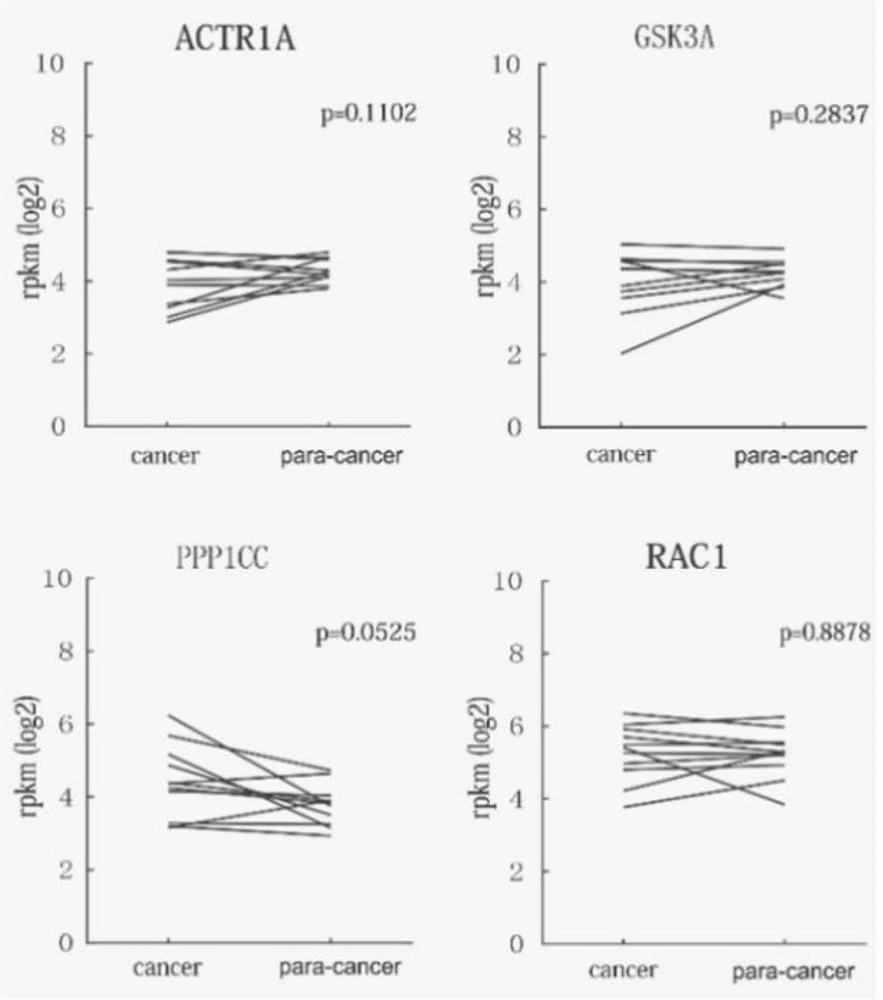
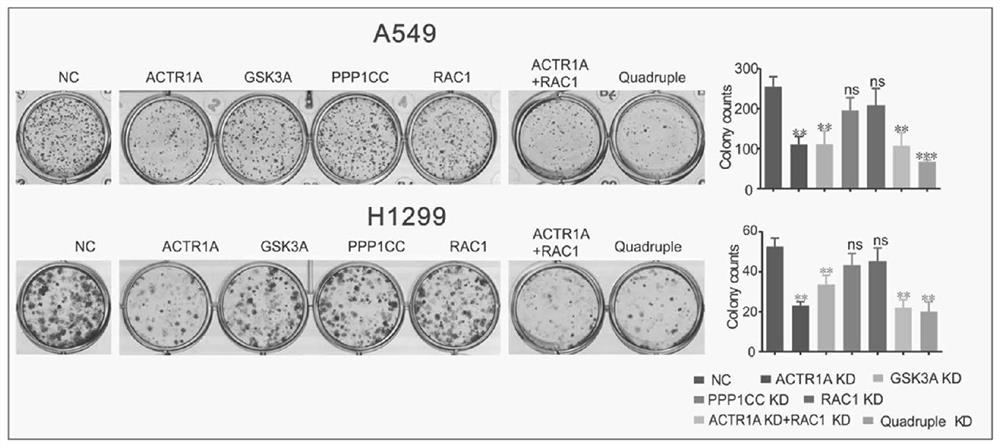
Patents
Literature
30 results about "Malignant phenotype" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In many cases, the gain of a malignant phenotype is not the result of a direct effect of the stimuli on tumor cells but, rather, a stimulus‐promoted cross‐talk between tumor cells and other cell types within the tumor microenvironment.
Method for restoration of normal phenotype in cancer cells
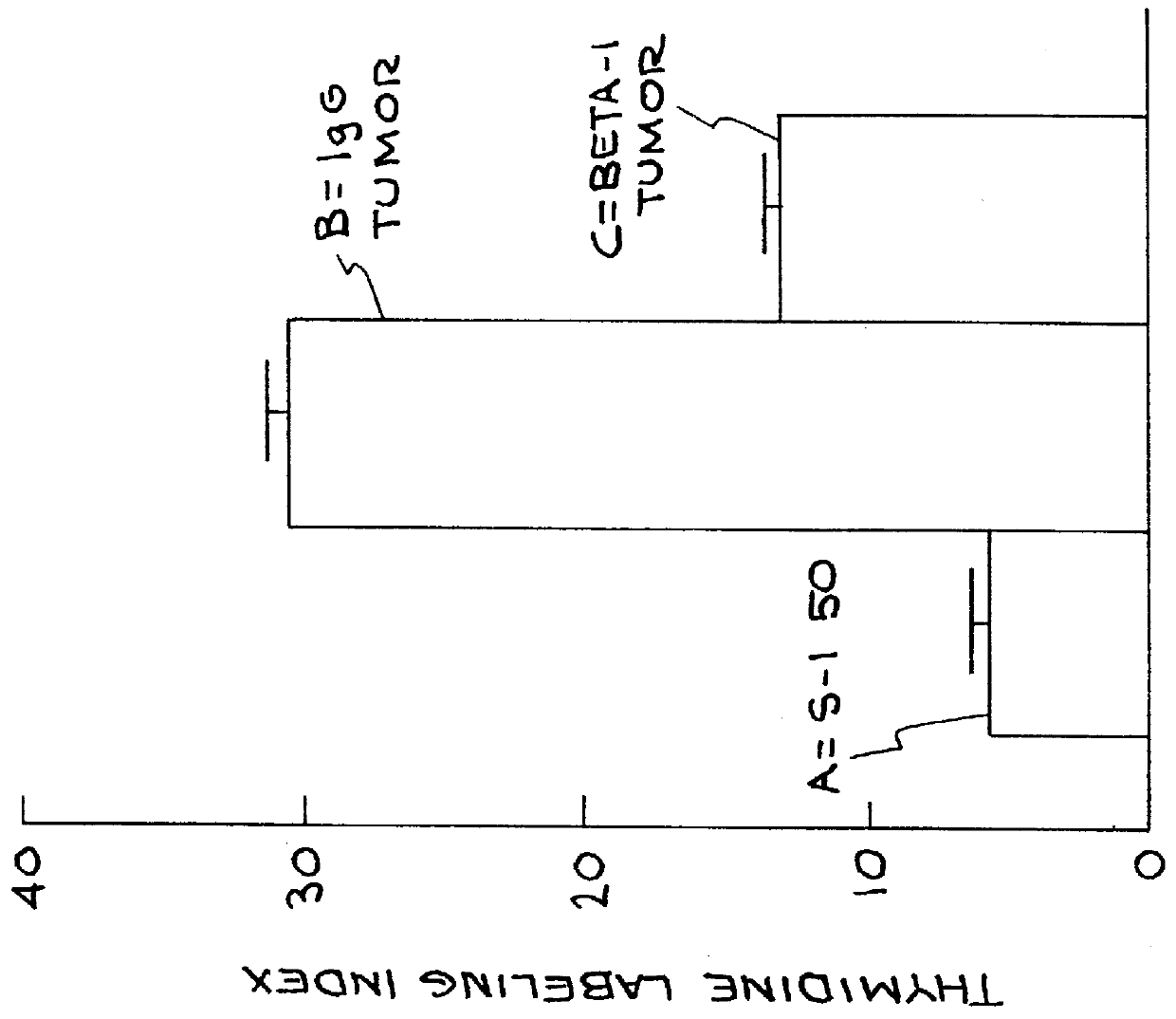
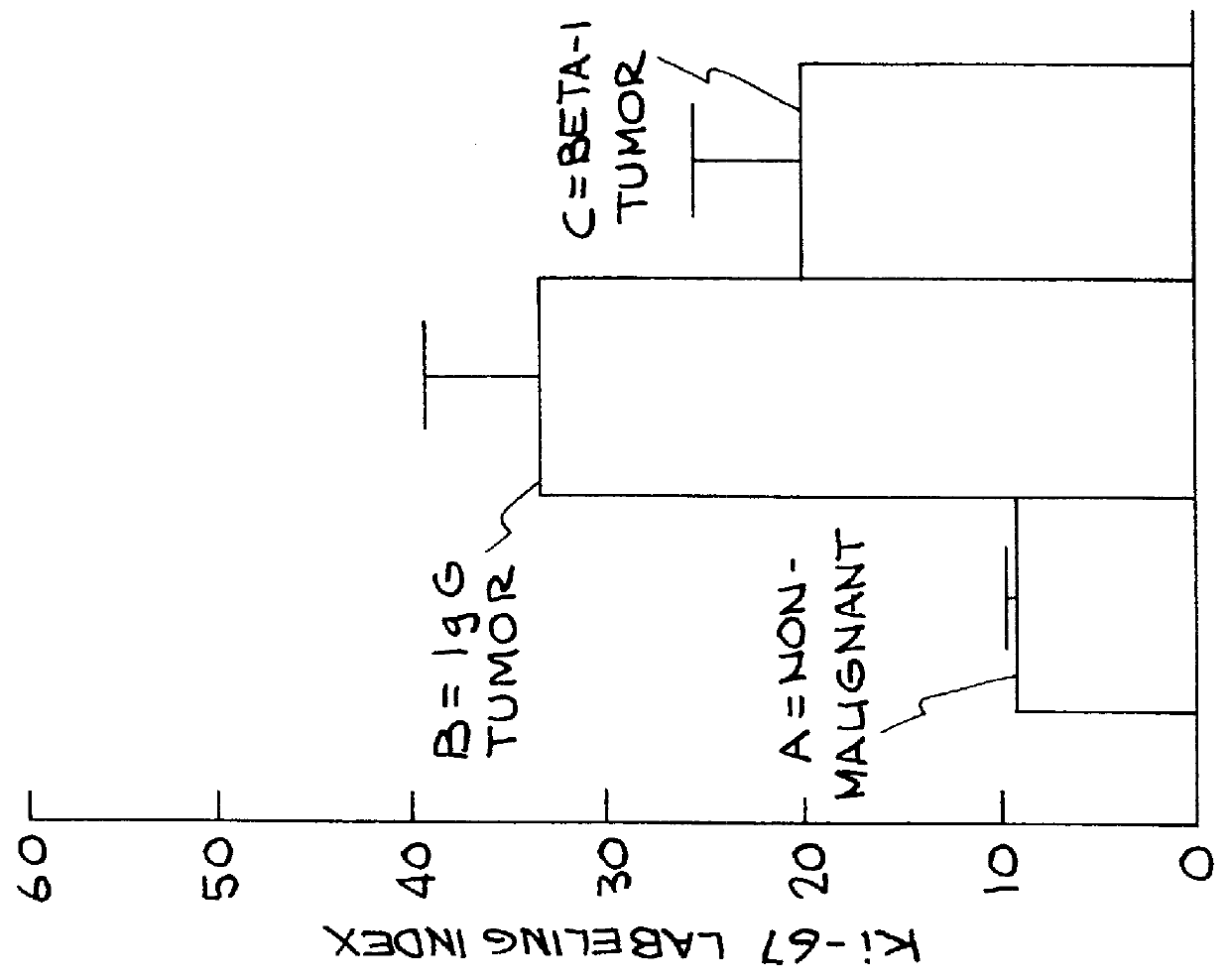
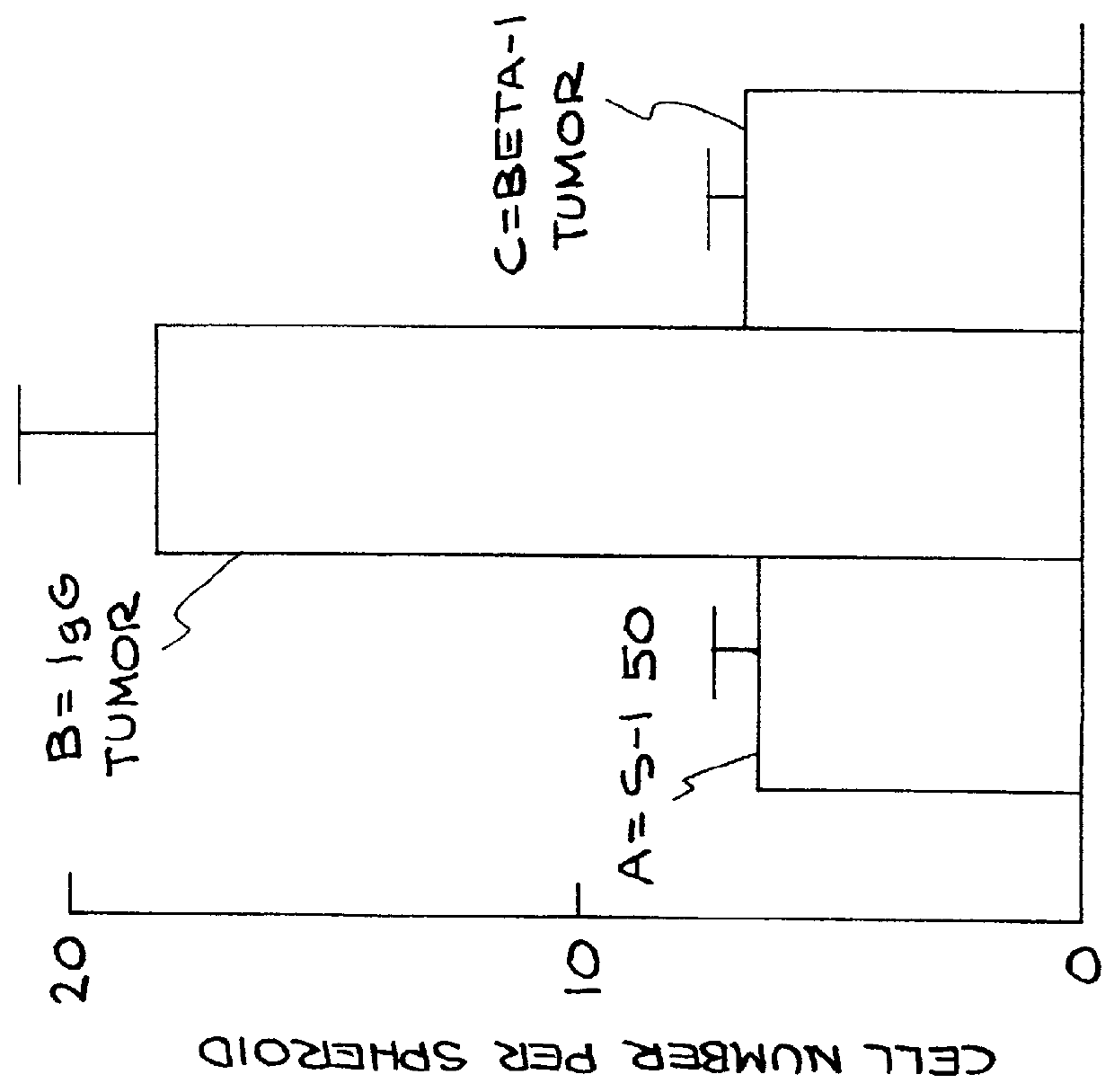
InactiveUS6123941AReverse malignant behaviorRapid assessmentPeptide/protein ingredientsCulture processMalignant phenotypeHuman Mammary Epithelium
A method for reversing expression of malignant phenotype in cancer cells is described. The method comprises applying beta 1 integrin function-blocking antibody to the cells. The method can be used to assess the progress of cancer therapy. Human breast epithelial cells were shown to be particularly responsive.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
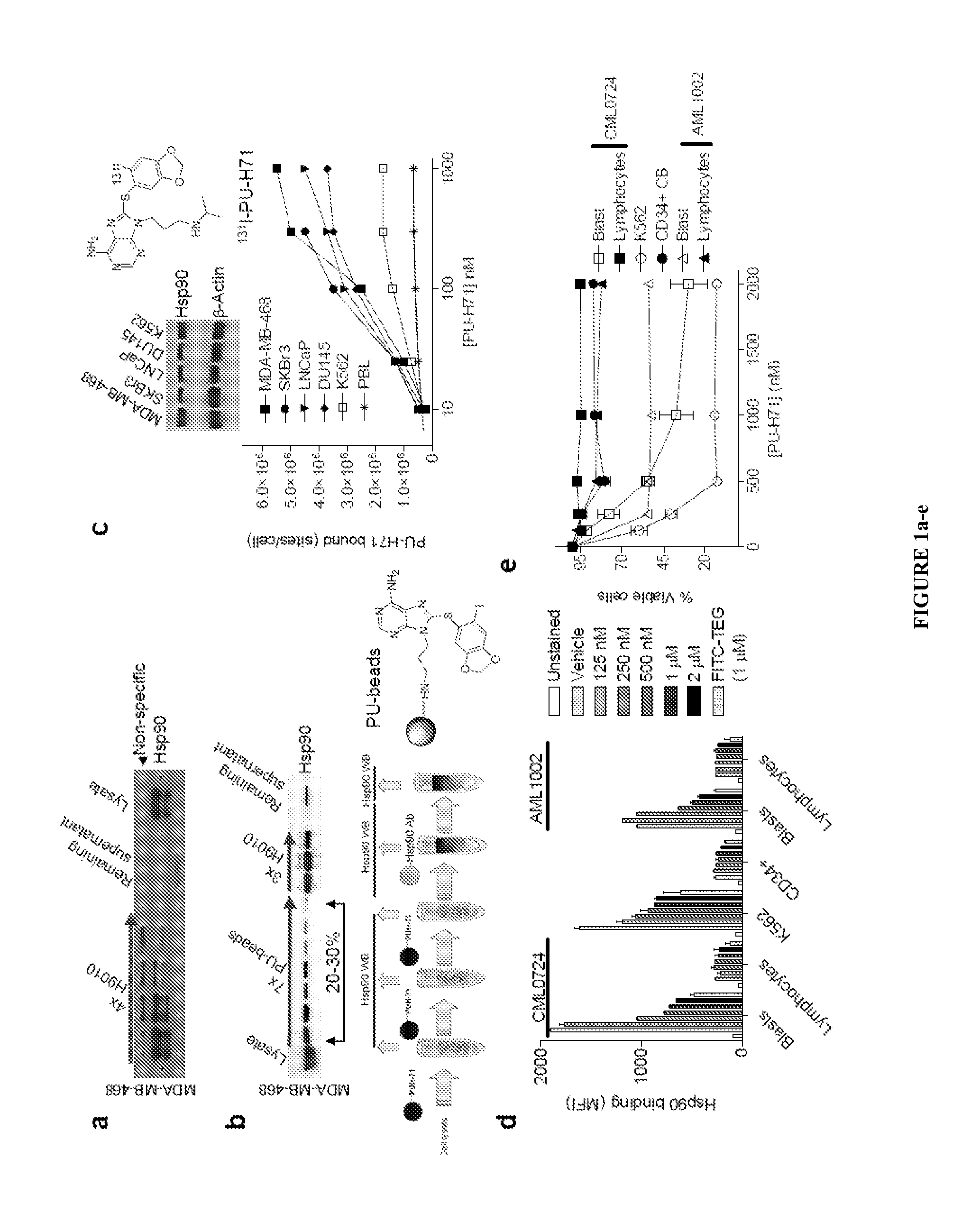
Uses of labeled hsp90 inhibitors
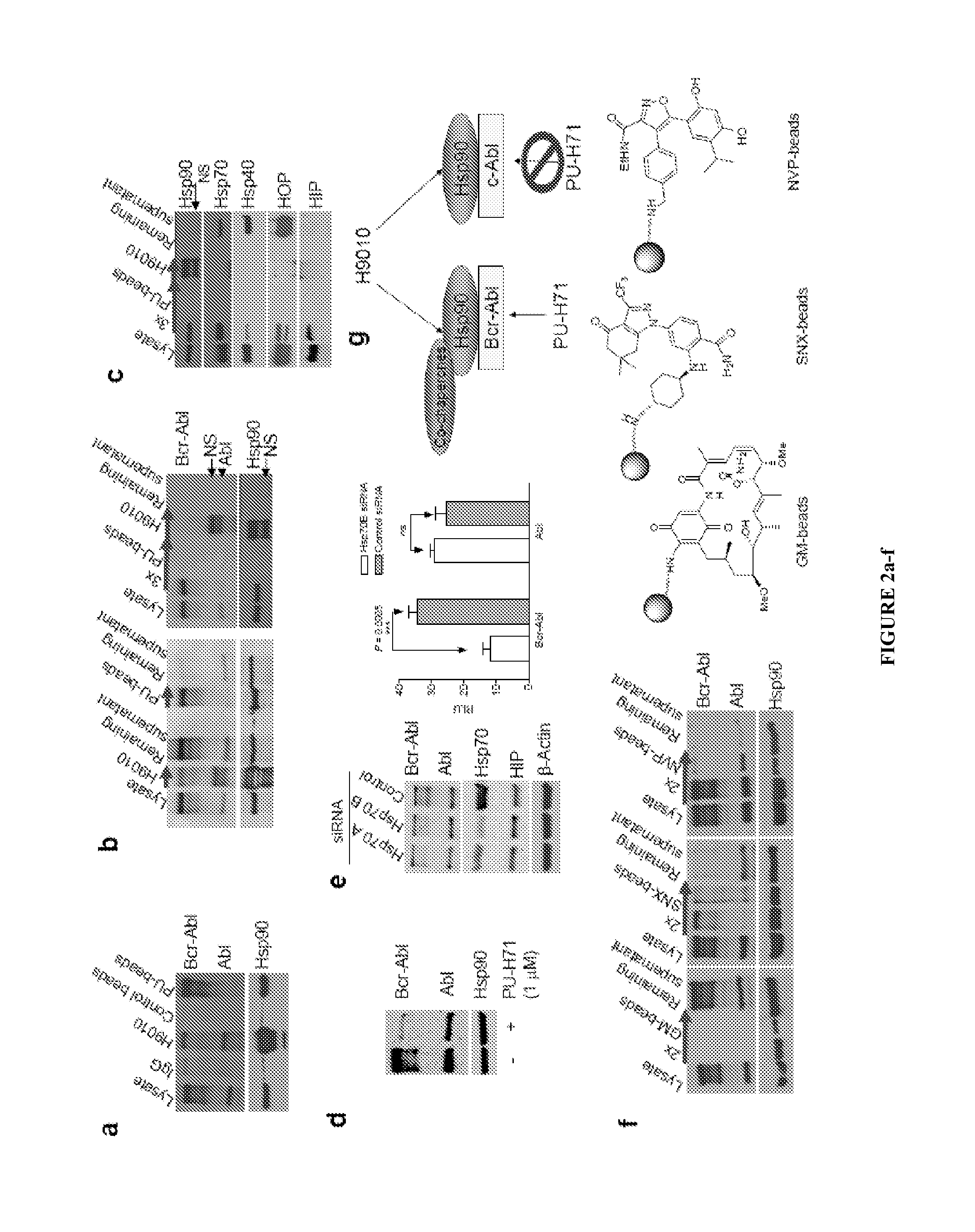
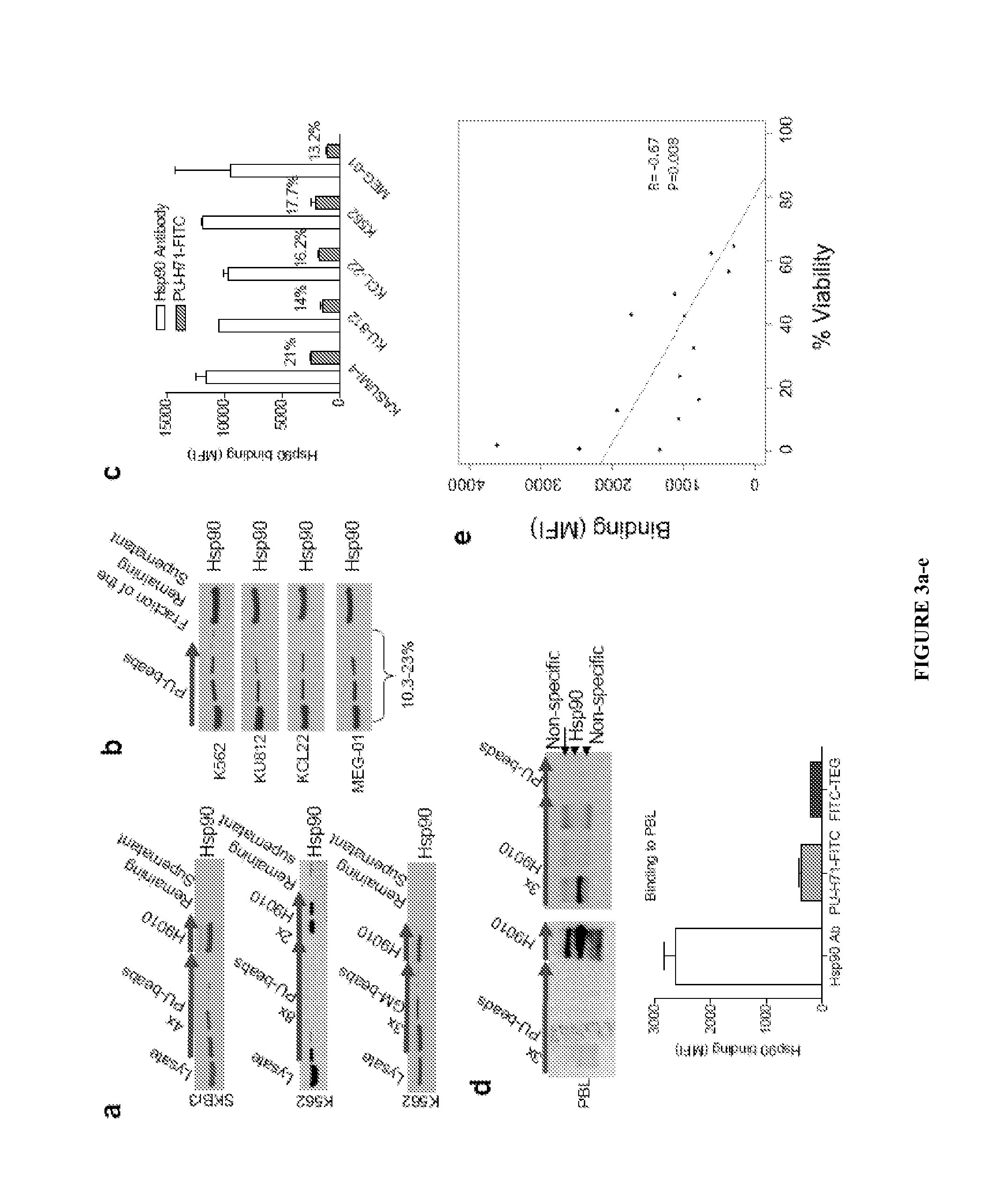
The disclosure provides evidence that the abundance of this particular “oncogenic HSP90” species, which is not dictated by HSP90 expression alone, predicts for sensitivity to HSP90 inhibition therapy, and thus is a biomarker for HSP90 therapy. The disclosure also provides evidence that identifying and measuring the abundance of this oncogenic HSP90 species in tumors predicts of response to HSP90 therapy. “Oncogenic HSP90” is defined herein as the HSP90 fraction that represents a cell stress specific form of chaperone complex, that is expanded and constitutively maintained in the tumor cell context, and that may execute functions necessary to maintain the malignant phenotype. Such roles are not only to regulate the folding of overexpressed (i.e. HER2), mutated (i.e. mB-Raf) or chimeric proteins (i.e. Bcr-Abl), but also to facilitate scaffolding and complex formation of molecules involved in aberrantly activated signaling complexes (i.e. STATS, BCL6).
