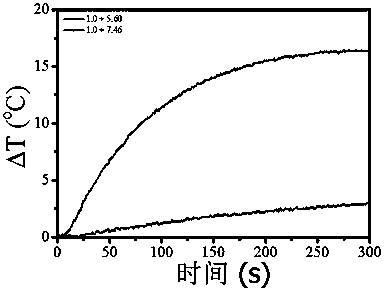
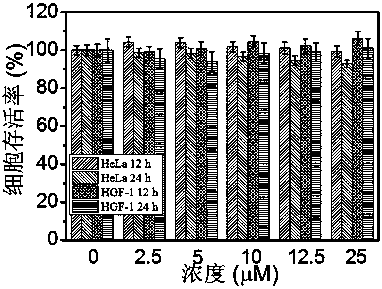
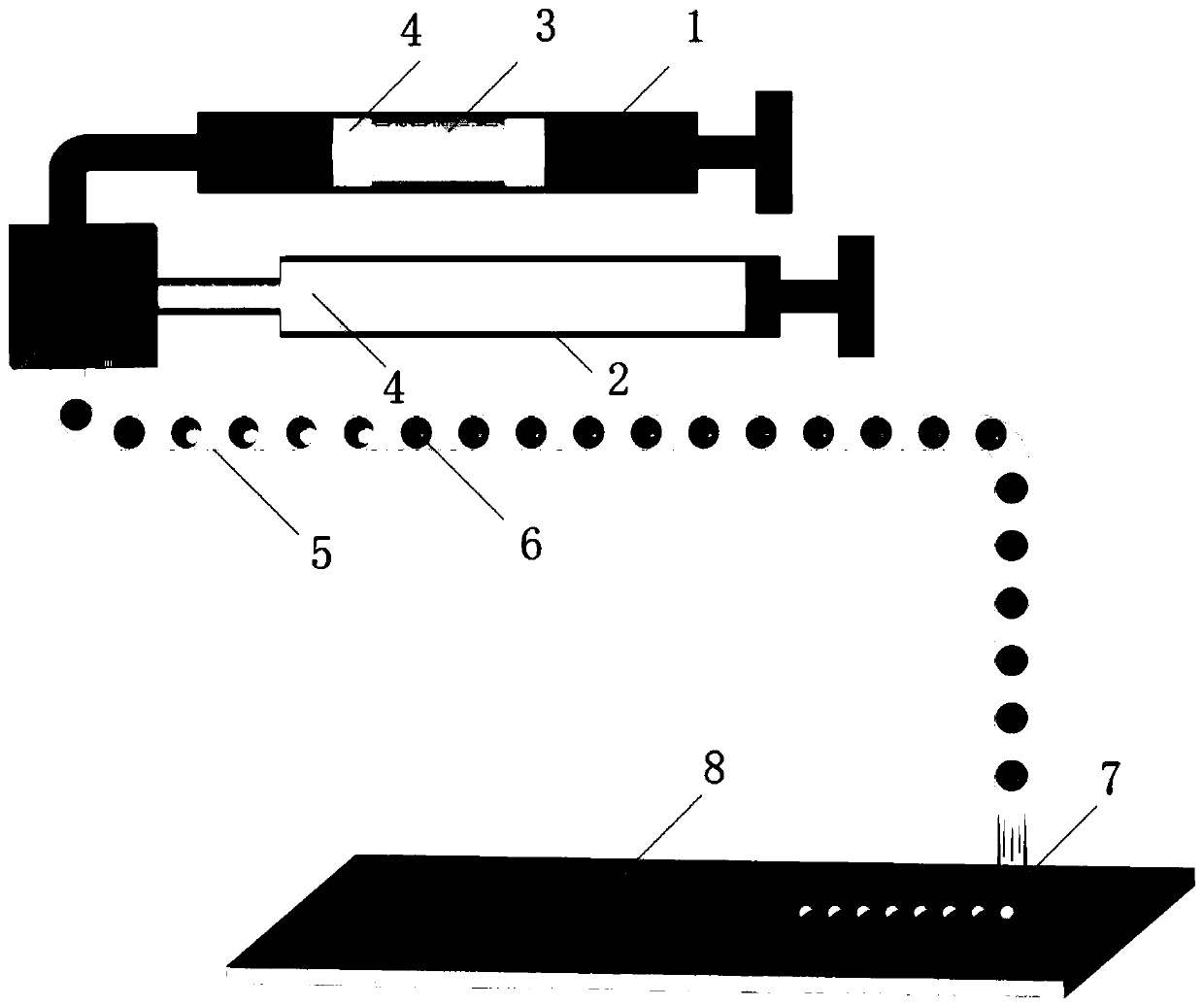
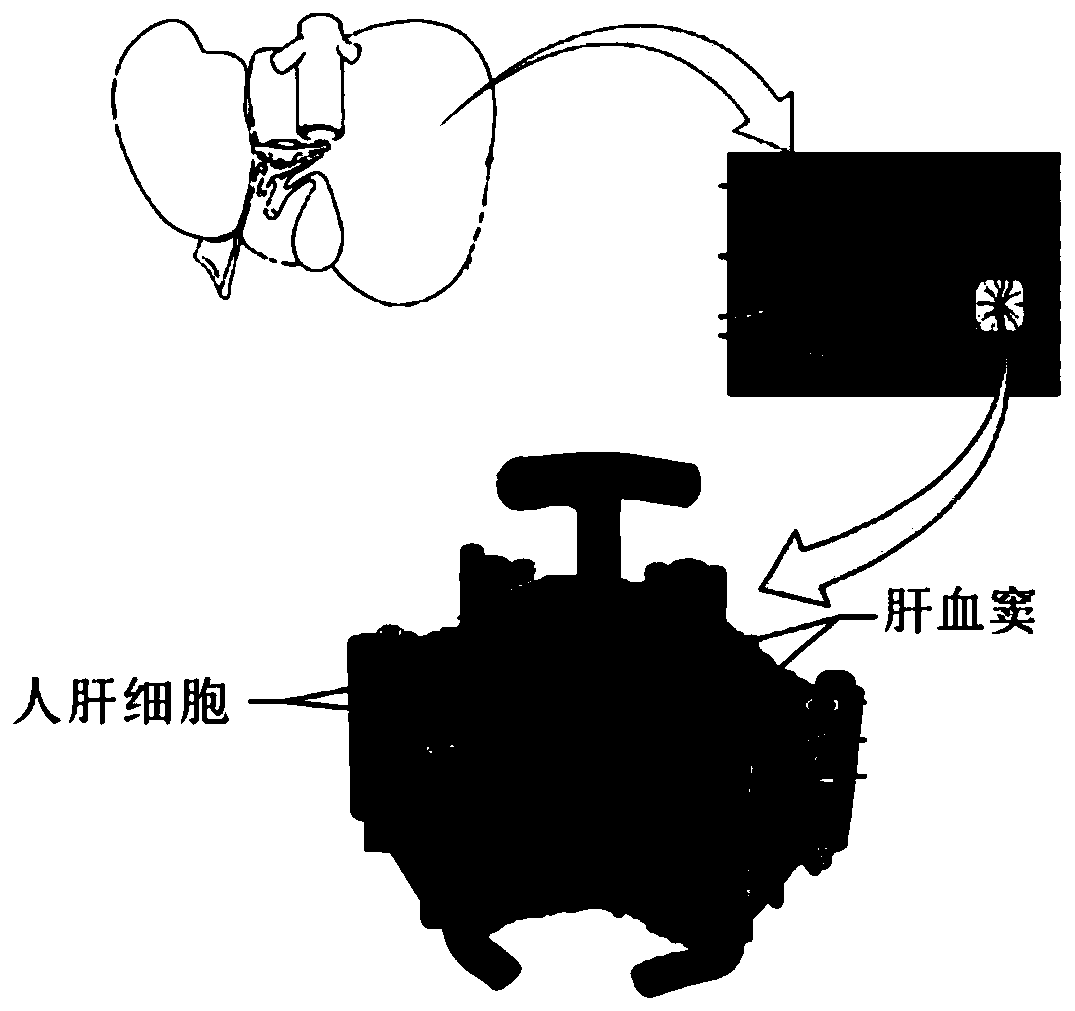
Patents
Literature
45 results about "Cellular Microenvironment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
BioMed Research International is a peer-reviewed, Open Access journal that publishes original research articles, review articles, and clinical studies covering a wide range of subjects in life sciences and medicine. ... The use of microfluidic systems in controlling the cellular microenvironment offers numerous advantages, such as the following ...
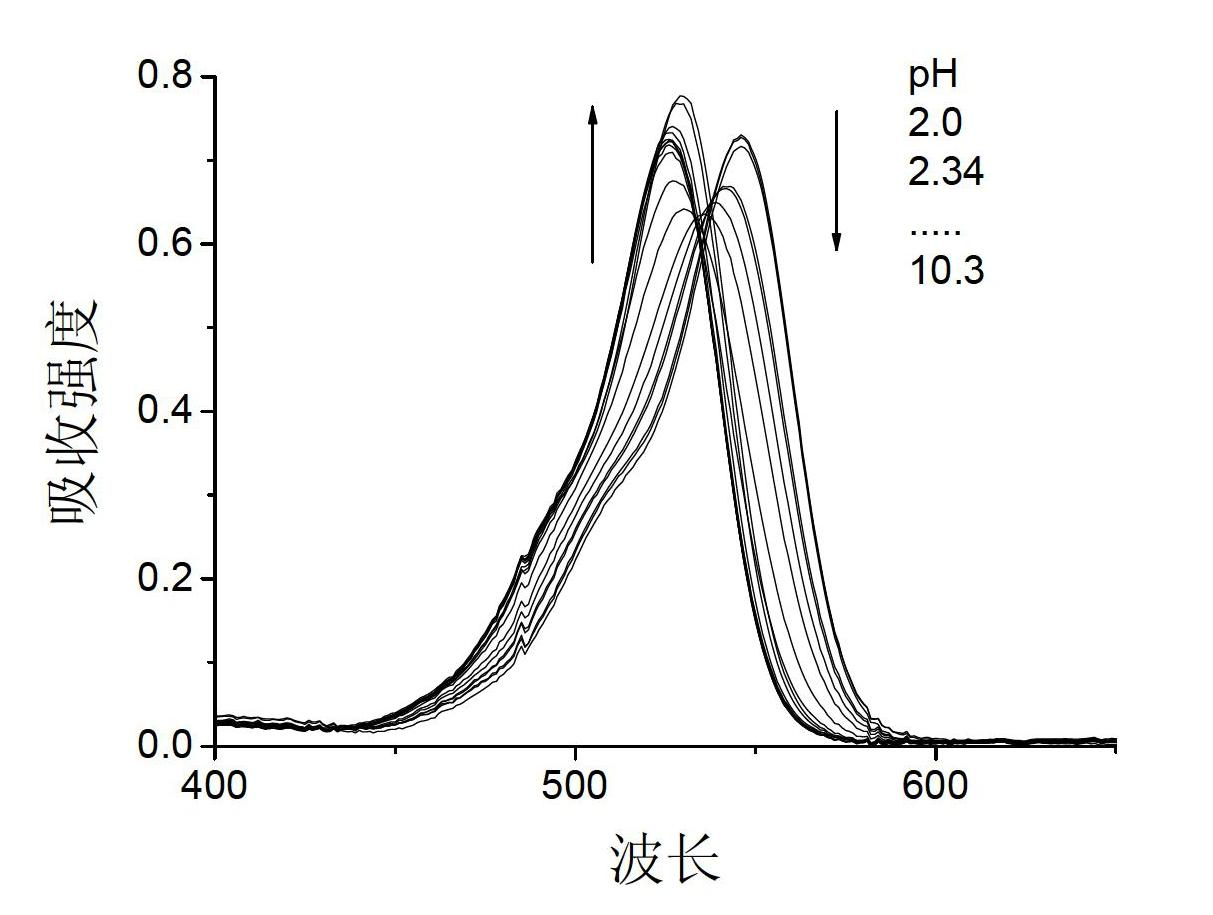
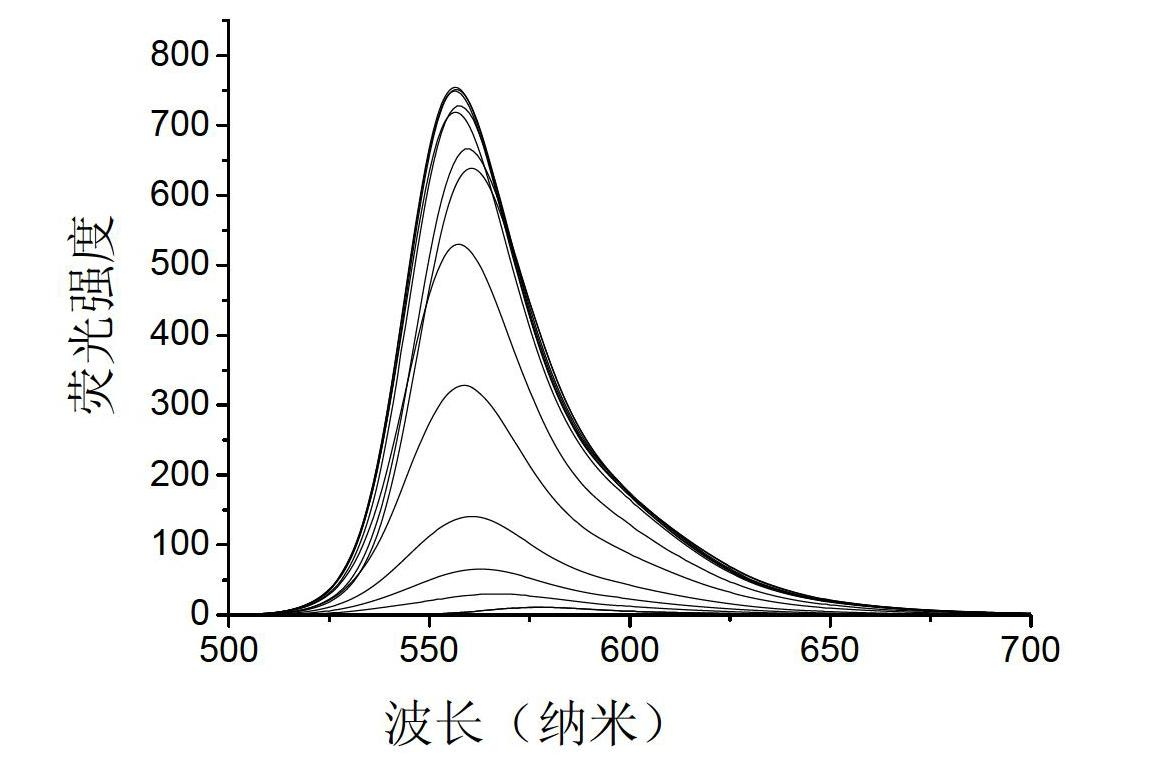
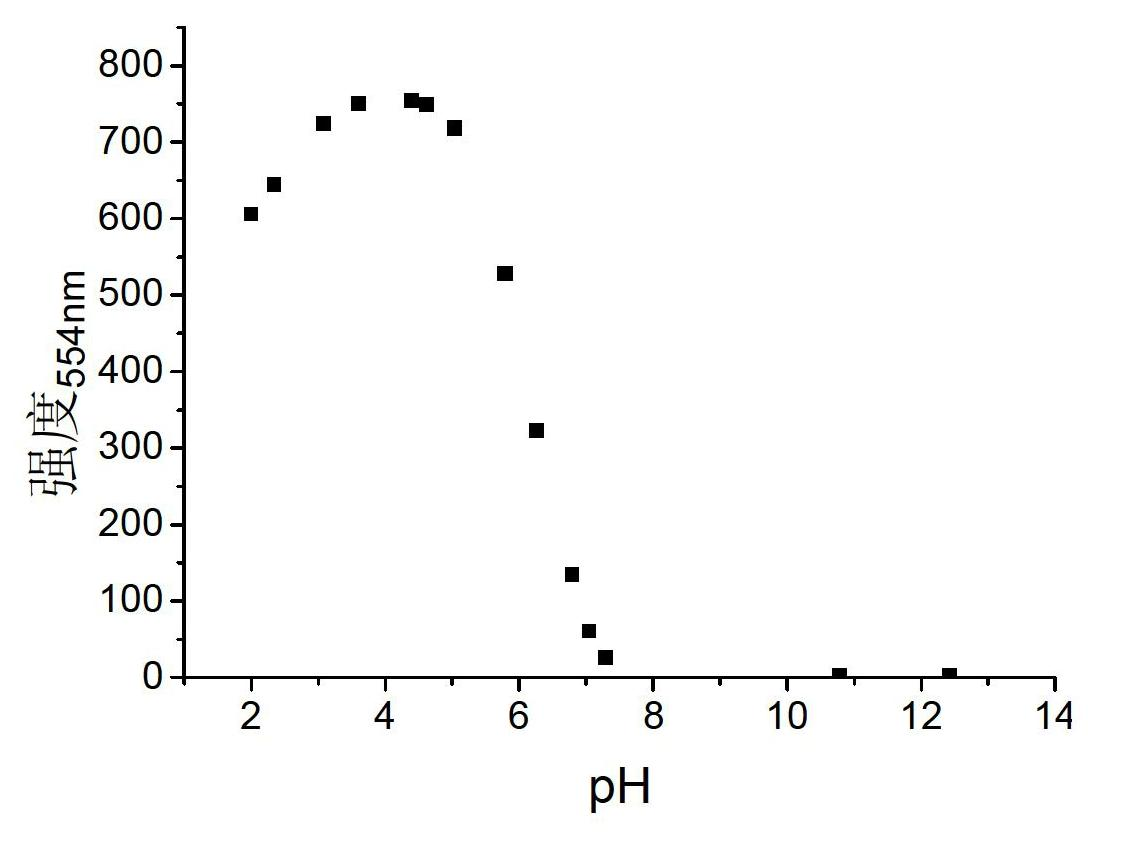
Rhodamine fluorescent probe sensitive to pH change, synthetic method and application
InactiveCN102659744AEasy to synthesizeHigh sensitivityOrganic chemistryMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorCellular MicroenvironmentSolubility
The invention relates to a class of rhodamine fluorescent probe sensitive to pH change. The fluorescent probe has the following structural general formula, the molecules of the fluorescent probe have a simple synthetic process and better chemical and light stability, fluorescence is sensitive to pH change, and the fluorescent probe has different protein kinase A (pKa) values by introducing different amine groups. Meanwhile, the rhodamine fluorescent probe sensitive to the pH change has very good water solubility and biological compatibility and higher fluorescent quantum yield and has the function of cellular localization. Meanwhile, the pH value of a cellular microenvironment can be detected.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
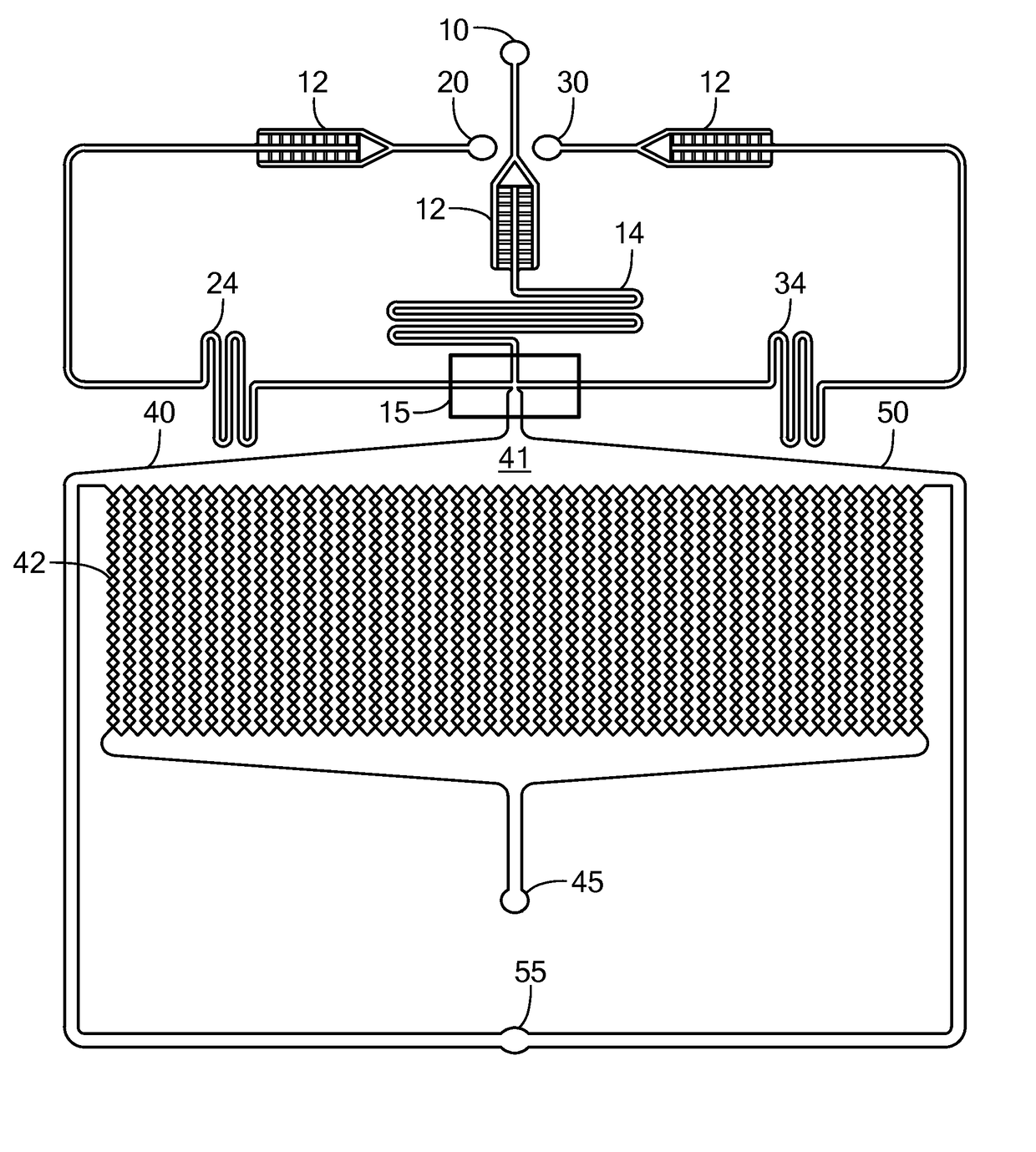
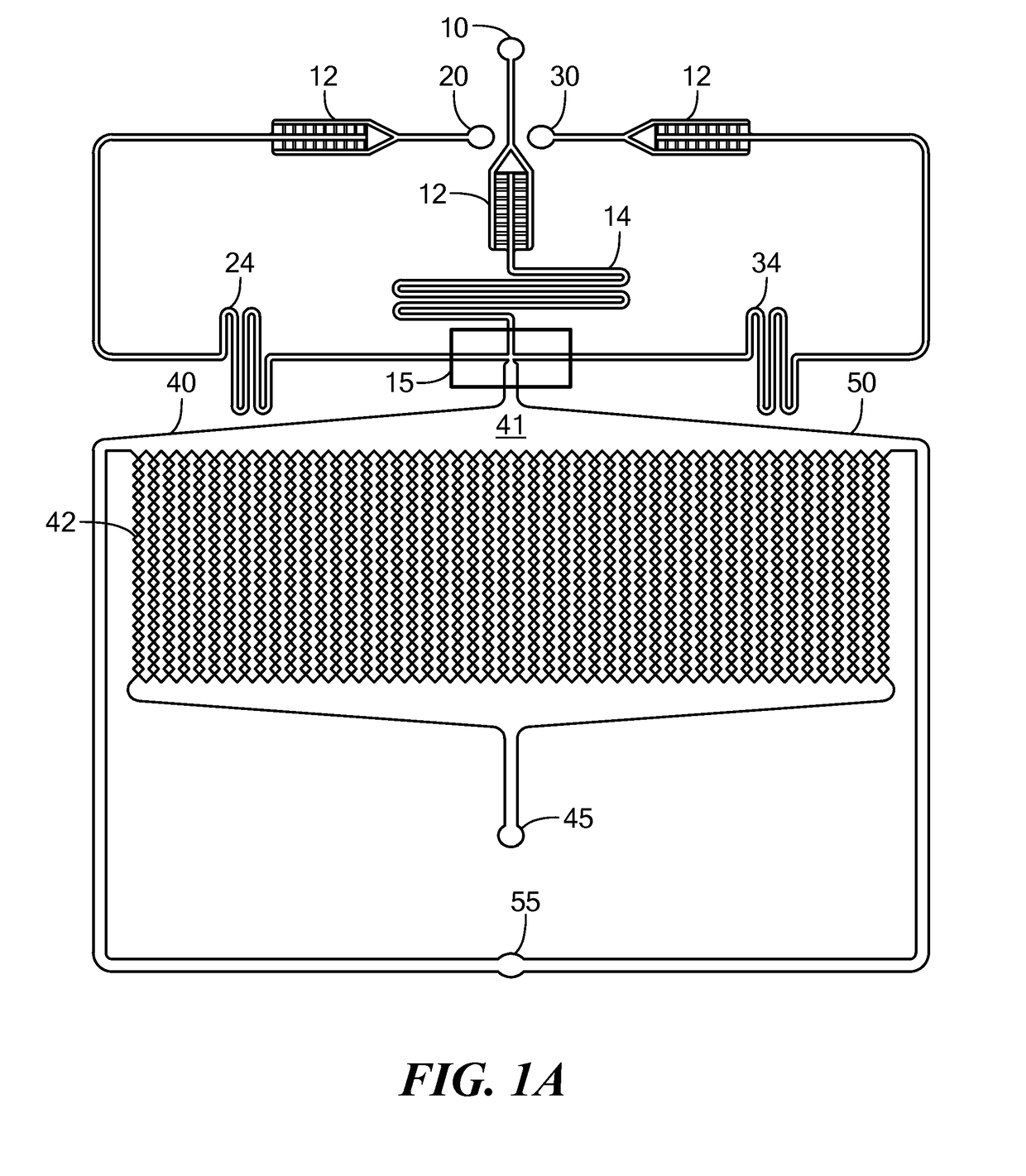
Microfluidic Device and Method for Analysis of Tumor Cell Microenvironments
ActiveUS20170199173A1High throughput generationRealistic drug responseLaboratory glasswaresCell culture supports/coatingCellular MicroenvironmentMicrofluidics
