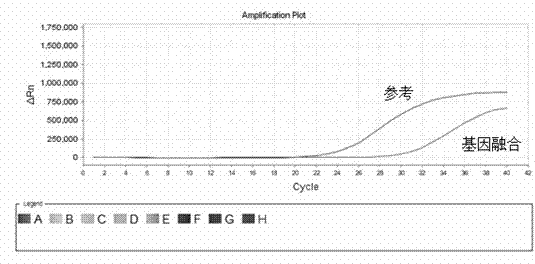
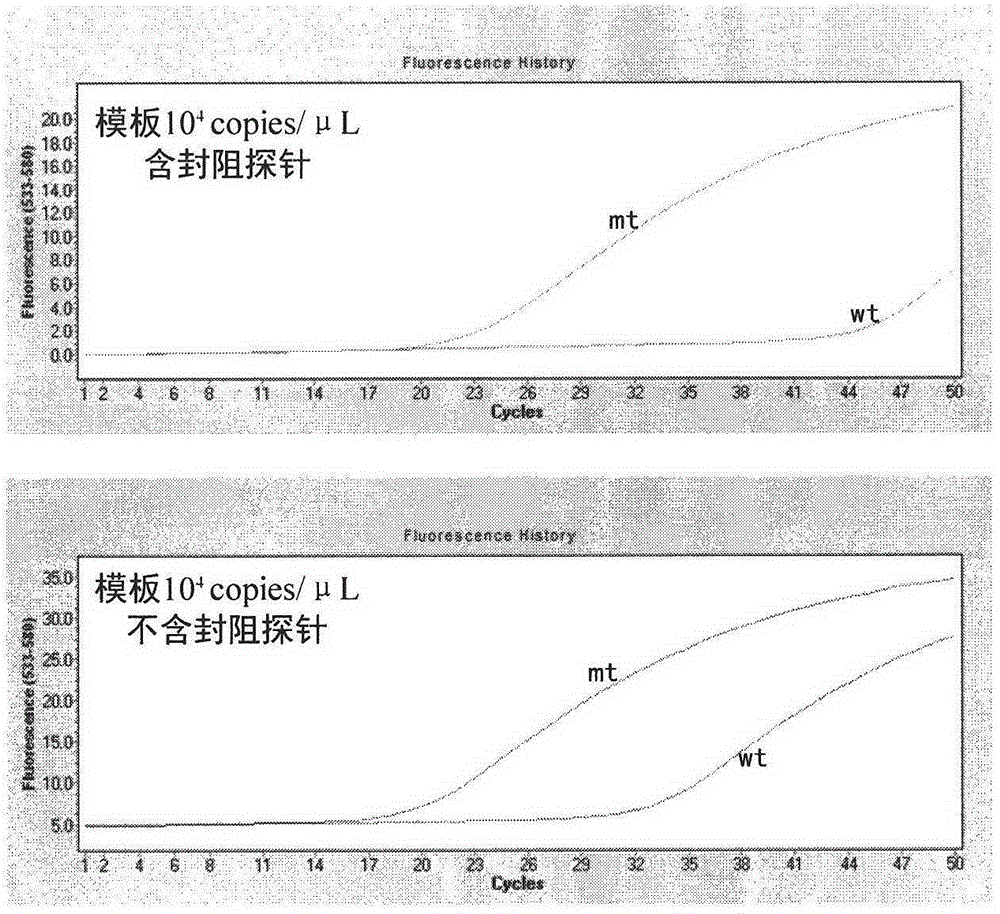
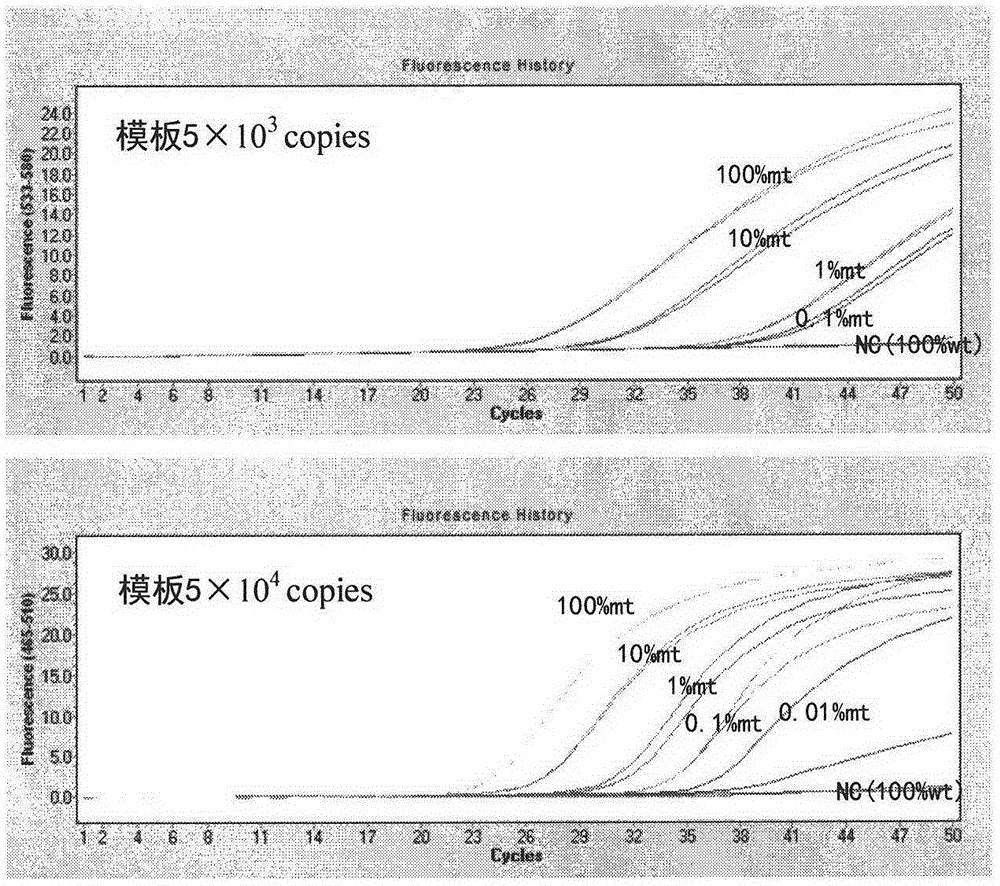
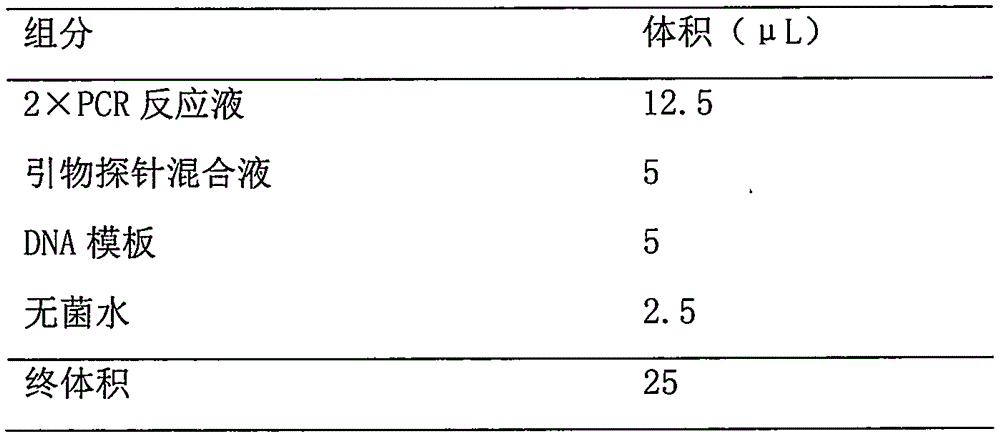
Patents
Literature
78 results about "Pleural fluid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Integrated body fluid collection and analysis device with sample transfer component
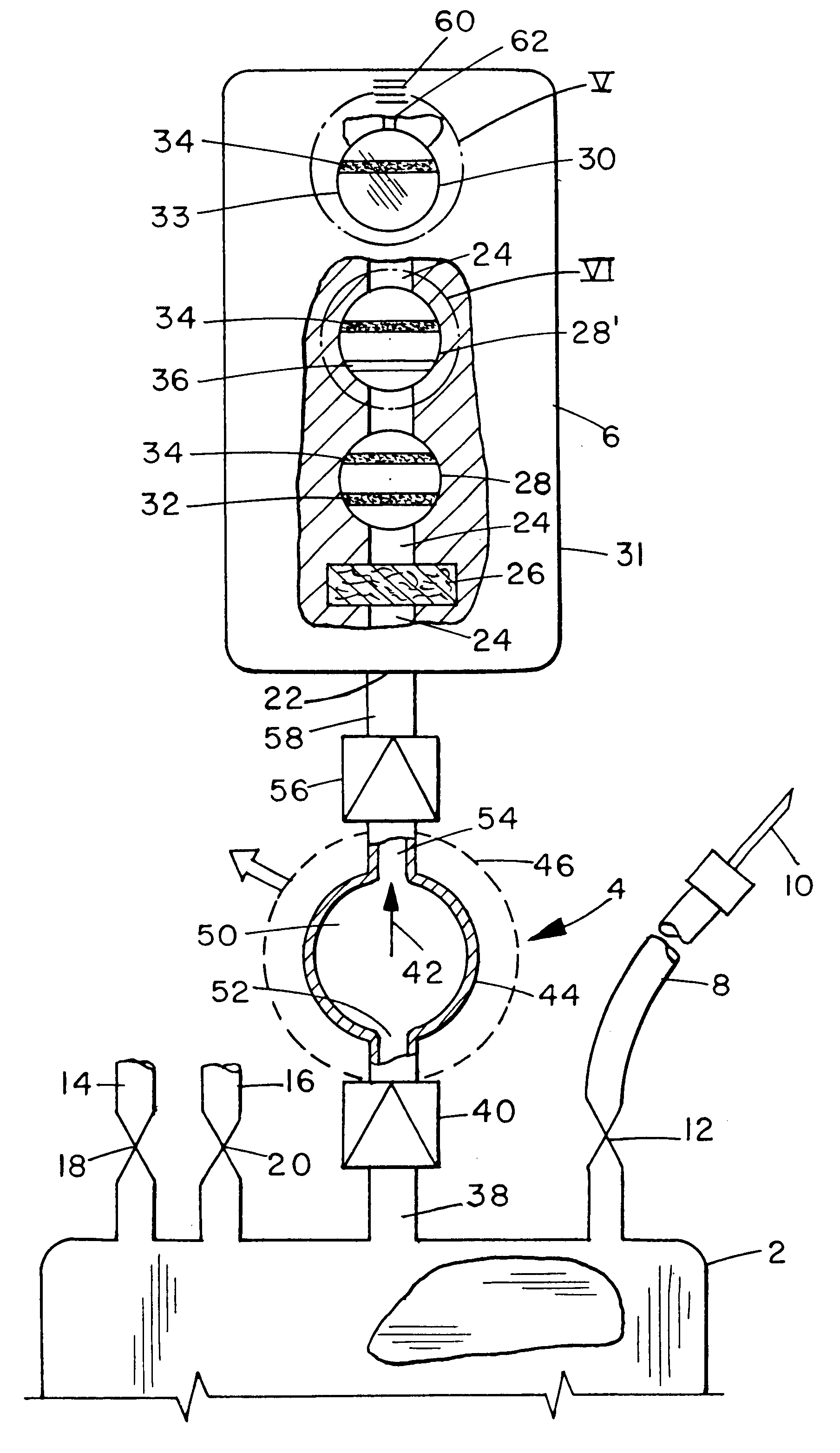
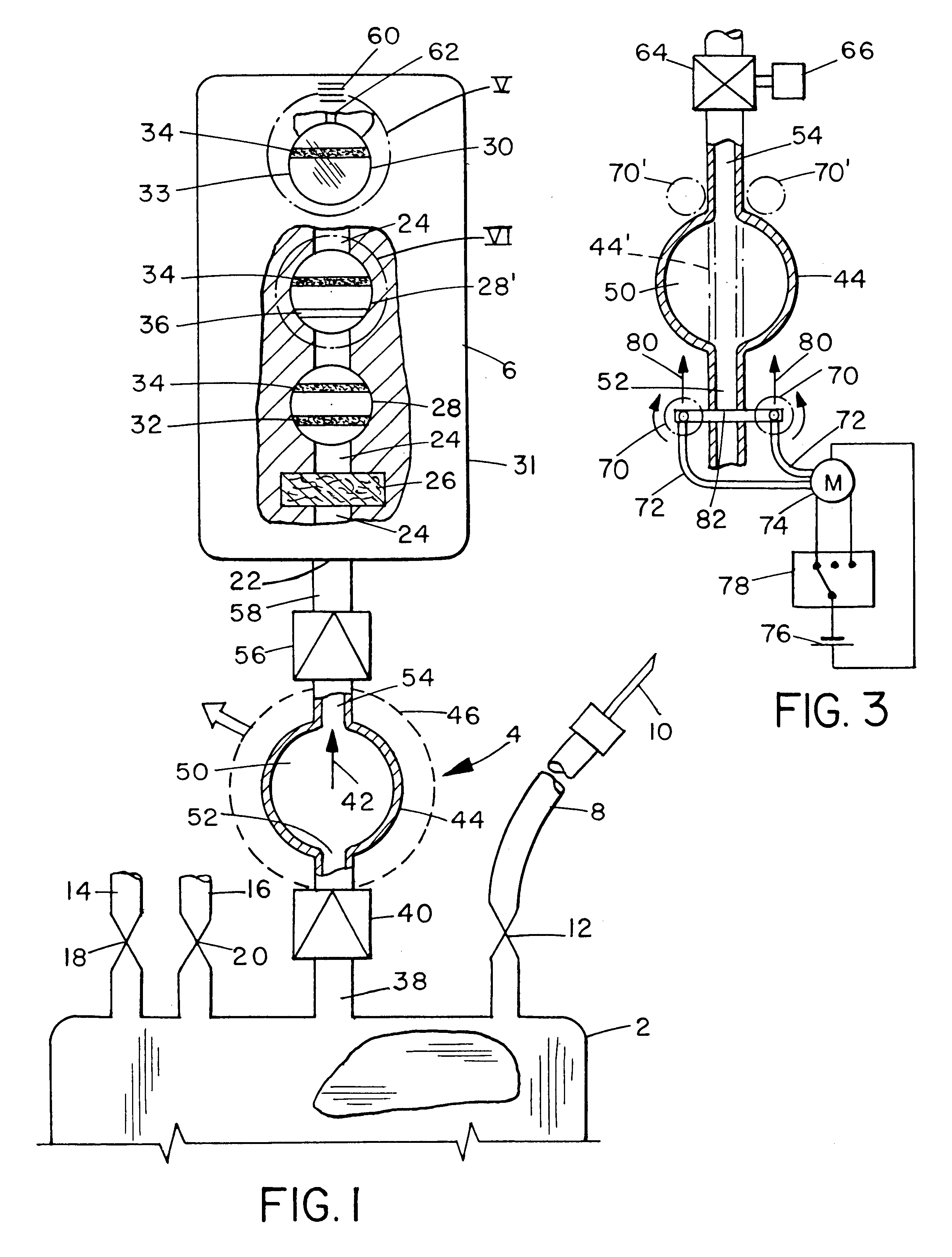
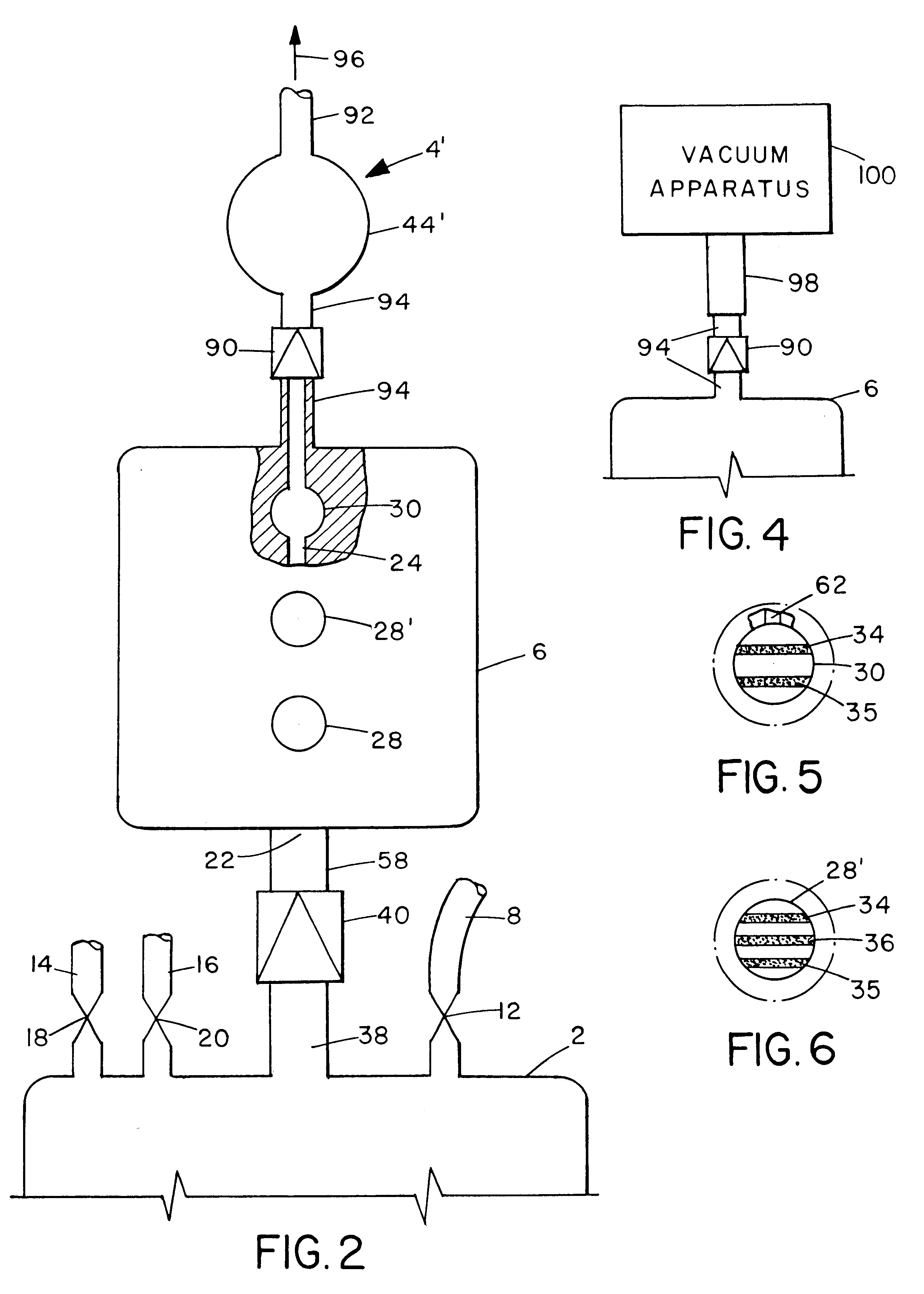
A single, integrated device in which a body fluid (e.g., blood) of a human or animal can be both collected and analyzed easily and without risk of contamination is disclosed. The collection portion and analysis portion of the device are permanently joined to permit movement of small quantities of body fluid under controlled conditions, to minimize any waste of the body fluid, to ensure that no contamination reaches the main body fluid volume, and to create a permanent physical record of the results of the analysis in association with the fluid sample itself: A wide variety of different body fluid components which may be indicative of various diseases, dysfunctions and abnormalities of the human or animal or the body fluid itself can be tested for. The device includes a container for collecting human or animal body fluid, one or more testing chambers containing one or more analysis units activated by body fluid; a transfer pump or vacuum assembly to transfer one or more samples into the analysis units; and one-way valves or the equivalent to prevent any portion of the withdrawn sample from being returned to the collection container. The body fluid acted upon may be blood, blood plasma, urine, bile, pleural fluid, ascites fluid, stomach or intestine fluid, colostrom, milk or lymph.