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES +1
Fusion protein for treating breast cancer and application thereof
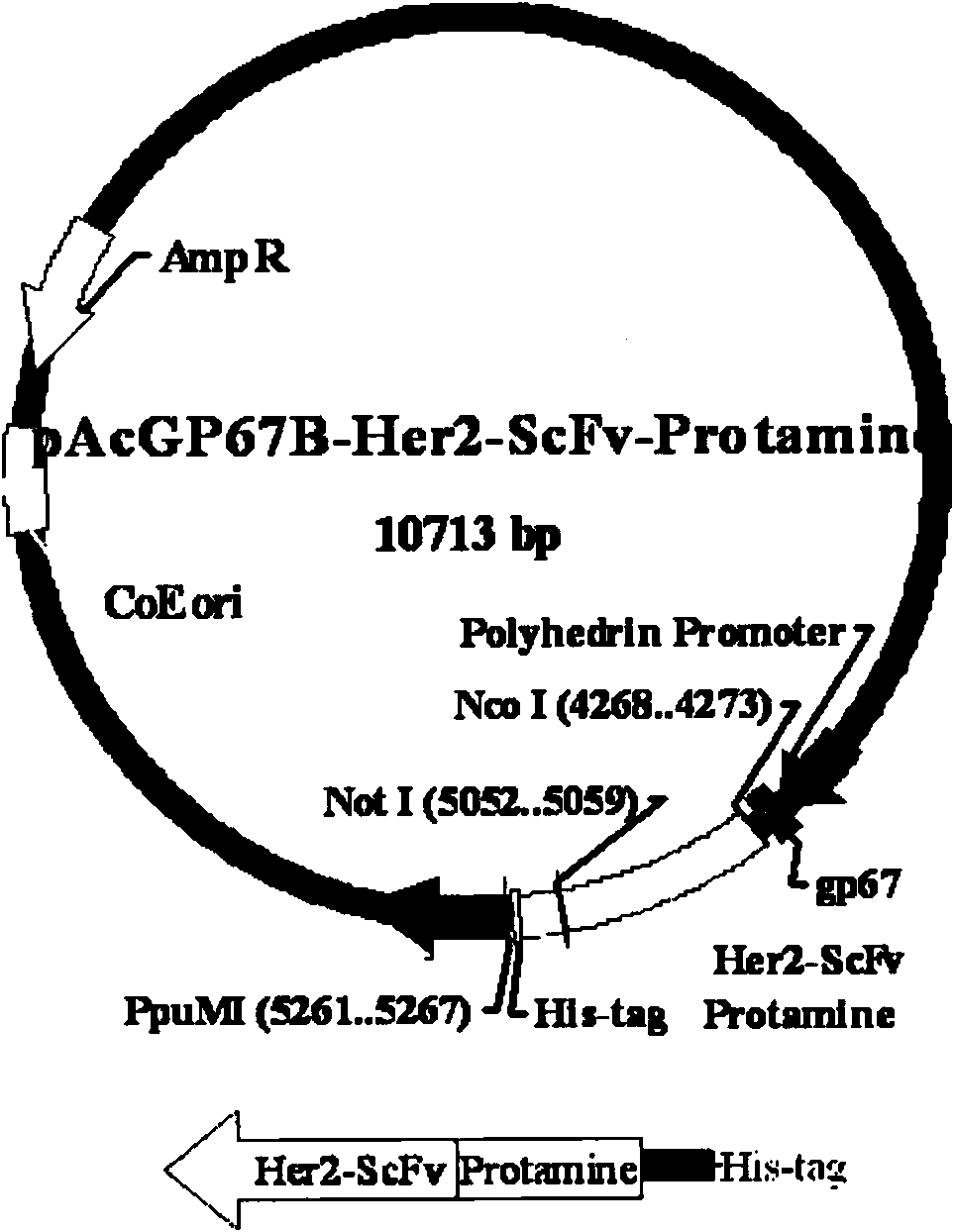
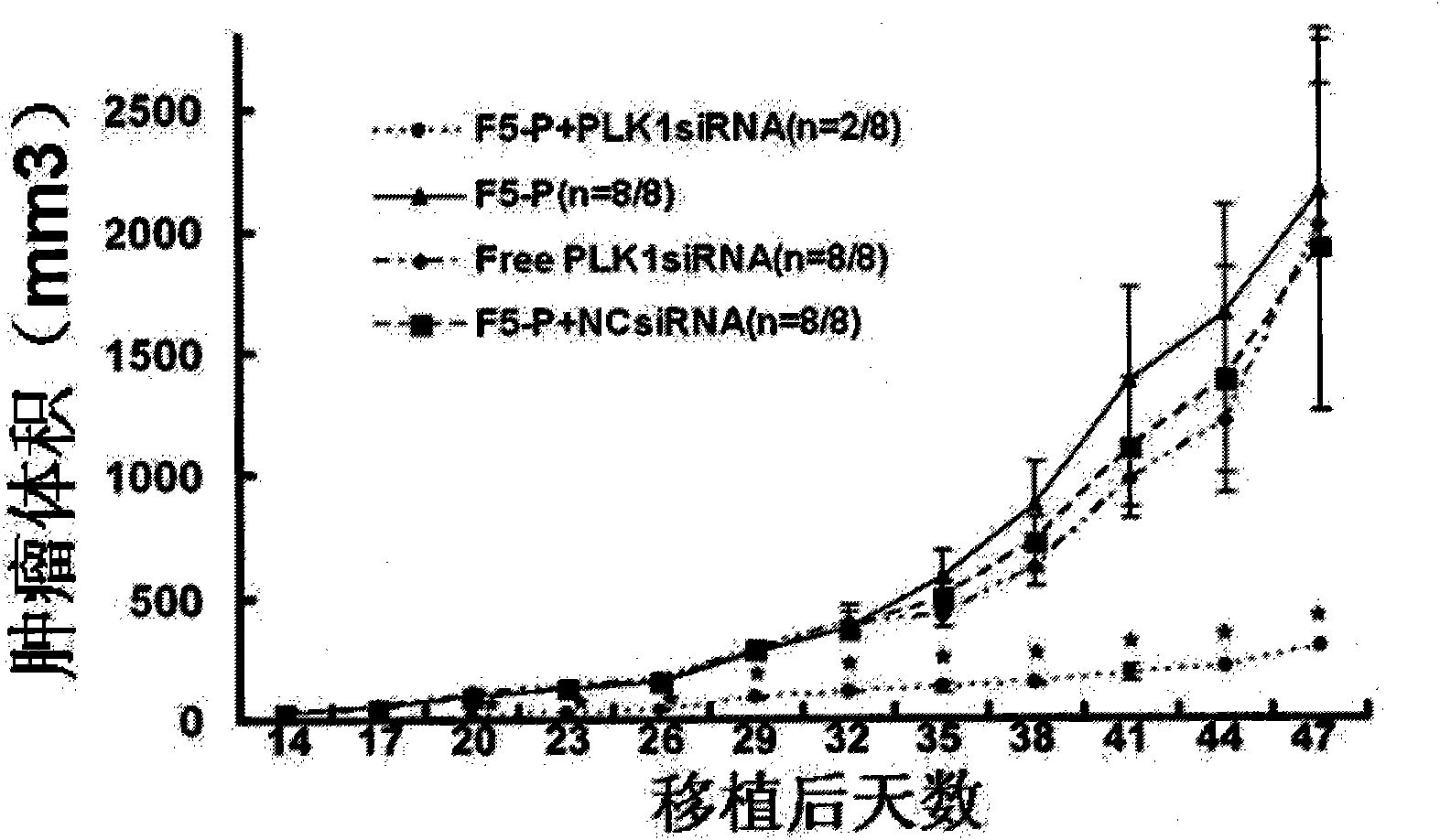
InactiveCN101585882AGenetic material ingredientsMacromolecular non-active ingredientsHER2 Positive Breast CancerMalignant phenotype
The present invention discloses a fusion protein for treating a breast cancer, wherein the fusion protein is Her2 single-chain fragment antibody-polypeptide, the Her2 single-chain fragment antibody is capable of targeting a Her2 receptor locating on a surface of a breast cancer cell, and the polypeptide is capable of carrying siRNA. The polypeptide includes a protamine polypeptide. The siRNA includes PLK1-siRNA, which is capable of restraining an expression of a knubble malignant phenotype gene. The fusion protein for treating the breast cancer is capable of carrying the PLK1-siRNA, and targeting and importing a Her2 positive breast cancer cell specifically, so as to bring the medicament into the cell. The treatment of the breast cancer is capable of generating a strong effect for restraining the breast cancer growth and transfer, may break a gene suppression effect of the existing antisense oligonucleotide and ribozyme, and becames a novel anti-Her2 gene medicament for treating the breast cancer.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV +2
Altered DNA synthesome components as biomarkers for malignancy
InactiveUS20060073477A1Guaranteed functionChange activityPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementMalignant phenotypeNeoplasm
Owner:SCHNAPER LAUREN
Application of gap junction protein and coding gene thereof in preparing medicament for reversing malignant phenotype of cancer stem cell
ActiveCN101966332AReduced self-renewalReduce tumorigenesisPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsCancer cellMalignant phenotype
The invention discloses application of gap junction protein and coding gene thereof in preparing medicament for reversing malignant phenotype of a cancer stem cell, and investigates the functional state of gap junction communication in the tumor stem cell, expression condition of the gap junction protein and relation between the gap junction protein and special biological characteristics of tumorstem cells. Results prove that compared with differentiated tumor cells, gap junction communication obstacle exists in the tumor stem cell, no clear gap junction like structure is found among the cells, and expressions of various gap junction protein, particularly gap junction protein 43(Cx43), is down regulated; the down regulation of the expression of the Cx43 is related to promoter methylationof coding gene GJA1 thereof and expression of micro RNA; recovering of the expression of the Cx43 in the tumor stem cell can remarkably reduce the self-renew ability, tumor forming ability and invasion ability of the tumor stem cells, which is related to partial recovery of the gap junction communication function, up regulation of E-cadherin expression and inactivity of SDF-1 / CXCR4 downstream signal path (AKT and ERK1 / 2); and the gap junction protein and coding gene thereof can be used for preparing the medicament for reversing malignant phenotype of the cancer stem cell.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
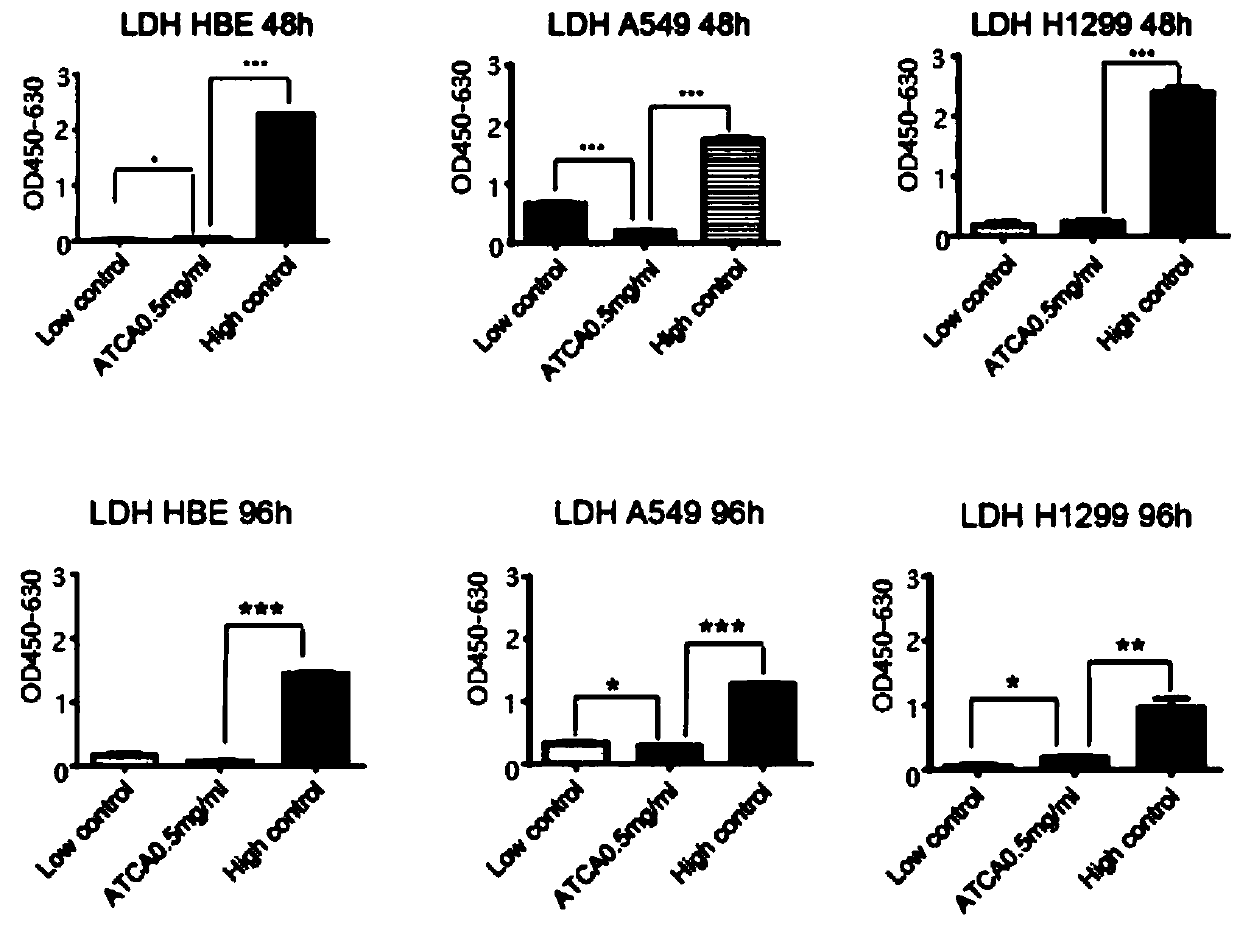
Purpose of ATCA to preparation of medicines for tumors
PendingCN110638802AMalignant phenotype suppressionMinimized damageOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsCancer cellSide effect
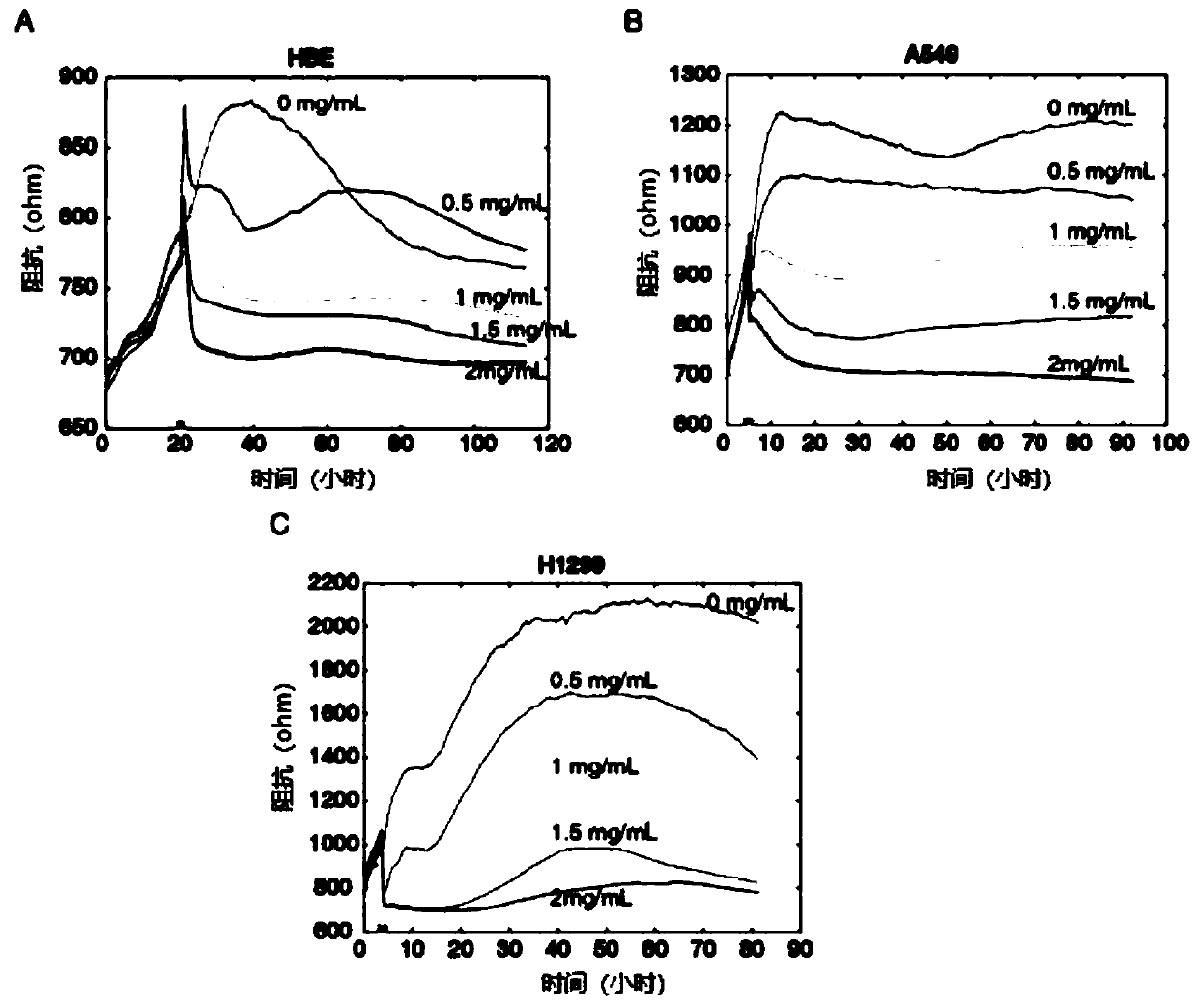
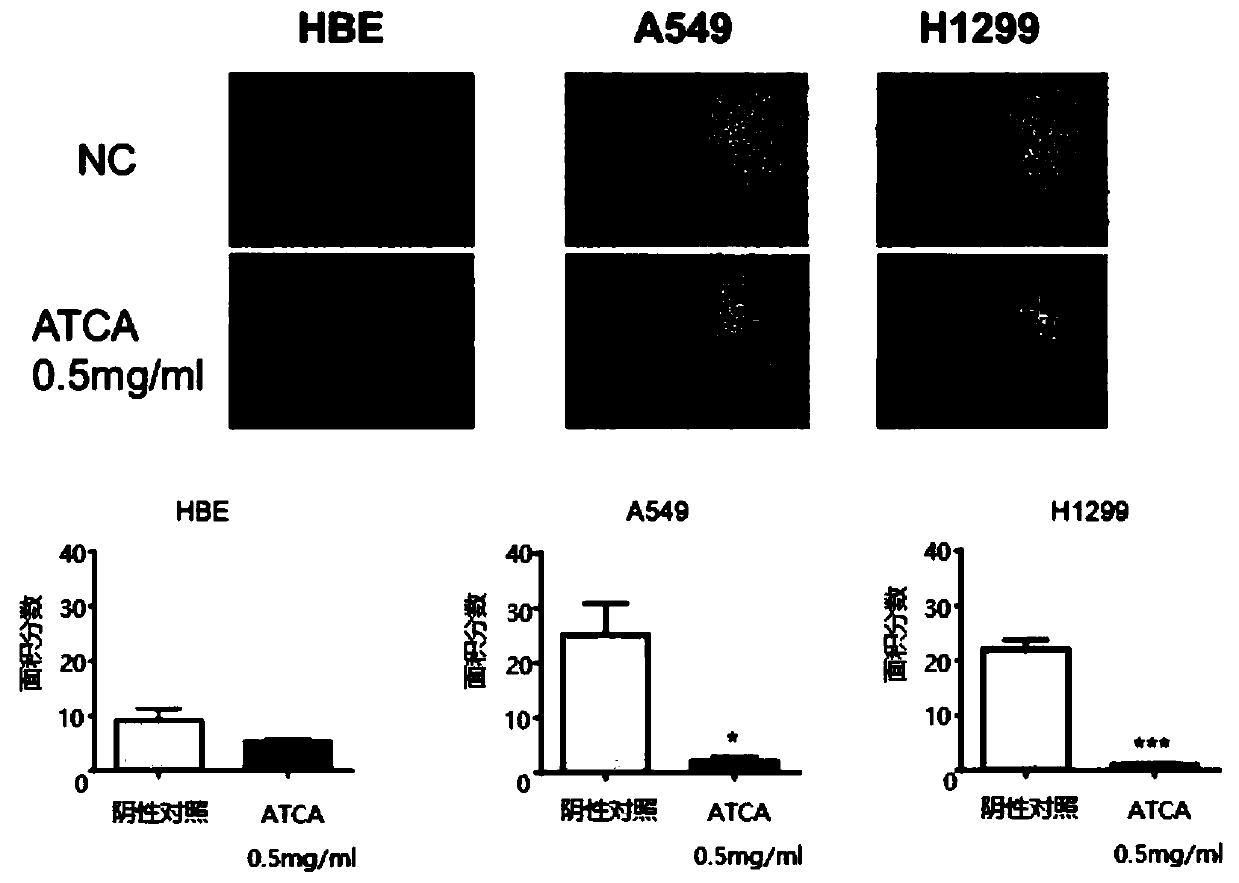
The invention discloses a purpose of ATCA (Aurintricarboxylic acid, aurin tricarboxylic acid) to preparation of medicines for treating tumors. Through experiment, the inventor of the invention finds that through specifically intervening a translation initiation process, the ATCA can enable cancer cells not to strengthen malignant phenotypes through slowing down cancer gene translation elogation rate, so that the malignant phenotypes of the cancer cells can be restrained, besides, lethal effects on normal cells can be minimized, the effect of resisting cancer is achieved, and besides, the sideeffects are effectively controlled. The ATCA disclosed by the invention has important application value on tumor treatment.