A microfluidic device provides high throughput generation and analysis of defined three-dimensional cell spheroids with controlled geometry, size, and cell composition. The cell spheroids of the invention mimic tumor microenvironments, including pathophysiological gradients, cell composition, and heterogeneity of the tumor mass mimicking the resistance to drug penetration providing more realistic drug response. The device is used to test the effects of antitumor agents.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
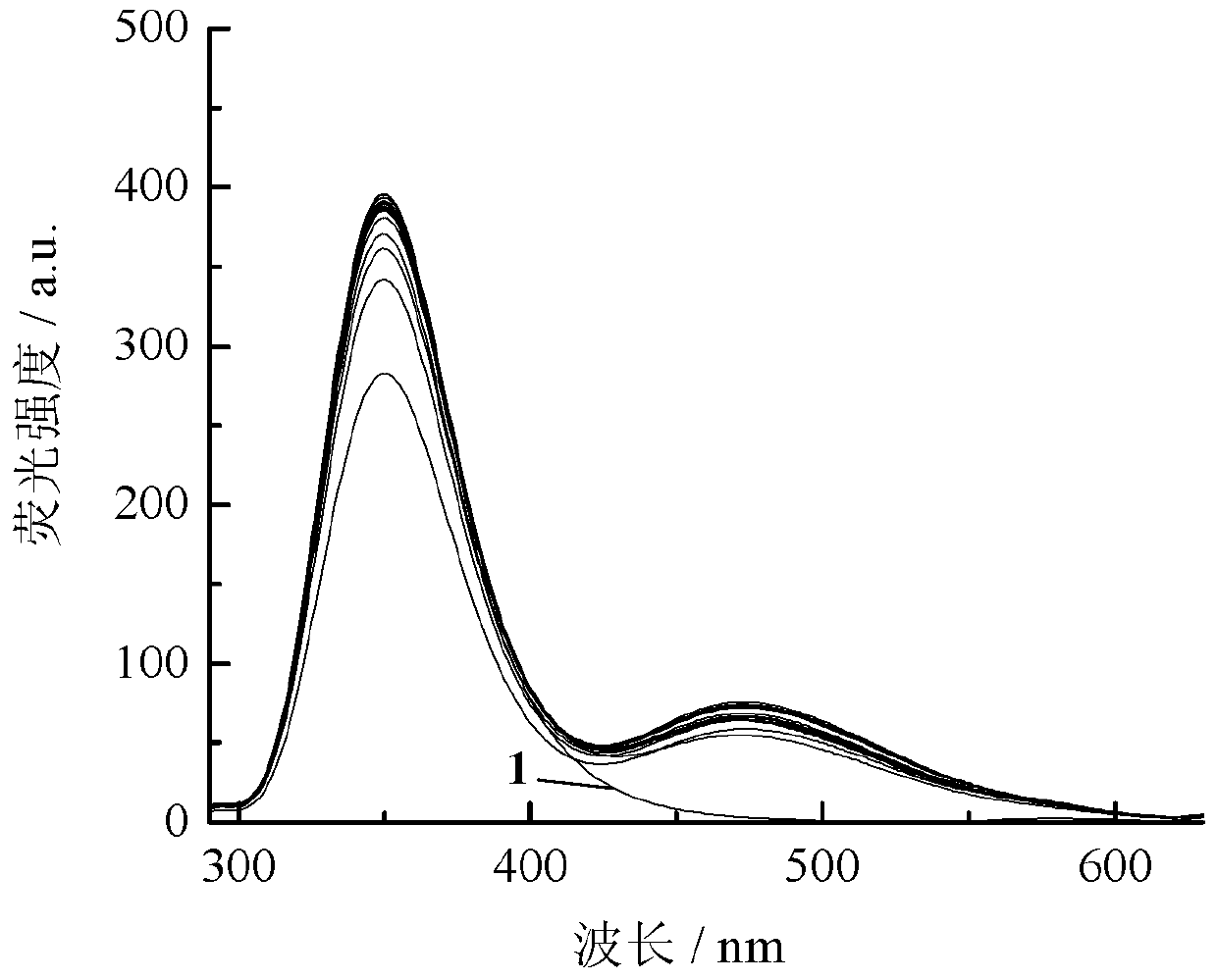
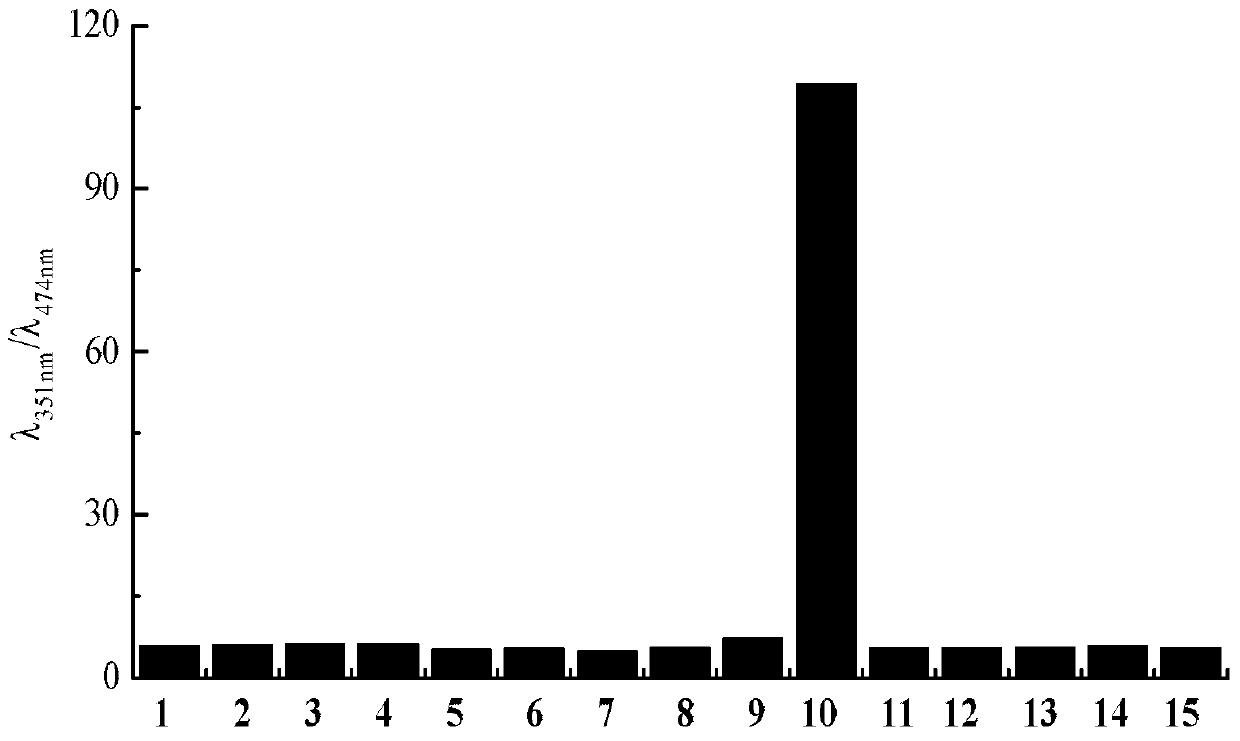
Dual-fluorophore ratio fluorescence molecular probe for non-fluorescence resonance energy transfer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103342698AHigh selectivityHigh sensitivityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceImage detectionFluorophore
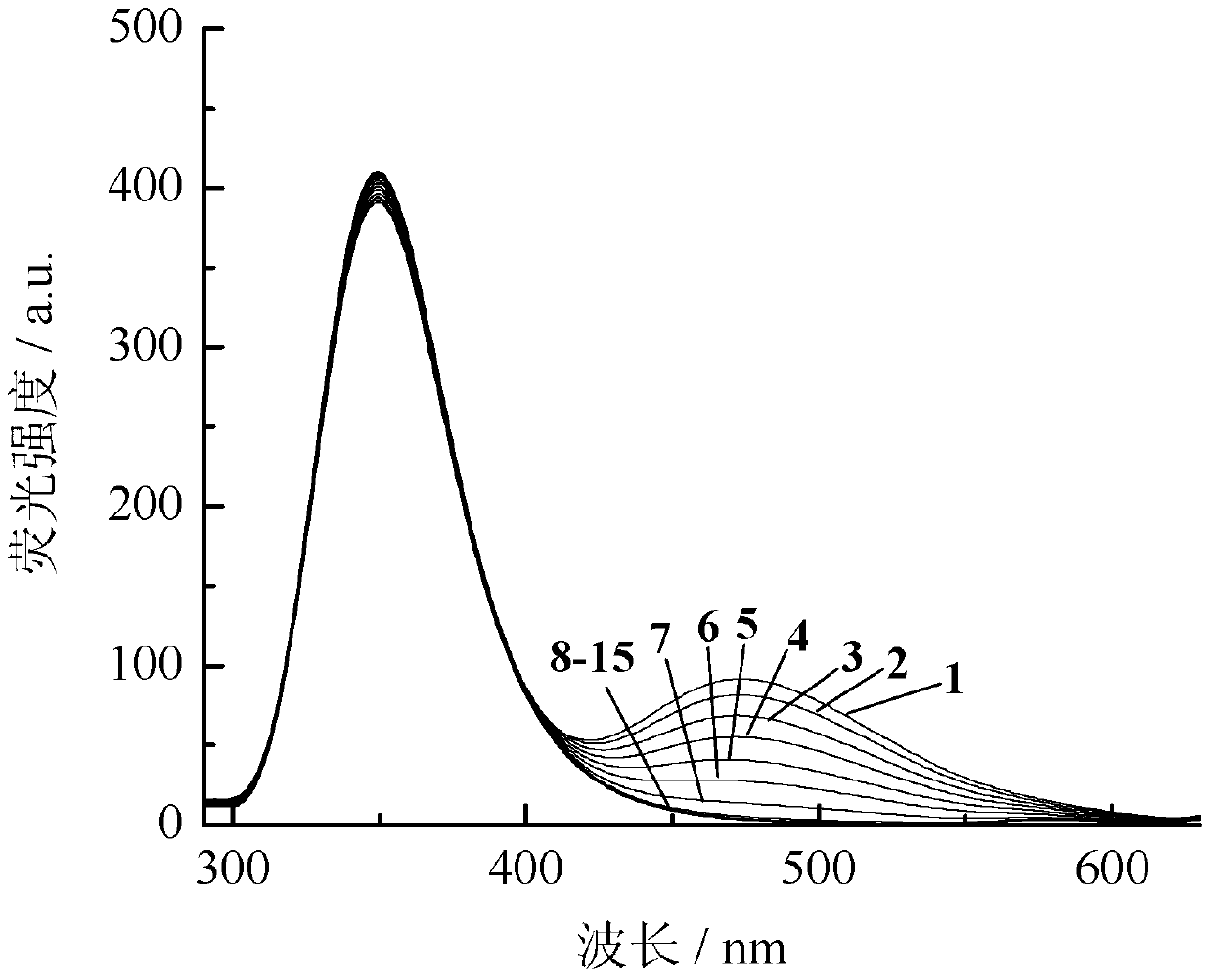
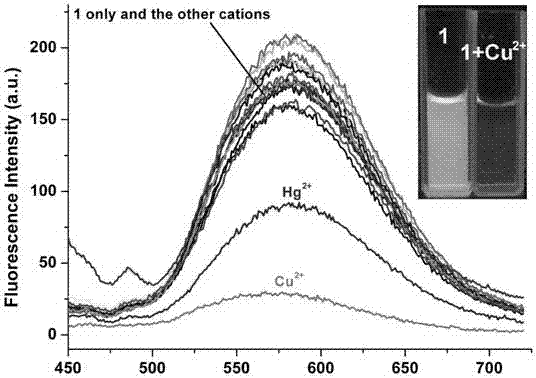
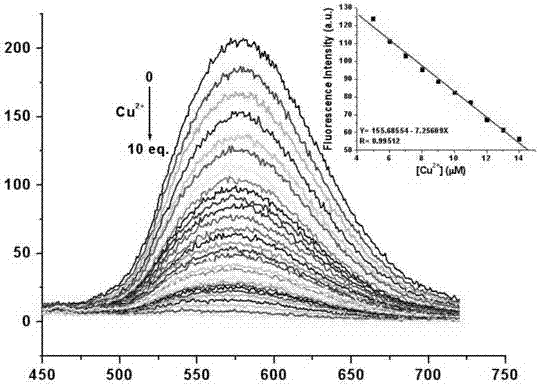
The invention discloses application of dual-fluorophore ratio fluorescence molecular probe for non-fluorescence resonance energy transfer, and relates to application of the dual-fluorophore ratio fluorescence molecular probe. The dual-fluorophore ratio fluorescence molecular probe disclosed by the invention is designed for solving the technical problems that due to energy loss caused by energy transfer between double fluorophores when the existing dual-fluorophore ratio fluorescence molecular probes are excited, the probes are poor in fluorescence, and not high in metal ion selectivity and sensitivity. The dual-fluorophore ratio fluorescence molecular probe for non-fluorescence resonance energy transfer is used for identifying fluorescence peak quenching of Cu2+, Cu2+ to the dual-fluorophore ratio fluorescence molecular probe for non-fluorescence resonance energy transfer at the position of 474nm, while the fluorescence peak strength at the wavelength of 351nm basically remains unchanged. The dual-fluorophore ratio fluorescence molecular probe disclosed by the invention can be applied to the fluorescence imaging detection of metal ions in biological tissue and cell microenvironments.
