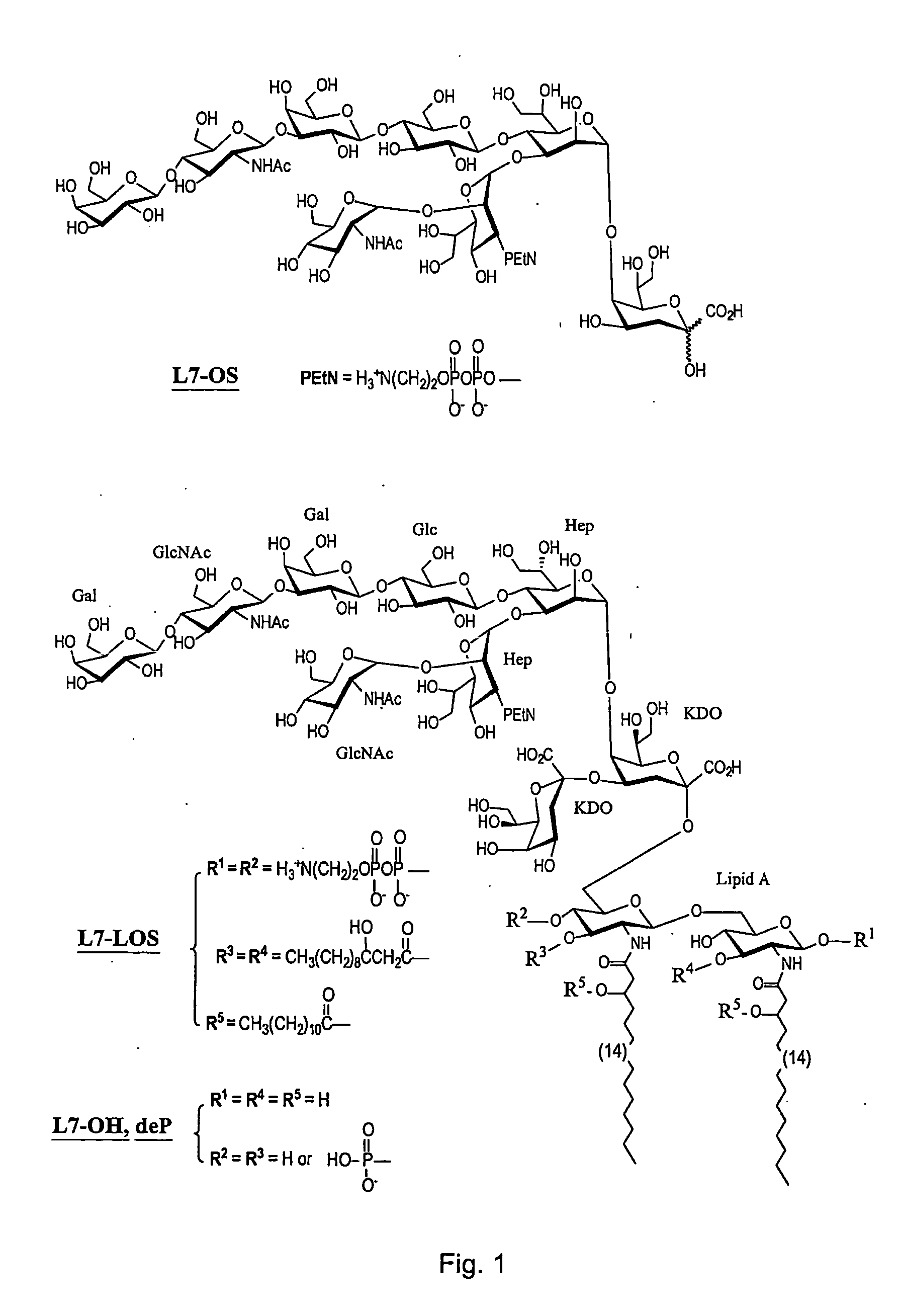
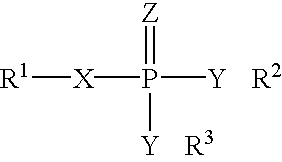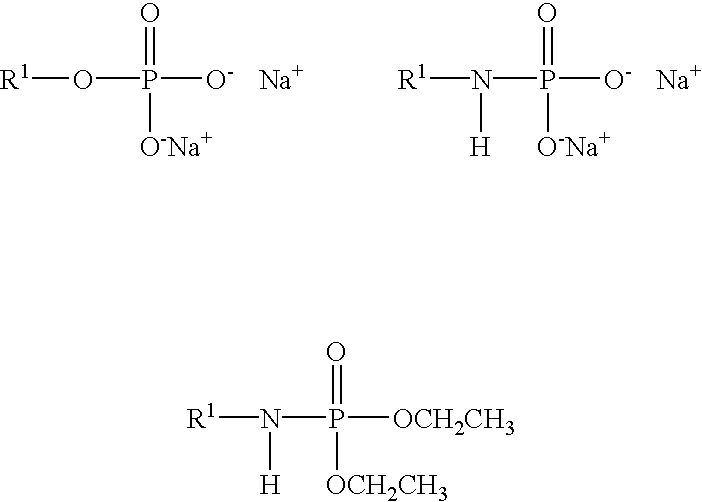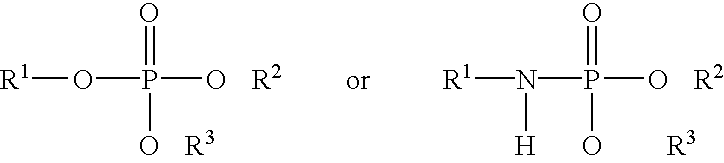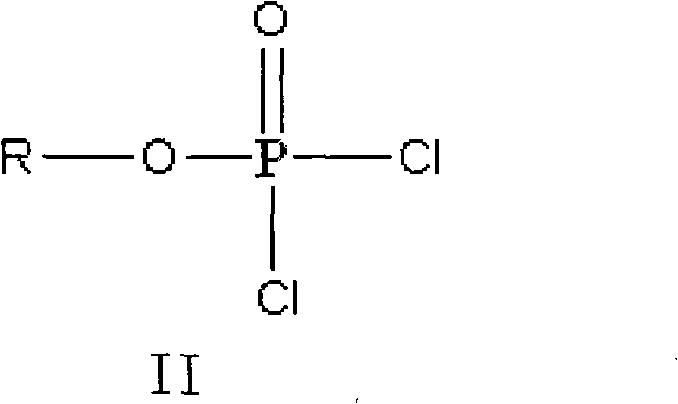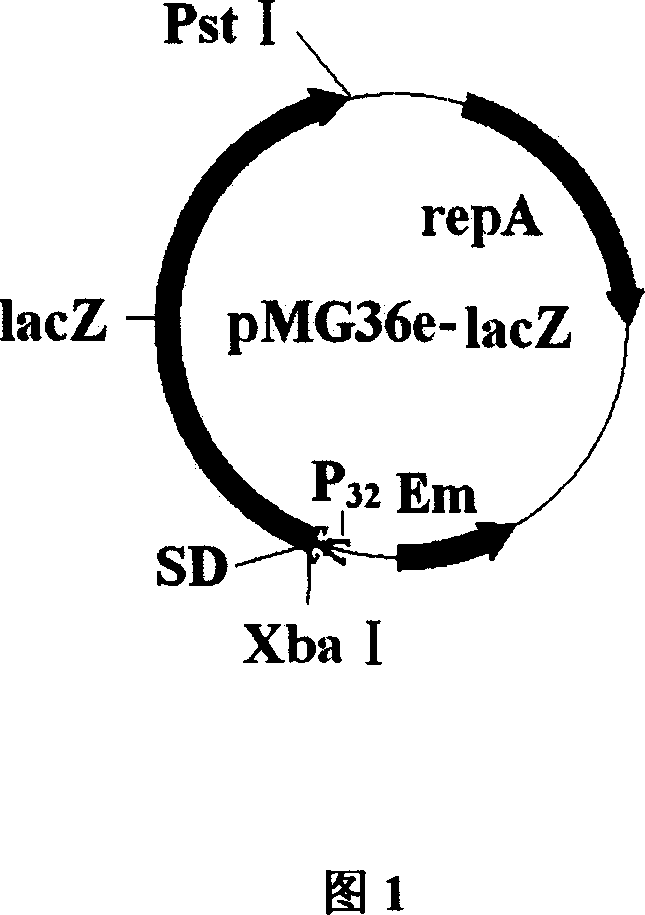Patents
Literature
231 results about "Dephosphorylation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
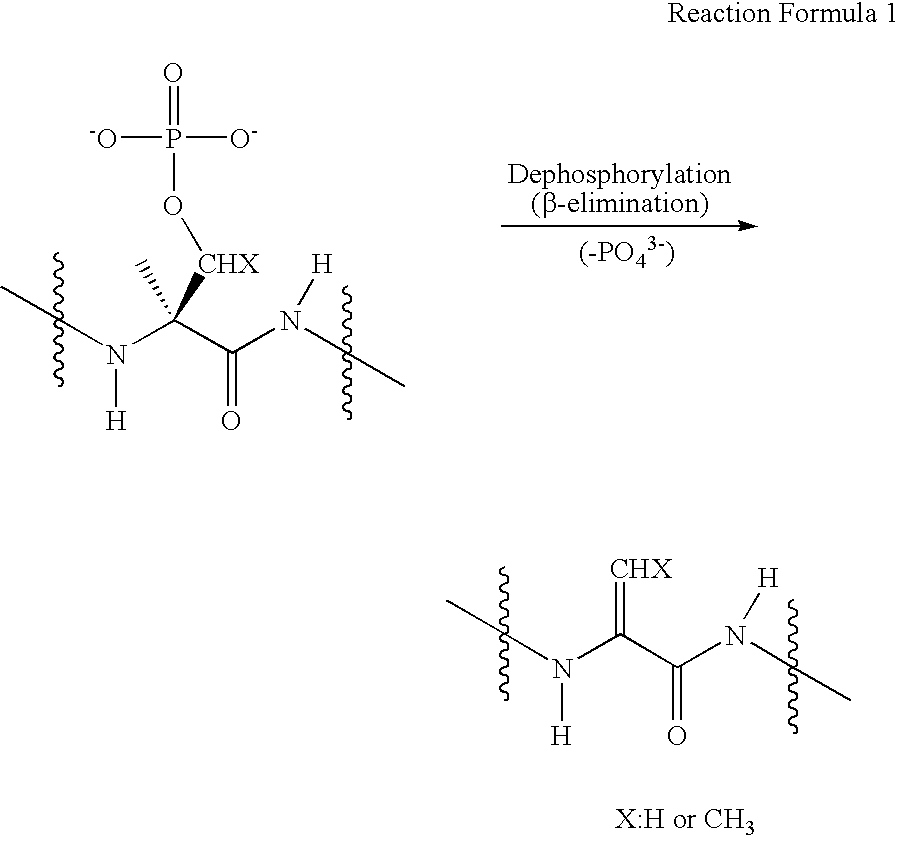
Dephosphorylation is the removal of a phosphate (PO₄³⁻) group from an organic compound by hydrolysis. It is a reversible post-translational modification. Dephosphorylation and its counterpart, phosphorylation, activate and deactivate enzymes by detaching or attaching phosphoric esters and anhydrides. A notable occurrence of dephosphorylation is the conversion of ATP to ADP and inorganic phosphate.
Compositions and methods for use in targeting vascular destruction
Treatment of warm-blooded animals having a tumor or non-malignant hypervascularation, by administering a sufficient amount of a cytotoxic agent formulated into a phosphate prodrug form having substrate specificity for microvessel phosphatases, so that microvessels are destroyed preferentially over other normal tissues, because the less cytotoxic prodrug form is converted to the highly cytotoxic dephosphorylated form.
Owner:MATEON THERAPEUTICS INC
Synthesis of lipopolysaccharide-protein conjugate vaccines via the lipid a region following removal of the glycosidic phosphate residue
InactiveUS20050147624A1Avoid bacterial infectionImproving immunogenicityBacterial antigen ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsConjugate vaccinePhosphorylation
This invention relates to lipopolysaccharide-protein conjugate vaccines with appropriate presentation of conserved inner core oligosaccharide epitopes having improved immunogenic properties. These are based upon antigenic, detoxified bacterial lipopolysaccharides which optimally present an inner core oligosaccharide epitope following removal of at least a glycosidic phosphate of the lipid A region. These partially or completely dephosphorylated antigenic, detoxified bacterial lipopolysaccharides are linkable to an immunologically acceptable carrier and can be used in polyvalent or multivalent vaccines.
Owner:THE CHANCELLOR MASTERS & SCHOLARS OF THE UNIV OF OXFORD +1
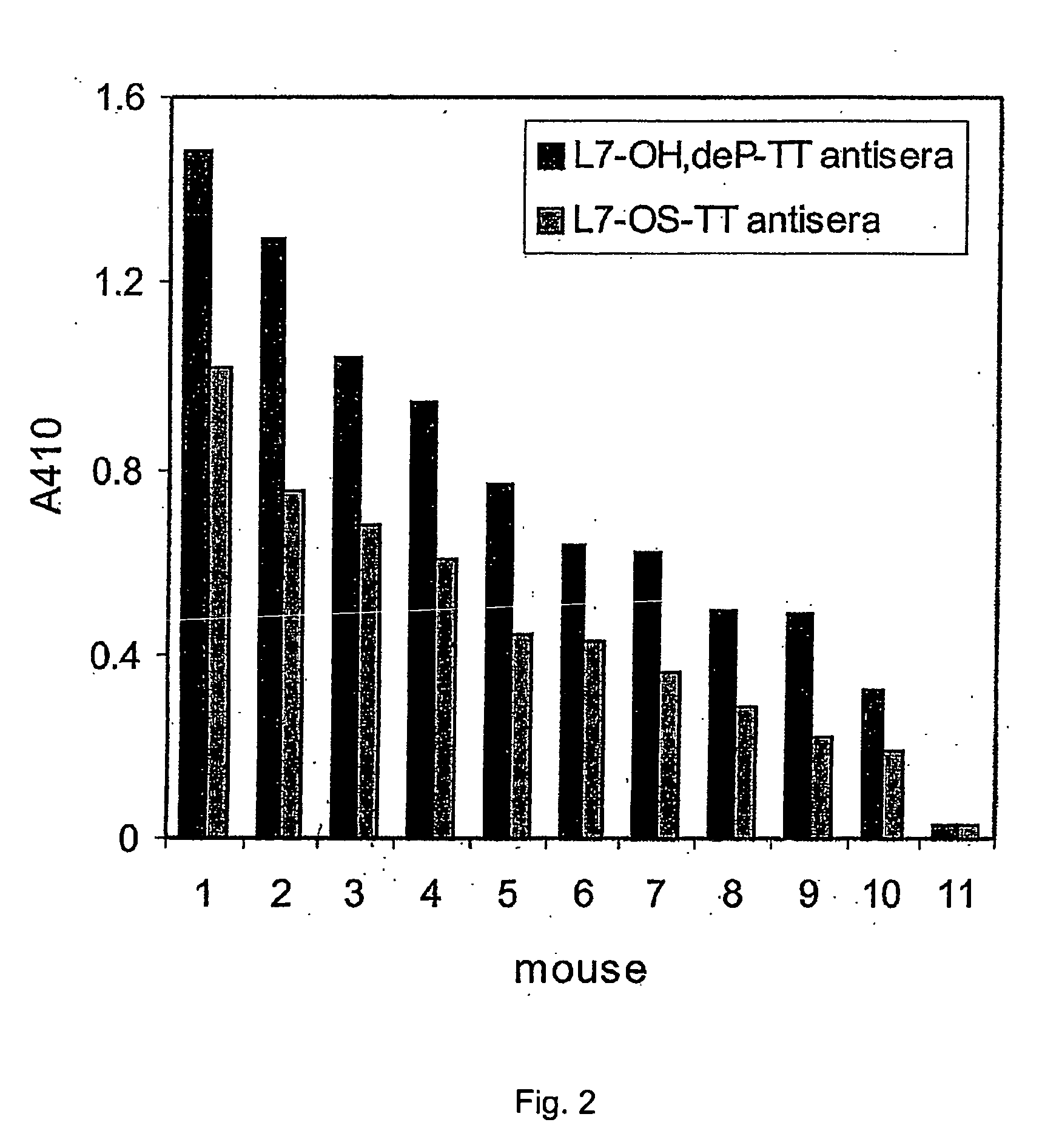
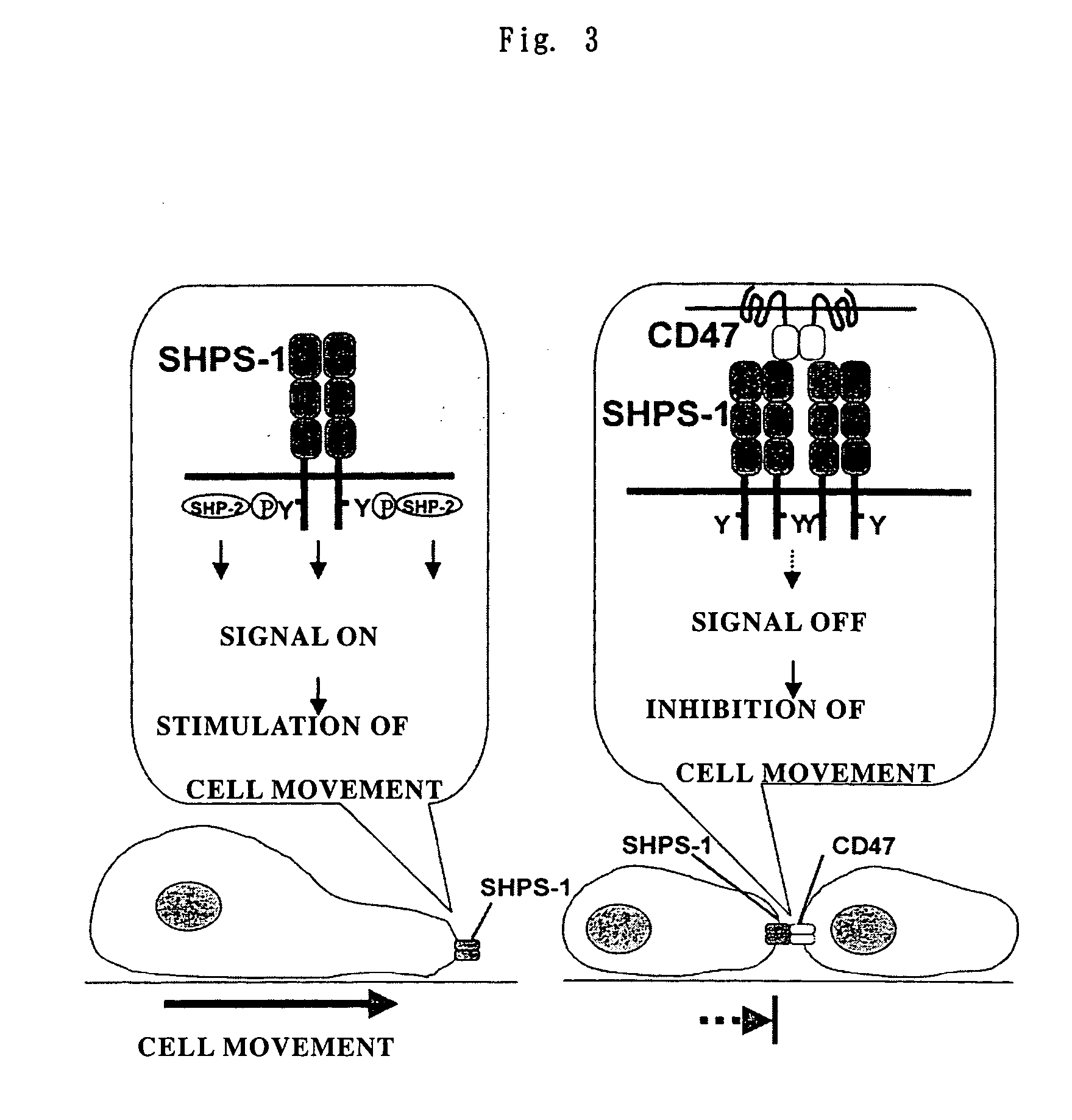
Cd47 partal peptdie and anti-shps-1 monoclonal antibody
A CD47 partial peptide which has an amino acid sequence constituting an extracellular region having an immunoglobulin-like structure of a CD47 protein, which is specifically bound to an N-terminal immunoglobulin-like structure of a dephosphorylation substrate protein SHPS-1 of an SH2 domain-containing protein, and which can act on a function of cell response mediated by SHPS-1, and an anti-SHPS-1 monoclonal antibody.
Owner:GUNMA UNIVERSITY
Method for connecting DNA molecule fragment with carrier and application thereof in construction of high-capacity antibody library
InactiveCN101619323AEfficient connectionImprove connection efficiencyVector-based foreign material introductionProtein nucleotide librariesRestriction Enzyme Cut SiteAgricultural science
The invention discloses a method for connecting a DNA molecule fragment with a carrier. The carrier comprises at least three different restriction enzyme cutting sites E1, E2 and E3, wherein the E2 is located between the E1 and E3; the DNA molecule fragment to be connected at least comprises the restriction enzyme cutting sites E1 and E3. The method comprises the following steps: firstly carrying out enzyme cutting and dephosphorylation on the restriction enzyme cutting sites E1 and E2 of the carrier; and then carrying out a first step of the enzyme cutting and connection on the restriction enzyme cutting site E1 of the DNA molecule fragment to obtain a linear connection product of the DNA molecule fragment and the carrier, and then recycling the connection product with a correct size; finally carrying out a second step of the enzyme cutting and connection on the restriction enzyme cutting site E3 of the connection product to obtain a self-connected annular connection product. The invention can realize the effective connection between the DNA molecule fragment and the carrier, so that the generation of incorrect connected polymers with different forms is reduced, the proportion of the correct connected product accounts for over 30% in the connection system so as to realize an efficient electro-transformation.