Owner:AALTO SCI
Intrathecal and intratumoral superantigens to treat malignant disease
InactiveUS20060052295A1Improve effectivenessStrong specificityPeptide/protein ingredientsSnake antigen ingredientsDiseaseAbnormal tissue growth
The presence of tumor nodules in organs often results in serious clinical manifestations and the permeation by cancer cells of sheaths surrounding organs often produces clinical manifestations of pleural effusion, ascites or cerebral edema. The present invention addresses this problem by providing a method for treating tumors comprising (a) intratumoral administration of a superantigen and / or (b) intrathecal or intracavitary administration of a superantigen directly into the sheath. Intratumoral superantigen results in significant and sustained reduction of the tumor size. Intrathecal administration produces significant sustained reduction of the fluid accumulation associated with clinical improvement and prolonged survival. Useful superantigen compositions for intrathecal and intratumoral injection include tumoricidally effective homologues, fragments and fusion proteins of native superantigens. Also disclosed is combined therapy that includes intratumoral or intrathecal superantigen compositions in combination with (i) intratumoral low, non-toxic doses of one or more chemotherapeutic drugs or (ii) systemic chemotherapy at reduced and non-toxic doses of chemotherapeutic drugs.
Owner:JENQUEST
A liquid-based cell preservation solution
The invention relates to a pathological examination, in particular to a liquid-based cell preservation solution used in cytopathological examination of human cervical mucus, sputum, urine, pleural fluid, tracheal mucus and the like. It is characterized in that it is prepared from alcohols, sodium phosphate buffer, edetate disodium, sodium chloride 0.08%-0.12%, potassium chloride, formaldehyde, dithiothreitol, calcium acetate, magnesium acetate, etc. As a result, it can not only maintain the stability of the cell structure. It can reduce the agglomeration and precipitation of cell mucus and the loss of cell rupture, and can also make cells easy to stain, improve the clarity of cell preparation, facilitate the smooth progress of pathological examination, and the cost is low, which is conducive to popularization and use.
Owner:XIAOGAN CENT HOSPITAL +1
Methods for Diagnosing Cancer by Characterization of Tumor Cells Associated with Pleural or Serous Fluids
InactiveUS20140295426A1High diagnostic sensitivityImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationCellular componentCell Fraction
A method for diagnosing or differentially diagnosing a cancer characterized by the presence of cancer cells in the pleural fluid of a mammalian subject, the method comprising contacting a sample of pleural fluid of the subject with colloidal magnetic particles coupled to a ligand which binds to a determinant on a cancer cell, but does not bind above a baseline threshold to other cellular and non-cellular components in pleural fluid; subjecting the pleural fluid-magnetic particle mixture to a magnetic field to produce a cell fraction enriched in ligand coupled-magnetic particle-bound cancer cells, if present in the pleural fluid; and analyzing the enriched fraction for the number of cancer cells in the pleural fluid. In certain aspects, this method involves preparing the pleural fluids for the above-noted method steps by, e.g., dilution of unprocessed pleural fluid. In certain aspect, the pleural fluid is subjected to the diagnostic method within 24 hours of withdrawal from the subject. This method has advantages to present diagnostic procedures for identifying malignant pleural effusions. The tumor cells present in pleural fluid can be characterized with cellular and molecular markers to determine prognostic and predictive factors.
Owner:JANSSEN DIAGNOSTICS LLC
Kit for detecting EGFR gene mutation and application of kit
ActiveCN104946739ADoes not generate non-specific signalStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementSerum igeFluorescence
The invention discloses a kit for detecting EGFR gene mutation and an application of the kit. The kit is characterized by containing 20 specific amplification primers for an EGFR gene mutation site, 5 efficient blocking probes for wild sequences, and 4 EGFR gene specific TaqMan fluorescent probes. The kit can be used for detecting samples of which the mutation copy number is as low as 5-10 copies and the mutation content is as low as 0.1%. The kit disclosed by the invention can be used for simultaneously detecting 5 types of gene mutations of an EGFR gene, is high in sensitivity, simple to operate, low-cost in detection and wide in clinical application range, the samples can be fresh pathological tissues, paraffin embedded tissues, pleural fluid, serum or plasma, the detection speed is high, and the detection process can be finished in only 90 minutes.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Method and kit for separating rare cells from peripheral blood
ActiveCN105891165AAvoid damageEnrich the connotation of stagingBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceTumor cellsDensity gradient
The invention discloses a method for separating rare cells from peripheral blood and a kit using the same. The method integrates a negative enrichment technology and a density gradient centrifugation technology, has the advantages of high recovery rate, simpleness, and convenience, and generates little damage to rare cells in peripheral blood. By using the provided kit, tumor cells such as breast cancer cells can be separated from peripheral blood through the separation method. The kit and method can also be applied to early diagnosis, relapse monitoring, and drug effect evaluation, can be used to separate rare cells in body liquids such as pleural fluid, ascitic fluid, and the like, and have a wide application prospect.
Owner:郝淮杰
Primer, probe and detection kit for detection of EML4-ALK fusion gene mutation
ActiveCN102719525AHigh sensitivityEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceSpecific detectionPleural fluid
The invention discloses a primer, a probe and a detection kit for detection of an EML4-ALK fusion gene mutation. The primer and probe provided by the invention are SEQ ID NO 1-SEQ ID NO 24. The primer and probe of the invention can carry out specific detection on EML4-ALK fusion gene mutation. The present invention has the following advantages: (1) an established real-time fluorescent PCR system capable of simultaneously detecting 9 kinds of fusion mutation of EML4-ALK gene; (2) high sensitivity capable of detecting mutation of 5-10 copies; (3) simple operation, cheap detection and wide clinical application range; (4) a wide range of samples from fresh pathological tissue to paraffin embedded tissue or pleural fluid; and (5) high speed detection with a detection procedure taking only 90 minutes.
Owner:AMOY DIAGNOSTICS CO LTD
Nucleic acid mass spectrometry method for detecting 10 common pathogenic bacteria of clinical infection
InactiveCN107964565AHigh detection sensitivityOperational securityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesRational useFluorescence
The invention discloses a primer system for detecting 10 common pathogenic bacteria of clinical infection. The detection system is used for detecting blood or body fluid (pleural fluid, ascitic fluid,drainage fluid, synovial fluid and cerebrospinal fluid) infected samples of patients infected by the pathogenic bacteria; detection results are combined with other clinical indicators, reference canbe provided for early diagnosis for clinicians and rational use of antibiotics, and treatment delaying and nonstandard use of the antibiotics are avoided. Virulence factor gene loci of 10 differentpathogenic bacteria can be simultaneously detected in two reaction systems; compared with sequencing, real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR and other technologies, the cost is lower, the operation is more convenient, and the accuracy and sensitivity are improved.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
Traditional Chinese medicine composition for curing tuberculous exadative pleurisy and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103041341AAlleviate malabsorption reactionsFast absorptionAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryDiseaseChangium
