Methods, compositions and kits for assaying mitochondrial function
a technology of mitochondrial function and kits, applied in the field of methods, compositions and kits for assaying mitochondrial function, can solve the problems of difficult to establish the concentration of detergents under which mitochondrial function is sustained, and achieve the effect of accurate evaluation of intracellular mitochondrial activities
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Experimental Design and Methodology
[0097]PFO-Based Cell Permeabilization Methods for Mitochondrial Function Assays:
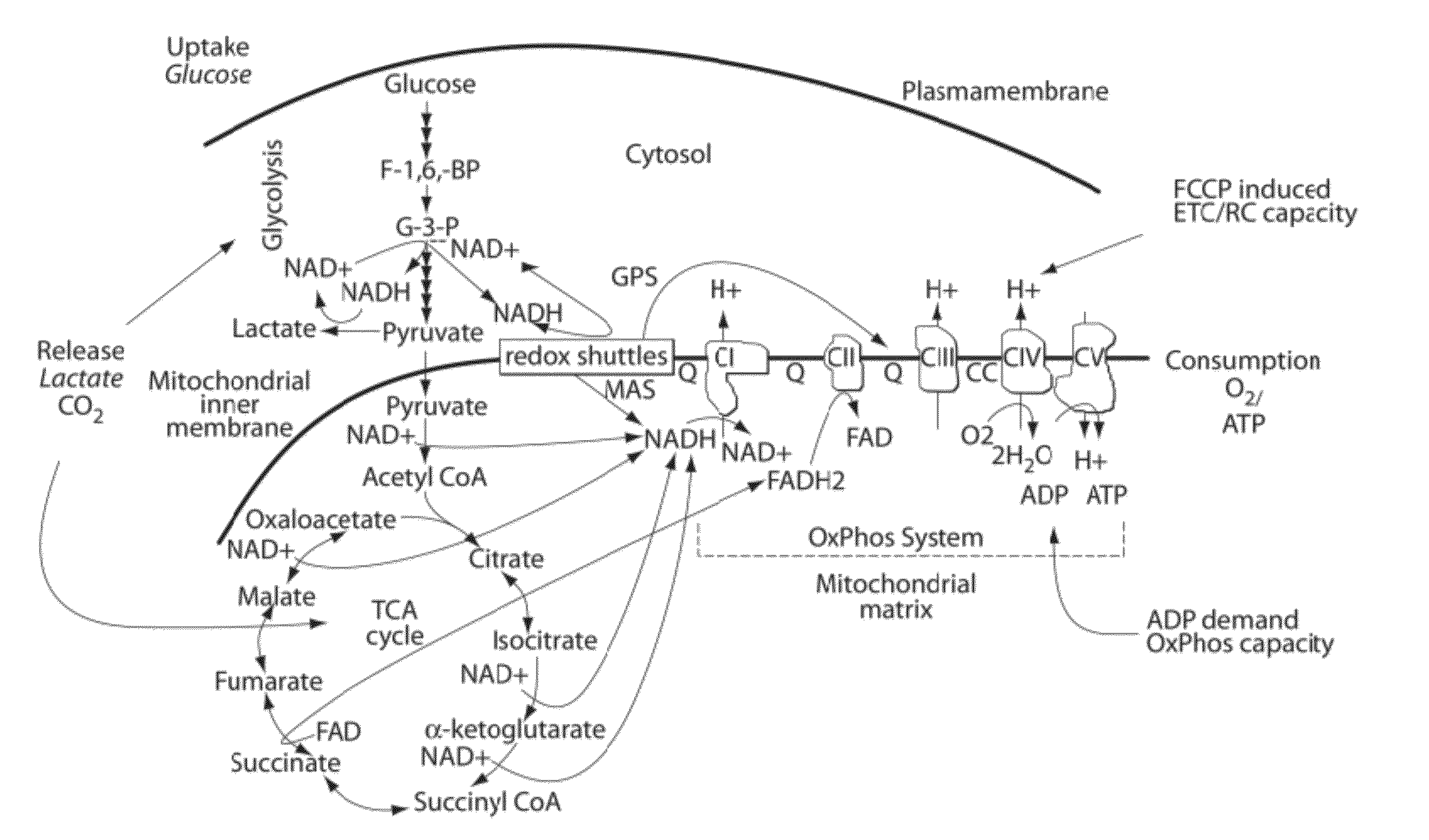
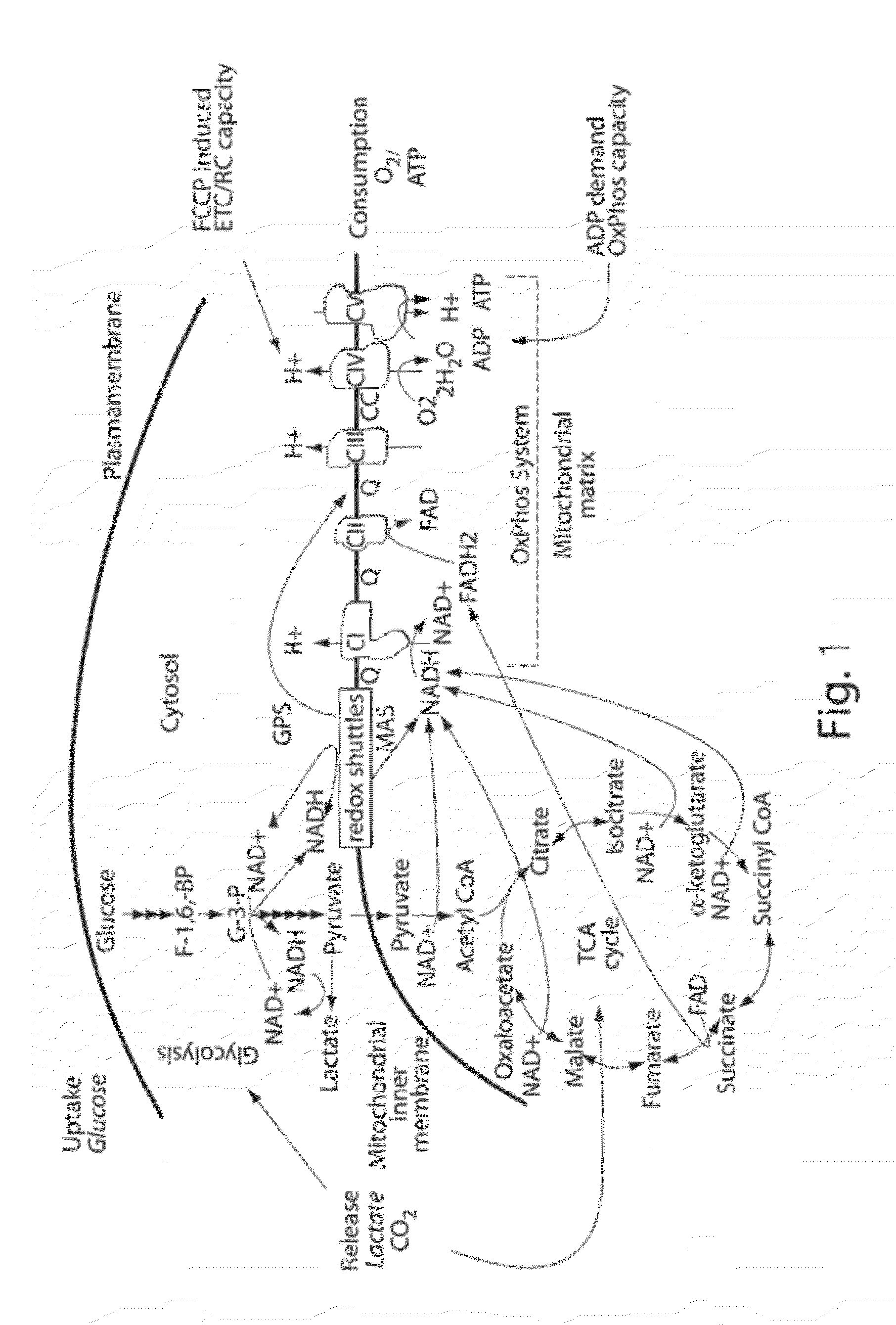
[0098]Wild type PFOs and variants have been tested for maximal mitochondrial performance (see Table 1 for examples of PFOs) using methods disclosed herein. Specific assays for different OxPhos components applicable to a wide variety of were developed based on cell permeabilization methods described herein. Both established and primary cells were utilized to test the general applicability of PFO-based assays.
[0099]It has been recognized that a reducing agent may be used to increase shelf life of wild-type PFO. PFO contains only one Cys residue at position 459. To avoid the need of a reducing agent in