Targeting the histone code as a bacterial strategy for selectively modulating gene expression
a bacterial strategy and gene expression technology, applied in the field of targeting the histone code as a bacterial strategy for selectively modulating gene expression, can solve the problems of excessive inflammation, ineffective invading the apical pole of polarized iec, and detrimental to i>shigella/i>'s survival in the hos
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Materials and Methods
[0086] Cell Culture. The human intestinal epithelial cell line Caco-2, derived from a colonic carcinoma, and HeLa cells were used. Synchronization of the cells by a double thymidine block was performed as described previously (Harper, 2005).
[0087] Bacterial strains. The wild-type (WT) invasive strain of S. flexneri serotype 5a and a noninvasive variant (VP−) of the WT strain lacking the 220 kB virulence plasmid were used. The ipa mutants strains have been described previously (Mavris et al., 2002a). To construct the ospF mutant, a PCR amplified DNA fragment encompassing nucleotides 61 to 420 of ospF was cloned between the XbaI and EcoRI sites of the suicide plasmid pSW23T, generating pSWOspFTr. This plasmid was transferred by conjugation to the WT strain WT-Sm. A plasmid expressing the ospF gene was constructed by inserting a PCR fragment encompassing the ospF gene between the EcoRI and HindIII sites of pUC18, forming pUC18-OspF. This plasmid was used to compl...
example 2
Shigella Inactivates Erk and Sequesters Erk into the Nucleus
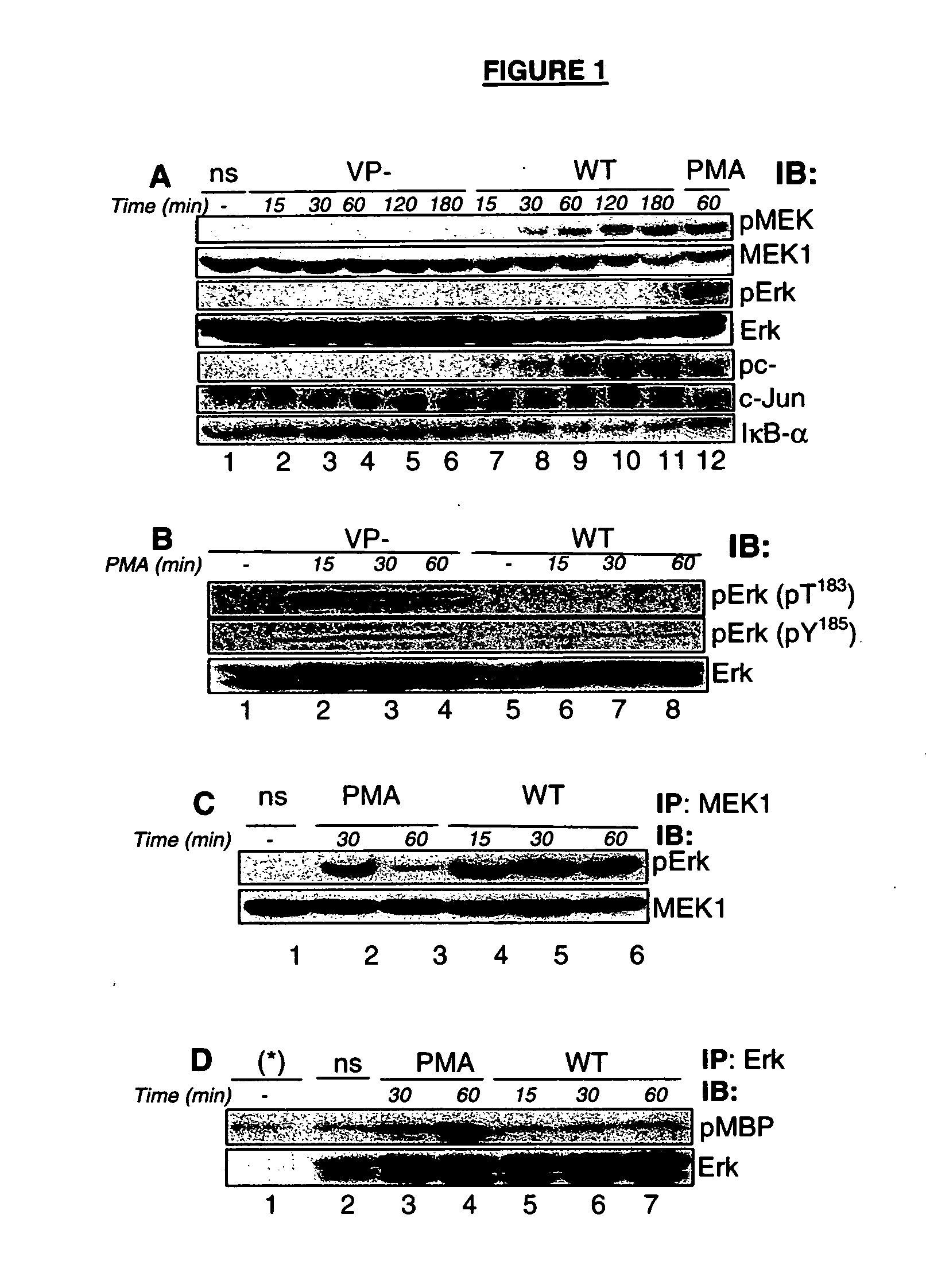
[0098] MAPK pathways play important roles in regulating gene expression in eukaryotic cells by phosphorylating transcription factors, co-regulators, and chromatin remodelling components. The three major subfamilies of MAPKs in mammalian cells include the Erk 1 and 2, JNK 1, 2, and 3, and p38 proteins (p38α / β / γ / δ). MAPK kinases (MAPKKs) activate MAPKs by phosphorylating threonine (Thr) and tyrosine (Tyr) residues at TEY sequences located in the MAPK's activation loop domain. MAPKKs are in turn activated by phosphorylation at serine (Ser) and Thr residues performed by MAPKK kinases (MAPKKKs). In quiescent cells, the two isoforms of MAPKs, Erk1 and Erk2, are inactive and retained in the cytoplasm via a direct association with their upstream activator, the kinase MEK1. Upon cell activation, activated MEK1 phosphorylates Erk1 and Erk2 on the TEY sequence leading to dissociation of the MEK-Erk complex before Erk translocates int...
