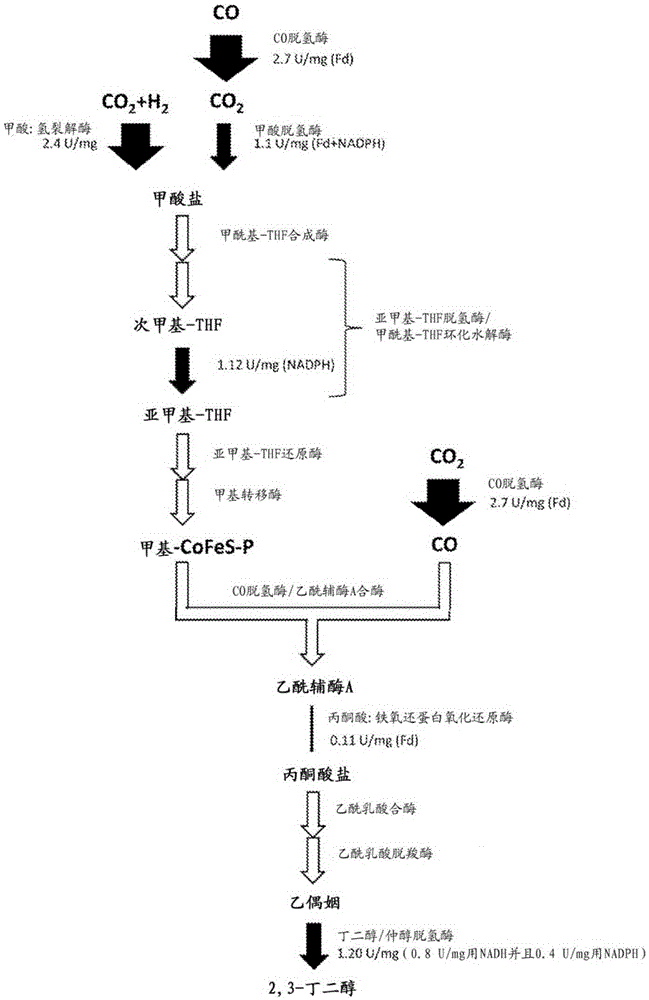
Conditioning of SO2-ethanol-water spent liquor for fermentation by clostridia
The present invention relates to producing chemicals and biofuels from wood material, e.g. mixed forest biomass. Specifically, the invention concerns a process for conditioning spent liquor produced by SO2-ethanol-water (SEW) fractionation of wood chips for fermentation to butanol, ethanol and acetone / isopropanol (so called ABE process) by Clostridia bacteria.
Owner:GRANBIO INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY HOLDINGS LLC
Recombinant microorganisms exhibiting increased flux through a fermentation pathway
Owner:LANZATECH NEW ZEALAND LTD
Novel Ethanologenic Clostridium species, Clostridium coskatii
Owner:SYNATA BIO INC
Methods and compositions for treating dysbiosis and gastrointestinal and inflammatory disorders
InactiveUS20170290889A1Promote wound healingReduce the amount of solutionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsWound healingClostridia
The present invention relates to the use of type 2 cytokines and mucins for increasing the amount or activity of bacterial species of the Clostridia class in the gastrointestinal tract, for treating dysbiosis in the gastrointestinal tract, for treating gastrointestinal and inflammatory disorders, and for promoting wound healing in the gastrointestinal tract.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Method for improving fermentation efficiency of anaerobic qi-eating microorganisms
ActiveCN105039416ARealize interconnectionRealize suction filtrationFermentationCellulosePeristaltic pump
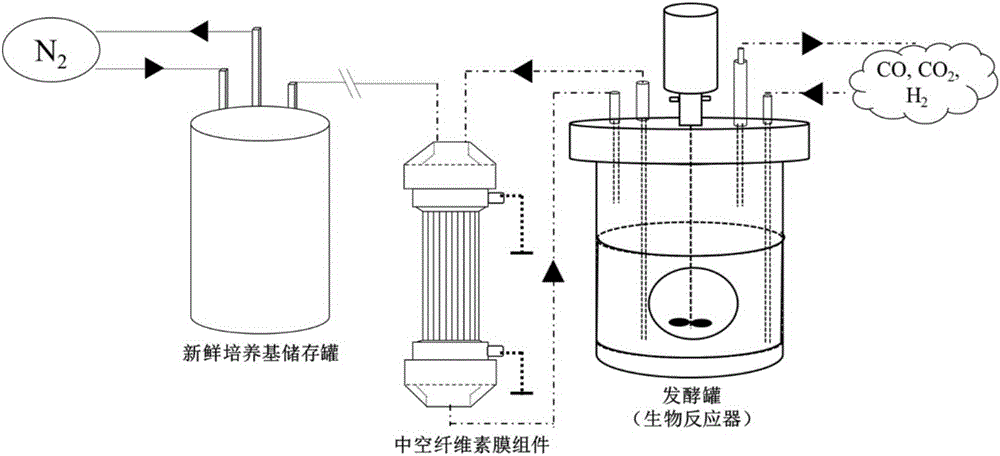
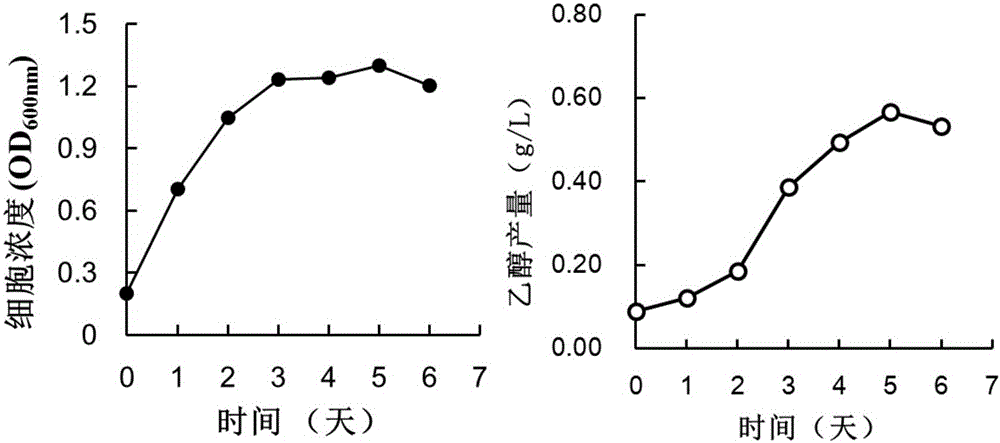
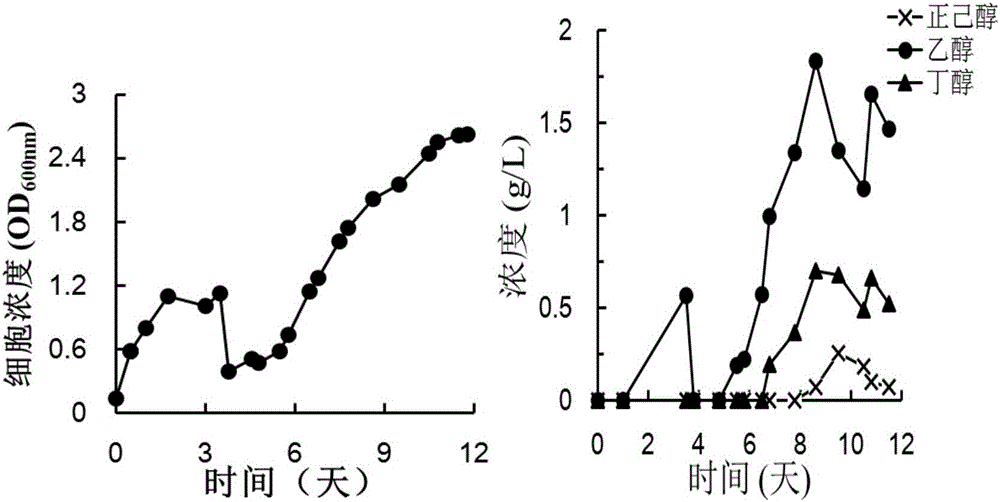
The invention aims at providing a method for improving fermentation efficiency of anaerobic qi-eating microorganisms. The method for improving the fermentation efficiency of the anaerobic qi-eating microorganisms comprises the following steps: firstly carrying out filtration interception on an anaerobic qi-eating microorganism