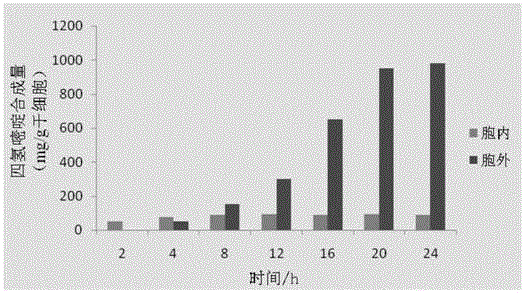
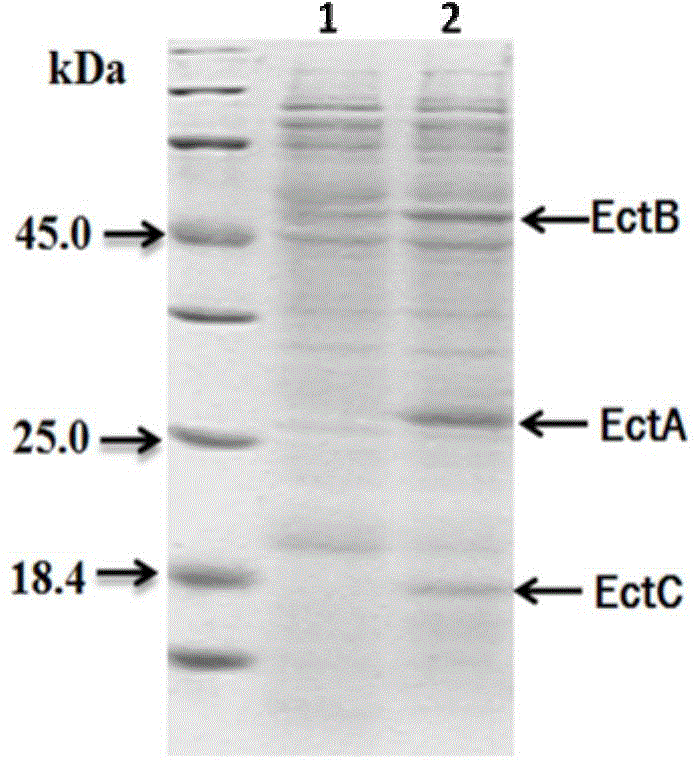
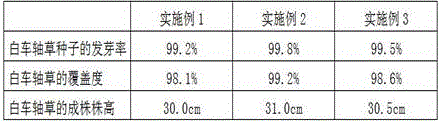
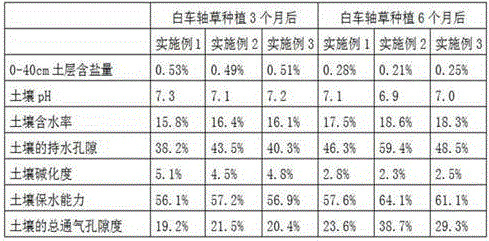
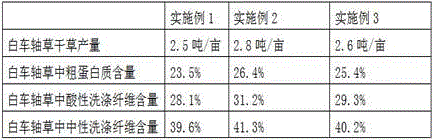
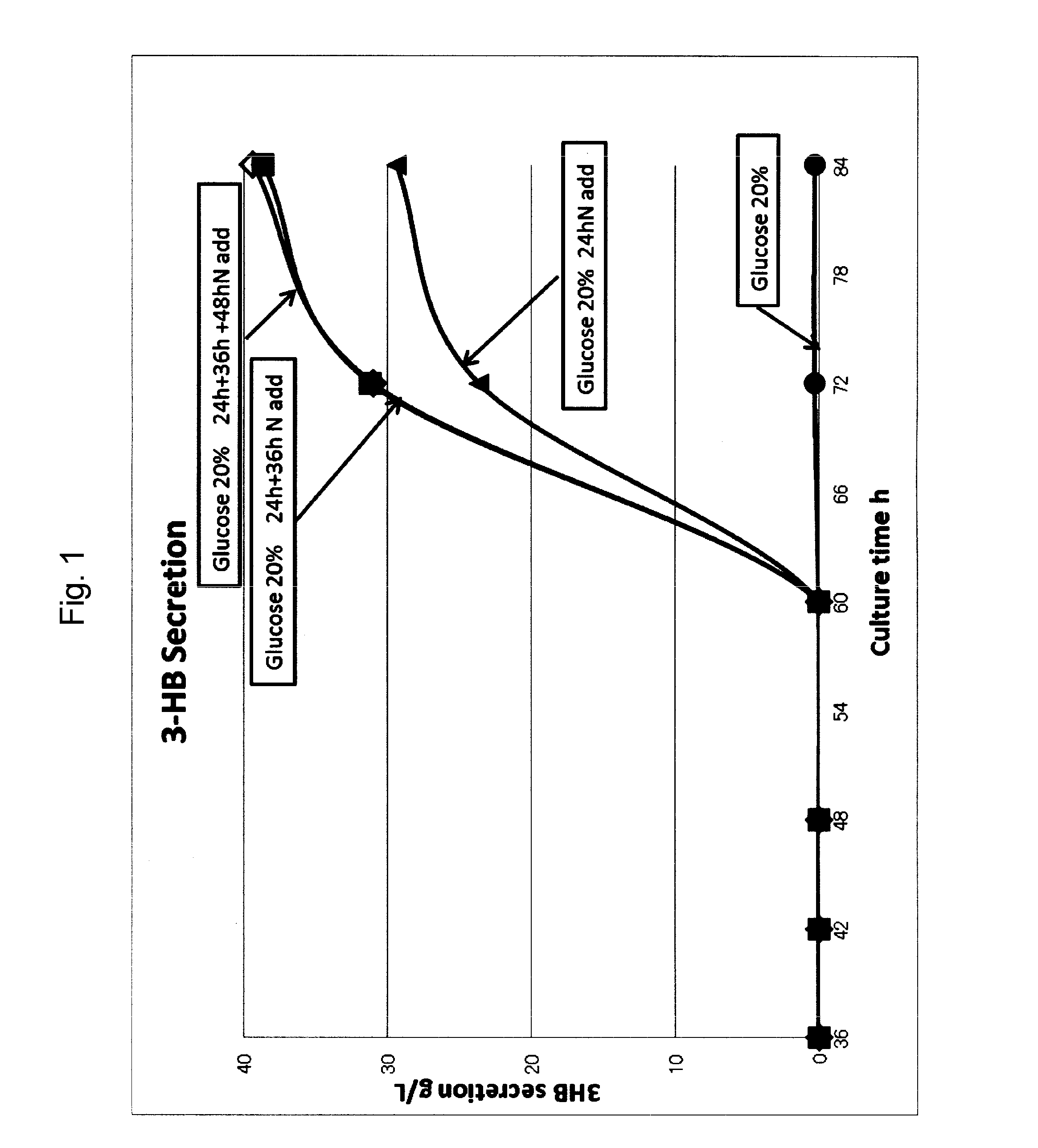
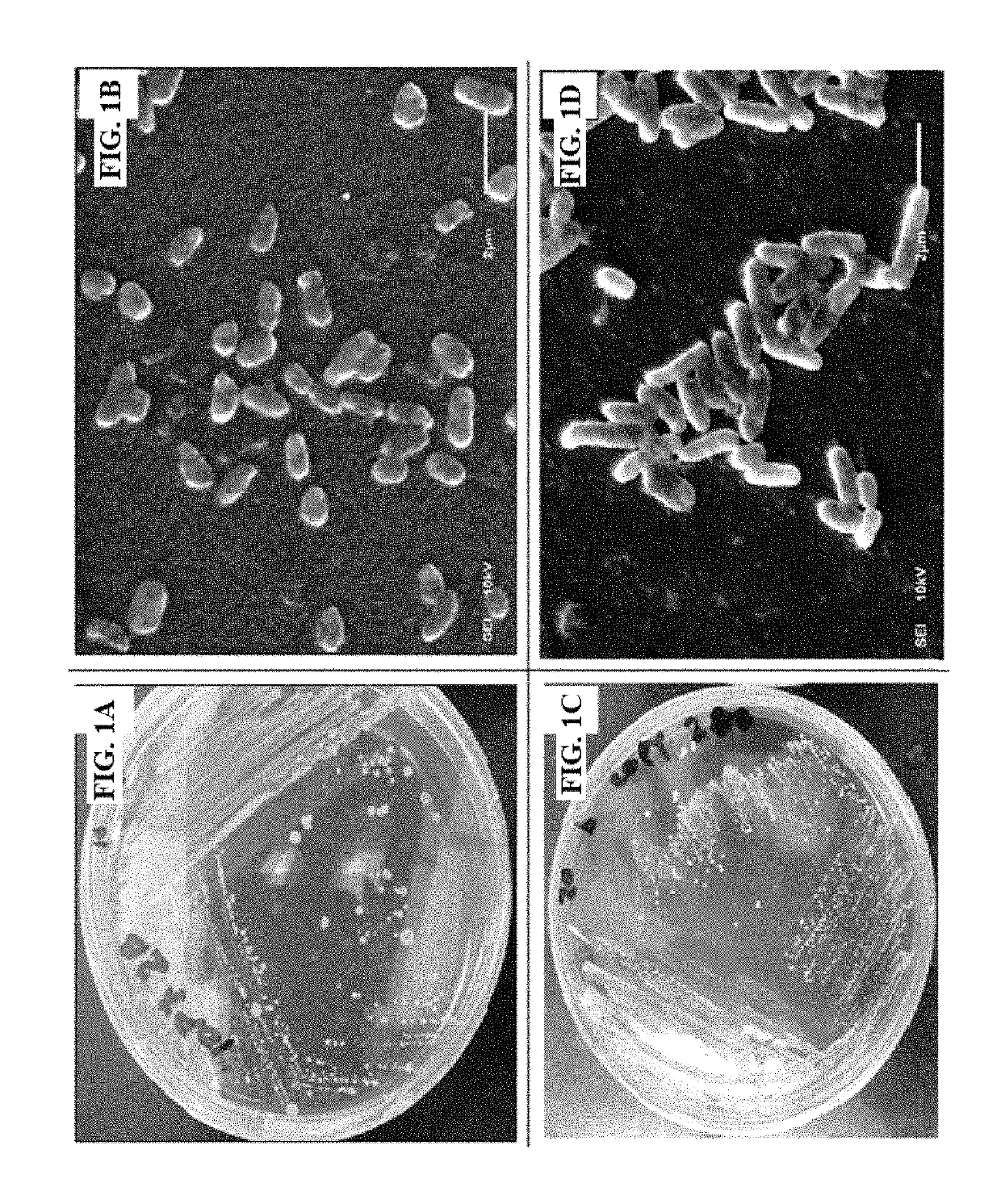
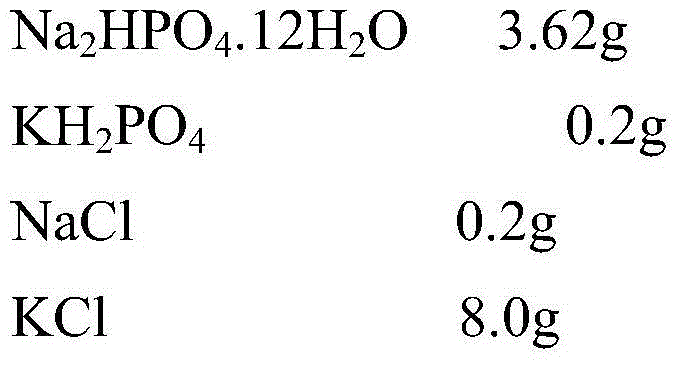Patents
Literature
52 results about "Halomonas" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Halomonas is a genus of halophilic (salt-tolerating) proteobacteria. It grows over the range of 5 to 25% NaCl. The type species of this genus is Halomonas elongata.
