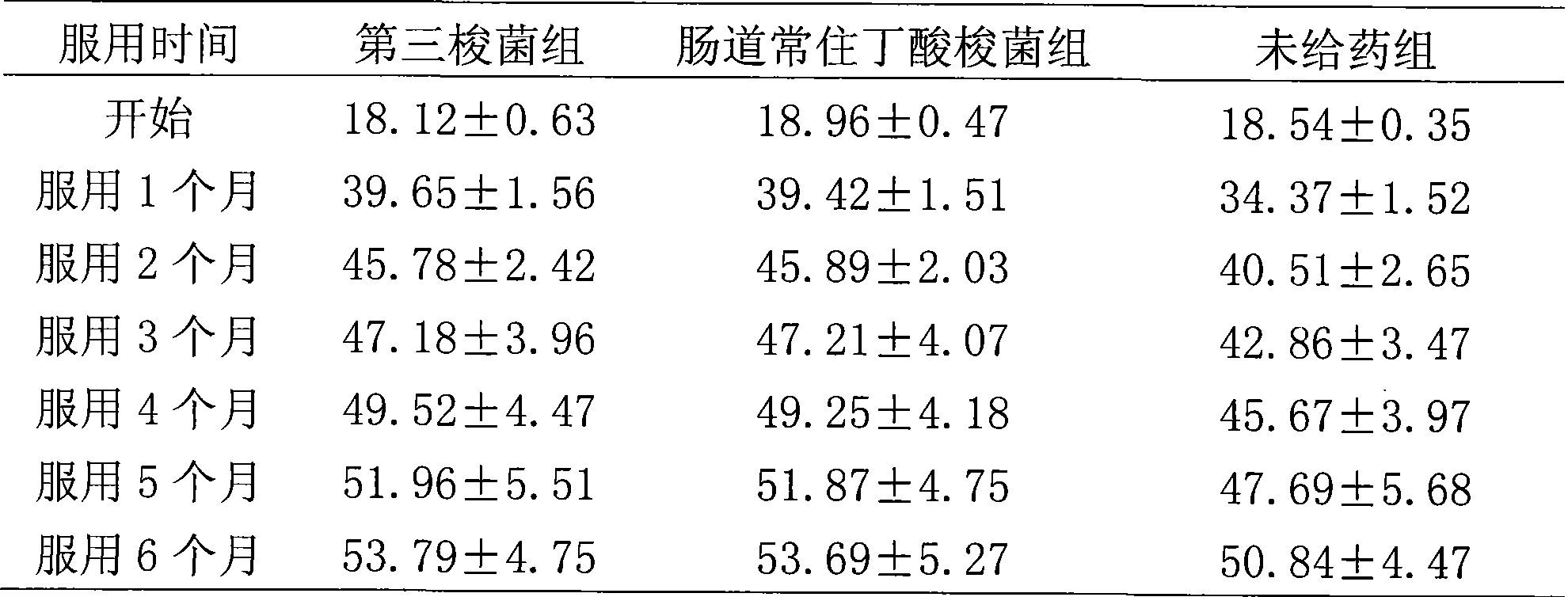
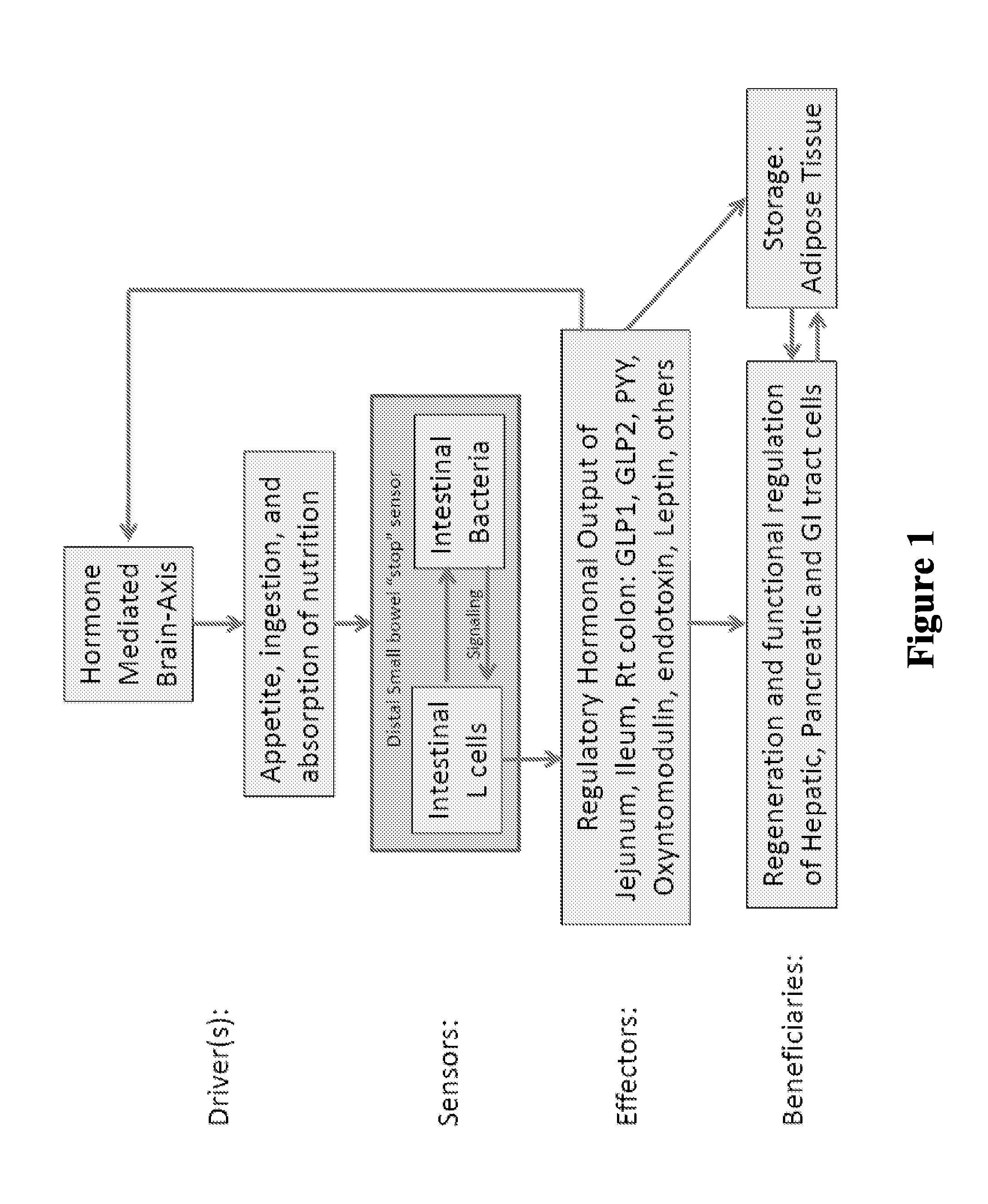
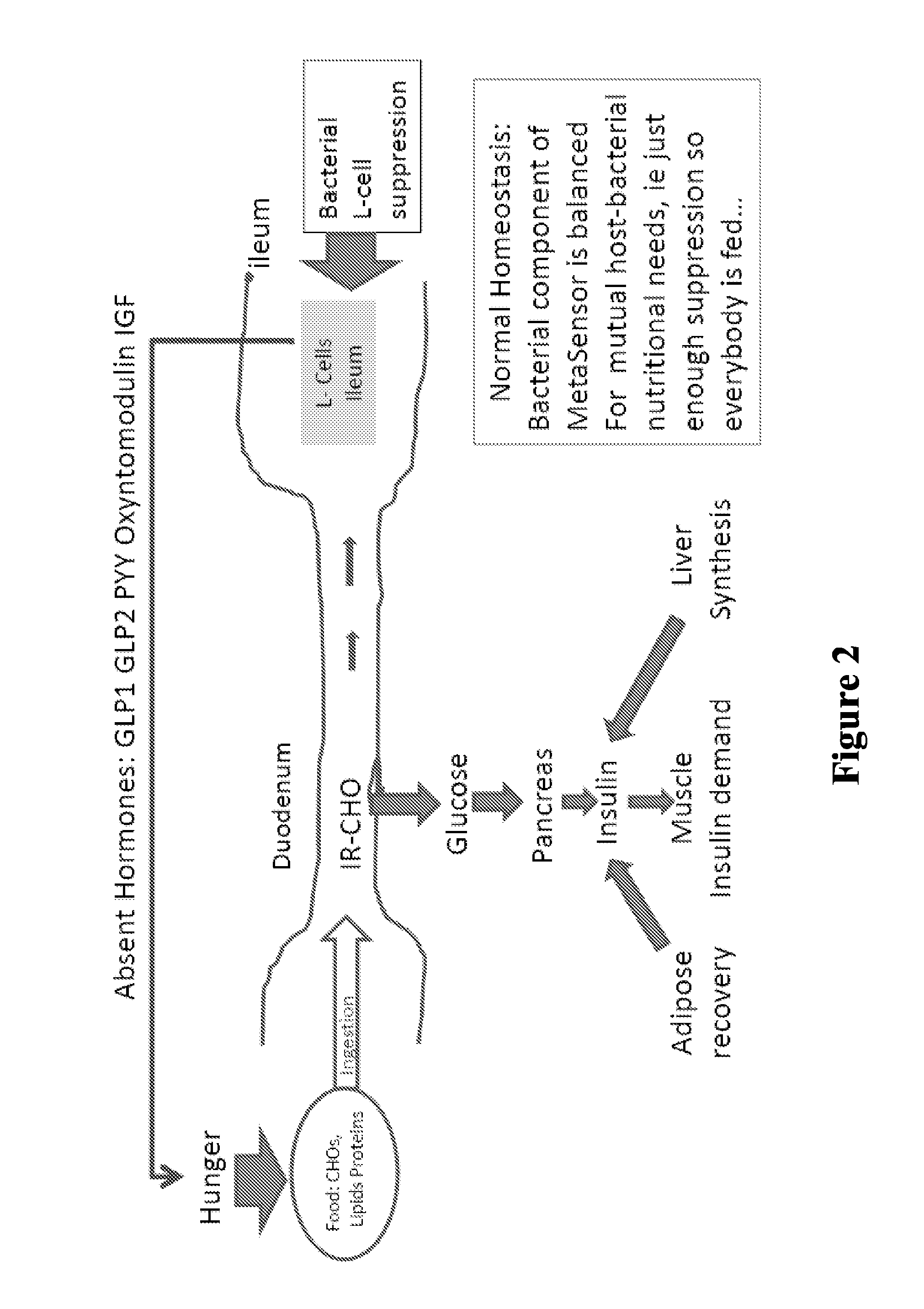
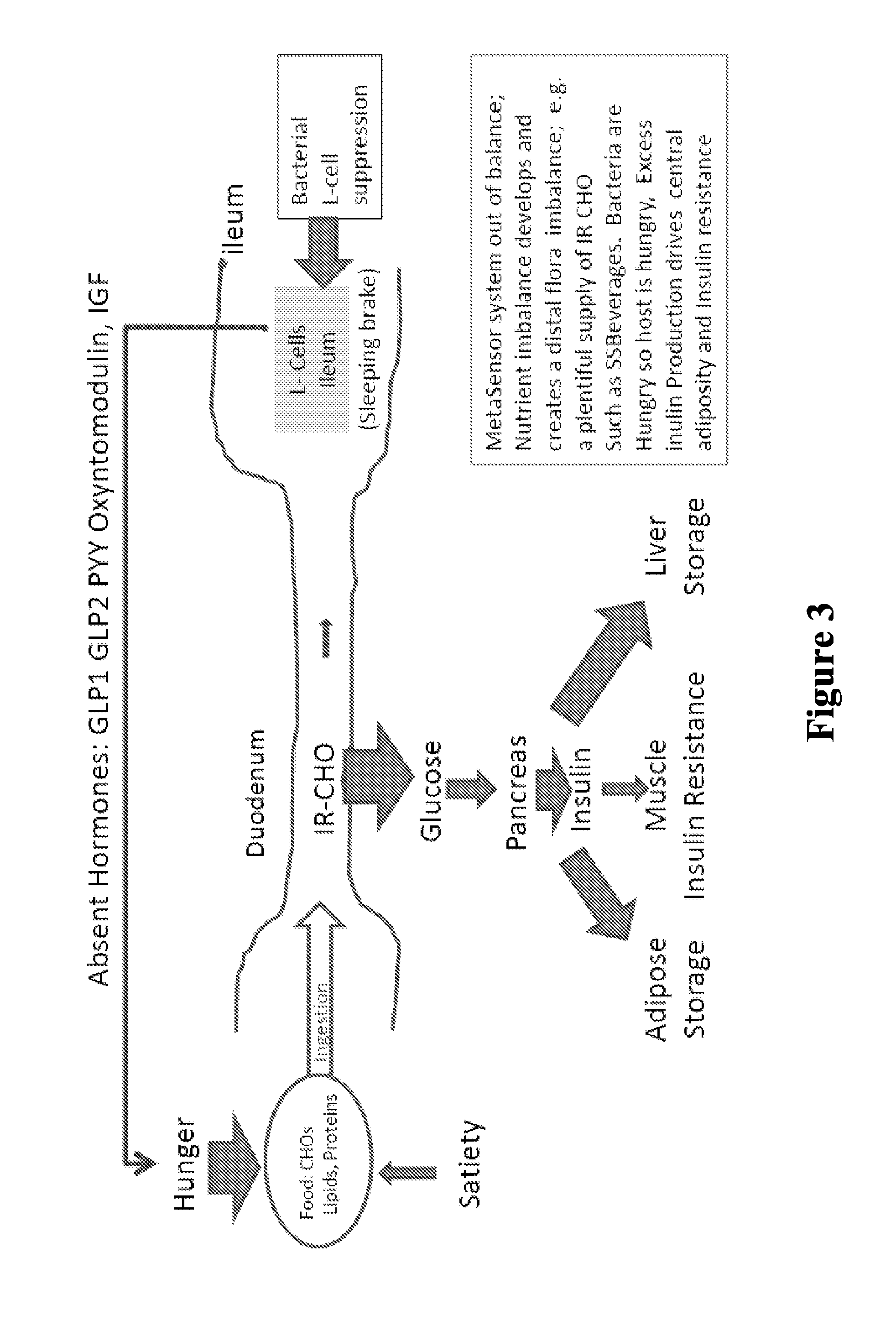
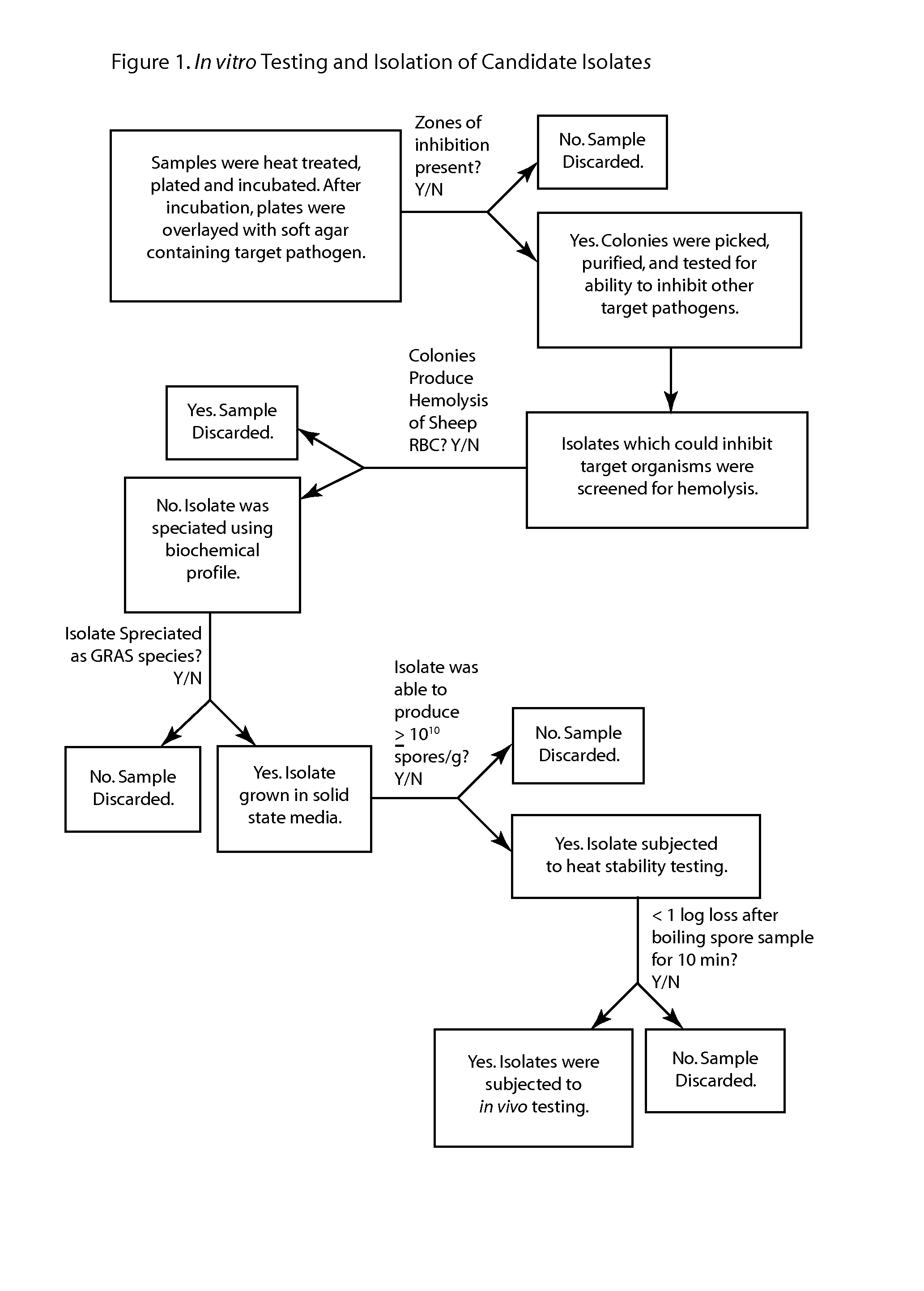
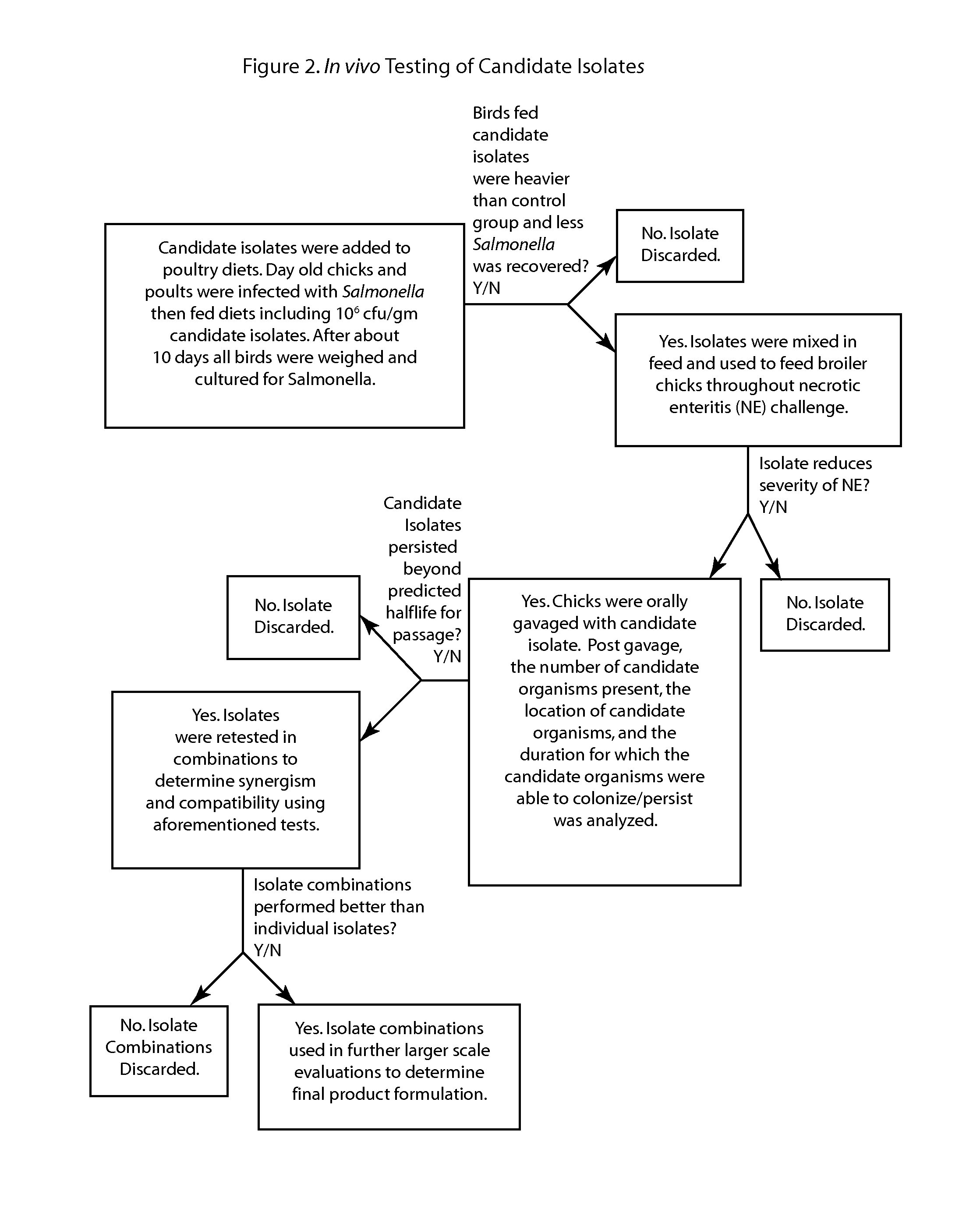
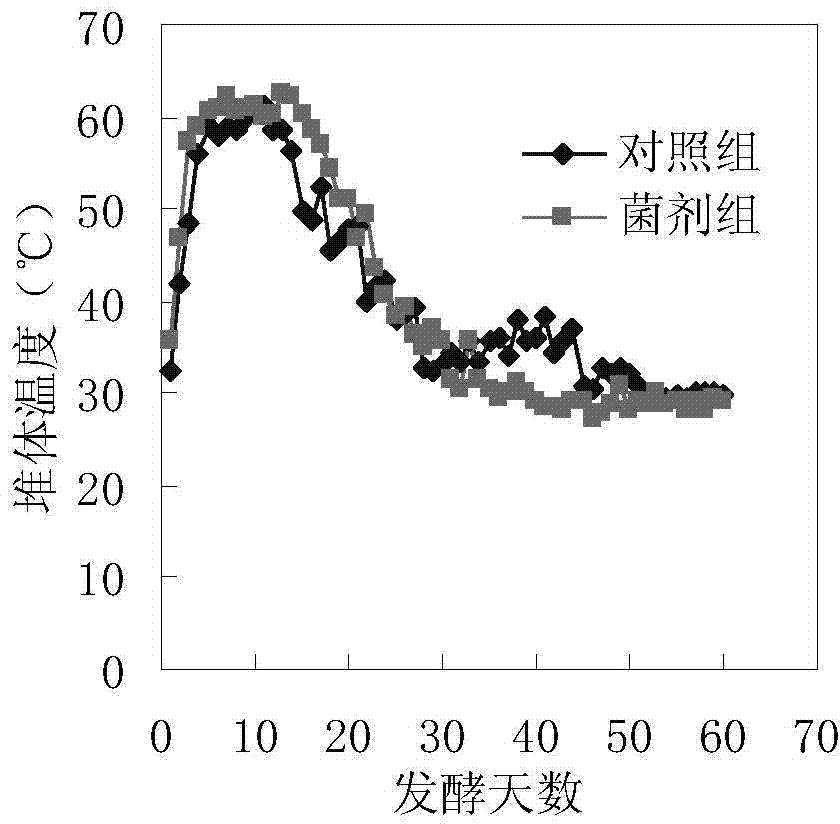
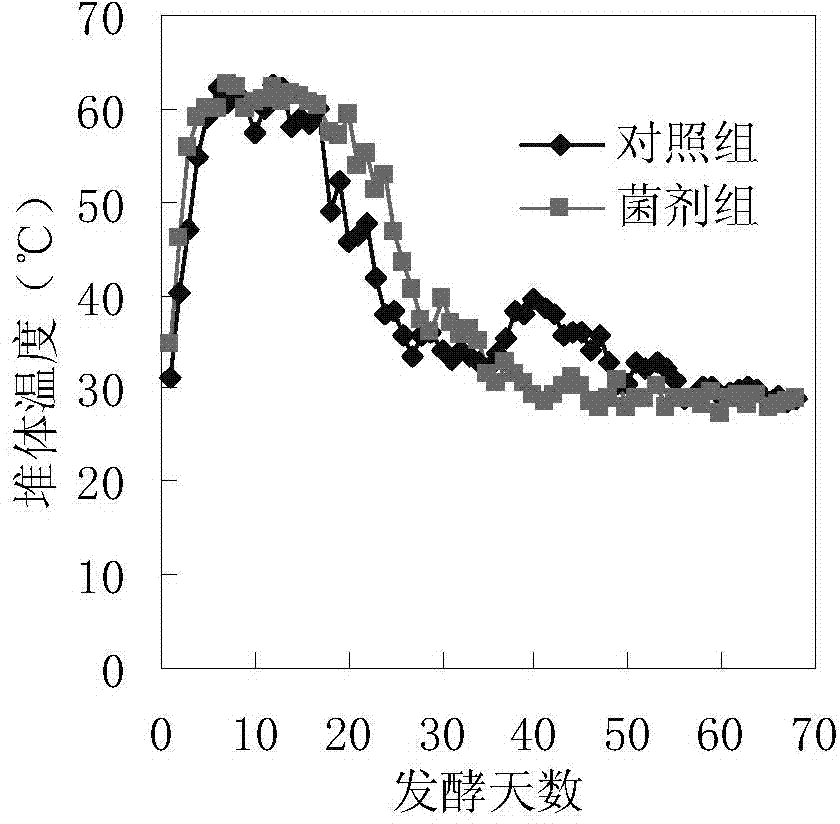
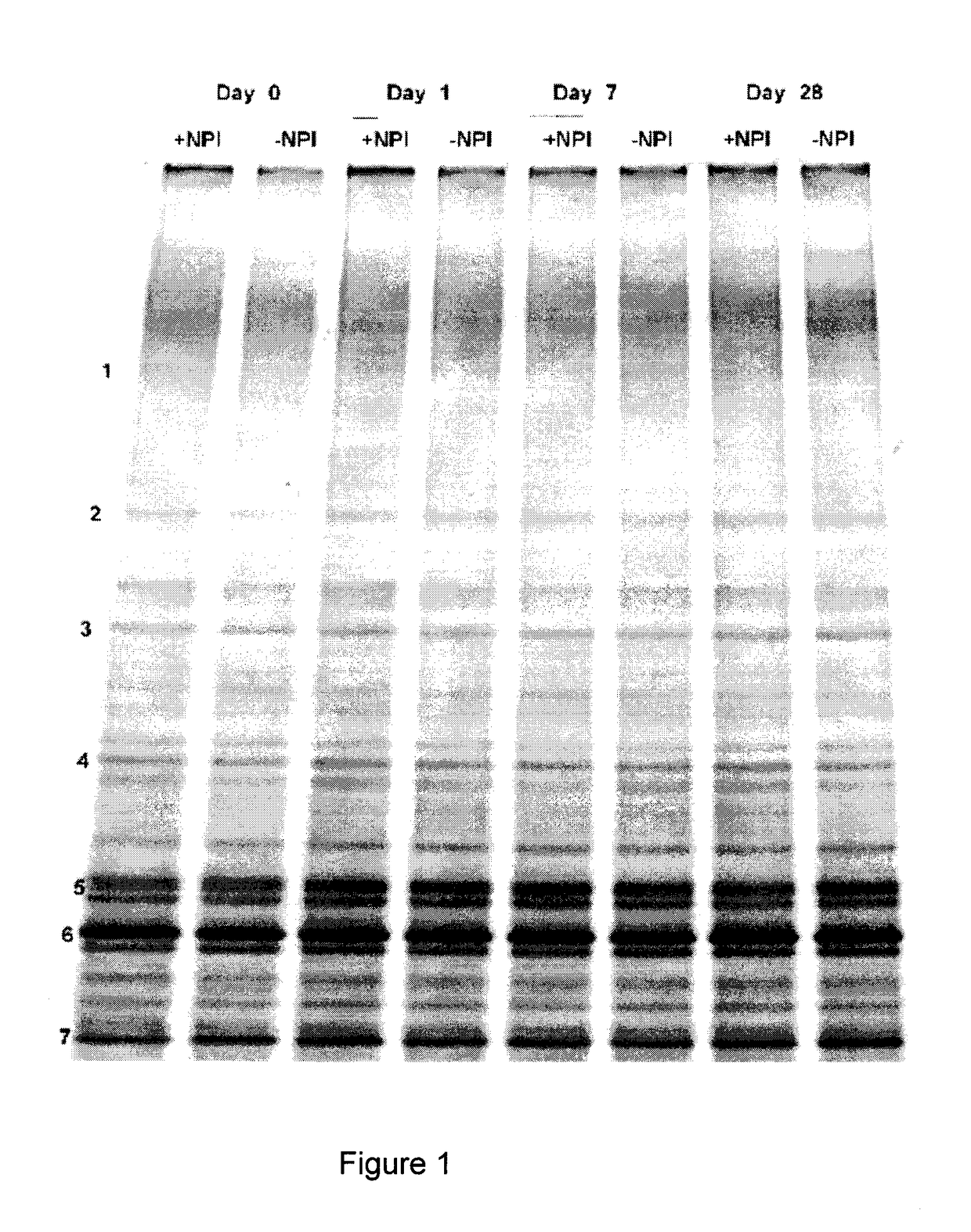
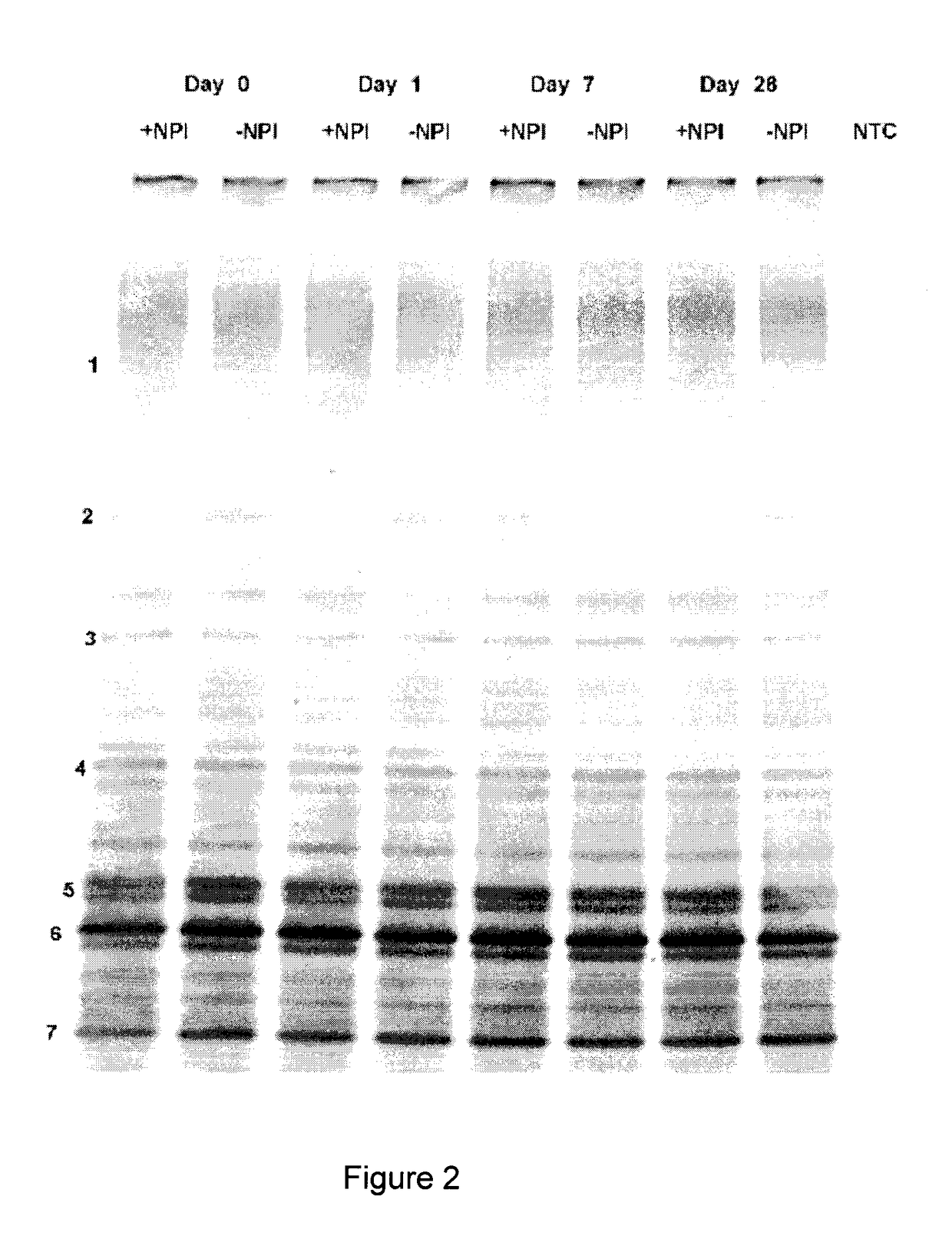
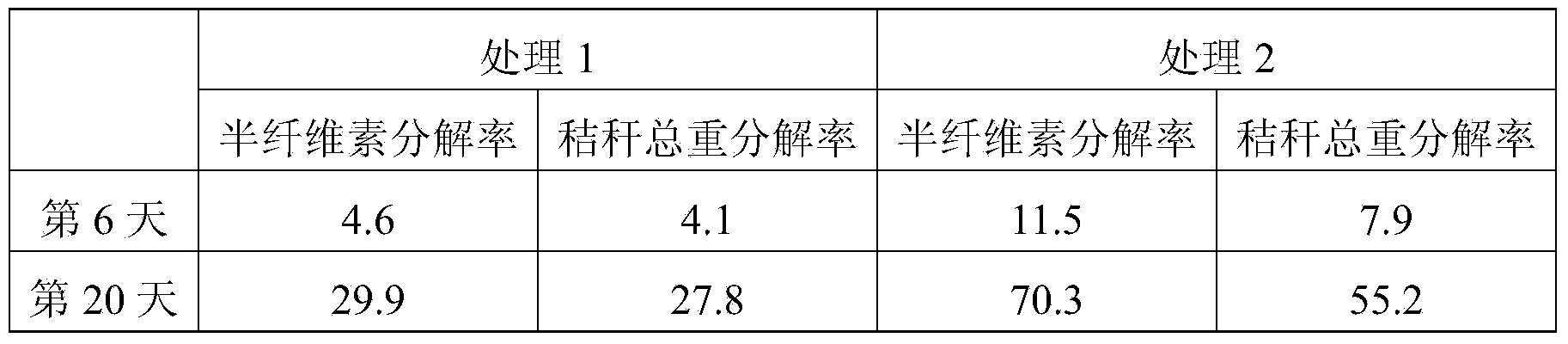
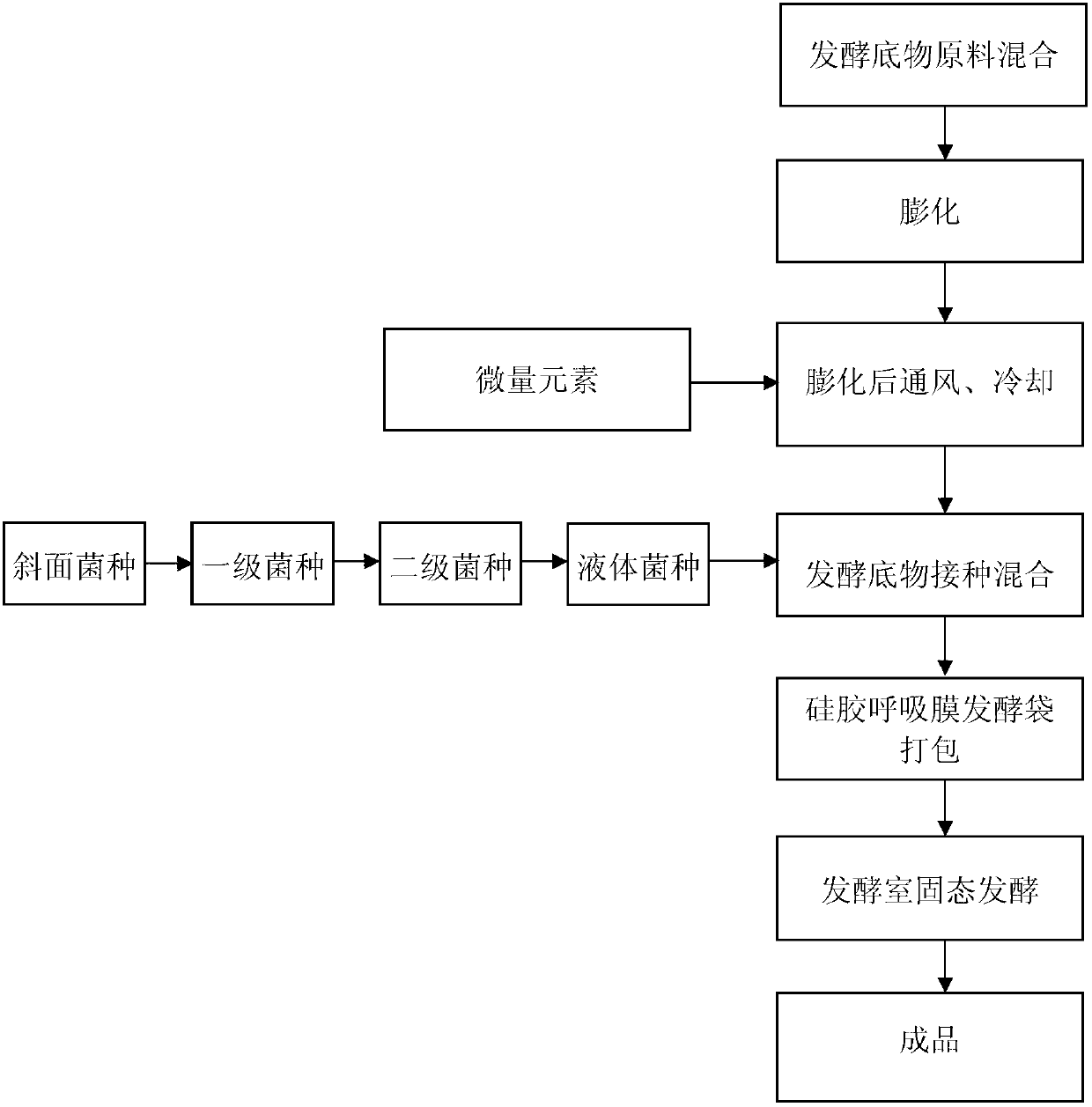