The invention provides a traditional Chinese medicine composition for curing tuberculous exadative pleurisy. The bulk drugs of the traditional Chinese medicine composition include flos farfarae, root bark of white mulberry, Chinese yam, euphorbia kansui, rhizoma panacis majoris, folium eriobotryae, radix stemonae, Chinese-date, inula flower, Chinese mahonia stems, rhizoma zingiberis, rhizoma sparganii, flowers carthami, folia perillae acutae, allium macrostemon, selaginella tamariscina, vine of multiflower knotweed, exocarpium, changium smyrnioides, poria cocos, semen coicis, turmeric, schisandra chinensis, semen lepidii, radix polygonati officinalis, rhizoma anemarrhenae, dayflower, polygonum cuspidatum, adenophora tetraphylla and kaladana. The traditional Chinese medicine composition reduces untoward effect of hydrothorax absorption, shortens course of disease, reduces pleural adhesions, pleural thickening and chest pain, enables hydrothorax absorption of patients to be quick, remarkably alleviates chest pain, and greatly reduces rate of pachynsis pleurae or pleural adhesion, thereby overcoming side effects caused by western drug therapy and having a certain curative effect on curing tuberculous exadative pleurisy.
Owner:CHONGQING XUANNU BIOTECH
Effective culturing method for body fluid derived tumor cells and application of effective culturing method
PendingCN108707582AMaintain gene mutation profilesEasy to trainMicrobiological testing/measurementCell culture active agentsCell-Extracellular Matrix3D cell culture
The invention relates to a culturing method for body fluid derived tumor cells and a tumor medium. The method comprises the steps of enriching body fluid tumor cells; mixing the body fluid tumor cellswith an extracellular matrix; and in the presence of a basic medium, adding corresponding pleural effusion, ascites or cerebrospinal fluid and the like to carry out 3D cell culture. By the method, apatient derived tumor analog (PDTA) can be obtained effectively, and a novel detecting tool is provided for detection of sensitivity of clinical tumor patients to drugs and measurement of in-vitro metabolic stability, metabolic profiling, toxicity and the like of drug candidates.
Owner:上海赫佰生物医药科技有限公司
Primer, probe and detection reagent kit for detecting RET fusion gene
InactiveCN104745719AHigh sensitivityEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationRet genePcr dgge
The invention discloses a primer and a probe for detecting an RET fusion gene. The primer comprises an RET fusion mutation specificity reverse transcription primer, an RET gene fusion mutation detection specificity primer and a probe nucleotide sequence. The invention discloses a detection reagent kit for detecting the RET fusion gene. The detection reagent kit comprises an mRNA reverse transcription cDNA system, wherein the mRNA reverse transcription cDNA system is used for detecting the PCR reaction of the detection reagent. The specific primer and probe technology is adopted, so that the human RET gene fusion mutation can be specifically detected; a real-time fluorescent PCR system is established, and 17 fusion mutations of the RET genes can be simultaneously detected; the sensitivity is high, the mutation of 5 to 10 copies can be detected; the operation is simple, the detection is cheap, and the clinical application range is wide; the specimen detection range is wide, and the specimen can be fresh pathological tissues, paraffin-embedded tissues or pleural fluid; the detection speed is high, and the detection process can be completed in 90 minutes.
Owner:张道允 +1
BRAF gene mutation detection kit and application thereof
InactiveCN106148497AHigh sensitivityThe detection process is fastMicrobiological testing/measurementBraf genesBRAF Gene Mutation
The invention discloses a detection kit and detection method for BRAF gene mutations, and belongs to the technical field of B2D10 currently first developed high-tech industrialization important field guide / biology / novel medical precise diagnosis and treatment equipment. The detection kit is characterized by comprising two pairs of specifically amplified primers for BRAF gene mutation loci, an efficient blocking probe of a wild sequence and a BRAF gene specific TaqMan fluorescent probe. The kit can detect specimens of which the number of the mutant copies is as low as 5 to 10, and the mutation content is as low as 0.1%. The detection kit can detect five gene mutations of a BRAF gene simultaneously, the sensitivity is high, operation is easy, detection is low in price, the clinical application range is wide, samples can adopt fresh pathological tissue or paraffin-embedded tissue or a pleural fluid or serum or plasma, the detection speed is high, and only 90 minutes are needed for completing the detection process.
Owner:上海济远生物科技有限公司
Stock solution concentrating device, stock solution treatment device, and circulation-type treatment device
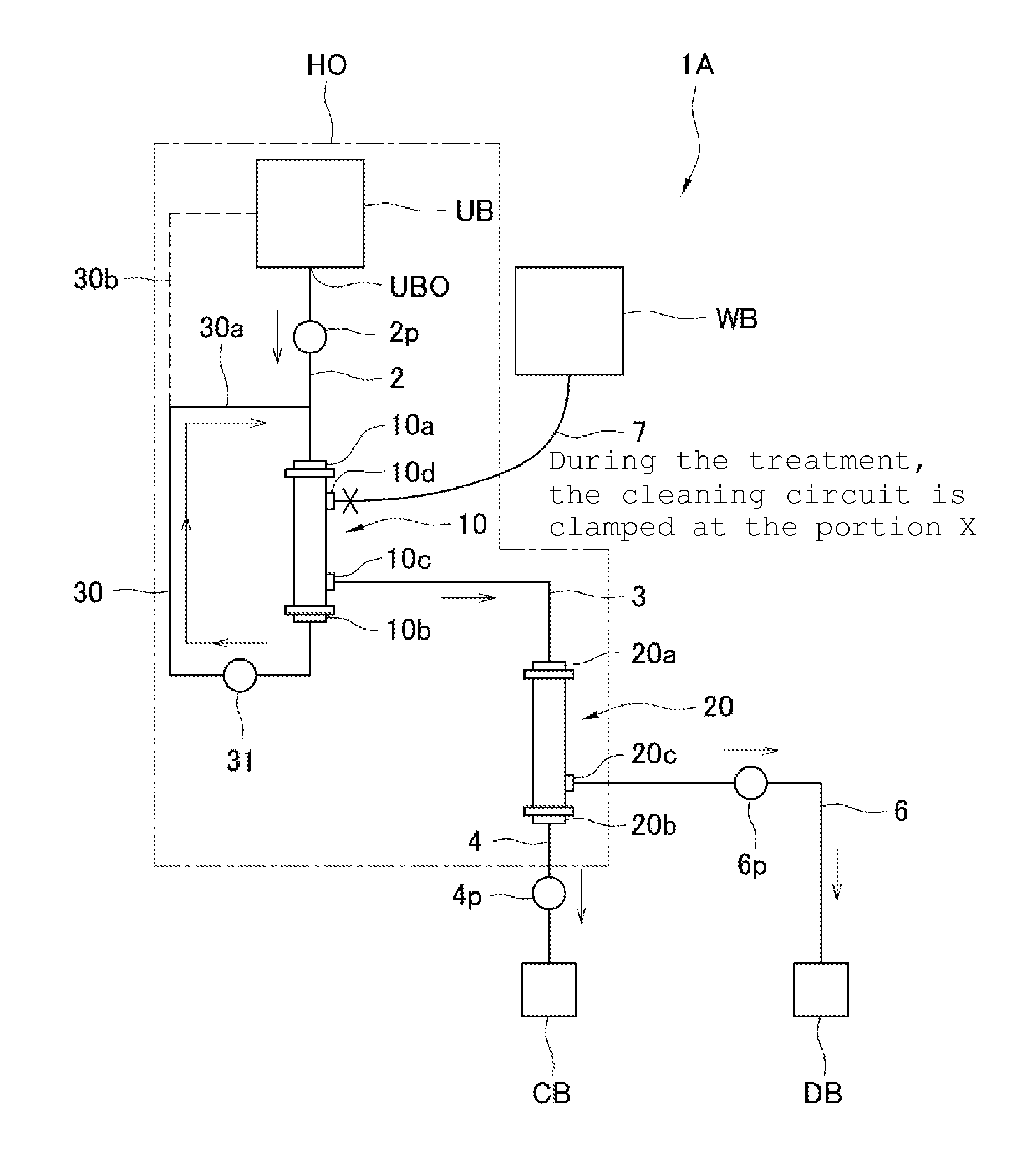
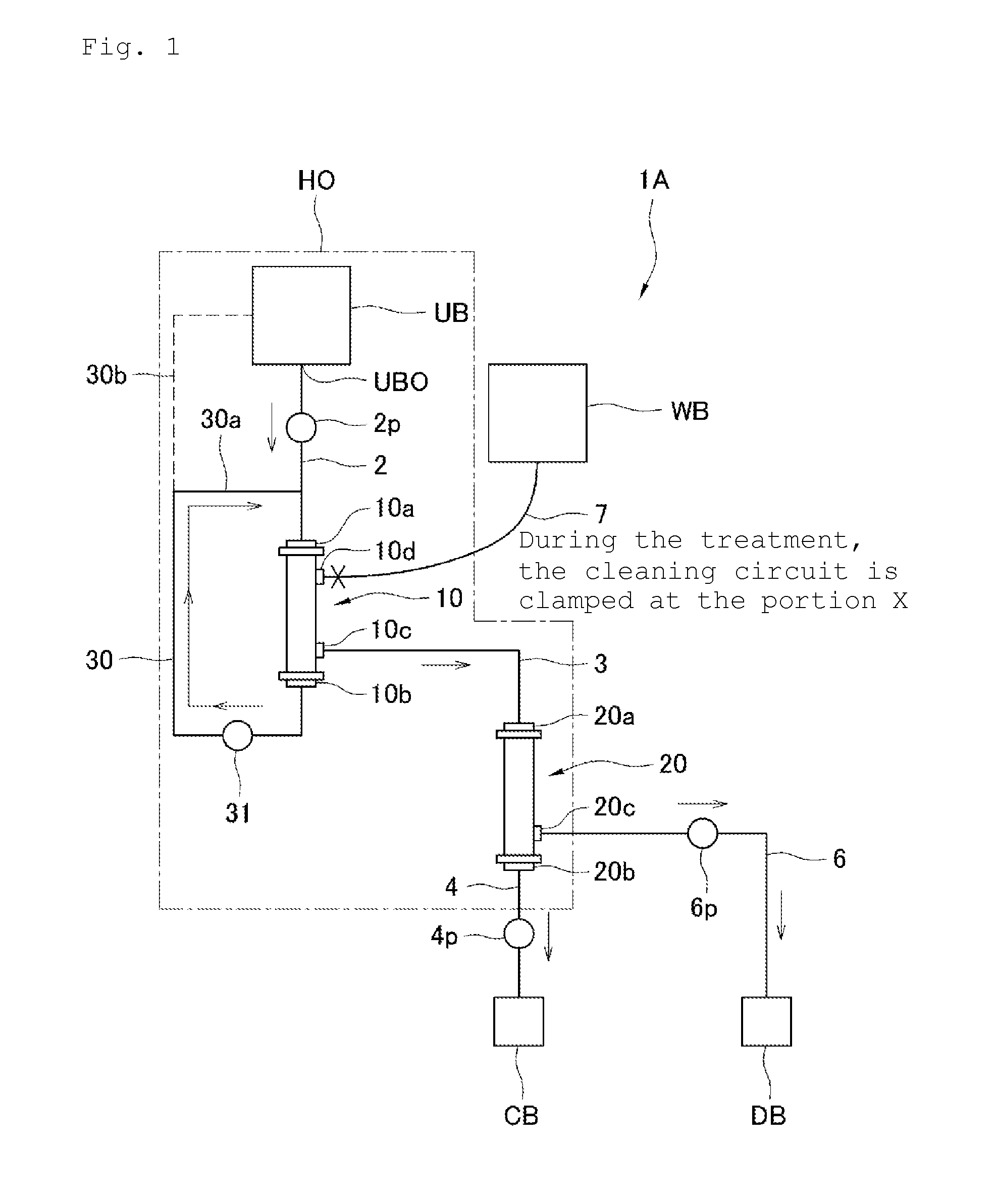
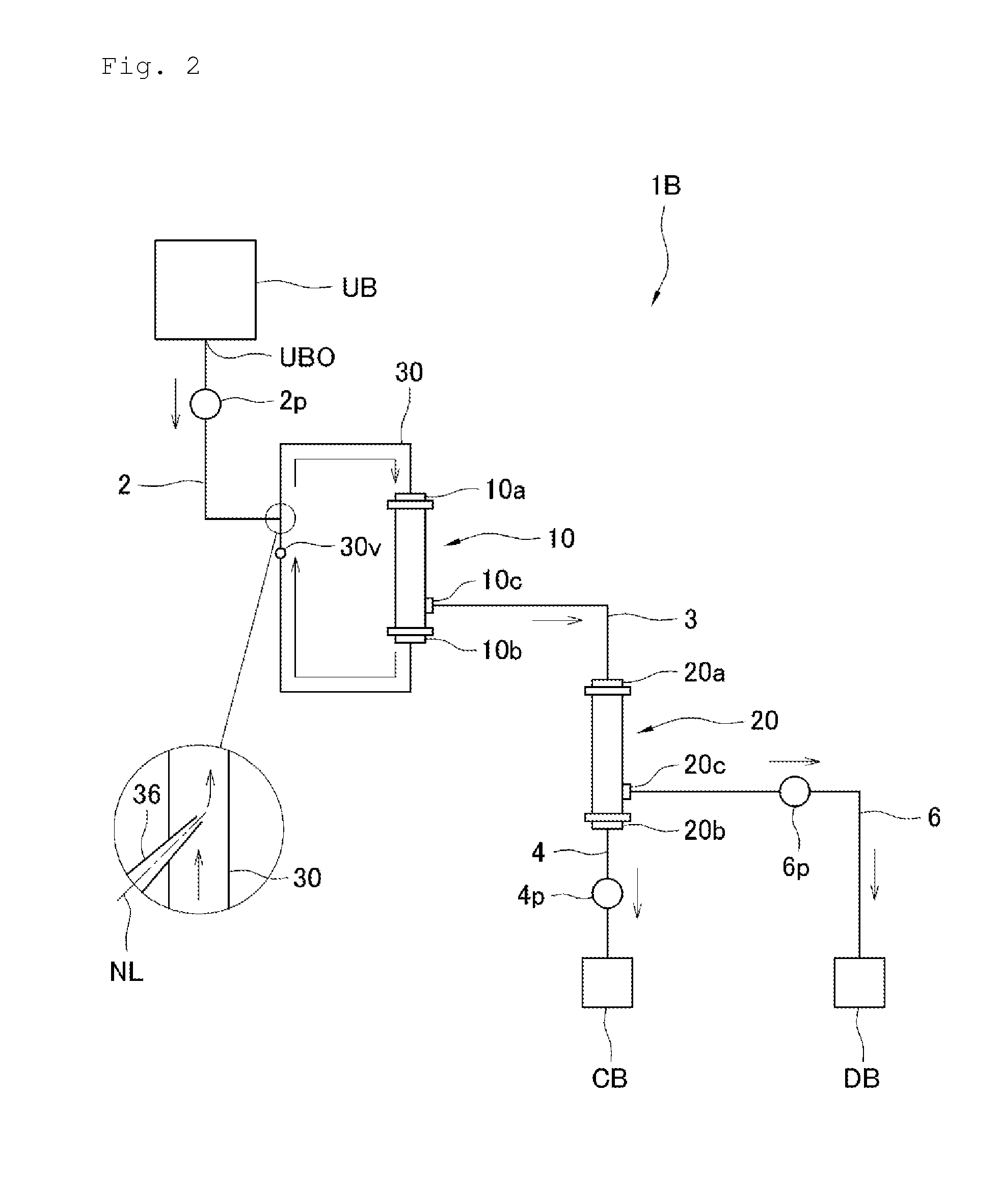
InactiveUS20160022895A1Avoid treatmentImprove efficiencySemi-permeable membranesHaemofiltrationAscitic fluidPleural fluid
Provided are a stock solution concentrating device, a stock solution treatment device and a circulation-type treatment device that can prevent the deposition of cells and the like on a filtration member and that can continuously filter and concentrate a stock solution such as pleural and ascitic fluid or blood plasma. The stock solution concentrating device concentrates a stock solution such as pleural and ascitic fluid or blood plasma to form a concentrated solution, and is equipped with: a filter (10) having a filtration member that filters the stock solution; a concentrator (20) to which the filtrate which has been filtered is supplied, and which concentrates the filtrate to form a concentrated solution; and a stock solution supply unit that supplies the stock solution to the filter (10). The stock solution supply unit has a supply amount adjustment function for adjusting the amount of the stock solution supplied to the filter.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TOKUSHIMA +1
Human epidermal growth factor tyrosine kinase inhibitor acquired drug-resistance lung cancer cell line and establishing method and application thereof
ActiveCN108866000AHigh tumorigenic activityLow tumor formation rateCell dissociation methodsMicrobiological testing/measurementCancer cellTyrosine-kinase inhibitor
The invention relates to a human epidermal growth factor tyrosine kinase inhibitor acquired drug-resistance lung cancer cell line and an establishing method and application thereof. The establishing method comprises the following steps: collecting and confirming precipitates containing cancer cells from pleural fluid of a lung cancer patient with human epidermal growth factor tyrosine kinase inhibitor acquired drug-resistance, culturing in vitro, inoculating to mouse underarm, taking tumor tissue after tumor formation, carrying out primary culture, and confirming drug-resistance tumor cells with purity being more than 90%, thereby establishing the human epidermal growth factor tyrosine kinase inhibitor acquired drug-resistance lung cancer cell line with preservation number of CCTCC NO: C2018121. The cell line keeps main clinical biological characteristics, can reflect a drug resistance mechanism more truly, has a high tumor formation rate, stable biological characteristics and strong vitality, and is an ideal cell line material for basic research and preclinical testing of human epidermal growth factor tyrosine kinase inhibitor acquired drug-resistance.
Owner:SHANGHAI PULMONARY HOSPITAL
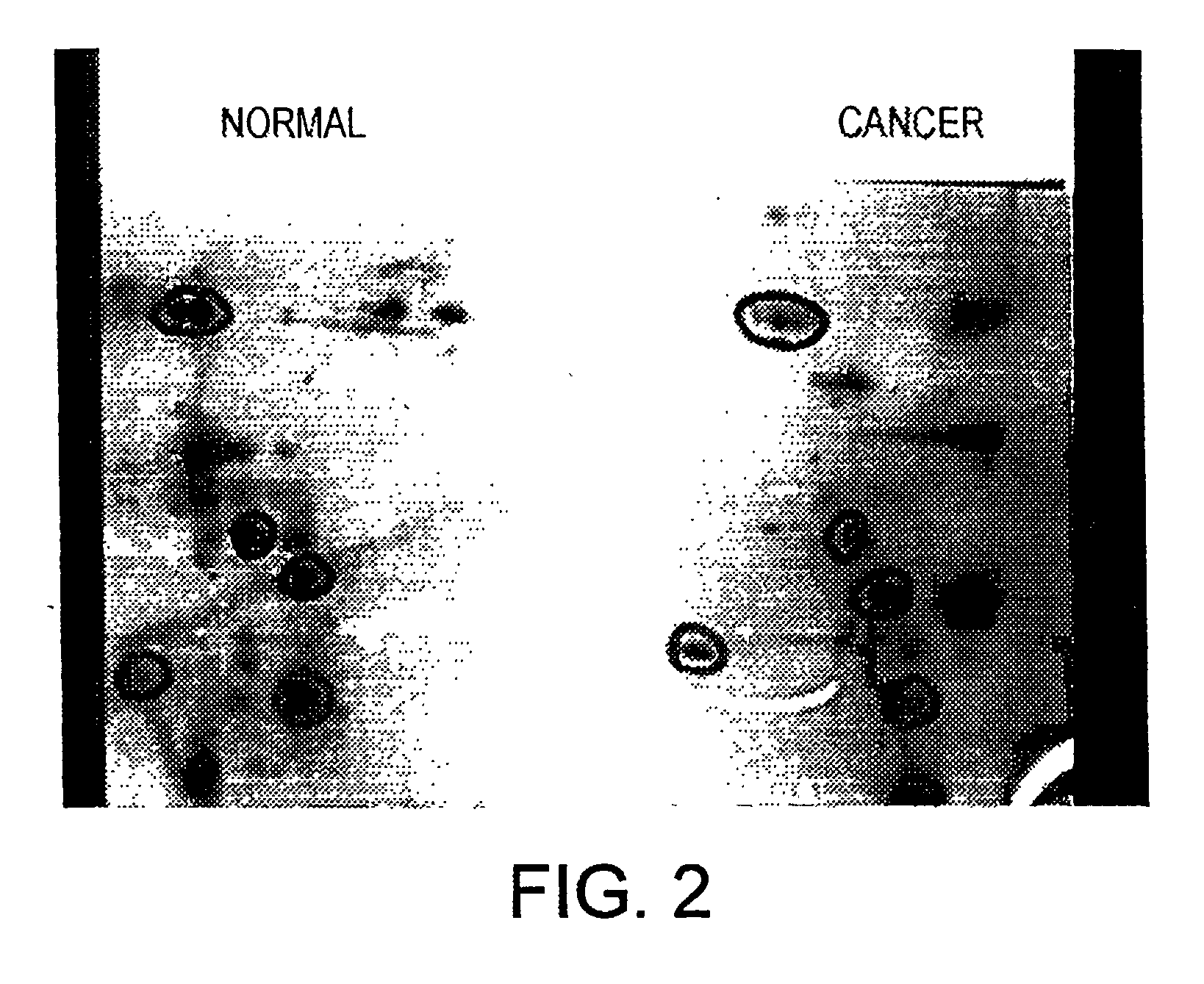
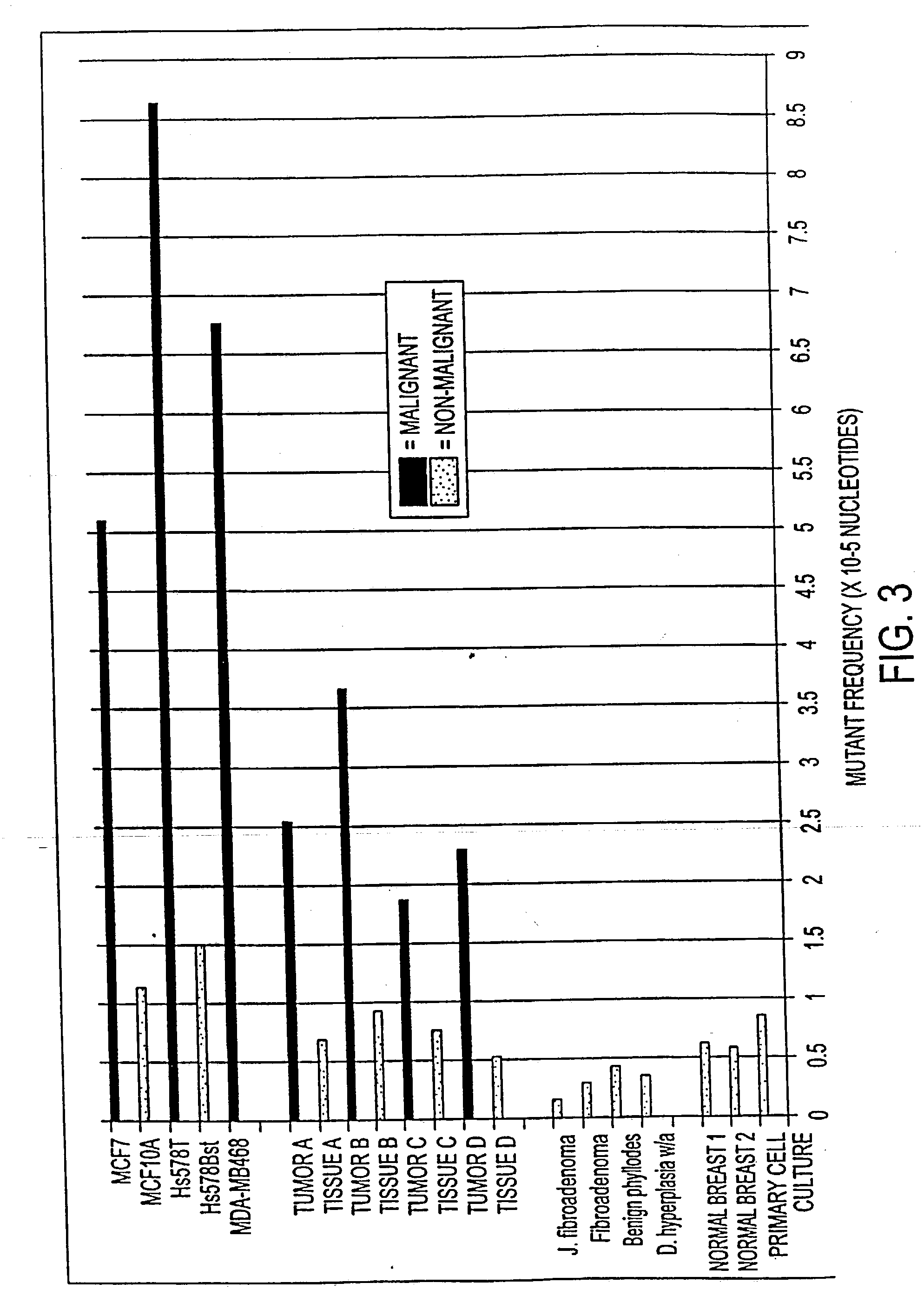
Altered DNA synthesome components as biomarkers for malignancy
InactiveUS20060073477A1Guaranteed functionChange activityPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementMalignant phenotypeNeoplasm
Owner:SCHNAPER LAUREN
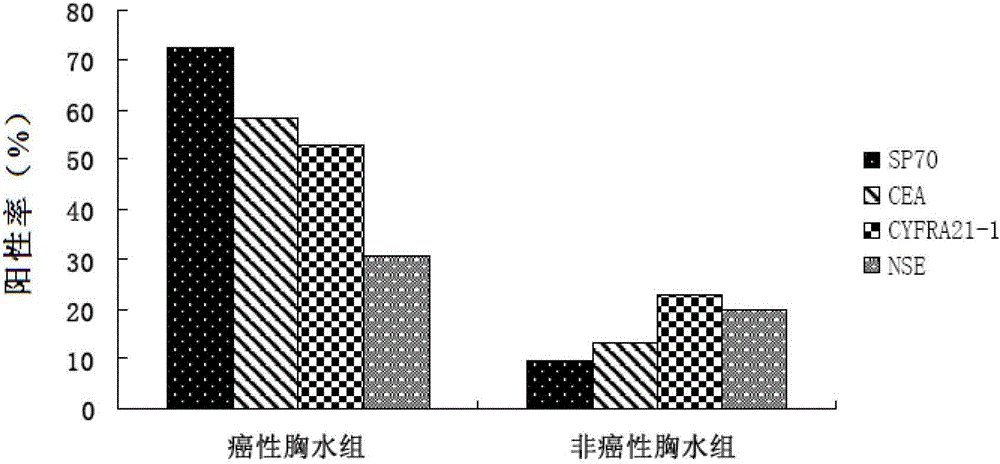
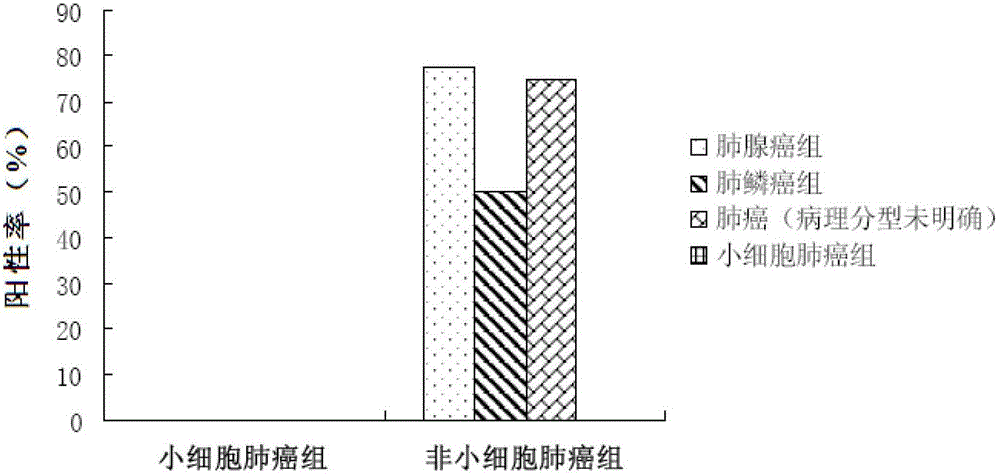
Application of non-small cell lung cancer pleural effusion tumor marker
InactiveCN102944681AMake up for the shortcomings that are not easy to identifyHard to identify shortcomings to overcomeBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceAntigenFluorescence
The invention belongs to the field of biological sample detection and discloses an application of a non-small cell lung cancer pleural effusion tumor marker. SP70 is used as the non-small cell lung cancer pleural effusion tumor marker to be applied to preparation of non-small cell lung cancer pleural effusion and / or pleural effusion cast-off cell diagnostic reagents. A monoclonal antibody of the SP70 is applied to preparation of the non-small cell lung cancer pleural effusion and / or pleural effusion cast-off cell diagnostic reagents. A direct immunofluorescence detection kit of non-small cell lung cancer pleural effusion cast-off cells contains the fluorescently-labeled monoclonal antibody of the SP70, 5% of bovine serum albumin (BSA) and 1% of a phosphate buffer solution (PBS). According to a great quantity of experimental researches, SP70 antigens can serve as a sensitive and specific detection index of malignancy pleural effusion caused by non-small cell lung cancers, simultaneously, the SP70 antigens in the pleural effusion and the pleural effusion cast-off cells can be detected, and sensitivity and specificity of carcinogenic pleural effusion diagnosis can be greatly improved.