Halomonas strain and application thereof
ActiveCN102120973AIncrease productionReduce manufacturing costBacteriaFermentationBiotechnologyNutrient
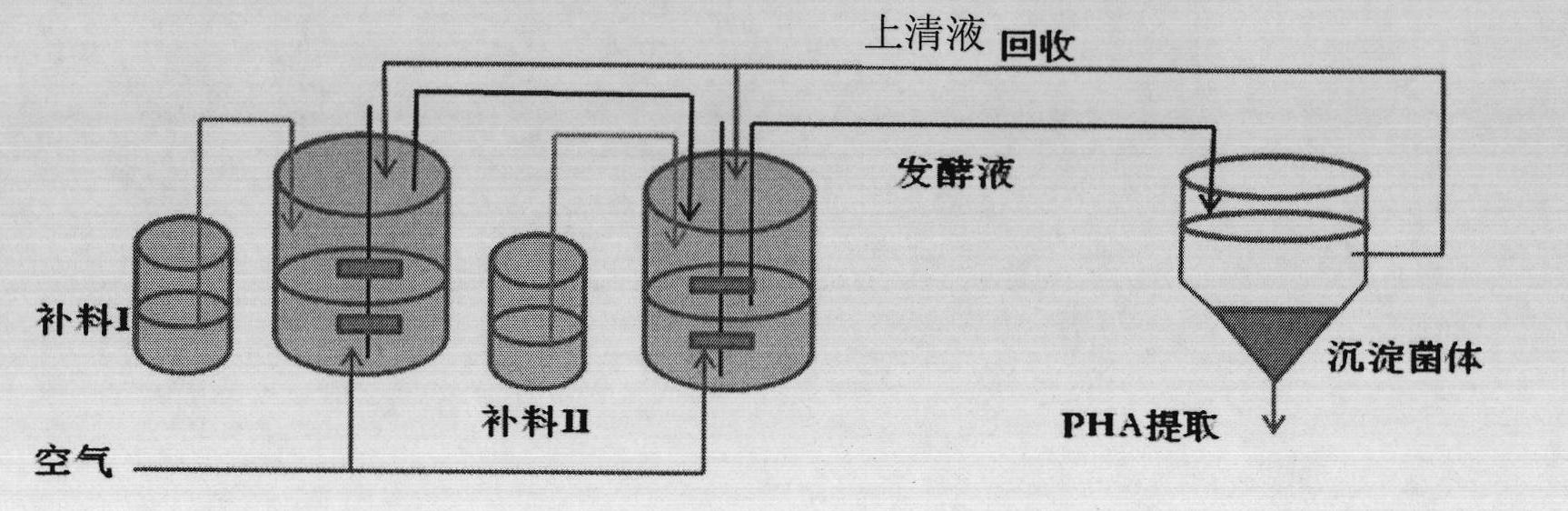
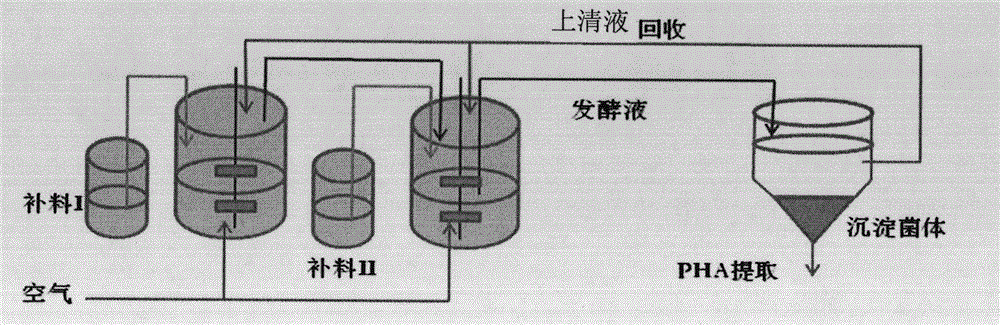
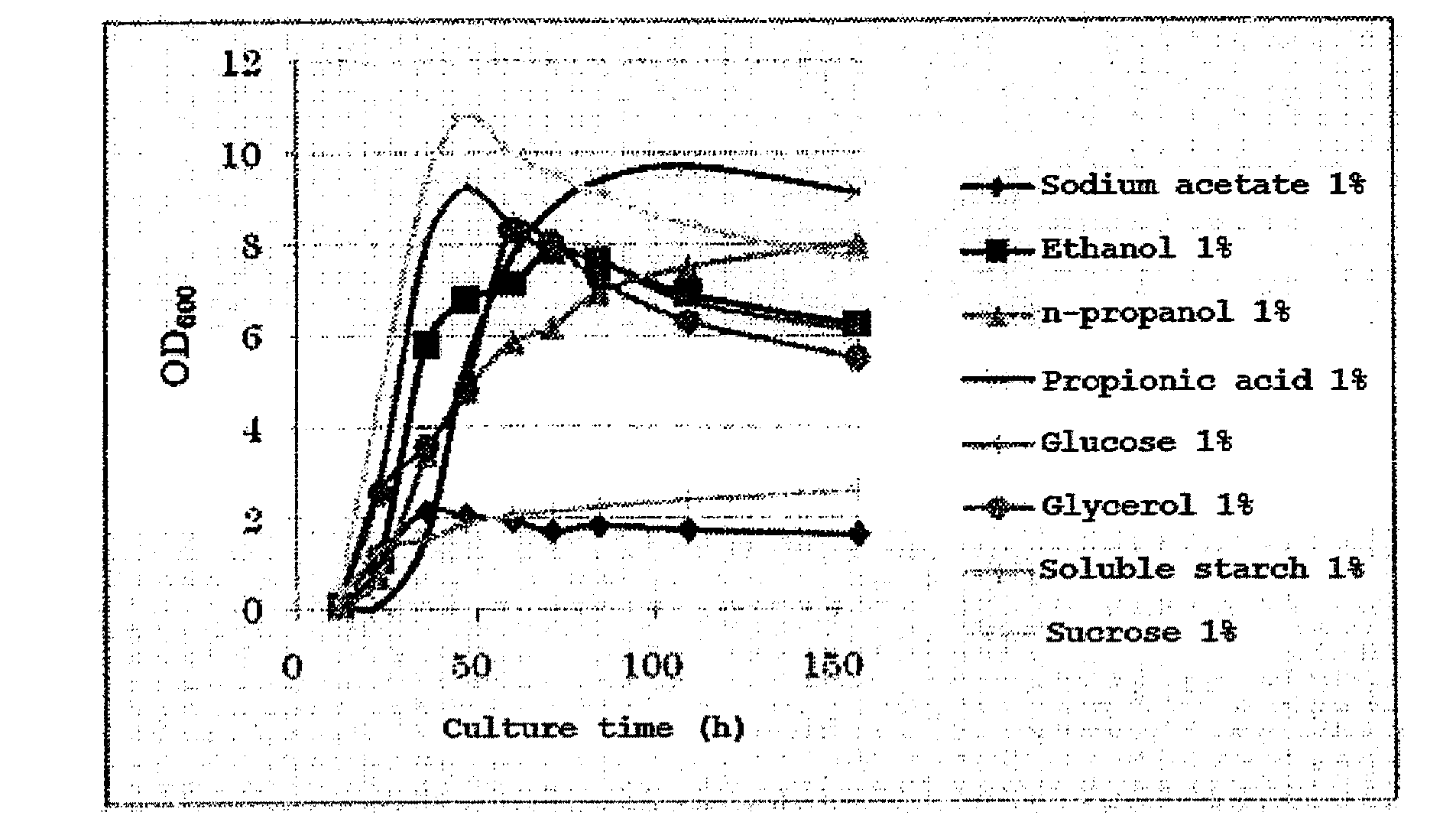
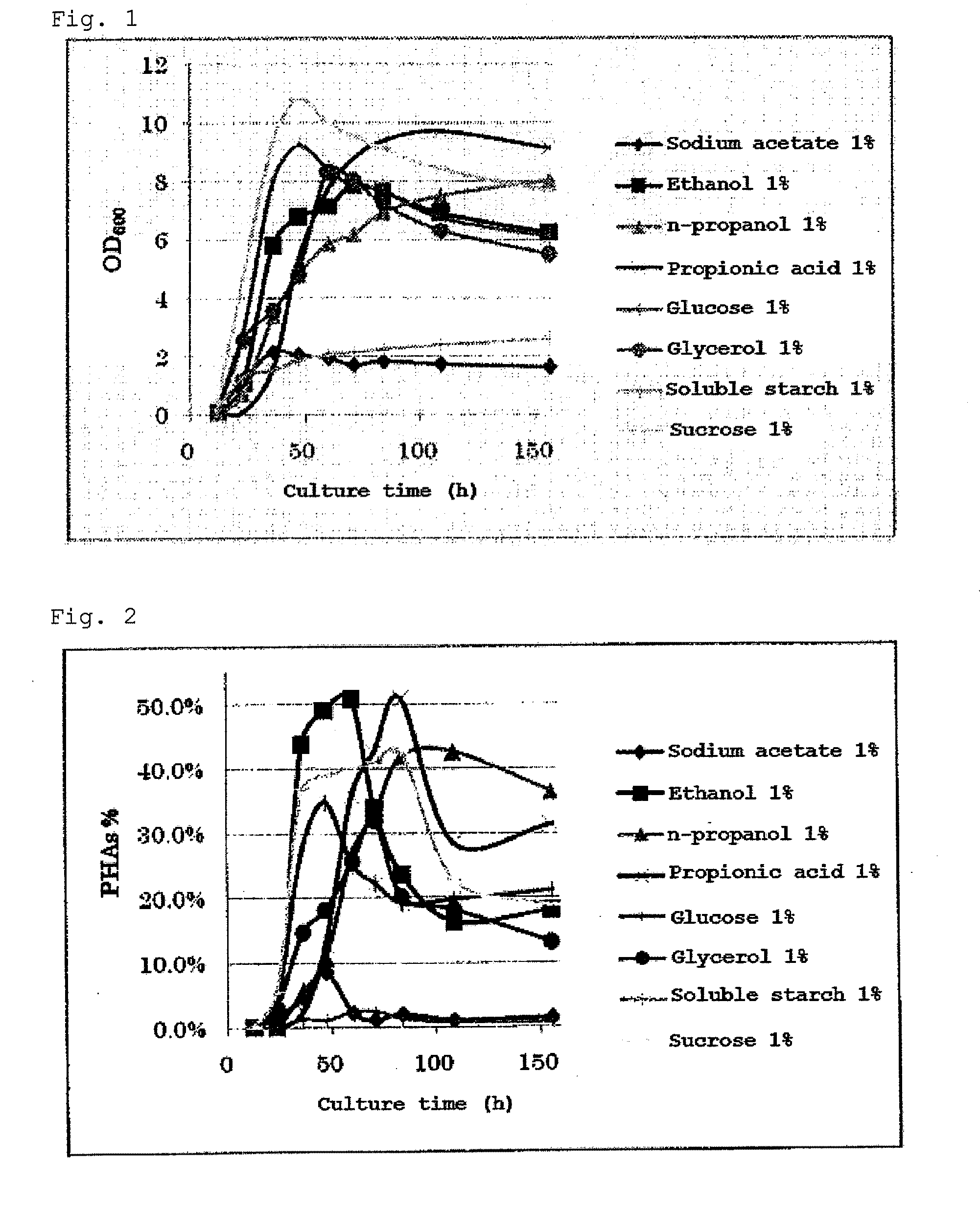
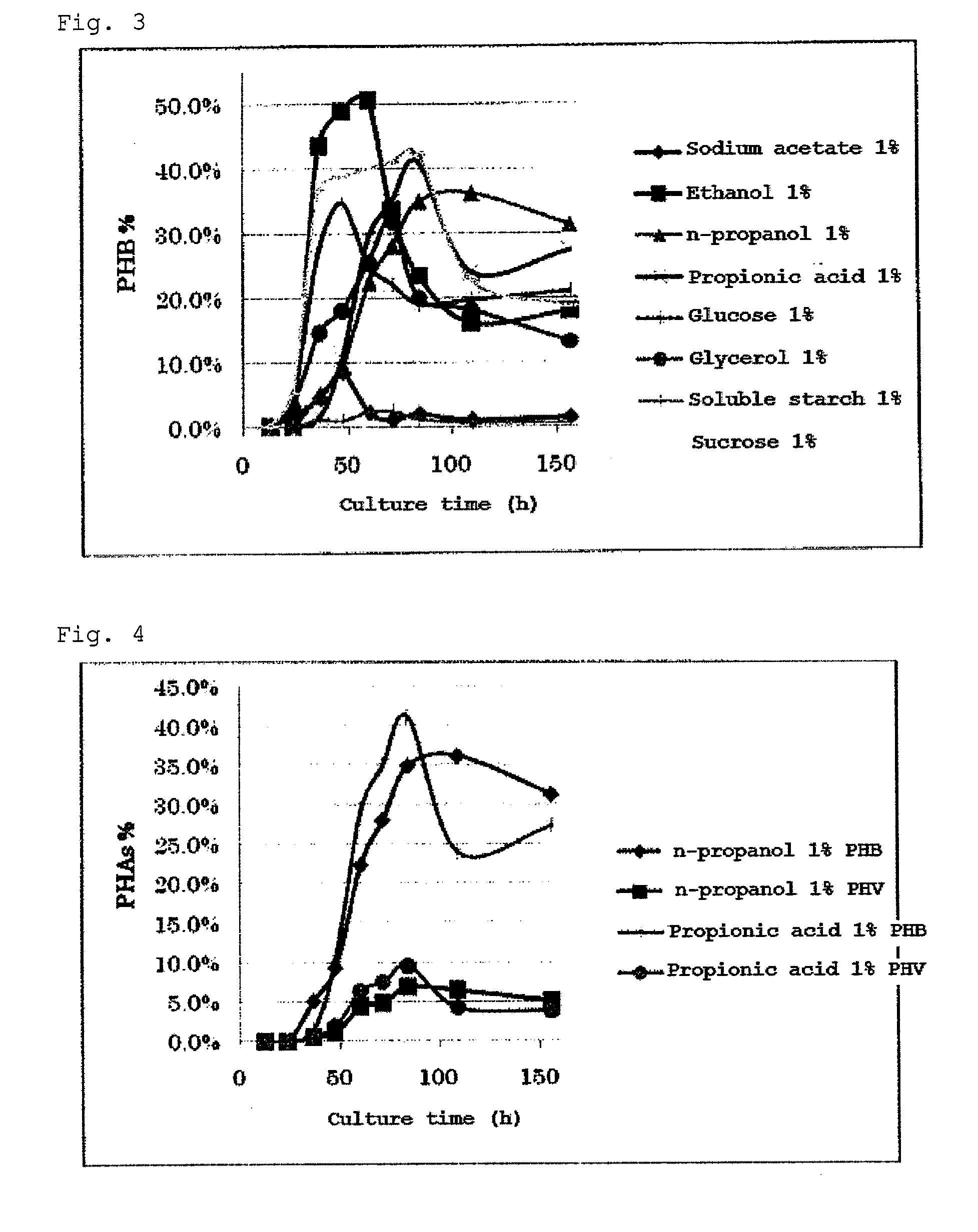
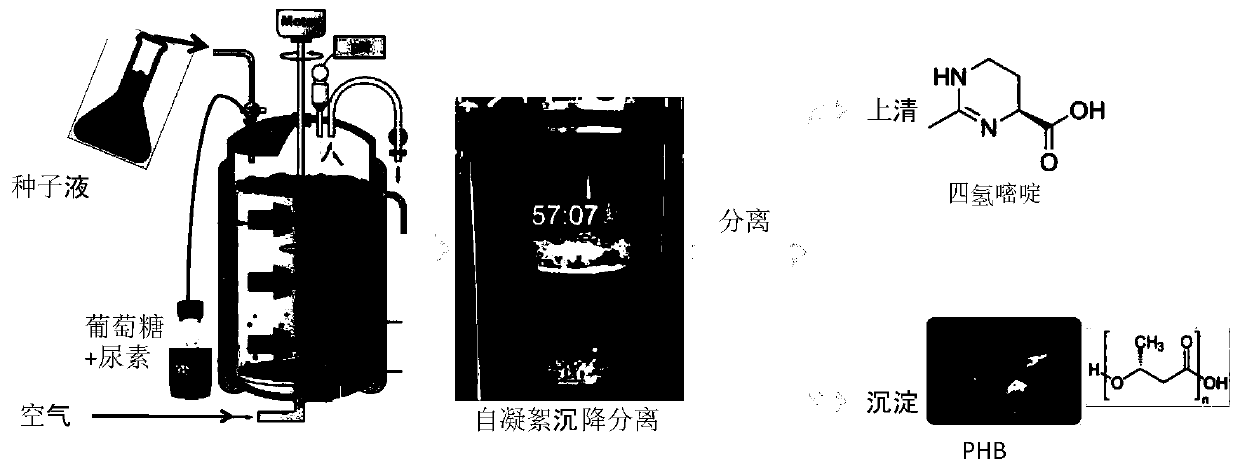
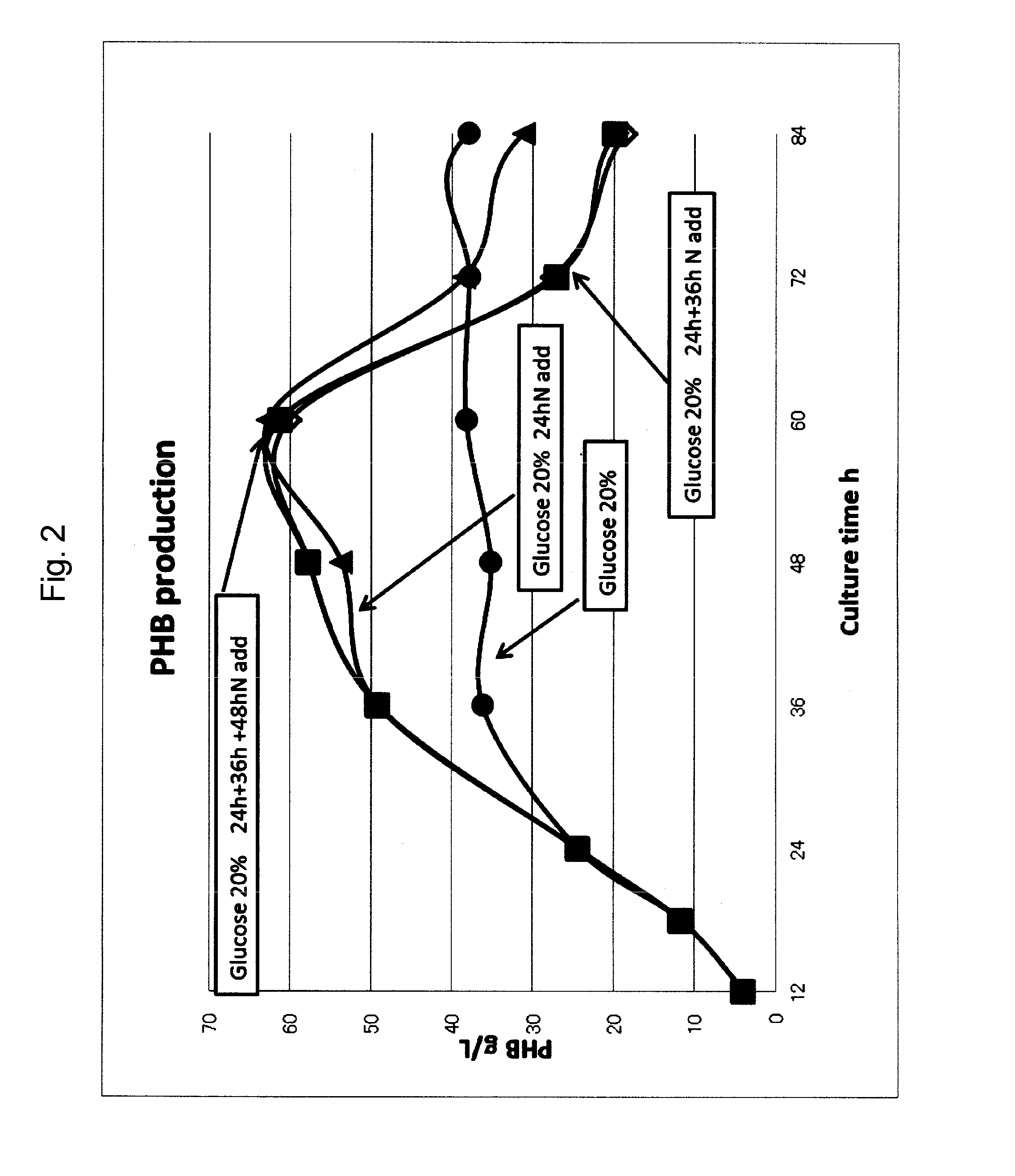
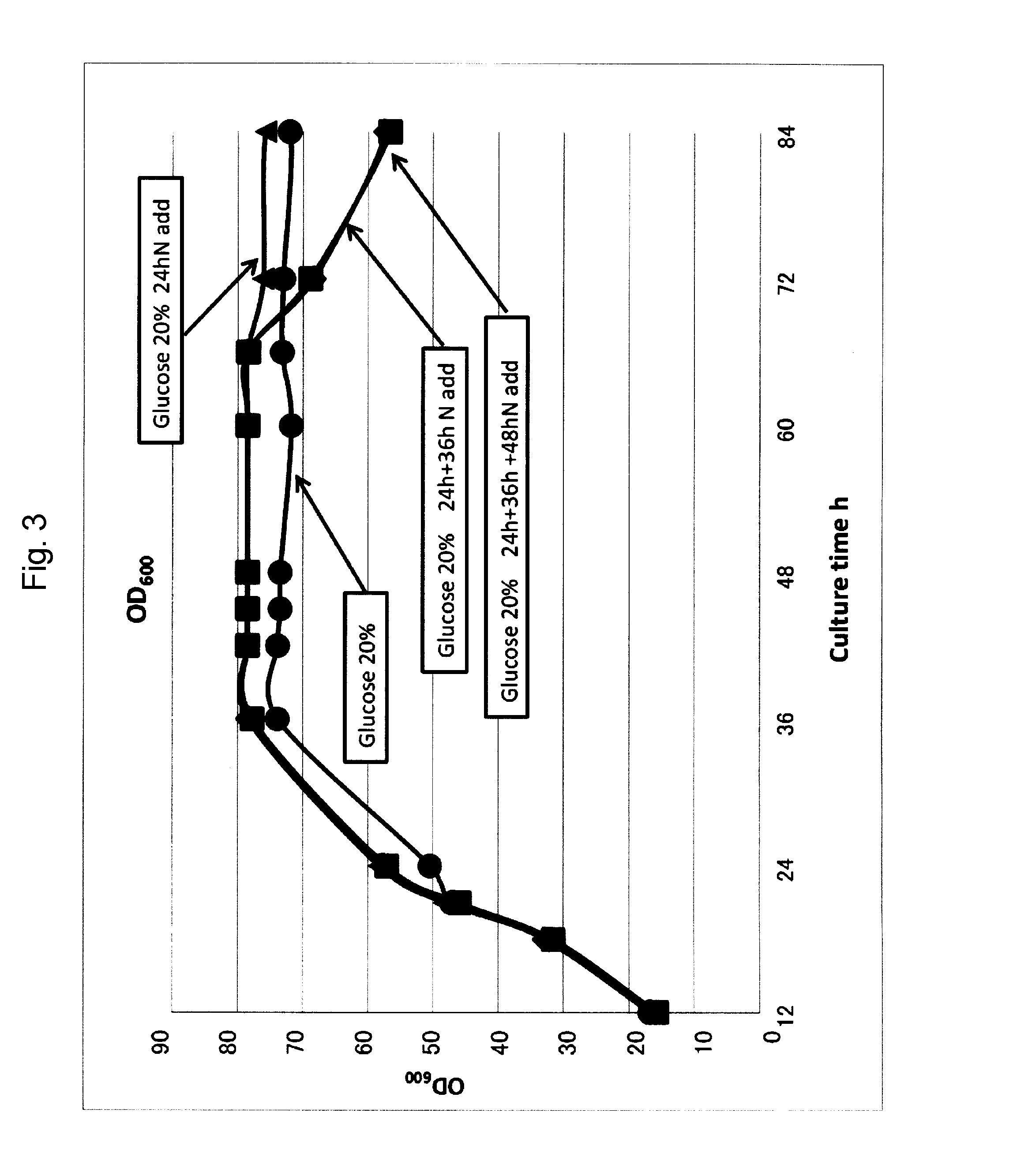
The invention discloses a halomonas strain and application thereof. The halomonas strain is a halomonas sp. TD01 with a preservation number of CGMCC NO.4353. Experiments indicate that the halomonas sp. TD01 can effectively accumulate polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) in a mineral medium (MM) and provides a better guarantee for the biosynthesis of the PHA and PHBV (poly(hydroxybutyrate-hydroxyvalerate)). The halomonas strain has the advantages of simple nutrient requirement, no need of sterilization in a fermenting process, capability of continuous implantation and simpleness and easiness in control. Methods for preparing the PHA by using the halomonas sp. TD01 all lower the production cost from varying degrees and increase the yield of the PHA; and the obtained PHA has the molecular weight of above 500kDa and has an industrial application value.