Owner:CHI BIOTECH CO LTD
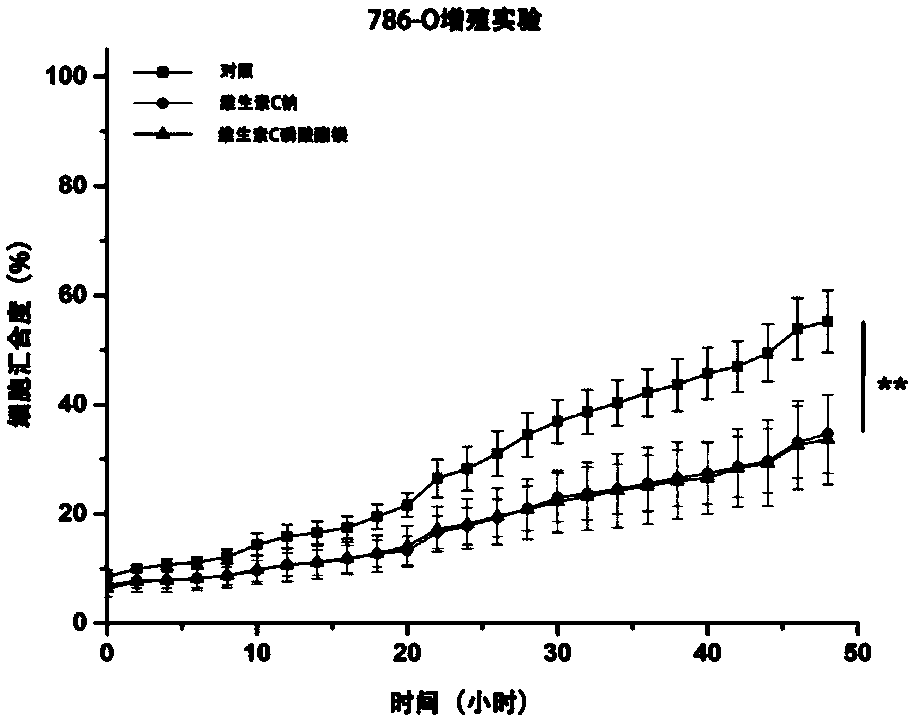
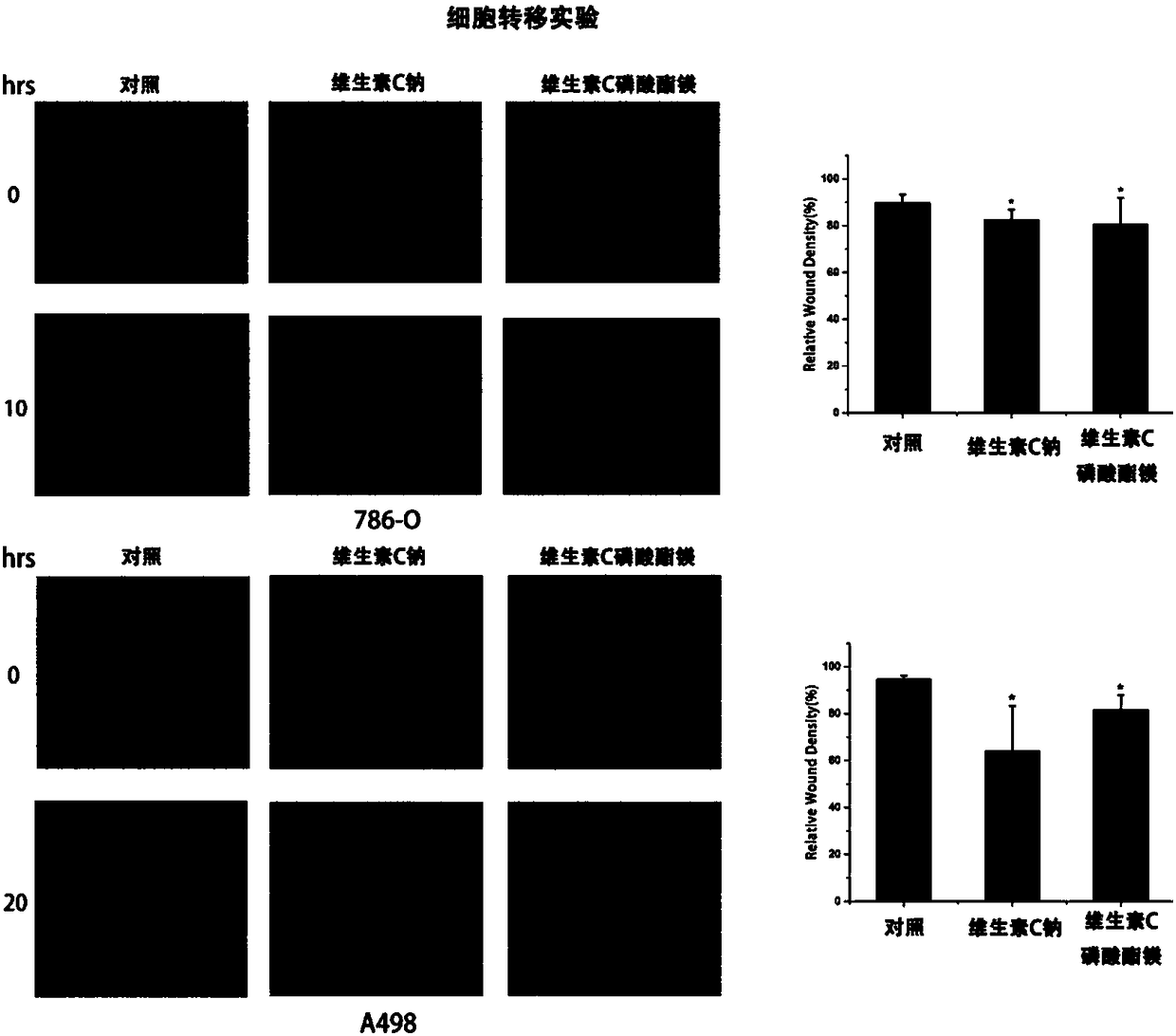
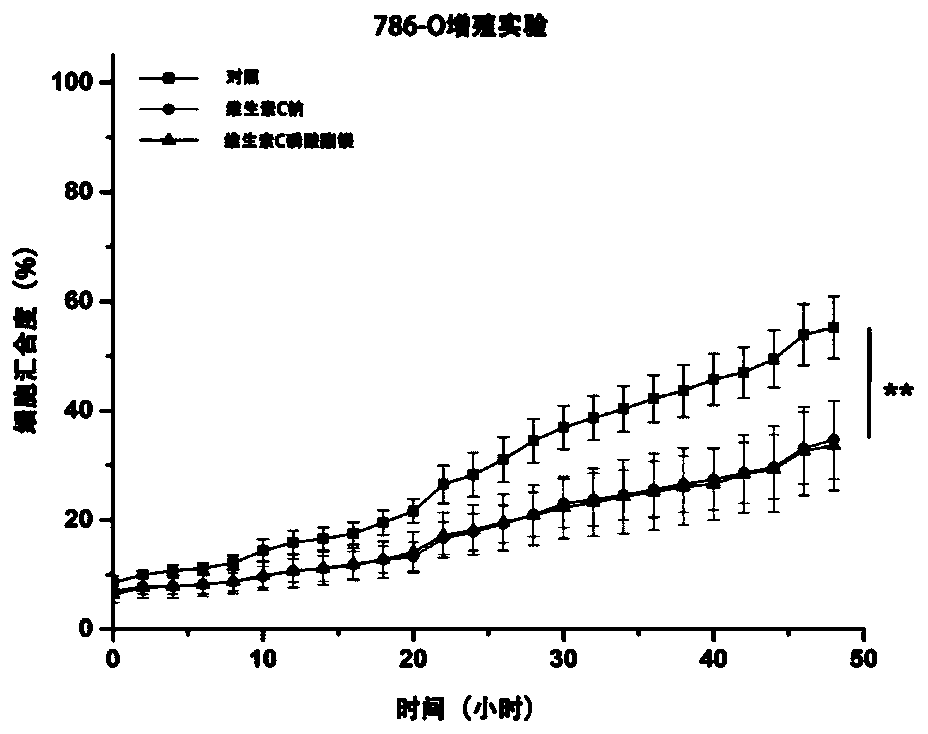
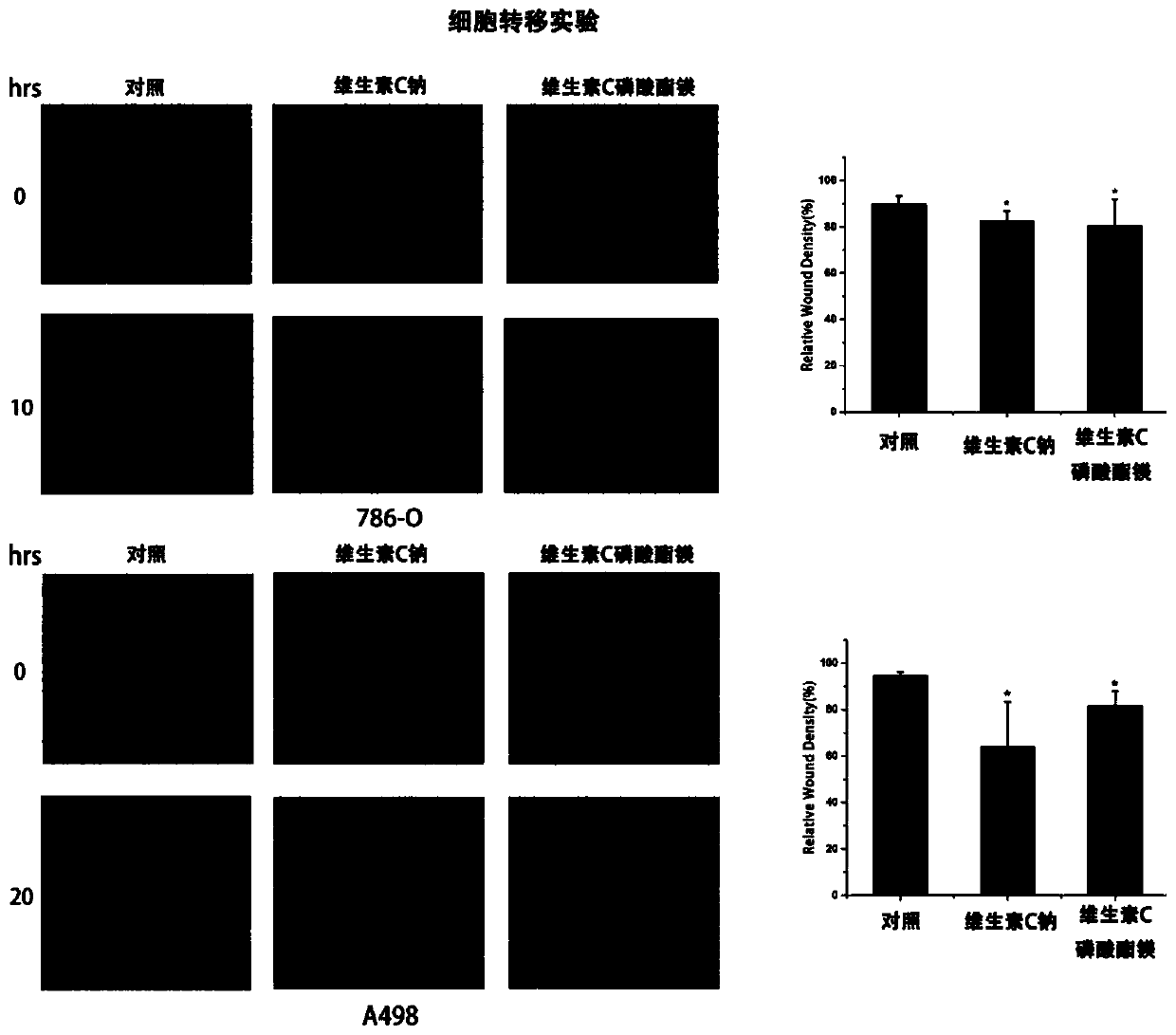
Applications of vitamin C derivatives in antitumor products
ActiveCN108567774ALow toxicityPrevent proliferationOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsCancer cellVitamin C
The invention relates applications of vitamin C derivatives in antitumor products. According to the present invention, with the continuous and long-time administration of the low-dose vitamin C derivatives, the differentiation of cancer cells can be inhibited, and the malignant phenotype of cancer cells can be effectively inhibited, such that the evidence can be provided for the application of thevitamin C derivatives in tumor differentiation therapy.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF GENOMICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI CHINA NAT CENT FOR BIOINFORMATION
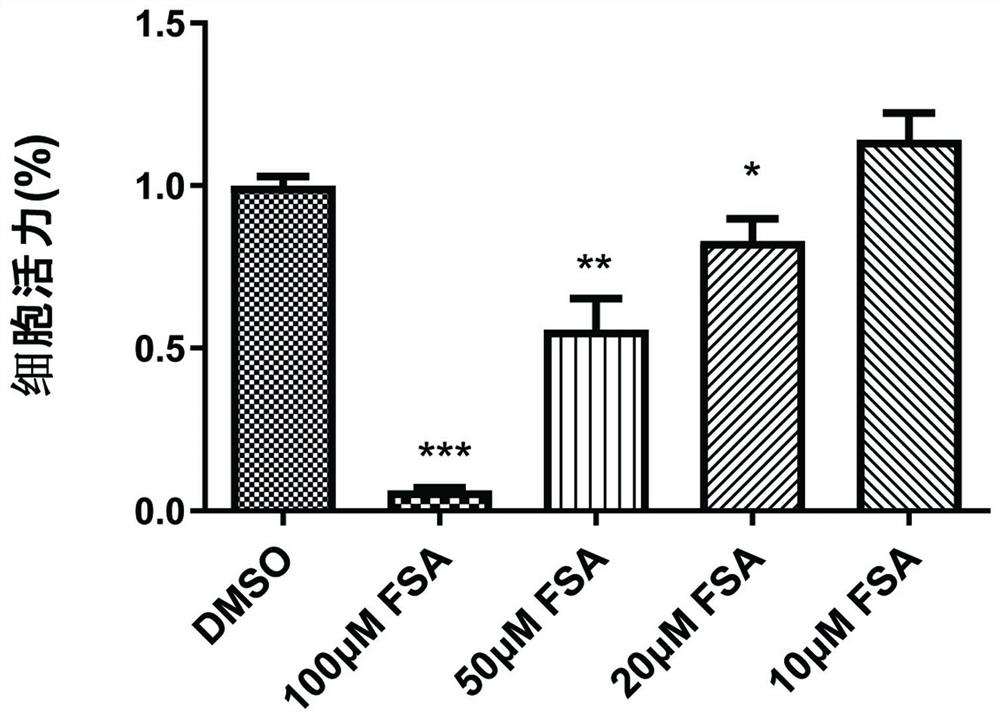
Application of forsythiaside A to preparation of anti-esophageal cancer medicine
ActiveCN113209113APromote apoptosisTo achieve the purpose of resisting esophageal squamous cell carcinomaOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsMalignant phenotypeOncology
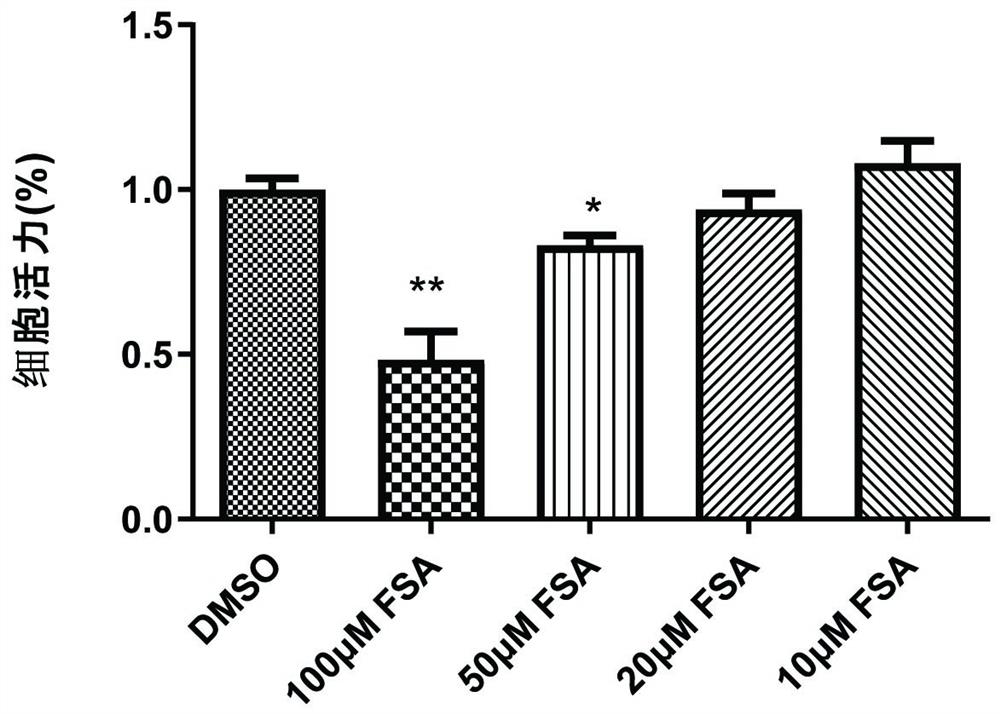
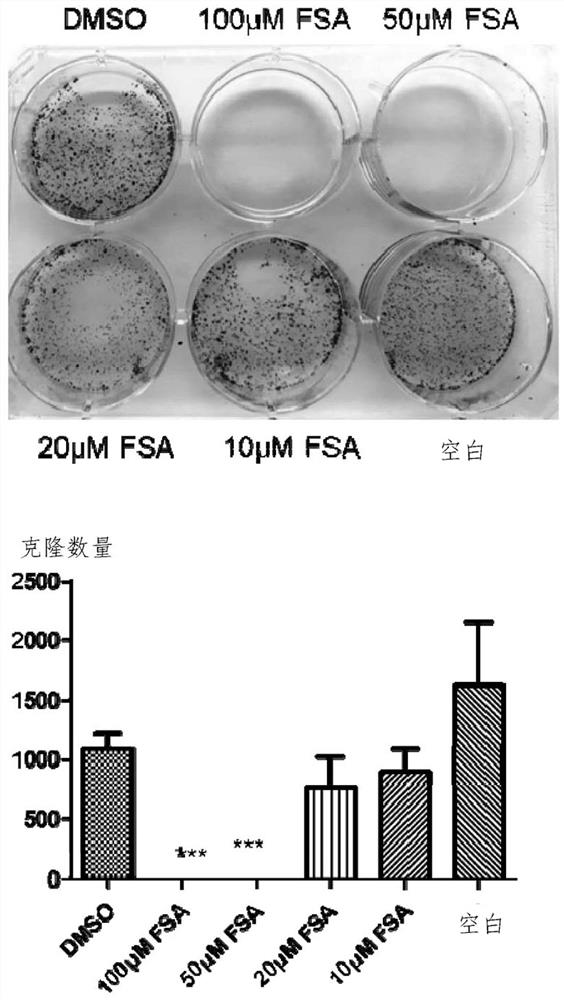
The invention provides an application of forsythiaside A to preparation of an anti-esophageal squamous cell carcinoma medicine. The forsythiaside A is used as an active component in the anti-esophageal squamous cell carcinoma medicine, and the molecular formula of the forsythiaside A is C29H36O15. The forsythoside A mainly inhibits proliferation, clone formation and cell migration of esophageal squamous carcinoma cells, or promotes apoptosis of the esophageal squamous carcinoma cells by retarding the cycle of the esophageal squamous carcinoma cells so as to achieve the purpose of resisting the esophageal squamous carcinoma. Therefore, the forsythiaside A has an inhibiting effect on the malignant phenotype of the esophageal squamous carcinoma.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU NORMAL UNIV
Application of malignant glioma biomarker
PendingCN111996251APrevent proliferationPrevent invasionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisMalignant phenotypeBiologic marker
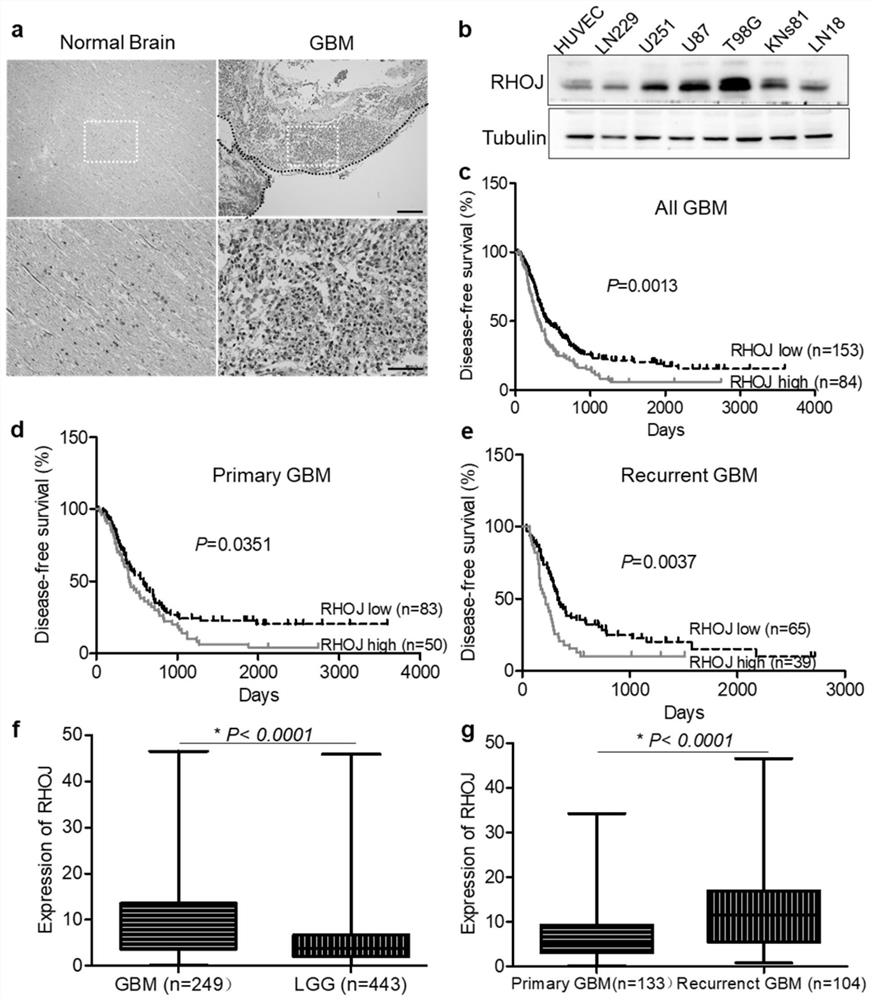
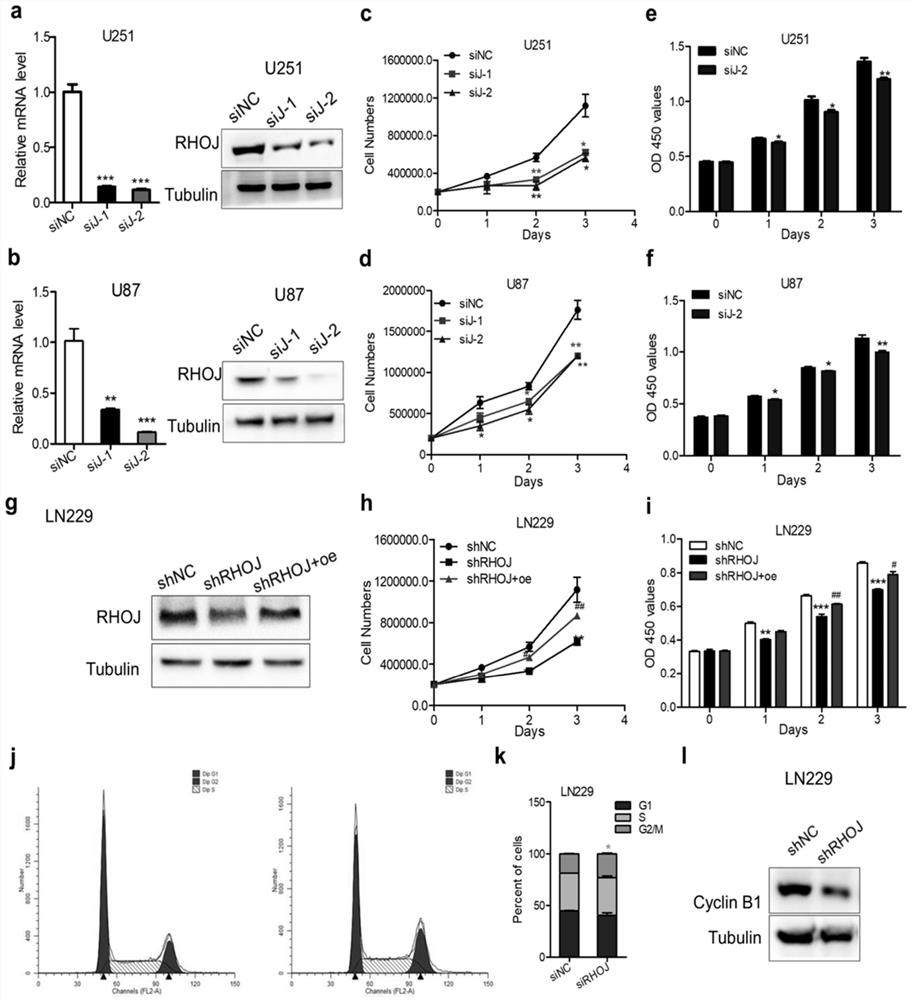
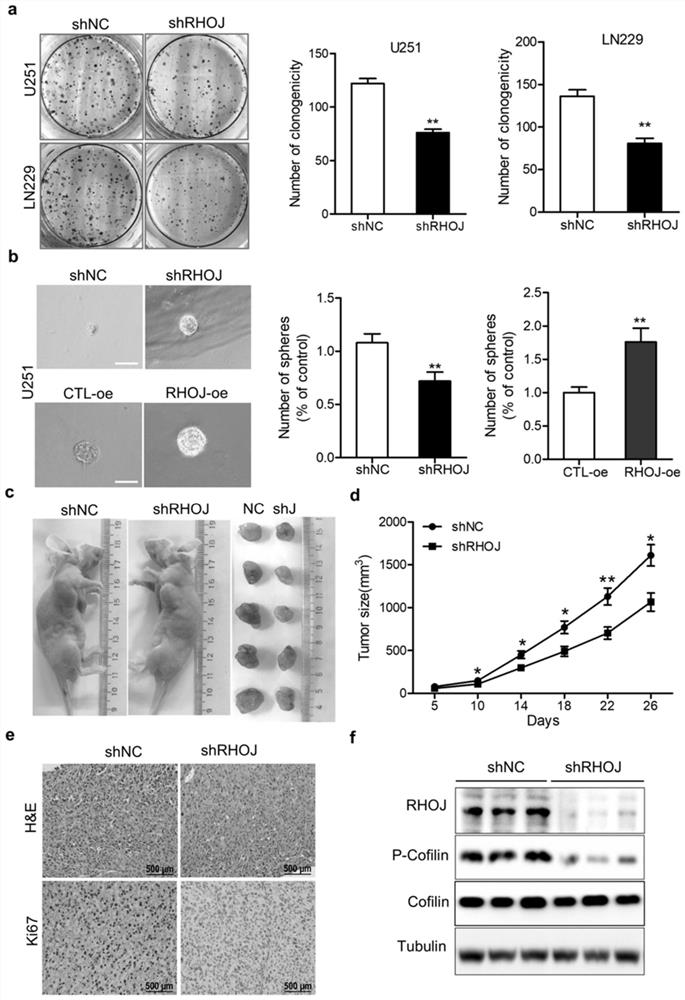
The invention relates to application of a malignant glioma biomarker, in particular to application of RHOJ mRNA shown in SEQ ID No:1 and RHOJ protein shown in SEQ ID No:2 as detection targets in preparation of a kit for diagnosing, treating or prognostically judging malignant glioma. We find that silence of RHOJ expression significantly inhibits malignant phenotypes such as glioma cell proliferation and invasion, RHOJ can be used as a molecular marker for malignant glioma diagnosis and prognostic judgment, and treatment strategies such as an RHOJ-targeting antibody or small molecule inhibitorare expected to improve malignant glioma treatment.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF WANNAN MEDICAL COLLEGE YIJISHAN HOSPITAL OF WANNAN MEDICAL COLLEGE
Functional assay for cancer recurrence and malignant potential
ActiveUS20150212072A1Promote rapid proliferationPoor prognosisCompound screeningApoptosis detectionCancer pharmacotherapyMalignant phenotype
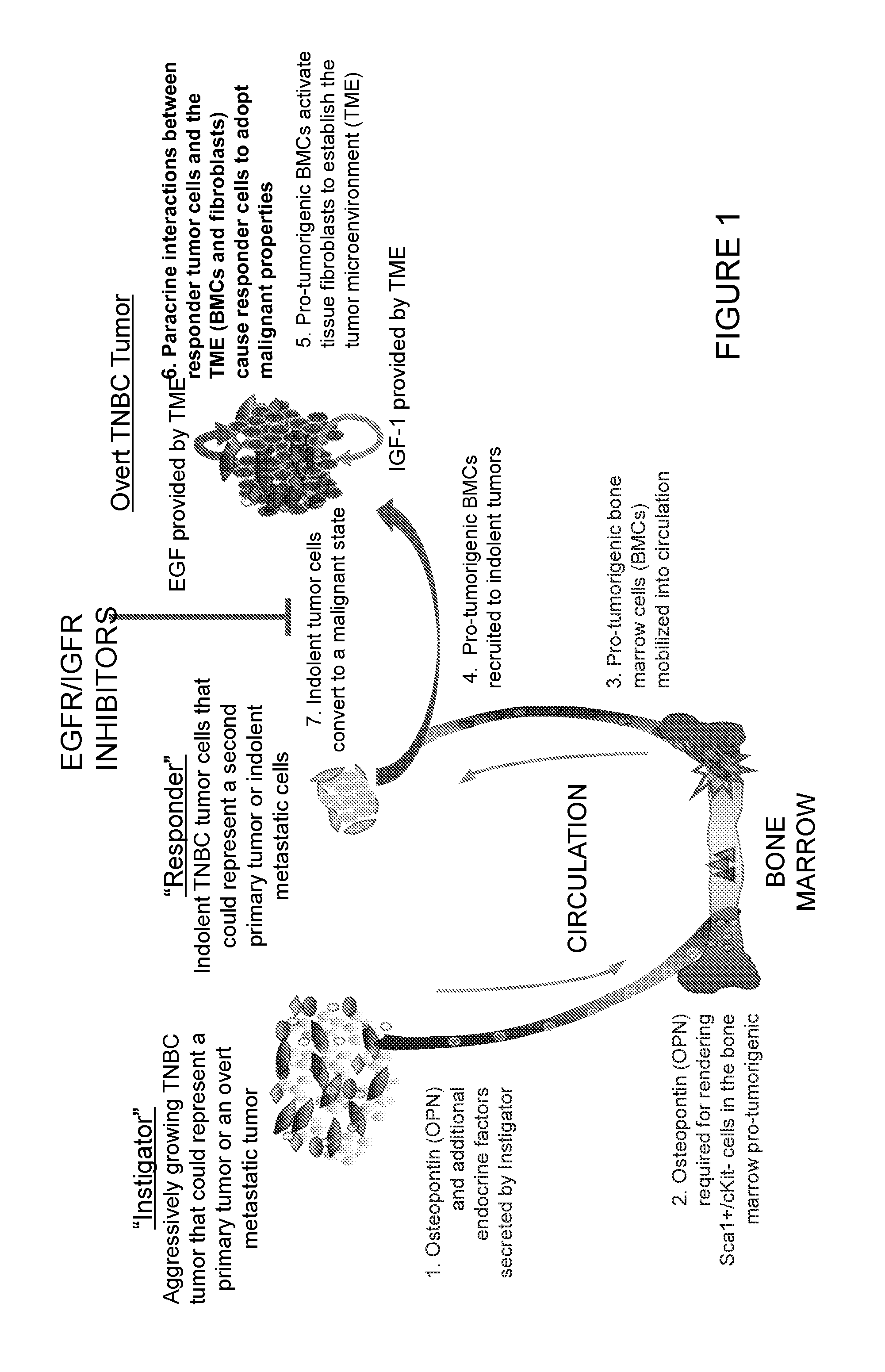
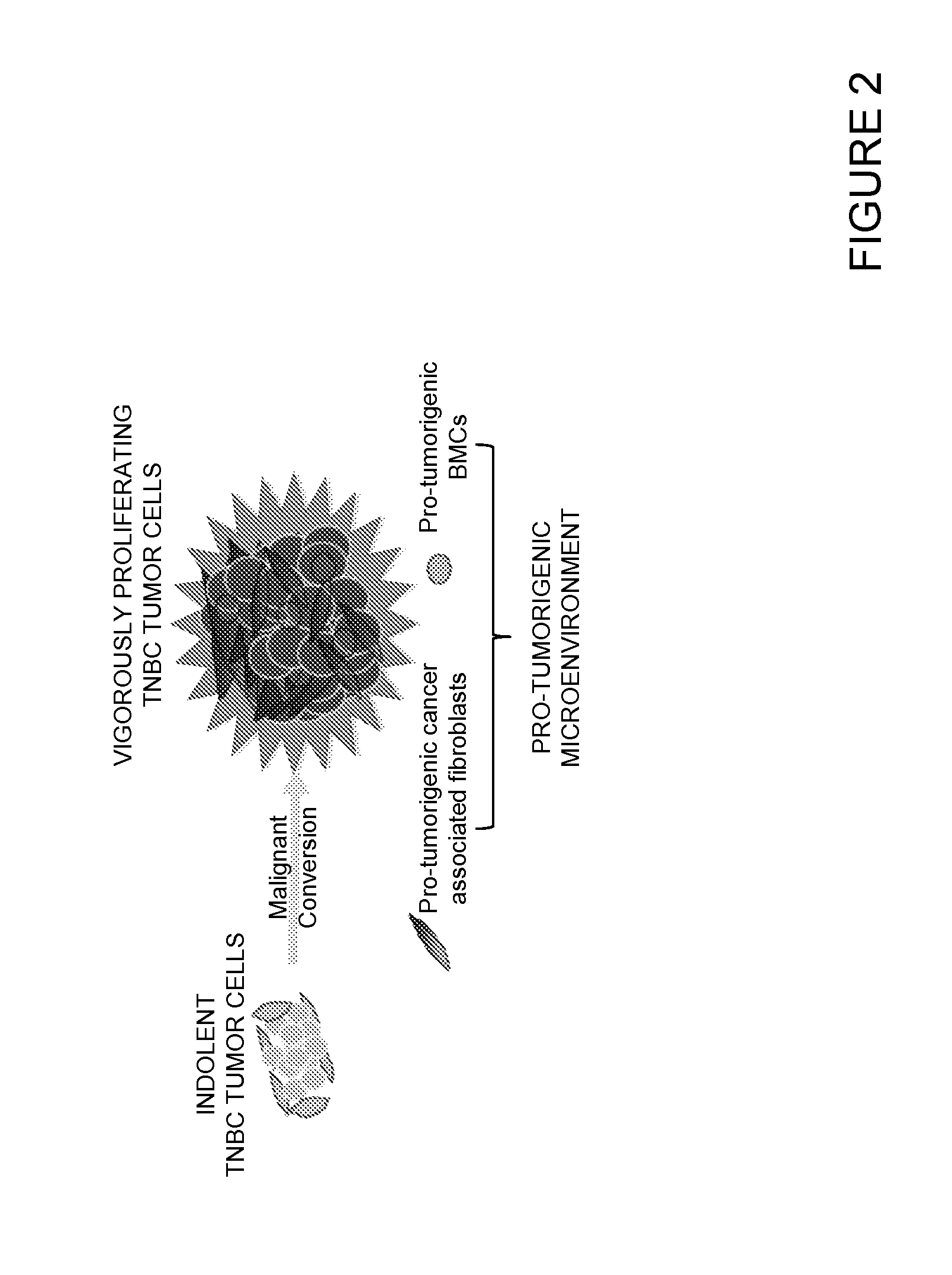
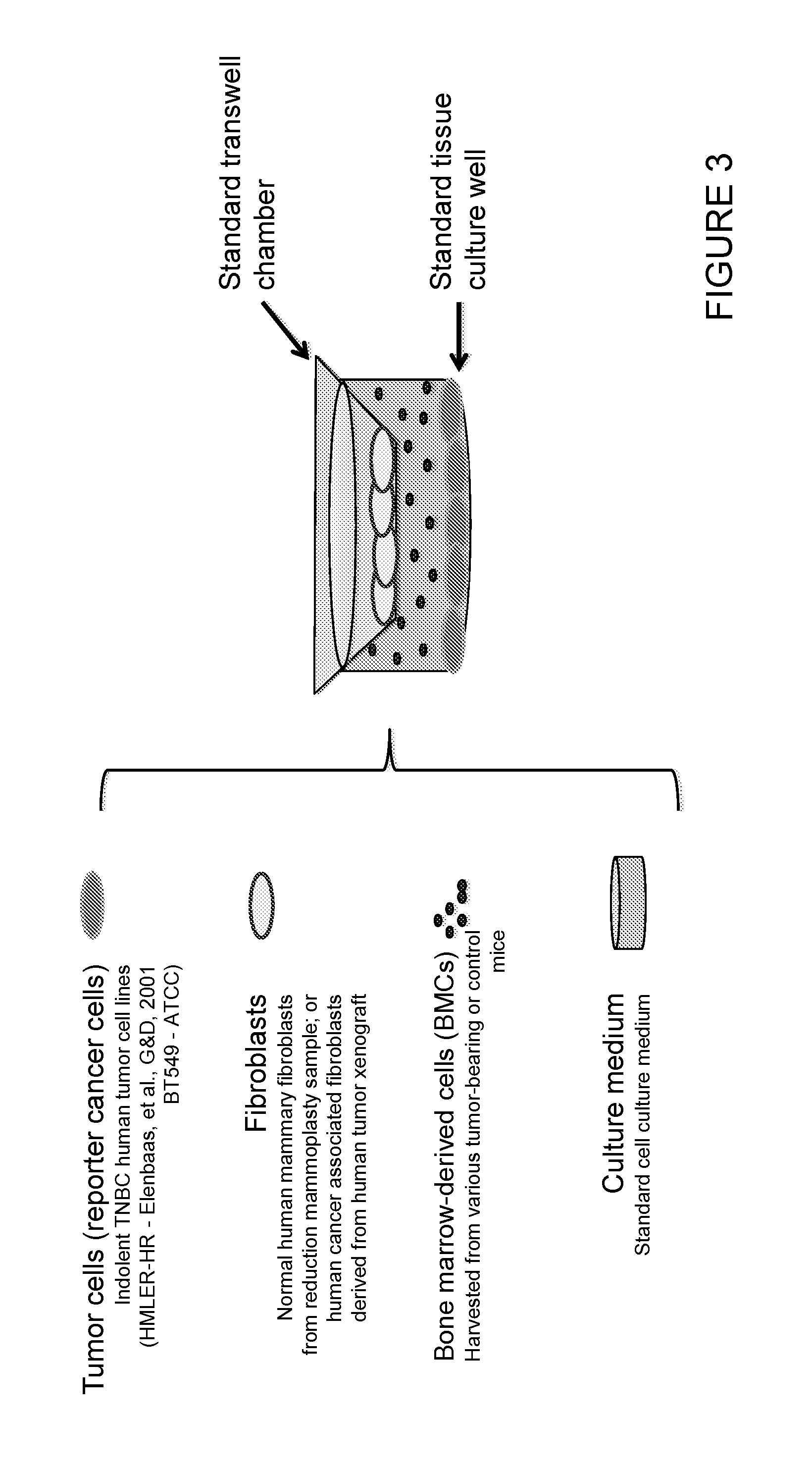
Embodiments herein provides an in vitro co-culture system comprising a population of cancer responder cells and a population of non-tumor cells wherein the cancer responder cells can convert to a malignant state and exhibit hallmark malignant phenotype when the cells are placed in a tumor supportive environment. The system is useful for prognosis evaluation of cancer recurrence, malignancy development, cancer drug screening and surveillance for resistance to cancer drug therapy.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Application of ILF3 detection reagent in preparation of colorectal cancer diagnosis reagent
ActiveCN111012913APrevent proliferationHigh expressionOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementMalignant phenotypeMalignancy
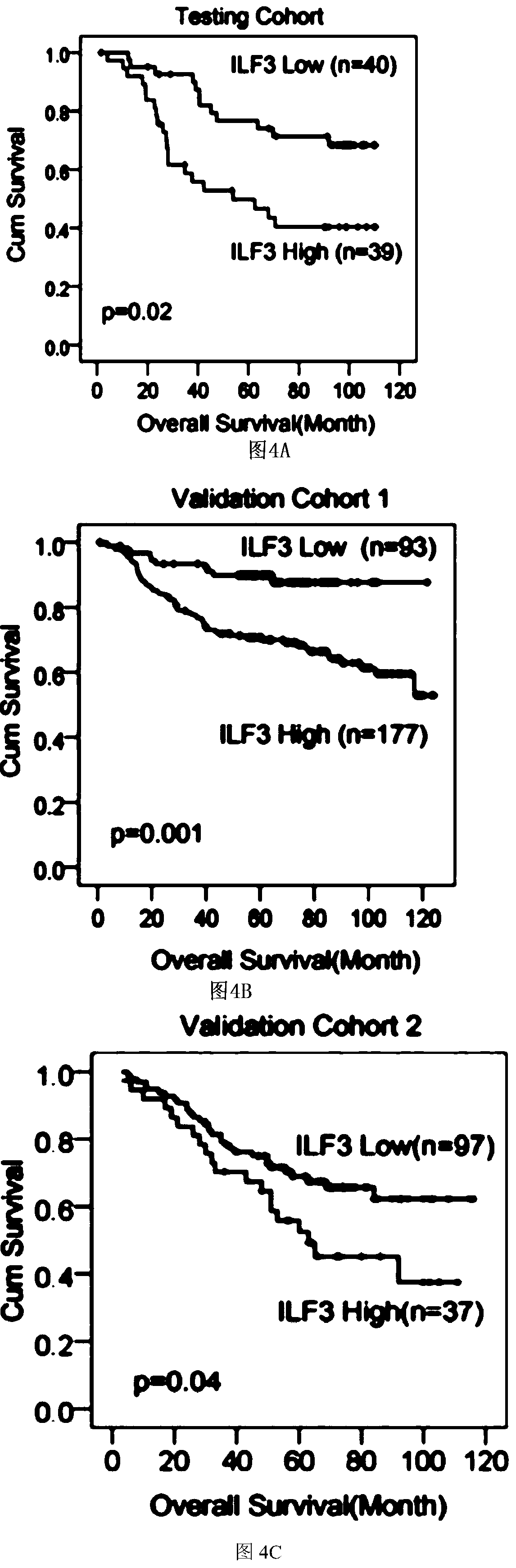