permeabilization reactions, a Cys free derivative, PFOC459A, has been used. This variant has activity comparable to wild type PFO. A mutant rPFOT319C-V334C provides for conditional cell permeabilization, as it does not form pore in the membrane following insertion until a re...
example 2
Experimental Evaluations Using Different Cell Types
[0107]Similar experimental conditions may be used for assays of Complexes I-V, and OxPhos and ETC / RC capacity and across different cells (see Table 4 for a non-limiting list of cells).
TABLE 4Cells for PFO-based mitochondrial function assays.CategorySubcategoryCellsCell linesAdherent cellsHEK293, C2C12, HepG2, A549, H460, MCF7Adherent cells withINS1, SHSY-5YcoatingNon-adherent cellsCell seeding, spin down, and measurements onsame day with above cellsCells may be grouped with respect to their OxPhos capacity vs. ETC / RCcapacity to provide a reference for each enlisted cell line.Primary cellsAdherent cellsβ-cells, astrocytes,Note: primary cellsneurons, fibroblasts,may require coatinghepatocytes, mammaryof plates (e.g., V7epithelial cells,plates) with PEI ormyocytes / blastssimilar reagents e.g.(cardiac, skeletal),PDL, CellTak.Adipocytes(WAT / BAT), adultstem cellsNon-adherent cellsPeripheral bloodMay involve coatingwith coatingsmonocytesof ...
