Patents
Literature
954 results about "Gene cluster" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A gene family is a set of homologous genes within one organism. A gene cluster is part of a gene family. A gene cluster is a group of two or more genes found within an organism's DNA that encode for similar polypeptides, or proteins, which collectively share a generalized function and are often located within a few thousand base pairs of each other. The size of gene clusters can vary significantly, from a few genes to several hundred genes. Portions of the DNA sequence of each gene within a gene cluster are found to be identical; however, the resulting protein of each gene is distinctive from the resulting protein of another gene within the cluster. Genes found in a gene cluster may be observed near one another on the same chromosome or on different, but homologous chromosomes. An example of a gene cluster is the Hox gene, which is made up of eight genes and is part of the Homeobox gene family.
Methods and compositions for cellular and metabolic engineering
InactiveUS7105297B2Improve abilitiesExcellent catalytic performanceImmunoglobulinsFermentationIndividual geneOrganism
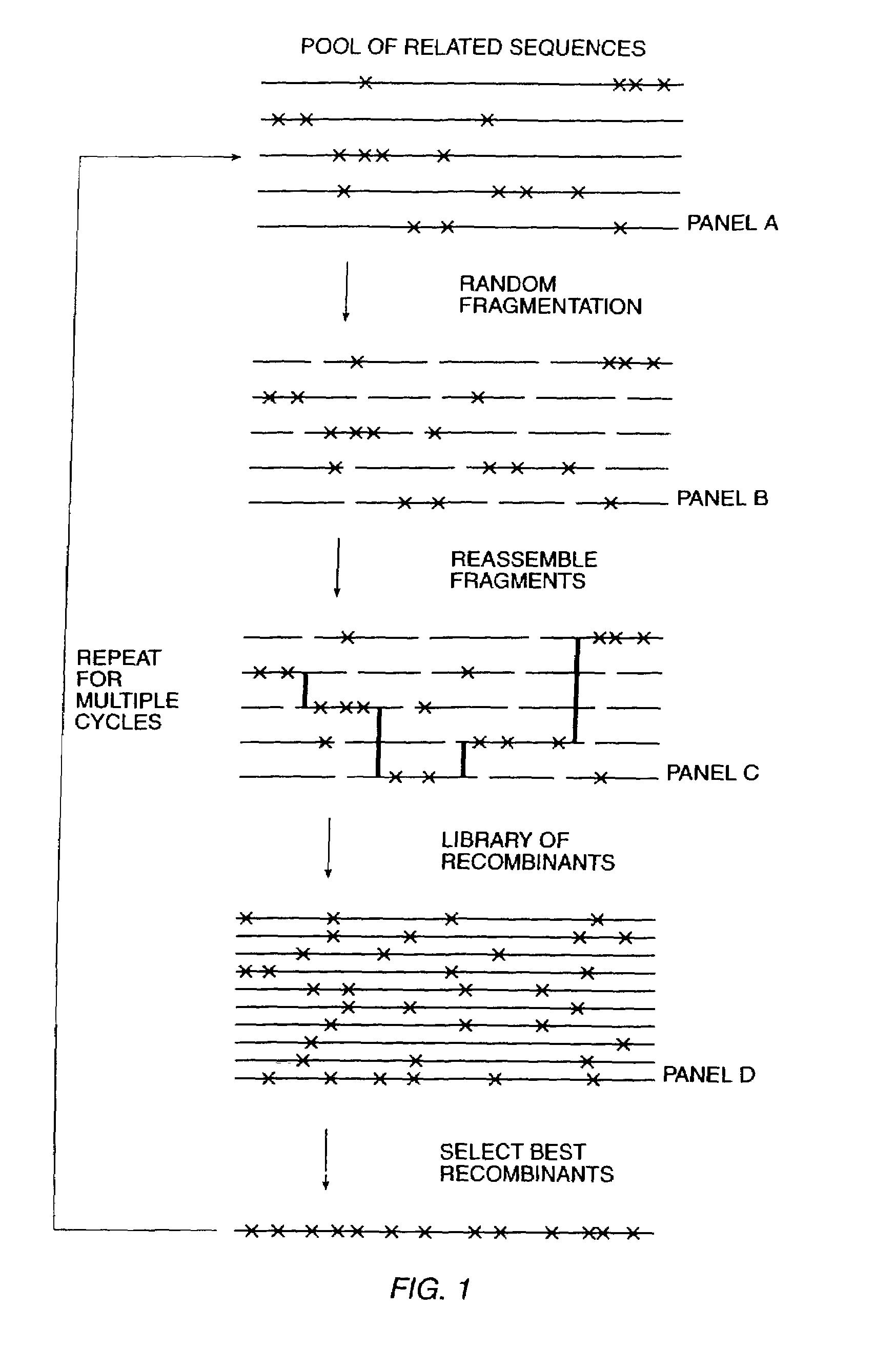
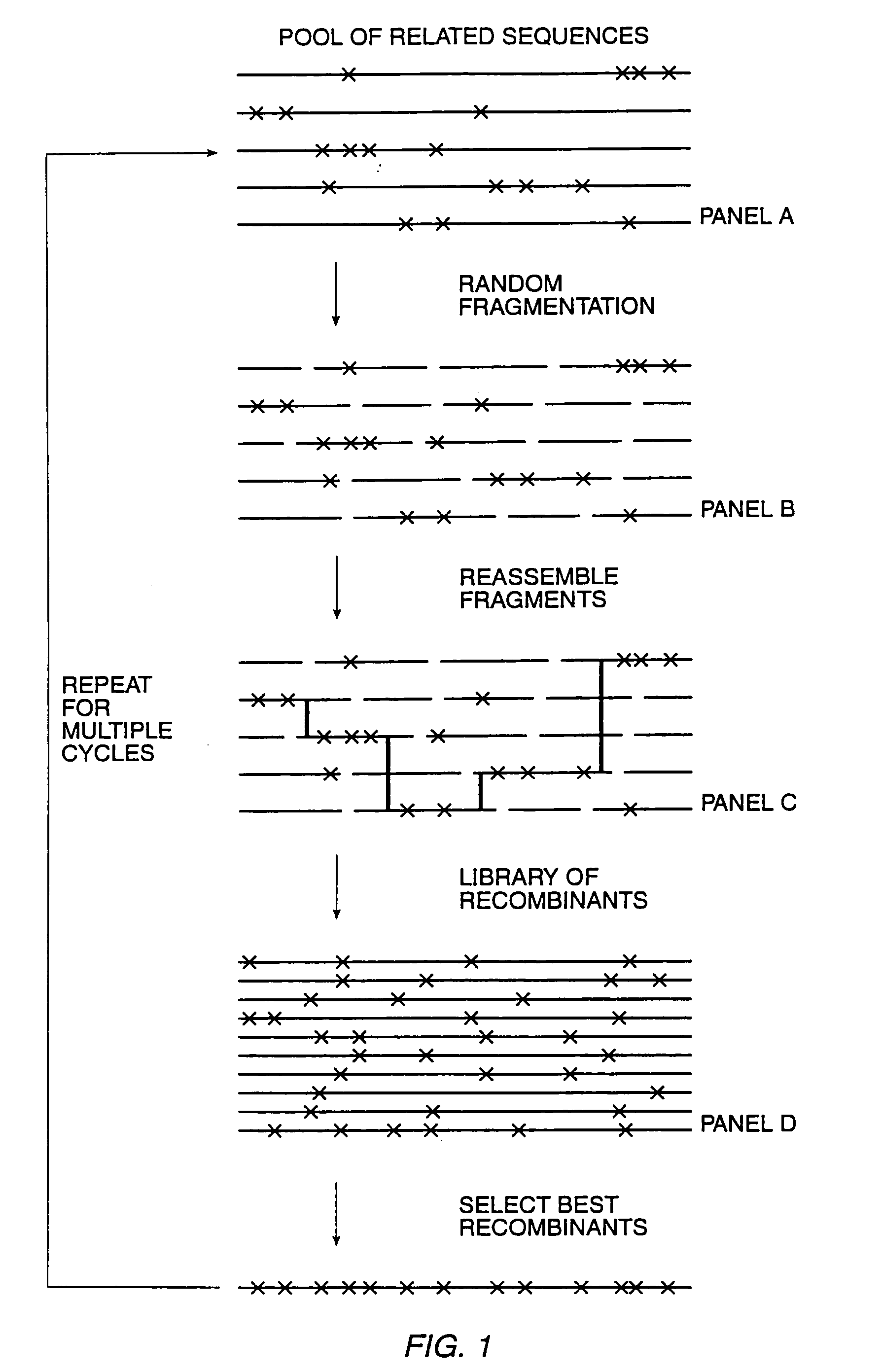
The present invention is generally directed to the evolution of new metabolic pathways and the enhancement of bioprocessing through a process herein termed recursive sequence recombination. Recursive sequence recombination entails performing iterative cycles of recombination and screening or selection to “evolve” individual genes, whole plasmids or viruses, multigene clusters, or even whole genomes. Such techniques do not require the extensive analysis and computation required by conventional methods for metabolic engineering.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Computer systems and methods for identifying genes and determining pathways associated with traits
ActiveUS7035739B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological bodyQuantitative trait locus
Owner:ROSETTA INPHARMATICS LLC
Computer systems and methods for identifying genes and determining pathways associated with traits
ActiveUS20030224394A1Improve artBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological bodyQuantitative trait locus
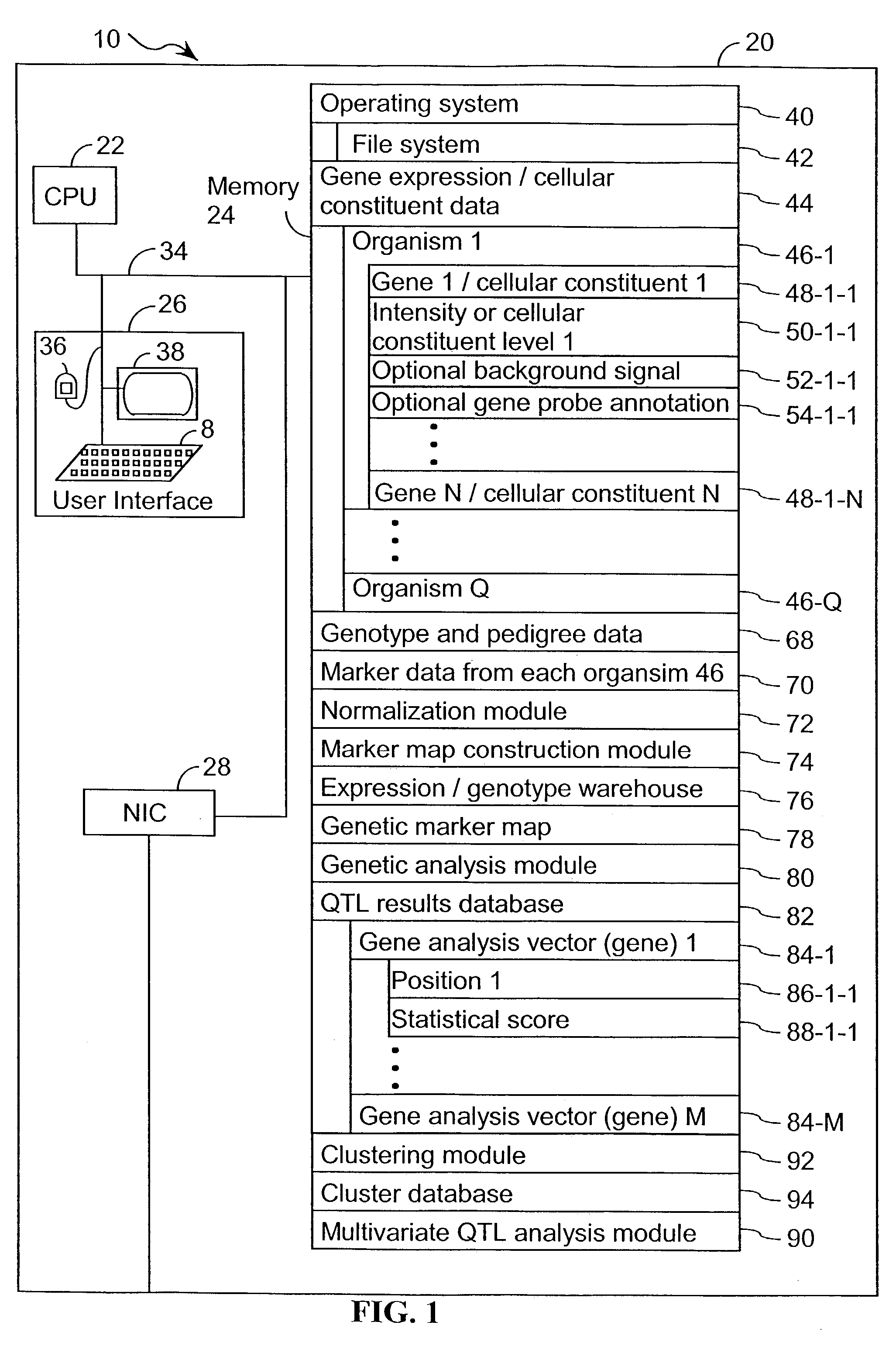
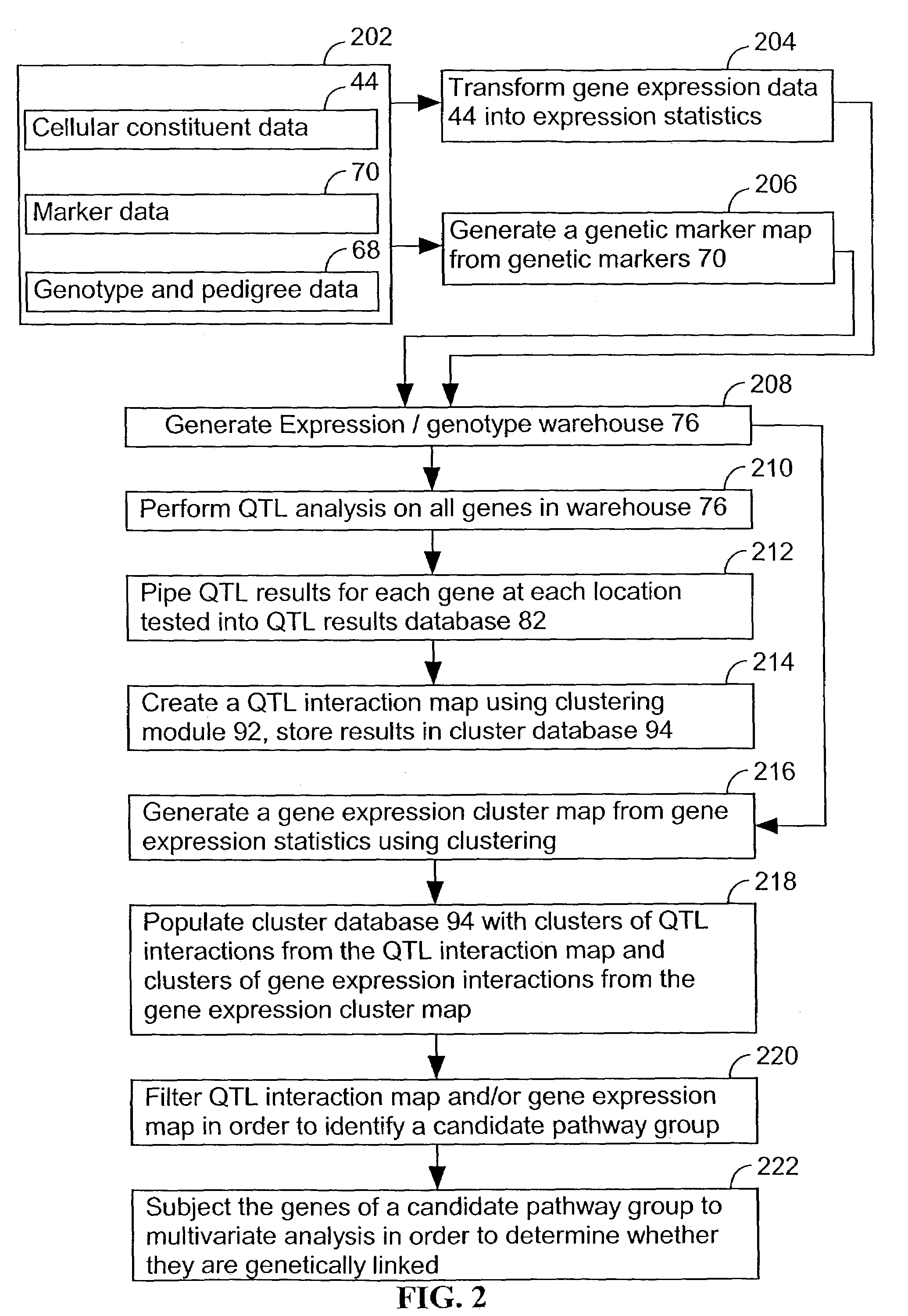
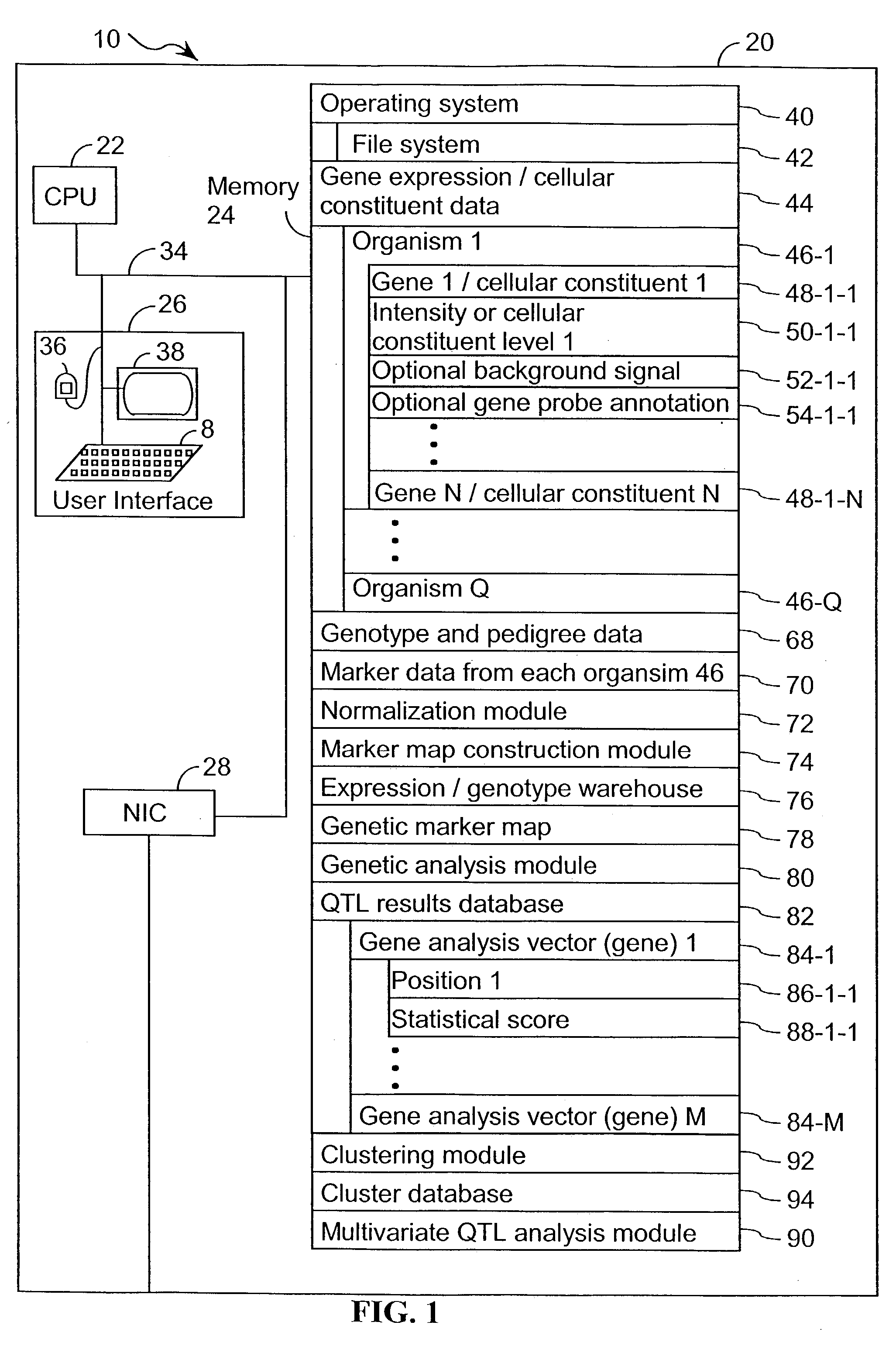
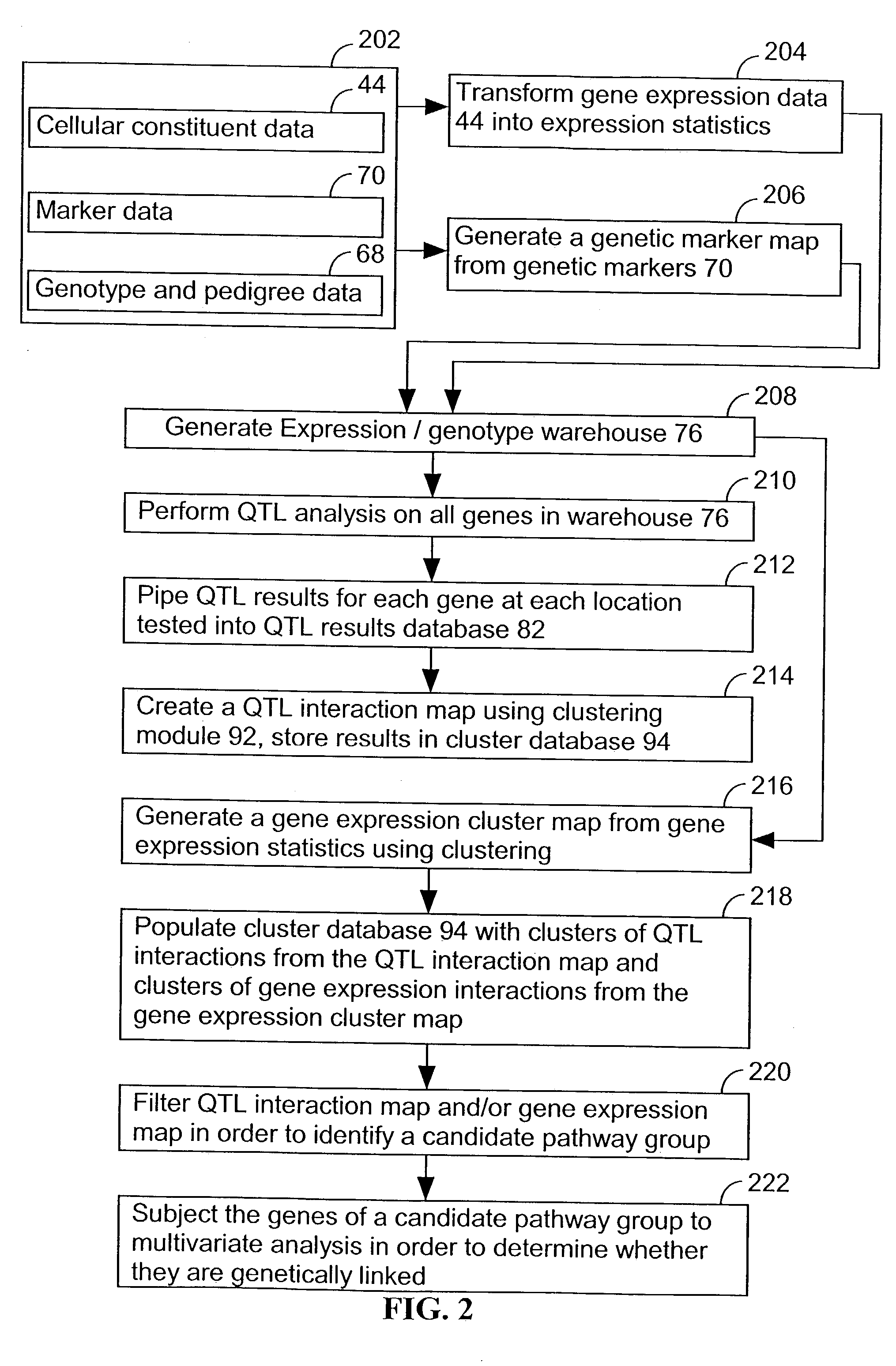
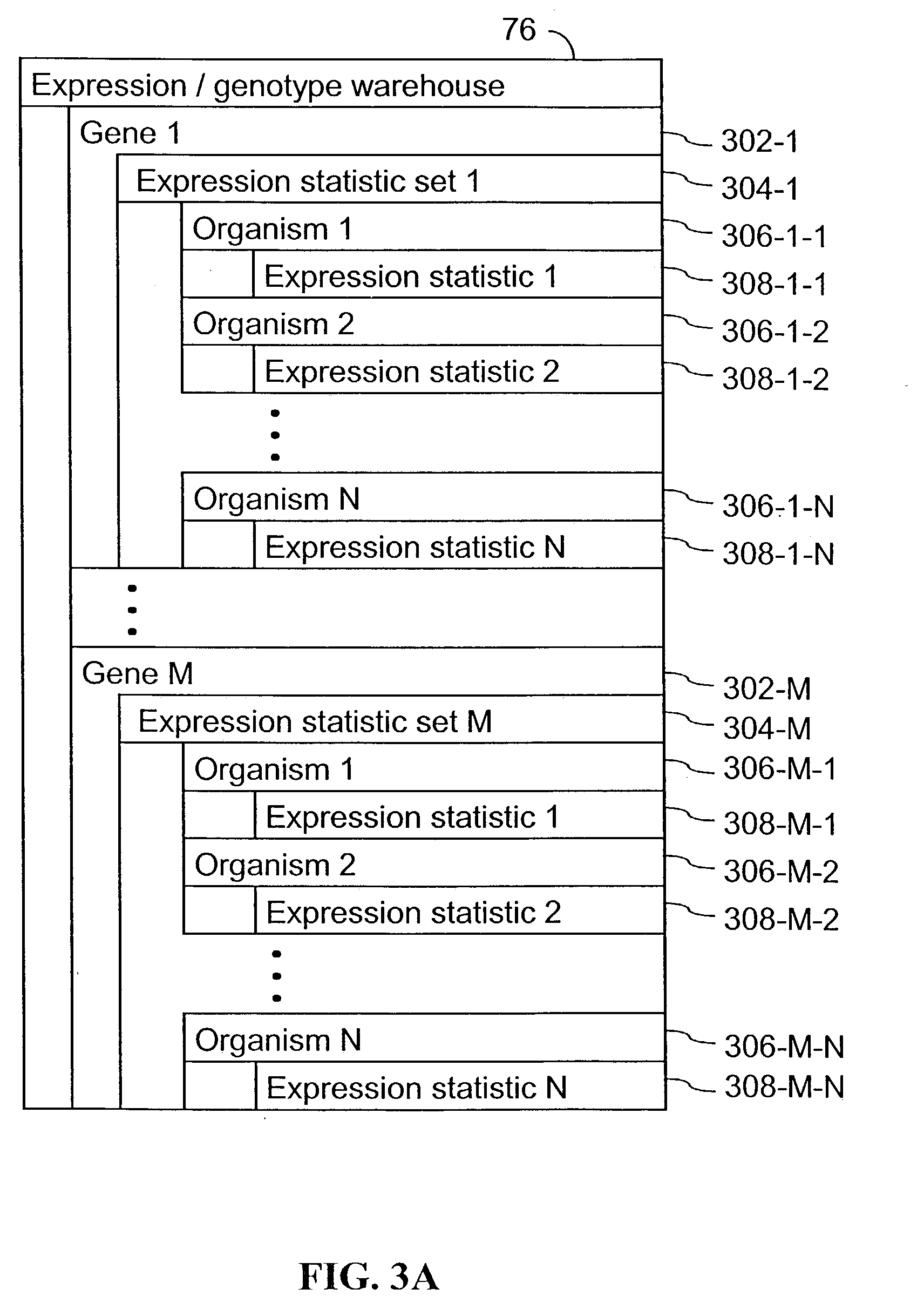
A method for associating a gene with a trait exhibited by one or more organisms in a plurality of organisms from a species. A genetic marker map is constructed from a set of genetic markers associated with the plurality of organisms. For each gene in a plurality of genes, a quantitative trait locus analysis is performed using the genetic marker map and a quantitative trait. The quantitative trait locus analysis produces quantitative trait locus data. A quantitative trait comprises an expression statistic for a gene. The expression statistic for a gene is derived from a cellular constituent level that corresponds to the gene in each organism in the plurality of organisms. The quantitative trait locus data are clustered from each quantitative trait locus analysis to form a quantitative trait locus interaction map. Clusters of genes in the map are identified as a candidate pathway group. An expression cluster map is used to refine the candidate pathway group. Multivariate analysis is used to validate the candidate pathway group as a set of genes that are genetically interacting.
