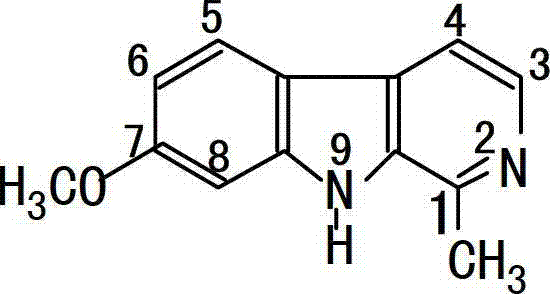
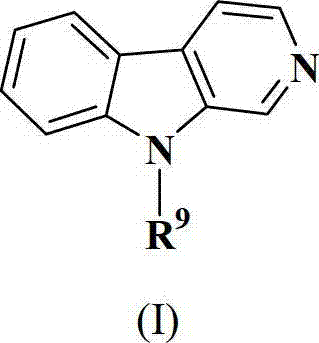
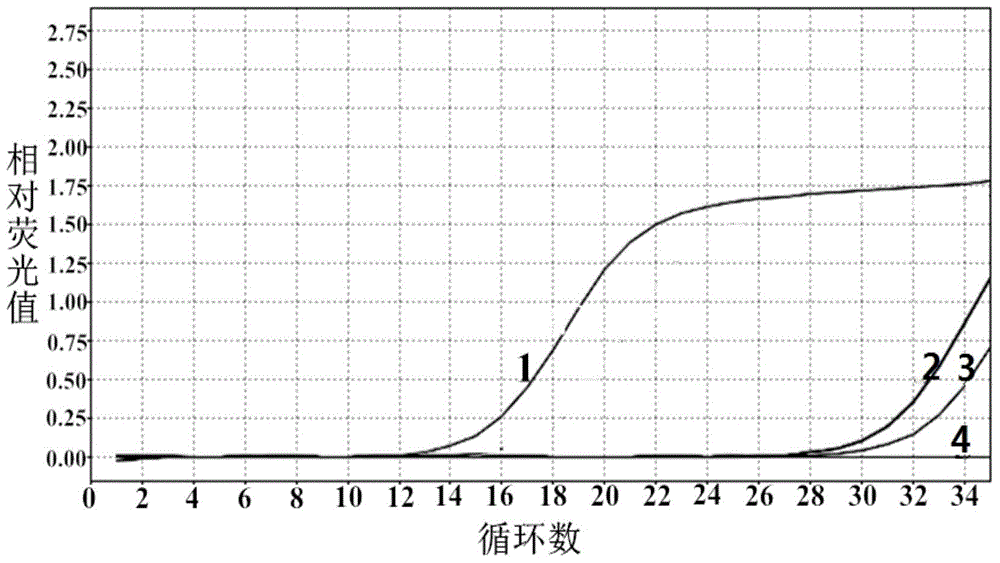
Patents
Literature
277 results about "Klebsiella" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Klebsiella is a genus of Gram-negative, oxidase-negative, rod-shaped bacteria with a prominent polysaccharide-based capsule. Klebsiella species are found everywhere in nature. This is thought to be due to distinct sublineages developing specific niche adaptations, with associated biochemical adaptations which make them better suited to a particular environment. They can be found in water, soil, plants, insects and other animals including humans.
Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteriophage and application thereof
ActiveCN106754745AEnhance killing activityBroad cracking spectrumAntibacterial agentsViral/bacteriophage medical ingredientsK pneumoniaeInduced infections
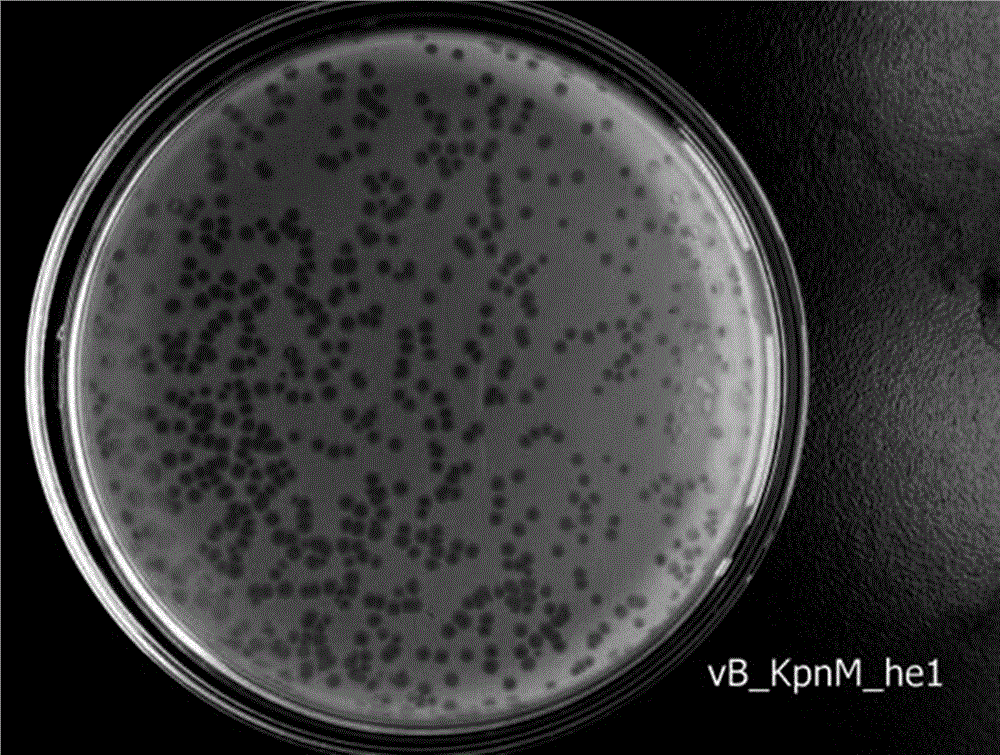
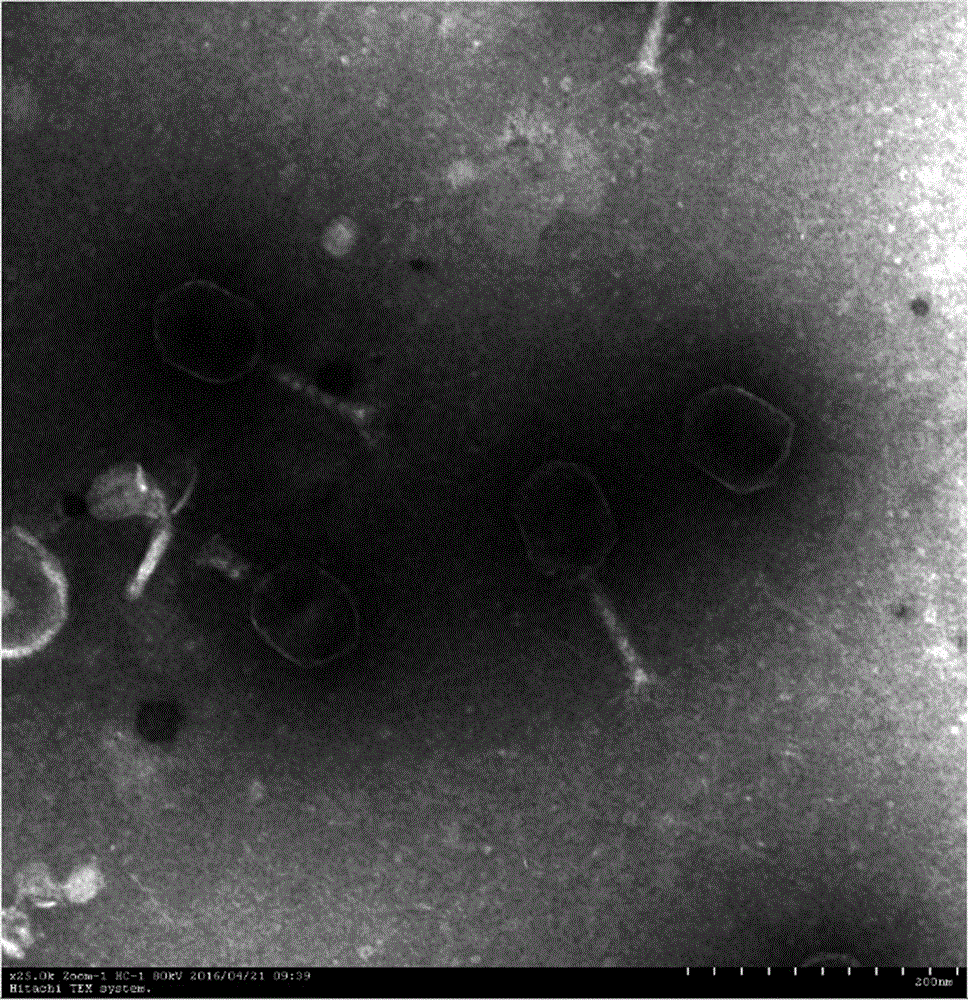
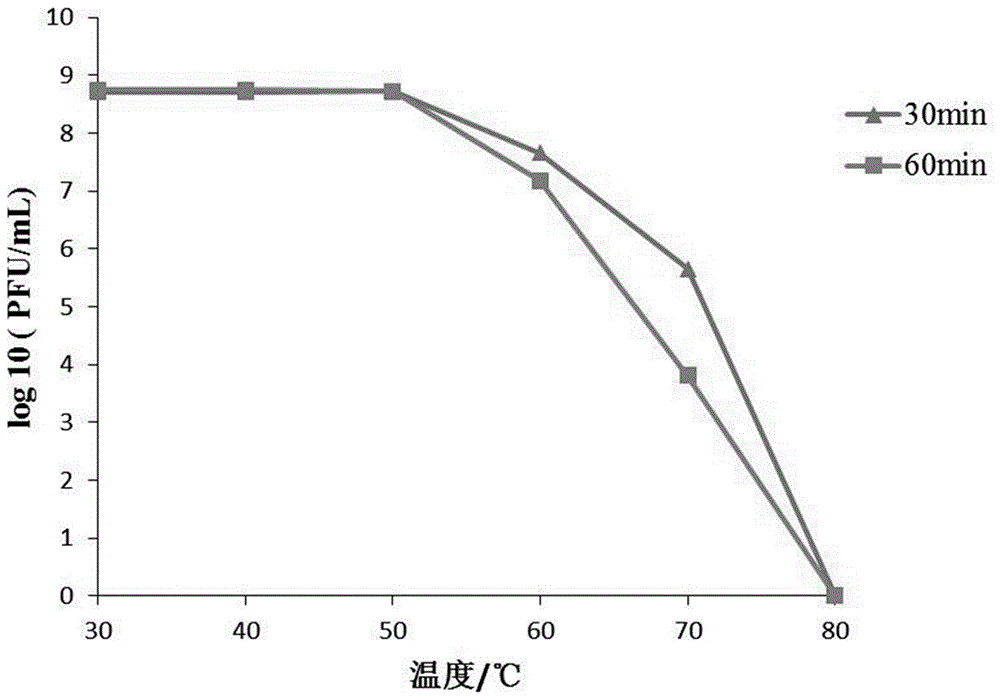
The invention discloses a strong lysis bacteriophage for splitting NDM-1 positive Klebsiella pneumoniae clinical isolates, and an application of the strong lysis bacteriophage used as a biological preparation in the prevention and treatment of NDM-1 Klebsiella pneumoniae induced infection and pollution. The preservation number of the bacteriophage is CCTCC M 2015760, and the bacteriophage has a regularly icosahedral head and a telescopic tail, and belongs to a Myoviridae double-stranded DNA bacteriophage. The bacteriophage has strong kilign activity and wide bacteriophage lysis spectrum, can be used for preparing medicines for preventing and treating NDM-1 Klebsiella pneumoniae induced bacterium infection, and also can be used for killing NDM-1 positive Klebsiella pneumoniae in culture environment and medical environment.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Environmentally-friendly breeding of bacillus subtilis for producing 2,3-butanediol by fermentation with glucose substrate
InactiveCN101851598AImprove protectionHigh utilization rate of raw materialsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesChemical synthesisPolyester
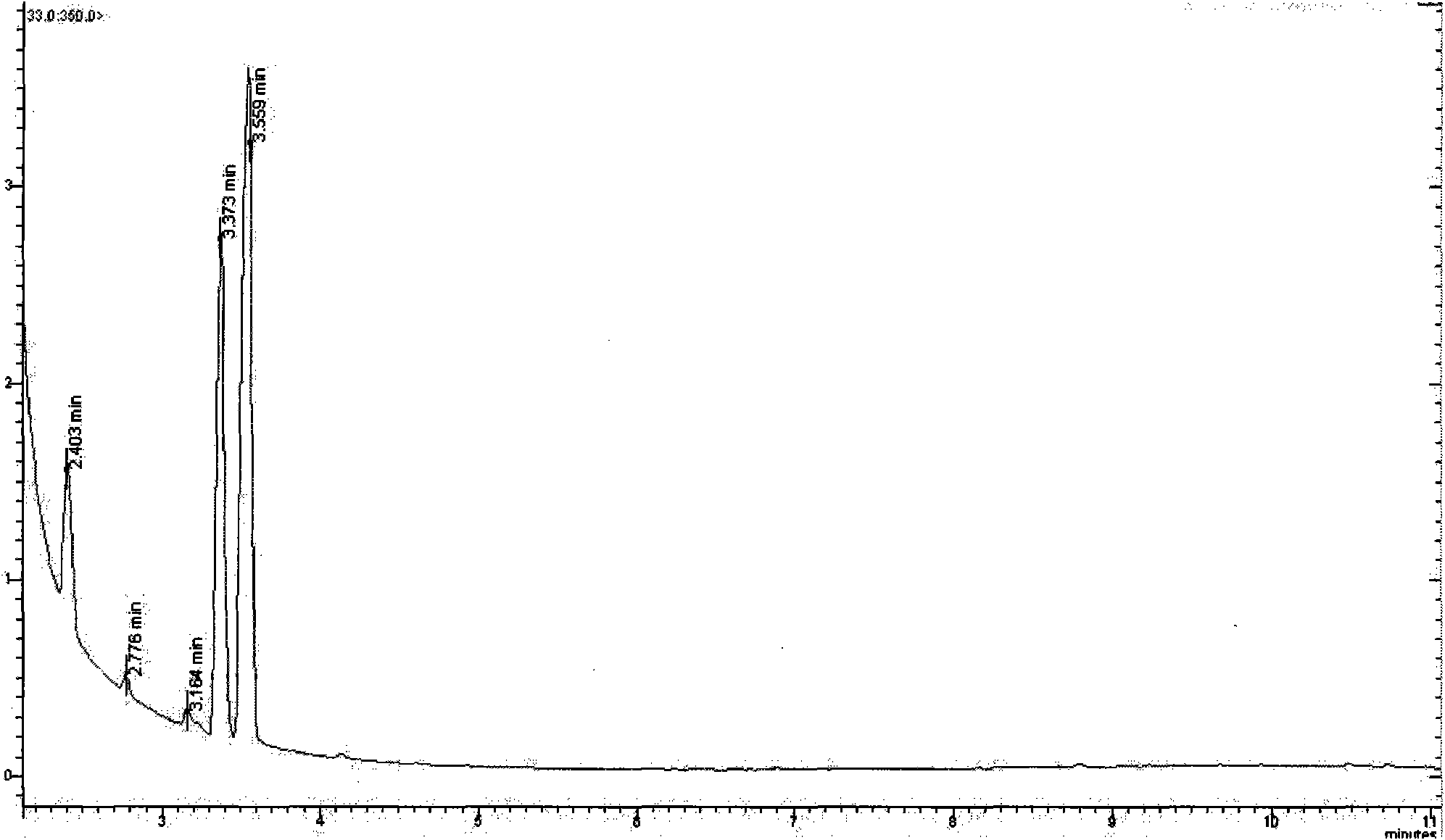
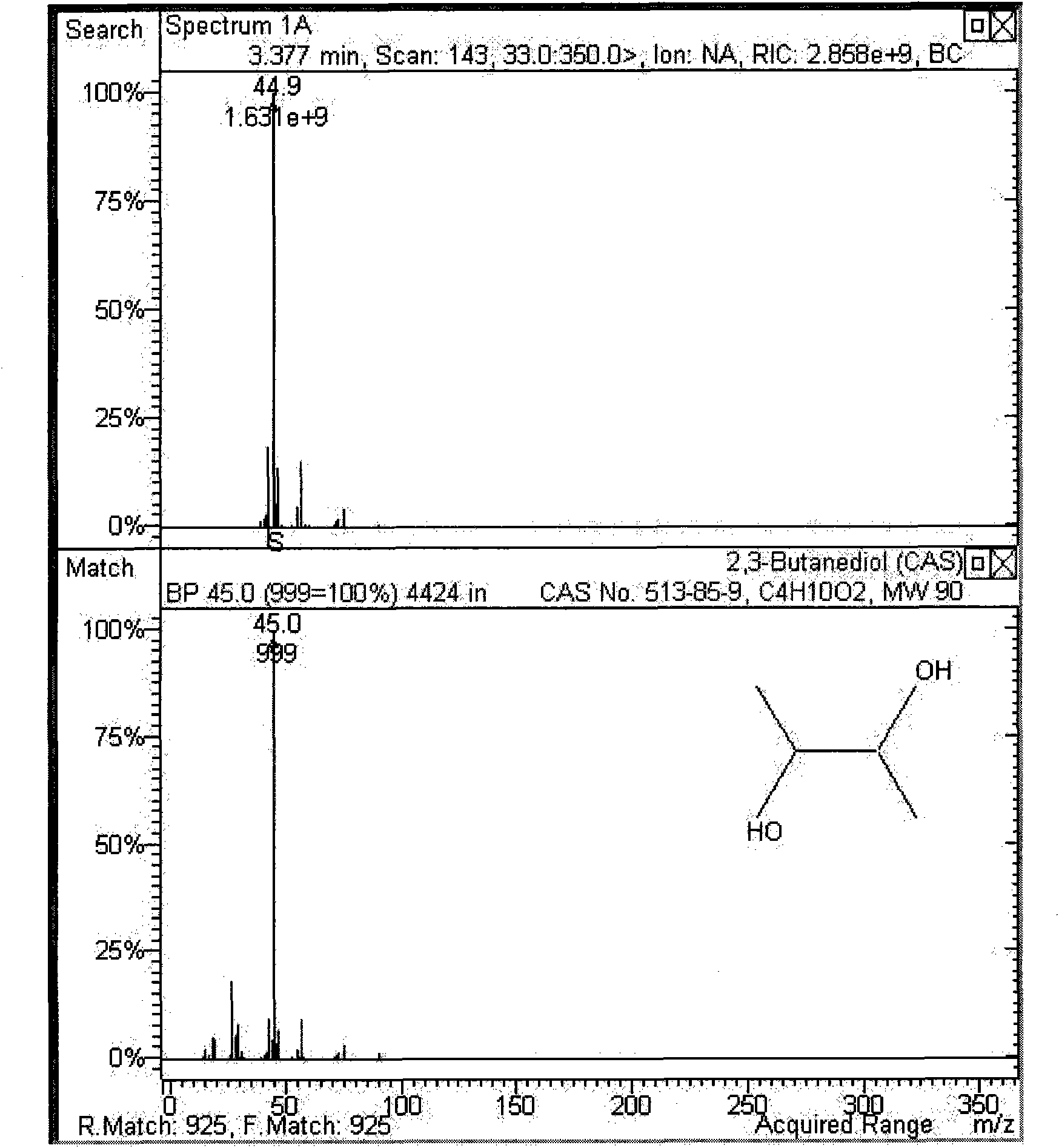
2,3-BDO is important industrial chemicals and a medicinal precursor, for example, the 2,3-BDO can form 1,3-butadiene through dehydration and can be used for synthesizing rubber, polyester and polyurethane; the esterified 2,3-BDO is a precursor of synthetic polyimine, and can be applied to medicaments, cosmetics, washing liquor liquid and the like; and in addition, the 2,3-BDO can also be used as a flavor substance to be added into distilled spirit and cream. The 2,3-BDO can be prepared by a chemical synthesis method and a microorganism production method, and