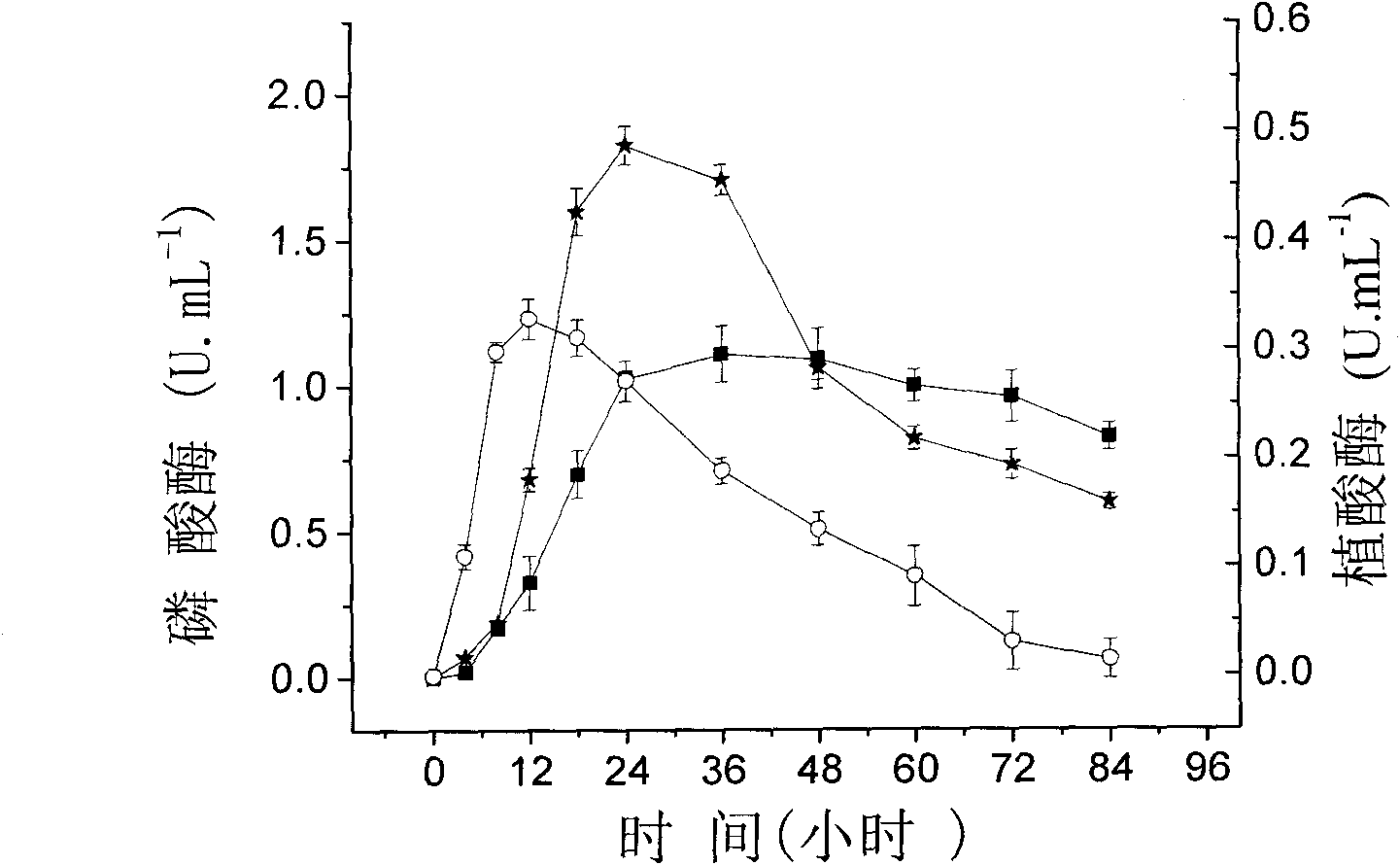
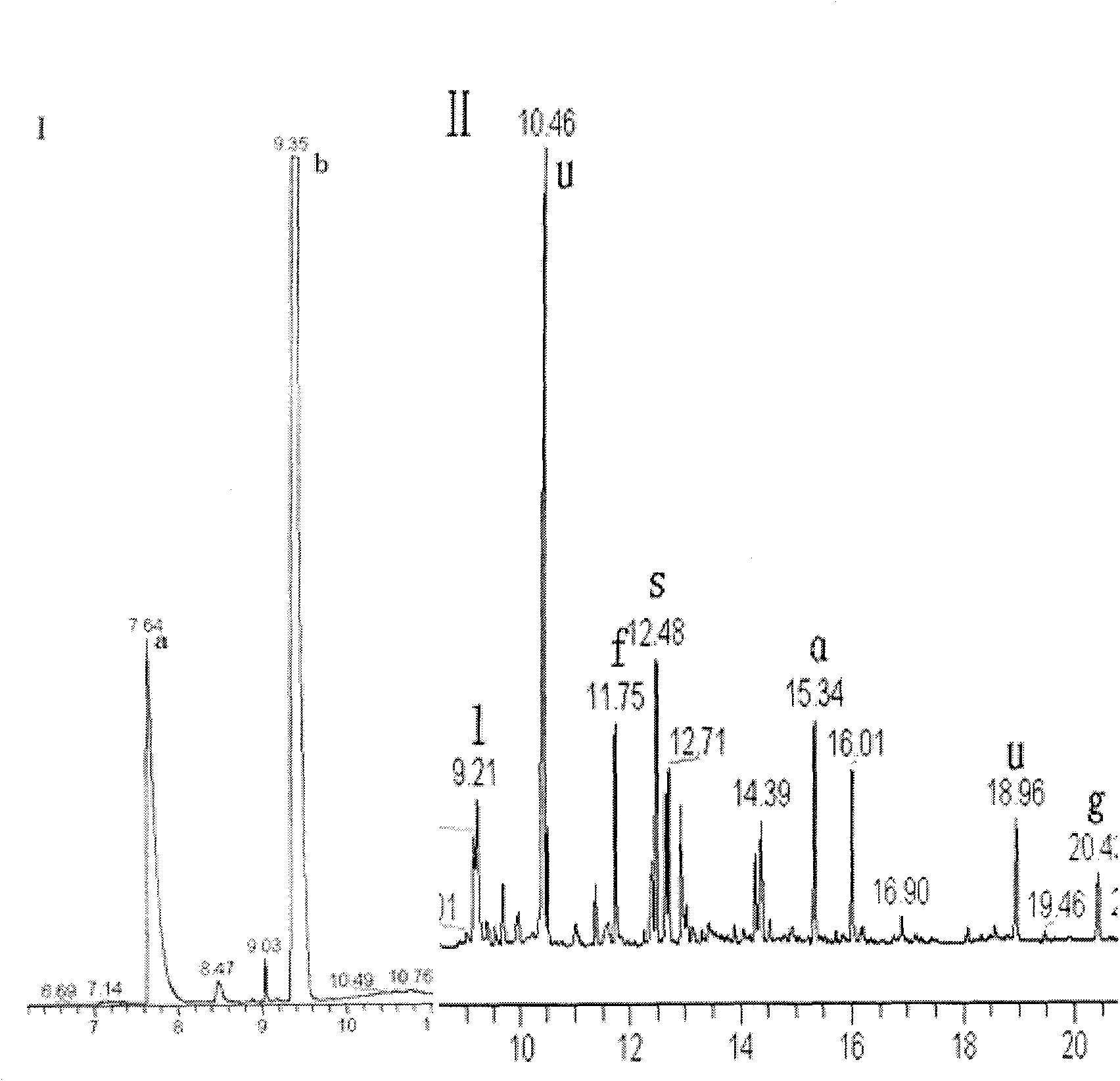
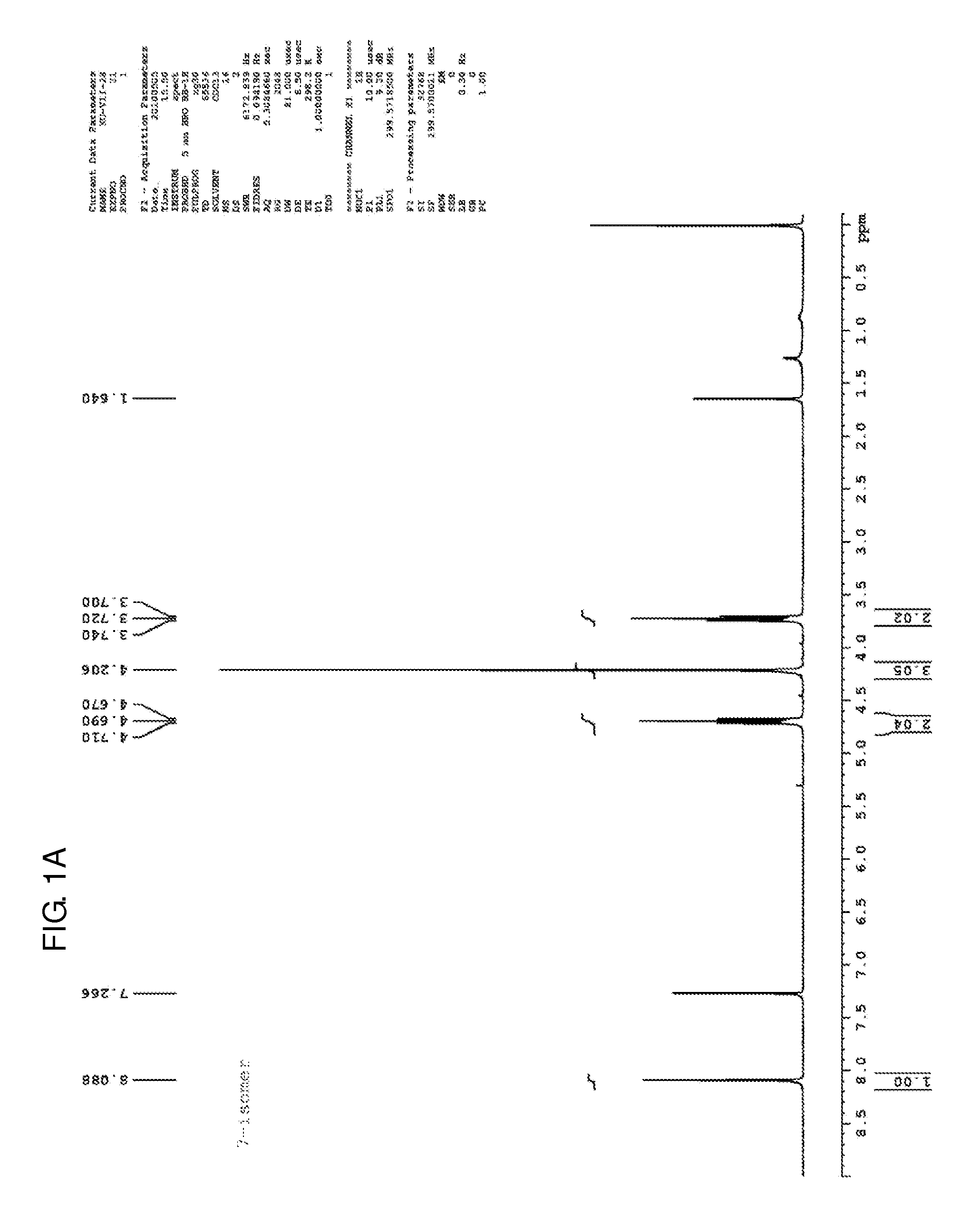
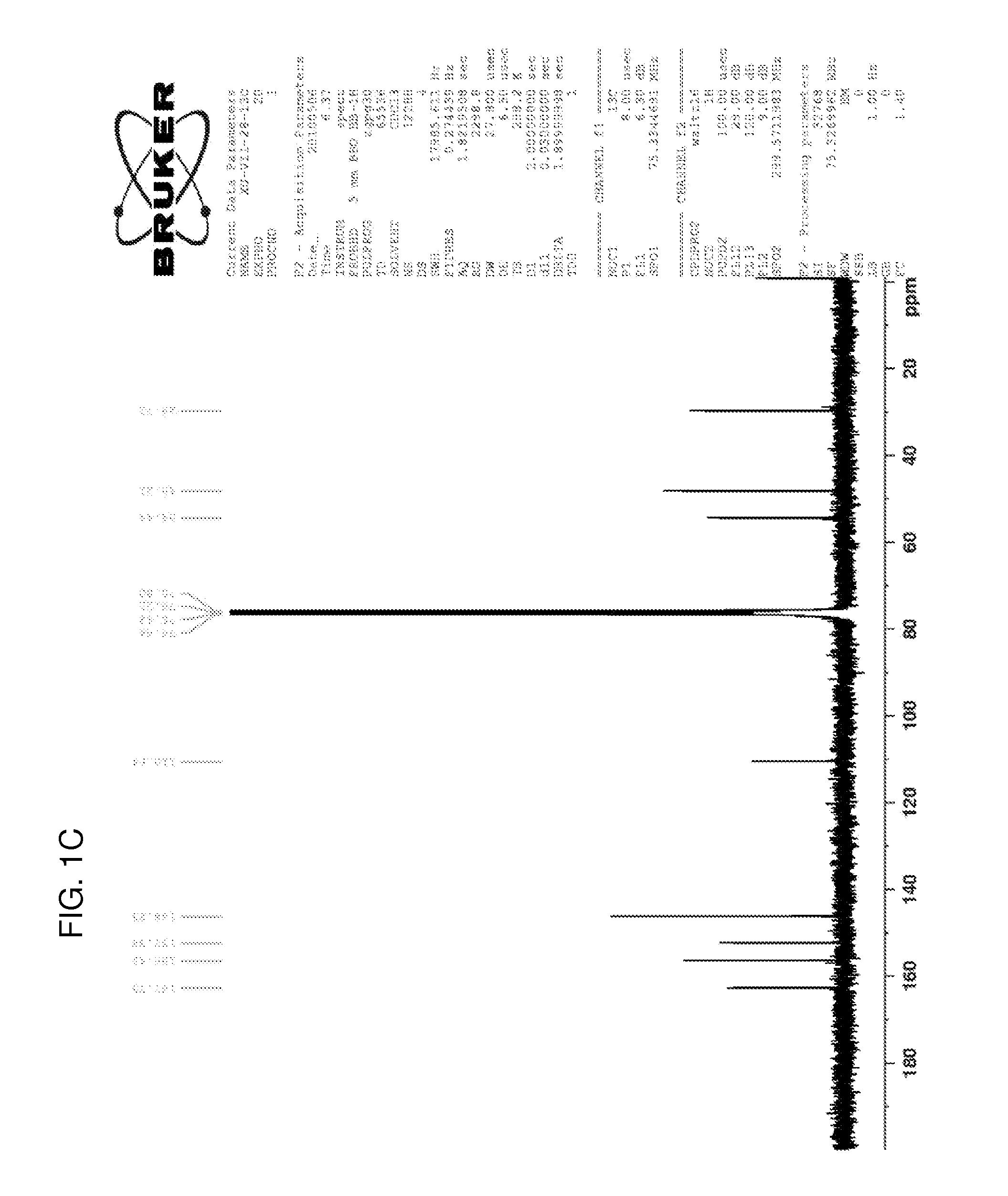
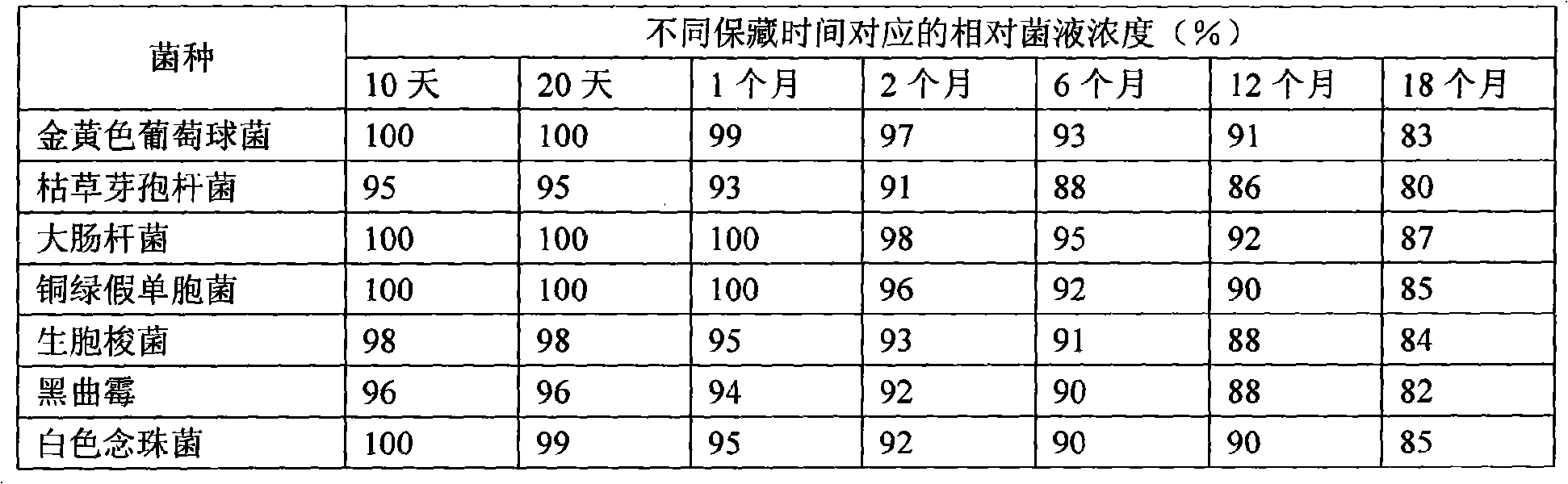
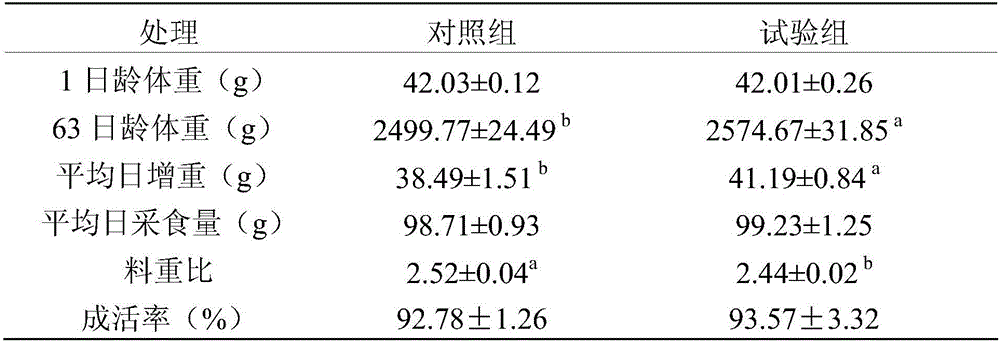
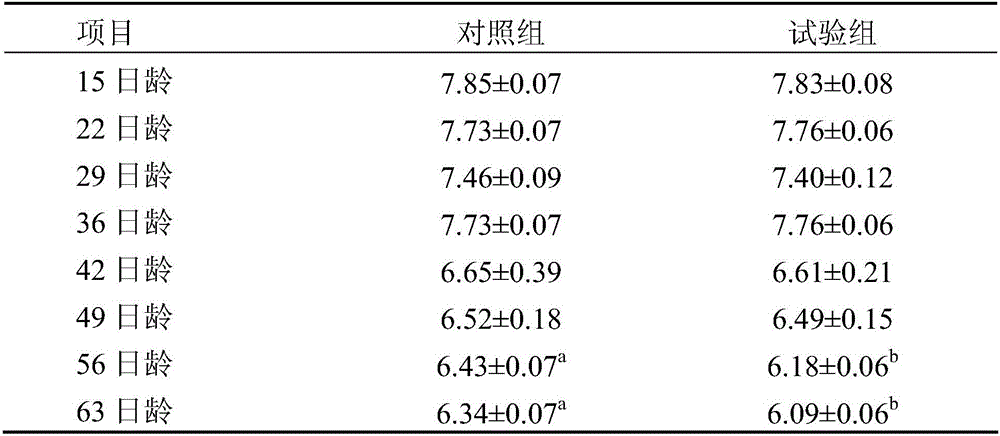
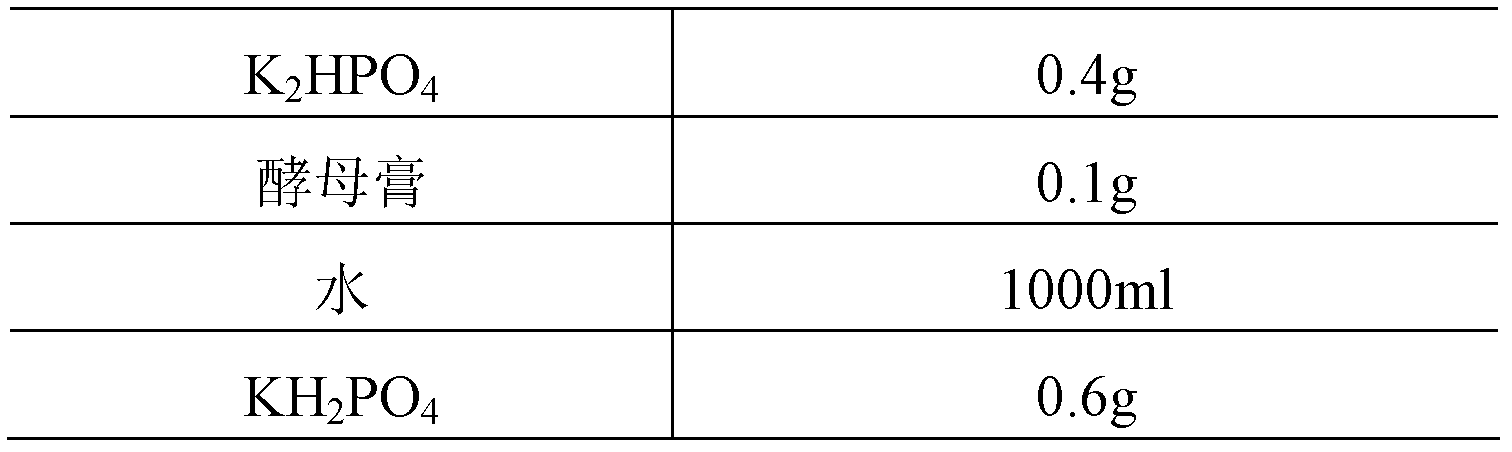
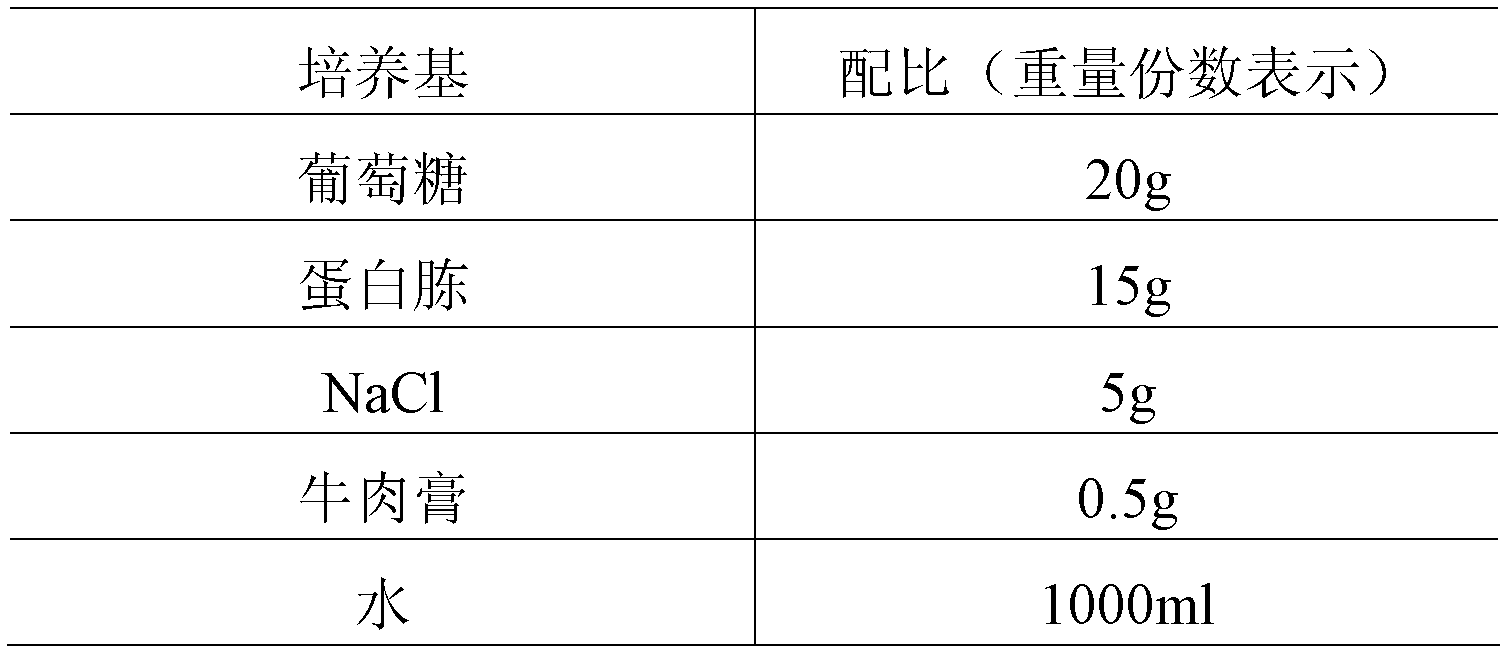
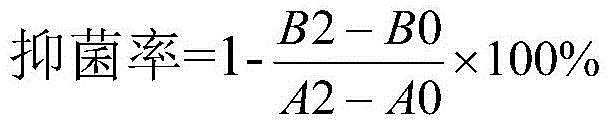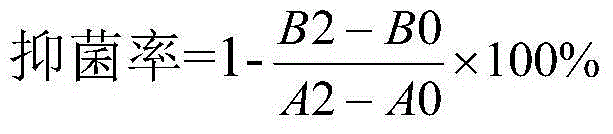Patents
Literature