Owner:ROSETTA INPHARMATICS LLC
Methods for the detection and treatment of cancer
InactiveUS20070231822A1Raise the possibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseLymphatic Spread
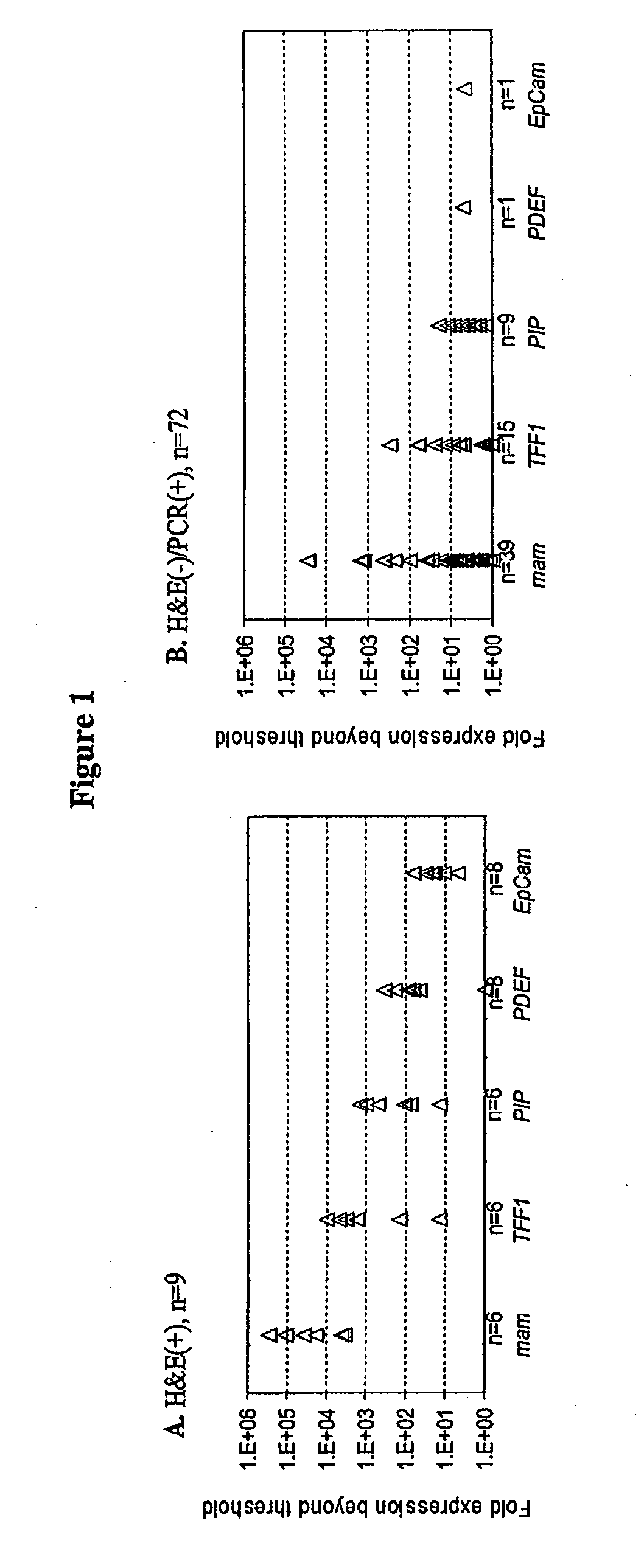
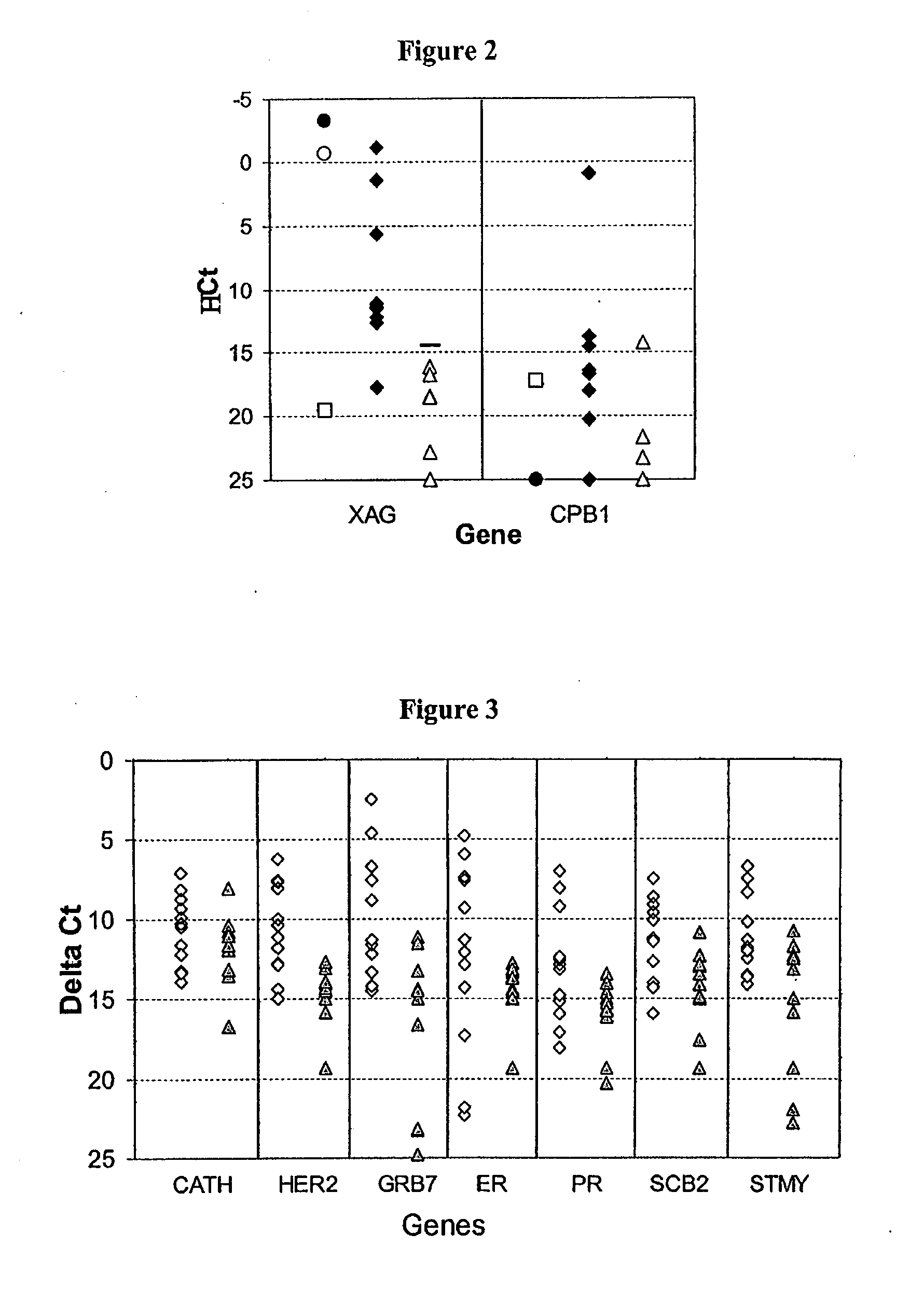
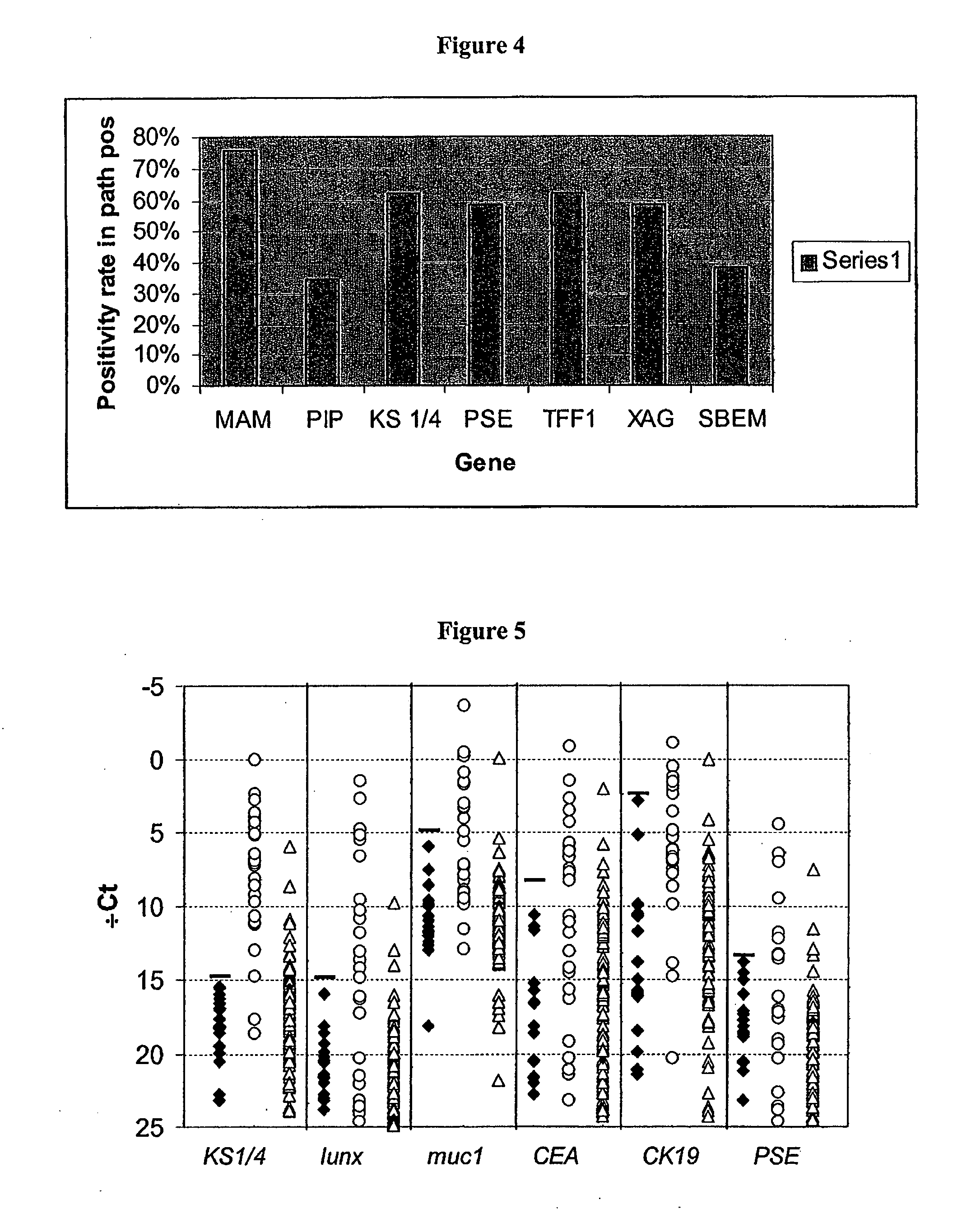
Methods are provided for the detection of and determining prognosis of metastatic breast, lung, prostate, and / or pancreatic cancer using various genetic markers, including markers for gene clusters linked by Esx. In one method, breast cancer micrometastases and non-small cell lung cancer metastases or micrometastases are detected in a patient by determining whether the AGR2 or TFF1 genes are overexpressed in a cell sample compared to control lymph node tissue cells. In a further method, the likelihood that a patient diagnosed with breast cancer will respond to hormonal therapy is predicted by determining a higher expression level of the AGR2 gene compared to a control gene. In a further method, a decreased probability of survival for a patient diagnosed with early stage non-small cell lung cancer is predicted by determining a higher expression level of the AGR2 gene compared to a control gene. Kits for practicing the methods of the invention are further provided. Methods are also provided for the identification of markers for which overexpression is indicative of the presence of micrometastatic disease.