Owner:QIQIHAR UNIVERSITY
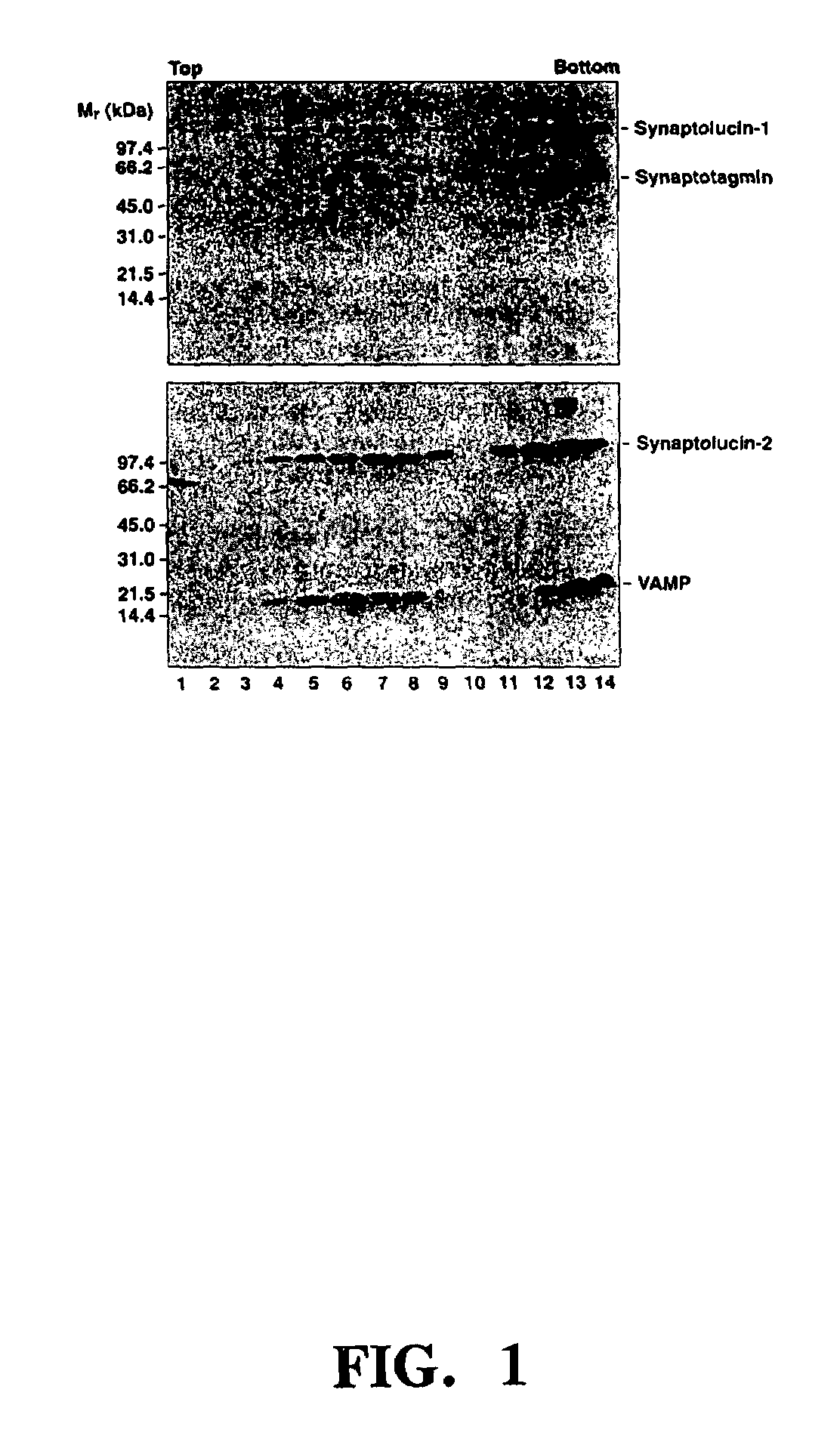
Hybrid molecules and their use for optically detecting changes in cellular microenvironments
The invention relates to methods and compositions which utilize the emission of light to monitor changes in microenvironments involving cells. The invention is especially useful for monitoring exocytotic activity such as detecting quantal release of synaptic vesicles. Fusion proteins of Cypridina luciferase and synaptotagmin-I or VAMP / synaptobrevin-2 were targeted to synaptic vesicles and, upon exocytosis, formed light-emitting complexes with luciferin present in the extracellular medium. Photon emissions in the presence of a depolarizing stimulus can be observed with these systems. pH-sensitive mutants of green fluorescent protein are also provided, which are useful for visualizing exocytosis and for imaging and measuring the pH of intracellular compartments.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
Fluorescent probe based on pyrrole-cumarin dihydrazone derivatives as well as preparation method and application of fluorescent probe
InactiveCN107382981AEasy to synthesizeRaw materials are easy to getOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceChemical structureCellular Microenvironment
The invention provides a fluorescent probe based on pyrrole-cumarin dihydrazone derivatives as well as a preparation method and application of the fluorescent probe. The chemical structural formula of the pyrrole-cumarin dihydrazone derivatives is shown in the description. The fluorescent probe based on the pyrrole-cumarin dihydrazone derivatives is prepared by using condensation reaction; the fluorescent probe is simple to synthesize and easy for obtaining raw materials; the fluorescent probe shows higher selective fluorescence identification performance for copper ions in multiple common metal ions, thus enabling the fluorescence of a solution containing the copper ions to be significantly quenched. More importantly, the fluorescent probe also can be used for biological tissues for detecting the fluorescence imaging of the copper ions in cellular microenvironment; the fluorescent probe has the characteristics of being rapid, simple and convenient and high in sensitivity and selectivity as well as wide potential application value.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Photothermal reagent for identifying tumor cells through pH control and preparation method and application thereof
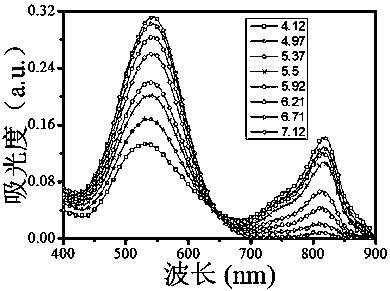
InactiveCN105693590APH sensitiveRealize photothermal therapyOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryCellular MicroenvironmentNear infrared laser
The invention belongs to the technical field of photothermal reagents, and particularly relates to a photothermal reagent and synthesis thereof and application of serving as the photothermal reagent under the excitation of a near-infrared 808-nm laser.The designed compound has a property of pH sensitivity and can identify tumor cells by responding to a cellular microenvironment.In the tumor cells, the compound in a weak acid environment can serve as the photothermal reagent to achieve a photothermal therapy under the induction of near-infrared light.In normal cells, due to the fact that the normal cells are alkalescent, a photothermal reaction almost does not exist under the induction of the near-infrared light.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
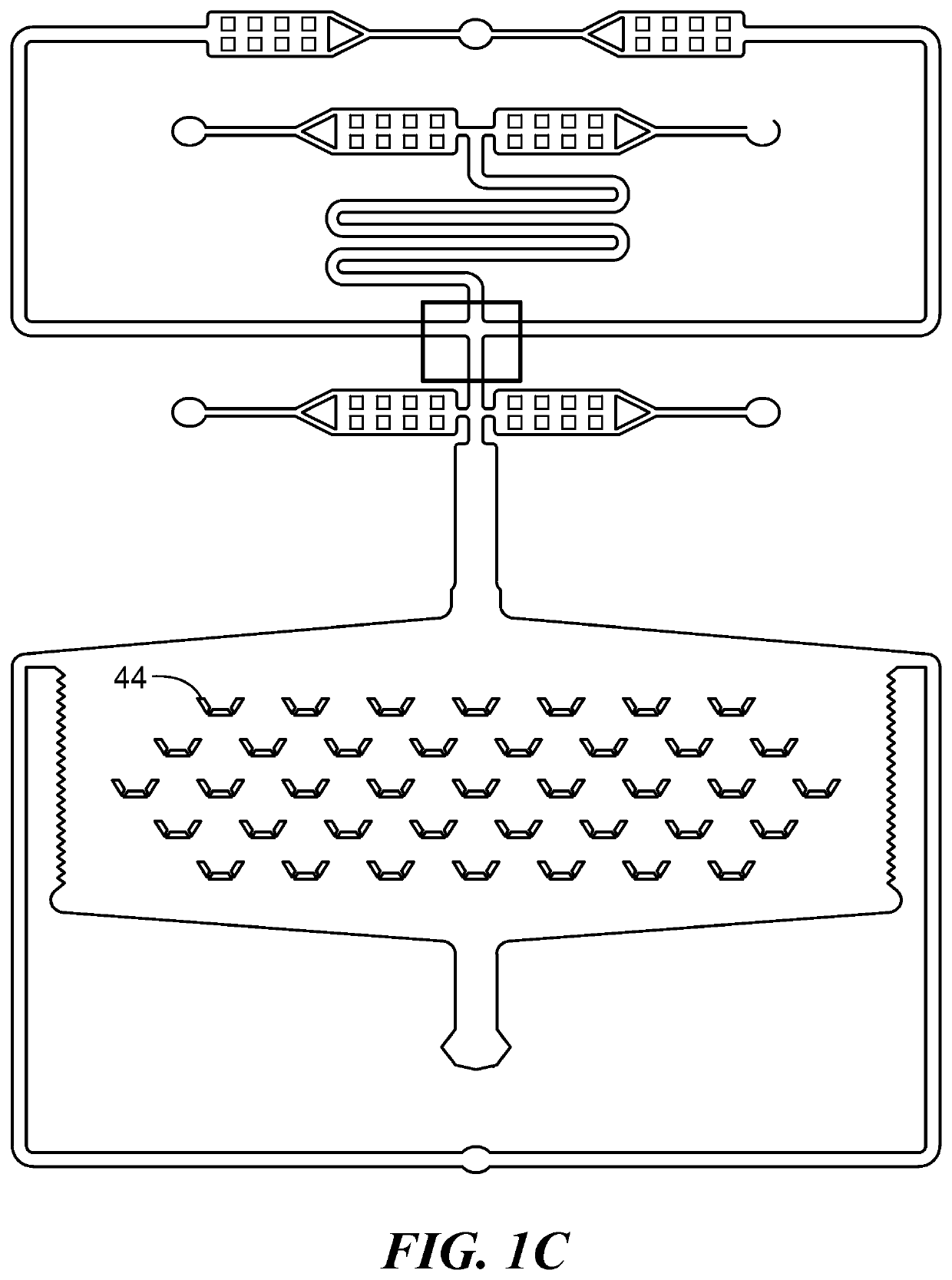
3D voxel printing device based on cell soft spheres and method thereof
ActiveCN111269834AReduce hardnessEfficient reductionAdditive manufacturing apparatusHepatocytesCellular MicroenvironmentTissue architecture
The invention discloses a 3D voxel printing device based on cell soft spheres and a method thereof. The device comprises a water phase input part, an oil phase input part and a microfluidic microtube,wherein the water phase input part inputs an extracellular matrix material loaded with cells, namely bio-ink, into the microfluidic microtube; and the oil phase input part synchronously inputs a low-viscosity and low-boiling-point oil phase meeting set requirements into the microfluidic microtube. The extracellular matrix material loaded with the cells is separated into monodisperse microdropletsembedded with the cells through an oil phase, the microdroplets are gelled into cell soft spheres in the flowing process in the microtube, the cell soft spheres are sequentially shot onto a substrateby utilizing rapid expansion and volatilization of the oil phase at an outlet of the microfluidic microtube, and the cell soft spheres are adhered together through an incompletely gelled ink material. An in-vitro model capable of highly reducing the human organ or tissue structure and the cell microenvironment can be printed under the condition that a printing material does not contain a biological inert material for assistance.
Owner:杭州济扶科技有限公司
Compositions, devices and methods for the control in vitro of chemical microambient in cell cultures
PendingCN110036106AEffective therapeutic strategiesAdjust oxygen gradientCulture processCell culture mediaCellular MicroenvironmentChemical compound
The present invention relates to compositions comprising a polymeric matrix or a gel containing functional enzymes capable of re-creating under culture conditions the cell microenvironment existing invivo. The present invention also relates to devices for cell cultures comprising such compositions, in particular hydrogel and the use thereof to control the chemical microenvironment of a cell culture or mimic physiological or pathological conditions of the in vivo cells. The compositions and the devices described herein could be also used in vitro for evaluating the therapeutic effect of a compound on a determined cell line or on primary cells.