due to a special structure of 2,3-butanediol, in the chemical method for producing the 2,3-butanediol, the 2,3-butanediol is mainly prepared by hydrolyzing four-carbon hydrocarbon generated during the splitting decomposition of petroleum at the high temperature and under the high pressure and has the disadvantages of high cost, complicated processes and difficult operation, so the large-scale industrial production is difficult to realize all the time. With the increasing rise in oil price, people pay close attention to the production of the 2, 3-butanediol by using the microbial fermentation method and the developmental research of derivatives thereof gradually. The fermentation method for producing the 2,3-butanediol has the following advantages that: firstly, the fermentation method has the superiority in cost, and the chemical method has high production cost; secondly, the fermentation method has an environmental-friendly characteristic, and the 2,3-butanediol is used as an organic synthesis intermediate to occupy markets of a number of compounds and other petroleum chemicals, has wide prospect, obvious social and environmental benefits, and is particularly favorable for the extensive application of the products; and thirdly, in the fermentation method for producing the 2,3-butanediol, renewable resources are used as raw materials, so the fermentation method does not depend on the petroleum chemicals.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Klebsiella pneumoniae detection kit and use method thereof
ActiveCN101892300AHigh yieldHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementK pneumoniaeKlebsiella
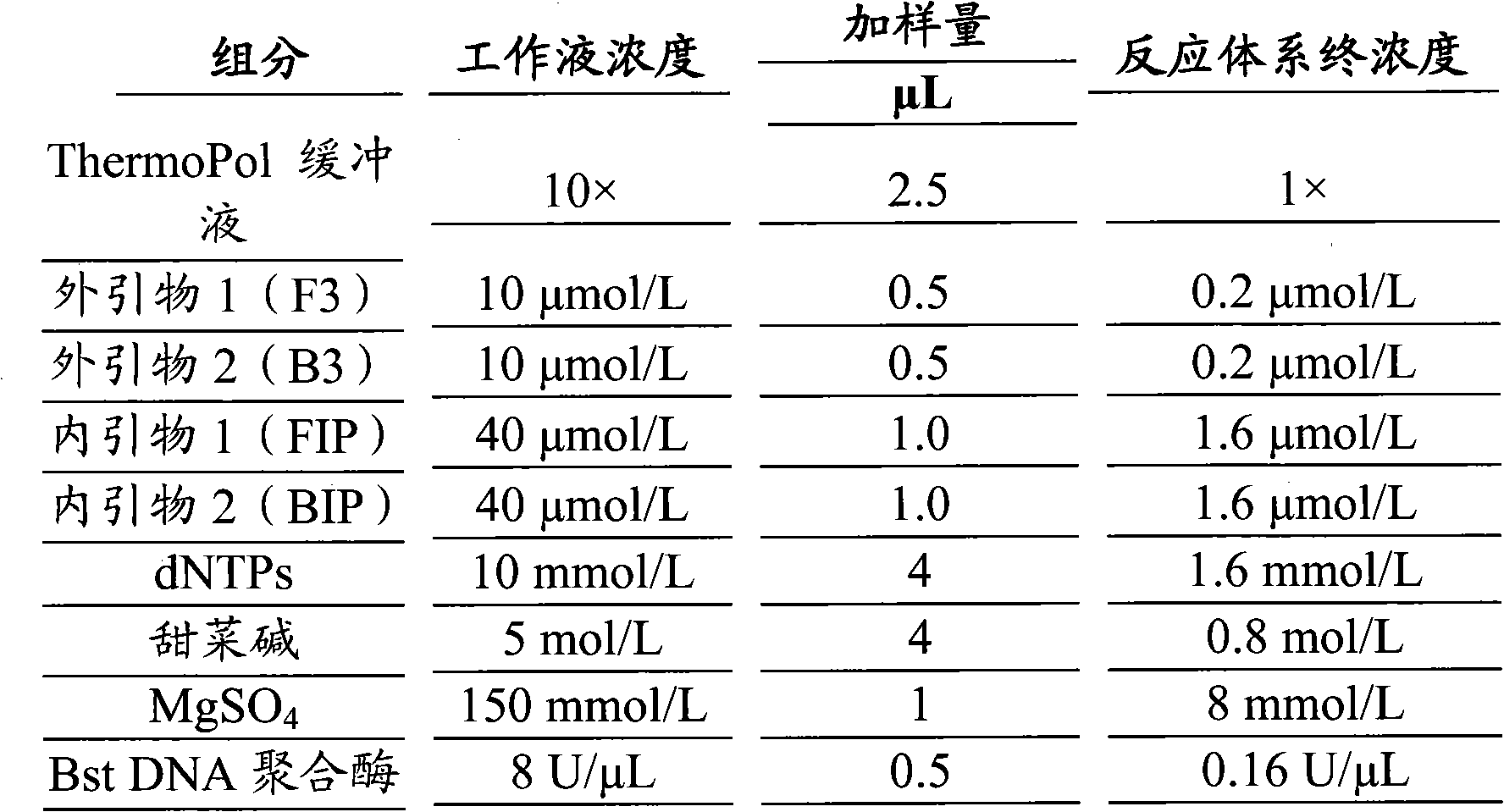
The invention provides a klebsiella pneumoniae detection kit. The klebsiella pneumoniae detection kit comprises two pairs of primers, i.e., an inner primer FIP / BIP and an outer primer F3 / B3, which use oppA gene of klebsiella pneumoniae as the target gene and is designed based on the loop-mediated constant-temperature amplification technology. The klebsiella pneumoniae detection kit has more comprehensive detection effect and low omission ratio.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HUAFENG BIOTECH
Application of Harmine derivative to preparation of antibacterial medicine
The invention discloses application of a Harmine derivative to preparation of antibacterial medicines. The bacteria is selected from Acinetobacter, Bacillus, Campylobacter, Chlamydia, Chlamydia trachomatis, Clostridium, Citrobacter, Escherichia, enterohemorrhagic escherichia coli, enteric bacteria, Enterococcus, Francisella, Haemophilus, helicobacter, Klebsiella Bacillus, Lester monocytogenes, Moraxella, Mycobacterium, Neisseria, proteus, Pseudomonas, Salmonella, shewanella oneidensis, Shigella, Stenotrophomonas, Staphylococcus, Streptococcus and Yersinia.