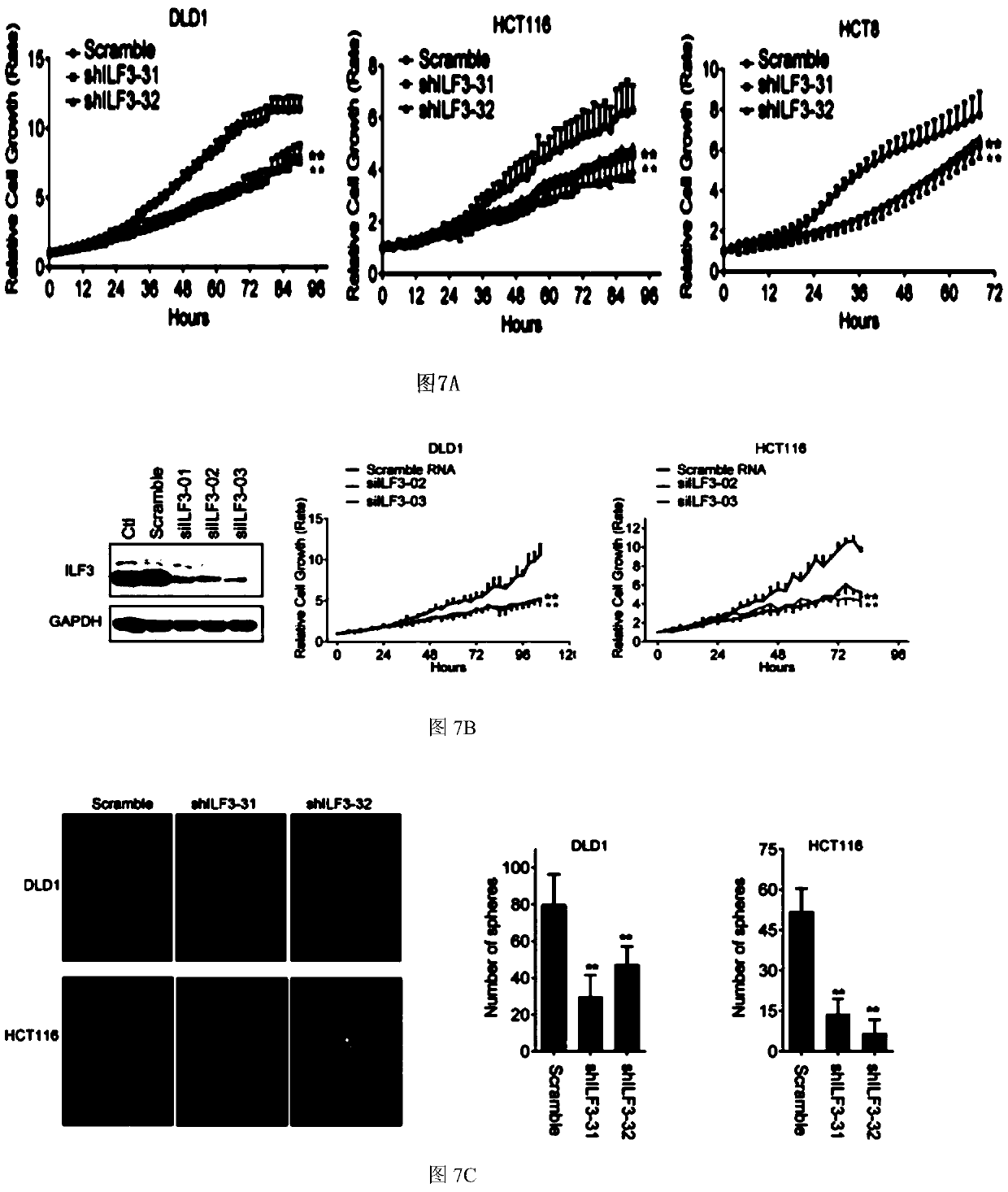
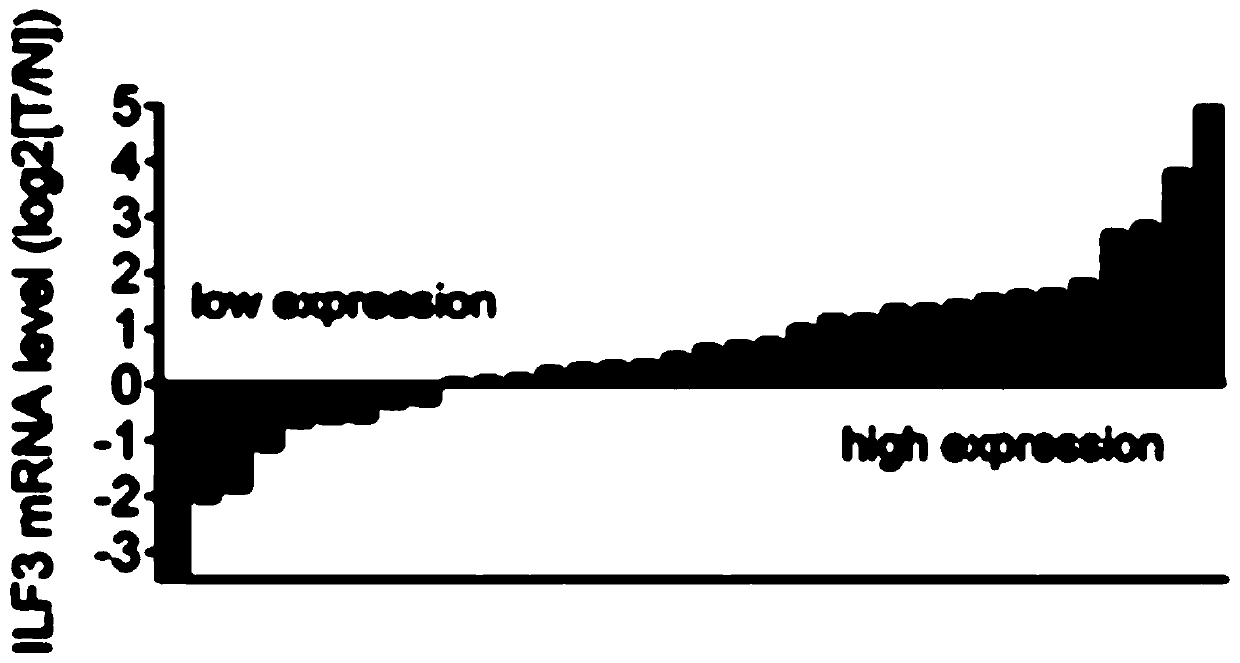
The invention, which belongs to the field of biological medicines, particularly relates to application of an ILF3 detection reagent in preparation of a colorectal cancer diagnosis reagent and a colorectal cancer prognosis diagnosis reagent / kit. The research finds that ILF3 is overexpressed in a specimen of a primary CRC patient and is related to poor prognosis; and the gene is suggested to be possibly related to the malignant phenotype of CRC at the clinical level. With the molecular biological means, interference of ILF3 can significantly inhibit CRC proliferation, so that the ILF3 is shown to have an important function in colorectal cancer occurrence and development. In addition, the invention also discovers that the ILF3 promotes tumor growth by directly adjusting the mRNA stability ofthe SGOC gene and increasing the expression of the SGOC gene for the first time; that is, the ILF3 influences tumors by adjusting the SGOC pathway. Researches show that the SGOC inhibitor can be usedfor treating CRC patients with ILF3 overexpression and has important clinical significance.
Owner:THE SIXTH AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Non-differential gene associated with malignant phenotype of tumor cell as well as screening method and application of non-differential gene
ActiveCN114388063AGuaranteed stabilityNormal growth effectsCharacter and pattern recognitionProteomicsParanasal Sinus CarcinomaMalignant phenotype
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioinformatics, and discloses a non-differential gene associated with tumor cell malignant phenotypes and a screening method and application thereof, the non-differential gene interacts with a plurality of differential genes of cancerous tissues, is ubiquitous in the cancerous tissues and para-carcinoma tissues, has relatively high abundance expression and no differential expression, and can be used for screening tumor cell malignant phenotypes. And the characteristic of playing a heavy role in a network path is realized. And sorting the genes to be distinguished through an SVM model for distinguishing cancerous tissues and para-carcinoma tissues, and removing differential genes from the genes at the first 5% of the sorted genes to obtain the non-differential genes. With the non-differential gene as a target, the non-differential gene can be used for preparing drugs for preventing or treating tumors related to the non-differential gene. Whether the non-differential genes are knocked down for preventing tumors or knocked down after tumors are formed for controlling tumor development, the screened non-differential genes can inhibit the sizes of mice tumors.
Owner:CHI BIOTECH CO LTD
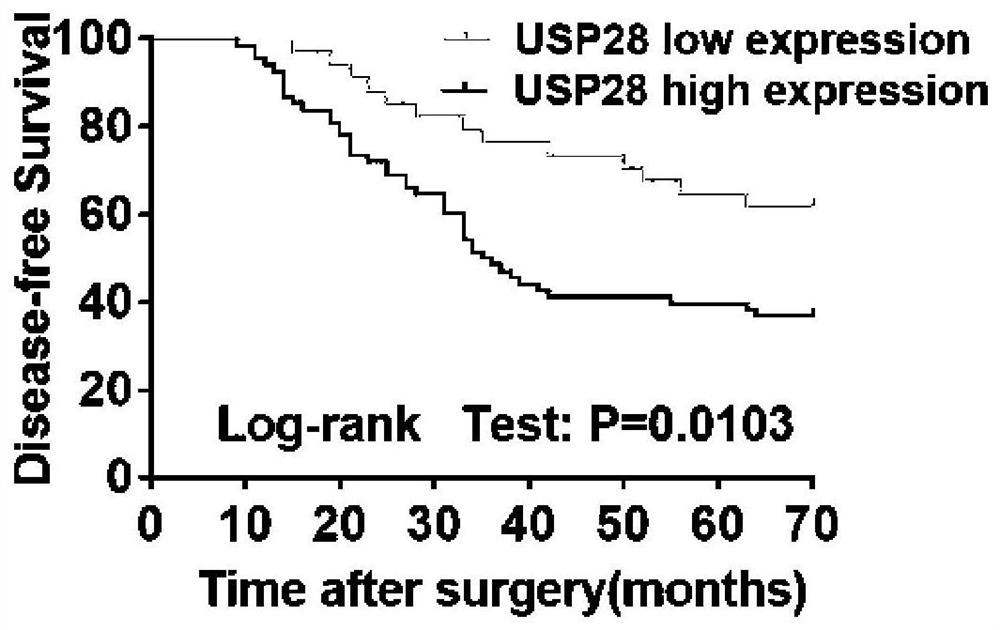
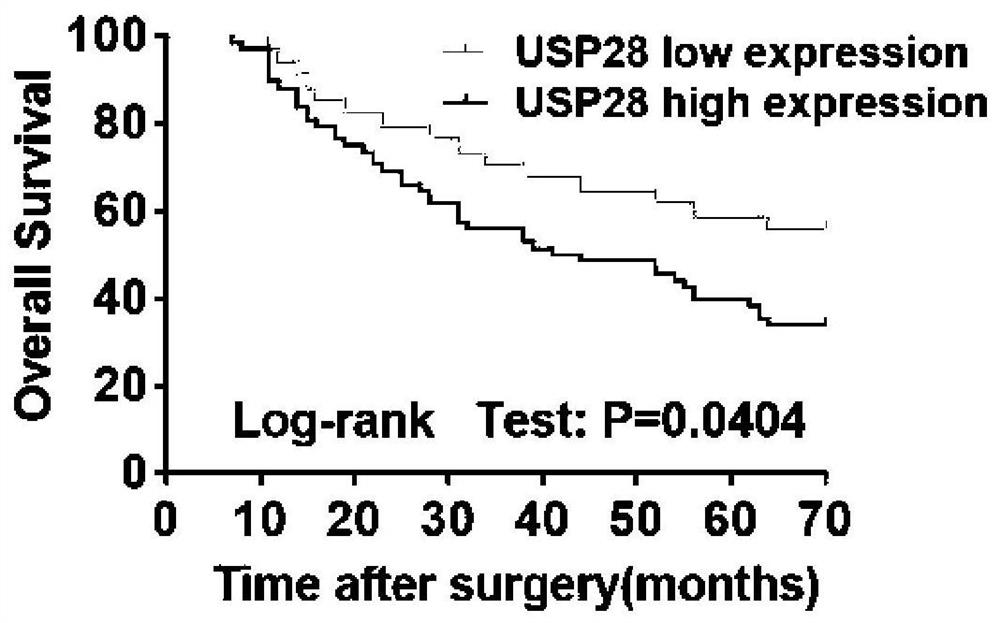
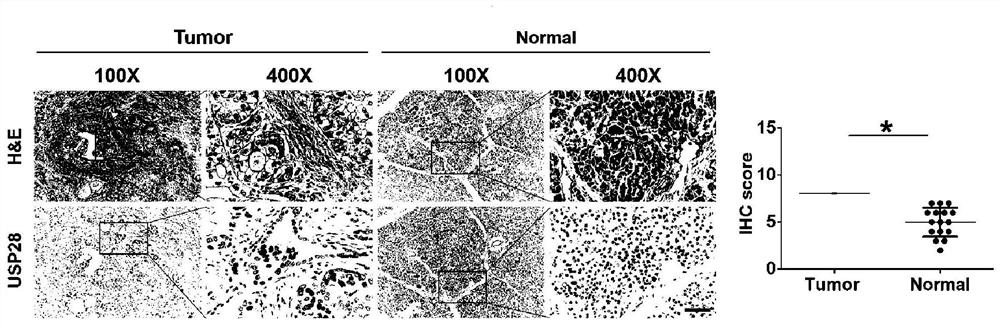
Application of deubiquitinating enzyme USP28 in preparation of medicine for preventing or treating pancreatic cancer
The invention discloses an application of deubiquitinating enzyme USP28 in preparation of a medicine for preventing or treating pancreatic cancer. Research finds that USP28 expression in pancreatic cancer tumor tissue is higher than that in normal pancreatic tissue, and USP28 high expression is remarkably related to malignant phenotype and lifetime shortening of pancreatic cancer patients; overexpression of the USP28 can accelerate growth of pancreatic cancer cells, and down-regulation of the USP28 can inhibit in-vitro and in-vivo growth of the pancreatic cancer cells; USP28 promotes the growth of pancreatic cancer cells by accelerating the cell cycle process and inhibiting cell apoptosis. In the aspect of mechanism, USP28 is subjected to ubiquitination and stabilizes a transcription factor FOXM1, which is a key medium for Wnt / beta-catenin signal transduction, USP28-mediated FOXM1 stabilizes and significantly promotes beta-catenin nucleation so as to further cause activation of a Wnt / beta-catenin pathway, and recovery of FOXM1 expression can alleviate the antitumor effect caused by down regulation of USP28. The deubiquitinating enzyme USP28 promotes the development of the pancreatic cancer by enhancing FOXM1 mediated Wnt / beta-catenin signal channel activation, and a powerful means is provided for potential targeted treatment and prevention of pancreatic cancer patients in the future.