bacterial liquid in a fermentation system by virtue of a hollow cellulose membrane, then carrying out back flushing by virtue of a culture medium, and carrying out fermentation on intercepted thalli again. The method for improving the fermentation efficiency of the anaerobic qi-eating microorganisms has the advantages that interconnection between a fermentation tank and a hollow cellulose membrane component is realized in a gaseous fermentation process of the anaerobic qi-eating microorganisms, so that fermentation liquor circulates between the inner cavity of the hollow cellulose membrane and the fermentation tank; meanwhile, a peristaltic pump connected with the outer wall of the hollow cellulose membrane component is used for pumping and drainage, realizing suction filtration on the fermentation liquor and intercepting the thalli, then a fresh culture medium is used for washing the thalli adhered in the cavity of the hollow cellulose membrane into the fermentation tank, and repeated and continuous fermentation is carried out; and the method for improving the fermentation efficiency of the anaerobic qi-eating microorganisms can be used for improving biomass accumulation of anaerobic qi-eating clostridia in the gaseous fermentation process and effectively improving yield of ethyl alcohol, butyl alcohol and hexyl alcohol which are produced by utilizing synthesis gas.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Treatment of fine wrinkles with clostridia neurotoxins
Owner:SANDERS +1
Microecological feed additive capable of improving eggshell quality and application method thereof
InactiveCN102499324AImprove qualityReduce quality degradationAnimal feeding stuffClostridiaSide effect
The invention provides a microecological feed additive capable of improving the eggshell quality and an application method thereof. The microecological feed additive comprises the following components: bacillus subtilis, bacillus natto, clostridia butyricum, lactobacillus metabolites, lactobacillus activators and carriers. By adopting the