Owner:INST OF BIOENG ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE CHINESE
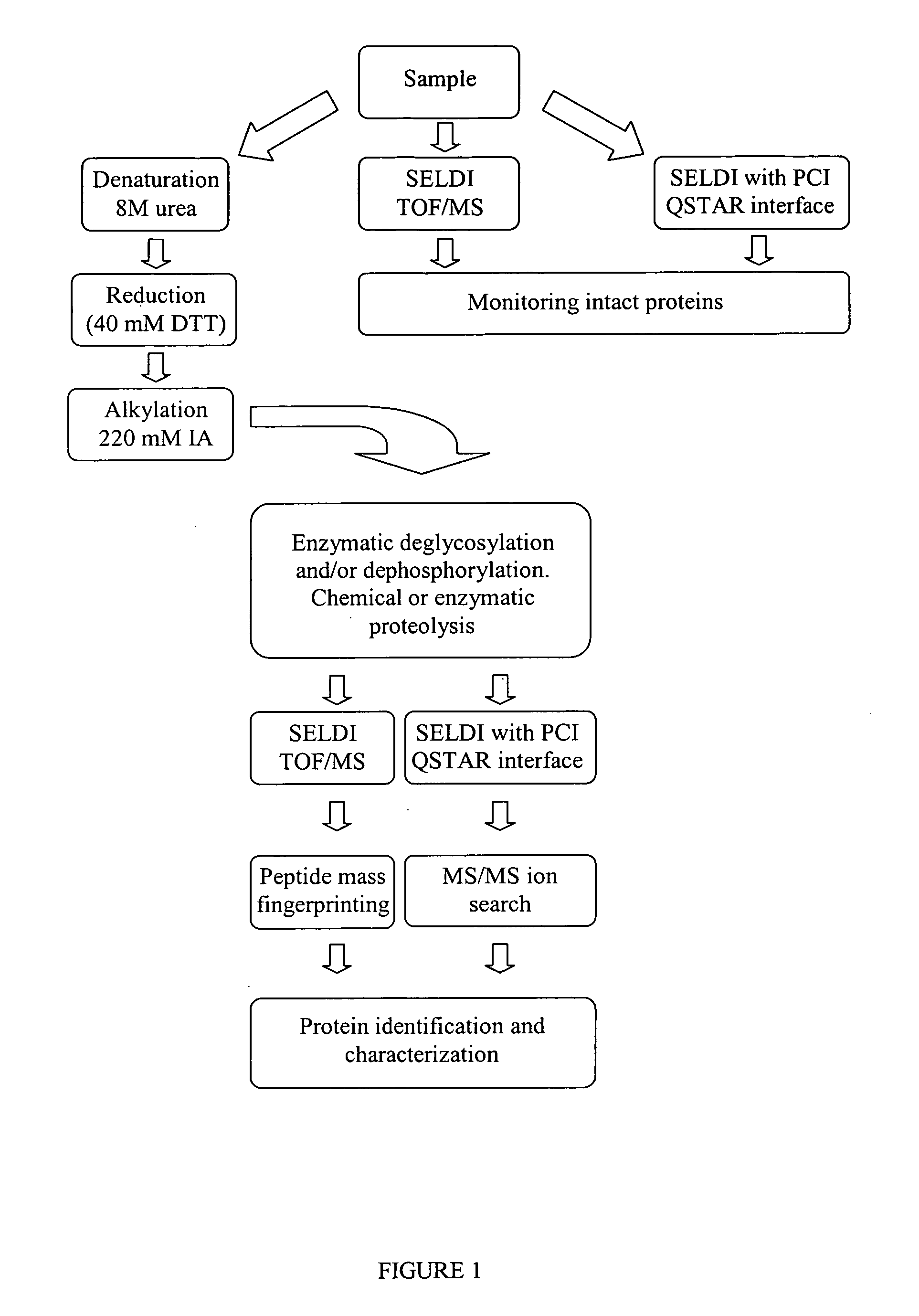
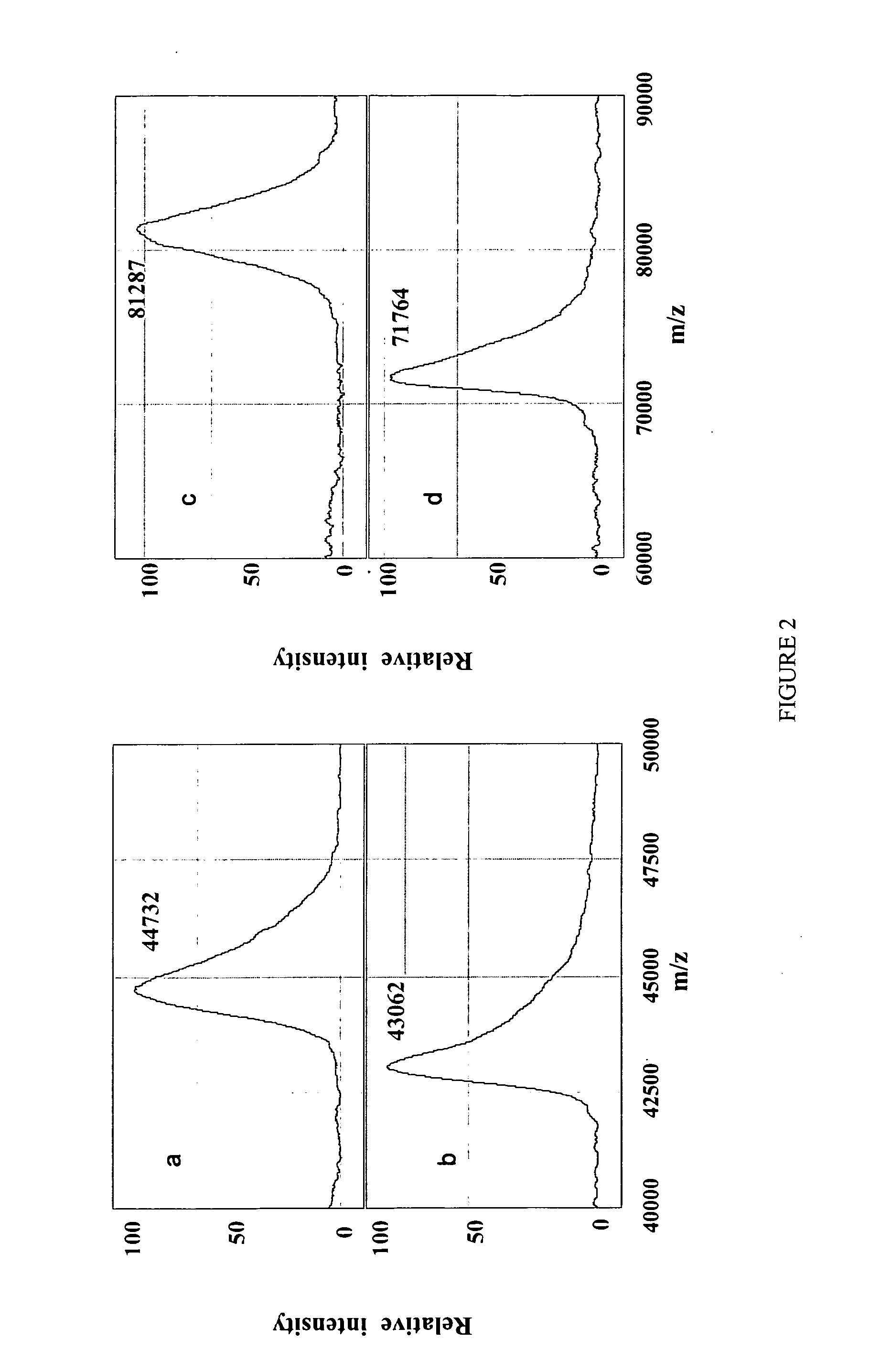
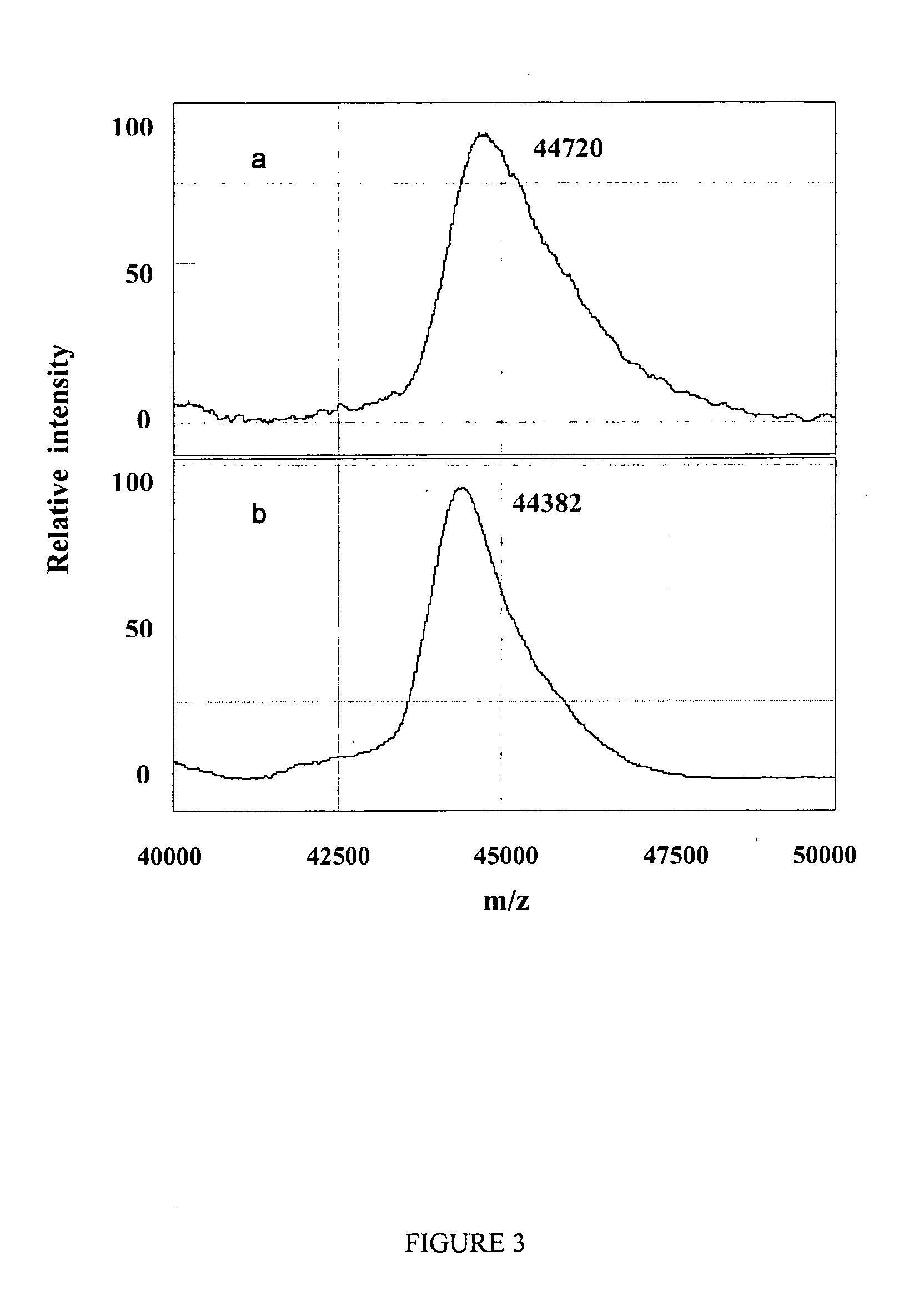
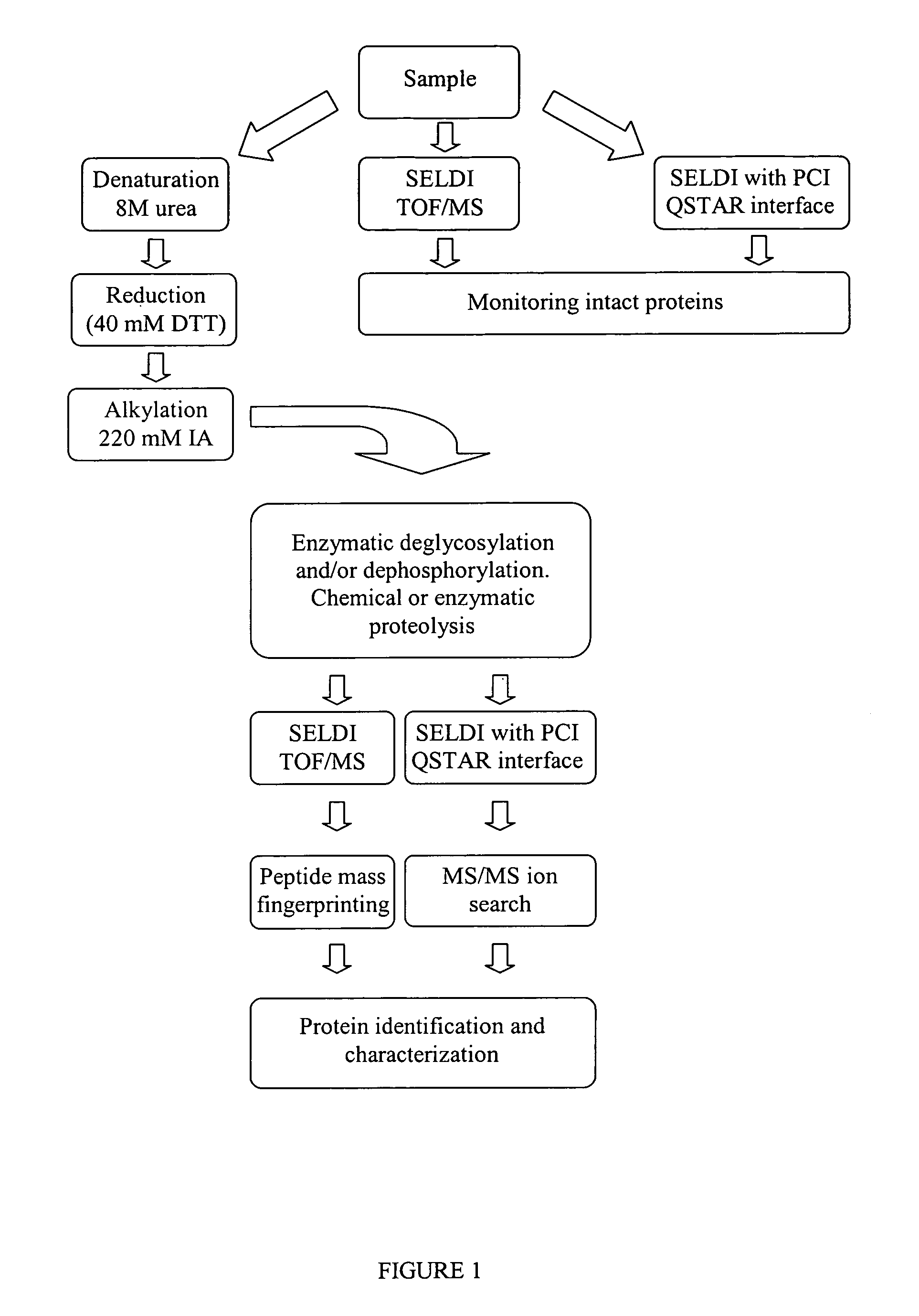
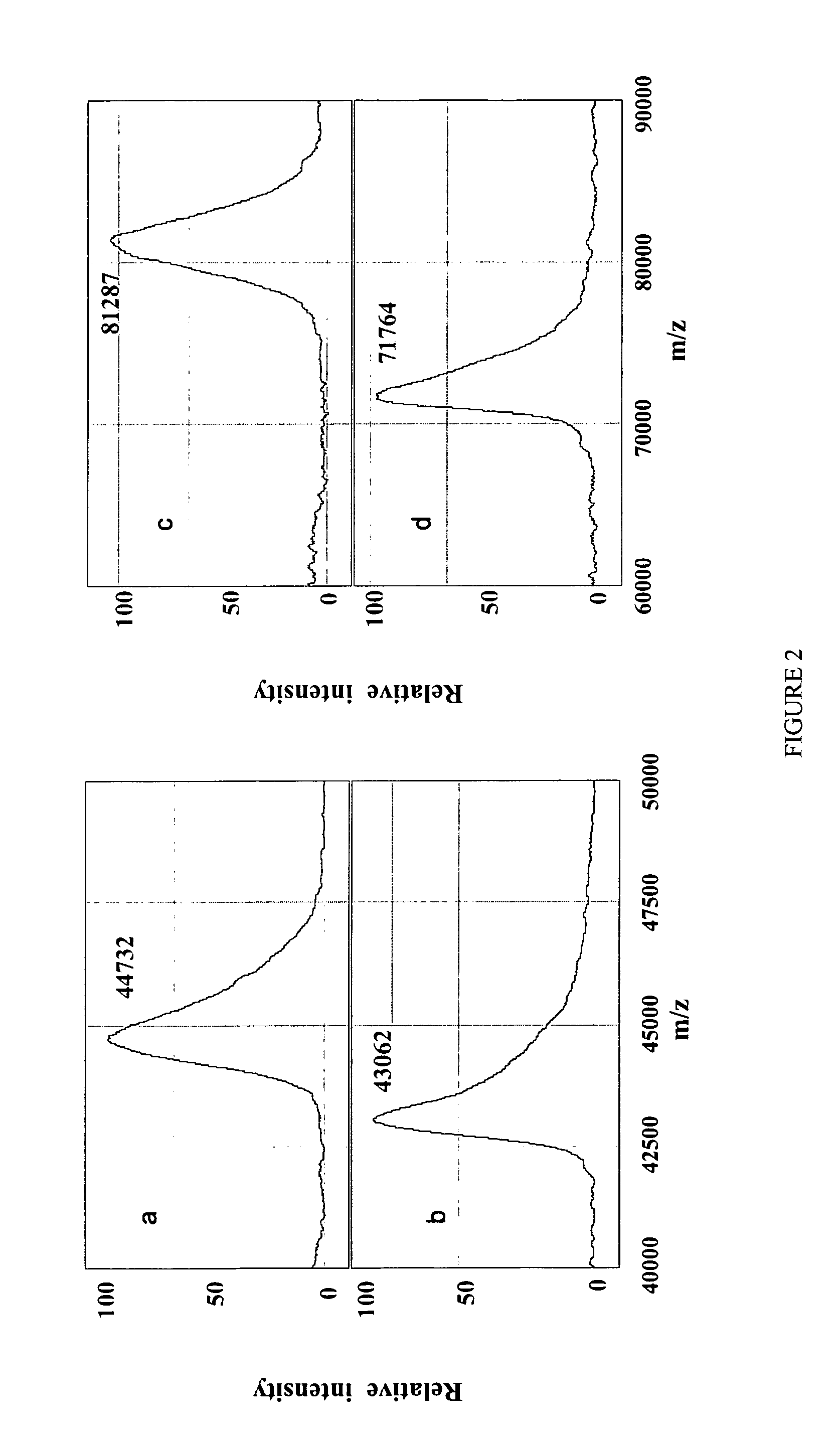
Complete chemical and enzymatic treatment of phosphorylated and glycosylated proteins on protein chip arrays
InactiveUS20060269980A1Quick upgradeSimpler, more sensitive methodologiesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisEnzymatic digestionChemical treatment
A simple and quick protocol for chemical treatment, enzymatic or chemical digestion, and subsequent identification of proteins on protein chip arrays is disclosed, together with kits therefor. The chemical treatment comprises denaturation, reduction and alkylation while enzymatic digestion encompasses deglycosylation, dephosphorylation, and digestion by various proteases. Digestion is also accomplished by various chemicals that are known to induce proteolysis. All reactions are carried out sequentially on chip. Subsequent peptide mass fingerprinting or product ion searches allow the identification of specific peptides which can be correlated to proteins. The method of the present invention can be applied to the analysis of biological samples such as urine and plasma to identify biomarkers in diseased states. The methods of the present invention allow complete on chip treatment, which can be used for rapid protein identification and structural characterization of heavily posttranslationally modified proteins.
Owner:GIBBS BERNARD F
Construction method of genome presumptive area nucleic acid sequencing library and device thereof
ActiveCN105624272ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEnzyme digestionGenomic DNA
The invention discloses a construction method of a genome presumptive area nucleic acid sequencing library and a device thereof. The method comprises the following steps: genomic DNA undergoes fragmentation treatment; DNA fragment undergoes fragment selection; the DNA fragment which has undergone fragment selection successively undergoes dephosphorylation, first end repairing and connection with first sequencing linker; a first connection product is screened by a probe; target fragment successively undergoes double-strands cyclization treatment and enzyme digestion; and an enzyme digestion product successively undergoes second end repairing, connection with second sequencing linker and DNA double-strands separation treatment so as to obtain single-stranded DNA which forms a genome presumptive area sequencing library, wherein the probe satisfies at least one condition selected from ten conditions. The probe has good specificity, high sensitivity and coverage in the aspect of target enrichment. By the method, the sequencing library for SNP enrichment detection can be effectively constructed.
Owner:BGI SHENZHEN CO LTD
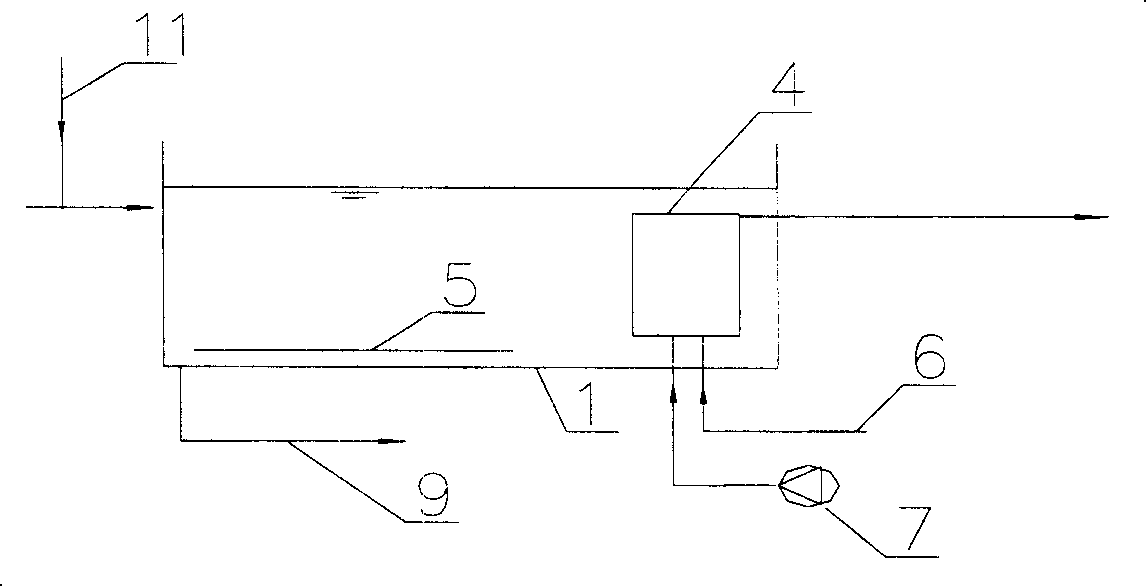
Sewage denitrogenation dephosphorylation treatment method by using biological film to filter
InactiveCN101168461ALow costEasy to operateSustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentSludgePhosphor
The invention relates to a sewage denitrification dephosphorization treatment method which uses biologic film to filter, wherein the invention arranges a biologic film filter in an aeration tank, which uses stainless steel or filter cloth as screen to replace traditional two deposit tanks to separate sludge and water. The invention is characterized in that the average aperture of stainless steel or filter cloth screen of the biologic film filter is 10-200mum, the screen is arranged with a biologic film to stop active sludge, the water flux at unit screen can reach more than 100l / h.m2, the highest filter resistance is controlled under 0.5m, the sludge of aeration tank can reach at least 2-3 times of general one, and the phosphor in the outlet water filtered by the biologic film filter is flocculated and deposited to reach denitrification and dephosphorization demands, the resistance of biologic filter is increased when serves some time, while the water flux is reduced, and the biologic film filter can come back to normal running after being blown reversely and washed reversely via a water pump.
Owner:SHANGHAI MUNICIPAL ENG DESIGN INST GRP
Selective labeling agent for phosphoproteome analysis and phosphorylated site analysis
InactiveUS20050176093A1High detection sensitivityOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsPhosphopeptideSlurry
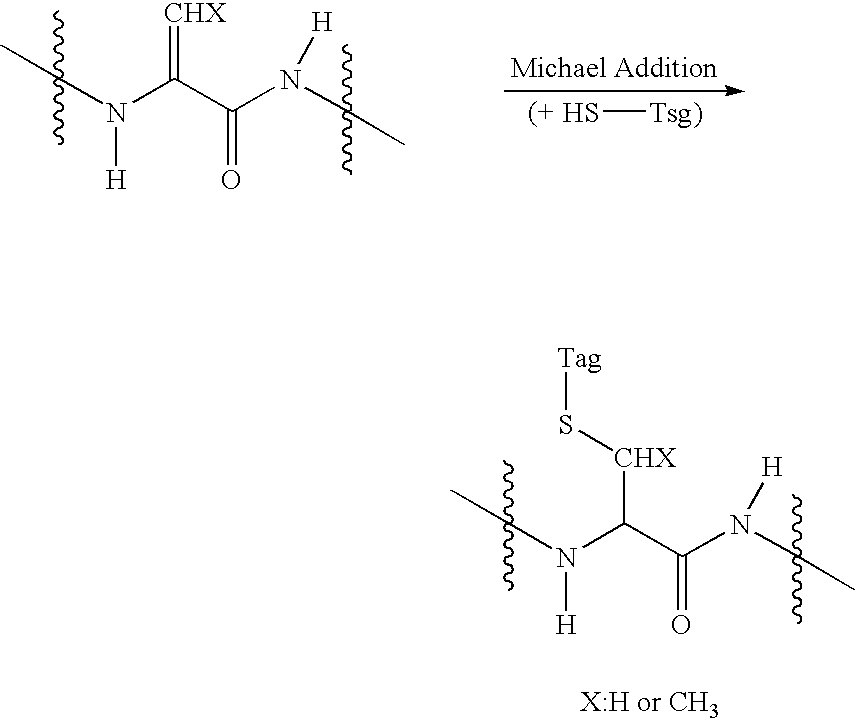
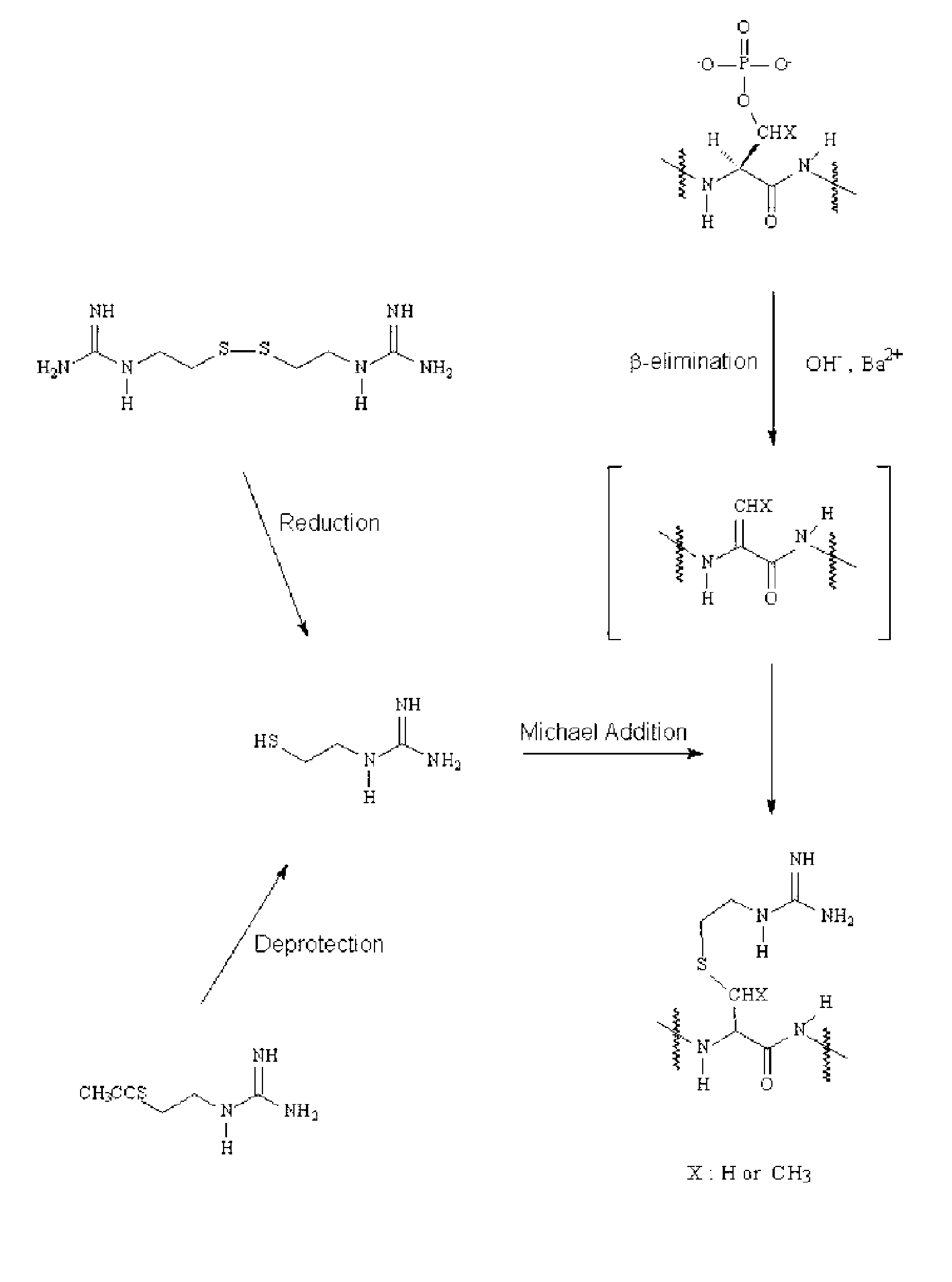
Disclosed is a method of analyzing mass of the phosphoproteins or phosphopeptides and of analyzing phosphorylated positions at a phosphoprotein or phosphopeptide, comprising the steps of: 1) dephosphorylating at least one Ser and / or Thr residue of the phosphoprotein or phosphopeptide; 2) tagging the dephosphorylated amino acid residues with a tag having a R-L-G moiety wherein R is a nucleophilic functional group that selectively bind with dephosphorylated amino acid residues, G is selected from the group consisting of guanidine moiety or protected guanidine moiety such as a mono-N-protected guanidino group, a di-N,N′-protected guanidino group and an N′-protected guanidino group, and L is a linker linking the R and the G; and 3) subjecting the tagged proteins or peptides to mass spectrometry. The method is capable of precisely analyzing mass of phosphoproteins of trace amounts as well as positions of phosphoryated amino acids.