Owner:潘世扬
Pleural effusion tumor cell detection kit
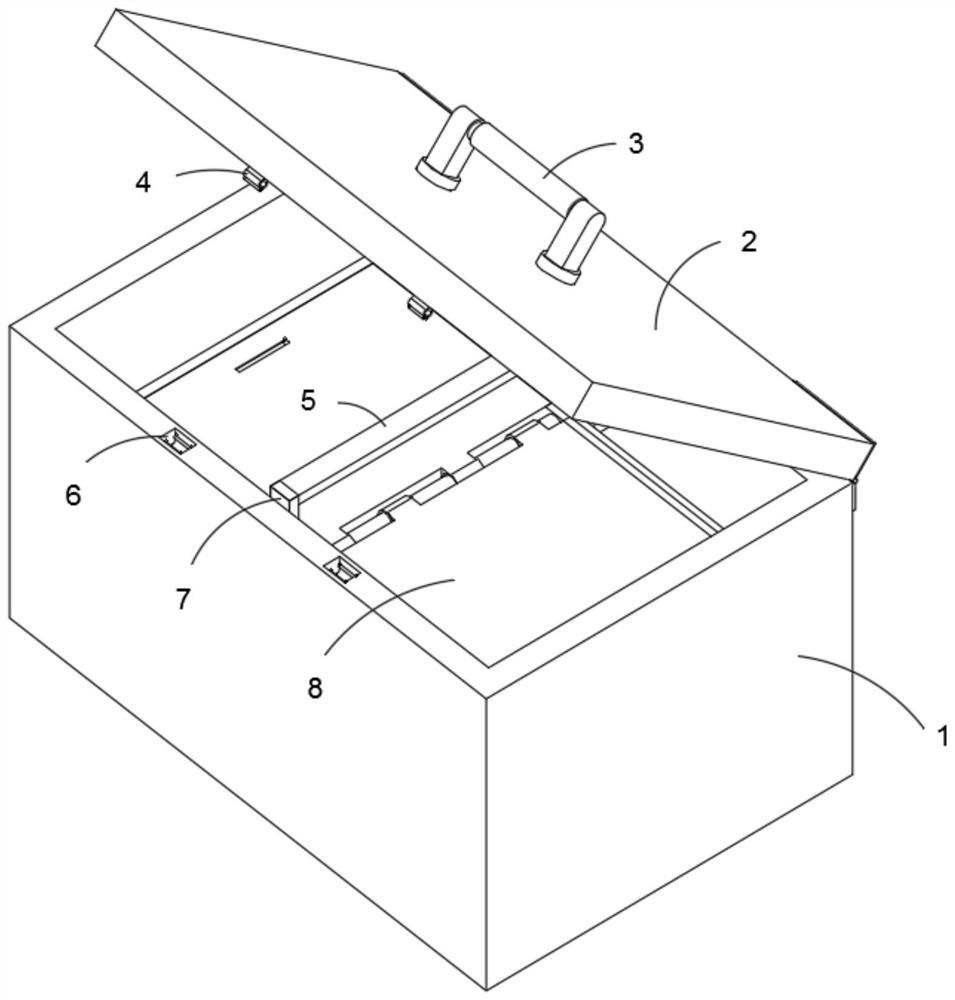
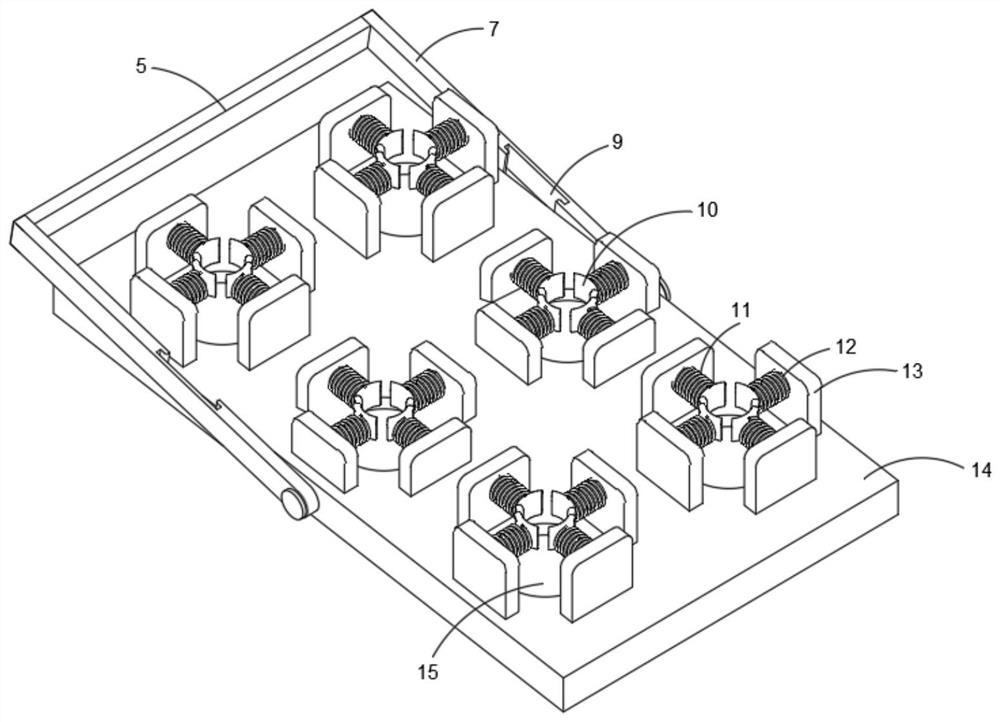
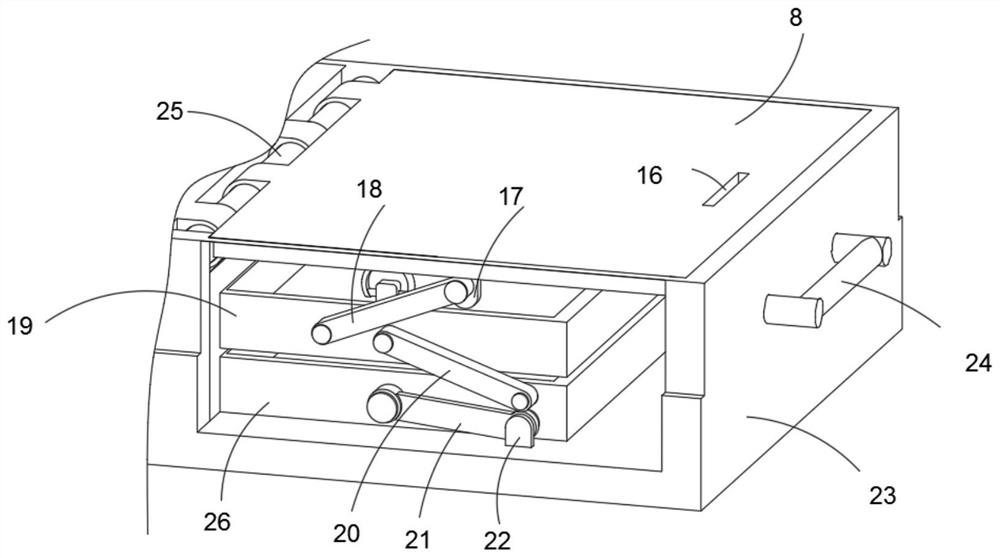
InactiveCN112078934AEasy to carryReduce wasteContainers to prevent mechanical damageInternal fittingsPlastic materialsEngineering
The invention discloses a pleural effusion tumor cell detection kit, and relates to the technical field of medical treatment. The pleural effusion tumor cell detection kit comprises a kit shell, a reagent tube fixing base and a sliding box, wherein the reagent tube fixing base is located in the kit shell; and the sliding box is located over the reagent tube fixing base and is located in the kit shell. The pleural effusion tumor cell detection kit further comprises supporting rods arranged on two sides of the reagent tube fixing base respectively, wherein the sides, close to the bottom edge, ofthe two supporting rods are rotatably connected with the centers of the outer surfaces of the two sides of the reagent tube fixing base correspondingly; and a connecting rod is fixedly connected between the adjacent sides, close to the top edge, of the two supporting rods. The pleural effusion tumor detection kit provided by the invention can carry more detection devices, and the detection kit ismade of a medical plastic material, so that the pleural effusion tumor detection kit can be recycled, deformation can be effectively prevented, and compared with a disposable kit, the pleural effusion tumor detection kit has the advantage that the phenomenon of resource waste is greatly reduced.
Owner:深圳市森盈生物科技有限公司
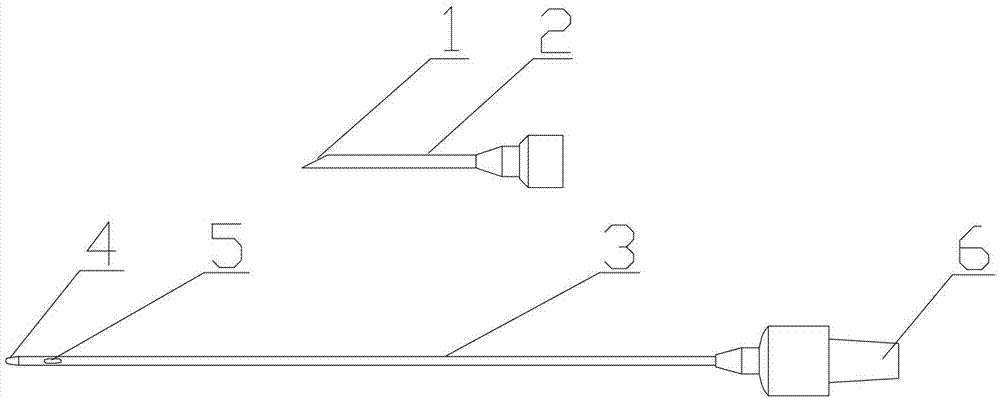
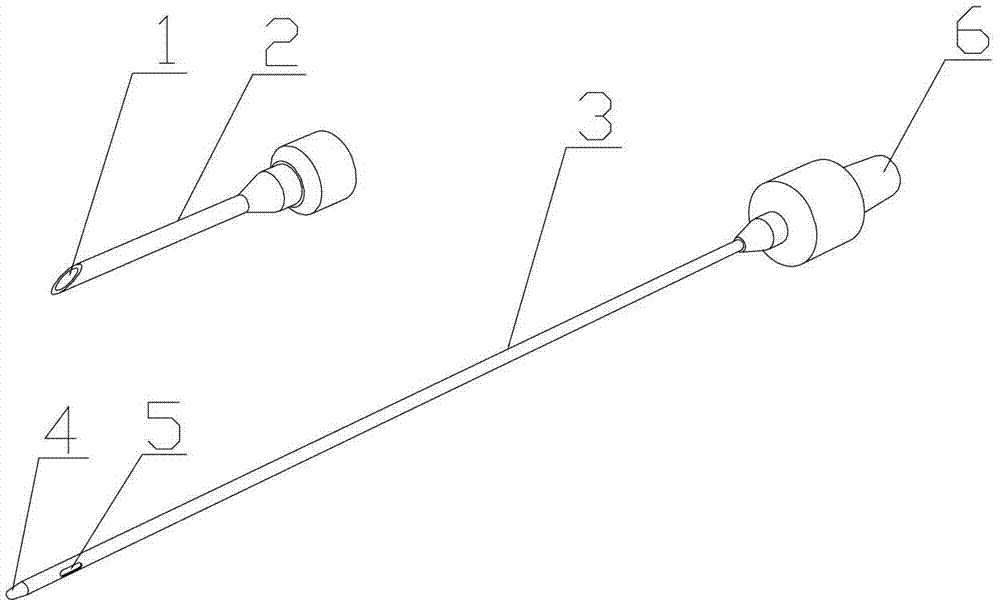
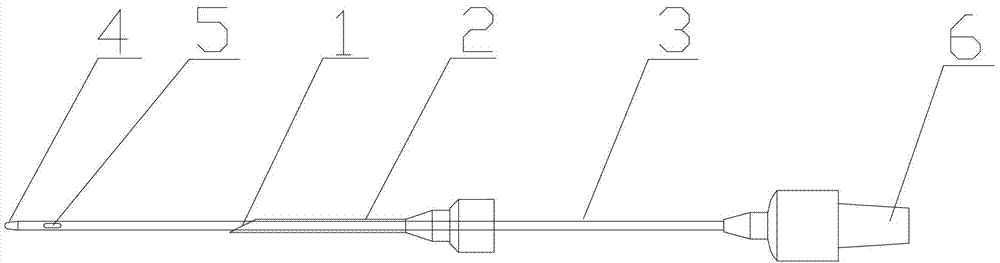
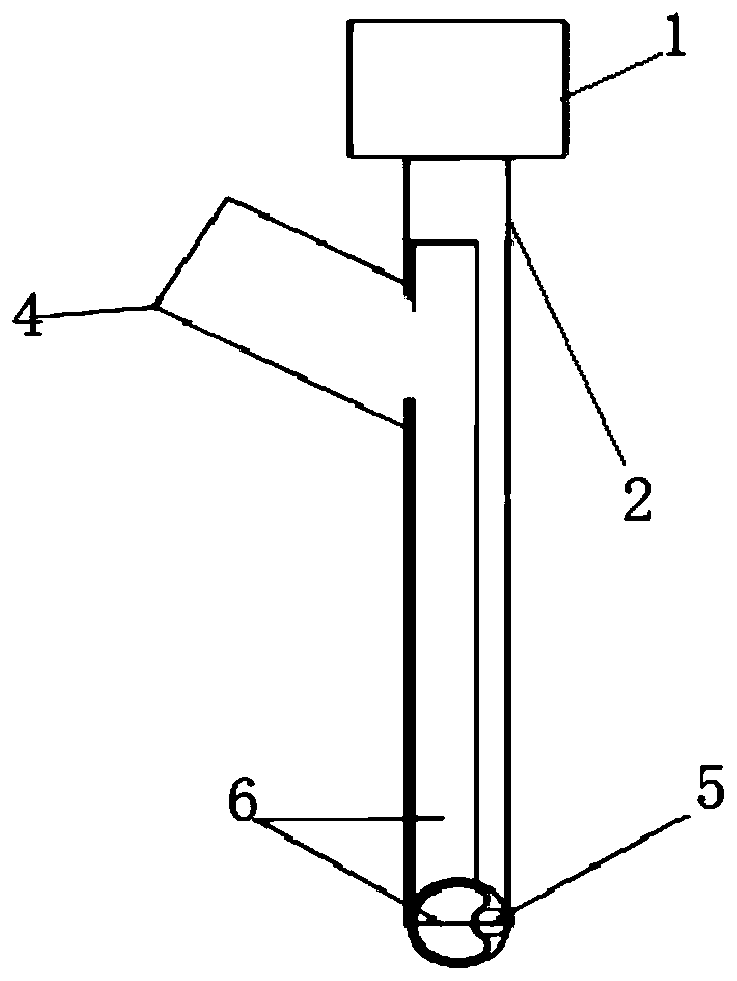
Thoracocentesis drainage needle
InactiveCN103040504AAvoid cloggingLow operating pressureGuide needlesSurgical needlesGynecologyHydrothorax
Owner:JIANGSU BLUE AREA INNOVATION TECH INVESTMENT
Preparation method for thyroid and mammary fine needle aspiration cell tissue blocks
ActiveCN109975090ASimple structureNo privacy involvedPreparing sample for investigationHydrothoraxThyroid
The invention provides a preparation method for thyroid and mammary fine needle aspiration cell tissue blocks. The method includes the following steps: a, performing centrifugation on hydrothorax or ascites in advance, and obtaining hydrothorax or ascites supernatant; b, taking the hydrothorax or ascites supernatant to inject into a centrifuge tube; c, injecting a fine needle punctured thyroid andmammary specimen into the centrifuge tube, and then immediately taking 95% of ethanol to inject into the centrifuge tube; and d, performing centrifugation on the centrifuge tube and abandoning the supernatant so that cell sediment can be obtained, adding 4% of neutral buffer formaldehyde fixative, and adopting a paraffin tissue specimen processing program to perform conventional embedding after the cell sediment in the centrifuge tube is solidified. The preparation method can guarantee that tissue fragments and free-floating single cells are not lost; and cytoplasm is good in form and structure preservation, can be sliced continuously or for many times, and is suitable for a plurality of dyeing, and therefore, diagnosis efficacy can be enhanced.
