Patents
Literature
41 results about "CREB" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
CREB-TF (CREB, cAMP response element-binding protein) is a cellular transcription factor. It binds to certain DNA sequences called cAMP response elements (CRE), thereby increasing or decreasing the transcription of the genes. CREB was first described in 1987 as a cAMP-responsive transcription factor regulating the somatostatin gene.
Augmented cognitive training
InactiveUS7947731B2Improve performanceNormally performanceBiocideNervous disorderNeuronal circuitsClinical psychology
The present invention provides methods of therapy of cognitive deficits associated with a central nervous system disorder or condition, methods of enhancing cognitive performance and methods for repeated stimulation of neuronal activity or a pattern of neuronal activity, such as that underlying a specific neuronal circuit(s). The methods comprise combining cognitive training protocols and a general administration of CREB pathway-enhancing agents.
Owner:COLD SPRING HARBOR LAB INC
Transcription factor RNA interference reagents and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20050197312A1High-efficiency intracellular deliveryInhibit bindingGenetic material ingredientsEnzymesDouble strandGenome
The present invention concerns methods and reagents useful in modulating transcription factor gene expression in a variety of applications, including methods of use in therapeutic, diagnostic, target validation, and genomic discovery applications. Specifically, the invention relates to small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siRNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), and doublestranded RNA (dsRNA) molecules capable of mediating RNA interference (RNAi) against E2F1, NFkB, CREB-1, and / or CDC2A gene expression, useful in the treatment of cell cycle disorders, inflammatory conditions, reproductive disorders, cancers and any other condition that responds to modulation of E2F1, NFkB, CREB-1, and / or CDC2A expression and / or activity.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Method for classification of anti-psychotic drugs
The present invention provides a method for identifying an agent to be tested for an ability to treat a psychotic disorder in a patient in need of such treatment. The invention provides a method for screening candidate drugs for anti-psychotic drug activity, preferably atypical anti-psychotic activity, comprising contacting cells or tissues with a candidate drug, determining levels of phosphorylation of the intracellular signaling proteins, DARPP-32, ERK1, ERK2 and CREB, in said cells or tissues and determining the pattern of the levels of phosphorylation of the proteins. The pattern of the levels of phosphorylation of DARPP-32, ERK1, ERK2 and CREB is, in certain embodiments, compared with the pattern of the levels of phosphorylation of DARPP-32, ERK1, ERK2 and CREB in the presence of an atypical anti-psychotic drug.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Method for screening compounds & uses therefor
InactiveUS20060246418A1Modulate levelPromotes rapid Ser17 dephosphorylationCompound screeningApoptosis detectionHeterologousCytoplasm
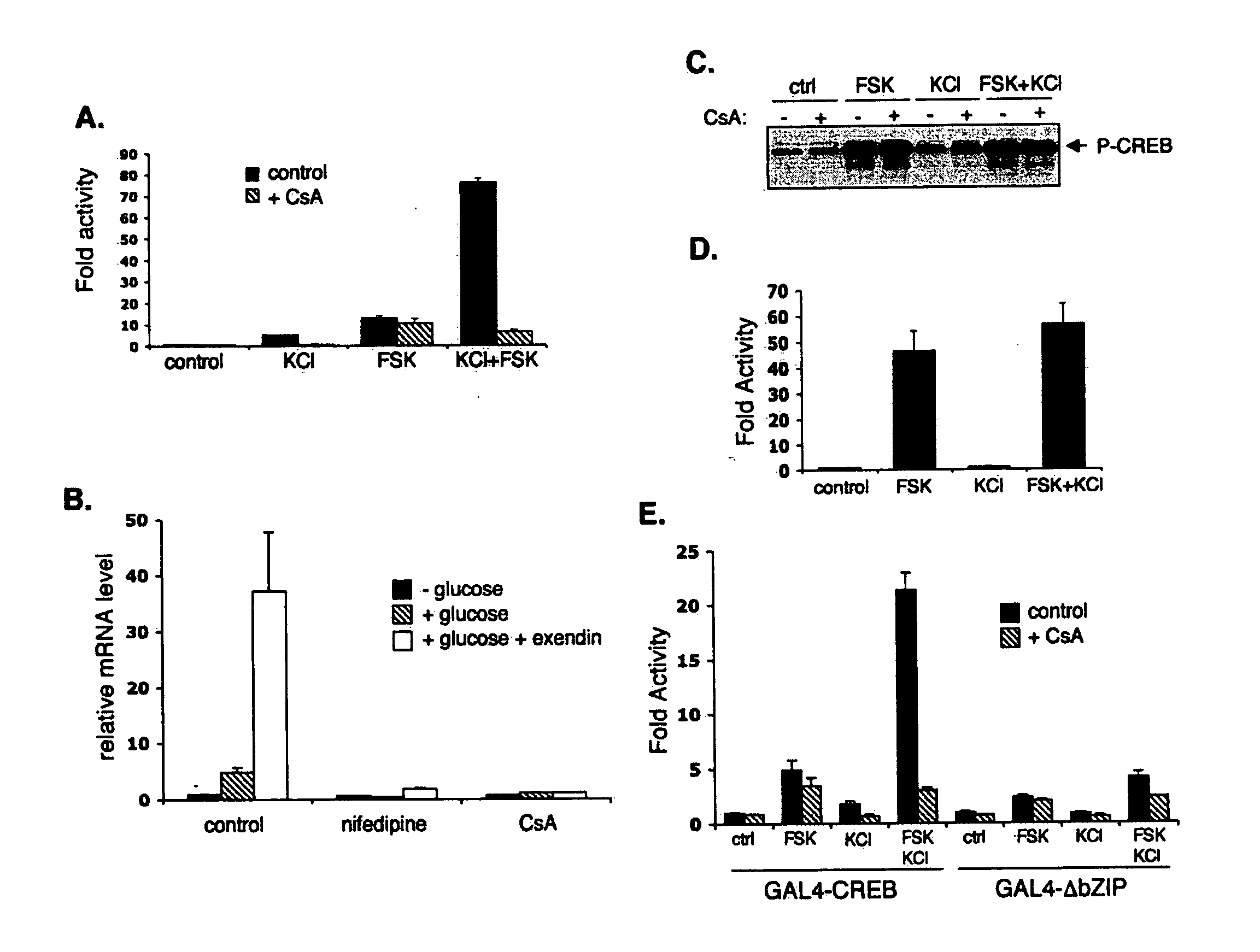
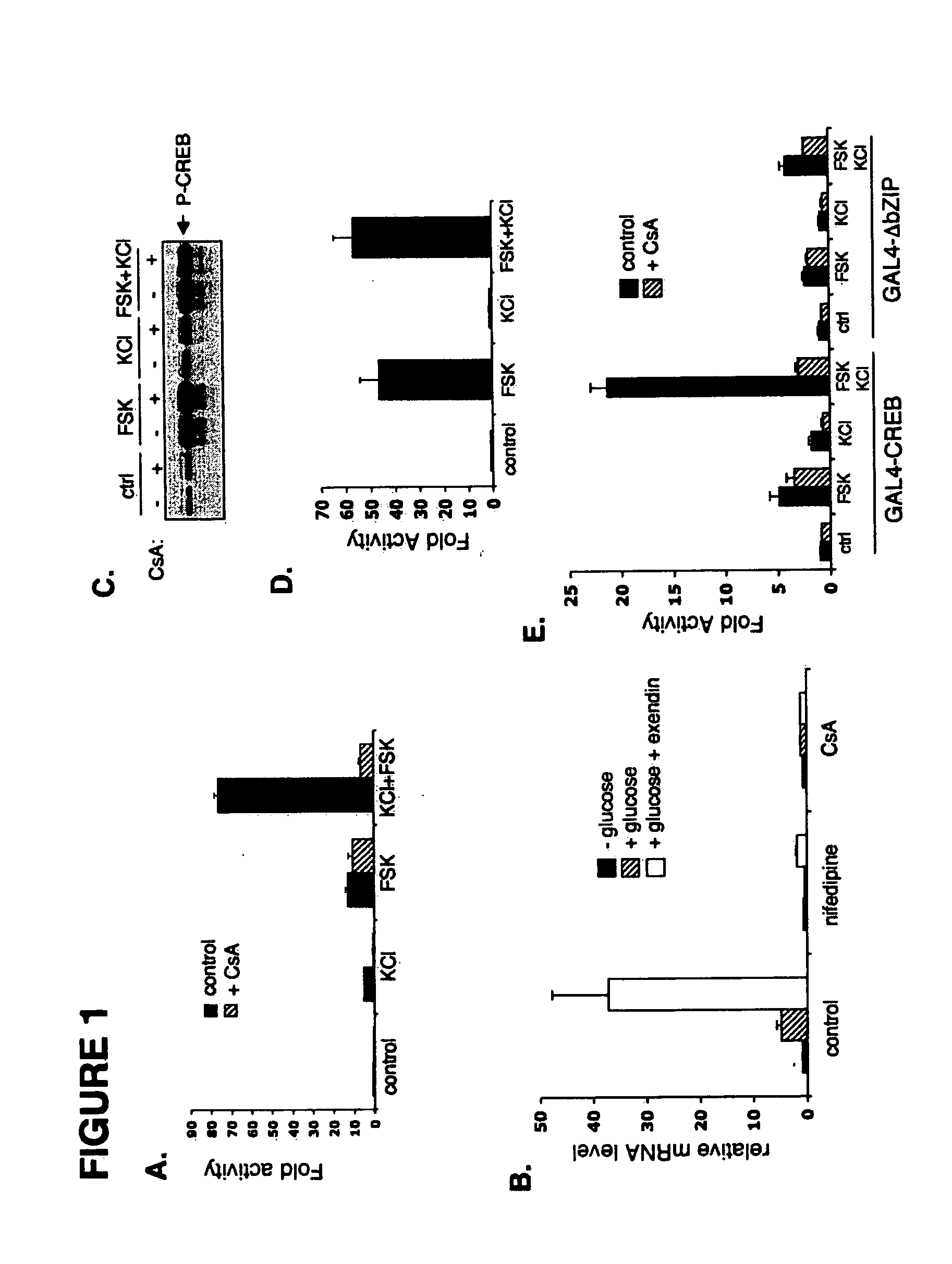
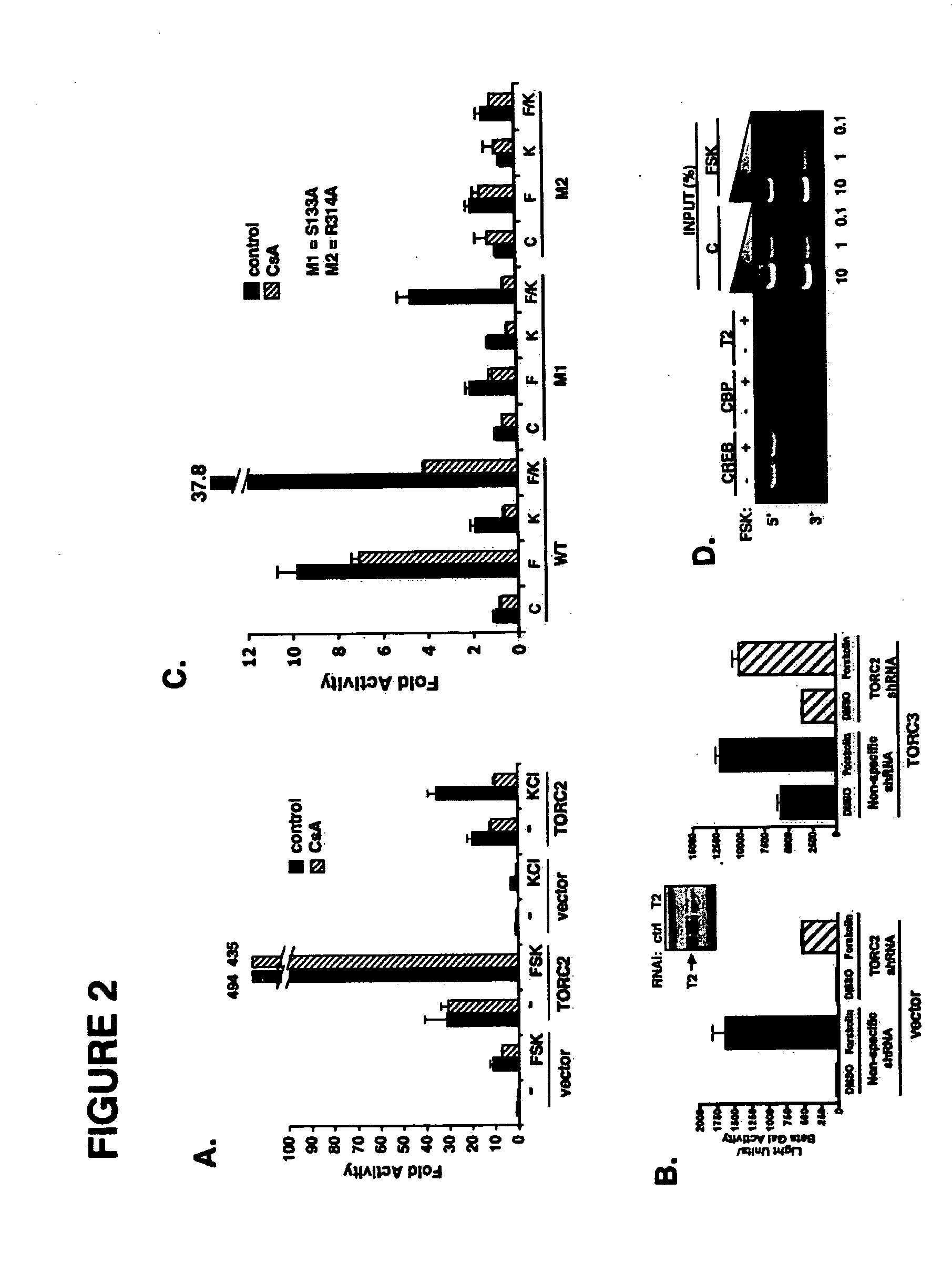
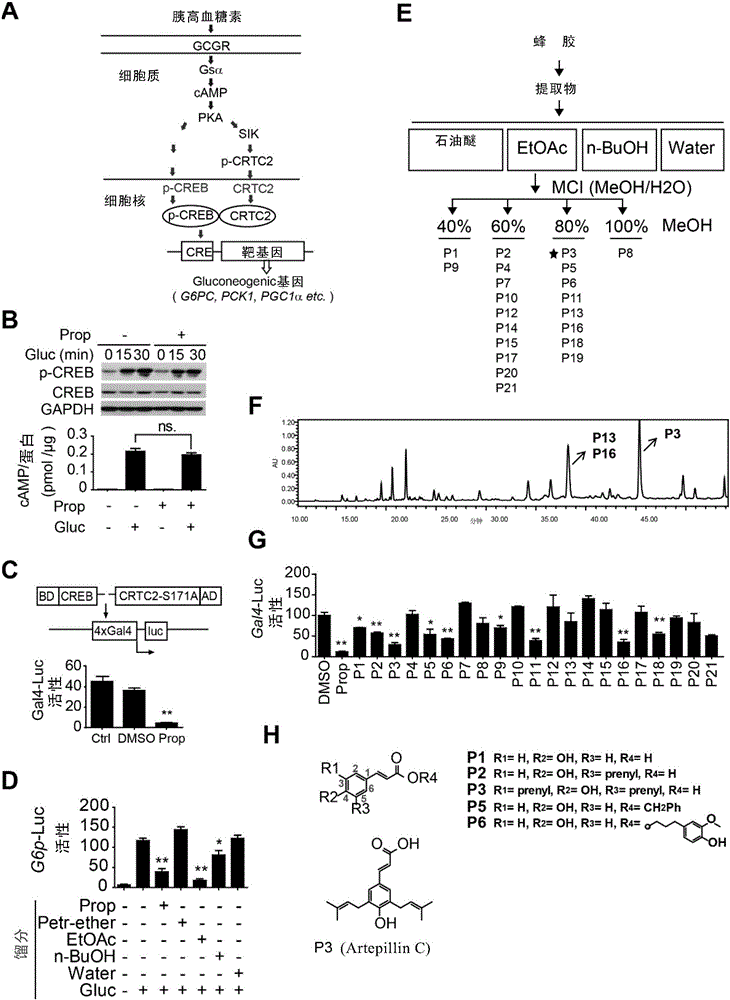
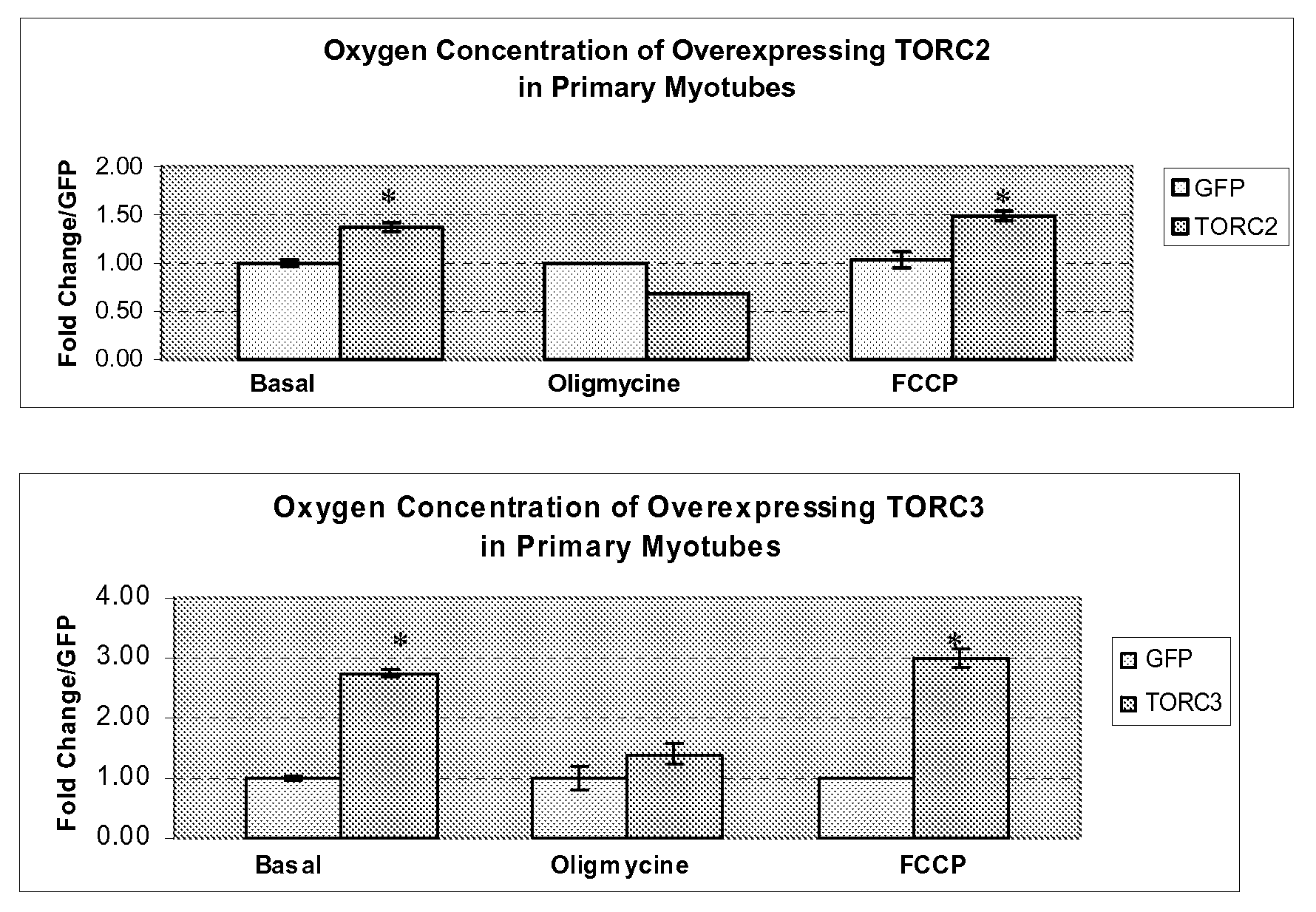
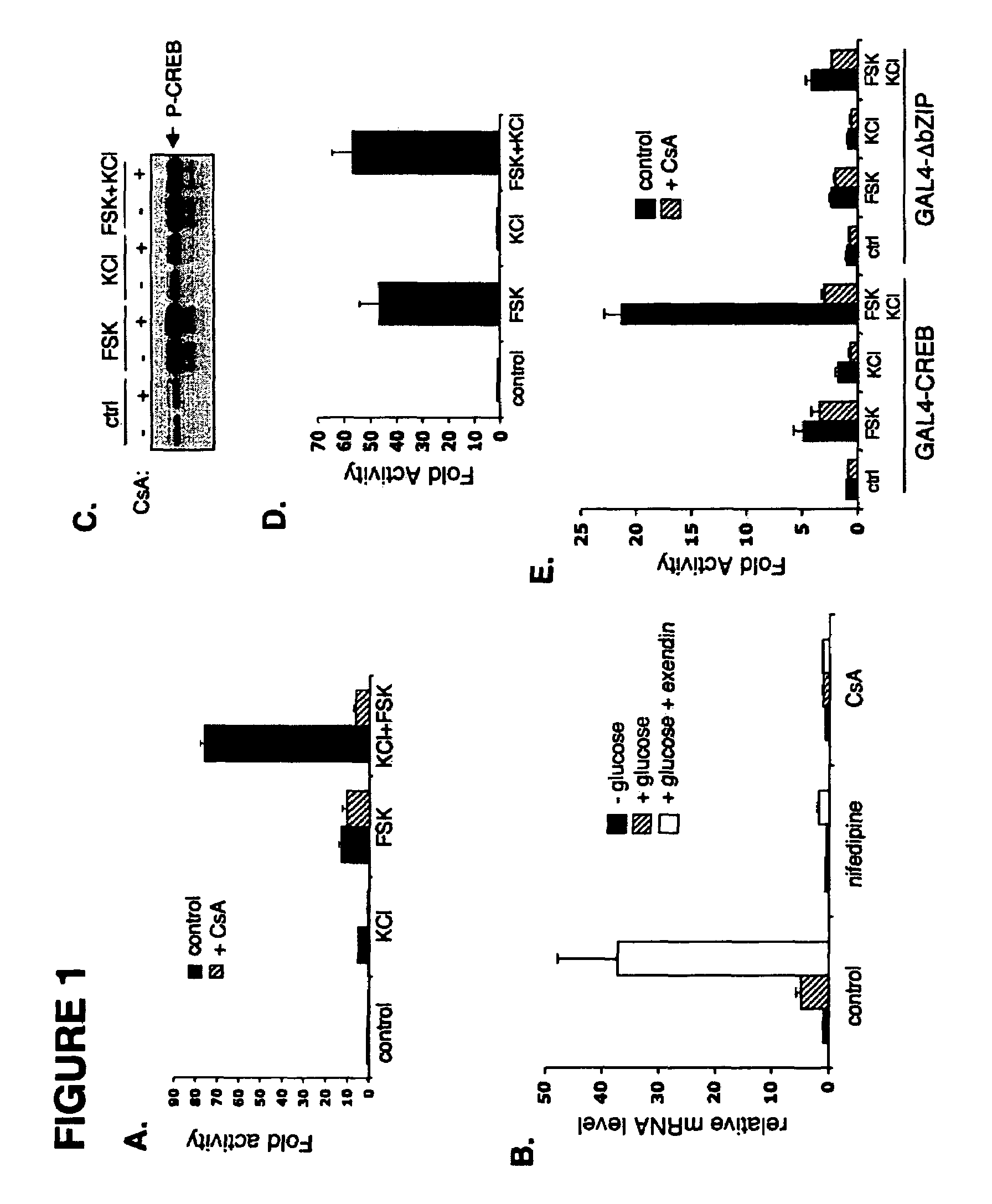
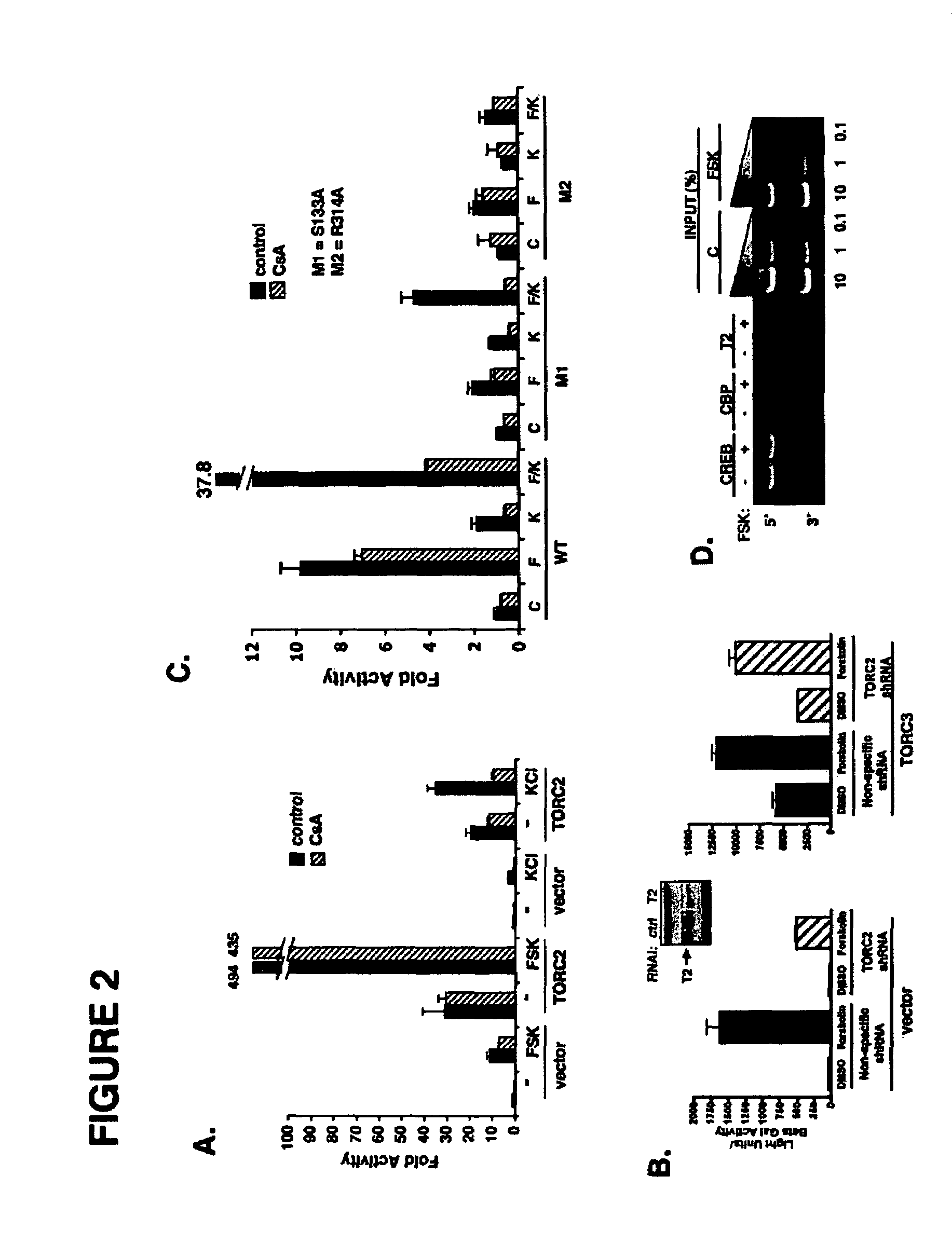
In accordance with the present invention, it has been discovered that glucose and incretin hormones promote pancreatic islet cell survival via the calcium and cAMP dependent induction, respectively, of the transcription factor CREB. Specifically, a signaling module has been identified which mediates cooperative effects of calcium and cAMP on islet cell gene expression by stimulating the dephosphorylation and nuclear entry of TORC2, a cytoplasmic CREB coactivator. The module comprises a cAMP regulated snf1-like kinase called SIK2 and the calcium regulated phosphatase calcineurin, both of which associate with TORC2 in the cytoplasm. TORC2 is repressed under basal conditions through a phosphorylation dependent interaction with 14-3-3 proteins. cAMP and calcium signals stimulate CREB target gene expression via complementary effects on TORC2 dephosphorylation; cAMP disrupts TORC2-associated activity of SIK2 or related family members, whereas calcium induces TORC2 dephosphorylation via calcineurin. These findings provide a novel mechanism by which CREB activates cellular gene expression, depending on nutrient and energy status, and facilitate development of assays to identify compounds which modulate the role of TORCs. In accordance with the present invention, it has been discovered that fasting and energy-sensing pathways regulate the gluconeogenic program in liver by modulating the nuclear entry of a transcriptional coactivator called Transducer of Regulated CREB Activity 2 (TORC2). Hepatic TORC2 over-expression induces fasting hyperglycemia, whereas knockdown of TORC2 leads to fasting hypoglycemia and silencing of the gluconeogenic program. Since a majority of individuals with Type II diabetes exhibit fasting hyperglycemia due to elevated hepatic gluconeogenesis, compounds that enhance TORC2 phosphorylation will find use as therapeutic agents in this setting.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
Applications of Artepillin C and analogue thereof in preparing drugs used for preventing metabolic diseases
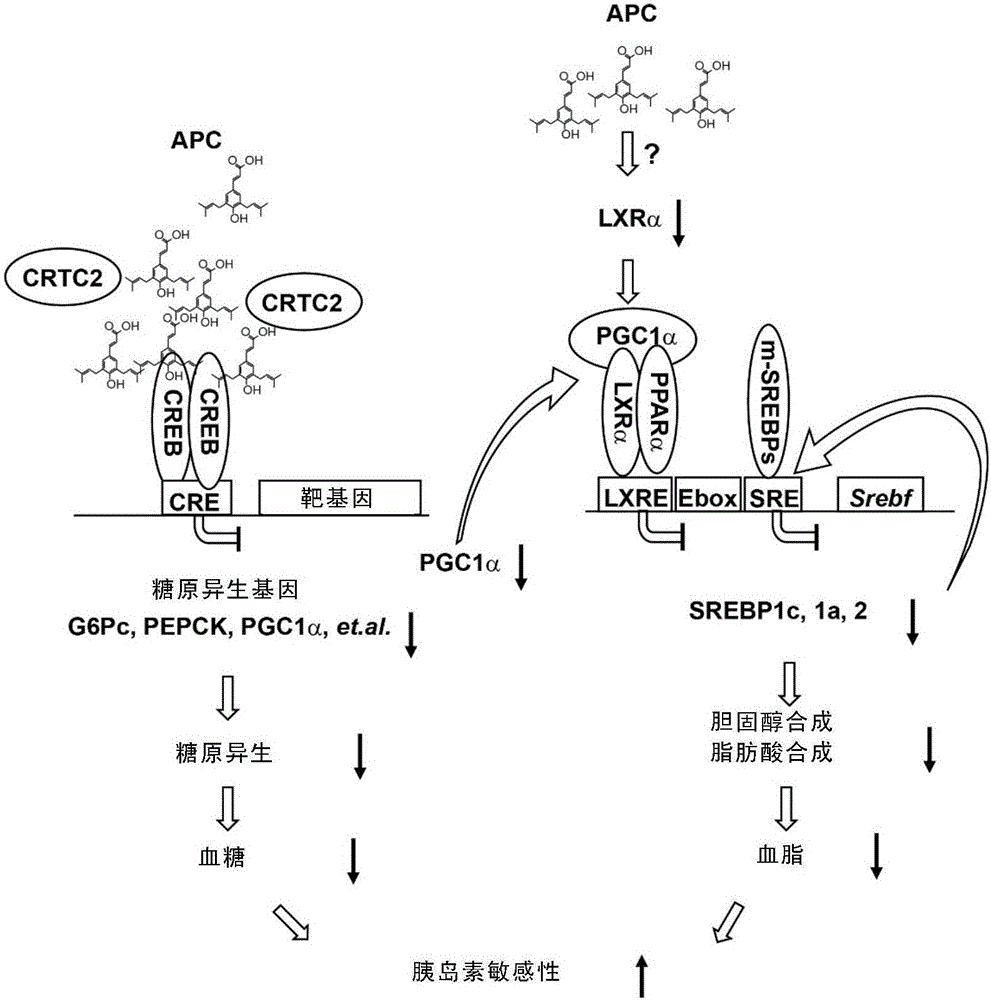
The invention relates to applications of Artepillin C and an analogue thereof in preparing drugs used for preventing metabolic diseases. The extremely excellent effect of Artepillin C or the analogue in preventing metabolic diseases is disclosed for the first time, and multifunctional drugs used for conditioning taking CREB / CRTC2 and SREBP as target spots are provided.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Torc polynucleotides and polypeptides and method of use
