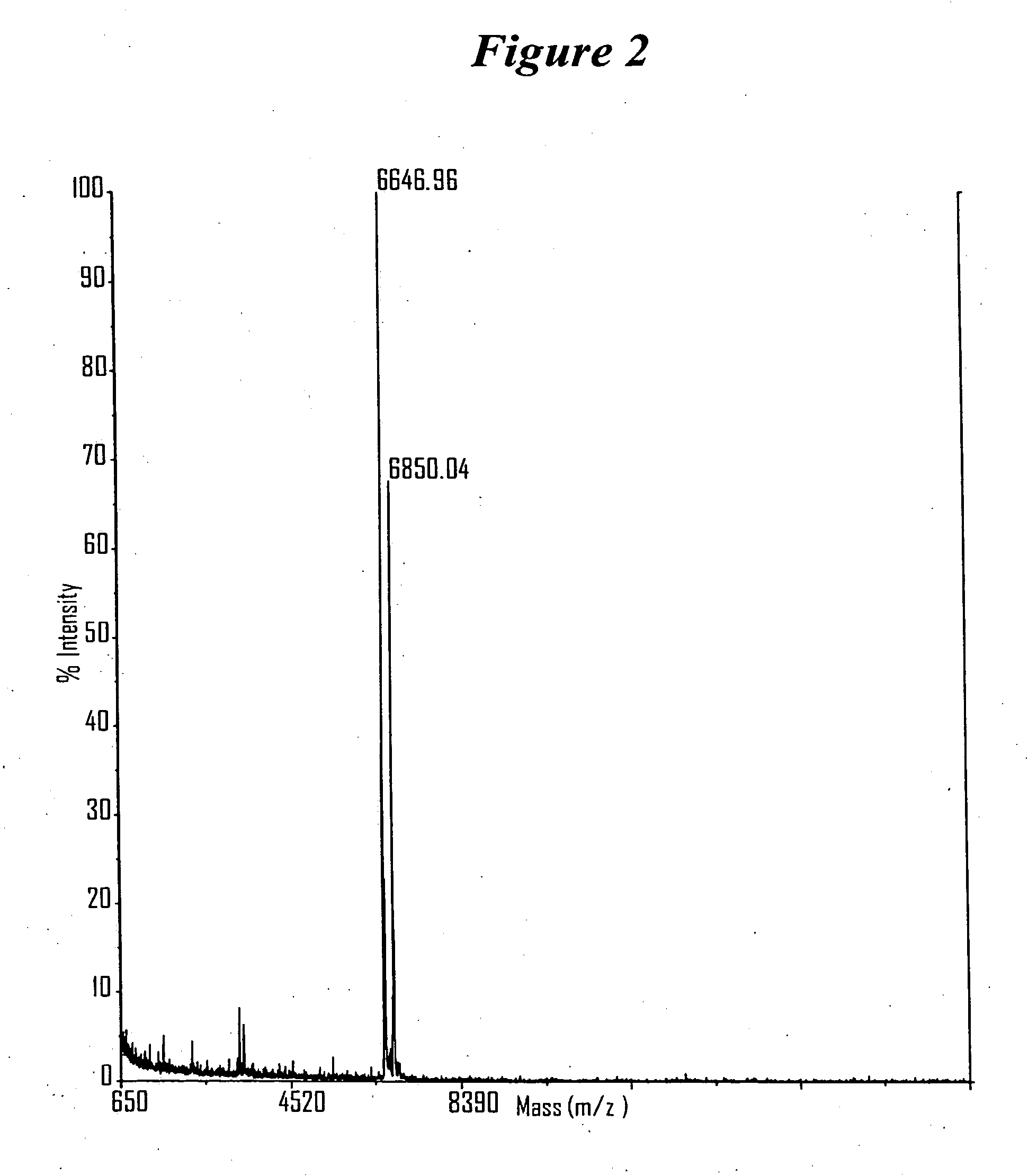
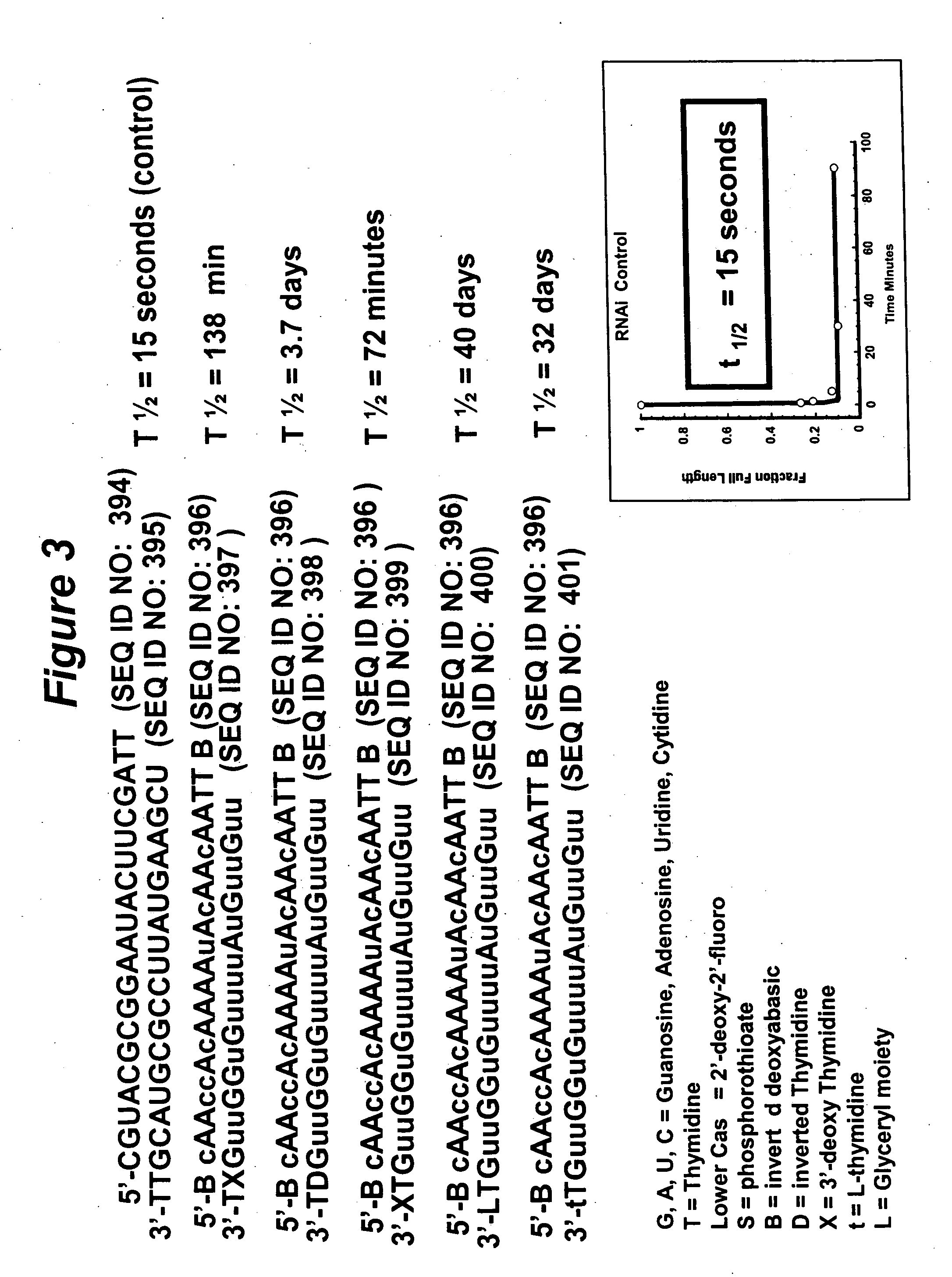
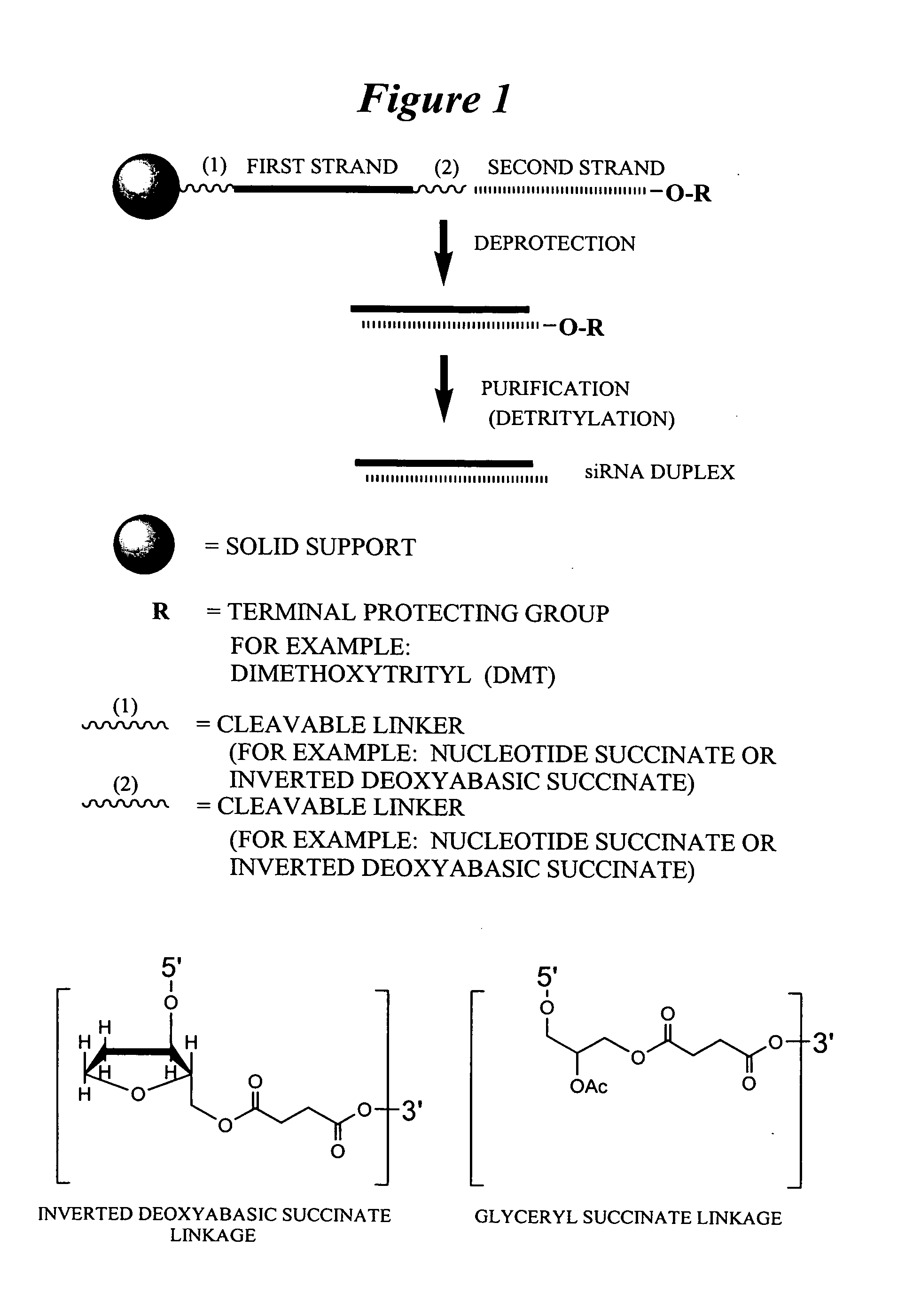
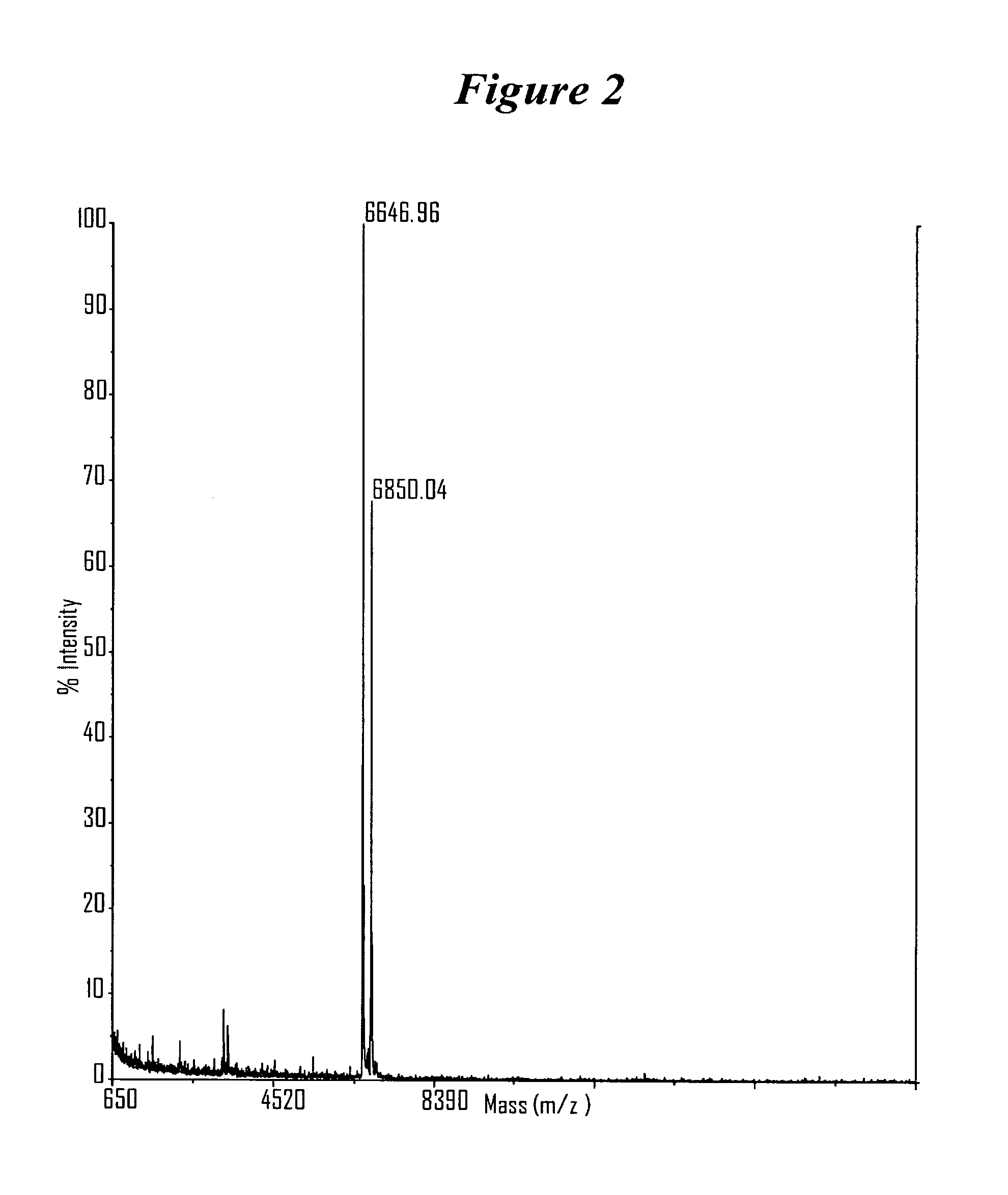
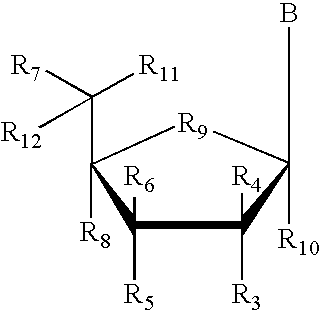
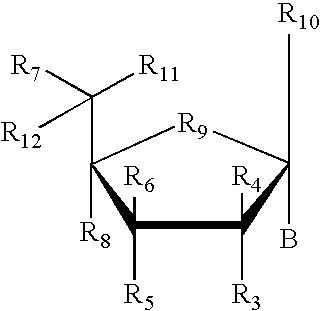
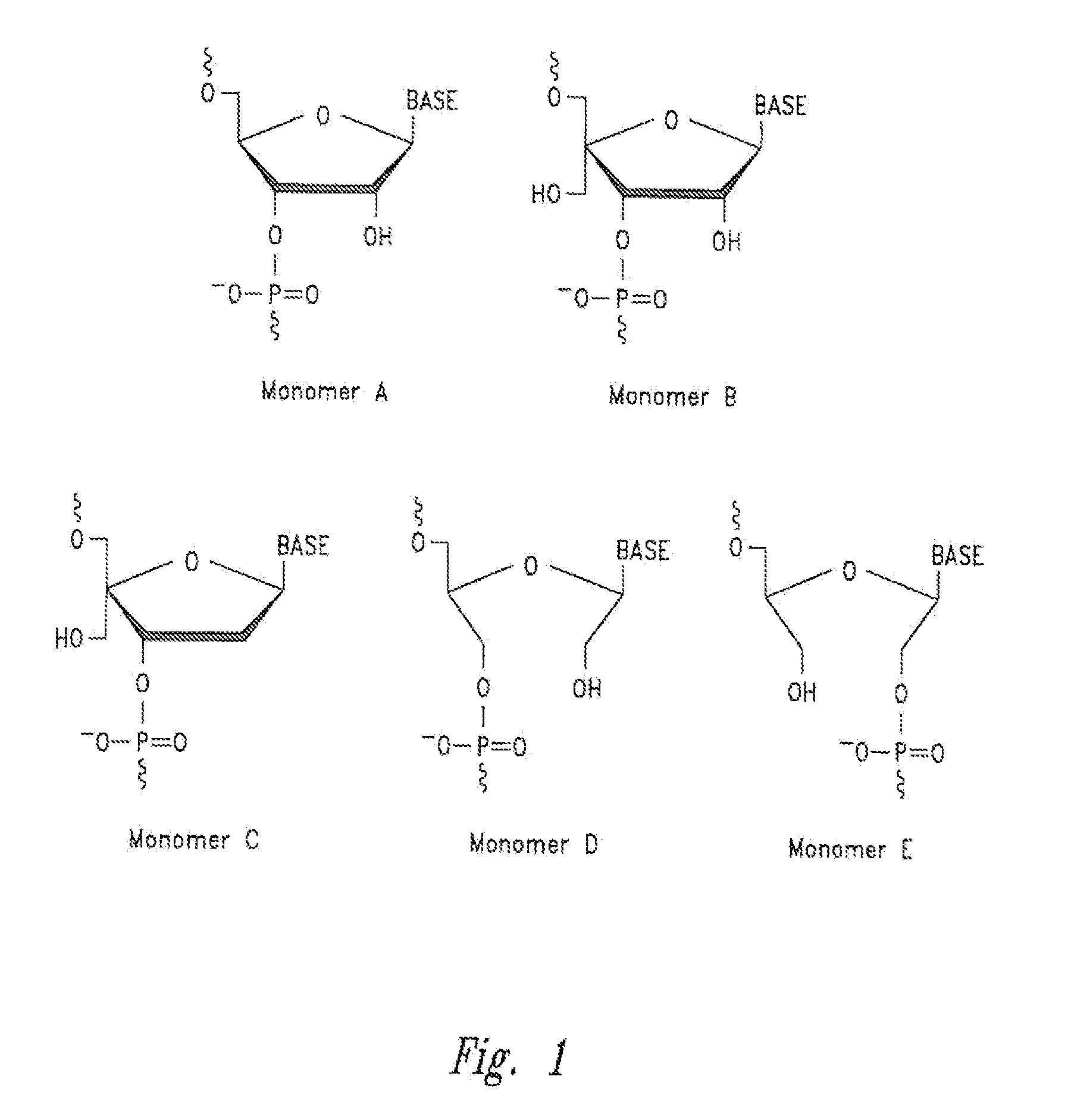
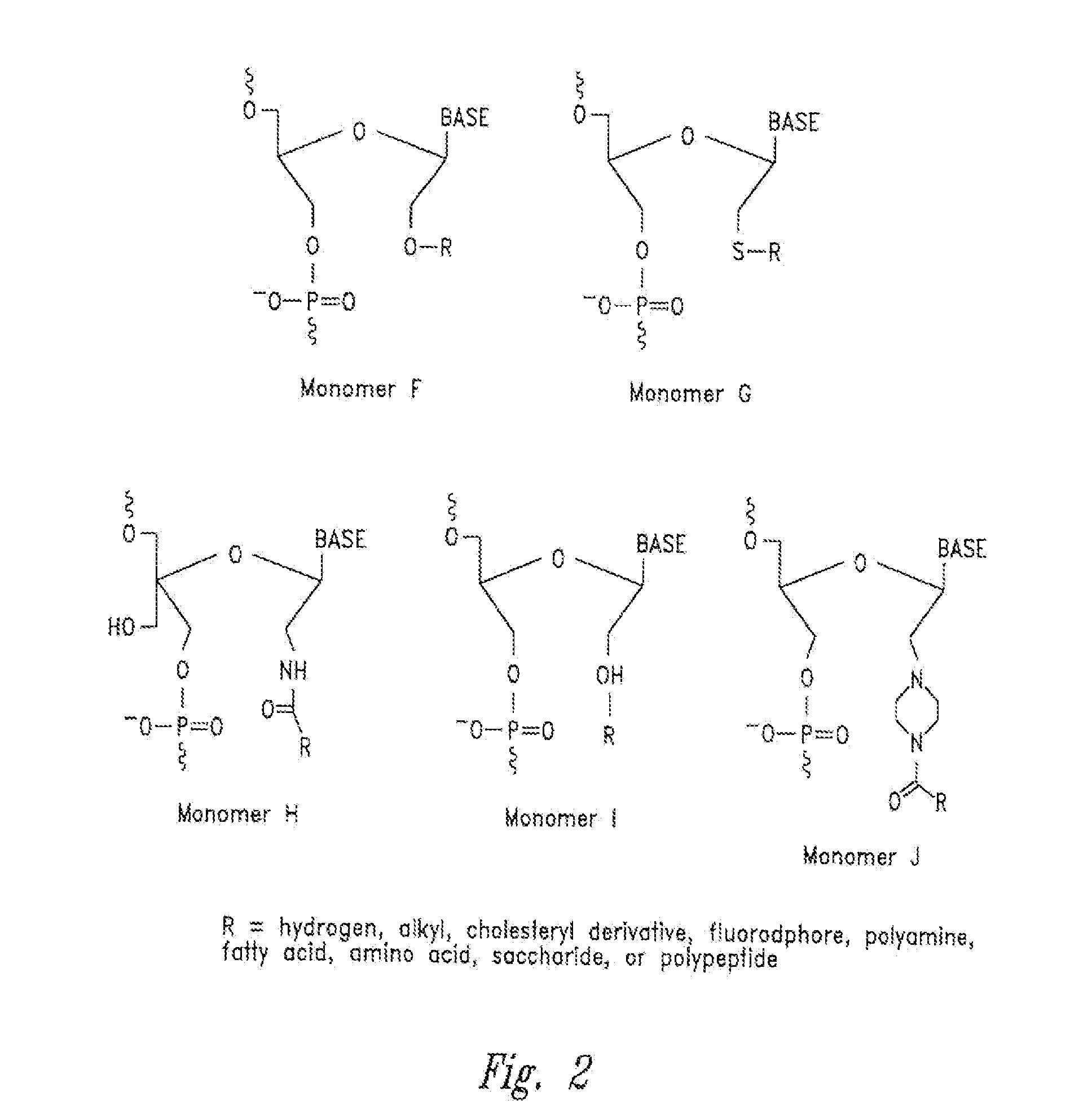
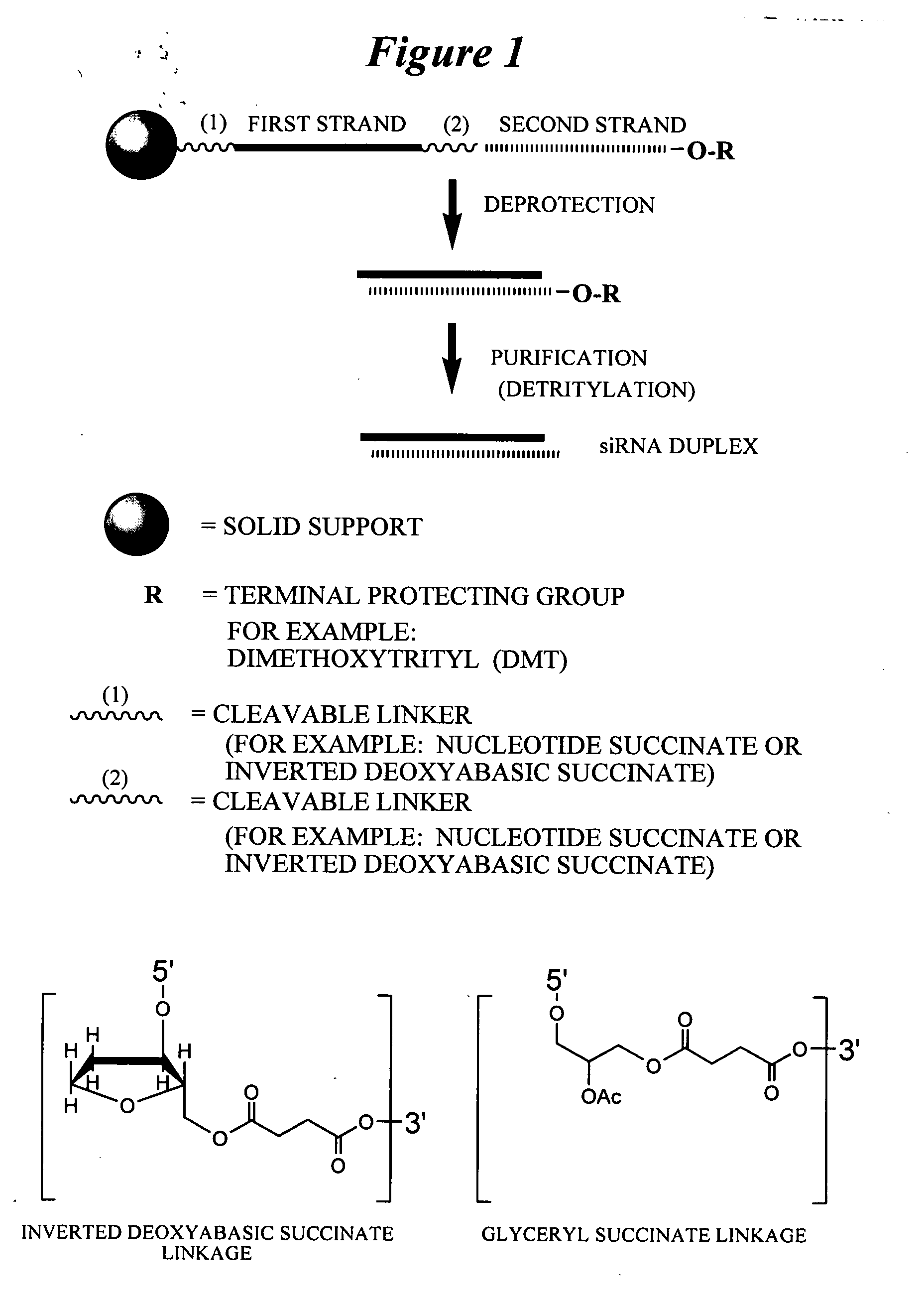
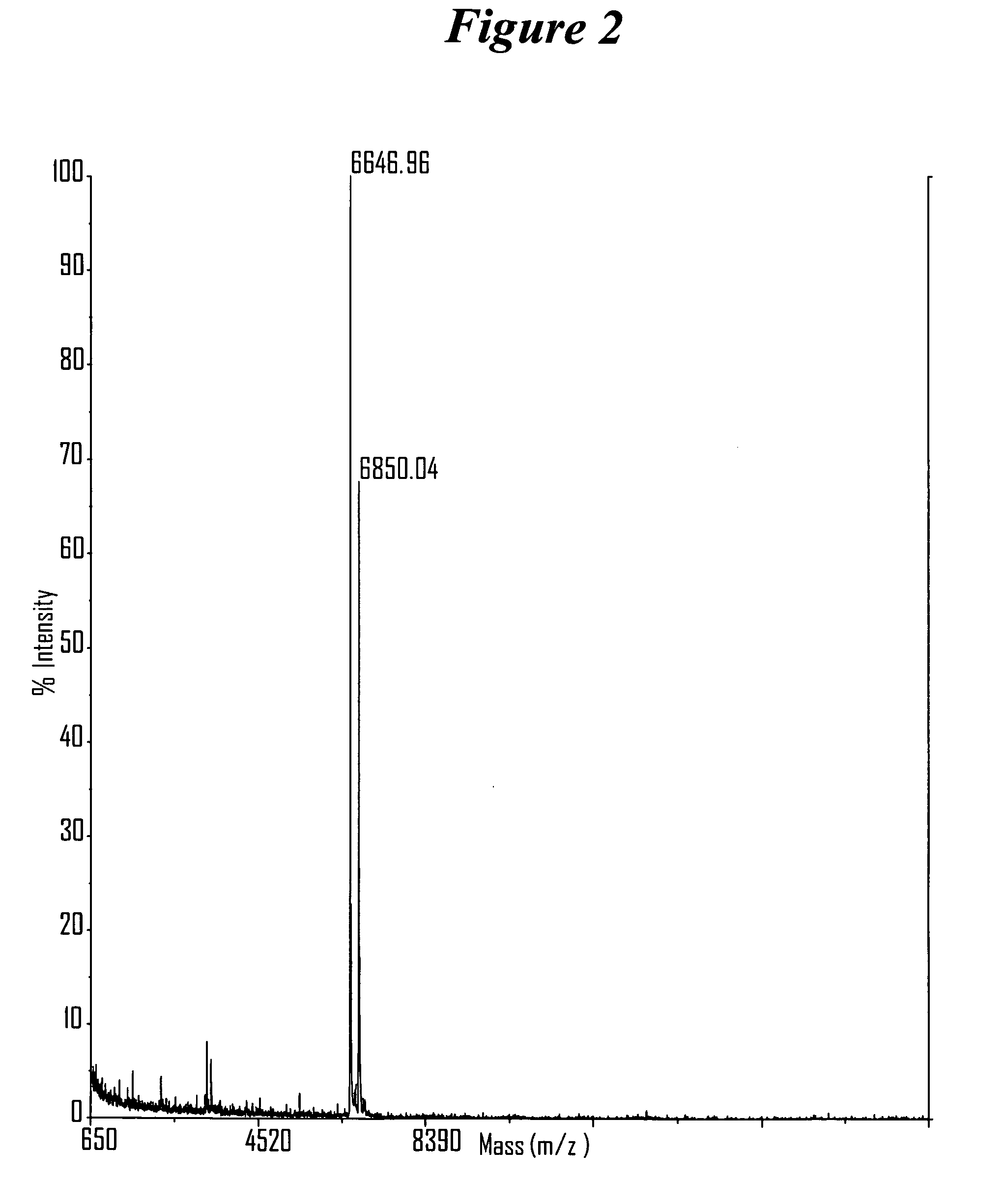
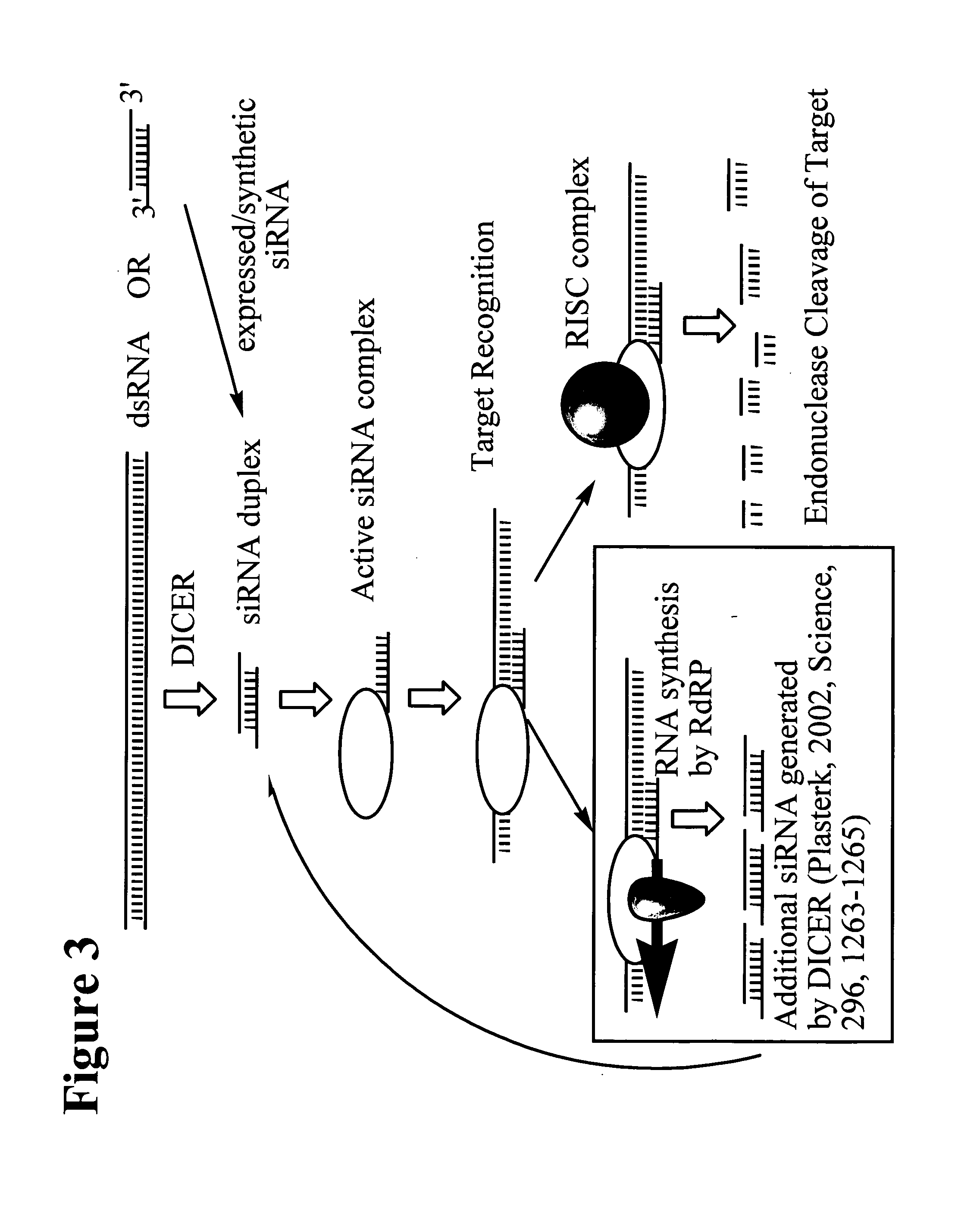
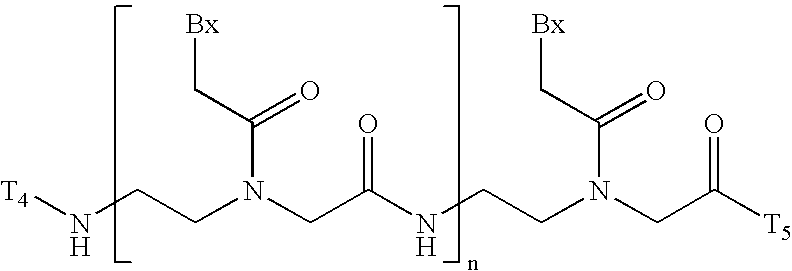
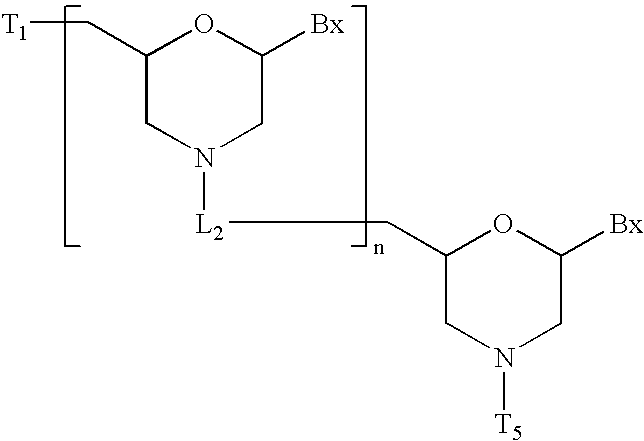
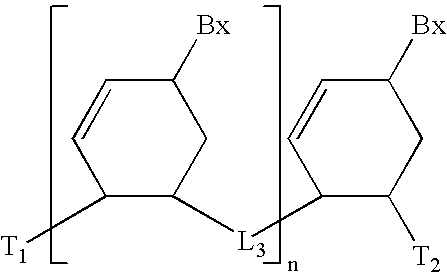
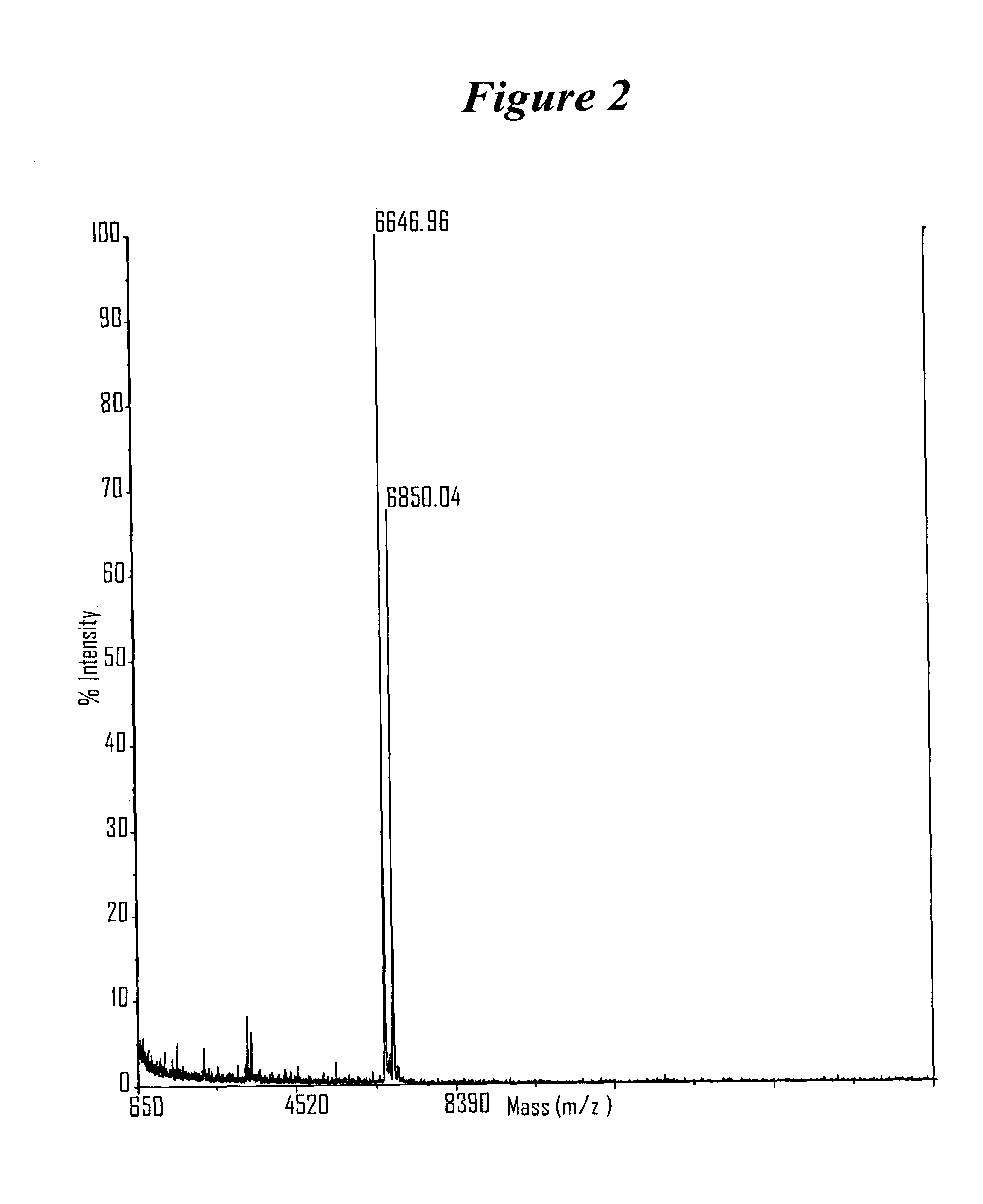
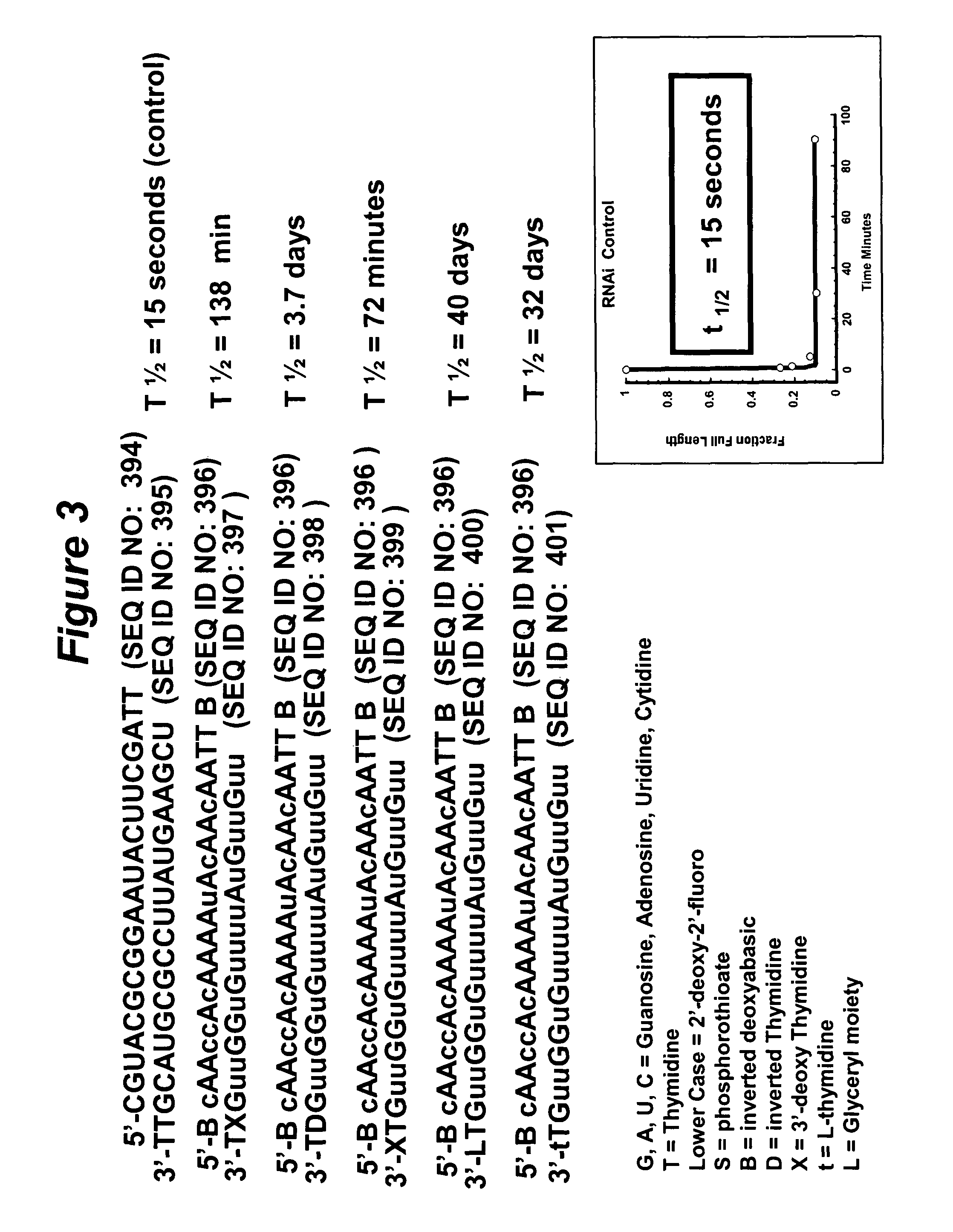