Owner:ALMA MATER STUDIORUM UNIV DI BOLOGNA
Double-cell and microenvironment-sensitive anti-tumor drug-loaded nanocapsule and preparation method
ActiveCN105878212AEffectively play the role of medicineAcid sensitiveOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsHigh concentrationCellular Microenvironment
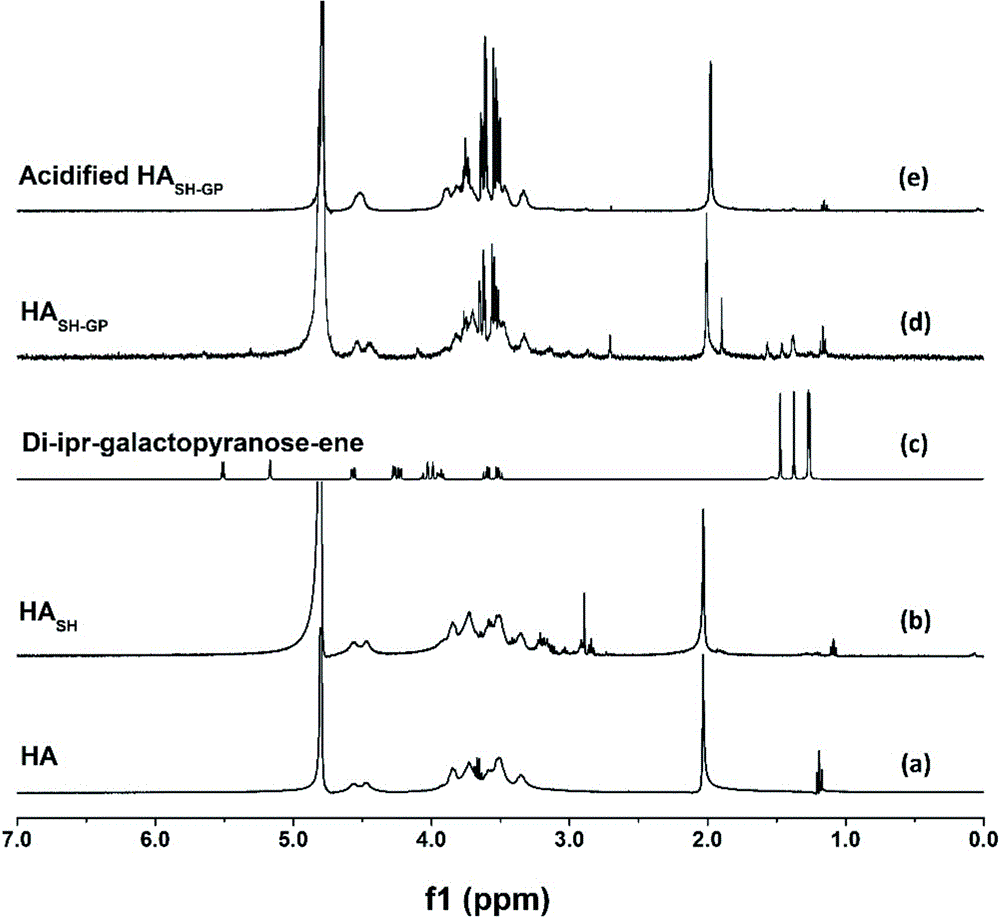
The invention provides a preparation method of a double-cell and microenvironment-sensitive anti-tumor drug-loaded nanocapsule. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a thiol hyaluronic acid; (2) preparing vinyl-functional second-generation isopropylidene-protected galactopyranose; (3) grafting the second-generation isopropylidene-protected galactopyranose on the thiol hyaluronic acid; and (4) preparing the drug-loaded nanocapsule. The drug-loaded nanocapsule prepared by the method is high in compatibility with a tumor cell, has dual high-sensitive responsiveness on high-concentration glutathione and acid environment, achieves high-selectivity rapid release in the tumor cell, and is high in anti-tumor efficiency and good in safety.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Method for screeing cancer metastasis inhibitor using culture of cells or spheroidically aggregated cells in which lysyl-trna synthetase is regulated to be expressed or unexpressed
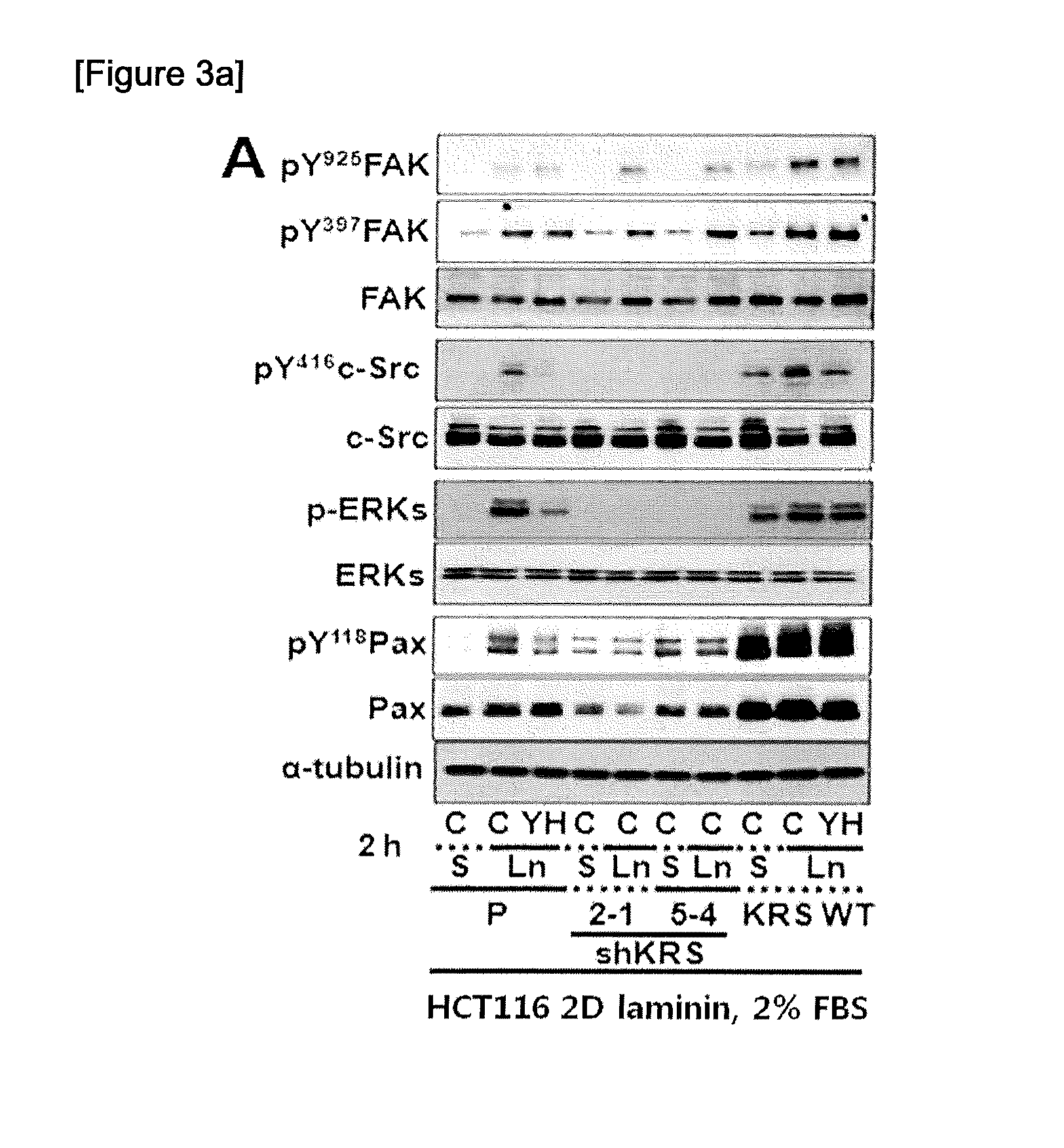
InactiveUS20160146815A1Increase valueEfficient processCompound screeningApoptosis detectionAminoacyl-tRNA synthetasesHCT116 Cell
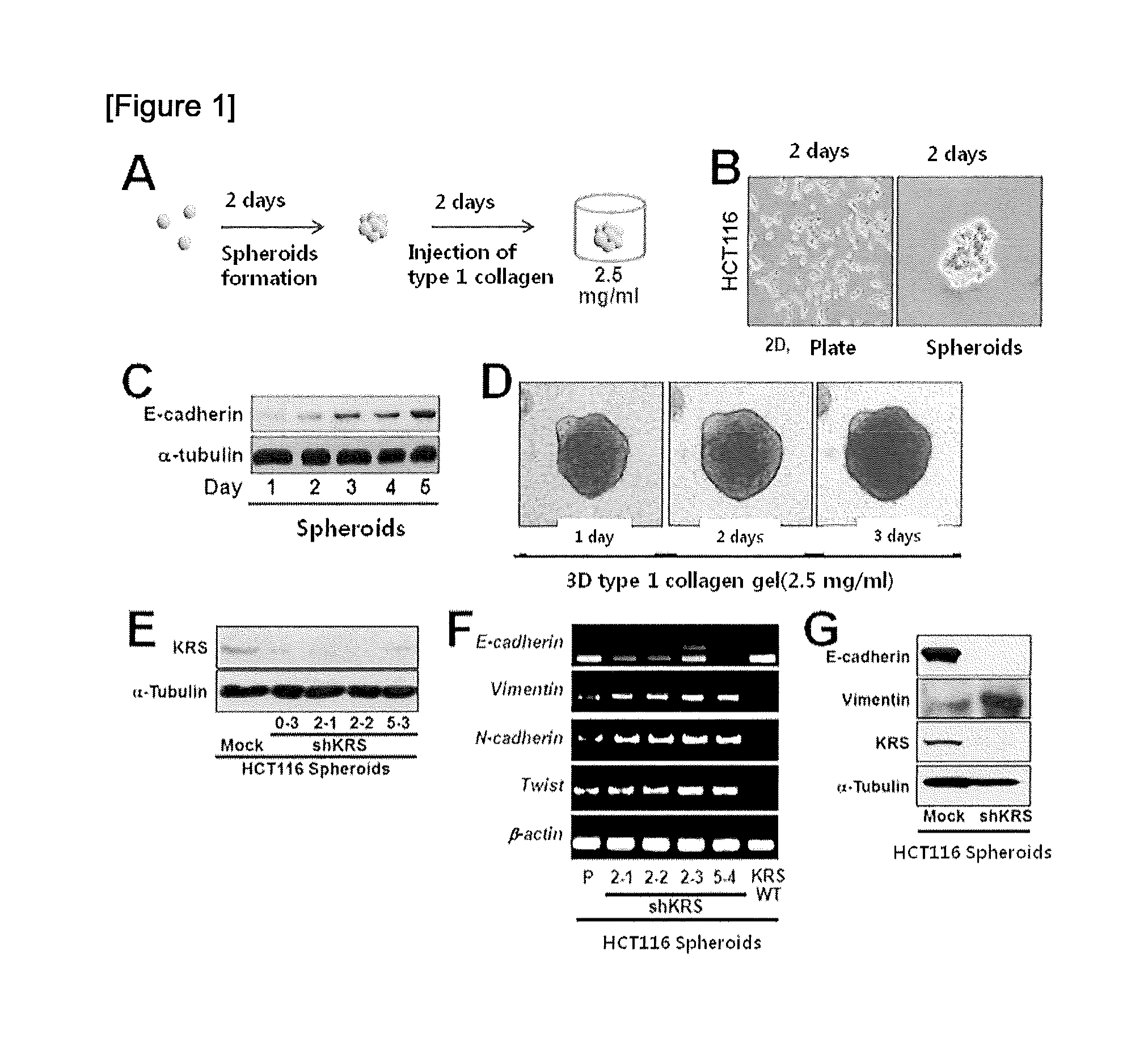
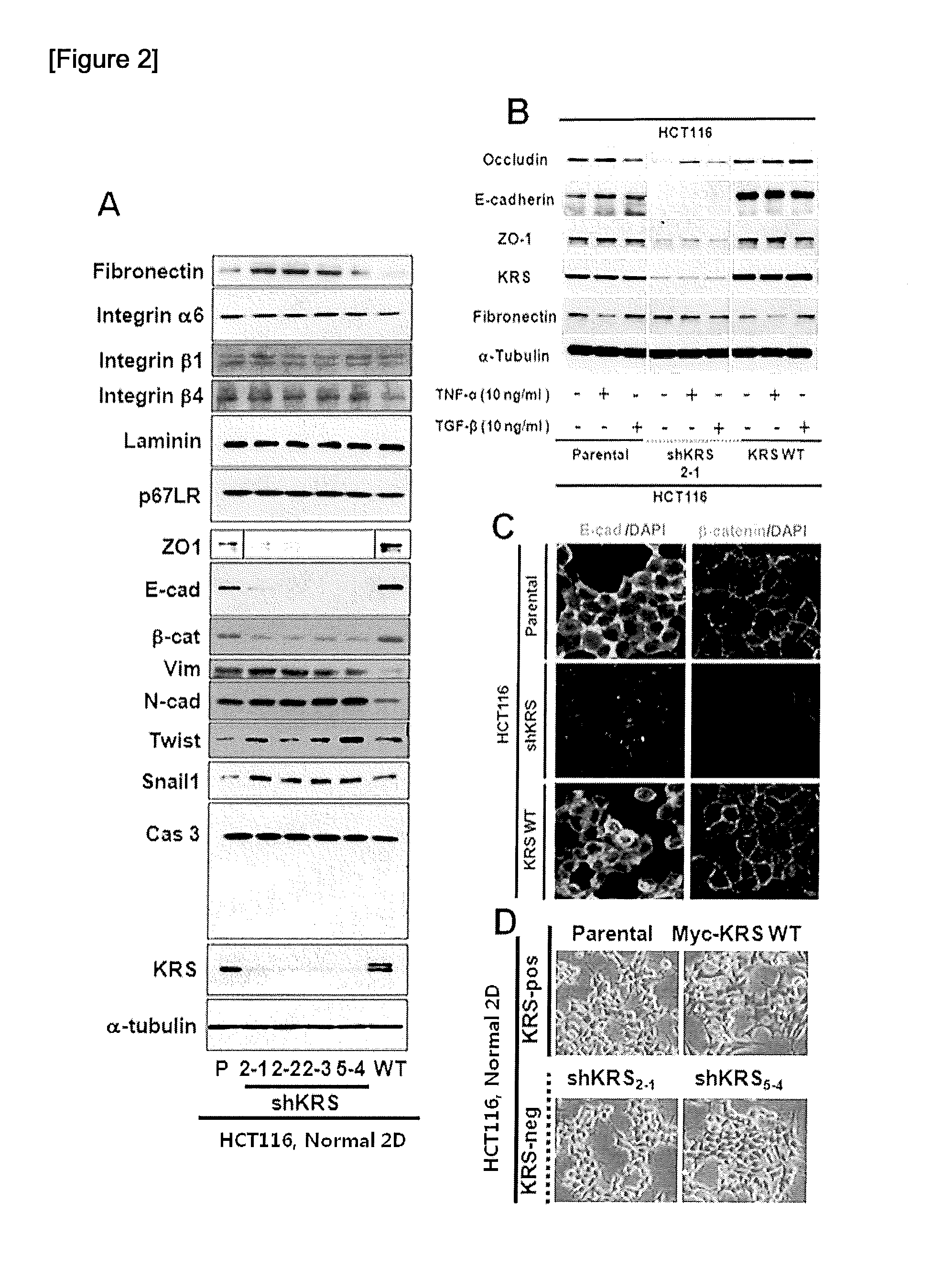
The present invention relates to a method for scanning a cancer metastasis inhibitor by analyzing the activity of lysyl-tRNA synthetase (KRS) in a cancer cell line cultured in a three-dimensional collagen gel environment, and to a method for monitoring the dissemination of cancer cells from aggregated cancer cells, and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition, migration, invasion, and metastasis of cancer cells. Specifically, it was verified that, in the case where a cell line or a spheroidically aggregated cell line, in which KRS has been regulated to be expressed or unexpressed, was constructed by using various colorectal cancer cells including HCT116 cell line and then cultured in a two-dimensional environment, the incomplete epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition phenotype (incomplete ECM phenotype) was induced in the cell line inhibiting KRS expression, and the inhibition of KRS expression inhibited cell-extracellular matrix (ECM) adhesion and cell-ECM signaling activity. In addition, it was verified that, in the case where the constructed spheroid cell line was cultured in an aqueous environment or a three-dimensional collage gel culture environment, the inhibition of KRS expression induced cells into mesenchymal cells but failed to reach the disintegration of cell-cell adhesion; inhibited the cell-ECM adhesion and the related signaling activity, causing the inhibition of the dissemination of cells from spheroid cells cultured in a three-dimensional collagen gel culture environment; and failed to induce the dissemination of cells through TGFβ1 present in the cellular microenvironment. Thus, the present invention can be used as a method for screening a cancer metastasis inhibitor and a method for monitoring the migration, invasion and metastasis of cancer cells, and will be useful as one of the screening methods capable of creating low-cost, high-efficient added value at the time of pre-clinical tests required for drug development.
Owner:MEDICINAL BIOCONVERGENCE RES CENT
Nucleic Acid Based Sensor and Methods Thereof
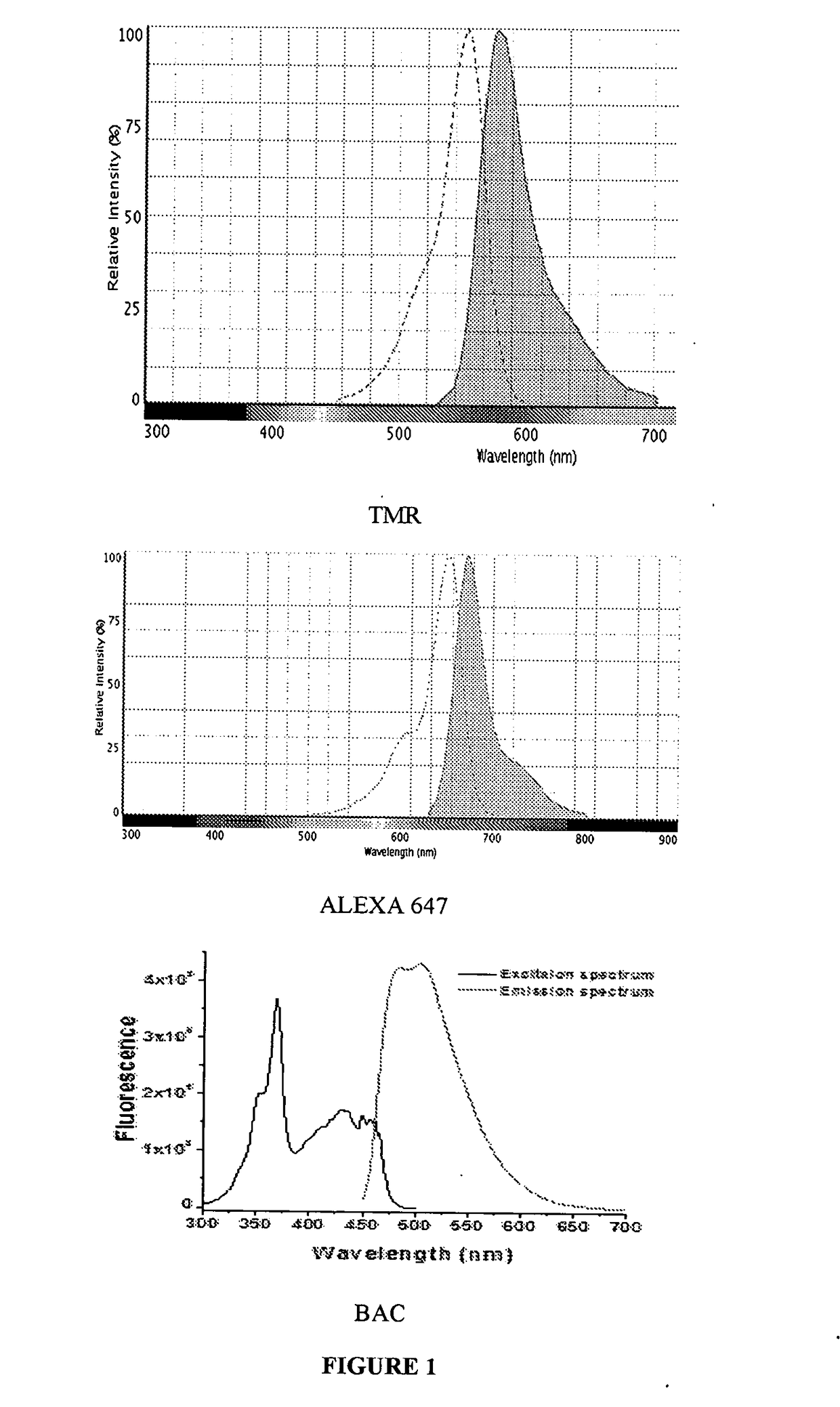
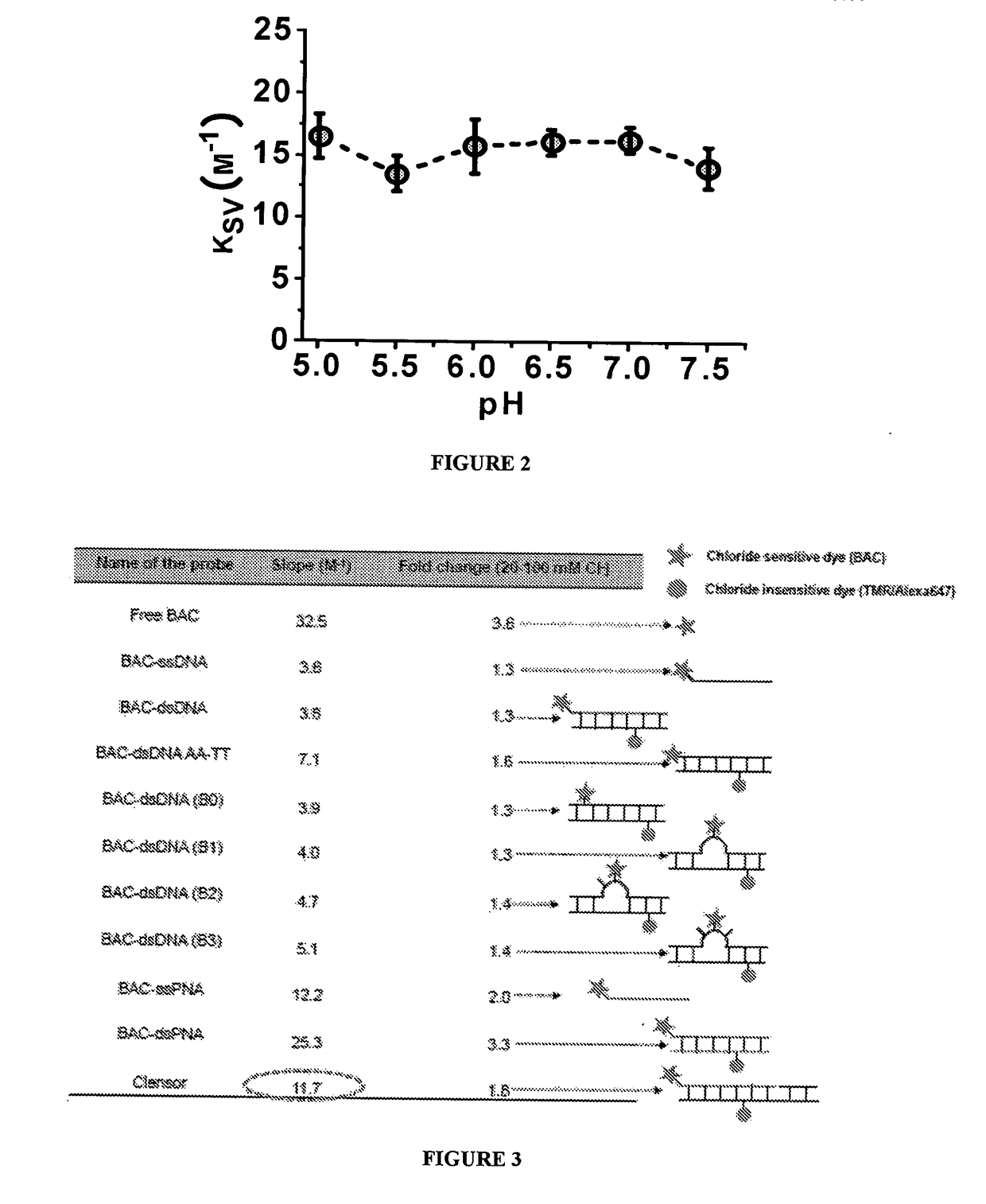
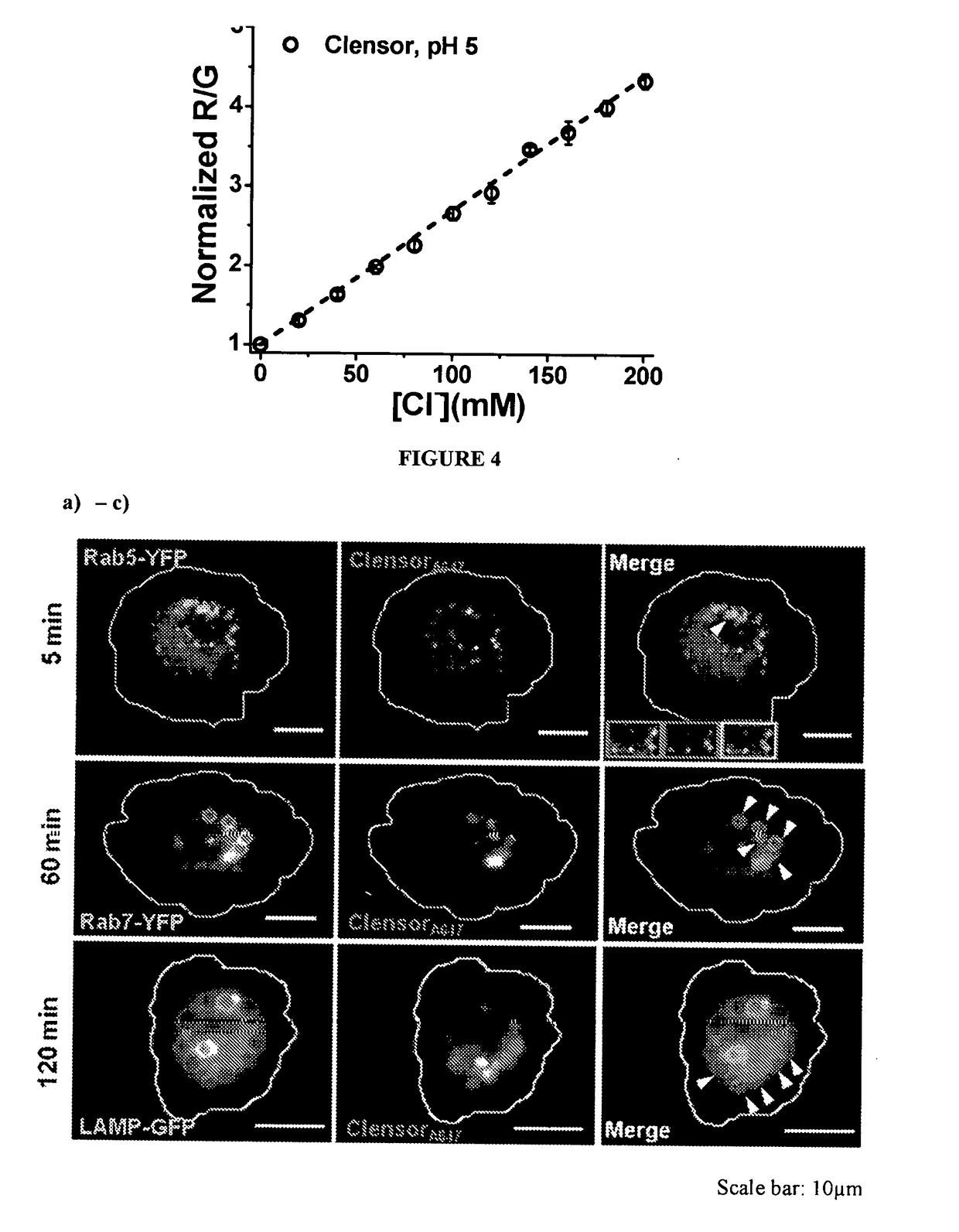
The present disclosure relates to a nucleic acid based sensor, comprising a sensing 5 module, a normalizing module and a targeting module. It also relates to a method of obtaining and targeting the sensor and its use to identify and optionally quantify a target in a specific cellular microenvironment.