Owner:马晓丽
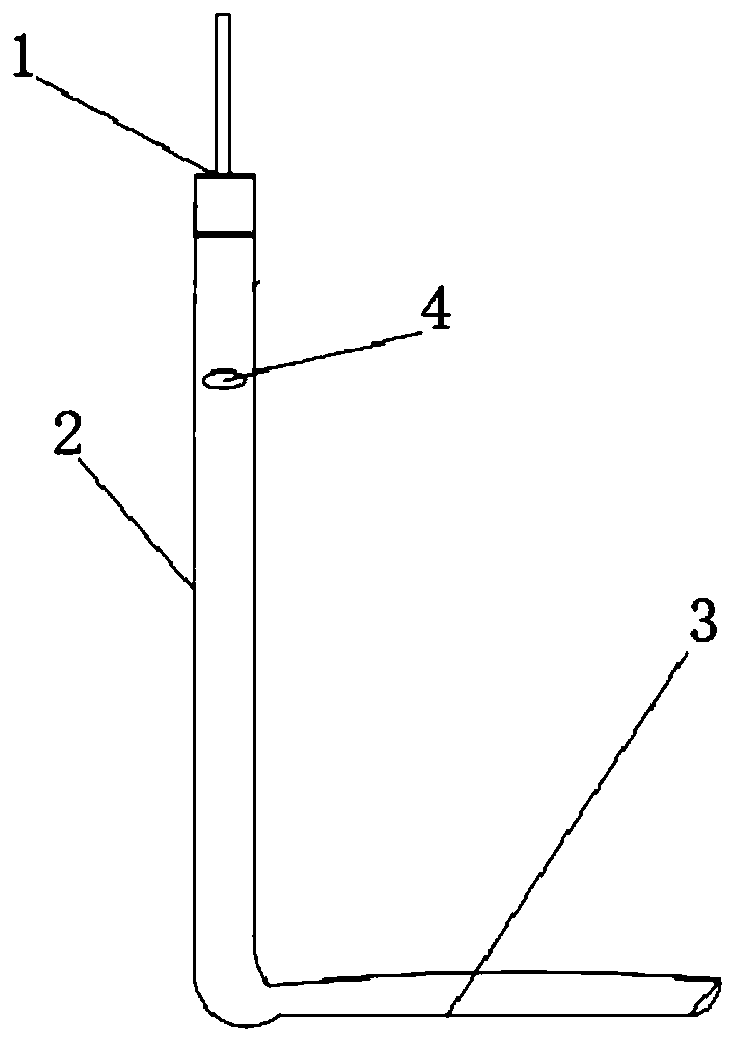
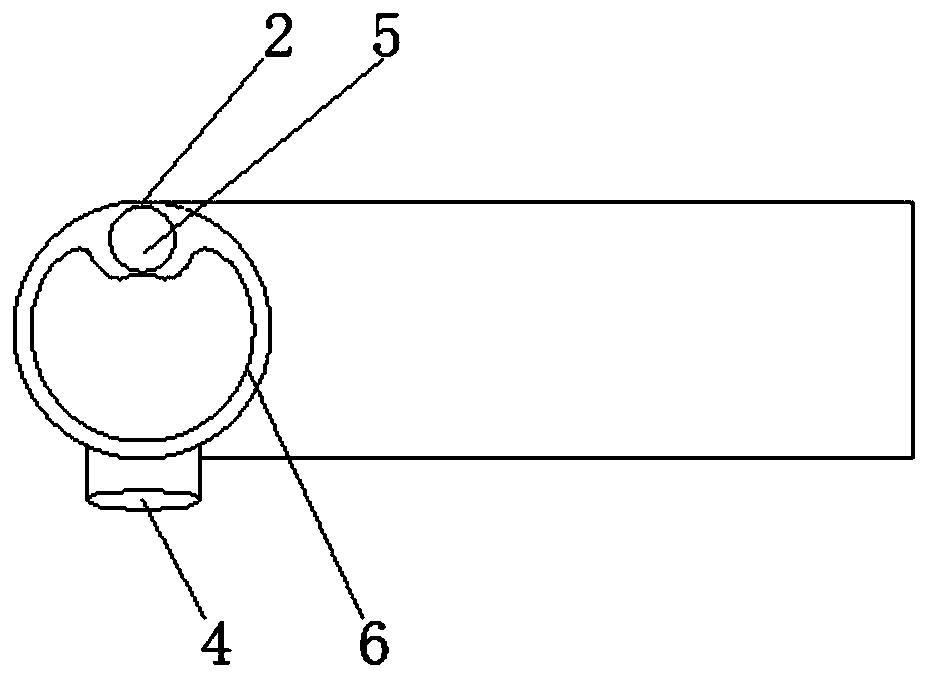
Visualized pleura brush cytology instrument
PendingCN111227875AReduce washoutImprove fitSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsBrushing cytologyMedicine
The invention discloses a visualized pleura brush cytology instrument. The visualized pleura brush cytology instrument comprises a main body and an image acquisition mechanism, wherein the main body is in the shape of an L; a biopsy channel is formed in the main body; a displayer and a light source host machine are mounted at the top of the vertical part of the main body; a biopsy hole is formed in the side wall of the vertical part of the main body; and the image acquisition mechanism is located at the tail end of a horizontal part of the main body, and is electrically connected with the displayer and the light source host machine. According to the visualized pleura brush cytology instrument disclosed by the invention, the brush cytology device is firstly a visual device, so that the risks of blind brushing and blind test are avoided; through the L-shaped design, a cell brush is preferably jointed to the chest wall; besides, through the protecting effect of a brush cytology groove, the scouring action of hydrothorax to the cell brush is reduced, so that the brush cytology positive rate is increased, and the risk is reduced; and the visualized pleura brush cytology instrument has the advantage of being portable and small in damage, so that the visualized pleura brush cytology instrument is suitable for developing brush cytology at bedside and in an endoscope chamber.
Owner:郝登荣 +1
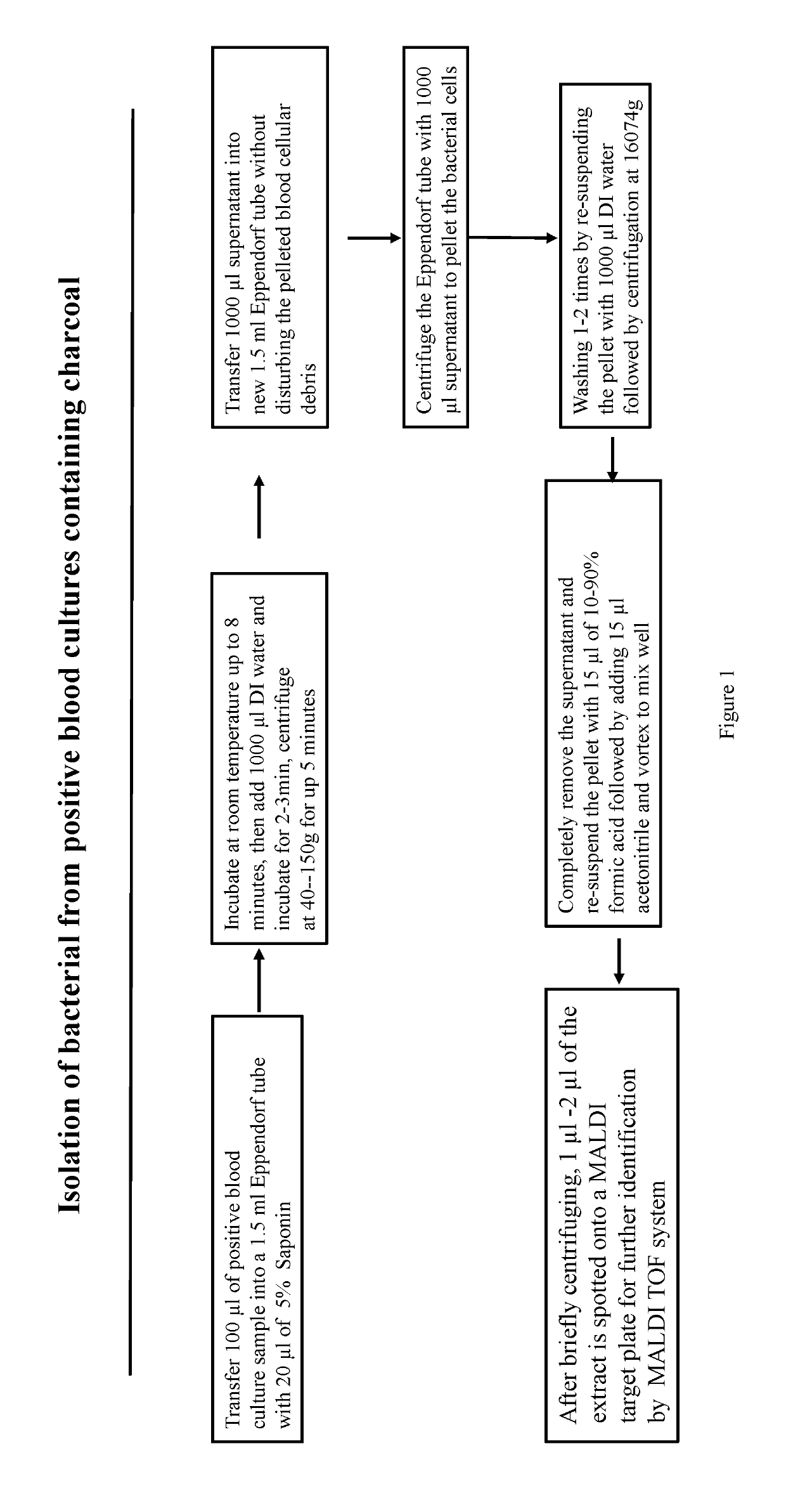
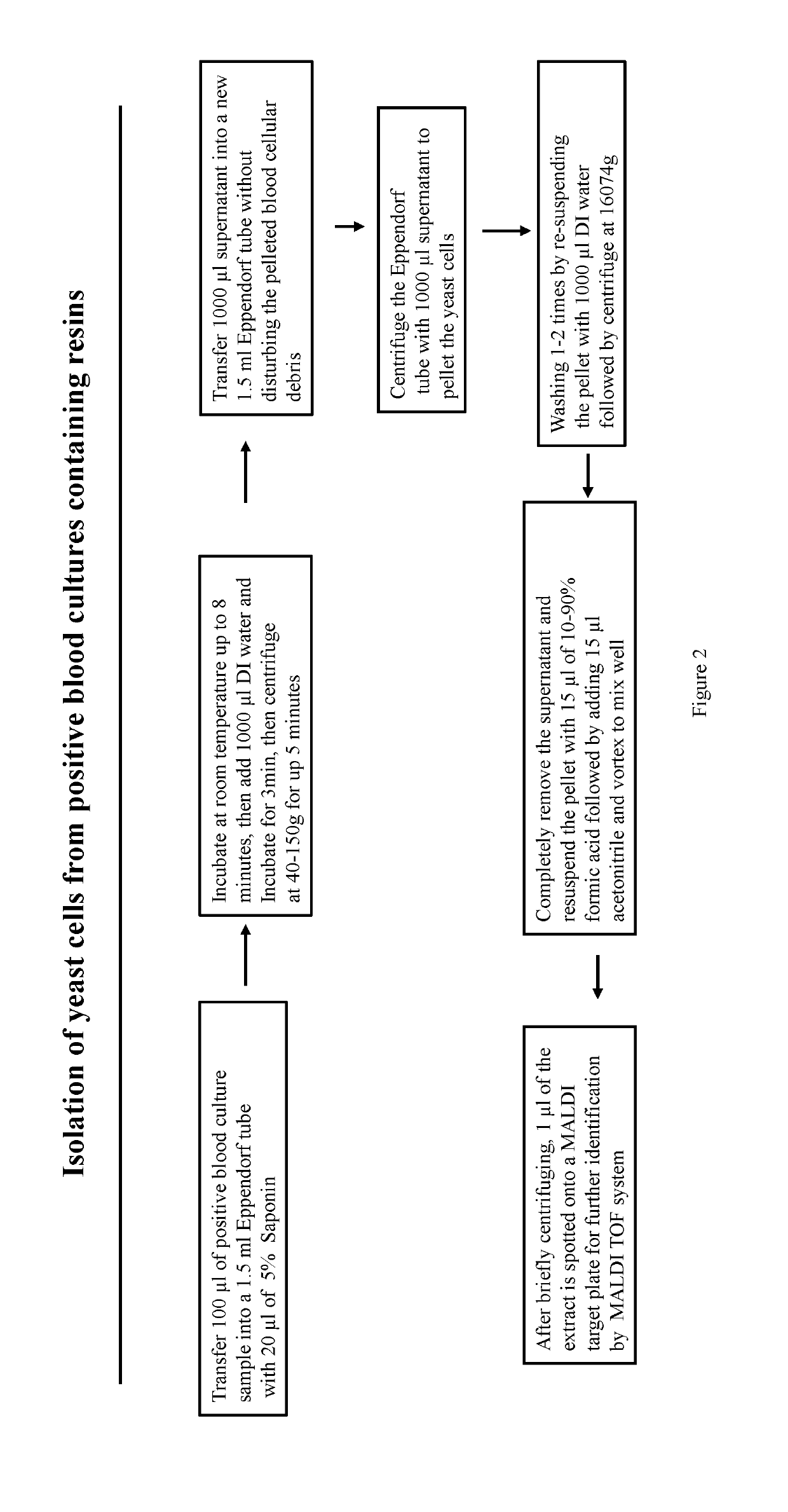
Method for rapid and direct identification of microbial pathogen from positive culture sterile body fluids using mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20190293646A1Accurate mass spectrometryShort timeMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingClinical settingsLow speed
The invention provides methods for rapid isolation of microorganisms from positive culture sterile body fluids, including blood, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), pleural fluid, ascitic fluid, pericardial effusion, joint cavity fluid, vitreous fluid, and amniotic fluid for mass spectrometry identification. Whenever the subject of blood culture is discussed, the intended sample used is always related to blood sample. However, it is also necessary to be aware that other than the blood sample, sterile fluids can also be inoculated as samples for blood culture testing. Among the sterile fluids that are commonly known are CSF, pleural fluid, ascitic fluid, pericardial effusion, joint cavity fluid, vitreous fluid, amniotic fluid etc. The methods involve combining micro-volume positive blood culture sample with detergent solution to lyse human blood cells, then isolating the microorganism by differential centrifugation process that first removes interfering substances such as charcoal (when present), resins and human blood cellular debris through a low speed centrifugation, then isolates the microorganisms in the sample supernatant through a fast centrifugation. The methods not only apply to regular blood culture media but also apply to antimicrobial removal containing media such as resin containing BD BACTEC™ Plus-Aerobic media and charcoal-containing Biomerieux BacT / Alert® FA media. In addition, the methods can isolate a variety of Gram-positive bacteria, Gram-negative bacteria, and yeast in clinical settings. The isolated microorganism(s) from positive blood culture can be used for multiple downstream analyses, including identification of the microorganism(s) by mass spectrometry, phonotypical, or molecular identification methods.
Owner:FENG LIPING
Drainage tube for gathered tumor cast-off cells
ActiveCN104771826AIncreased stay enrichment opportunitiesImprove the detection rateSurgical needlesCatheterHuman bodyAbdominal cavity
The invention discloses a drainage tube for gathered tumor cast-off cells. The drainage tube comprises a drainage tube body. The end, located in the thoracic and abdominal cavity, of the drainage tube body is provided with a platform type bent portion. A step, opposite to the flowing direction of seroperitoneum, of the platform type bent portion is provided with a groove used for depositing the tumor cast-off cells. The portion, located in a human body, of the drainage tube is set to be of a bent structure, the groove is formed in the step corresponding to the flowing direction of seroperitoneum, the chance of staying and gathering of the tumor cast-off cells is increased, and it can be guaranteed that the tumor cast-off cells will be deposited and sucked into the drainage tube when passing through the drainage tube; the tumor cell detection rate is improved, missed diagnosis of tumorous pleural fluid and ascites is effectively avoided, and a reliable guarantee is provided for pretreatment of a patient.