Owner:KOREA BASIC SCI INST
Kit for detecting alkaline phosphatase and method thereof
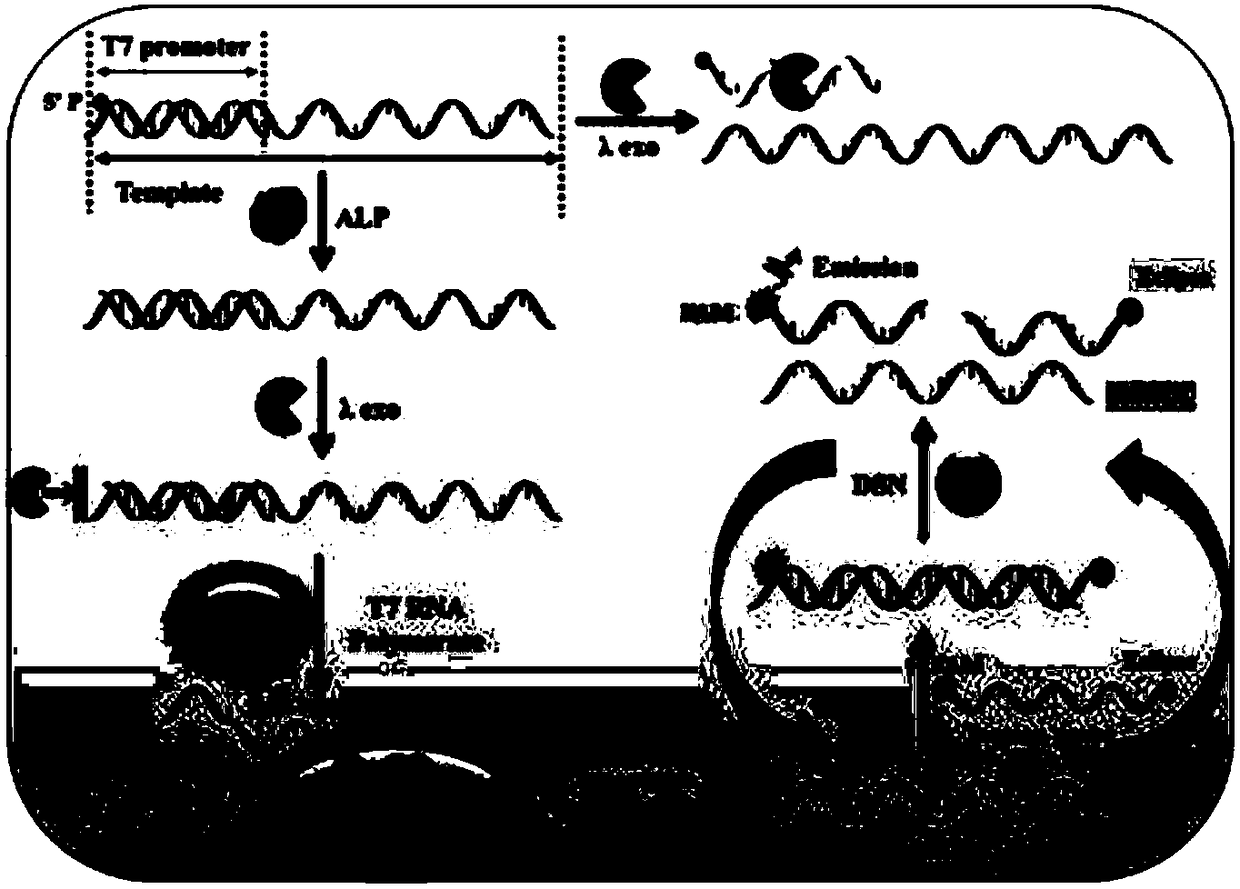
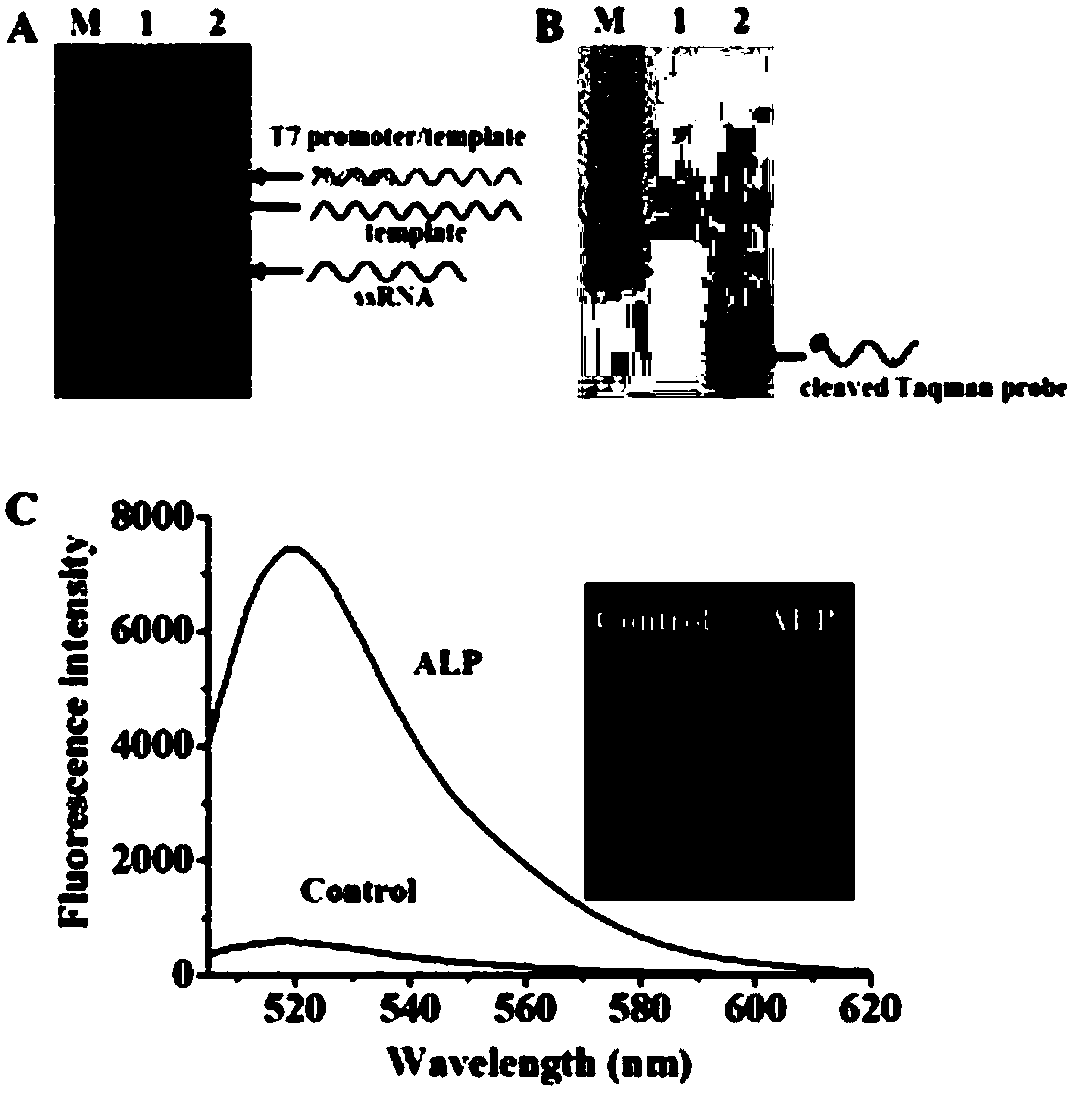
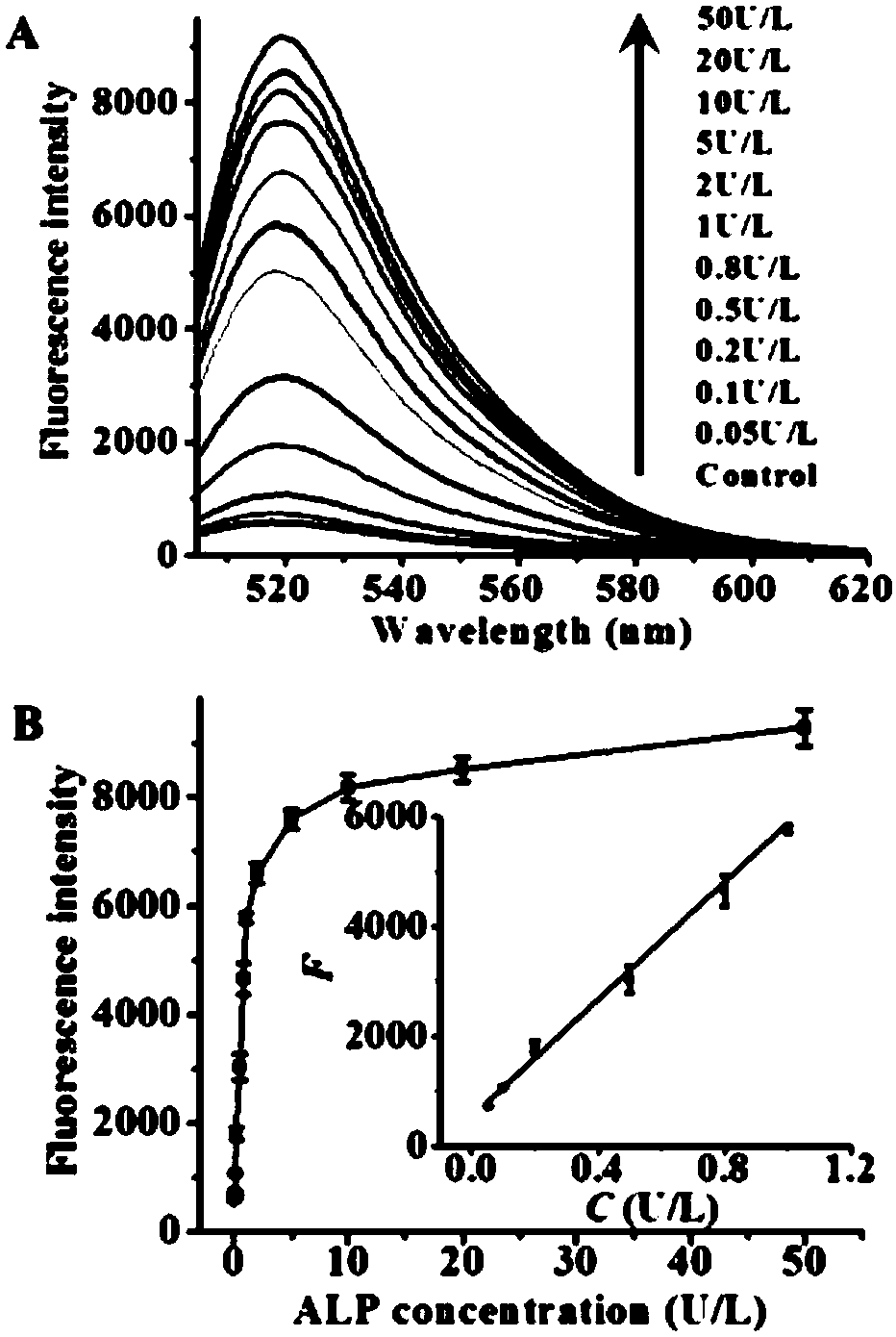
ActiveCN108588178AAvoid design complexityInhibit synthesisMicrobiological testing/measurementT7 RNA polymeraseFluorescence
The invention relates to a method for sensitively detecting alkaline phosphatase by double-signal amplification mediated by a transcription reaction initiated by dephosphorylation. The method comprises the steps that a 5'-phosphorylated T7 promoter single chain is designed, alkaline phosphatase can catalyze 5'-phosphorylated T7 promoter to be dephosphorylated to protect the T7 promoter chain frombeing digested by Lambada exonuclease, the remaining T7 promoter can activate transcription reaction mediated by T7 RNA polymerase, and thus a large number of RNA transcripts are produced; and subsequently, the RNA transcripts complement and pair with Taqman probes to form a RNA-DNA duplex, duplex-specific nucleases is introduced to initiate circular cutting of the Taqman probes, and a significantly enhanced fluorescence signal is produced. The method is simple and convenient to operate, has high sensitivity and high specificity, and can be applied to the screening of target inhibitors in complex biological samples and the quantitative detection of targets in cervical cancer cells.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
DSP-10 dual-specificity phosphatase
Compositions and methods are provided for the treatment of conditions associated with cell proliferation, cell differentiation and cell survival. In particular, the dual-specificity phosphatase DSP-10, and polypeptide variants thereof that stimulate dephosphorylation of DSP-10 substrates, are provided. The polypeptides may be used, for example, to identify antibodies and other agents that inhibit DSP-10 activity. The polypeptides and agents may be used to modulate cell proliferation, differentiation and survival.
Owner:CEPTYR
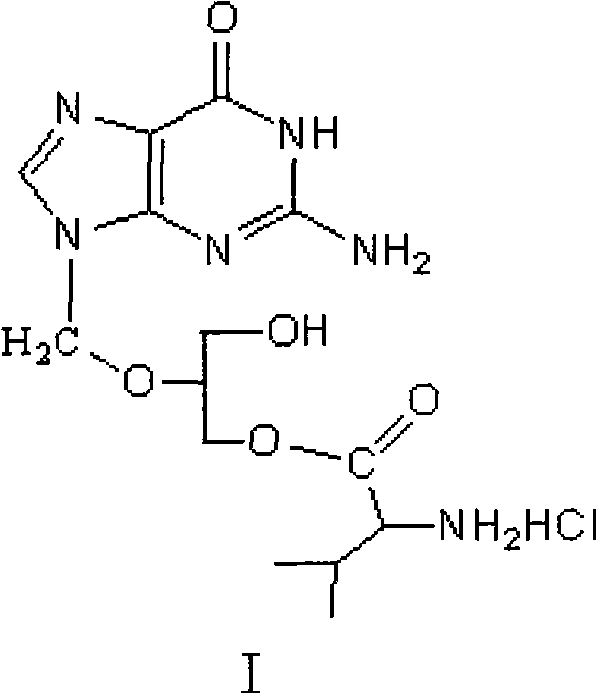
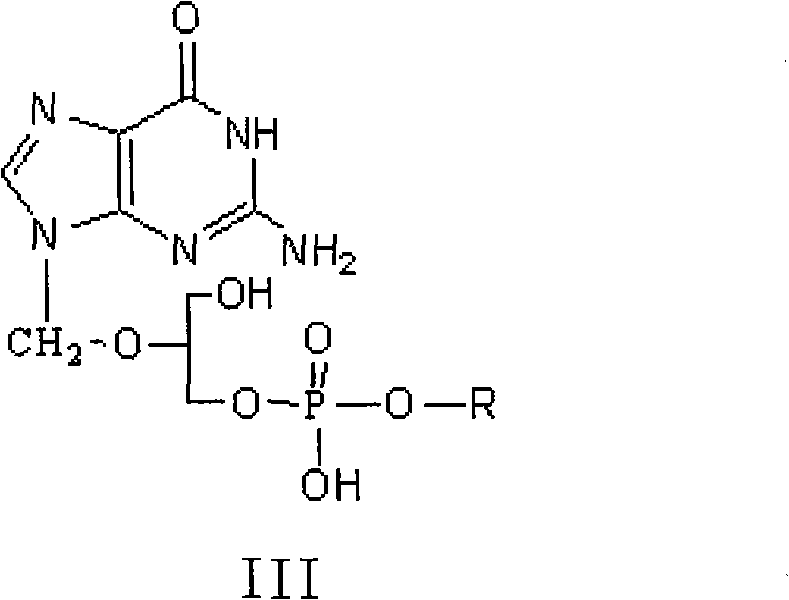
Method for preparing valganciclovir hydrochloride
InactiveCN101955481AEnhanced steric effectHigh yieldOrganic chemistryValganciclovir HydrochlorideHydrogenation reaction
The invention discloses a method for preparing valganciclovir hydrochloride I. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, dissolving phosphorus oxychloride into an inert solvent, and performing a reaction of the mixture and the alcoholic liquor to obtain phosphoryl halide II; 2, performing a reaction of ganciclovir and the phosphoryl halide II obtained in the step to obtain ganciclovir monoester III; 3, esterfying the ganciclovir monoester III in the step 2 and N-carbobenzoxy-L-valine to obtain ganciclovir diester IV; 4, acidizing the ganciclovir diester IV in the step 3 for dephosphorylation to obtain N-carbobenzoxy-L-valine ganciclovir monoester V; and 5, performing a hydrogenation reaction on the product in the step 4 to prepare the valganciclovir hydrochloride I. By the method, the ganciclovir monoester with high purity and yield can be produced, the post-processing is easy, and the post-processing difficulty is reduced.
Owner:STAR LAKE BIOSCI CO INC ZHAOQING GUANGDONG
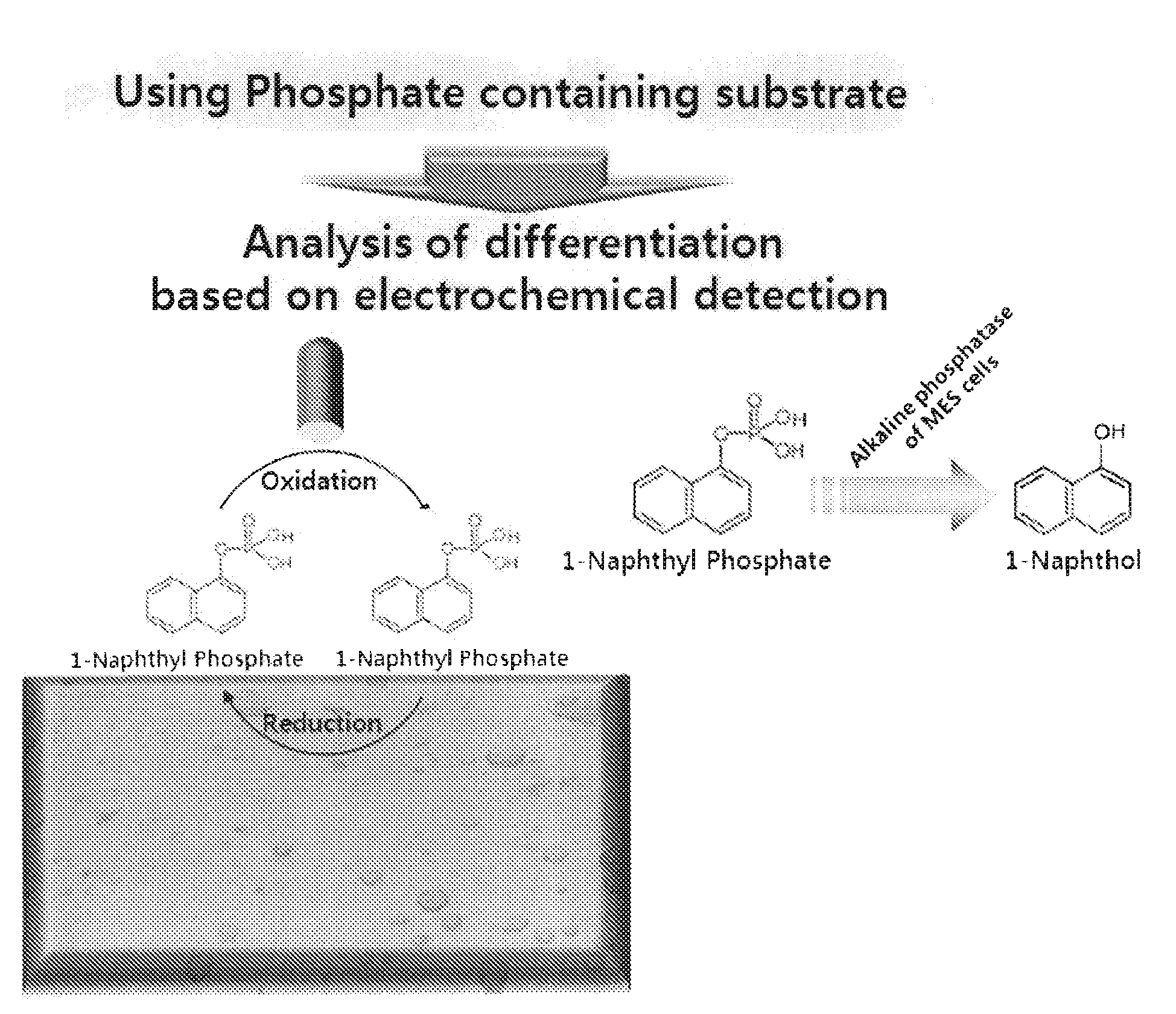
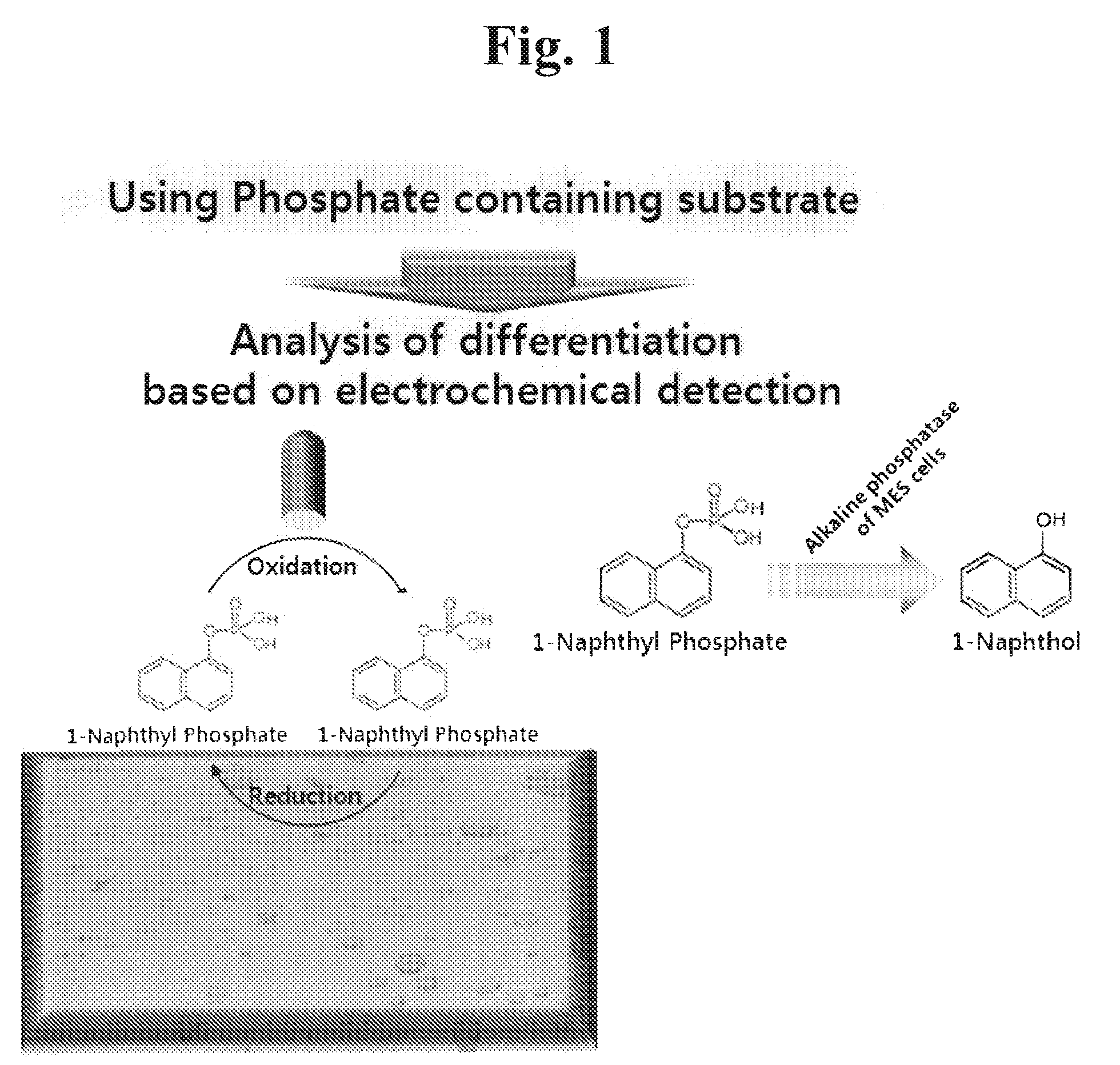
Sensor for detecting stem cell differentiation based on electrochemical methods
InactiveUS20100243479A1Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsPhosphorylationAbnormal alkaline phosphatase
This invention relates to a sensor for detecting a stem cell differentiation, including (a) an electrode; and (b) a substrate of an alkaline phosphatase. The phosphorylation or dephosphorylation of the substrate for an alkaline phosphatase as a stem cell undifferentiation marker which dephosphorylates its substrate may be measured using an electrical signal in the present sensor. Therefore, the sensor of the present invention enables to electrically detect a stem cell status in a high-throughput manner and to determine the stem cell differentiation.