422 results about "Clostridium bacteria" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Clostridium difficile (etymology and pronunciation), also known as C. difficile, C. diff (/siː/ /dɪf/), or sometimes CDF/cdf, is a species of Gram-positive spore-forming bacterium. Clostridia (members of the genus Clostridium and of the Clostridiaceae family) are anaerobic, motile bacteria, ubiquitous in nature, and especially prevalent in soil.
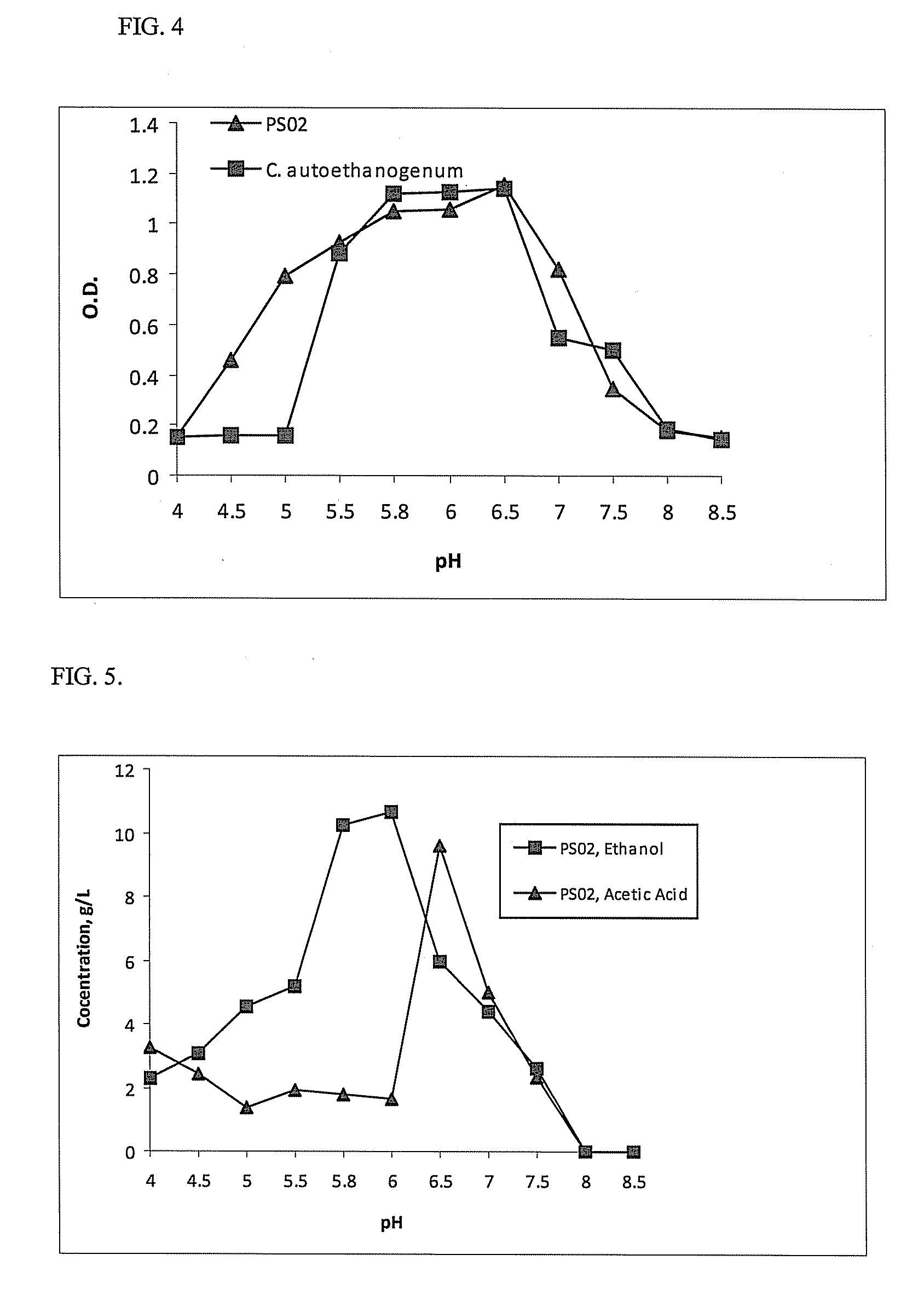
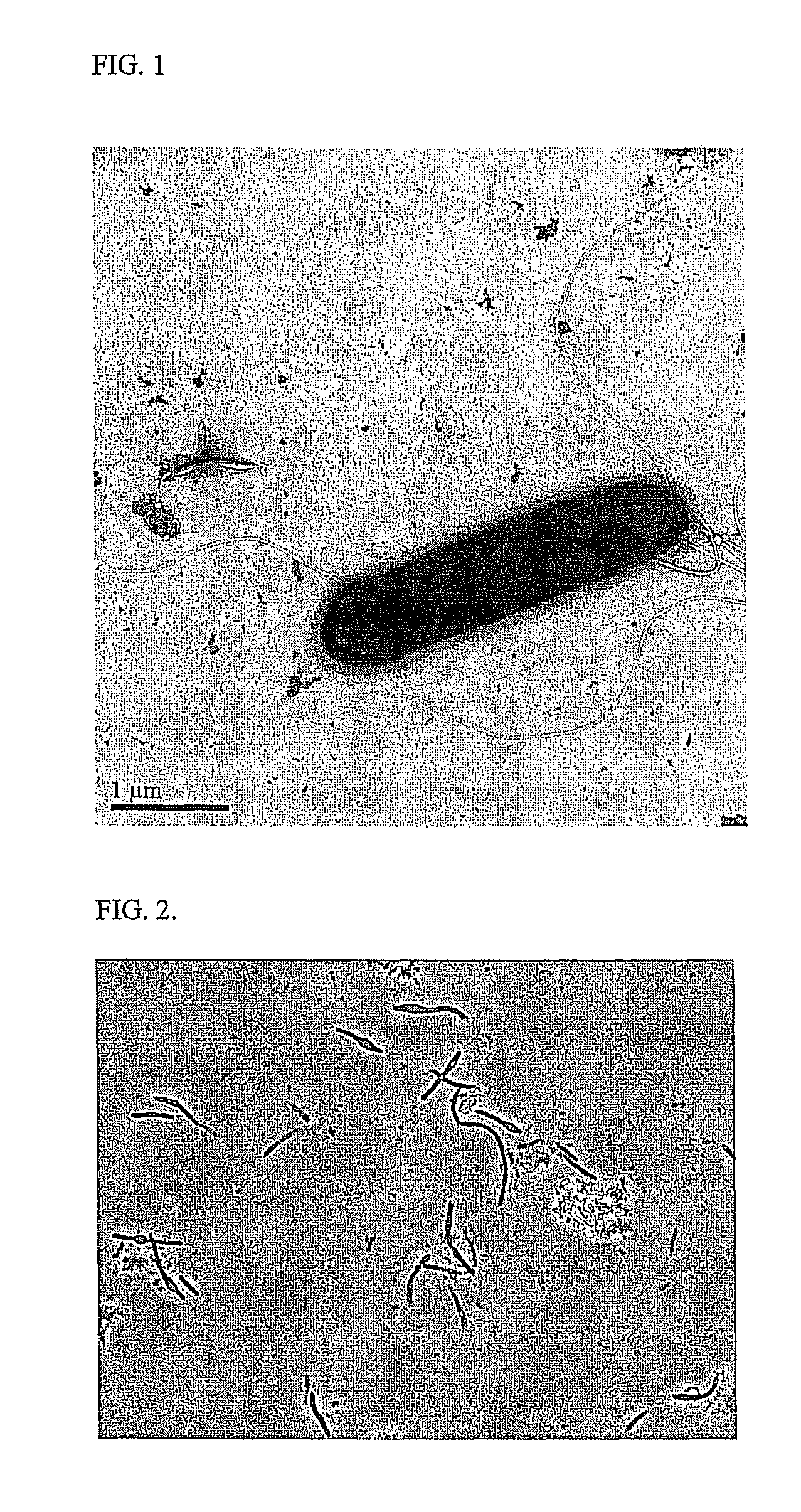