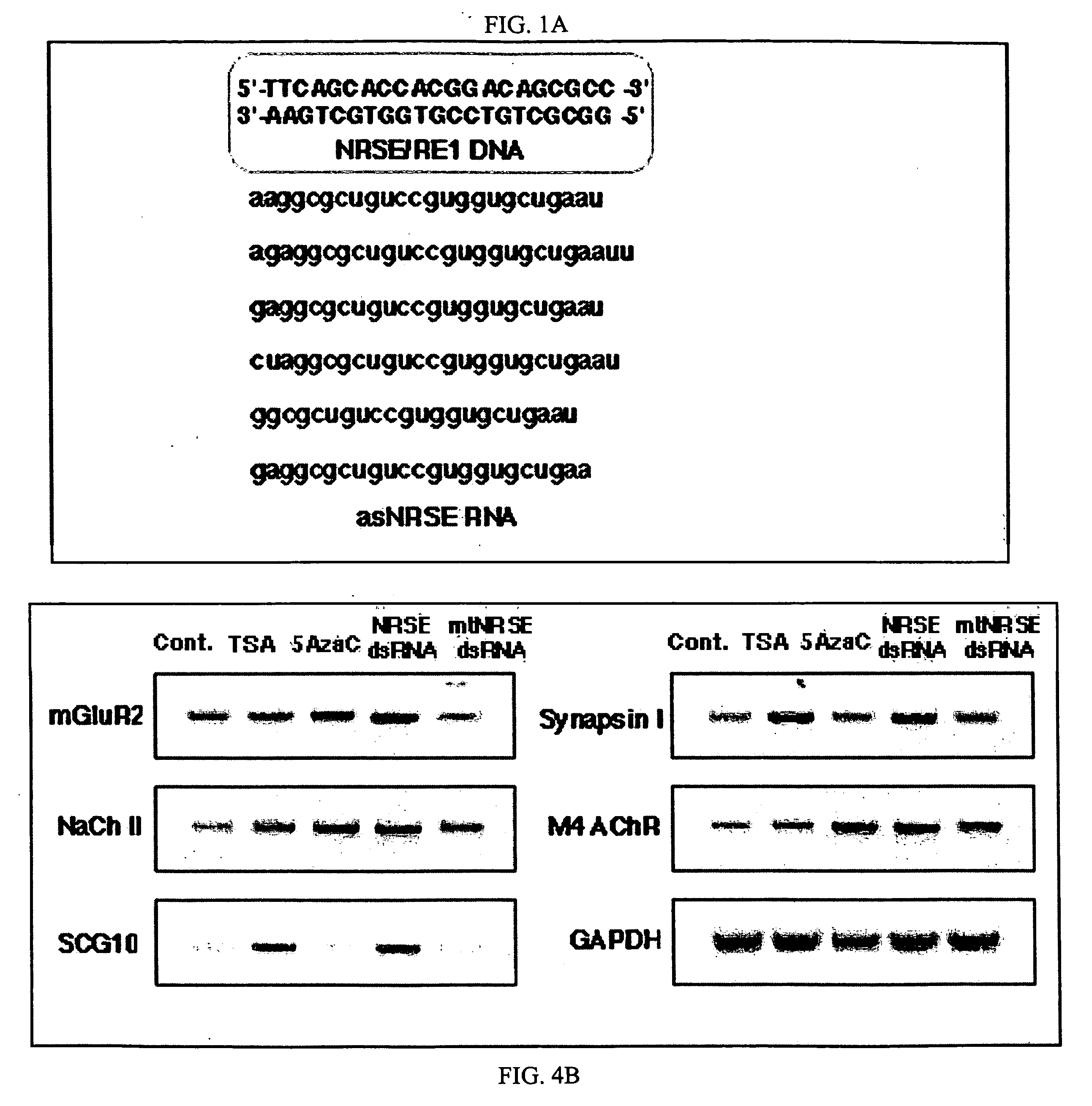
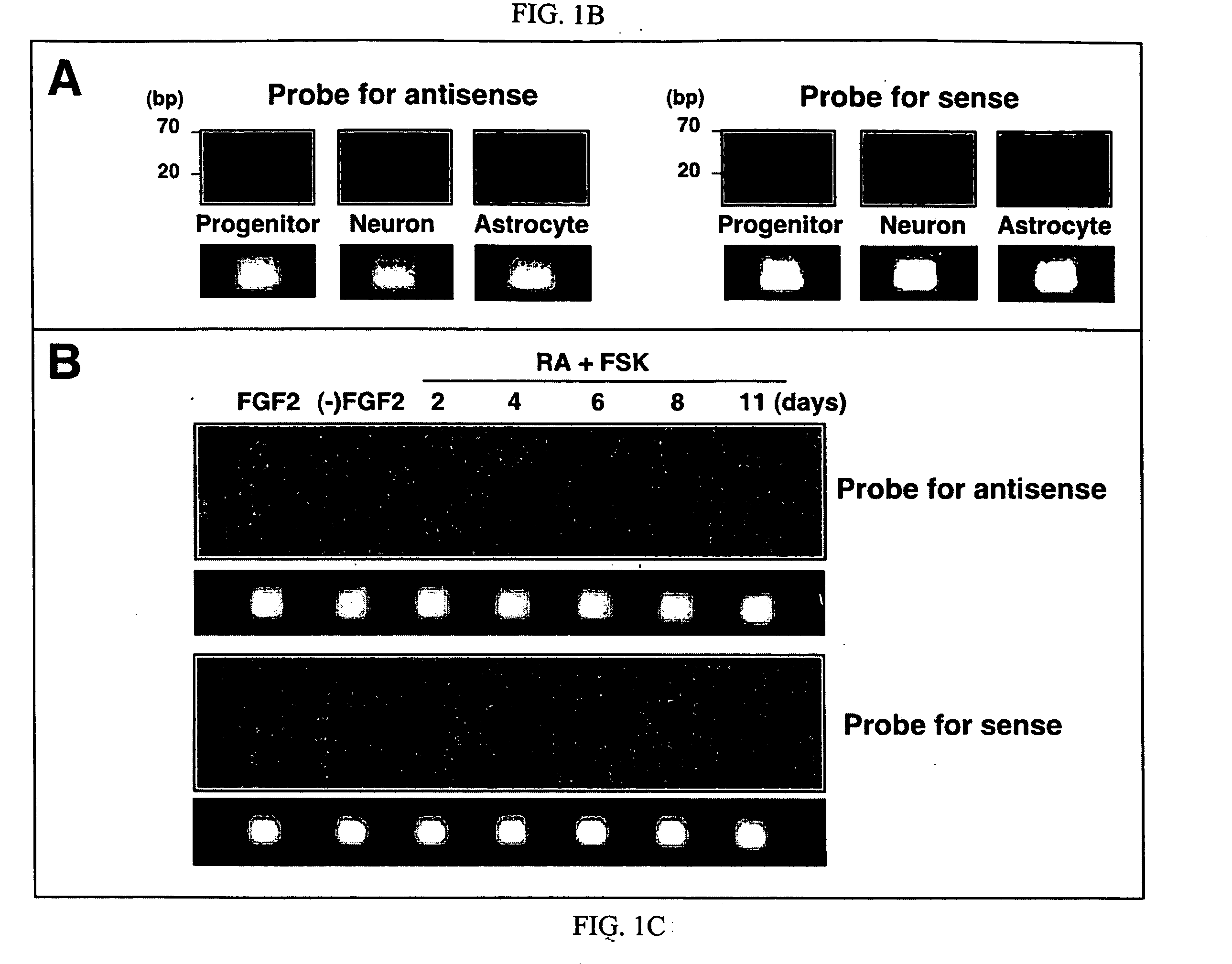
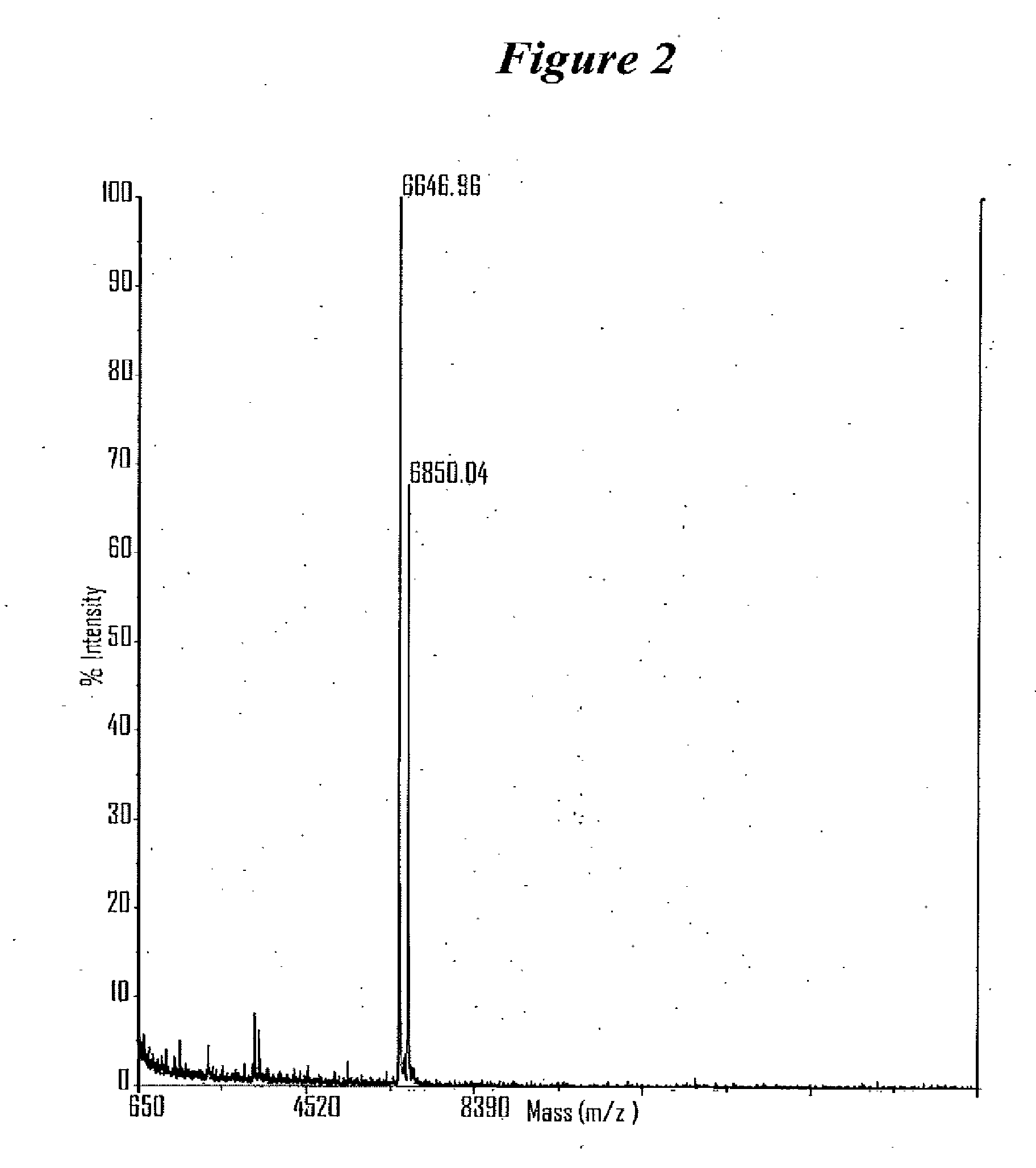
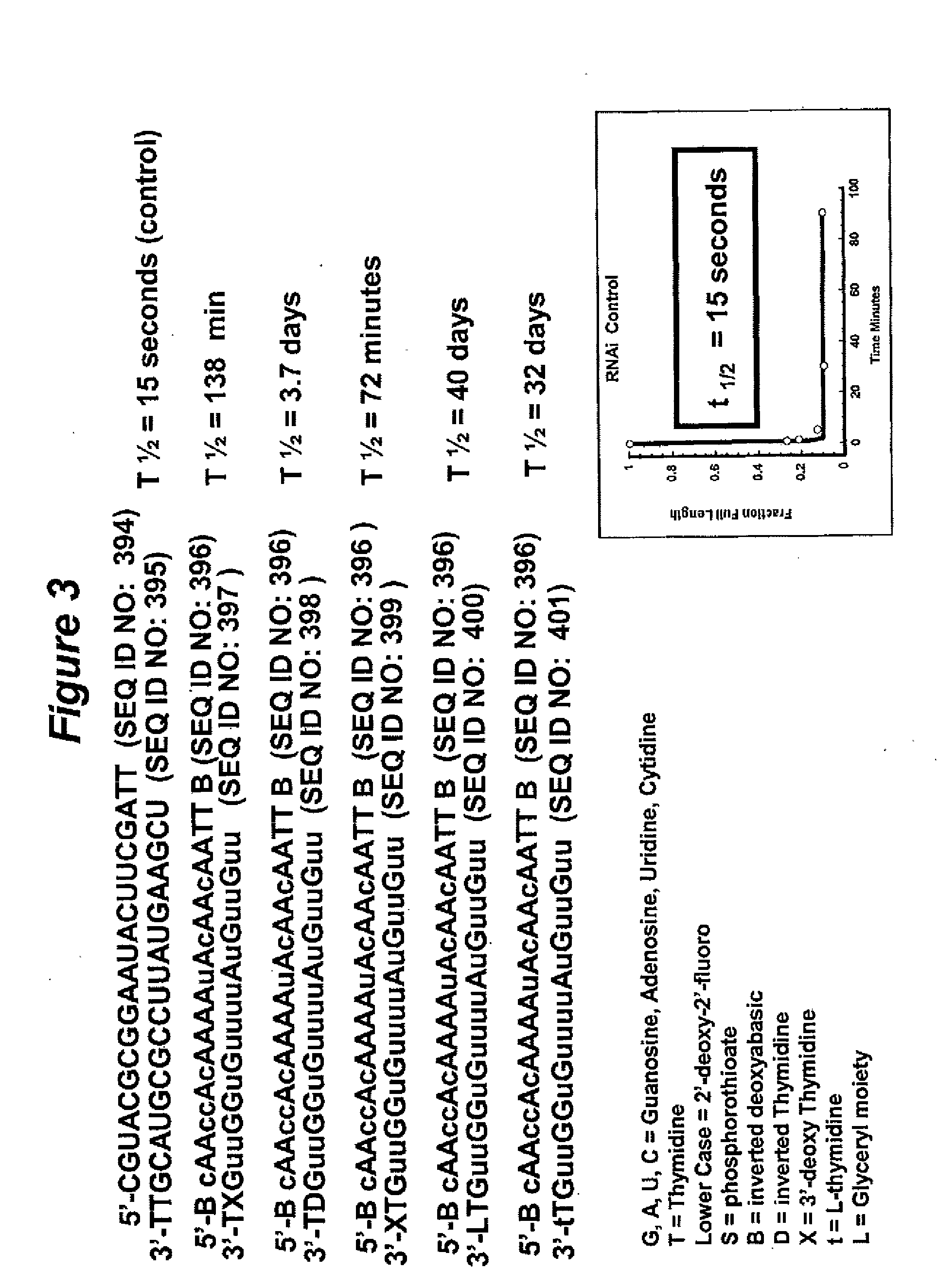
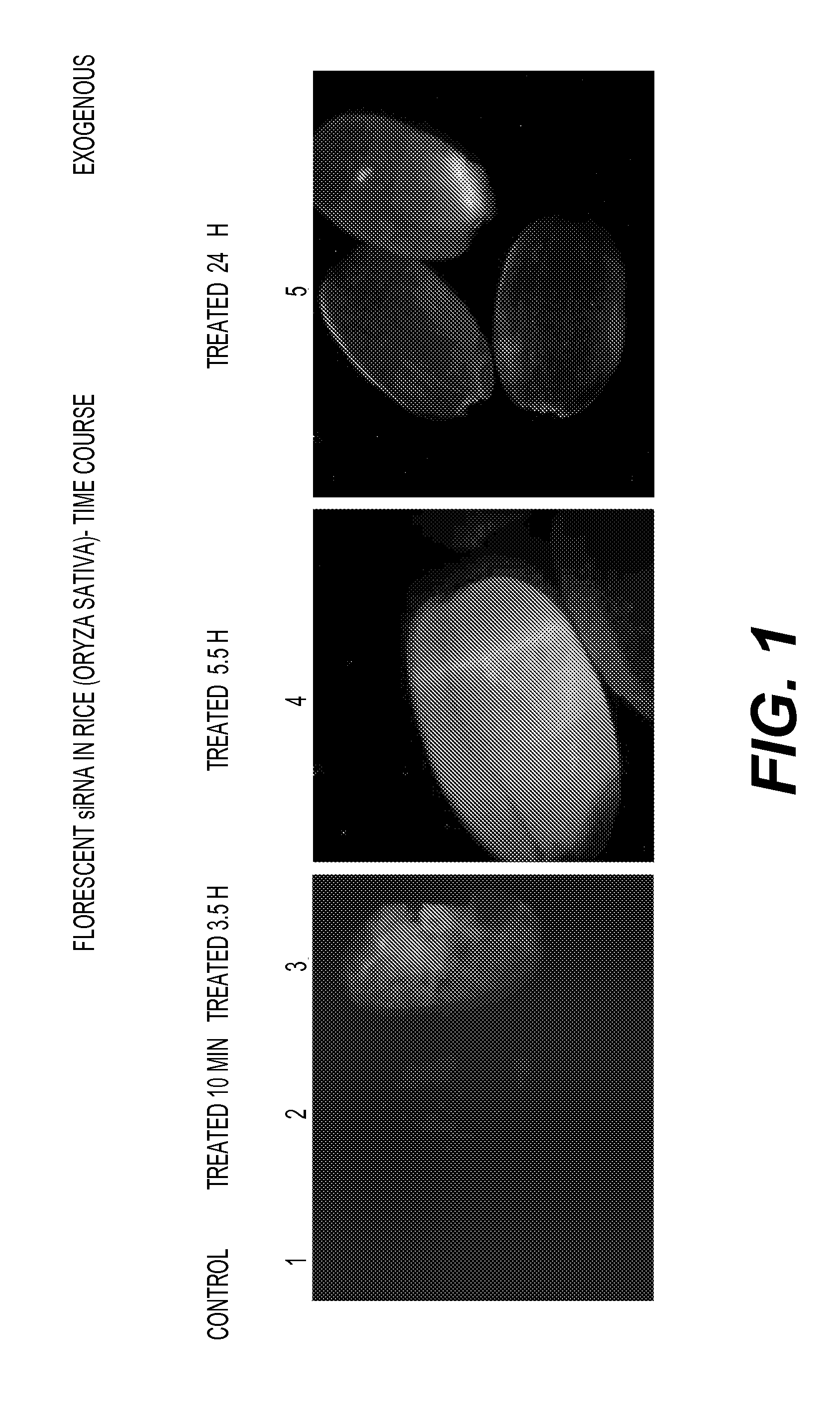
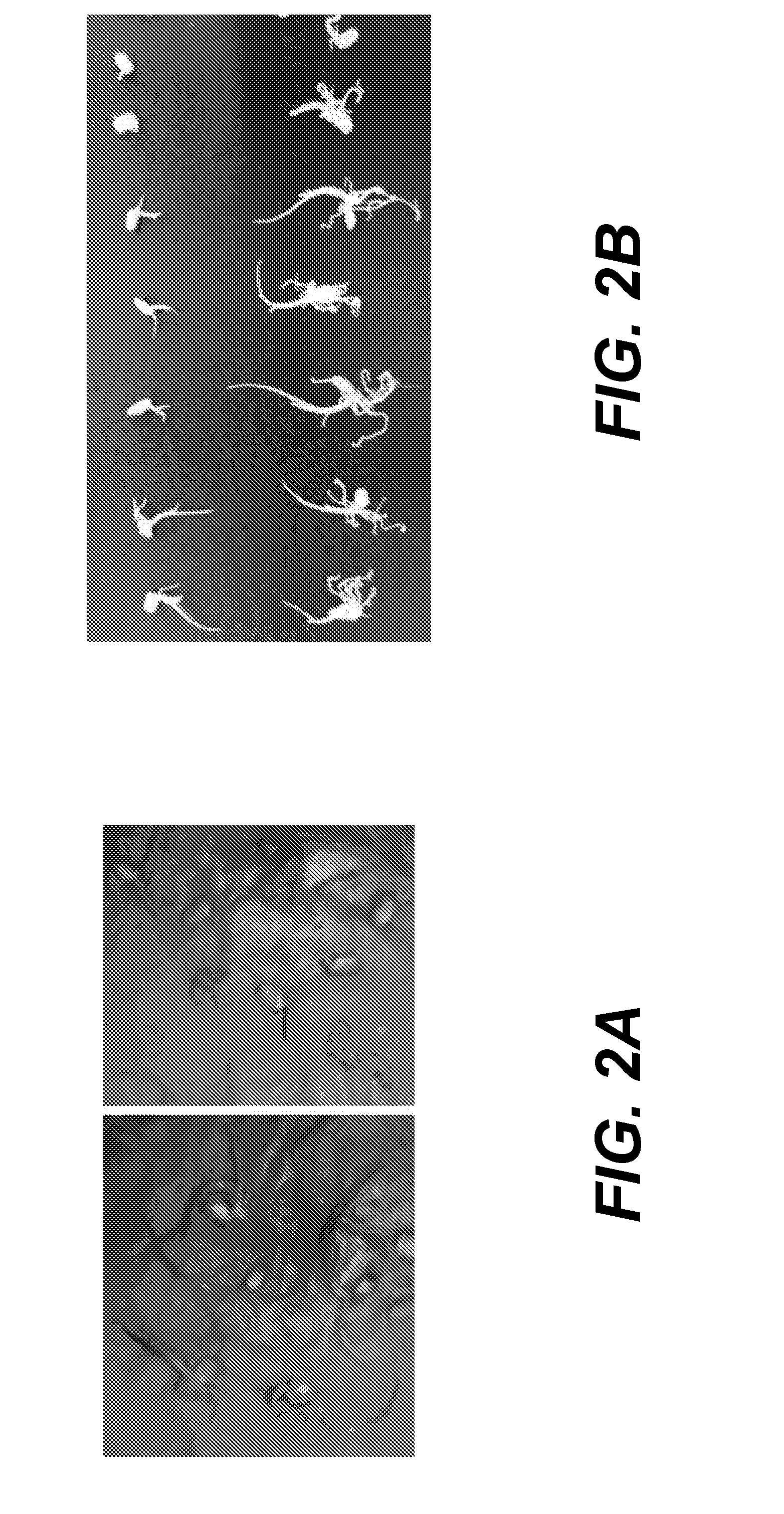
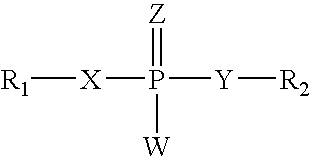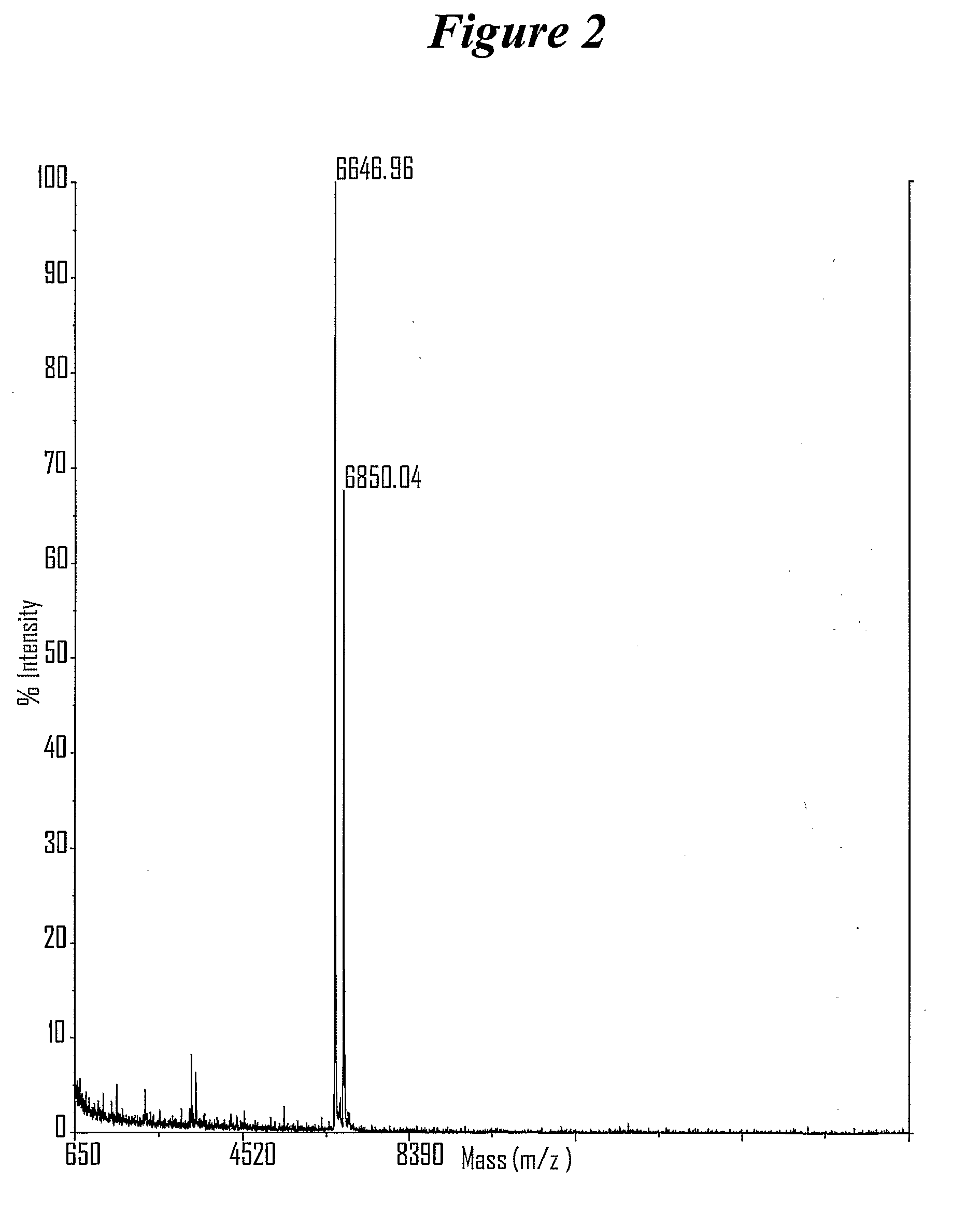Patents
Literature
643 results about "Regulator gene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A regulator gene, regulator, or regulatory gene is a gene involved in controlling the expression of one or more other genes. Regulatory sequences, which encode regulatory genes, are often at the five prime end (5') to the start site of transcription of the gene they regulate. In addition, these sequences can also be found at the three prime end (3') to the transcription start site. In both cases, whether the regulatory sequence occurs before (5') or after (3') the gene it regulates, the sequence is often many kilobases away from the transcription start site. A regulator gene may encode a protein, or it may work at the level of RNA, as in the case of genes encoding microRNAs. An example of a regulator gene is a gene that codes for a repressor protein that inhibits the activity of an operator (a gene which binds repressor proteins thus inhibiting the translation of RNA to protein via RNA polymerase).