Owner:MUSC FOUND FOR RES DEV
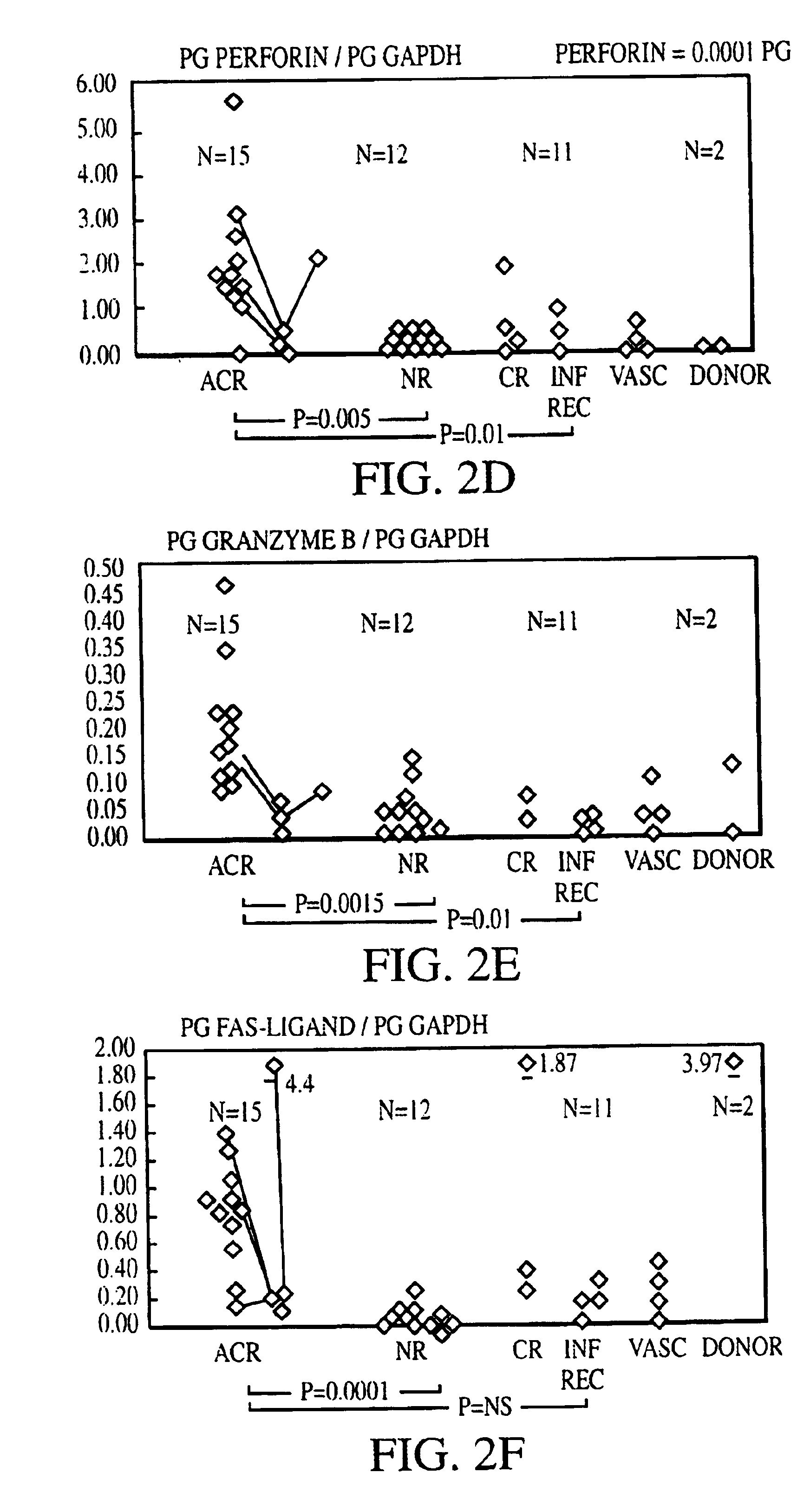
Measurement of protective genes in allograft rejection
InactiveUS6900015B2Quantitative precisionAccurately allograft rejectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisCytotoxicityAllograft rejection
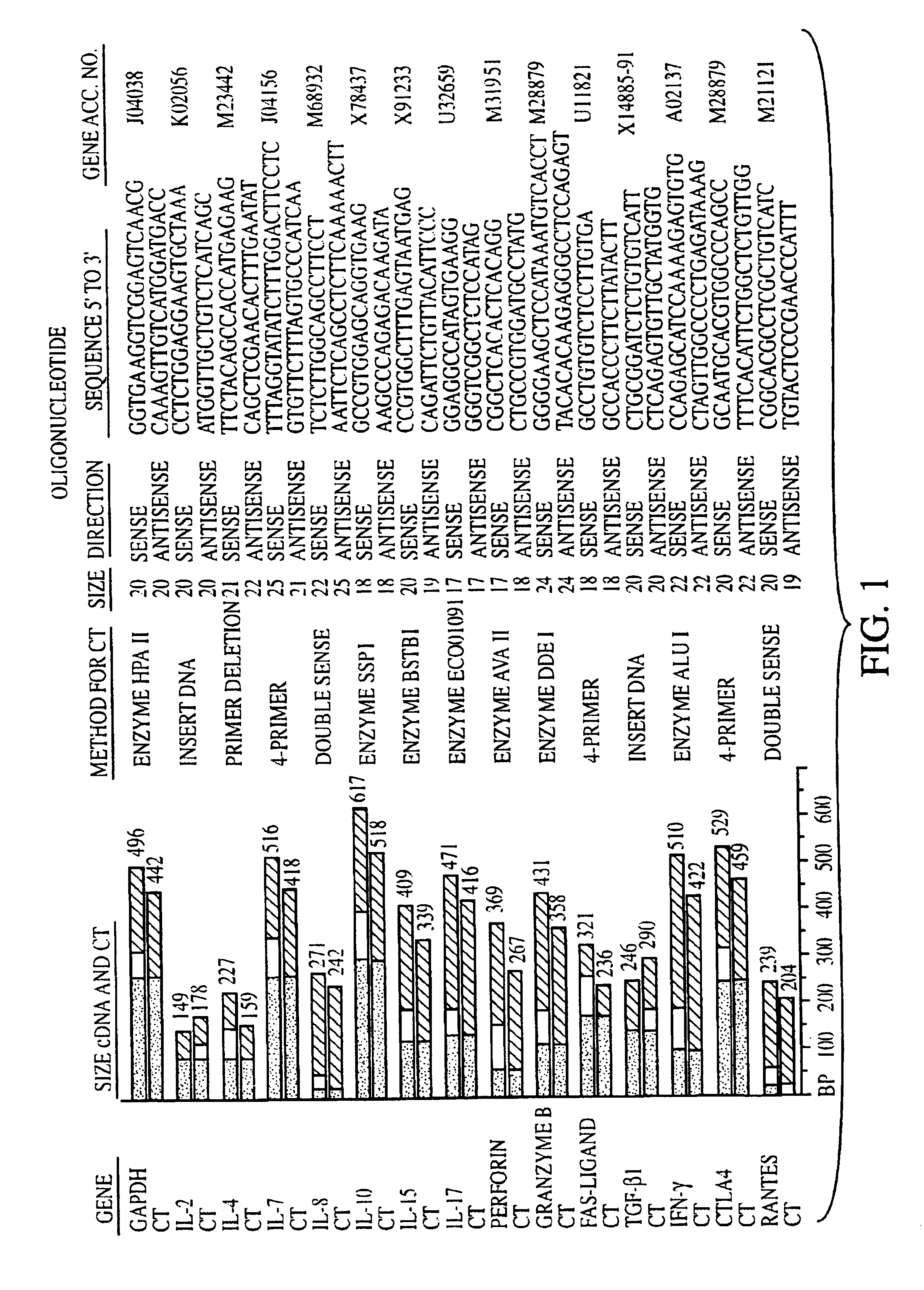
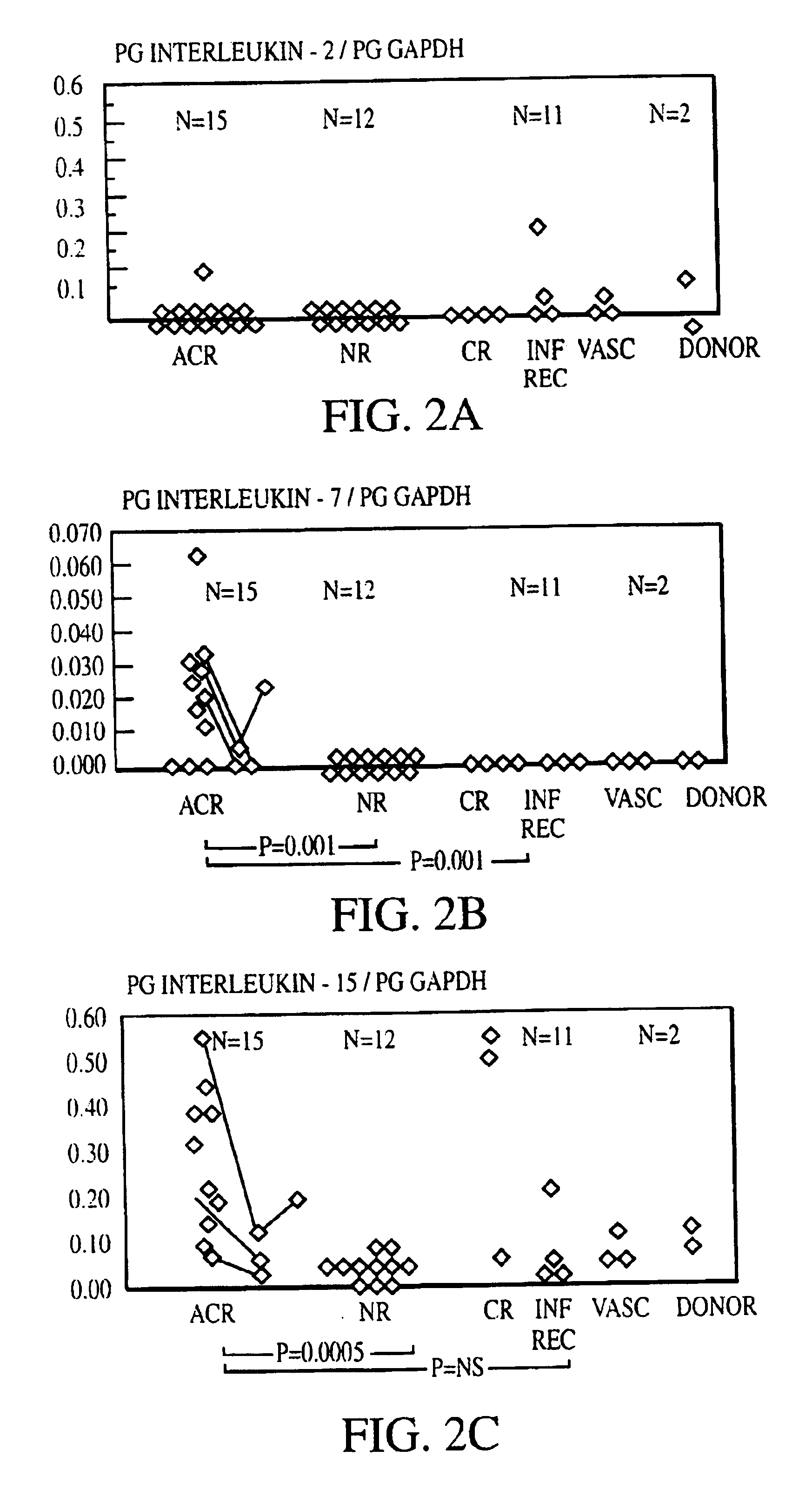
The invention relates to methods of evaluating transplant rejection in a host comprising determining a heightened magnitude of gene expression of genes in rejection-associated gene clusters. The disclosed gene clusters include genes that are substantially co-expressed with cytotoxic lymphocyte pro-apoptotic genes, cytoprotective genes and several other cytokine and immune cell genes.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC +1
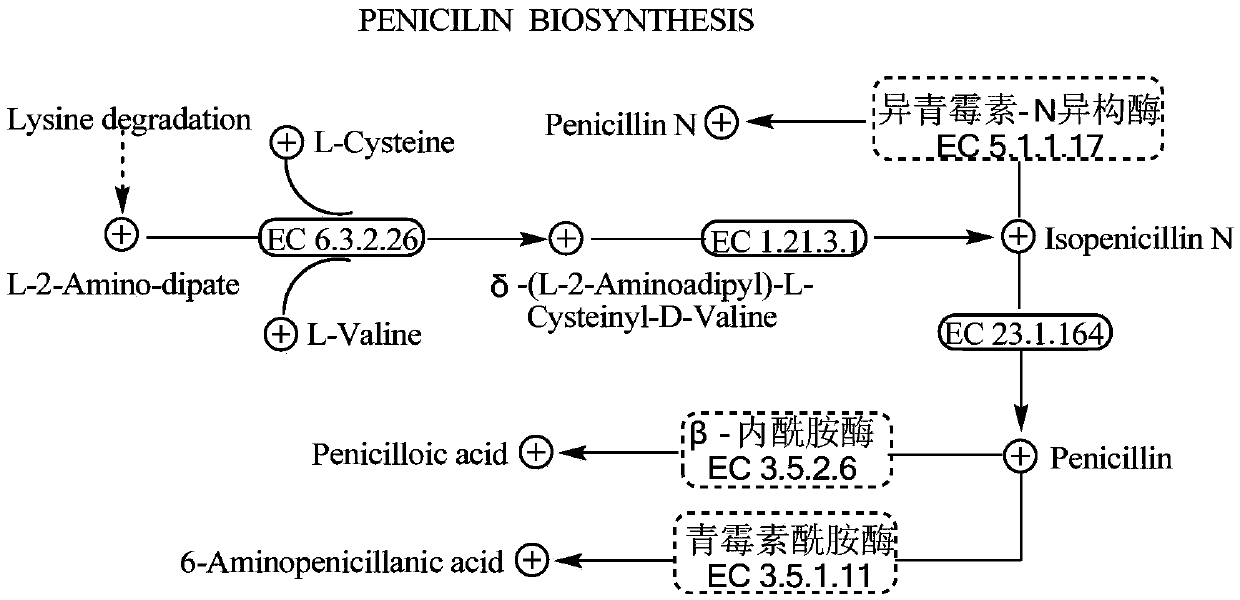
Construction method of penicillin-producing recombined strain of streptomyces virginiae IBL14
InactiveCN105505976AEasy to editChange genetic traitsNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionGene clusterMicrobiology
The invention discloses a construction method of a penicillin-producing recombined strain of streptomyces virginiae IBL14. The method involves sequence properties of a beta-lactamase gene containing hydrolysis penicillin and gene clusters producing penicillin, and the whole process of a construction method of the penicillin-producing recombined strain constructed on this basis. Related genes are compiled through the penicillin-producing gene and the CRISPR-Cas I-B gene of streptomyces virginiae IBL14, and therefore the aim of increasing the penicillin yield is achieved. A new route and method are provided for increasing the types of biological medicine, improving the production level and improving the product quality.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Synthetic gene clusters
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
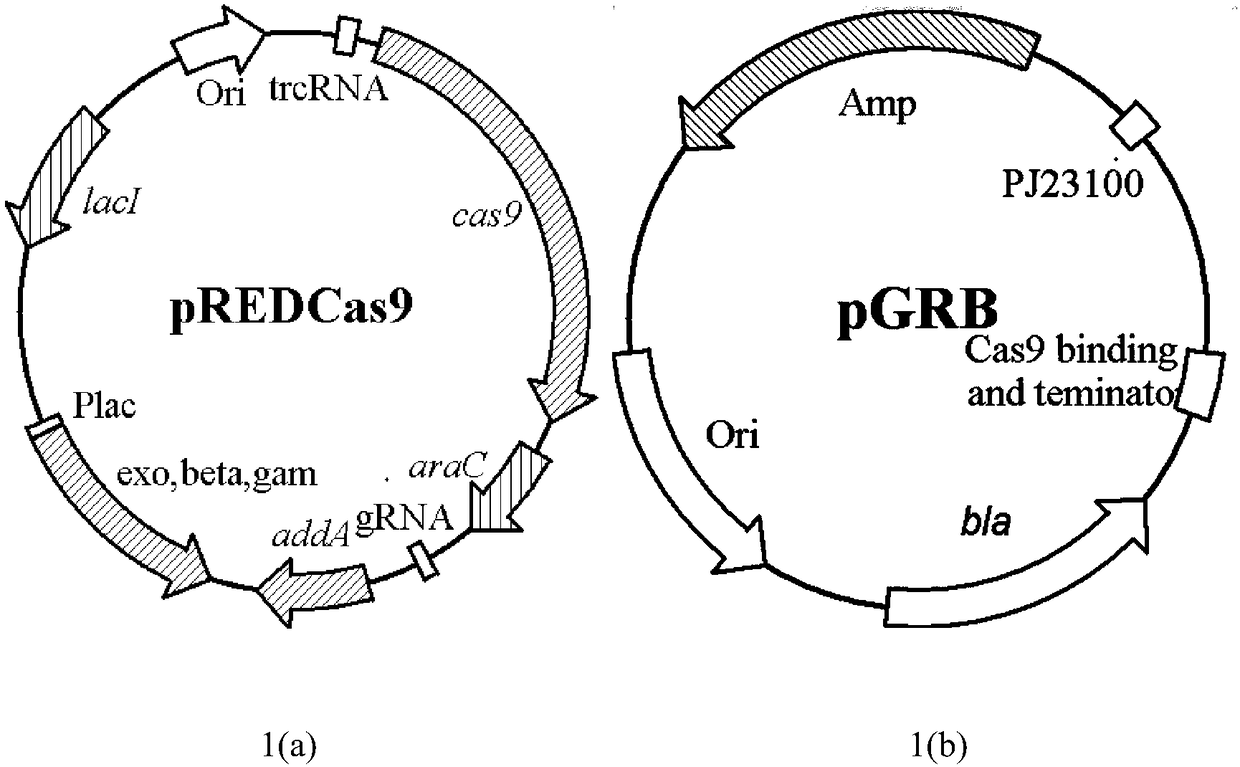
Dual-spacer sequence recognition and cleavage CRISPR-Cas9 vector construction, and application thereof in verrucosispora
ActiveCN107058358ACost advantageImprove stabilityHydrolasesVector-based foreign material introductionGene clusterVerrucosispora
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Streptococcus suis vaccines and diagnostic tests
InactiveUS7125548B2ImmunogenicityImproving immunogenicityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaAntigenSpecific detection
The invention relates to Streptococcus suis infection in pigs, vaccines directed against those infections and tests for diagnosing Streptococcus suis infections. The invention provides an isolated or recombinant nucleic acid encoding a capsular gene cluster of Streptococcus suis or a gene or gene fragment derivated thereof. The invention further provides a nucleic acid probe or primer allowing species or serotype-specific detection of Streptococcus suis. The invention also provides a Streptococcus suis antigen and vaccine derived thereof.
Owner:STICHTING DIENST LANBOUWKUNDIG ONDERZOEK
Bioinformatically detectable human herpesvirus 5 regulatory gene
ActiveUS7696334B1Preventing and treating viral diseasesSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementOperonVirus attack
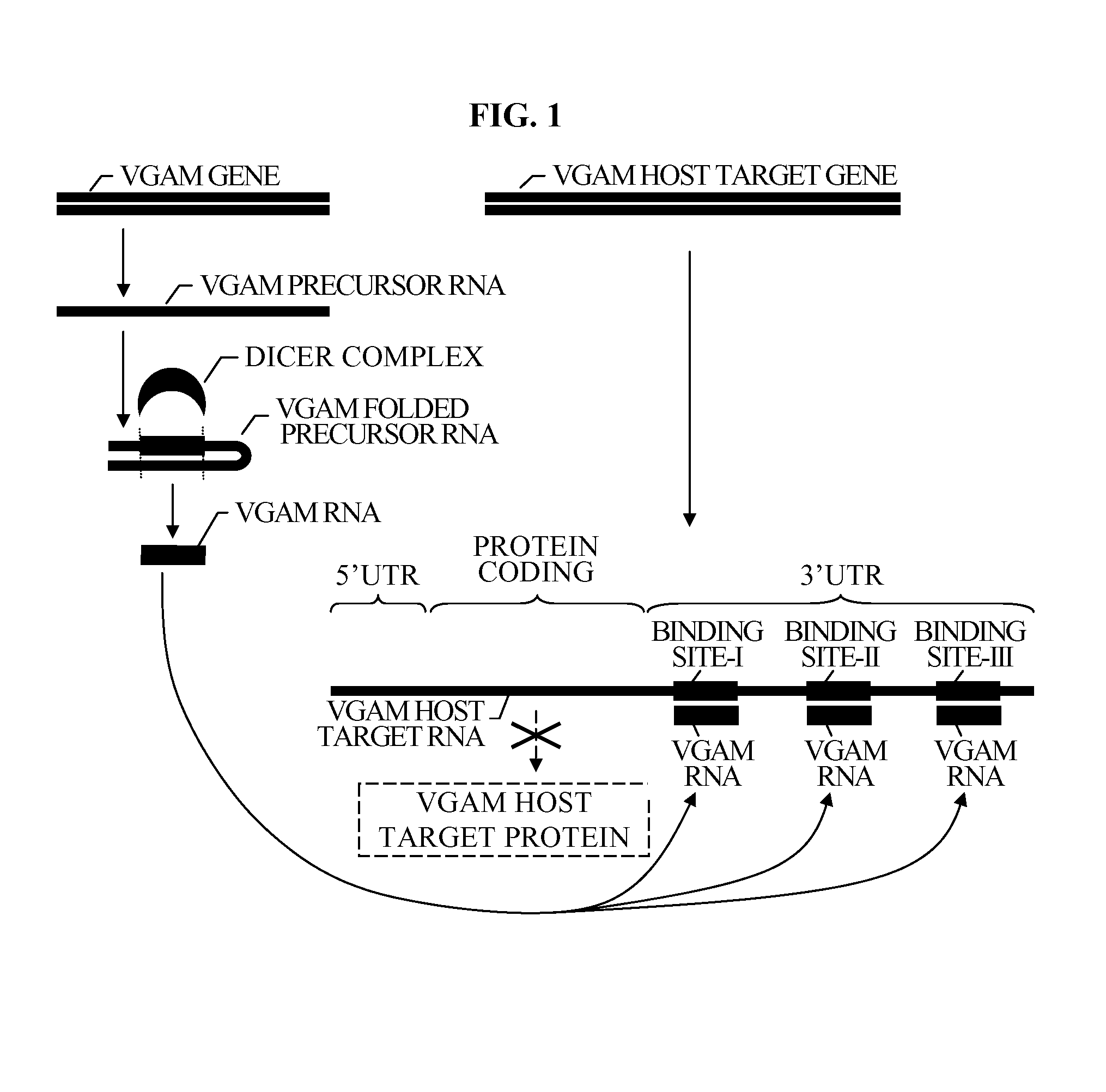
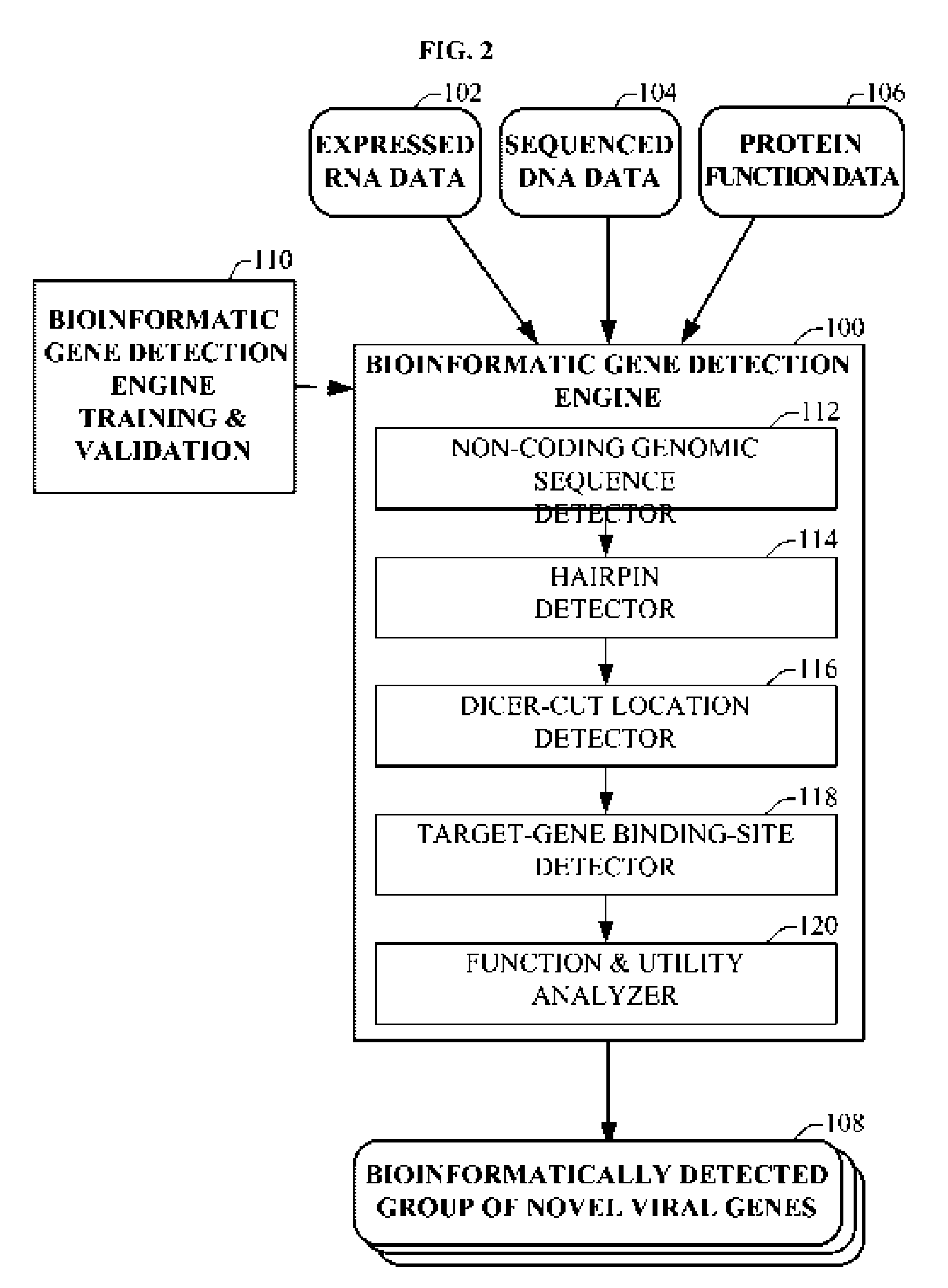
The present invention relates to a group of novel viral RNA regulatory genes, here identified as “viral genomic address messenger genes” or “VGAM genes”, and as “genomic record” or “GR” genes. VGAM genes selectively inhibit translation of known host target genes, and are believed to represent a novel pervasive viral attack mechanism. GR genes encode an operon-like cluster of VGAM genes. VGAM and viral GR genes may therefore be useful in diagnosing, preventing and treating viral disease. Several nucleic acid molecules are provided respectively encoding several VGAM genes, as are vectors and probes, both comprising the nucleic acid molecules, and methods and systems for detecting VGAM genes, and for counteracting their activity.