Owner:THE SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL TO NANCHANG UNIV
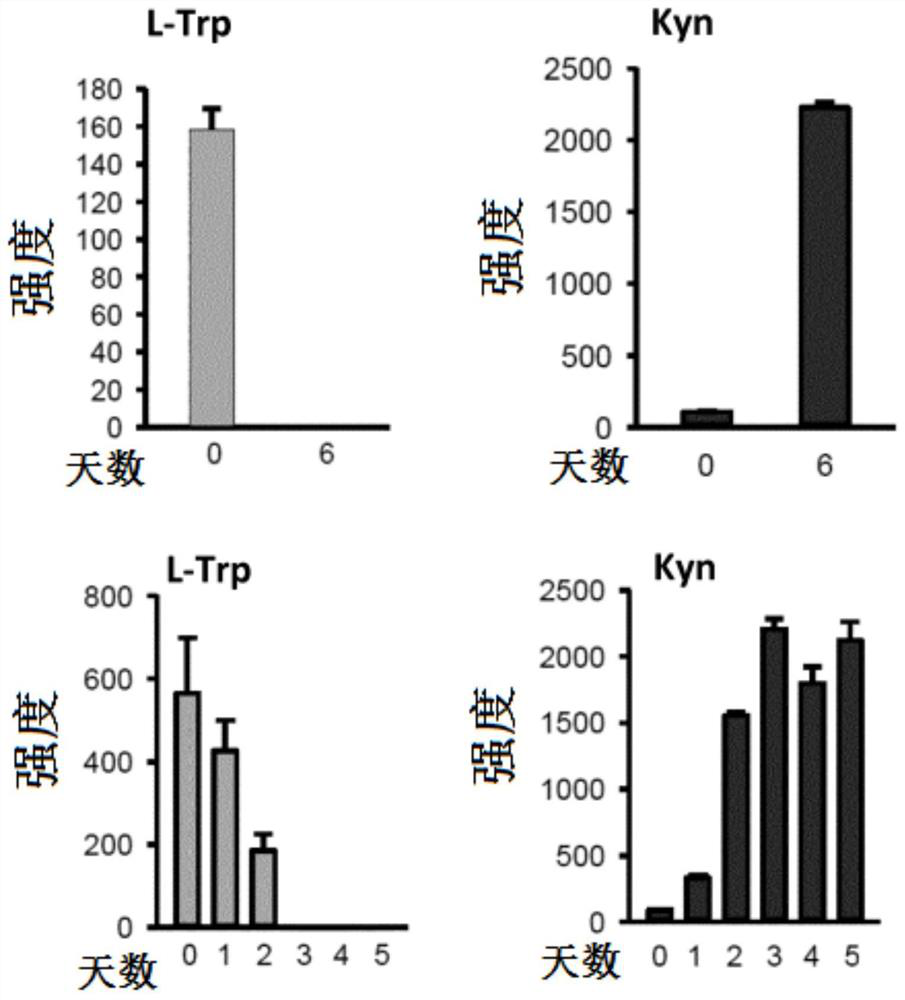
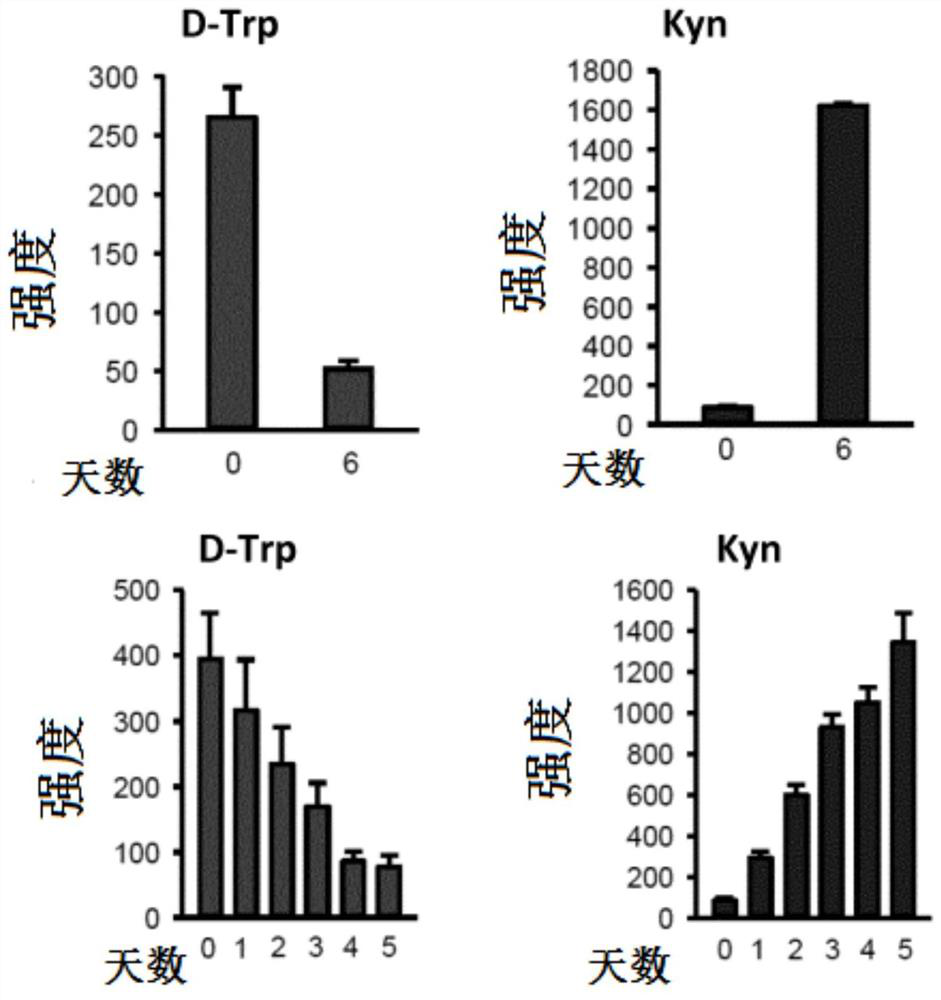
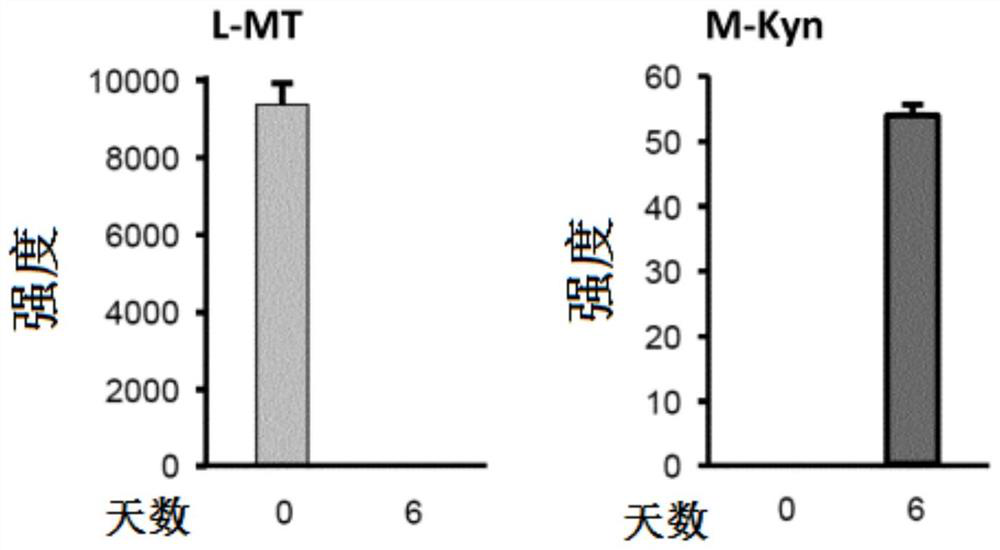
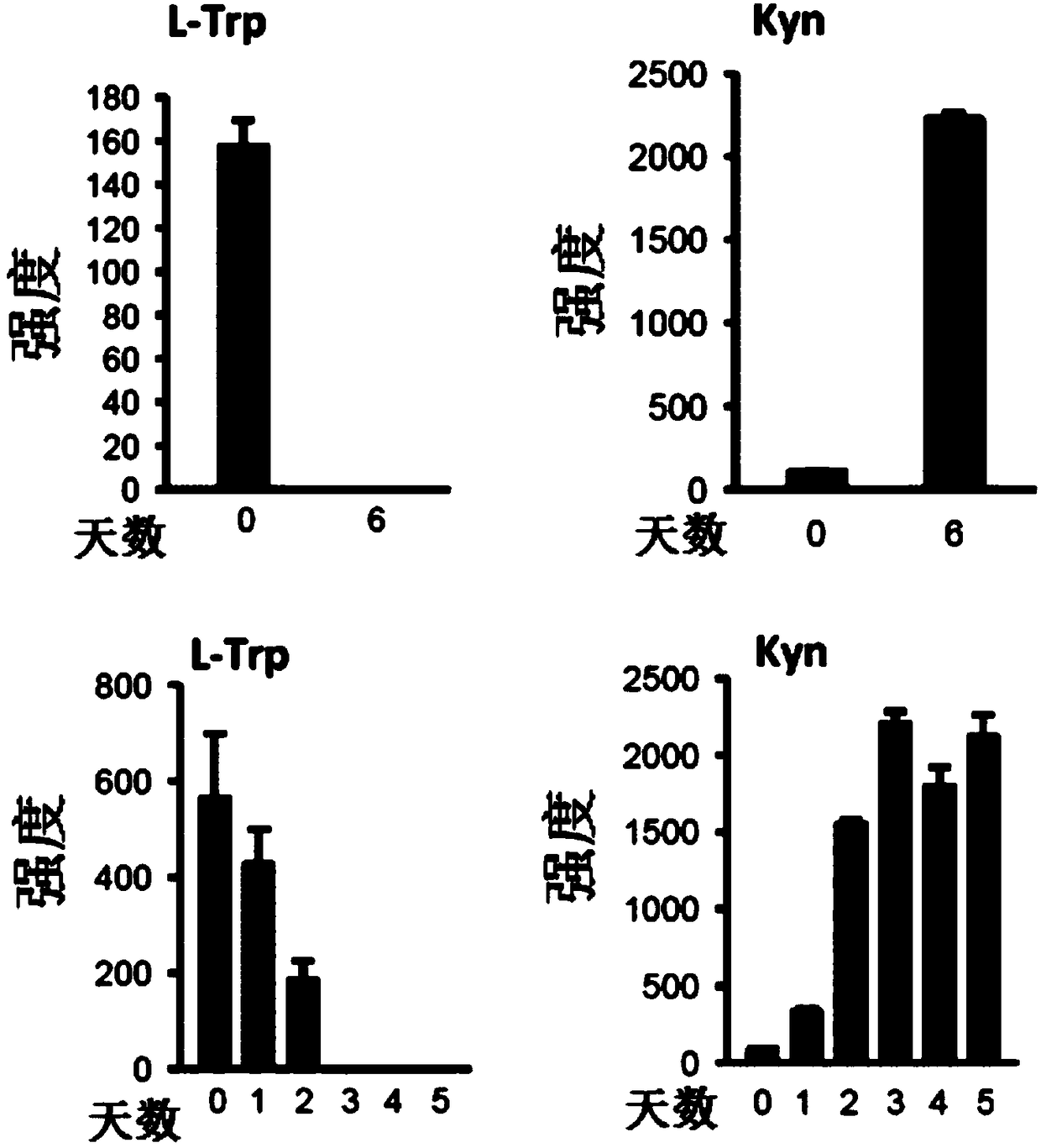
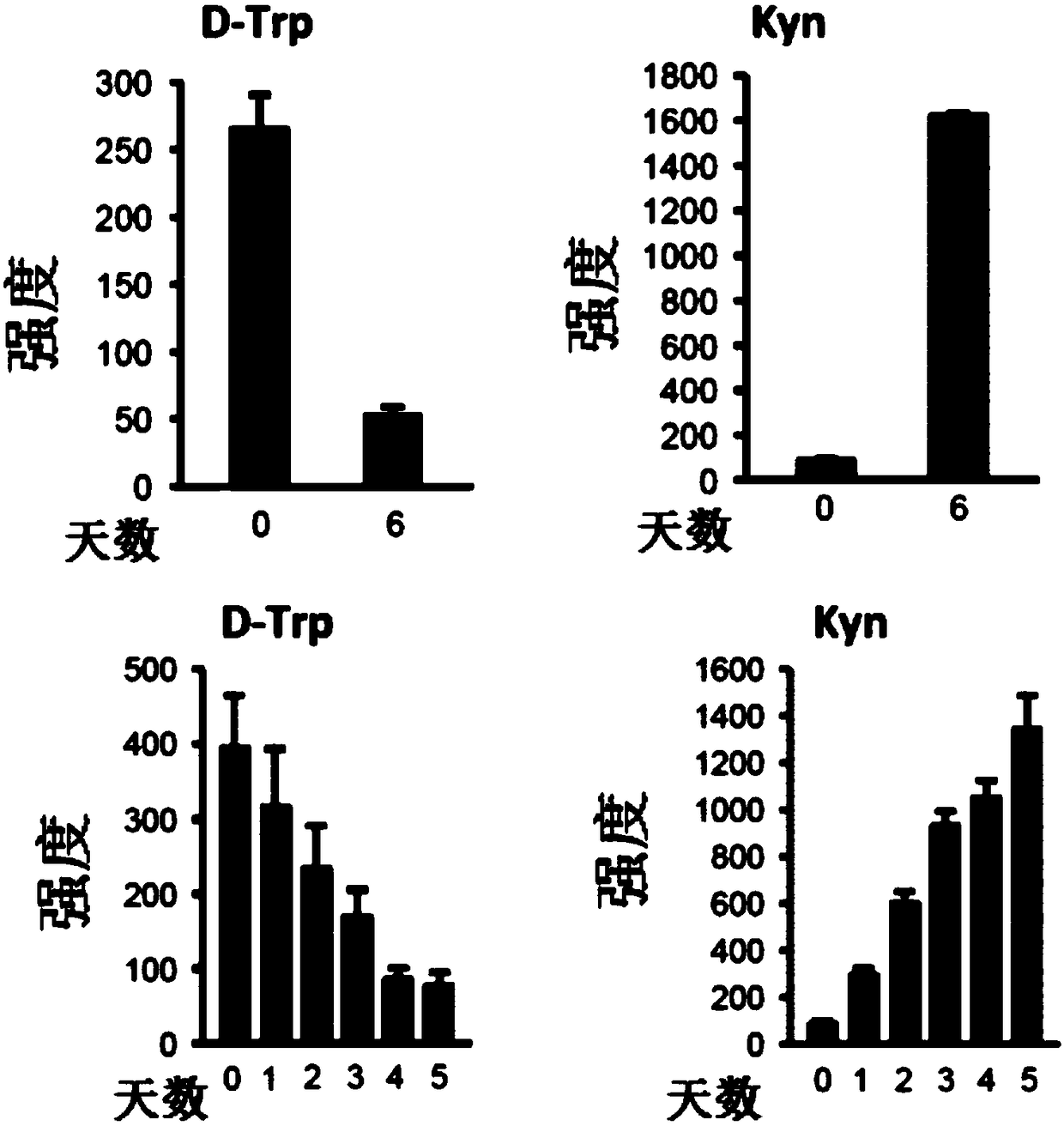
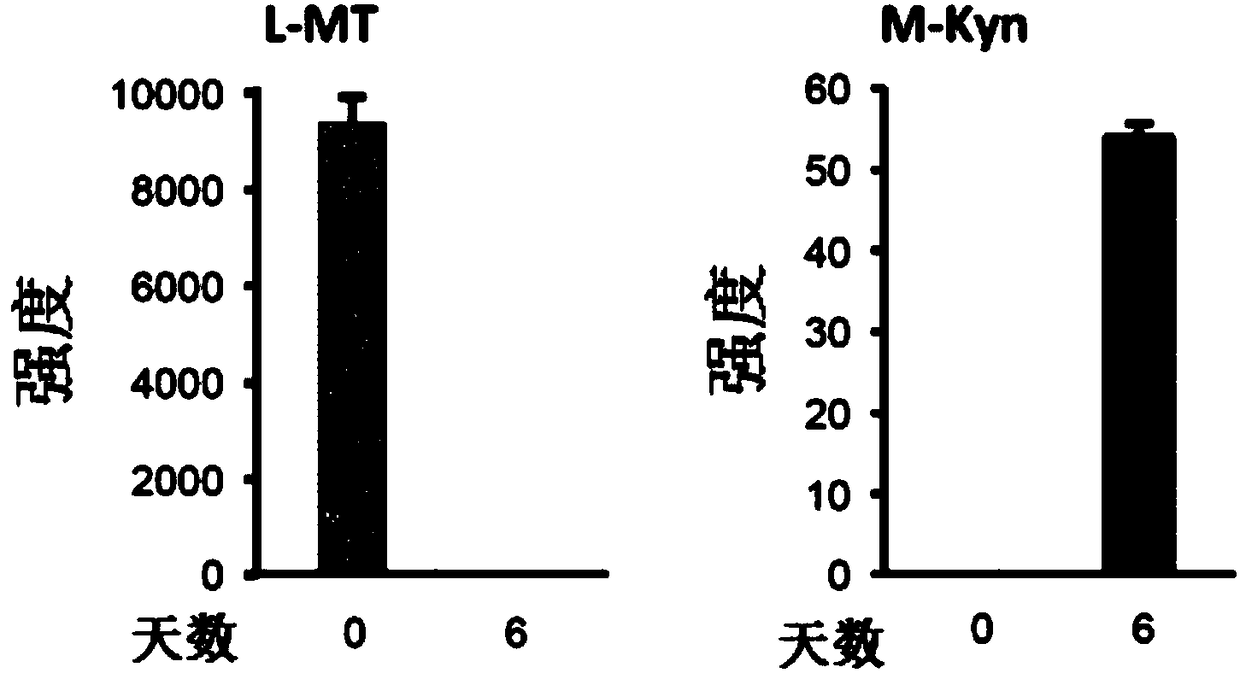
Isotopic methods for the measurement of tryptophan and its metabolites
Owner:ELECTROPHORETICS LTD +2
Isotopic methods for measurement of tryptophan and metabolites thereof
Tryptophan degradation is a key metabolic pathway controlling immune reactions and evidence suggests that during cancer progression generation of tryptophan metabolites may be fundamental for immune escape promoting the malignant phenotype of cancer cells in an autocrine fashion. The invention relates to methods of measuring mass tag labelled tryptophan and metabolites thereof and methods using the labelled molecules for monitoring in a subject the effectiveness of a treatment and of disease recurrence after treatment, for stratifying patients and for diagnosing suppression of an immune response in a subject.