The present invention relates to a broad range of methods that utilize a transducer of regulated CREB (TORC)-related polynucleotide, polypeptide, or TORC-specific antibody. In addition the invention relates to TORC-related polynucleotide, polypeptide, or TORC-specific antibody compositions, including variants of TORC wild-type sequences. Exemplary methods include a method of stimulating a TORC related process in a cell as well as a method of inhibiting a TORC-related process in a cell, and a method of inhibiting TORC-related processes in a cell. The invention additionally discloses therapeutic methods of substantially inhibiting the development of, treating, or ameliorating a disease or pathological condition in a subject related to an abnormal level of a TORC-activated process in a cell that includes administering one or more therapeutically effective doses to the subject of either a substance that modulates accumulation of a TORC polypeptide in a subcellular region of the cell, or of a substance that inhibits expression of a TORC polypeptide in the cell. In an additional aspect a method of identifying an agent that modulates the activity of a TORC-related process in a cell is disclosed. In still a further aspect the invention relates to a method of detecting the presence or quantifying the amount of a TORC polypeptide in a sample. In a further aspect, a method is disclosed of determining whether the amount of a TORC polypeptide in a sample differs from the amount of the TORC polypeptide in a reference. An additional aspect relates to a method of contributing to the diagnosis or prognosis of, or to developing a therapeutic strategy for, a disease or pathology in a first subject, wherein the subcellular localization of a TORC polypeptide in the pathology is known to differ from the subcellular localization of the TORC polypeptide in a nonpathological state.
Owner:LABOW MARK ARON +1
Detecting method for evaluating tumor growth safety promotion of cell growth factor
InactiveCN101419222AReliable detection methodIn vivo and in vitro test results are reliableMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingAbnormal tissue growthPhosphorylation
The invention discloses a detection method for evaluating the safety of cell growth factor to promote tumor growth, which comprises the following steps: firstly, using a CFSE marker flow cytometry and a [<3>H] incorporation method to measure the speeds of cell division and cell growth respectively; secondly, measuring CREB passageway related genes and protein expression level, and measuring the phosphorylation level of a CREB protein, and the combination of CREB, CREM, ICER, CBP, P300 and a growth regulatory gene promoter; and finally, evaluating the clone forming number and the tumor volume. The method applies the molecular biology and the cell biological technology combining with in vitro and in vivo test results to evaluate the safety of the cell growth factor to promote the tumor growth. The method can also be used for evaluating the safety of other genetic engineering drugs.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Methods for modulating expression of creb
InactiveUS20110177097A1Lower Level RequirementsDownsized mannerOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsLipid levelCREB
Methods are provided for modulating CREB by administering a CREB-specific modulator. Also provided are methods for treating cardiovascular and metabolic disorders in a subject or delaying or preventing risk factors thereof through the modulation of CREB. The present invention is also directed to methods of decreasing lipid levels in a subject or for preventing or delaying the onset of a rise in lipid levels in a subject, comprising administering to said subject a CREB-specific inhibitor.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC +1
Targeting the histone code as a bacterial strategy for selectively modulating gene expression
InactiveUS20070077254A1Reduce transcriptionAvoid changeAntibacterial agentsHydrolasesDiseaseShigella flexneri
The ospF gene of Shigella flexneri encodes a phosphatase, which is a member of a new class of phosphatases. The OspF phosphatase inhibits the activity of several proteins either by direct protein modification or transcription downregulation. These proteins include MAP kinase, IL-8, CCL20, IL-12, AP1, CREB, RPA p32, and BCL2 related proteins. Methods for treating diseases using OspF phosphatase, methods for identifying agents that modulate OspF phosphatase's activity, methods for identifying agents that mimic OspF phosphatase's activity, and immunogenic compositions comprising OspF phosphatase are provided. A strain of Shigella flexneri containing an inactivated ospF gene is also provided.
Owner:INST PASTEUR
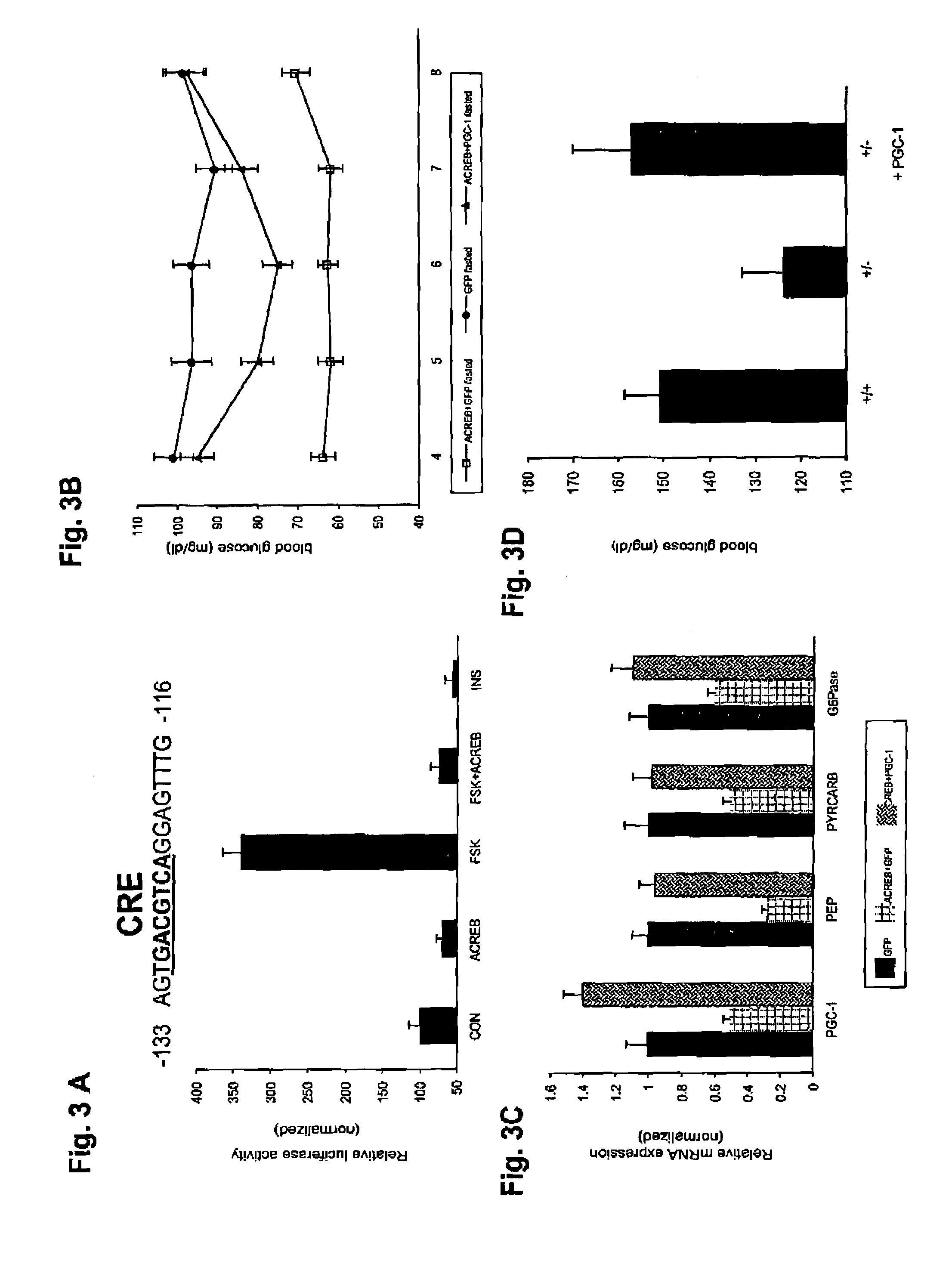
Methods for indentifying compounds that modulate gluconeogenesis through the binding of CREB to the PGC-1 promoter
InactiveUS6974671B1Restored glucose homeostasisRescued expressionElectrolysis componentsGenetic material ingredientsDiabetes mellitusGlucocorticoid
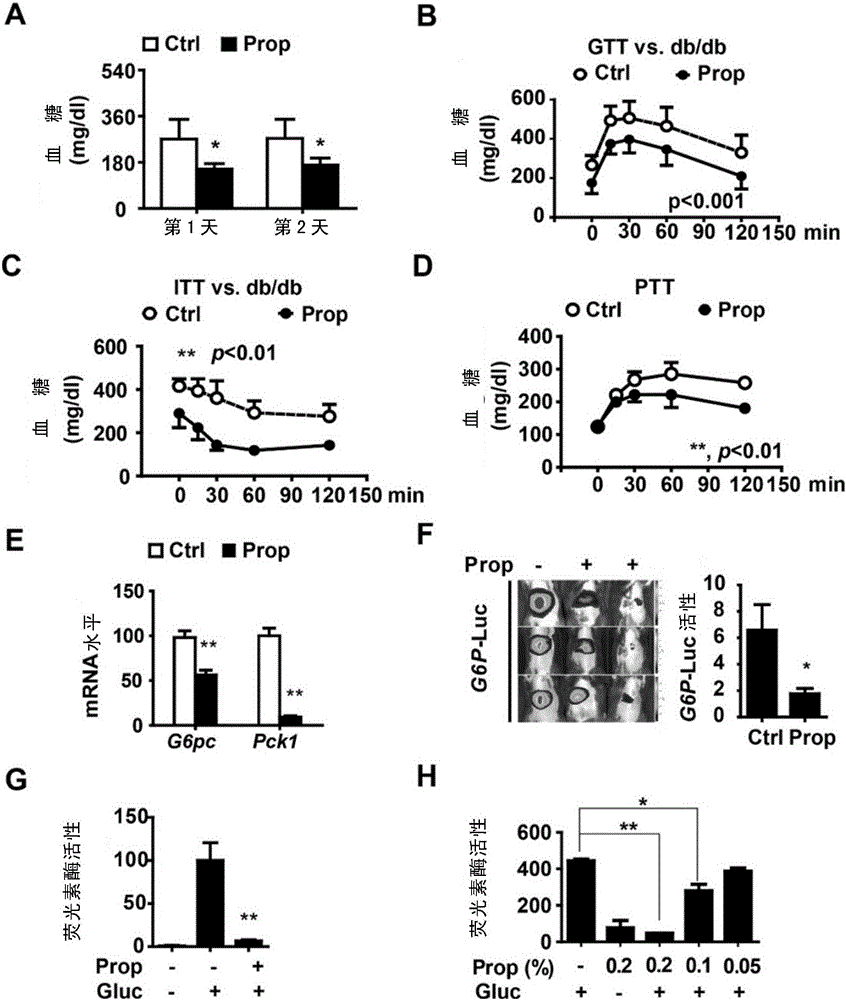
In accordance with the present invention, it has been discovered that CREB regulates hepatic gluconeogenesis via the co-activator, PGC-1. PGC-1 potentiated glucocorticoid induction of the gene for PEPCK, the rate limiting enzyme in gluconeogenesis, via the glucocorticoid response unit in the promoter, indicating that activation of PGC-1 by CREB in liver contributes to the pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus. In accordance with the above discoveries, the present invention provides a method of identifying a compound that modulates gluconeogenesis. The invention method comprises contacting CREB and a nucleic acid comprising a PGC-1 promoter with a test compound, and determining if the test compound modulates binding between CREB and the PGC-1 promoter.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
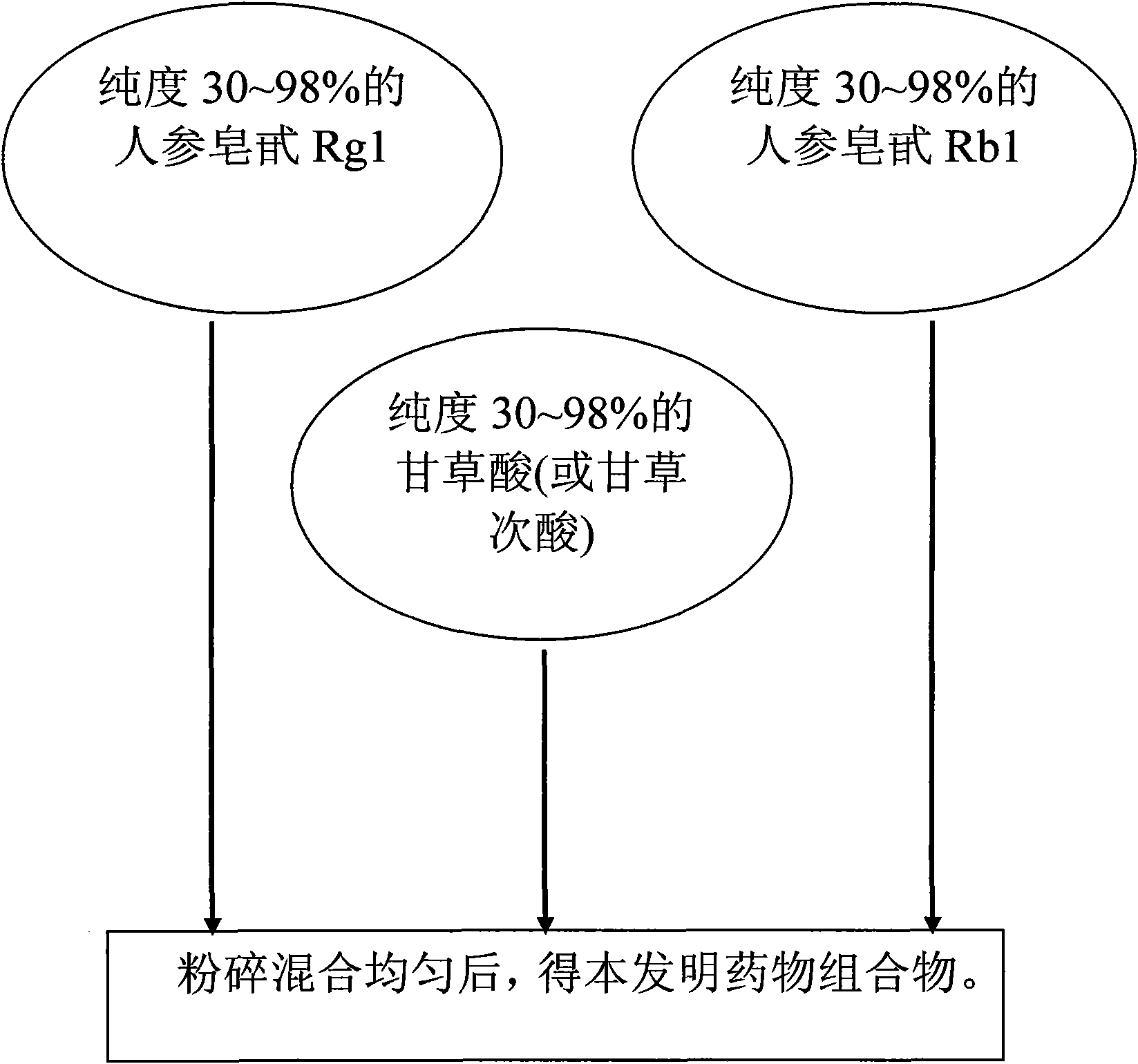
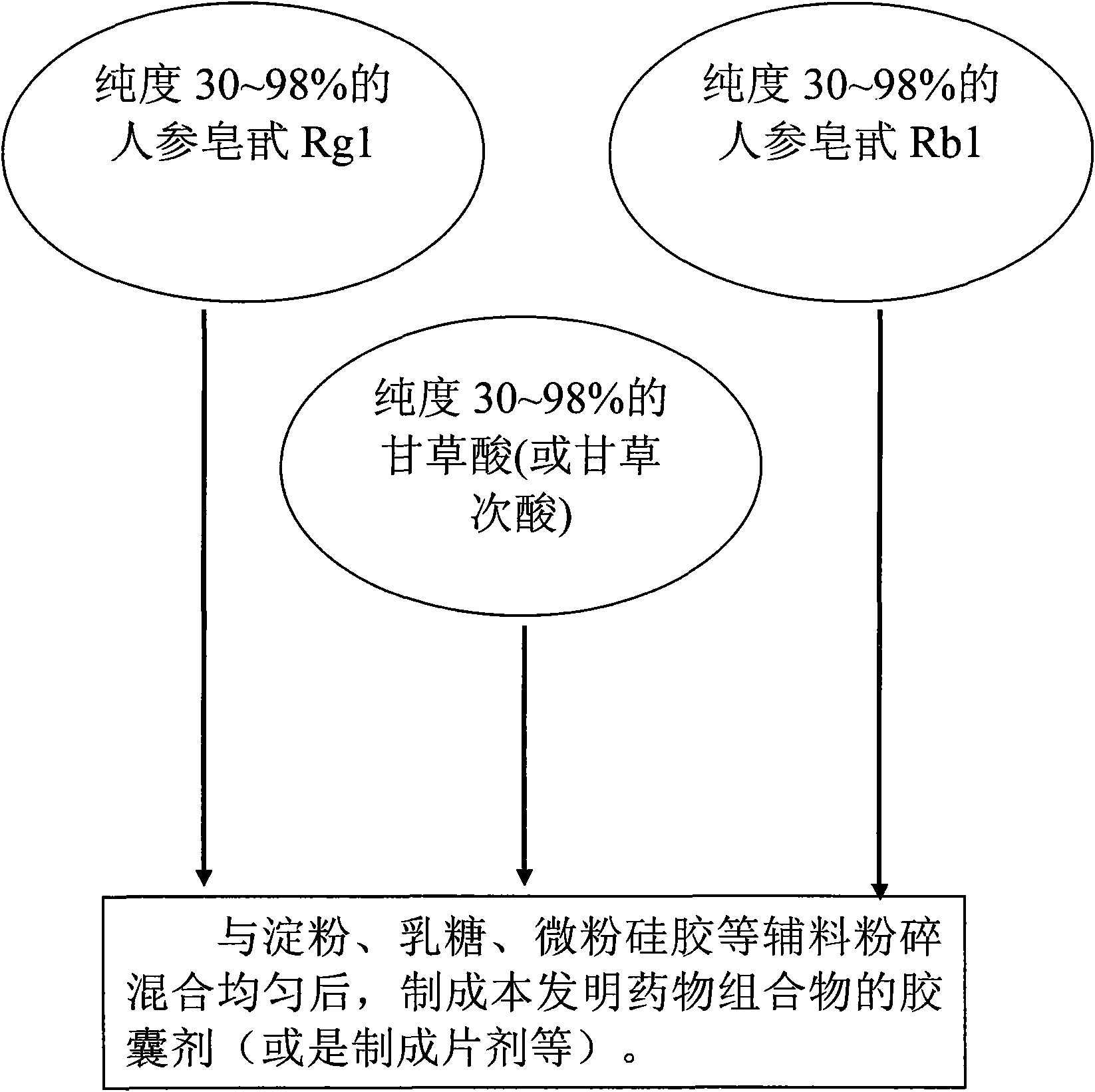
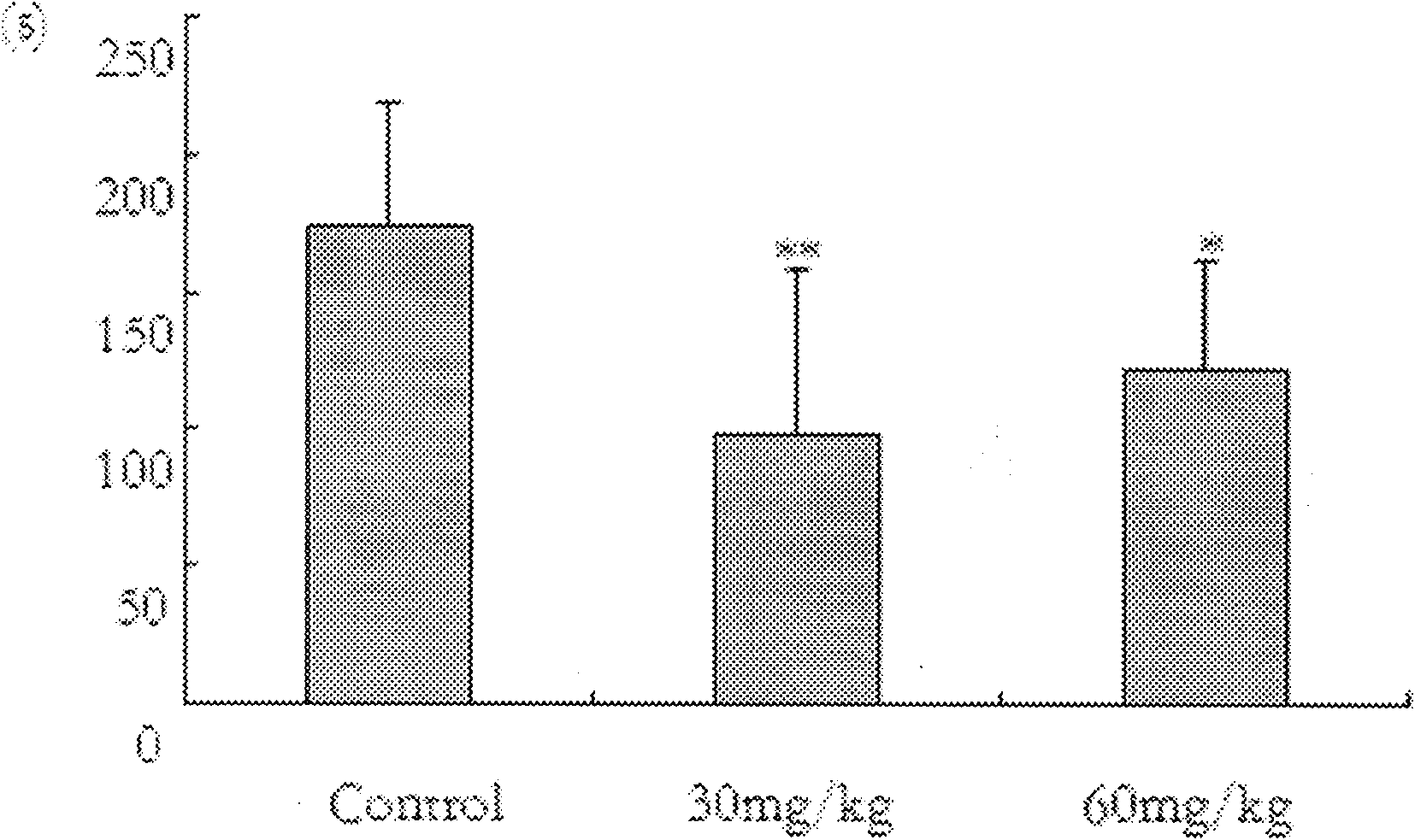
Medicine composition for treating depression with formulation of Rg1, Rb1 and glycyrrhizic acid and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101890032AQuality is easy to controlQuality improvementOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderMechanism of actionTail Suspension
The invention discloses a medicine composition for treating depression, which is prepared from panaxoside Rg1, Rb1 and glycyrrhizic acid (glycyrrhetinic acid), and a preparation method of the medicine composition. Proven by a test, the medicine composition can obviously reduce the tail suspension and immobility time during forced swimming, can rapidly arouse the CAMP-PKA access of a hippocampus and improves the expressions of CREB and BDNF. Accordingly, the medicine composition can be used for treating depression acted on the body.