Owner:ROSETTA GENOMICS
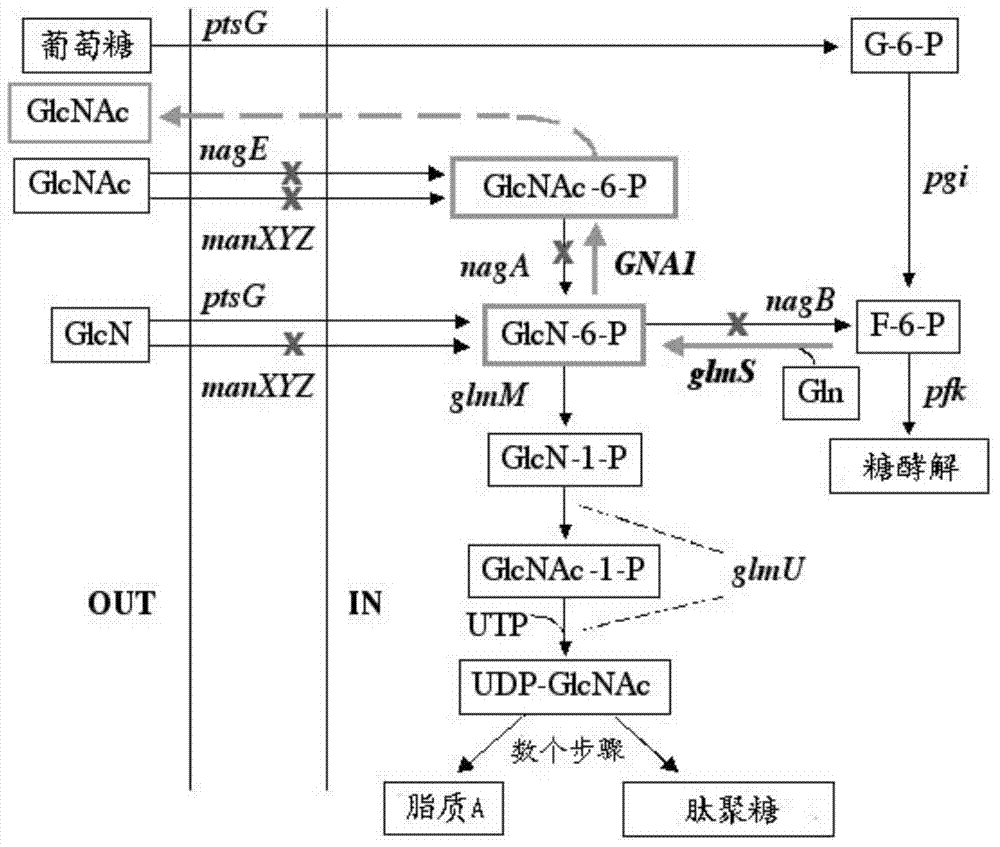
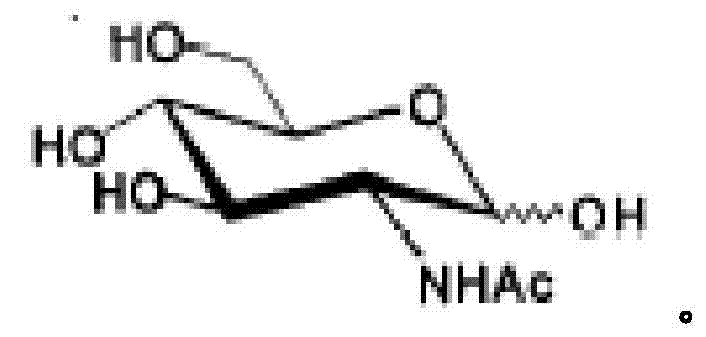
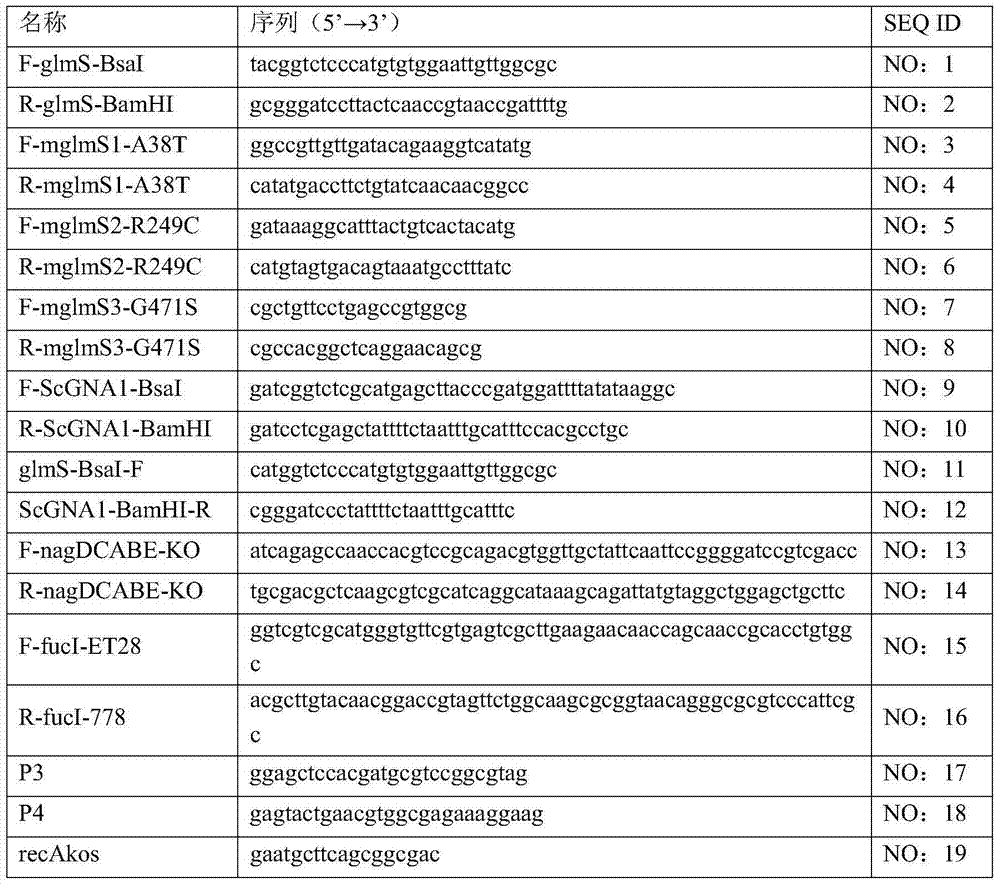
Genetically engineered bacteria for efficiently producing N-acetylglucosamine
InactiveCN104293724AImprove fermentation yieldImprove stabilityBacteriaHydrolasesEscherichia coliBiotechnology
The invention provides genetically engineered bacteria for efficiently producing N-acetylglucosamine. The genetically engineered bacteria are prepared by the following steps: integrating chromosome deficiency nag DCABE gene clusters of Escherichia coli, respectively connecting 6-glucosamine phosphate synthetase mutant genes and N-acetylglucosamine transferase genes which are respectively mediated by a T7 promoter and a Trc promoter with a gene expression cassette in series, wherein the 6-glucosamine phosphate synthetase mutant genes are obtained by mutating wild 6-glucosamine phosphate synthetase genes from an Escherichia coli W3110 strain source into A38T / R249C / G471S mutants. The genetically engineered bacteria constructed by the invention have the advantages of high N-acetylglucosamine fermentation yield and high strain stability and have wide industrial application prospects.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES & DEV CENT OF INDAL BIOTECH +1
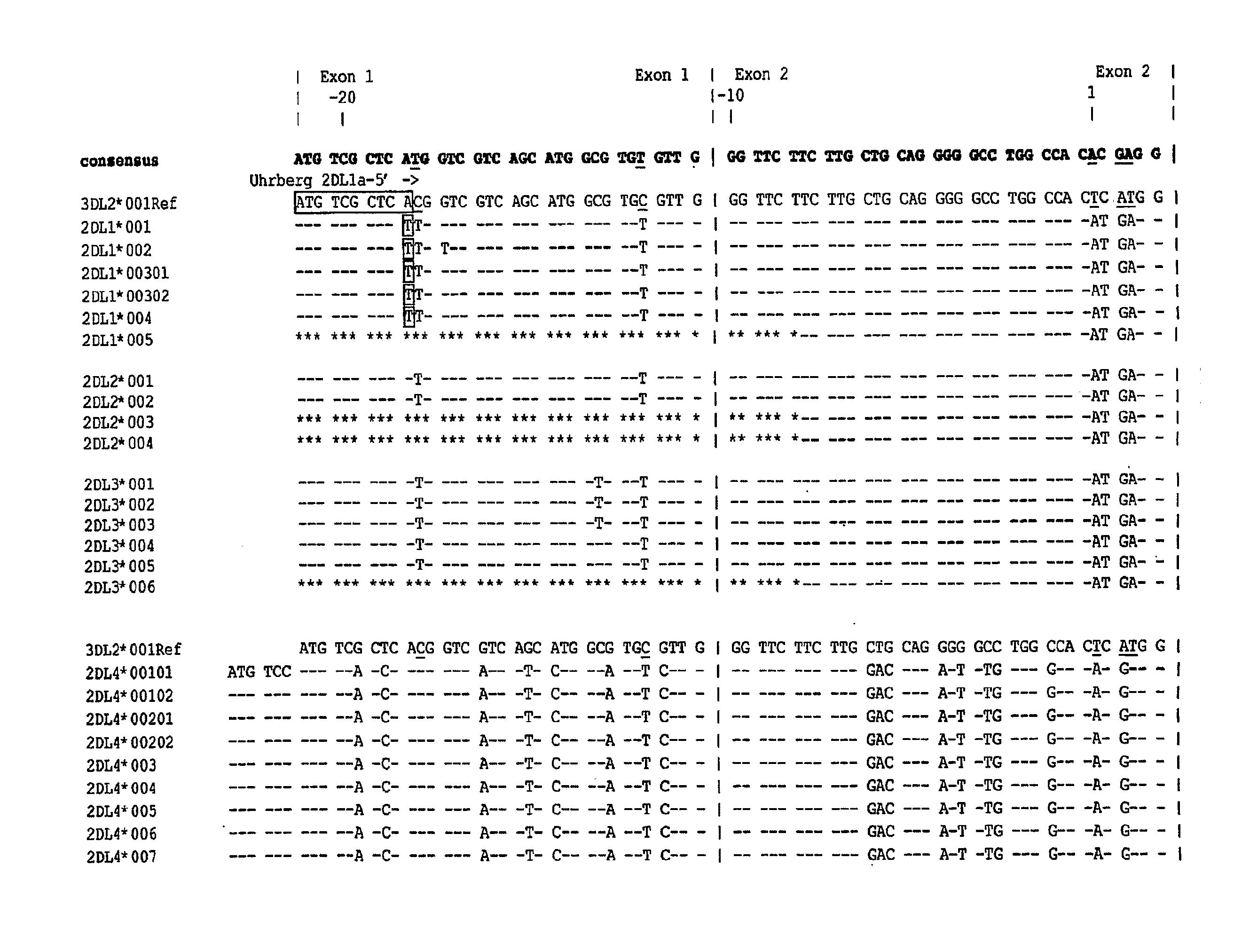
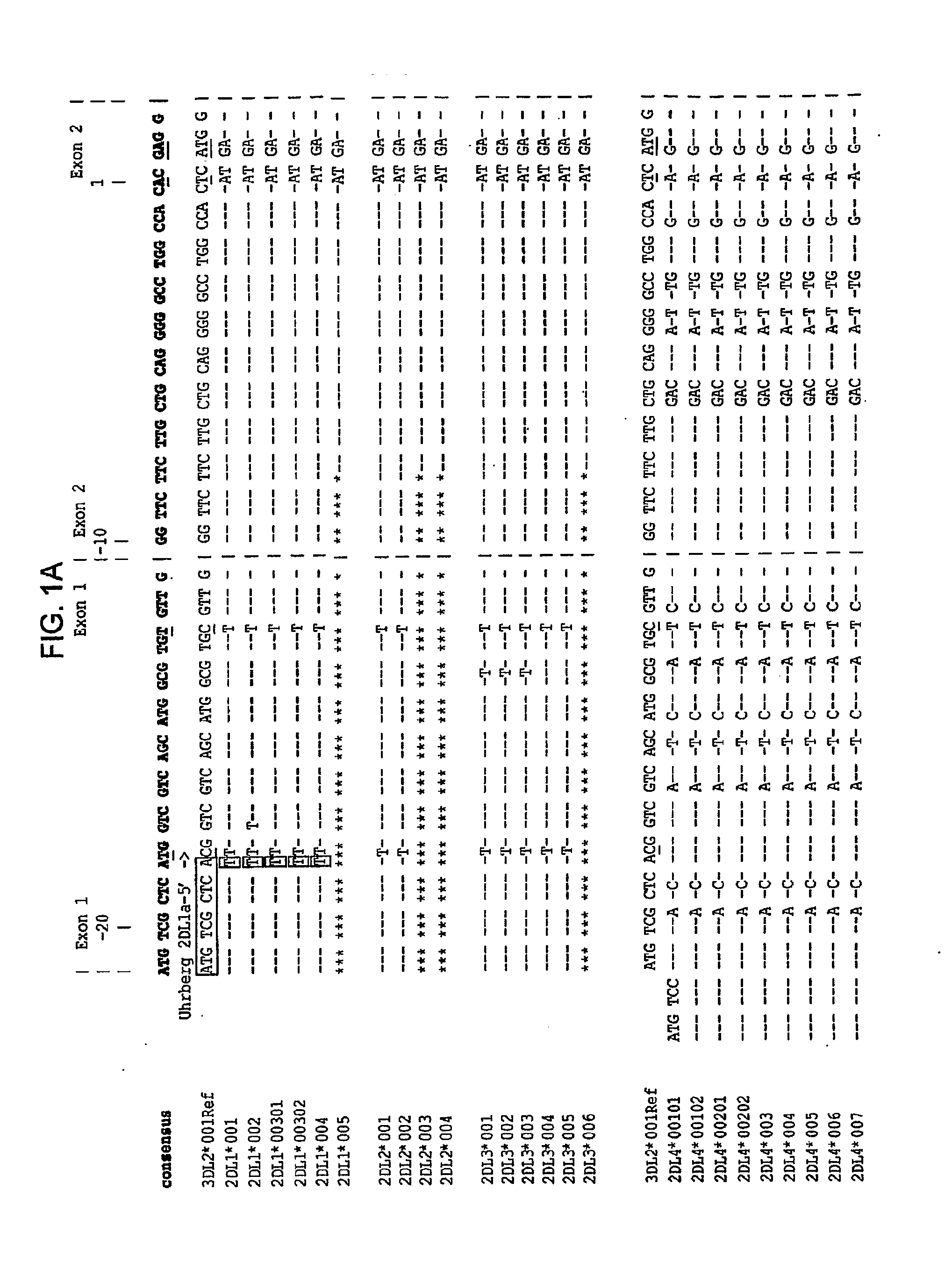
Methods and Compositions for Kir Genotyping
InactiveUS20080213787A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGene clusterIonization time of flight
The present invention provides methods for single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)-based killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) gene cluster genotyping using the matrix-assisted laser desorption / ionization time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometer. In general, the methods involve amplifying a plurality of target sequences of a plurality of KIR genes, and detecting the presence or absence of a plurality of single SNPs of the plurality of KIR genes by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. The invention also features compositions, including arrays of capture primers and optionally extension primers on a substrate surface, and kits, for use in the methods of the invention.
Owner:CHILDREN S HOSPITAL &RES CENT AT OAKLAN
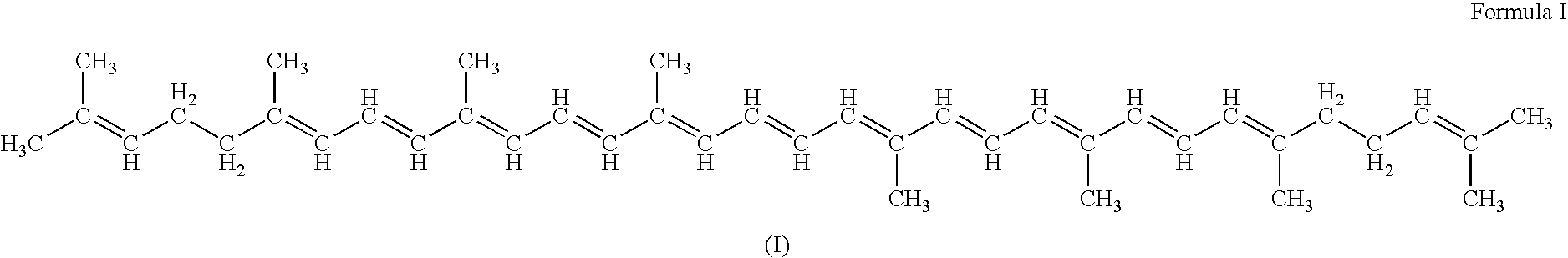
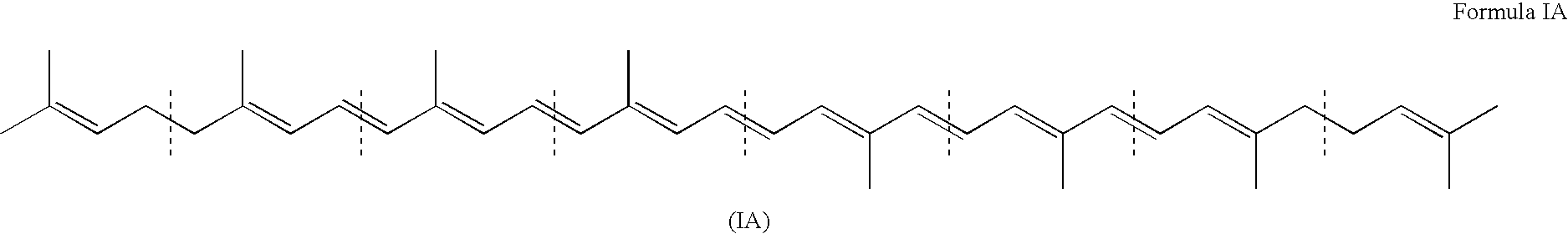
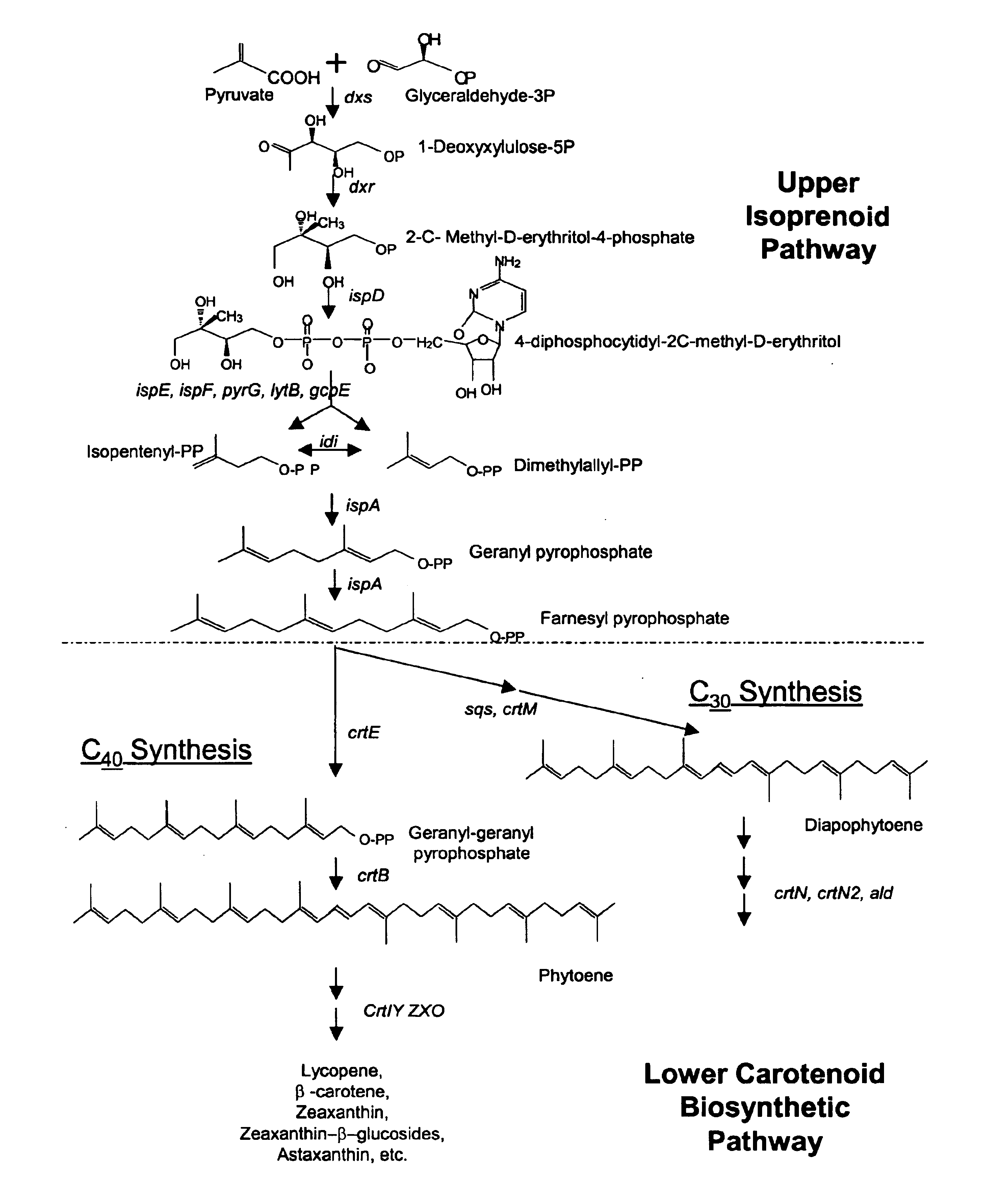
Genes encoding carotenoid compounds
A unique carotenogenic biosynthetic gene cluster has been isolated from Panteoa agglomerans strain DC404, wherein the genetic organization of the cluster is crtE-idi-crtY-crtI-crtB-crtZ. The genes contained within this cluster encode geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP) synthetase (CrtE), isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase (Idi), lycopene cyclase (CrtY), phytoene desaturase (CrtI), phytoene synthase (CrtB), and β-carotene hydroxylase (CrtZ). The gene cluster, genes and their products are useful for the conversion of farnesyl pyrophosphate to carotenoids. Vectors containing those DNA segments, host cells containing the vectors and methods for producing those enzymes by recombinant DNA technology in transformed host organisms are disclosed.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
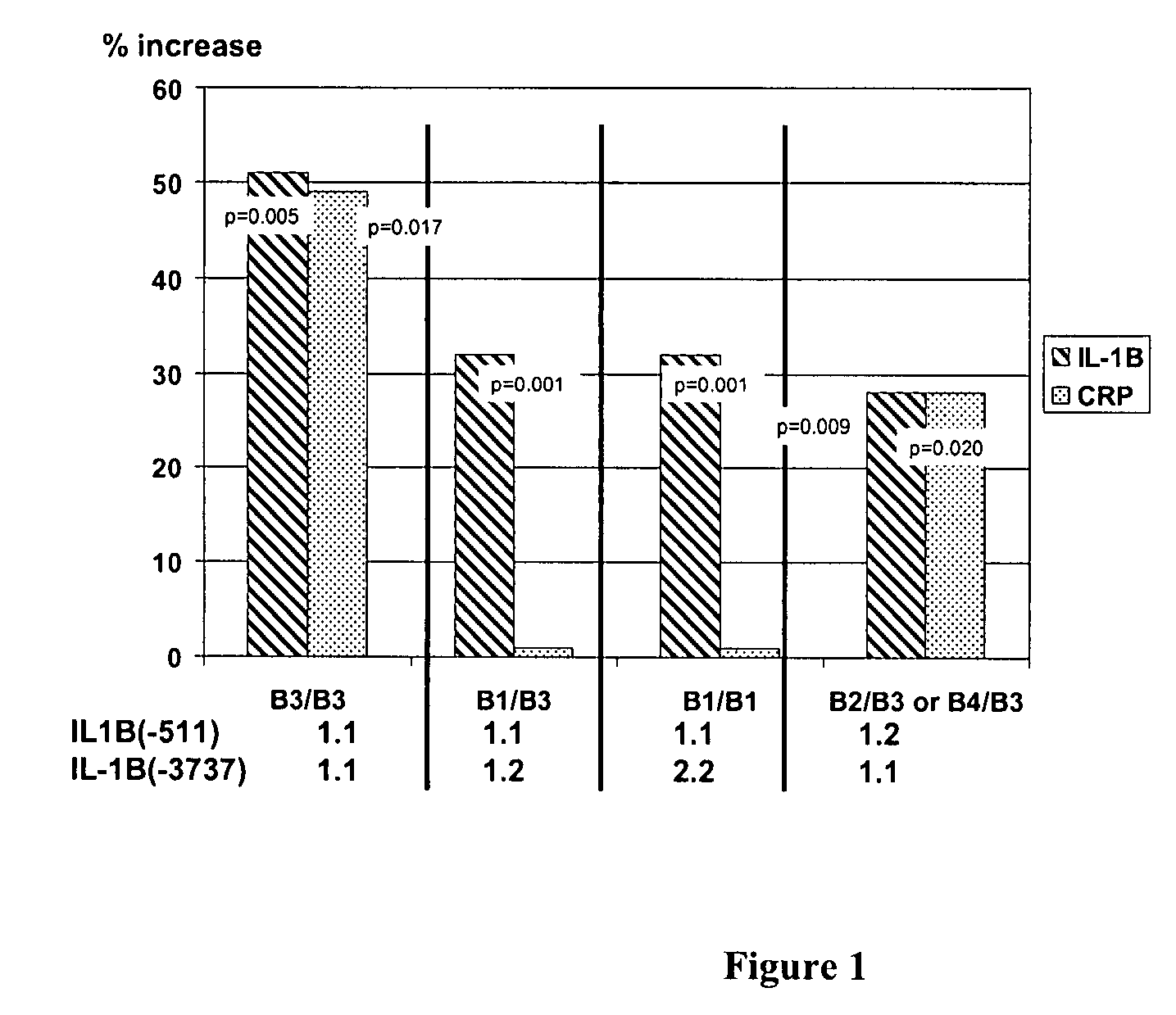
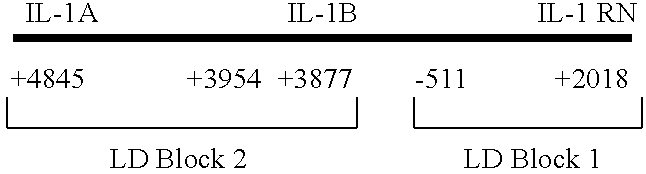
IL-1 gene cluster, insulin resistance and coronary artery disease associated polymorphisms and haplotypes and methods of using same
The invention provides methods and compositions relating to identification and use of genetic information from the IL-1 gene cluster—including the structure and organization of novel IL-1-like genes found within the IL-1 locus as well as polymorphisms and associated haplotypes within these genes. The invention thereby expands the repertoire of useful genetic information available from the IL-1 locus—which contains the previously-identified IL-1α, IL-1β and IL-1RN genes, for predicting IL-1 associated phenotypes (e.g. increased or decreased risks of insulin resistance associated pathologies) and for treating IL-1 haplotype associated insulin resistance associated pathologies.