Owner:BLUEPHA CO LTD
Genetically engineered bacterium producing tetrahydropyrimidine and structuring method and application thereof
ActiveCN105018403AIncrease productivityLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesChemical synthesisBiotechnology
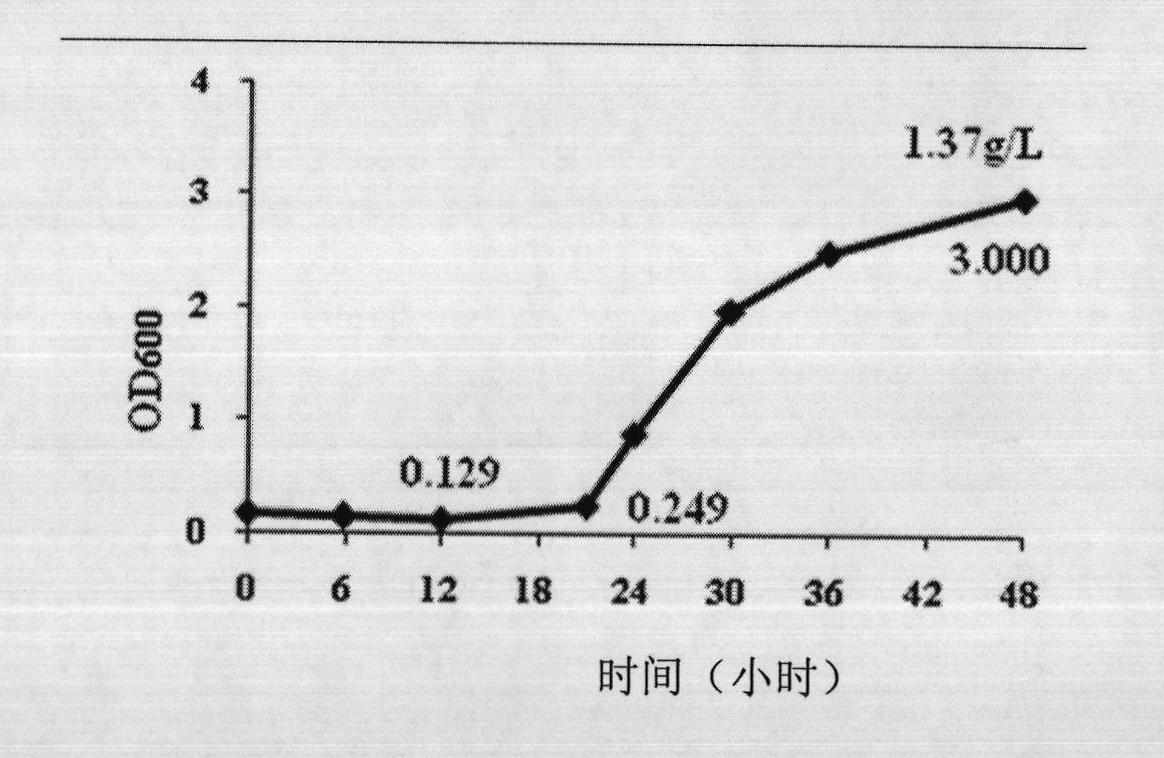
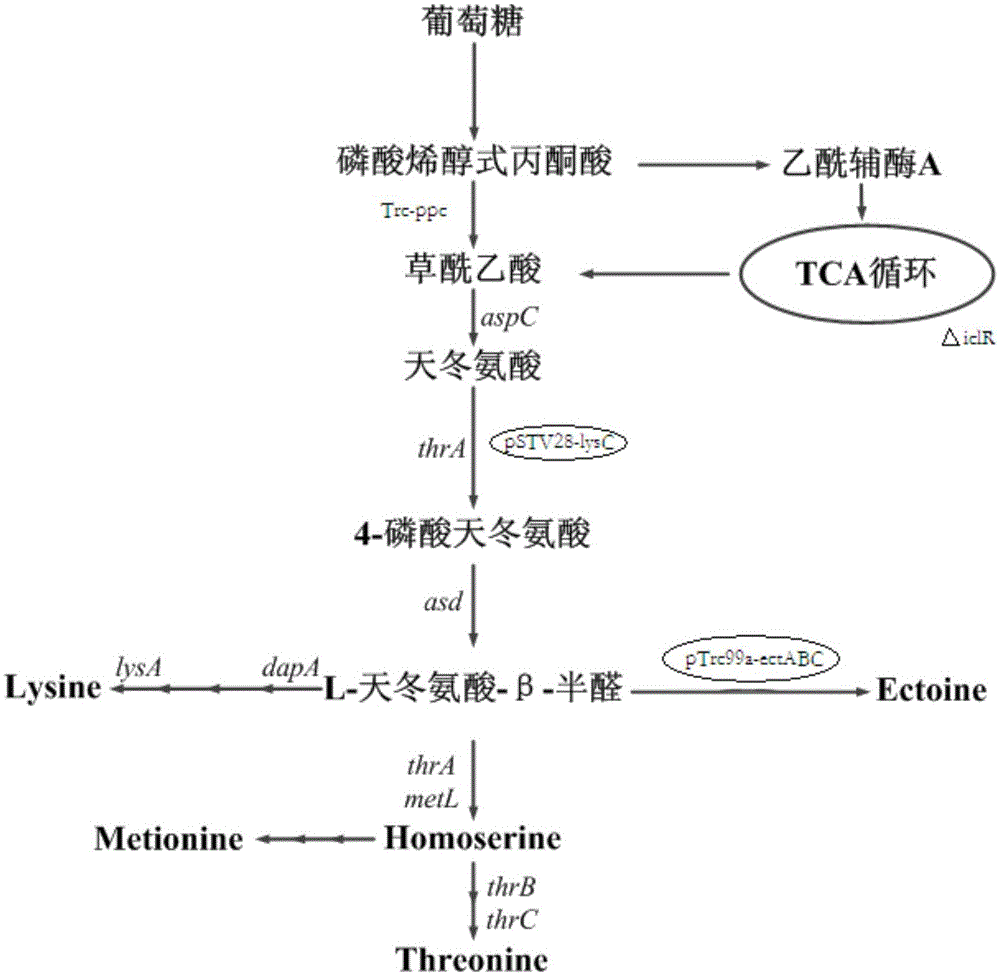
The invention relates to a genetically engineered bacterium producing tetrahydropyrimidine and a structuring method and application thereof. The genetically engineered bacterium is Escherichia coli with a specific genotype, comprises Halomonas-elogata-derived ectABC gene, has three gene deficiency variants including lysA, thrA and iclR and has corynebacterium glutamicum lysC gene controlled by a lac promoter and ppc gene controlled by a trc promoter. The defect that chemical synthesis methods have harsh reaction conditions and high energy consumption can be overcome by using the genetically engineered bacterium and utilizing glucose fermentation to produce tetrahydropyrimidine. The defect that Halomonas-elogata fermentation or enzyme-catalyzed methods are complex in process and high in production cost can be overcome. After fermentation for 20-28h, yield of tetrahydropyrimidine reaches 12-18g / L, and the genetically engineered bacterium has high industrial application value.