Owner:张作光
Method for classification of anti-psychotic drugs
The present invention provides a method for identifying an agent to be tested for an ability to treat a psychotic disorder in a patient in need of such treatment. The invention provides a method for screening candidate drugs for anti-psychotic drug activity, preferably atypical anti-psychotic activity, comprising contacting cells or tissues with a candidate drug, determining levels of phosphorylation of the intracellular signaling proteins, DARPP-32, ERK1, ERK2 and CREB, in said cells or tissues and determining the pattern of the levels of phosphorylation of the proteins. The pattern of the levels of phosphorylation of DARPP-32, ERK1, ERK2 and CREB is, in certain embodiments, compared with the pattern of the levels of phosphorylation of DARPP-32, ERK1, ERK2 and CREB in the presence of an atypical anti-psychotic drug.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
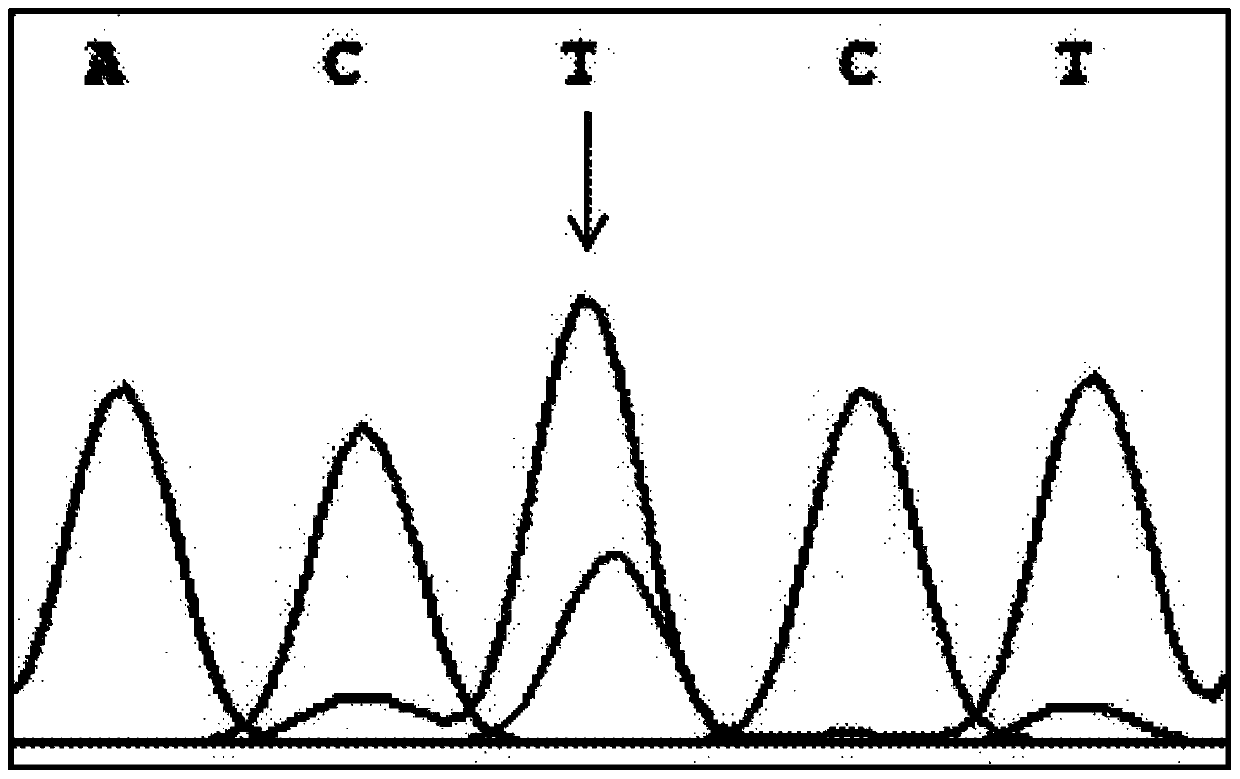
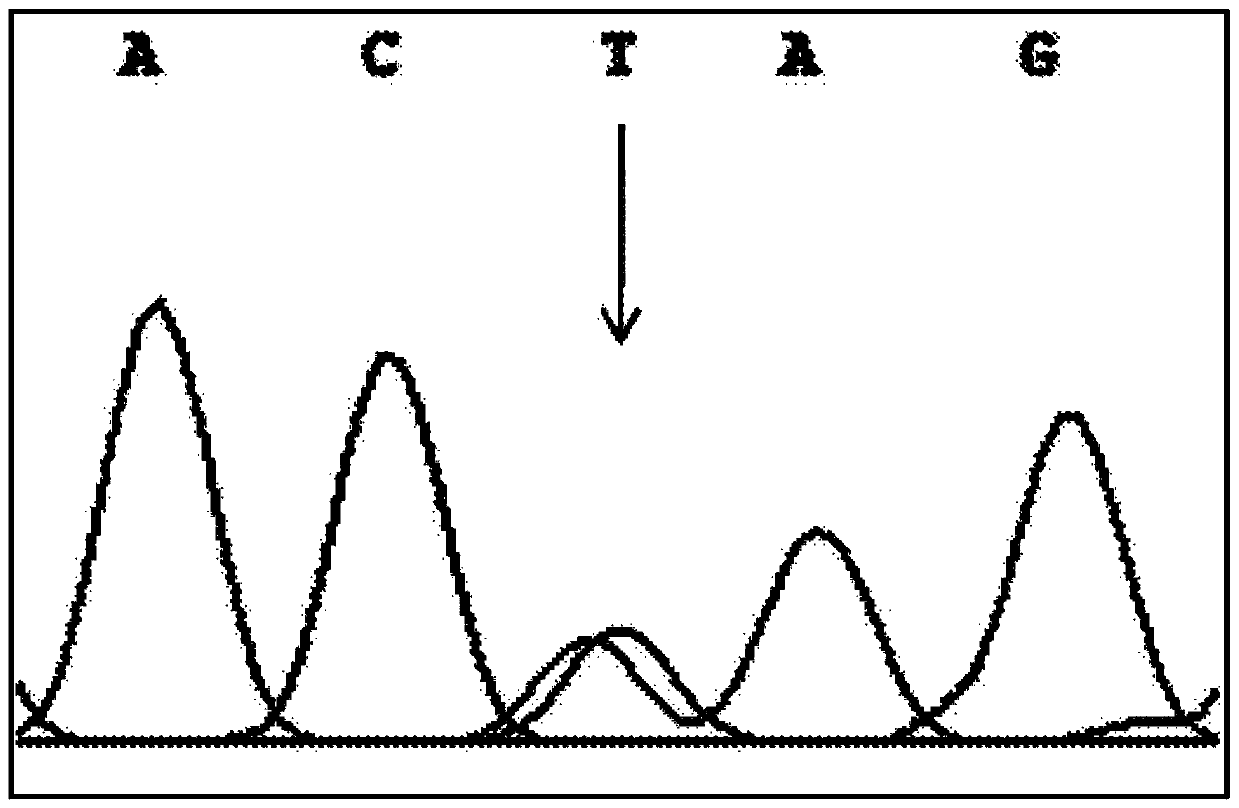
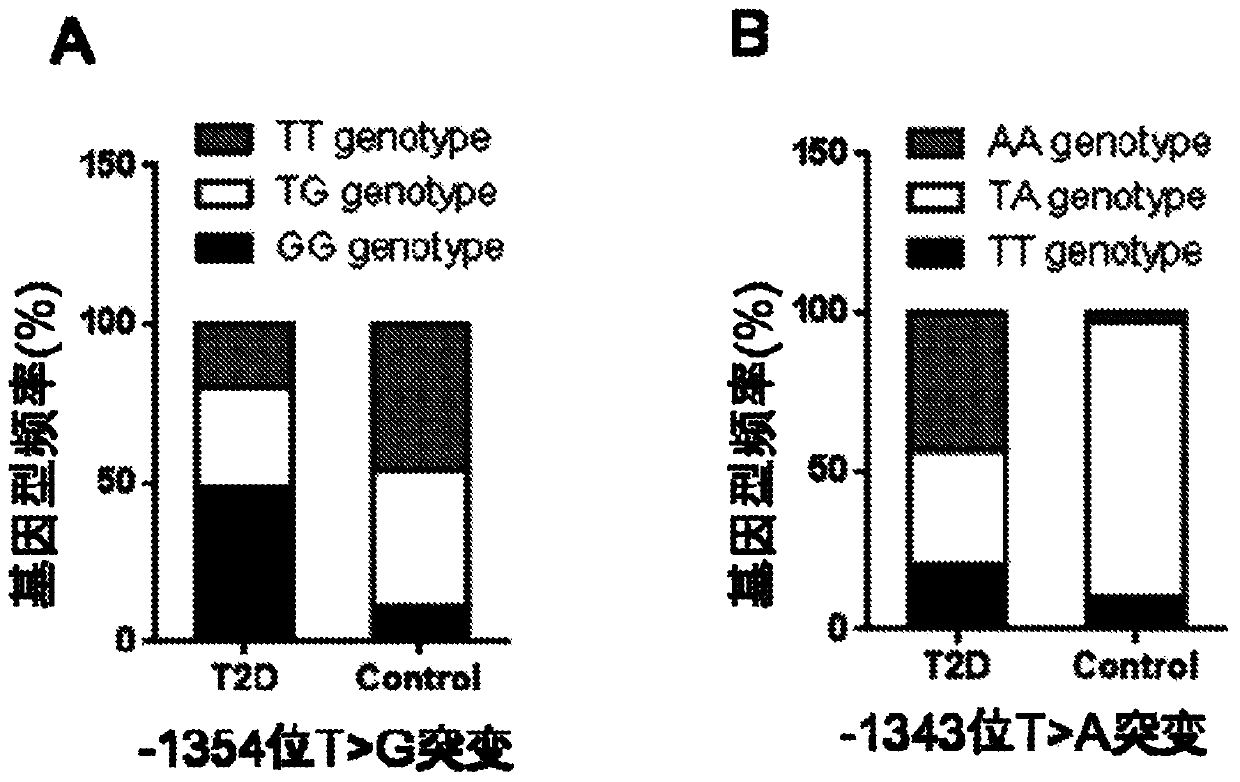
PCR-RFLP method for detecting single nucleotide polymorphism of gene CREB 1
InactiveCN110734969ASolve the cumbersomeFix instabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme digestionNucleotide
The invention discloses a PCR-RFLP method for detecting the single nucleotide polymorphism of a gene CREB 1. Firstly, according to a DNA pool sequencing result, the detected gene polymorphism comprises single nucleotide polymorphism of T or G at the 1354th site from a CREB1 gene promoter region to a transcription starting point and single nucleotide polymorphism of T or A at the 1343th site. PCR amplification is conducted on a CREB1 gene sequence containing polymorphic sites in the presence of Taq DNA polymerase, Buffer (a buffer environment), Mg++ and dNTPs by taking genome DNA of a to-be-detected sample as a template and a primer pair P as a primer, a PCR product is divided into two parts, the two parts are digested by using restriction enzymes Hha I and Xsp I respectively, and enzyme digestion products are subjected to typing through agarose gel electrophoresis.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
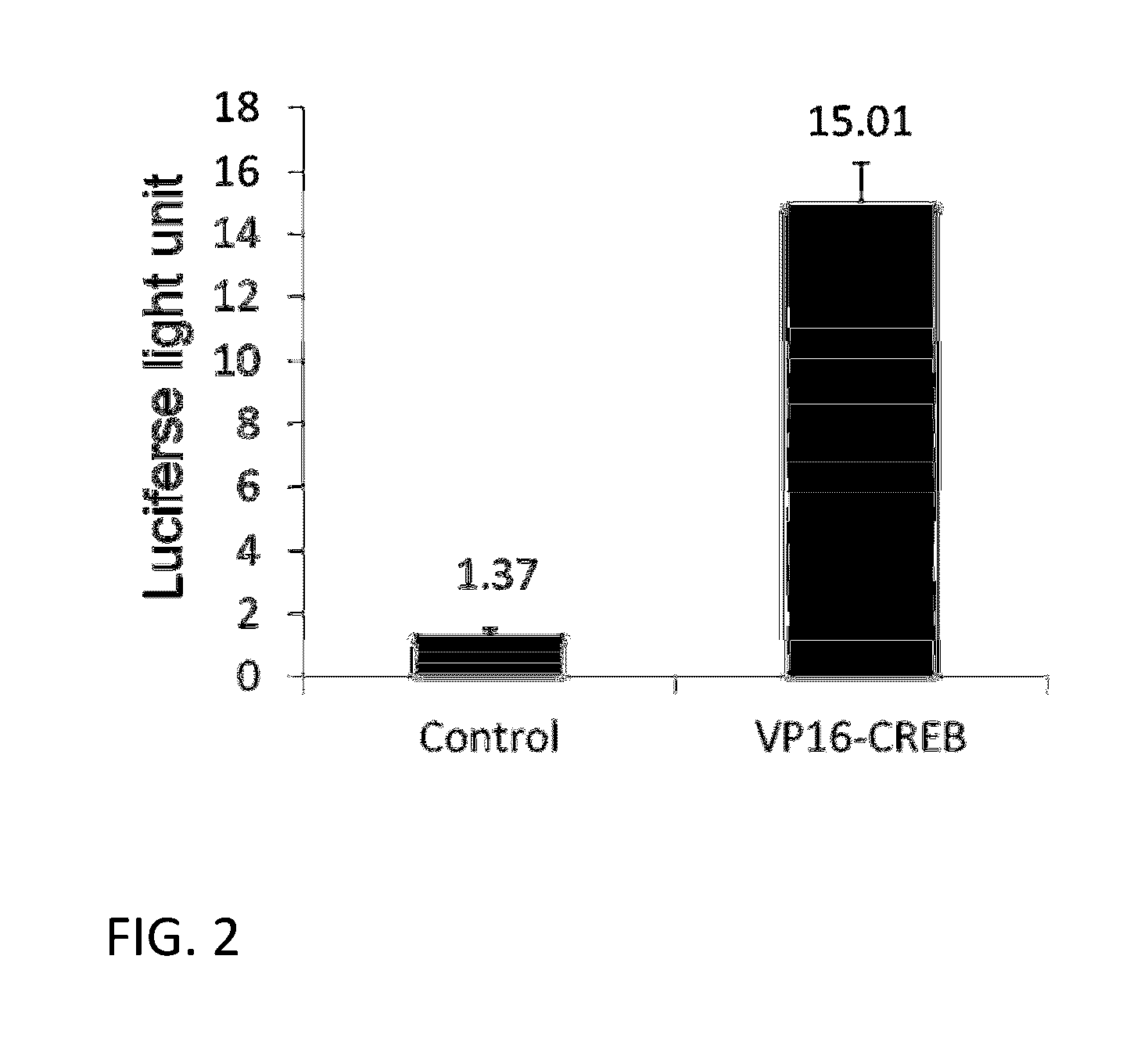
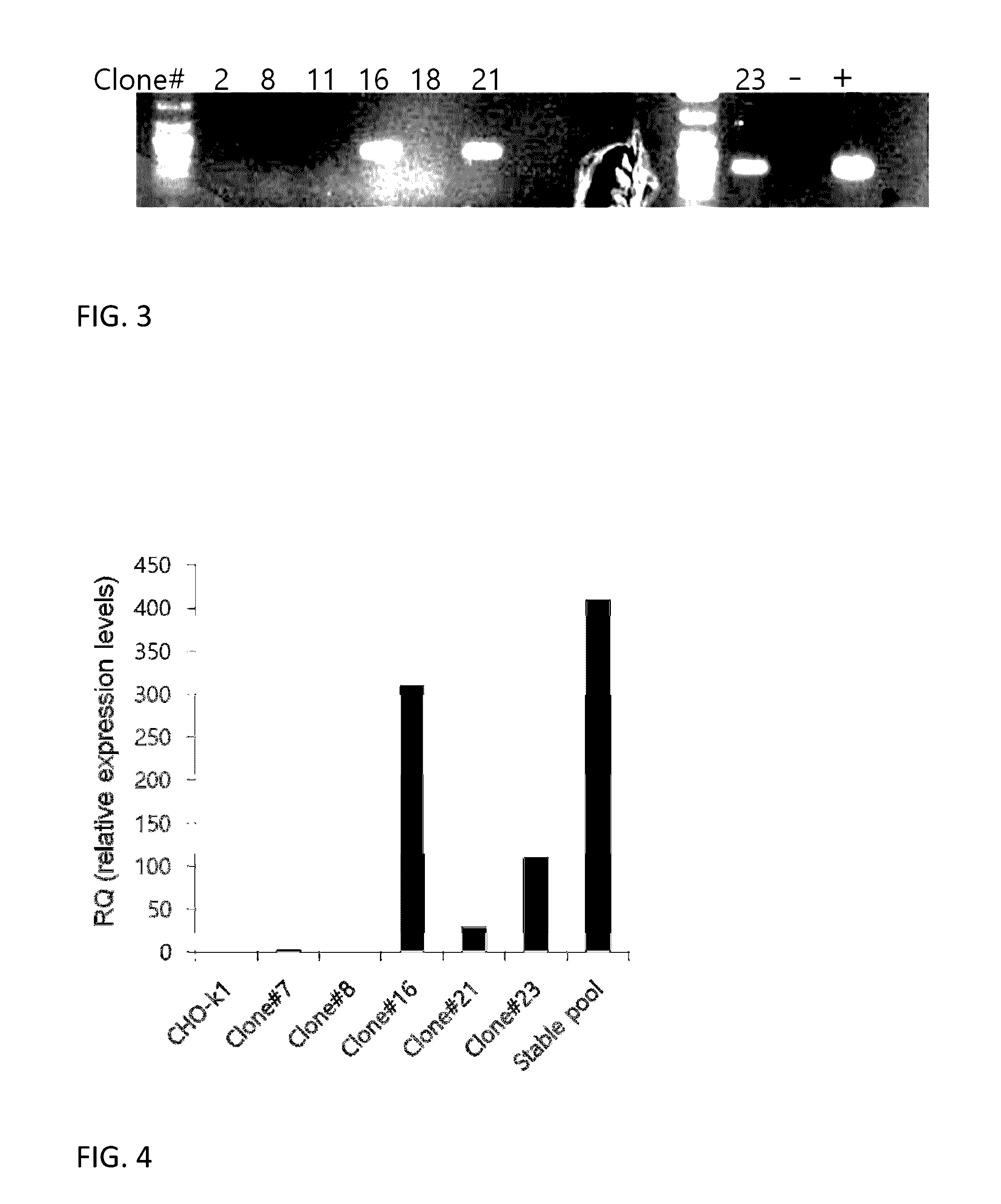
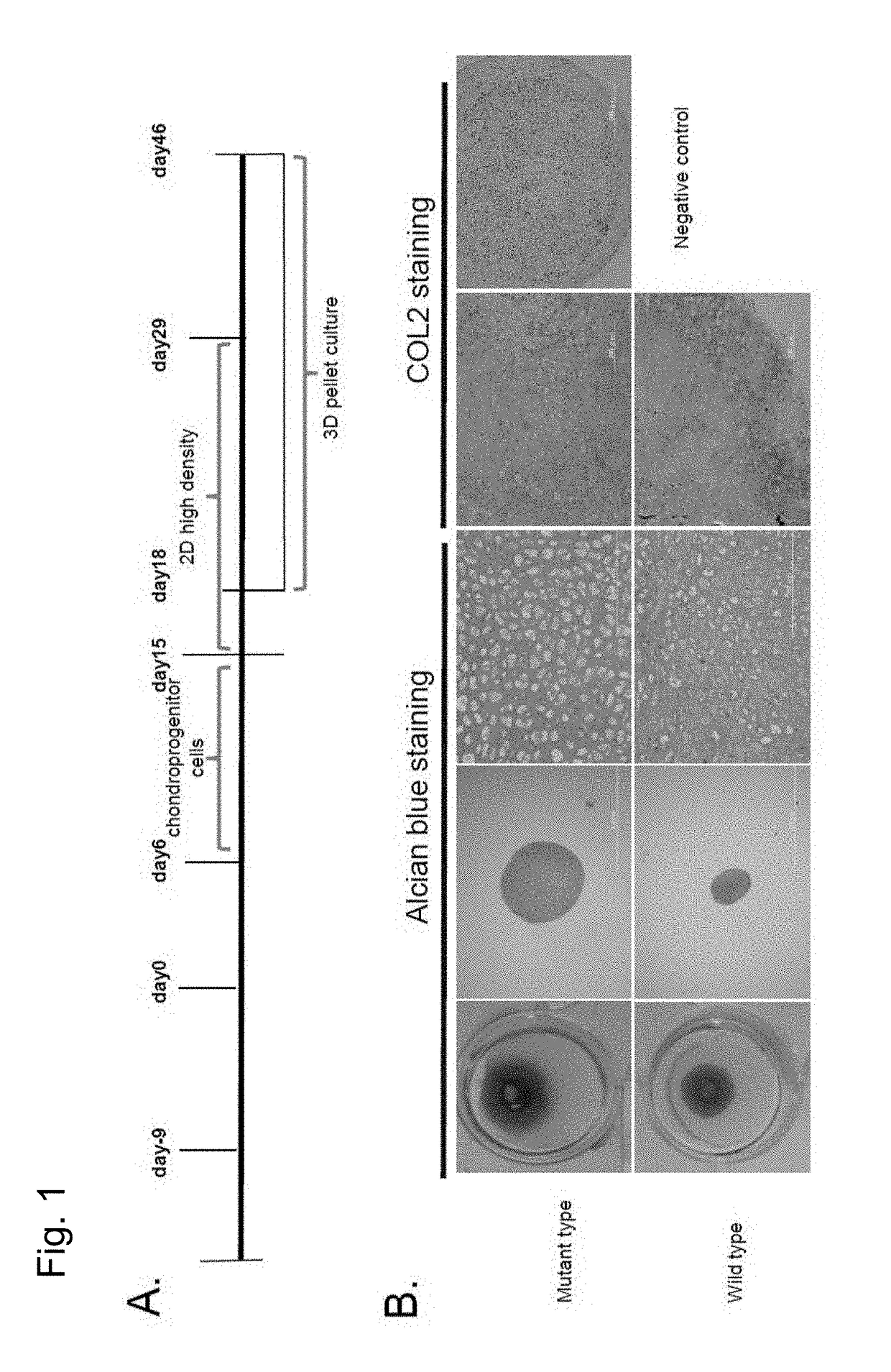
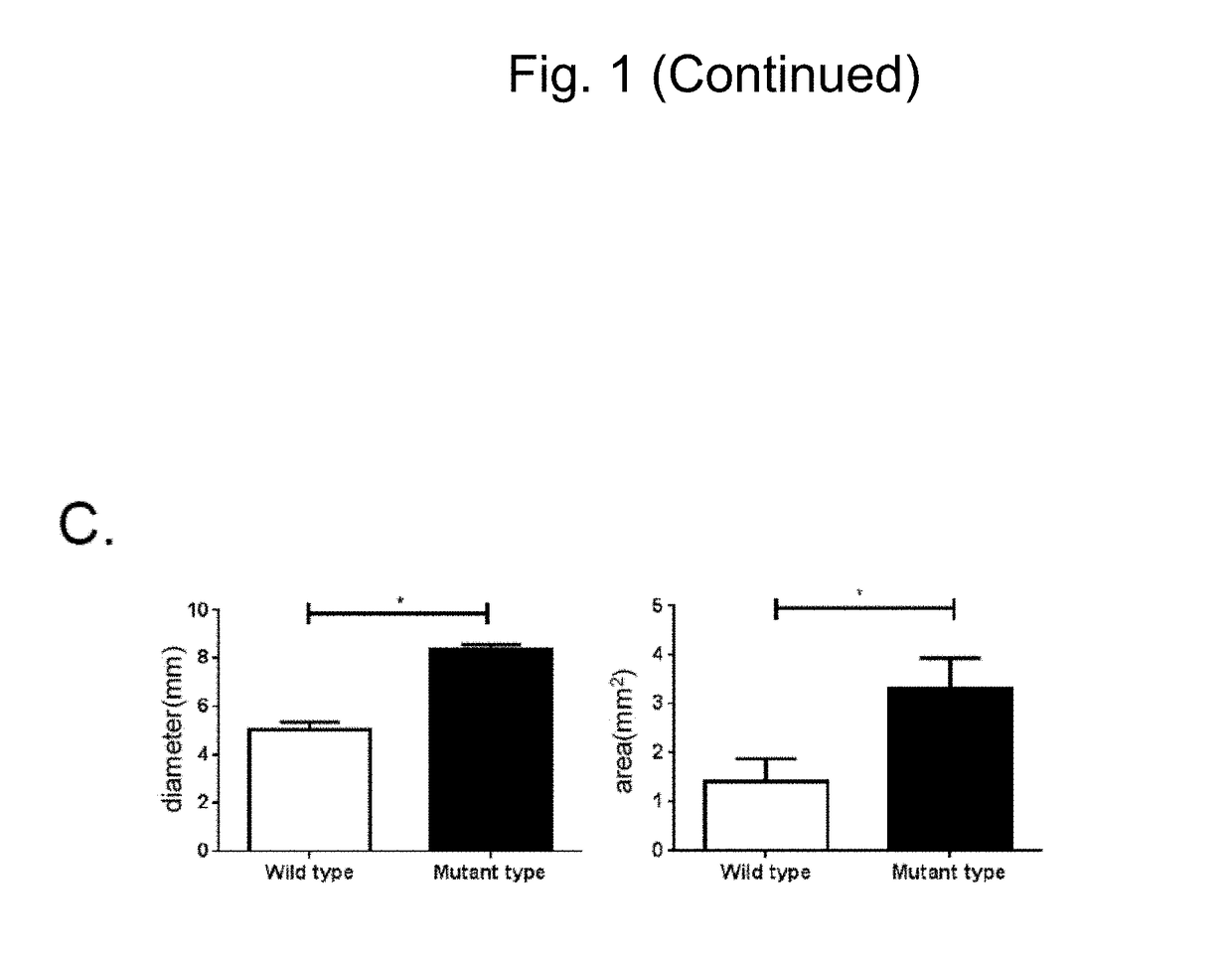
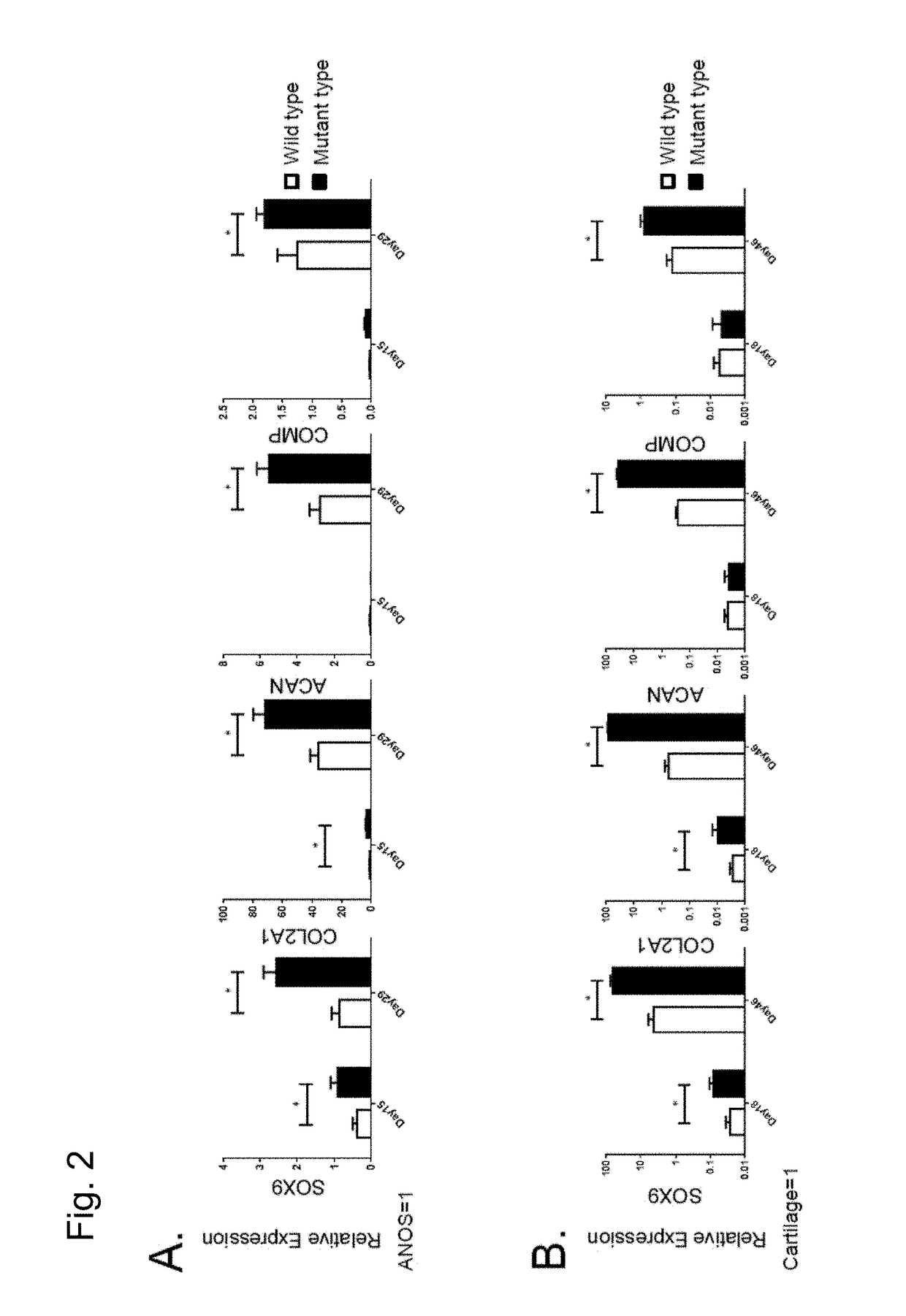
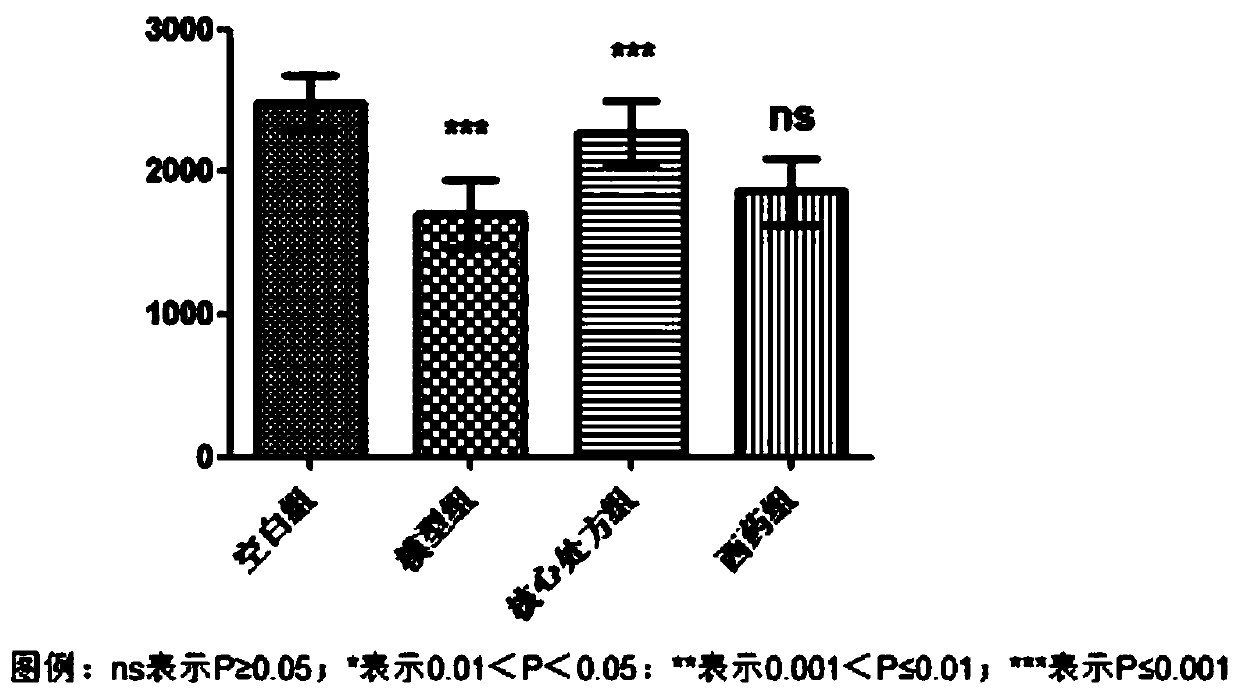
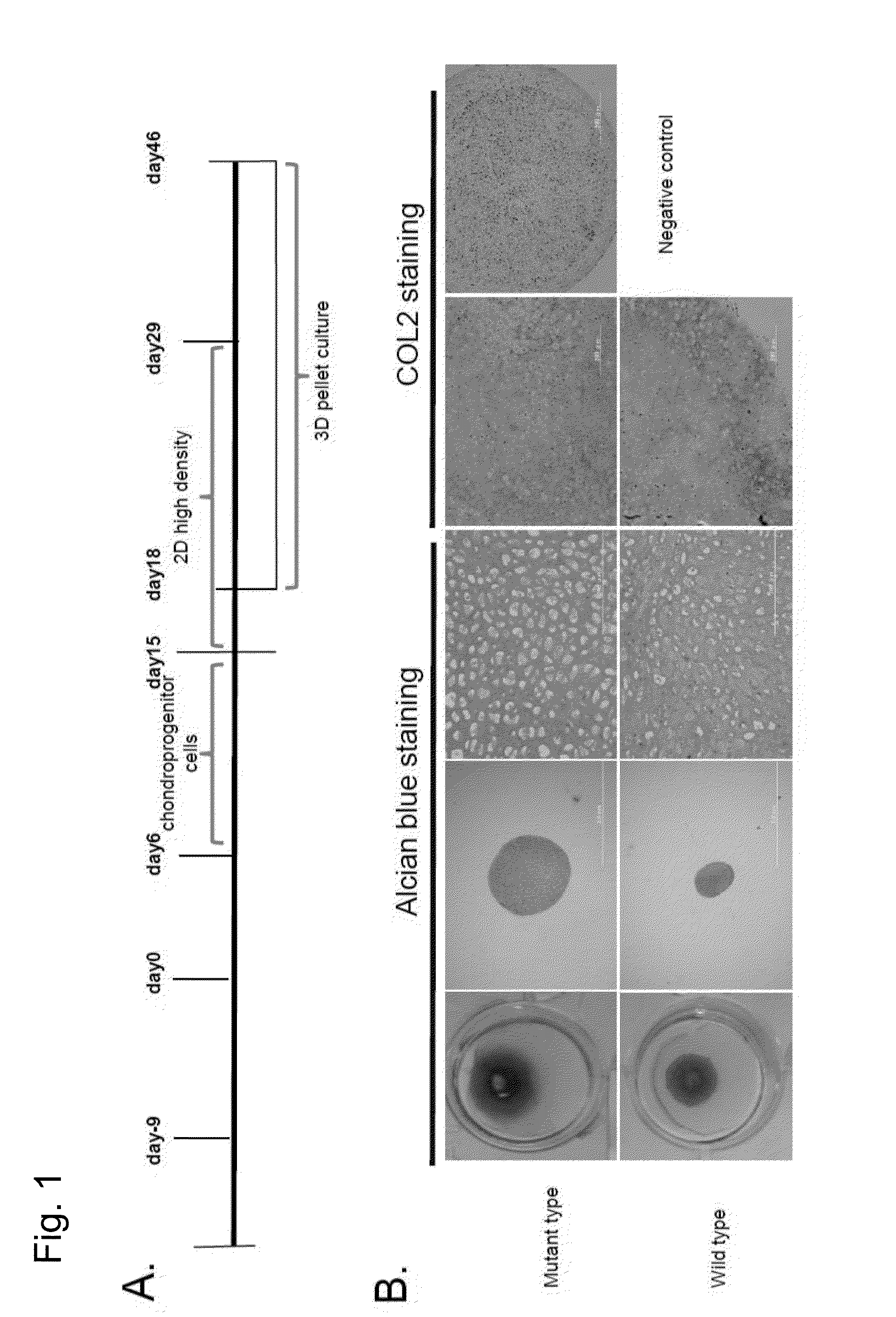
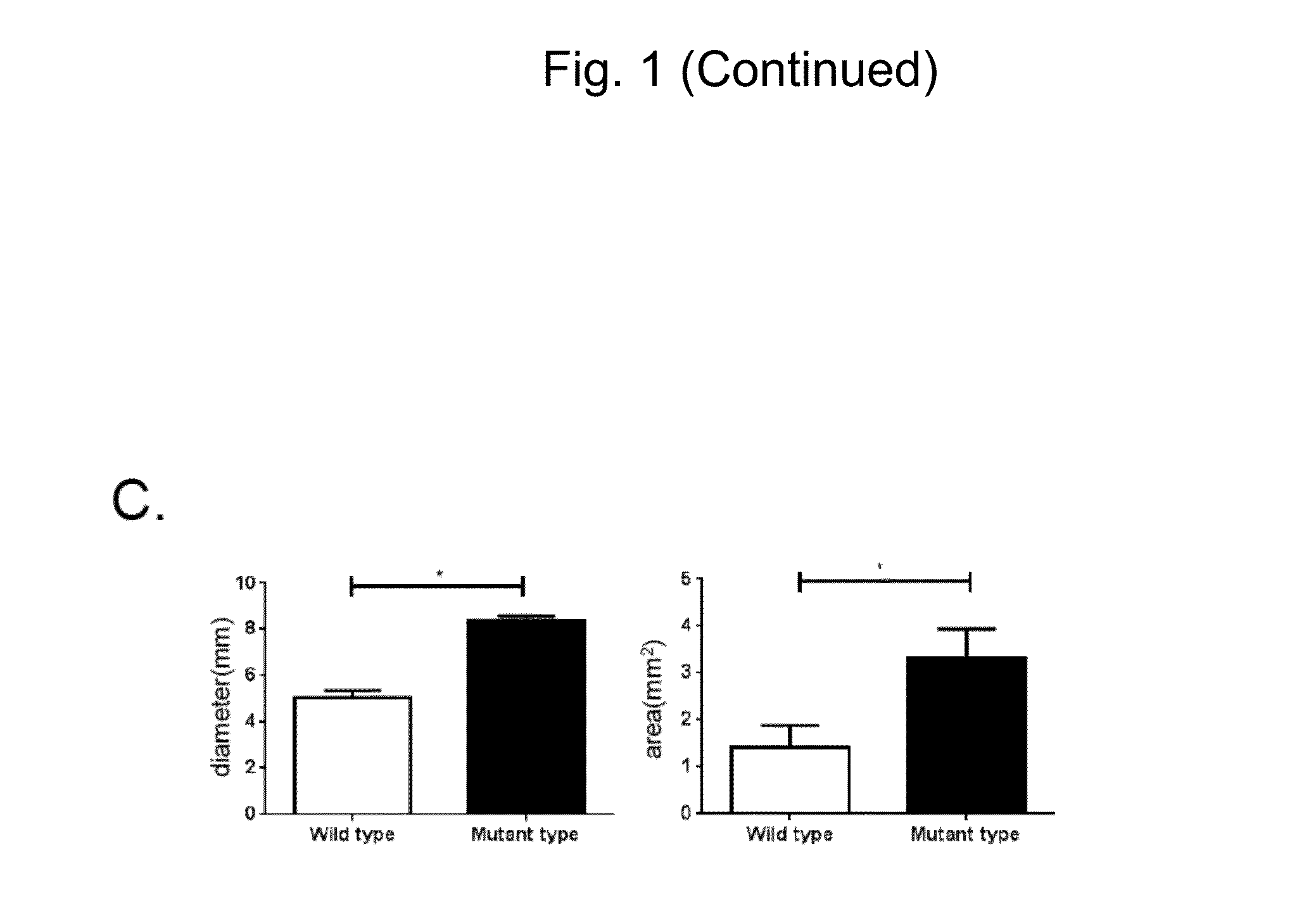
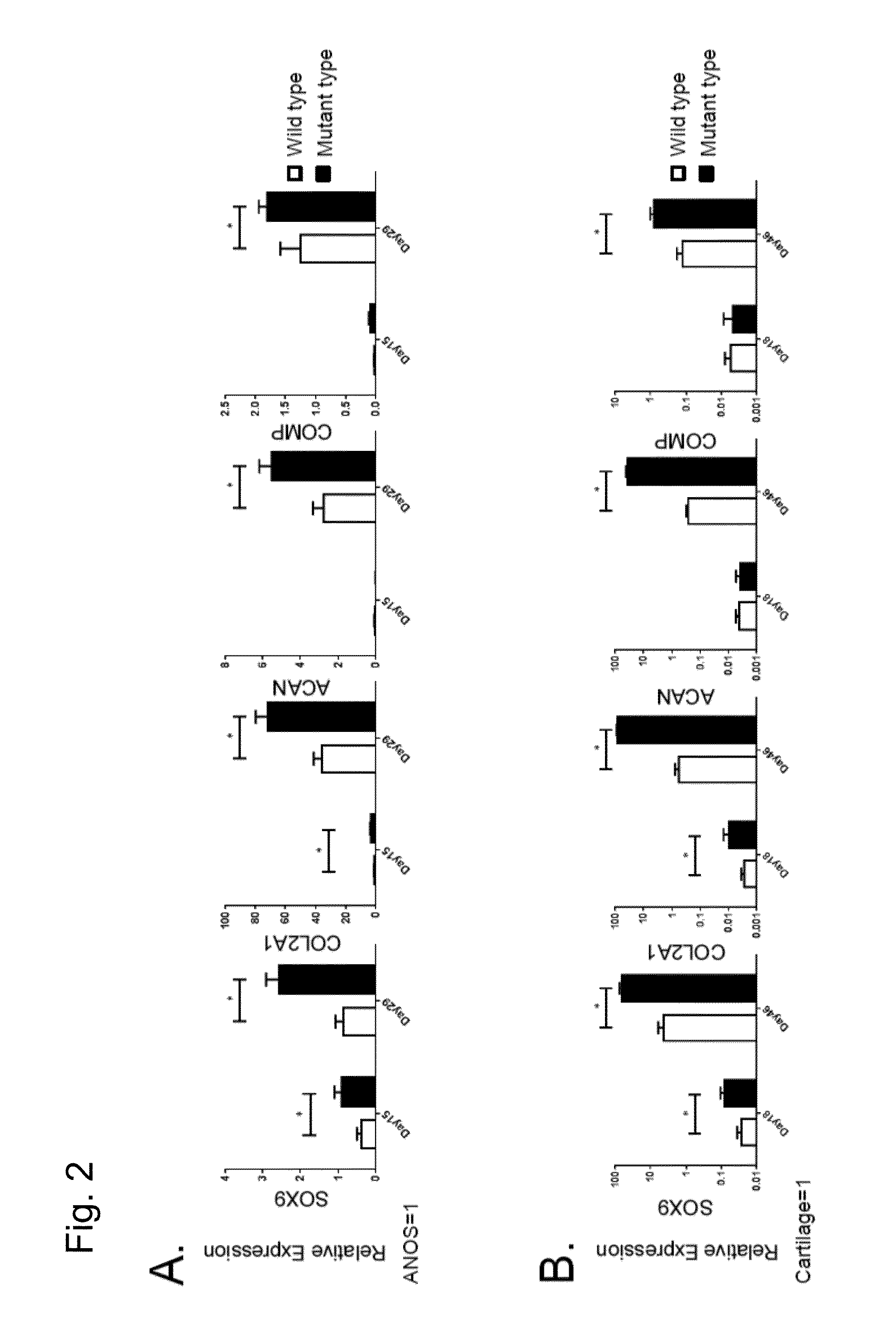
Preventive and therapeutic drug for cartilaginous hyperplasia and method of screening for the same
