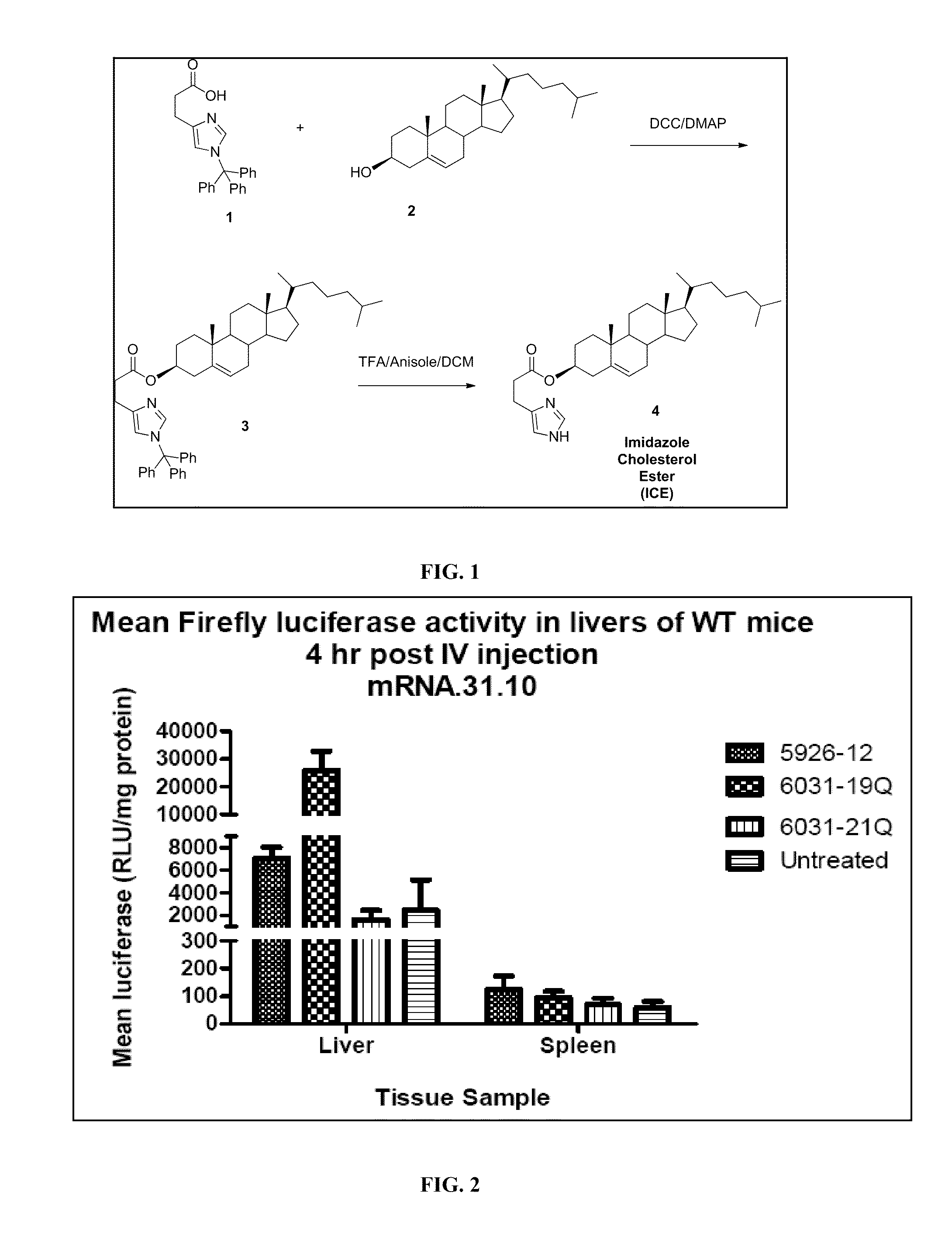
Delivery of mRNA for the augmentation of proteins and enzymes in human genetic diseases
a technology for enhancing proteins and enzymes, applied in the direction of non-active genetic ingredients, genetic material ingredients, drug compositions, etc., can solve the problems of affecting the expression of proteins or enzymes, and reducing the synthesis of proteins, so as to facilitate the transfection and enhance the affinity of compositions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
General Preparation of Transfer Vehicles by Solvent Dilution Technique
[0098]This example generally illustrates a process for the manufacture of small (<100 nm) liposomal formulations containing mRNA and the means to evaluate the amount of mRNA encapsulated. Parameters which may be modified to further optimize transfection efficiency include, but are not limited to, the selection of lipid, the ratio of lipids, the molar ratio of the PEG-containing lipid, the length of the lipid anchor of the PEG-containing lipid and the sizing of the liposomal transfer vehicles.
[0099]Appropriate quantities of lipids (e.g., DSPC / CHOL / DODAP / C8-PEG2000-Cer) to construct a transfer vehicle of a desired lipid ratio (e.g., a molar ratio of 31:40:25:4) were weighed and dissolved in absolute ethanol at 70° C. to obtain the desired lipid ratios and concentrations. In order to monitor the lipid, a small amount (typically 0.05 mole %) of rhodamine-dioleoylphosphatidylethanolamine (Rh-PE) was routinely added to ...
example 2
Preparation of DSPC / CHOL / DODAP / C8-PEG-2000 Ceramide (Molar Ratio of 31:40:25:4) / Renilla Luciferase mRNA (Formulation I)
[0108]Formulation 1 was prepared by dissolving the appropriate masses of DSPC, CHOL, DODAP and C8-PEG-2000 ceramide in absolute ethanol, then adding this to a solution of Renilla Luciferase mRNA in buffer to produce MLVs at 10.8 mg / mL lipid, 250 μg / mL mRNA, 20% solvent. The MLVs were extruded to produce LUVs, and then passed through a 0.2 μm filter. The pH was increased by combining with an equal volume of 100 mM NaCl-50 mM borate pH 8.0 and the external mRNA removed by anion exchange using the DEAE-Sephacel centrifugation method, as described in Example 1. The solvent was removed, the external buffer exchanged and the sample concentrated by diafiltration / ultrafiltration. The concentrated sample was then passed through a 0.2 μm filter and aliquots were transferred to vials and stored at 2-8° C.
example 3
Preparation of DSPC / CHOL / DOTAP / C8-PEG-2000 Ceramide (Molar Ratio of 31:40:25:4) / Renilla Luciferase mRNA (Formulation 2)
[0109]Formulation 2 was prepared using a similar methodology as Formulation 1 with minor changes. In brief, the appropriate masses of DSPC, CHOL, DOTAP and C8-PEG-2000 ceramide were dissolved in absolute ethanol and then added to a solution of Renilla Luciferase mRNA in buffer to produce MLVs at 10.8 mg / mL lipid, 250 μg / mL mRNA, 20% solvent. The MLVs were extruded to produce LUVs. As DOTAP was used in this formulation, the external mRNA could not be effectively removed by anion exchange and therefore this step was omitted. The solvent was removed, the external buffer exchanged and the sample concentrated by diafiltration / ultrafiltration. The concentrated sample was then passed through a 0.2 μm filter and aliquots were transferred to vials and stored at 2-8° C.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molar ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molar ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com