Owner:IND UNIV COOP FOUND SOGANG UNIV
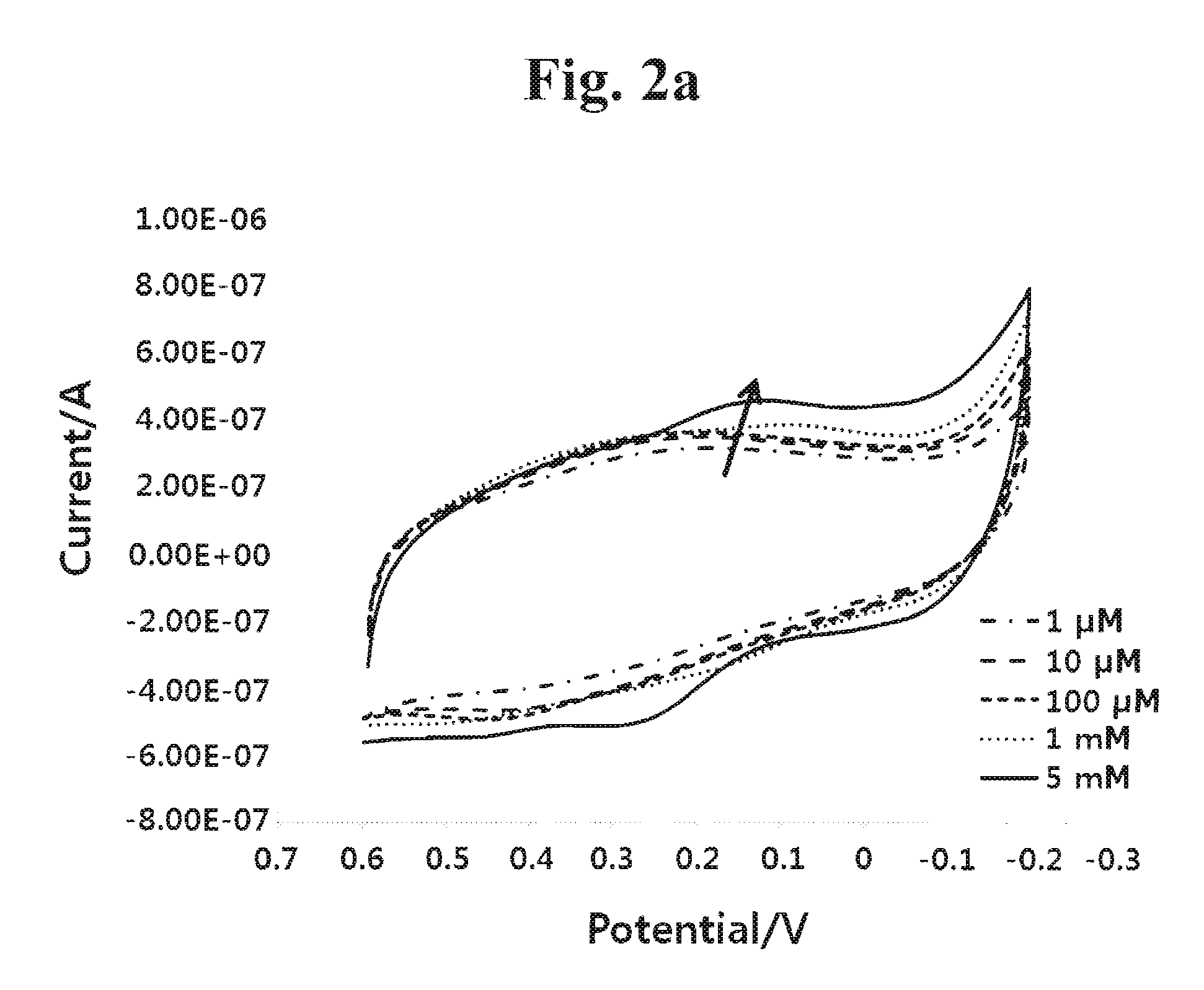
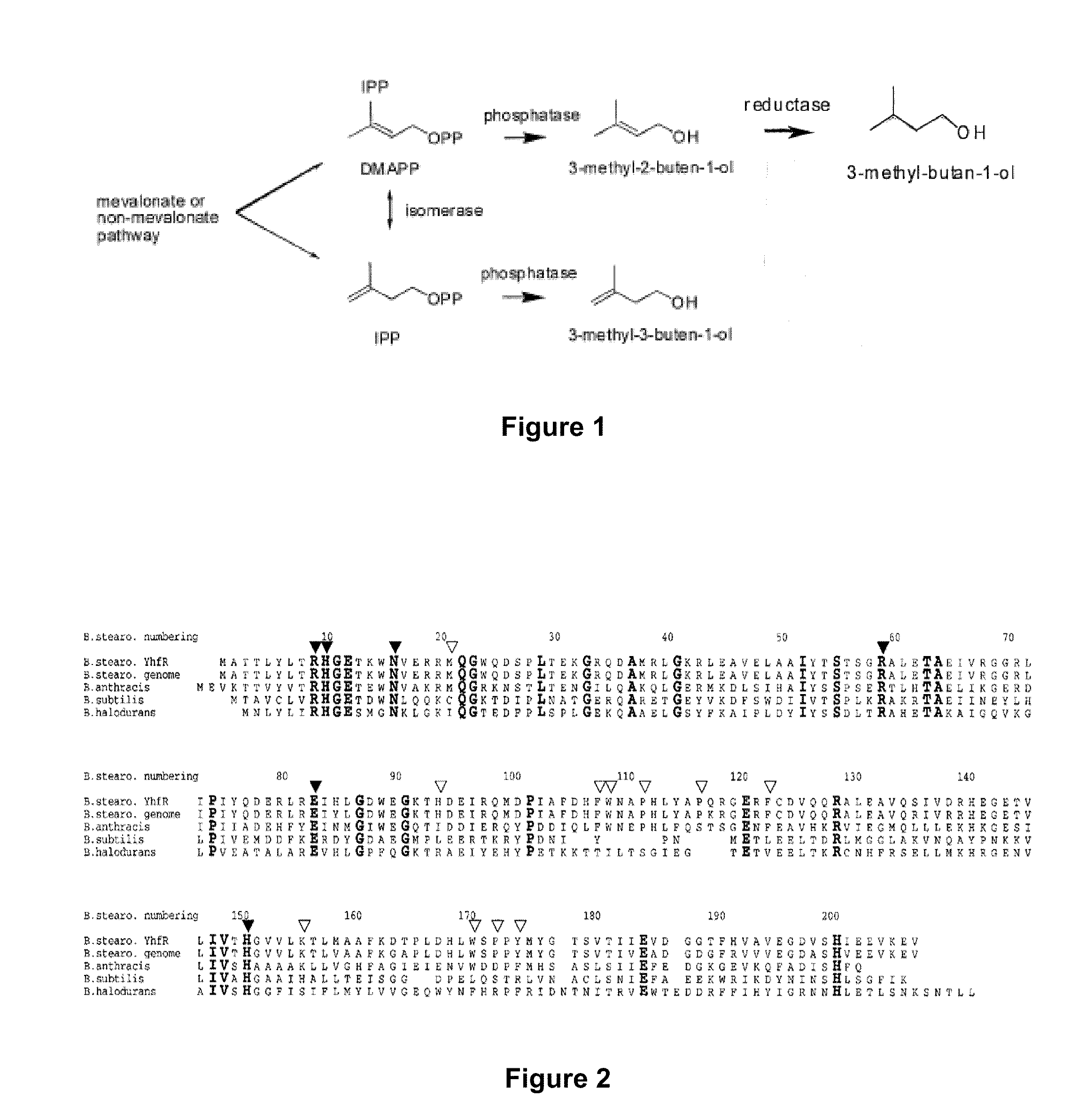
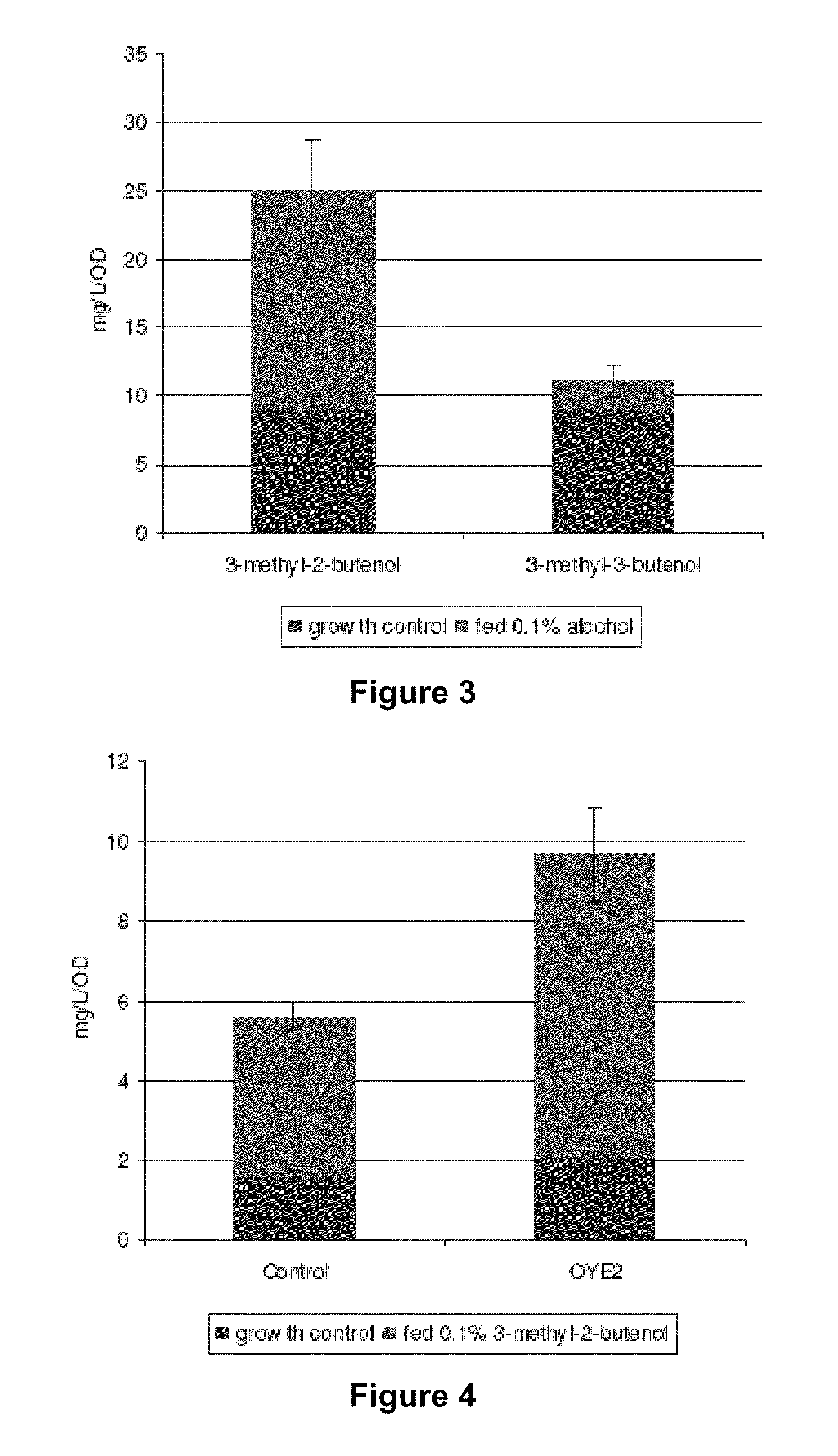
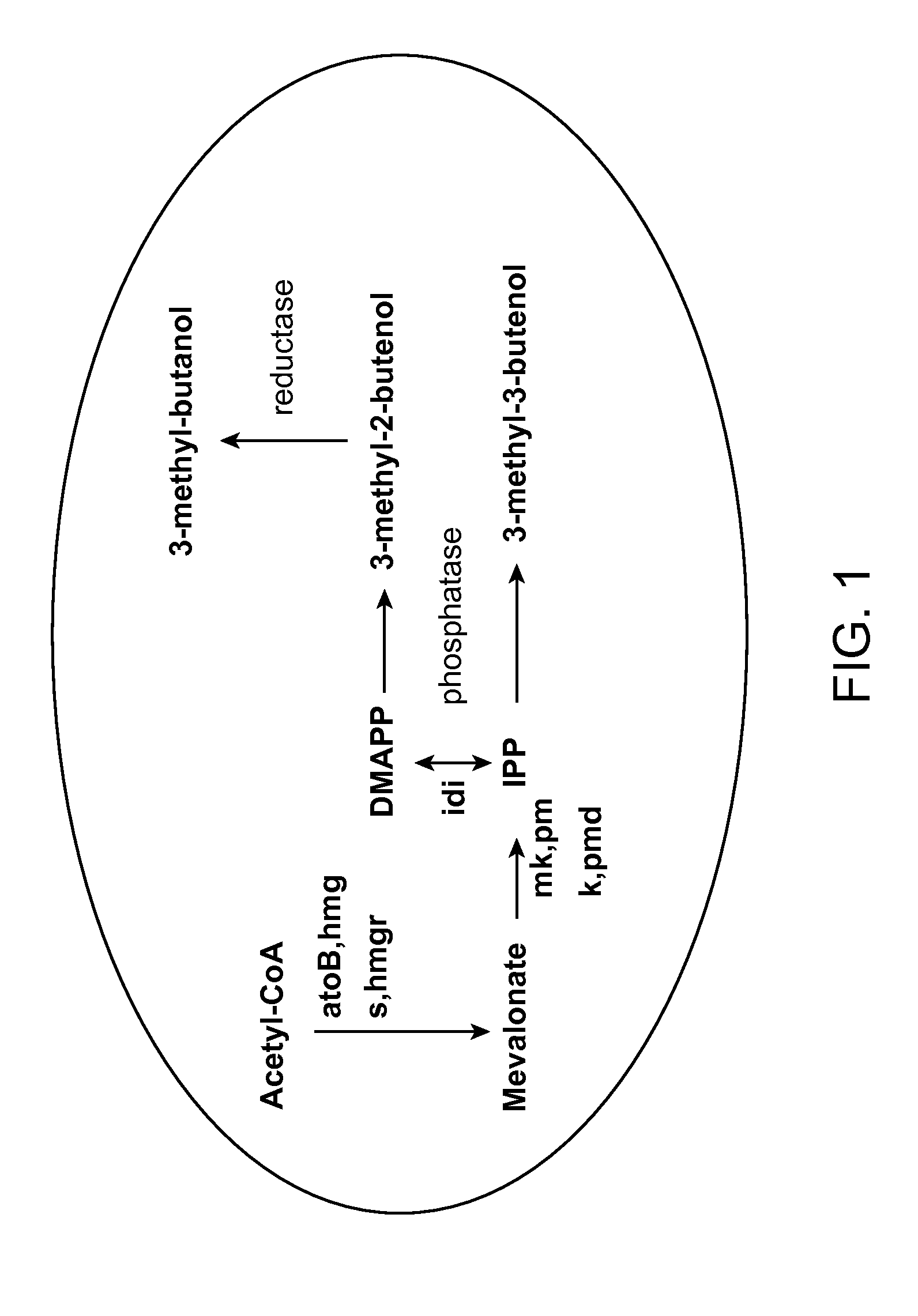
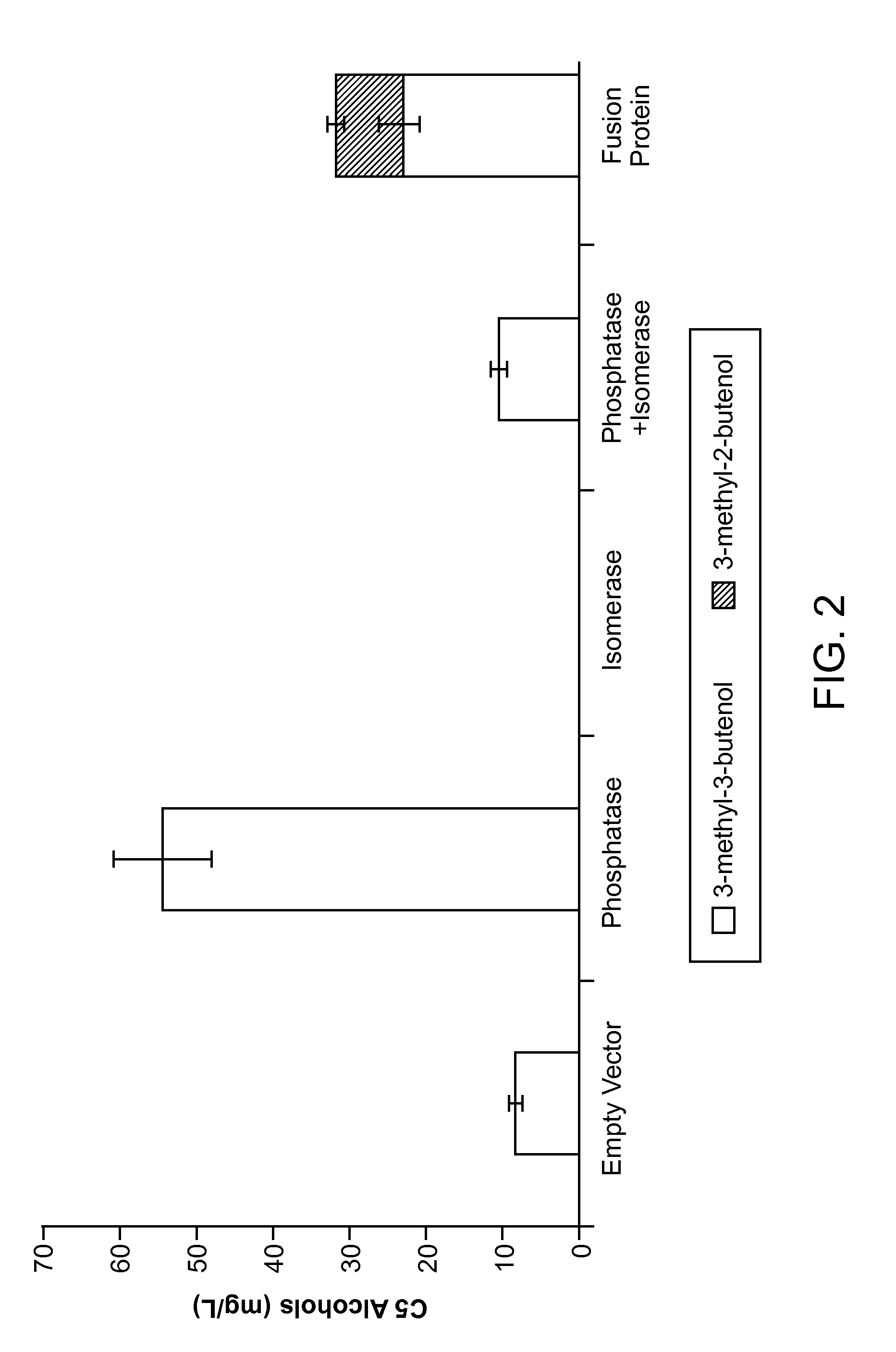
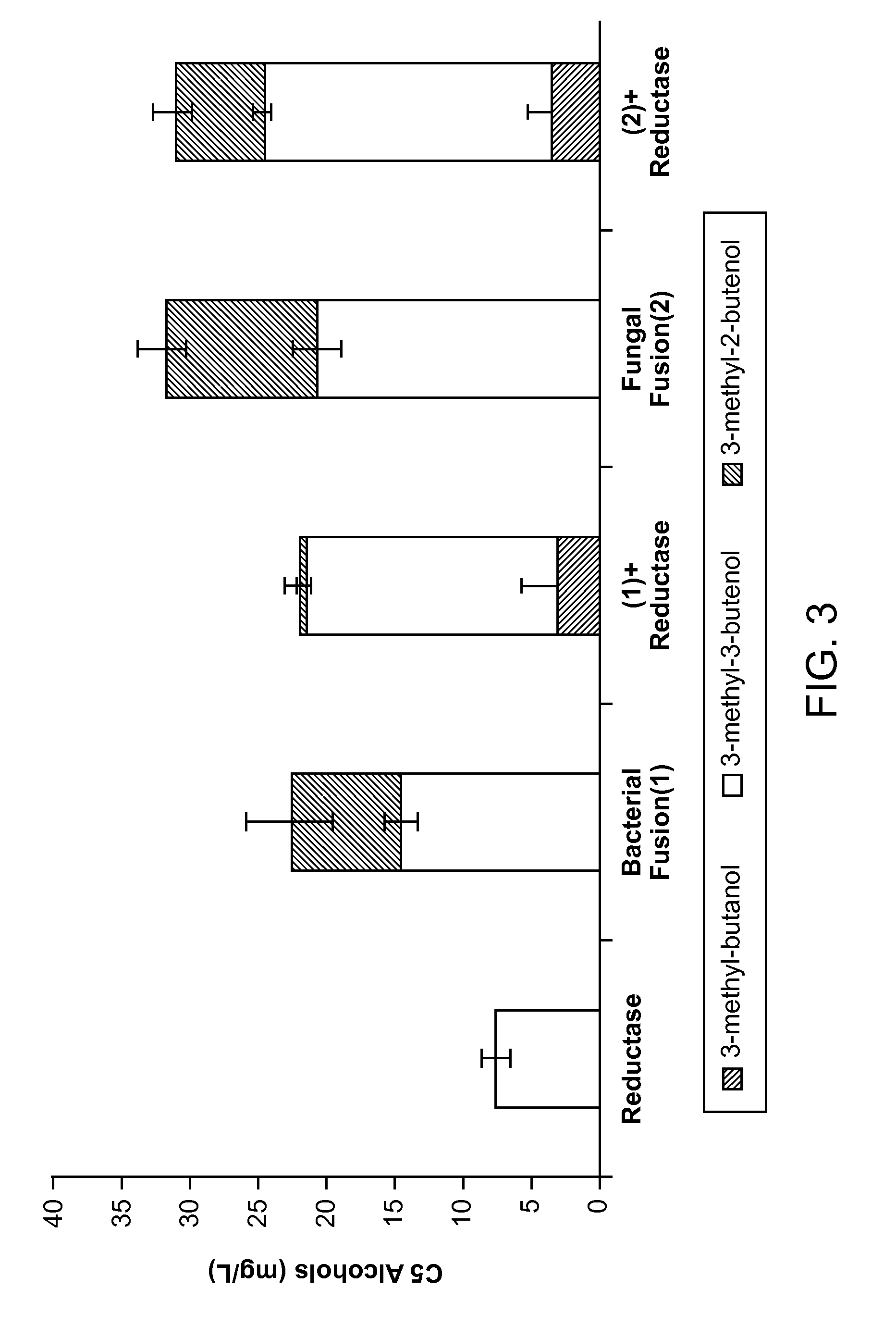
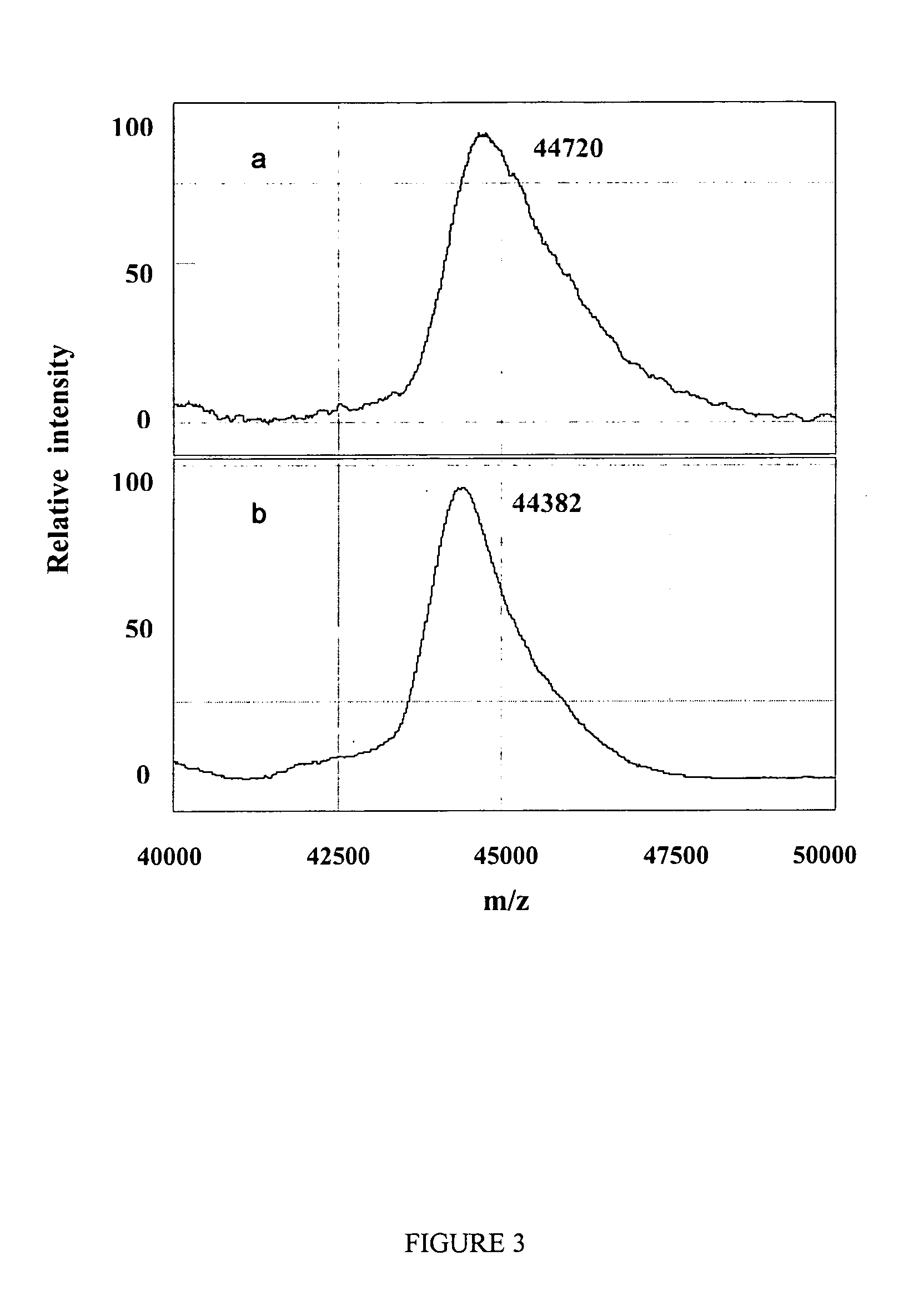
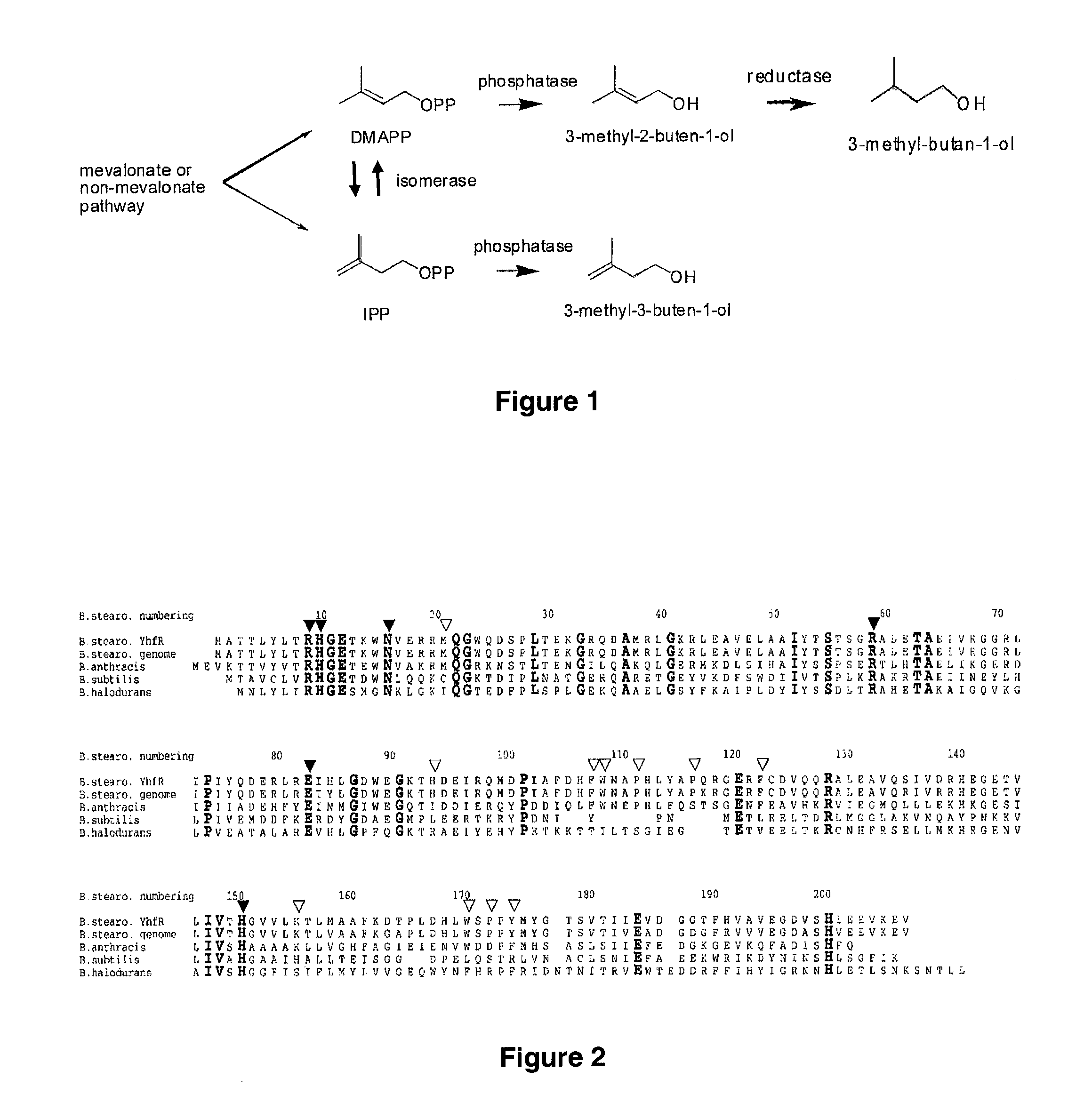
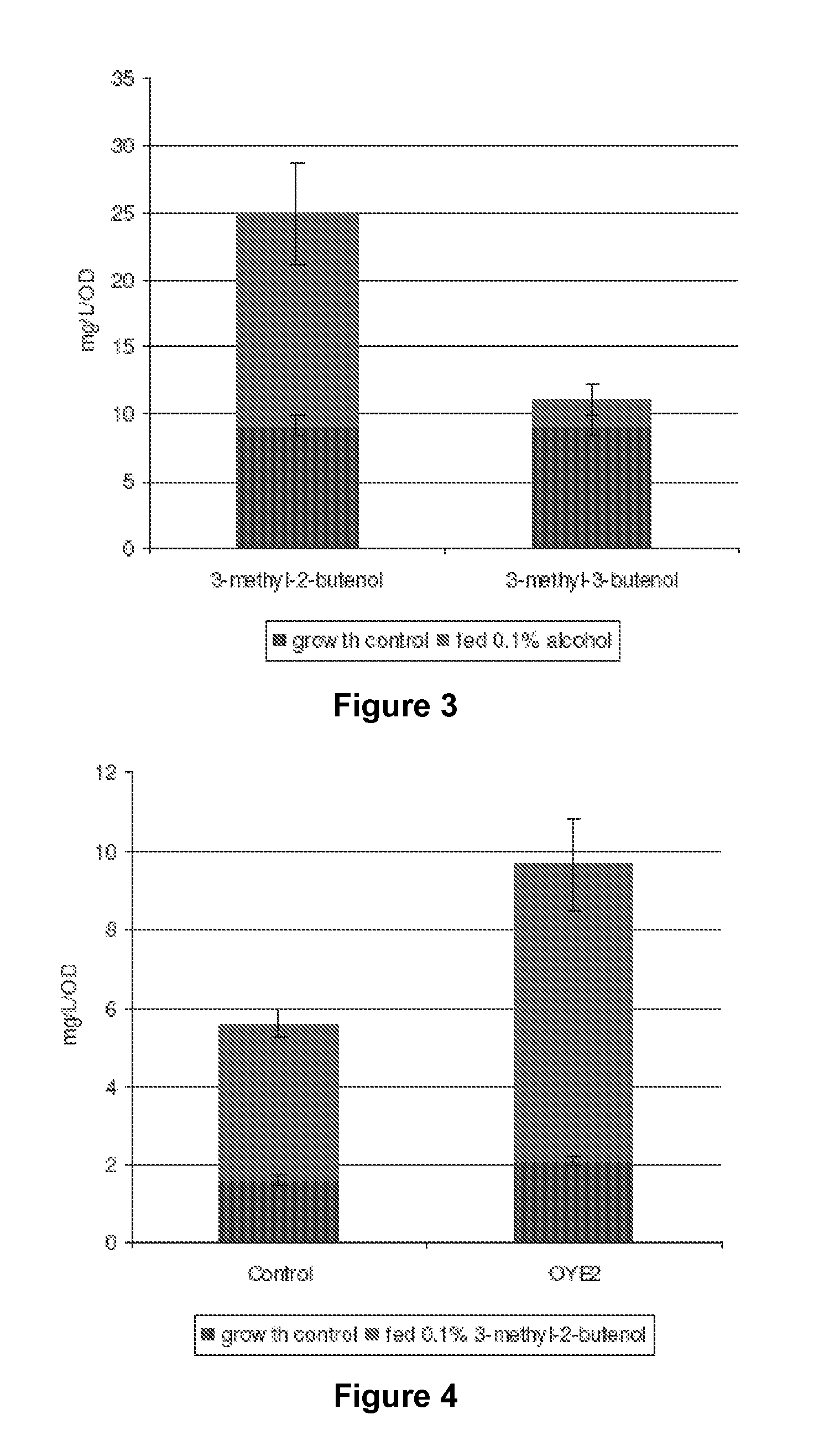
Host Cells and Methods for Producing 3-Methyl-2-buten-1-ol, 3-Methyl-3-buten-1-ol, and 3-Methyl-butan-1-ol
The invention provides for a method for producing a 5-carbon alcohol in a genetically modified host cell. In one embodiment, the method comprises culturing a genetically modified host cell which expresses a first enzyme capable of catalyzing the dephosphorylation of an isopentenyl disphosphate (IPP) or dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP), such as a Bacillus subtilis phosphatase (YhfR), under a suitable condition so that 5-carbon alcohol is 3-methyl-2-buten-1-ol and / or 3-methyl-3-buten-1-ol is produced. Optionally, the host cell may further comprise a second enzyme capable of reducing a 3-methyl-2-buten-1-ol to 3-methyl-butan-1-ol, such as a reductase.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
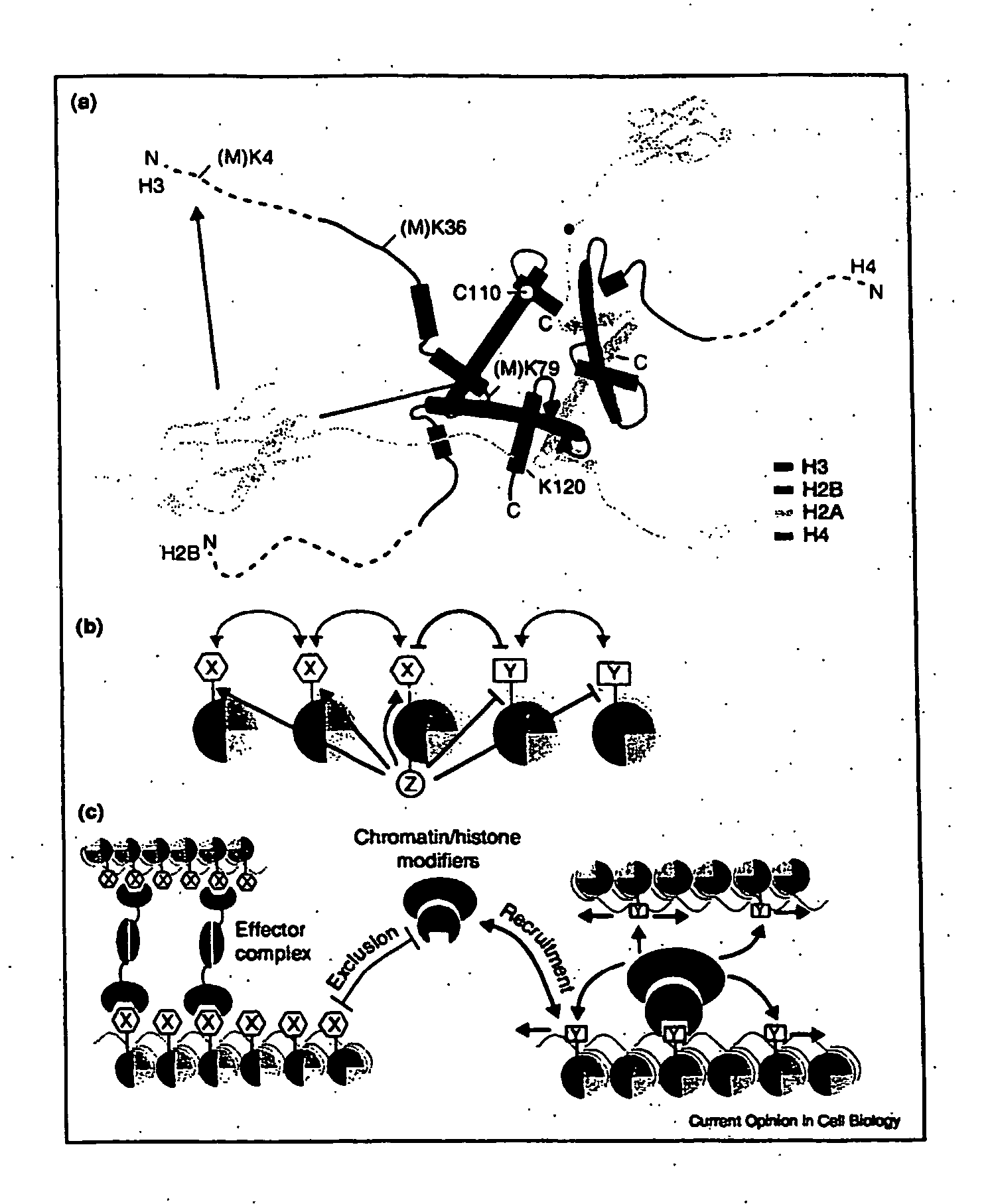
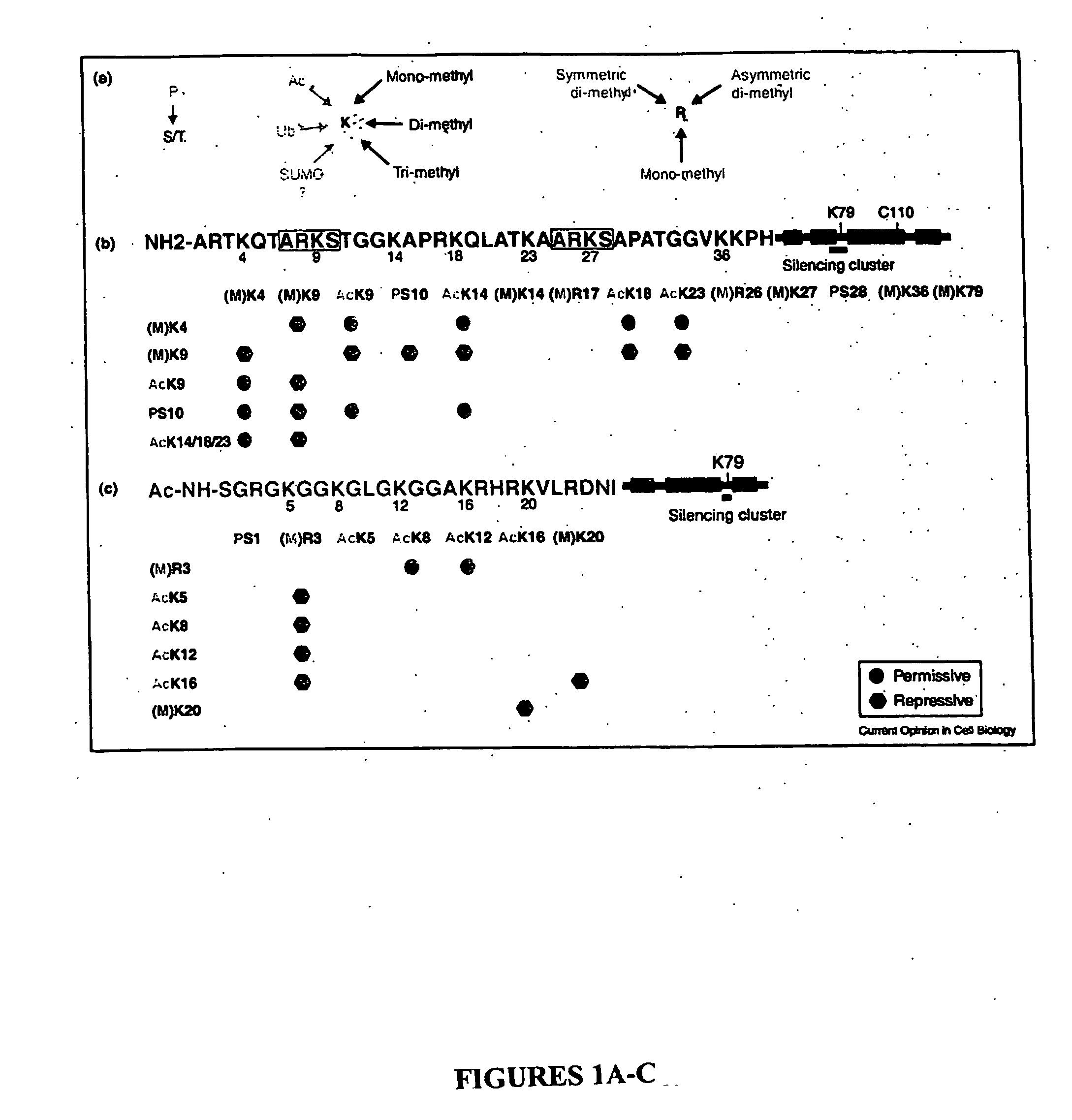
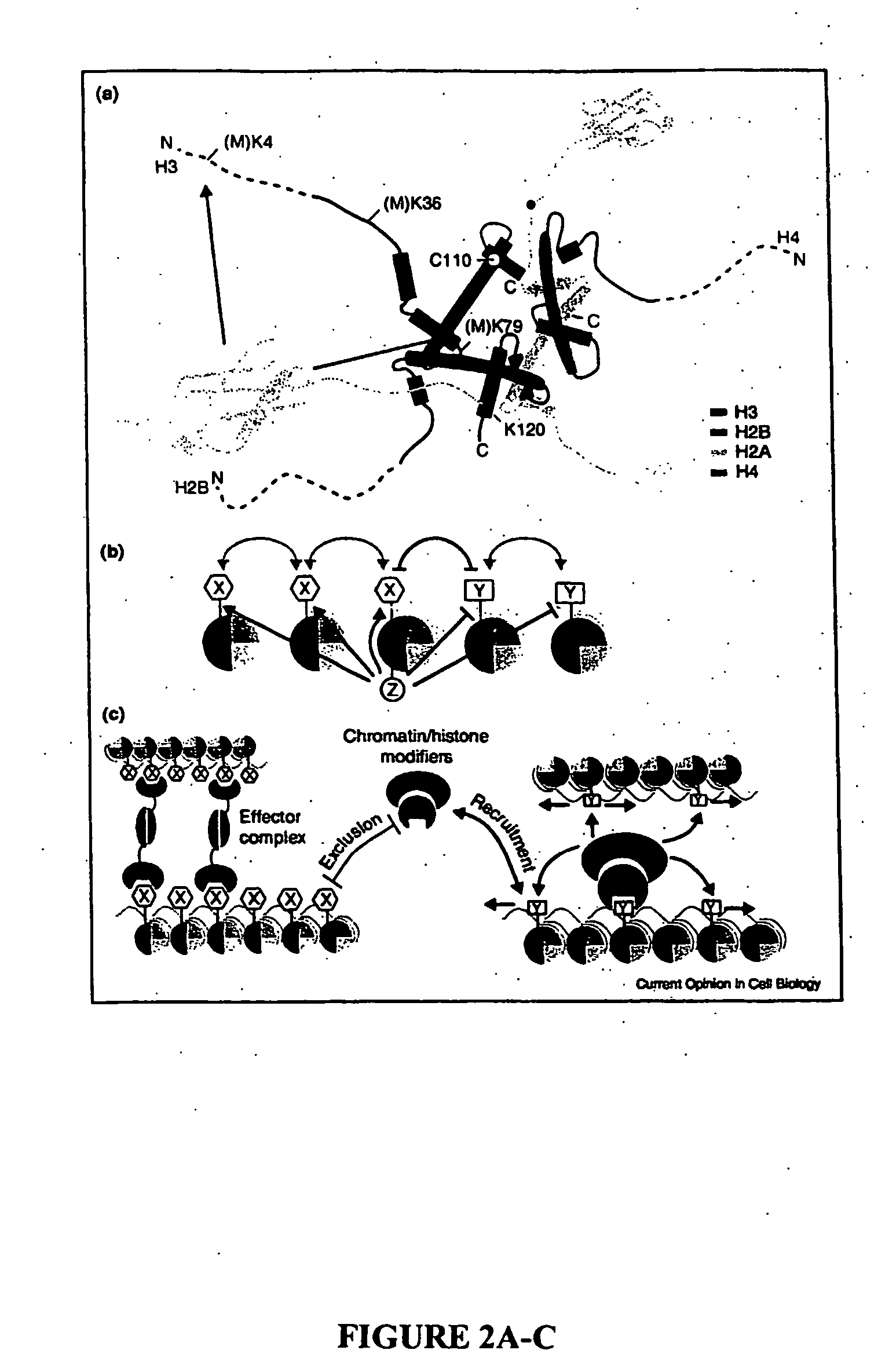
Histone Modifications as Binary Switches Controlling Gene Expression
InactiveUS20070274912A1Optimize dwell timeEasy to detectCompound screeningApoptosis detectionAmino acid bindingAntiendomysial antibodies
The present invention relates to a method of modulating a chromatin binding protein or complex which binds to a functional group on an amino acid of a histone. This method involves phosphorylating or dephosphorylating a serine or threonine on the histone proximate to the amino acid under conditions effective to modulate the chromatin binding protein or complex. This method is