Owner:SAPPHIROS LAB LLC
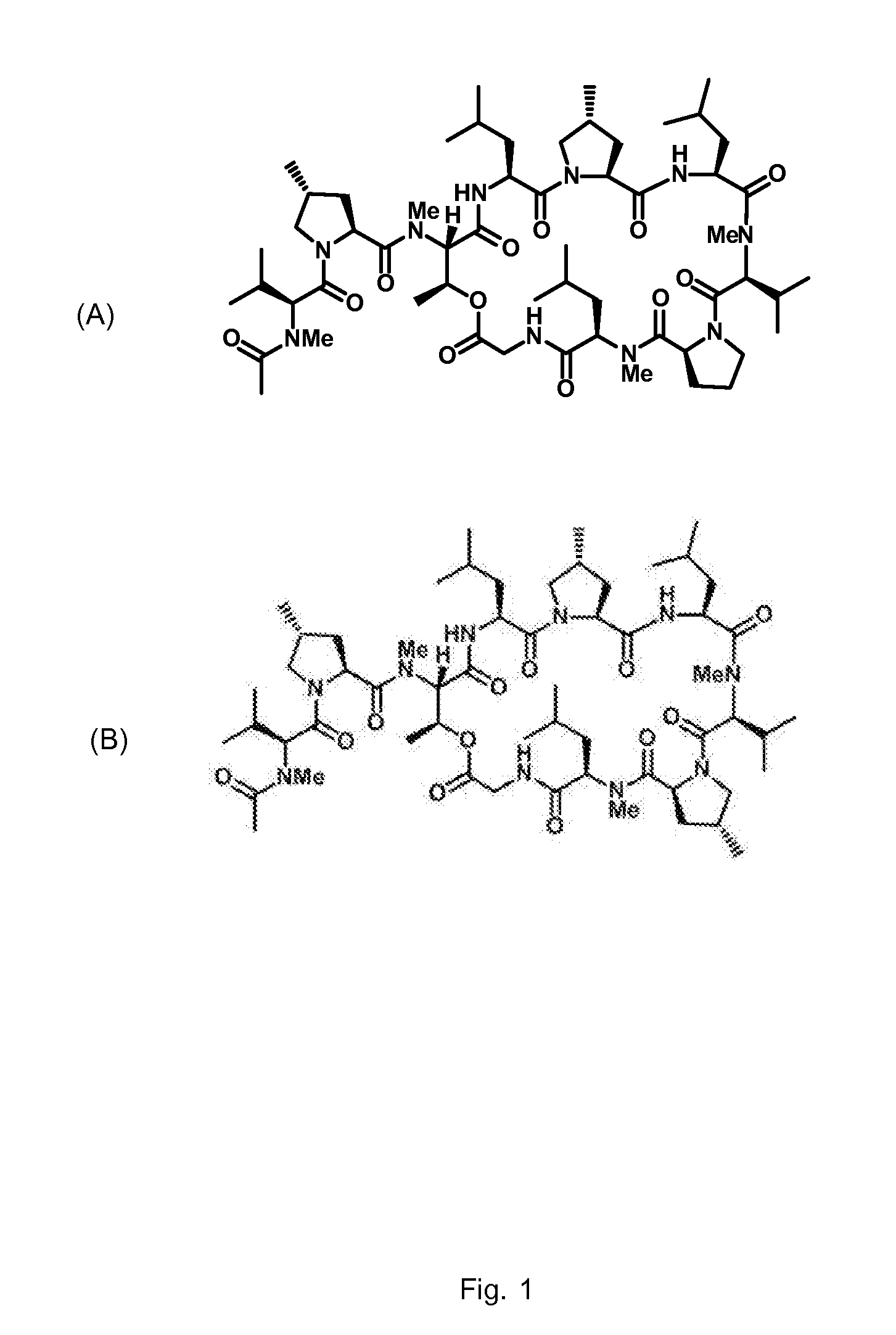
Gene cluster for biosynthesis of griselimycin and methylgriselimycin
ActiveUS20140295457A1Increase productionEasy to produceBacteriaHydrolasesAntibiotic AgentsGene cluster
The present invention refers to the gene cluster and genes comprised by the gene cluster which are involved in the biosynthesis of griselimycin and methylgriselimycin and to the use of the gene cluster, genes comprised thereby and proteins encoded thereby for the production of antibiotic agents.
Owner:SANOFI SA
Transformant and process for production thereof, and process for production of lactic acid
The present invention relates to a transformant, containing a lactate dehydrogenase gene which is introduced into Schizosaccharomyces pombe as a host, in which a part of a gene cluster encoding a pyruvate decarboxylase in the Schizosaccharomyces pombe host is deleted or inactivated.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
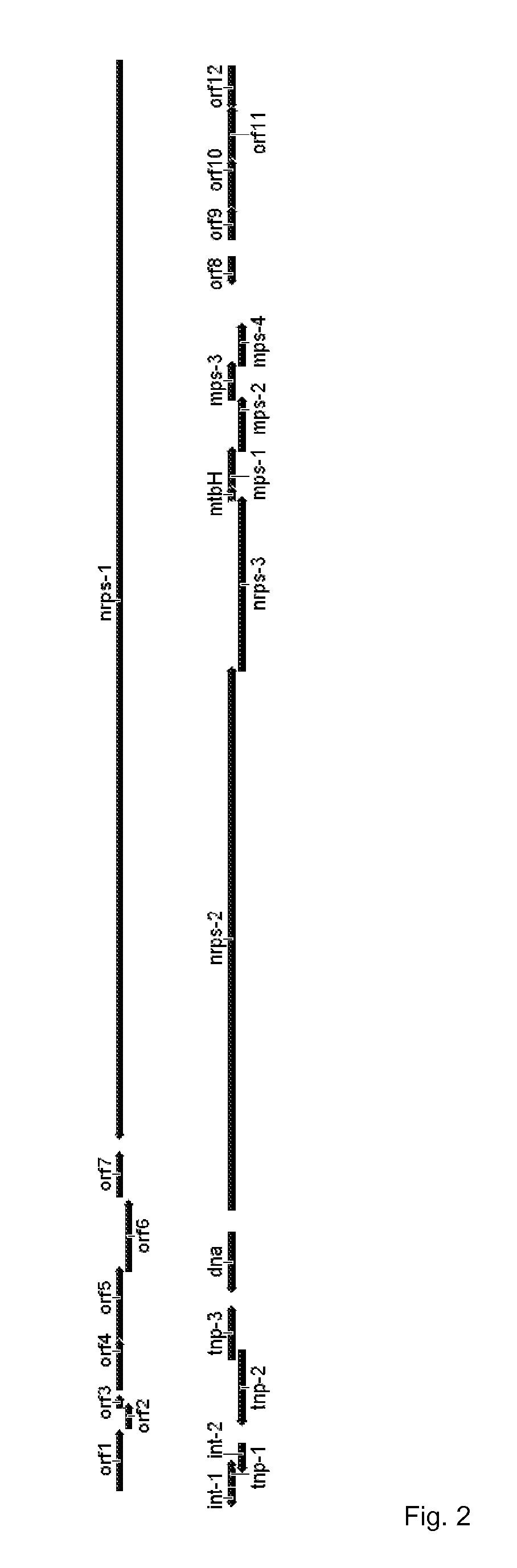
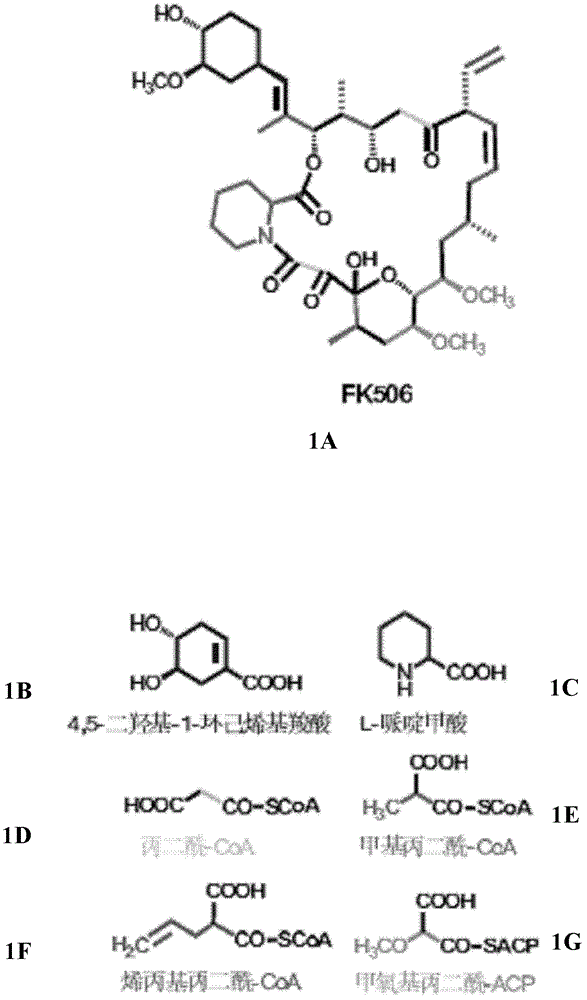
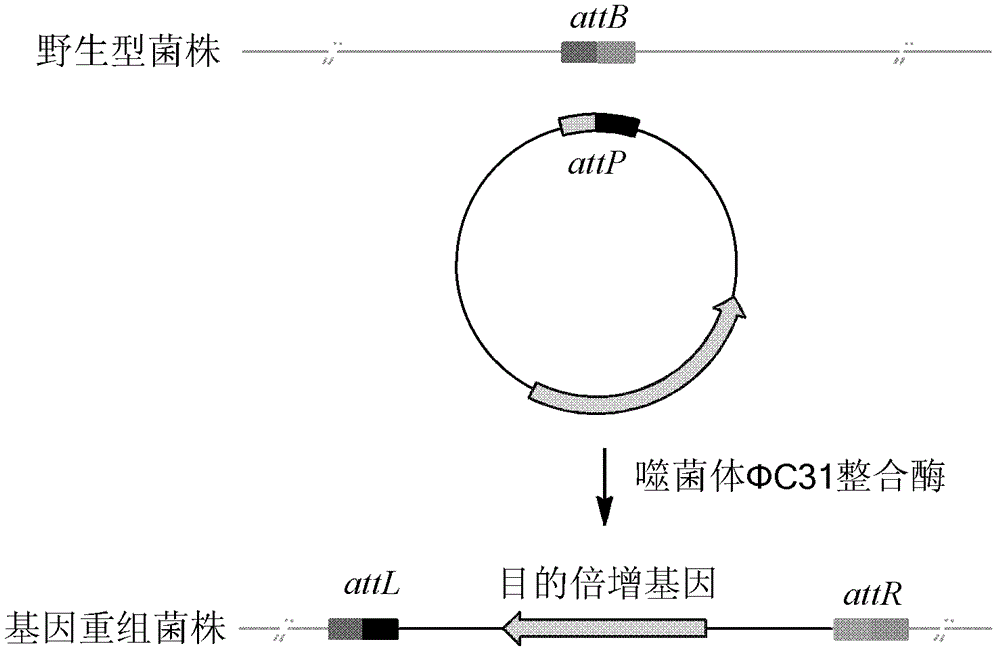
Method for constructing gene engineering FK506 high-producing strain and streptomyces tsukubaensis high-producing strain
The invention discloses a method for constructing a gene engineering FK506 (tacrolimus) high-producing strain and a streptomyces tsukubaensis high-producing strain. A receptor strain integrated in genome with a multiplication expression box expressing genes associated with biosynthesis of FK506 has the ability of stably producing FK506 in high yield. Specifically, in a site-specific integration mechanism mediated gene recombination way, endogenous genes associated with precursor biosynthesis in an FK506 gene cluster are multiplied to a streptomyces chromosome to directionally reconstruct the streptomyces producing FK506, so as to obtain an FK506 high-producing strain. The invention also discloses the application of the FK506 high-producing strain.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Methods and systems for gene expression array analysis
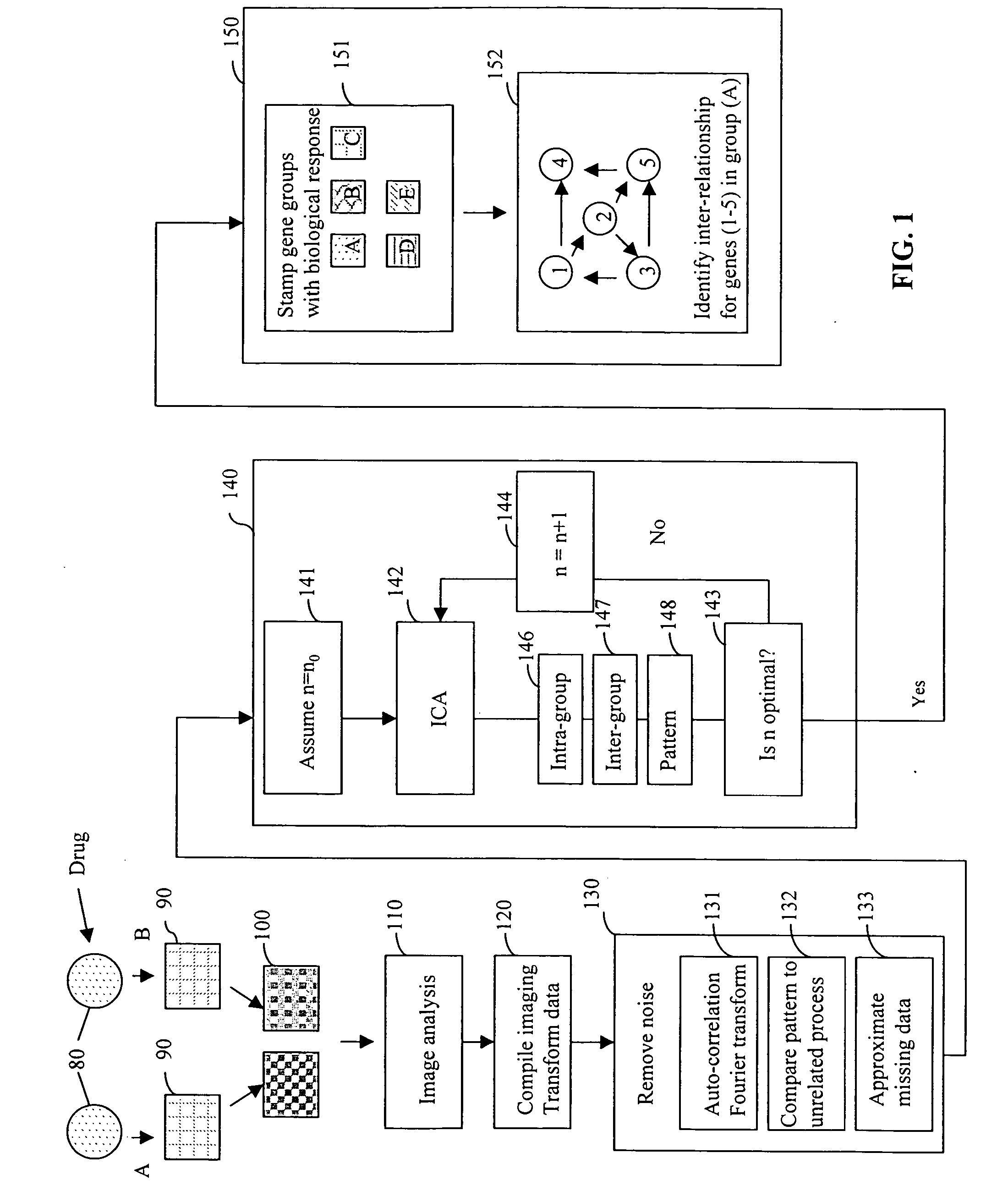
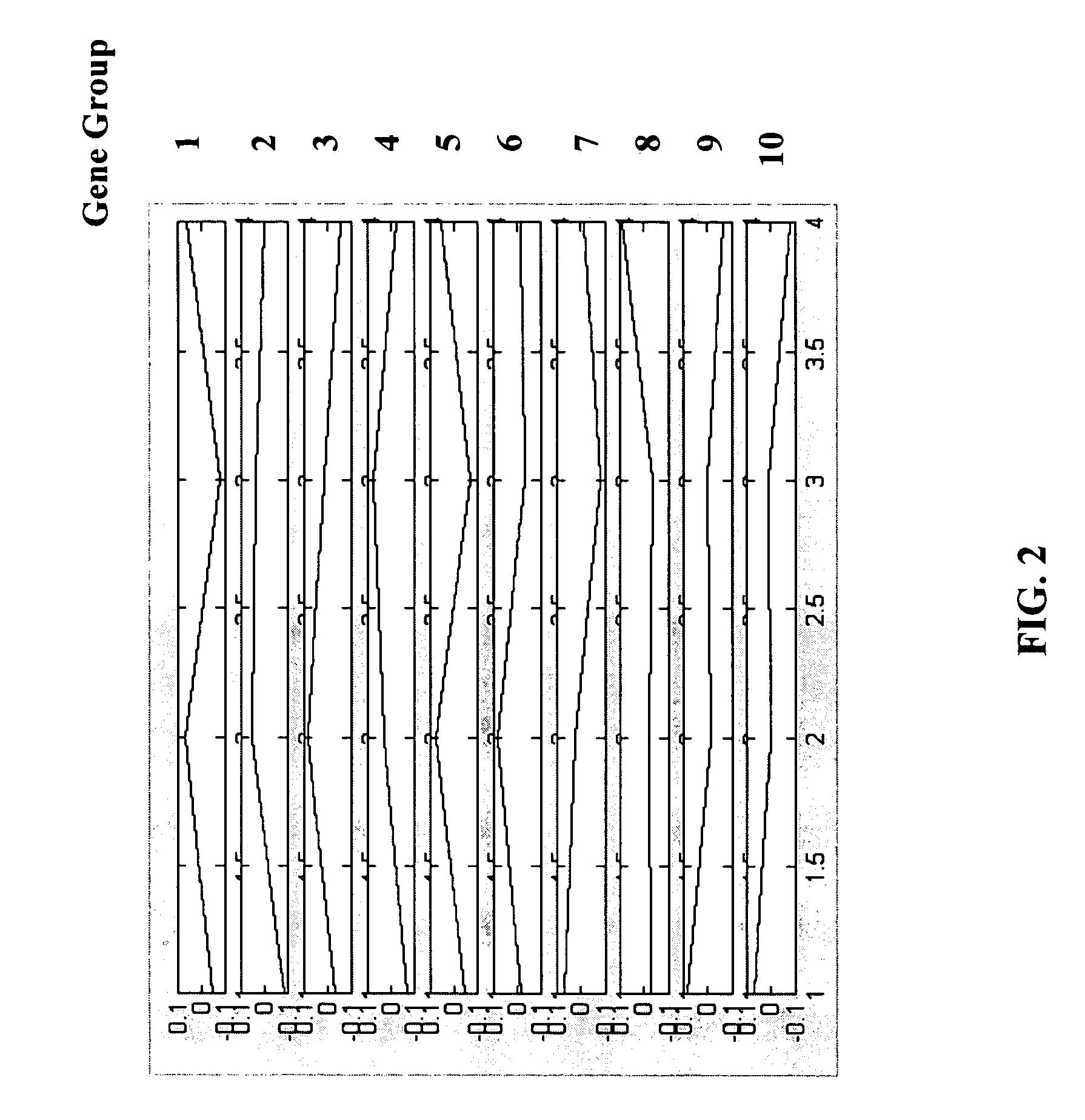
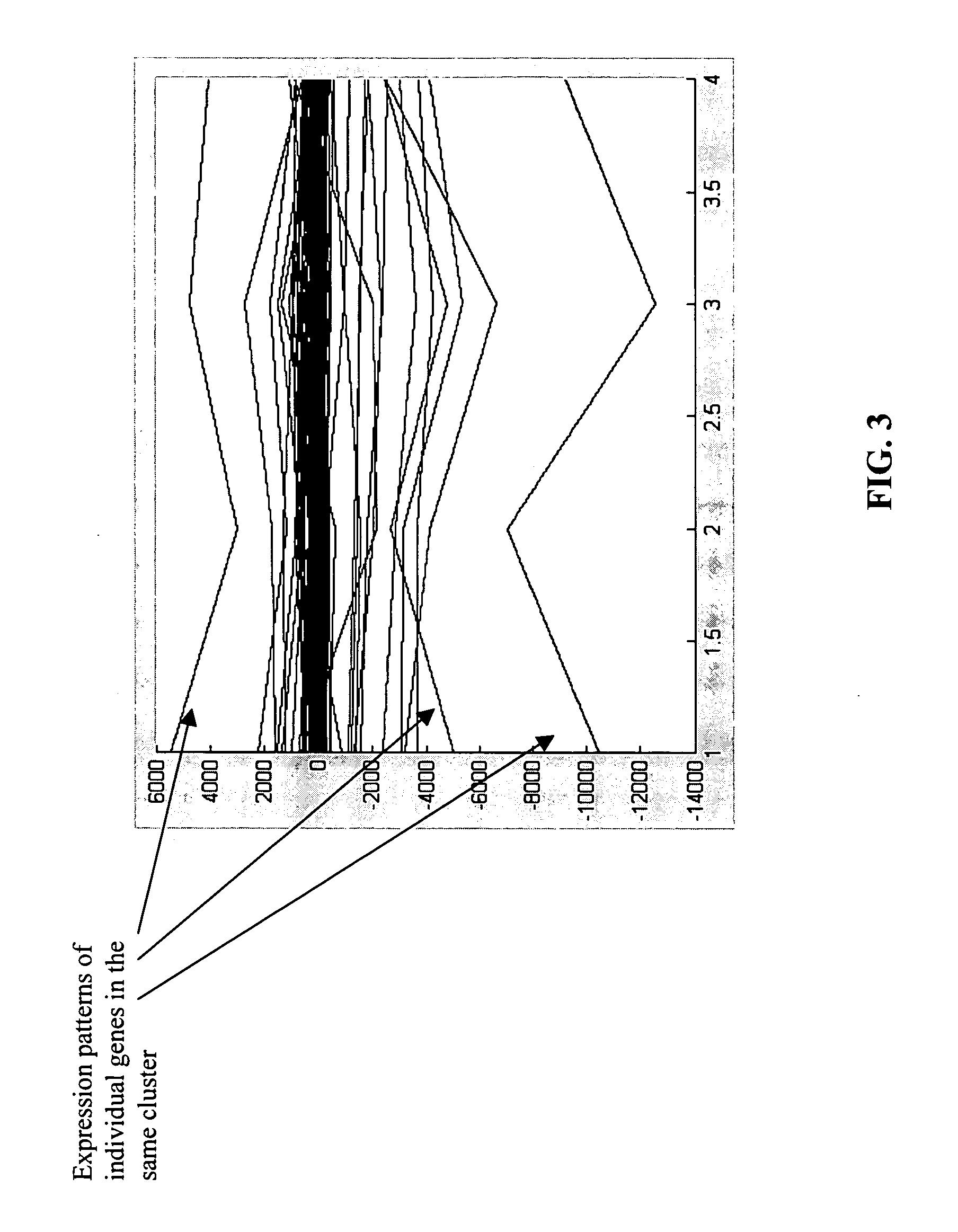
InactiveUS20060074566A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsGene clusterIndependent component analysis
Disclosed are methods and systems for applying independent component analysis (ICA) and other advanced signal processing techniques to automatically identify an optimal number of independent gene clusters and to efficiently separate gene expression data into biologically relevant groups. Embodiments of the methods and systems of the present invention provide an interface that allows the user to review the results at various stages during the analysis, thereby optimizing the type of analysis performed for a specific experiment. Also disclosed are methods and systems to mathematically define the relationship for gene expression within a group of interrelated genes.