A method of screening for a therapeutic and / or preventive drug for cartilaginous hyperplasia and a therapeutic and / or preventive drug for cartilaginous hyperplasia are provided.The following are provided: a method of screening for a therapeutic and / or preventive drug for cartilaginous hyperplasia, comprising a step of culturing chondroprogenitor cells under conditions in which the cells are brought into contact with a test substance and conditions in which the cells are not brought into contact with the test substance and a step of determining the SOX9 promoter activity, cAMP level, or degree of phosphorylation of CREB in the cells or the extracellular matrix volume in a culture; and a therapeutic and / or preventive drug for cartilaginous hyperplasia, comprising as an active ingredient an adenylate cyclase inhibitor.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Efficient mammalian cell gene recombination protein expression vector
InactiveCN102787137AHigh expressionIncrease productionVector-based foreign material introductionProtein targetBinding site
The invention relates to an efficient mammalian cell gene recombination protein expression vector, wherein expression of target protein in mammalian cells by the existing commonly-used mammalian cell gene recombination protein expression vectors can be performed by the efficient mammalian cell gene recombination protein expression vector of the present invention, and the efficient mammalian cell gene recombination protein expression vector of the present invention provides higher expression efficiency compared with the existing vectors. According to the efficient mammalian cell gene recombination protein expression vector of the present invention, a section of DNA sequence with a length of 363 base pairs is inserted into a position at the upstream of a promoter of a vector, wherein the DNA sequence contains a large number of transcription factor binding sites, transcription factors such as SP, AP, CREB / CBP, and the like can bind with the corresponding binding sites so as to provide a transcription enhancement effect and increase a protein expression level, wherein the transcription factors such as SP, AP, CREB / CBP, and the like provide enhancement effects for transcription. The DNA fragment-containing expression vector is introduced into mammalian cells, and the DNA fragment can attract a large number of transcription factors such as SP, AP, CREB / CBP, and the like, such that an expression level of the target protein can be increased by 3-50 times so as to achieve a purpose of protein yield improvement.