Methods and agents for screening for compounds capable of modulating gene expression
InactiveUS20050048549A1Modulate expressionLibrary screeningTissue cultureRegulator geneProtein level
The invention relates to the fields of screening assays, compounds, and methods for altering gene expression and protein levels. In particular, the invention includes assays to screen for agents capable of modulating gene expression in a UTR-dependent manner and agents capable of modulating gene expression.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
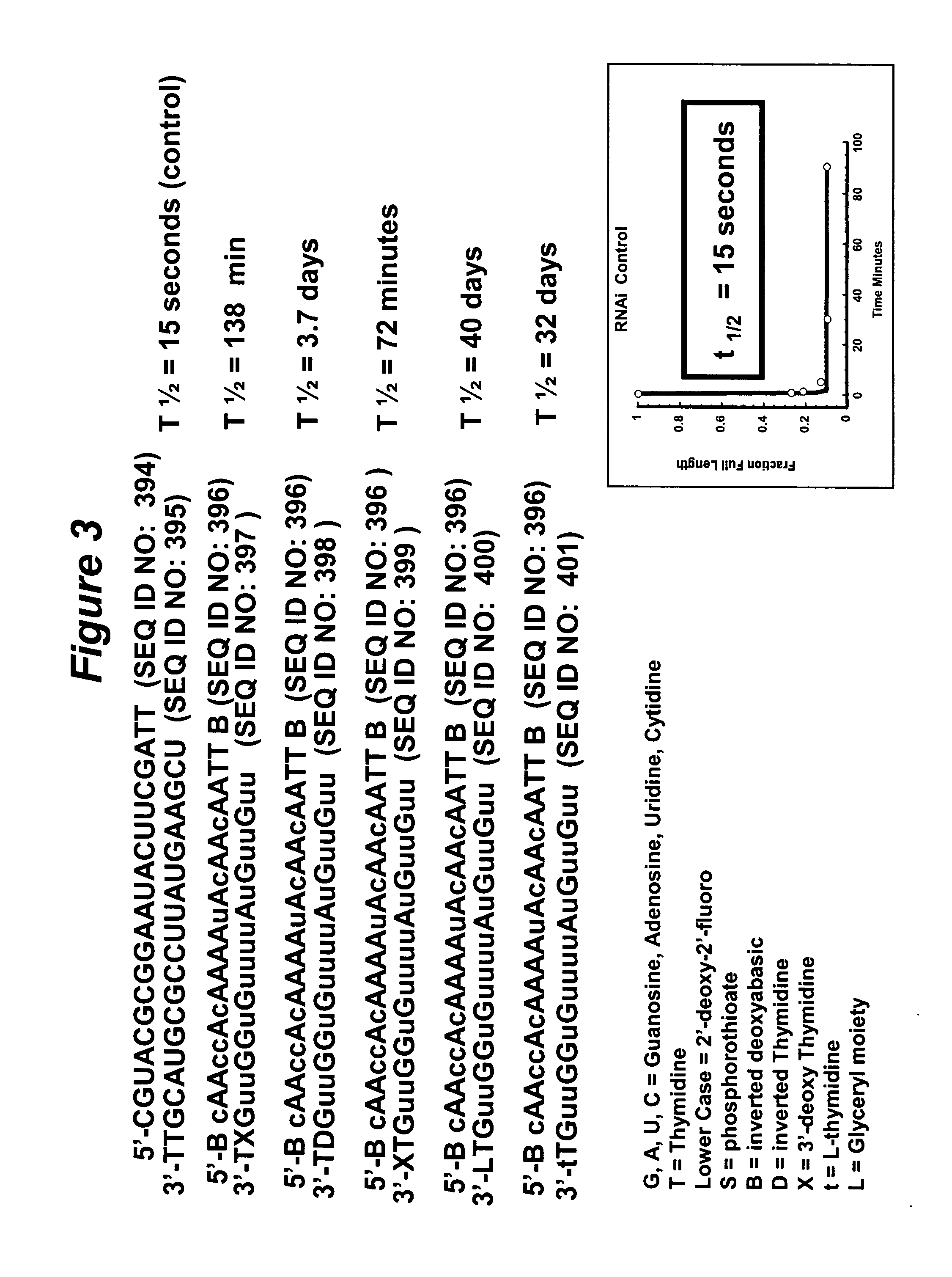
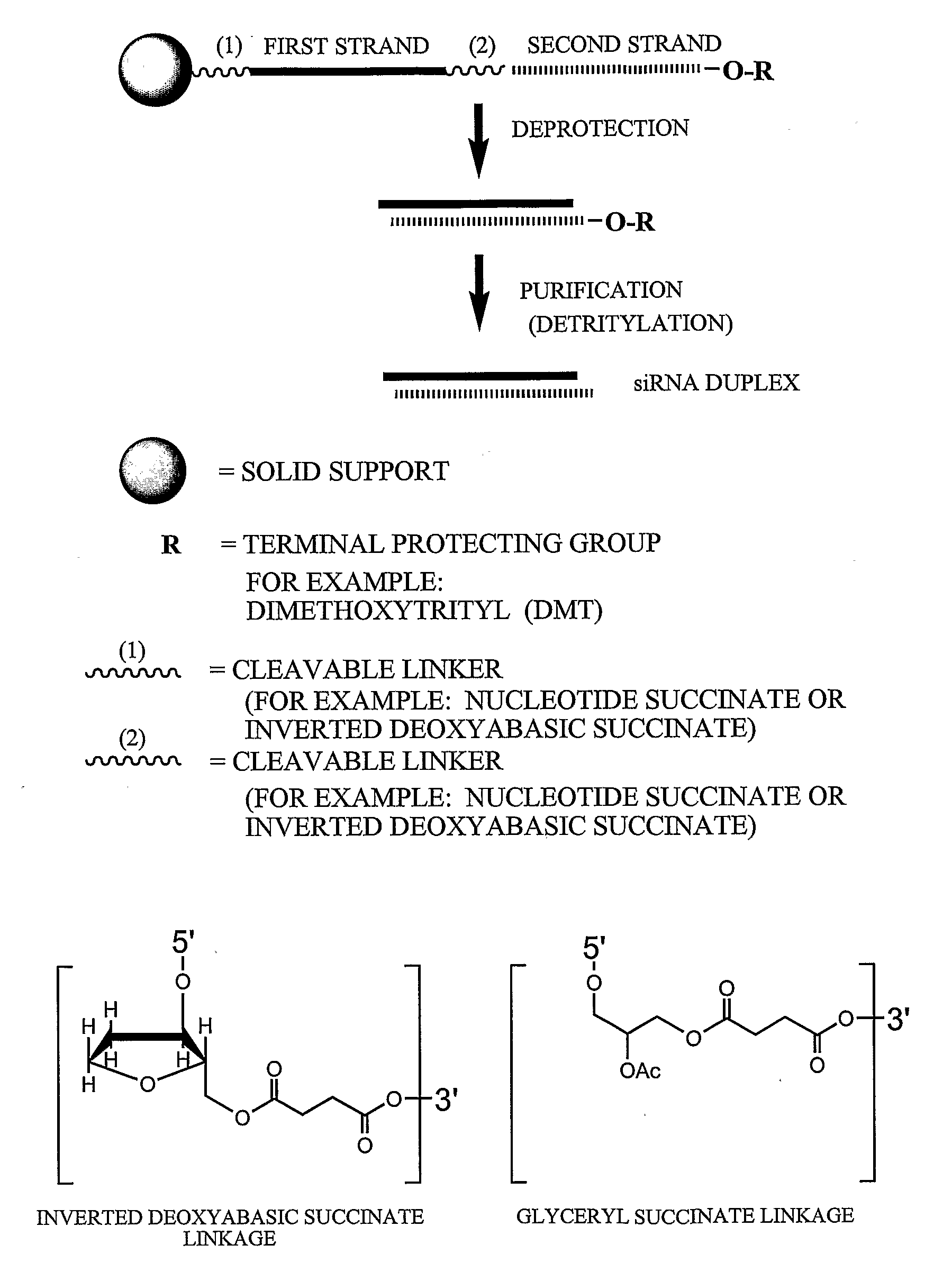
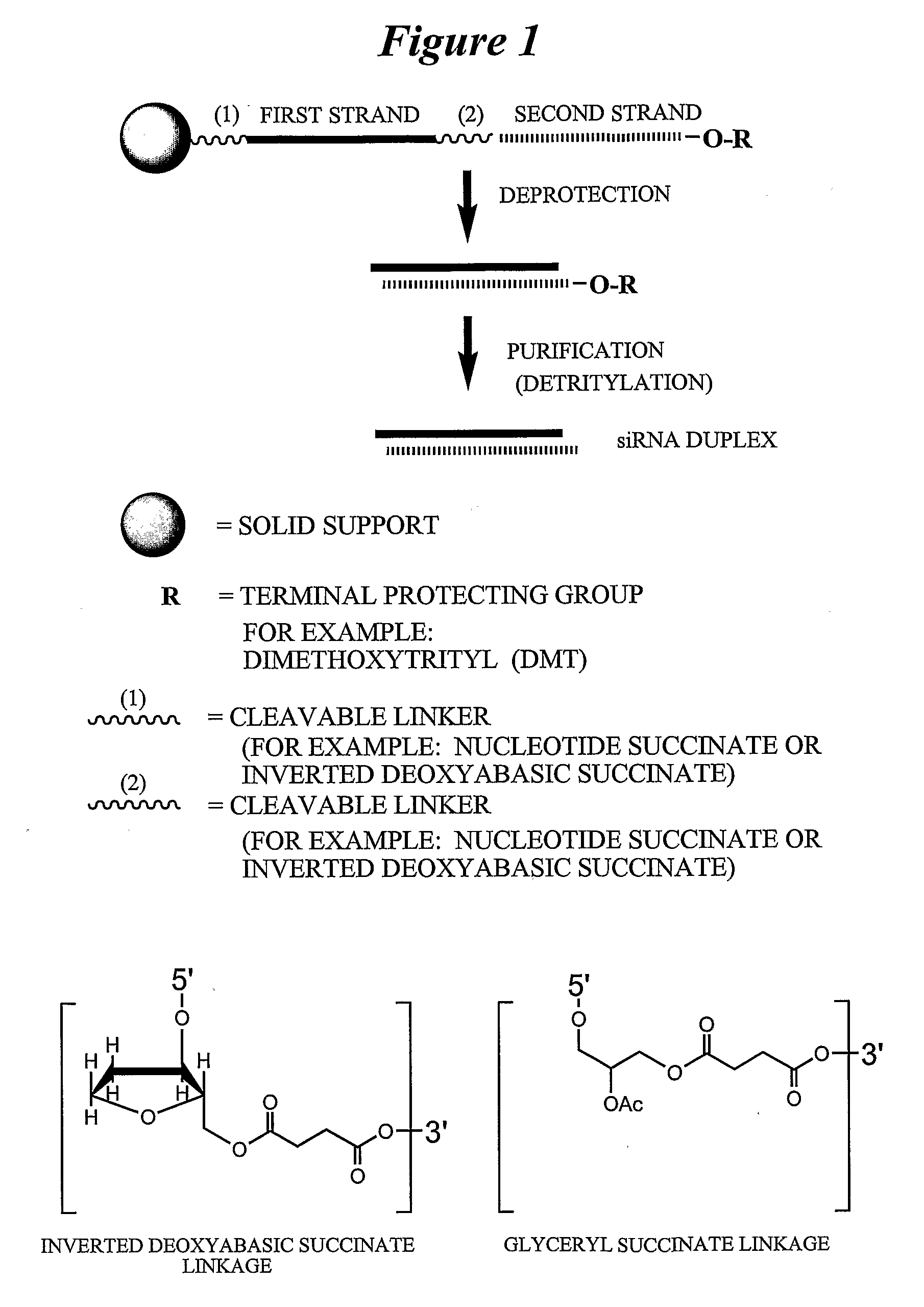
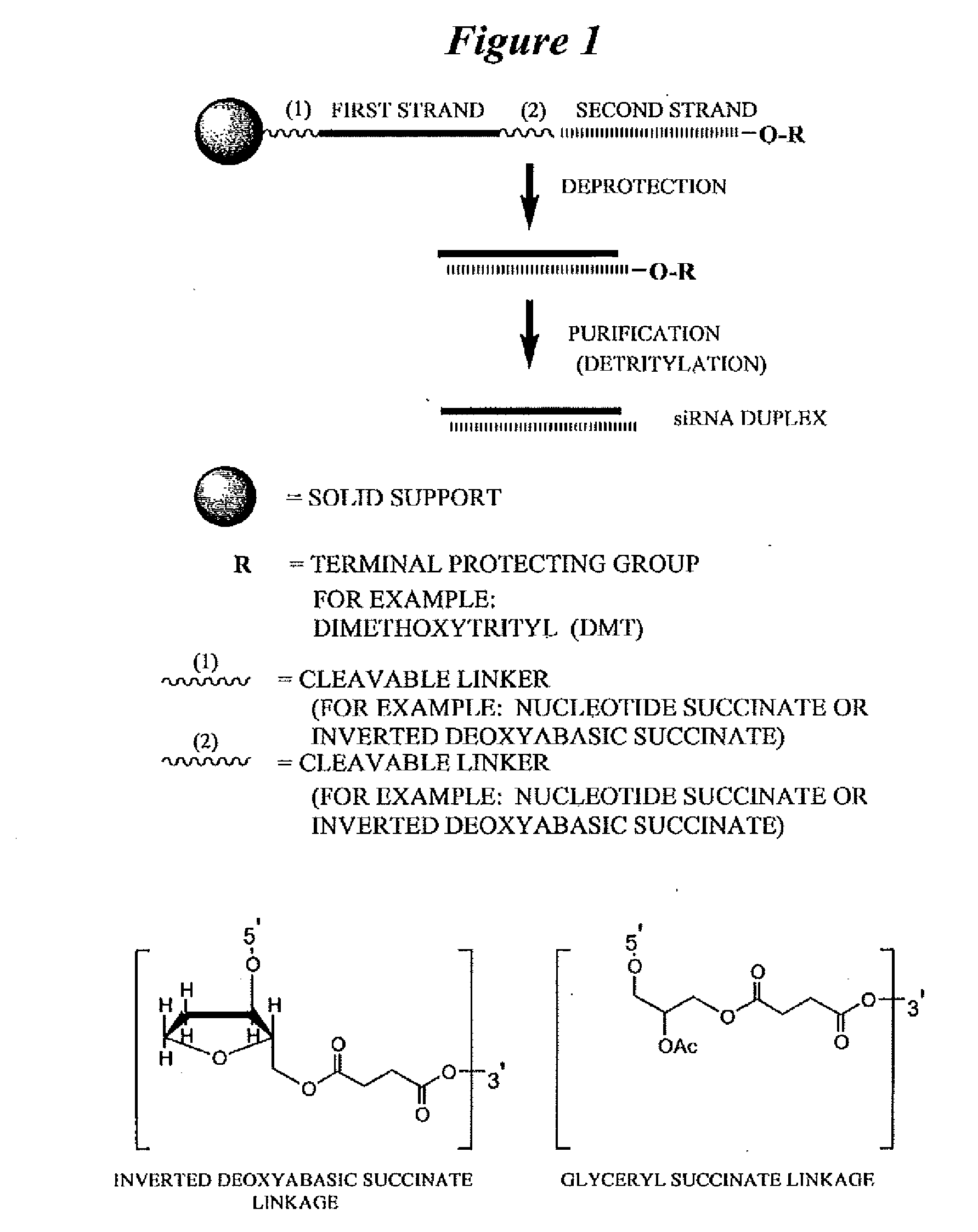
RNA interference mediated inhibition of gene expression using chemically modified short interfering nucleic acid (siNA)
InactiveUS20050020525A1Improve various propertyModulate its functionCompounds screening/testingSugar derivativesDouble strandOrganism
The present invention concerns methods and reagents useful in modulating gene expression in a variety of applications, including use in therapeutic, diagnostic, target validation, and genomic discovery applications. Specifically, the invention relates to synthetic chemically modified small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules capable of mediating RNA interference (RNAi) against target nucleic acid sequences. The small nucleic acid molecules are useful in the treatment of any disease or condition that responds to modulation of gene expression or activity in a cell, tissue, or organism.
Owner:SIMA THERAPEUTICS ICN
RNA interference mediated inhibition of gene expression using chemically modified short interfering nucleic acid (SiNA)
InactiveUS20050032733A1Improve various propertyModulate its functionCompounds screening/testingSpecial deliveryBiological bodyNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention concerns methods and reagents useful in modulating gene expression in a variety of applications, including use in therapeutic, diagnostic, target validation, and genomic discovery applications. Specifically, the invention relates to synthetic chemically modified small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules capable of mediating RNA interference (RNAi) against target nucleic acid sequences. The small nucleic acid molecules are useful in the treatment of any disease or condition that responds to modulation of gene expression or activity in a cell, tissue, or organism.
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
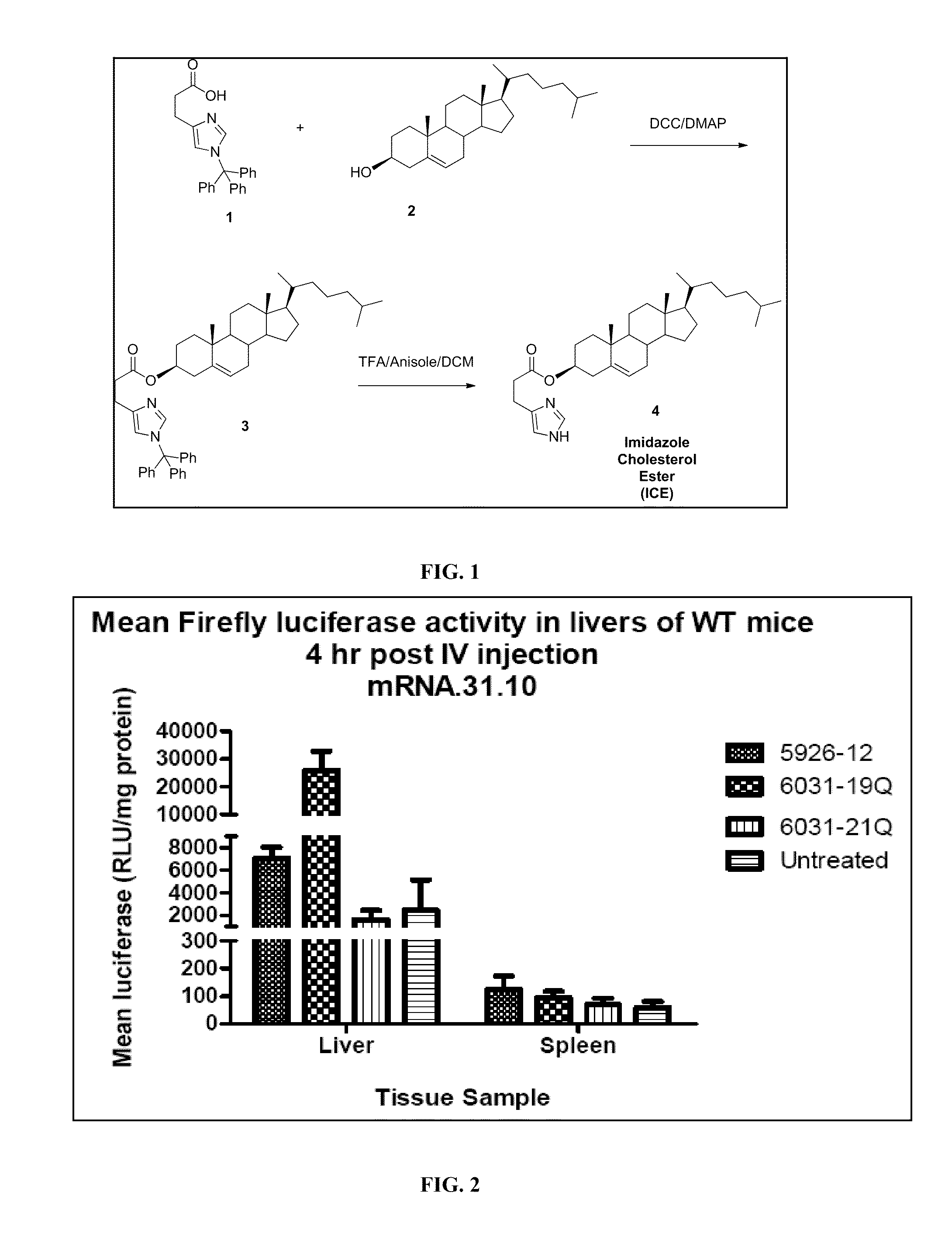
Delivery of mRNA for the augmentation of proteins and enzymes in human genetic diseases
InactiveUS20110244026A1Facilitating transfectionReduce deliveryOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemDiseaseADAMTS Proteins
Disclosed herein are compositions and methods of modulating the expression of gene or the production of a protein by transfecting target cells with nucleic acids. The compositions disclosed herein demonstrate a high transfection efficacy and are capable of ameliorating diseases associated with protein or enzyme deficiencies.