particularly useful in treating or preventing cancer in a subject. In addition, the histone comprising a serine or threonine proximate to an amino acid capable of binding to a functional group can be used to screen for compounds which prevent or treat cancer. Also disclosed is an antibody or binding portion thereof raised against a binary switch on a histone comprising a phosphorylated serine or threonine proximate to an amino acid bound to a functional group and its use in detecting a condition mediated by that switch.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
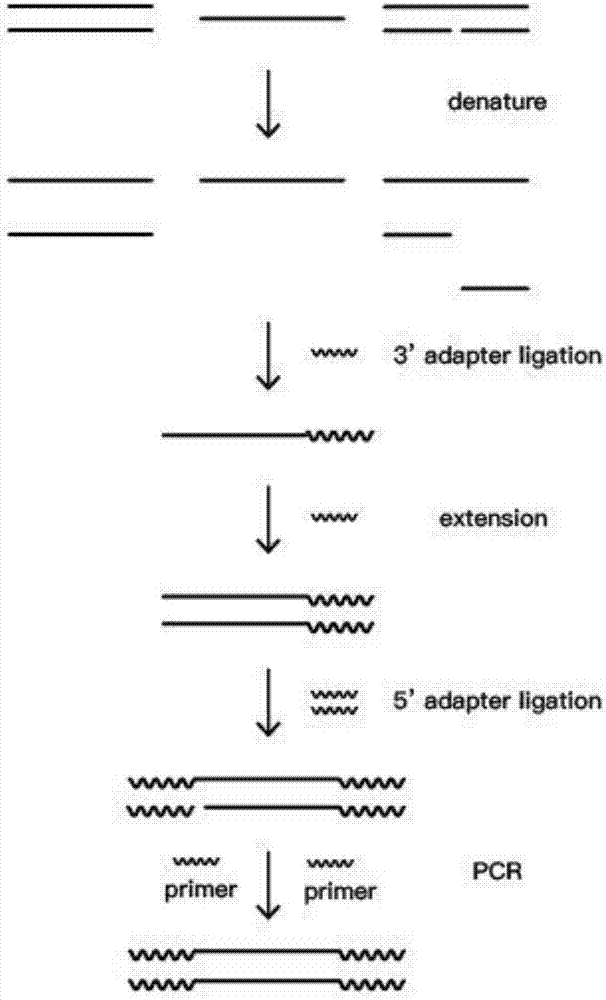
Construction method of single stranded DNA next generation sequencing library specific to cfDNA
ActiveCN106987585AAchieve capture enrichmentEfficient detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationSequence designPhosphorylation
The invention discloses a construction method of single stranded DNA next generation sequencing library specific to cfDNA. The construction method includes steps of 1), cfDNA extraction; 2), dephosphorylation; 3), denaturation to be single stranded cfDNA; 4), intermolecular single stranded connection on 3' end single stranded DNA interface; 5), extension: the acquired single stranded connection product is a template, and the known sequence design primer of the 3' end interface is extended; 6), intermolecular double stranded connection between the acquired double stranded DNA product and a 5' end double stranded DNA interface; 7), PCR amplification: use the acquired complete double stranded DNA interface connection product as a template, and take the known sequences of the interfaces at 3' end and the 5' end as forward and reverse products, and perform PCR amplification; 8), PCR product purification by a paramagnetic particle method, and library recycling. The original cfDNA gathering efficiency is high, and the double stranded, the single stranded and damaged DNA can be effectively detected.