Owner:朱燕华
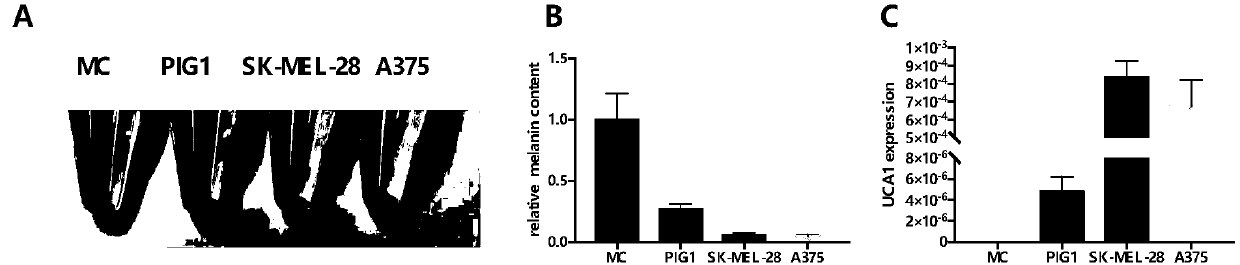
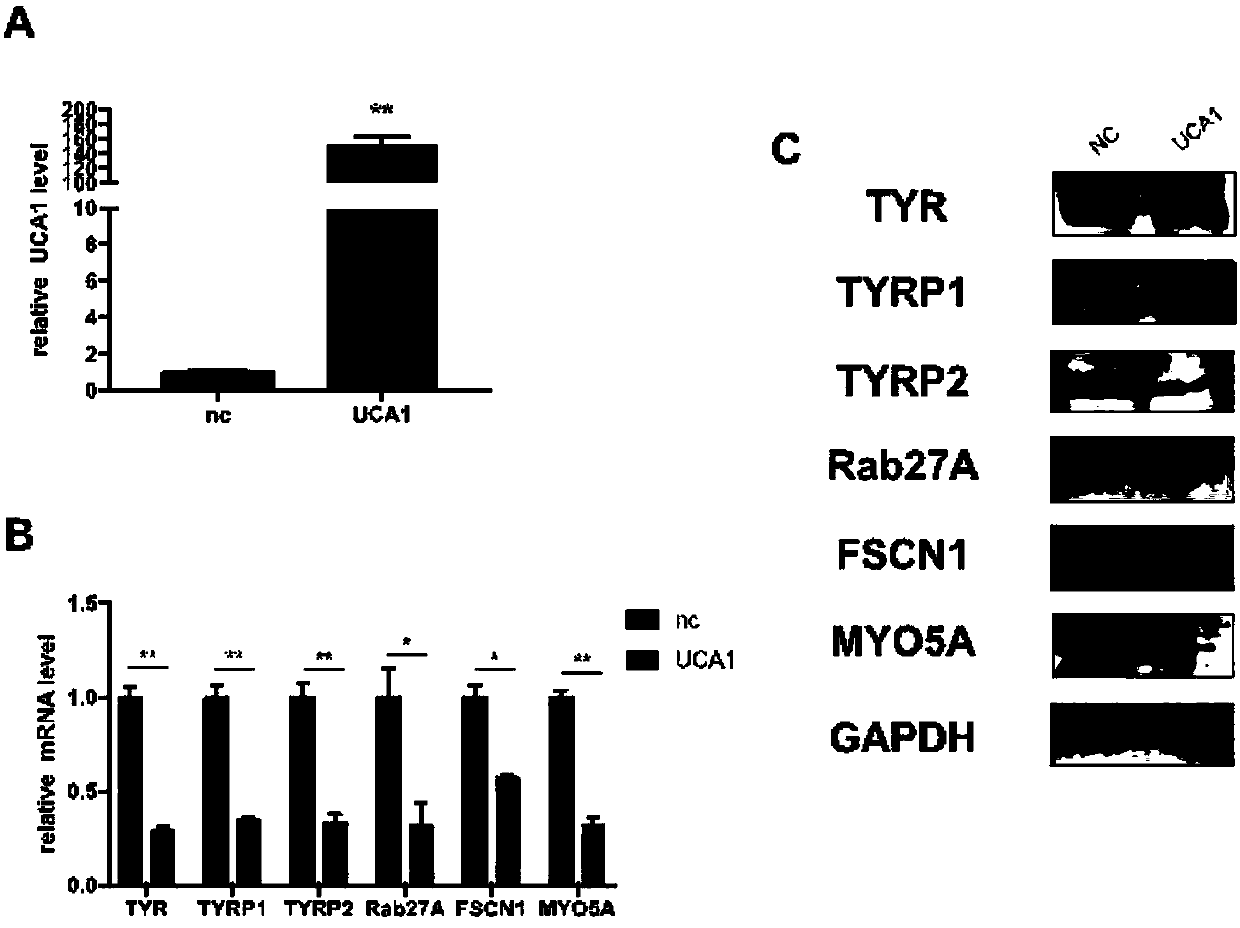
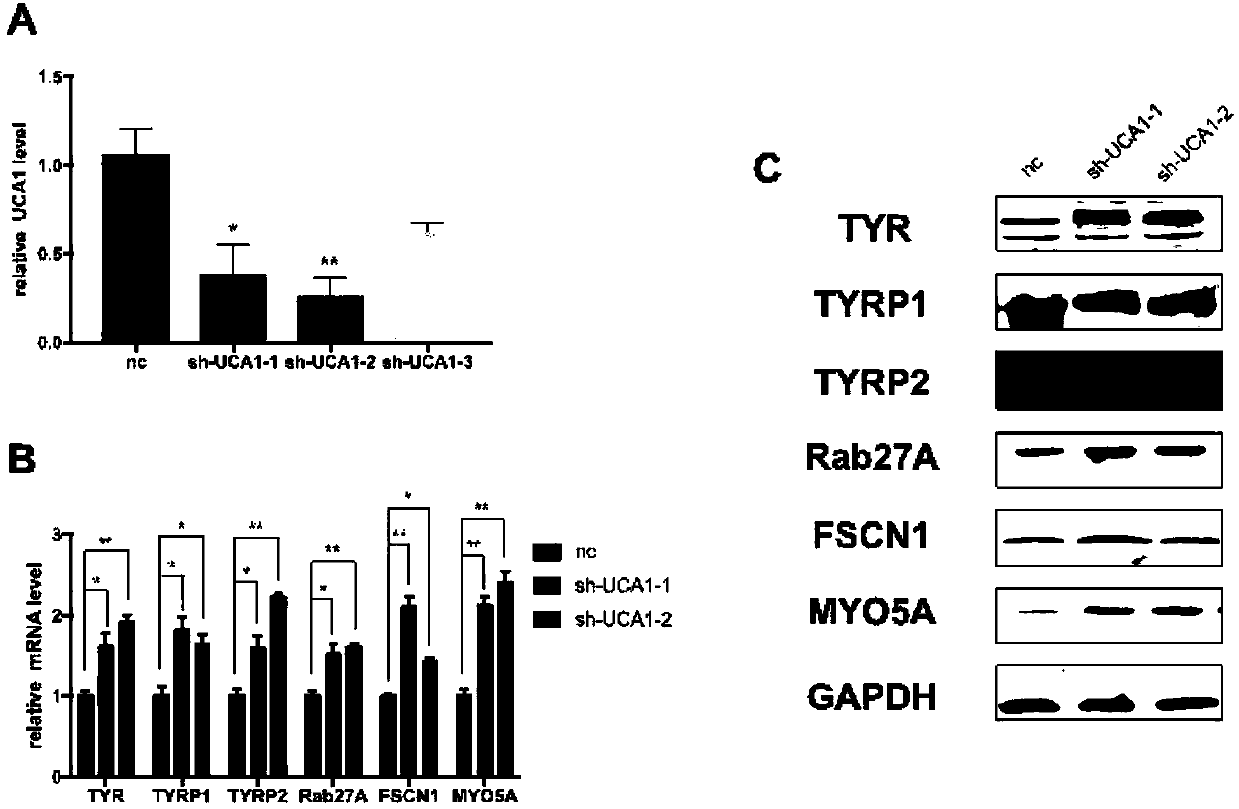
Application of UCA1 as target site to preparation of drugs for treating hyperpigmentation dermatoses
ActiveCN108451969ANegative regulationReduced expression levelOrganic active ingredientsDermatological disorderMelanocyteTreatment modality
According to the experimental results of the invention, UCA1 has a negative regulatory effect on melanogenesis of melanocytes, and the expression level of melanogenesis-related genes is decreased after overexpression of UCA1 in melanocytes, and is obviously enhanced after UCA1 is knocked out, and UCA1 negatively regulates melanogenesis mainly through a cAMP / PKA / CREB pathway. The results of this study suggest that UCA1 is a potential therapeutic target for regulating melanogenesis in melanocytes, and the development of drugs or treatments that regulate the expression level of UCA1 is expected to bring new hope to the treatment of hyperpigmentation dermatoses.
Owner:THE THIRD XIANGYA HOSPITAL OF CENT SOUTH UNIV
Association of biomarkers with patient outcome
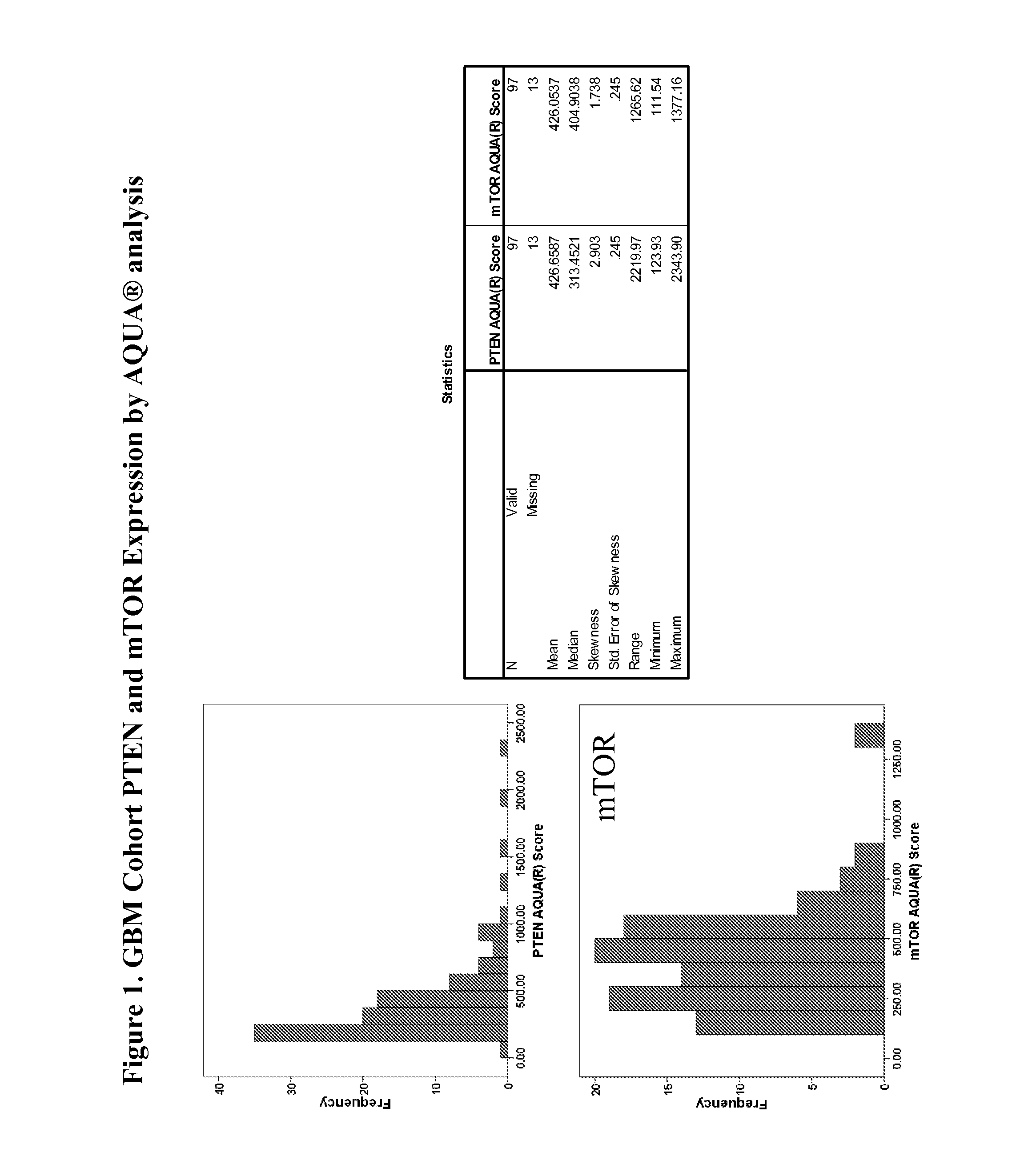
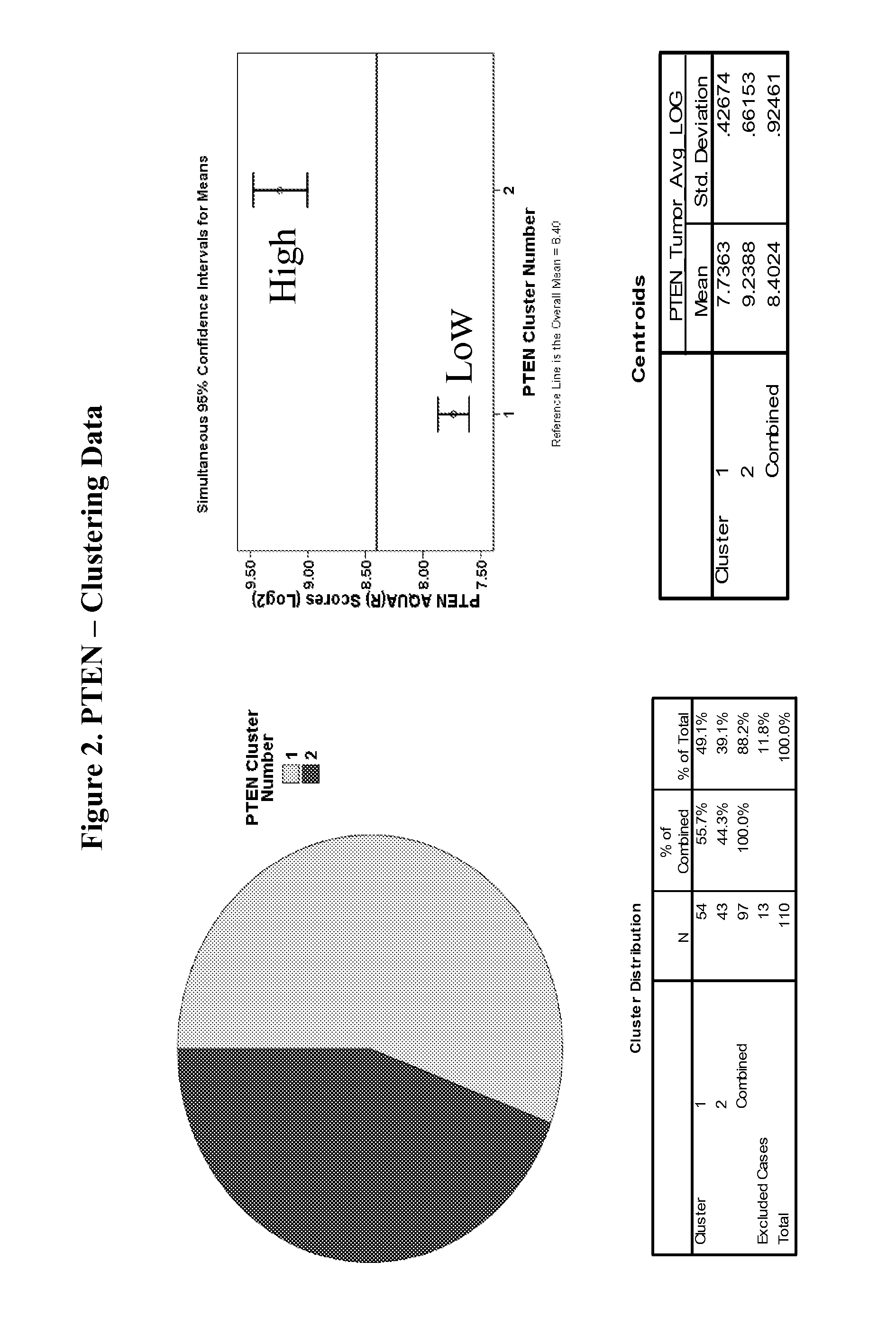
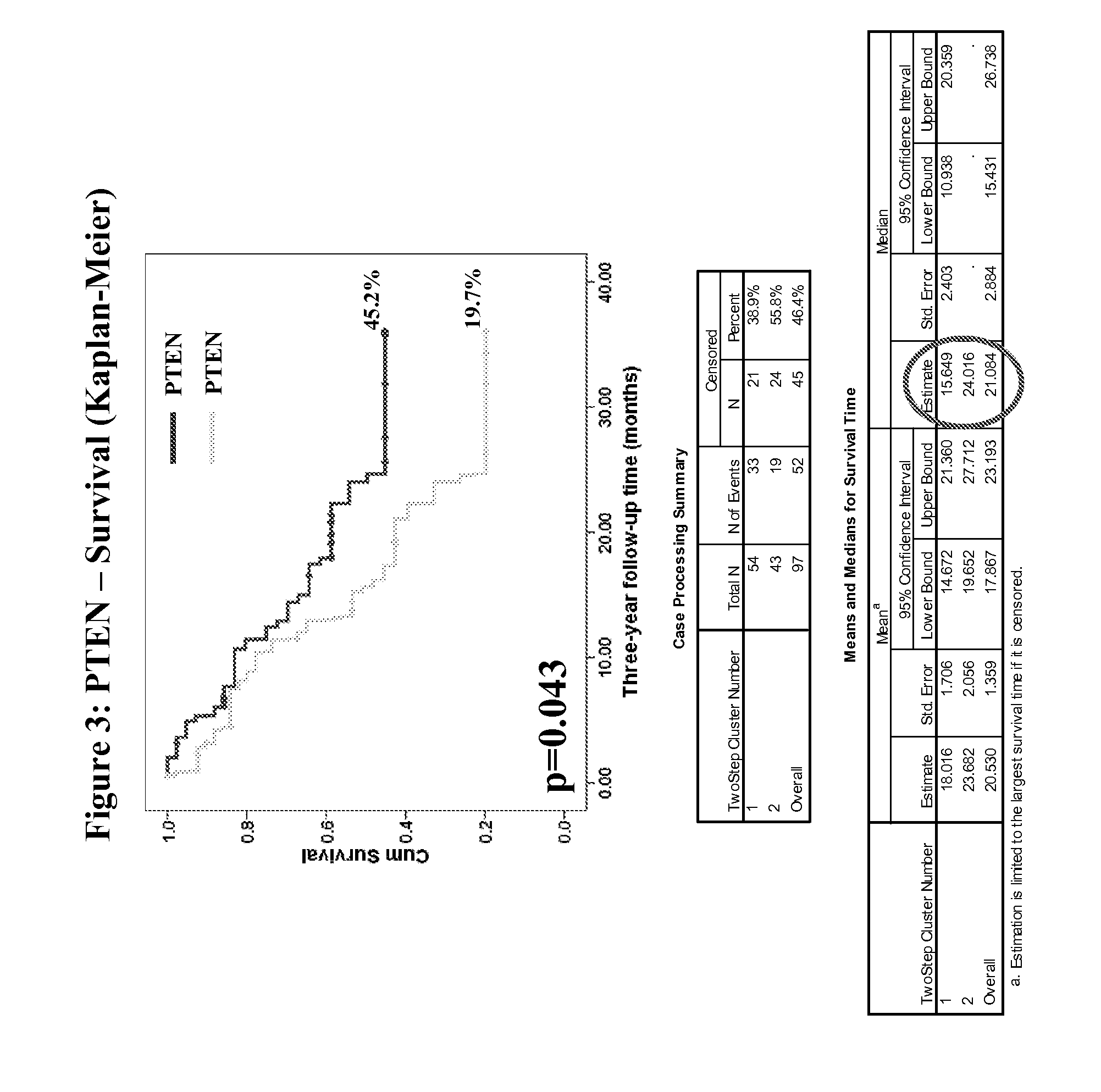
InactiveUS20120270233A1Improved prognosisHigh expression of PTENMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisPresent methodClinical settings
The present method relates to quantification of prognostic and predictive biomarkers of the PDK / AKT / mTOR pathway, such as GSK3β, S6, CREB, PTEN, AKT and mTOR, using AQUA® analysis to estimate both patient risk and benefit of treatment to patients diagnosed with glioblastoma. Unlike traditional IHC, the AQUA® system is objective and produces quantitative in situ protein expression data on a continuous scale. Taking advantage of the power of the AQUA system, the present method provides a highly robust and standardized diagnostic assays that can be used in the clinical setting to provide physicians with reliable prognostic and predictive information. Glioblastoma multiform (GBM) remains one of the most aggressive human cancers, and biomarkers that provide prognostic and predictive information would be extremely valuable to both the physician and the patient. A patient's risk may be determined using the prognostic biomarkers of the present method. Such a prognostic determination will allow physicians to identify patients with a relatively ‘good’ or a relatively ‘poor’ prognosis. The benefit of treating specific patients with a specific therapy, may be determined usin̂ the predictive markers of the present method. Treatment with the AGC-family kinase inhibitor enzastaurin, for example, identifies patients that will likely benefit from treatment or not.
Owner:HISTORX INC
Applications of pegylated curcumin derivative
InactiveCN106581044AOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticReverse cholesterol transportPhosphorylation
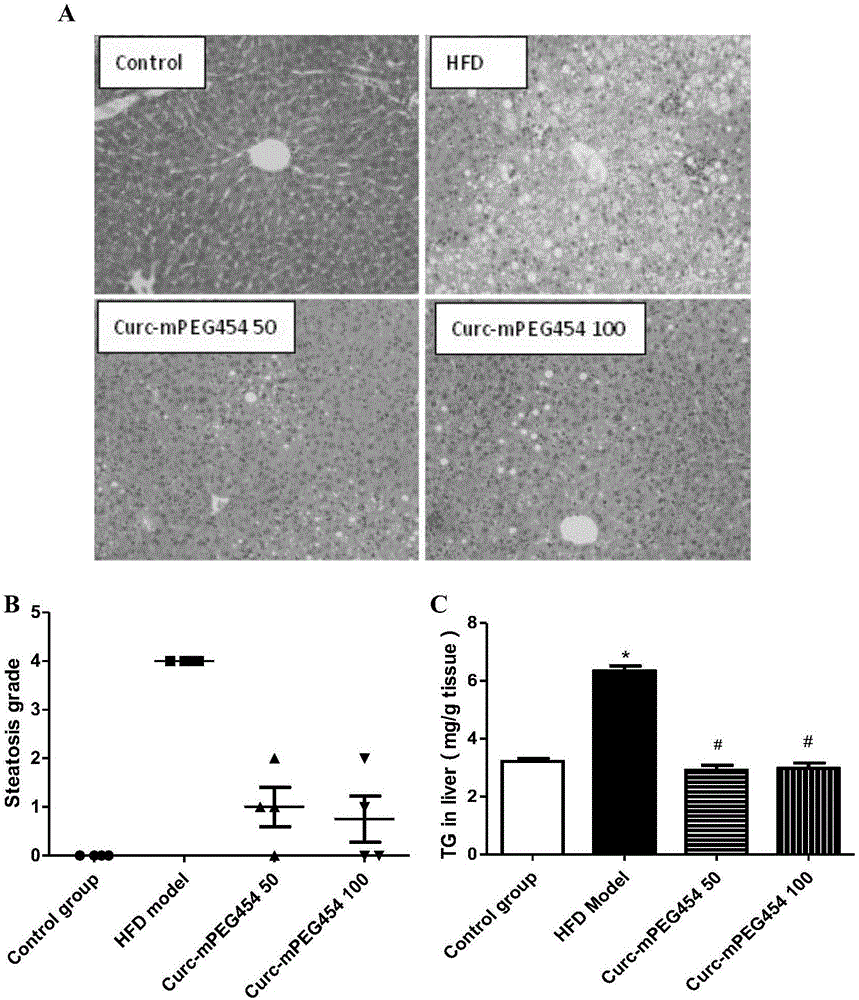
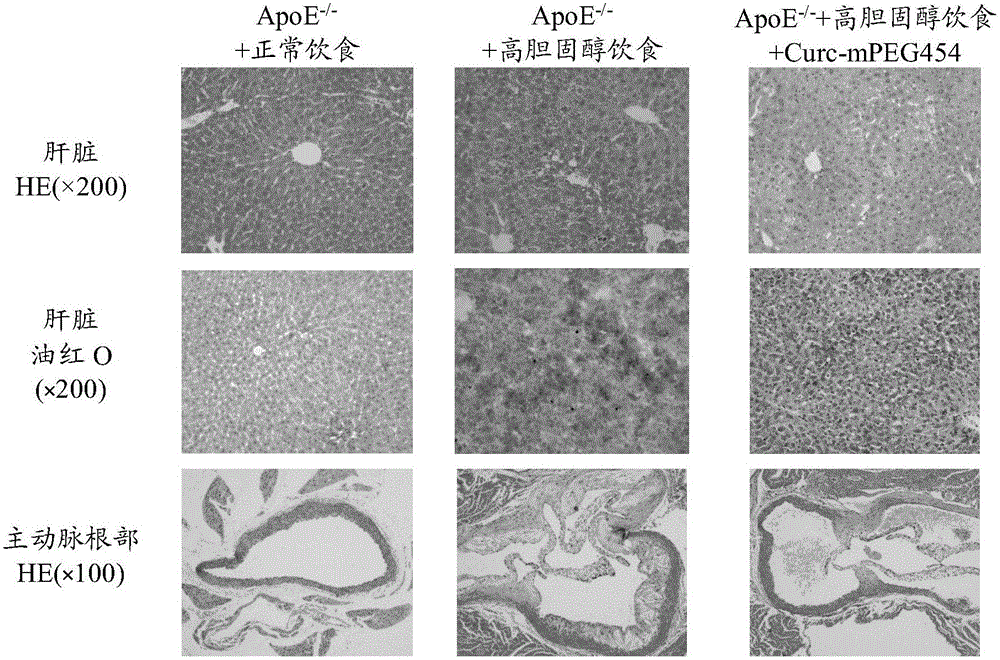
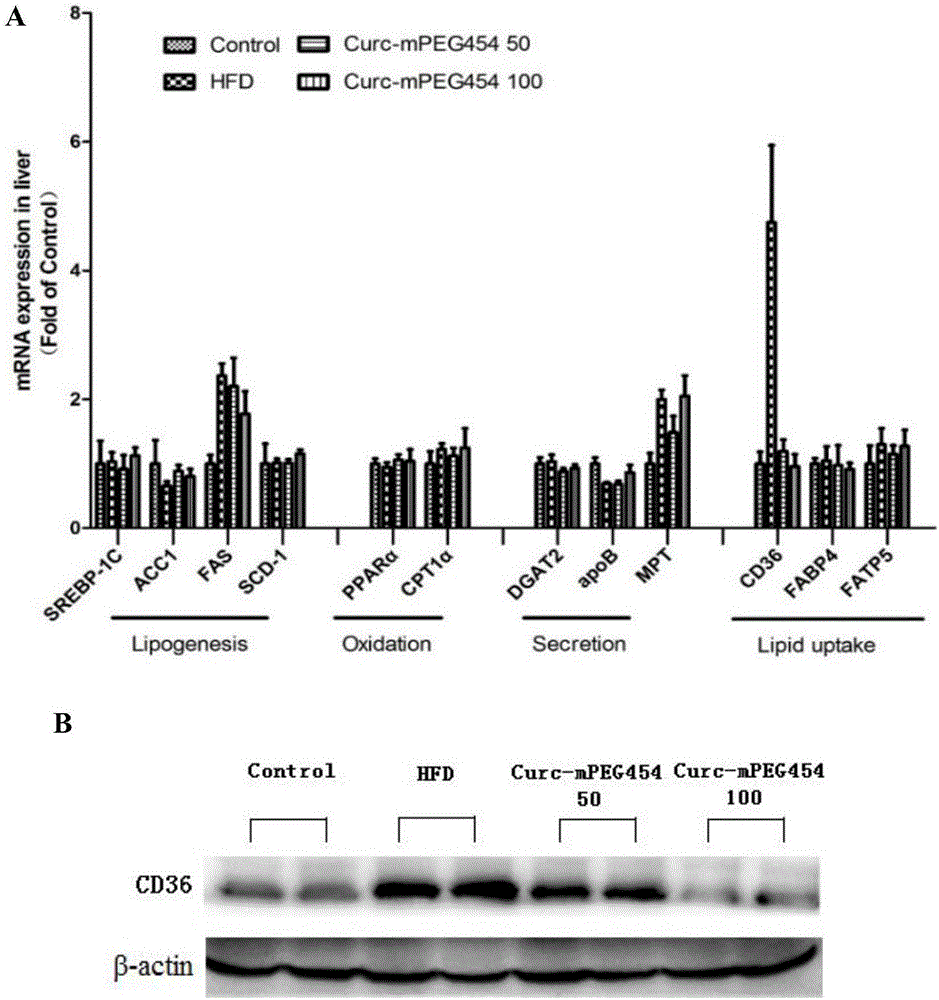
The invention belongs to the field of pharmaceutical chemistry, and in particular relates to novel applications of pegylated curcumin derivative, especially the applications of the pegylated curcumin derivative in preparing medicines for preventing or treating fatty liver diseases and atherosclerosis. The experiment proves that the pegylated curcumin derivative can reduce the level of triglyceride in the blood, activate the phosphorylation of cyclic-AMP response element binding protein (CREB), negatively regulate nuclear transcription receptor PPAR gamma closely related to lipid metabolism, reduce the CD36 expression of the lever tissue caused by high fat diet, reduce the intake of fatty acid of the liver, reduce the lipid formation of the liver, and improve the fatty degeneration of the liver. The pegylated curcumin derivative further can improve the level of high density lipoprotein cholesterol, promote the reverse cholesterol transport, reduce the CD36 expression of macrophages, reduce the intake of oxidized low density lipoprotein, alleviate the bubblization of the macrophages, and reduce the deposition of lipid on the endangium and the formation of artery atherosclerotic plaque.