Owner:XINJIANG HUASHIDAN PHARMA RES
Kit for detecting klebsiella pneumoniae
ActiveCN104946762ASimplify testing proceduresShort detection cycleMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationK pneumoniaeNucleotide
The invention discloses a kit for detecting klebsiella pneumoniae, and belongs to the technical field of PCR detection. The kit comprises specific primers and a probe for detecting klebsiella pneumoniae; the nucleotide sequences of the specific primers and the probe are as shown in SEQ ID NO.1-3; a detected target gene is a sequence of a pho gene, and has a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID No.4. The kit has the advantages of being accurate in detection, high in sensitivity, strong in specificity, and simple and quick to operate, has a favorable sample detection capacity, can replace a traditional bacterial isolated cultivation and diagnosis method, and the novel kit for quick detection is provided for klebsiella pneumoniae.
Owner:BIOSINO BIO TECH & SCI
Bamboo forest biological fertilizer
InactiveCN1443729AIncrease nitrogen fixation intensityIncrease productionBacteriaHorticulture methodsBacillus licheniformisK pneumoniae
The bamboo forest biolgoical fertilizer capable of meeting the requirements for biological organic fertilizer in production of nuisance-free green bamboo shoots and organic bamboo shoots for reducingor substituting chemical fertilizer is formed from matrix and bamboo plant rhizospheric combined nitrogen-fixing bacteria which are separated from bamboo plant rhizosphere, can be used for fixing molecular nitrogen in atmosphere and are any one strain or combination of any two kinds of strains or more than two kinds of (Bacillus polymyxa mace) WG-1 strain, (Bacillus polymyxa mace) WG-2 strain, (Bacillus licheniformis Chester) WG-3 strain and (Klebsiella pneumoniae (Schroeter) Trevisan) WG-4 strain. Said fertilizer can be used for cultivating bamboo forest.
Owner:吴晓丽 +1
Klebsiella sp. P5 with phosphorus dissolving function and application of Klebsiella sp. P5
ActiveCN110438037AIncrease available phosphorus contentIncrease profitPlant growth regulatorsBiocideGrowth plantGrowth promoting
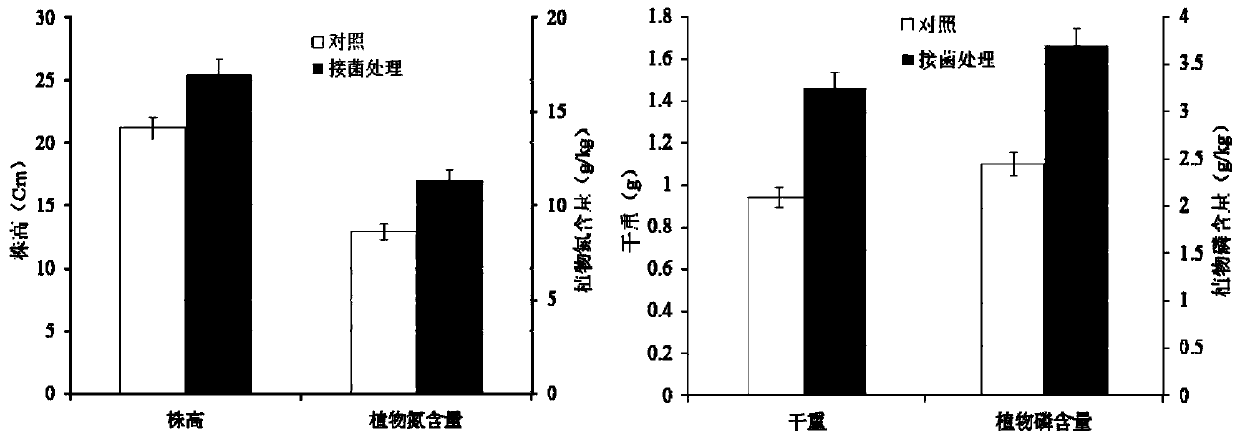
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant rhizosphere growth-promoting bacteria and particularly discloses Klebsiella sp. P5 with a phosphorus dissolving function and application of the Klebsiella sp. P5. The Klebsiella sp. CCNWSX1902 P5 is collected in the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) on April 22, 2019, with the collection number of CCTCC NO:M 2019280. The phosphorus dissolving bacterium P5 is separated from wheat rhizosphere soil and identified as the Klebsiella sp. CCNWSX1902 in the aspects of morphology, physiological-biochemical characteristics and genetics. The strain can effectively dissolve indissolvable phosphorus in plant rhizosphere soil, substantially increase the content of rapidly available phosphorus in the soil and increase the utilization rate of phosphorus in the soil by plants to promote plant growth, reduce the dosage of chemical fertilizer and increase the yield of crops, and has important significance in agricultural production.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Primer and probe for quantitative determination of klebsiella pneumonia, and application of primer and probe
ActiveCN103642910AAccurate quantification of DNA contentMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationK pneumoniaeFluorescence
The invention discloses a primer and a probe for quantitative determination of klebsiella pneumonia, and an application of the primer and the probe. Nucleotide sequences of the primer are a sequence 3 and a sequence 4 in a sequence table; a nucleotide sequence of the probe is a sequence 5 in the sequence table. The primer and the probe have the beneficial effects that the specific primer and probe sequences of the klebsiella pneumonia disclosed by the invention can be applied to qualitative and quantitative detection of the klebsiella pneumonia, the target of accurately and quantitatively determining the deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) content of the klebsiella pneumonia in a specimen to be detected can be achieved by extracting the DNA in the sample to be detected and combining with a real-time fluorescence quantification polymerase chain reaction (PCR) detection technology, and the primer and the probe can be applied to food detection, scientific research and clinical diagnosis and used for carrying out qualitative and quantitative analysis on the klebsiella pneumonia DNA in samples such as a food sample, a suffer throat swab, nasopharyngeal secretion, people sputum specimens and blood samples. Thus, the primer and the probe have an important significance on judgment of klebsiella pneumonia infection, evaluation of treatment effectiveness and dynamic observation of the state of an illness, and simultaneously play an important role in the field of detection of clinical medicine.
Owner:SUZHOU BAIYUAN GENT CO LTD
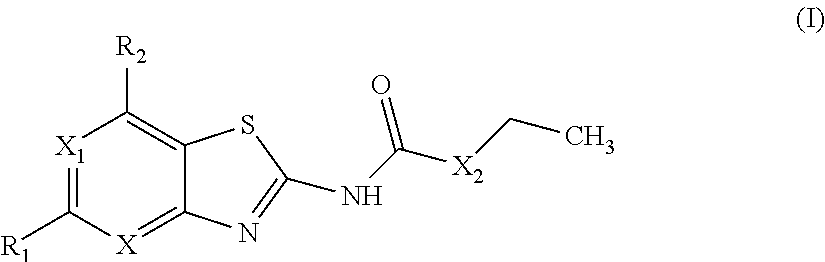
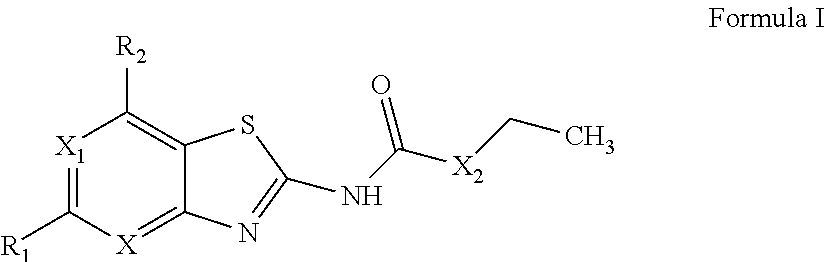
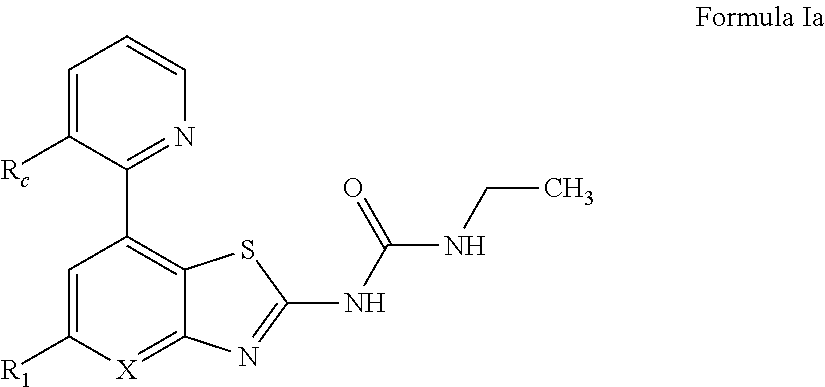
Benzothiazoles and aza-analogues thereof use as antibacterial agents
The present invention provides Gyrase B and / or Topoisomerase IV par E inhibitors, which can be used as antibacterial agents. Compounds disclosed herein can be used for treating or preventing conditions caused by or contributed by gram positive, gram negative and anaerobic bacteria, more particularly against, for example, Staphylococci, Streptococci, Enterococci, Haemophilus, Pseudomonas spp., Acenetobacter spp., Moraxalla spp., Chlamydia spp., Mycoplasma spp., Legionella spp., Ktycobacterium spp., Helicobacter, Clostridium spp., Bacteroides spp., Corynebacterium, Bacillus spp., Enterobactericeae,’ (E. coli, Klebsiella spp., Proteus spp., etc.) or any combination thereof. Also provided, are processes for preparing compounds disclosed herein, pharmaceutical compositions containing compounds disclosed herein, and methods of treating bacterial infections. (Formula)
Owner:RANBAXY LAB LTD
Acid-producing Klebsiella bacterium and uses thereof
InactiveCN101063095AReduce outputIncrease profitBacteriaMicroorganism based processesUltravioletKlebsiella species
The invention discloses a generating acid klebsiella and appliance, which is characterized by the following: setting the preserved number at CCTCC NO: M 207023; adopting ultraviolet and diethyl sulfate; composite-treating strain CCTCC NO: M 207023; seeding on selective solid medium with bromide of sodium and sodium bromate; culturing; sorting single bacterial colony; yeasting; preparing 2, 3-butylene glycol. This invention possesses simple operation, low cost, high efficiency and short period, which can increase receiving ratio of 2, 3-butylene glycol.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Klebsiella pneumoniae and its application in preparing 2,3-butanediol
ActiveCN101457211AIncrease productionHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesK pneumoniaeProduction rate
The invention discloses a Klebsiella pneumoniae SDM CCTCC M 208097 and applications in preparing 2, 3-butanediol. The Klebsiella pneumoniae SDM CCTCC M 208097 has features of wide nutritional requirement range, high outcome concentration and short production period or the like. The culture medium and the operation method are simple, the cost is low. The outcome of the 2, 3-butanediol prepared by a fermenter feeding batch fermentation can reach 120-160g / L, the conversion can reach 90-940f the theoretic conversion, the most production rate of the 2, 3-butanediol is 4. 05g / (L. h). The invention has very large commercial use prospect.