Owner:合肥和晨生物科技有限公司
Escherichia coli engineering bacterium for high-yield tetrahydropyrimidine and applications of escherichia coli engineering bacterium
ActiveCN104560844AHigh synthesis efficiencyFacilitate downstream purification and separationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliRecombinant escherichia coli
The invention provides a recombinant escherichia coli for high-yield tetrahydropyrimidine and a method for preparing tetrahydropyrimidine by using the recombinant escherichia coli. The recombinant escherichia coli provided by the invention is prepared by importing Halomonas elongate EctABC containing recombinant plasmids into escherichia coli. The recombinant escherichia coli disclosed by the invention realizes the soluble expression of three key enzymes synthesized by tetrahydropyrimidine under the adjustment and control of an arabinose promoter. Thalli subjected to induced expression implements the efficient secretory expression of tetrahydropyrimidine by taking sodium aspartate as a precursor through a bioconversion method. Thalli per gram can synthesize 1.1 grams of tetrahydropyrimidine, and more than 90% of tetrahydropyrimidine is secreted to extracellular receptors. The method for preparing tetrahydropyrimidine by using the recombinant escherichia coli provided by the invention facilitates the downstream purification and separation of products, and has great significance on the industrial production and large-scale application of tetrahydropyrimidine.
Owner:南京众惠生物材料科技有限公司
Genetically engineered bacterium for high-yield production of hydroxytetrahydropyrimidine as well as construction method and application of genetically engineered bacterium
InactiveCN108441460AIncrease productivityImprove growth traitsBacteriaTransferasesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention relates to a genetically engineered bacterium for high-yield production of hydroxytetrahydropyrimidine as well as a construction method and application of the genetically engineered bacterium. The strain integrates RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) polymerase which is controlled by a xylose promoter and is derived from T7 bacteriophage; a thrA gene for encoding homoserine dehydrogenase I is knocked out; a lysC gene derived from corynebacterium glutamicum, an ectABC gene cluster derived from halomonas elongate and an ectD gene for encoding tetrahydropyrimidine hydroxylase are integrated andare promoted by a strong promoter PT7; a hydroxytetrahydropyrimidine synthesis way is reconstructed; the ectD gene is integrated at a sucCD site of succinyl coenzyme A synthetase and is started by thestrong promoter PT7; the genetically engineered bacterium has the highest level of producing the hydroxytetrahydropyrimidine by a fermentation method which is reported at present.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Halomonas strain and application thereof
ActiveCN102120973BIncrease productionReduce manufacturing costBacteriaFermentationBiotechnologyNutrient
The invention discloses a halomonas strain and application thereof. The halomonas strain is a halomonas sp. TD01 with a preservation number of CGMCC NO.4353. Experiments indicate that the halomonas sp. TD01 can effectively accumulate polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) in a mineral medium (MM) and provides a better guarantee for the biosynthesis of the PHA and PHBV (poly (hydroxybutyrate-hydroxyvalerate)). The halomonas strain has the advantages of simple nutrient requirement, no need of sterilization in a fermenting process, capability of continuous implantation and simpleness and easiness in control. Methods for preparing the PHA by using the halomonas sp. TD01 all lower the production cost from varying degrees and increase the yield of the PHA; and the obtained PHA has the molecular weight of above 500kDa and has an industrial application value.
Owner:BLUEPHA CO LTD
Saline-alkaline tolerant microbial flora and applications thereof
ActiveCN104403967AWide adaptabilityStable adaptabilityWaste water treatment from quariesBacteriaEndurance capacityHazardous substance
The invention provides a saline-alkaline tolerant compound active microbial flora, which is used to process waste drilling well slurry and oil-containing slurry with a high saline-alkaline content. The provided saline-alkaline tolerant active microbial flora contains shewanella mac donell, pseudomonas, and halomonas, wherein the preferable number ratio of shewanella mac donell to pseudomonas to halomonas is 4:3:1. The provided flora has a strong endurance capacity on pH and salt content, and can well adapt to the various environments of waste slurry in drilling well and soil polluted by petroleum. The additives and harmful substances in the waste slurry do not have a prominent inhibition effect on the active microbial flora. The growth speed of the flora is quick, the activity of the flora is stable, and the adaptability of the flora is strong. The production cost is low. The flora can be applied to the biodegradation of waste slurry in drilling wells, repairmen of environment destroyed by petroleum, and chemical engineering industry. The provided flora can increase the biodegradation efficiency on slurry in drilling wells and further improve the related processing technology.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
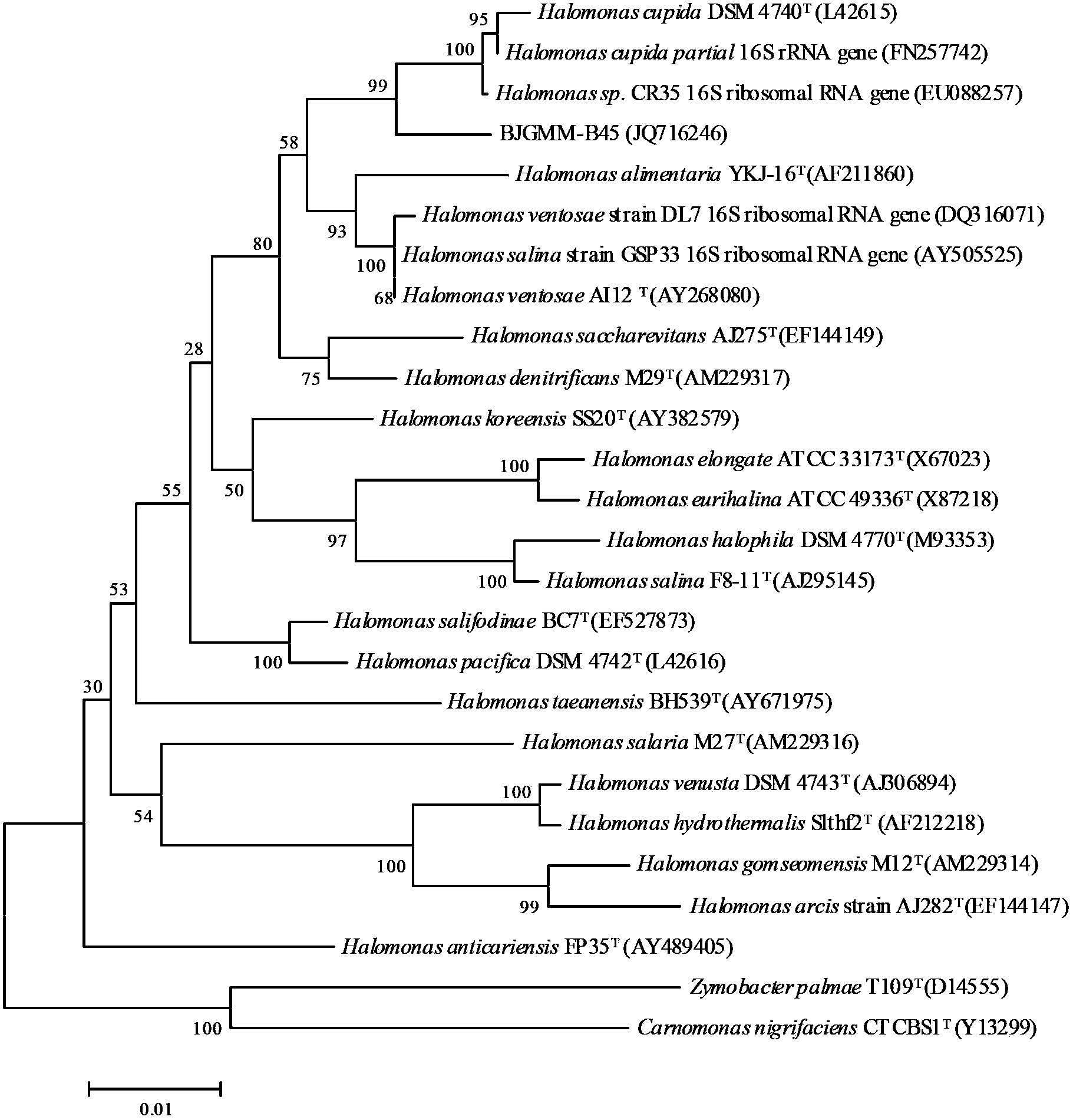
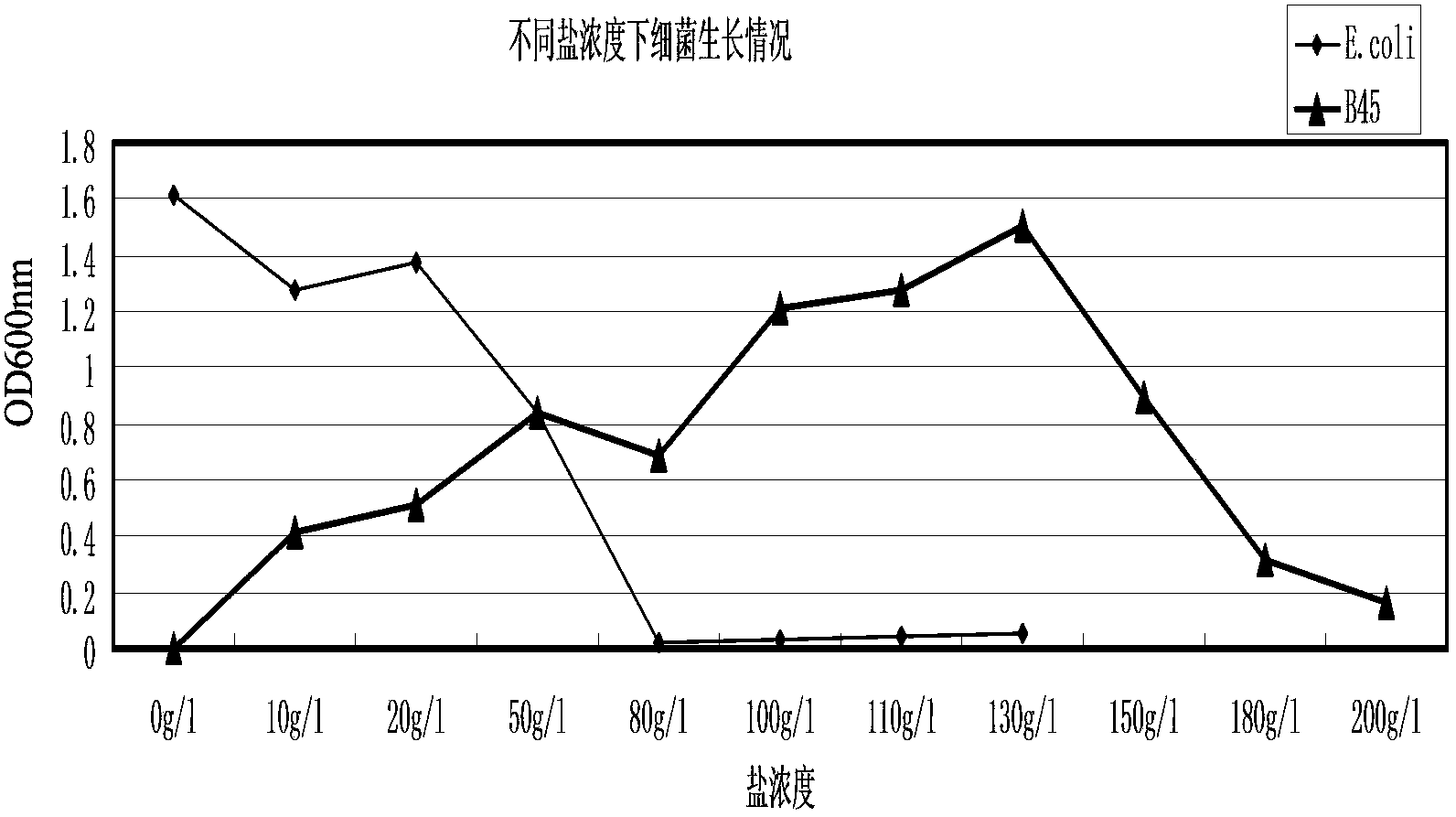
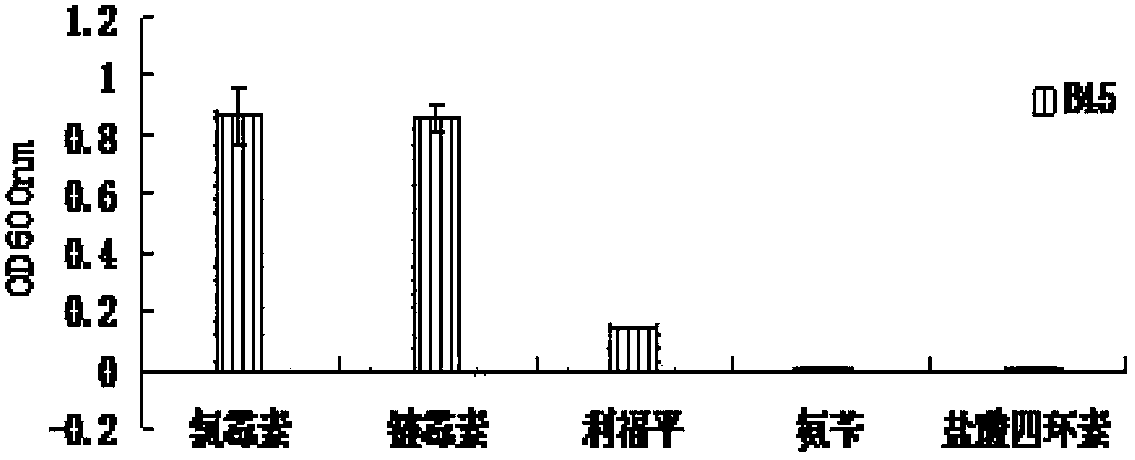
Halomonas huanghegensis BJGMM-B45 and application thereof
InactiveCN103805531AGood characterImproved stress resistance traitsAgriculture tools and machinesBacteriaBiotechnologyAlkali soil
The invention provides a bacteria halomonas huanghegensis BJGMM-B45, which has excellent salt tolerance. The preservation number of the halomonas huanghegensis BJGMM-B45 is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) NO.7022. The bacteria not only can be directly used as functional bacteria for improvement of saline-alkali soil, but also can be used as a gene donor of a novel transgenic organism; the organism can obtain excellent stress resistance if an excellent salt tolerance gene is transferred into the organism; in addition, the bacteria also can be used as a novel gene engineering bacteria, and can obtain more excellent properties by accepting other foreign excellent genes; furthermore, more mutant strains with excellent properties can be obtained through improvement of properties by traditional mutation breeding manner.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
High-salinity nitrogen-containing wastewater stress resistance auxiliary nitrogen removal method
ActiveCN106754504ASolve the problem of low nitrogen removal efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesOxygenSeawater
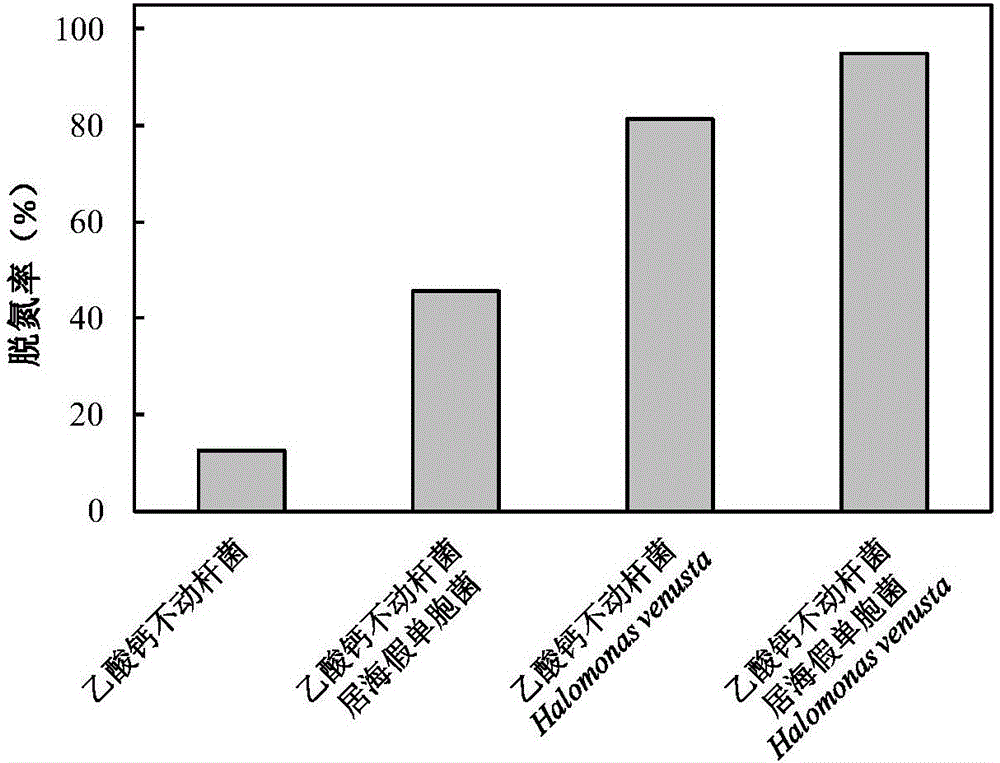
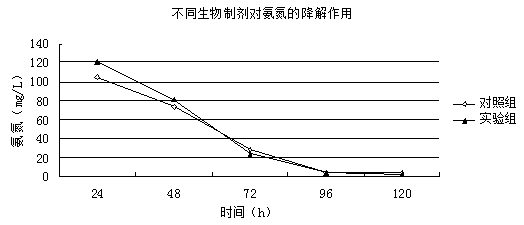
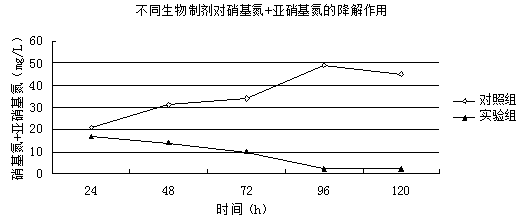
The invention discloses a high-salinity nitrogen-containing wastewater stress resistance auxiliary nitrogen removal method, and belongs to the technical field of microorganism nitrogen removal. By constructing a tetrahydro-2-pyrimidinone secreting type halomonas meridian and traditional denitrifier strain combined stress resistance auxiliary synchronous heterotrophic nitrification aerobic denitrification nitrogen removal mode, the high-salinity nitrogen-containing wastewater nitrogen removal technology is provided. The problem that according to existing high-salinity nitrogen-containing wastewater nitrogen removal, the nitrogen removal efficiency is low due to inhibition of high salinity on denitrifier strain growth and metabolism is solved, and the application prospect on the aspects of high-salinity nitrogen-containing wastewater treatment and seawater aquatic water purification is achieved.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