Owner:NAT CENT FOR BIOLOGICAL SCI
Methods for therapeutics prescreening in bodily fluids
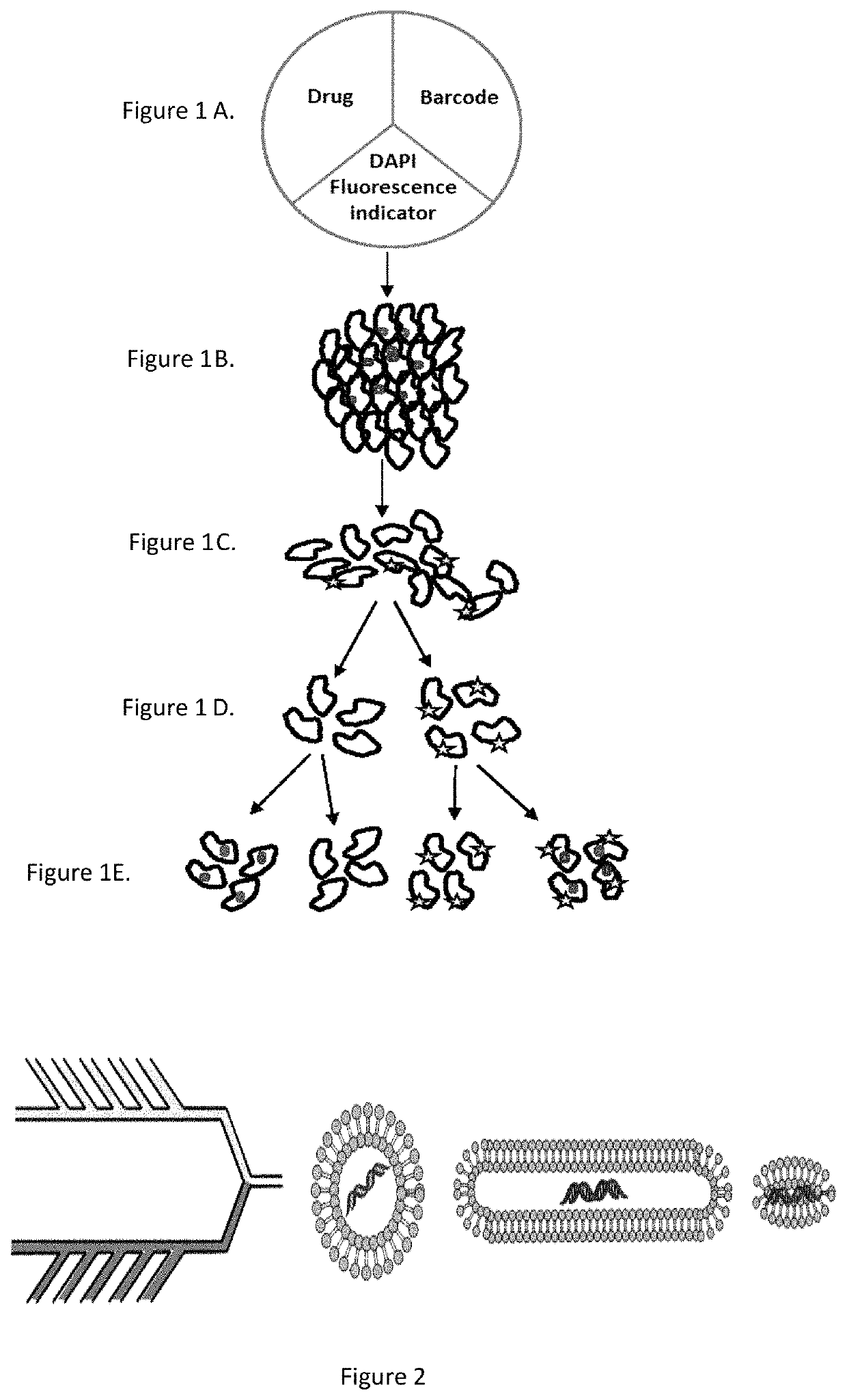
PendingCN111051521AMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisCellular MicroenvironmentPharmaceutical drug
A method for using bodily fluids in determining the cell-specific potency of drugs is provided. A composition comprising a plurality of types of carriers, wherein each carrier comprises a single-celllethal amount of a therapeutic agent and a unique barcode identifying that agent and wherein the composition comprises equal numbers of each carrier type, equal concentrations of the agent and equal concentrations of each barcode is also provided. Further, methods useful for studying the therapeutic profile of one or more drugs within a cell microenvironment, including but not limited to a tumor,are provided.
Owner:BARCODE DIAGNOSTICS LTD
Preparation method of cellular microenvironment pH-sensitive micelle
InactiveCN104415011AHas a nanoscale structureLow critical micelle concentrationOrganic active ingredientsNanomedicineFreeze-dryingTert butyl
The invention discloses a preparation method of a cellular microenvironment pH-sensitive micelle. The preparation method comprises the following steps: polymerizing acrylic acid by utilizing an atom transfer radical polymerization method, thus obtaining polyacrylic acid; modifying polyacrylic acid by utilizing folic acid molecules; polymerizing O-tert-butyl-L-threonine carboxylic acid anhydride by utilizing a ring opening polymerization method, thus obtaining poly(O-tert-butyl-L-threonine); grafting adriamycin onto poly(O-tert-butyl-L-threonine) via hydrazone bonds; connecting polyacrylic acid with poly(O-tert-butyl-L-threonine) with bonds through click chemistry, thus obtaining block copolymers; after dissolving the block copolymers in tetrahydrofuran respectively, transferring the solutions into a dialysis bag, dialyzing the solutions with pure water, and filtering the dialysate with a filter membrane; freeze-drying the solutions after filtration, thus obtaining a drug loading micelle. The drug carrier micelle has a core / shell double-layer structure, wherein the outer layer is formed by hydrophilic polyacrylic acid, and the inner layer is a drug molecule coated layer. The material has the advantages that the material belongs to nanoparticles; the drug can achieve targeting delivery of cancer cells and pH-sensitive release in the cancer cells; the material has high drug loading capacity and good stability; the toxic and side effects of the drug on normal tissues and organs can be effectively reduced via the targeting function of the drug.
Owner:CHENGDU LVKE HUATONG TECH
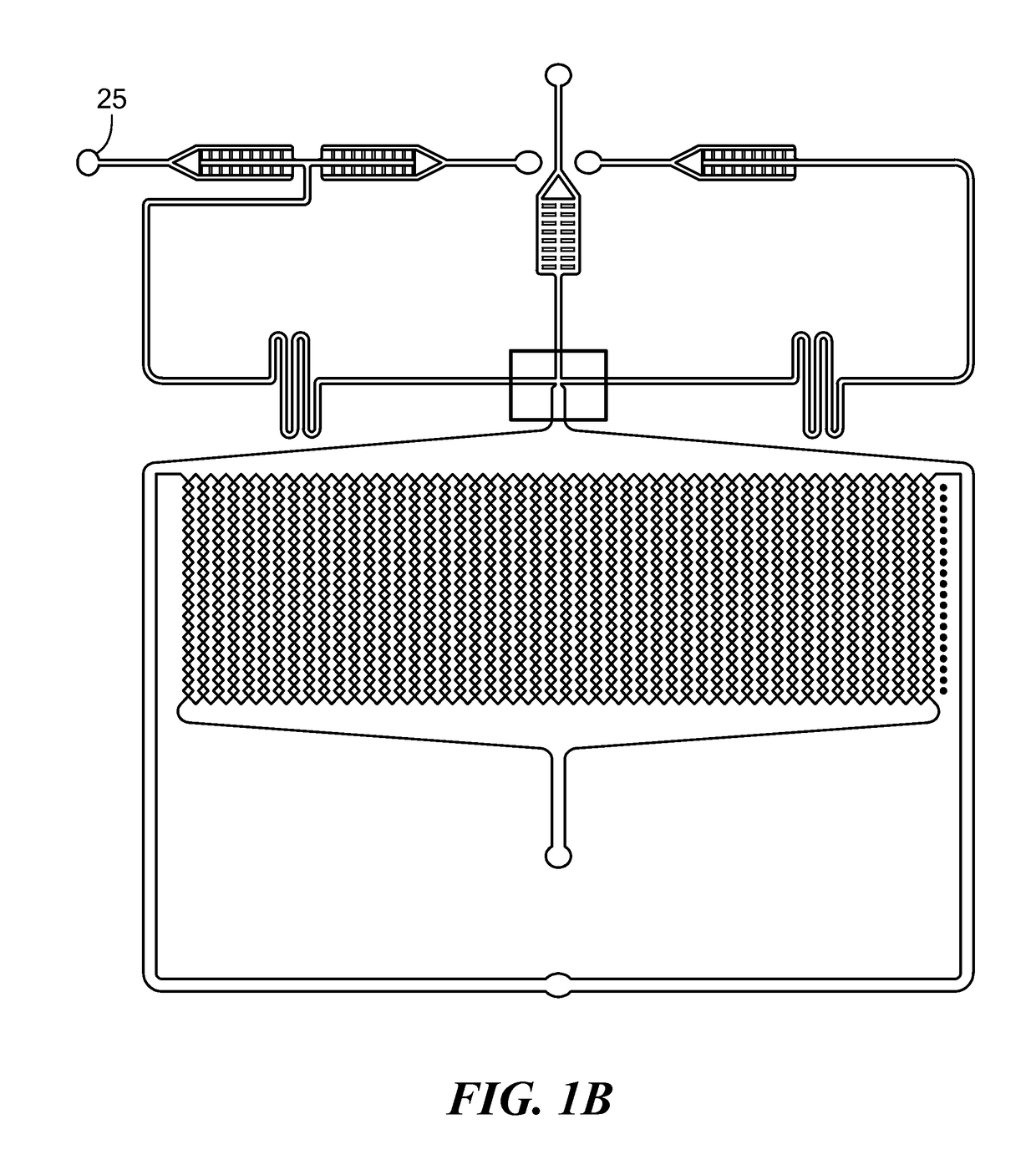
Microfluidic device and method for analysis of tumor cell microenvironments
ActiveUS10928382B2High throughput generationUniform geometryBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCellular MicroenvironmentMicrofluidics
A microfluidic device provides high throughput generation and analysis of defined three-dimensional cell spheroids with controlled geometry, size, and cell composition. The cell spheroids of the invention mimic tumor microenvironments, including pathophysiological gradients, cell composition, and heterogeneity of the tumor mass mimicking the resistance to drug penetration providing more realistic drug response. The device is used to test the effects of antitumor agents.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
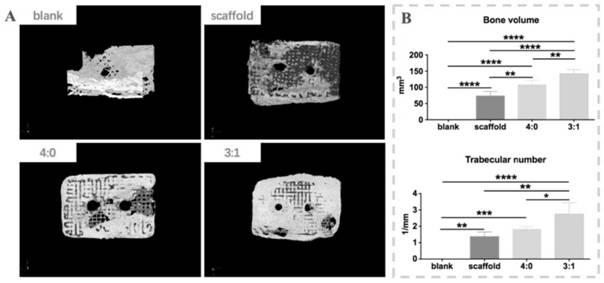
Vasculation bone cell membrane sheet stent complex and preparation thereof
PendingCN114045257AHigh strengthEliminate lossBone implantCell culture supports/coatingCell-Extracellular MatrixCell membrane
According to the vascularization bone cell sheet scaffold complex and the preparation method thereof, a method for co-culturing osteoblast cells and angiogenic cells is adopted, through a cell sheet technology, the loss of extracellular matrixes caused by a traditional cell digestion technology is eliminated, the original cell microenvironment is reserved, and the cell sheet scaffold complex has the advantages that the cell sheet scaffold complex is simple in structure and convenient to use. Through the synergistic effect of osteogenesis and vascularization, the survival and outcome of osteoblasts in the bone tissue engineering scaffold are facilitated; furthermore, the organic combination of the 3D printing bone tissue engineering scaffold and the cell sheet solves the problems that a pure cell sheet is low in strength and cannot maintain an osteogenesis space.