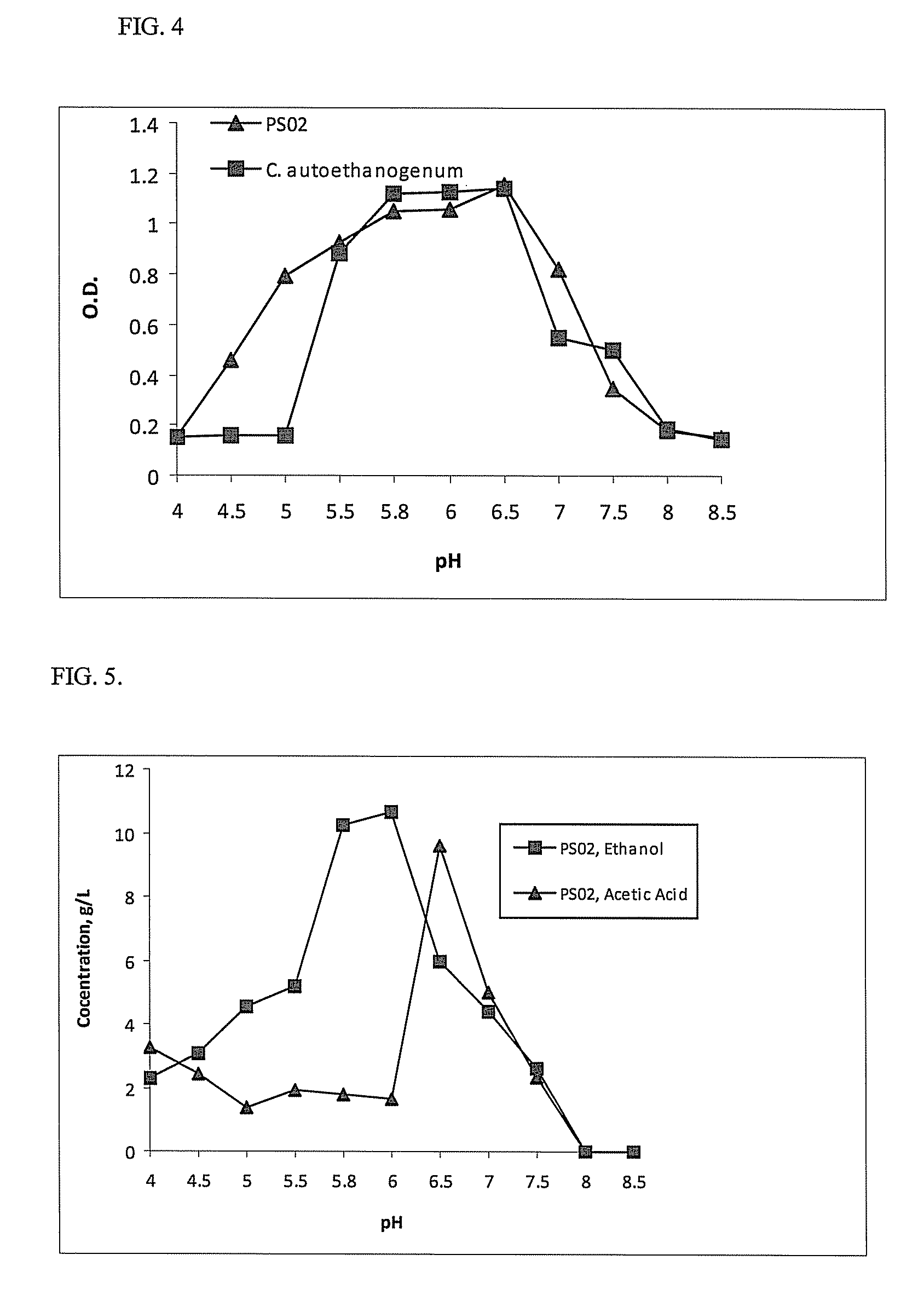
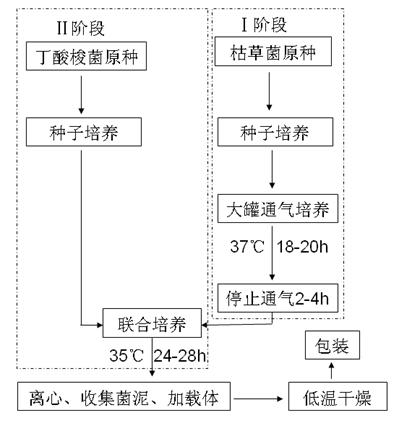
Novel Ethanologenic Clostridium species, Clostridium coskatii
A novel clostridia bacterial species (Clostridium coskatii ATCC No. PTA-10522, “PS02”) is provided. Under anaerobic conditions C. coskatii can convert CO and / or H2 and / or CO2 to ethanol or acetate. Thus, this novel bacterium is capable of transforming waste gases (e.g. syngas and refinery wastes) into useful products.