Owner:上海肆芃科技有限公司
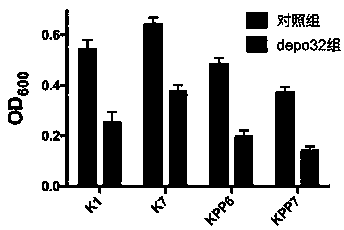
Bacteriophage depolymerase capable of degrading Klebsiella pneumoniae capsular polysaccharides and biofilms
ActiveCN109536459AHigh inhibitory effectSignificant clinical effectAntibacterial agentsBiocideK pneumoniaeBiofilm
The invention discloses a bacteriophage depolymerase capable of degrading Klebsiella pneumoniae capsular polysaccharides and biofilms. By prokaryotic expression and purification of a 32nd open readingframe in a genome of Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteriophage GH-K3, a brand-new depolymerase depo32 with high activity is obtained. The depolymerase has high-efficiency degradation effect on the capsularpolysaccharides and biofilms formed by Klebsiella pneumoniae.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
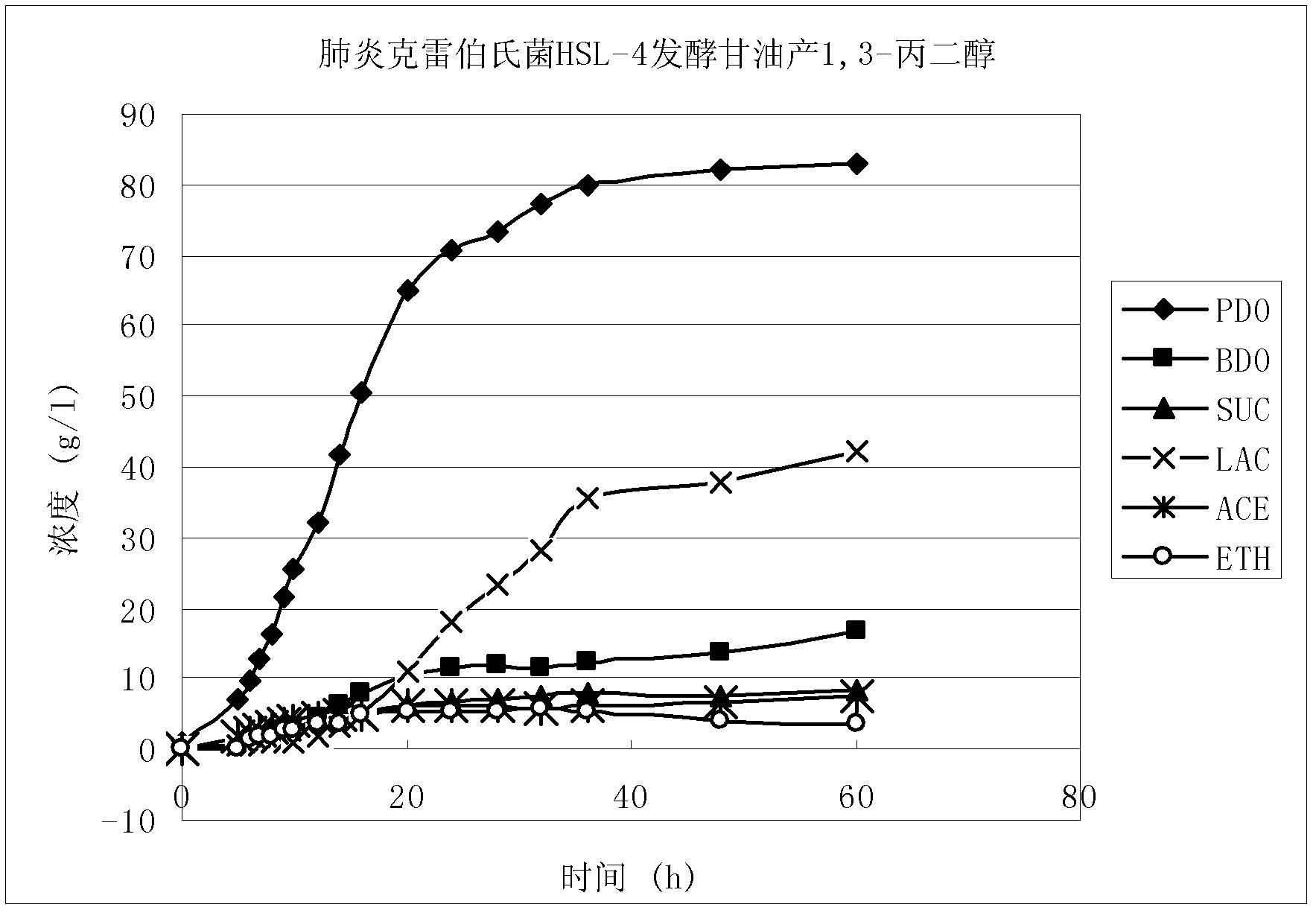
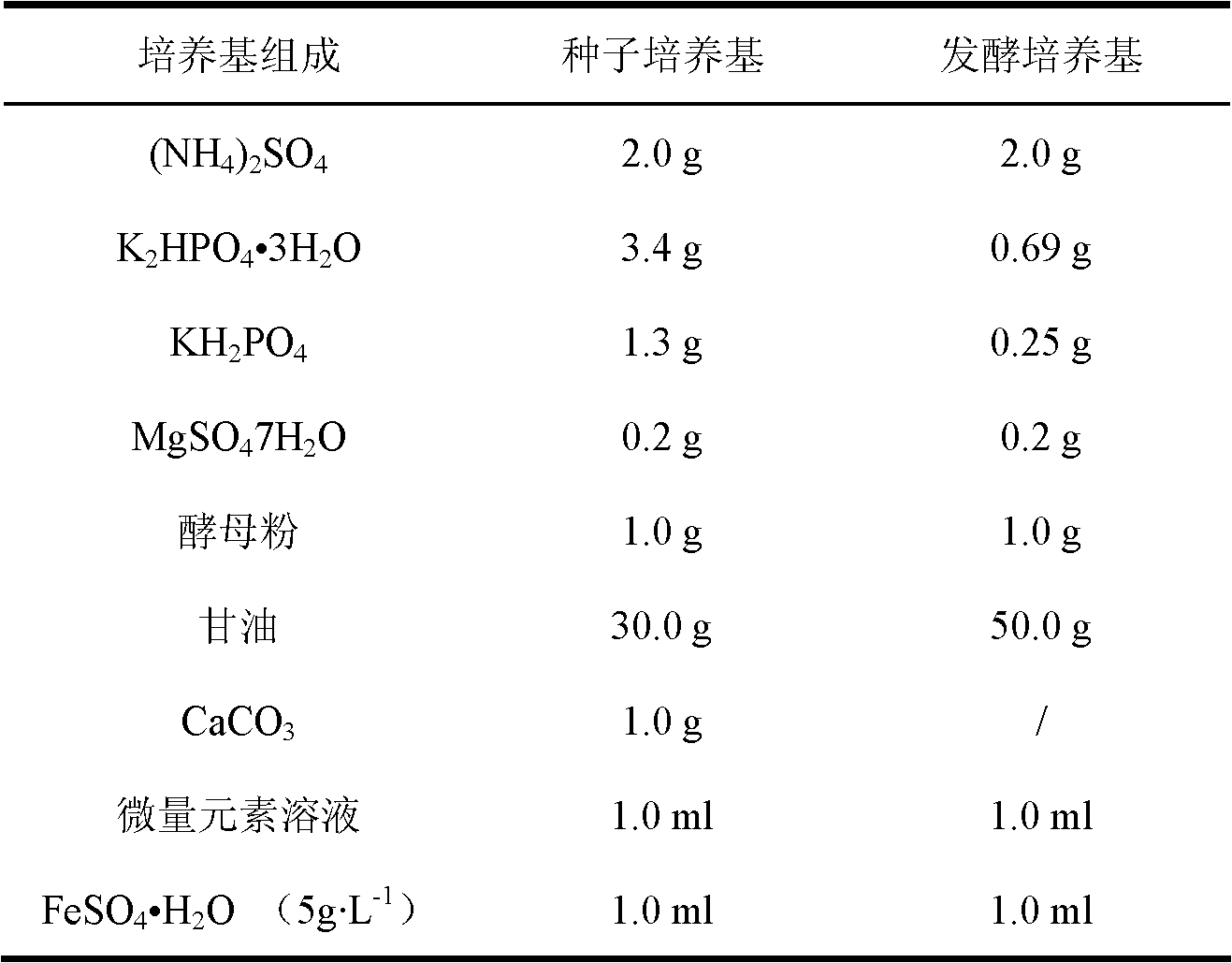
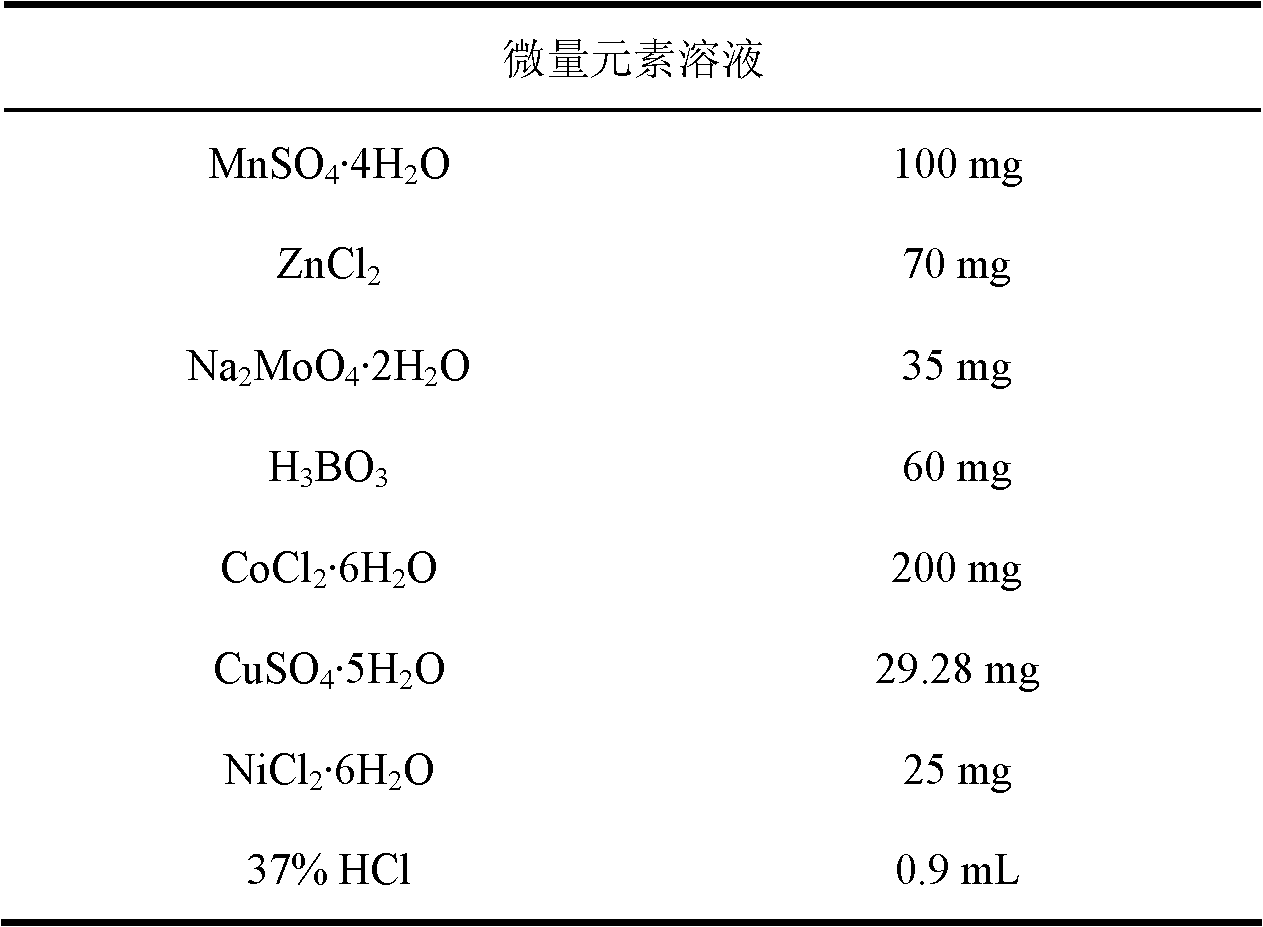
Klebsiella pneumoniae from mangrove forest and application thereof in producing 1,3-propylene glycol
ActiveCN102604863AStrong toleranceStrong 1,3-propanediol production capacityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesK pneumoniaeOrganic acid
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Novel klebsiella pneumoniae strain as well as isolation method and application thereof
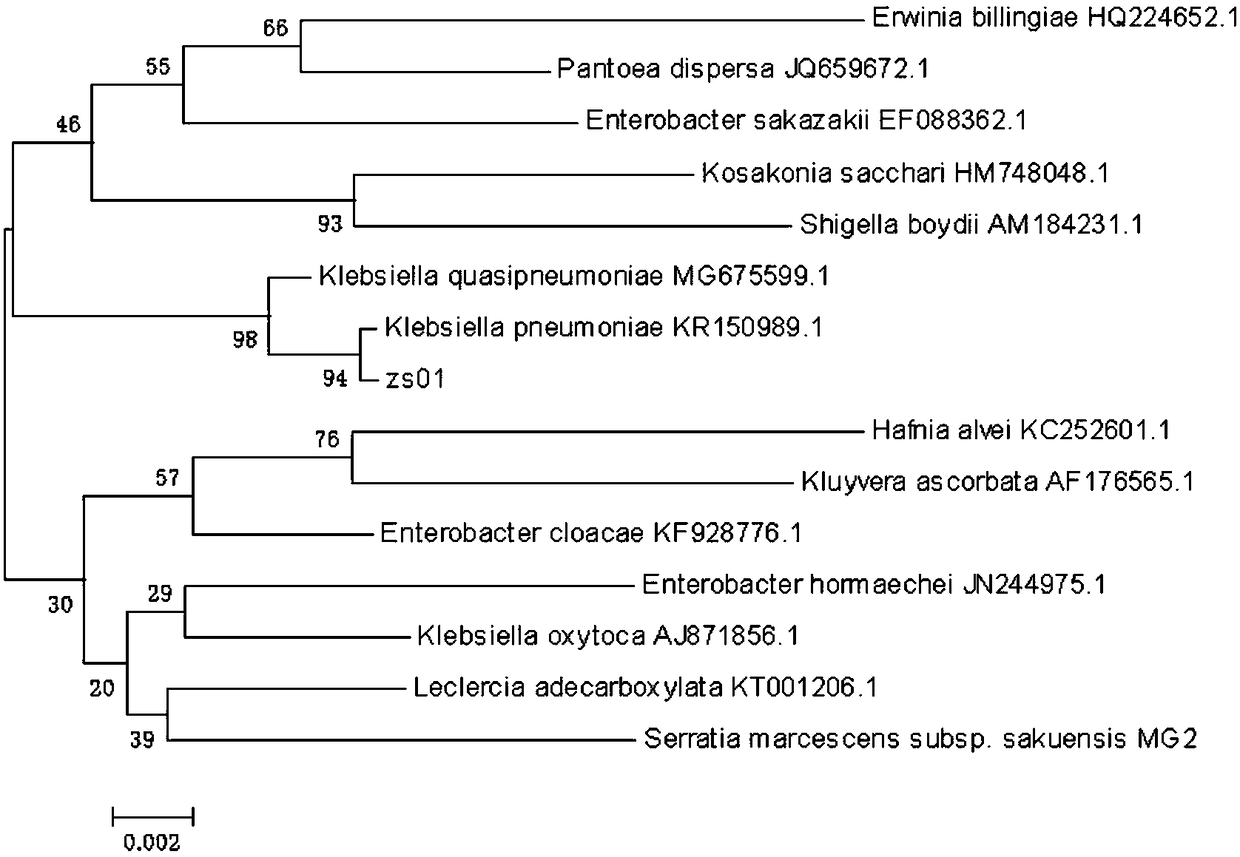
ActiveCN109055282AHas the ability to degradeImprove toleranceBacteriaWater contaminantsHigh concentrationK pneumoniae
The invention discloses a novel klebsiella pneumoniae strain as well as an isolation method and application thereof. The novel strain is isolated and screened from activated sludge in an aeration tankof a papermaking sewage treatment plant and is collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, the collection name is ZS-01, the collection number is 16041, and the collection date is June 30, 2018. The strain has the characteristics and performance as follows: (1), the characteristics are: colonies formed on a phenol MedA solid culture medium are relatively short and thickbacilli, have the sizes of (0.5-0.8)*(1-2)[mu]m, are arranged separately or in pairs, and are pale yellow, uniform in texture and opaque; relatively large gray white sticky colonies are formed on an MPYE solid culture medium, are flagella-free, have capsules, belong to enterobacteriaceae and are Gram-negative short and thick bacilli; (2), the performance is: the strain has certain phenol degradingcapability and has relatively high tolerance to phenol. The strain has the advantages as follows: the strain can degrade the phenol with relatively high concentration, and provides a new bacterial source for effectively treating phenol-containing wastewater with relatively high concentration.
Owner:XIAN LONGHUA ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECHCO LTD
Klebsiella pneumoniae and method of preparing hydrogen and 2, 3-butanediol thereby
InactiveCN101531979AEasy to separateImprove conversion efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesLiquid productK pneumoniae
The invention relates to Klebsiella pneumoniae and a method of preparing hydrogen and 2, 3-butanediol thereby. The Klebsiella pneumoniae is Klebsiella pneumoniae ECU-21 with the preservation number of CGMCC No. 2850. In the preparation method, a ring colony taken from a panel is inoculated to a seed culture medium, the inoculated seed culture medium is arranged in an incubator of 37 DEG C for the static culture, and the seed culture medium which is cultured for 12 hours is switched to a fermentation medium for the fermentation culture; after the inoculation, a rubber stopper is used for