example 3
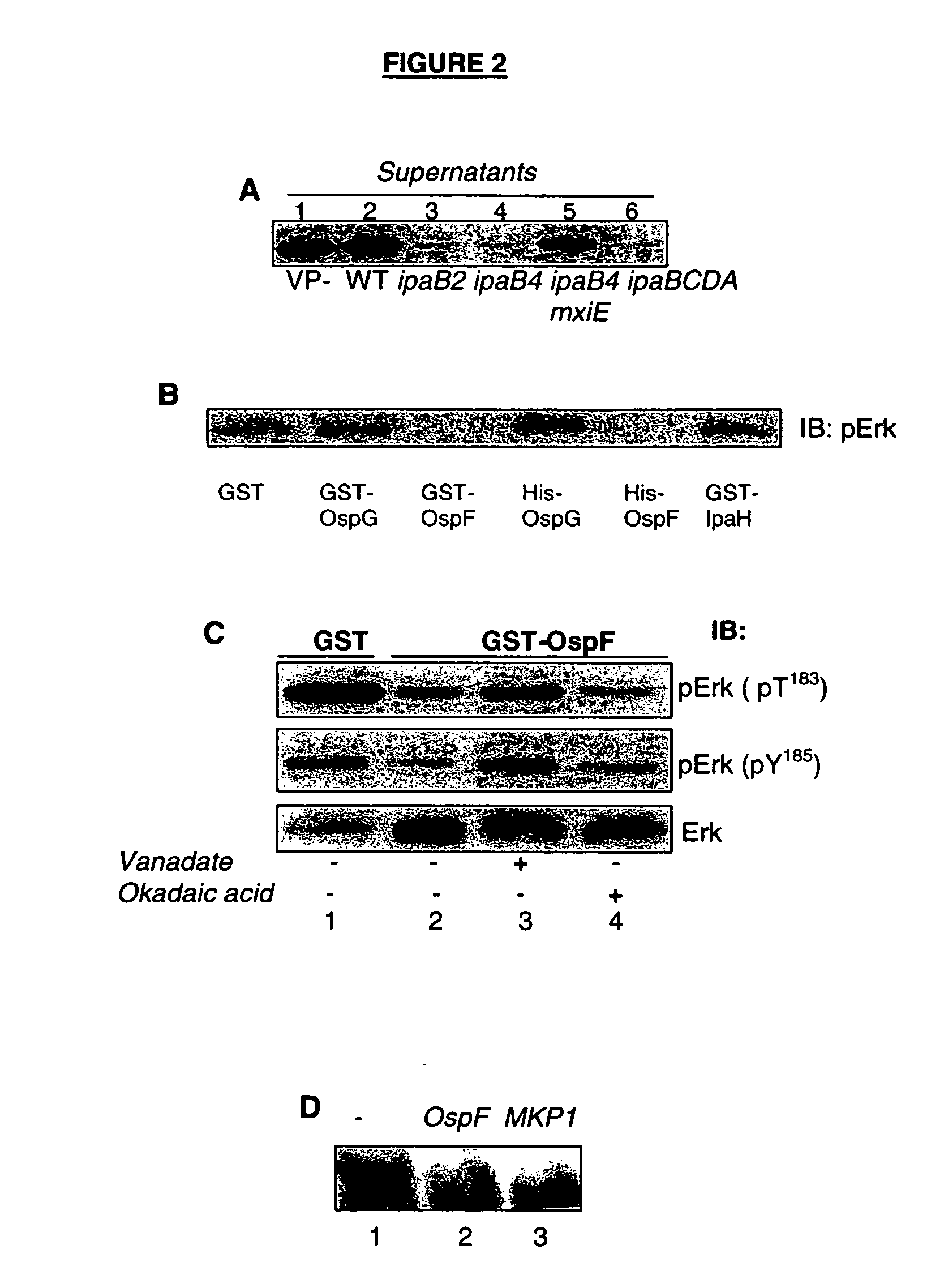
The ospF Gene Encodes a Bacterial Phosphatase that Directly and Dually Dephosphorylates Erk
[0103] Upon contact with the epithelial cell surface, the Shigella TTSS apparatus activates and approximately 20 proteins are secreted through this secreton. The TTSS apparatus is weakly active during bacterial growth in vitro at 37° C. and is deregulated by inactivation of the ipaB or ipaD genes (Menard et al., 1994).
[0104] Since the major Erk phosphatases described in mammals are soluble enzymes, a strategy was developed to identify a putative bacterial DSP using bacterial supernatants from deregulated mutant strains in which the ipaB gene has been either inactivated (ipaB2 strain) or disrupted, leading to a truncated version of the ipaB protein (ipaB4 strain) (Mavris et al., 2002a). Supernatants from these mutant strains were assayed for the phosphatase activity using a commercial phospho-Erk2-glutathione S transferase (pErk2-GST) fusion peptide as a substrate.
[0105] The supernatant from...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| chemical | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com