Owner:ELECTROPHORETICS LTD +2
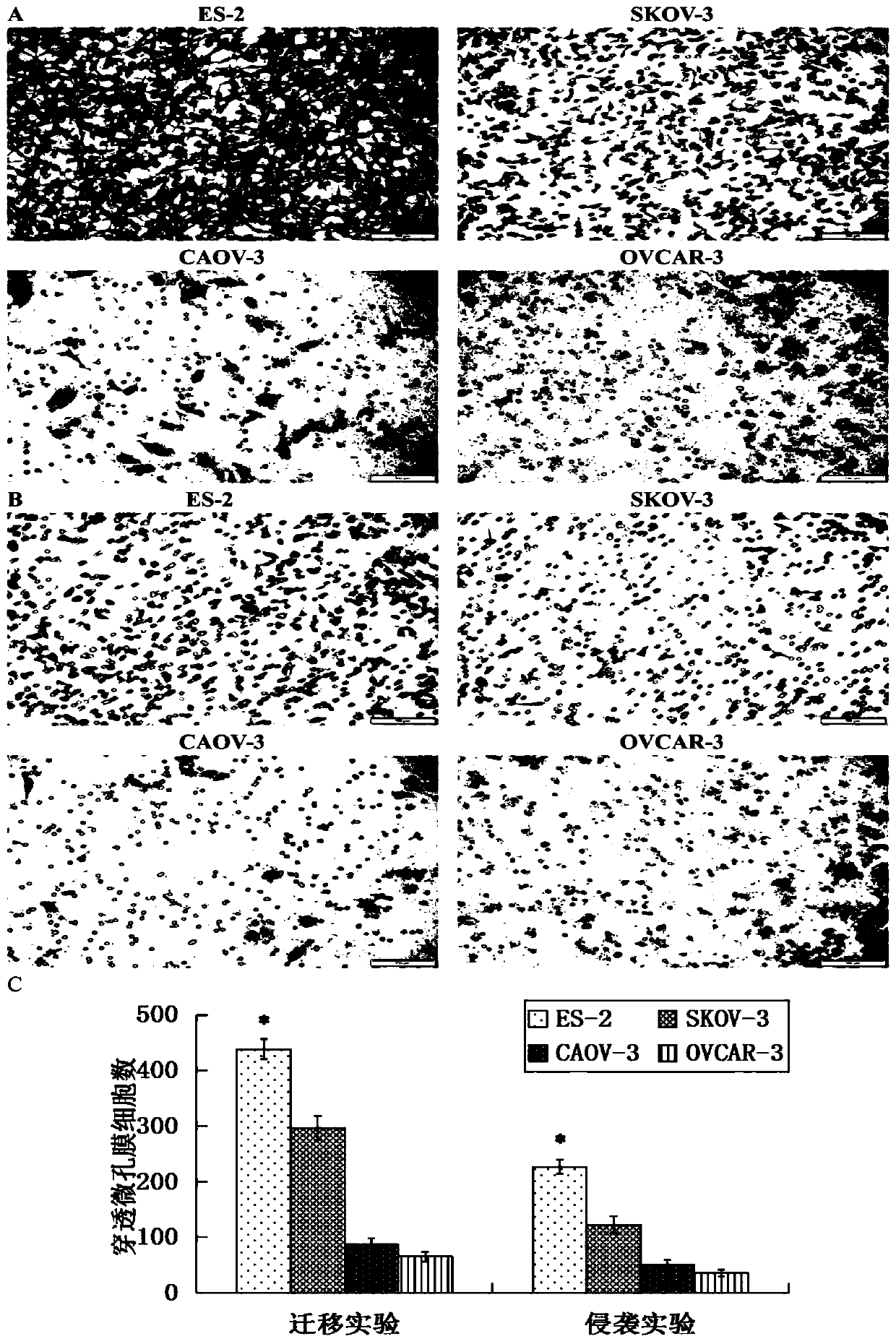
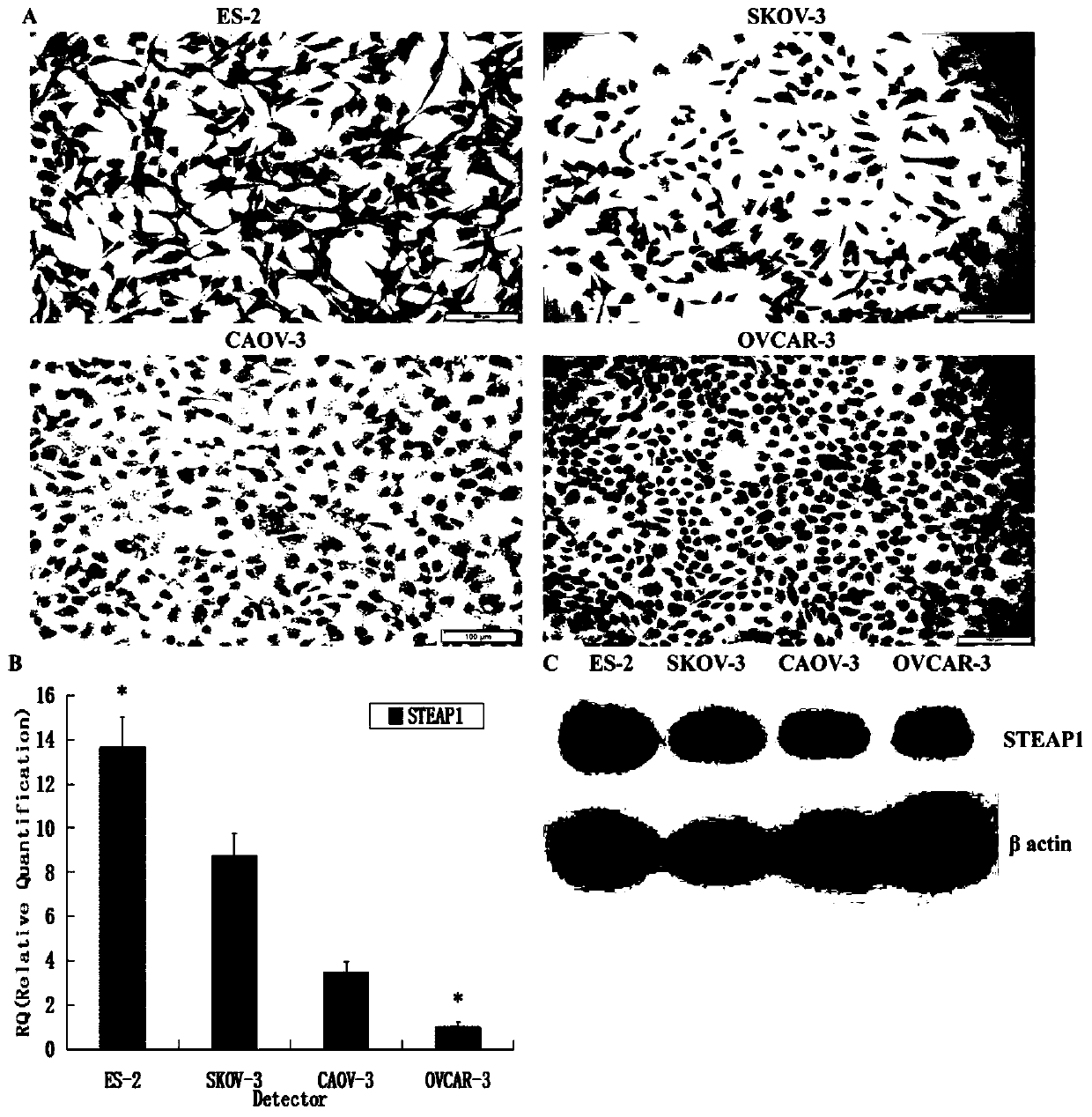
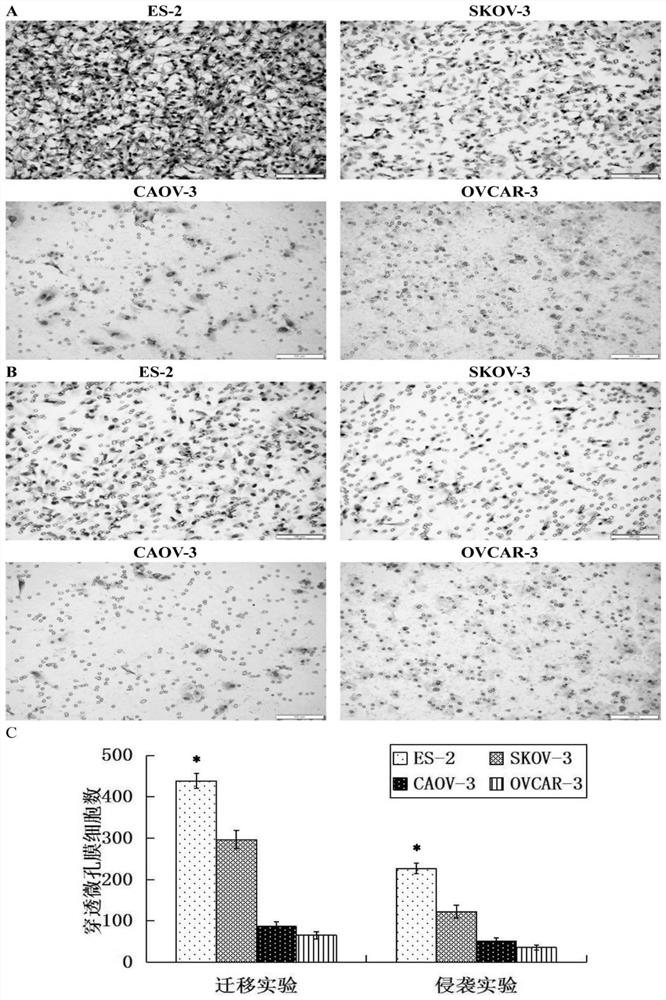
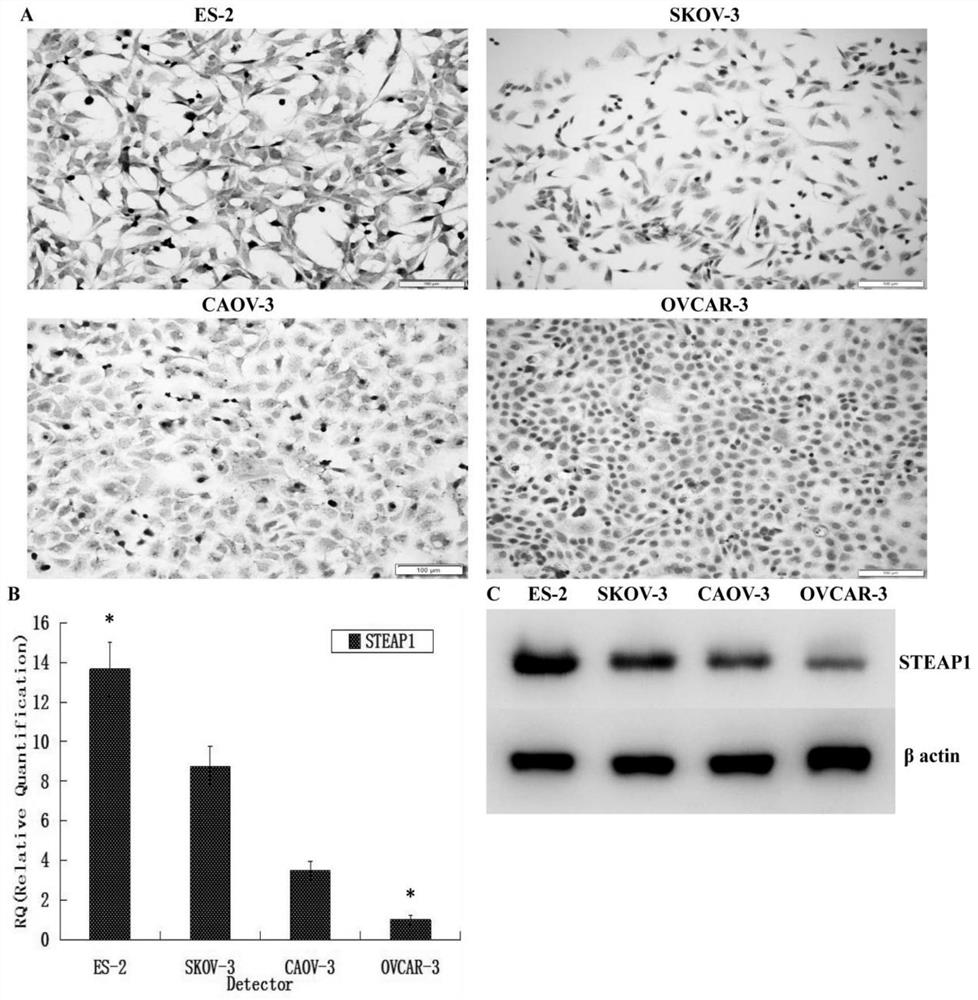
Application of STEAP1 in diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of ovarian cancer
ActiveCN110229896APromote proliferationPromote invasionMicrobiological testing/measurementSexual disorderLymphatic SpreadApoptosis
The present invention provides application of STEAP1 in diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of ovarian cancer. The research shows that STEAP1 plays an oncogene role in the ovarian cancer, and the highexpression of the STEAP1 is positively related to the malignant phenotype of the ovarian cancer and the poor prognosis of a patient; the STEAP1 can promote the proliferation of ovarian cancer cells and inhibit the apoptosis of the cells. The STEAP1 can promote invasion and metastasis of ovarian cancer cells by promoting the progression of EMT. The invention shows that the STEAP1 is an oncogene participating in the generation and development of the ovarian cancer, can be used as a biological marker and a treatment target of the the ovarian cancer, and has good practical application value.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
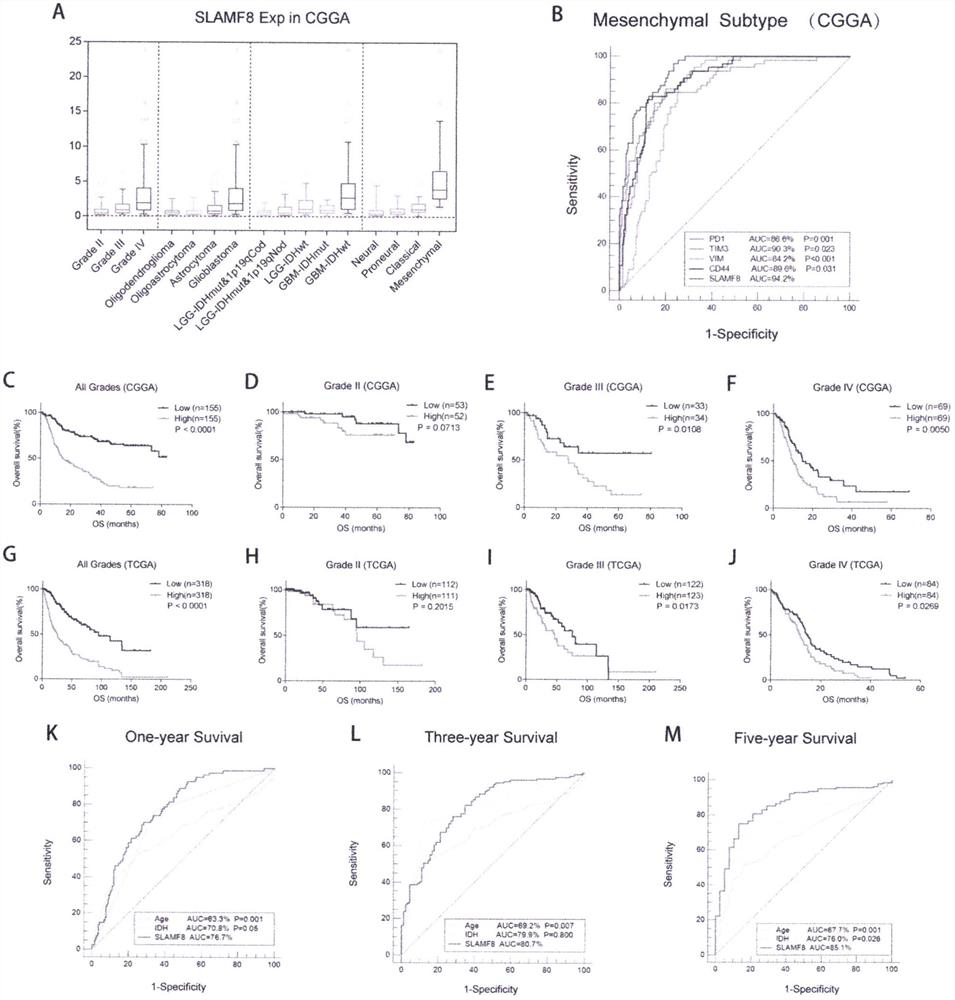
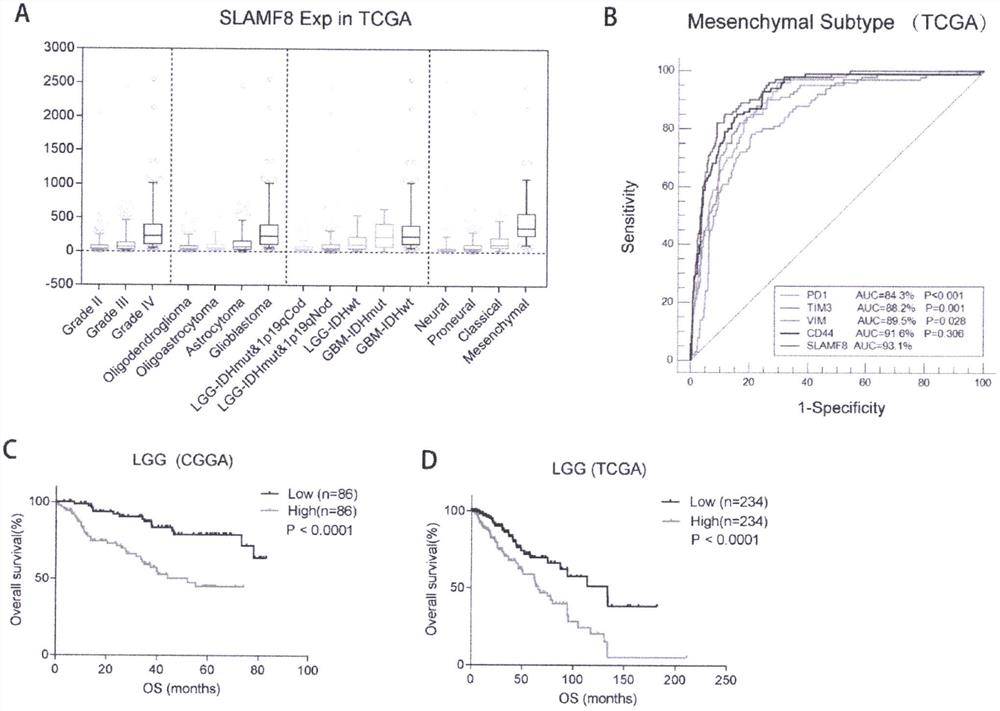
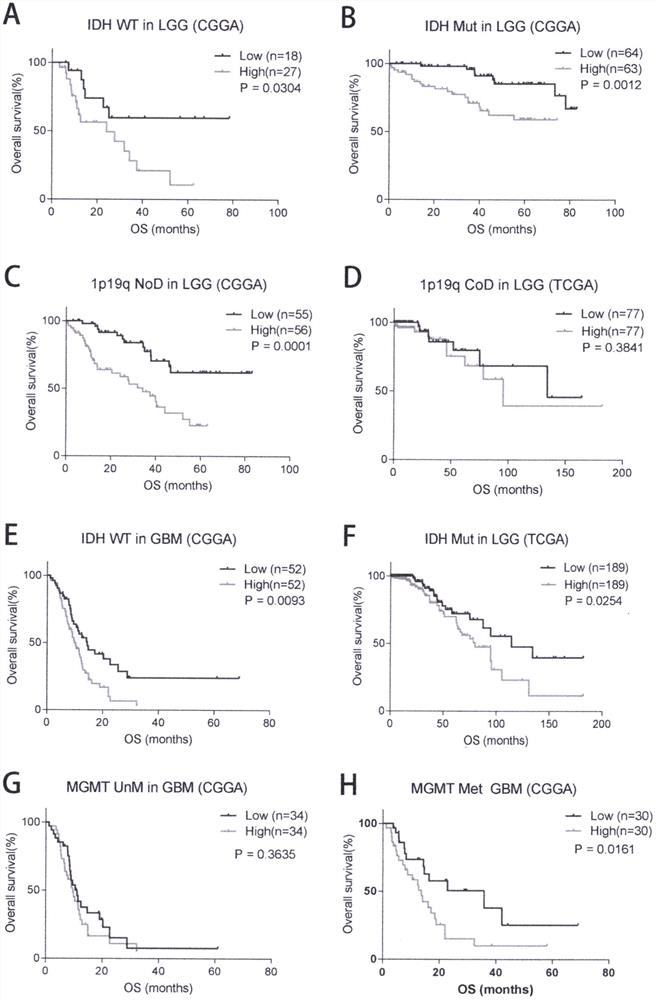
A method for evaluating clinical prognosis of glioma using immune co-stimulatory molecules
The invention discloses the application of SLAMF8 in preparing preparations of tumor tissue markers or serum markers for evaluating the prognosis of human glioma, and as a marker for evaluating the prognosis of human glioma. The present invention also provides a method for evaluating the clinical prognosis of glioma by using immune co-stimulatory molecules. The present invention finds through research that SLAMF8 is highly expressed in the malignant phenotype of glioma and glioblastoma, and is closely related to the poor prognosis of glioma, and the high expression of SLAMF8 is an important sign of the poor prognosis of glioma. Moreover, high expression of SLAMF8 is associated with chemotherapy resistance. The present invention suggests that SLAMF8 mainly affects the glioma microenvironment through monocytes and dendritic cells, and is closely related to immune response. SLAMF8 can affect glioma immune function, inhibit glioma immune response and promote inflammatory response. In conclusion, SLAMF8 can be used as an important clinical prognostic marker for glioma.
Owner:THE FIRST HOSPITAL OF CHINA MEDICIAL UNIV
Application of Steap1 in the diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of ovarian cancer
ActiveCN110229896BPromote proliferationPromote invasionMicrobiological testing/measurementSexual disorderMalignant phenotypeTreatment targets
The present invention provides application of STEAP1 in diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of ovarian cancer. The research shows that STEAP1 plays an oncogene role in the ovarian cancer, and the highexpression of the STEAP1 is positively related to the malignant phenotype of the ovarian cancer and the poor prognosis of a patient; the STEAP1 can promote the proliferation of ovarian cancer cells and inhibit the apoptosis of the cells. The STEAP1 can promote invasion and metastasis of ovarian cancer cells by promoting the progression of EMT. The invention shows that the STEAP1 is an oncogene participating in the generation and development of the ovarian cancer, can be used as a biological marker and a treatment target of the the ovarian cancer, and has good practical application value.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
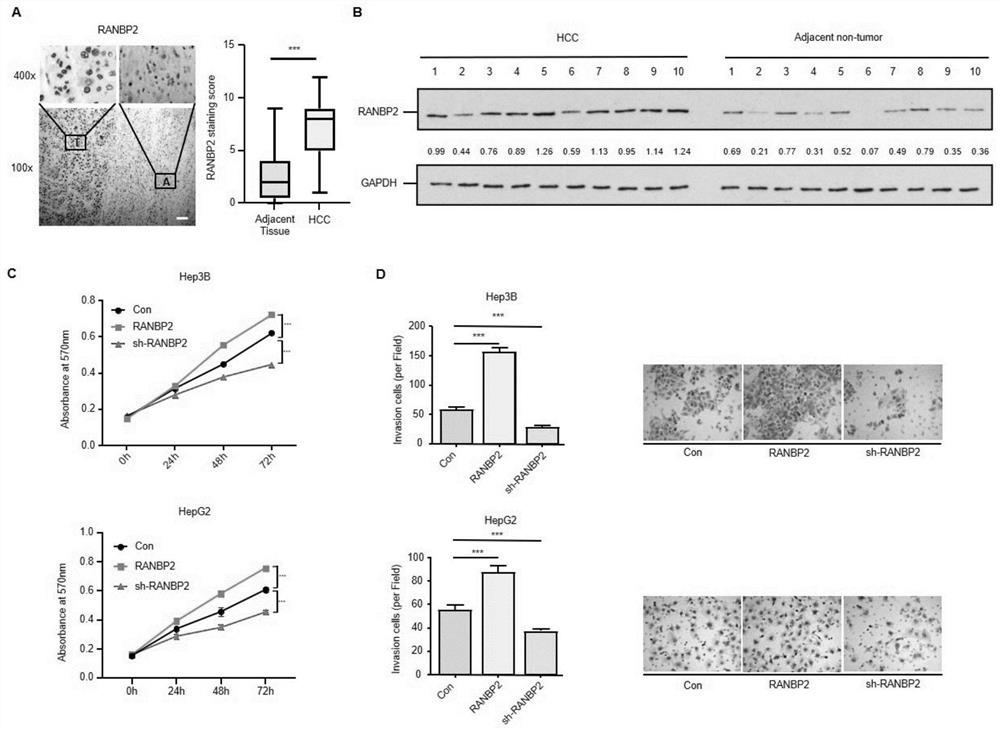
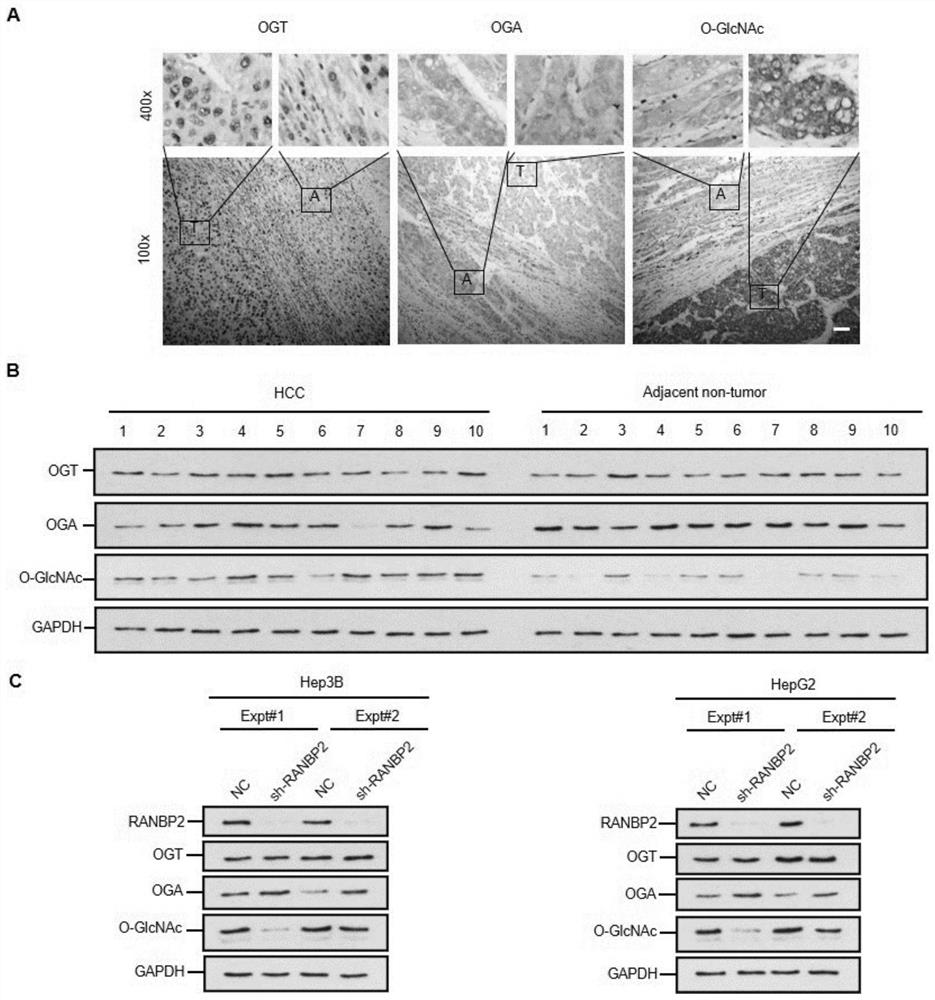
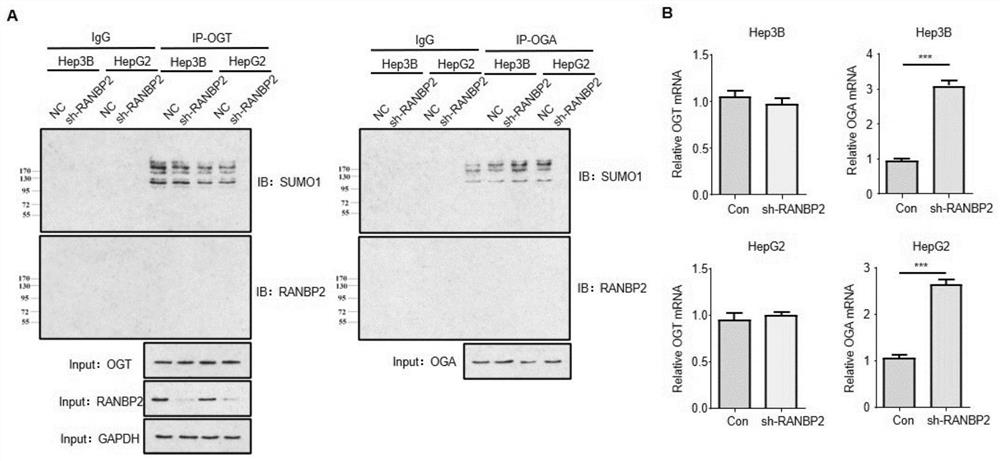
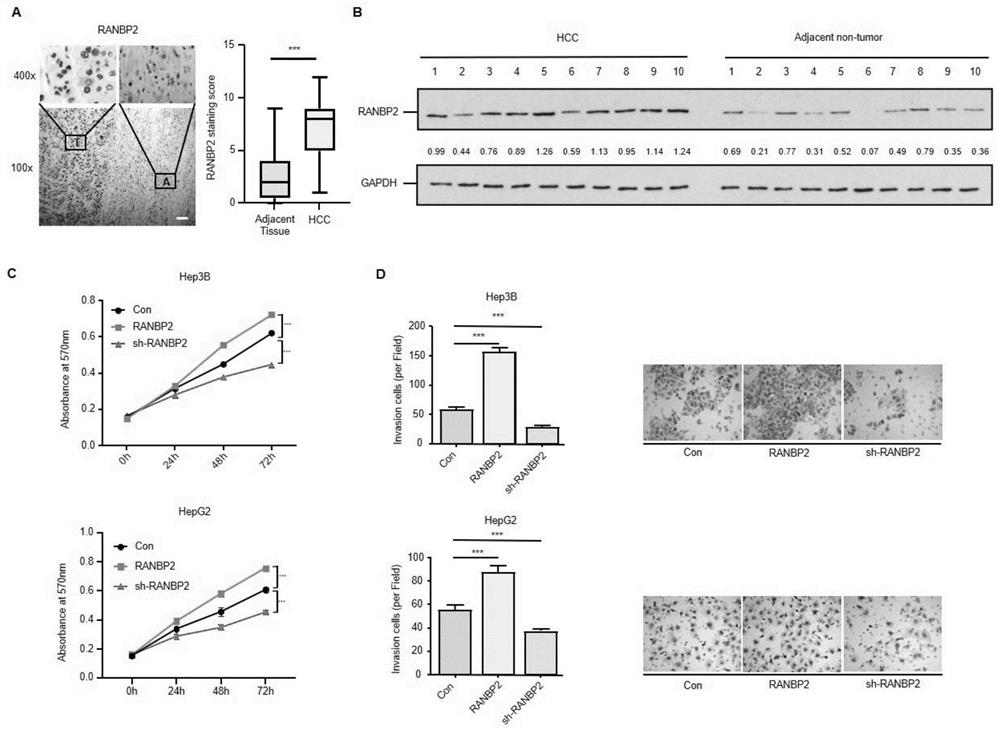
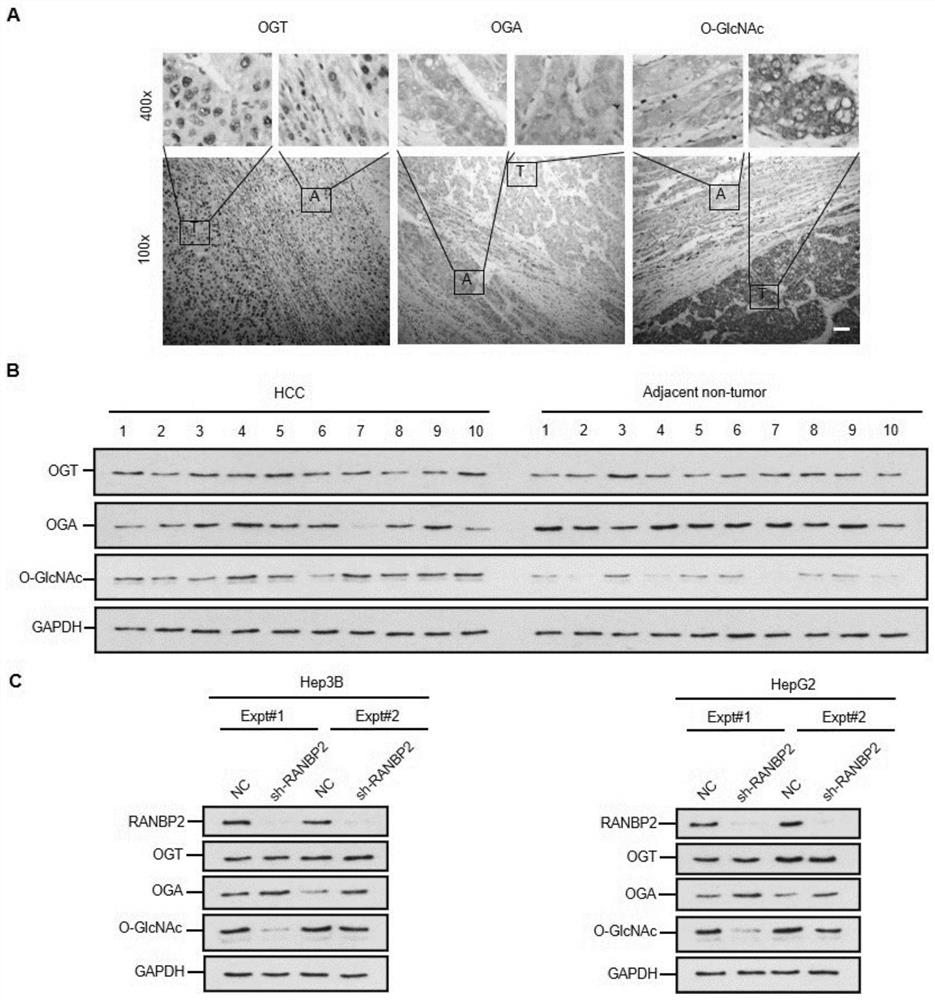
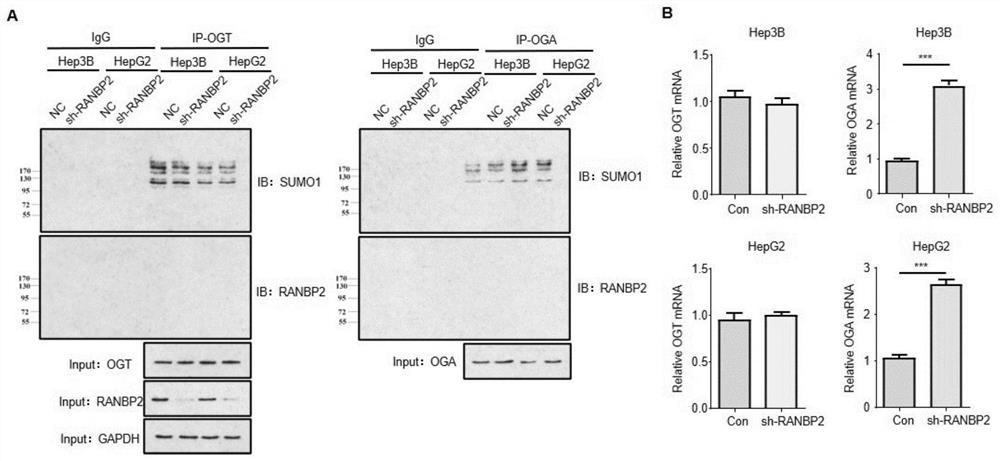
Application of cebpα as the target site of ranbp2 in the preparation of glycosylation drugs for the treatment of liver cancer
ActiveCN113499438BAntineoplastic agentsPharmaceutical active ingredientsMalignant phenotypePharmaceutical drug
The invention discloses the application of CEBPα as a detection reagent of RANBP2 target site in the preparation of glycosylation-related drugs for treating liver cancer. The study of the present invention shows that the high expression of RANBP2 in liver cancer cells is positively correlated with the malignant phenotype of liver cancer. RANBP2 down-regulates the expression of OGA, increases O-glycosylation modification, and then increases the proliferation and invasion ability of liver cancer cells. As a key transcription factor CEBPα that positively regulates OGA, RANBP2 can induce the SUMOylation of CEBPα, and experiments have confirmed that the K196 site of CEBPα is the key SUMO target site of RANBP2, and SUMOylation of this site can promote the degradation of CEBPα protein. Protecting the K196 site of CEBPα from SUMOylation or increasing the expression of CEBPα itself can slow down the OGA-mediated O-glycosylation pathway.