Owner:TRANSLATE BIO INC
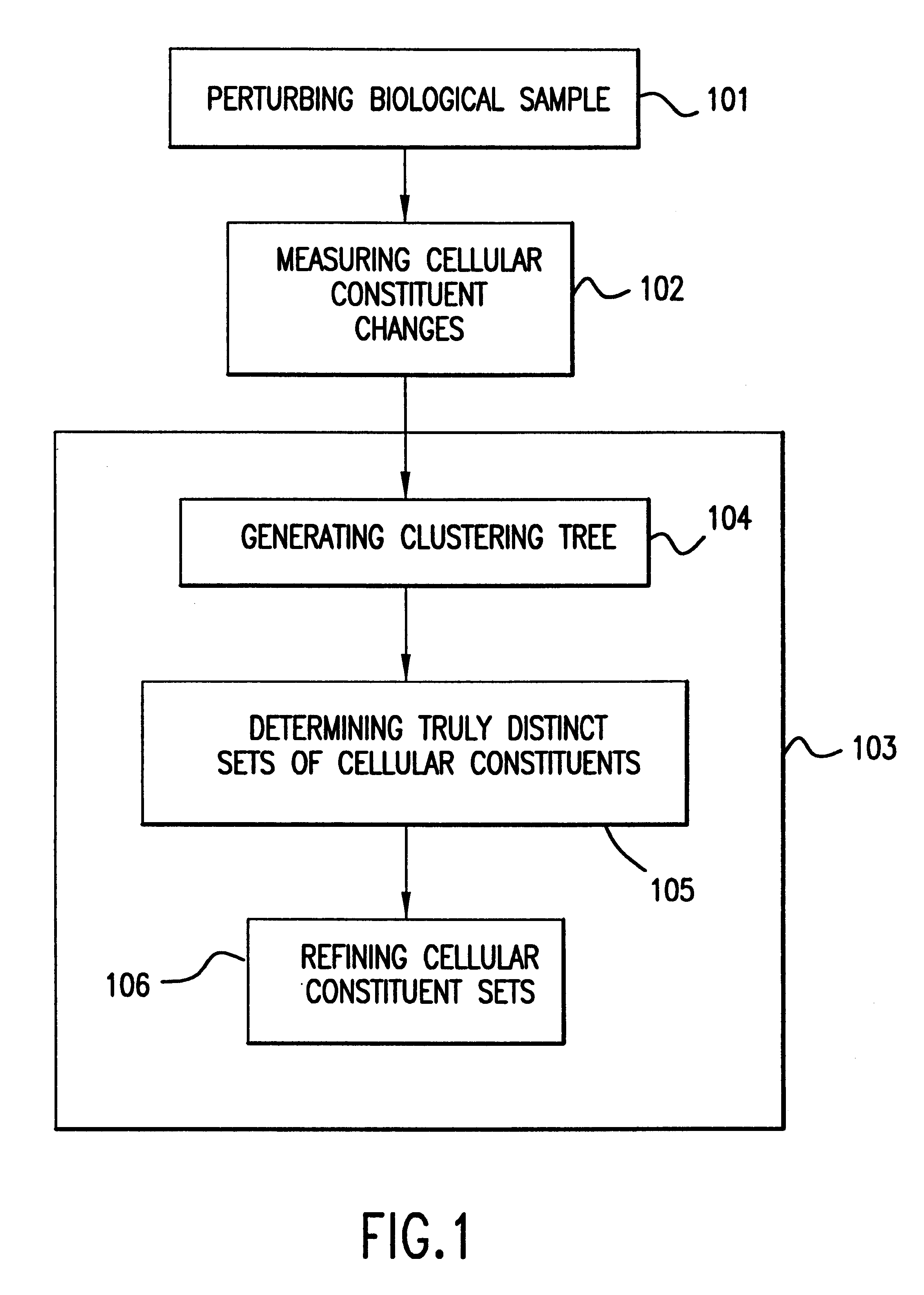
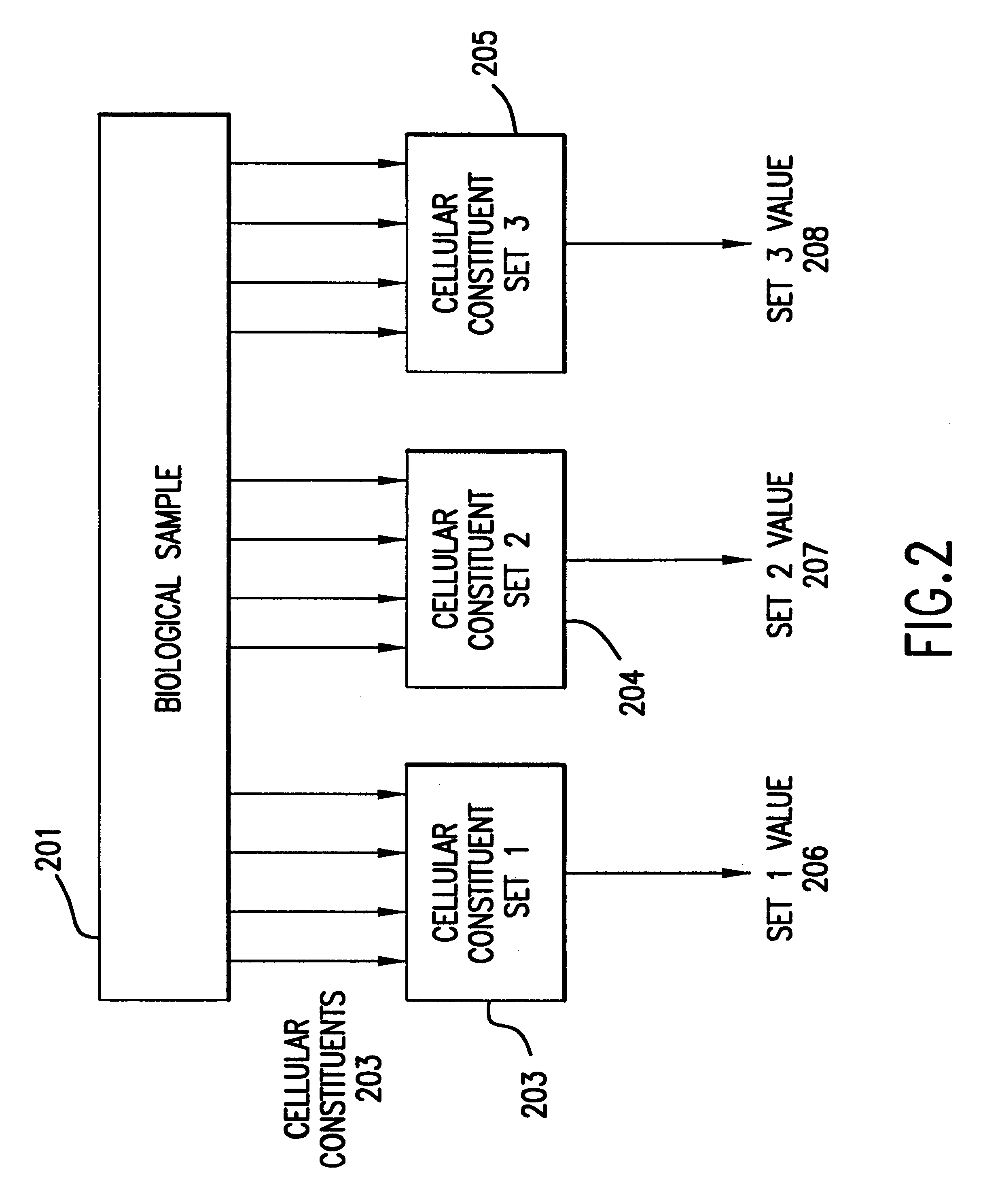
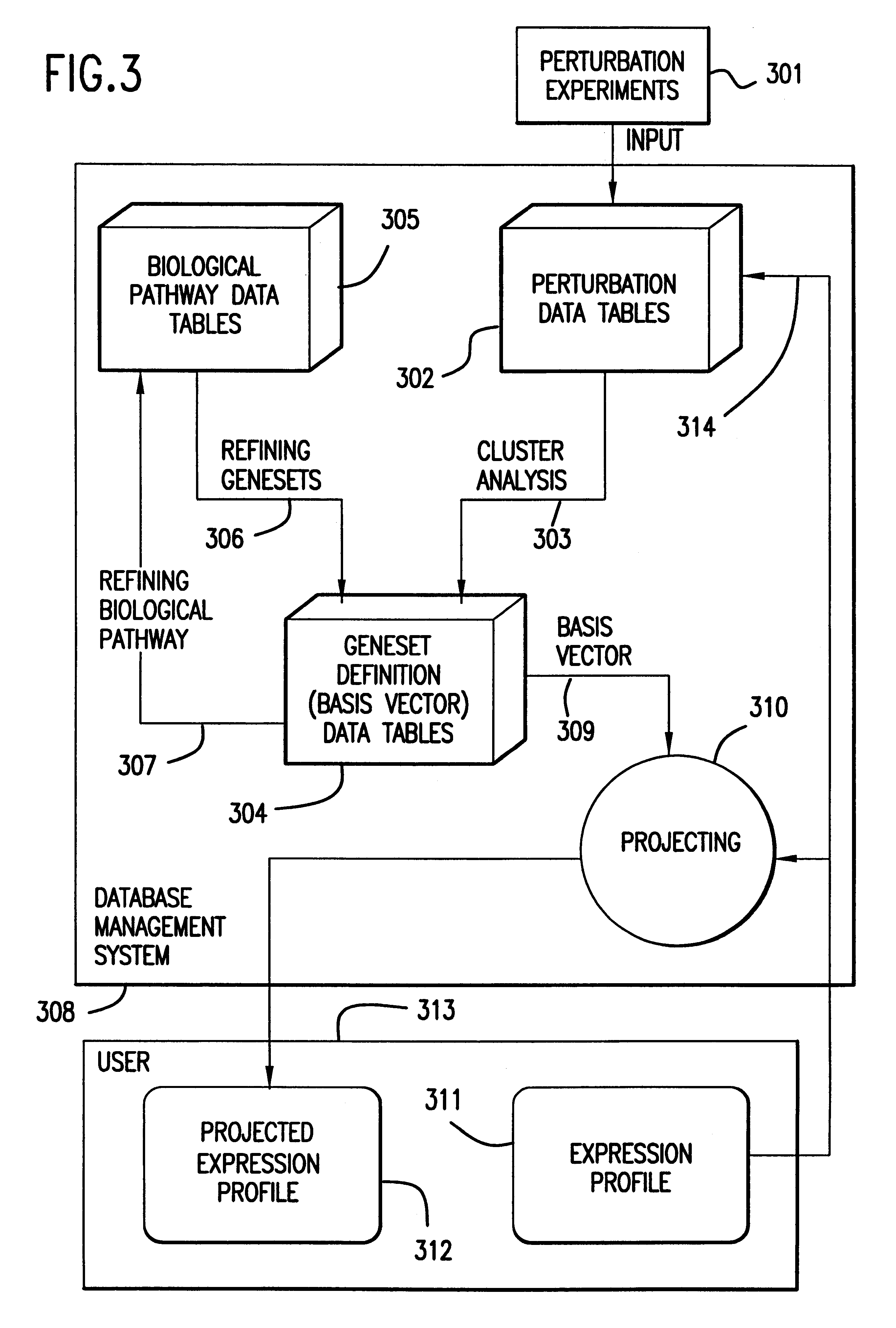
Methods for using co-regulated genesets to enhance detection and classification of gene expression patterns
InactiveUS6203987B1Peptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementCo-regulationIndividual gene
The present invention provides methods for enhanced detection of biological response patterns. In one embodiment of the invention, genes are grouped into basis genesets according to the co-regulation of their expression. Expression of individual genes within a geneset is indicated with a single gene expression value for the geneset by a projection process. The expression values of genesets, rather than the expression of individual genes are then used as the basis for comparison and detection of biological responses with greatly enhanced sensitivity.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Liver specific delivery of messenger RNA
Disclosed herein are compositions and methods of modulating the expression of gene or the production of a protein by transfecting target cells with nucleic acids. The compositions disclosed herein demonstrate a high transfection efficacy and are capable of ameliorating diseases associated with protein or enzyme deficiencies.
Owner:TRANSLATE BIO INC
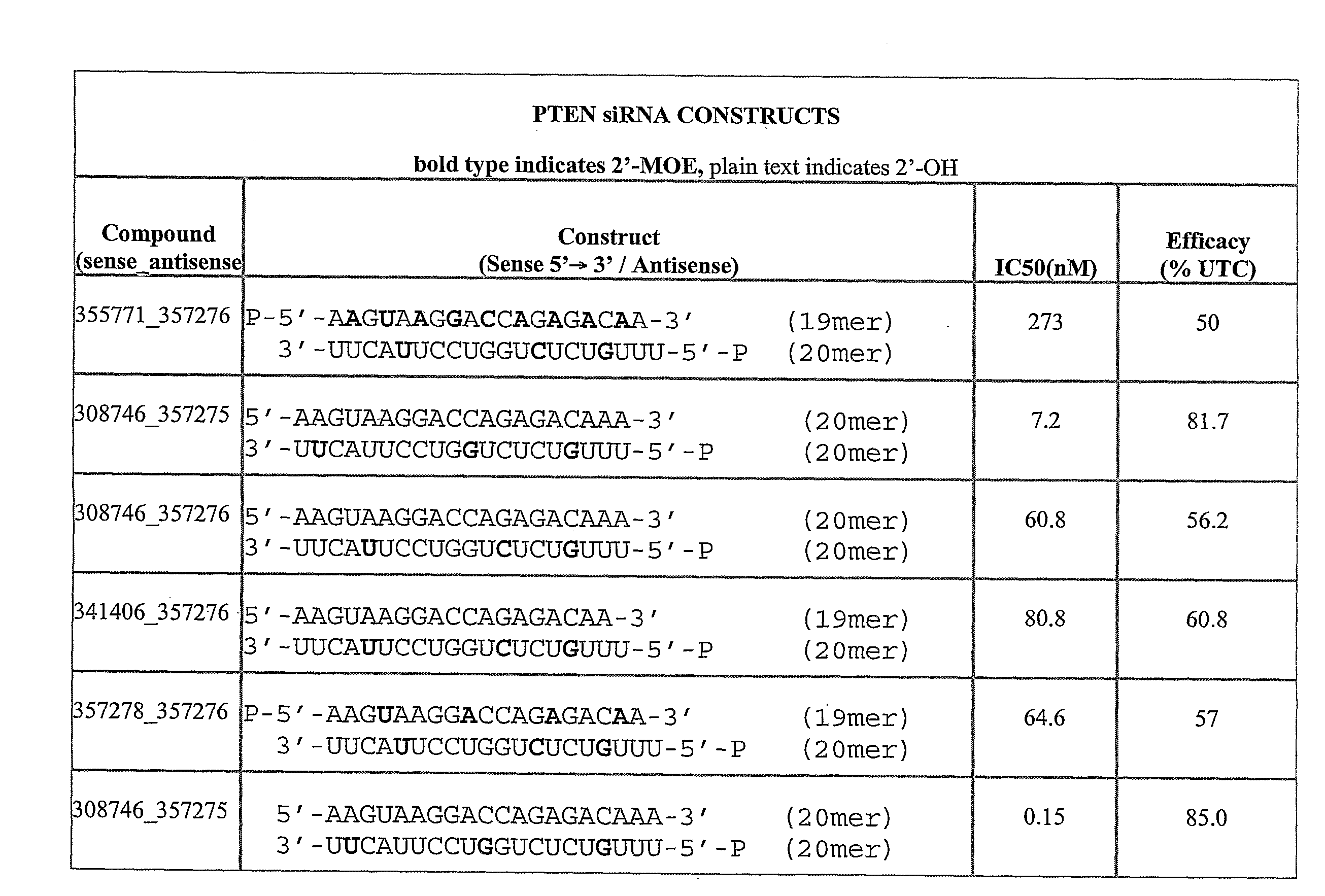
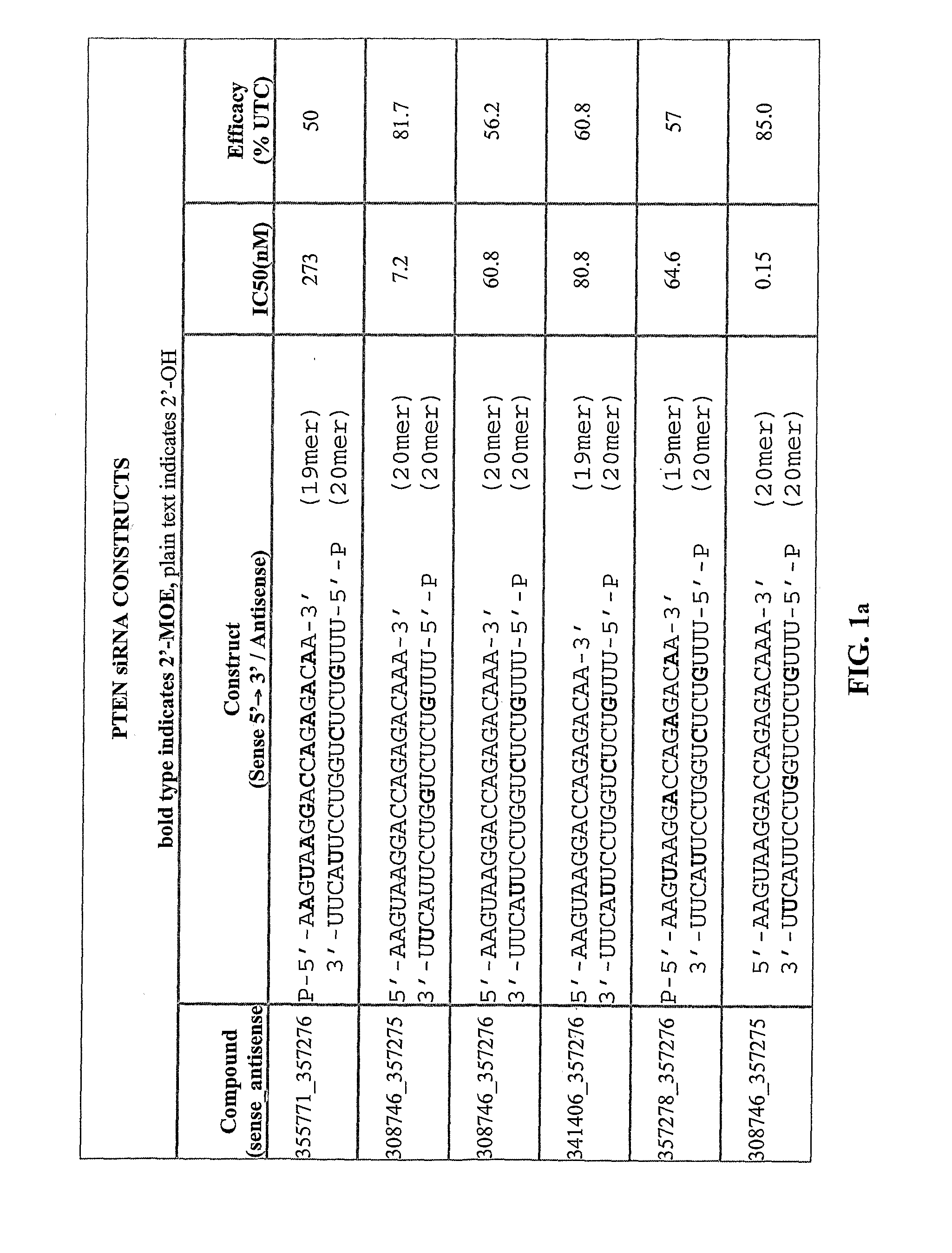
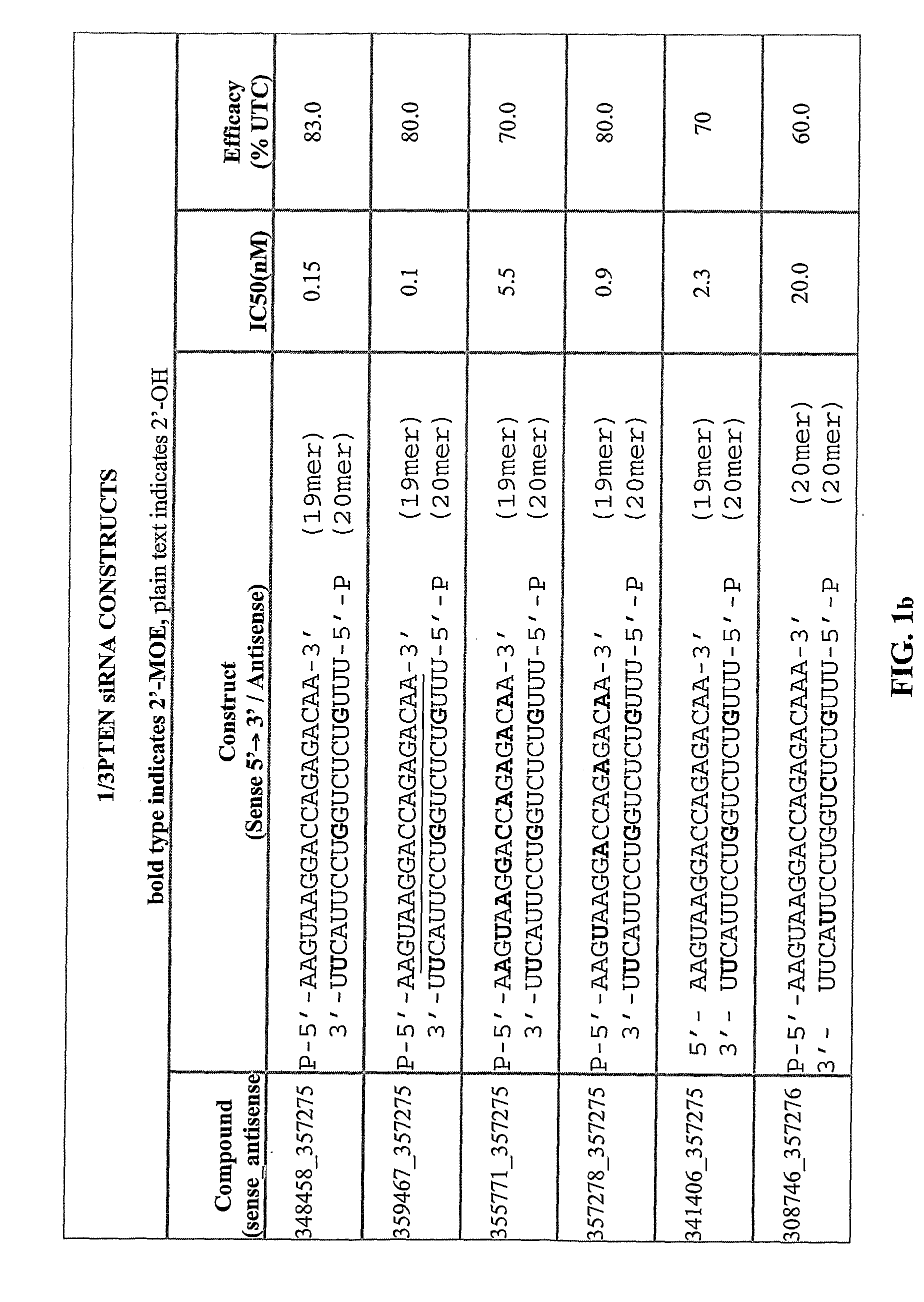
Positionally Modified Sirna Constructs
The present invention provides oligomeric compounds having sufficient complementarity to hybridize to a nucleic acid target and methods for their use in modulating gene expression. In one embodiment the oligomeric compounds comprise double stranded constructs wherein one of the strands capable of hybridizing to a nucleic acid target, and has a plurality of modified ribofuranosyl nucleosides at defined locations. The presence of modifications at such defined positions greatly enhances the properties of the corresponding compositions.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
RNA interference mediated inhibition of gene expression using short interfering nucleic acid (siNA)
InactiveUS20050282188A1Improve bioavailabilityMinimize the possibilitySugar derivativesActivity regulationPseudogeneRegulator gene
This invention relates to compounds, compositions, and methods useful for modulating gene expression using short interfering nucleic acid (siNA) molecules. In particular, the instant invention features small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules and methods used to modulate the expression of genes, such as expressed pseudogenes associated with the maintenance or development of diseases, disorders, traits, and conditions in a subject or organism. The invention also provides small nucleic acid molecules with reduced or attenuated immunostimulatory properties and methods for designing and synthesizing such small nucleic acid molecules having improved toxicologic properties while retaining RNAi activity.
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
UsiRNA Complexes
ActiveUS20110313020A1Reduce off-target effectsImprove propertiesOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderNucleotideSense strand
This disclosure provides double-stranded RNA complexes having one or more hydroxymethyl substituted nucleomonomer(s) in the passenger strand (or sense strand) of an RNA complex. RNA complexes of the disclosure may be useful for therapeutic applications, diagnostic applications or research applications. RNA complexes include short interfering RNA complexes (siRNA) capable of modulating gene expression comprising an antisense strand and a continuous or a discontinuous passenger strand (“sense strand”). Further, one or more hydroxymethyl substituted nucleomonomer(s) of this disclosure may be positioned at the 3′-end, at the 5′-end, at both the 3′-end and 5′end.
Owner:ARCTURUS THERAPEUTICS
RNA interference mediated inhibition of gene expression using chemically modified short interfering nucleic acid (siNA)
InactiveUS20070004664A1Improve various propertyModulating gene expressionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsBiological bodyNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention concerns methods and reagents useful in modulating gene expression in a variety of applications, including use in therapeutic, diagnostic, target validation, and genomic discovery applications. Specifically, the invention relates to synthetic chemically modified small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules capable of mediating RNA interference (RNAi) against target nucleic acid sequences. The small nucleic acid molecules are useful in the treatment of any disease or condition that responds to modulation of gene expression or activity in a cell, tissue, or organism.