Owner:WUXI PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Methods for classifying pleural fluid
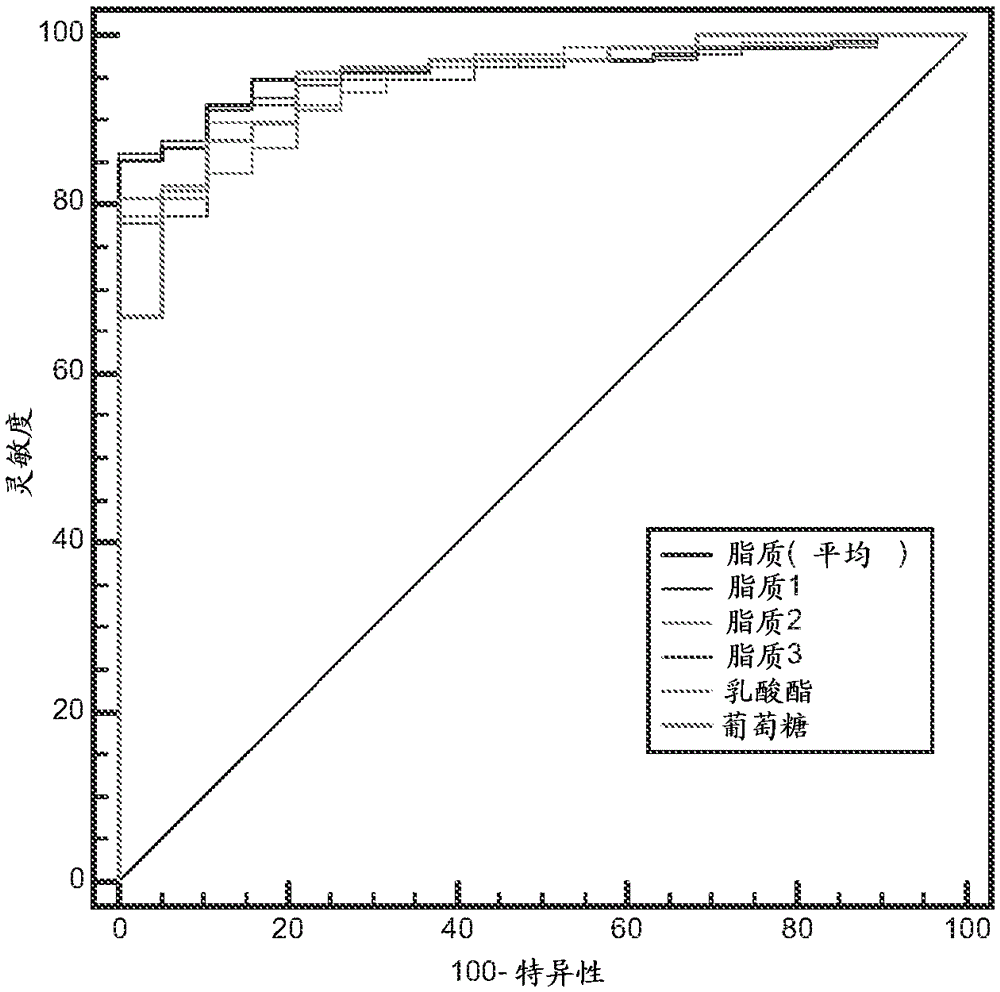
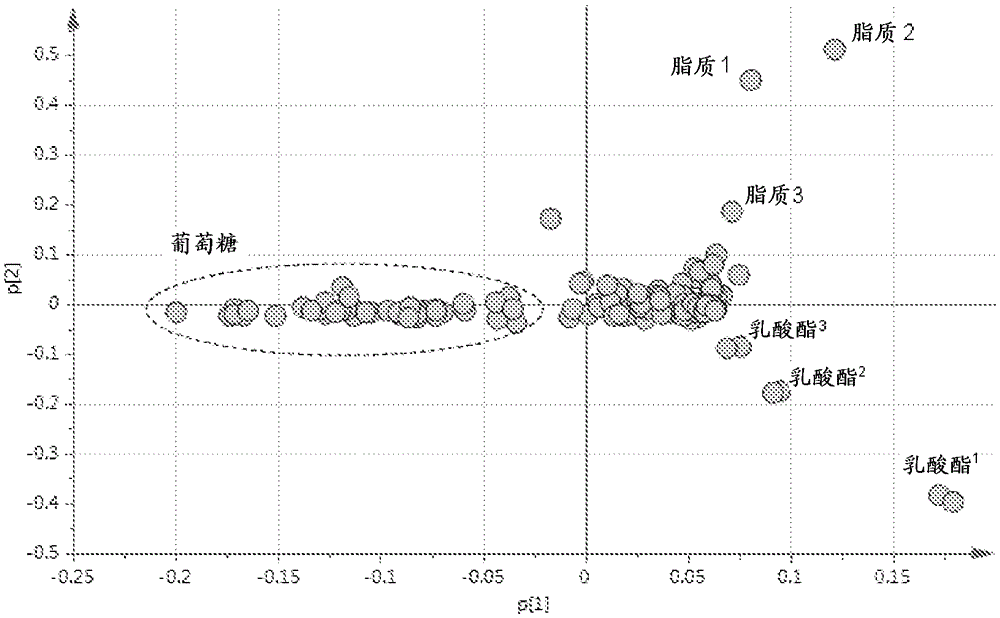
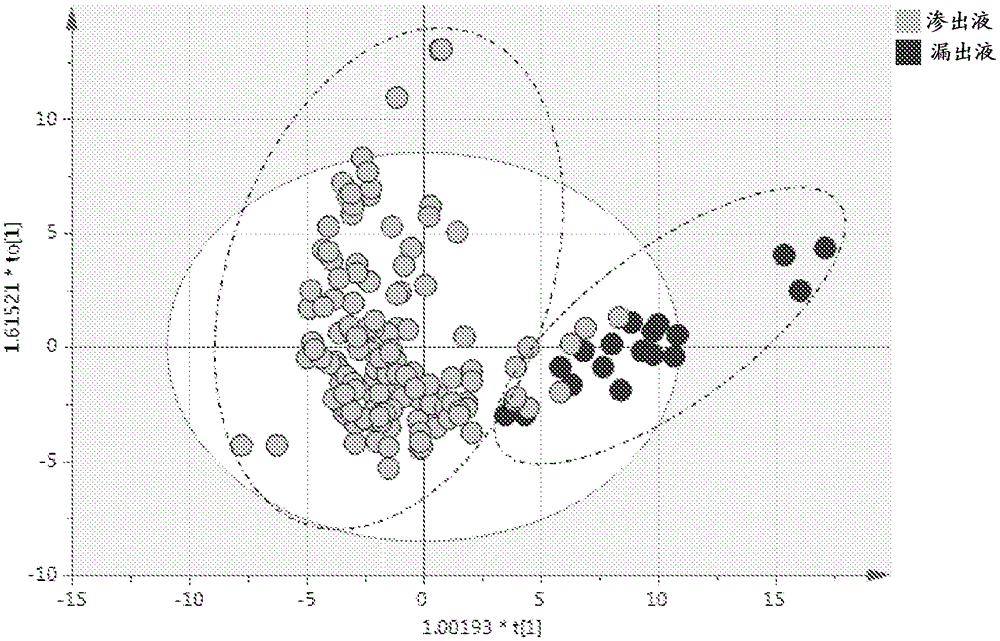
InactiveCN105555318AMicrobiological testing/measurementRespiratory organ evaluationDiseaseNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
Methods of classifying pleural fluid are disclosed. The methods typically include determining the level of indicator nanoparticles, such as lipids, particularly large lipids, in the pleural fluid of a subject. The level of lipids can be determined by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), such as proton NMR (1H-NMR) by measuring the NMR signal corresponding to methyl protons, methylene protons, methene protons, or combinations thereof. The level of large lipids in pleural fluid can be carried out in vitro on a sample of pleural fluid obtained from the subject or in vivo using magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS). The pleural fluid can be classified as exudate or transudate with a sensitivity, selectivity, or combination thereof of 85%, 90%, 95%, 99%, or high, a selectivity of 85%, 90%, 95% and 99%. The method can be coupled with diagnosing and / or treating the subject with a disease, disorder, or condition.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
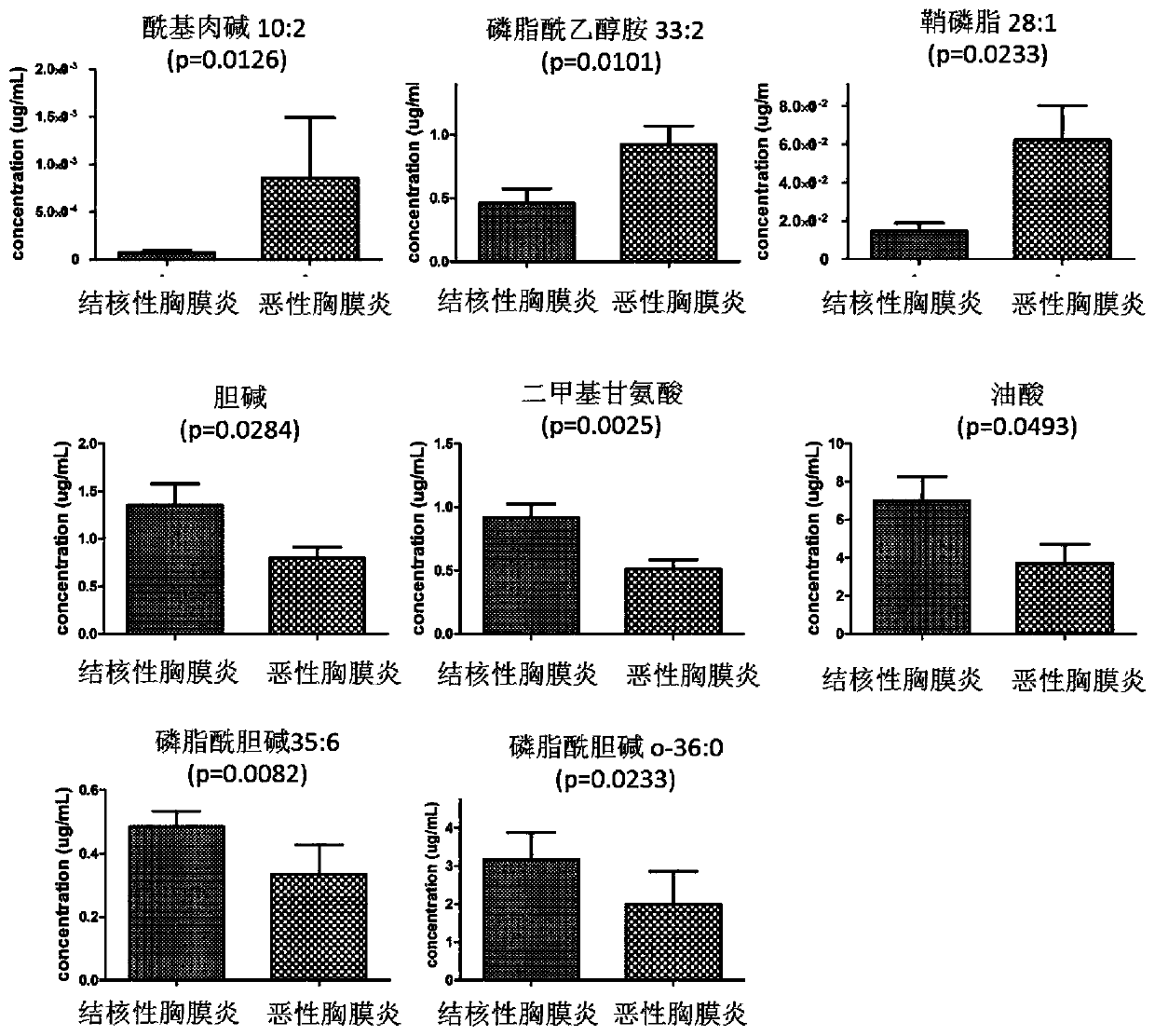
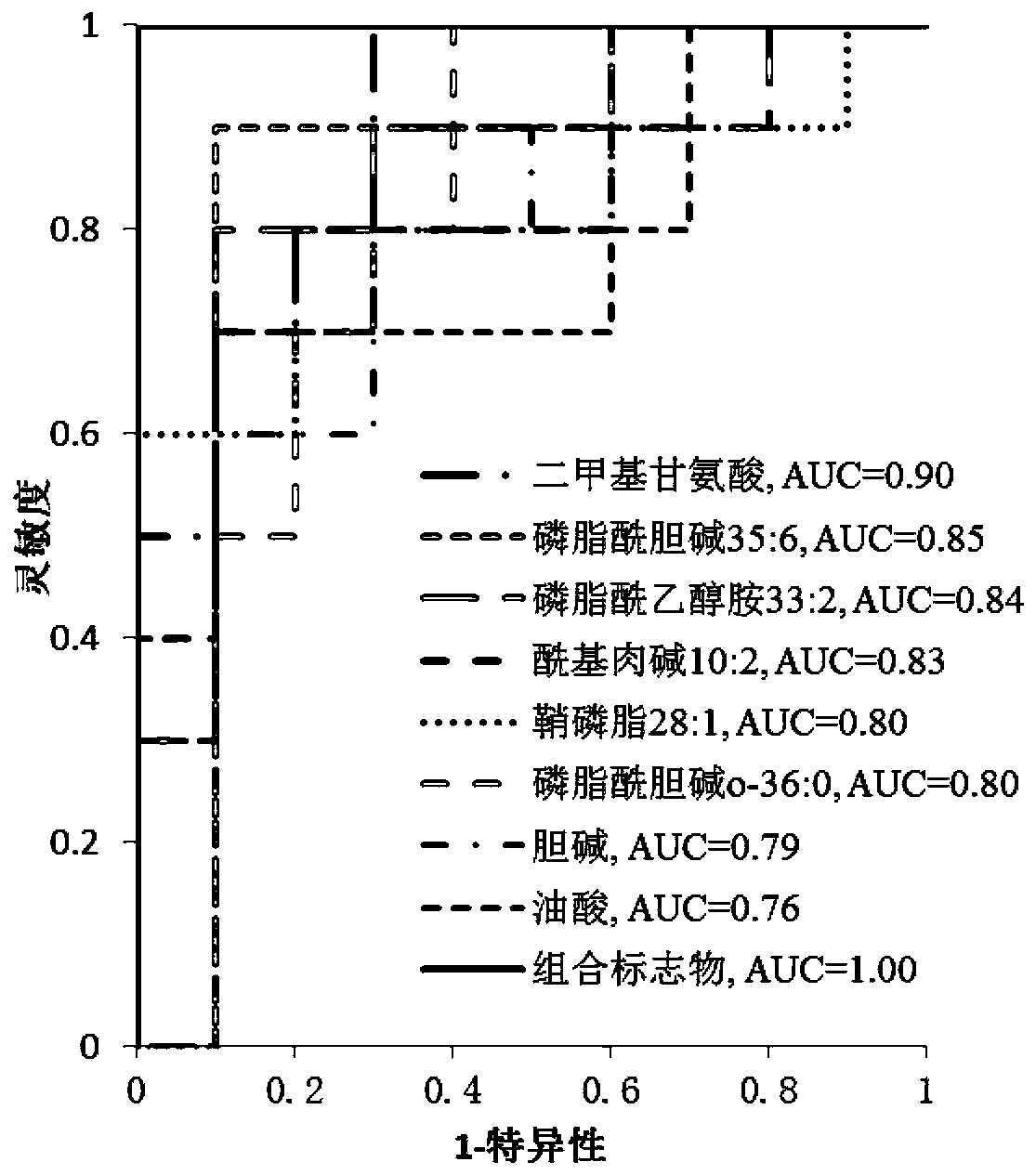
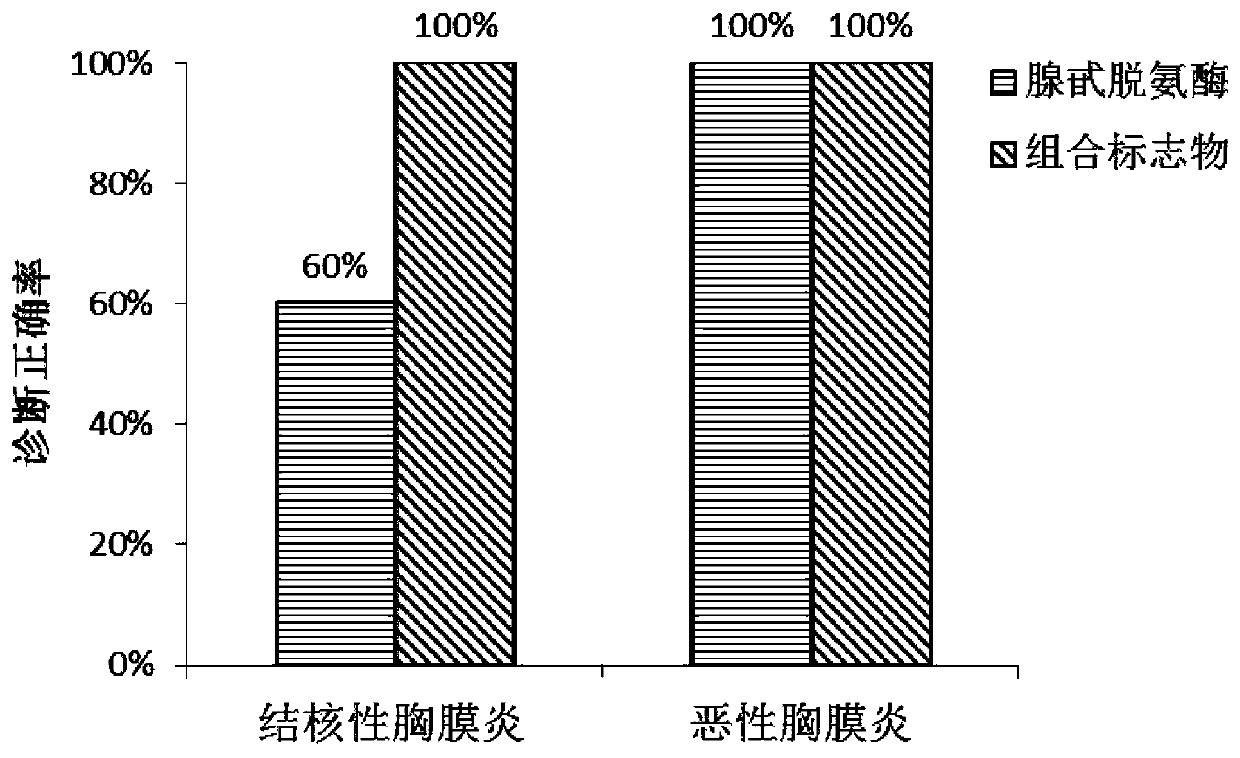
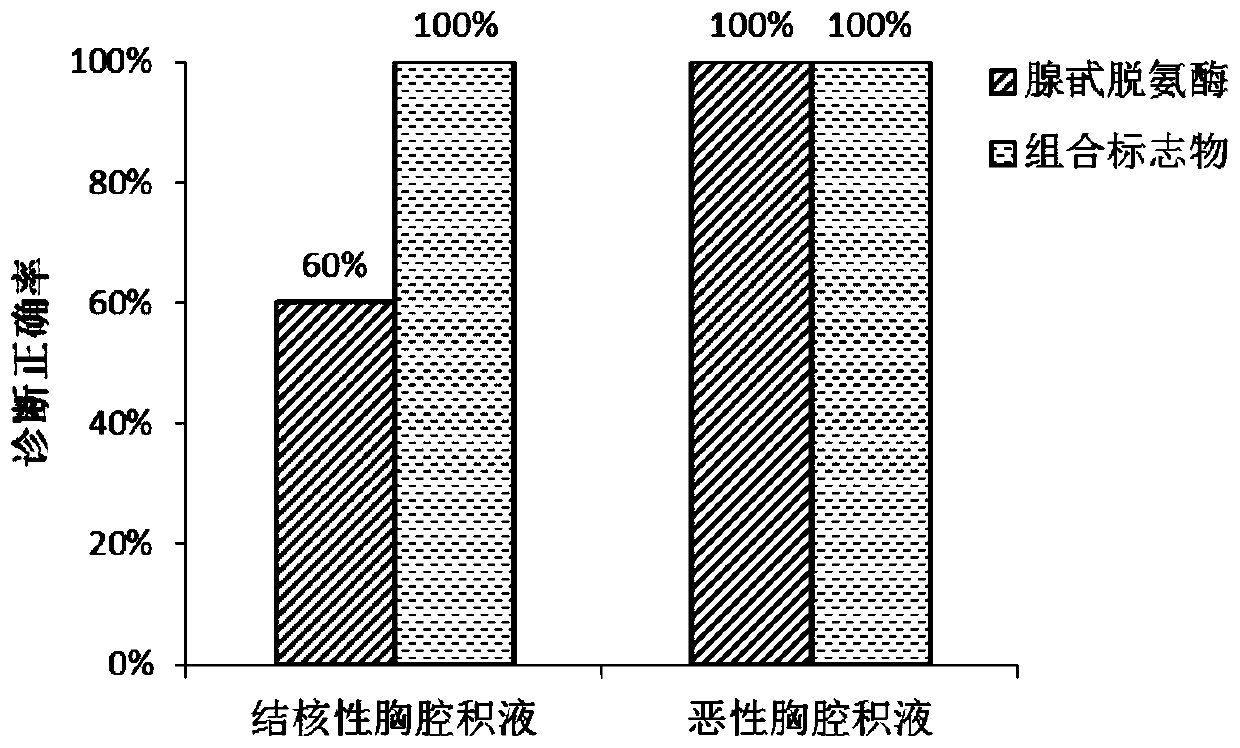
Hydrothorax exosome metabolite combination, kit and method for diagnosing tuberculous pleurisy
ActiveCN110954607AHigh diagnostic sensitivityHighly specific featuresComponent separationHydrothoraxAcyl group
The invention relates to a hydrothorax exosome metabolite combination, a kit and a method for diagnosing tuberculous pleurisy. The hydrothorax exosome metabolite combination for diagnosing the tuberculous pleurisy is prepared from dimethylglycine, choline, acyl carnitine with the ratio of 10: 2, phosphatidylcholine with the ratio of 35: 6, phosphatidylcholine o with the ratio of -36: 0, phosphatidylethanolamine with the ratio of 33: 2, sphingomyelin with the ratio of 28: 1 and oleic acid. The kit for diagnosing the tuberculous pleurisy comprises an internal standard substance required for detecting the concentration of the metabolites in the hydrothorax exosome sample extraction solution. A combined marker provided by the invention has the characteristics of high sensitivity and high specificity for the diagnosis of tuberculous pleurisy, and meanwhile, can be complementary with the traditional marker adenosine deaminase, and can be used for the auxiliary diagnosis of the tuberculous pleurisy by being combined with the traditional marker adenosine deaminase.