Owner:STOMATOLOGY AFFILIATED STOMATOLOGY HOSPITAL OF GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
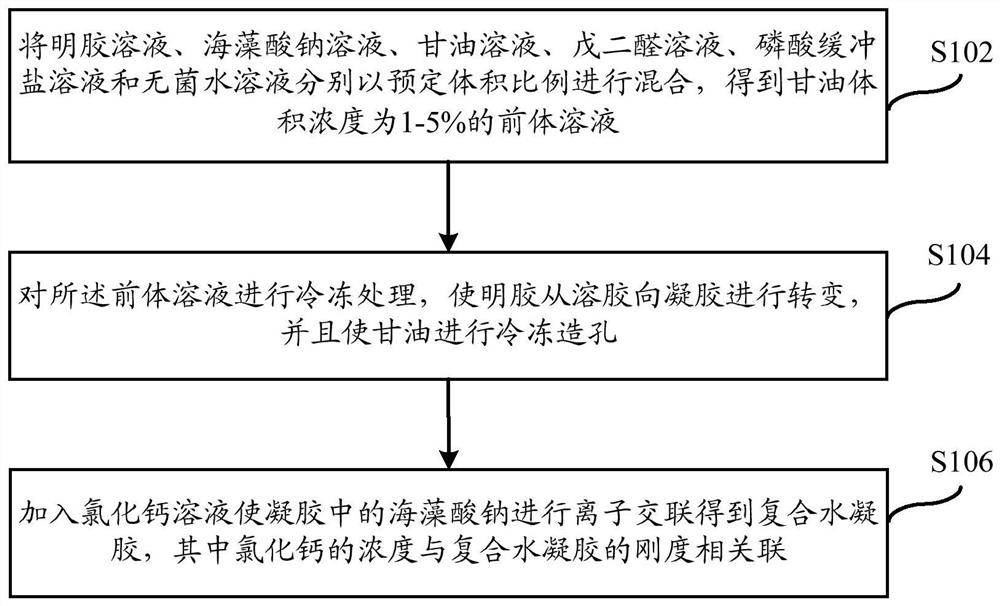
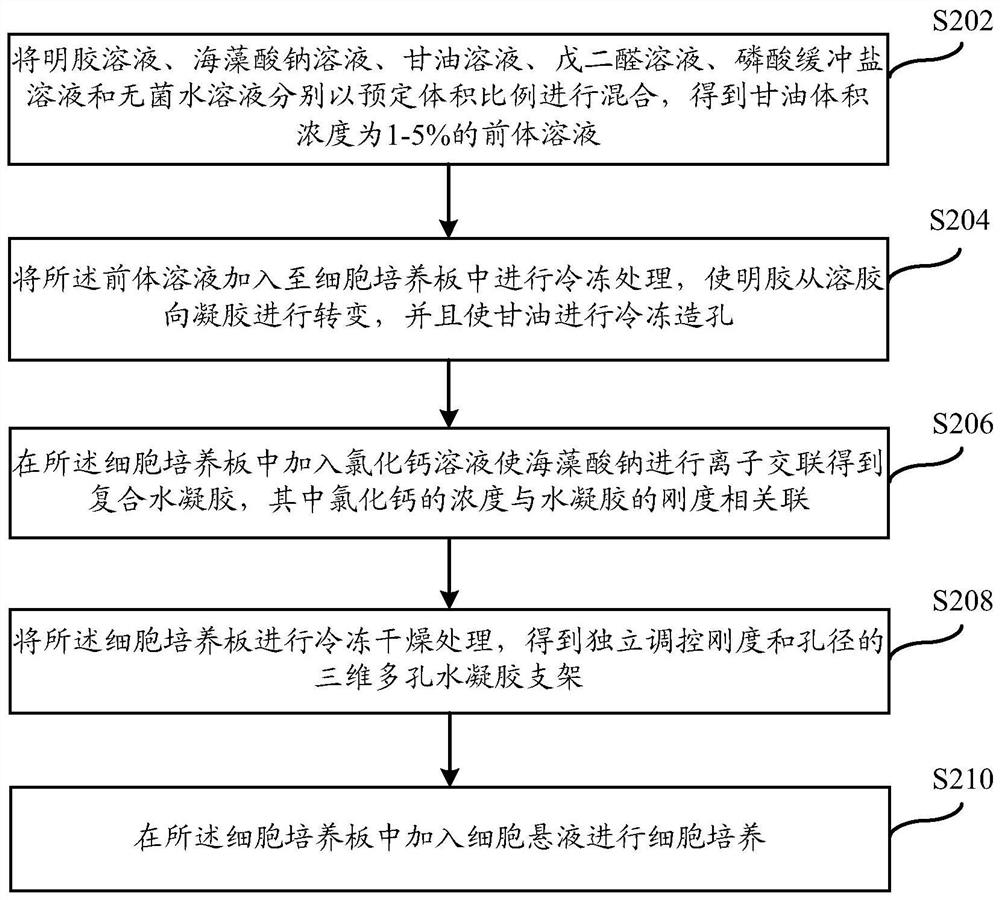
Preparation method of composite hydrogel, and construction method of cell microenvironment bionic system
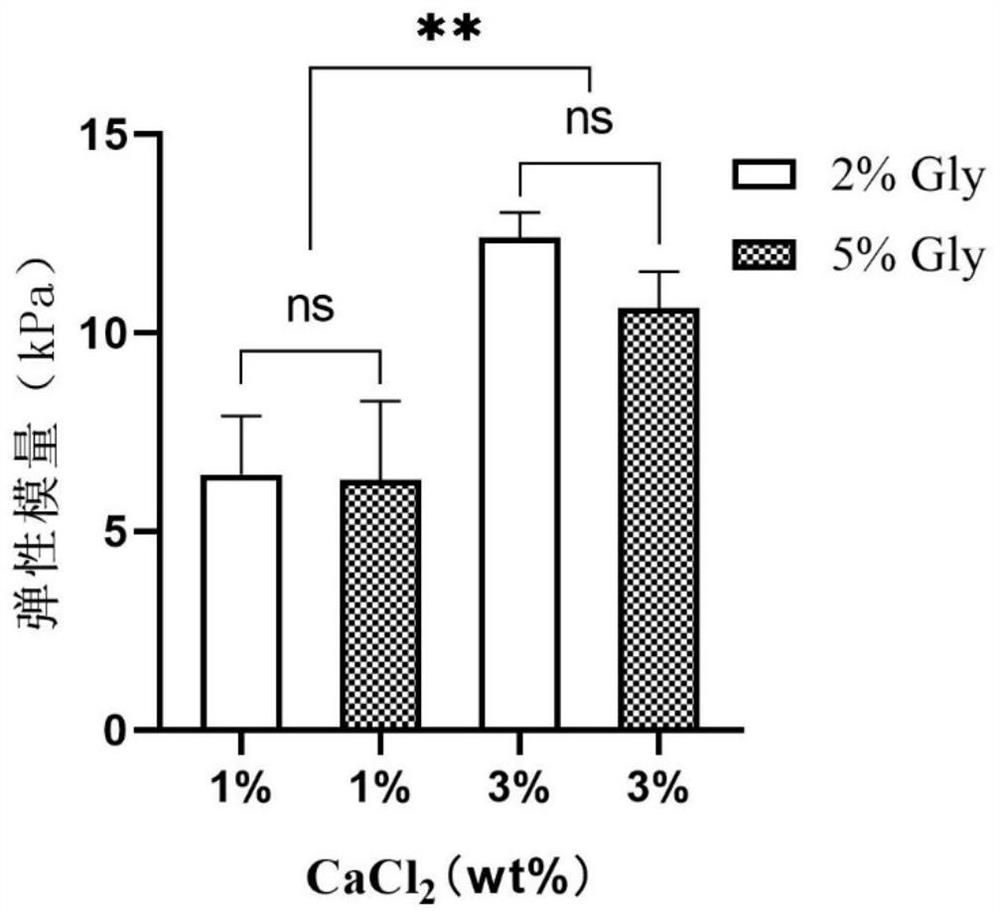
PendingCN113372580AWell formedStable mechanical propertiesCell culture supports/coating3D cultureCell-Extracellular MatrixGlycerol
The invention discloses a preparation method of composite hydrogel, and a construction method of a cell microenvironment bionic system. The preparation method of the composite hydrogel comprises the following steps: mixing a gelatin solution, a sodium alginate solution, a glycerin solution, a glutaraldehyde solution, a phosphate buffer salt solution and a sterile aqueous solution according to a preset volume ratio to obtain a precursor solution the glycerol volume concentration being 1-5%; freezing the precursor solution to convert gelatin from sol to gel, and freezing glycerol to form pores; and adding a calcium chloride solution to carry out ionic crosslinking on sodium alginate in the gel to obtain the composite hydrogel, wherein the concentration of calcium chloride is associated with the rigidity of the composite hydrogel. The composite hydrogel prepared by the embodiment of the invention is good in forming, stable in mechanical property and uniform in pore structure, and can be used for simulating an extracellular matrix microenvironment in vitro.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Preparation method and application of cobalt-doped metal organic framework nanoparticles
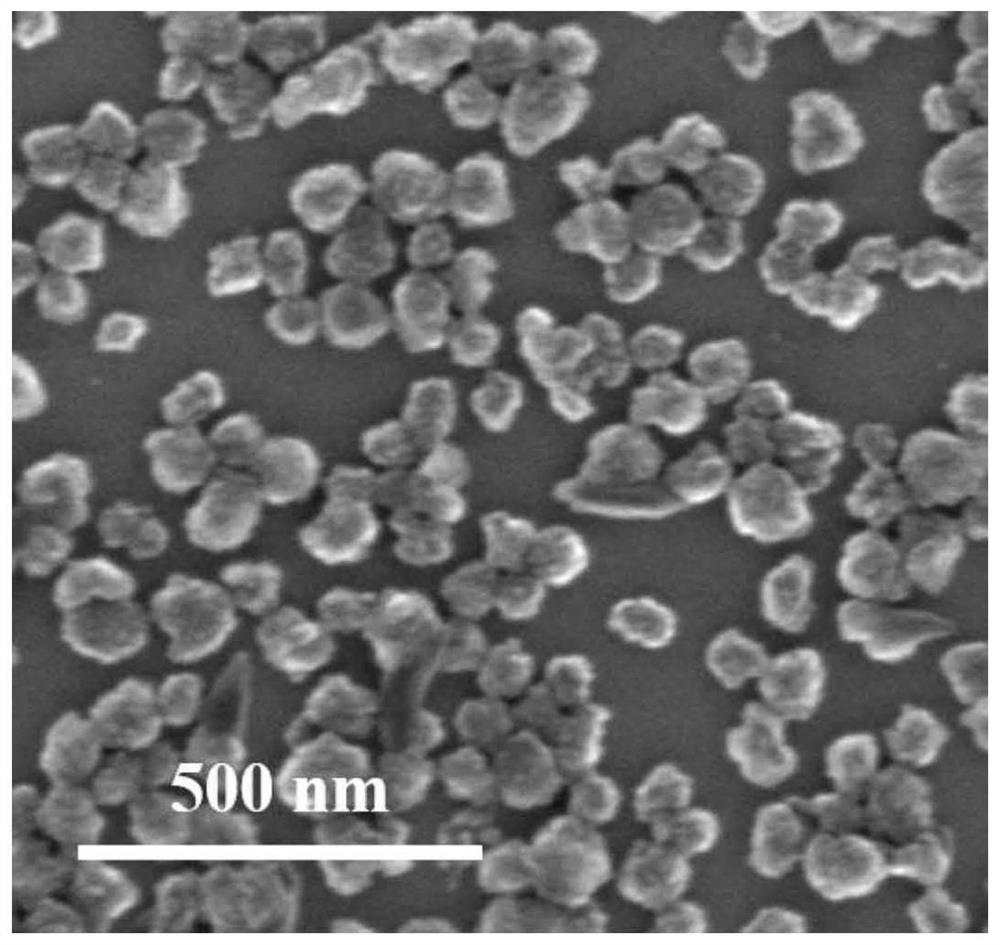
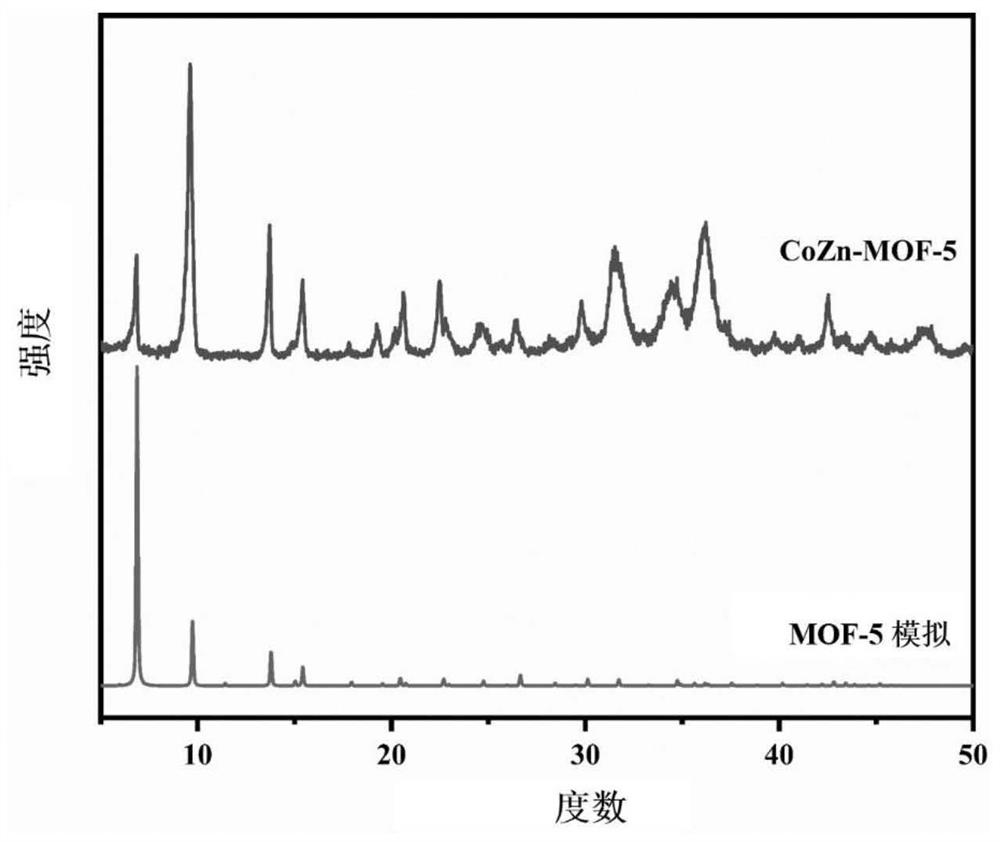
ActiveCN113750252AEasy to manufactureSmall sizeOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMetal-organic frameworkPyrrolidinones
The invention belongs to the technical field of materials, and relates to a preparation and application of cobalt-doped metal organic framework nanoparticles, and the cobalt-doped metal organic framework nanoparticles have good hydroxyl radical generation capability and good drug loading performance. Doped cobalt metal ions enable the nucleation number in a reaction system to be increased, the concentration of relative ligands is greatly consumed, polyvinylpyrrolidone is used as a stabilizer, the nano-particles are protected and dispersed, the nanoparticles stop growing in a small size, and therefore synthesis of small-size CoZn-MOF-5 materials is achieved. The nanoparticle material is small in size, good in dispersity and high in loading capacity, and can be sensitively controlled to be released under the high glutathione expression acidic tumor cell microenvironment, meanwhile, cobalt ions doped in the material can react with hydrogen peroxide overexpressed by tumor cells to generate hydroxyl free radicals, the coordination of a chemical kinetic therapy and a chemical therapy is realized, and the cobalt-doped metal organic framework nanoparticles are a good nano anti-cancer drug carrier.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Compositions and methods for therapeutics prescreening
ActiveUS10815530B2Compounds screening/testingMicrobiological testing/measurementCellular MicroenvironmentPharmaceutical drug
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
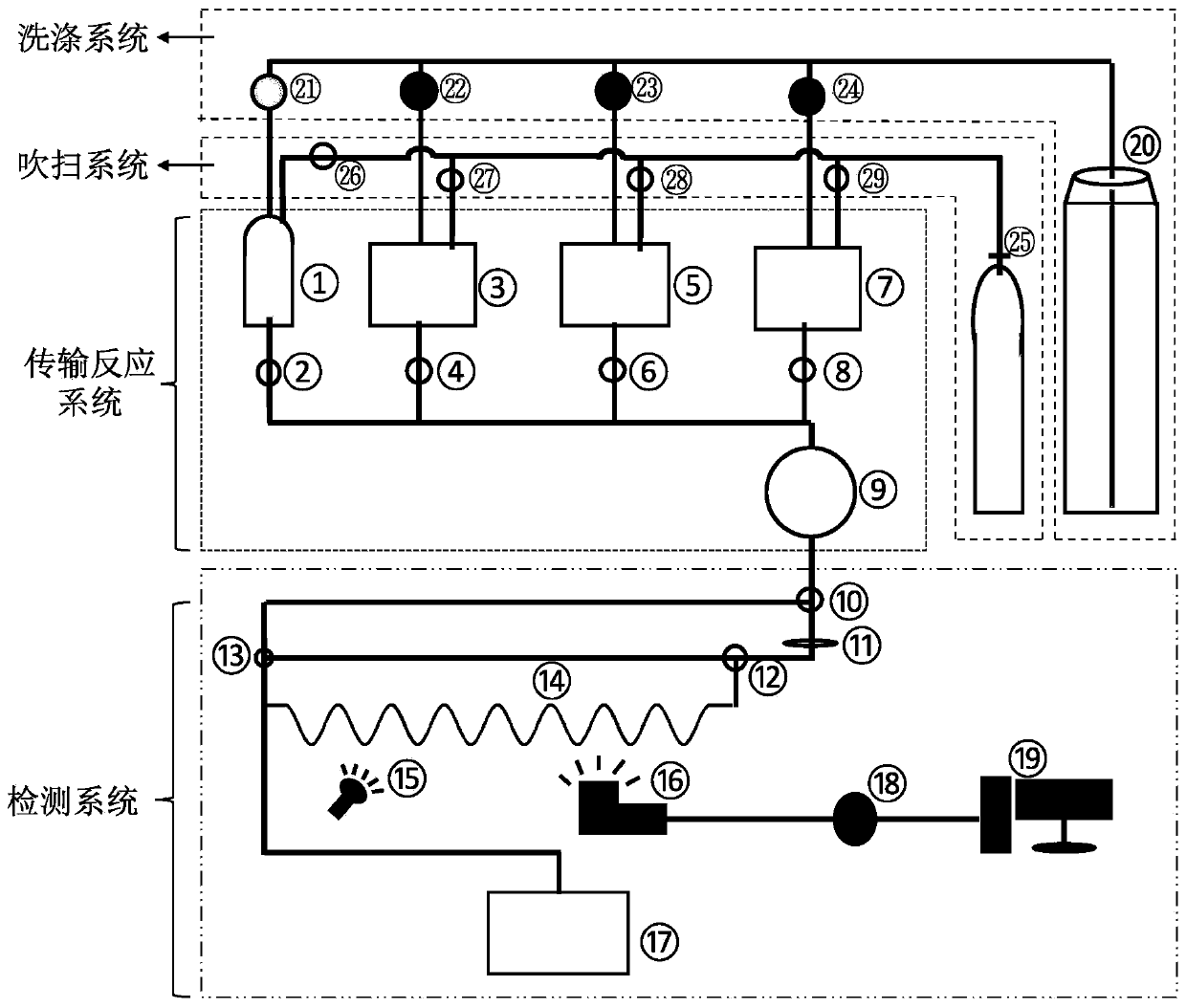
Active oxygen content automatic detection system suitable for cell microenvironment
PendingCN111426663AHigh sensitivityHigh precisionFluorescence/phosphorescencePeritoneal fluidBiophysics
The invention relates to a biochemical detection instrument. The invention aims to provide a rapid, accurate and automatic detection system for realizing the trace volume of a large number of ROS content samples aiming at cell, tissue and organ microenvironments such as pleural fluid, peritoneal fluid, cerebrospinal fluid, amniotic fluid, follicular fluid, cell culture fluid and the like. The technical scheme is as follows: the active oxygen content automatic detection system suitable for a cell microenvironment is characterized in that the automatic detection system comprises a sample transmission reaction system, a detection system, a washing system communicated with the sample transmission reaction system through a water pipe pipeline and a purging system communicated with the sample transmission reaction system through an air pipe pipeline, wherein the sample transmission reaction system and the detection system are sequentially communicated through a light shielding pipeline; thesample transmission reaction system comprises a sample injector and a DCFH supply bin which are connected in parallel and then communicated with a reaction bin through a light shielding pipeline; andsample injection valves are respectively arranged between the sample injector and the reaction bin and between the DCFH supply bin and the reaction bin.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
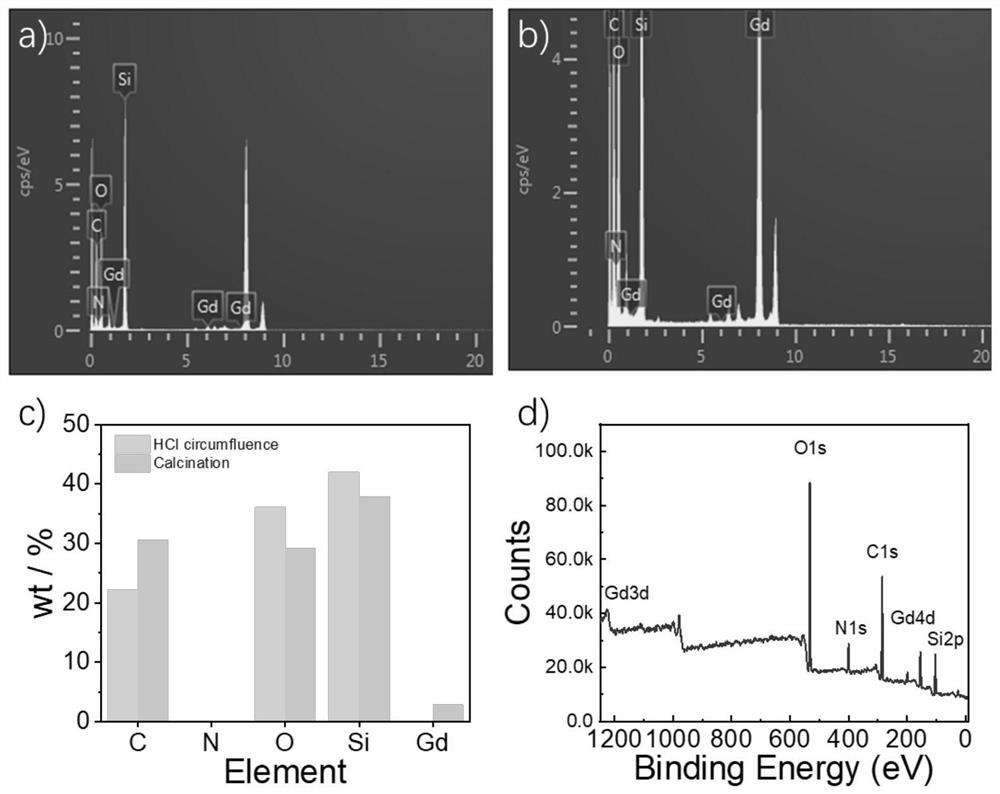
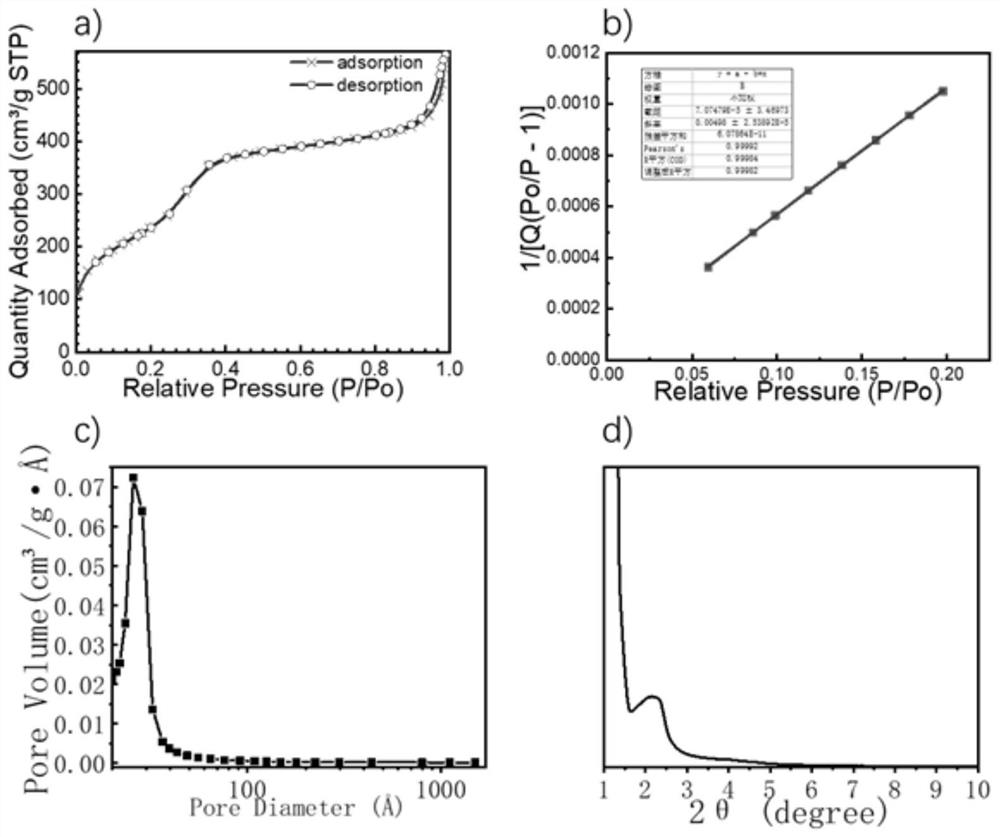
Preparation and application of polyelectrolyte-coated drug-loaded Gd2O3@mesoporous silica nanoparticles
InactiveCN113730609ATargetedRealize the integration of diagnosis and treatmentPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsCancer cellMRI contrast agent