Owner:SYNATA BIO INC
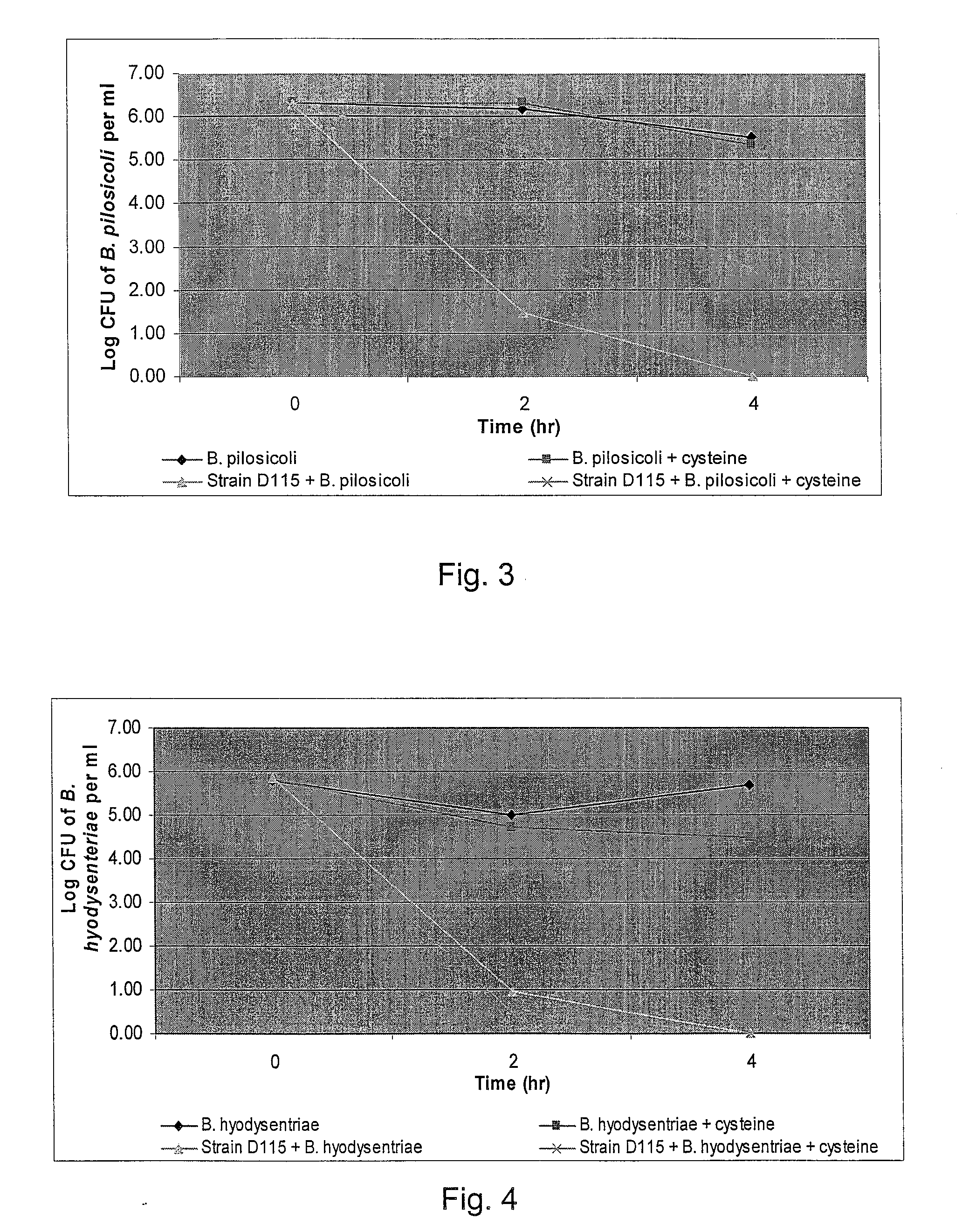
Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial and Antifungal Activity of Lactobacillus Johnsonii D115
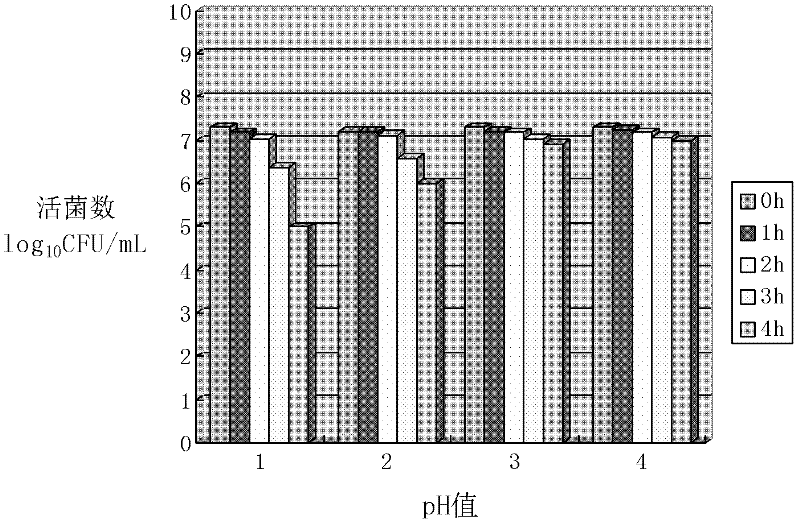
The present invention demonstrated the potential use of Lactobacillus johnsonii D115 as a probiotic, as a prophylactic agent or as a surface treatment of materials against human and animal pathogens such as Brachyspira pilosicoli, Brachyspira hyodysenteriae, Shigella sonnei, Vibrio cholera, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, Campylobacter jejuni, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Enterococcus faecalis, Enterococcus faecium, Clostridium perfringens, Yersinia enterocolitica, Escherichia coli, Klebbsiella pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella spp., Bacillus cereus, Aspergillus niger and Fusarium chlamydosporum. The proteineous antimicrobial compound was partially characterized and found to be heat tolerant up to 121° C. for 15 min, and acid tolerant up to pH1 for 30 min at 40° C. The compound is also stable to enzymatic digestion, being able to retain more than 60% antimicrobial activity when treated with pepsin and trypsin.
Owner:KEMIN IND INC
Eubacterium, Clostridium preparation and use thereof
The invention relates to a eubacterium and clostridium preparation and application of the same, in particular to a microecological preparation which is prepared for replenishing butyric acid bacteria and butyric acid produced by intestinal tract by taking single eubacterium, single clostridium or a eubacterium and clostridium composition as a main active composition, and application of the same in treating related diseases through butyric acid production, and belongs to the field of biological medicine.
Owner:QINGDAO EASTSEA PHARMA +1
Targeted gastrointestinal tract delivery of probiotic organisms and/or therapeutic agents
ActiveUS20160022592A1Improve imbalanceAntibacterial agentsBiocideAntibiotic-associated diarrhoeaClostridium difficile infections
The present invention relates to the development of a targeted delivery system for the oral delivery of probiotics or therapeutic agent for various indications, including and not limited to active and prophylaxis treatment of Clostridium difficile infection, antibiotic associated diarrhea, irritable bowel syndrome, Crohn's disease, intestinal flora replacement, supplemental flora treatments for patients taking antibiotics, and for restoration of balance and signaling between the intestinal microbiome and the intestinal cells in patients under treatment of metabolic syndrome manifestations, specifically diabetes, insulin resistance, obesity, hyperlipidemia and hypertension.
Owner:THERABIOME
Ethanologenic Clostridium species, Clostridium coskatii
Owner:SYNATA BIO INC
Preparation and use of bacillus subtilis and clostridium butyricum composite bacterial preparation
ActiveCN102220261AImprove efficiencyReduce energy consumptionBacteriaAnimal feeding stuffPeristaltic pumpMicrobiology
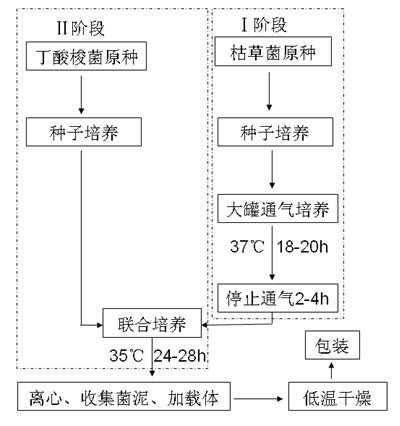
The invention discloses a method for preparing a bacillus subtilis and clostridium butyricum composite bacterial preparation, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) preparing seed culture solution, namely preparing a seed solution containing clostridium butyricum and a seed solution containing bacillus subtilis respectively, wherein the concentration of the bacterial solution is 0.5*10<8> to 1.0*10<8>CFU / ml; (2) preparing a coculture medium; (3) adding the seed solution of the bacillus subtilis into the coculture medium prepared by the step (1) according to a ratio of 2 percent, automatically regulating the pH value to 6.5 to 7.0 by using 10-percent diluted hydrochloric acid or 10-percent sodium hydroxide, introducing gas, stirring, controlling dissolve oxygen content to be 20 to 50 percent, culturing for 18 to 20 hours at 37 DEG C, stopping introducing gas, and continuing to stir and culture for 2 to 4 hours; and (4) adding the seed solution of the clostridium butyricum prepared by the step (1) into the coculutre medium by using a peristaltic pump according a ratio of 2 percent, standing at 35 DEG C and culturing for 24 to 28 hours to obtain the bacillus subtilis and clostridium butyricum composite bacterial preparation. In the invention, a microecological preparation is mixed with feed according to a ratio of 0.5 percent, the feed is directly used to feed livestock, the diarrhea rate and death rate of the livestock are lowered effectively, yield is increased, and medicine administration cost is saved.
Owner:山东亚太海华生物科技有限公司 +1
Enzyme and microbial inoculum for decomposing lignocellulose
InactiveCN101560488AImprove degradation rateLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroides xylanisolvensFlavobacterium aquatile
The invention discloses a microbial inoculum for decomposing lignocellulose and application thereof. The active component of the microbial inoculum consists of Alcaligenes faecalis, Bacteroides xylanisolvens, Clostridium xylanolyticum, Clostridium lentocellum, Flavobacterium aquatile, and Pseudomonas stutzeri. Experiments prove that the microbial inoculum has high degradation rate to the lignocellulose, and the degradation rate can reach between 60 and 70 percent. The microbial inoculum has low cost and simple preparation, breaks through the limitation that a purification bacterium and a clastic enzyme thereof cannot decompose the lignocellulose efficiently, provides a key technique for decomposing, saccharifying biomass containing cellulose and converting the biomass into an energy source, and has extensive application prospect in the field of decomposing the lignocellulose.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Sporicidal composition for clostridium difficile spores
A cleaning medium or formulation that contains a sporicidal composition is described. The composition includes about 0.1-20% weight / weight of a germinant agent, about 0.01-75% w / w of an antimicrobial agent, in terms of dry or wet total weight, and which is admixed with water to generate a solution with a pH of 3.5-9.5. The composition can help trigger the germination of spores, in particular C. difficile, and subsequently deactivate or kill the spores. A means of applying the cleaning formulation in a medium and process for cleaning are also described.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
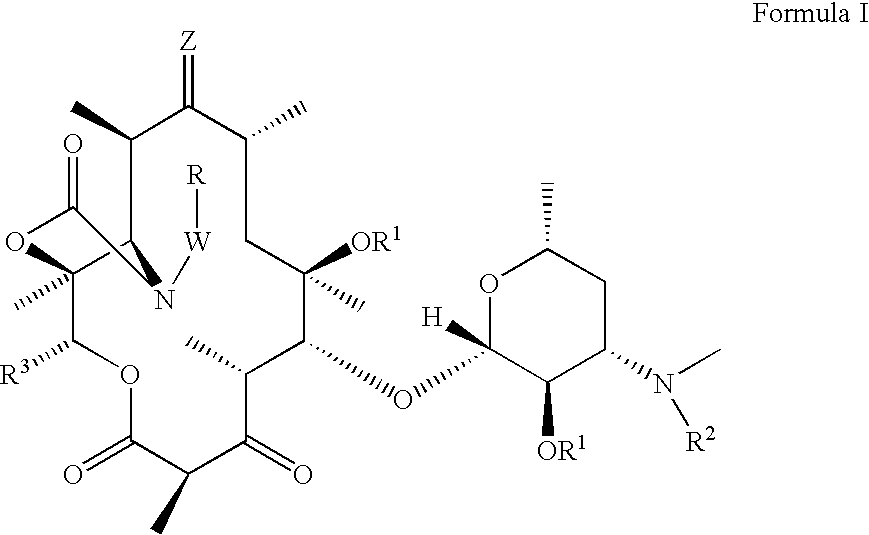
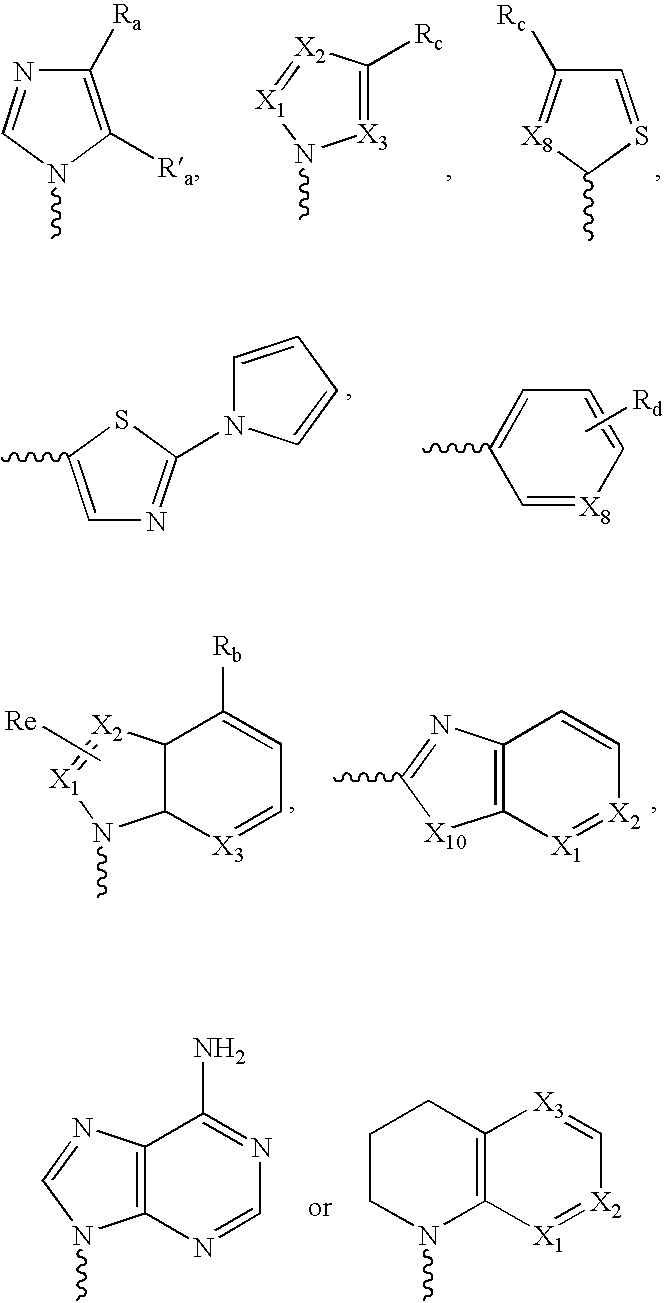
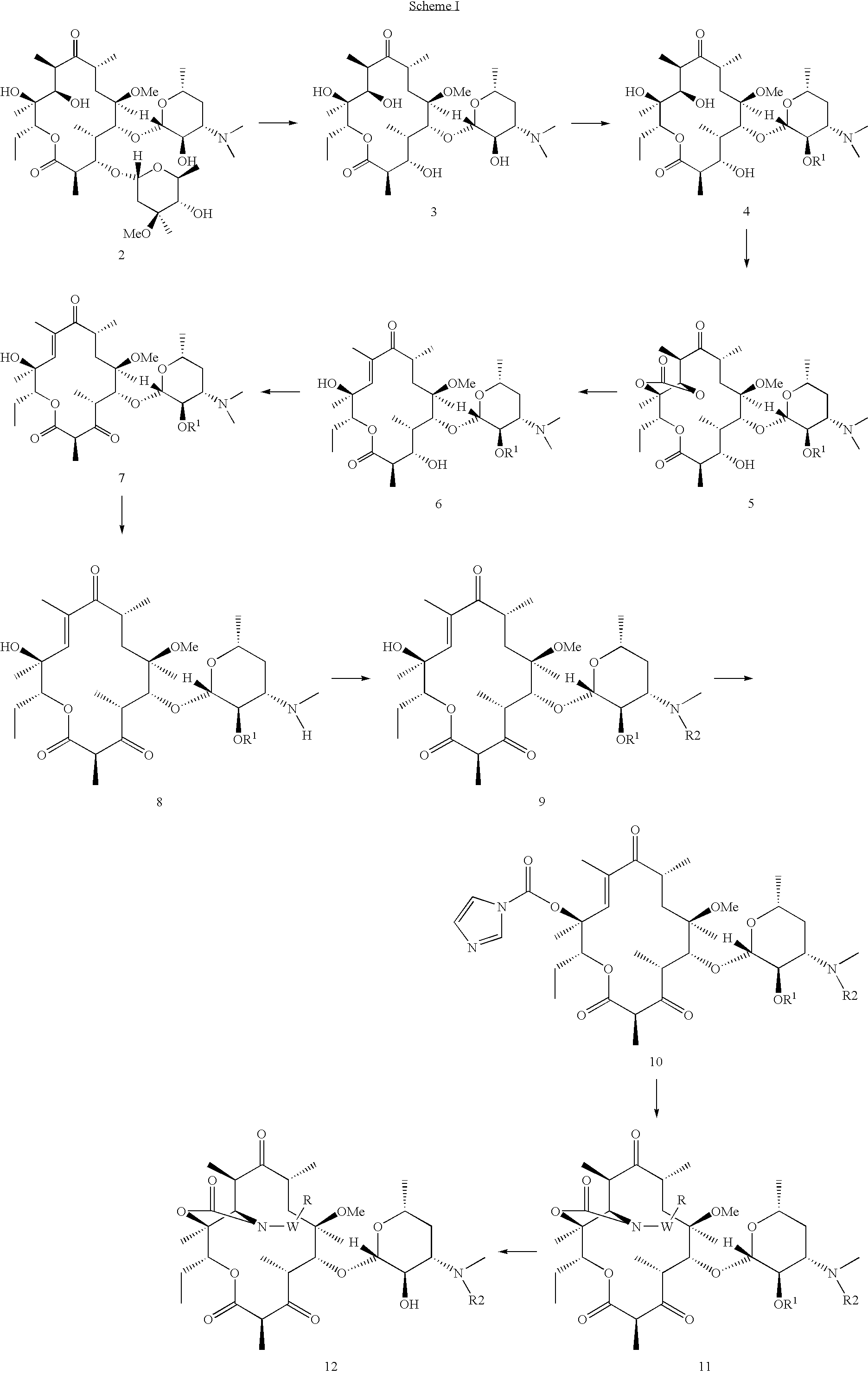
Antibacterial compounds
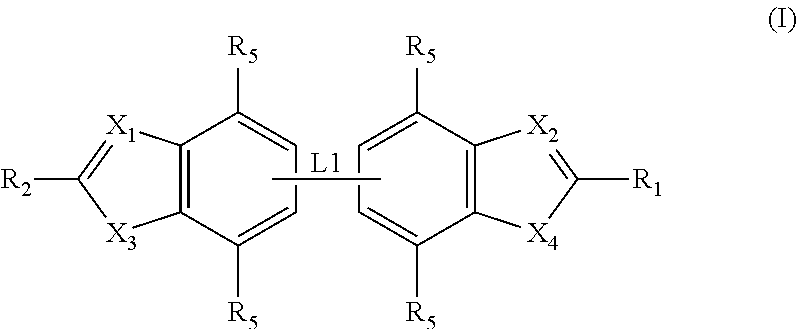
ActiveUS20120020950A1Augment other biological activityHigh activityAntibacterial agentsBiocideClostridium difficileBacterial Disorder
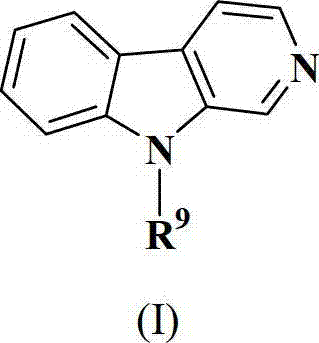
Disclosed are compounds of formula (I), which are of use in the treatment of bacterial diseases and infections, to compositions containing those compounds and to methods of treating bacterial diseases and infections using the compounds. In particular, the compounds are useful for the treatment of infection with, and diseases caused by, Clostridium difficile.