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
Modulation of gene expression by oligomers targeted to chromosomal DNA
Synthesis of a target transcript of a gene is selectively increased in a mammalian cell by contacting the cell with a polynucleotide oligomer of 12-28 bases complementary to a region within a target promoter of the gene under conditions whereby the oligomer selectively increases synthesis of the target transcript.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
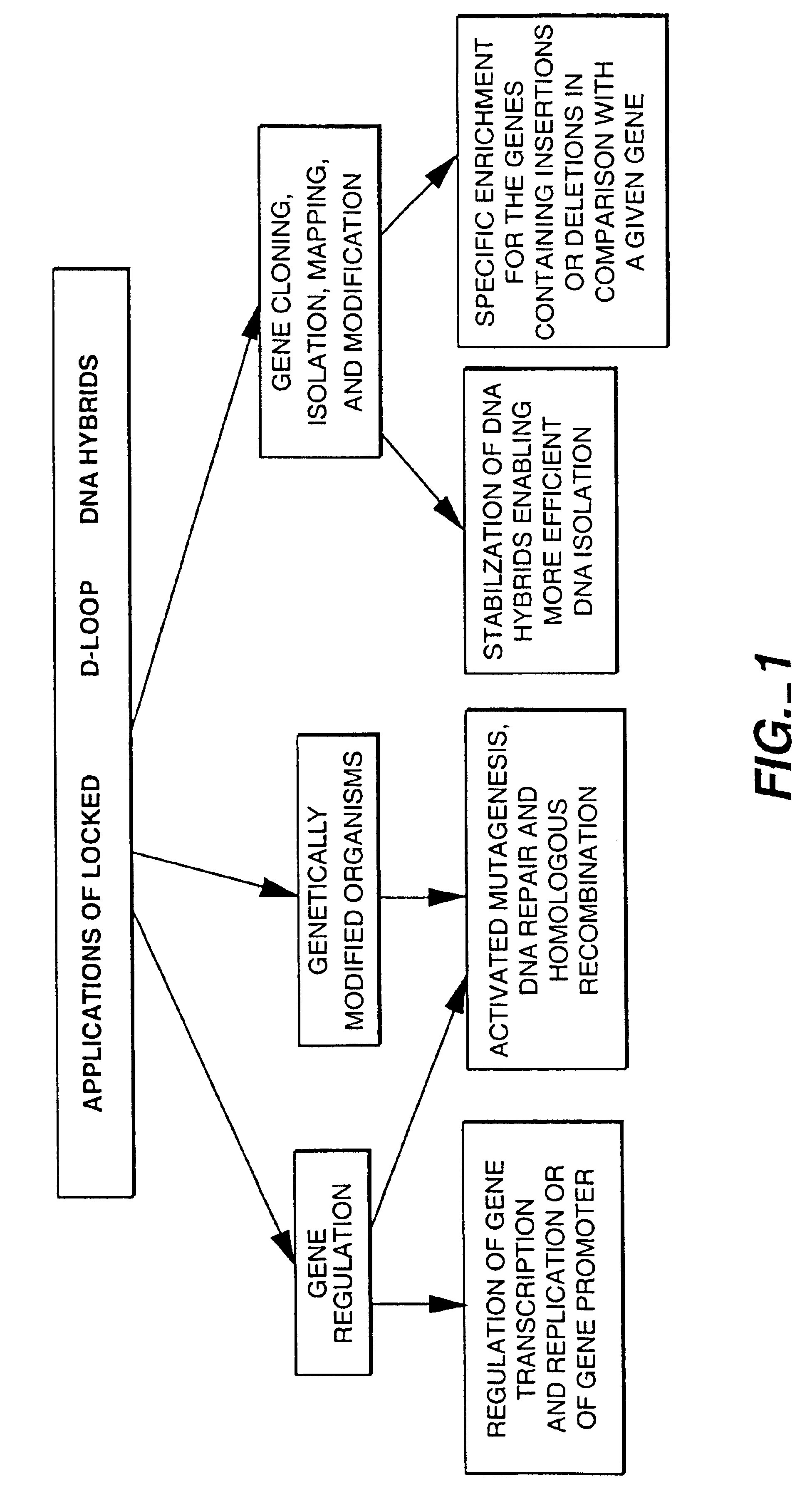
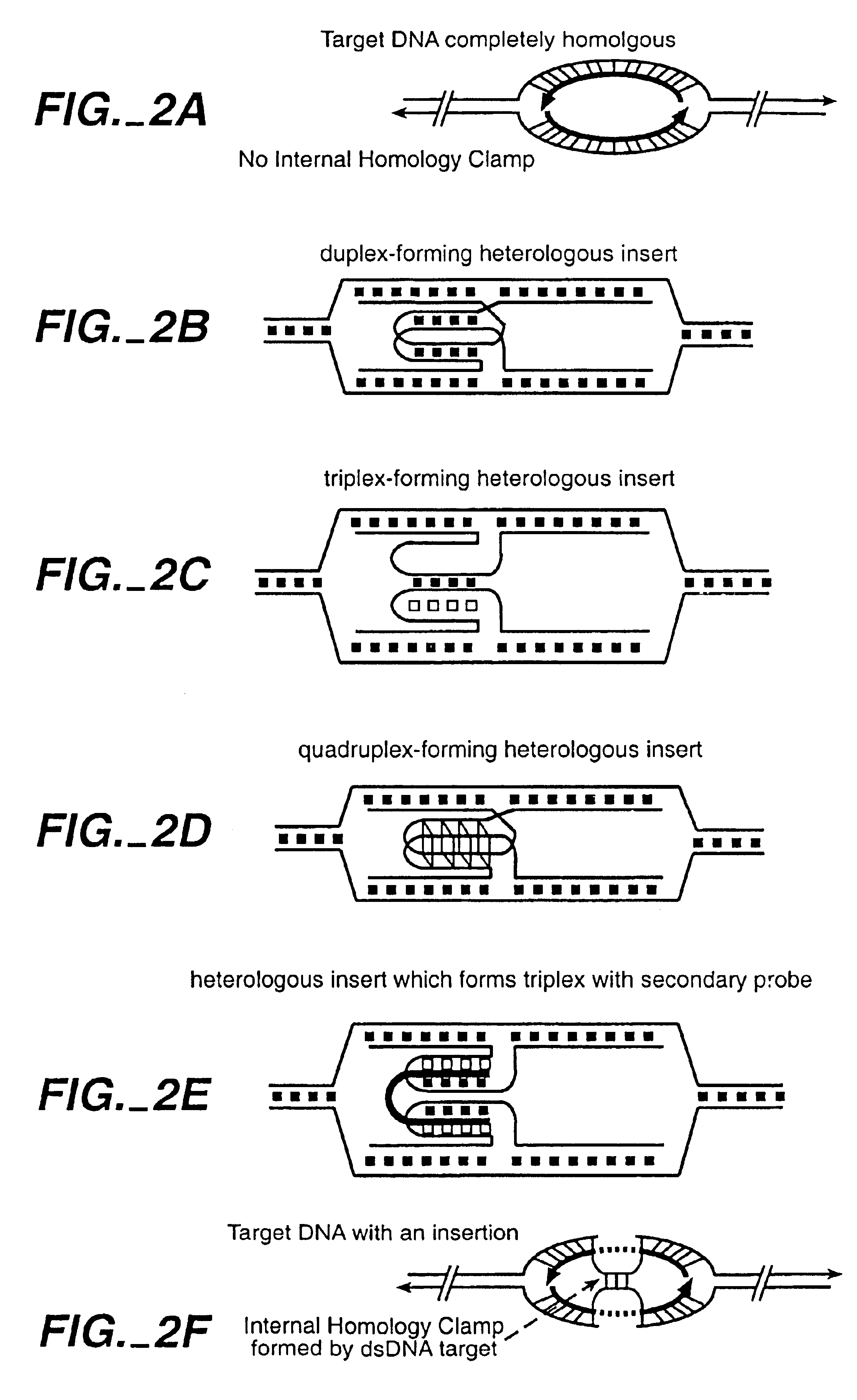
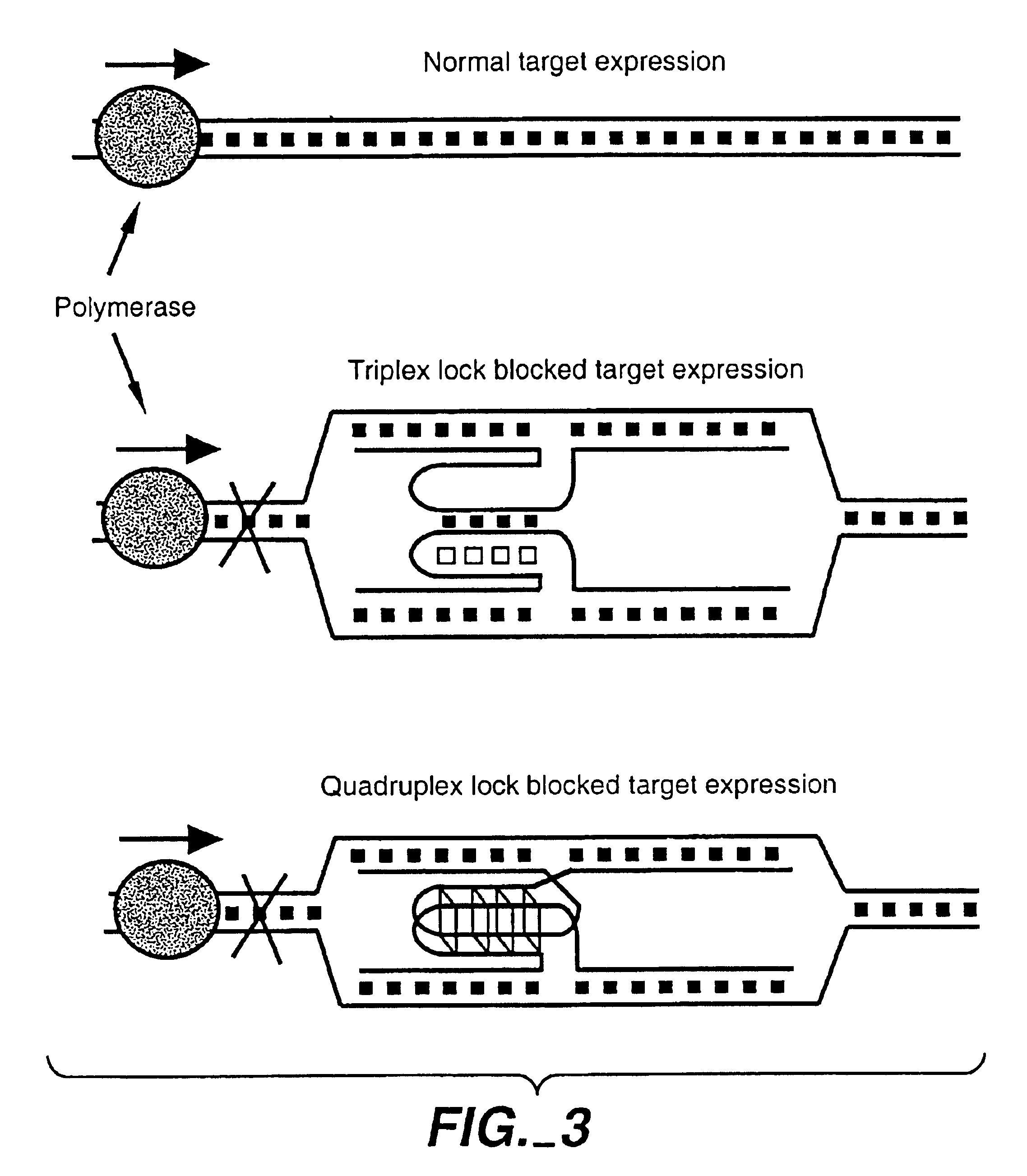
Locked nucleic acid hybrids and methods of use
InactiveUS6977295B2Inhibit migrationPrevent rotationBacteriaSugar derivativesNucleotideRegulator gene
The invention relates to methods for inhibiting, cloning, modifying or labelling an endogenous DNA sequence using compositions comprising recombinases in combination with exogenous polynucleotides containing “anchoring” or “locking” sequences. The anchoring sequences serve to stabilize structures formed by the exogenous polynucleotides and the endogenous DNA. The stabilized structure thus can either serve to regulate gene transcription or replication, or can allow the endogenous sequences to be labelled or pulled out, i.e. cloned, or modified.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
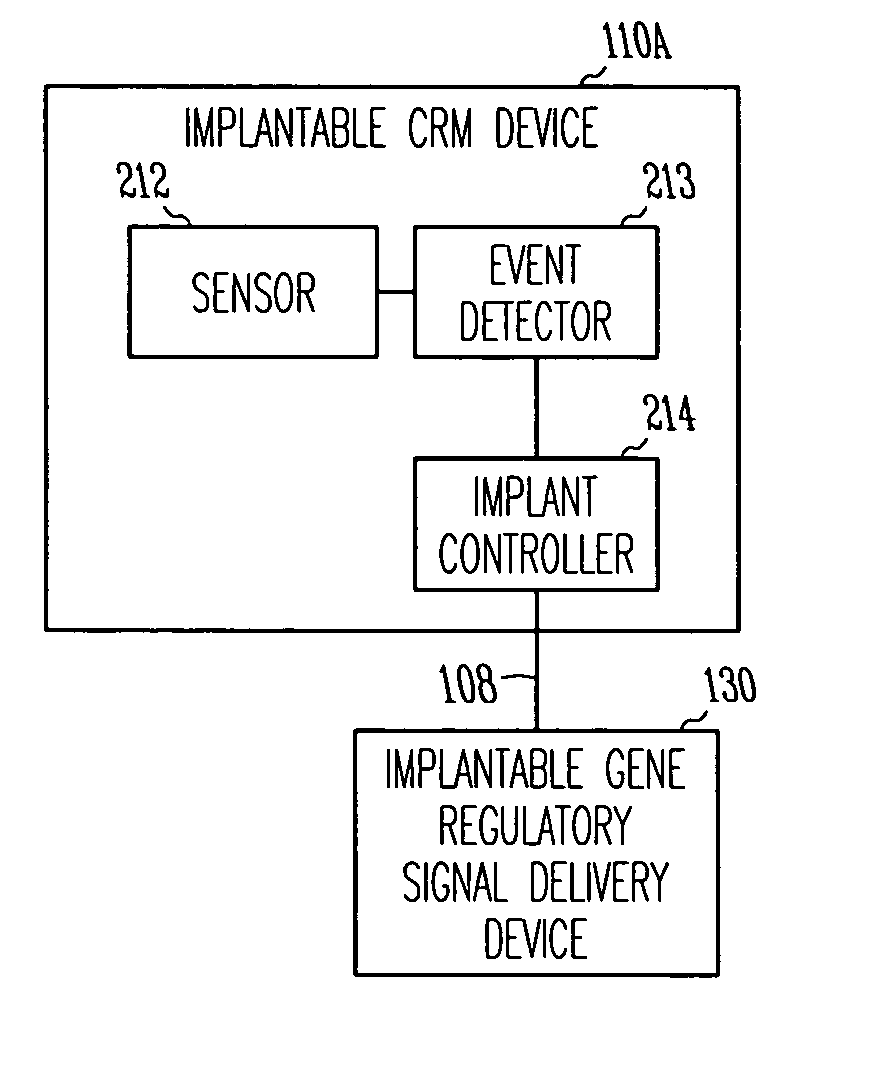
Method and apparatus for device controlled gene expression
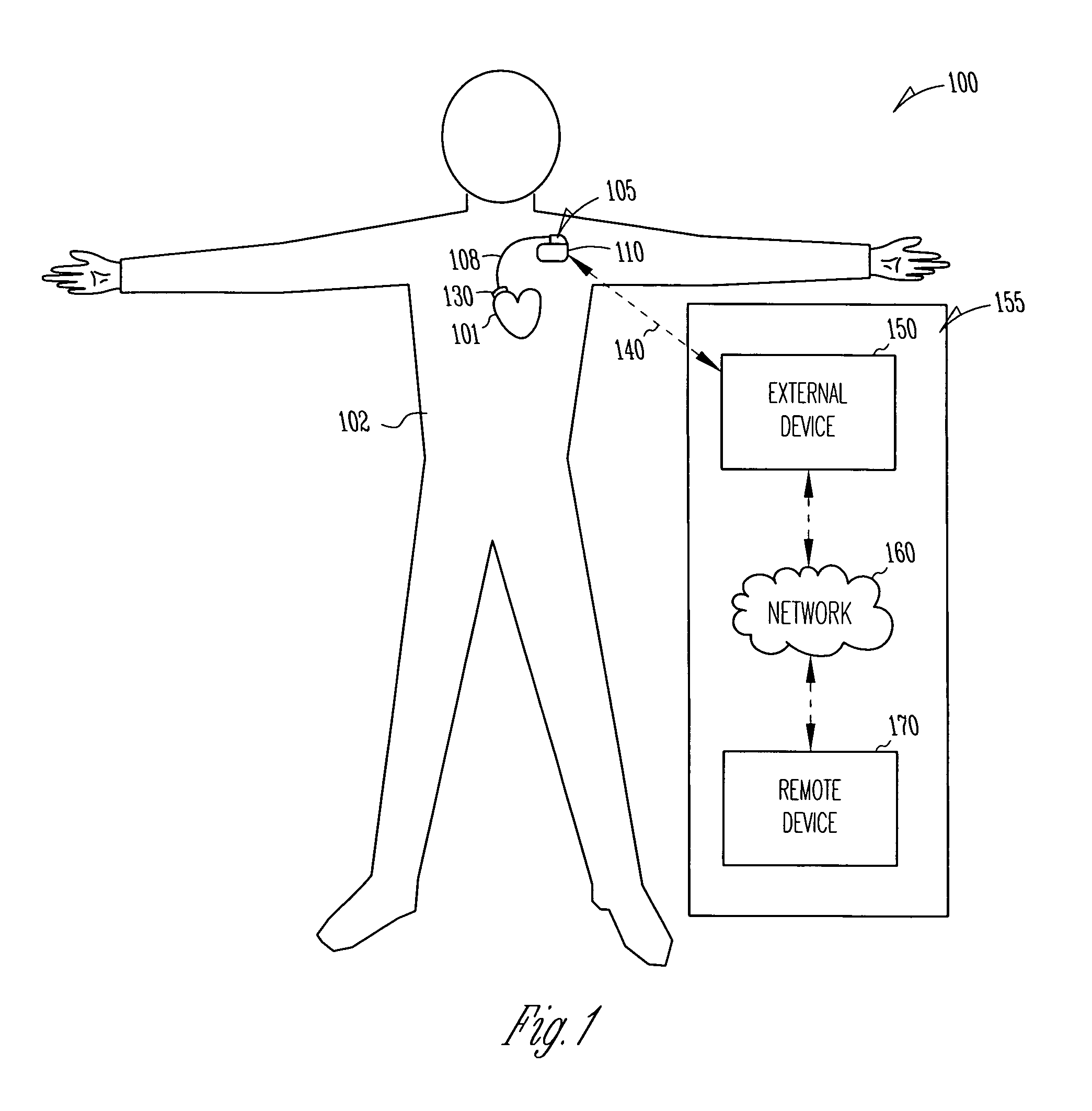
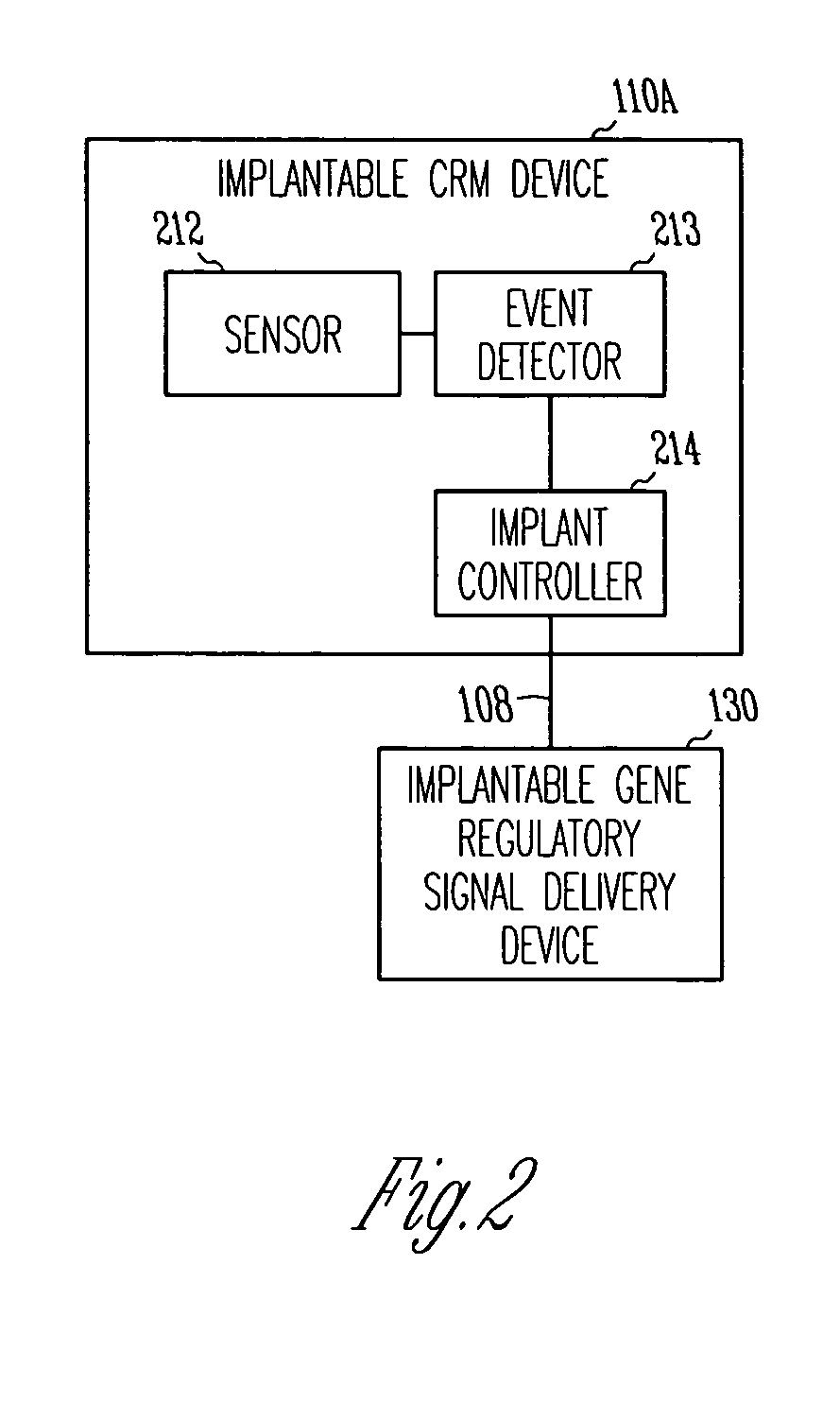
InactiveUS20050192637A1Readily be titratedPreventing and inhibiting and cardiac conditionGenetic material ingredientsHeart defibrillatorsForms of energyRegulator gene
A gene regulatory system controls gene therapy by emitting one or more forms of energy that regulate gene expression by triggering promoters. The system includes a sensor to sense a signal indicative of a need for the gene therapy as well as responses to the gene therapy. The regulation of the gene expression is controlled based on the sensed signal and / or a user command. In one embodiment, the system delivers one or more electrical therapies in conjunction with the gene therapy.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Regulation of gene expression
InactiveUS6022863APrevention of fetal rejectionSugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsMHC class IDisease
The present invention relates to utrons, RNA molecules which contain promoter regulatory motif(s) and DNA analogs thereof and DNA molecules that can be transcribed to produce the foregoing. In particular, the invention provides gene promoter suppressing nucleic acids which suppress transcription from a promoter of interest. In a preferred embodiment, the invention provides the TSU gene, nucleotide sequences of the TSU gene and RNA, as well as fragments, homologs and derivatives thereof. Methods of isolating TSU genes are also provided. Therapeutic and diagnostic methods and pharmaceutical compositions are also provided. In particular, the invention relates to methods for cell replacement therapy, gene therapy or organ transplantation wherein TSU nucleic acids suppress MHC class I and II gene expression, thus preventing immuno-rejection of non-autologous cells or organs. The invention also provides methods for treatment of diseases or disorders by suppression of MHC class I, MHC class II, ICAM-1, B7-1, B7-2, and / or Fc gamma R expression by provision of TSU function.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Sugar modified oligonucleotides that detect and modulate gene expression
Compositions and methods are provided for the treatment and diagnosis of diseases amenable to modulation of the production of selected proteins. In accordance with preferred embodiments, oligonucleotides and oligonucleotide analogs are provided which are specifically hybridizable with a selected sequence of RNA or DNA wherein at least one of the 2'-deoxyfuranosyl moieties of the nucleoside unit is modified. Treatment of HIV, herpes virus, papillomavirus and other infections is provided.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
METHODS AND COMPOSITIONS FOR IMPROVED THERAPEUTIC EFFECTS WITH siRNA
InactiveUS20080311040A1Improve in vivo stabilityImprove efficacyBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsTherapeutic effectProtein
The present invention relates to chemically modified, linked double-stranded (ds)RNA compositions comprising two or more double-stranded (ds) oligoribonucleotides linked by at least one linking moiety and methods of formulating and delivering such compositions to modulate gene expression through target-specific RNA co-interference (RNAco-i). The compositions of the invention may optionally comprise a conjugation or a complex with one or more small molecule drugs, protein therapeutics, or other dsRNA molecules. The present invention is directed at the methods of production for, methods of use of, and therapeutic utilities for RNAi co-interference therapy utilizing the compositions of the invention.
Owner:FLAGSHIP VENTURES
RNA interference mediated inhibition of proprotein convertase subtilisin Kexin 9 (PCSK9) gene expression using short interfering nucleic acid (siNA)
InactiveUS20070173473A1Improve stabilityModulating RNAi activitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementLipid formationProprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin 9
The present invention relates to compounds, compositions, and methods for the study, diagnosis, and treatment of traits, diseases and conditions that respond to the modulation of Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin Kexin 9 (PCSK9) gene expression and / or activity. The present invention is also directed to compounds, compositions, and methods relating to traits, diseases and conditions that respond to the modulation of expression and / or activity of genes involved in Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin Kexin 9 (PCSK9) gene expression pathways or other cellular processes that mediate the maintenance or development of such traits, diseases and conditions. Specifically, the invention relates to double stranded nucleic acid molecules including small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules capable of mediating RNA interference (RNAi) against Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin Kexin 9 (PCSK9) gene expression, including cocktails of such small nucleic acid molecules and lipid nanoparticle (LNP) formulations of such small nucleic acid molecules. The present invention also relates to small nucleic acid molecules, such as siNA, siRNA, and others that can inhibit the function of endogenous RNA molecules, such as endogenous micro-RNA (miRNA) (e.g, miRNA inhibitors) or endogenous short interfering RNA (siRNA), (e.g., siRNA inhibitors) or that can inhibit the function of RISC (e.g., RISC inhibitors), to modulate PCSK9 gene expression by interfering with the regulatory function of such endogenous RNAs or proteins associated with such endogenous RNAs (e.g., RISC), including cocktails of such small nucleic acid molecules and lipid nanoparticle (LNP) formulations of such small nucleic acid molecules. Such small nucleic acid molecules and are useful, for example, in providing compositions to prevent, inhibit, or reduce metabolic diseases traits and conditions, including but not limited to hyperlipidemia, hypercholesterolemia, cardiovascular disease, atherosclerosis, hypertension, diabetis (e.g., type I and / or type II diabetis), insulin resistance, obesity and / or other disease states, conditions, or traits associated with PCSK9 gene expression or activity in a subject or organism.