The invention discloses preparation and application of polyelectrolyte-coated drug-loaded Gd2O3@mesoporous silica nanoparticles, and relates to the technical field of medicinal chemistry. The preparation method comprises the following steps: loading synthesized Gd2O3 nanoparticles on mesoporous walls of MSN by adopting a one-step method, removing a synthesis template CTAB by adopting a calcination method, loading DOX in mesopores of MSN by utilizing an ultrasonic oscillation method, coating the surface of MSN with a pH responsive substance PAH / P (DMA-co-TPAMA) by using an LBL method, connecting folic acid to the outermost layer of the coating material to serve as a targeting agent, and therefore the pH responsive polyelectrolyte-coated drug-loaded Gd2O3@mesoporous silica nanoparticles are prepared and have the cancer cell targeting property, the cancer cell microenvironment response drug controlled release property and the MRI contrast agent enhancement effect, and the purposes of diagnosis and treatment integration, anti-cancer drug tracing, real-time curative effect monitoring and the like are achieved.
Owner:贺克武
Methods for therapeutics prescreening in bodily fluids
ActiveUS20200216907A1Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisCellular MicroenvironmentPharmaceutical drug
A method for using bodily fluids in determining the cell-specific potency of drugs is provided. A composition comprising a plurality of types of carriers, wherein each carrier comprises a single-cell lethal amount of a therapeutic agent and a unique barcode identifying that agent and wherein the composition comprises equal numbers of each carrier type, equal concentrations of the agent and equal concentrations of each barcode is also provided. Further, methods useful for studying the therapeutic profile of one or more drugs within a cell microenvironment, including but not limited to a tumor, are provided.
Owner:BARCODE DIAGNOSTICS LTD
Membrane protein dimerization state in situ detection kit and its application
ActiveCN114624225BHigh sensitivityStrong specificityRaman scatteringNanosensorsCellular MicroenvironmentCell to cell signaling
The invention discloses a membrane protein dimerization state in-situ detection kit and application thereof. The kit includes a membrane protein anchor chain, an identification probe and a SERS label. Proximity hybridization of strands upon membrane protein dimerization triggers catalytic hairpin self-assembly to form a networked assembly of recognition probes and SERS tags, enabling SERS detection of a highly specific event in cell communication, membrane protein dimerization With imaging, it is suitable for high-sensitivity monitoring of membrane protein dimerization-based intercellular signaling in complex cellular microenvironments.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
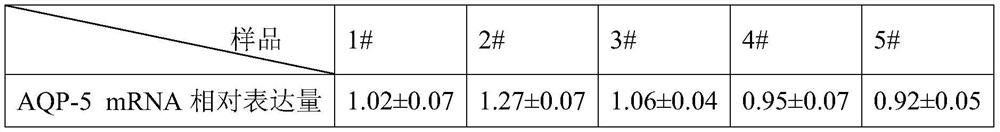
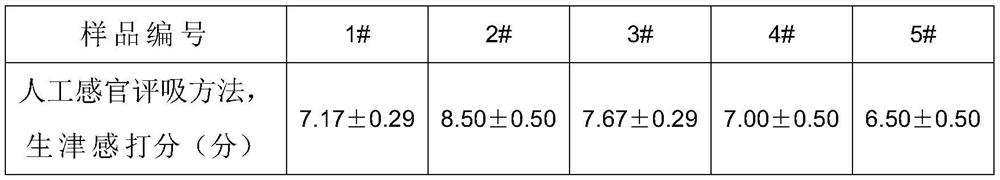
A method for detecting the influence of cigarette smoke on the mRNA expression of aquaporin 5 cells
ActiveCN107586830BShort experiment cycleMicrobiological testing/measurementTumor/cancer cellsMrna expressionCell
The invention relates to a method for detecting the influence of cigarette smoke on the mRNA expression of aquaporin 5 cells, belonging to the technical field of biological applications. The present invention uses biochemical and cytological methods, uses BMP6 to treat cells, and simulates the cell microenvironment when Sjögren's syndrome occurs, so as to study the influence of cigarette smoke on the expression of AQP‑5, which is simpler than animal experiments , high efficiency; the oral bionic simulation device is used in the capture of cigarette smoke, which is more suitable for the actual human smoking state; at the same time, the fluorescence quantitative PCR method is used to compare the influence of different samples on the expression of AQP‑5 mRNA in real time , thus providing a new rapid method for evaluating the efficacy of cigarette smoke.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO YUNNAN IND
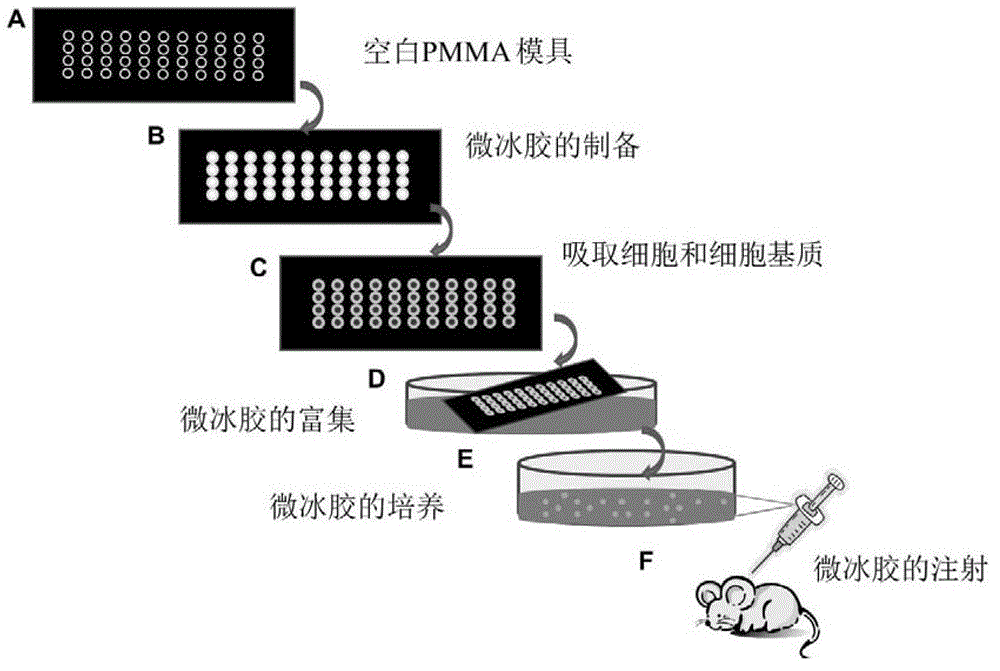
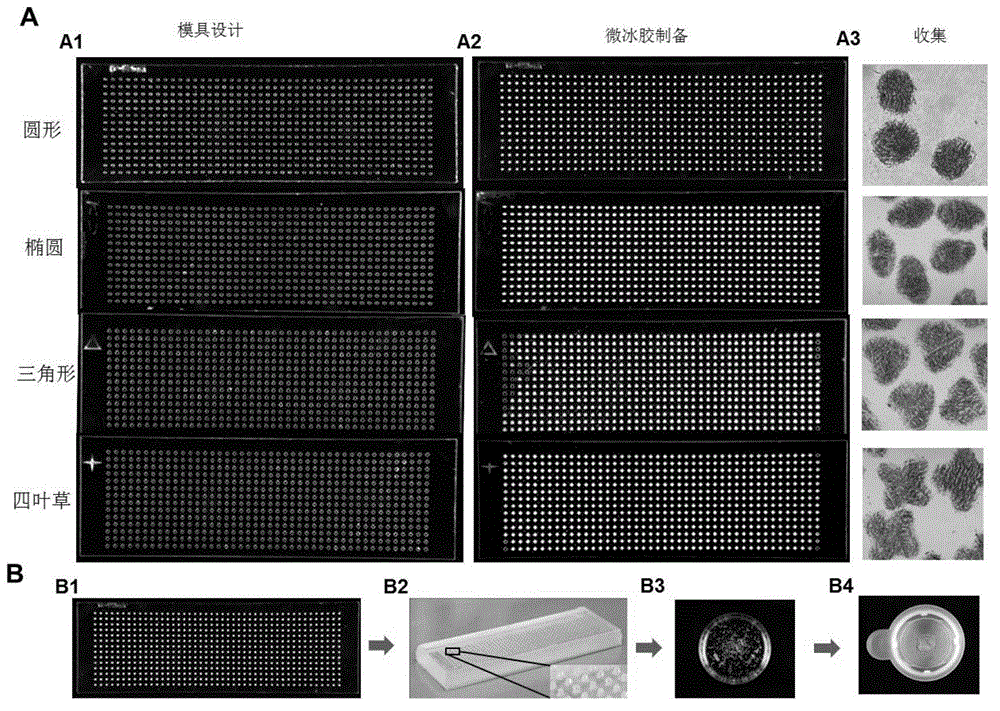
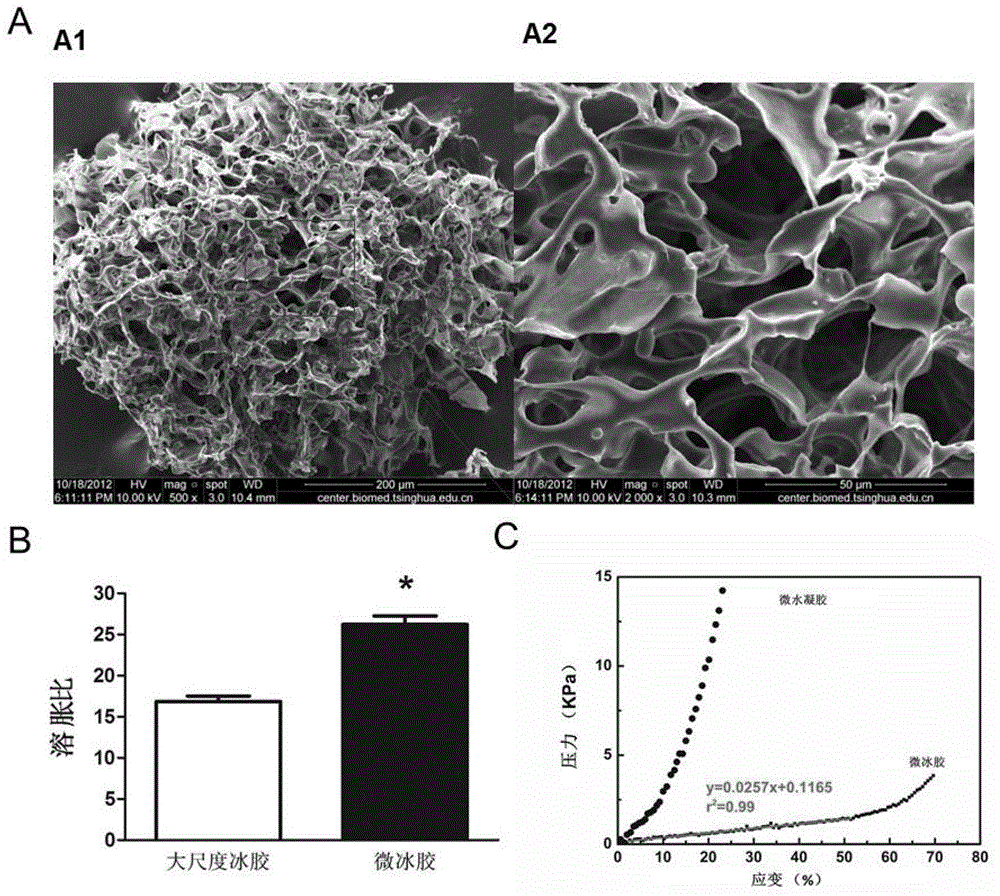
System and method for constructing injectable three-dimensional cell microenvironment based on microcryogel
ActiveCN103877613BSyringability GuaranteeMeet the requirements for injectable therapyProsthesisTreatment fieldIn vivo
The invention discloses a system and a method for constructing an injected three-dimensional cell microenvironment based on microfrozen gel. A microfrozen gel three-dimensional microenvironment vector is made of the frozen gel and in micro scale size. Experiments demonstrate that the prepared microfrozen gel three-dimensional microenvironment vector has the following characteristics that mechanical properties are good; whole morphology can be kept after being injected; the vector can load cells effectively; compared with conventional large-scale frozen gel, the microfrozen gel three-dimensional microenvironment vector can absorb the cells uniformly and has good material transmission performance; the microfrozen gel three-dimensional microenvironment vector has a protection effect for loaded cells in an injection process; and the microfrozen gel loaded with the cells can be injected into an animal body at specific sites and keep original functions and activities in in-vivo cells. The microfrozen gel three-dimensional microenvironment vector plays an important role in the field of cell injection therapy, and has wide application prospects in animal model establishment and the drug screening field.