METHOD FOR PRODUCING POLYHYDROXYALKANOATE (PHAs) USING HALOBACTERIUM AND HALOBACTERIUM
ActiveUS20110104767A1High salt concentrationImprove the use environmentBacteriaUnicellular algaeInorganic saltsHalobacterium
Disclosed are a method for producing polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) using a halobacterium belonging to the genus Halomonas, wherein the halobacterium can grow in a medium consisting of an inorganic salt and a single organic carbon source and having a pH of 8.8 to 11, and produce PHAs in an amount of 20 wt. % or more based on the dry cell weight, and the halobacterium is cultured in an alkaline medium containing an inorganic salt and one or more organic carbon sources to produce PHAs in an amount of 20 wt. % or more based on the dry cell weight; and the halobacterium belonging to the genus Halomonas, which can grow in a medium consisting an inorganic salt and a single organic carbon source and having a pH of 8.8 to 11, and produce PHAs in an amount of 20 wt. % or more based on the dry cell weight.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Strain for producing alginate lyase and use thereof
ActiveCN103911315AReduce manufacturing costSimple ingredientsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses a strain for producing alginate lyase and a use thereof. The strain is preserved in the China general microbiological culture collection center on October 9, 2013, has an accession number of CGMCC No.8312 and is named as Halomonas elongata SH-19. A 16S rDNA polynucleotide sequence of the strain is shown in the formula of SEQ ID No.1. The strain SH-19 can efficiently express alginate lyase and can be used for high-efficiency production of alginate lyase. A strain SH-19 fermentation medium comprises simple ingredients commonly used in a laboratory, has substantial fermentation effects, greatly reduces an alginate lyase production cost and can be used for large-scale production.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Biochemical coupling-effect blocking remover and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110951472AWith oil displacement functionRestore permeabilityDrilling compositionSodium acetateMicrobial oil
The invention discloses a biochemical coupling-effect blocking remover and a preparation method thereof, and relates to the technical field of preparation of blocking removers. The blocking remover comprises a chemical composite blocking remover and a microbial oil displacement blocking remover; the chemical composite blocking remover is composed of the following raw material components: sodium polyepoxysuccinate, sodium ethylene diamine tetracetate, ammonium hydroxysuccinate, diisobutyl methanol, sodium allysulfonate, sodium lignin sulfonate and sodium succinic acid ester sulfonate. The microbial oil displacement blocking remover is composed of the following raw material components: halomonas, bacillus subtilis, bacillus chlamydosporium and pseudomonas. The blocking remover disclosed by the invention not only has an oil displacement function, but also has a blocking removing function of dissolving organic and inorganic blocking substances of stratum and recovering the permeability ofan oil layer; after the blocking remover enters the stratum, no by-product is generated, various material scales can be rapidly dissolved, and blocking removing products and working fluid do not needto flow back; the corrosion rate is less than 0.9 g / m<2>*h, the highest scale dissolving rate can reach 95%, and the highest rock core permeability recovery rate can reach 93.79%.
Owner:李国斌
Cosmetic composition containing halomonas ferment extract, and use thereof
ActiveUS20170224602A1Improve cell communicationCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsMedicineBacterial strain
Ferment extract and exopolysaccharide of a bacterial strain for its use in treatment and / or care of the skin, as well as its cosmetic and / or dermopharmaceutical compositions. In particular, its use for skin aging, skin firmness and hydration.
Owner:LUBRIZOL ADVANCED MATERIALS INC
Self-flocculation halomonas aydingkolgenesis M1 and application thereof
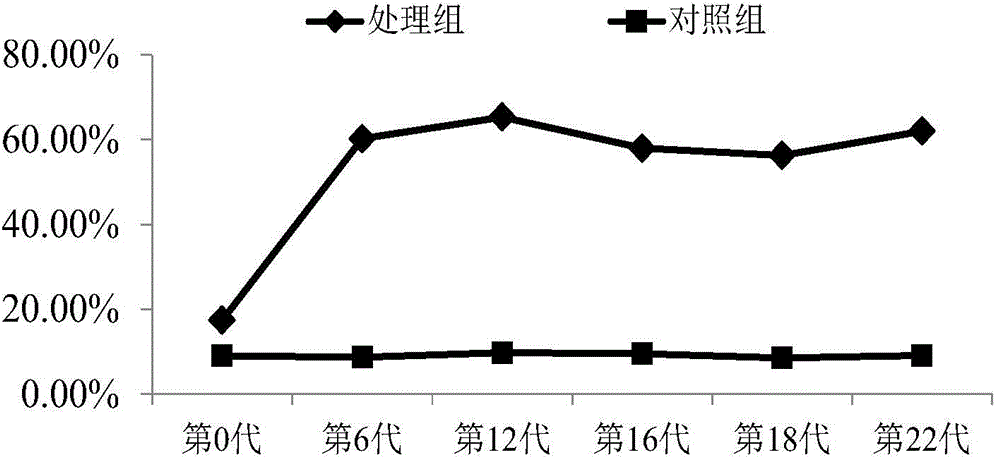
ActiveCN111593006AAchieve separationImprove survivabilityBacteriaTransferasesBiotechnologyEngineering
The present invention discloses a halomonas aydingkolgenesis strain and an application thereof. The strain is halomonas aydingkolgenesis M1 and has a deposit number of CGMCC NO.19880 in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center. Studies show that the halomonas aydingkolgenesis M1can be cultured without sterilization under fermentation conditions in an opening way and can efficiently accumulate polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) and / or a small molecule compound of tetrahydropyrimidine, etc. A method for continuous culture of the halomonas aydingkolgenesis M1 is established and a method for co-producing the PHA and tetrahydropyrimidine is successfully established. The method by using the halomonas aydingkolgenesis M1 to produce the PHA and / or tetrahydropyrimidine can realize high yield, is low in production cost, and has broad application prospects.
Owner:北京微构工场生物技术有限公司
Method for performing raw soil greening on coast saline land through biological modifier containing fly ash
InactiveCN106034443AImprove water retentionIncreased total vented porosityBiocideOther chemical processesCelluloseTrichoderma longibrachiatum
The invention relates to a method for performing raw soil greening on coast saline land through a biological modifier containing fly ash. The biological modifier comprises the following components in weight part: 8-12 parts of ceramsite, 11-15 parts of vermiculite, 1-5 part of fly ash, 0.5-2 parts of iron chloride, 0.5-2 parts of calcium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.2-1 parts of formic acid, 1-4 parts of amino acid salt, 2-6 parts of fermented sheep manure, 2-7 parts of capsicum straw powder, 0.3-1 parts of compound sodium nitrophenolate, 0.3-1 parts of amino-oxyacetic acid, 0.3-1 parts of soybean germ extract, 0.5-2 parts of potassium ferrocyanide, 0.2-0.5 parts of cellulose cellulose grafted acrylic acid salt, 0.1-0.5 parts of halomonas, 0.1-0.5 parts of Bacillus subtilis, 0.1-0.5 parts of azotobacter vinelandii, 0.1-0.5 parts of Aspergillus oryzae and 0.1-0.5 parts of Trichoderma longibrachiatum.
Owner:SHANDONG SUNWAY LANDSCAPE TECH
Compound microbial preparation and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107267407ANo wasteImprove processing efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationResource saving
The invention discloses a compound microbial preparation and a preparation method thereof. The compound microbial preparation contains bacillus amyloliquefaciens CGMCC1.7463, halomonas halophila CGMCC1.9009, virgibacillus halodenitrificans and pseudonocardia ammonioxydans MCCC1B00742 and pseudomonas fluorescens CGMCC1.6279 and is prepared after the four bacteria are subjected to enlarged culture and fermented products are uniformly mixed in a certain proportion. The compound microbial preparation can be directly applied to treatment of wastewater containing high-concentration salt substances and organic matter, has the removal rate of CODCr up to 50%-90% and the removal rate of ammonia nitrogen up to 40%-80%, has the advantages of being simple to operate and resource-saving, can be widely applied to biological treatment of high-salinity organic wastewater and has broad application prospects.