Owner:JUNIVERSITI OF NORT KAROLINA EHT SHARLOTT
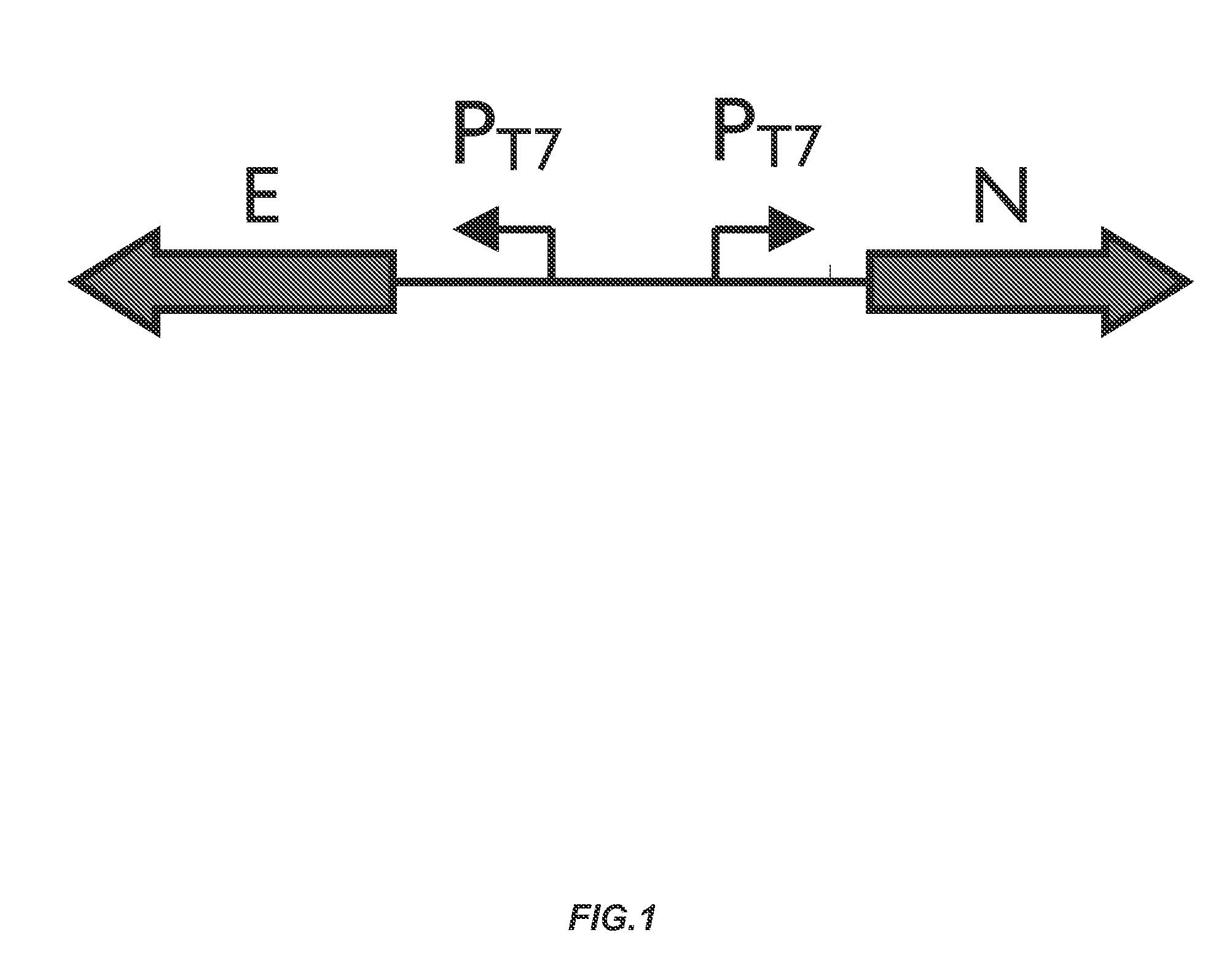
Genetically engineered bacterium for high-yield production of hydroxytetrahydropyrimidine as well as construction method and application of genetically engineered bacterium
InactiveCN108441460AIncrease productivityImprove growth traitsBacteriaTransferasesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention relates to a genetically engineered bacterium for high-yield production of hydroxytetrahydropyrimidine as well as a construction method and application of the genetically engineered bacterium. The strain integrates RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) polymerase which is controlled by a xylose promoter and is derived from T7 bacteriophage; a thrA gene for encoding homoserine dehydrogenase I is knocked out; a lysC gene derived from corynebacterium glutamicum, an ectABC gene cluster derived from halomonas elongate and an ectD gene for encoding tetrahydropyrimidine hydroxylase are integrated andare promoted by a strong promoter PT7; a hydroxytetrahydropyrimidine synthesis way is reconstructed; the ectD gene is integrated at a sucCD site of succinyl coenzyme A synthetase and is started by thestrong promoter PT7; the genetically engineered bacterium has the highest level of producing the hydroxytetrahydropyrimidine by a fermentation method which is reported at present.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
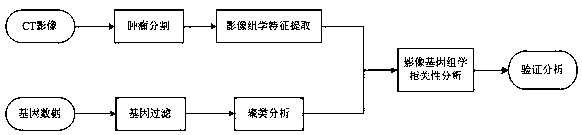
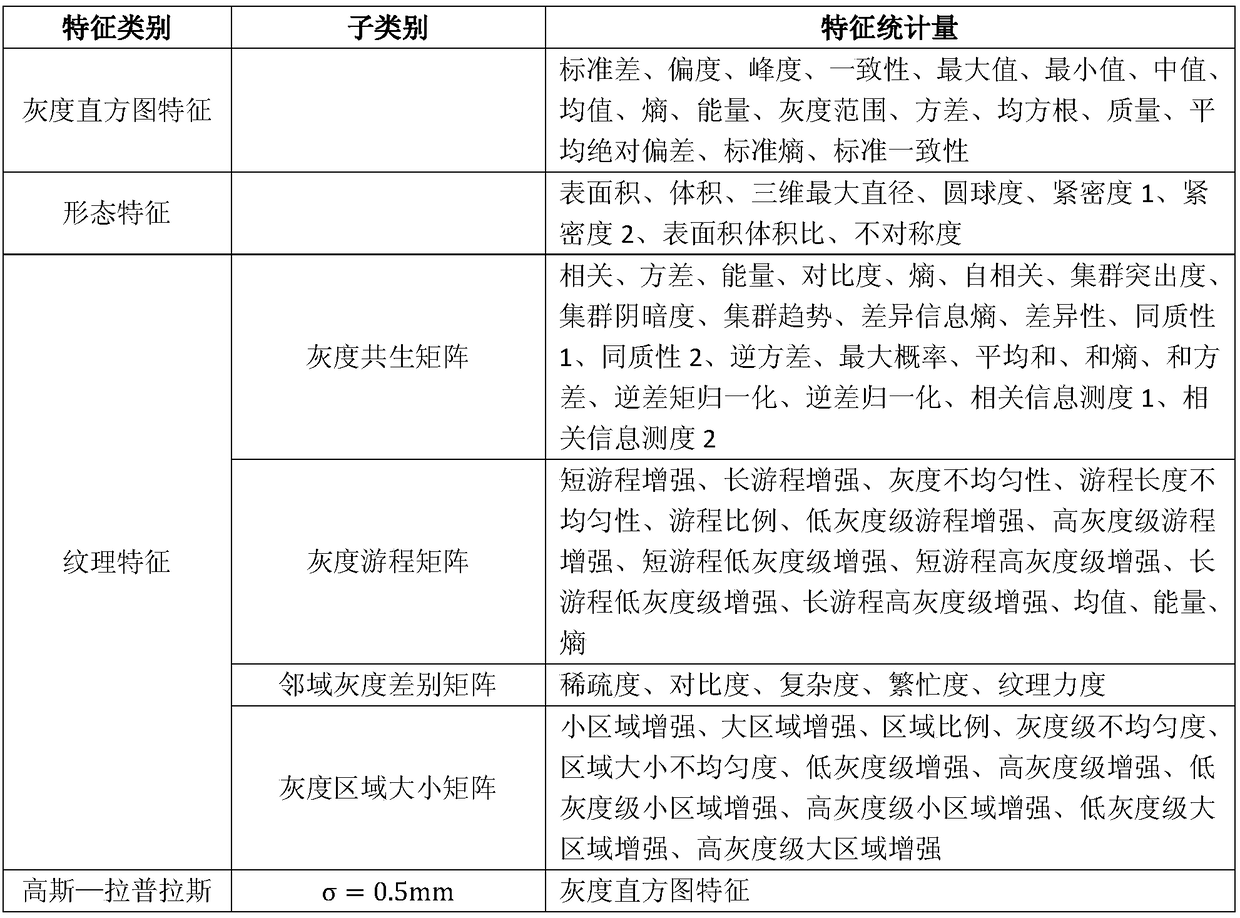
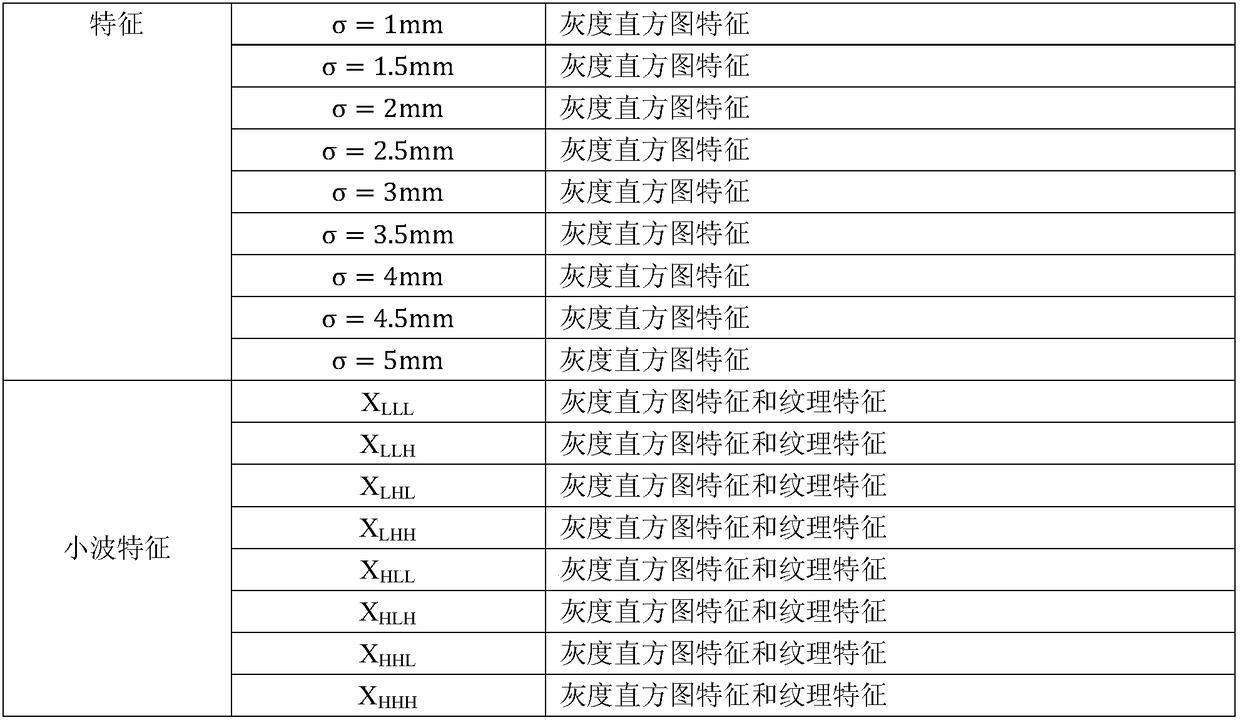
Method for analyzing correlation between CT imaging genomics characteristics and gene expression in lung cancer
InactiveCN108897984AAdjunctive Personalized TherapyImage enhancementImage analysisPersonalizationGenomics
The invention relates to a method for analyzing the correlation between CT imaging genomics characteristics and gene expression in lung cancer. The method includes: using a semi-automatic segmentationmethod to extract CT imaging genomics characteristics of a segmented tumor were; performing clustering analysis on the basis of preprocessed gene data, and taking a first principal component as a representative of a gene clustering result with a similar expression profile; and finally, using a gene chip saliency analysis algorithm to find the correlation between CT imaging genomics characteristics and gene expression in lung cancer, and verifying and analyzing the result. The invention provides a novel scheme for exploring the relationship between the image characteristics and the gene data,and attempts to find an imaging substitute of the gene, interprets the image characteristics from the gene level, and assists the personalized treatment of the tumor well.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Methods and compositions for cellular and metabolic engineering
InactiveUS20060257890A1Improve abilitiesExcellent catalytic performanceMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningIndividual geneGene cluster
The present invention is generally directed to the evolution of new metabolic pathways and the enhancement of bioprocessing through a process herein termed recursive sequence recombination. Recursive sequence recombination entails performing iterative cycles of recombination and screening or selection to “evolve” individual genes, whole plasmids or viruses, multigene clusters, or even whole genomes. Such techniques do not require the extensive analysis and computation required by conventional methods for metabolic engineering.
Owner:MAXYGEN
Production of modified polysaccharide S-7
A modified S7 polysaccharide is disclosed. The polysaccharide contains 20% less glucose that S7. An S7c6 gene cluster is disclosed. A mutated Sphingomonas is also disclosed.