microecological feed additive, the microecological flora balance of laying poultry can be adjusted, the oviduct inflammation of the laying poultry can be reduced, and the calcium-phosphorus ratio in the blood of the laying poultry can be adjusted. Compared with similar additives, the microecological feed additive has the advantages of high effectiveness, good specificity, no residues and no side effects. When the microecological feed additive is used, the eggshell quality can be improved.
Owner:SHANDONG YISHENGYUAN MICROBIOLOGY TECH +2
Treatment of fine wrinkles with clostridia neurotoxins
Methods of using clostridial toxins and other biological agents to thin skin and control fine wrinkles in humans are provided. In preferred embodiments the methods provide beneficial effects in humans.
Owner:SANDERS
Novel efficient synbiotics intestines-targeting microspheric capsule and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a novel efficient synbiotics intestines-targeting microspheric capsule and a preparation method of the novel efficient synbiotics intestines-targeting microspheric capsule. The novel efficient synbiotics intestines-targeting microspheric capsule comprises 30-40% of probiotics and 60-70% of prebiotics, wherein the probiotics is a mixture composed of 40 to 50% of clostridia butyricum and 50 to 60% of lactobacillus sporogenes; and the prebiotics is the mixture composed of 60 to 70% of cerevisiae zymosan and 30 to 40% of sulphated cerevisiae zymosan. The novel micro-capsule synbiotics additive for the feed, prepared by the method disclosed by the invention, plays the effects of both the probiotics and the prebiotics, has remarkable effects of improving the utilization rate of the feed, promoting the growth of animal and improving the resistance and immunity of the human body; and the novel efficient synbiotics intestines-targeting microspheric capsule is sable in quality, safe, and free from toxic and side effect, brings no residues and pollution, and is beneficial for the human health and environmental protection.