sealing a fermentation shake flask, the anaerobic culture environment is formed by introduced N2 sweeping, superfluous gas is discharged via an exhaust port, a gas bag is used to be connected with the exhaust port for collecting hydrogen produced during the fermentation after the gas discharge is finished, and the 2, 3-butanediol is obtained in liquid product; the culturing temperature is 37 DEG C, a magnetic stirrer is adopted for stirring, the rotation speed is 150rpm, and the culturing time is 12-15h. The invention has the advantages that the hydrogen and the 2, 3-butanediol are produced by the fermentation under the anaerobic condition, the additional value of the production is increased, the reaction conditions are easy and wide industrial application development prospect is provided.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation of microbial oligosaccharide with prebiotic function
InactiveCN101503720APromote growthImprove micro-ecological environmentMicroorganism based processesFermentationEcological environmentOligosaccharide
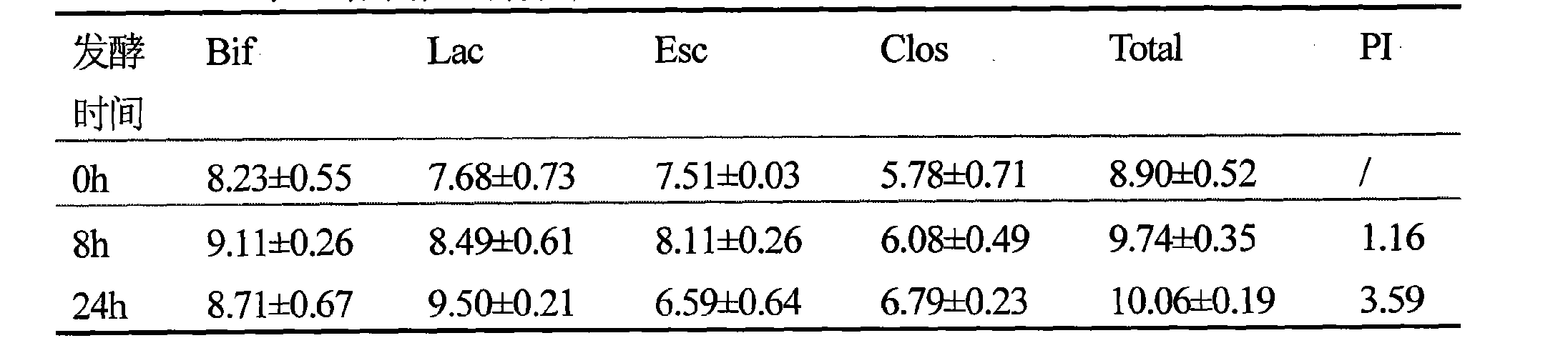
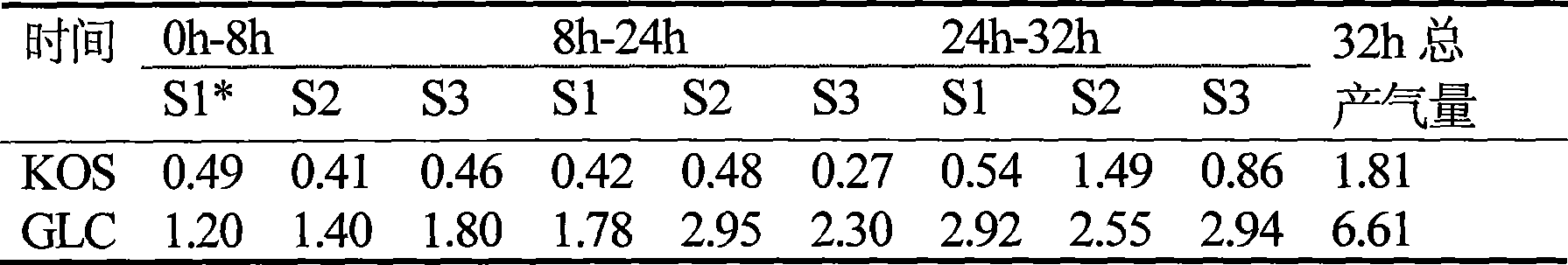
The invention provides a method for preparing microbial oligosaccharide with probiotic action. The method is characterized in that: a sugar producing culture medium is used for liquid fermentation of K.rhinoscleromatis K13 to extract extracellular polysaccharide; enzymatic solution of phage glycanase is prepared, the enzymatic solution and water solution of extracellular polysaccharide are mixed for enzymolysis, the undegraded macro molecular sugar is removed by ultrafiltration, and the obtained filtrate is refined and condensed to obtain the microbial oligosaccharide KOS. Tests show that the microbial oligosaccharide KOS is non-digestible oligosaccharide which can promote the growth of probiotics such as bifidobacterium, lactobacillus and the like, inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria such as pathogenic bacteria, putrefying bacteria and the like, and has the functions of improving the micro ecological environment of the intestinal tract and cleaning the intestinal tract. The microbial oligosaccharide KOS is novel probiotics, which is novel microbial oligosaccharide which is obtained by degrading the extracellular polysaccharide of the K.rhinoscleromatis K13 through the phage glycanase, and the raw materials used in the method are different from those of other polysaccharides, and the result repeatability is good due to the degradation by an enzyme method, so that the application prospect is wide.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Identification method for Klebsiella pneumoniae and adopted primers
ActiveCN104531887AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
The invention relates to an identification method for Klebsiella pneumoniae and adopted primers, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. The two pairs of primers (artificially synthesized gene sequences) are acquired through creative labor and used for conducting PCR amplification on the Klebsiella pneumoniae, escherichia coli and pseudomonas aeruginosa, and an amplified product is a specificity sequence of the Klebsiella pneumoniae. Thus, the Klebsiella pneumoniae can be distinguished from the escherichia coli and the pseudomonas aeruginosa. The primers for identifying the Klebsiella pneumoniae comprise the primer pair K1 or / and the primer pair K2, wherein the primer pair K1 comprises K1-F and K1-R, and the primer pair K2 comprises K2-F and K2-R. Nucleotide sequences of K1-F, K1-R, K2-F and K2-R are SEQ ID NO.1, SEQ ID NO.2, SEQ ID NO.3 and SEQ ID NO.4 in a sequence table.