Owner:THE SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIV
Ameliorative effects of a whole coffee fruit extract on age-related neurodegenerative disease
InactiveUS20190159474A1Reduce expressionReduce depositionNervous disorderRoasted coffee treatmentDiseaseChlorogenic acid
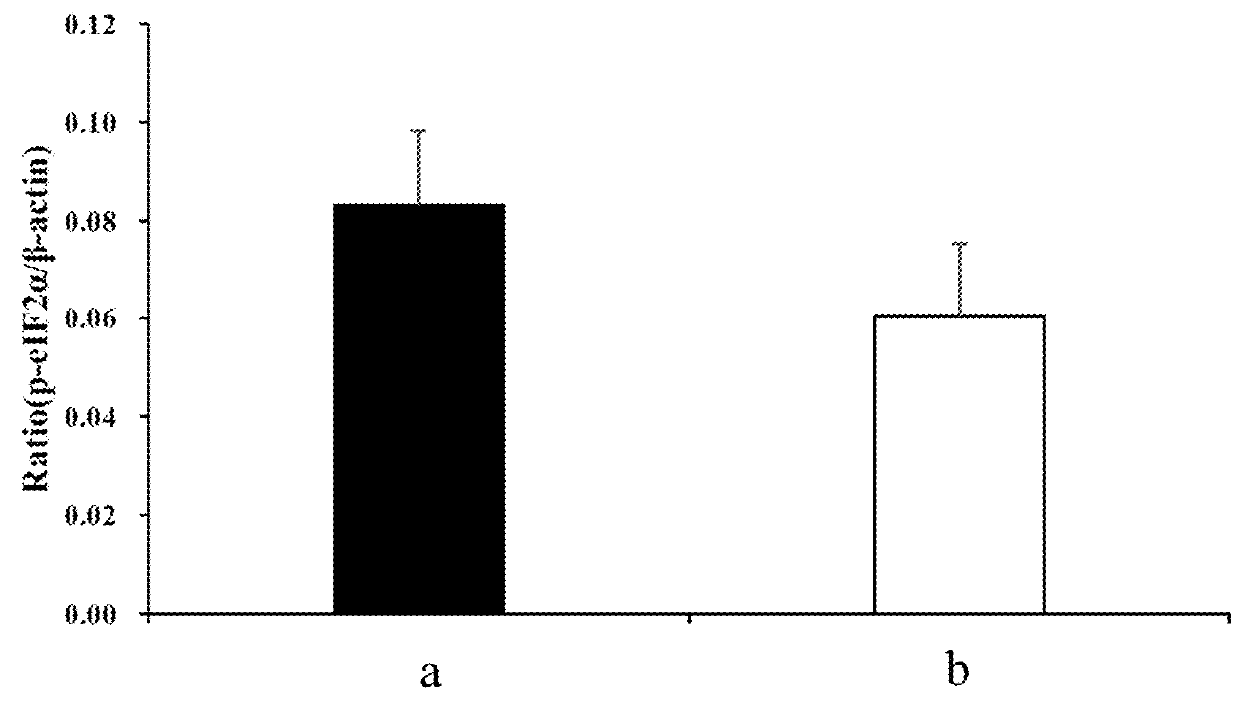
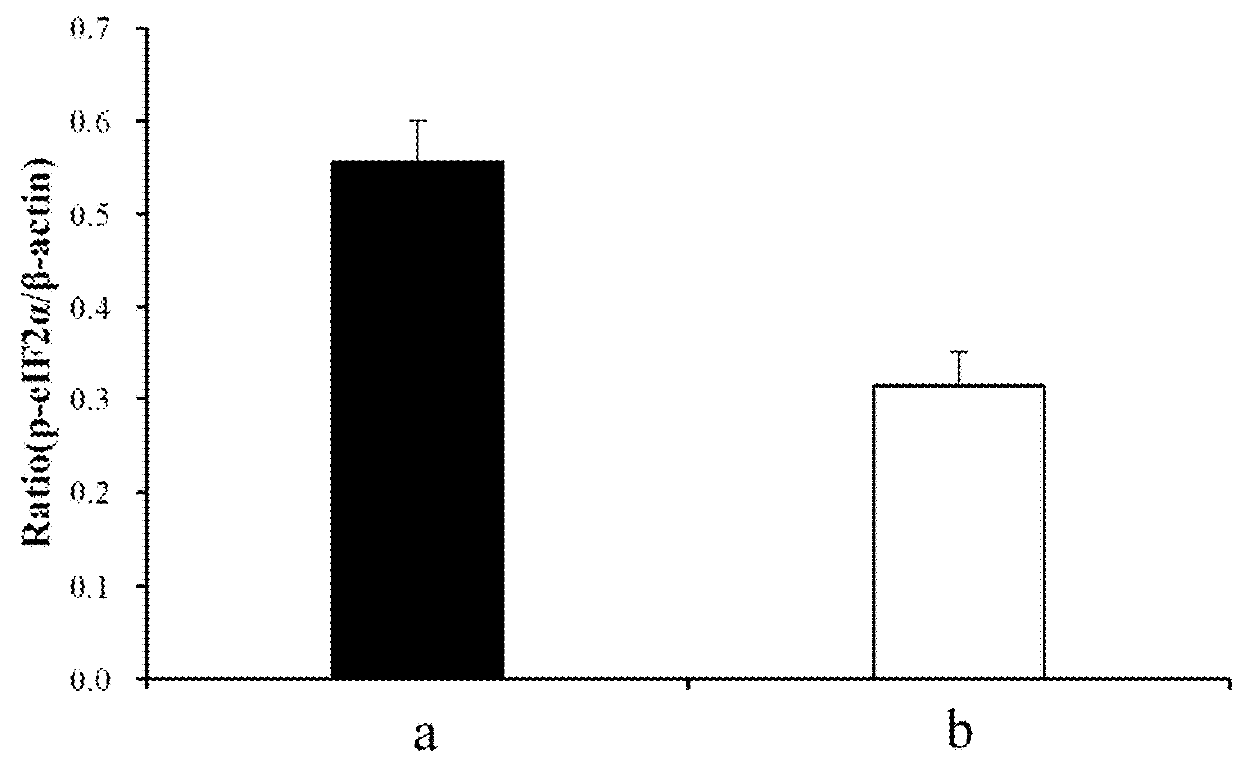
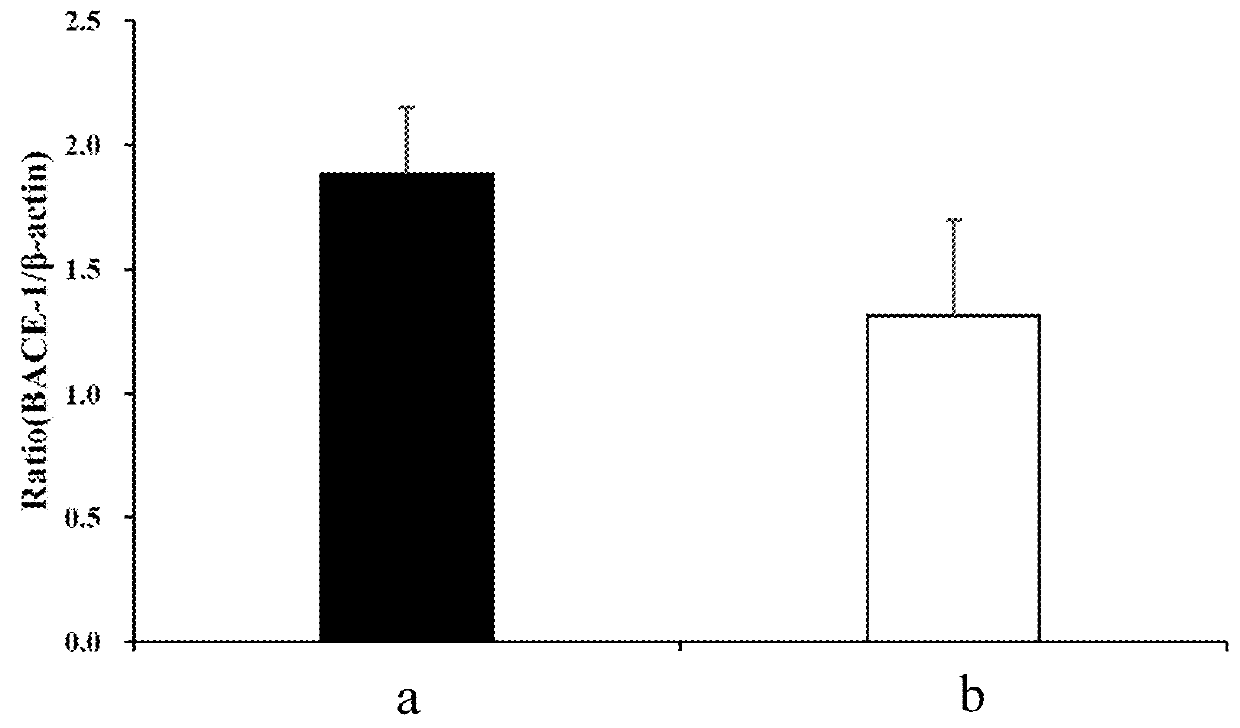
The invention provides a method of extracting whole coffee fruit, an extract obtained from the method, and method of ameliorating age-related neurodegenerative diseases using said extract. The whole coffee fruit extract may be extracted by water, methanol, ethanol, or acetone and may comprise chlorogenic acid (CA) and procyanidine. The expression levels of p-CREB, BDNF, p-eIF2α, BACE-1, Aβ, NLRP3, caspase-1, IL-1β and COX-2 which may relate to age-related neurodegenerative diseases can be modulated.
Owner:LYTONE ENTERPRISE INC
Traditional Chinese medicine composition for promoting regeneration of hippocampal neurons
ActiveCN109700973APromote regenerationEffective in treating depressionNervous disorderPlant ingredientsPinelliaMedicine
The invention provides a traditional Chinese medicine composition for promoting regeneration of hippocampal neurons. The composition is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 5-20parts of acanthopanax roots, 5-20 parts of medicinal Indian mulberry roots, 5-20 parts of turmeric root tuber, 1-15 parts of polygala roots, 5-20 parts of platycladi seeds, 3-15 parts of Chinese magnoliavine fruits, 5-20 parts of nutgrass galingale rhizome, 1-10 parts of lotus plumules, 3-15 parts of prepared pinellia tubers and 1-10 parts of pseudo-ginseng. The traditional Chinese medicine composition can be used for promoting regeneration of hippocampal neurons and regulating 5-HT1AR mediated CAMP-CREB-BDNF channel so as to achieve the effect of treating depression.
Owner:何原
Preventive and therapeutic drug for cartilaginous hyperplasia and method of screening for the same
A method of screening for a therapeutic and / or preventive drug for cartilaginous hyperplasia and a therapeutic and / or preventive drug for cartilaginous hyperplasia are provided.The following are provided: a method of screening for a therapeutic and / or preventive drug for cartilaginous hyperplasia, comprising a step of culturing chondroprogenitor cells under conditions in which the cells are brought into contact with a test substance and conditions in which the cells are not brought into contact with the test substance and a step of determining the SOX9 promoter activity, cAMP level, or degree of phosphorylation of CREB in the cells or the extracellular matrix volume in a culture; and a therapeutic and / or preventive drug for cartilaginous hyperplasia, comprising as an active ingredient an adenylate cyclase inhibitor.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Method for efficiently inducing human cells to be reprogrammed into neuronal cells
PendingCN113278585AShorten induction timeImprove induction efficiencyNervous system cellsCell culture active agentsReprogrammingNeuro-degenerative disease
The invention provides a method for efficiently inducing human cells to be reprogrammed into neuronal cells. The concentration of cAMP is improved or the expression of PKA and CREB is up-regulated or the expression of AMPK, ALK2, ALK3, P38 and JNK is inhibited through a single small molecule compound or gene knockout or gene overexpression. The induced small molecule compound is single and safe, short in induction time, high in induction efficiency, clear in induction action site and gene and clear in molecular regulation mechanism, can be applied to clinical treatment of human neurodegenerative diseases, and provides a safer and more efficient treatment means for treatment of the neurodegenerative diseases. As neurons do not have division and proliferation capacities, fibroblasts and astrocytes with division and proliferation capacities can be induced in vivo and in vitro by utilizing the method; and a large number of induced neurons can be continuously obtained in vivo and in vitro.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV +1