Owner:ANHUI ZHENGDAYUAN FEED GRP CO LTD
Oxazolidinone derivatives as antimicrobials
InactiveUS20060293307A1High antibacterial activityTreatment safetyAntibacterial agentsBiocideAcid-fastMycobacterium
The present invention relates to certain substituted phenyl oxazolidinones and to processes for the synthesis of the same. This invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions containing the compounds of the present invention as antimicrobials. The compounds are useful antimicrobial agents, effective against a number of human and veterinary pathogens, including gram-positive aerobic bacteria such as multiple-resistant staphylococci, streptococci and enterococci as well as anaerobic organisms such as Bacterioides spp. and Clostridia spp. species, and acid fast organisms such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Mycobacterium avium and Mycobacterium spp.
Owner:RANBAXY LAB LTD
Microbial fermentation and detoxification method of rapeseed cake
ActiveCN102919624AGood detoxification stabilityPromote growthFood preparationNutritive valuesRapeseed
The invention discloses a microbial fermentation and detoxification method of rapeseed cake. The method comprises the following steps: adding a crushed detoxification synergist to the rapeseed cake; inoculating a bacillus subtilis, a clostridia butyricum, a lactobacillus acidophilus and a saccharomyces cerevisiae solid strain to the mixture and mixing evenly; fermenting, drying the mixture to obtain a detoxified rapeseed cake product. According to the invention, the content of glucoside sulphate in the detoxified rapeseed cake product does not exceed a safety level specified by the feed, the nutritional value is higher than that of the unfermented and undetoxified rapeseed cake, the protein content reaches 42 to 45%, and the content of disassociated amino acid reaches more than 10%, so that the detoxified rapeseed cake product can be directly used as protein feed for livestocks and aquatic products. The method provided by the invention