Owner:SUMMIT OXFORD
Control of acidosis
InactiveUS7011826B1Enhance immune responseBetter establishment of favourable starch utilising organismsOrganic active ingredientsBacteriaBiotechnologyBacteroides
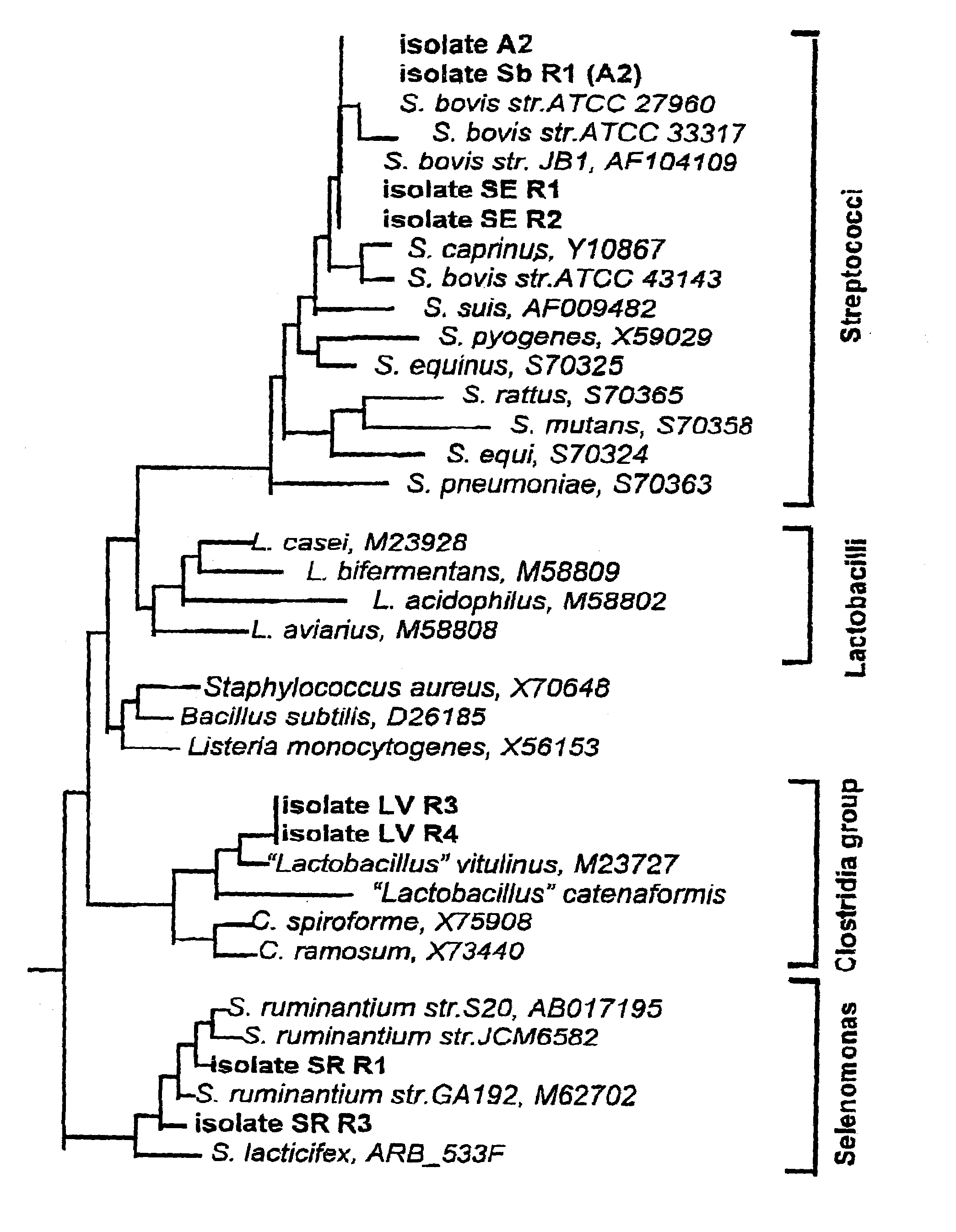
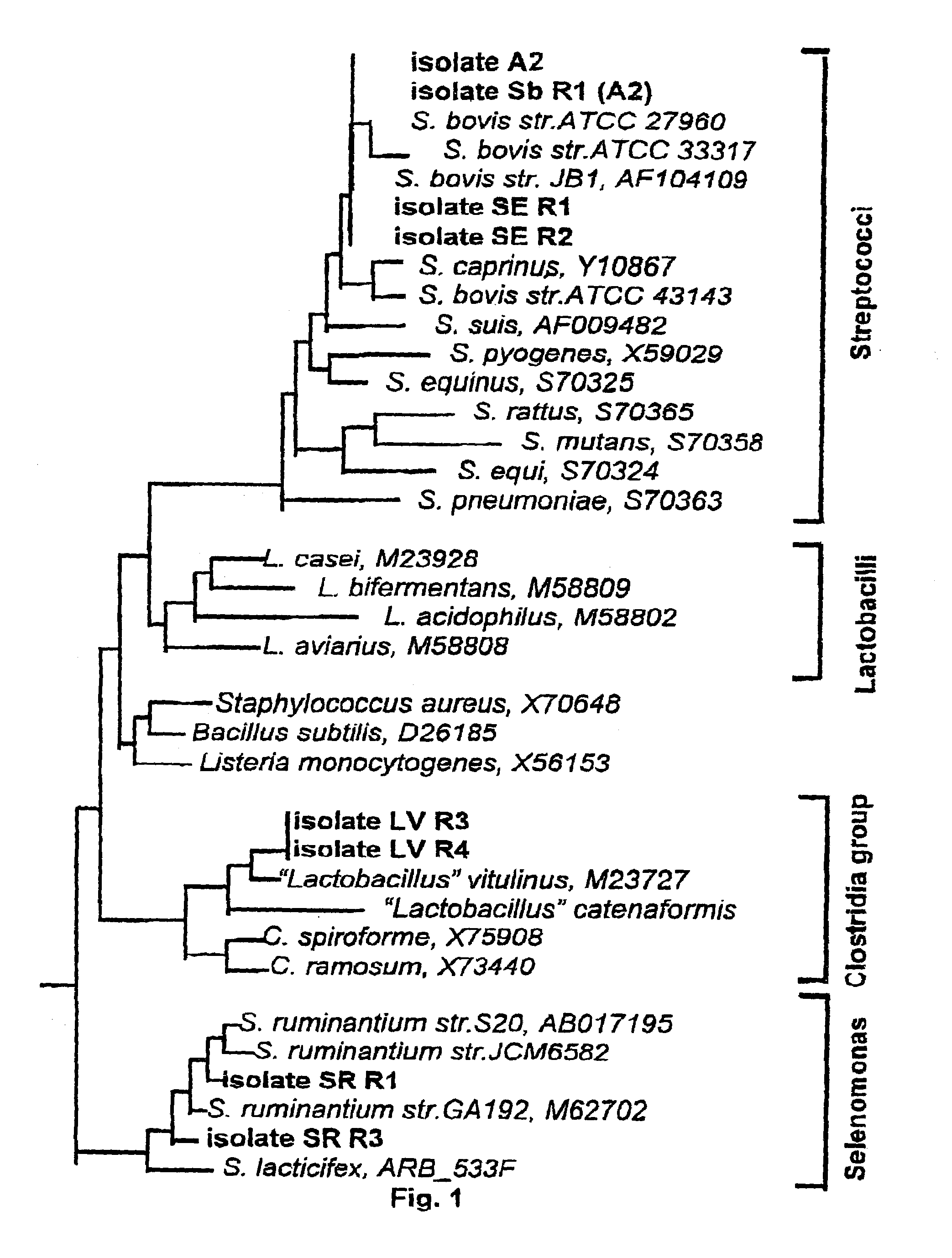
The present invention relates to a vaccine for the prevention of lactic acidosis in a vertebrate, said vaccine comprising at least one isolated microorganism, or fragment or fragments thereof, wherein said microorganism is capable of producing lactic acid within the gut of said vertebrate, and wherein said microorganism is selected from the group consisting of: Clostridium-like species, Prevotella-like species, Bacteroides-like species, Enterococcus-like species, Selenomonas species, non-dextran slime producing Streptococcus species and non-slime producing lactic acid bacterial isolates.
Owner:SPRUSON & FERGUSON +1
Clostridium butyricum having diarrhea treating effect and application of clostridium butyricum as substitute of sodium butyrate
ActiveCN102559550AIncrease acidityRepair mucous membraneBacteriaAnimal feeding stuffChronic diarrheaActive component
The invention discloses a clostridium butyricum having a diarrhea treating effect. The strain is named as clostridium butyricum Cb-2 which is conserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection with the conservation number of CCTCC M2011384, in November 9th, 2011. A test proves that the clostridium butyricum disclosed by the invention has strong acid producing capability especially butyric acidproducing capability; and the clostridium butyricum has obvious effects on diseases, such as intestinal tract flora infection, acute and chronic diarrhea, irritable bowel syndrome and non-ulcer dyspepsia, caused by various reasons, and has no toxicity and harm. Thus, the clostridium butyricum or clostridium butyricum powder disclosed by the invention is used as a raw material for preparing a micro-ecological preparation and used for replacing sodium butyrate to be applied; and when a specific application is carried out, a clostridium butyricum preparation can be singly used as an active component to be prepared into the micro-ecological preparation together with corn starch, or, the clostridium butyricum preparation is mixed with at least one of other bacterial preparations and the corn starch to prepare a composite micro-ecological preparation.
Owner:山东宝来利来生物工程股份有限公司
Bacillus subtilis and application thereof to livestock breeding
ActiveCN103555640AHigh antibacterial ratePromote reproductionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationEscherichia coli
The invention aims to provide bacillus subtilis WL-04 and application thereof to livestock breeding. The preservation number of the bacillus subtilis WL-04 is CCTCC NO:M 2013343. The bacillus subtilis WL-04 can be used for remarkably inhibiting the growth of Escherichia coli, salmonella, clostridium pefringens and other conditional pathogenic bacteria of the intestinal canal of livestock, and particularly, the bacteriostasis rate of the bacillus subtilis WL-04 to Escherichia coli and clostridium perfingens is above 75%; the enzyme production is stable; the average activity of alpha-amylase is 22U / mL, and the average activity of neutral protease is 170U / mL; the reproduction of probiotics of intestinal canal can be promoted; high temperature for pelletizing can be endured; the influence of inverse environments with low-pH gastric fluid and high-concentration cholate is endured; the production performance of breeding animals can be effectively improved; immune organ development can be promoted. The bacillus subtilis WL-04 can be widely applied to livestock feeds as a feed additive.
Owner:山东蔚蓝生物科技有限公司 +1
Antibodies for the treatment of Clostridium difficile-associated infection and disease
ActiveUS8986697B2Improve the quality of lifeImprove survivabilityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenDisease
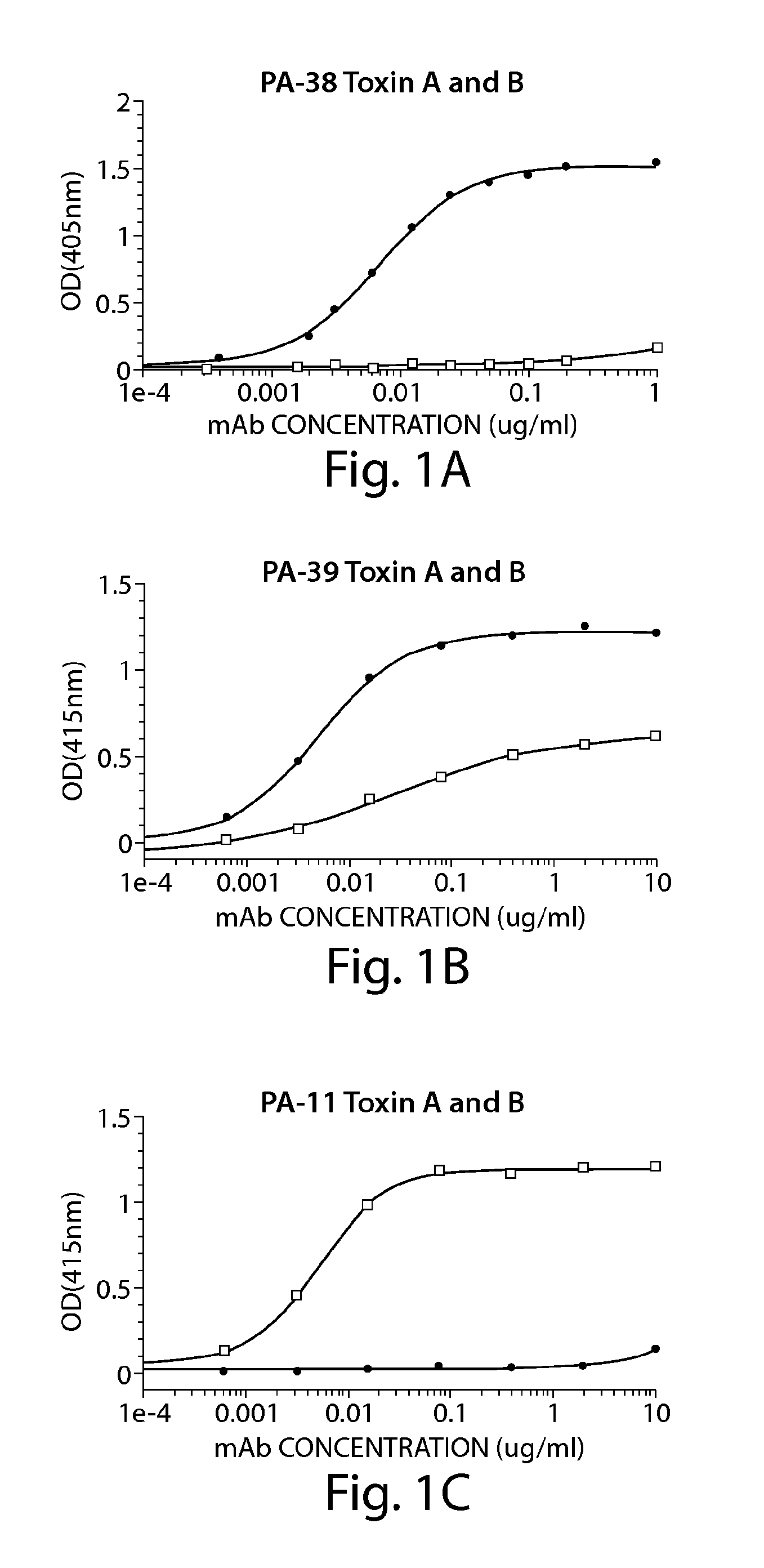
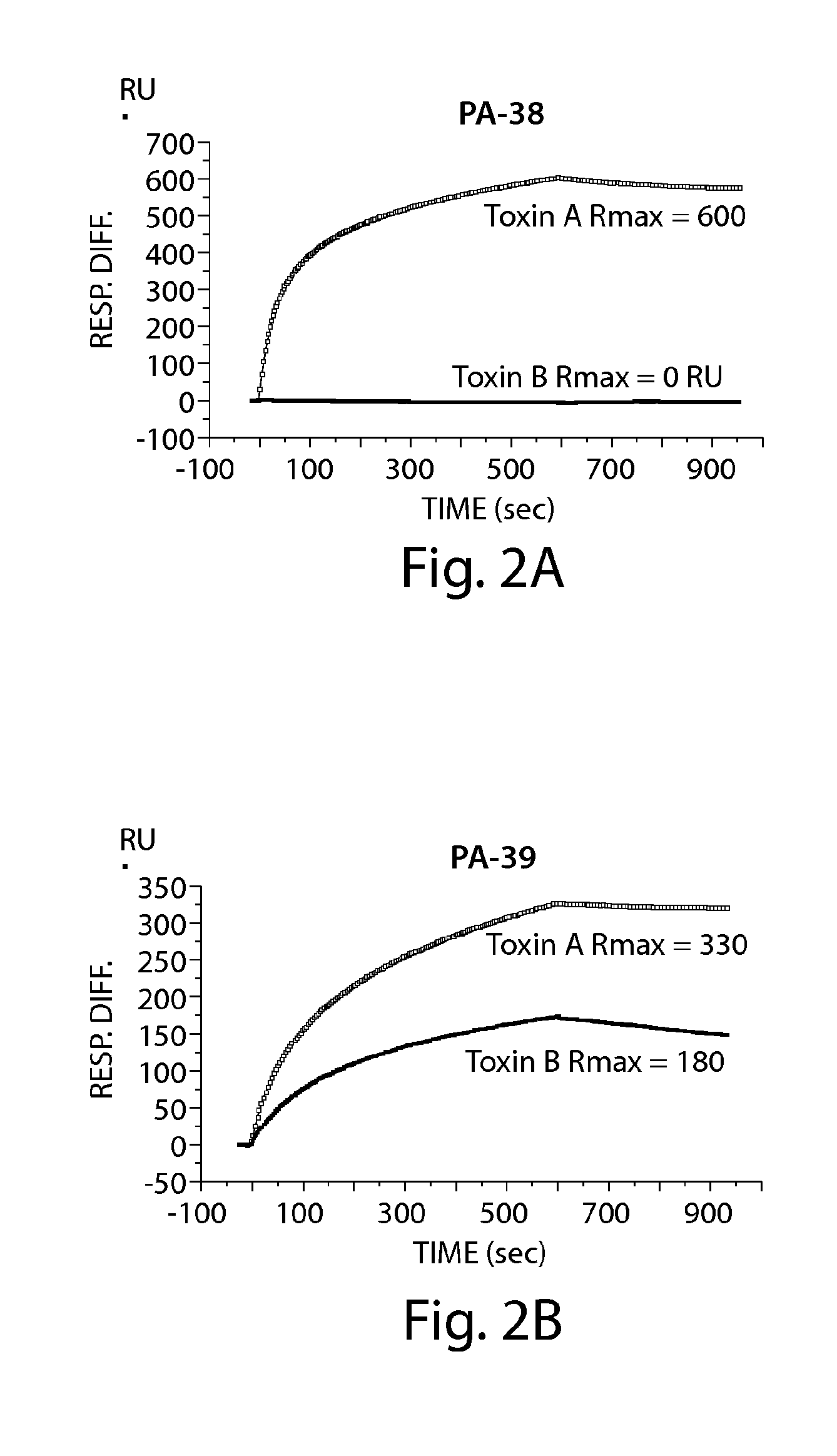
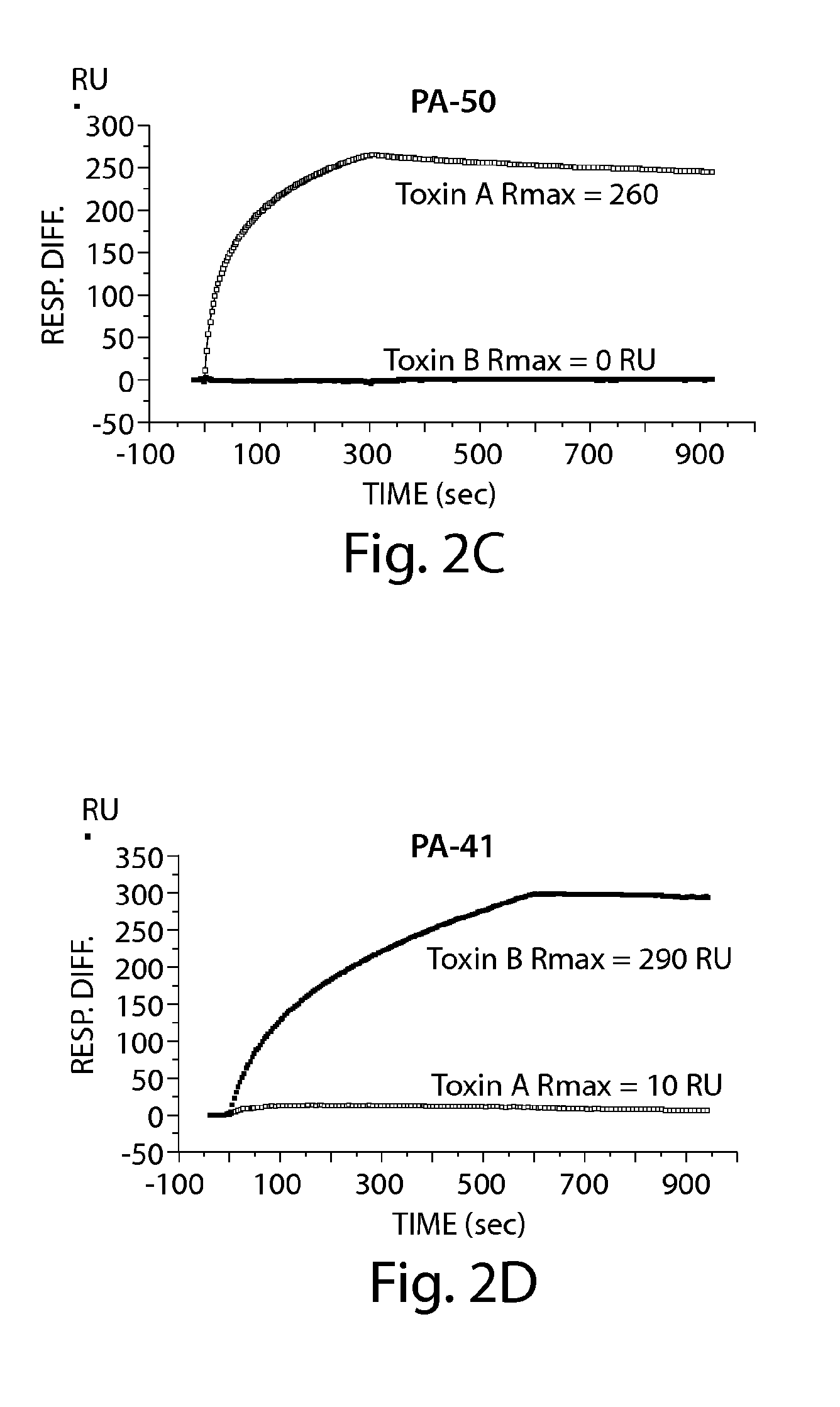
Provided herein are reagents, compositions, and therapies with which to treat Clostridium difficile infection and related disease conditions and pathologies, such as Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea, resulting from infection by Clostridium difficile bacteria and the enterotoxins produced by these bacteria. In particular, antibodies or antigen-binding fragments thereof that bind specifically to toxin A and / or toxin B of C difficile and neutralize the activities of these toxins; compositions comprising such antibodies; and methods of using the antibodies and the compositions are provided.