Owner:王贵升
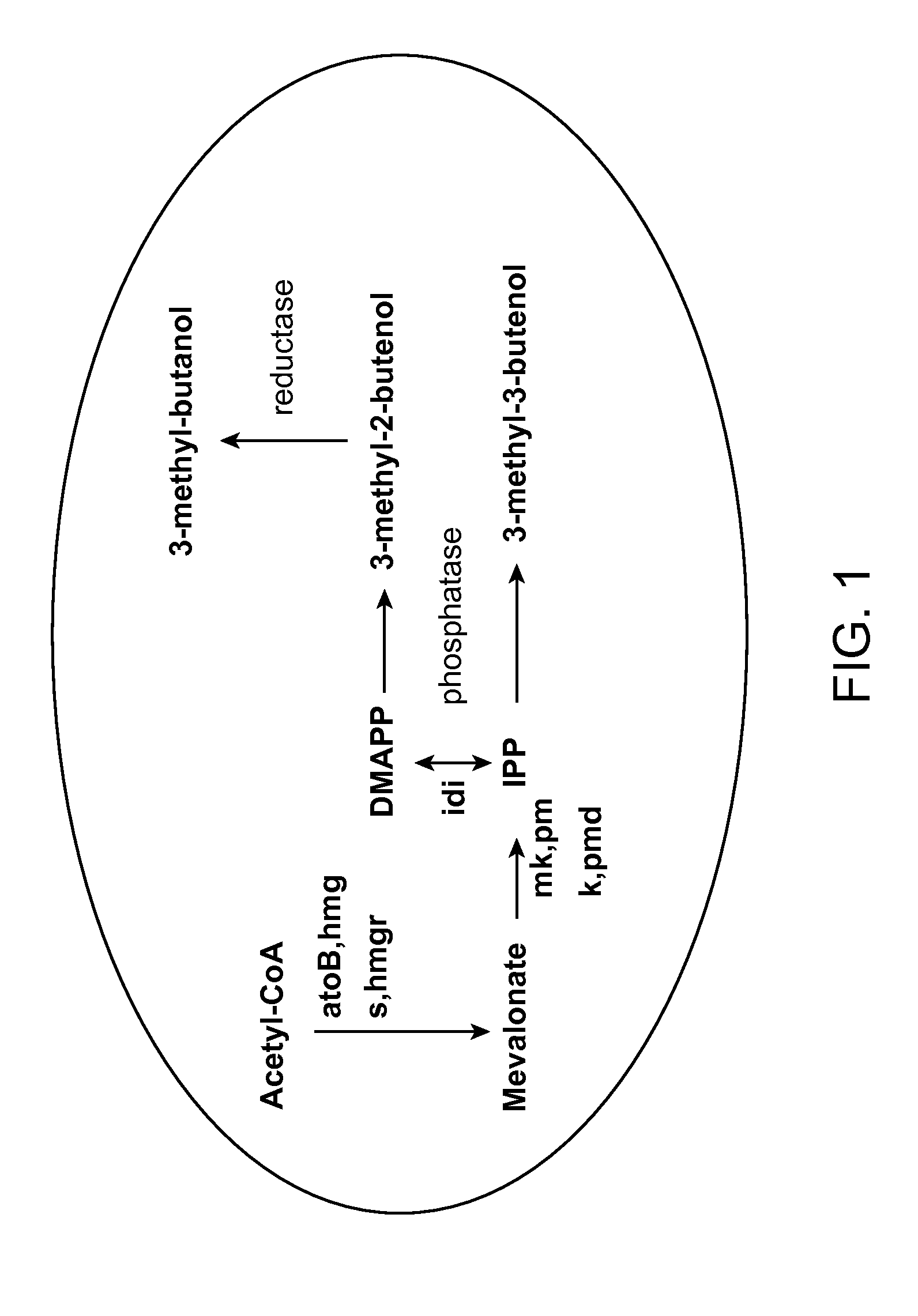
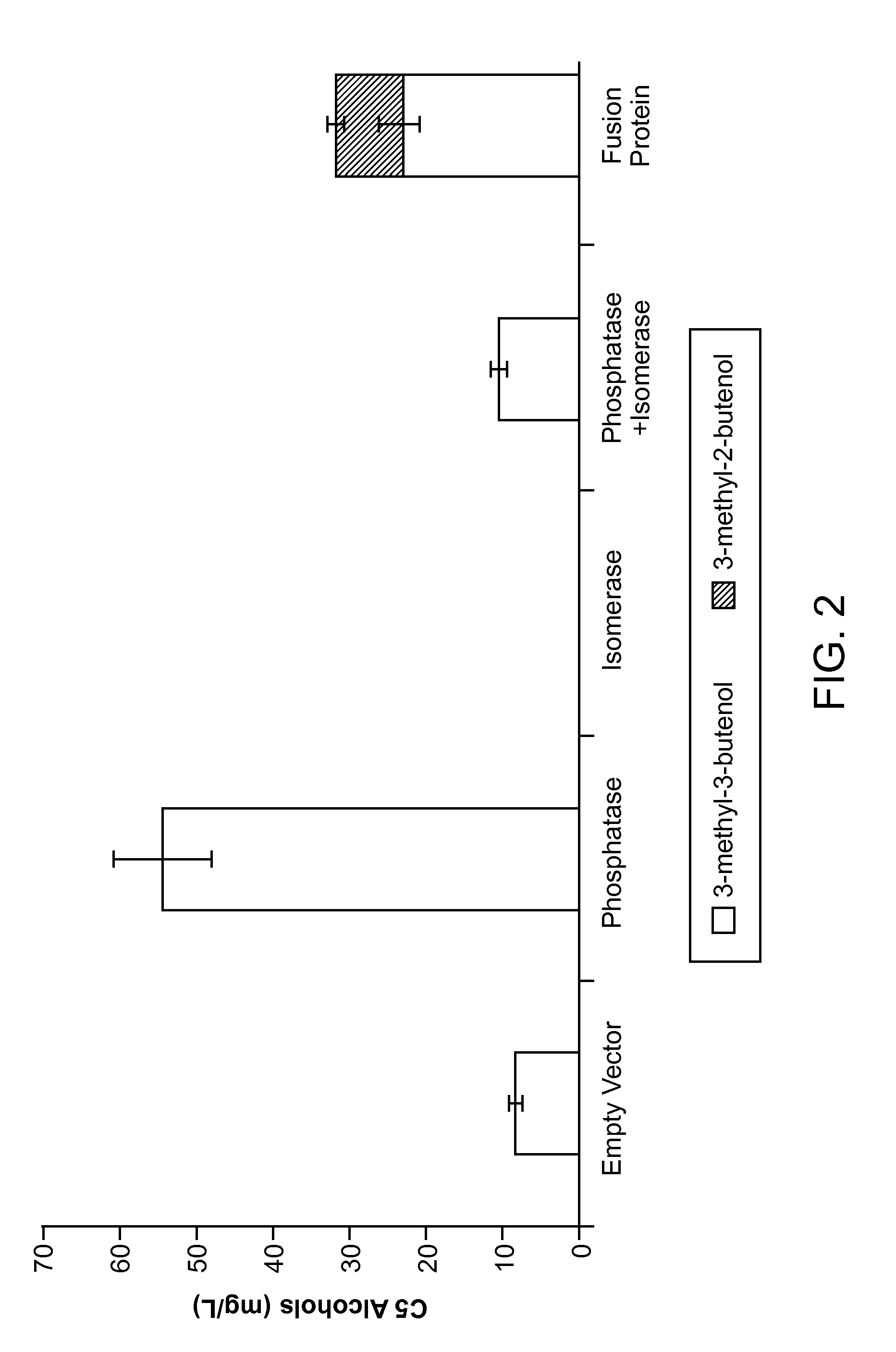
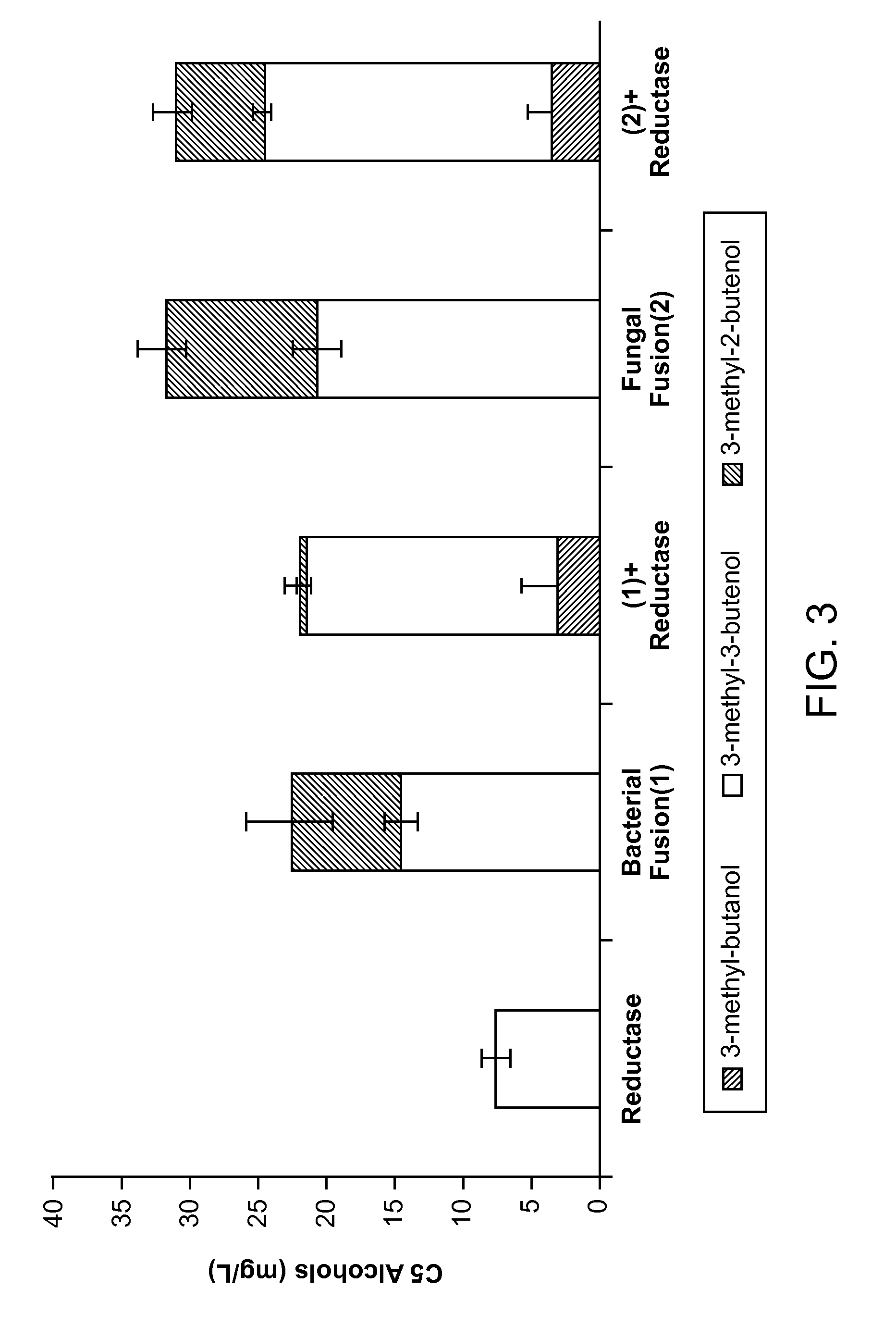
Methods for increasing production of 3-methyl-2-butenol using fusion proteins
The invention relates, in part, to nucleic acid constructs, genetically modified host cells and methods employing such constructs and host cells to increase the production of 3-methyl-2-butenol from IPP. Thus, in some aspects, the invention provides a genetically modified host cell transformed with a nucleic acid construct encoding a fusion protein comprising a phosphatase capable of catalyzing the dephosphorylation of dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP) linked to an IPP isomerase capable of converting IPP to DMAPP, wherein the nucleic acid construct is operably linked to a promoter. In some embodiments, the genetically modified host cell 5 further comprises a nucleic acid encoding a reductase that is capable of converting 3-methyl-2-butenol to 3-methyl-butanol. In some embodiments, the reductase is encoded by a nucleic acid construct introduced into the cell. In some embodiments, the IPP isomerase is a Type I isomerase. In some embodiments, the IPP isomerase is a Type II isomerase. In some embodiments, the host cell is selected from a group of taxonimcal classes consisting of 20 Escherichia, Enterobacter, Azotobacter, Erwinia, Bacillus, Pseudomonas, Klebsiella, Proteus, Salmonella, Serratia, Shigella, Rhizobia, Vitreoscilla, Synechococcus, Synechocystis, and Paracoccus taxonomical classes. In some embodiments, the host cell is an Escherichia coli cell. In some embodiments, the host cell is a fungal cell, such as a yeast cell. In some embodiments, the yeast cell is a Saccharomyces sp. cell. In some embodiments, the host cell is an algal, insect or mammalian cell line. In some embodiments, the phosphatase is nudB from E. coli. In some embodiments, the IPP isomerase is encoded by an idi gene from E. coli or idil gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Specific primer pair for assisting identification of Klebsiella pneumoniae
InactiveCN102367483AImprove detection efficiencyHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesK pneumoniaeAgricultural science
The invention discloses a specific primer pair for assisting identification of Klebsiella pneumoniae. The primer pair provided in the invention consists of DNA shown in sequence 1 of the sequence table and DNA shown in sequence 2 of the sequence table. The specific primer pair designed in the invention can be used for assisting identification about whether Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel) carries Klebsiella pneumoniae only by means of PCR (polymerase chain reaction) and electrophoresis, and the identification is characterized by high sensitivity, simple process and no need for cloning. In order to increase accuracy, a PCR amplified product can be subjected to sequencing. The specific primer pair provided in the invention improves the efficiency of Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel) symbiotic bacteria (Klebsiella pneumoniae), and creates conditions for further study of the coevolution relation between Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel) and Klebsiella pneumoniae.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for quickly detecting klebsiella pneumoniae triple qPCR in respiratory tract sample
InactiveCN107058511AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesRespiratory tract diseasePneumonitis
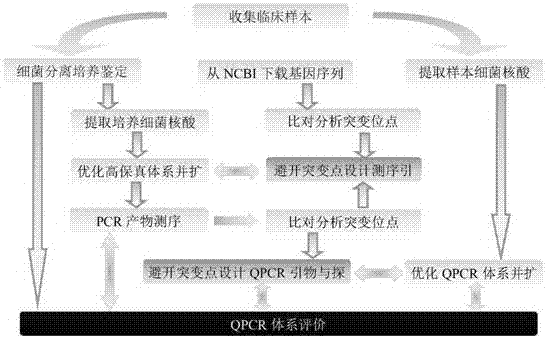
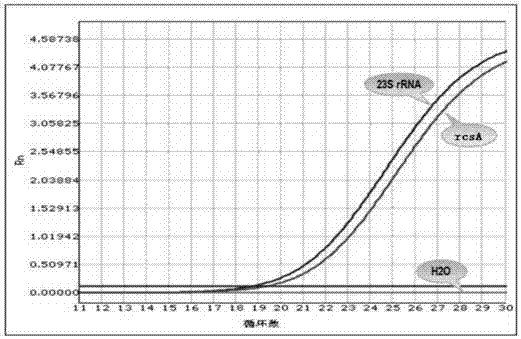
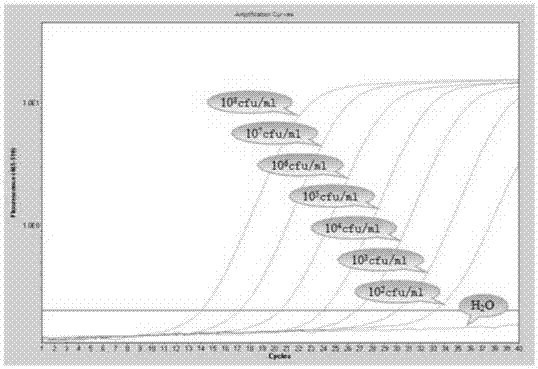
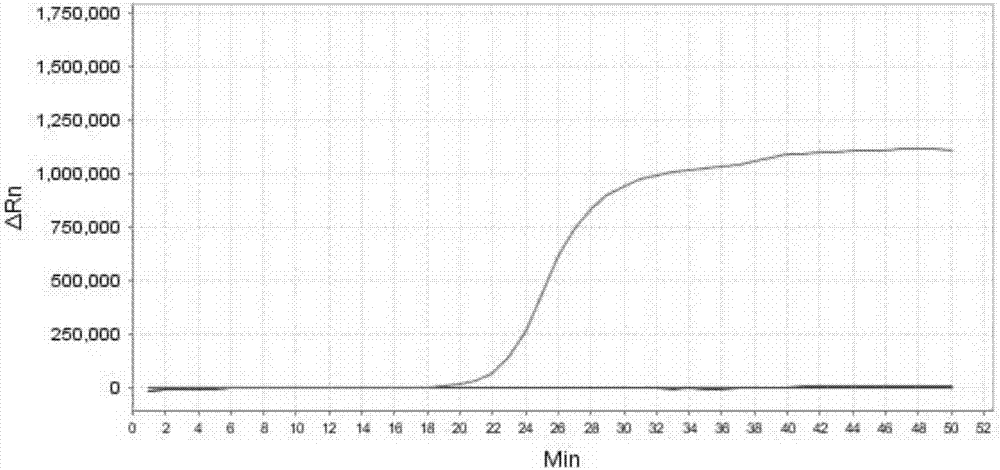
The invention provides a method for quickly detecting klebsiella pneumoniae triple qPCR in a respiratory tract sample. The method comprises the following steps: collecting and selecting a clinical respiratory tract sample; performing bacterial culture and identifying; extracting and purifying nucleic acid; constructing quality control / interior label plasmid; designing and compounding a sequencing primer; optimizing a clinical isolate high-fidelity system, amplifying and judging a result; sequencing a high-fidelity PCR product and controlling quality; designing a triple qPCR primer and a probe and compounding a marker; and optimizing a triple qPCR system, amplifying and judging the result. The method has the beneficial effects that klebsiella pneumoniae rcsA and 23s RNA housekeeping genes can be simultaneously detected, and the adopted primer and probe are designed in the manner of effectively avoiding a variation area or a mutational site according to a gene sequencing result of popular distribution strain in China; a quick sputum liquefying bactericide is added into a sputum sample, so that the sputum can be quickly liquefied, pathogenic microorganisms can be killed, and an operator can be protected from being infected; and compared with the traditional method, the method provided by the invention can reduce the time by about 1 hour and has the characteristics of simple and convenient operation, high speed, safety and sensitivity.
Owner:深圳市宝安区沙井人民医院 +1
Compound microbial agent for treating dye waste water as well as preparation and application of compound microbial agent
InactiveCN102080057AStrong broad spectrumGood decolorization and degradationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAcinetobacter haemolyticusMicroorganism
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
LAMP primer combination for detecting 8 environmental pathogens of dairy cow mastitis and application thereof
ActiveCN107541567AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesK pneumoniaeMastitis