Owner:SHIN ETSU BIO INC +1
Genes and enzymes for the production of adipic acid intermediates
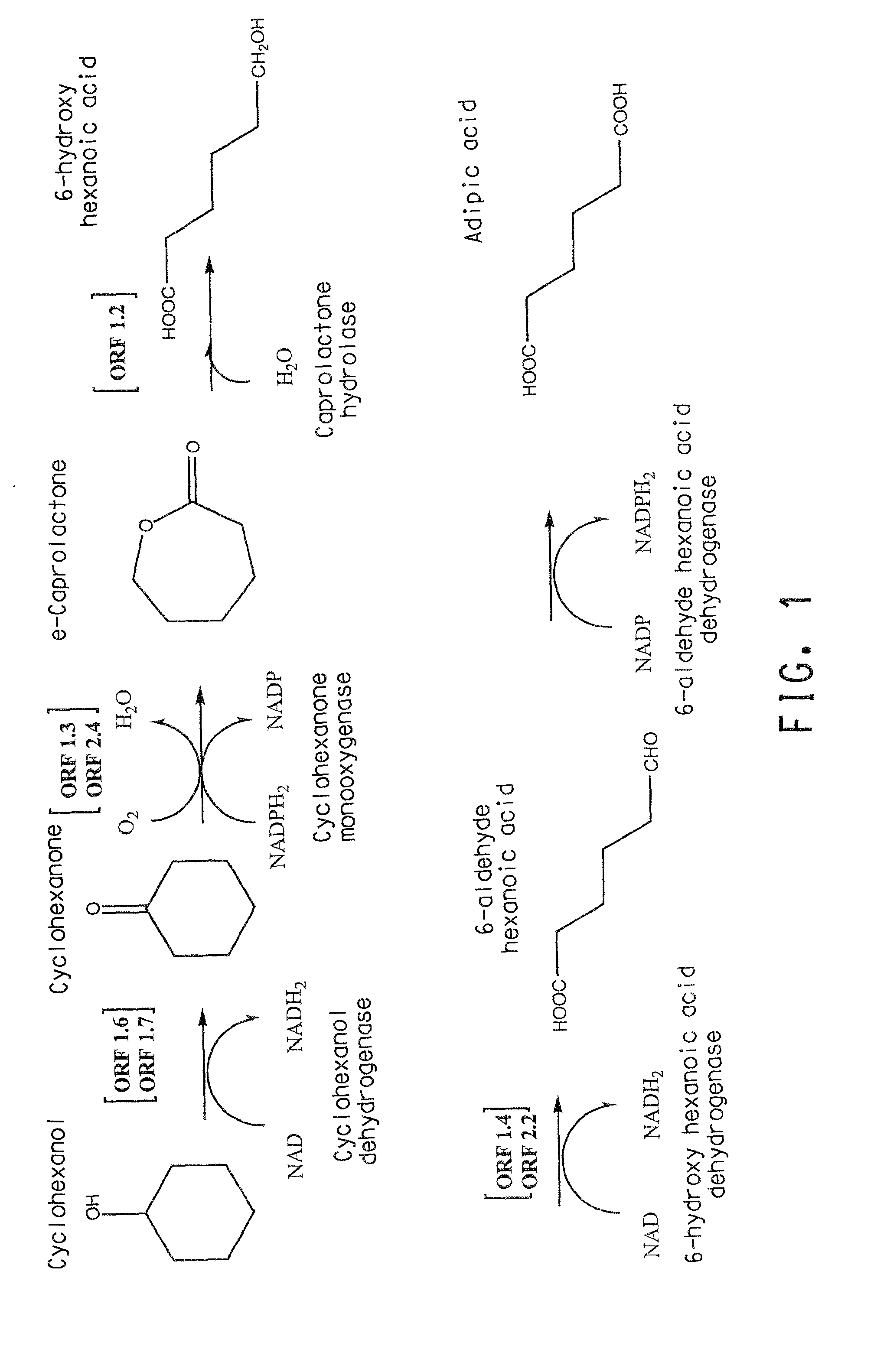
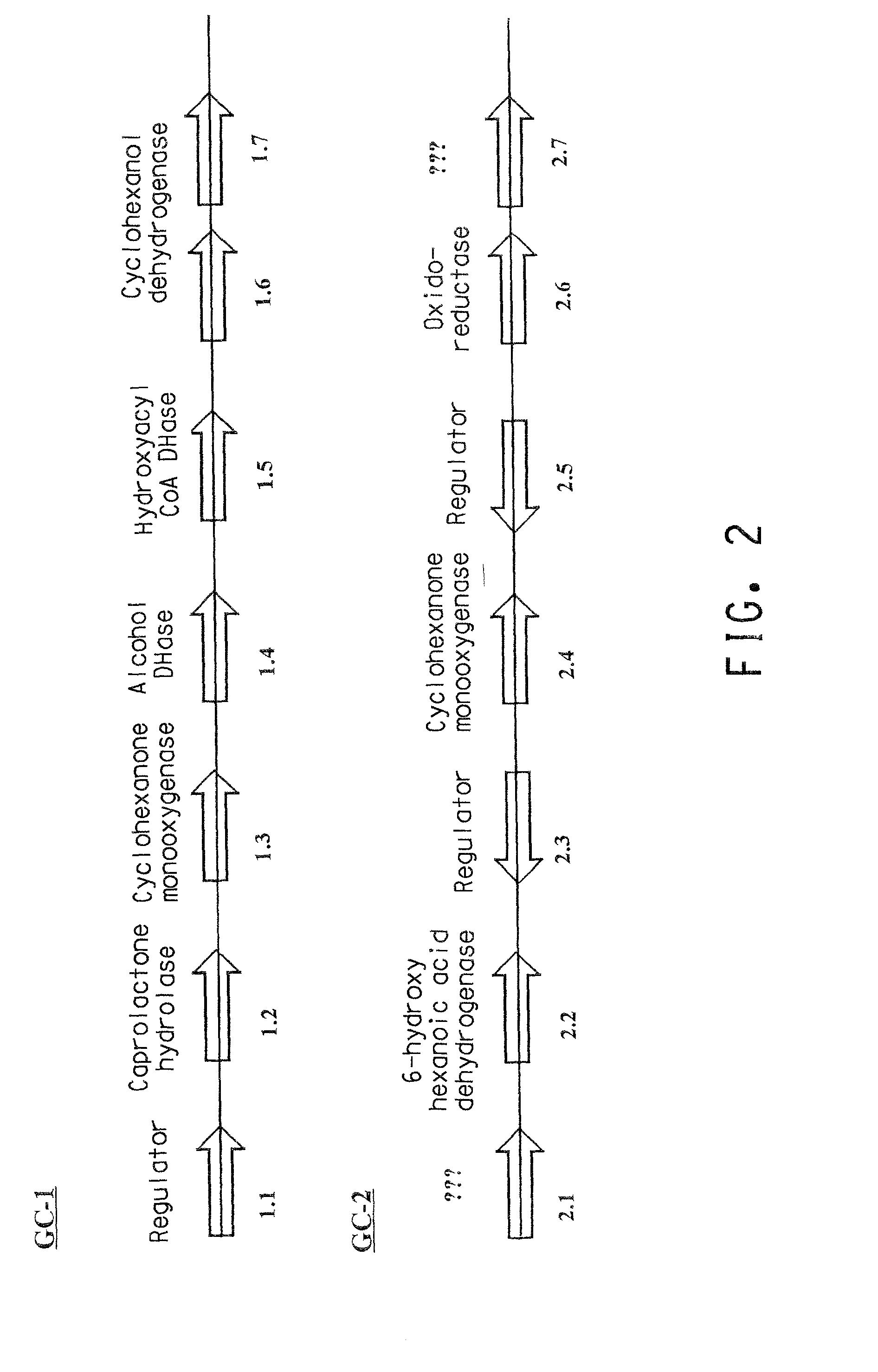
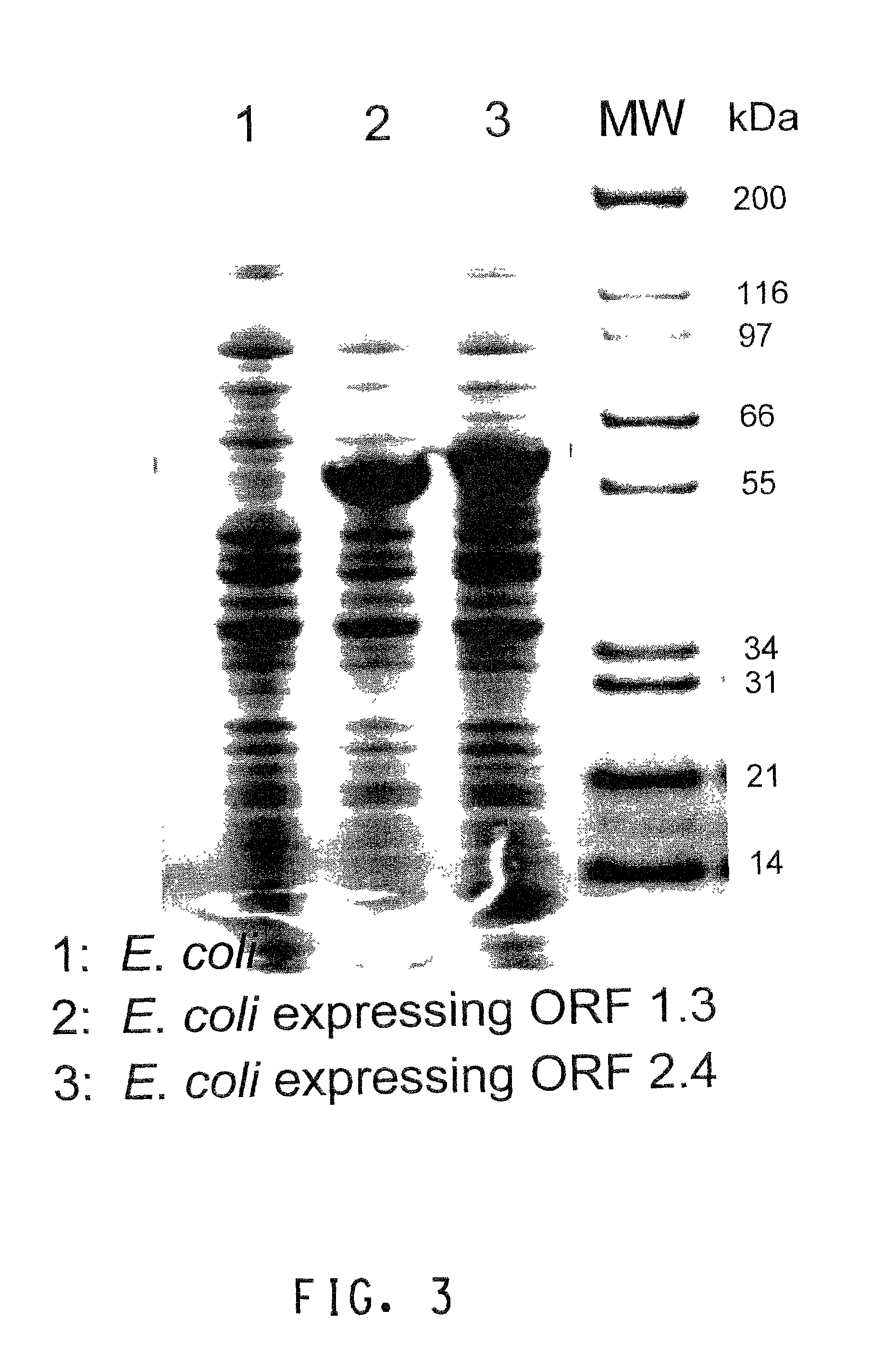
Two gene clusters have been isolated from an Brevibacterium sp HCU that encode the enzymes expected to convert cyclohexanol to adipic acid. Individual open reading frames (ORF's) on each gene cluster are useful for the production of intermediates in the adipic acid biosynthetic pathway or of related molecules. All the ORF's have been sequenced. Identification of gene function has been made on the basis of sequence comparison and biochemical analysis.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
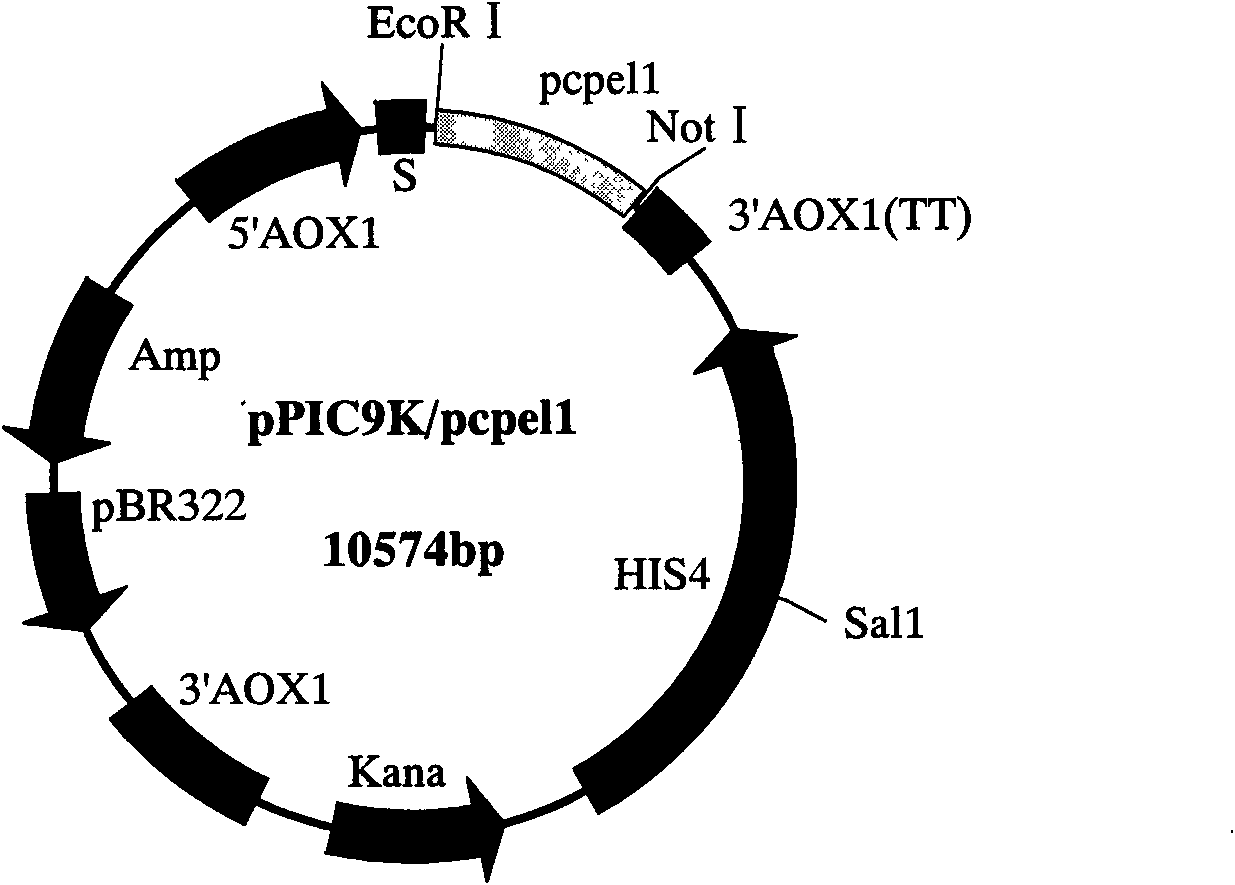
Phytophthora capsici pectate lyase (PL) Pcpel1 gene, protein preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101638663AObvious symptomsSufficient technical reservesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesCytochemistryPlant pathology
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology and in particular provides a pectate lyase (PL) gene Pcpel1 which is cloned from phytophthora capsici and protein preparation technology thereof. Gene and protein levels prove that the gene is effectively involved in the process that the phytophthora capsici infects hot pepper hosts and results in occurrence of the course of diseases on hot pepper leaves. Plant pathology and cytochemistry technology further prove that after the protein coded by the gene is inoculated onto the hot pepper leaves, obvious withering and shrinking occur on theinoculated parts of the leaves and the cell walls on the affected parts of the leaves are obviously degraded, namely the gene code is an important protein related to the course of diseases or is possibly an important target pathogenic gene of a phytophthora capsici PL gene cluster. The invention provides important technical reserve for further developing phytophthora capsici molecule detection technology.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Platensimycin biosynthetic gene cluster of streptomyces platensis
The present invention relates to the cloning and sequence of a biosynthetic gene cluster from Streptomyces platensis that produces platensimycin and platencin. Also provided are engineered micro-organisms for the production of these compounds, and analogs thereto, as well as methods of screening for compounds with anti-bacterial activity.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Biological synthesis gene cluster for Azintamide
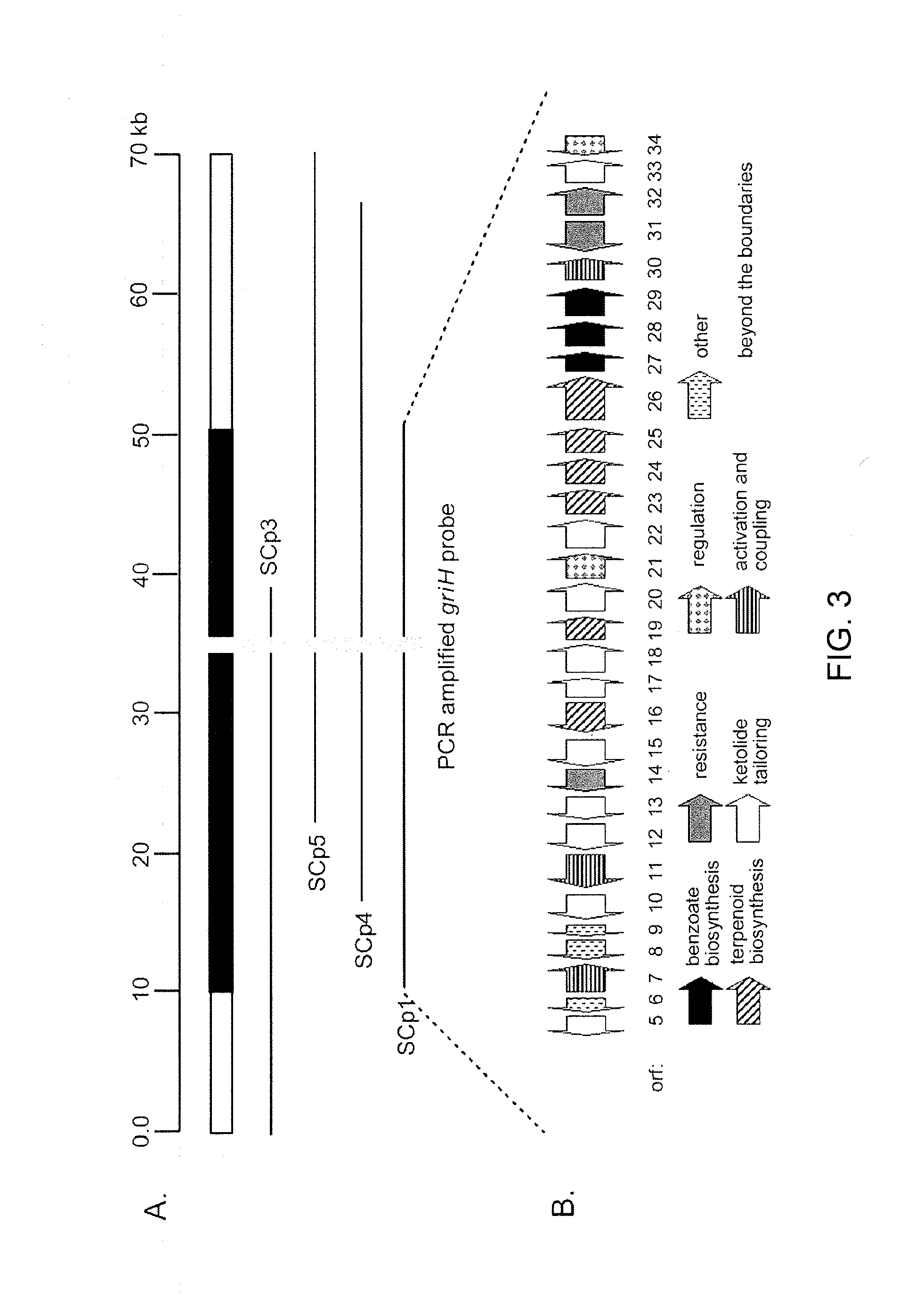
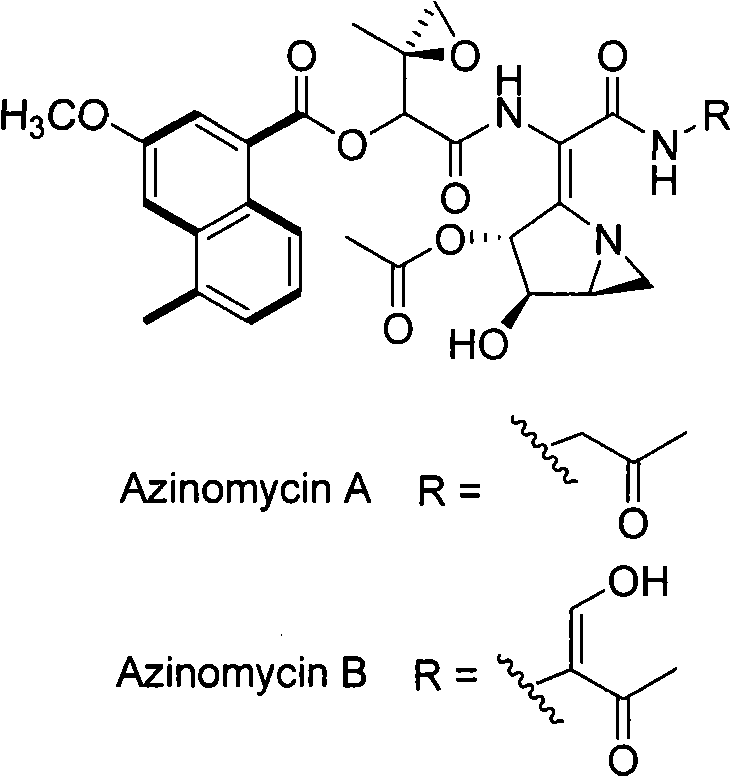
InactiveCN101275141AUnderstanding Biosynthetic MechanismsFermentationPlant genotype modificationHeterologousEnzyme Gene
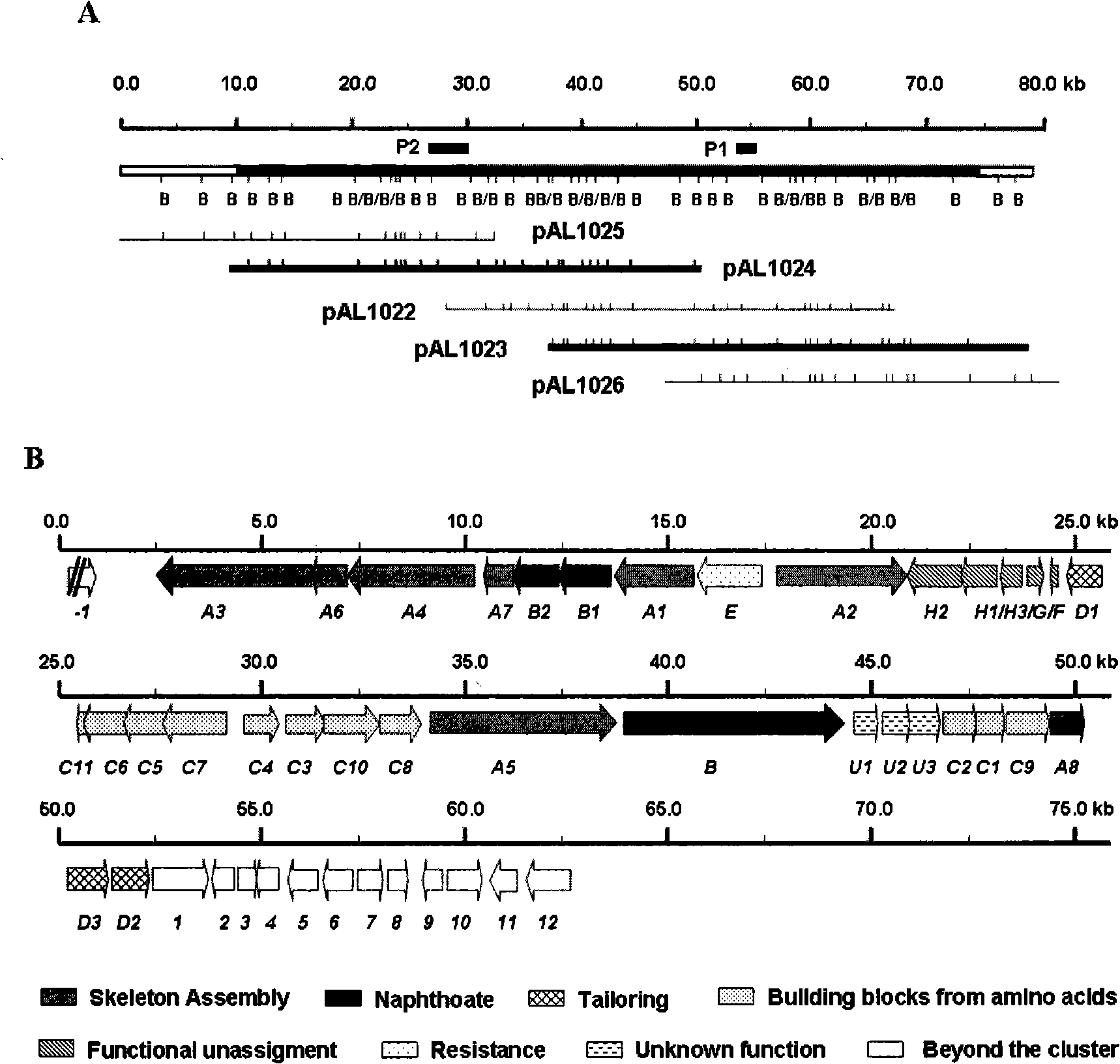
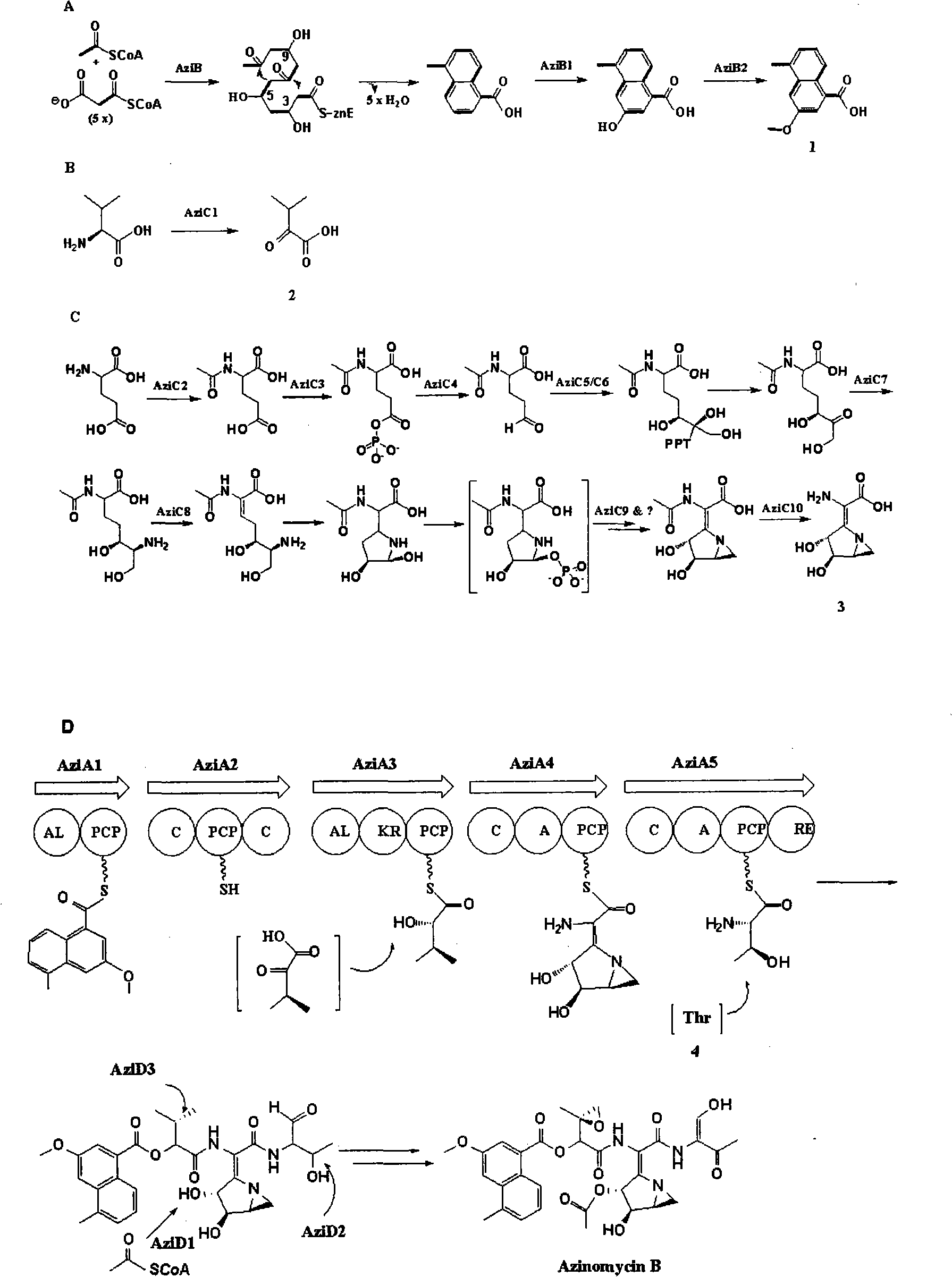
The present invention provides cloning sequencing, analyzing, function research of a biosynthesis gene cluster of an antibiotic-Azinomycin B having antitumor activity produced by streptomyces, and its application. The whole gene cluster includes 34 genes: one repeatedly using I type polyketide synthase gene; two naphthalene ring modification enzyme genes; 8 non-ribosomal polypeptide skeleton synthesis and modification enzyme genes; 11 non-natural amino acid structure unit synthase genes; 1 resistance gene; 3 post modification enzyme genes and 8 genes which functions are not determined. The genetic operation of the biosynthesis gene breaks the synthesis of Azinomycin B; the precursor compound is produced by the heterologous expression of synthesis gene and modification gene of naphthalene ring. The gene of the invention and the protein can be used for searching and finding compound or gene, protein applied in medical, industry or agriculture.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