Owner:GUANGDONG PROVINCIAL ACADEMY OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI +1
Biological seaweed fertilizer, bacterial liquid for biological fertilizer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN112358345AExtended storage timePromote absorptionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPseudomonas
The invention provides a biological seaweed fertilizer. The biological seaweed fertilizer is obtained by culturing a seaweed water extracting solution and a bacterial solution, wherein the bacterial liquid comprises halomonas, shewanella, Marinobacter, pseudomonas and nitrate reducing bacteria. Compared with the prior art, the microbial preparation is added into the seaweed water extracting solution for culture, plants can be promoted to absorb nutrient substances in the seaweed water extracting solution, then the quality of fruits and vegetables is improved, the content of soluble solids andVC is increased, fruit coloring is promoted, and the salt tolerance of the plants is improved; the preservation time of the biological seaweed fertilizer can be prolonged, and tropical agricultural areas are convenient to use.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY +1
Marine halomonas for producing low-temperature beta-galactosidase and application thereof
The invention relates to the technical field of marine microorganisms. Since milk is generally conveyed and preserved at a low temperature, the capability of decomposing lactose at the low temperature is one of conditions which are necessary for industrially applying the beta-galactosidase. A marine halomonas strain P6006-1 provided by the invention is separated from sea water of an East China Sea region through culturing and has been preserved at the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC for short) in Wuhan city on January 7th, 2011, with a collection number of CCTCC No. M2011001. The invention also provides a method for producing the low-temperature beta-galactosidase by using the marine halomonas. The low-temperature beta-galactosidase produced by using the marine halomonas can be used for decomposing the lactose in cow milk; and the most proper reaction temperature is 30 DEG C.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
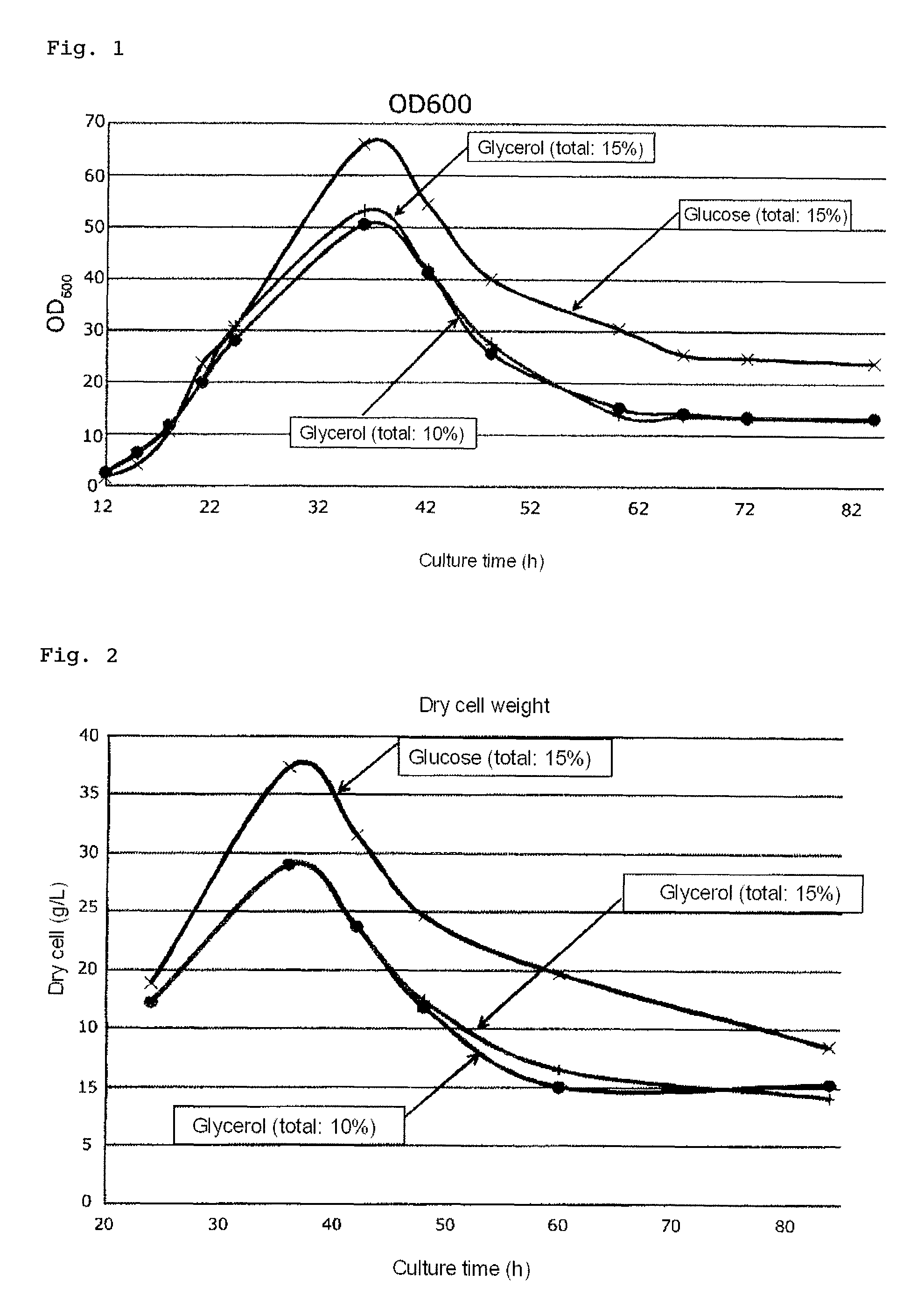
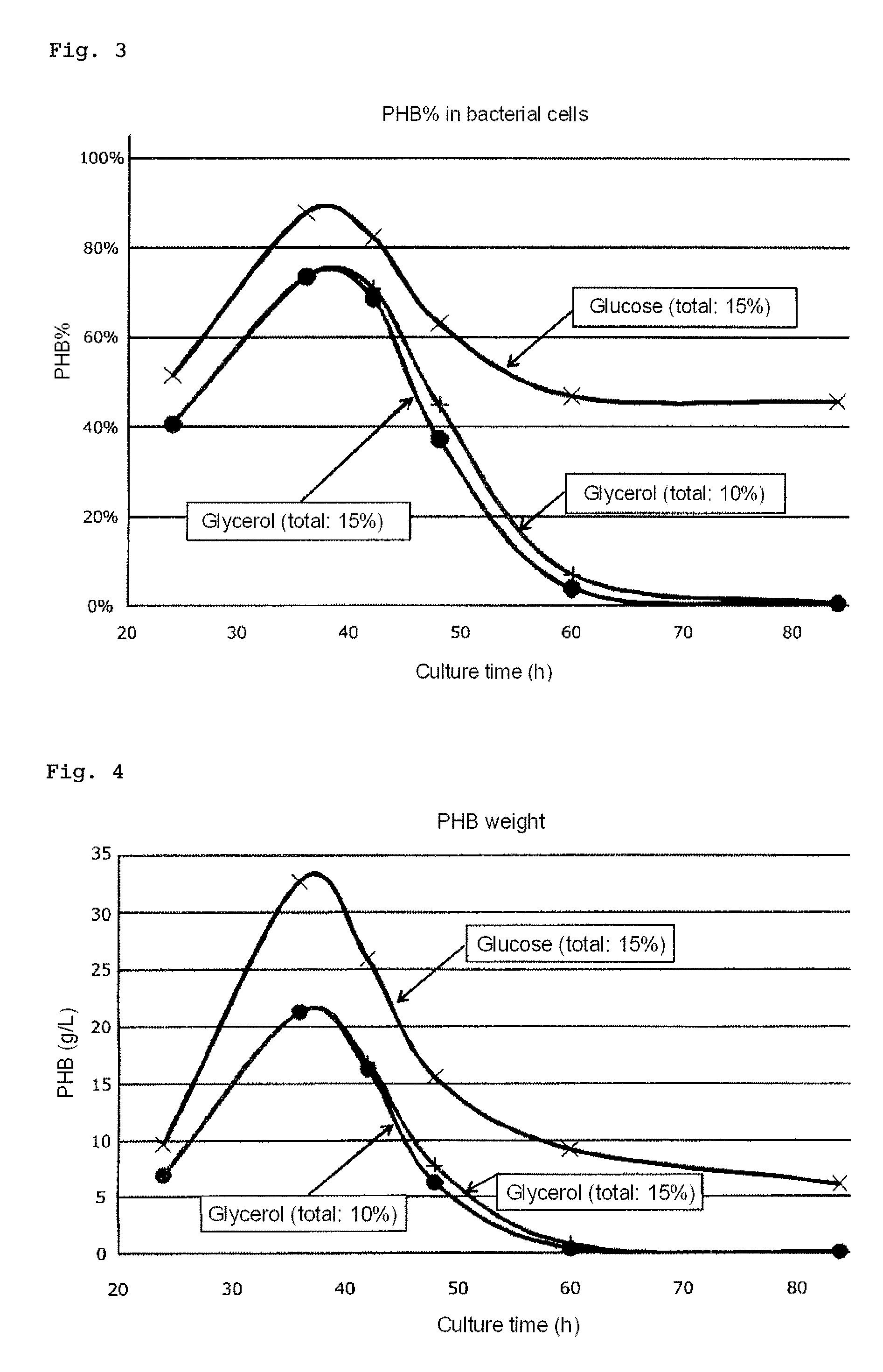
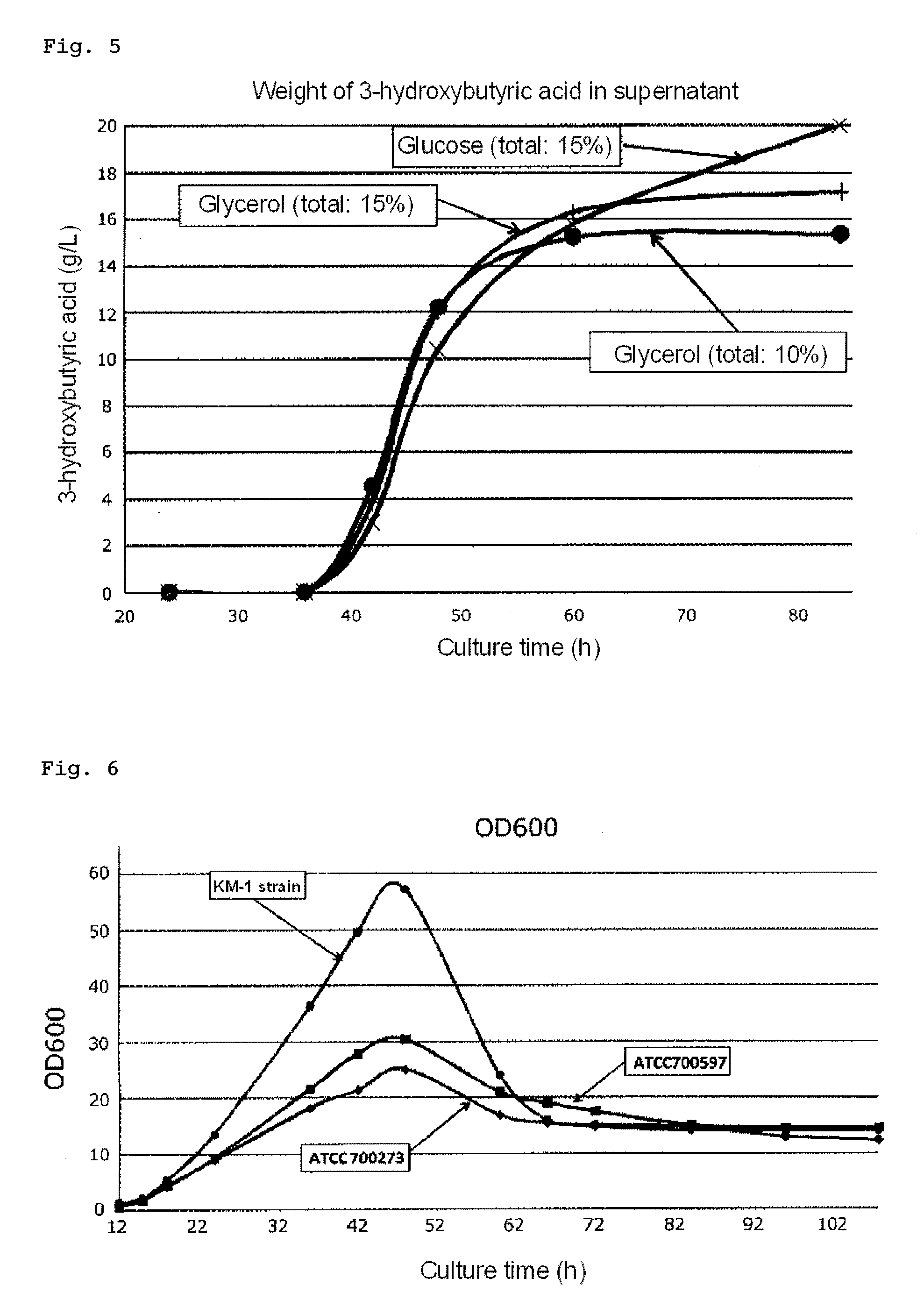
Method for manufacturing 3-hydroxybutyric acid using halomonas sp.
ActiveUS20160265007A1Easy to changeSimple production processBacteriaFermentationGenus3-Hydroxybutyric Acid
The invention provides a process for producing 3-hydroxybutyric acid or a salt thereof, the process comprising culturing one or more halophilic bacteria belonging to the genus Halomonas under specific conditions.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
Biological preparation for treating xanthan gum fermentation process wastewater
ActiveCN110092526AHigh porosityChemically stableSpecific water treatment objectivesWater contaminantsWastewaterBacillus perfringens
The invention belongs to the technical field of organisms, and discloses a biological preparation for treating xanthan gum fermentation process wastewater. The biological preparation includes a combination of any two or more of Paracoccus denitrificans, Clostridium perfringens and Halomonas elogata. The bacteria in the biological preparation can form shortcut positive cycle, so the biological preparation has good synergistic performances, and can effectively treat pollutants in the wastewater.
Owner:内蒙古阜丰生物科技有限公司
EPSP synthase of variable halomonas high resistance glyphosate and its encoding sequence
The invention discloses a novel 5-enol pyruvyl shikimate3-phosphate (EPSP), the polynucleotide for encoding the EPSP and the method for producing the EPSP through recombination technology. The invention also discloses the use of the polynucleotide for encoding the EPSP.