The invention discloses an LAMP primer combination for detecting 8 environmental pathogens of dairy cow mastitis and application thereof. The primer combination provided by the invention is composed of 48 primers shown in sequence 1 to sequence 48. The primer combination provided by the invention can be used for detecting whether a to-be-detected bacterium is Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Streptococcus dysgalactiae, Streptococcus uberis, Salmonella typhimurium, Proteus mirabilis or Candida albicans, and can be used for detecting whether a to-be-detected sample contains Escherichia coli and / or Klebsiella pneumonia and / or Pseudomonas aeruginosa and / or Streptococcus dysgalactiae and / or Streptococcus uberis and / or Salmonella typhimurium and / or Proteus mirabilis and / or Candida albicans. The primer combination provided by the invention is used for identifying and detecting the 8 environmental pathogens of dairy cow mastitis, has high specificity and high sensitivity, and can realize simple, rapid and accurate detection, thus having great popularization value.
Owner:CAPITALBIO CORP
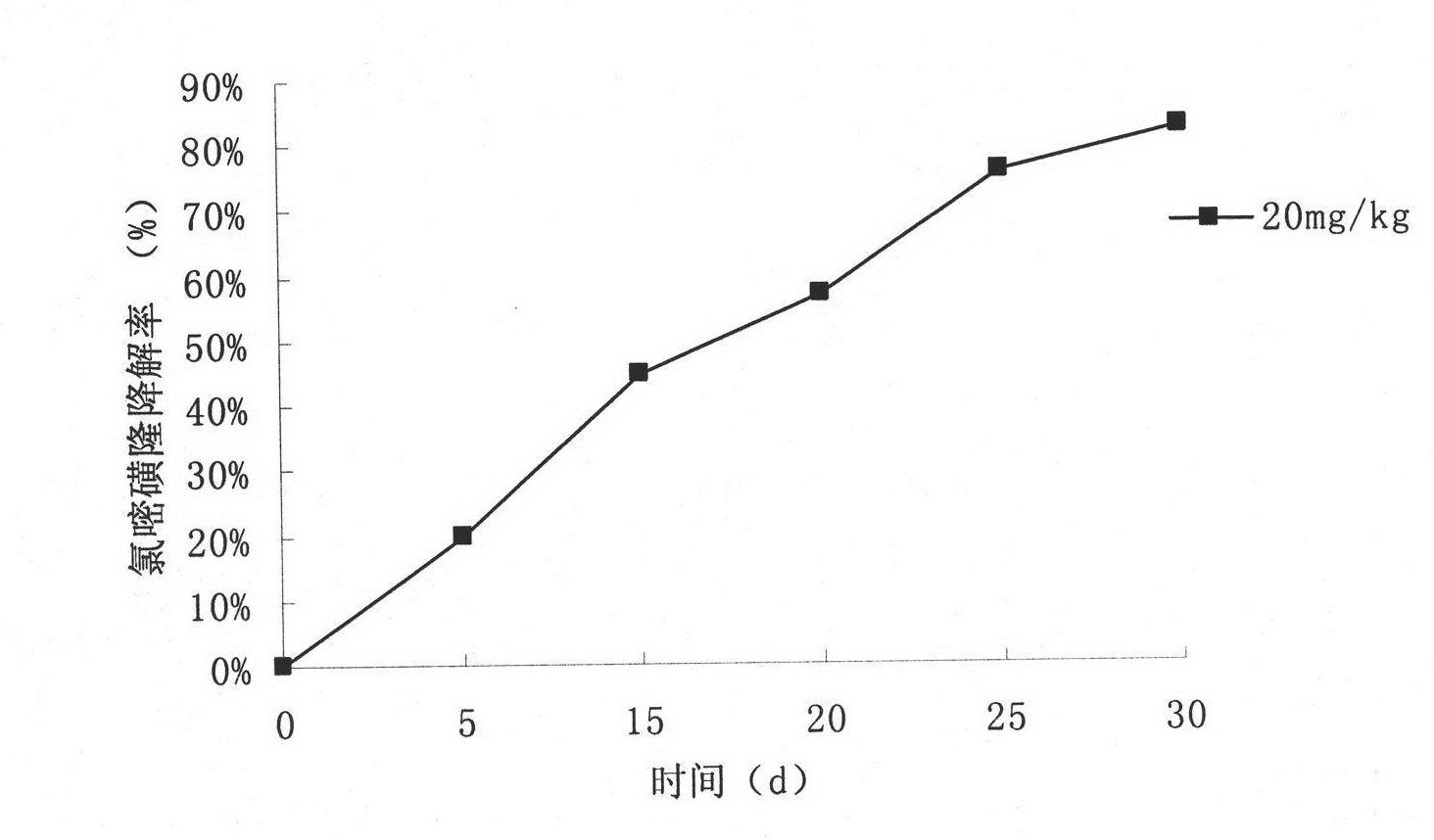
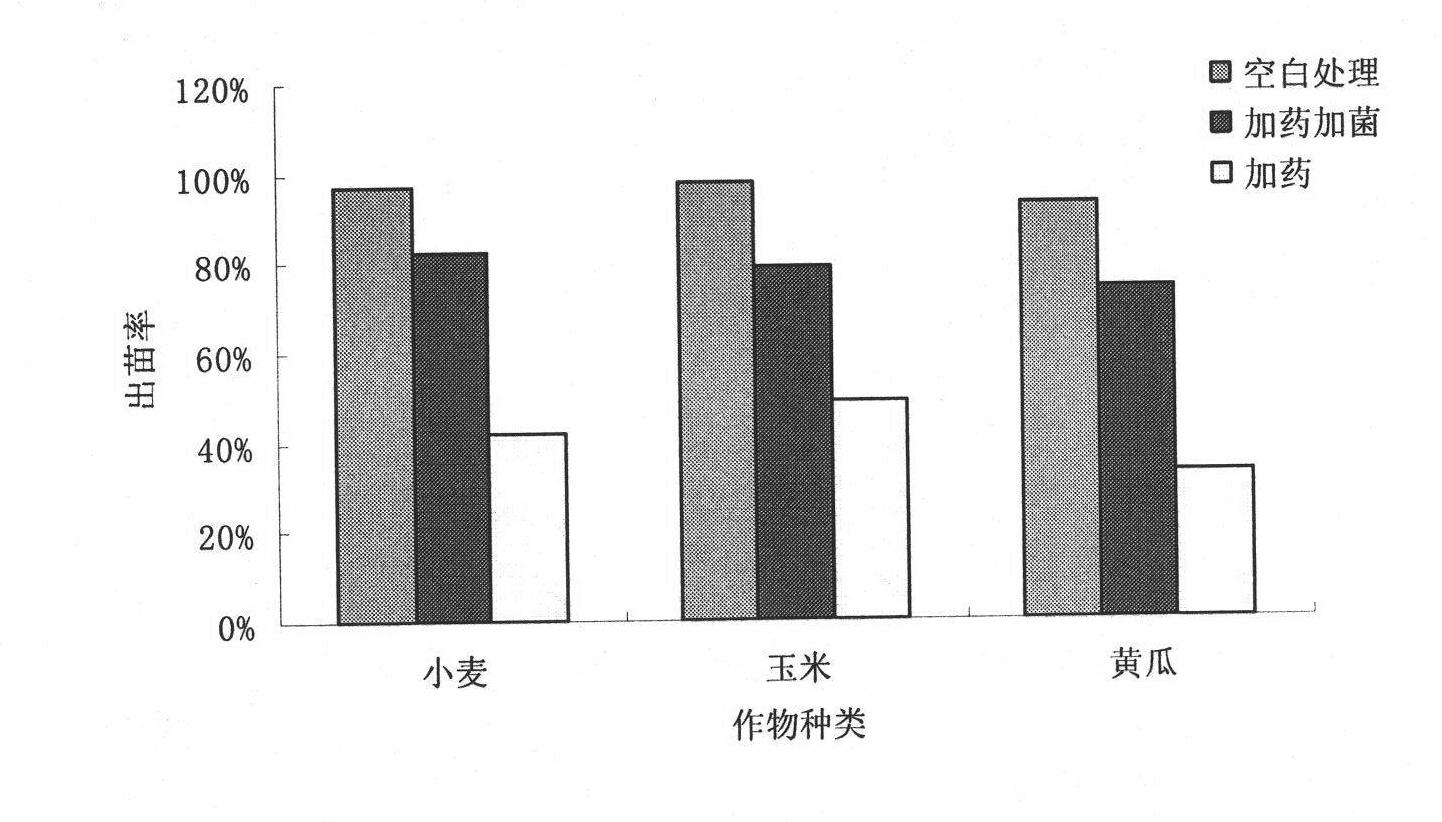
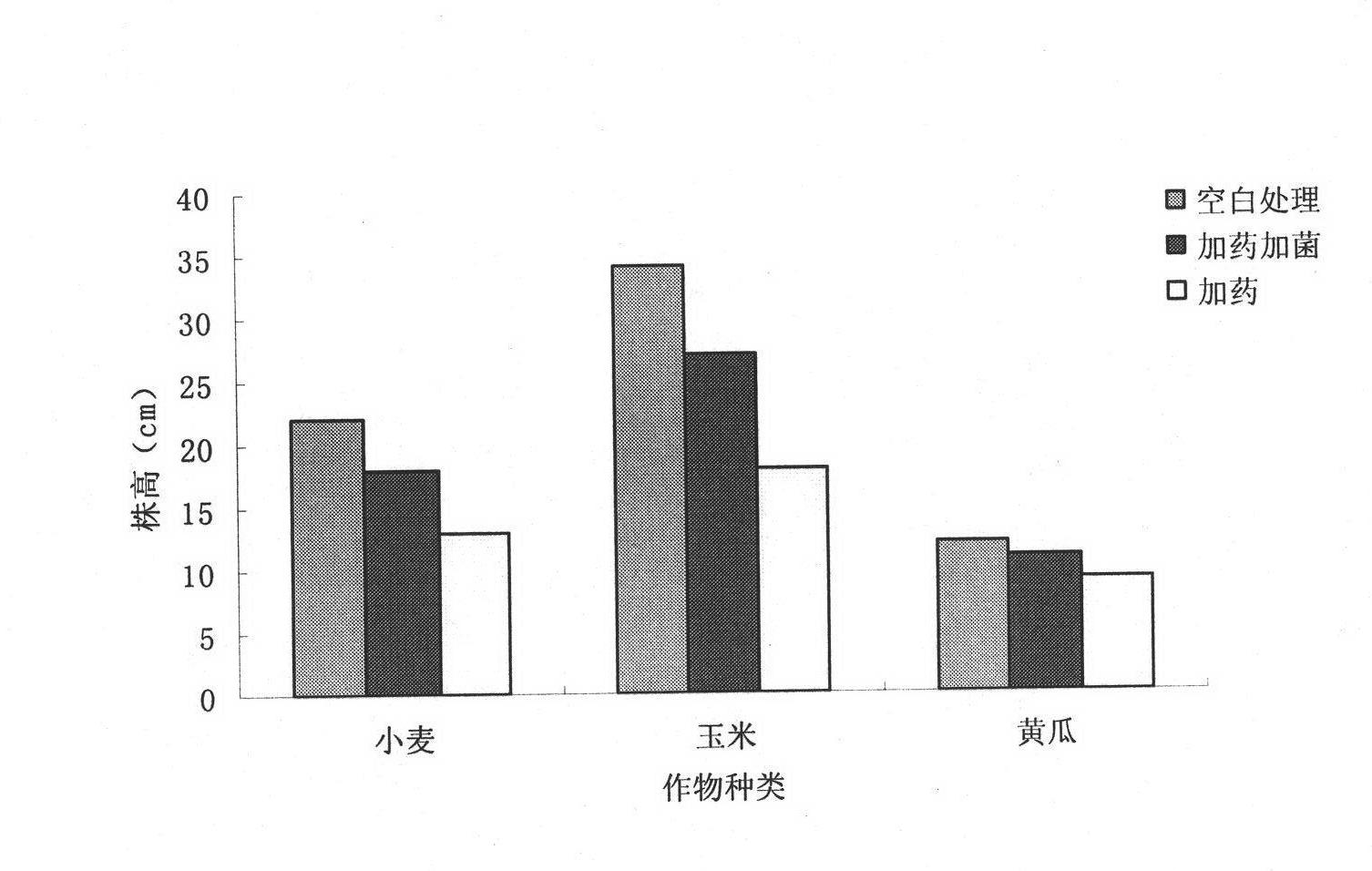
Klebsiella inoculum capable of biodegrading residual chlorpyrifos pesticide on surfaces of garden stuffs and soil
A microbial strain capable of degrading chlorpyrifos pesticide residue in soil with the chlorpyrifos pesticide residue is isolated. The microbial strain is klebsiella sp. dsp-B by identification, Genbank accession number is HQ836365, and the strain preservation number is CCTCC: NO: M2012477. The characteristic of chlorpyrifos pesticide degradation of klebsiella is utilized for development of biodegrading inoculum applicable to the surfaces of garden stuffs and soil. The klebsiella inoculum belongs to the field of microbial environment modification, and the process flow comprises: purified strain preserving, shaking culture, seeding tank enlargement culture, fermentation tank secondary enlargement, and product split charging. The inoculum is simple in preparation technology, low in production cost and easy to popularize and apply, and the application characteristic is direct spraying. The klebsiella inoculum is capable of fast effectively degrading residual chlorpyrifos pesticide on the surfaces of garden stuffs and soil, so that the exceeding standard problem of the residue is solved; and the klebsiella inoculum has direct economical value for production nontoxic nuisance-free greed agricultural products.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Heterotrophic nitrification bacterial strain
InactiveCN104152367APromote degradationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesTotal nitrogen
The invention discloses a heterotrophic nitrification bacterial strain which is named as Klebsiella sp.HLNR02 and is collected in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) in 3#, No.1 Courtyard, West Beichen Road, Chaoyang District, Beijin in October, 2013, and the collection number is CGMCC No.8397. The heterotrophic nitrification bacterial strain has the beneficial effects that the heterotrophic nitrification bacterial strain is relatively high in degradation effect on ammonia nitrogen and total nitrogen in a eutrophic water body, and a good microorganism material is provided for biological treatment on a water body polluted by ammonia nitrogen wastewater by further using the stain.
Owner:JINGGANGSHAN UNIVERSITY
Process for the biological production of 1,3-propanediol with high titer
The present invention provides an improved method for the biological production of 1,3-propanediol from a fermentable carbon source in a single microorganism. In one aspect of the present invention, an improved process for the conversion of glucose to 1,3-propanediol is achieved by the use of an E. coli transformed with the Klebsiella pneumoniae dha regulon genes dhaR, orfY, dhaT, orfX, orfW, dhaB1, dhaB2, dhaB3, and orfZ, all these genes arranged in the same genetic organization as found in wild type Klebsiella pneumoniae. In another aspect of the present invention, an improved process for the production of 1,3-propanediol from glucose using a recombinant E. coli containing genes encoding a G3PDH, a G3P phosphatase, a dehydratase, and a dehydratase reactivation factor compared to an identical process using a recombinant E. coli containing genes encoding a G3PDH, a G3P phosphatase, a dehydratase, a dehydratase reactivation factor and a 1,3-propanediol oxidoreductase (dhaT). The dramatically improved process relies on the presence in E. coli of a gene encoding a non-specific catalytic activity sufficient to convert 3-hydroxypropionaldehyde to 1,3-propanediol.
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
Method for producing 1,3-propanediol and 2,3-butanediol from raw starch material
The invention discloses a method for producing 1,3-propanediol and 2,3-butanediol from raw starch materials, including the following steps: 1) Candida krusei or Hansenula Arabitolgens Fang are inoculated into a fermentation medium with the saccharifying liquid of the raw starches as a carbon source; the yeast cells are cultured on an aerobic condition until glucose-consuming-rate is significantly reduced, and then fermented anaerobically to a glucose concentration from 5 to 10 g / L; the fermentation broth is collected and filtered to remove the yeast cells in the broth, and the resultant filtrate is glycerin fermentation broth; 2) Klebsiella, Clostridium butyricum, or Clostridium pasteurianum are inoculated into a fermentation medium in which the glycerin fermentation broth obtained from step 1) serves as a carbon source; the bacteria are fermented anaerobically for 30-32 hours, and then fermented aerobically when the production rate of 1,3-propanediol decreased obviously, and the fermentation was stopped when the concentration of glycerin is reduced to a level below 10 g / L, and finally 1,3-propanediol and 2,3-butanediol are obtained. The method of the present invention can effectively reduce production cost and increase productivity.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for treating chemical industrial sewage with klebsiella pneumoniae