can better solve the problems of incomplete detoxification, difficult elimination of anti-nutritional factors, nutrition loss and complexity in preparation process in prior art. The method has the advantages of good detoxification effect, simplicityin preparation and low energy consumption, and can reach the standard feed requirement of producing the non-toxic rapeseed cake. Therefore, the problem of shortage of feed protein resources in China is solved.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
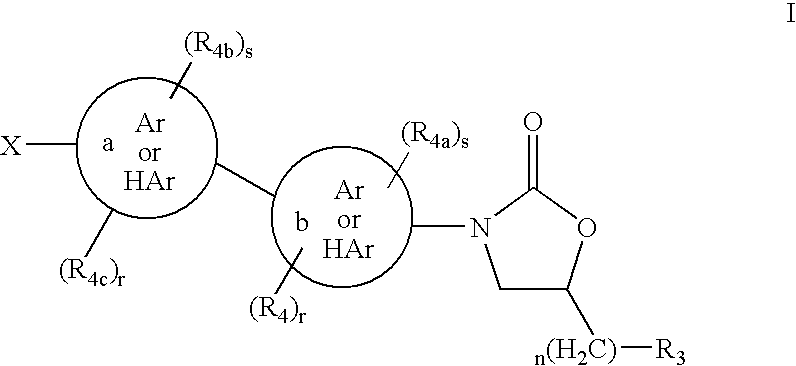
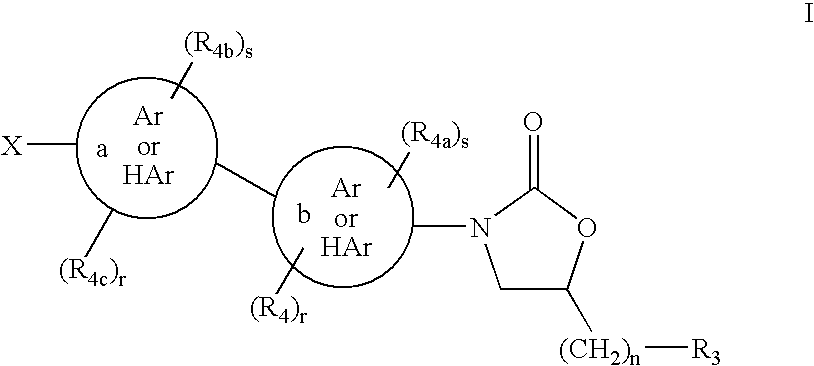
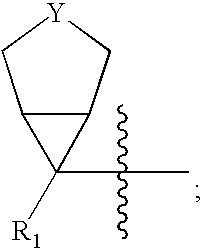
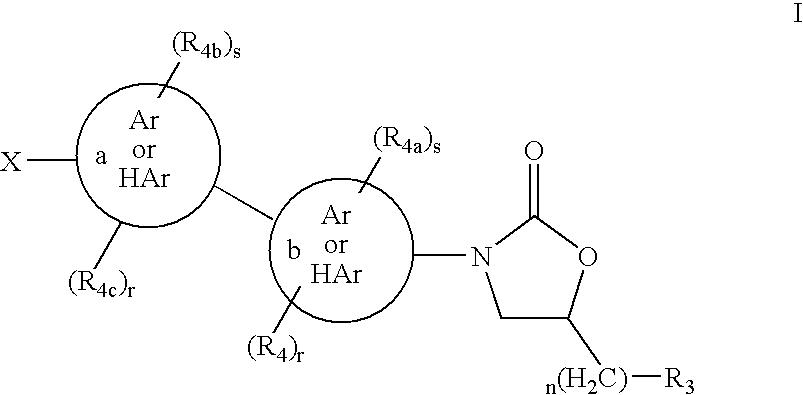
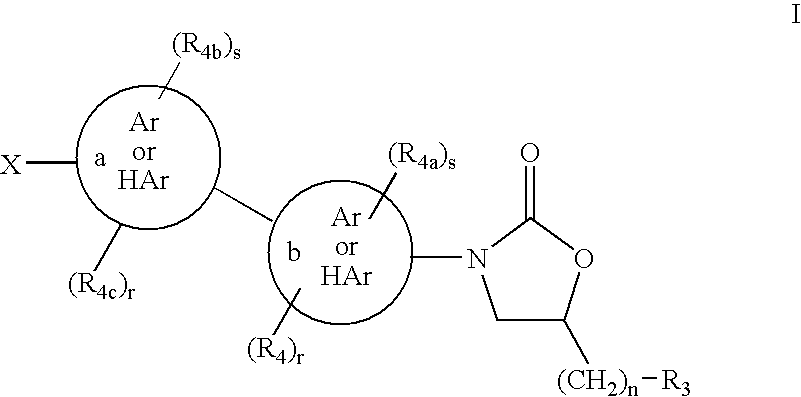
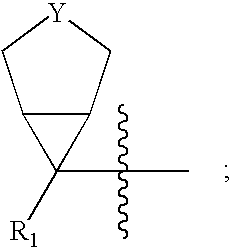
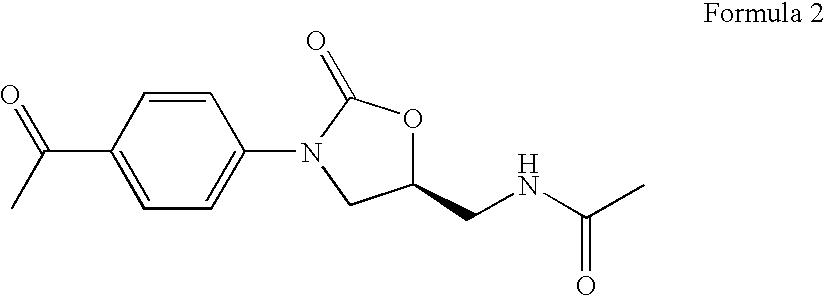
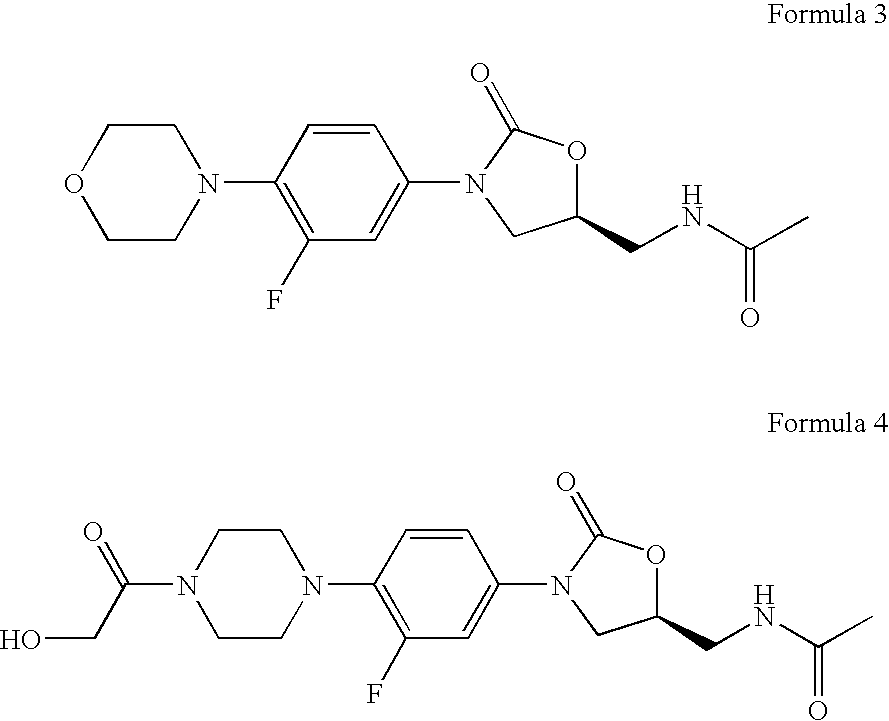
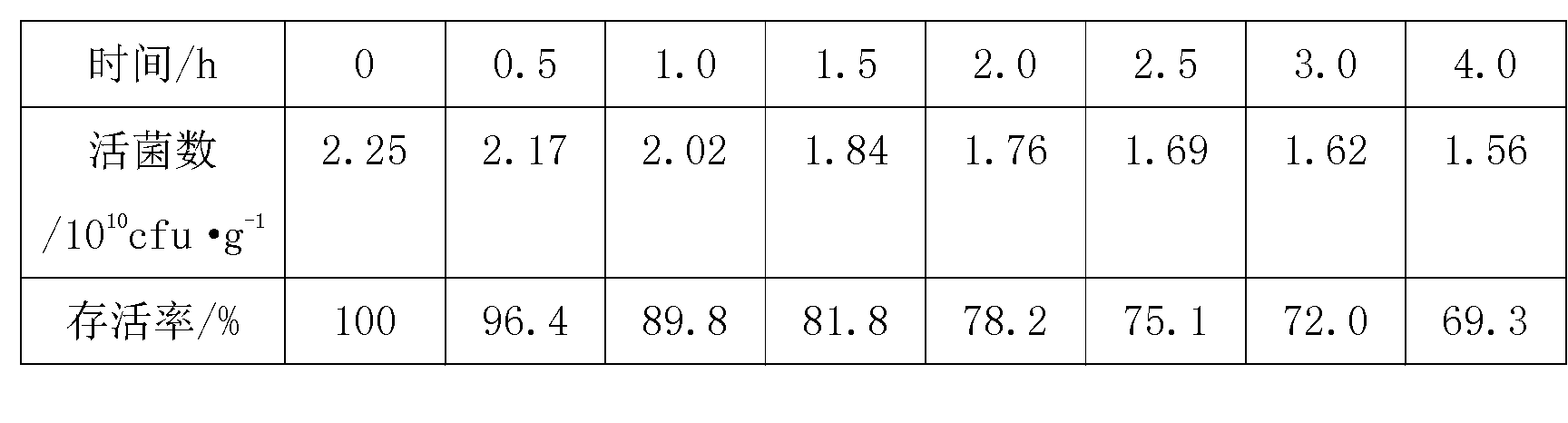
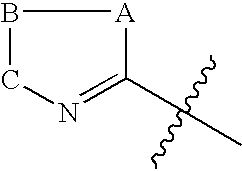
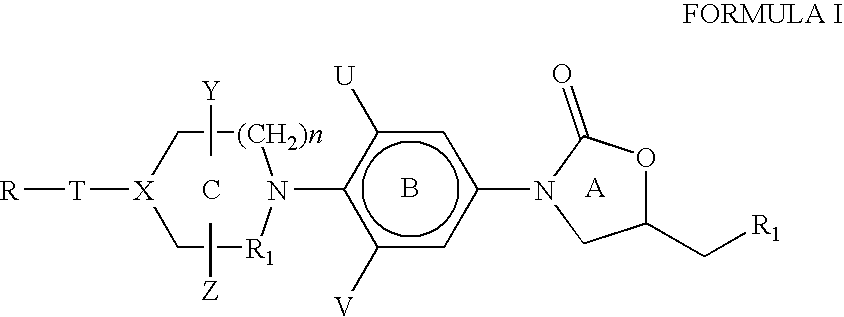
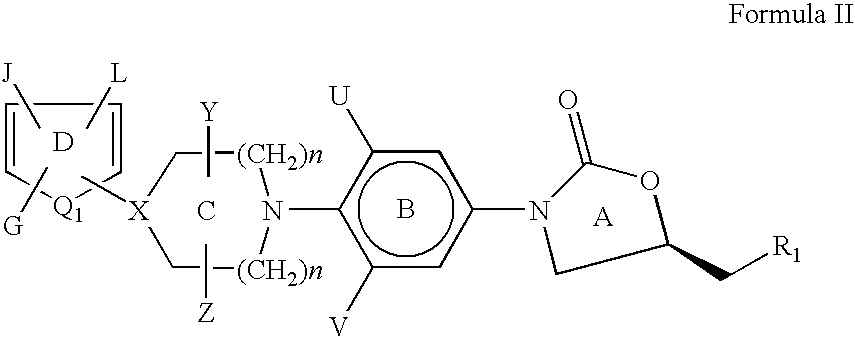
Bicyclo[3.1.0]hexane containing oxazolidinone antibiotics and derivatives thereof
Owner:KYORIN PHARMA CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com



![Bicyclo[3.1.0]hexane containing oxazolidinone antibiotics and derivatives thereof Bicyclo[3.1.0]hexane containing oxazolidinone antibiotics and derivatives thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/874c49f4-4960-4c13-9dbe-ceb734bb581c/US20050203144A1-20050915-C00001.png)
![Bicyclo[3.1.0]hexane containing oxazolidinone antibiotics and derivatives thereof Bicyclo[3.1.0]hexane containing oxazolidinone antibiotics and derivatives thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/874c49f4-4960-4c13-9dbe-ceb734bb581c/US20050203144A1-20050915-C00002.png)
![Bicyclo[3.1.0]hexane containing oxazolidinone antibiotics and derivatives thereof Bicyclo[3.1.0]hexane containing oxazolidinone antibiotics and derivatives thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/874c49f4-4960-4c13-9dbe-ceb734bb581c/US20050203144A1-20050915-C00003.png)