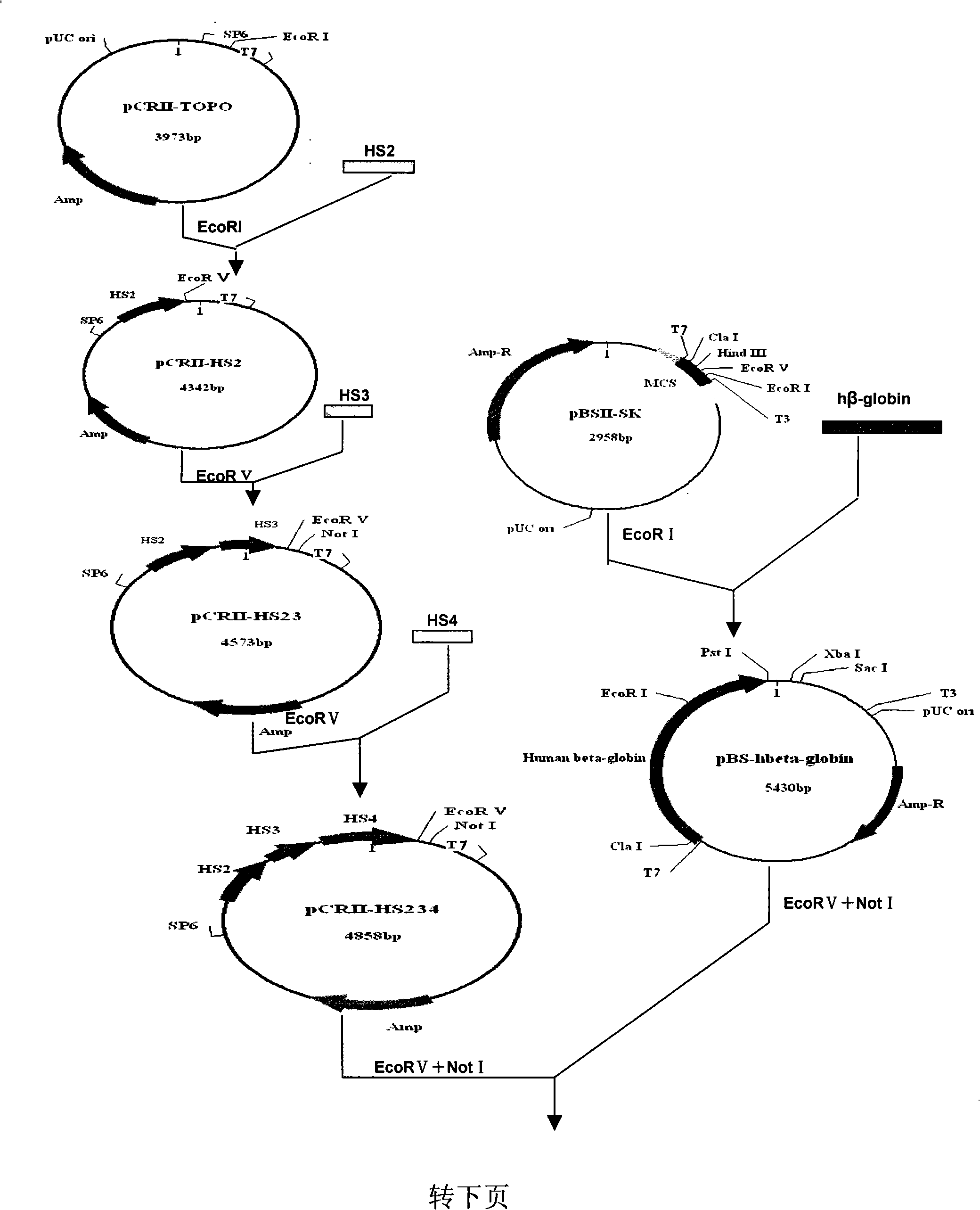
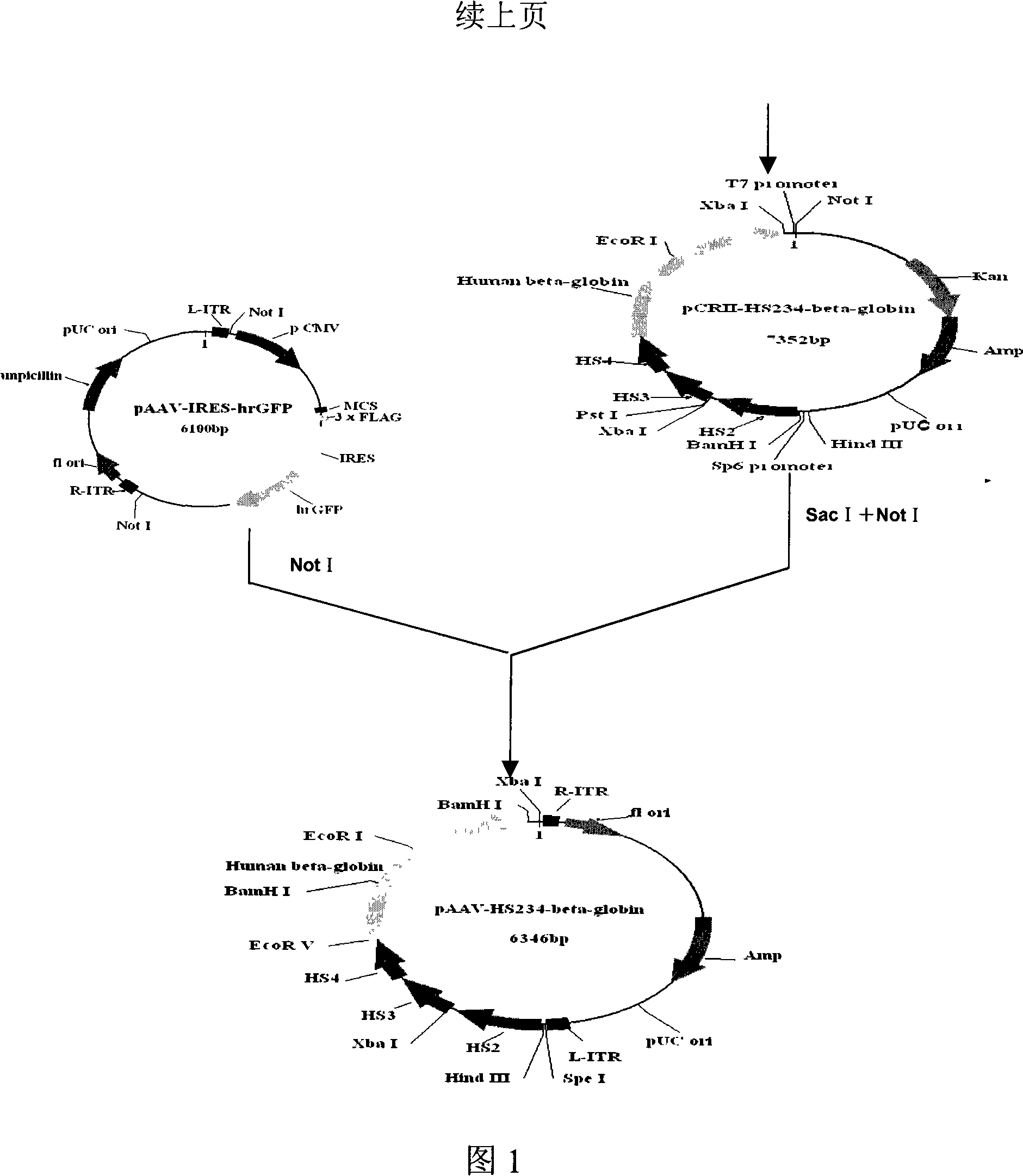
Human beta-globin gene and recombinant adeno related viral vector thereof
ActiveCN101348786AImprove expression efficiencyGenetic material ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsAdeno associate virusAdeno-associated virus
The invention discloses a human beta globin gene containing a human beta globin gene promoter, a recombinant adeno-associated virus vector containing the human beta globin gene, and a method for preparing the recombinant vector. The recombinant adeno-associated virus vector inserts an HS2 segment, an HS3 segment and an HS4 segment of a human beta globin gene cluster enhancer core sequence and a human beta globin gene sequence containing the human beta globin gene promoter into repeated sequence ITRs on the reverse terminal of an adeno-associated virus. The recombinant vector has high transfection efficiency; and mediated exogenous genes can be expressed in vivo for a long time, have good safety and can be used for gene therapy of beta Mediterranean anemia.
Owner:DONGGUAN ZHENGXING BEITE MEDICINE TECH CO LTD
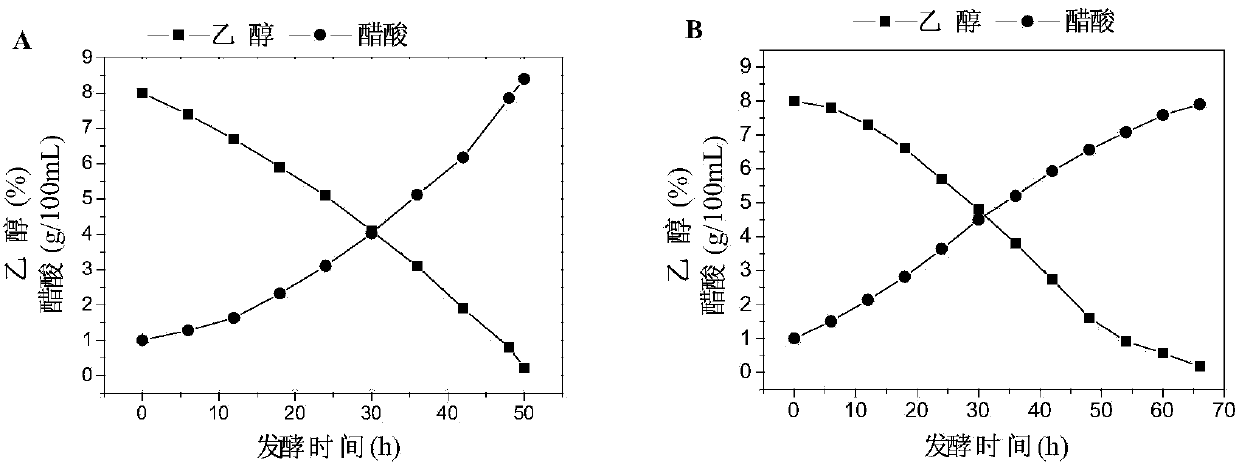
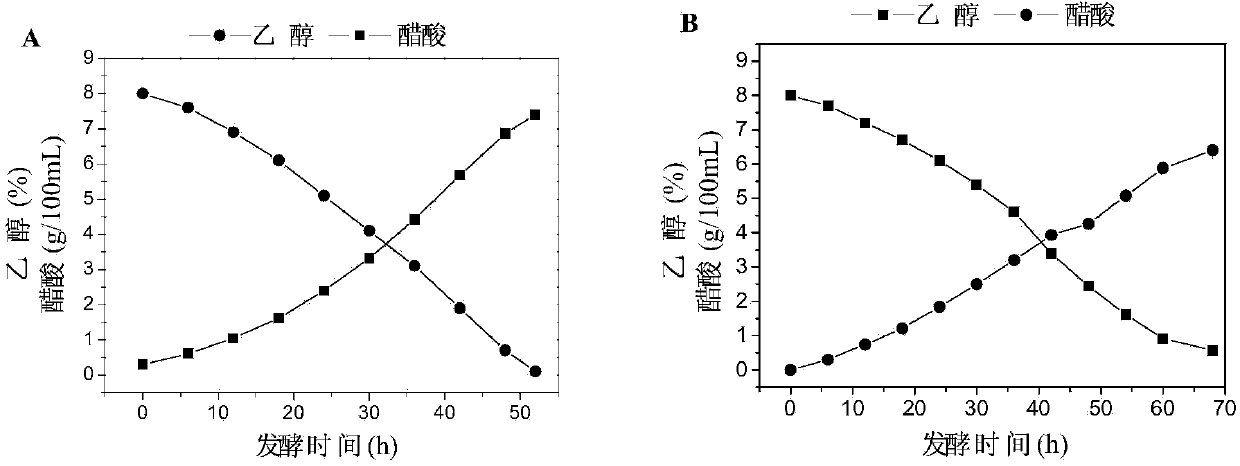
Genetic engineering acetic acid bacteria of overexpressing coenzyme PQQ (pyrroloquinoline quinone) synthetic proteins and application of bacteria
ActiveCN103740629AIncrease concentrationSimultaneous synthesisBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEthanol dehydrogenaseIn vivo
The invention relates to a building method of genetic engineering acetic acid bacteria of recombinantly expressing coenzyme PQQ (pyrroloquinoline quinone) synthetic proteins. The PQQ biosynthetic proteins are PqqA, PqqB, PqqC, PqqD, PqqE, and functional equivalents thereof. An alcohol dehydrogenase promoter from acetobacter pasteurianus and a coenzyme PQQ synthetic protein gene cluster pqqABCDE sequence are orderly connected into plasmids which can be stably copied in the acetic acid bacteria, so as to recombine pBBR-padh-pqq; recombinant plasmid pBBR-padh-pqq is transferred into the acetic acid bacteria, so as to obtain the genetic engineering acetic acid bacteria of overexpressing the coenzyme PQQ synthetic proteins. Thus, the concentration of in vivo coenzyme PQQ of the acetic acid bacteria in the fermentation process of acetic acid is improved. Acetic acid fermentation is carried out by using the genetic engineering bacteria disclosed by the invention, the fermentation delay phase can be shortened, and the fermentation rate of the acetic acid is increased. Thus, the production cost is reduced.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
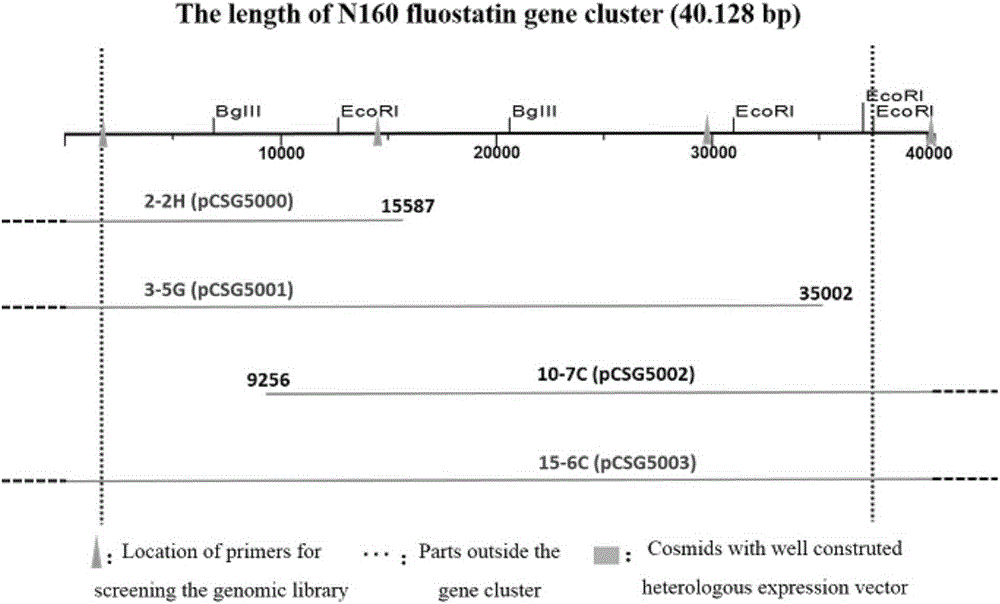
Biosynthetic gene cluster of romatic-polyketide atypical fluostatins and applications of biosynthetic gene cluster
The invention discloses a biosynthetic gene cluster of romatic-polyketide atypical fluostatins and applications thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the biosynthetic gene cluster of fluostatins derived from micromonospora rosaria SCSIO N160 (preservation No: CCTCC NO: M2012392) is shown in the 1st-40128th base sequences in SEQ ID NO. 1, and contains 32 genes. Genes and proteins thereof provided by the invention can be used for seeking and finding compounds or genes and proteins for medicine, industry or agriculture.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
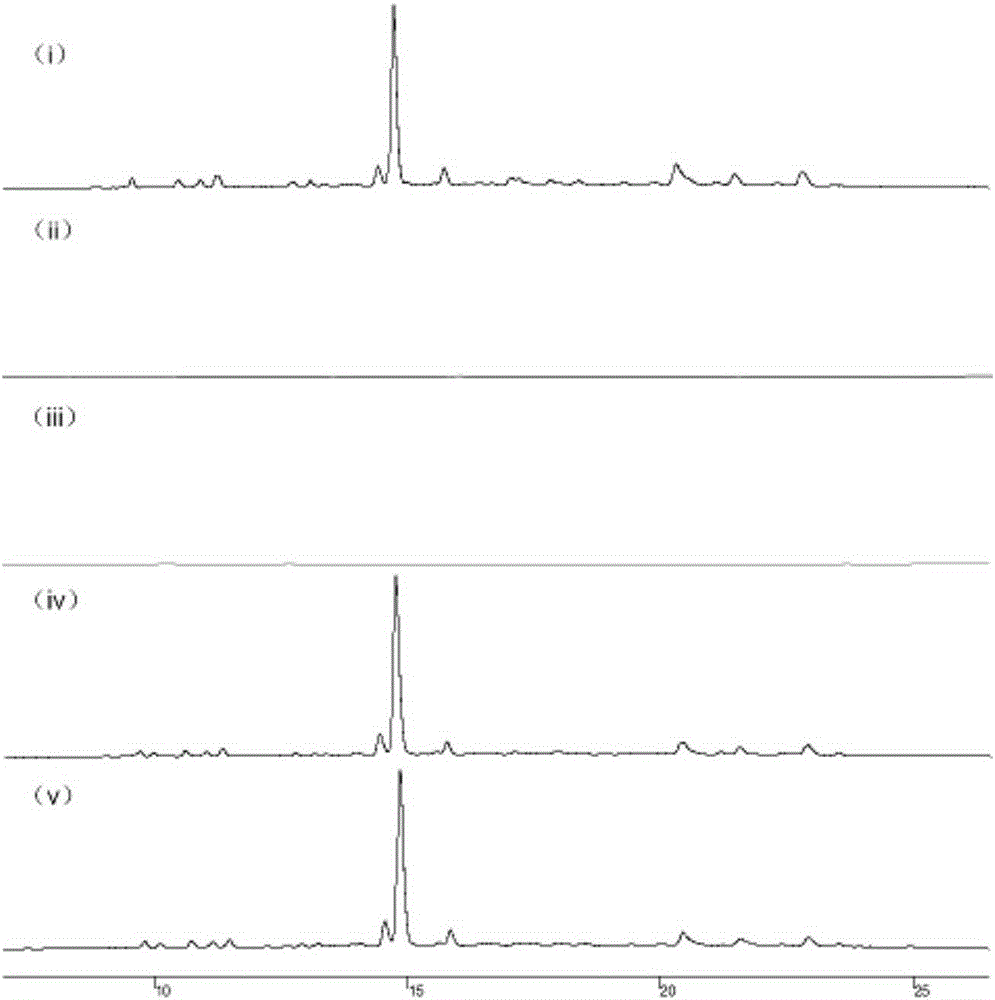
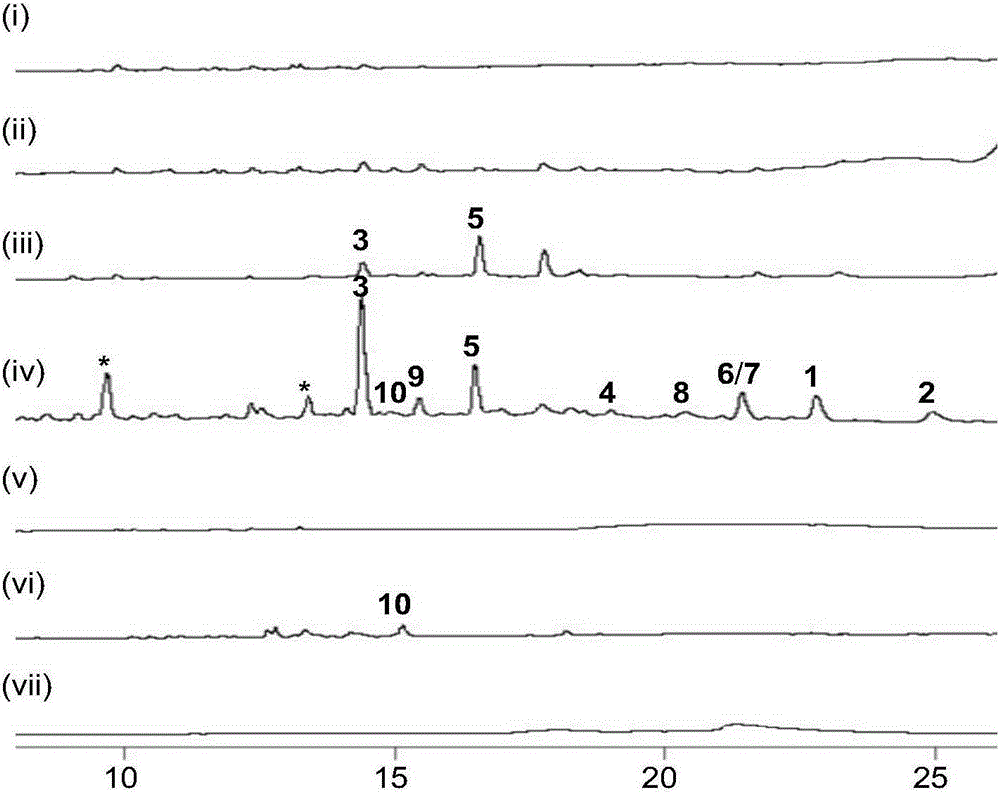
Directed evolution of synthetic gene cluster
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com