Owner:BEIJING CYTONICHE BIOTECH CO LTD
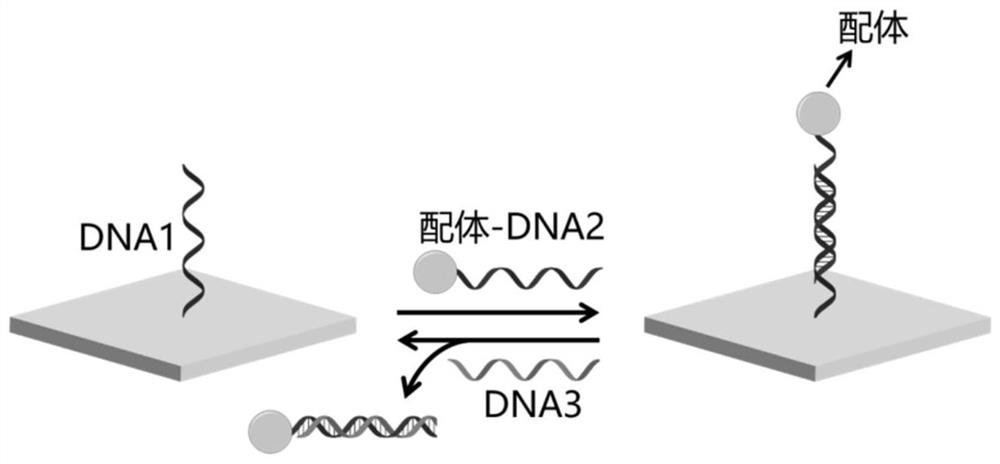
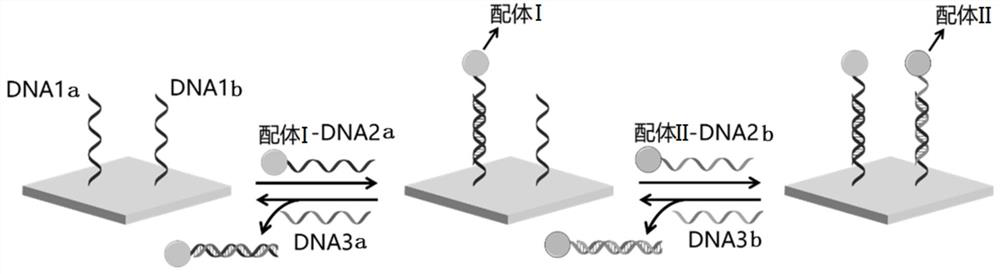
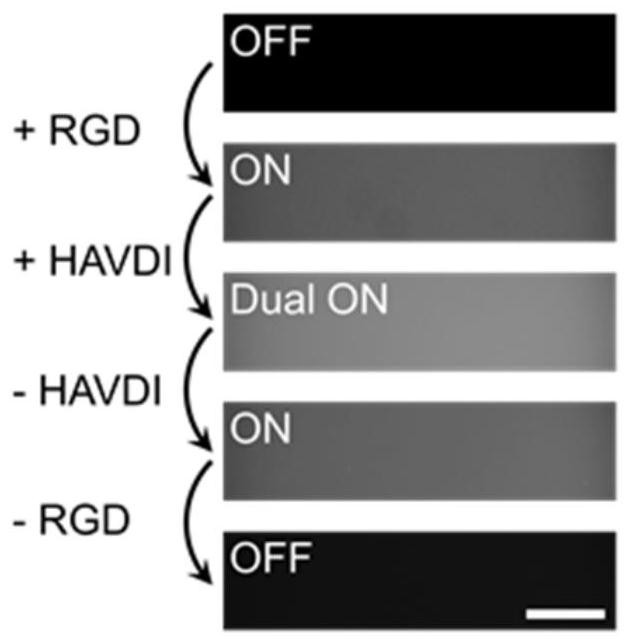
Dynamic cell microenvironment simulation platform and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN113621551AEasy to operateGood biocompatibilitySkeletal/connective tissue cellsCell culture supports/coatingEngineeringBiocompatibility
The invention discloses a dynamic cell microenvironment simulation platform and a preparation method thereof. The platform takes hydrogel as a cell culture carrier, and can selectively regulate and control the combination and dissociation of one or more ligands in the hydrogel and a cross-linked network structure of the hydrogel in real time, wherein the ligands are proteins and polypeptides with specific structures determined according to the types of cells and receptor types expressed by the cells, and are modified in the hydrogel based on a DNA hybridization principle, so that a dynamic cell microenvironment is simulated in vitro, and the platform can be used for regulating and controlling the interaction between the cells and the microenvironment. The platform is simple in preparation method, easy to operate and good in biocompatibility, and meanwhile, the physical and chemical properties in a biological environment are stable.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
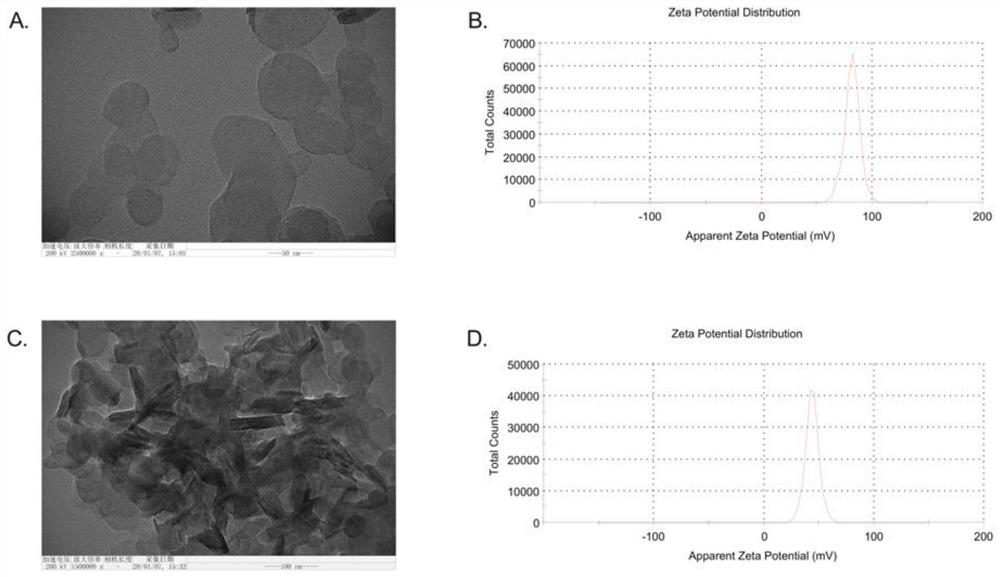
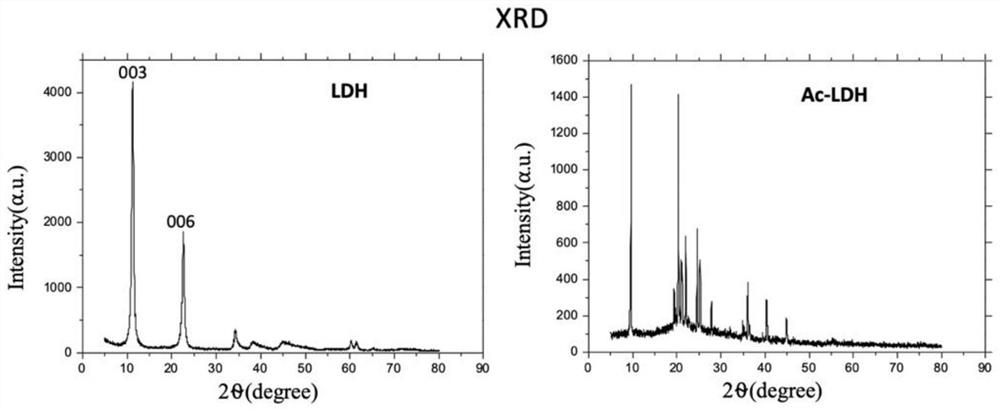
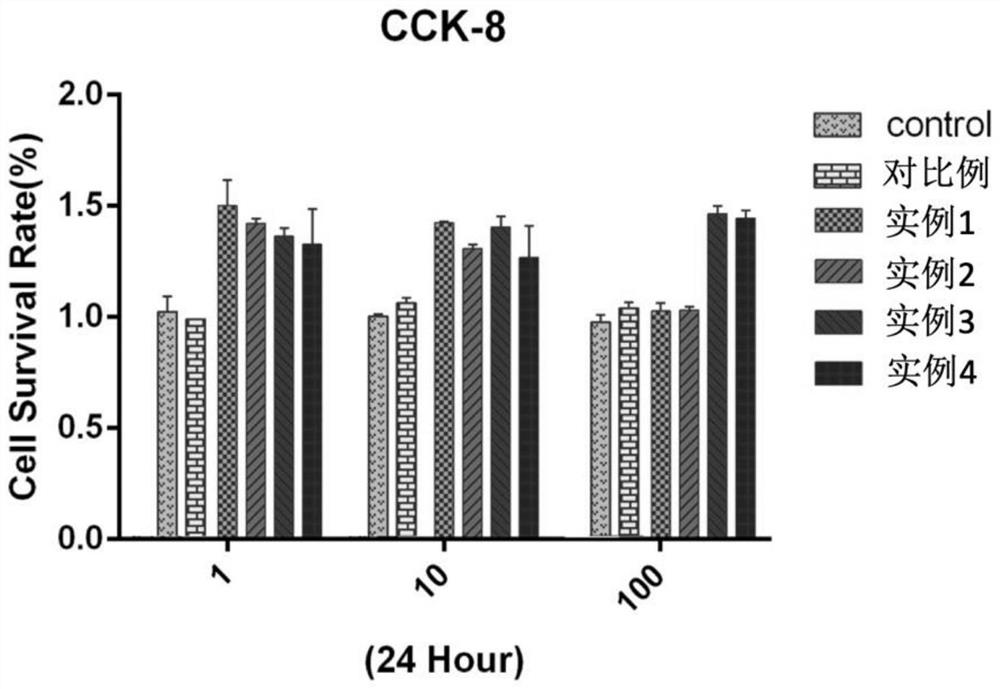
Ac-SDKP-LDH nanocrystallization preparation as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112587669AHigh biosecurityHas anti-fibrotic effectTetrapeptide ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCellular MicroenvironmentControl release
The invention discloses an Ac-SDKP-LDH nanocrystallization preparation as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The Ac-SDKP-LDH nanocrystallization preparation comprises LDH and Ac-SDKP inserted between LDH layers and is prepared through the following steps that the LDH and the Ac-SDKP are fully mixed and react at the temperature of 2-8 DEG C for 8-24 h, the Ac-SDKP is inserted between the LDH layers through ion exchange, and the Ac-SDKP-LDH nanocrystallization preparation is obtained. The Ac-SDKP-LDH nanocrystallization preparation disclosed by the invention can be used for preparing anti-silicofibrosis medicines. The method for preparing the Ac-SDKP-LDH nanocrystallization preparation is simple and easy to operate, and according to the prepared Ac-SDKP-LDH nanocrystallization preparation, under the action of a cell microenvironment, a cationic laminate of LDH dissolves in inorganic metal ions, so that the Ac-SDKP is released, the effect of protecting the Ac-SDKP is achieved, the anti-EMT effect can be sufficiently exerted, and the Ac-SDKP-LDH nanocrystallization preparation is used for preventing and treating silicosis fibrosis and has the medicine controlled release characteristics of long lasting time, high biological safety and pH sensitivity. In addition, the LDH has a certain anti-fibrosis effect, and the anti-fibrosis effect of the LDH is enhanced by compounding the LDH and the Ac-SDKP.
Owner:复旦大学附属中山医院青浦分院
Method and device for constructing three-dimensional microenvironment
ActiveCN103131625BBridging barriers in practical applicationEffective combinationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCellular MicroenvironmentLiquid layer
Provided are a method and a device for constructing a three-dimensional cellular microenvironment. The method comprises the following steps: 1) establishing a three-dimensional transparent sponge scaffold or a three-dimensional transparent sponge scaffold array; 2) establishing a thin sample liquid layer containing molecules, a material, cells, and a mixture thereof; 3) combining the transparent sponge scaffold or transparent sponge scaffold array in 1) with the thin liquid layer in 2), and completing loading of a sample liquid, thereby achieving construction of a three-dimensional microenvironment. The method and device provide a simple and practical platform for research on the growth, proliferation, label-free observation, and functional analysis of cells in a three-dimensional microenvironment in the fields such as the biomedical research and the drug research and development, and rapidly and losslessly realize the patterning of the three-dimensional microenvironment of molecules, a material, cells, and a mixture thereof, high flux synchronous loading, and label-free real-time observation.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for detecting influence of cigarette smoke on expression quantity of aquaporin 5 cells
ActiveCN107513552AFast and accurate detectionShort experiment cycleMicrobiological testing/measurementDiagnosticsCellular MicroenvironmentHigh flux
The invention relates to a method for detecting the influence of cigarette smoke on the expression quantity of aquaporin 5 (AQP-5) cells, and belongs to the technical field of biological application. According to the method, biochemical and cytological methods are used, BMP6 is used to process the cells, and the cellular microenvironment when sjogren syndrome happens is simulated so as to study the influence of cigarette smoke on the expression quantity of AQP-5; compared with animal experiments, the method is simpler and more efficient; an oral cavity biomimetic-simulation device is used for collecting cigarette smoke, which is closer to the actual state of human smoking; meanwhile, a high content system is used and can detect the influence of multiple samples on the expression quantity of the AQP-5 cells in a high flux, the multi-sample detection can be conducted rapidly, accurately and visually, and a novel rapid means is provided for the efficiency evaluation of cigarette smoke.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO YUNNAN IND
Achilles tendon repairing patch and preparation method thereof
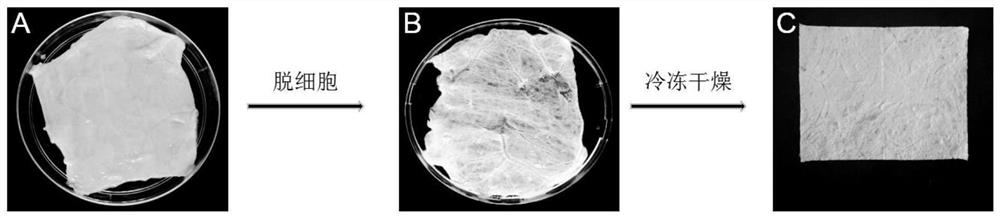
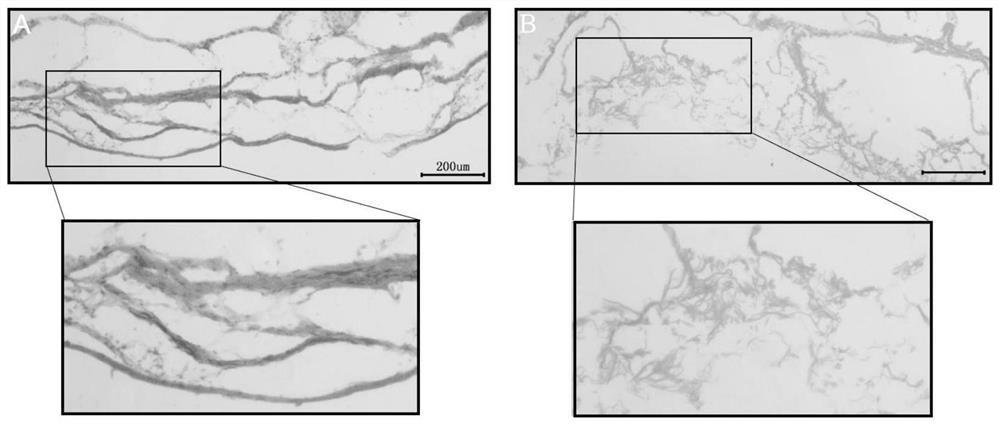
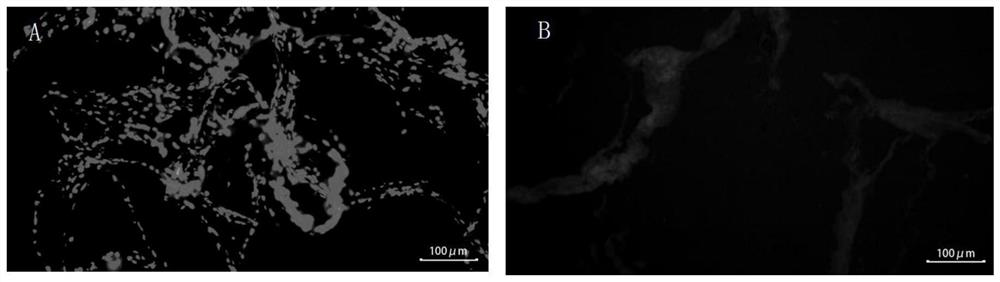
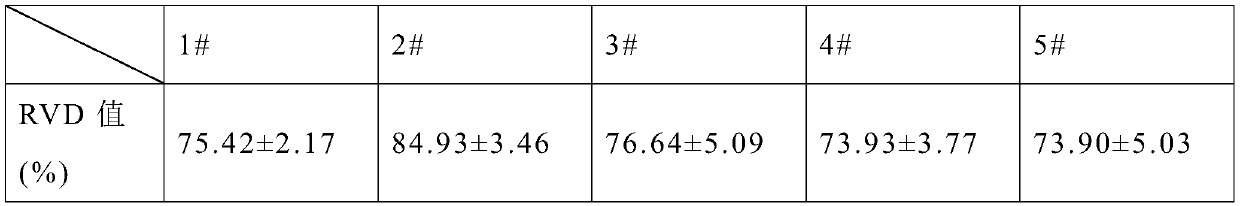
PendingCN114344567AIsolation of adhesionsGood biocompatibilityProsthesisBiologic scaffoldCellular Microenvironment
The invention provides an achilles tendon repair patch and a preparation method thereof.The achilles tendon repair patch comprises a flaky SIS matrix, tendon stem cells are planted on the SIS matrix, the achilles tendon repair patch takes the flaky SIS matrix as a biological scaffold and the tendon stem cells as seed cells, has good biocompatibility and strong tendon differentiation capacity, and can be used for repairing achilles tendons. The sheet-shaped SIS matrix can wrap the achilles tendon broken end during tendon repair, so that adhesion between surrounding soft tissues and the achilles tendon broken end is isolated, meanwhile, the tendon stem cells carried by the sheet-shaped SIS matrix are accurately attached to the broken end, a good cell microenvironment is provided for proliferation and migration of the tendon stem cells, and a good achilles tendon repair effect is achieved.
Owner:THE AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF MEDICAL SCHOOL NINGBO UNIV
A method for detecting the influence of cigarette smoke on cellular water permeability
ActiveCN107764716BShort experiment cycleHigh-precision detectionPermeability/surface area analysisCellular MicroenvironmentCytology
The invention relates to a detection method for influence of cigarette smoke on cell water permeability, which belongs to the technical field of biological application. A biochemical and cytology method is adopted, BMP6 is used for processing cells, a cell micro environment when a sjogren syndrome occurs is simulated, so that the influence of the cigarette smoke on the water permeability is researched, and compared with the animal experiment, the detection method is simpler and more efficient; an oral bionic simulation apparatus is adopted for trapping the cigarette smoke, thereby being closerto the actual human smoking state; and meanwhile, by adopting a high content system, the influence of a plurality of samples on the cell water permeability can be simultaneously detected at differenttime, the multi-sample detection can be rapidly, accurately and visibly performed, and a novel rapid means can be provided for the efficacy evaluation of the cigarette smoke.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO YUNNAN IND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com