Owner:SHENZHEN HAPLOX BIOTECH
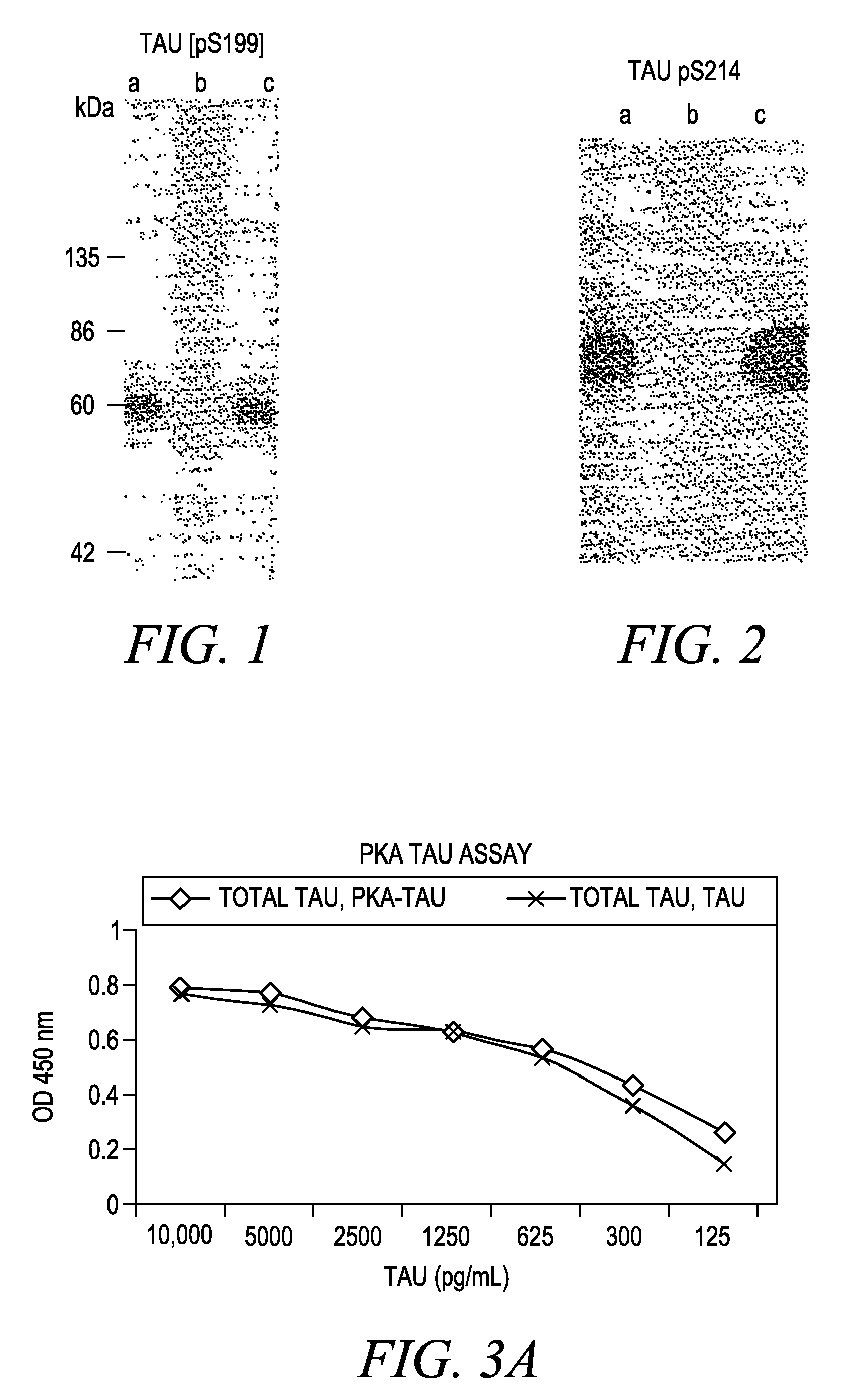
Method for quantifying phosphokinase activity on proteins
InactiveUS7888050B2Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisProtein targetTyrosine
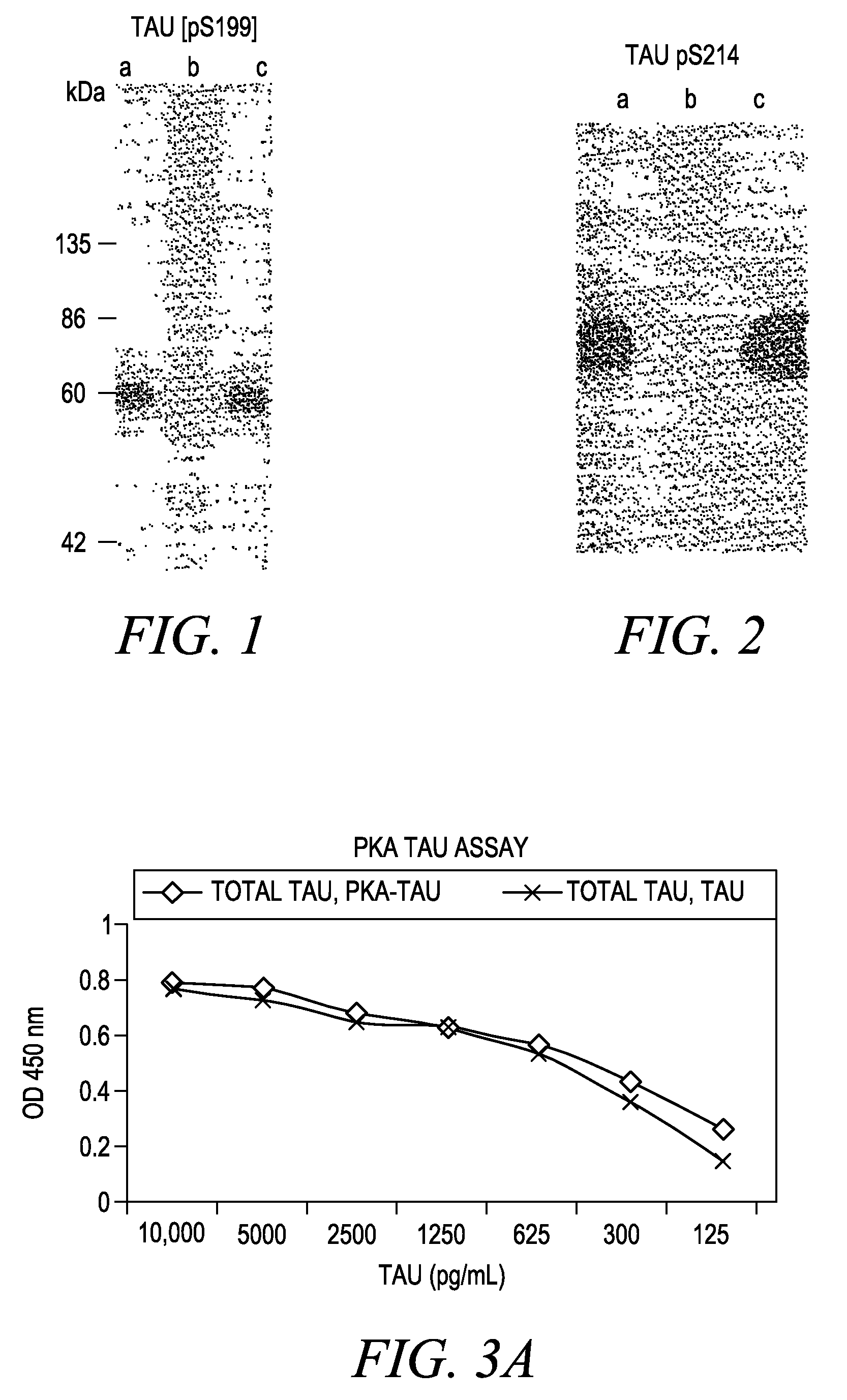
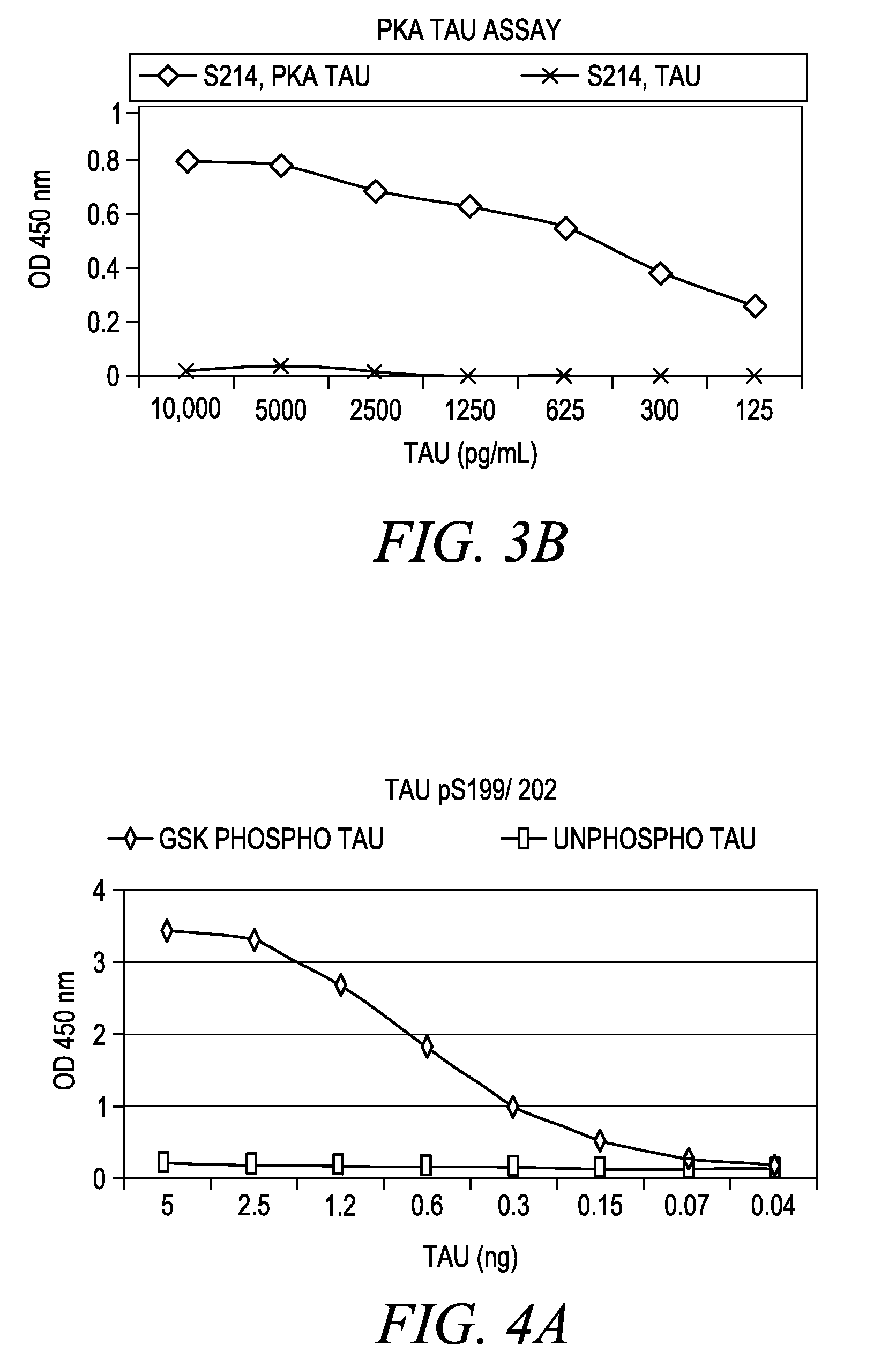
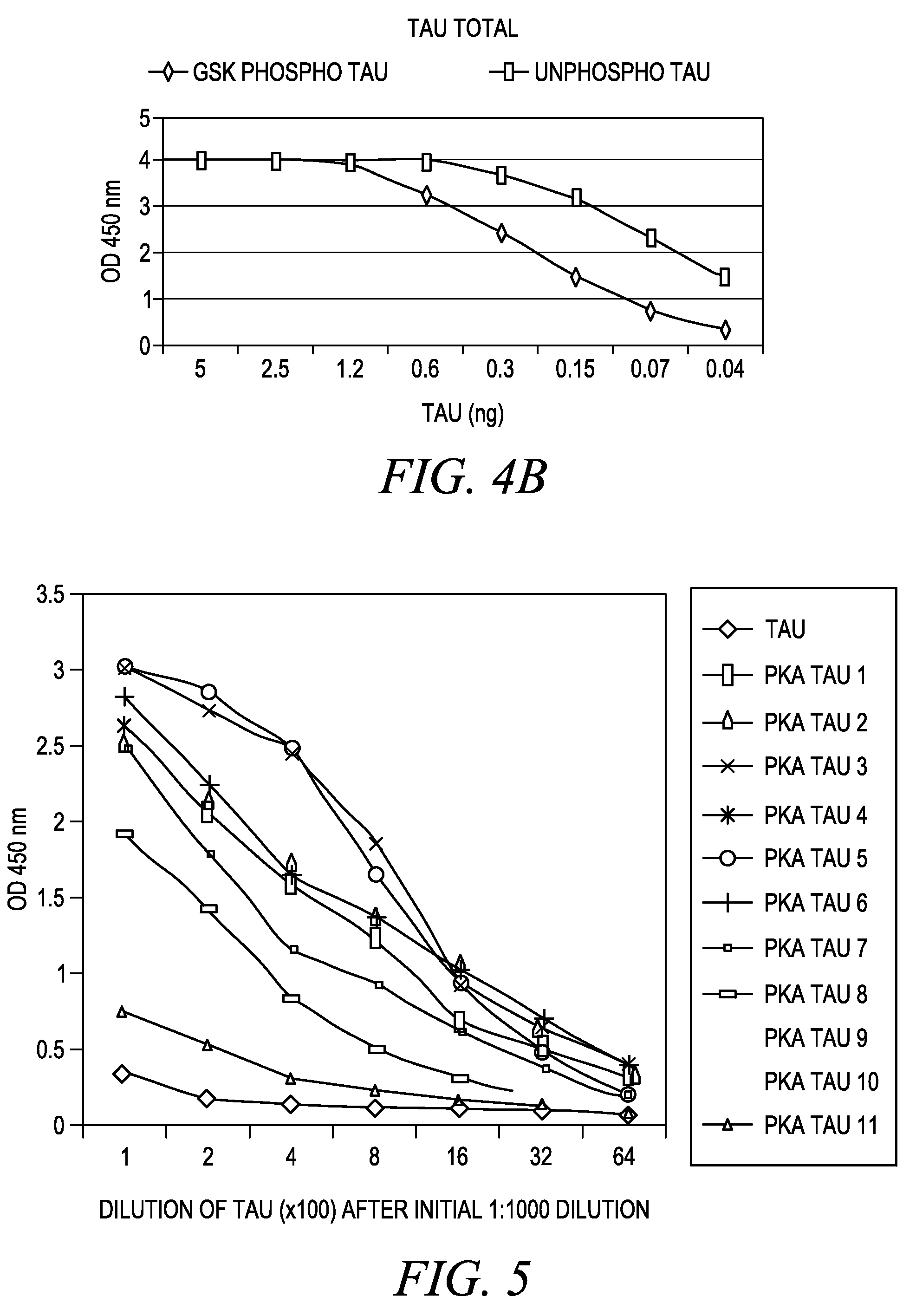
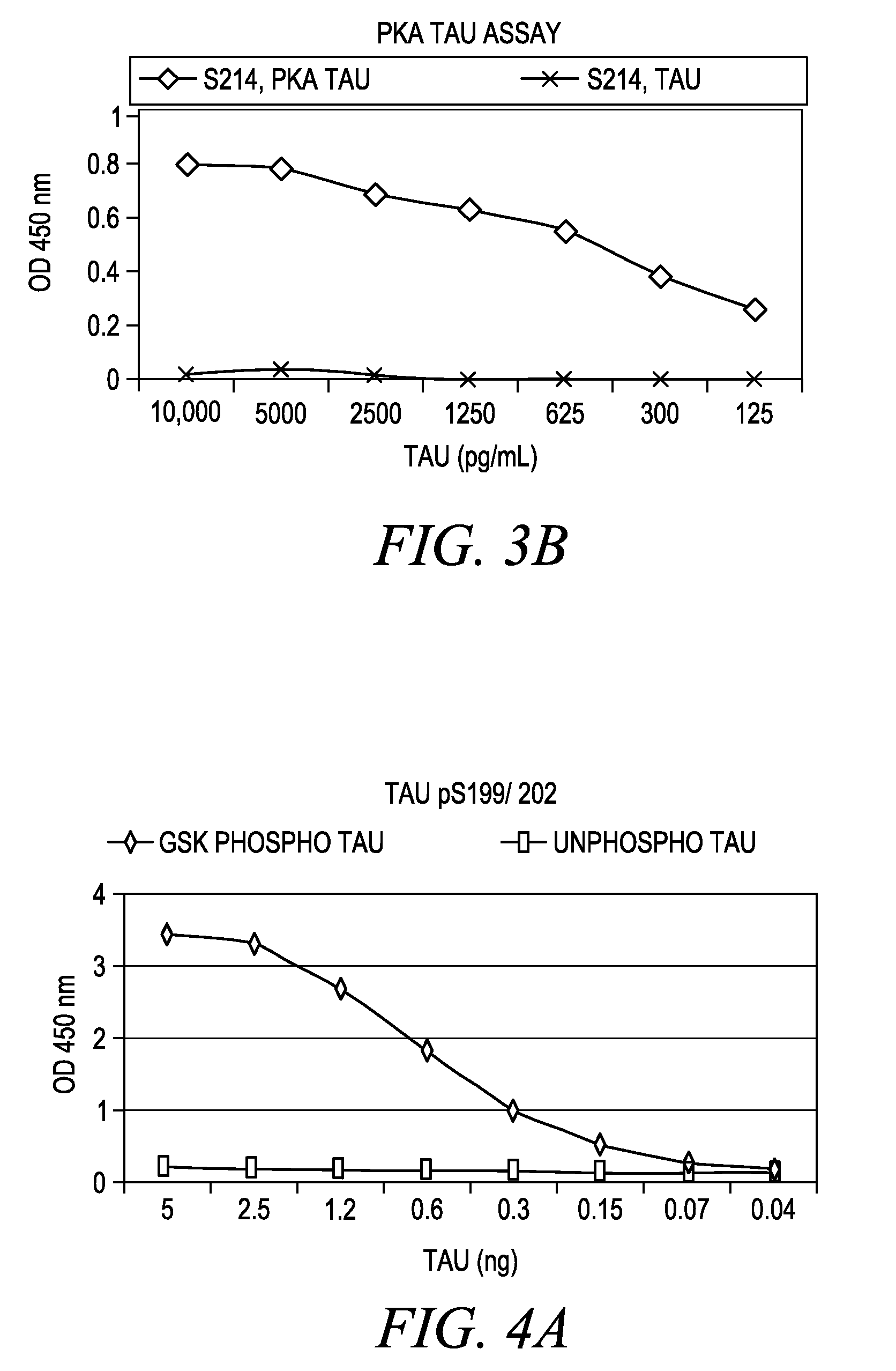
The invention involves a method for measuring phosphorylation of proteins at specific sites and, as such, is an indicator of the protein kinase activity of enzymes capable of phosphorylating those sites. The method involves the in vitro or in vivo phosphorylation of a target protein at a specific serine, threonine or tyrosine residue, subjecting that protein (non-phosphorylated) to reaction mixture containing all reagents, including phosphokinase which allow the creation of a phosphorylated form of protein. The phosphorylated protein is measured by contacting it with an antibody specific for the phosphorylation site(s). The invention includes antibodies useful in practicing the methods of the invention. The invention particularly relates to all proteins modified by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation as illustrated by Tau, Rb and EGFR proteins and antibodies specific for the site of phosphorylation of the Tau, Rb or EGFR proteins.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Production of mouse model of viral hepatitis B with high expression HBsAg
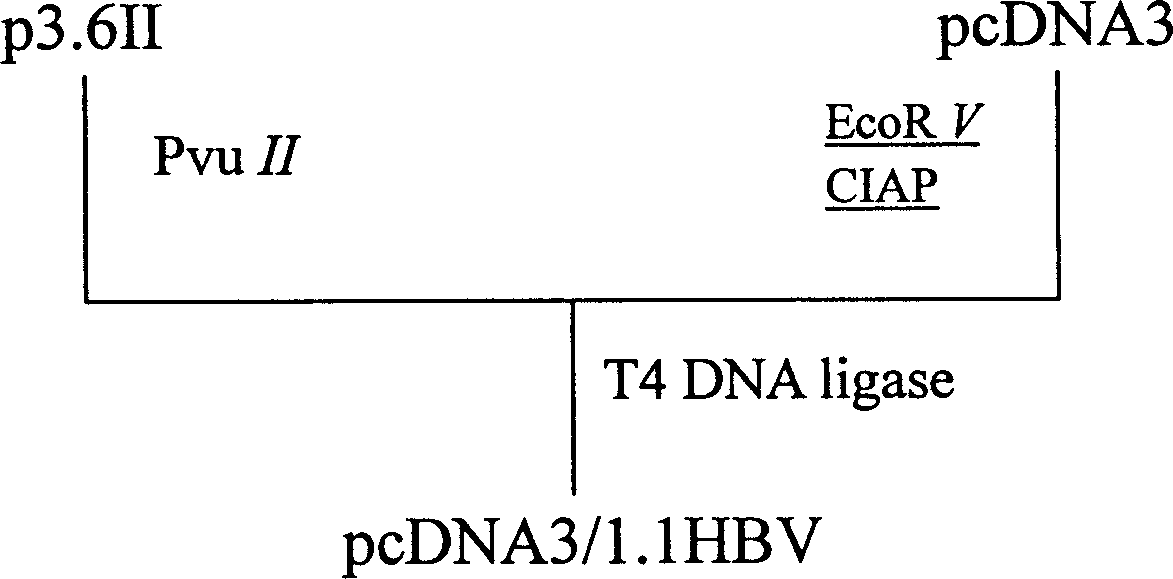
InactiveCN1679967AOvercome injectionOvercoming disadvantages of portal vein injection of naked DNAIn-vivo testing preparationsEscherichia coliPhosphorylation
A process for preparing VHB mouse model with high expression of HBsAg includes such steps as linearizing carrier pcDNA3 by EcoRV, dephosphorylating by alkaline phosphatase of ox's small intestine, recombining the clonal carrier p3.6II, enzyme severing by PvuII to obtain 1.1-time HBV gene fragment, linking it with linear pcDNA3, transforming colibacillus competent cell DH5 alpha, screening resistance, enzyme serving, sequencing to verify the recombinant plasmid, injecting it in the mouse body via tail vein, and verifying the model.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for screening compounds & uses therefor
InactiveUS20060246418A1Modulate levelPromotes rapid Ser17 dephosphorylationCompound screeningApoptosis detectionHeterologousCytoplasm
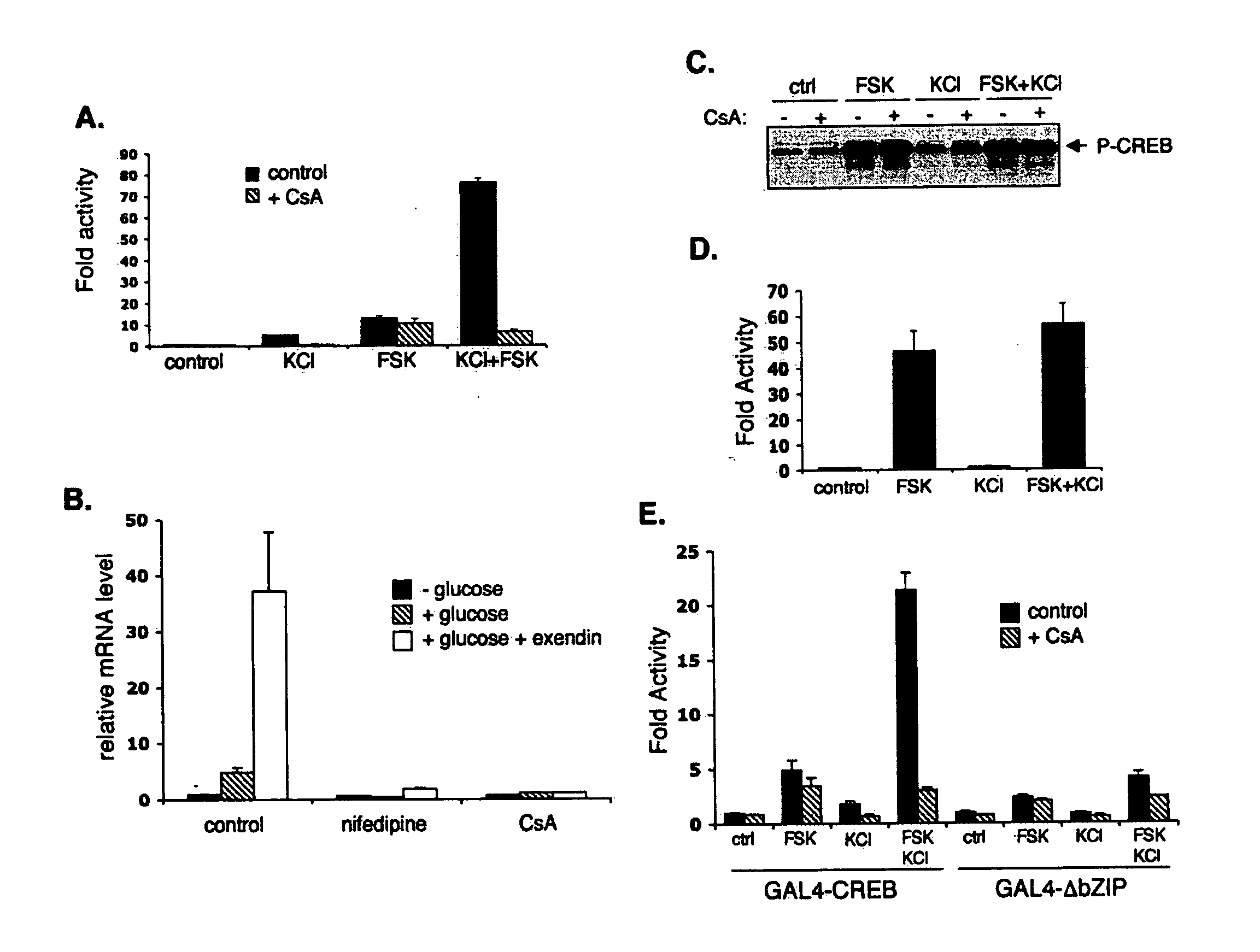
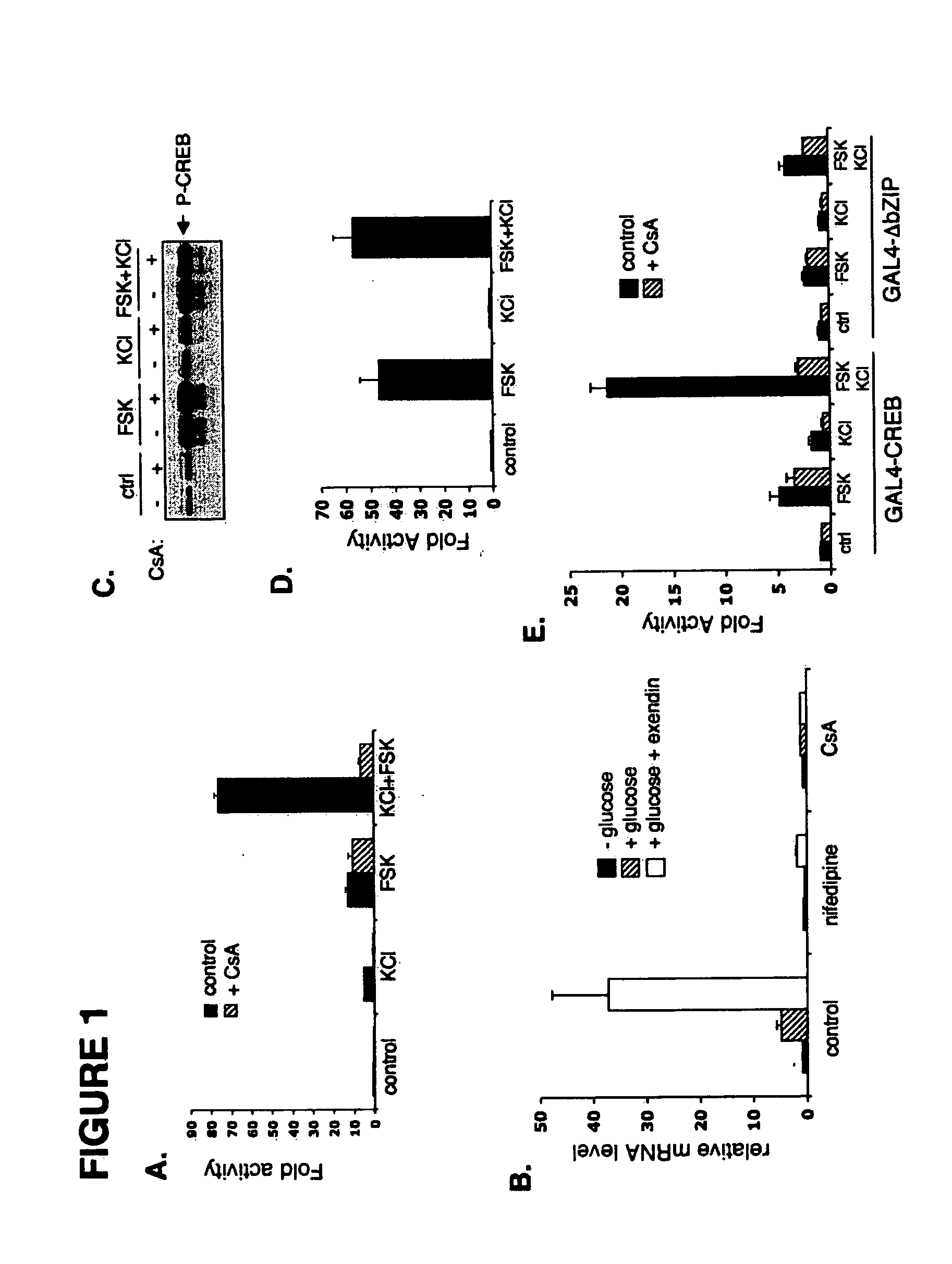
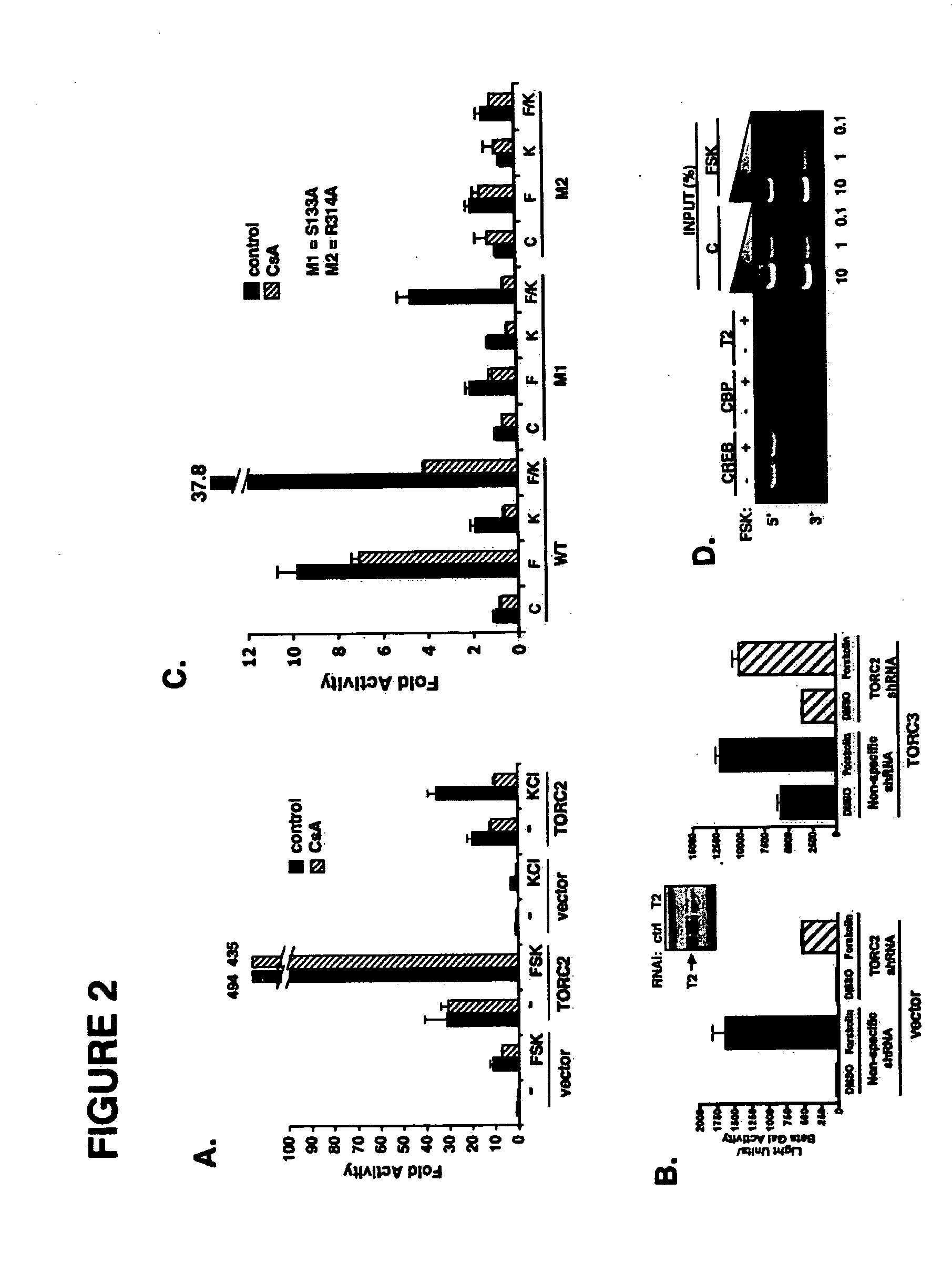
In accordance with the present invention, it has been discovered that glucose and incretin hormones promote pancreatic islet cell survival via the calcium and cAMP dependent induction, respectively, of the transcription factor CREB. Specifically, a signaling module has been identified which mediates cooperative effects of calcium and cAMP on islet cell gene expression by stimulating the dephosphorylation and nuclear entry of TORC2, a cytoplasmic CREB coactivator. The module comprises a cAMP regulated snf1-like kinase called SIK2 and the calcium regulated phosphatase calcineurin, both of which associate with TORC2 in the cytoplasm. TORC2 is repressed under basal conditions through a phosphorylation dependent interaction with 14-3-3 proteins. cAMP and calcium signals stimulate CREB target gene expression via complementary effects on TORC2 dephosphorylation; cAMP disrupts TORC2-associated activity of SIK2 or related family members, whereas calcium induces TORC2 dephosphorylation via calcineurin. These findings provide a novel mechanism by which CREB activates cellular gene expression, depending on nutrient and energy status, and facilitate development of assays to identify compounds which modulate the role of TORCs. In accordance with the present invention, it has been discovered that fasting and energy-sensing pathways regulate the gluconeogenic program in liver by modulating the nuclear entry of a transcriptional coactivator called Transducer of Regulated CREB Activity 2 (TORC2). Hepatic TORC2 over-expression induces fasting hyperglycemia, whereas knockdown of TORC2 leads to fasting hypoglycemia and silencing of the gluconeogenic program. Since a majority of individuals with Type II diabetes exhibit fasting hyperglycemia due to elevated hepatic gluconeogenesis, compounds that enhance TORC2 phosphorylation will find use as therapeutic agents in this setting.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
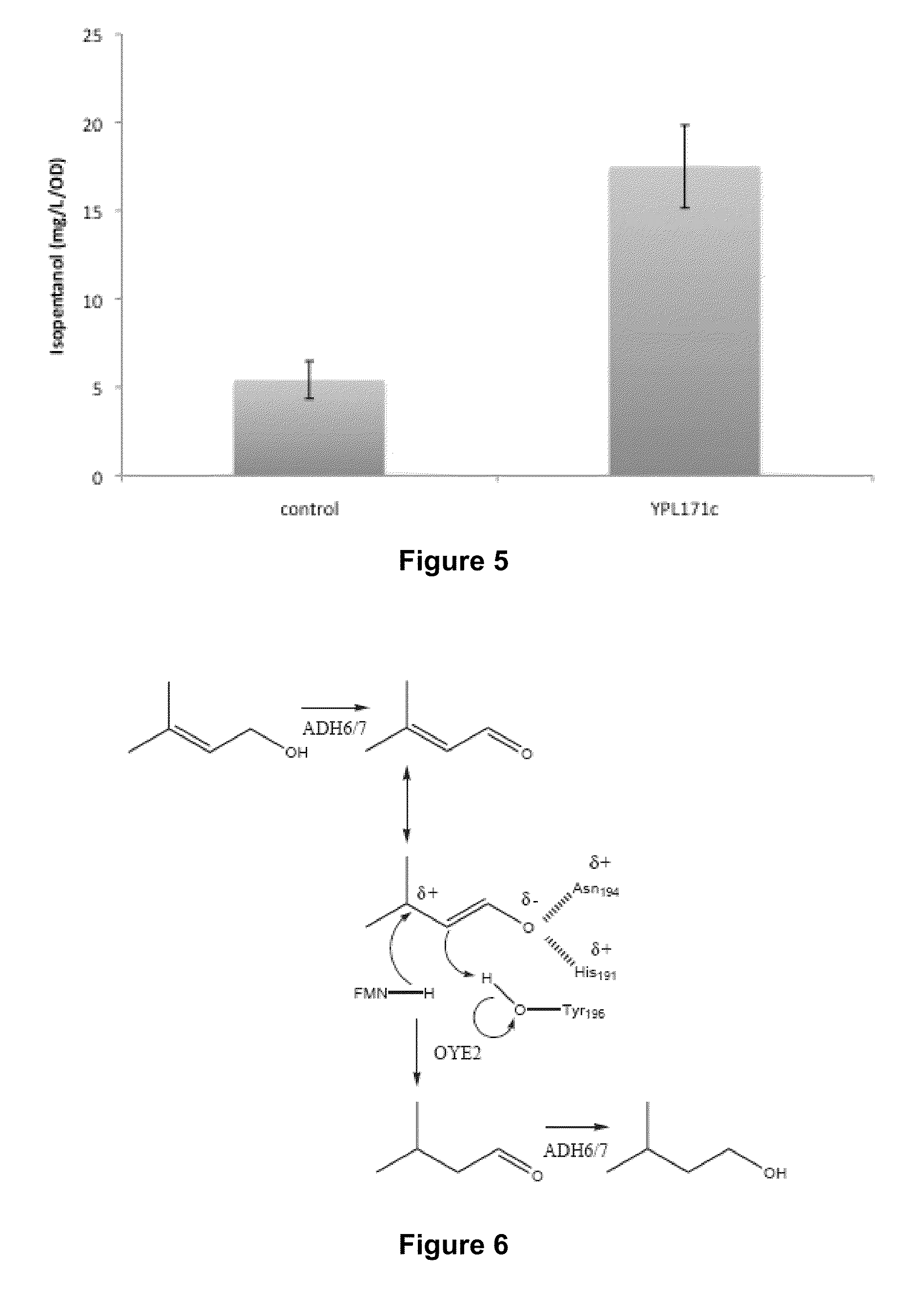
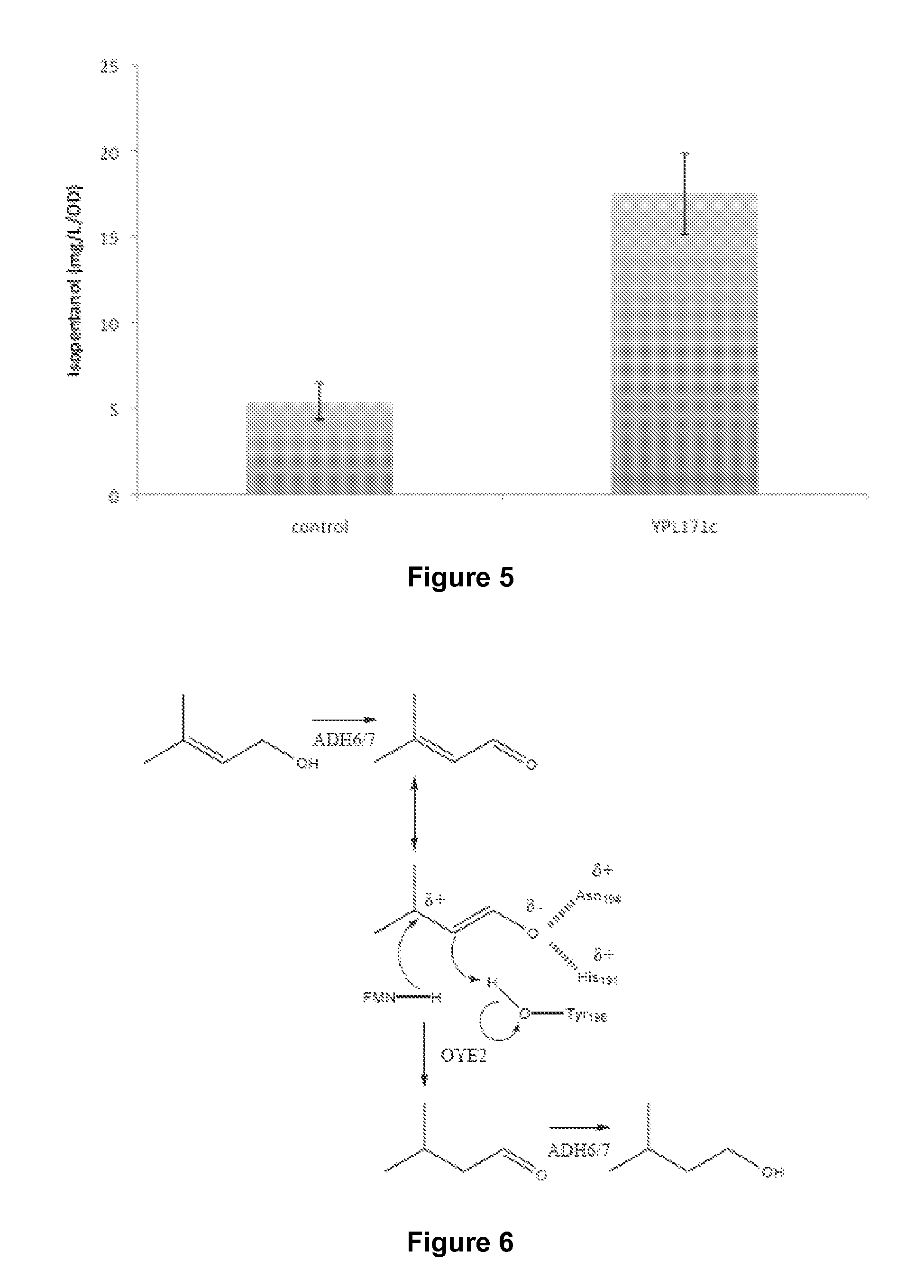
Methods for increasing production of 3-methyl-2-butenol using fusion proteins
The invention relates, in part, to nucleic acid constructs, genetically modified host cells and methods employing such constructs and host cells to increase the production of 3-methyl-2-butenol from IPP. Thus, in some aspects, the invention provides a genetically modified host cell transformed with a nucleic acid construct encoding a fusion protein comprising a phosphatase capable of catalyzing the dephosphorylation of dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP) linked to an IPP isomerase capable of converting IPP to DMAPP, wherein the nucleic acid construct is operably linked to a promoter. In some embodiments, the genetically modified host cell 5 further comprises a nucleic acid encoding a reductase that is capable of converting 3-methyl-2-butenol to 3-methyl-butanol. In some embodiments, the reductase is encoded by a nucleic acid construct introduced into the cell. In some embodiments, the IPP isomerase is a Type I isomerase. In some embodiments, the IPP isomerase is a Type II isomerase. In some embodiments, the host cell is selected from a group of taxonimcal classes consisting of 20 Escherichia, Enterobacter, Azotobacter, Erwinia, Bacillus, Pseudomonas, Klebsiella, Proteus, Salmonella, Serratia, Shigella, Rhizobia, Vitreoscilla, Synechococcus, Synechocystis, and Paracoccus taxonomical classes. In some embodiments, the host cell is an Escherichia coli cell. In some embodiments, the host cell is a fungal cell, such as a yeast cell. In some embodiments, the yeast cell is a Saccharomyces sp. cell. In some embodiments, the host cell is an algal, insect or mammalian cell line. In some embodiments, the phosphatase is nudB from E. coli. In some embodiments, the IPP isomerase is encoded by an idi gene from E. coli or idil gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Ultra-low-frequency library building method for FFPE tissue samples