Owner:PROGENICS PHARMA INC
Methods and compositions including spore-forming bacteria for increasing the health of animals
ActiveUS20130136695A1Good for healthIncrease productionAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacteroidesBiology
Methods, compositions and bacterial isolates for improving the gastrointestinal health of animals and in particular of poultry are provided herein. The methods include administering an endospore-forming bacteria to an animal. The bacteria are selected for the ability to reduce the growth and presence of bacterial pathogens, such as Salmonella, Clostridium, and Campylobacter, in the gastrointestinal tract of the animal. The bacteria are also selected for the ability to improve at least one production parameter in the animal.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
High-temperature compost decay-promoting bacterial compound inoculant and applications thereof
InactiveCN103614326ASimplify the manufacturing processDecomposition function is stableBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaBiotechnologyXanthomonas campestris
The invention discloses a compost inoculant and applications thereof. The active ingredients of the composting inoculant provided by the invention include clostridium thermocellum, geobacillus stearothermophilus, Taiwan false xanthomonas, brevibacillus agri and bacillus licheniformis in a CFU (colony-forming unit) ratio of (3-5):(1-2):(1-2):(1-2):(1-2). Strains in the inoculant provided by the invention can grow in a symbiosis state well, and under the conditions of microaerobic co-culturing, lignocelluloses can be regularly proliferated and effectively decomposed in proportion. The inoculant is simple in manufacturing process due to co-culturing, stable in decomposition function, and long in quality ensured period. Experiments show that when the inoculant is adopted for fermenting composts, large gas feeding is not required, the energy is saved, and the nitrogen loss is reduced; composts can be thoroughly decomposed in advance, thereby improving the quality of fertilizers.
Owner:MOUNT EMEI GREEN LAND ECOLOGICAL AGRI DEV LIMITED
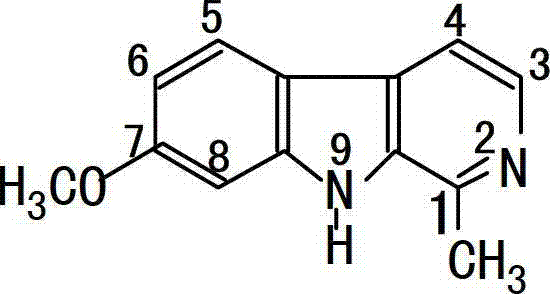
Application of Harmine derivative to preparation of antibacterial medicine
The invention discloses application of a Harmine derivative to preparation of antibacterial medicines. The bacteria is selected from Acinetobacter, Bacillus, Campylobacter, Chlamydia, Chlamydia trachomatis, Clostridium, Citrobacter, Escherichia, enterohemorrhagic escherichia coli, enteric bacteria, Enterococcus, Francisella, Haemophilus, helicobacter, Klebsiella Bacillus, Lester monocytogenes, Moraxella, Mycobacterium, Neisseria, proteus, Pseudomonas, Salmonella, shewanella oneidensis, Shigella, Stenotrophomonas, Staphylococcus, Streptococcus and Yersinia.
Owner:XINJIANG HUASHIDAN PHARMA RES
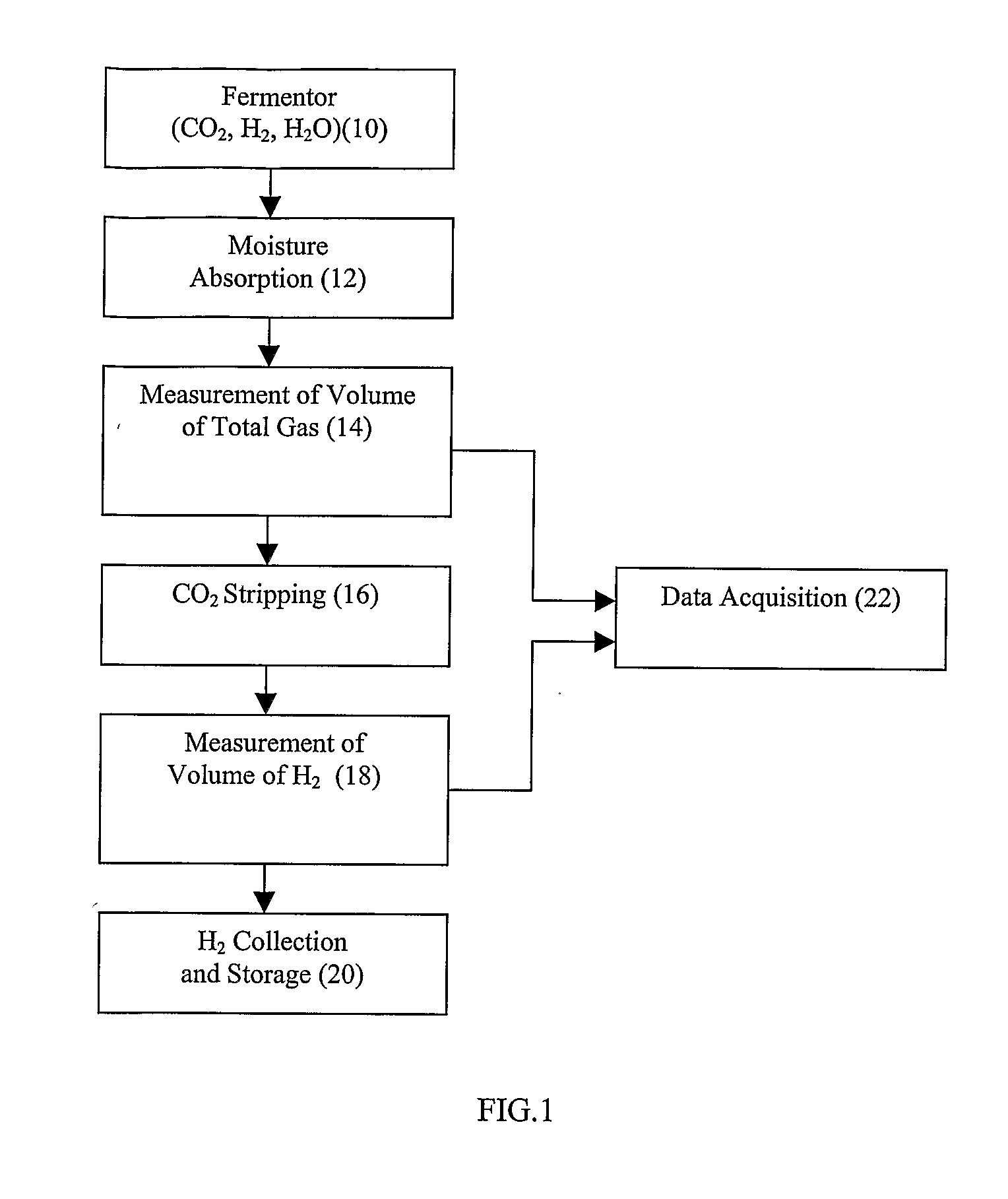
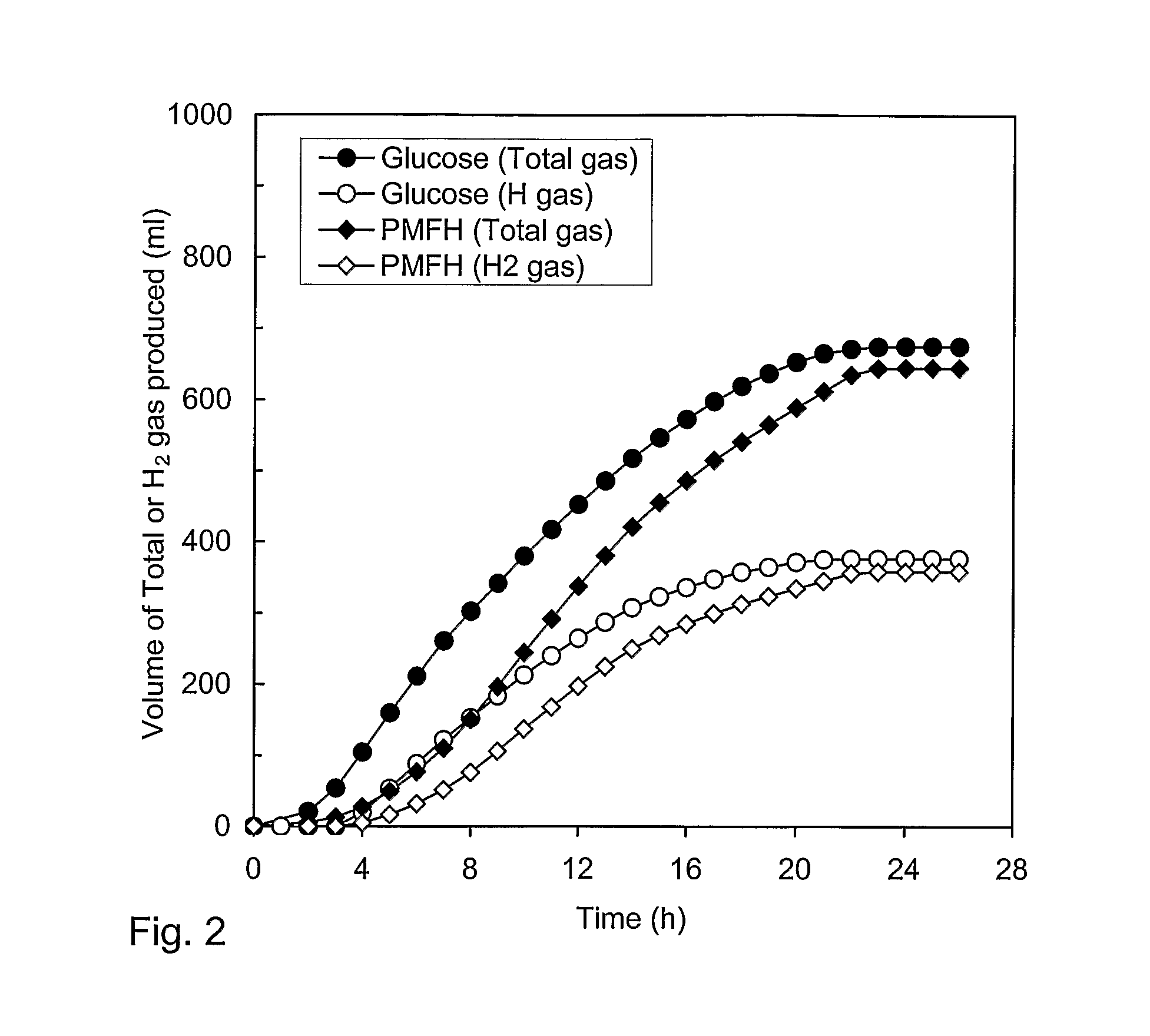
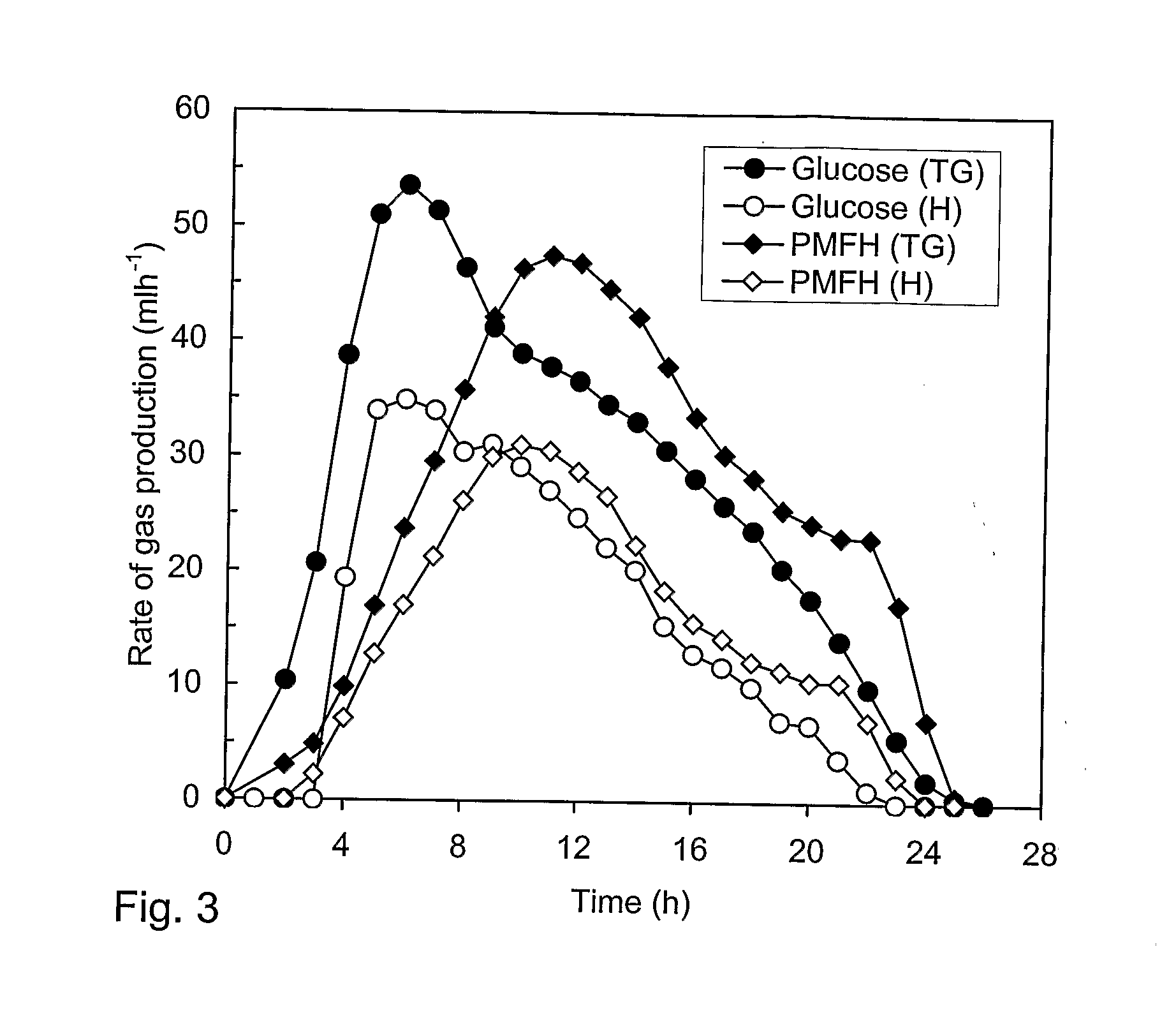
Methods and bacterial strains for producing hydrogen from biomass
A method is provided for producing hydrogen by fermenting a culture medium containing a sugar and maintained under substantially anaerobic conditions with a bacterium of the genus Clostridium. The bacterium may be Clostridium bifermentans and hydrogen may be produced with an efficiency of at least about 34% relative to the maximum theoretical possible yield. There are also disclosed substantially pure cultures of bacteria of the genus Clostridium which can ferment sugars present in a culture medium at a concentration of between about 1% and 10% under substantially anaerobic conditions to produce hydrogen with an efficiency of at least about 34% of the maximum possible theoretical yield
Owner:KAM BIOTECH
Composition And Method For Stabilizing And Maintaining The Viability Of Hardy Microorganisms
PendingUS20170226469A1Stabilizing and maintaining viabilityBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismBacteroides
The present application is to provide a composition and method for stabilizing and maintaining the viability of hardy microorganisms from sample collection to downstream analysis. In particular, there is a method for preserving viable hardy bacteria, such as Mycobacteria, Bacillus anthracis, or Clostridium difficile, in a biological sample, comprising contacting the biological sample with a stabilization composition, wherein the stabilization composition comprises a chelating agent, a denaturing, a salt and has a pH between about 6 and about 11.