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
Conjugated oligomeric compounds and their use in gene modulation
The present invention provides modified oligomeric compounds that modulate gene expression via an RNA interference pathway. The oligomeric compounds of the invention include one or more conjugate moieties that can modify or enhance the pharmacokinetic and phamacodynamic properties of the attached oligomeric compound.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
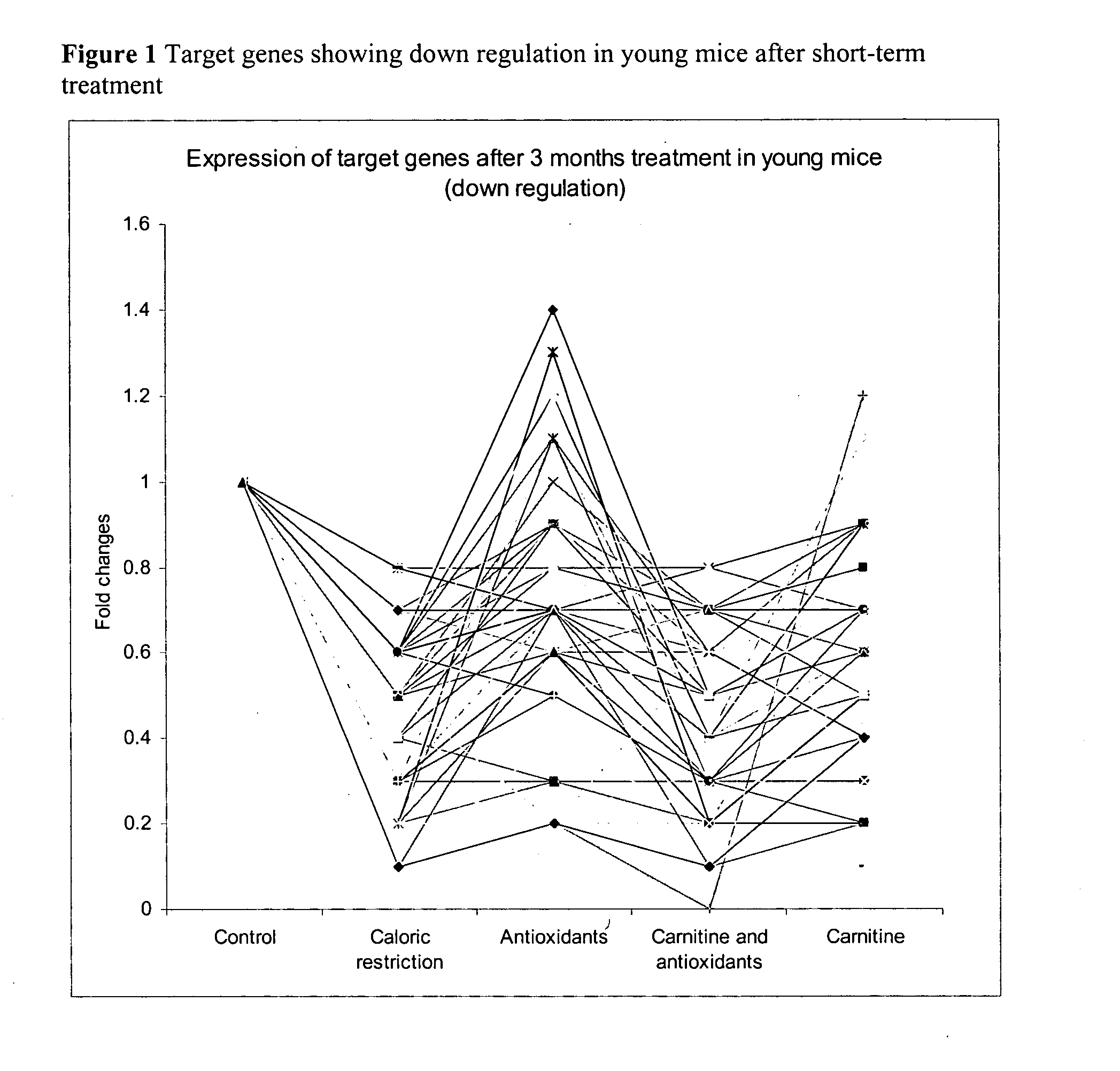
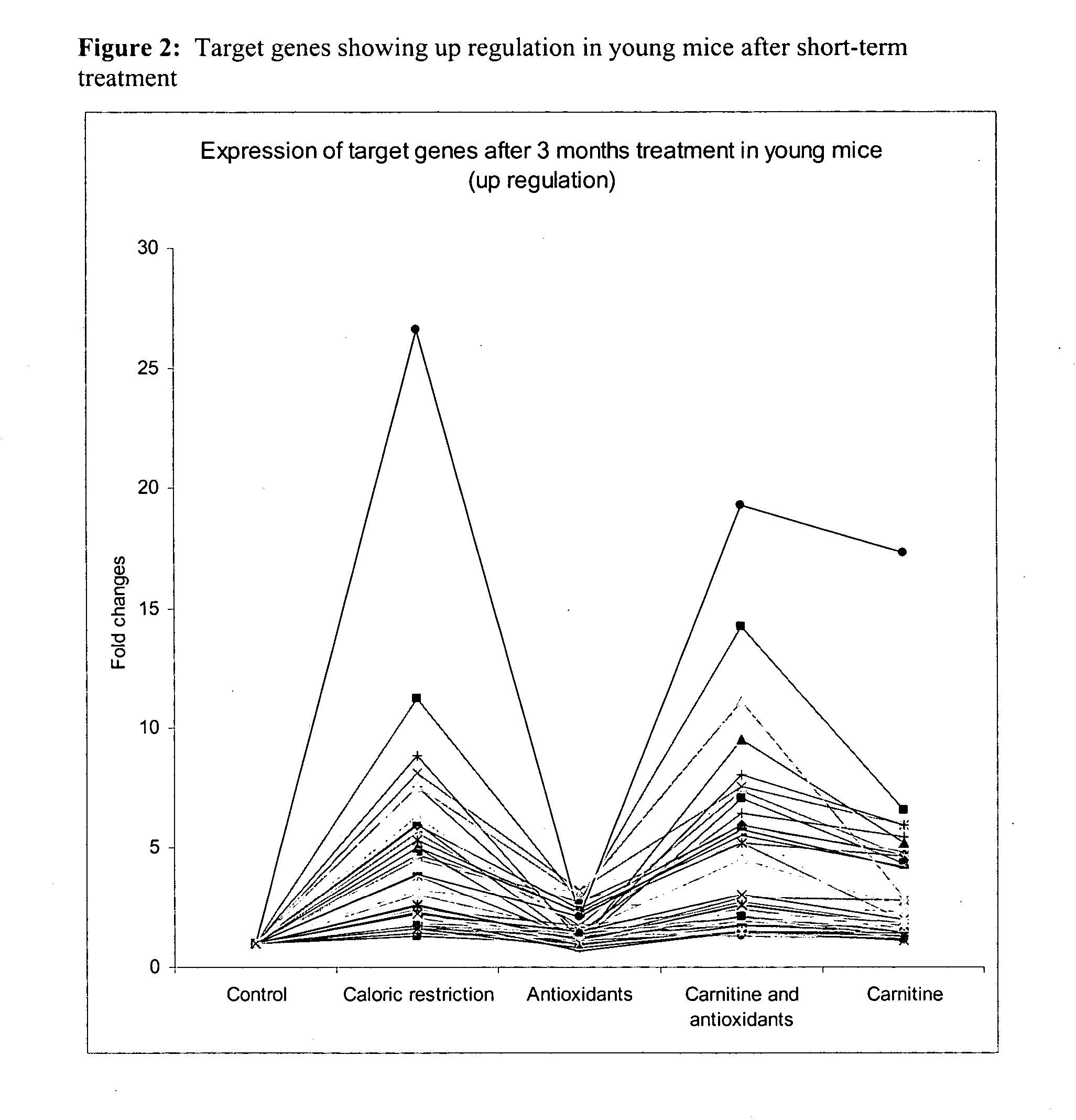
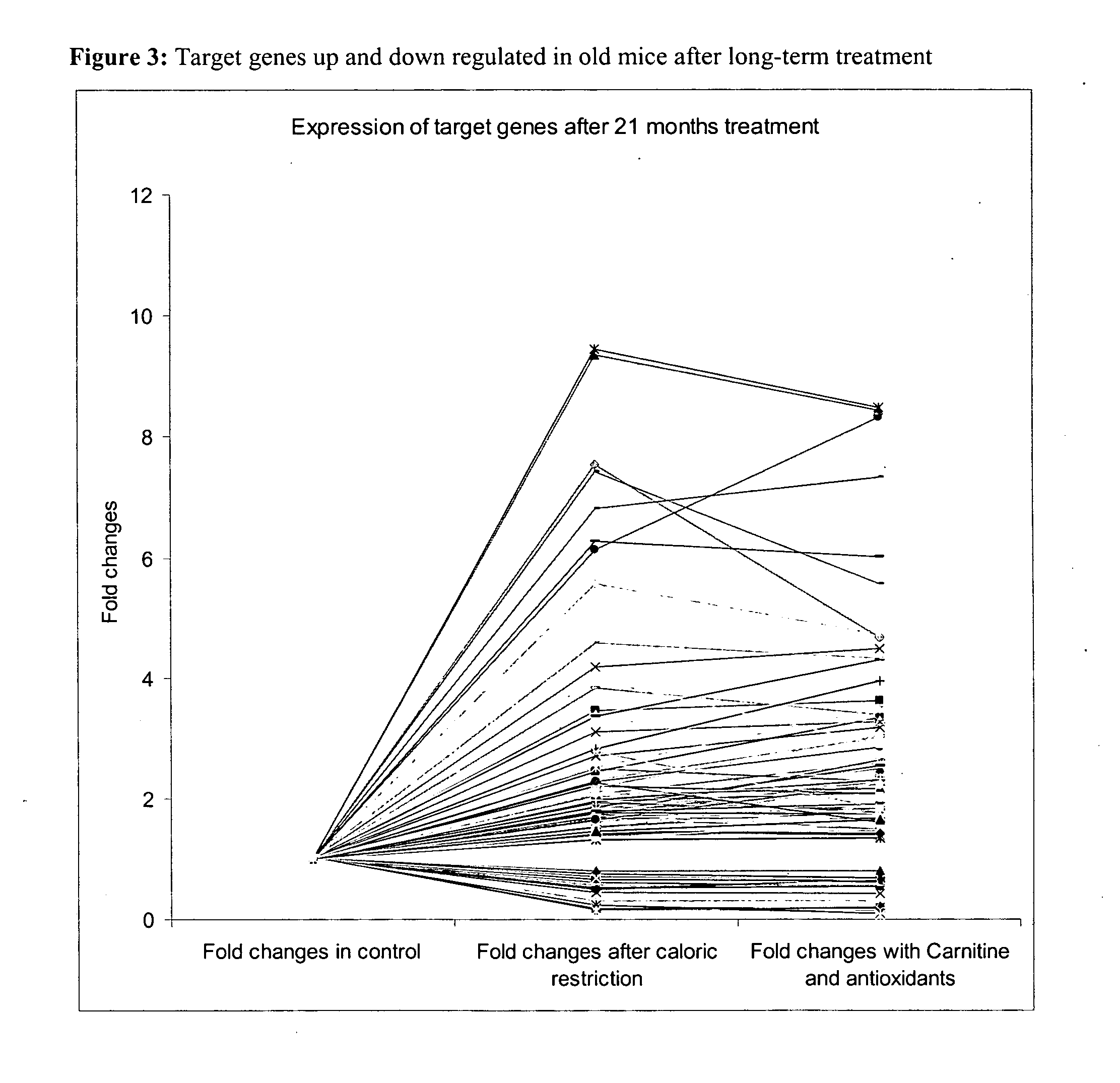
Method for improving age-related physiological deficits and increasing longevity
InactiveUS20050100617A1Retarding and reversing age associated oxidative damagePrevent and delay mitochondrial dysfunctionOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderCaloric restrictionsAntioxidant
A method for mimicking the effects of caloric restriction by administration of a food substrate having carnitine or a carnitine derivative and an antioxidant. The food substrate is capable of modulating gene expression in a way similar to caloric restriction.
Owner:NESTEC SA
Inhibition of gene expression using duplex forming oligonucleotides
InactiveUS20050233329A1Improve bioavailabilityHigh potencySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementOligonucleotideRegulator gene
The present invention concerns methods and nucleic acid based reagents useful in modulating gene expression in a variety of applications, including use in therapeutic, veterinary, agricultural, diagnostic, target validation, and genomic discovery applications. Specifically, the invention relates to double strand forming oligonucleotides (DFO) that can self assemble to form double stranded oligonucleotides, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA) molecules, and modulate gene expression, for example by RNA interference (RNAi). The self complementary DFO nucleic acid molecules are useful in the treatment of any disease or condition that responds to modulation of gene expression or activity in a cell, tissue, or organism.
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
Compostions and methods for enhancing delivery of nucleic acids into cells and for modifying expression of target genes in cells
InactiveUS20060040882A1Increase serum stabilityPreserve RNAi activity in cellsOrganic active ingredientsSpecial deliveryRegulator genePolynucleotide
Polynucleotide delivery-enhancing polypeptides are admixed or complexed with, or conjugated to, nucleic acids for enhancing delivery the nucleic acids into cells. The transported nucleic acids are active in target cells as small inhibitory nucleic acids (siNAs) that modulate expression of target genes, mediated at least in part by RNA interference (RNAi). The siNA / polypeptide compositions and methods of the invention provide effective tools to modulate gene expression and alter phenotype in mammalian cells, including by altering phenotype in a manner that eliminates disease symptoms or alters disease potential in targeted cells or subject individuals to which the siNA / polypeptide compositions are administered.
Owner:MDRNA
RNA interference mediated inhibition of gene expression using chemically modified short interfering nucleic acid (SINA)
InactiveUS8273866B2Modulating gene expressionImprove various propertySugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsDiseaseBiological body
The present invention concerns methods and reagents useful in modulating gene expression in a variety of applications, including use in therapeutic, diagnostic, target validation, and genomic discovery applications. Specifically, the invention relates to synthetic chemically modified small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules capable of mediating RNA interference (RNAi) against target nucleic acid sequences. The small nucleic acid molecules are useful in the treatment of any disease or condition that responds to modulation of gene expression or activity in a cell, tissue, or organism.
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
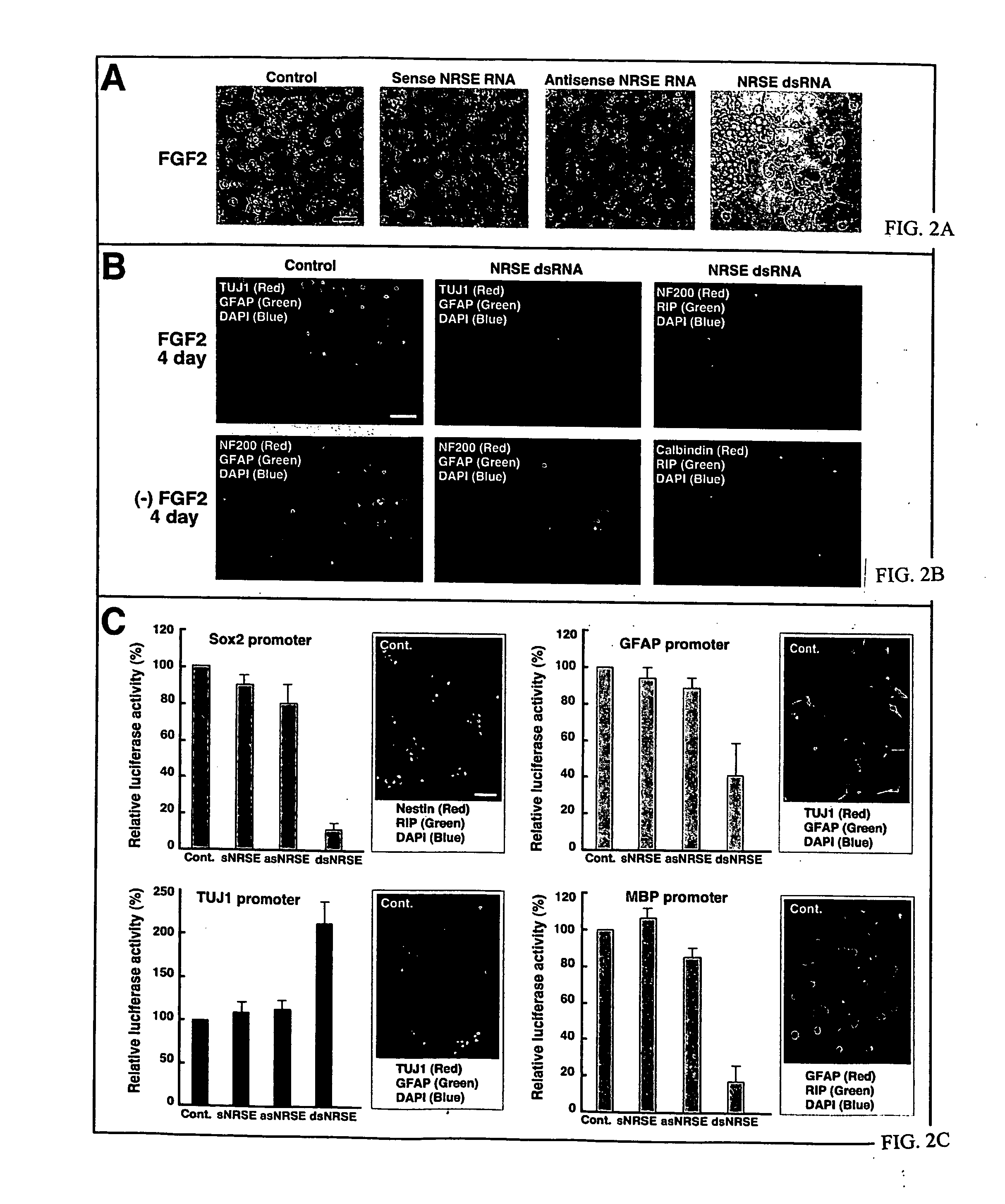
Transcriptional regulation of gene expression by small double-stranded modulatory RNA
The invention provides a method for modulating gene expression by contacting a cellular system with a double-stranded ribonucleic acid molecule capable of associating with a regulatory machinery that controls transcription of one or more genes, wherein the association results in altered expression of the one or more genes. The invention is further directed to method for directing the differentiation of neuronal stem cells into neurons by contacting a cellular system with a double-stranded ribonucleic acid molecule capable of associating with a regulatory machinery that controls transcription of one or more genes involved in neuronal differentiation and directing the transcription of the one or more genes. In related embodiments, the invention provides particular compositions of double-stranded ribonucleic acid molecules as well as therapeutic and screening applications of the invention.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
Oligomeric compounds for the modulation of Bcl-2
InactiveUS20050203042A1Comparable and enhanced biological effectInteresting biological propertiesBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseNucleobase
The present invention provides improved oligomeric compound, in particular oligonucleotide compounds, and methods for modulating the expression of the Bcl-2 gene in humans. In particular, this invention relates to oligomeric compounds of 10-30 nucleobases in length which comprise a target binding domain that is specifically hybridizable to a region ranging from base position No. 1459 (5′) to No. 1476 (3′) of the human Bcl-2 mRNA, said target binding domain having the formula: 5′-[(DNA / RNA)0-1-(LNA / LNA*)2-7-(DNA / RNA / LNA*)4-14-(LNA / LNA*)2-7-(DNA / RNA)0-1]-3 and said target binding domain comprising at least two LNA nucleotides or LNA analogue nucleotides linked by a phosphorothioate group (—O—P(O,S)—O—). In particular the oligo is predominantly or fully thiolated. The invention also provides the use of such oligomers or conjugates or chimera for the treatment of various diseases associated with the expression of the Bcl-2 gene, such as cancer.
Owner:SANTARIS PHARMA AS
RNA interference mediated inhibition of STAT3 gene expression using short interfering nucleic acid (siNA)
InactiveUS20050196781A1Improve bioavailabilityMinimize the possibilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDouble strandOrganism
This invention relates to compounds, compositions, and methods useful for modulating STAT3 gene expression using short interfering nucleic acid (siNA) molecules. This invention also relates to compounds, compositions, and methods useful for modulating the expression and activity of other genes involved in pathways of STAT3 gene expression and / or activity by RNA interference (RNAi) using small nucleic acid molecules. In particular, the instant invention features small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (mRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules and methods used to modulate the expression of STAT3 genes. Such small nucleic acid molecules are useful, for example, for treating, preventing, inhibiting, or reducing cancer, proliferative, and / or inflammatory diseases, disorders, or conditions in a subject or organism, such as psoriasis, eczema, dermatitis, Crohn's disease, and inflammatory bowel disease, and for any other disease, trait, or condition that is related to or will respond to the levels of STAT3 in a cell or tissue, alone or in combination with other treatments or therapies.