The invention discloses an ultra-low-frequency library building method for FFPE tissue samples. The ultra-low-frequency library building method for FFPE tissue samples comprises the following steps: DNA extraction of FFPE samples; DNA interruption; dephosphorylation and DNA denaturation; adding of biotin UID single-chain joints; capturing and elution of streptomycin magnetic beads; adding of double-chain second joints and elution of a library; adding of a second joint at the other end of a target DNA molecule by T4DNA ligase, and removal of excessive and residual joints by washing; LM-PCR amplification and introduction of barcode; and purification of a PCR amplification product by magnetic beads. Library building, capturing and sequencing are realized for some severely degraded FFPE DNA micro-samples, UID label joints are introduced before beginning of library building, and thus, preconditions are provided for follow-up exclusion of technical mutations introduced in library building, capturing and computerized sequencing process.
Owner:普瑞基准科技(北京)有限公司
Method for chemical and enzymatic treatment of posttranslationally modified proteins bound to a protein chip
InactiveUS7622273B2Quick upgradeSimpler, more sensitive methodologiesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisEnzymatic digestionChemical treatment
Owner:GIBBS BERNARD F
Host cells and methods for producing 3-methyl-2-buten-1-ol, 3-methyl-3-buten-1-ol, and 3-methyl-butan-1-ol
The invention provides for a method for producing a 5-carbon alcohol in a genetically modified host cell. In one embodiment, the method comprises culturing a genetically modified host cell which expresses a first enzyme capable of catalyzing the dephosphorylation of an isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) or dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP), such as a Bacillus subtilis phosphatase (YhfR), under a suitable condition so that 5-carbon alcohol is 3-methyl-2-buten-1-ol and / or 3-methyl-3-buten-1-ol is produced. Optionally, the host cell may further comprise a second enzyme capable of reducing a 3-methyl-2-buten-1-ol to 3-methyl-butan-1-ol, such as a reductase.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
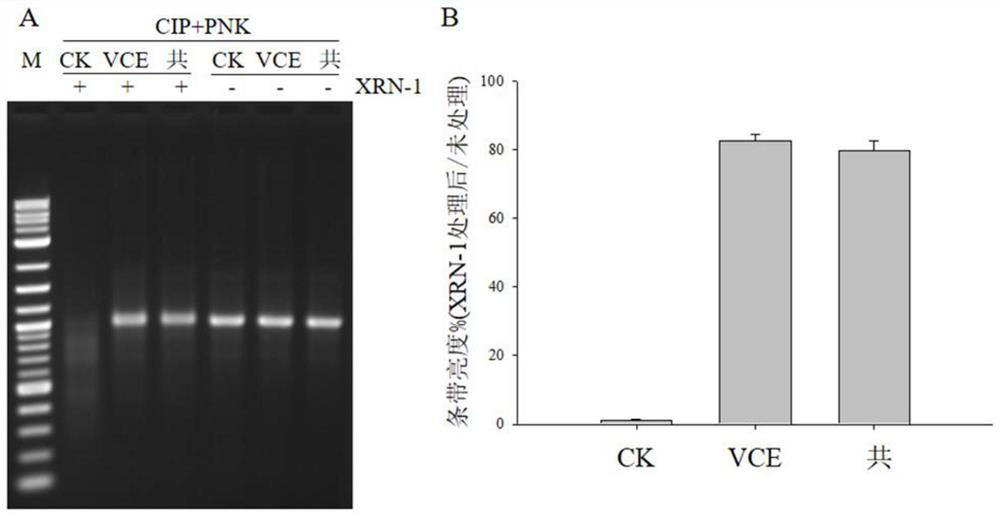
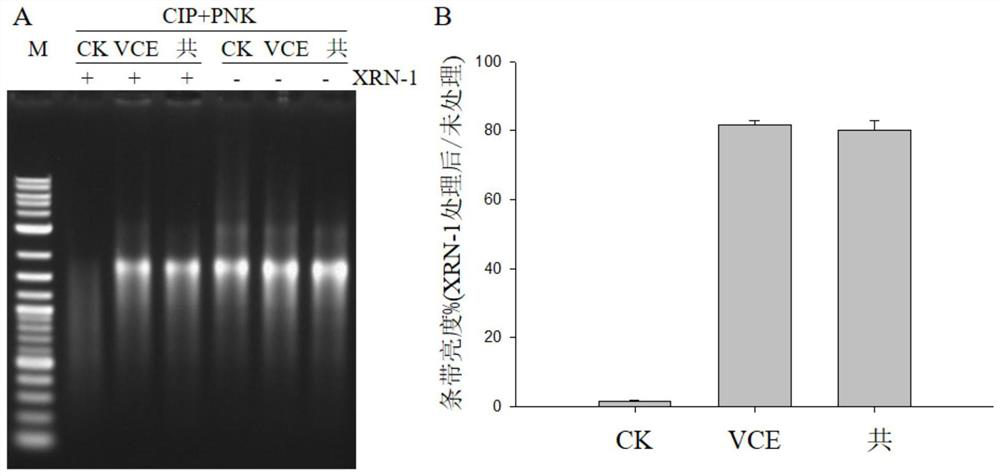
Method for rapidly and quantitatively detecting capping efficiency of RNA
PendingCN112626177ADetection of capping efficiencyEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementPhosphorylationKinase
The invention discloses a method for rapidly and quantitatively detecting the capping efficiency of RNA. The method comprises the following steps: S1, performing in-vitro transcription to synthesize uncapped RNA and removing template DNA; S2, carrying out capping treatment on the RNA; S3, performing mono-phosphorylation treatment on the RNA obtained in the steps S1 and S2: firstly, performing dephosphorylation by using alkaline phosphatase, purifying the RNA, and then adding monophosphate to the 5' end of the RNA by using polynucleotide kinase; S4, removing the RNA subjected to the monophosphorylation treatment by using monophosphatase, and setting a control group not treated with the monophosphatase; and S5, performing glue leaking detection: quantitatively determining the strip brightness (denoted as n) of the RNA treated by the monophosphatase and the strip brightness (denoted as N) of the RNA of the control group, and calculating the capping efficiency of the RNA: (n / N)*100%. The method has the beneficial effects that (1) the capping efficiency of the RNA can be rapidly and quantitatively detected, the operation is simple and rapid, and the result is effective and accurate; and (2) the method has less demand on samples, has no special requirements on RNA types, lengths and the like, and has a wide application range.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
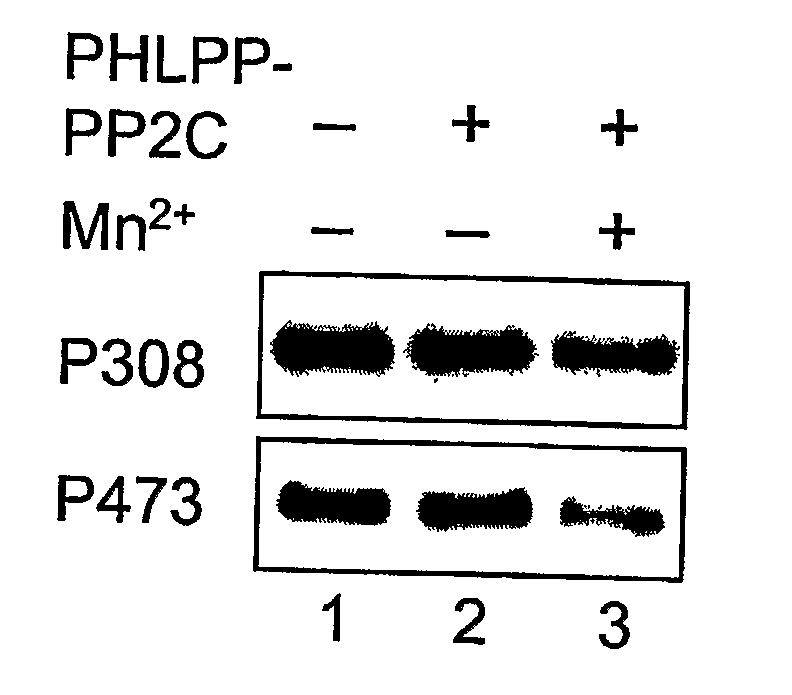
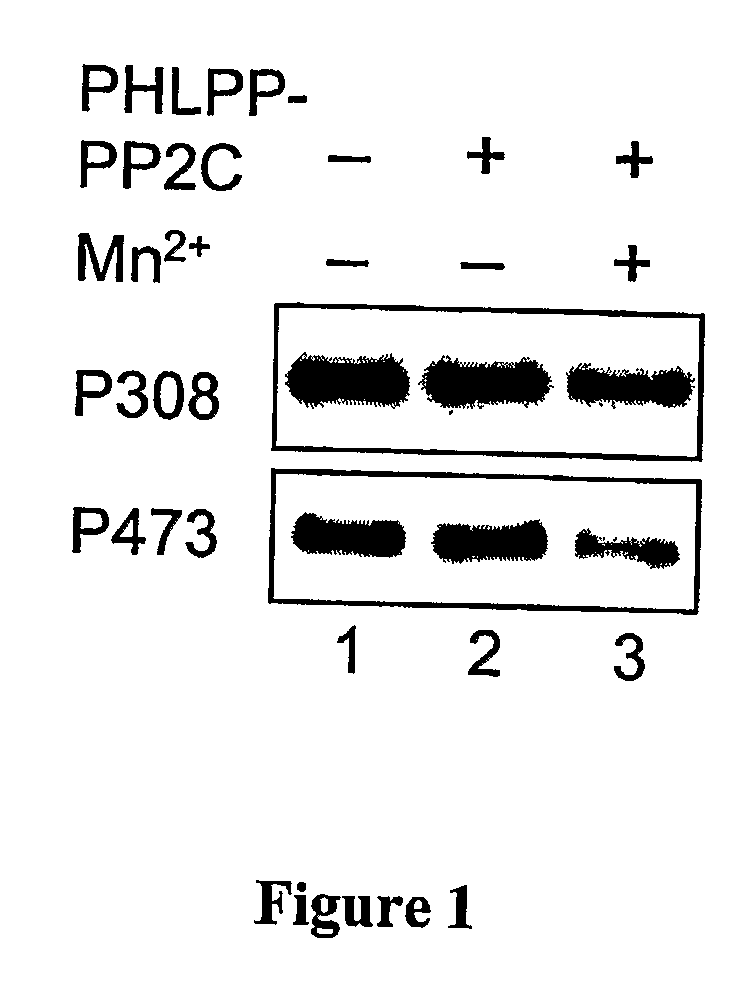
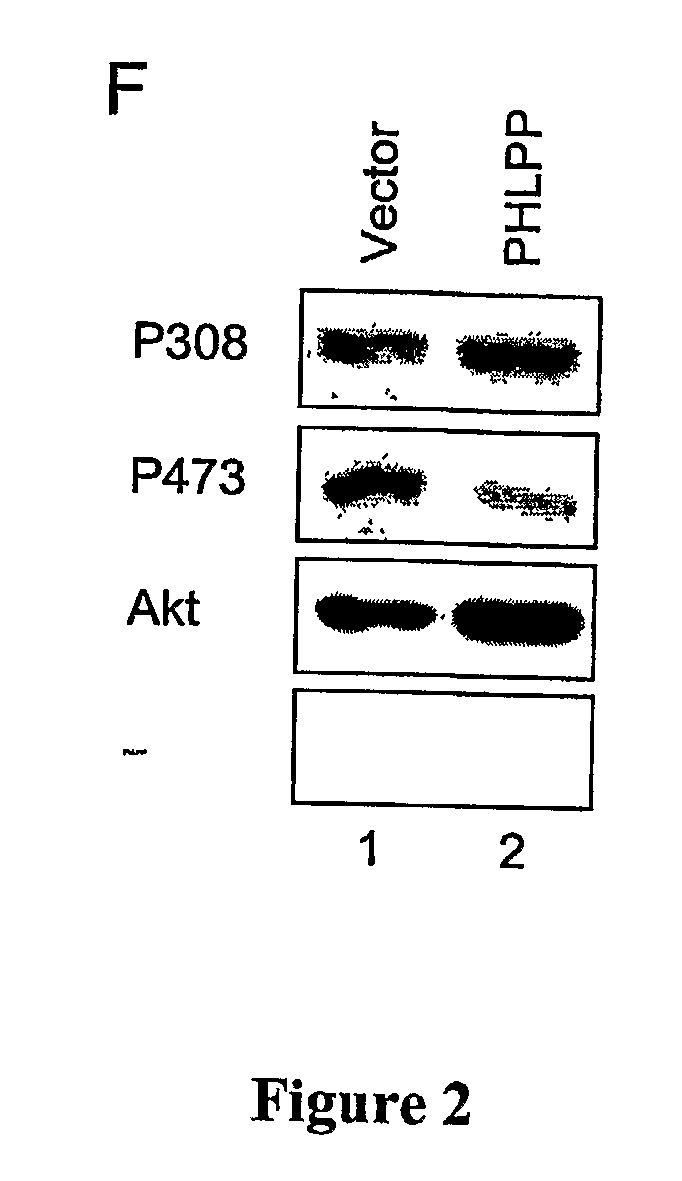
Compositions and Methods for Treating Diseases Associated With Phlpp
The present invention relates generally to PHLPP, a novel phosphatase that inactivates Akt (protein kinase B) by directly dephosphorylating the hydrophobic domain of the C-terminus. More specifically, the invention relates to PHLPP polynucleotides and the polypeptides encoded by these polynucleotides and the use of these polynucleotides and polypeptides in the treatment and diagnosis of biological conditions mediated by Akt phosphorylation, particularly cancer. This invention relates to PHLPP polynucleotides and polypeptides as well as vectors, host cells, antibodies directed to PHLPP polynucleotides and polypeptides and recombinant and synthetic methods for producing the same. The invention further relates to screening methods for identifying agonists and antagonists of PHLPP polynucleotides and polypeptides of the invention.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Application of compounds Pyrrocidines in preparation of anti-tuberculosis drug
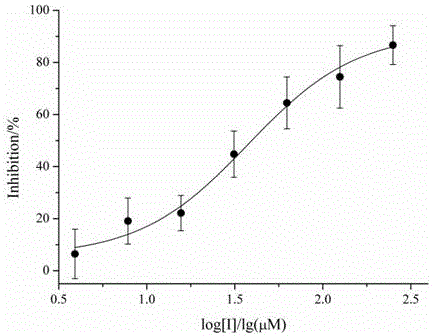
InactiveCN105687187AInhibition of dephosphorylation activityHas inhibitory activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsChemical synthesisPhosphorylation
The invention provides an application of compounds Pyrrocidines in preparation of an anti-tuberculosis drug, namely, an application of the compounds Pyrrocidines, derivatives of the compound Pyrrocidines or pharmaceutically acceptable salts of the compounds Pyrrocidines as tyrosine phosphatase inhibitors or in preparation of the tyrosine phosphatase inhibitors. The compounds 19-O-methyl-pyrrrocidine B and pyrrrocidine B have inhibitory activity on mycobacterium tuberculosis tyrosine phosphatase B, and IC50 of the compounds is 3.9 mu M and 75.5 mu M respectively. The compounds can effectively inhibit dephosphorylation activity of the mycobacterium tuberculosis tyrosine phosphatase B and has the clinical application potential for tuberculosis treatment; besides, the compounds Pyrrocidines are natural-metabolism active micro-molecular products separated from microorganisms and can be produced through chemical synthesis and large-scale fermentation separation, the sources are abundant, the production cost is low, and the possibility of medicine preparation is high.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV +1