Owner:LONGPING BIOTECHNOLOGY (HAINAN) CO LTD
Process for producing 3-hydroxybutyric acid or salt thereof
The invention provides a process for producing 3-hydroxybutyric acid or a salt thereof. The process includes (1) culturing one or more halophilic bacteria belonging to the genus Halomonas under aerobic conditions in a medium containing an inorganic salt and one or more organic carbon sources; (2) changing the culture conditions from aerobic culture to microaerobic culture, and culturing bacterial cells of the halophilic bacteria to produce 3-hydroxybutyric acid or a salt thereof in a culture medium; and (3) collecting the 3-hydroxybutyric acid or the salt thereof from the culture medium.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
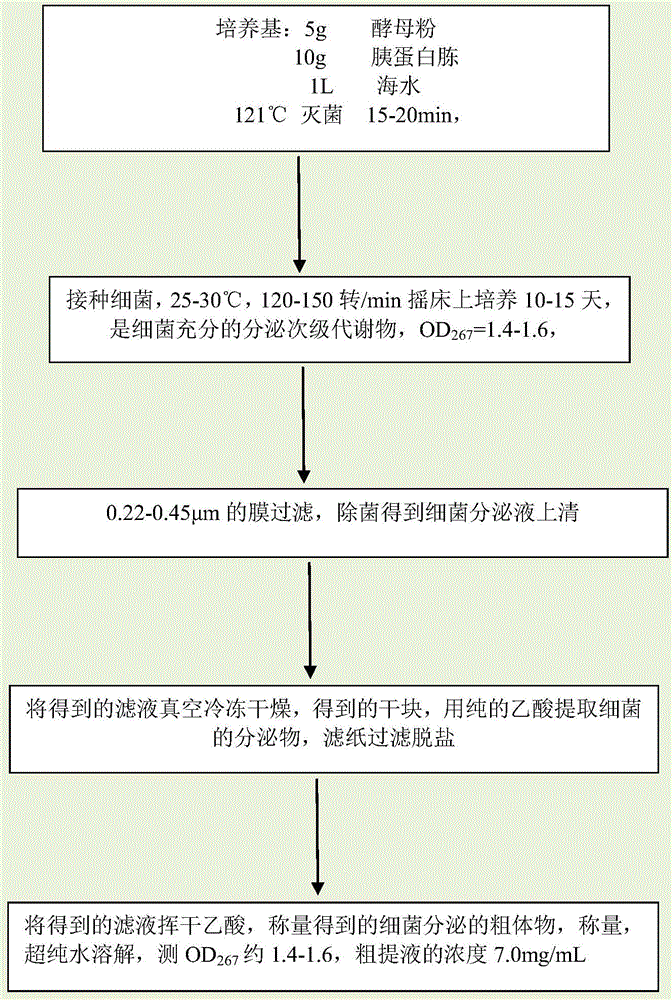
Secretions of marine halomonas and extraction method and application of secretions
InactiveCN104561104ASimple cultivation conditionsShort duration of actionBiocideMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesFiltration
The invention relates to secretions of marine halomonas, an extraction method of the secretions and the application of the secretions. The extraction method comprises the following steps: preparing a culture medium according to a formula of 5 g of yeast powder, 10 g of tryptone and 1L of seawater, and sterilizing the culture medium for 15-20 minutes at the temperature of 121 DEG C; inoculating the marine halomonas into the culture medium under aseptic conditions, culturing the culture medium inoculated with the marine halomonas for 10-15 days at the constant temperature of 25-30 DEG C on a backward rotating shaking table at the speed of 120-150 rpm, performing filtration with a film of 0.22-0.45 micrometers, and performing sterilization so as to obtain bacterial exudate supernatant; vacuum freezing and drying a filtrate, performing extraction through a pure acetic acid, and performing filtration and desalination through filter paper; volatilizing the acetic acid of the obtained filtrate so as to obtain coarse substances of the secretions of the marine halomonas. The secretions disclosed by the invention can be used for governing red tides, and have the effect of restraining dinoflagellates like Alexandrium tamarenses, prorocentrum donghaiense and Karenia mikimotoi of the red tides. According to the invention, the culture conditions are simple, products do not need to be refined, only the filtration is needed for removing thalli, and the secretions have a good effect of restraining the dinoflagellates of the red tides.
Owner:SHANTOU UNIV
Clostridium for producing acid and application thereof to paper-making wastewater treatment
The invention discloses a Clostridium strain for producing acid. The strain is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) in December 27, 2012, and the stain has a preserve number of CCTCC NO: M2012555 in Clostridium sp. YC3. The invention further discloses an application of a mixture of the strain and Halomonas to paper-making wastewater treatment. The stain disclosed by the invention not only has a capability of directly processing paper-making wastewater, but also can reduce the pH of the wastewater, thereby providing an agreeable environment for growth and colonization of methanogens in paper-making black liquid. According to the method which is a primary processing method, favorable conditions are provided for subsequent processes of the paper-making wastewater, the recovery efficiency is enhanced, the cost is lowered, and the secondary pollution is reduced; and the method has a wide application prospect in the paper-making wastewater treatment.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Salt-tolerant efficient denitrification-type microbial preparation for water treatment
InactiveCN110241039AAvoid restrictionsImprove denitrification abilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPseudomonas denitrificansNitrifying bacteria
The invention discloses a salt-tolerant efficient denitrification-type microbial preparation for water treatment. The microbial preparation consists of the following components in percentage: 2.5-5% of halophilic archaea, 5-10% of bacillus subtilis, 5-10% of pseudomonas denitrificans, 5-10% of halomonas and 5-10% of halophilic bacteria, and 5-10% (w / t) of bamboo charcoal particles are added. The microbial preparation for water treatment consisting of halophilic archaea, pseudomonas denitrificans, bacillus subtilis, nitrifying bacteria, denitrifying bacteria and coryneform bacteria still has good denitrification capacity under the condition of high salt, and solves the limitation of a high salt environment on traditional biological denitrification methods. The bamboo charcoal particles have good adsorption performance because of large specific surface area, can be in direct contact with microorganisms better, and can adsorb organic matters on the surface, so that the formation of a surface biological membrane is promoted; and on the other hand, a large amount of oxygen can be stored in the bamboo charcoal particles, so that oxygen-containing components in a water area are improved, and a water area recovery effect is improved.
Owner:天津金辰博科环保科技发展有限公司
Heat-resistant halomonas bacterium and application thereof
The invention discloses a heat-resistant moderately halophilic bacterium halomonas sp. LCB169 of which the preservation number is KCTC 52618. The strain is determined as a new species of halomonas bya polyphasic classification method. The halomonas bacterium disclosed by the invention has enzyme activities of oxidase, catalase, esterase, lipoesterase, leucine aminopeptidase, valine aminopeptidase, alkaline phosphatase and the like, and can be widely applied in related production fields of various bioengineering enzyme preparations. Moreover, the strain can grow normally at an NaCl concentration up to 17% and high temperature of 52 DEG C, indicating that the strain has high resistance to the environment. At the same time, the strain can secrete extracellular polysaccharides and accumulatepolyhydroxybutyrate abundantly under high NaCl concentration of up to 10%, so the strain can be further developed and applied to biomedicine and environmentally-friendly bioplastics related industriessuitable for extreme high-salt environments.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
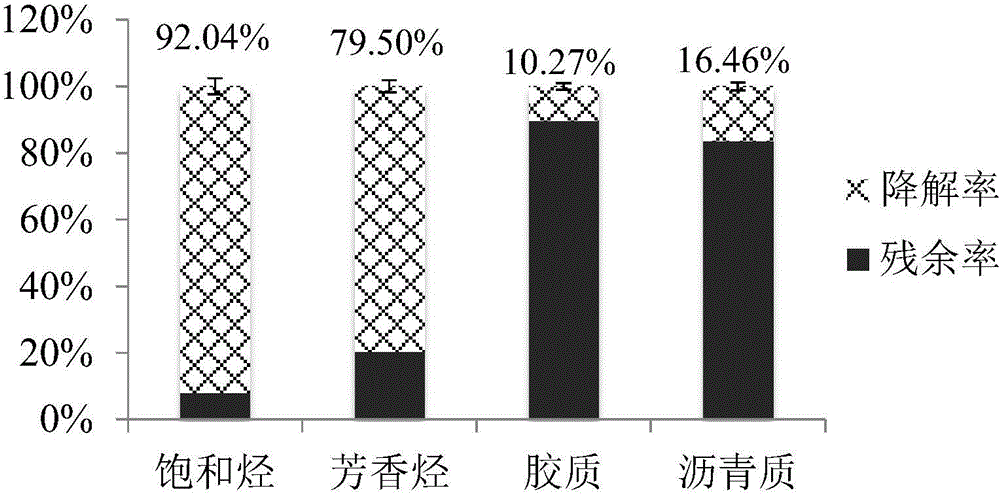
Method for biodegrading high molecular weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon pyrenes with halophilic bacteria
A method and composition for biodegrading or bioremediating a pyrene or other polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (“PAH”) with one or more bacteria of the genus Halomonas or Idiomarina. Bacterial strains useful for degrading or remediating pyrenes and other polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
Fermentation production process of alkaline mycose lyase and microbe for producing the lyase
The present invention provides one kind of special basophile N19-2 and the microbe fermentation production process of alkaline mycose lyase by using sodium alginate and peptone as material in the presence of the special basophile N19-2 strain. The method is simple, the enzyme activity of the fermented liquid reaches 100 u / ml, and the post-extraction rate is over 80 %. The enzyme has optimal reaction pH value of 9.5, optimal reaction temperature of 55 deg.c and important application value in the production of oligomycose.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
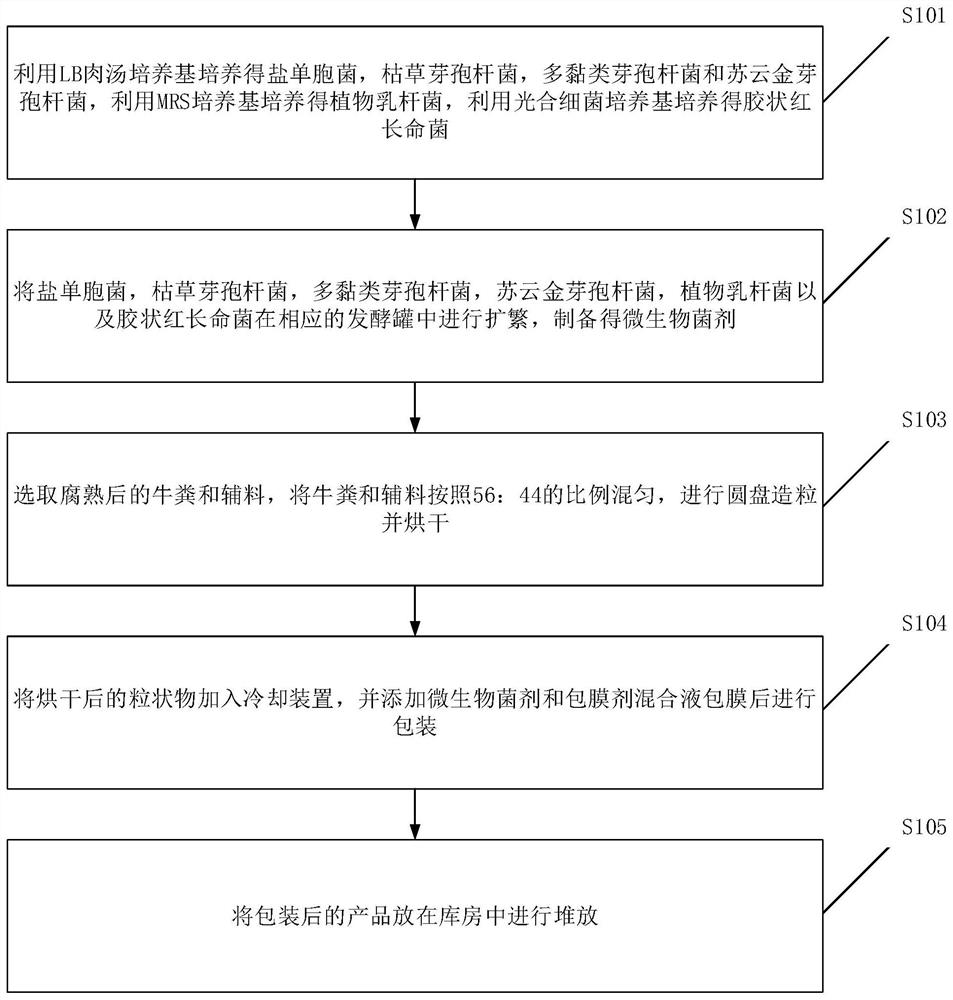
Special bio-organic fertilizer for rice planted in saline-alkali soil and preparation method of special bio-organic fertilizer
PendingCN113149786APromote growthImprove stress resistanceCalcareous fertilisersExcrement fertilisersRice plantsBacillus thuringiensis
The invention discloses a special bio-organic fertilizer for rice planted saline-alkali soil. The special bio-organic fertilizer is prepared from halomonas, bacillus subtilis, paenibacillus polymyxa, bacillus thuringiensis, lactobacillus plantarum, Rubrivivax gelatinosus and an organic fertilizer. In actual preparation, microorganisms are propagated to obtain a microbial agent, then decomposed cow dung and auxiliary materials are uniformly mixed, granulation and drying are performed, cooling treatment is performed, a mixed solution of the microbial agent and a coating agent is added through a coating barrel for coating treatment, packaging is performed, and the finished product can be used after being packaged and stacked in a warehouse for a period of time. The bio-organic fertilizer has a high organic matter content and a high viable count, and can improve the soil structure of saline-alkali soil, reduce soil salinity and a pH value, enhance crop stress resistance, promote rice growth, increase yield and achieve the effects of soil improvement, fertility improvement, stress resistance and growth promotion when used in cooperation with conventional irrigation and fertilization measures.