Owner:THE THIRD XIANGYA HOSPITAL OF CENT SOUTH UNIV
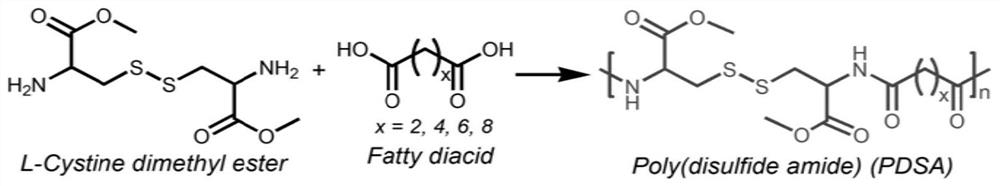
Novel intracellular response nanoparticle loaded with target gene siRNA and preparation method of novel intracellular response nanoparticle
PendingCN113209043AAccurate targetEasy to makeOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMalignant phenotypeMalignancy
Disclosed is a novel intracellular response nanoparticle loaded with target gene siRNA. The novel intracellular response nanoparticle comprises a high-molecular polymer PDSA which wraps the target gene siRNA and is decomposed under the glutathione concentration in cytoplasm, and the nanoparticle at least simultaneously wraps two kinds of target gene siRNA, namely MGLL-siRNA and CB2-siRNA. The nanoparticle capable of releasing siRNA through decomposition under the cytoplasmic glutathione concentration is utilized, the defect of siRNA transmission in the prior art is overcome, intracellular glutathione can be quickly responded, and the siRNA transmission efficiency is improved. The nanoparticles simultaneously wrap MGLL-siRNA and CB2-siRNA, so that malignant phenotype genes of malignant tumors can be silenced, repolarization of tumor-related macrophages to anti-cancer phenotypes can be promoted, MGLL expression is knocked down to directly act on the malignant tumors for inhibition, and CB2 is knocked down to promote repolarization of the tumor-related macrophages to M1 type to synergistically resist tumors.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN MEMORIAL HOSPITAL SUN YAT SEN UNIV
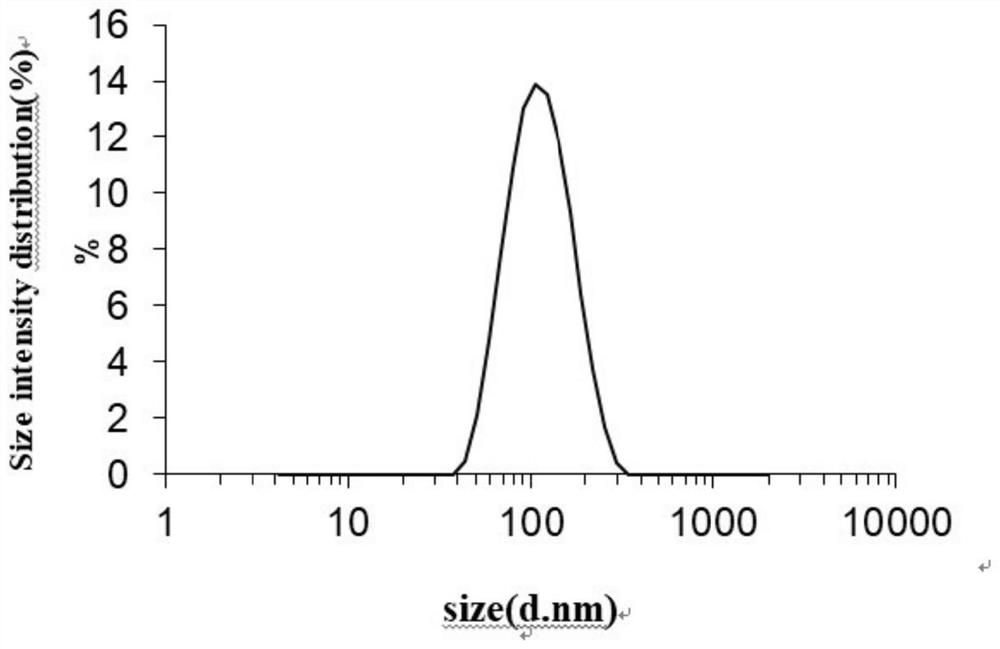
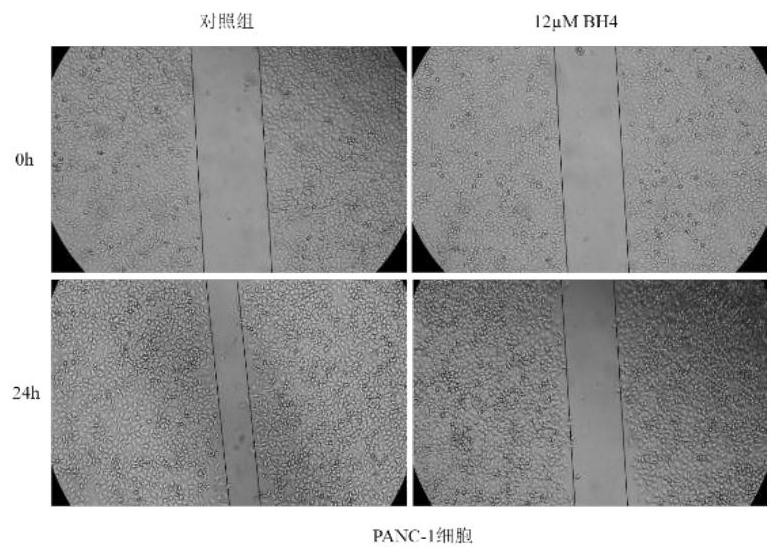
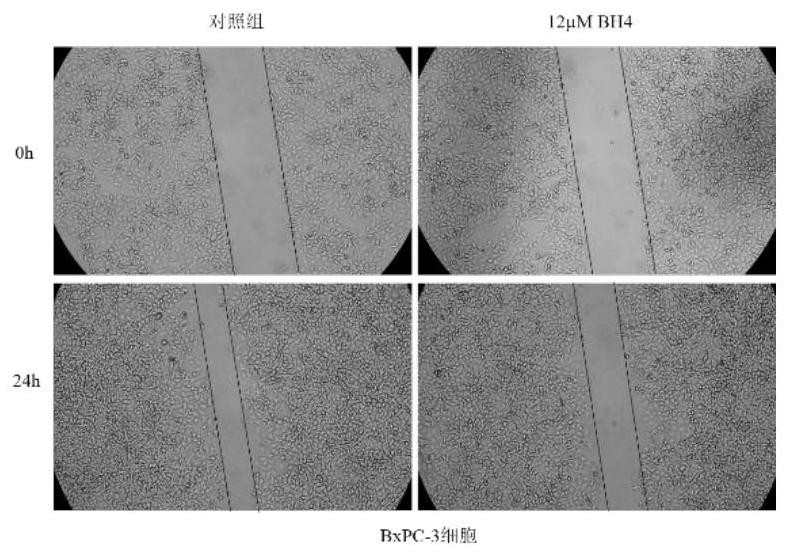
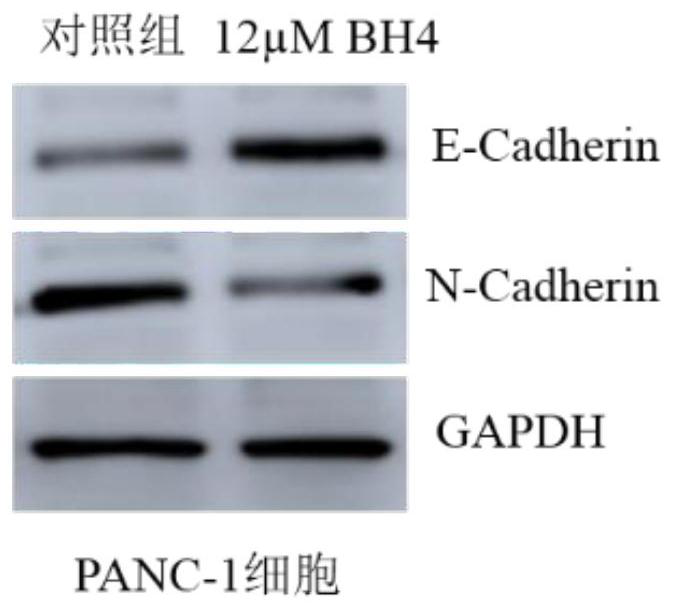
Promoter for reducing malignant phenotypes of pancreatic cancer cells, pharmaceutical composition and application thereof
PendingCN114558141AReduced activityReduce apoptosisOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemParanasal Sinus CarcinomaPancreas Cancers
The invention relates to the technical field of tumor medicine research and development, in particular to an accelerant for reducing malignant phenotypes of pancreatic cancer cells, a pharmaceutical composition and application of the accelerant and the pharmaceutical composition. According to the invention, tetrahydrobiopterin acts on PANC-1 and BxPC-3 cells, along with the increase of the concentration of tetrahydrobiopterin, the activity of cancer cells is gradually reduced, the apoptosis number of cancer cells is gradually increased, and the apoptosis rate is increased; the tetrahydrobiopterin can reduce the healing area of the two cancer cells, promote the expression of E-cadherin in the cancer cells, inhibit the expression of N-cadherin, inhibit the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of pancreatic cancer cells and reduce the malignant phenotype of the cancer cells, thereby reducing the migration and invasion ability of the cancer cells. It is indicated that the BH4 bioactive activator can inhibit pancreatic cancer cell proliferation activity and cell migration ability, promote cell apoptosis and inhibit cancer cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition, so that the malignant phenotype of cancer cells is reduced, and the BH4 bioactive activator can be used as a treatment target of pancreatic cancer.
Owner:XINXIANG MEDICAL UNIV
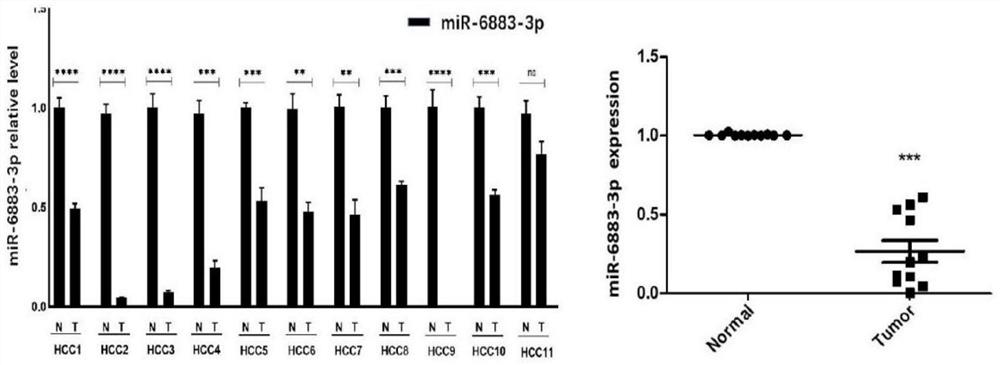
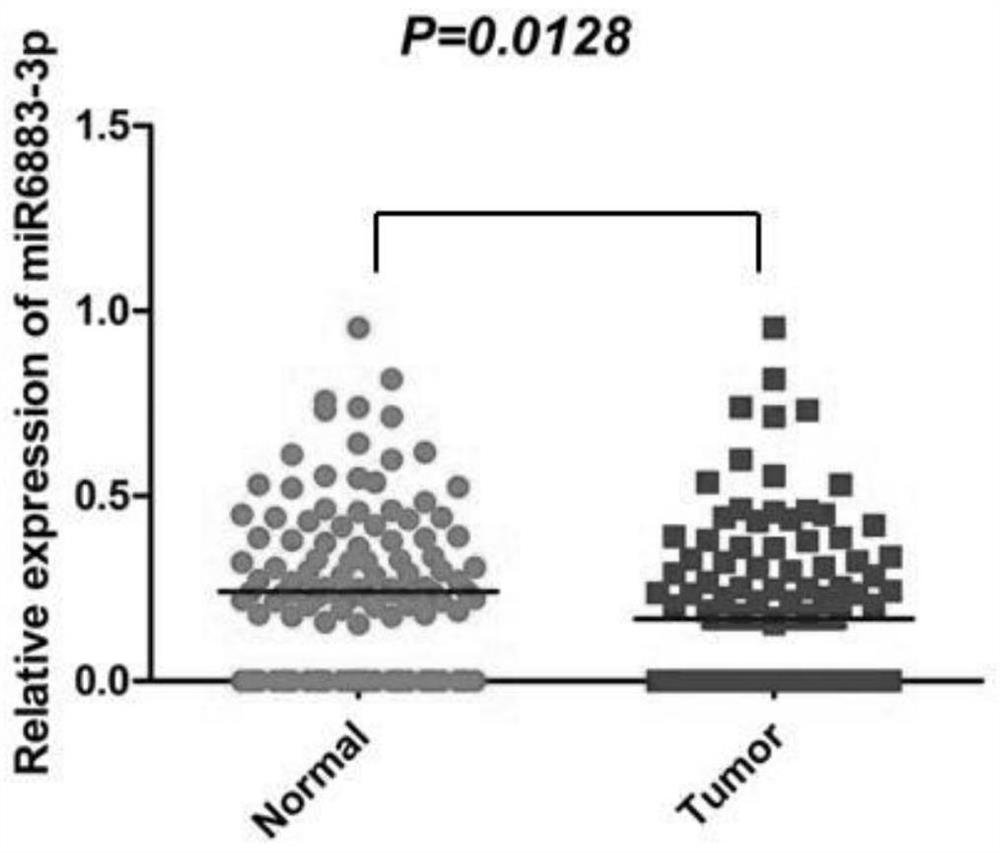
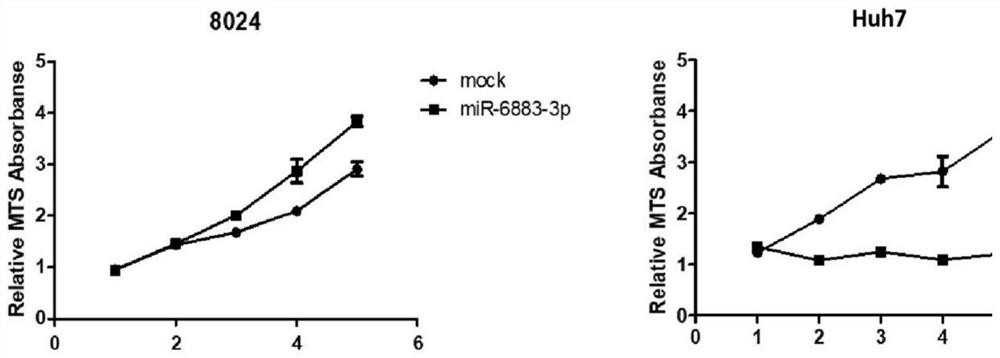
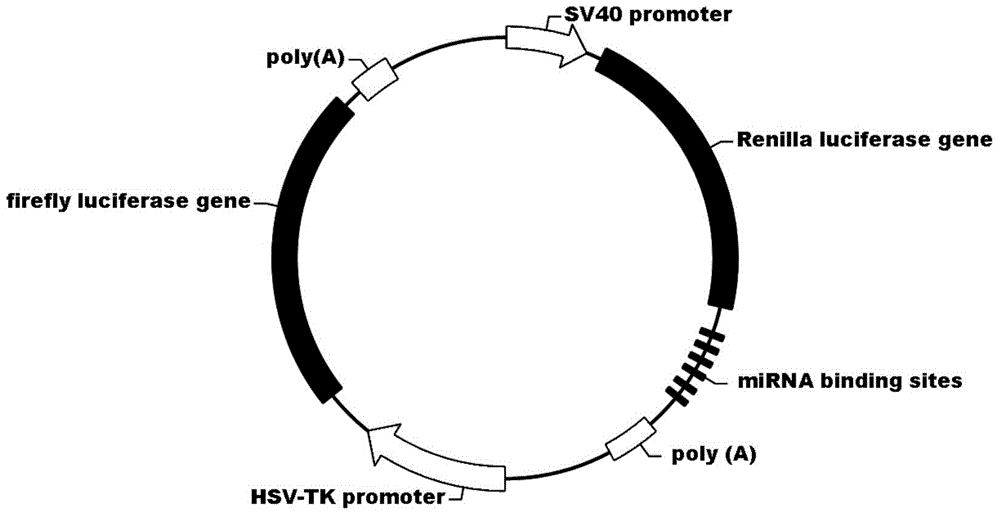
Application of miR-6883-3p in preparation of anti-liver cancer or liver cancer prognosis evaluation product
PendingCN113604569APrevent proliferationInhibit migrationOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementParanasal Sinus CarcinomaMalignant phenotype
The invention relates to the technical field of biomedicine, discloses an application of miR-6883-3p in preparation of an anti-liver cancer product or a liver cancer prognosis evaluation product, and particularly relates to an application of miR-6883-3p in preparation of an anti-liver cancer drug or a liver cancer prognosis evaluation kit. The miR-6883-3p targeted gene regulation network provided by the invention is closely related to malignant phenotype and poor prognosis of tumors, overexpression of miR-6883-3p can effectively inhibit proliferation and migration of liver cancer cells, promote apoptosis of the liver cancer cells and reverse the differentiation state of the liver cancer cells, and the miR-6883-3p is low in expression in liver cancer tissues, so that the miR-6883-3p can be used for preparing antitumor drugs or detection kits and has good application prospects.The method has potential application value in treatment or prognosis evaluation of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Owner:GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
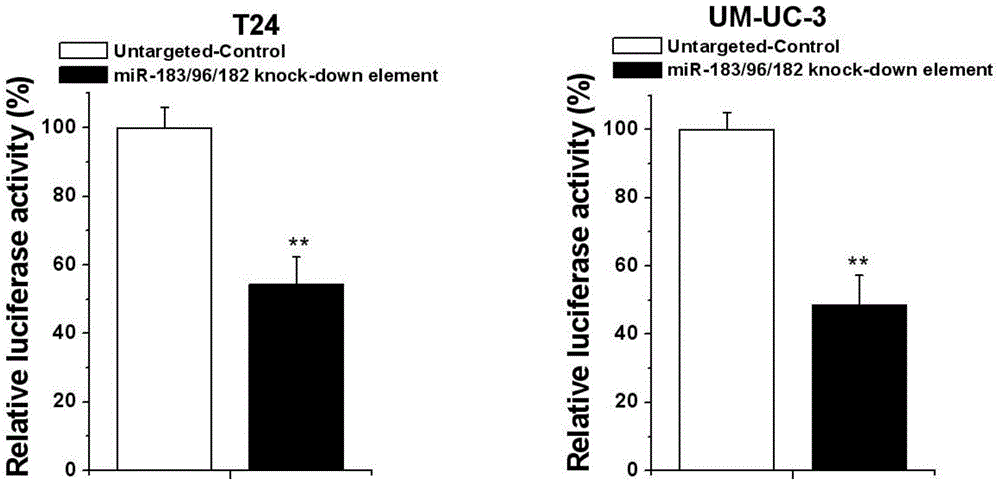
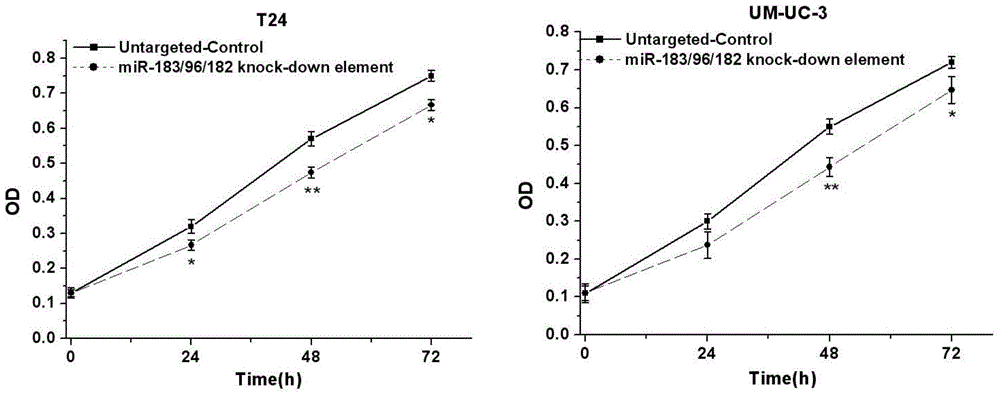
Human miR-183 gene cluster biological knock-down element, construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN105886504AEffective regulationFacilitate scientific researchMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic material ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthAbnormal expression
The invention discloses a human miR-183 gene cluster biological knock-down element, a construction method and an application thereof. Sequence is as shown in the SEQ ID NO:1. Abnormal expression of miR-183 gene cluster exists in many tumor cells, and the family participates in regulation of cell proliferation, apoptosis and cell migration related genes. Through design of the gene cluster knock-down element, expression of a gene cluster in bladder cancer cell can be effectively regulated. The knock-down element of the invention is convenient for scientific research and is also helpful for controlling tumor malignant phenotype and biological behavior.