InactiveCN104591406AEasy to handleNature of treatment waterBiological water/sewage treatmentBacteroidesK pneumoniae
The invention relates to a method for treating chemical industrial sewage with klebsiella pneumonia. The method comprises the following steps: arranging a bacterial carrier in a bioreactor so that klebsiella pneumoniae is adsorbed on the bacterial carrier; adding the chemical industrial sewage inside a bioreactor so that the concentration of klebsiella pneumoniae is 10.2 billion-10.8 billion per milliliter; and treating the chemical industrial sewage inside the bioreactor for 0.5-72 hours. According to the method of treating chemical industrial sewage with klebsiella pneumoniae, the organic pollutants in the chemical industrial sewage are decomposed with klebsiella pneumoniae, the chemical industrial sewage is efficiently treated and the treated drainage water can reach the industrial water standard.
Owner:苏忠
Method for preparing borneol by using microorganism separated from natural world
InactiveCN103290065AIncrease tolerance to substratesGood weather resistanceBacteriaMutant preparationBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The present invention relates to a method for preparing borneol by using a microorganism separated from natural world. The method sequentially comprises: bacterial screening and identification, bacteria induction mutation, and borneol preparation. According to the present invention, a microorganism klebsiella planticola acting on pinene is successfully separated, and plasma induction and chemical induction are performed, wherein solid culture is performed to obtain 5*10<8> cfu / g koji material, such that substrate tolerance, weathering resistance and stereoselectivity are increased, substrate tolerance concentration achieves 10%, and bornyl ester content in the produced bornyl acetate is 66-75%; and according to the method, the pinene microorganism method is adopted to produce the bornyl acetate, water vapor distillation is adopted to remove the unreacted pinene, and saponification hydrolysis is performed to prepare the borneol, such that the borneol produced by the method is close to nature borneol, the borneol content is 66-75%, quality of the borneol is higher than quality of the process product of the existing chemical method, and comprehensive cost of the method of the present invention is superior to comprehensive cost of the existing process.
Owner:ANHUI JIMIN MEDICAL TECH
Chlorimuron-ethyl degrading bacterium, soil bioremediation agent based on same, and application thereof
InactiveCN101798564ARemoval of pesticide residuesReduce manufacturing costBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationPesticide residueSludge
The invention relates to a chlorimuron-ethyl pesticide residue degrading bacterium which is named klebsiella 2N3 (Klebsiella jilinsis H.Zhang 2N3) with the storage No. of CCTCC NO: M 209248 in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC), a soil bioremediation agent prepared from the chlorimuron-ethyl pesticide residue degrading bacterium, and application thereof. The chlorimuron-ethyl pesticide residue degrading bacterium is a bacterial strain which has strong degradation capacity to chlorimuron-ethyl and is obtained by carrying out enrichment culture and separation on sludge at a drainage outlet of an insecticide factory for producing chlorimuron-ethyl, the bacterial strain grows by using the chlorimuron-ethyl as the unique nitrogen source, and the activity of the bacterium in a liquid nutrient medium is increased by the induction of the chlorimuron-ethyl so as to improve the degradation capacity to the chlorimuron-ethyl. The preparation method for the bacterium is simple, low in cost and convenient to use, and can be spread in the soil, and the degradation effect in the soil can reach 82.6 percent; therefore, the chlorimuron-ethyl pesticide residue degrading bacterium has good application prospect.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Laccase from Klebsiella pneumoniae, as well as recombinant strain and preparation method thereof
PendingCN106434579AImprove thermal stabilityGreat application potentialFungiBacteriaK pneumoniaePichia pastoris
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering of enzymes and relates to a novel laccase from Klebsiella pneumoniae and a preparation method thereof. The invention adopts the technical scheme comprising the following steps of: utilizing a molecular biology method and a gene engineering technology to obtain a plant of Klebsiella pneumoniae capable of generating the laccase by strain screening, amplifying genes of the novel laccase by a PCR technology, and then carrying out expression on the genes of the novel laccase in a bacillus subtillis expression system and a pichia pastoris expression system respectively to obtain a high-stability laccase recombinant strain of bacillus subtillis and a high-stability laccase free expression recombinant strain of pichia pastoris, thereby realizing preparation of the novel laccase. Simultaneously, the novel bacterial laccase has a better decoloring effect for azo and anthraquinone dyes.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com