Owner:NINGXIA UNIVERSITY
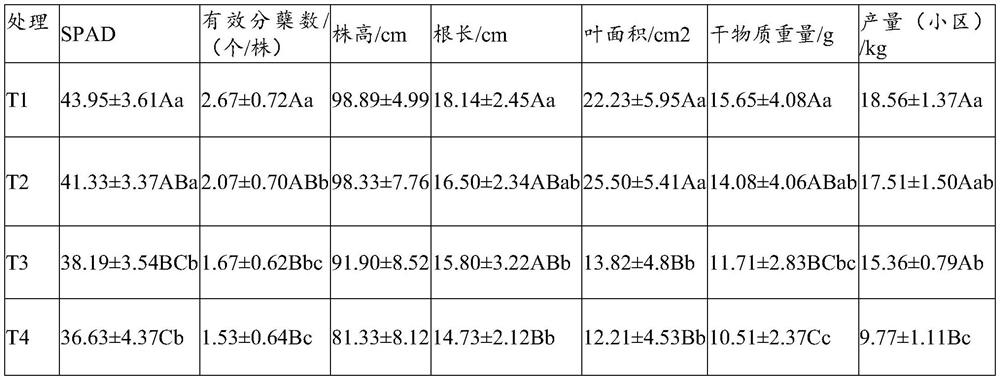
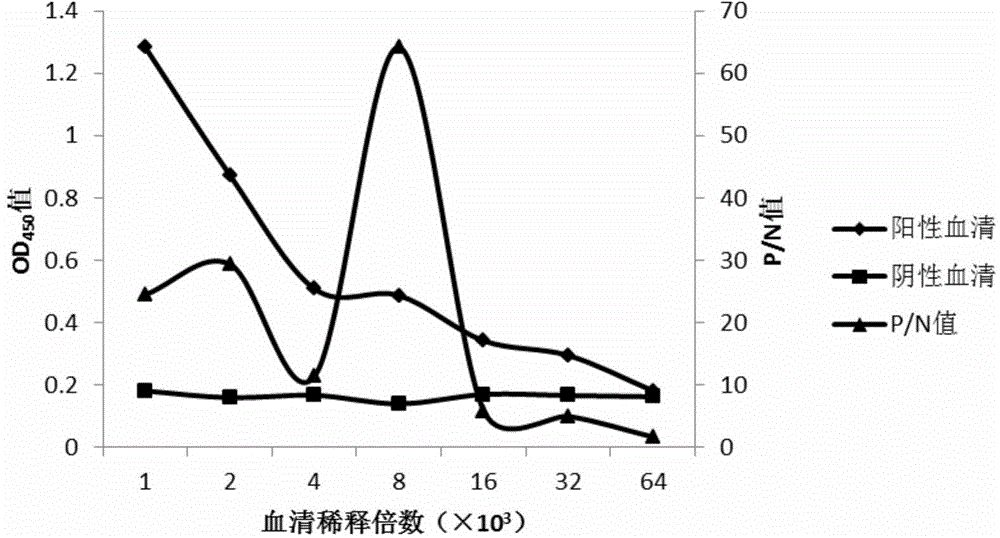
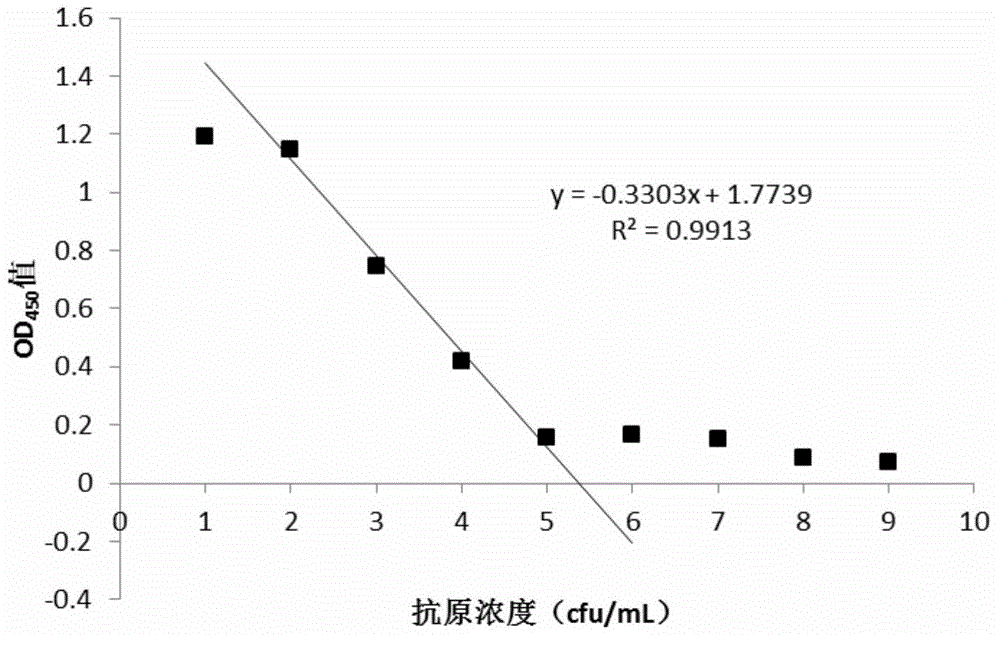
Quantitative detection method for halomonas strains by adopting indirect enzyme-linked immunosordent assay
ActiveCN104655842AStrong nitrite degradation abilityPlay a role in promotingMaterial analysisSerum igeAquatic product
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Microbial antibacterial deodorant preparation, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN111500490AImprove stabilityProlong the action timeBiocideGas treatmentBiotechnologyInfluenza A (H1N1) virus
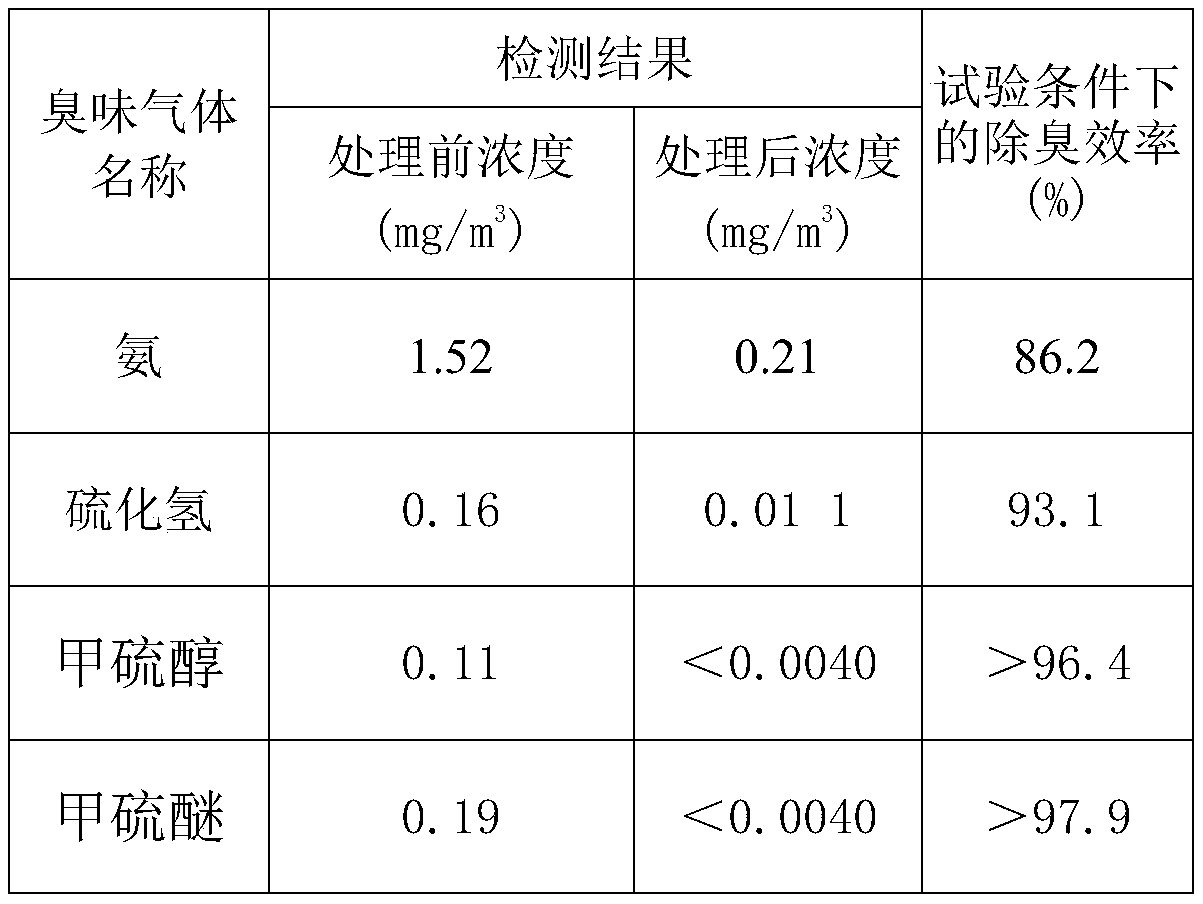
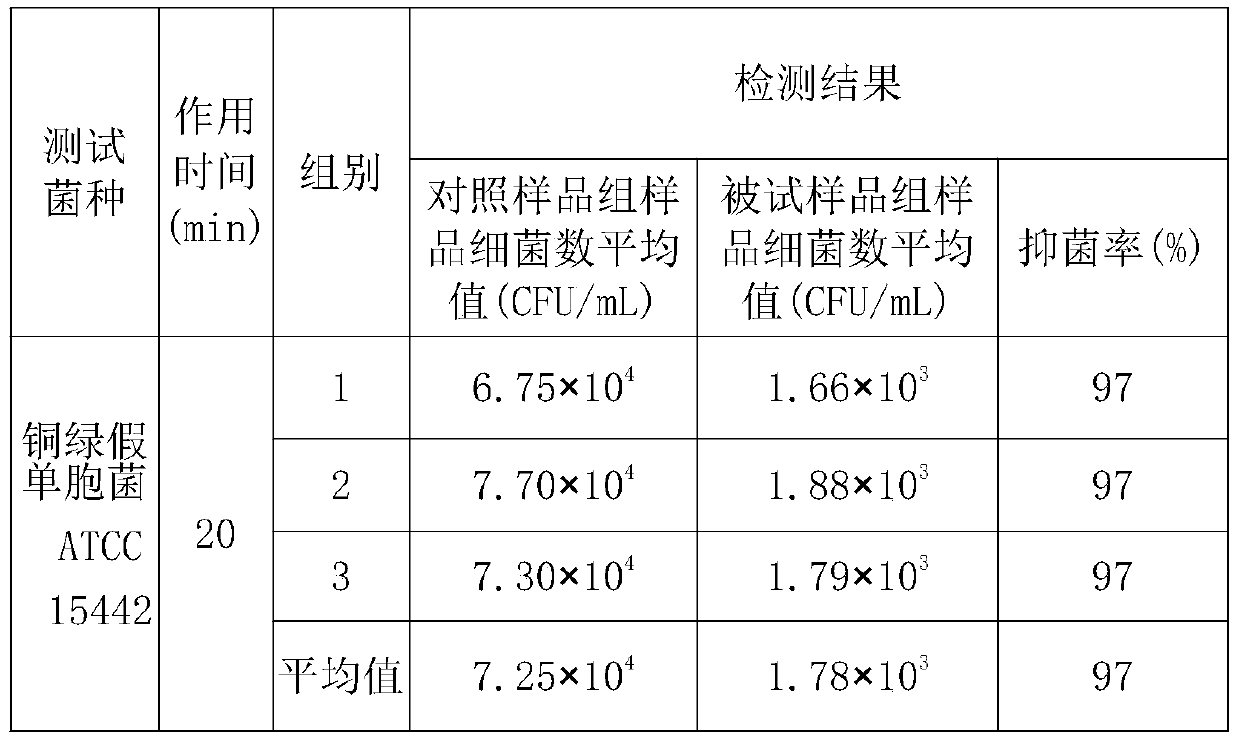
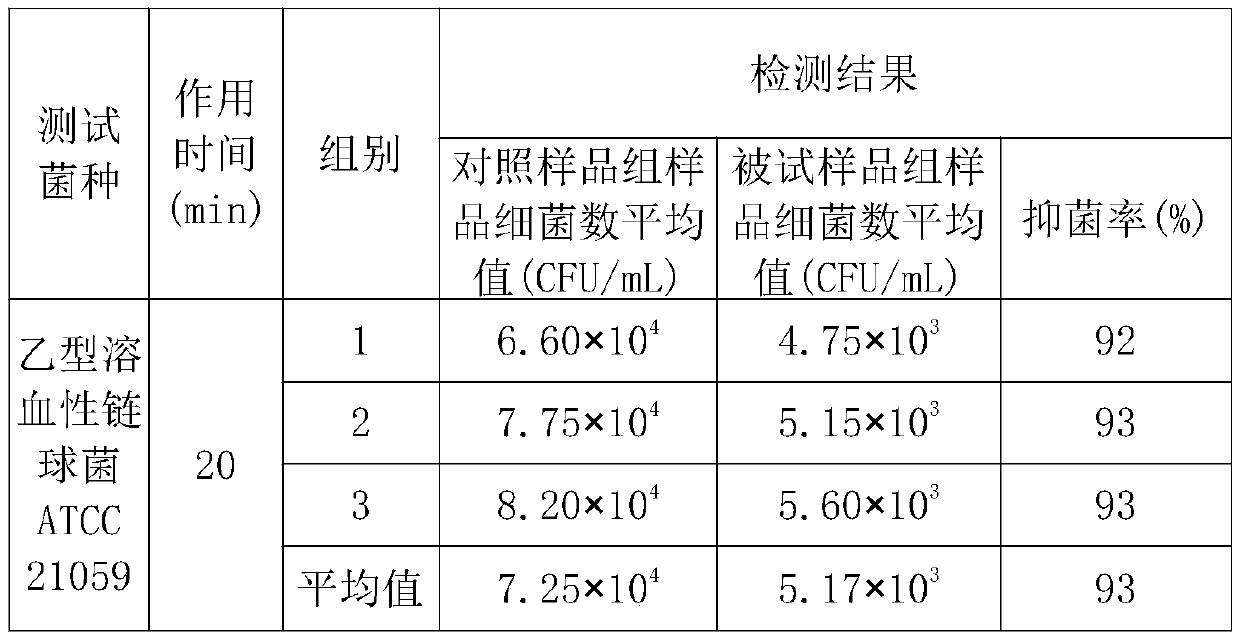
The invention belongs to the field of microorganisms, and particularly relates to a microbial antibacterial deodorant preparation, and a preparation method and application thereof. The microbial antibacterial deodorant preparation disclosed by the invention is prepared from functional bacteria including bacillus aceticus, halomonas, lactobacillus casei and saccharopolyspora chrysosporium; and theratio of colony count of the acetobacter aceticus to the halomonas to the lactobacillus casei to the saccharopolyspora chrysosporium is (3-7):(3-8):(1-6):(0.5-2). The microbial preparation disclosed by the invention does not contain chemical additives; all functional bacteria surviving in the microbial preparation are dominant bacteria; a microorganism interspecific competition principle is utilized; the killing effect of metabolic products of the strains on pathogenic microorganisms is also achieved; the microbial antibacterial deodorant preparation shows excellent antibacterial and virus inactivation effects, the antibacterial effects on pseudomonas aeruginosa, B hemolytic streptococcus, shigella dysenteriae, staphylococcus aureus and escherichia coli all reach 93% or above, and the inactivation rate on influenza A H1N1 viruses reaches 99% or above.
Owner:SHENZHEN HE MIN BIOTECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com