Application of rhodanine to treatment of metabolic diseases
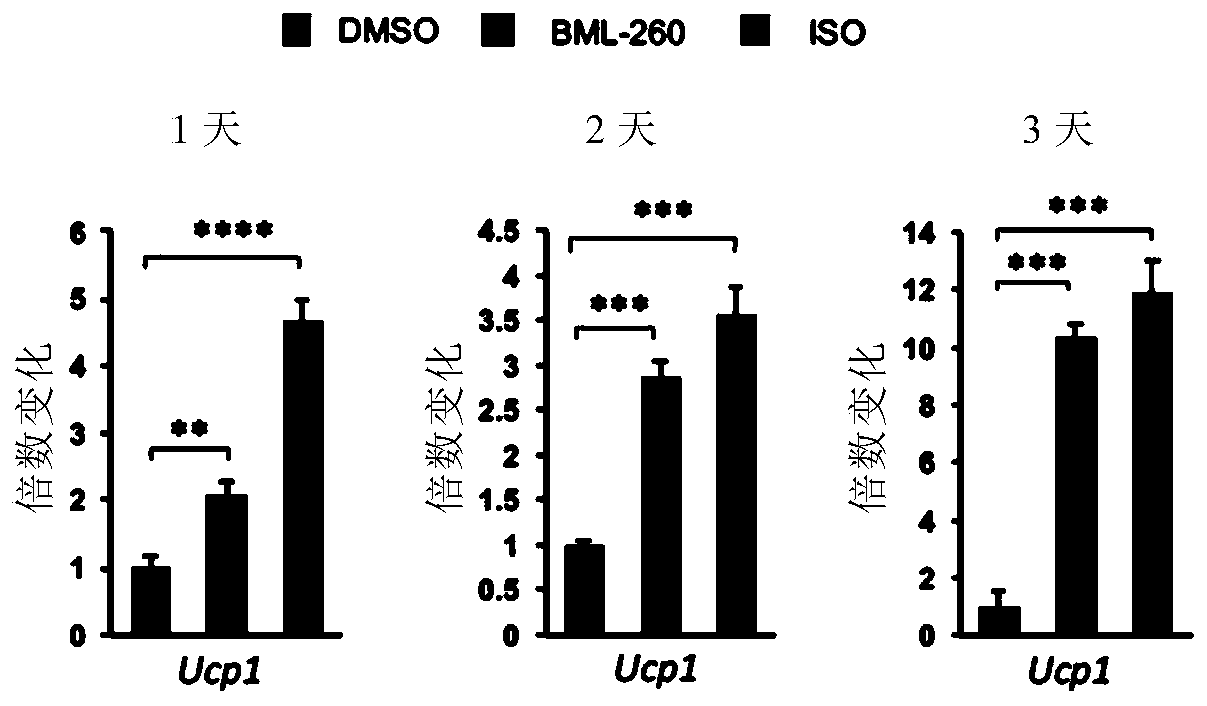
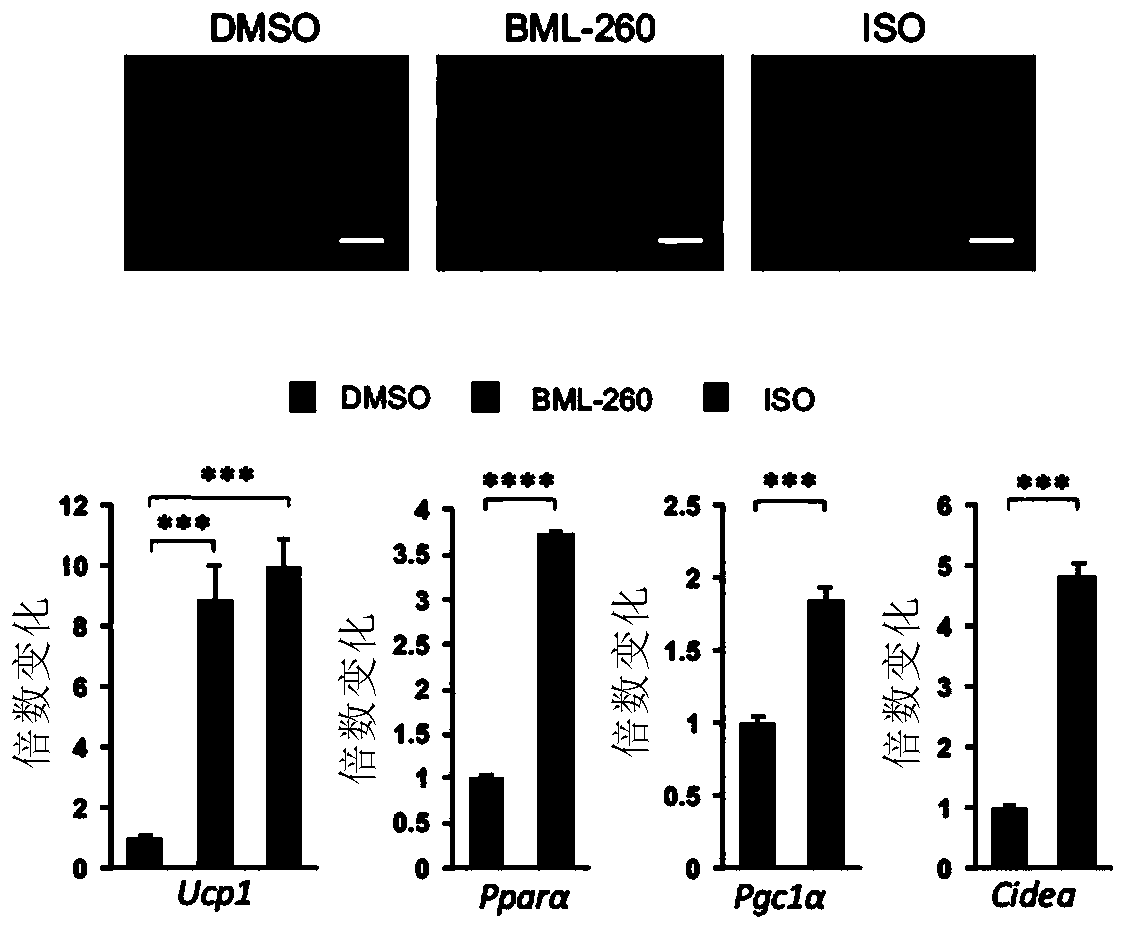
It is the first time for the invention to disclose that a rhodanine derivative can activate STAT3, CREB and PPARs signal paths, significantly increase expression of UCP1, enhance expression of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation genes, effectively increase thermogenesis, and can be used for treating the metabolic diseases. Accordingly, the invention relates to application of the rhodanine derivative to treatment of the metabolic diseases. The invention further relates to a pharmaceutical composition containing the rhodanine derivative as an active ingredient, and the pharmaceutical composition is used for treatment of the metabolic diseases.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
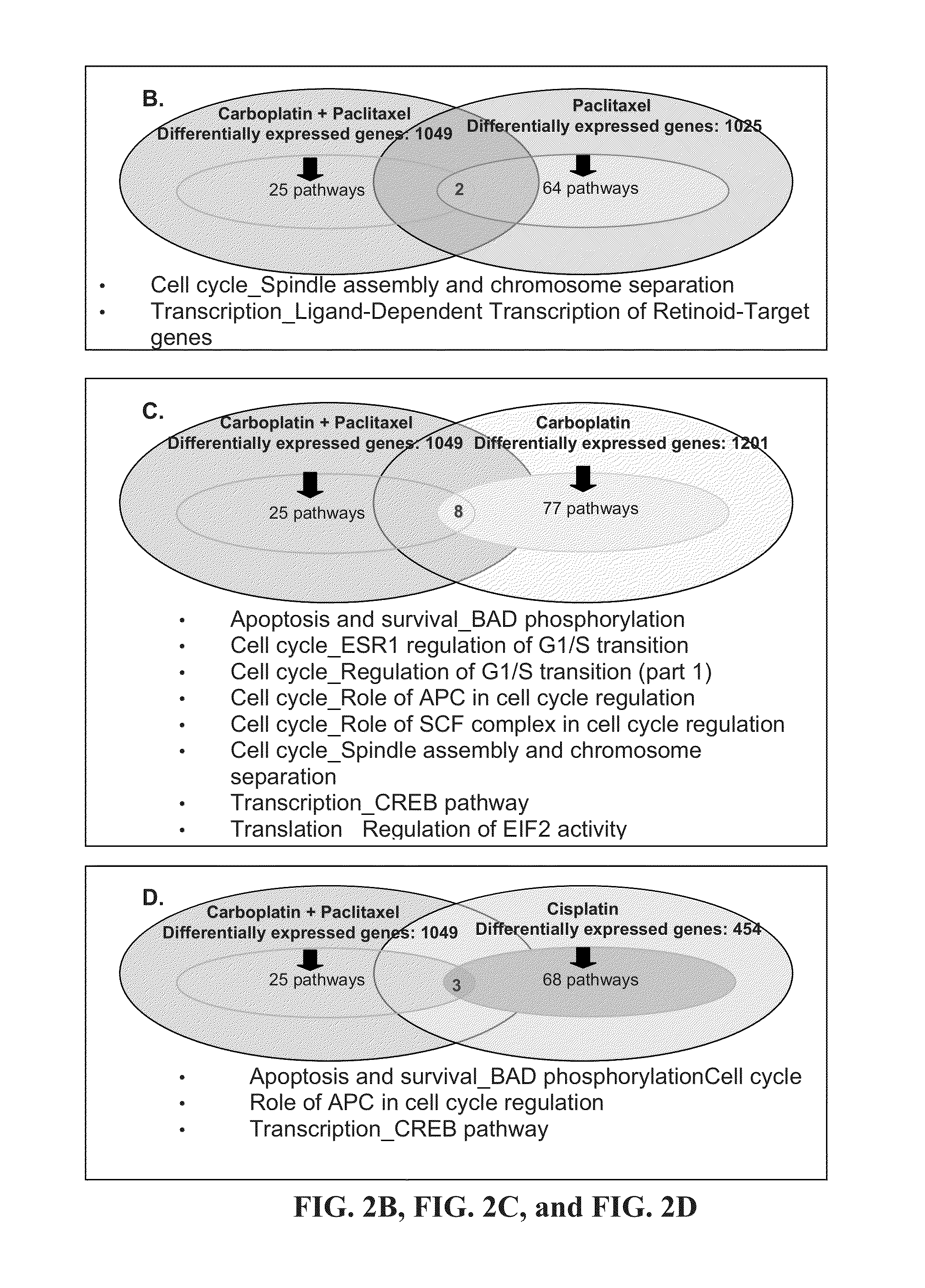
Compositions and Methods APC, CREB, and BAD Pathways to Assess and Affect Cancer
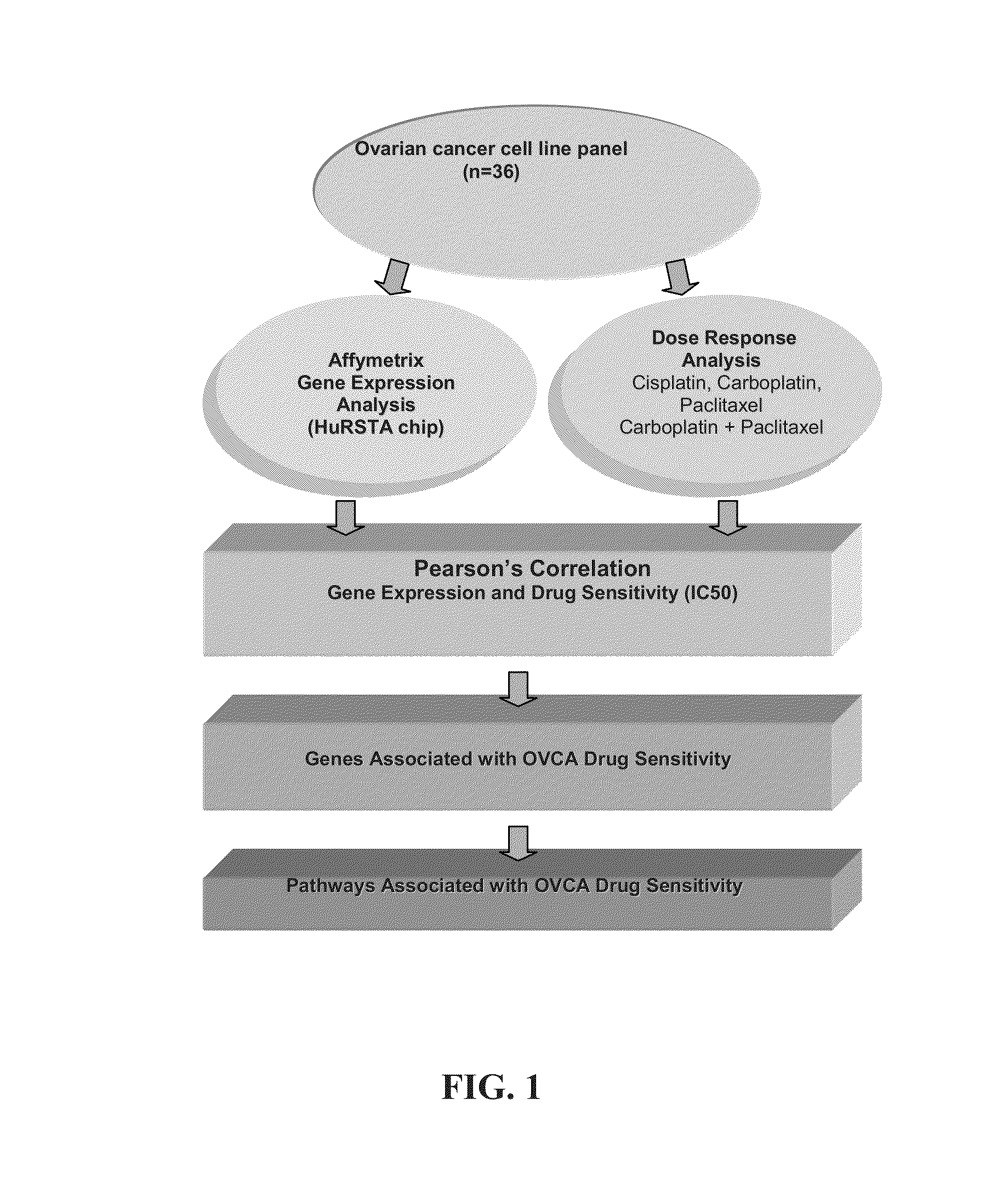
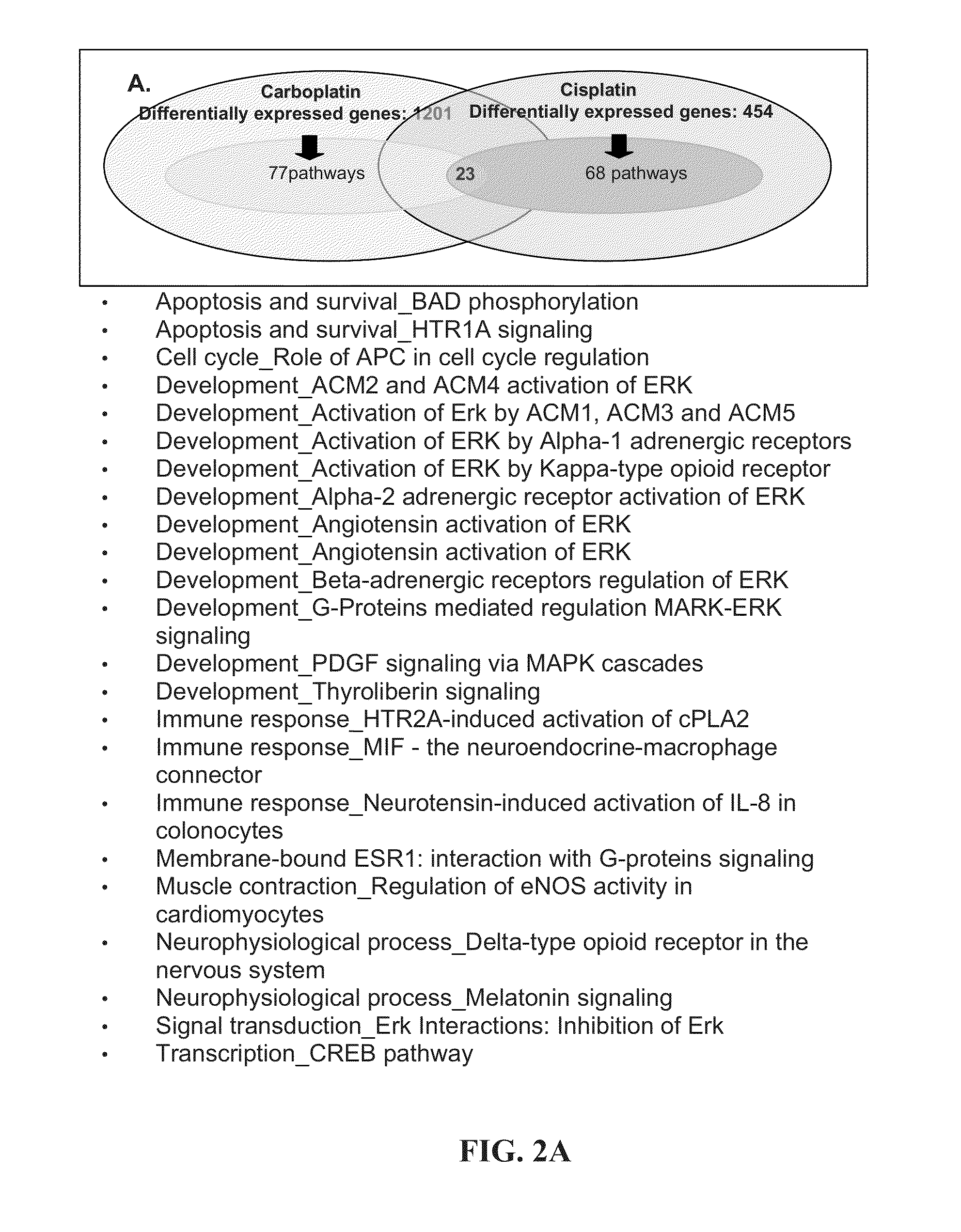
Disclosed are compositions and methods for assessing the apoptosis and survival BAD phosphorylation pathway (BAD pathway); and / or (2) the cell cycle role of APC in cell cycle regulation pathway (APC pathway); and / or (3) the transcription CREB pathway (CREB pathway) and for using these pathways to assess, treat, monitor, prognose, diagnose, etc. subjects with cancer. Also disclosed are compositions and methods for identifying molecular pathways that are common to one or more chemotherapeutic agents for the treatment of an oncological disorder, for screening for compounds or agents that can be used to treat ovarian cancer, and for selecting for compounds or agents that can enhance the cytotoxic response of cisplatin, carboplatin, and / or paclitaxel against a cancer cell, such as an ovarian cancer cell or cell line.
Owner:H LEE MOFFITT CANCER CENT & RES INST INC
Use of RET agonist molecules for haematopoietic stem cell expansion protocols and transplantation therapy and a RET agonist kit
InactiveUS9821026B2Reduce in quantityReturn to normal activitiesPeptide/protein ingredientsUnknown materialsProgenitorHsc transplantation
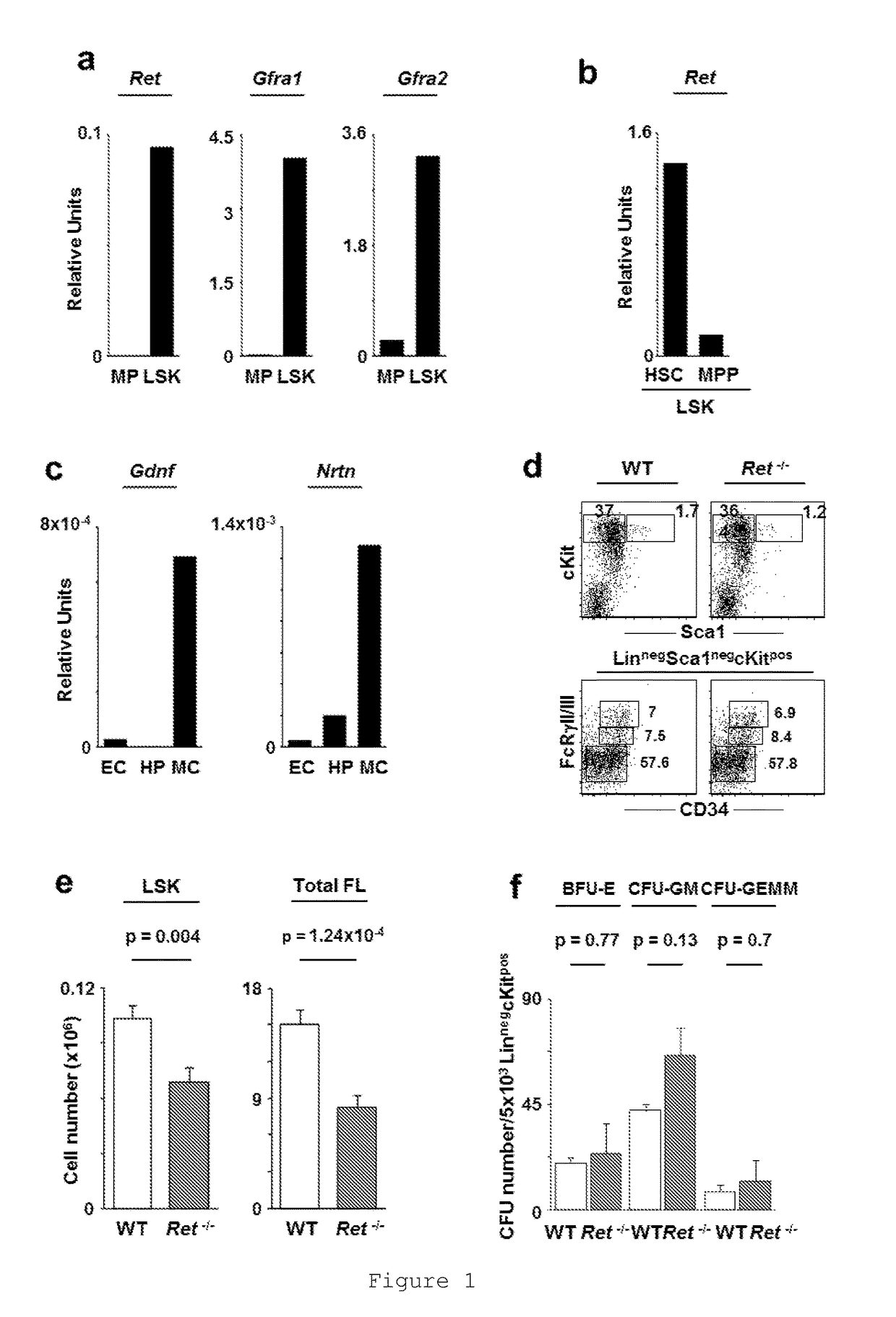
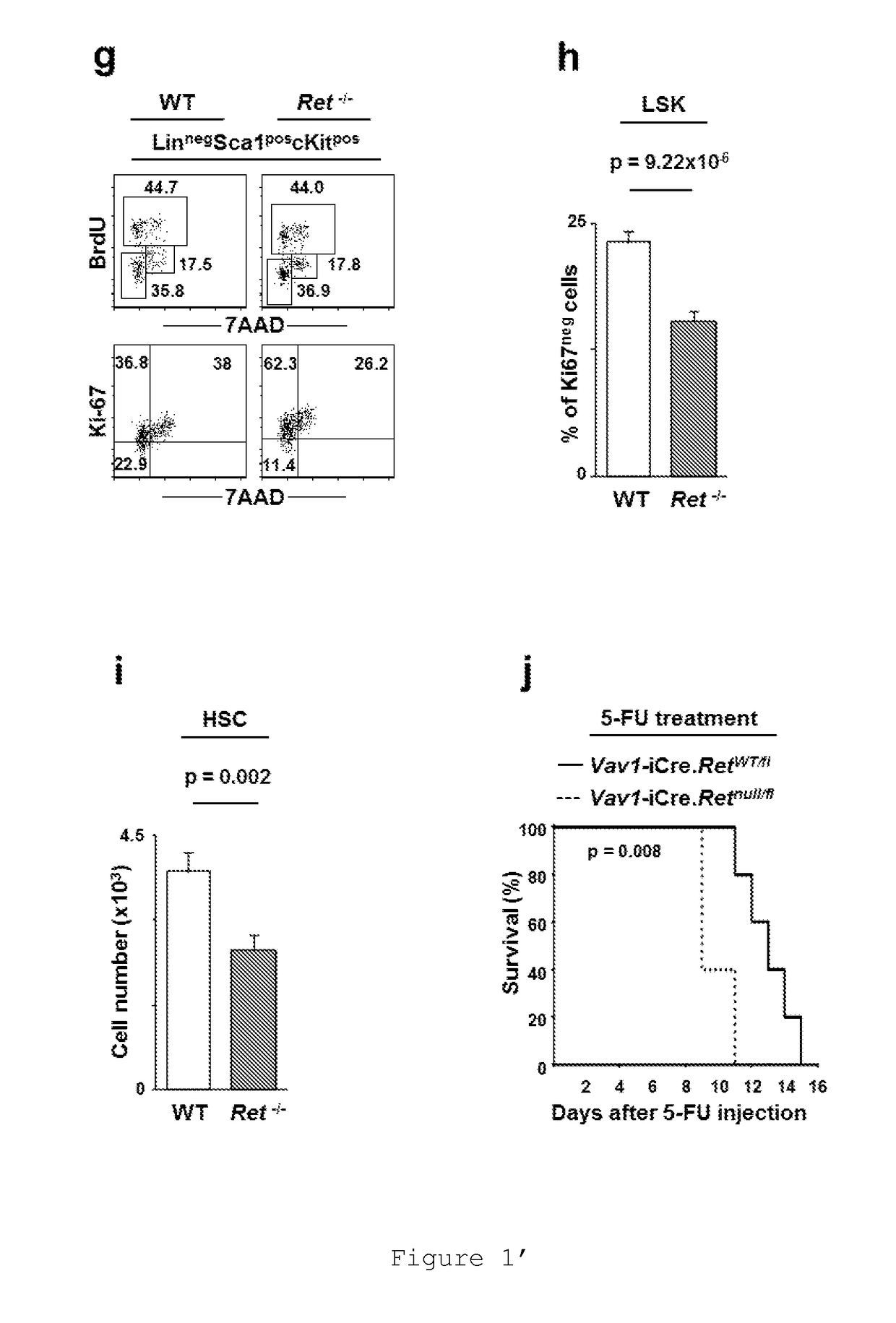
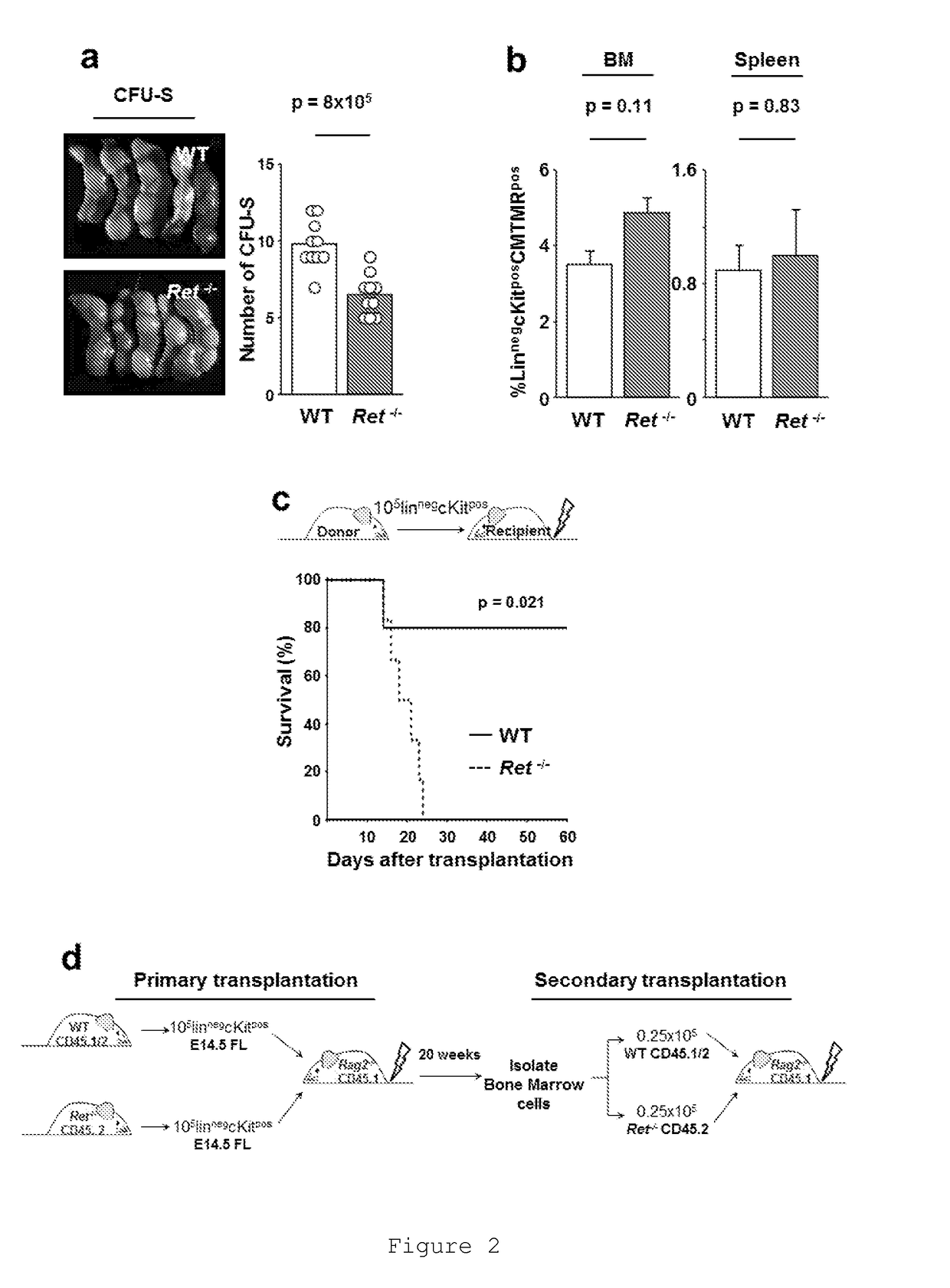
The present disclosure relates to the use of RET, a transmembrane tyrosine kinase receptor, agonist molecules for Haematopoietic Stem Cell (HSC) expansion protocols and HSC transplantation therapy.RET signaling molecules are expressed by HSCs and Ret ablation leads to reduced HSC numbers. RET signals provide HSCs with critical Bcl2 and Bcl2l1 surviving cues, downstream of p38 / MAP kinase and CREB activation. Accordingly, enforced expression of RET down-stream targets, Bcl2 or Bcl2l1, is sufficient to restore the activity of Ret null progenitors in vivo. Remarkably, activation of RET improves HSC survival or maintenance and in vivo transplantation efficiency, thus opening new horizons to the usage of RET agonist in HSC expansion and transplantation protocols.Additionally, the present disclosure describes a kit comprising RET agonist molecules, to be used in HSC expansion protocols and transplantation therapy.