example 3
Assay Using Digitonin as a Permeabilizing Reagent
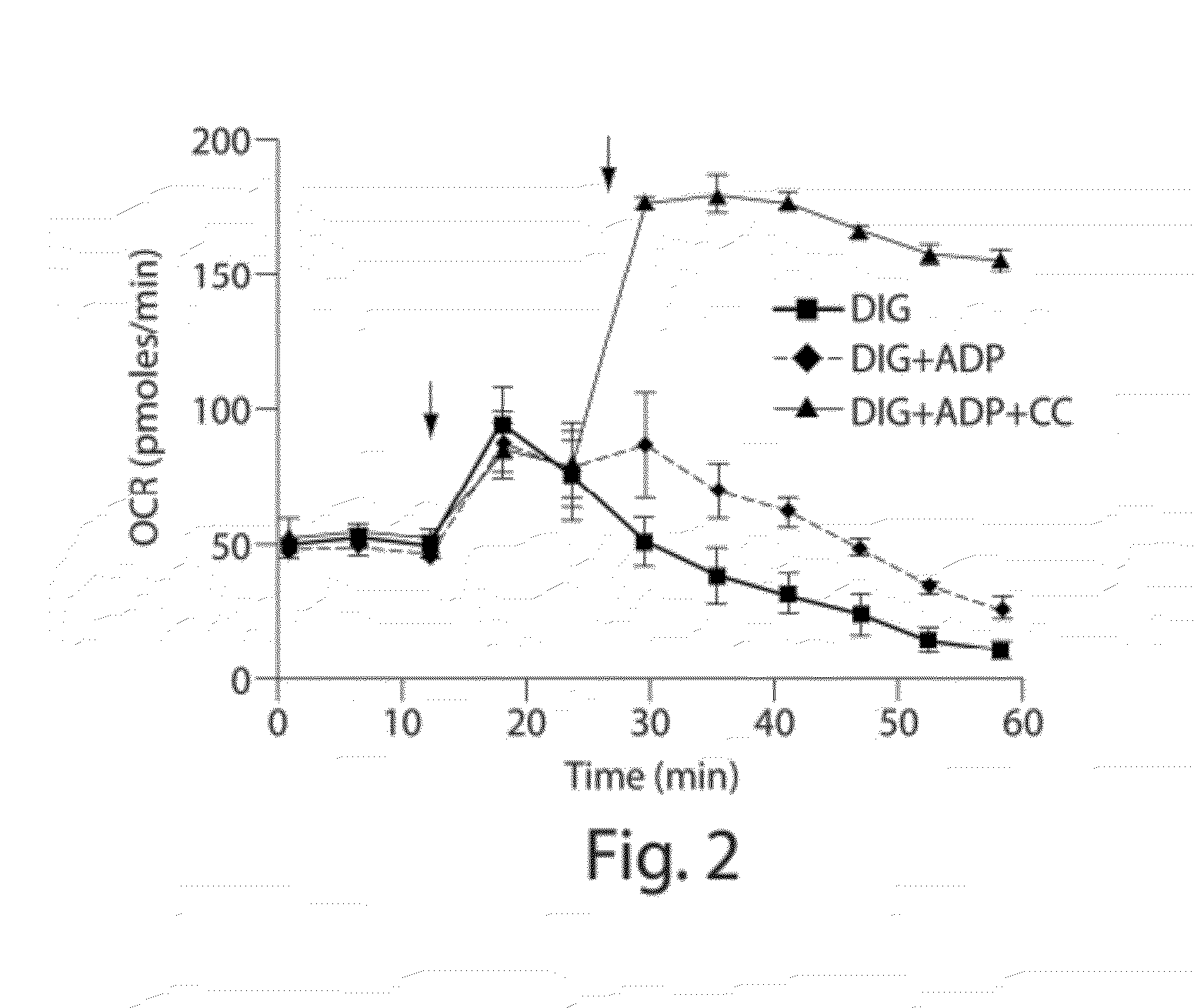
[0109]Digitonin concentration and respiration buffers were optimized for maximal ADP-stimulated respiration using succinate as substrate in the presence and absence of Cytochrome c. FIG. 2 shows representative data for conditions for INS1E cells that involve the addition of exogenous Cytochrome c. A Ca2+-free low K+ respiration buffer [20 mM TES pH7.4, 3.5 mM KCL, 120 mM NaCl, 0.4 mM KH2PO4, 1.2 mM Na2SO4, 2 mM MgSO4, 1 mM EGTA with 0.4% fatty acid free BSA] was used unless otherwise specified. Since, the intracellular K+ ion concentration is higher (˜120 mM), Ca2+-free high K+ buffers (25-120 mM NaCl replaced with equimolar KCL in the buffer) were tested to determine if mitochondria performed better. It was found that in certain instances high K+ buffers underperformed compared to the low K+ buffer using INS1E cells. Under the same conditions, the performance of two other commonly used permeabilizing agents, saponin, and alamethicin,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com