Owner:DNA GENOTEK
Straw in-situ decomposition microbial agent and application thereof
InactiveCN103642721AIncrease enzyme activityQuick destructionBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaCelluloseMicrobial agent
The invention discloses a straw in-situ decomposition microbial agent. Active ingredients of the microbial agent are formed by mixing clostridium xylanolyticum, xylan monad cellulolyticus, pseudomonas and bacillus subtilis in a CFU (Colony Forming Unit) ratio of (25-35): (25-30):(20-30):(15-20). Experiments prove that the microbial agent provided by the invention has degradation rate for straws, which can reach 70%-80% in a culture medium, and can reach over 50% when the straws are returned to the field for 20 days. The microbial agent disclosed by the invention is low in cost and simple to prepare. The microbial agent disclosed by the invention breaks through the limit that natural cellulose cannot be efficiently decomposed by purifying bacteria and clastic enzymes thereof, provides a key technology for straw in-situ rapid decomposition, and has a wide application prospect in the field of returning straws to the field and decomposing a lignocelluloses material.
Owner:MOUNT EMEI GREEN LAND ECOLOGICAL AGRI DEV LIMITED
Method for preparing environment-friendly and high-efficiency biological organic fertilizer by using distilled spirit vinasse
ActiveCN102992915ARelease fullyEffective activityClimate change adaptationBioloigcal waste fertilisersWater contentAmmonium sulfate
The invention provides a method for preparing environment-friendly and high-efficiency biological organic fertilizer by using distilled spirit vinasse, comprising the following steps of: puffing fermentation substrate by a threaded rod type puffing machine; transporting into a wet material mixing machine, cooling and adding microelement mineral salt, and inoculating bacterium liquid in proportion when the temperature is reduced to 30-35DEG C, completely mixing; and filling the inoculated and mixed fermentation substrate into a novel silica gel breathable membrane fermentation bag, packaging and sealing by an automatic metering and packing system, and fermenting for 5-7 at constant temperature in a fermentation room to obtain a finished product. The fermentation substrate is prepared by evenly mixing 50-60 parts by weight of distilled spirit vinasse, 5-10 parts by weight of humic acid, 5-15 parts by weight of sunflower husk powder, 5-10 parts by weight of ammonium sulfate, 5-10 parts by weight of potassium chloride and 5-10 parts by weight of corn steep liquor, wherein the water content of the fermentation substrate is 30-40 wt%; and the mixed bacterium liquid comprises bacterium liquid of streptomyces jingyangensis, clostridium butyricum, pseudomonas mendocina, azotobacter chroococcum and rhizopus oryzae.
Owner:张有聪
Clostridium beijerinckii strain and screening method and use thereof
InactiveCN102533612ALow costBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementPrimary screeningMicrobiology
The invention discloses high-butanol-yield clostridium beijerinckii, which is obtained by sampling, enriching, primary screening, separating and secondary screening. The strain is identified as clostridium beijerinckii which belongs to the class of clostridium beijerinckii gxas.28. The collection number of the strain is CCTCCM2011454. According to the invention, butanol is produced by using molasses as a raw material and by fermentation of clostridium beijerinckii. The butanol yield is 9.42 to 13.11g / L, and the ratio of the butanol to total solvent reaches 70 to 85 percent.
Owner:GUANGXI ACAD OF SCI
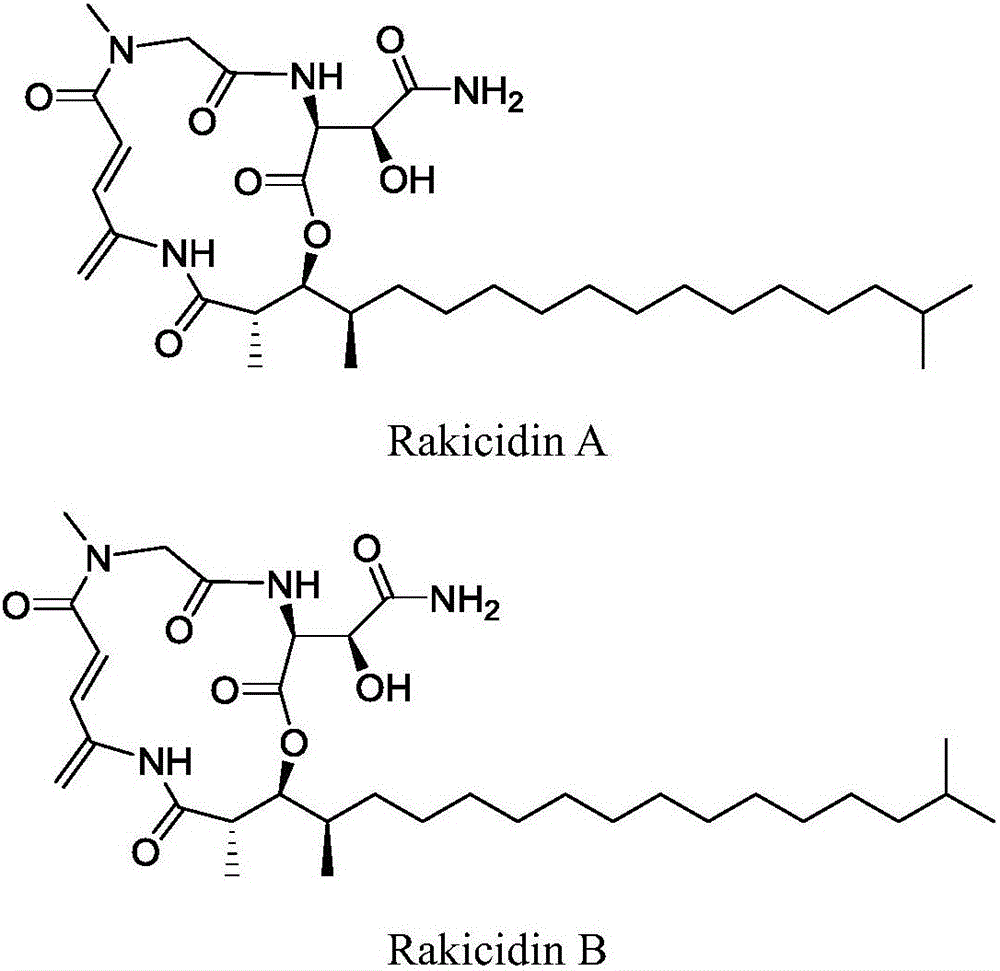
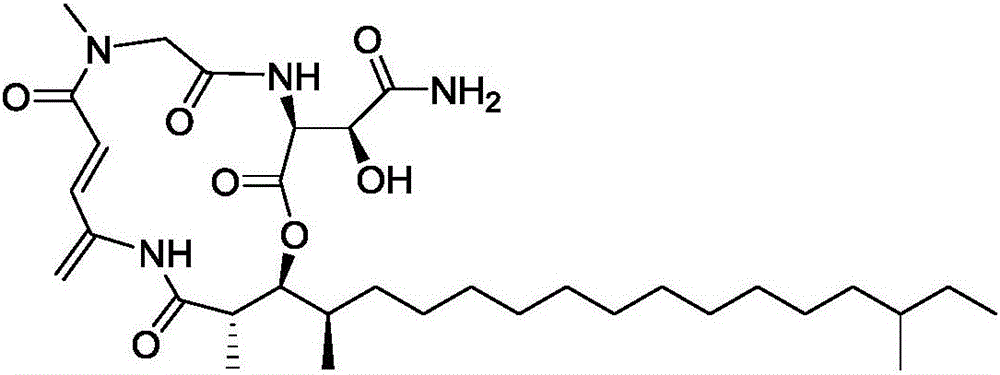
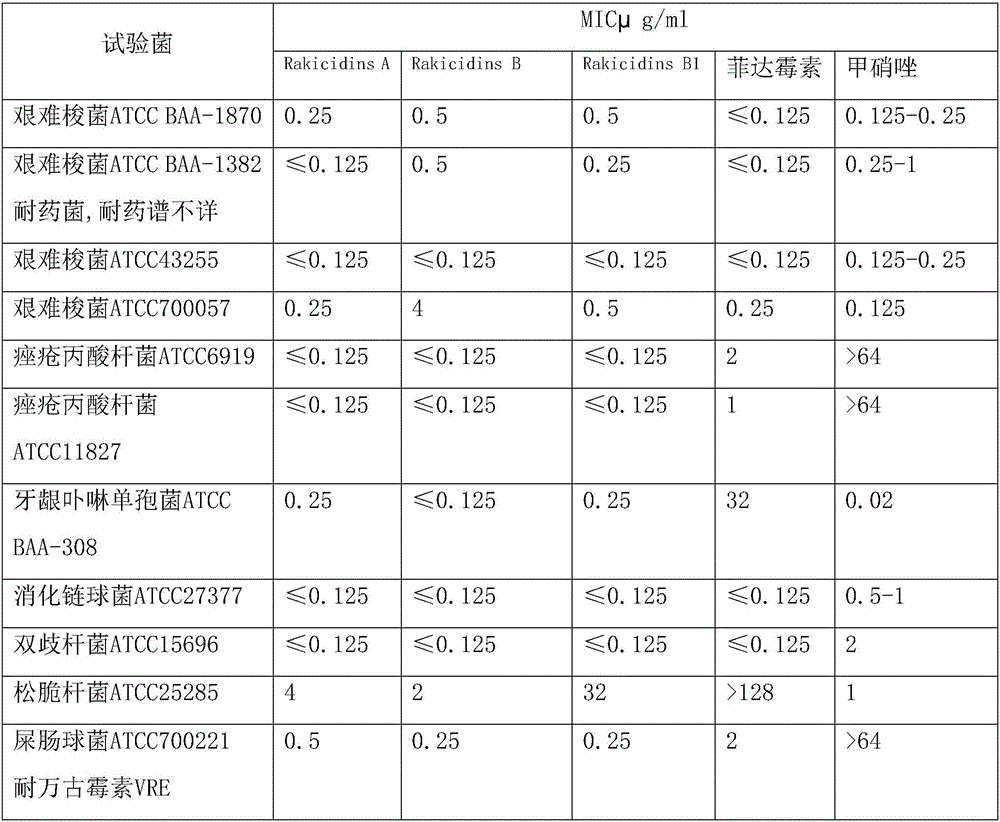
Application of Rakicidins compounds in resistance to clinical pathogenic anaerobic bacteria
ActiveCN105709205AQuite activeStrong inhibitory activityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaDiseaseUpper urinary tract infection
The invention relates to the field of biological medicine, in particular to an application of Rakicidins compounds in resistance to clinical pathogenic anaerobic bacteria. Pharmacodynamic experiments indicate that the Rakicidins compounds have good resistant effect on the clinical pathogenic anaerobic bacteria and have the resistant effect on vancomycin enterococcus infection diseases. The Rakicidins compounds can be used for treating diarrhea, enteritis, alimentary infection, oral infection or skin acne caused by clostridium difficile as well as diseases such as urinary tract infection, or skin soft-tissue infection and the like.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF MICROBIOLOGY
High-efficiency phosphate-solubilizing Clostridium butyricum A5-4 and applications
InactiveCN101851596AWill not cause pollutionEffective dissolutionBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaBacteroidesBiotechnology
The invention discloses high-efficiency phosphate-solubilizing Clostridium butyricum, a preparation method and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of agricultural microorganisms. In the invention, one high-efficiency phosphate-solubilizing Clostridium butyricum A5-4 strain is obtained through separation, and the strain is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC for short), wherein the preservation number is CCTCC NO: Ma010052. The bacterium is separate from the substrate sludge of a septic tank and has the capacity of efficiently dissolving calcium phosphate and calcium phytate under the anaerobic condition. The bacterium has wide nutrient requirement range, easy cultivation, low cost and storage property and can not cause environmental pollution after being reapplied to the environment. The strain can be developed into a novel microorganism agent applied to aquatic crop cultivation or aquaculture.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
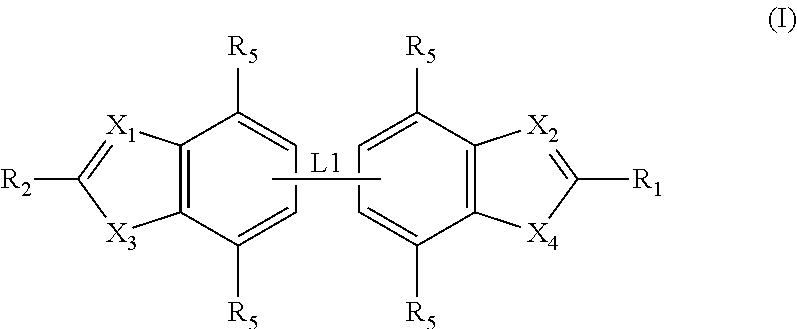
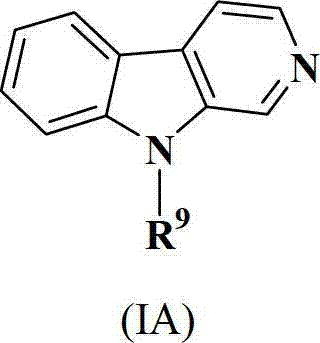
Selective antibacterials for clostridium difficile infections
ActiveUS8796292B2Reduce the possibilityHigh activityAntibacterial agentsBiocideDiseaseClostridium difficile infections
The invention features compounds of formula (I): The compounds are useful as antibacterial agents, especially again Clostridium difficile-associated diseases.
Owner:ACURX PHARMA LLC
Clostridium Daqing clostridium and application thereof
The present invention relates to clostridium 'daqing' clostridium and its uses. The present invention solves the problem it is difficult to remove or degrade polypropylene of oil field sewage. The clostridium 'daqing' clostridium -WL is preserved at CGMCC on January 10, 2007, preserving number being CGMCC No. 1911. The 'daqing' clostridium is Gram-positive bacilli, with endo-spore, facultative anaerobic, grows under pH 5.0-11.0,10-65 degree. The strain is variable in length, breadth being 0.4um-0.8um, length being 1.4um-4um, free of flagellum. The inventive 'daqing' clostridium -WL is a new strain, and can use polypropylene as unique carbon source which can be used in polypropylene biodegradation. 10ml 'daqing' clostridium -WL of concentration 6x10<6> per ml is added in oil field sewage with polypropylene concentration being 500mg / L and the polypropylene degradation rate is 35%-76% after 20 days.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Culture collection process
InactiveCN101307293ALong storage timeStable concentrationMicroorganism based processesMicroorganism preservationRefrigerated temperatureAspergillus niger
The invention provides a spawn preservation method adopting semisolid low-temperature air-tight culture. A spawn is inoculated in an aseptic semisolid culture medium which is vertically stored at an ambient temperature of between 6 and 8 DEG C after aseptic liquid paraffin is added into the culture medium. The spawn is staphylococcus aureus, escherichia coli, pseudomonas aeruginosa, bacillus subtilis, clostridium orogenes, aspergillus niger or candida albicans. The specific process is as follows: preparing the semisolid culture medium, carrying out sub-package and sterilization, and then culturing for 2 to 3 days, inoculating the spawn into the semisolid culture medium in a mode of stab inoculation after asepsis is ensured, with the number of stab inoculation points parallel with the plane of the culture medium being no less than 3; pouring the aseptic liquid paraffin with a height of 1 to 2 cm into the culture medium which is sealed by a sealing film and is stored in a refrigerator at a temperature of between 6 and 8 DEG C. The method can not only prolong the spawn preservation time but also keep a relatively stable spawn concentration, thereby saving much cost for production and test, reducing the treatment and discharge of rejected material after spawn use, and reducing environmental hazard.
Owner:药大制药有限公司
Feed additive premix capable of reducing excrement stink of broilers and application of feed additive premix
InactiveCN105746931ANo side effectsEasy to prepareAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsBiotechnologyDisease
The invention discloses a feed additive premix capable of reducing the excrement stink of broilers and application of the feed additive premix. The feed additive premix comprises the following components: bacillus licheniformis, bacillus subtilis, clostridium butyricum, enterococcus faecium, lactobacillus reuteri, a yucca extract, a camphor extract, fructooligosaccharide and rice protein peptide. The feed additive premix provided by the invention does not contain any antibiotic or drug residue and is an environment-friendly and pollution-free high-quality feed additive premix for broilers. The feed additive premix has the advantages of being free of toxic and side effects, being beneficial to growth of broilers and human health, and being simple and convenient to prepare and use. The feed additive premix has biological functions of promoting the growth and the intestinal health of broilers, improving the immune functions of organisms, and the like. The feed additive premix has the effects of effectively reducing stink gas including ammonia gas, hydrogen sulfide and the like produced by broilers, improving the growth environment of broilers, and reducing infection rates of diseases including respiratory diseases, intestine diseases and the like and the death rate of broilers.
Owner:ANIMAL SCI RES INST GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Methods and compositions for reducing clostridium difficile infection
InactiveUS20170087196A1Reduce riskReduce severityPeptide/protein ingredientsBacteria material medical ingredientsClostridial infectionClostridium difficile infections
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for reducing the risk and severity of C. difficile infection. It is based, at least in part, on the discovery that a restricted fraction of the gut microbiota, including the bacterium Clostridium scindens, contributes substantially to resistance against C. difficile infection. Without being bound by any particular theory, it is believed that this is achieved through the biosynthesis of secondary bile acids.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
Ketolide Derivatives as Antibacterial Agents
Provided herein are ketolide derivatives, which can be used as antibacterial agents. Compounds described herein can be used for treating or preventing conditions caused by or contributed to by gram positive, gram negative or anaerobic bacteria, more particularly against, for example, Staphylococci, Streptococci, Enterococci, Haemophilus, Moraxalla spp., Chlamydia spp., Mycoplasm, Legionella spp., Mycobacterium, Helicobacter, Clostridium, Bacteroides, Corynebacterium, Bacillus, Enterobactericeae, Propionibacterium acnes or any combination thereof. Also provided are processes for preparation of compounds described herein, pharmaceutical compositions thereof, and methods of treating bacterial infections.
Owner:RANBAXY LAB LTD
Microorganism bacterium agent for subtracting organic sludge, production method of microorganism bacterium agent and complex culture medium
ActiveCN102586111ANo secondary pollutionAvoid the limitations of prone to mutation and reduced effectFungiBacteriaBacteroidesSphaerotilus
The invention provides a microorganism bacterium agent for subtracting organic sludge. The microorganism bacterium agent is characterized in that: the microorganism bacterium agent per milliliter contains more than 2.7*10<9> of live bacteria, and the pH value is 3-4; the microorganism bacterium agent comprises photosynthetic bacteria, bacillus mucilaginosus, lactic acid bacteria, fusarium, anaerobic clostridium, denitrifying bacteria, sphaerotilus and zymogenous filamentous fungus. The invention also provides a corresponding production method of the microorganism bacterium agent and a complex culture medium. According to the invention, a mode of combining a plurality of floras is adopted to reduce and degrade the organic sludge and organic pollutants in water in a river (lake) or a municipal sewage treatment plant, and a limit that the effect is reduced due to single strain variation easily caused by environment change is avoided.
Owner:宗晓进 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com