Owner:INST DE MEDICINA MOLECULAR JOAO LOBO ANTUNES
Analytical method of CREB in Ang-2 regulating VEGFR2 expression
InactiveCN110333207AImprove the accuracy of image processingAccurately obtain expressionBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescencePartial systemAnalysis method
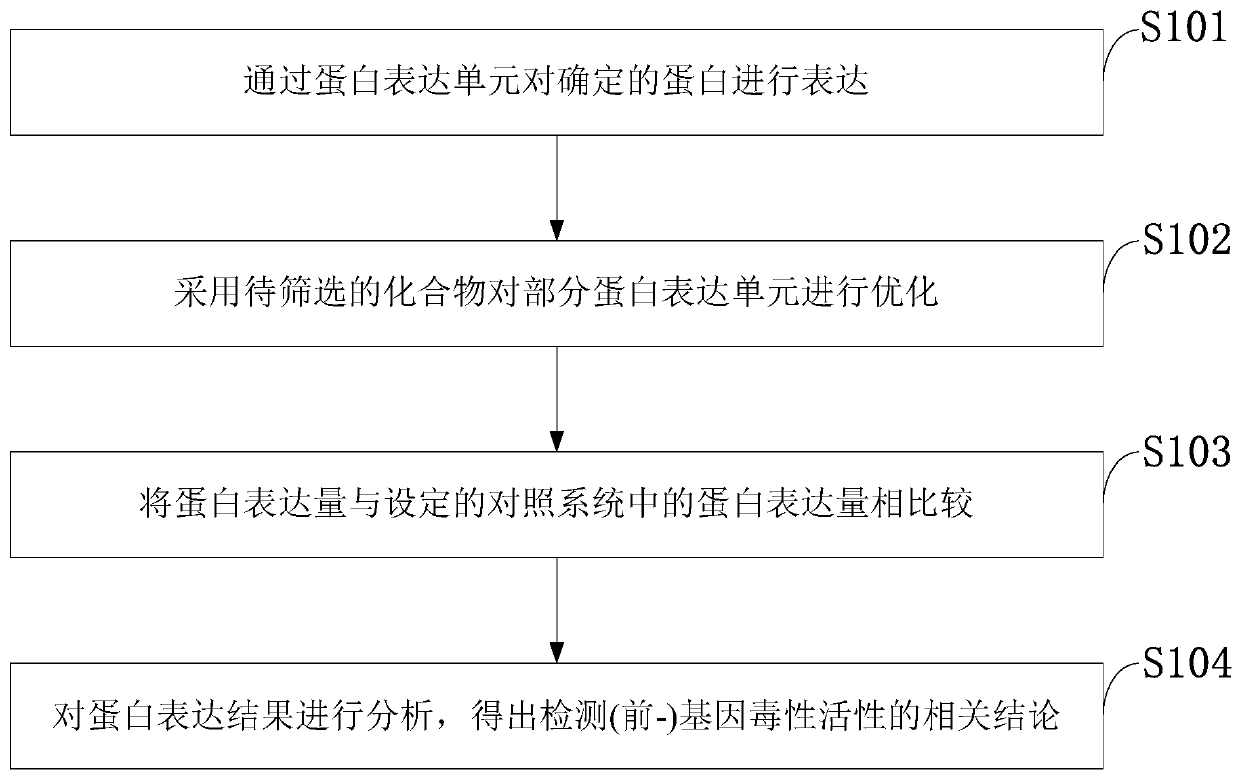
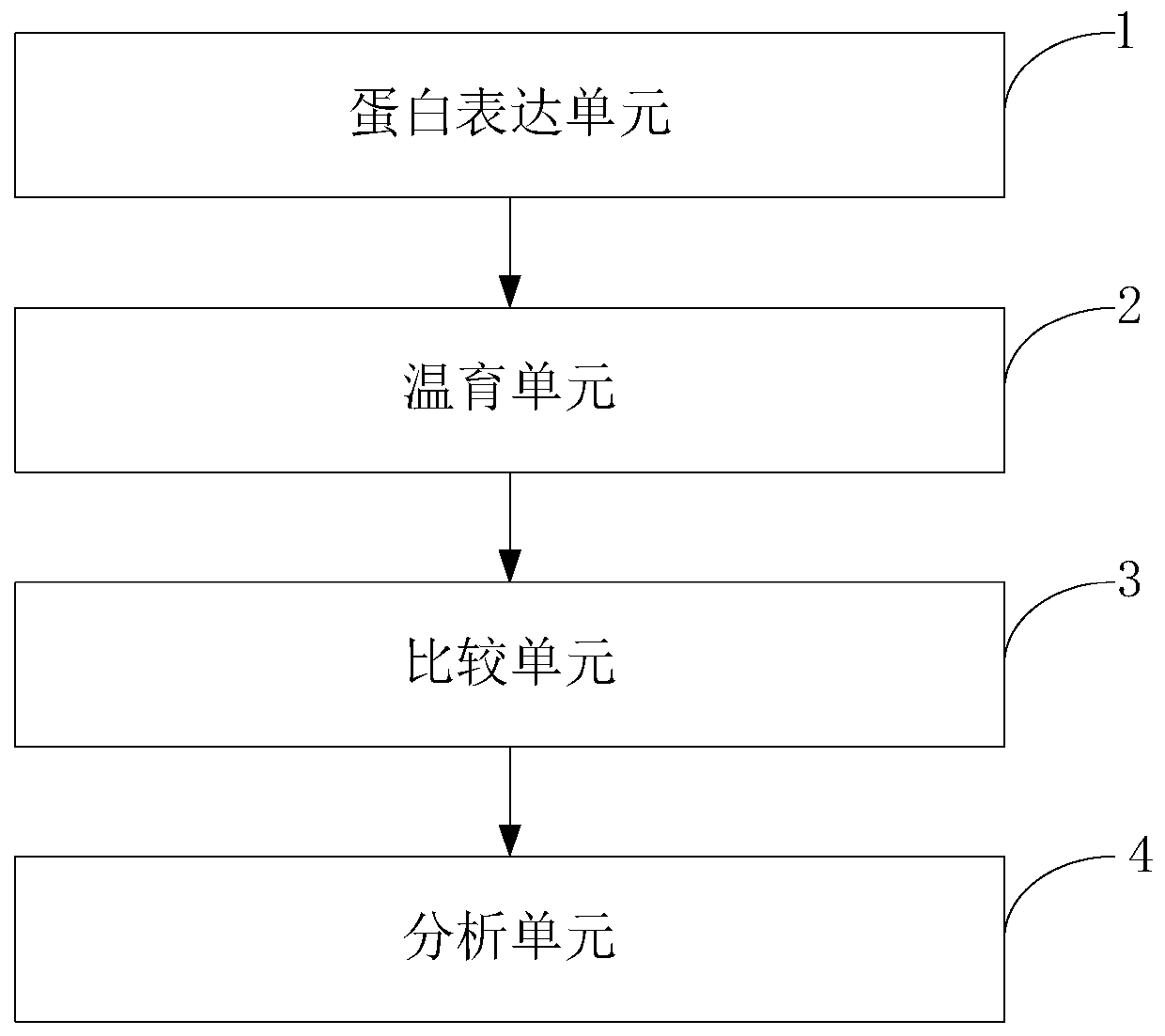
The invention belongs to the technical field of the biology, and discloses an analytical method of CREB in Ang-2 regulating VEGFR2 expression. By combining the gene knockout, signal channel inhibitionand like technical measures, the important effect of the CREB in the Ang-2 regulating VEGFR2 expression process is verified, and the determined protein is expressed through a protein expression unit;partial protein expression unit is optimized by adopting a to-be-screened compound; the protein expression quantity is compared with the protein expression quantity in a set reference system, a protein expression result is analyzed to obtain related conclusion for detecting gene toxicity activity. At least partial system is incubated by using the to-be-screened compound, and the protein expression in the system is compared with the protein expression in the reference system, thereby detecting the (front-) gene toxicity activity. The theoretical evidence is provided for the analysis of the CREB in the Ang-2 regulating VEGFR2 expression.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
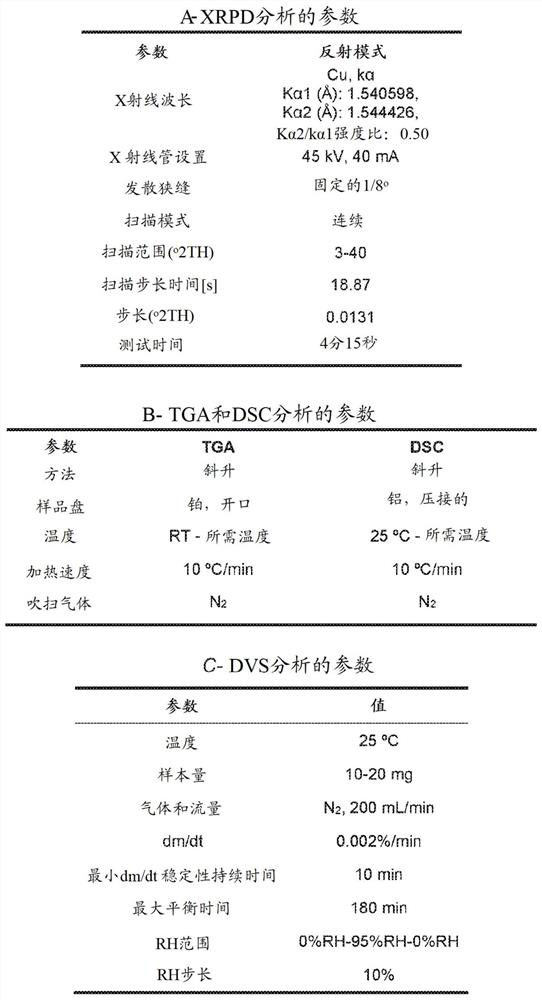
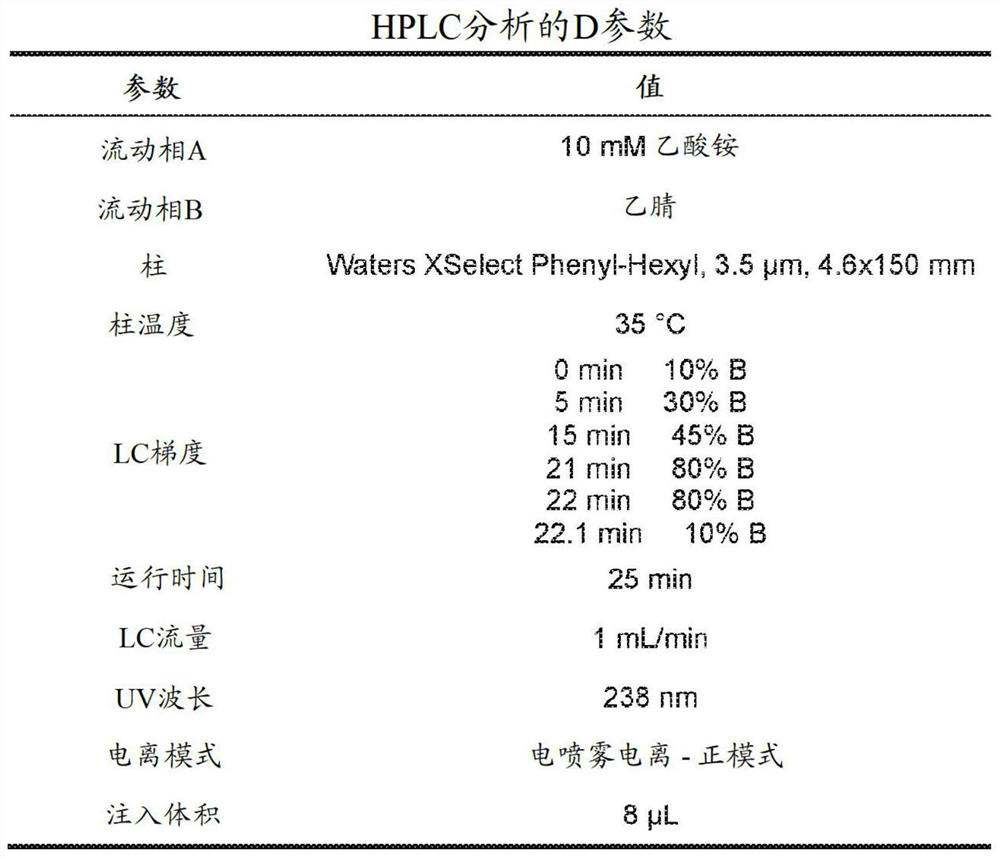
Inhibiting cyclic amp-responsive element-binding protein (CREB)
The present disclosure is directed to solid and salt forms of inhibitors of the CBP / p300 family of bromodomains made up of salts and crystalline forms of Formula (I). The compounds can be useful in the treatment of disease or disorders associated with the inhibition of the CBP / p300 family of bromodomains. For instance, the disclosure is concerned with compounds and compositions for inhibition of the CBP / p300 family of bromodomains, methods of treating diseases or disorders associated with the inhibition of CBP / p300 family of bromodomains (e.g., certain forms of cancer), and methods of synthesis of these compounds.
Owner:FORMA THERAPEUTICS INC
Method for screening compounds for those that modulate transducers of regulated CREB activity
InactiveUS7485434B2Modulate levelPromotes rapid Ser17 dephosphorylationCompound screeningApoptosis detectionCytoplasmCalcineurin phosphatase
In accordance with the present invention, it has been discovered that glucose and incretin hormones promote pancreatic islet cell survival via the calcium and cAMP dependent induction, respectively, of the transcription factor CREB. Specifically, a signaling module has been identified which mediates cooperative effects of calcium and cAMP on islet cell gene expression by stimulating the dephosphorylation and nuclear entry of TORC2, a cytoplasmic CREB coactivator. The module comprises a cAMP regulated snf1-like kinase called SIK2 and the calcium regulated phosphatase calcineurin, both of which associate with TORC2 in the cytoplasm. TORC2 is repressed under basal conditions through a phosphorylation dependent interaction with 14-3-3 proteins. cAMP and calcium signals stimulate CREB target gene expression via complementary effects on TORC2 dephosphorylation; cAMP disrupts TORC2-associated activity of SIK2 or related family members, whereas calcium induces TORC2 dephosphorylation via calcineurin. These findings provide a novel mechanism by which CREB activates cellular gene expression, depending on nutrient and energy status, and facilitate development of assays to identify compounds which modulate the role of TORCs. In accordance with the present invention, it has been discovered that fasting and energy-sensing pathways regulate the gluconeogenic program in liver by modulating the nuclear entry of a transcriptional coactivator called Transducer of Regulated CREB Activity 2 (TORC2). Hepatic TORC2 over-expression induces fasting hyperglycemia, whereas knockdown of TORC2 leads to fasting hypoglycemia and silencing of the gluconeogenic program. Since a majority of individuals with Type II diabetes exhibit fasting hyperglycemia due to elevated hepatic gluconeogenesis, compounds that enhance TORC2 phosphorylation will find use as therapeutic agents in this setting.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
Agents and methods for treating cbp-dependent cancers
ActiveUS20190276509A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifPeptide/protein ingredientsTat peptideBinding peptide
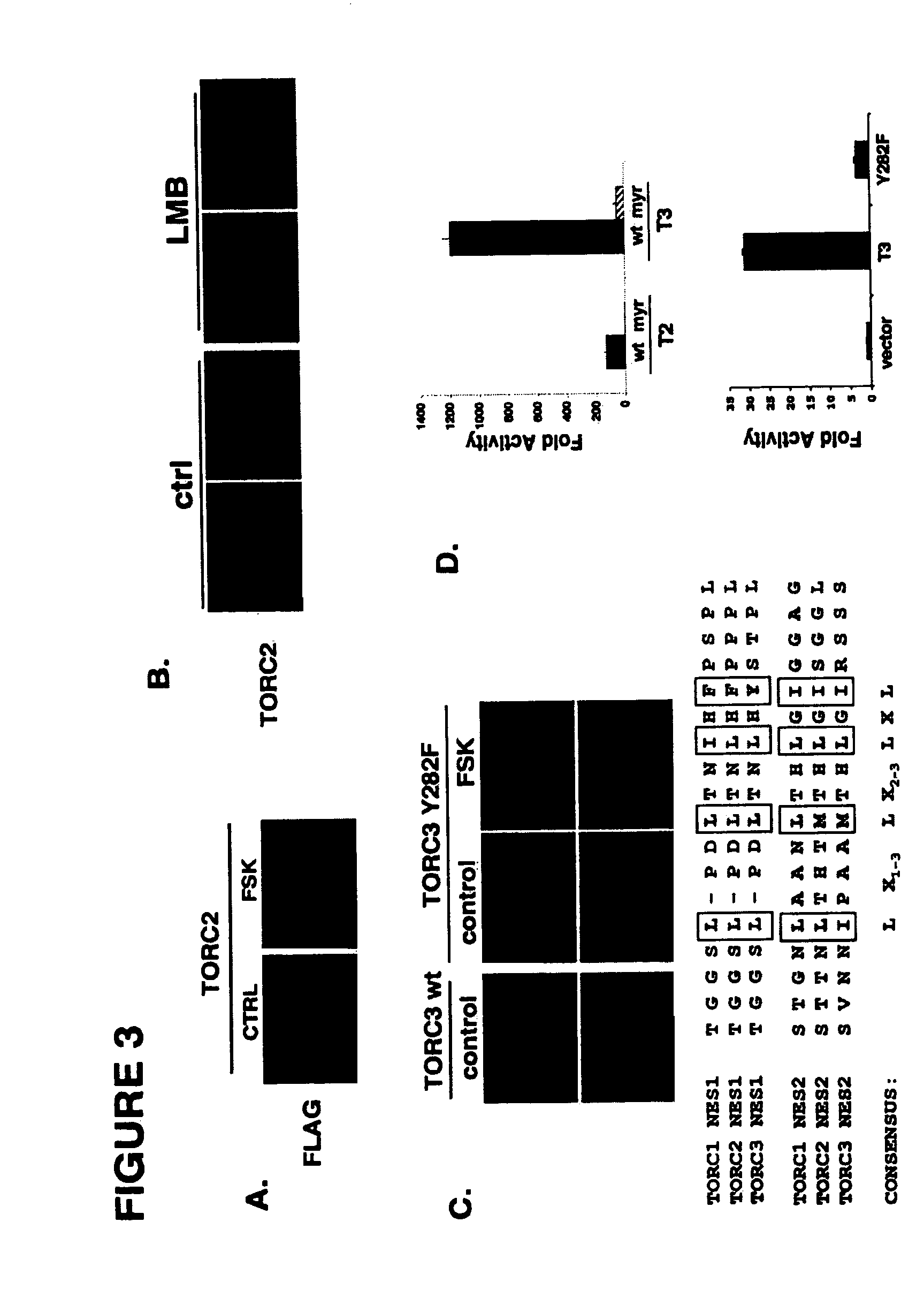
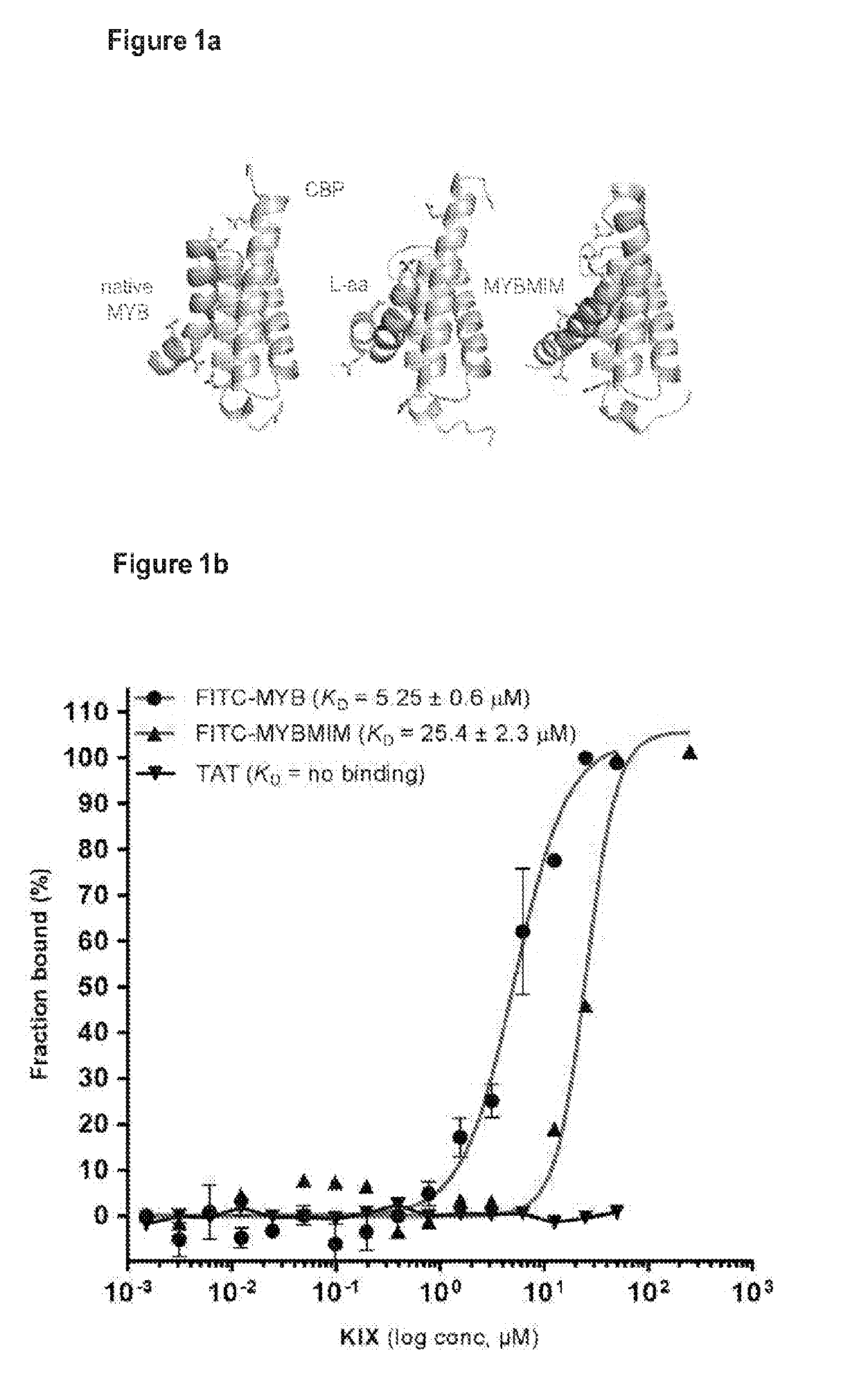
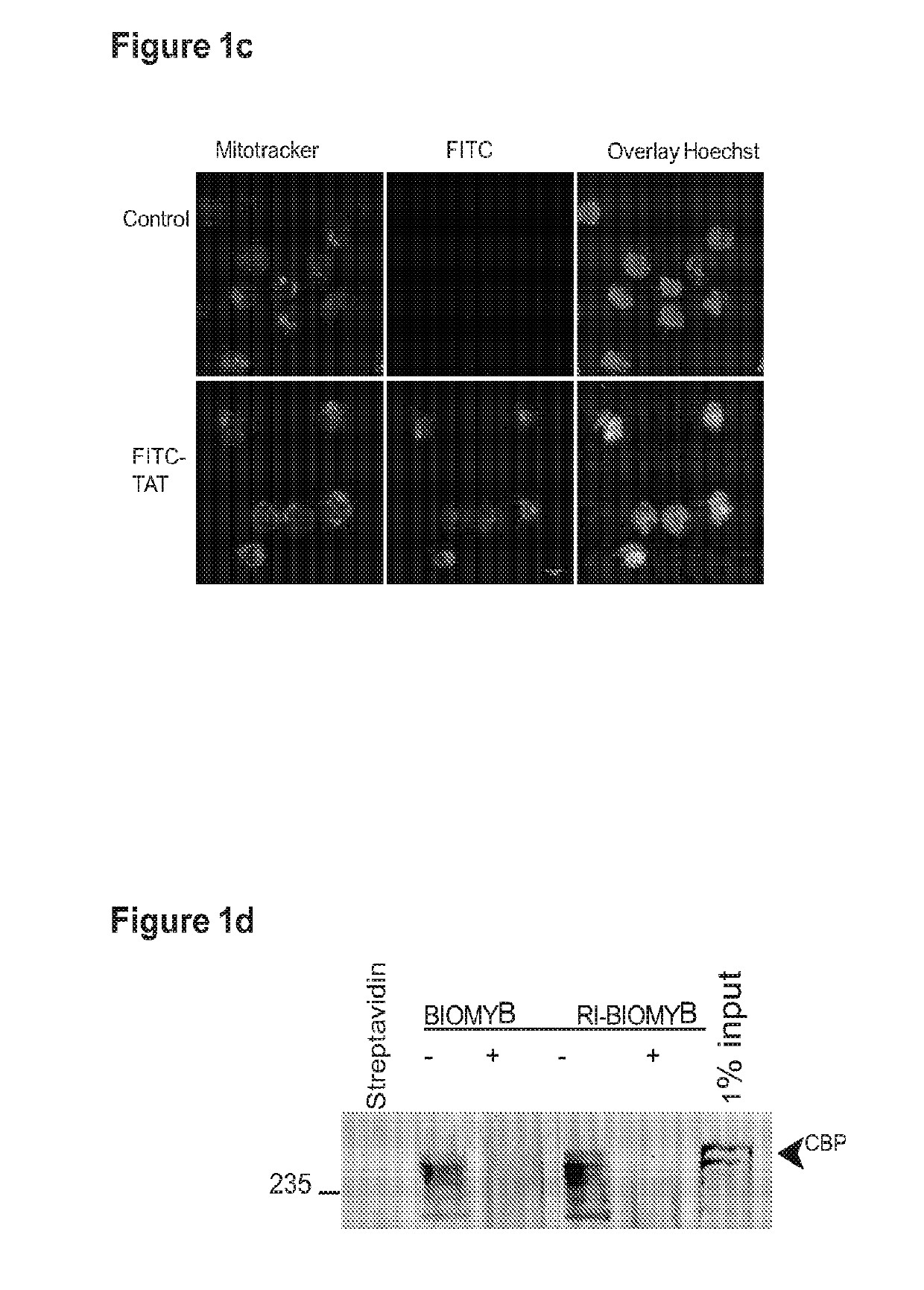
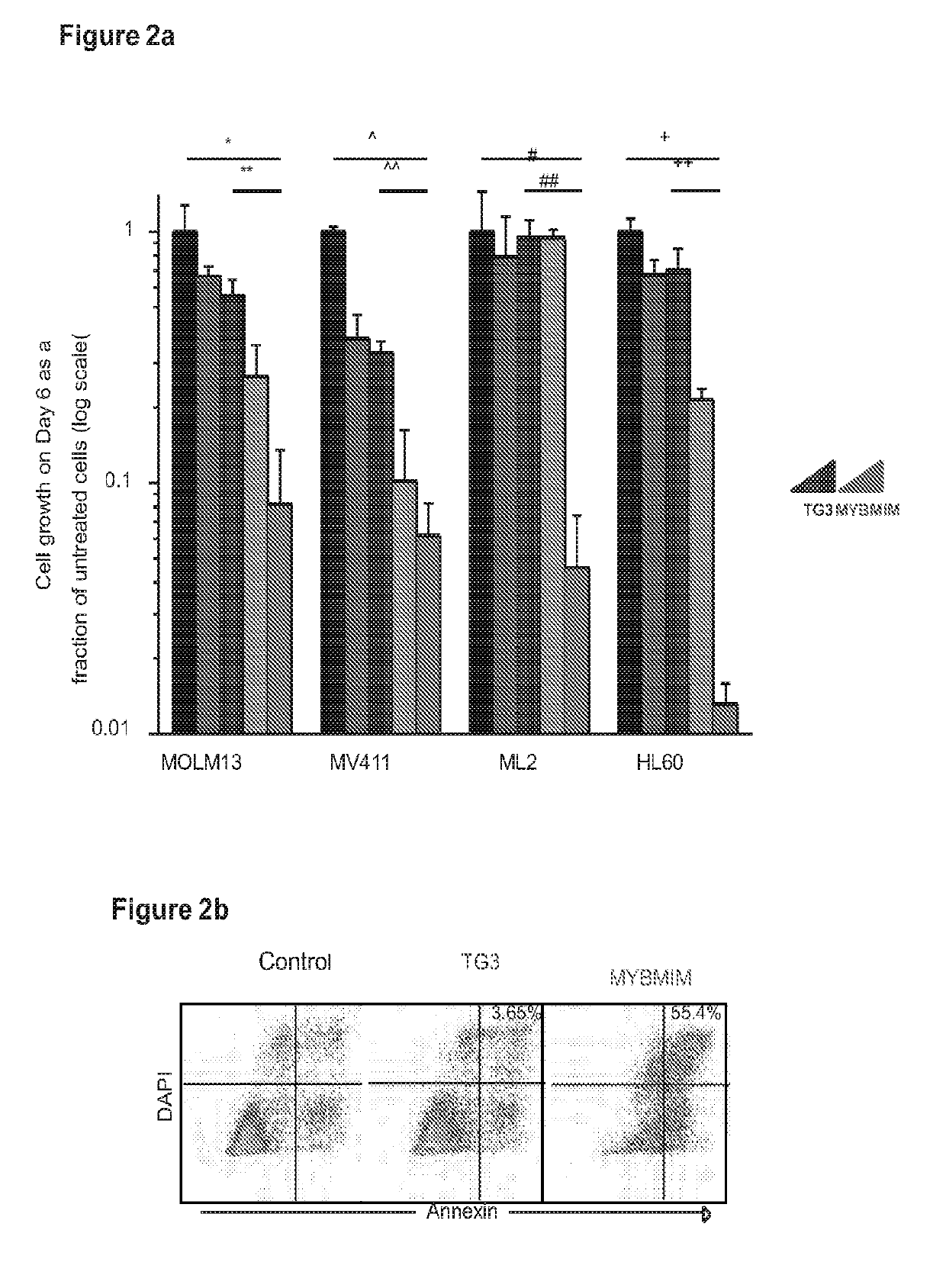
Single chain peptides comprising either a cell penetrating HIV-TAT peptide sequence and a MYB:CBP complex interfering peptide sequence from MYB, or comprising a cell penetrating HIV-TAT peptide sequence, a CBP binding peptide sequence from CREB and a MYB:CBP complex interfering peptide sequence from MYB, are provided for use in preventing MYB:CBP complex formation and downstream events leading to cancer, in particular a leukemia. Both L-amino acid single chain peptides and retro-inverso single chain peptides are provided.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com