Owner:XIEHE HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI & TECH UNIV
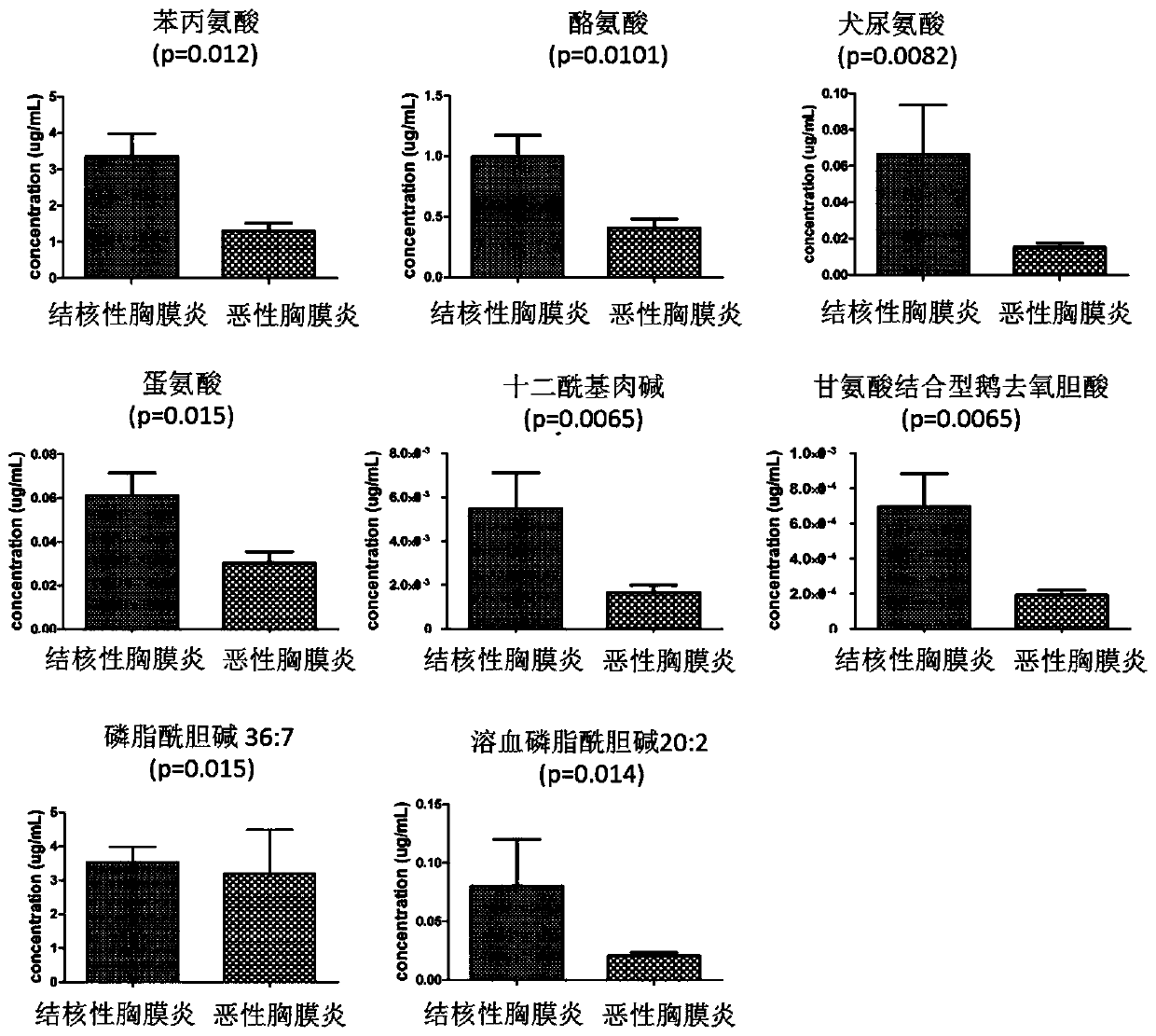
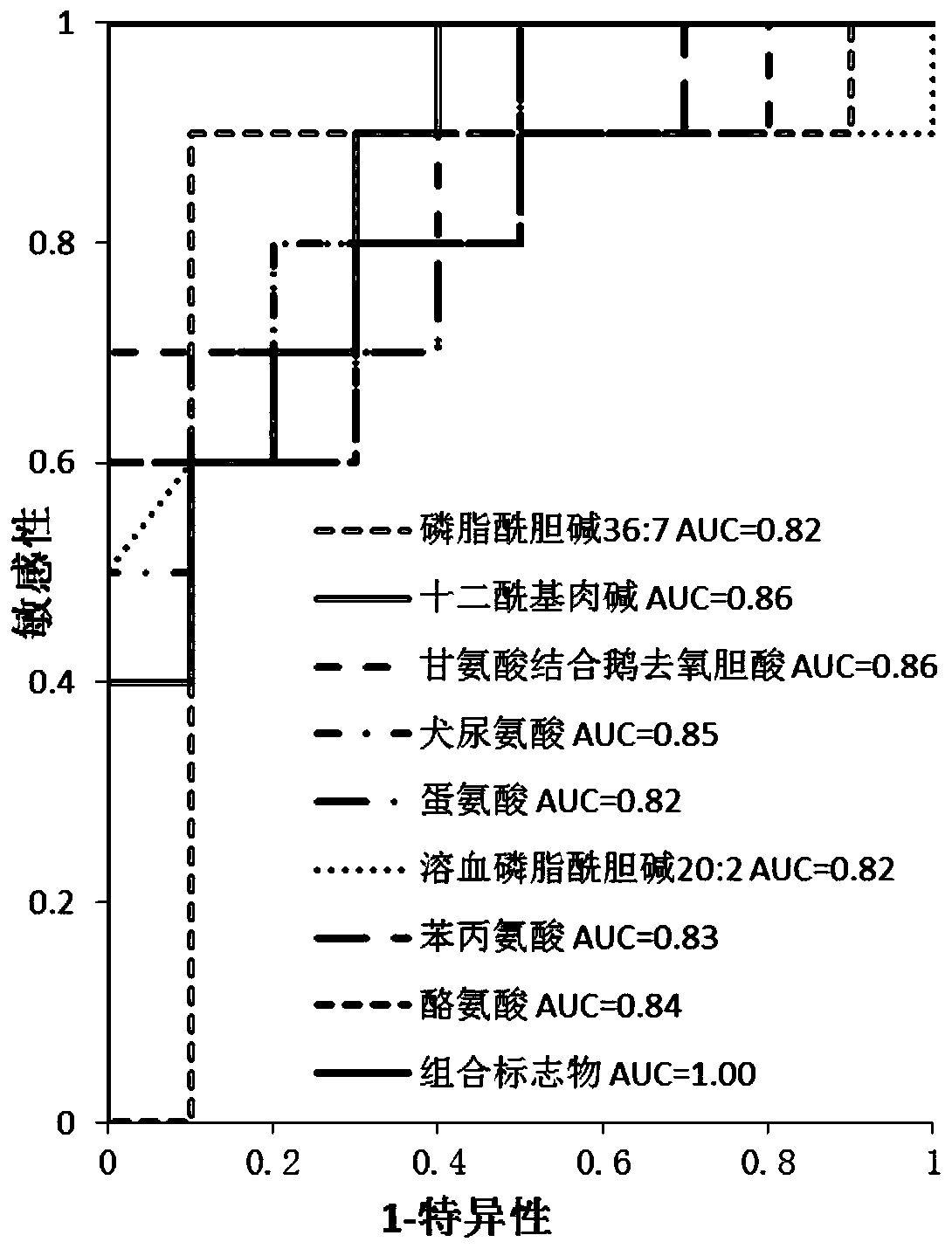
Hydrothorax fluid microparticle metabolite combination, kit and method for diagnosing tuberculous pleurisy
ActiveCN110954605AHigh diagnostic sensitivityHighly specific featuresComponent separationCholic acidPhenylalanine+Tyrosine
The invention relates to a hydrothorax microparticle metabolite combination, a kit and a method for diagnosing tuberculous pleurisy. The pleural effusion microparticle metabolite composition for diagnosing tuberculous pleurisy comprises phenylalanine, tyrosine, methionine, kynurenine, lauroyl carnitine, glycine-binding chenodeoxycholic acid, phosphatidylcholine with the ratio of 36: 7 and lysophosphatidylcholine with the ratio of 20: 2. The kit for diagnosing tuberculous pleurisy comprises an internal standard substance for detecting the concentration of metabolites in the pleural effusion microparticle sample extraction solution. A combined marker provided by the invention has the characteristics of high sensitivity and high specificity for the diagnosis of tuberculous pleurisy, at the same time, can be complementary with a traditional marker adenosine deaminase, and can be used for the auxiliary diagnosis of the tuberculous pleurisy by being combined with the traditional marker adenosine deaminase.
Owner:XIEHE HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI & TECH UNIV
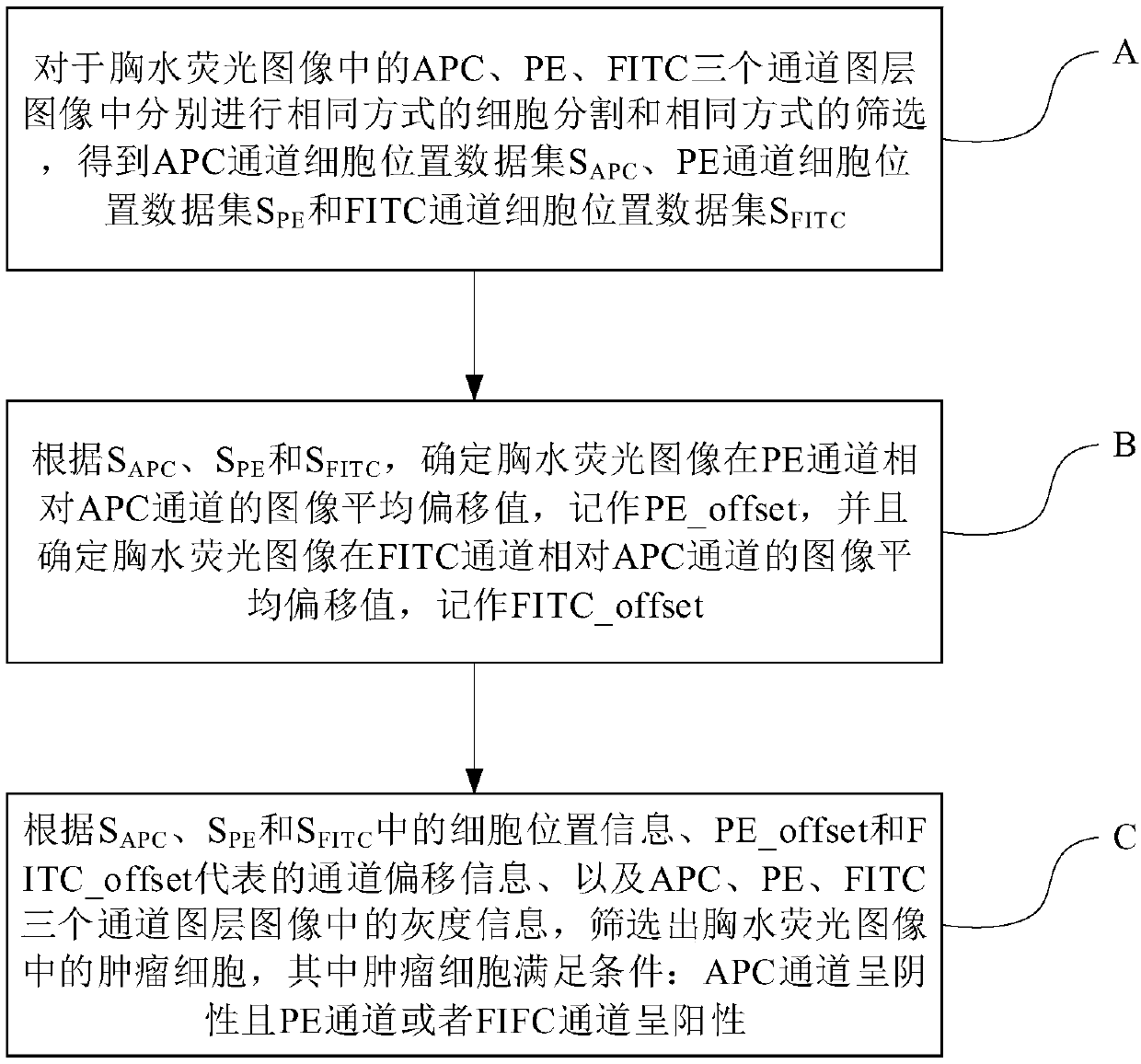
Method and device for detecting tumor cells in pleural fluid fluorescence image
InactiveCN109557000AReduce configuration requirementsImprove efficiencyBiological particle analysisDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionData setFluorescence
The invention provides a method and a device for detecting tumor cells in a pleural fluid fluorescence image. The method comprises the following steps: respectively performing cell segmentation in a same way and screening in a same way on APC, PE and FITC channel layer images in the pleural fluid fluorescence image to obtain a cell position data set SAPC of the APC channel, a cell position data set SPE of the PE channel, and a cell position data set SFITC of the FITC channel; determining an image average offset value of the pleural fluid fluorescence image in the PE channel relative to the APCchannel according to the SAPC, the SPE and the SFITC, marking as PE_offset, and determining the image average offset value of the pleural fluid fluorescence image in the FITC channel relative to theAPC channel, marking as FITC_offset; and screening the tumor cells in the pleural fluid fluorescence image according to the cell position information in the SAPC, the SPE and the SFITC, channel offsetinformation represented by the PE_offset and the FITC_offset, and gray information in the APC, the PE and the FITC channel layer images, wherein the tumor cells satisfy the following conditions: theAPC channel is negative and the PE channel or the FIFC channel is positive.
Owner:北京羽医甘蓝信息技术有限公司
Method for diagnosing cancer using cfdna
PendingCN113677808AEfficient detectionShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationHematological testPleural fluid
A diagnosis method according to the present invention relates to a technique for concentrating and separating small cfDNA from a liquid specimen such as urine, cerebrospinal fluid, plasma, blood, pleural fluid, or body fluid, and then detecting biomarkers, overexpressed in a specific cancer, with extreme sensitivity and without a PCR. A detection method according to one example of the present invention does not require a PCR amplification reaction, and thus can significantly reduce the time it takes to diagnose cancer. In addition, the method enables immediate on-site analysis, and can be used as point-of-care testing (POCT) that can simultaneously search a large number of genes in a short time.
Owner:GENOPSY CO LTD
Drug for treating pleural effusion
InactiveCN106109942ADispersion deliverySulfur/selenium/tellurium inorganic active ingredientsBletilla striataHouttuynia
A drug for treating pleural fluid is prepared from pepperweed seeds, rhubarb, red dates, unibract fritillary bulbs, platycodon roots, honeysuckle flowers, bletilla striata, bitter apricot kernels, heartleaf houttuynia herbs, rhizomes of manyleaf paris, ophiopogon japonicas, mulberry leaves, lily bulbs, mirabilite, prepared peking euphorbia roots, dried rehmannia roots, lilac daphne flower buds, radix kansui and the like through immersion and heating. Purgation therapy, resolving therapy and fluid-purging therapy of the traditional Chinese medicine are adopted, and the problem of pleural effusion is solved fundamentally.