Owner:THE SECOND PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF SHENZHEN
Application of Vitamin C Derivatives in Preparation of Antitumor Products
ActiveCN108567774BRole in inducing differentiationClarify the role and effectOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsCancer cellVitamin C
Owner:BEIJING INST OF GENOMICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI CHINA NAT CENT FOR BIOINFORMATION
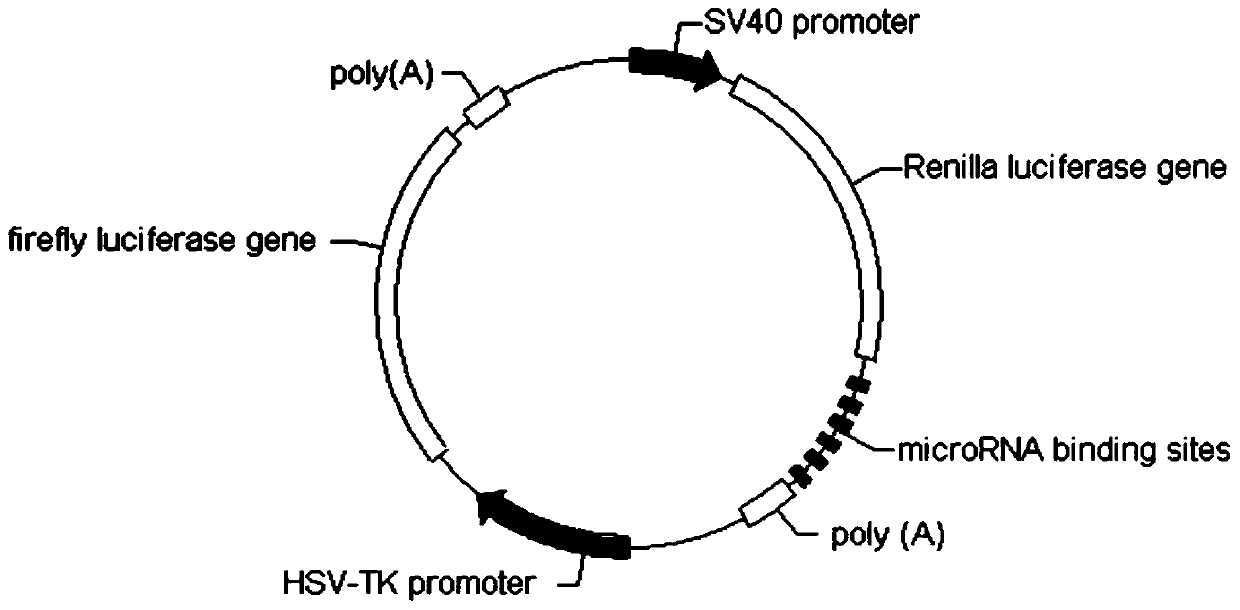
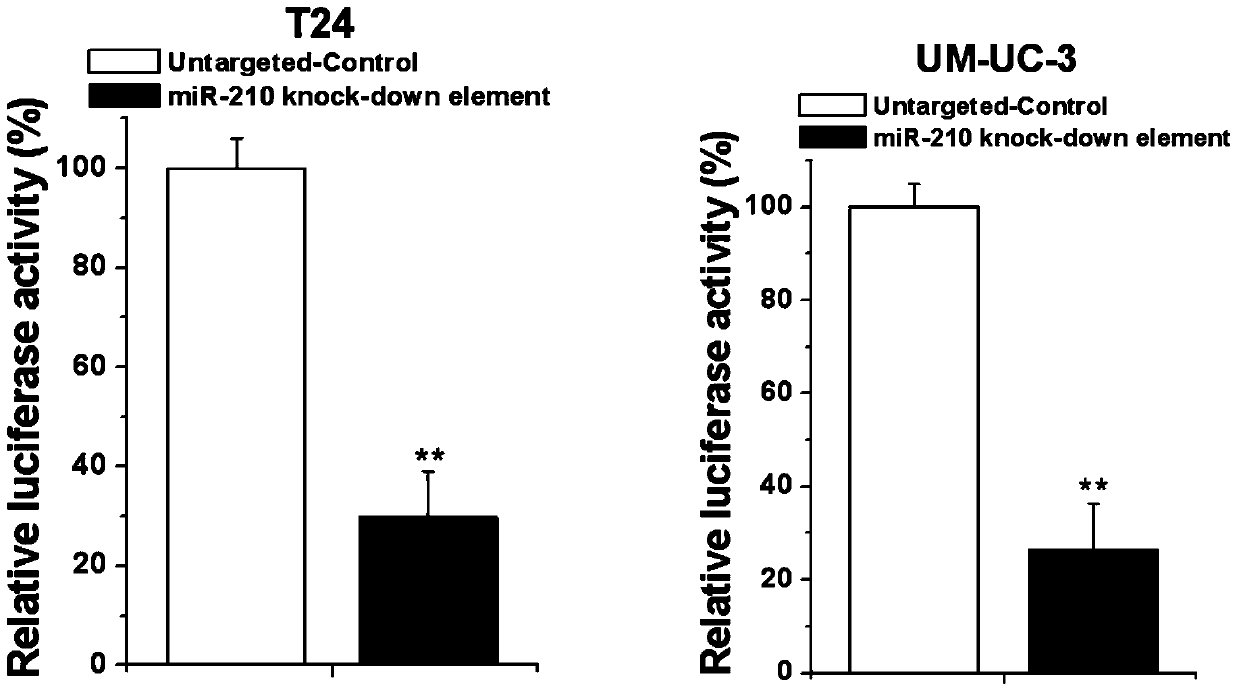
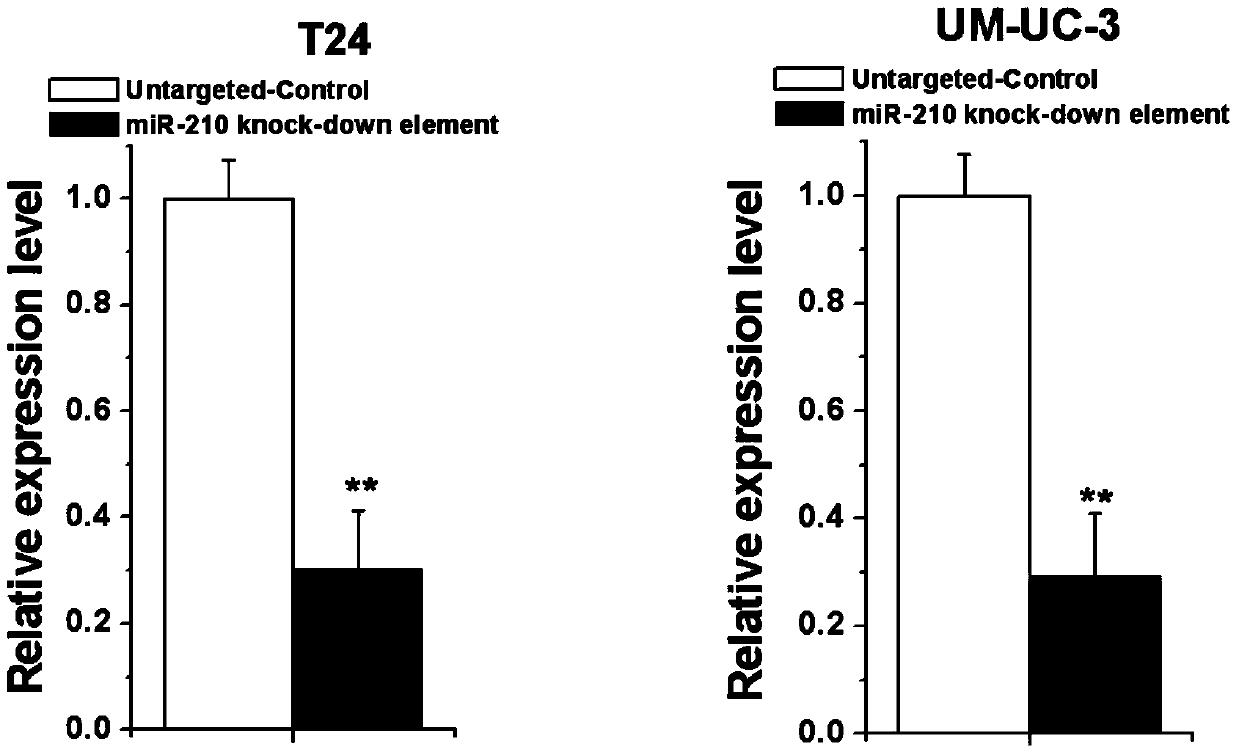
Human miR-210 biological knock-down element, construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN105886505AFacilitate scientific researchConducive to the control of tumor malignant phenotypeGenetic material ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementAbnormal tissue growthAbnormal expression
The invention discloses a human miR-210 biological knock-down element, a construction method and an application thereof. Sequence of the biological knock-down element is as shown in the SEQ ID NO:1. Abnormal expression of miR-210 exists in many tumor cells, and the family participates in regulation of cell proliferation, apoptosis and cell migration related genes. Through design of the knock-down element, expression of miR-210 in bladder cancer cell can be effectively regulated. The knock-down element of the invention is convenient for scientific research and is also helpful for controlling tumor malignant phenotype and biological behavior.
Owner:THE SECOND PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF SHENZHEN
Application of forsythiaside a in the preparation of anti-esophageal squamous cell carcinoma drugs
ActiveCN113209113BPromote apoptosisTo achieve the purpose of resisting esophageal squamous cell carcinomaOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsSquamous CarcinomasMalignant phenotype
The invention provides an application of forsythiaside A in the preparation of an anti-esophageal cancer drug, wherein, forsythiaside A is used as an active ingredient in the anti-esophageal squamous cell carcinoma drug, and its molecular formula is C 29 h 36 o 15 . Forsythiaside A mainly achieves the purpose of anti-esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by inhibiting the proliferation, colony formation, and cell migration of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells, or by blocking the cycle of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells and promoting the apoptosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells; therefore, even Arthrin A inhibits the malignant phenotype of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU NORMAL UNIV
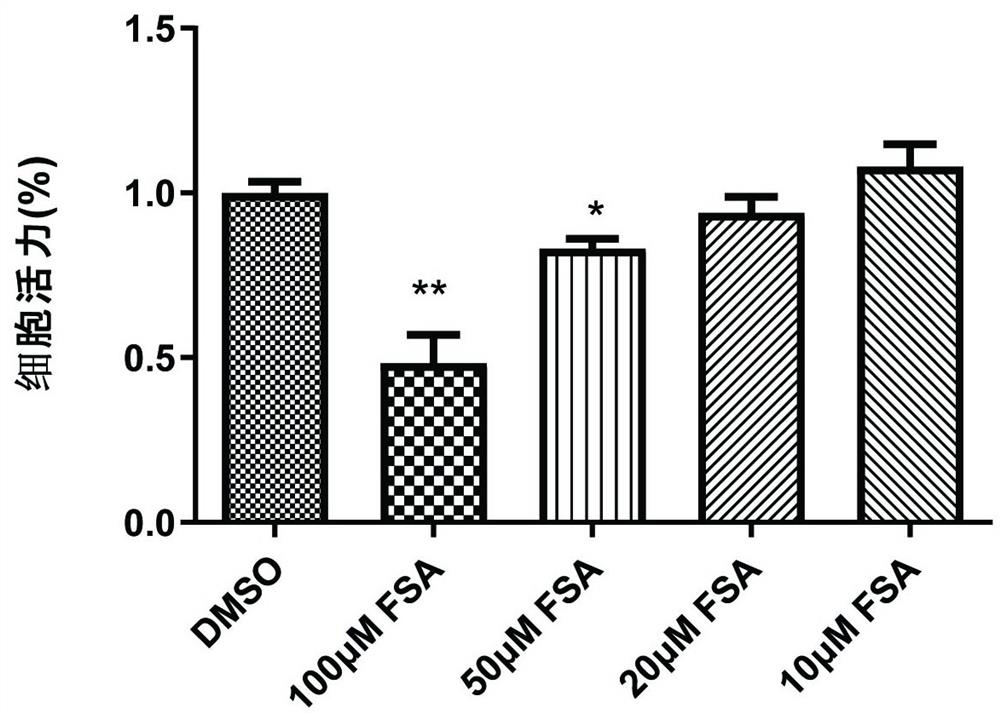
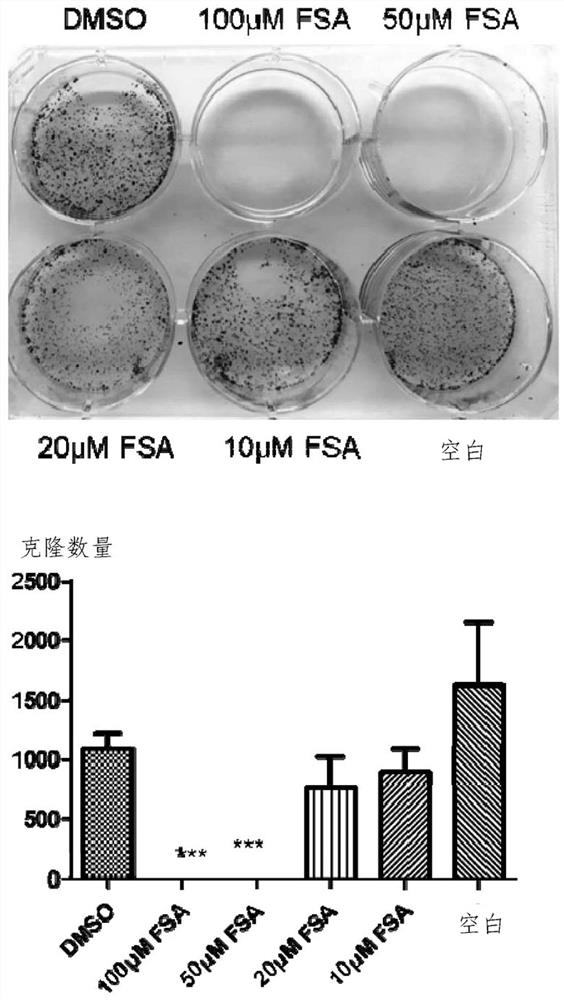
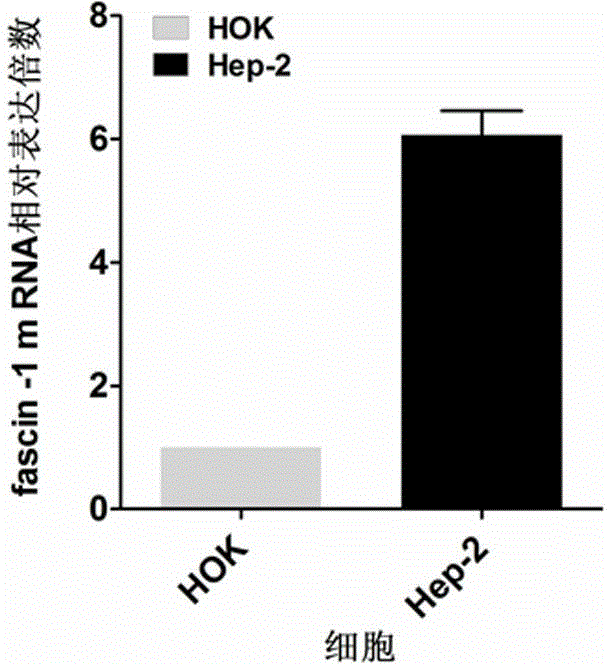
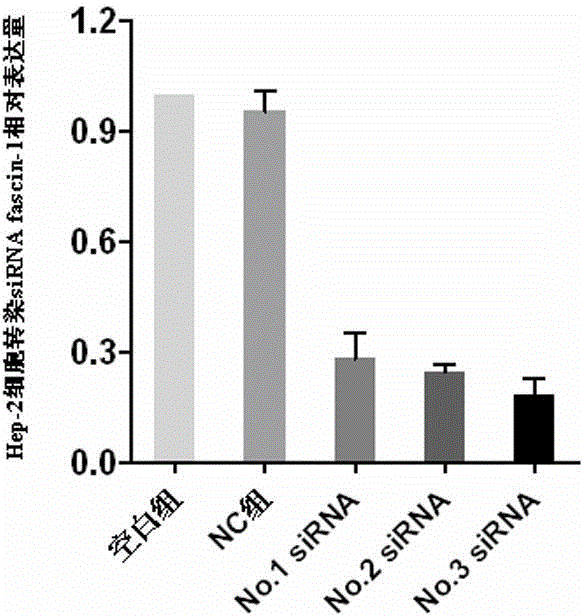
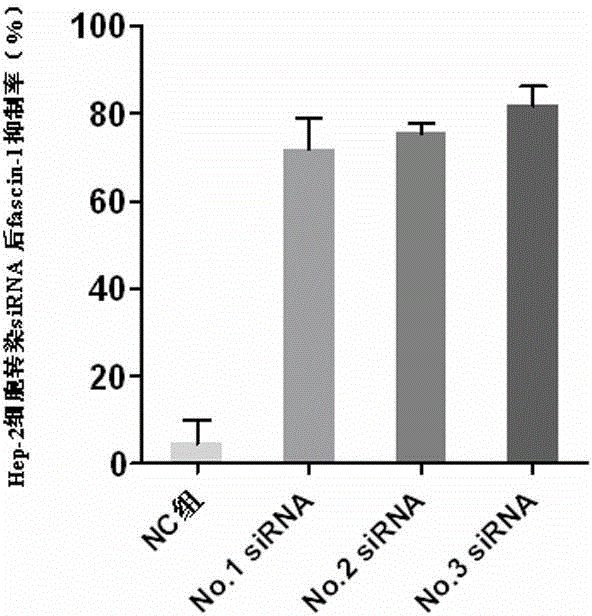
Human fascin-1 gene siRNA and applications thereof
ActiveCN103215268BInhibit malignant proliferationPrevent invasionGenetic material ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsMalignant phenotypeMalignancy
The present invention discloses a human fascin-1 gene siRNA and applications thereof, and belongs to the technical field of bio-engineering, wherein problems of malignant proliferation, invasion and metastasis of tumor cells fascin-1 are solved with the human fascin-1 gene siRNA. The human fascin-1 gene siRNA comprises the following sequences: a sense strand: 5'-CGACTATAACAAGGTGGCCATtt-3'; and an antisense strand: 5'-ATGGCCACCTTGTTATAGTCGtt-3'. According to the present invention, malignant biological phenotypes such as malignant proliferation, invasion and metastasis of tumor cells can be inhibited with the expressed human fascin-1 gene siRNA; and the human fascin-1 gene siRNA can be widely used for researching inhibition on malignant phenotypes of tumor cells, and can further be used for preparing anti-tumor biological targeting agents or drugs.
Owner:FIRST HOSPITAL OF SHANXI MEDICAL UNIV
Application of gap junction protein and coding gene thereof in preparing medicament for reversing malignant phenotype of cancer stem cell
ActiveCN101966332BReduce the ability to invadeGood potential application prospectsPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsCancer cellMalignant phenotype
The invention discloses application of gap junction protein and coding gene thereof in preparing medicament for reversing malignant phenotype of a cancer stem cell, and investigates the functional state of gap junction communication in the tumor stem cell, expression condition of the gap junction protein and relation between the gap junction protein and special biological characteristics of tumor stem cells. Results prove that compared with differentiated tumor cells, gap junction communication obstacle exists in the tumor stem cell, no clear gap junction like structure is found among the cells, and expressions of various gap junction protein, particularly gap junction protein 43(Cx43), is down regulated; the down regulation of the expression of the Cx43 is related to promoter methylation of coding gene GJA1 thereof and expression of micro RNA; recovering of the expression of the Cx43 in the tumor stem cell can remarkably reduce the self-renew ability, tumor forming ability and invasion ability of the tumor stem cells, which is related to partial recovery of the gap junction communication function, up regulation of E-cadherin expression and inactivity of SDF-1 / CXCR4 downstream signal path (AKT and ERK1 / 2); and the gap junction protein and coding gene thereof can be used for preparing the medicament for reversing malignant phenotype of the cancer stem cell.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
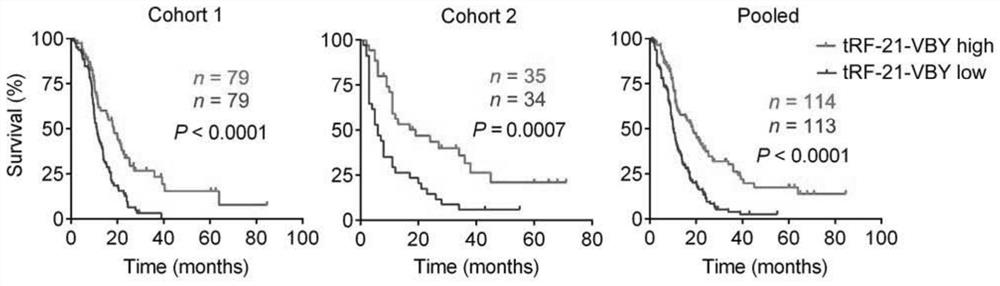
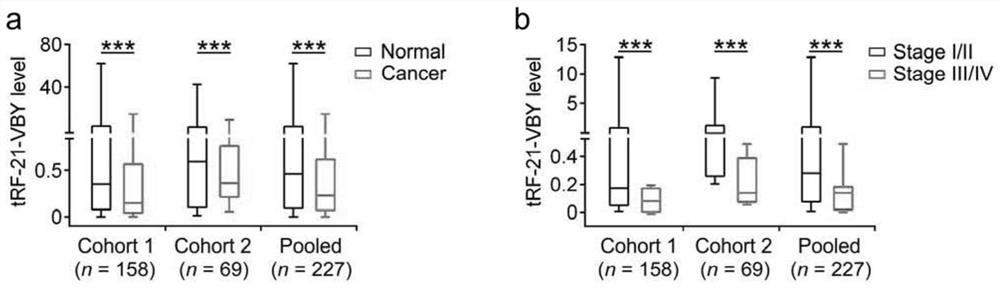
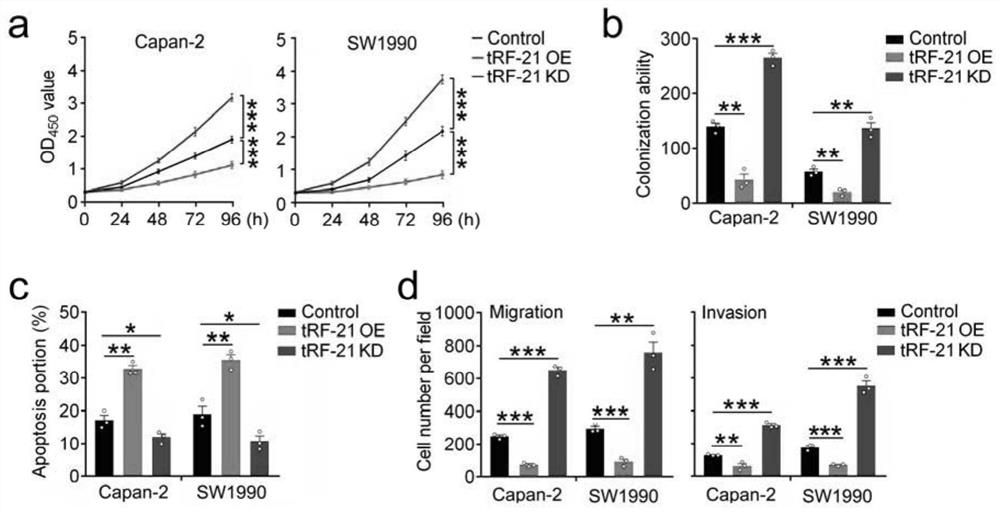
TRF related to pancreatic cancer and application thereof
ActiveCN112522262APrevent proliferationGrowth inhibitionOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementParanasal Sinus CarcinomaPancreas Cancers
The invention discloses tRF related to pancreatic cancer. The nucleotide sequence of the tRF related to pancreatic cancer is shown as SEQ ID No. 1. The present invention finds a tRNA-derived fragmenttRF-21-VBY having a function of highly expressing a malignant phenotypic function that significantly inhibits pancreatic cancer cells, which has the ability to inhibit cell proliferation, migration and invasion, promotes apoptosis, inhibits subcutaneous transplantation tumor growth and pancreatic cancer in-situ tumor growth, and can indicate the prognosis of pancreatic cancer patients. Therefore,the tRF-21-VBY or the activator thereof can be used for preparing a medicine for treating pancreatic cancer or screening a medicine suitable for treating pancreatic cancer; the reagent for detecting tRF-21-VBY can be used for preparing a pancreatic cancer prognosis prediction kit.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV CANCER CENT
Application of CEBP alpha as RANBP2 target site in preparation of glycosylation medicine for treating liver cancer
ActiveCN113499438AAntineoplastic agentsPharmaceutical active ingredientsMalignant phenotypeMalignancy
The invention discloses application of CEBP alpha as a detection reagent of an RANBP2 target site in preparation of glycosylation related medicine for treating liver cancer. Researches show that high expression of RANBP2 in liver cancer cells is positively correlated with liver cancer malignant phenotypes, and RANBP2 down-regulates OGA expression and increases O-glycosylation modification, so that proliferation and invasion abilities of the liver cancer cells are improved. As a key transcription factor CEBP alpha for forward regulation of OGA, RANBP2 can induce SUMOylation of the CEBP alpha, and experiments prove that the K196 site of the CEBP alpha is the SUMO key target site of the RANBP2, and the SUMOylation of the site can promote CEBP alpha protein degradation. OGA-mediated O-glycosylation pathways can be slowed down by protecting the K196 site of the CEBP alpha from being influenced by SUMOylation modification or improving the expression of the CEBP alpha.
Owner:THE THIRD XIANGYA HOSPITAL OF CENT SOUTH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com