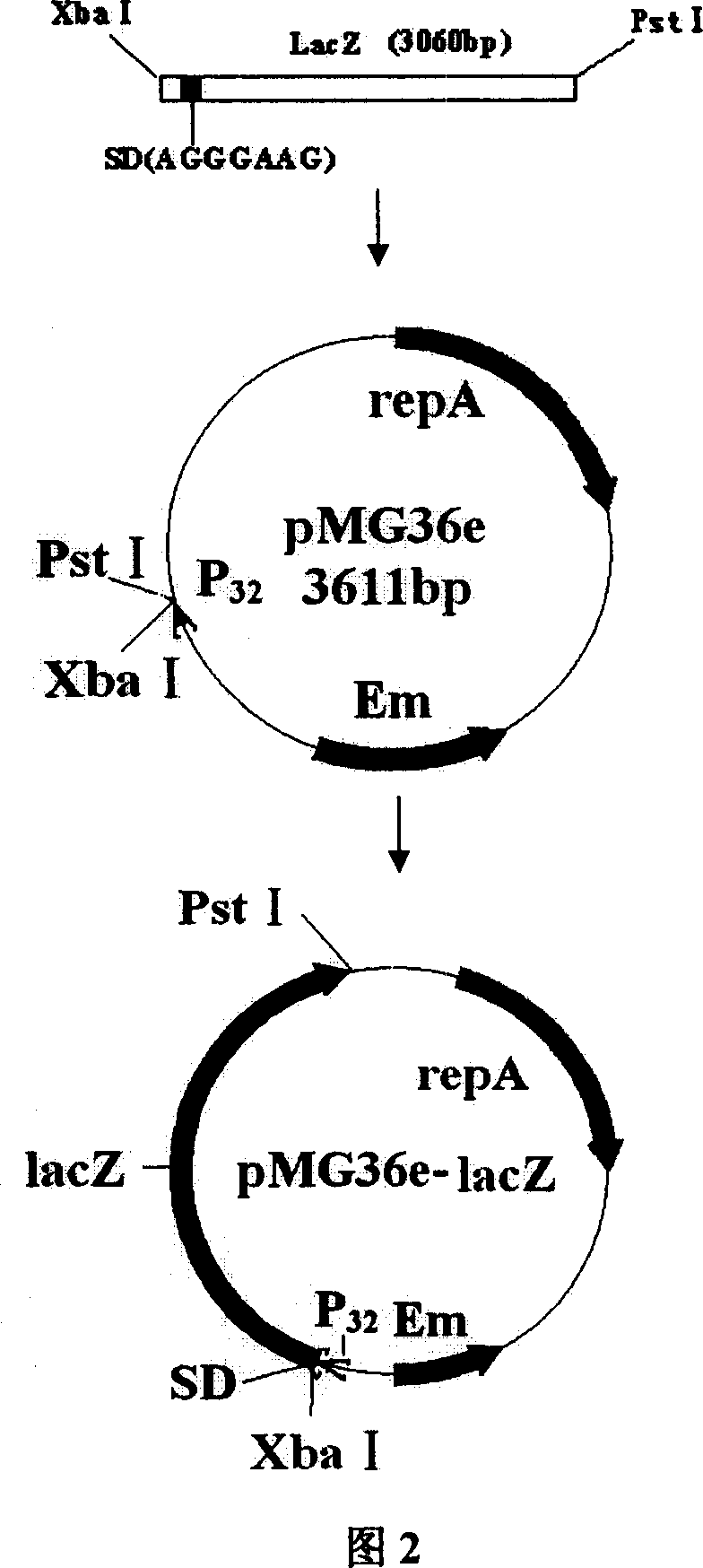
Colibacillus-lactic acid bacteria shuttle plasmid capable of expressing and excreting beta-galactosidase and its construction method and application
InactiveCN101033471AAchieve separationImmediate and broad application valueBacteriaFermentationPhosphorylationGenomic DNA
Gene of an E.coli-Lactobacillus shuttle plasmid expressing and secreting beta-galactosidase is composed of the gene encoding beta-galactosidase and its upstream regulatory sequence containing SD sites. Experiments proves that the recombinant plasmid can be transformed into Lactococcus lactis, and highly express the non-fused beta-galactosidase in E.coli and Lactococcus lactis, which is applicable in the lactic acid bacteria strain expressing beta-galactosidaseion. The construction method includes the following steps: taking Lactobacillus Bulgaria subspecies genomic DNA as template to amplify and obtain the beta-galactosidase gene containing the upstream regulatory sequence, digesting the gene to conjugate with the dephosphorylated vector digested with the same two enzymes and transform E.coli, then screening the positive one to extract the recombinant for enzyme identification and sequencing the inserted sequence.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Method for quantifying phosphokinase activity on proteins
InactiveUS20090104628A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisProtein targetTyrosine
The invention involves a method for measuring phosphorylation of proteins at specific sites and, as such, is an indicator of the protein kinase activity of enzymes capable of phosphorylating those sites. The method involves the in vitro or in vivo phosphorylation of a target protein at a specific serine, threonine or tyrosine residue, subjecting that protein (non-phosphorylated) to reaction mixture containing all reagents, including phosphokinase which allow the creation of a phosphorylated form of protein. The phosphorylated protein is measured by contacting it with an antibody specific for the phosphorylation site(s). The invention includes antibodies useful in practicing the methods of the invention. The invention particularly relates to all proteins modified by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation as illustrated by Tau, Rb and EGFR proteins and antibodies specific for the site of phosphorylation of the Tau, Rb or EGFR proteins.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Reagents and methods for phosphorylation/dephosphorylation analyses
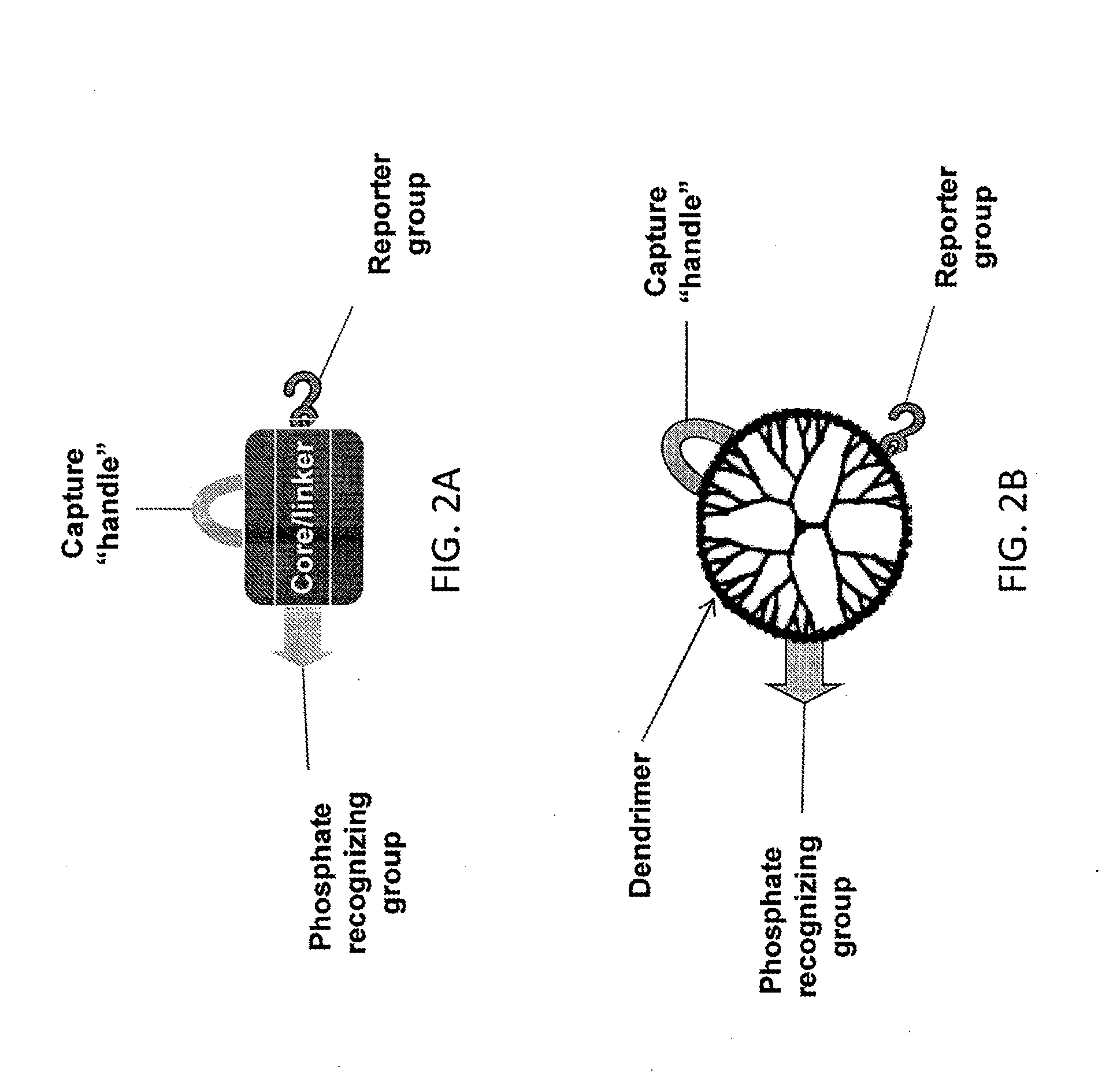
ActiveUS20130095502A1Maximize bindingMaximize generationOrganic chemistryEnzyme stabilisationDendrimerPhosphorylation
Disclosed herein are reagents that include a moiety that includes a metal such as titanium and that readily binds to phosphorylated molecules the reagents also include at least one moiety that produces a signal or that binds to a molecule that produces a signal. The reagent may also include a moiety that binds to a larger molecule or to a surface. Some forms of the reagent include a dendrimer that can simultaneously bind to multiple metal moieties that include a metal such as titanium and multiple moieties that can be used to detected bound molecules. These reagents can be used in detection and / or measurement and / or at least partial purification of phosphorylated molecules. These reagents and methods using them are used to analyze proteins, polypeptides, nucleic acids, phospholipids and the like. They are readily adapted for use in gels, blots, plate based high through put assays and for mass spectrometry.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
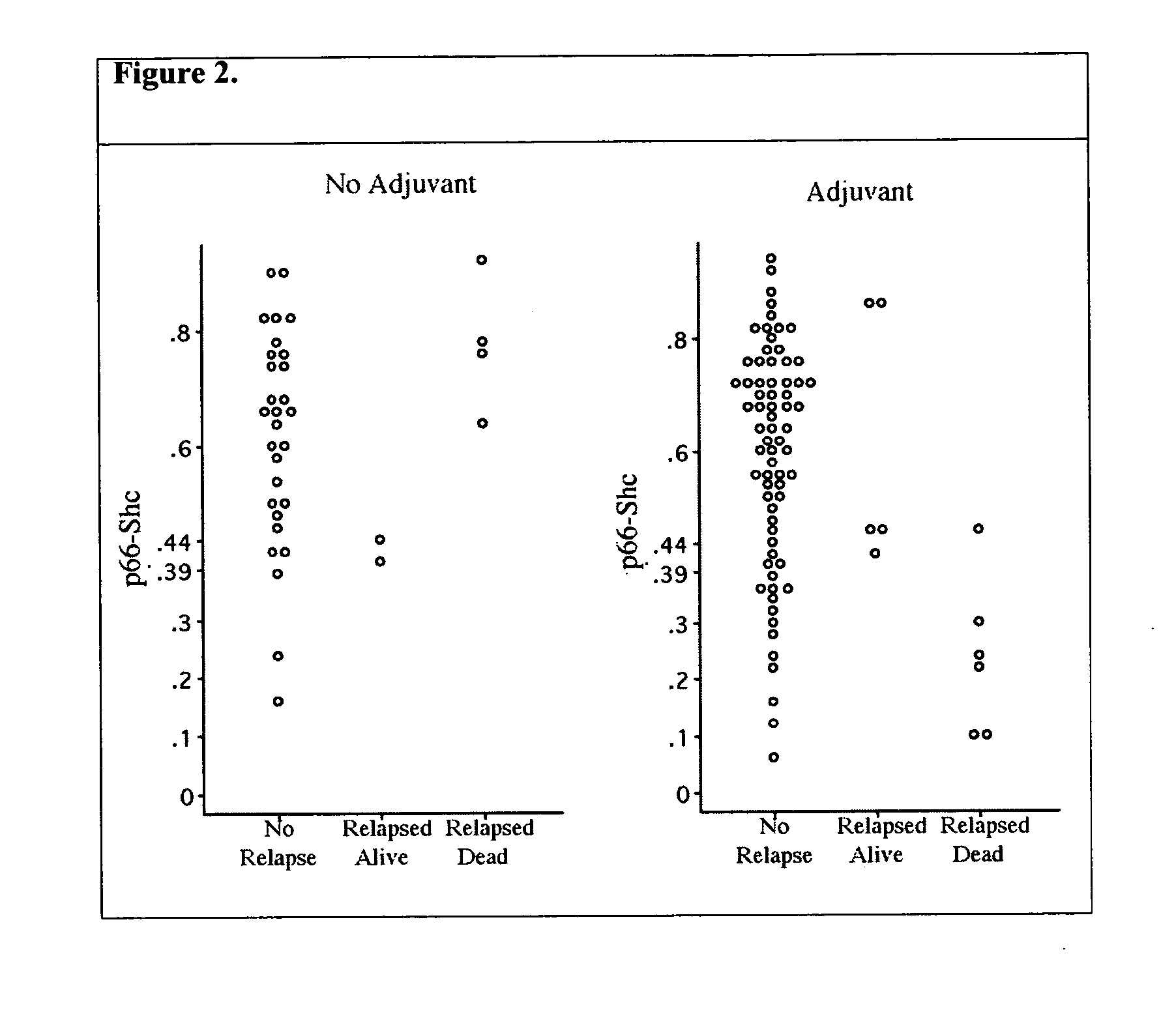
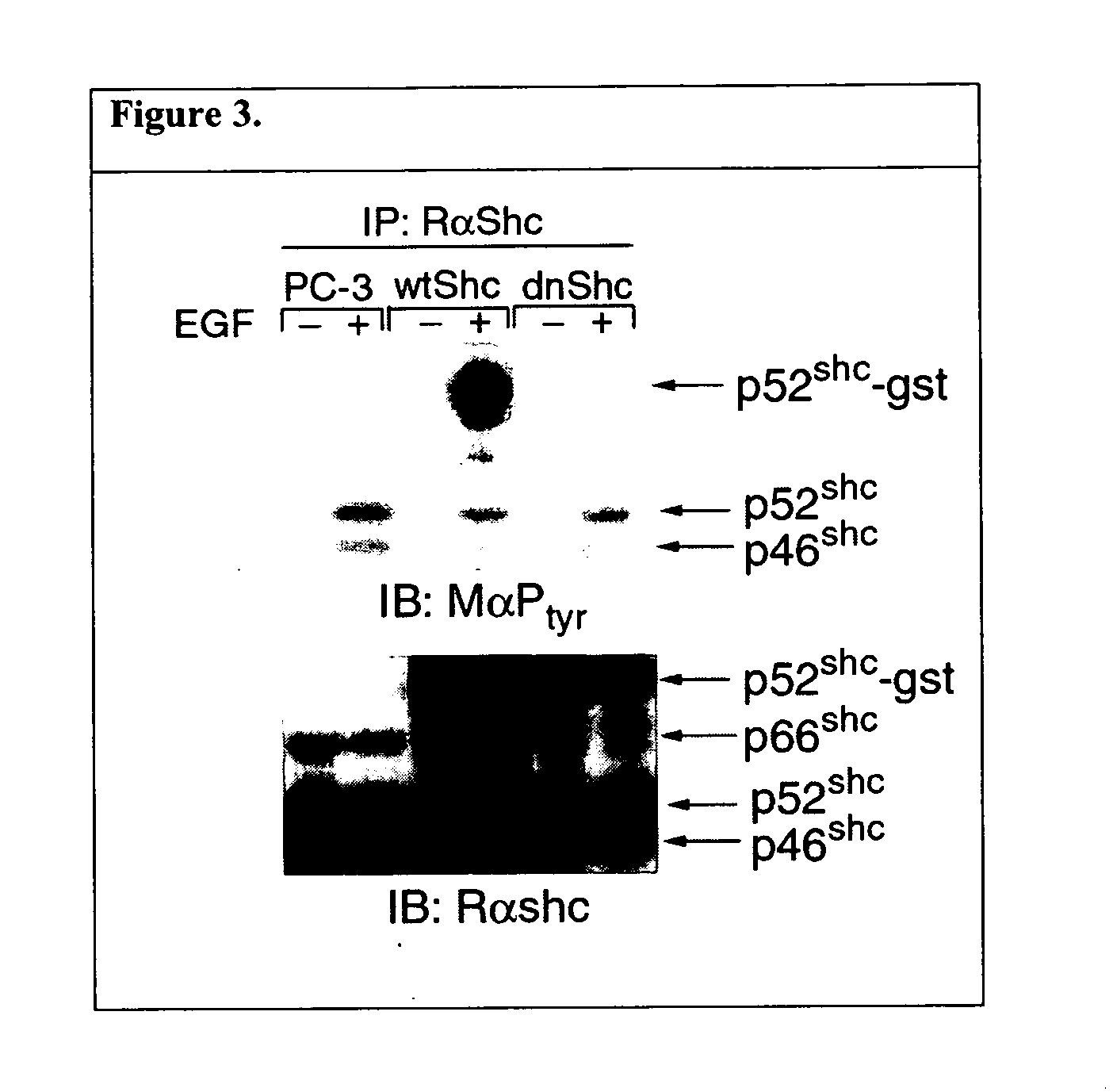
SHC proteins as therapeutic targets in proliferative diseases
This invention provides methods for treating a subject afflicted with a proliferative disorder comprising administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of an agent which inhibits the expression of p46 Shc and / or p52 Shc, inhibits the activity of p46 Shc and / or p52 Shc in the subject, or increases the level of phosphorylated p66 Shc in the subject. This invention also provides methods for determining whether an agent inhibits the phosphorylation of p46 Shc or p52 Shc; inhibits the dephosphorylation of p66 Shc comprising; or an agent inhibits the binding of a Shc A protein with a protein to which the Shc A protein must bind in a cell in order to carry out its proliferative function. This invention also provides articles of manufacture for use in treating a proliferative disorder in a subject.
Owner:ROGER WILLIAMS GEN HOSPITAL
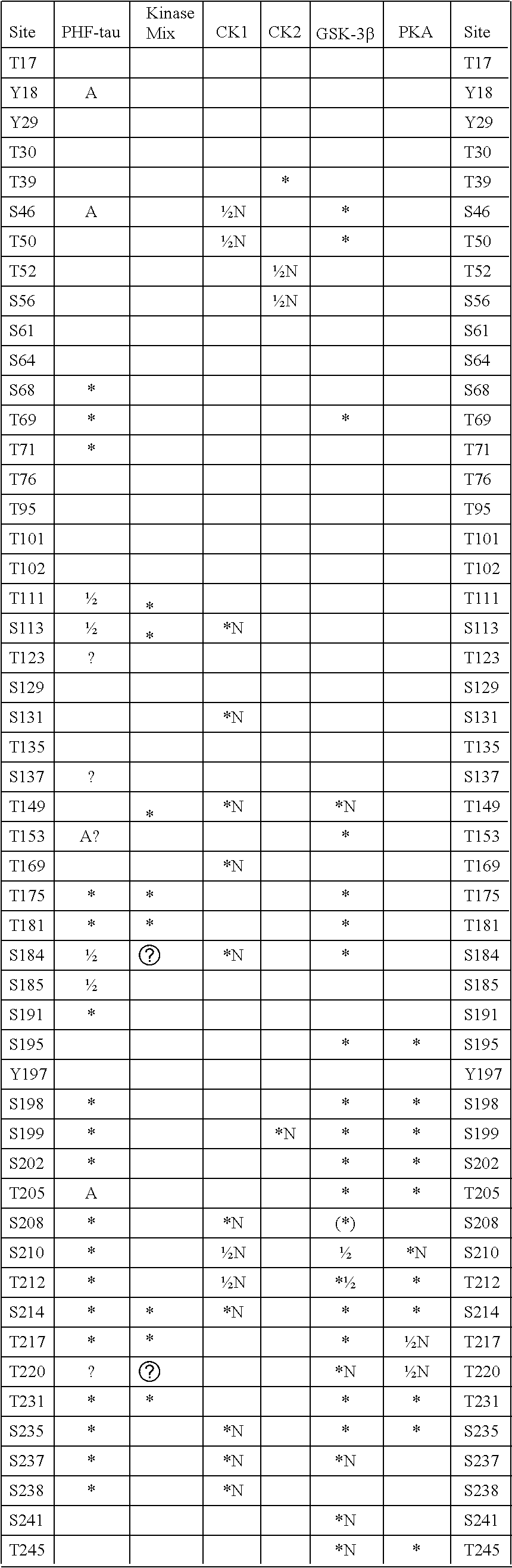
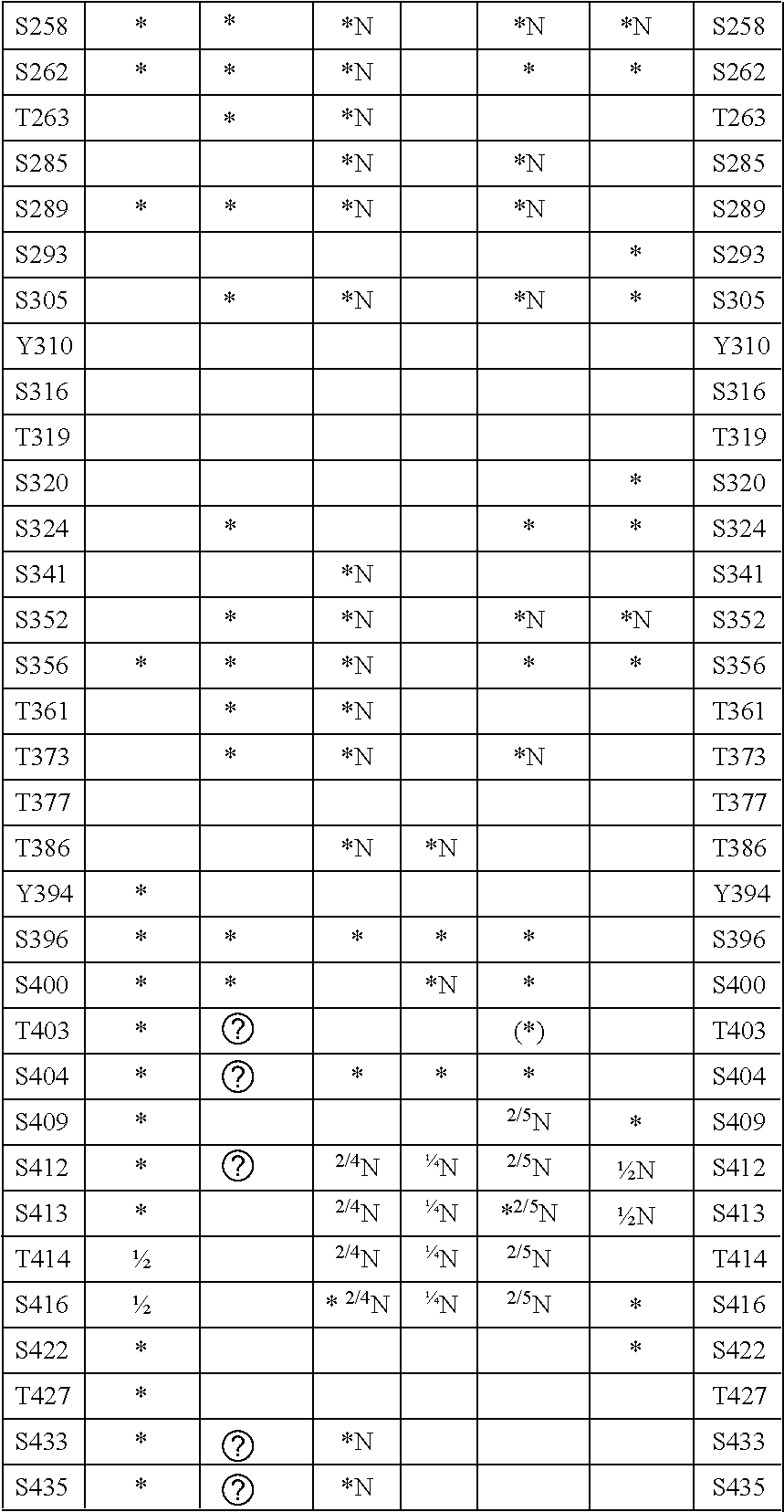
Methods for Screening Inhibitors of Tau Phosphorylation By Casein Kinase I
InactiveUS20150051097A1Compound screeningNervous disorderPhosphorylation InhibitionTau phosphorylation
Methods of screening for candidate compounds capable of inhibiting activity of fyn in phosphorylating tau protein at Y394 or binding to fyn to inhibit interaction with tau protein at Y394, including determining whether, and optionally the extent, the candidate compounds have these capabilities under conditions where fyn has these capabilities in the absence of the candidate compound. Methods of screening for substances capable of promoting dephosphorylation of tau protein by a phosphatase at a site of tau protein including contacting a candidate substance, the tau protein and a phosphatase capable of dephosphorylating the tau protein under conditions where the phosphatase is capable of dephosphorylating the site in absence of the candidate substance, where the kinase is fyn; determining whether, and optionally the extent, the candidate substance promotes dephosphorylation of the tau protein at the site; and selecting the candidate substance which promotes dephosphorylation of the tau protein the sites.
Owner:PROTEOME SCI +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com