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
Method of inhibiting prostaglandin synthesis in a human host
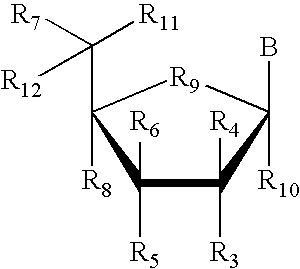
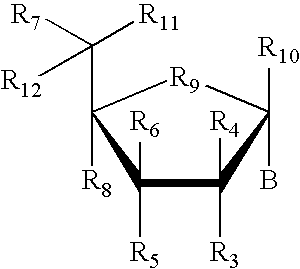
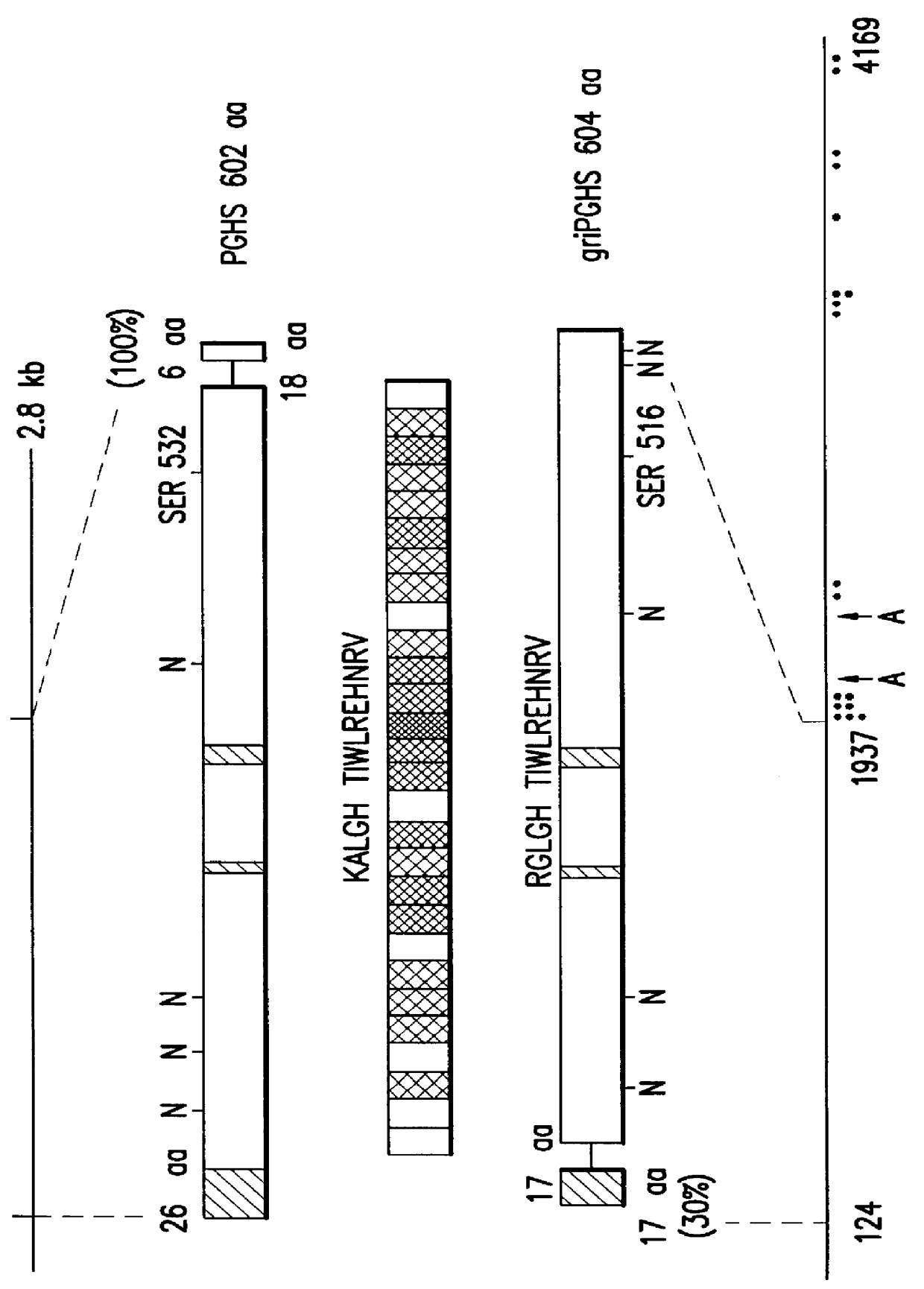
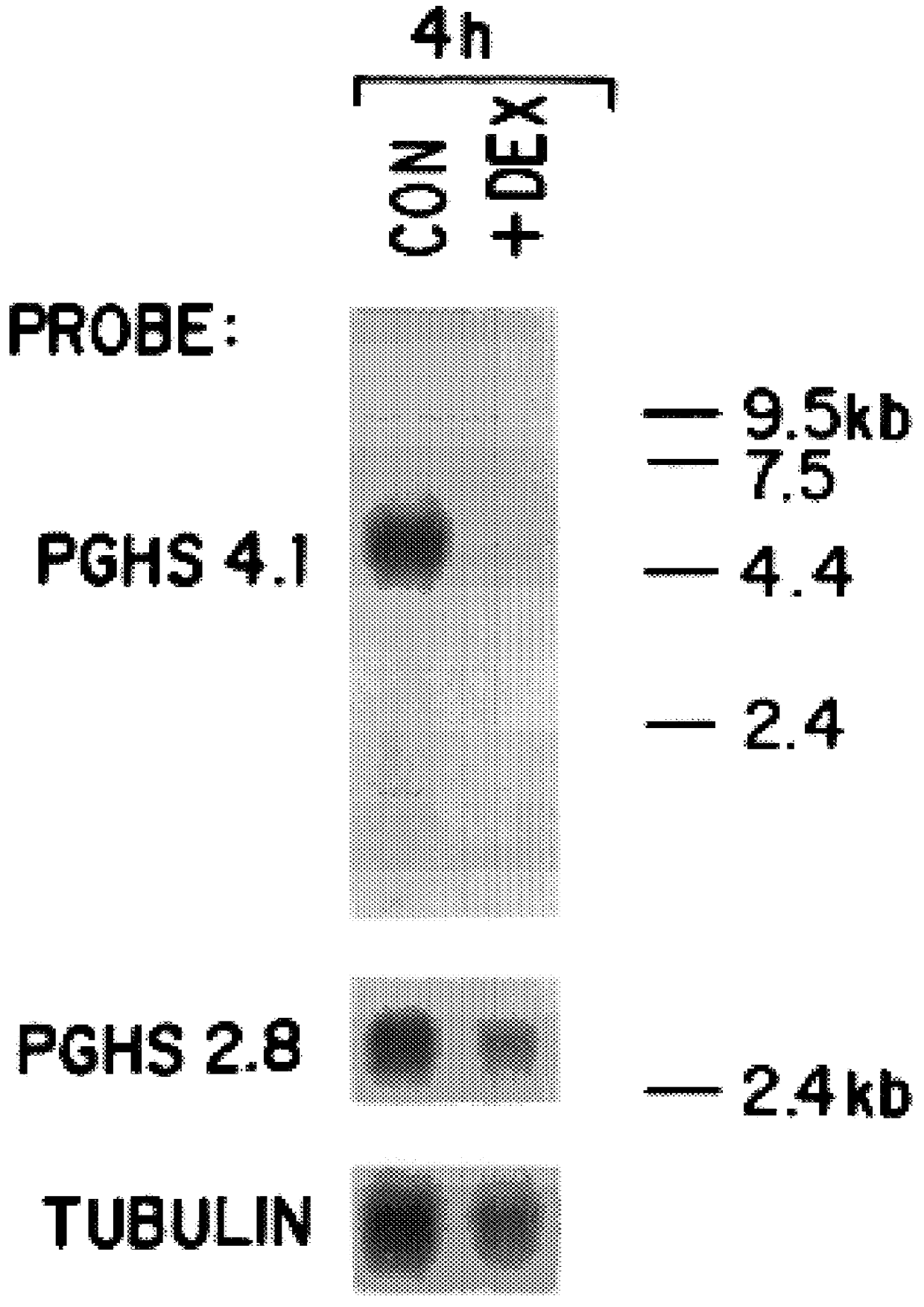
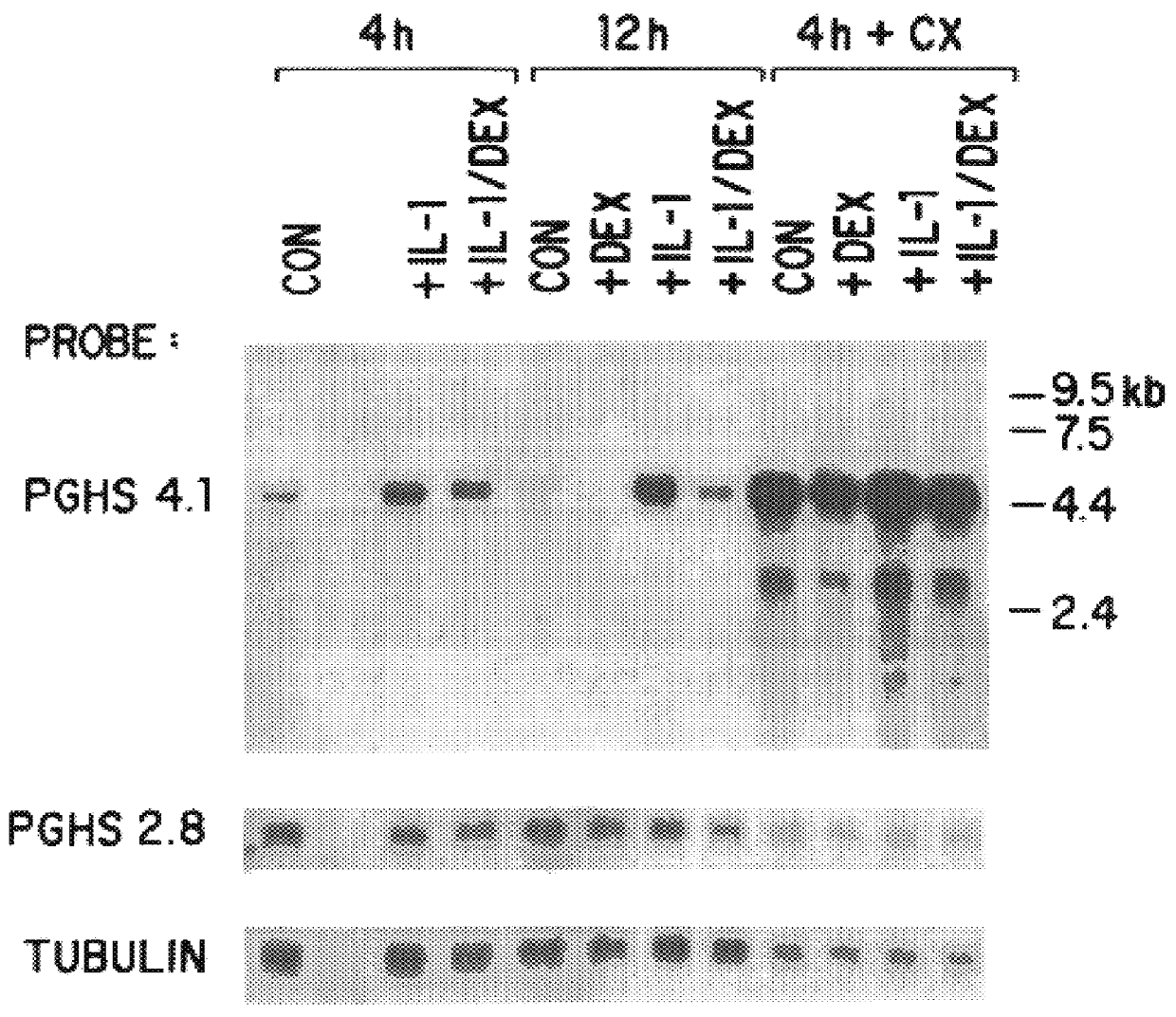
The invention relates to the gene encoding the mammalian prostaglandin H synthase-2 and its product. More specifically, the invention relates to the diagnosis of aberrant PGHS-2 gene or gene product; the identification, production, and use of compounds which modulate PGHS-2 gene expression or the activity of the PGHS-2 gene product including but not limited to nucleic acid encoding PGHS-12 and homologues, analogues, and deletions thereof, as well as antisense, ribozyme, triple helix, antibody, and polypeptide molecules as well as small inorganic molecules; and pharmaceutical formulations and routes of administration for such compounds.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Chemically modified short interfering nucleic acid molecules that mediate RNA interference
InactiveUS20090176725A1Improve stabilityModulating RNAi activitySugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsLipid formationDouble strand
The present invention relates to compounds, compositions, and methods for the study, diagnosis, and treatment of traits, diseases and conditions that respond to the modulation of gene expression and / or activity. The present invention is also directed to compounds, compositions, and methods relating to traits, diseases and conditions that respond to the modulation of expression and / or activity of genes involved in gene expression pathways or other cellular processes that mediate the maintenance or development of such traits, diseases and conditions. Specifically, the invention relates to double stranded nucleic acid molecules including small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules capable of mediating RNA interference (RNAi) against gene expression, including cocktails of such small nucleic acid molecules and lipid nanoparticle (LNP) formulations of such small nucleic acid molecules. The present invention also relates to small nucleic acid molecules, such as siNA, siRNA, and others that can inhibit the function of endogenous RNA molecules, such as endogenous micro-RNA (miRNA) (e.g., miRNA inhibitors) or endogenous short interfering RNA (siRNA), (e.g., siRNA inhibitors) or that can inhibit the function of RISC (e.g., RISC inhibitors), to modulate gene expression by interfering with the regulatory function of such endogenous RNAs or proteins associated with such endogenous RNAs (e.g., RISC), including cocktails of such small nucleic acid molecules and lipid nanoparticle (LNP) formulations of such small nucleic acid molecules. Such small nucleic acid molecules and are useful, for example, in providing compositions to prevent, inhibit, or reduce diseases, traits and conditions that are associated with gene expression or activity in a subject or organism.
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
Methods and compositions for the introduction and regulated expression of genes in plants
InactiveUS20110167516A1Minimize premature excisionSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyRegulator gene
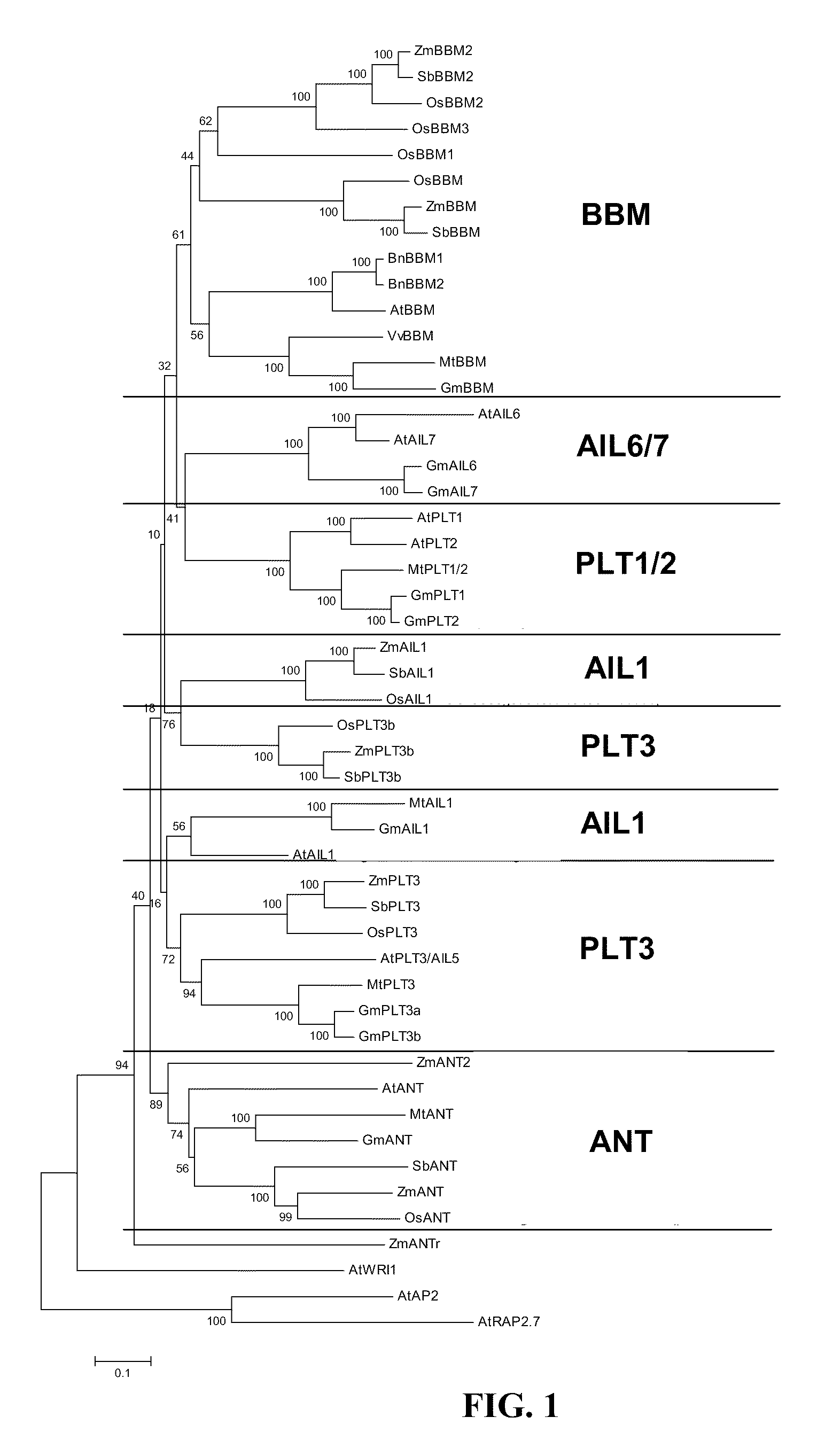
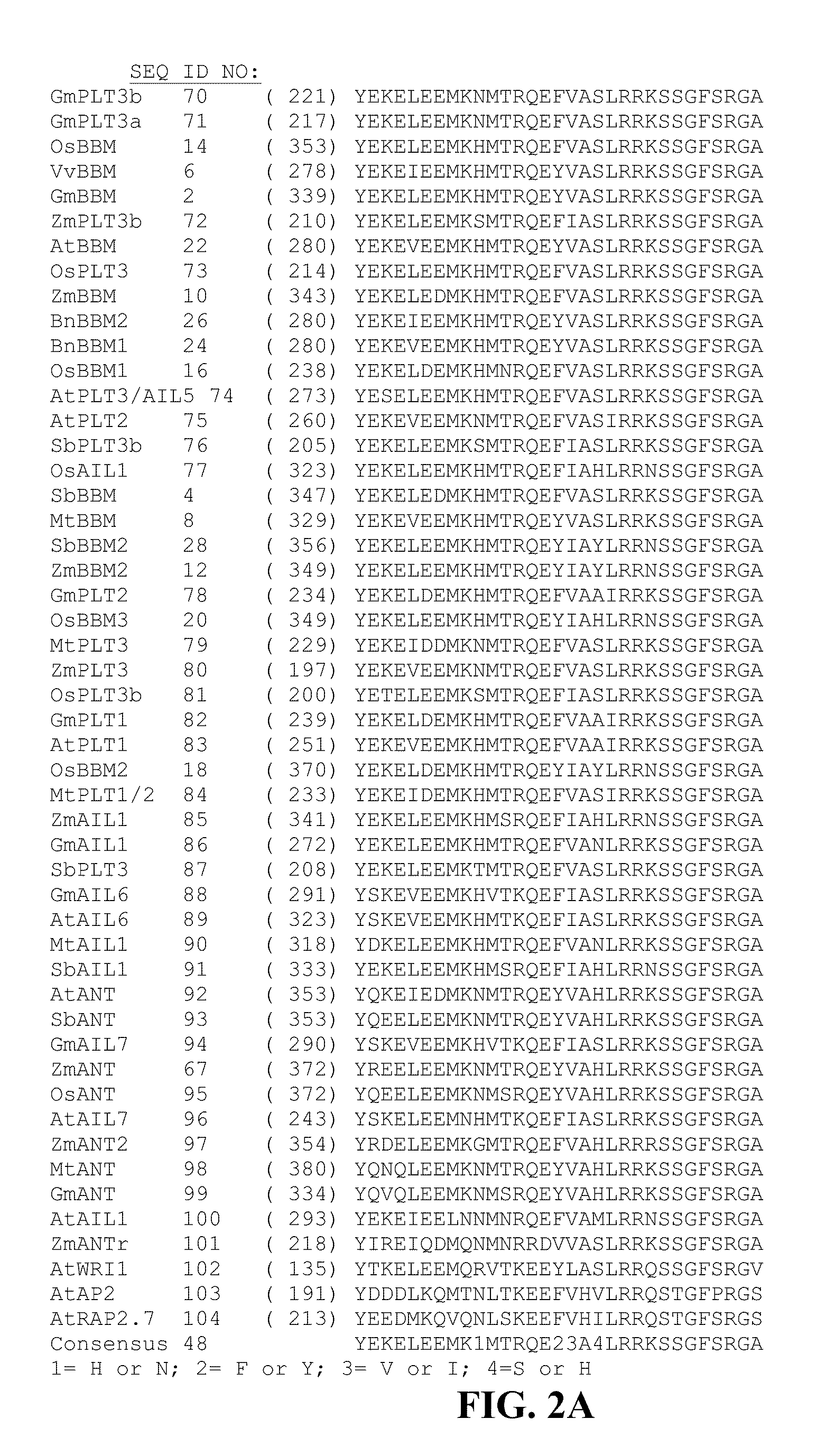
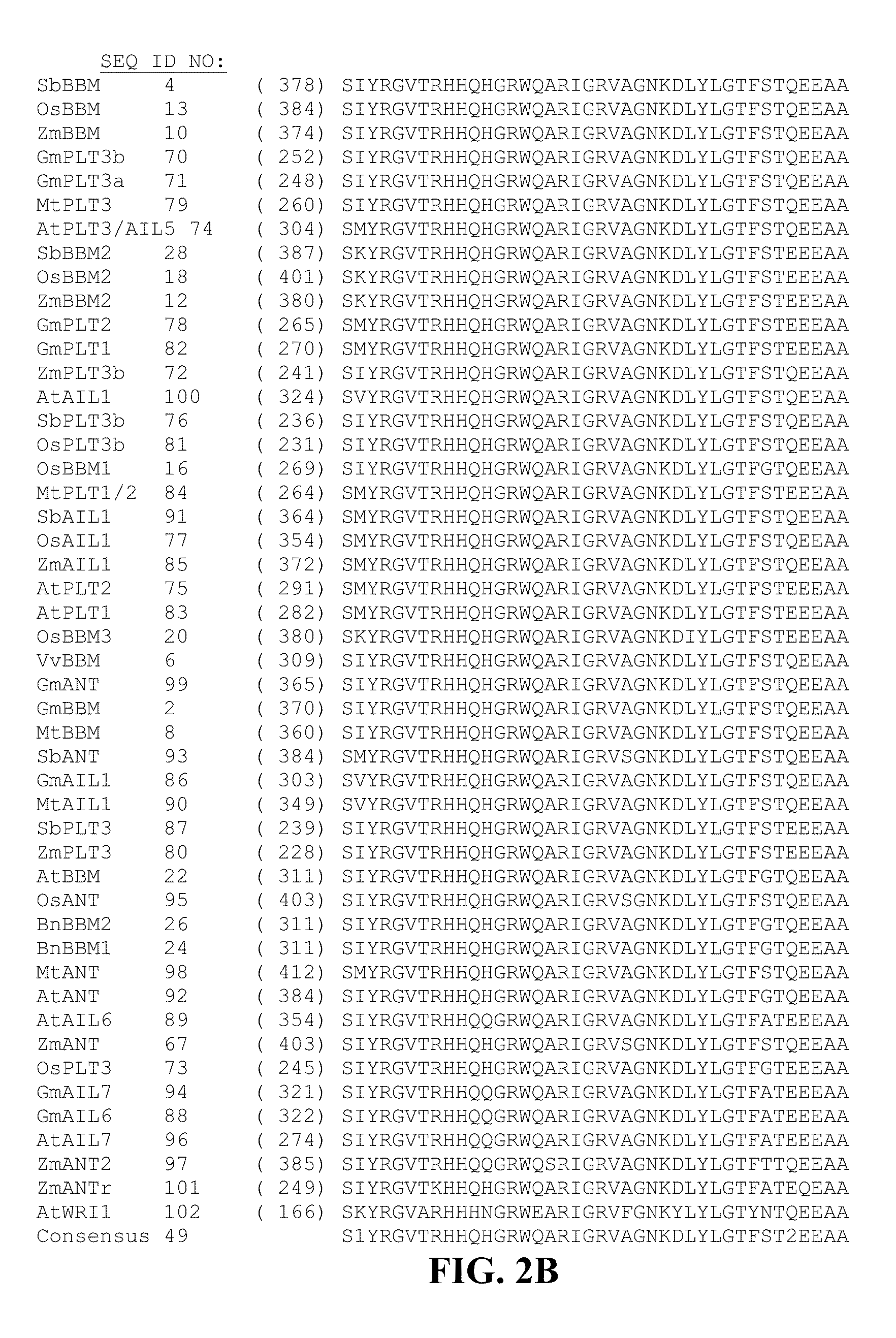
Compositions and methods are provided for the introduction and the regulated expression of genes in plants. Compositions include promoter constructs that provide a level of activity useful for the regulated expression of site-specific recombinases, while avoiding premature excision. Further provided are isolated polynucleotides encoding novel babyboom polypeptides, expression cassettes, and plants comprising the same. Methods for the introduction of genes into plants are provided, including methods for plastid transformation and methods for the transformation of tissues from mature seeds and leaves.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
RNA Interference Mediated Inhibition of Gene Expression Using Chemically Modified Short Interfering Nucleic Acid (siNA)
InactiveUS20090023675A1Modulate its functionImprove various propertySenses disorderNervous disorderDiseaseBiological body
The present invention concerns methods and reagents useful in modulating gene expression in a variety of applications, including use in therapeutic, diagnostic, target validation, and genomic discovery applications. Specifically, the invention relates to synthetic chemically modified small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules capable of mediating RNA interference (RNAi) against target nucleic acid sequences. The small nucleic acid molecules are useful in the treatment of any disease or condition that responds to modulation of gene expression or activity in a cell, tissue, or organism.
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
METHODS OF INTRODUCING dsRNA TO PLANT SEEDS FOR MODULATING GENE EXPRESSION
ActiveUS20140230090A1Improve plant resistanceIncreasing viral resistanceSpecial deliveryClimate change adaptationPlanting seedRegulator gene
A method of introducing an exogenous non-transcribable polynucleotide trigger, for example dsRNA, molecule into a seed is provided. The method comprises contacting the seed with the exogenous non-transcribable polynucleotide trigger, for example dsRNA, molecule under conditions which allow penetration of the exogenous non-transcribable polynucleotide trigger, for example dsRNA, molecule into the seed, thereby introducing the exogenous non-transcribable polynucleotide trigger, for example dsRNA, molecule into the seed.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com