Owner:李胜利
Molecular marker for the early detection of malignant pleural mesothelioma and the methods of its expression analysis using blood and pleural effusion samples
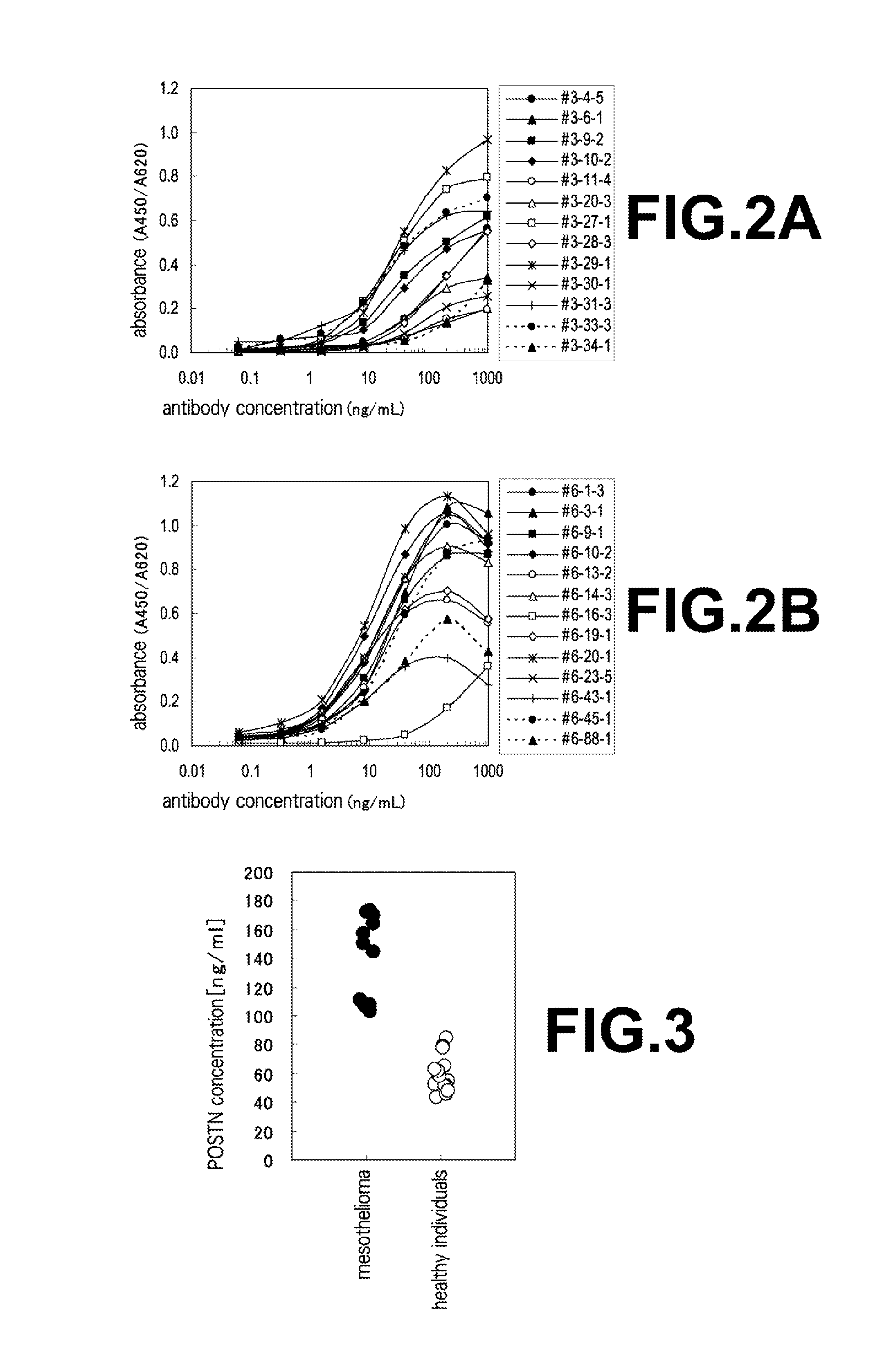
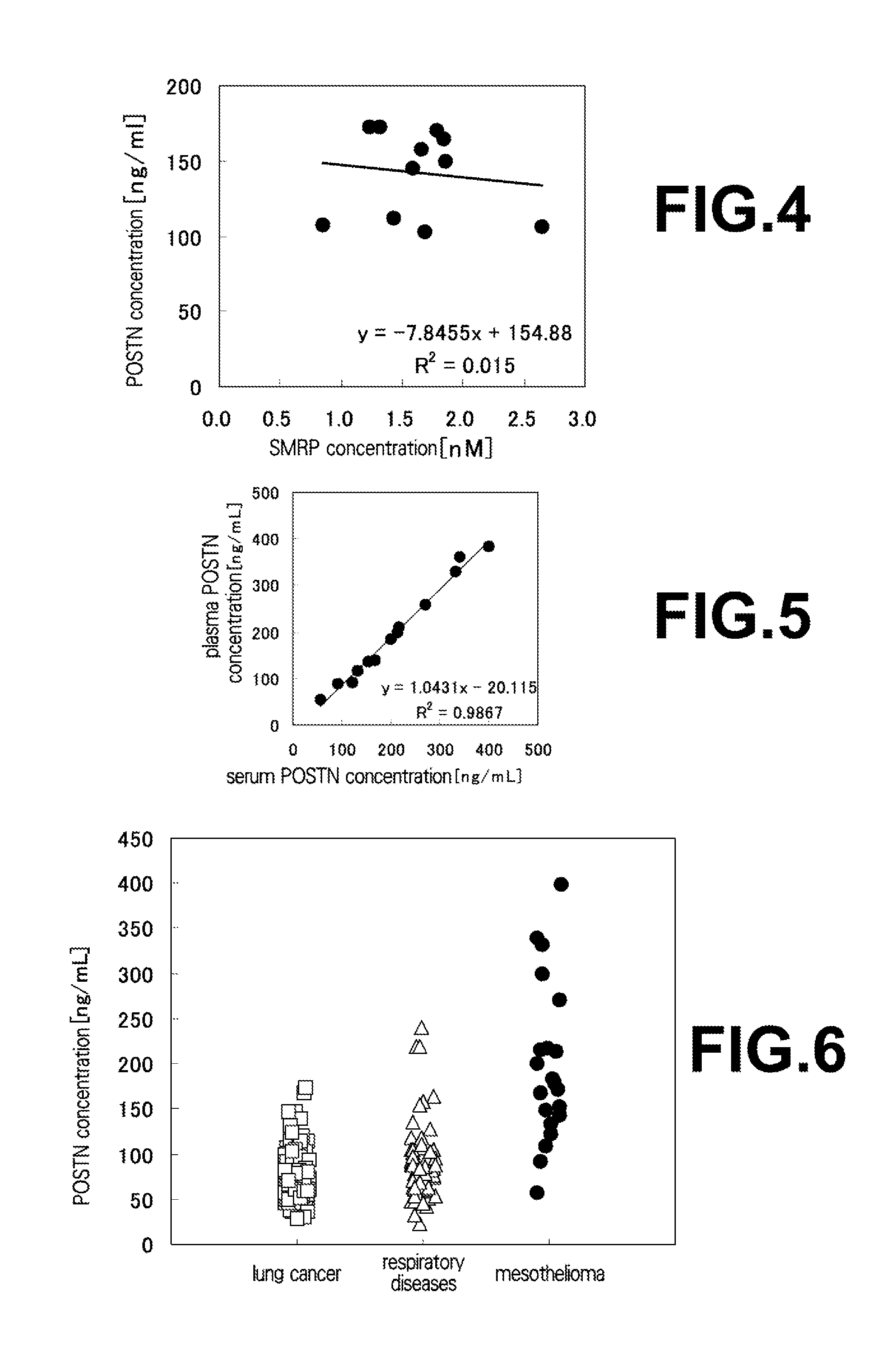
The present invention provides a method for testing mesothelioma comprising a step of determining a concentration of a human periostin protein in at least one type of sample of blood or pleural fluid of a subject. In the step of determining the concentration of human periostin protein, an antibody directed against human periostin protein may be used. The present invention further provides a kit for diagnosing mesothelioma, said kit comprising an antibody directed against human periostin protein. In the kit for diagnosing mesothelioma, the antibody directed against a human periostin protein may be an antibody that binds to a polypeptide consisting of an amino acid sequence set out in SE ID NO: 2.
Owner:NAGOYA UNIVERSITY +2
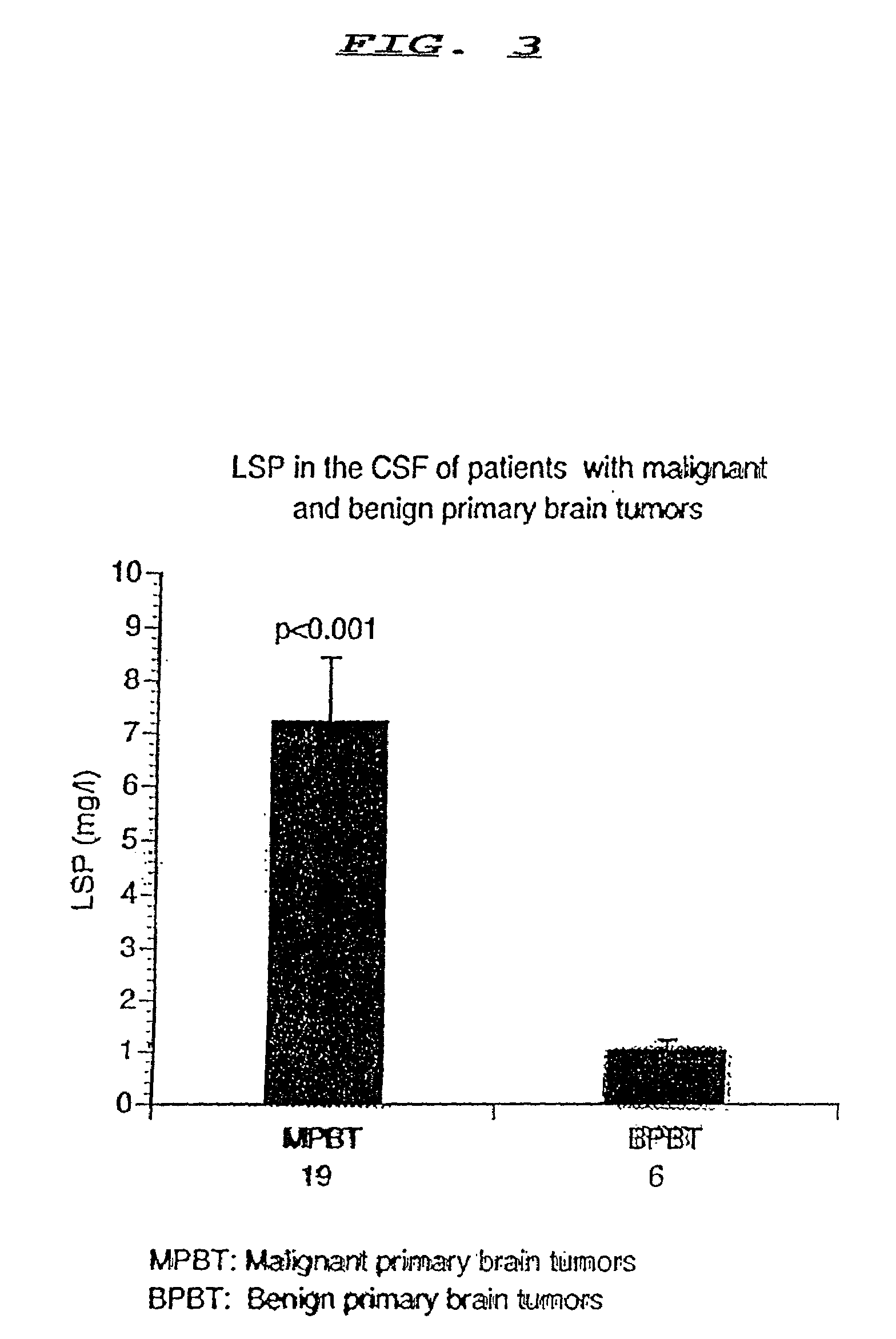
Method for determining lipid associated sialoprotein in body fluids
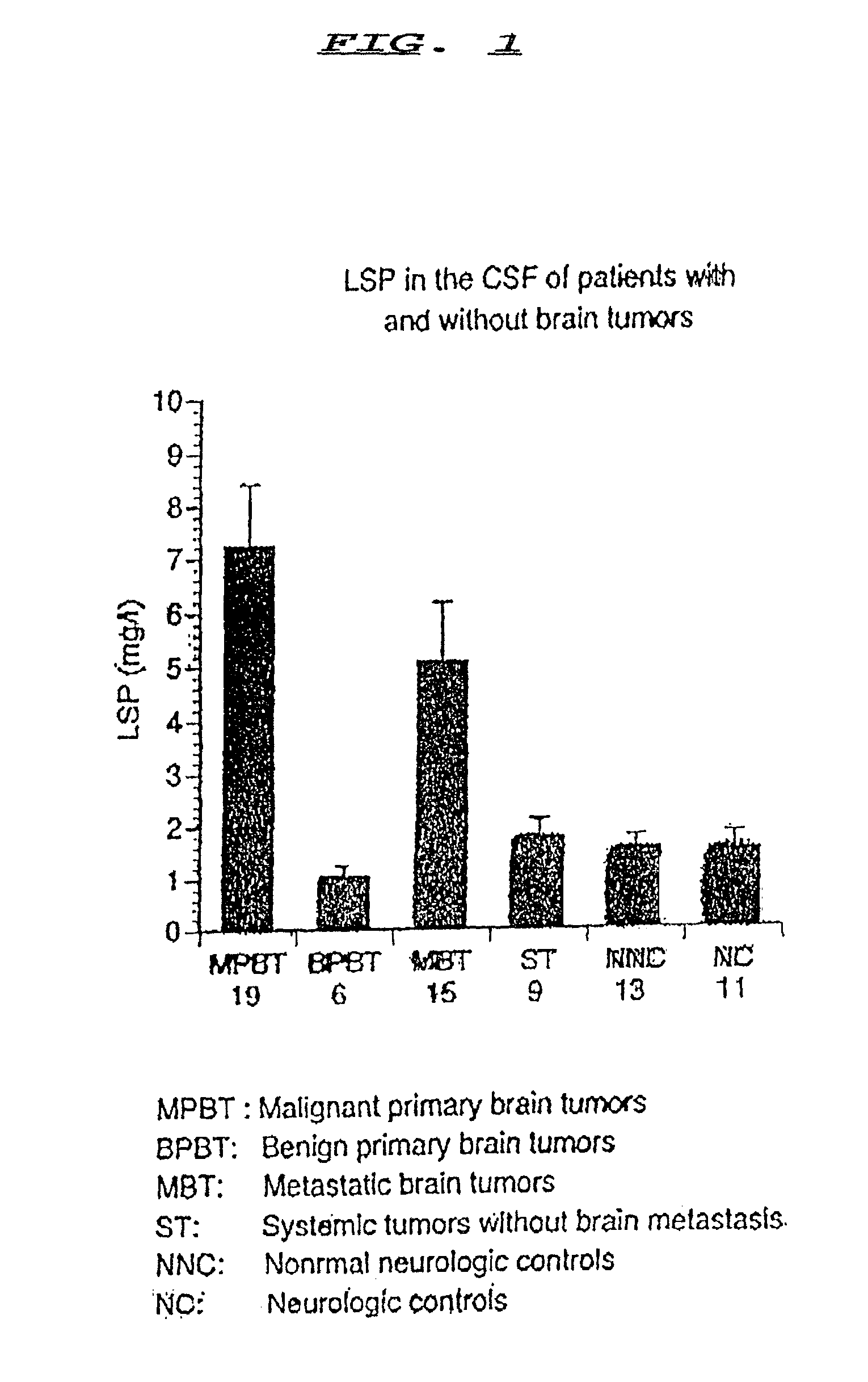
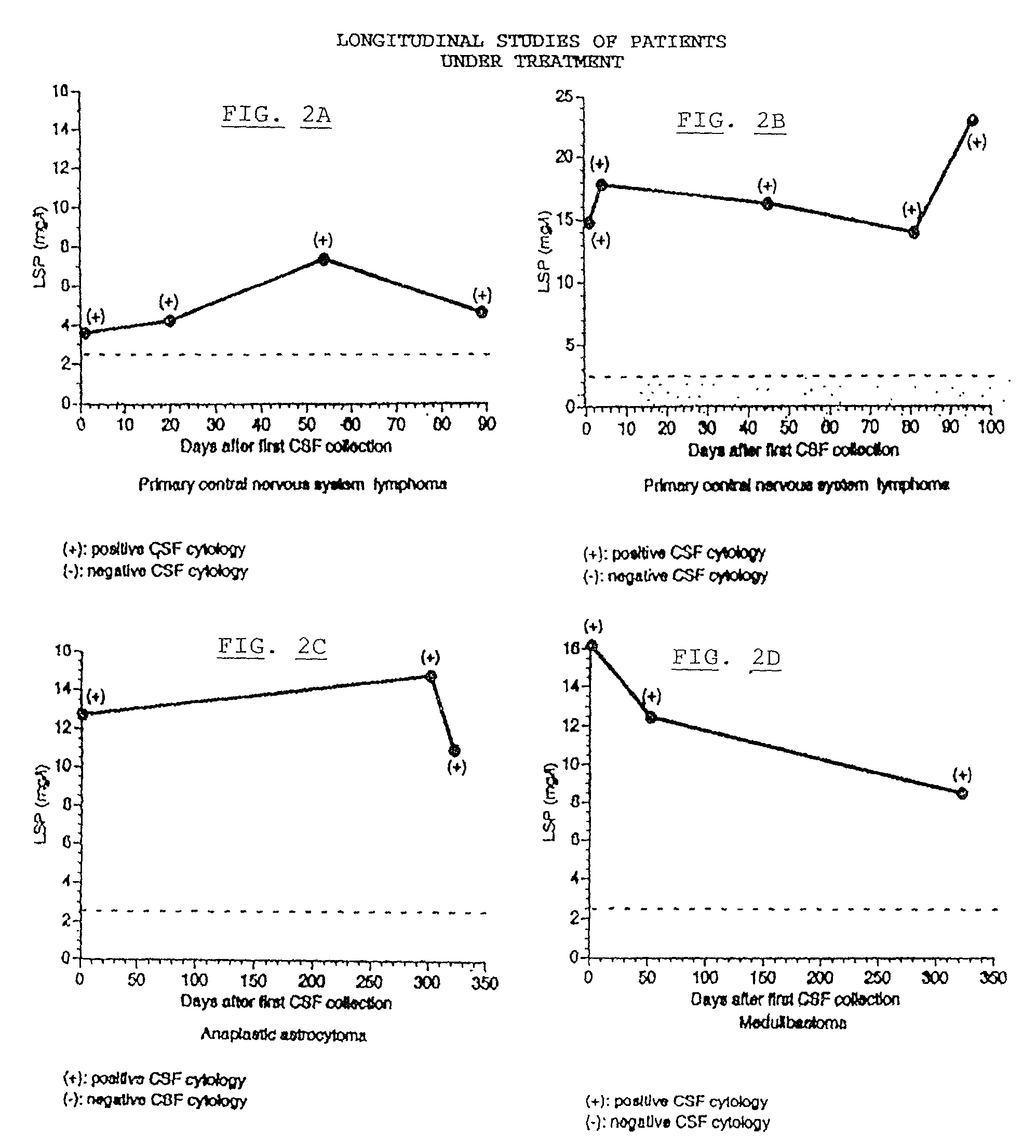
The amount of lipid associated sialoprotein (LSP) in body fluids such as cerebrospinal fluid, peritoneal fluid, pleural fluid, bronchial washings, saliva and sputum samples, may be determined by a method which may be automated, involving the following steps to be performed on the sample: adding a mixture of a chlorinated lower alkyl alcohol; centrifuging to yield a substantially clear upper phase; recovering the upper phase and adding to it a protein precipitating agent; mixing the resulting admixture; recovering the resulting precipitate; washing the precipitate with saline solution; centrifuging to recover the precipitate; dissolving the precipitate in water; mixing; adding to the resulting mixture an hydrolysis agent; heating; and determining the amount of lipid associated sialoprotein present by determining the optical density of the sample.
Owner:KATOPODIS NONDA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com