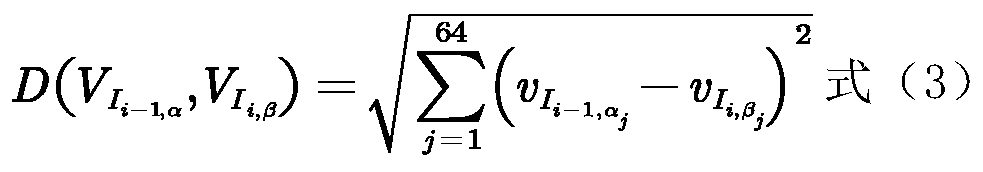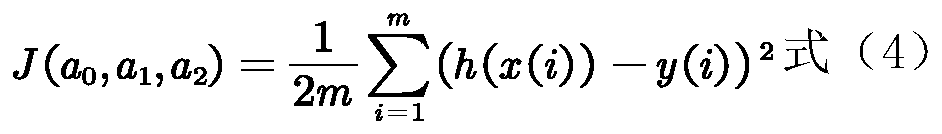Patents
Literature
111 results about "Colony count" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Colony count. A measurement of the growth of bacteria in a urine sample that has been cultured for 24 to 48 hours.
Test chip for fast detecting microorganism, preparation and use thereof
InactiveCN101497914AAvoid missingEasy to operateMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementFood borneColony count
The invention discloses a testing piece for quickly testing microorganisms, as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The testing piece comprises a soleplate, a film with a hollow part in the middle and a plastic film. The bottom surface of the film with the hollow part in the middle is adhered to the soleplate; a groove culture area is formed at the hollow part in the middle of the film; a color development culture medium is arranged in the groove culture area; a cold water condensable gellant is adhered to the bottom surface of the plastic film; and the bottom surface of the plastic film and the upper surface of the film are adhered to the edge at one side. After the upper and the lower layers of the testing piece are adhered, irradiation and sterilization packages are used for standby. The testing piece can be applied to the detection of total colony count, coliform bacteria, coliform group, salmonella, staphylococcus aureus, subsidiary haemolytic vibrio, pseudomonas aeruginosa and other food-borne causative organisms and has the advantages of simple operation, convenient carrying, short testing time, accurate result and double-sided bacteria count.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROORGANISM
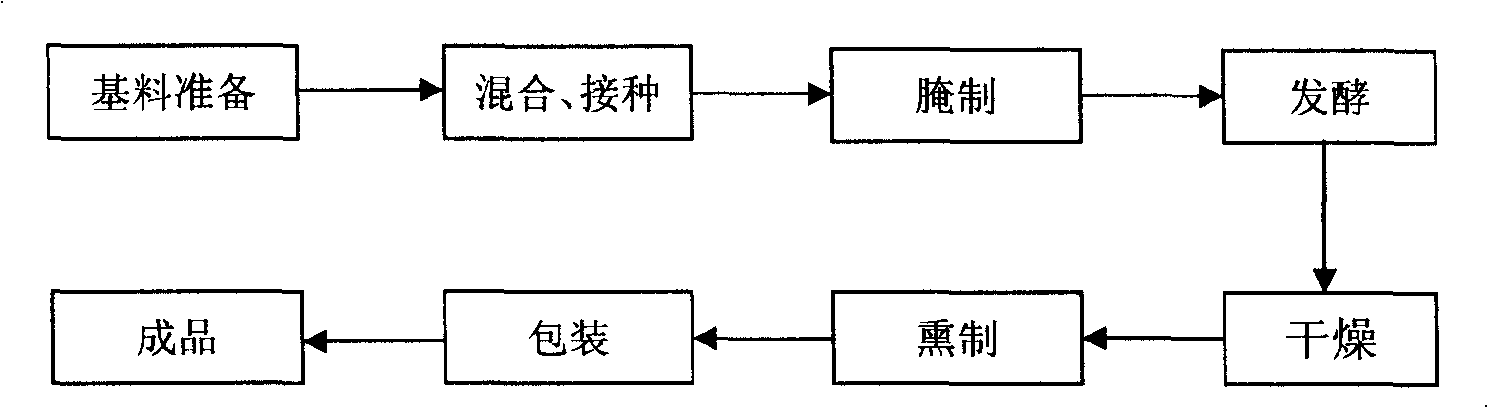
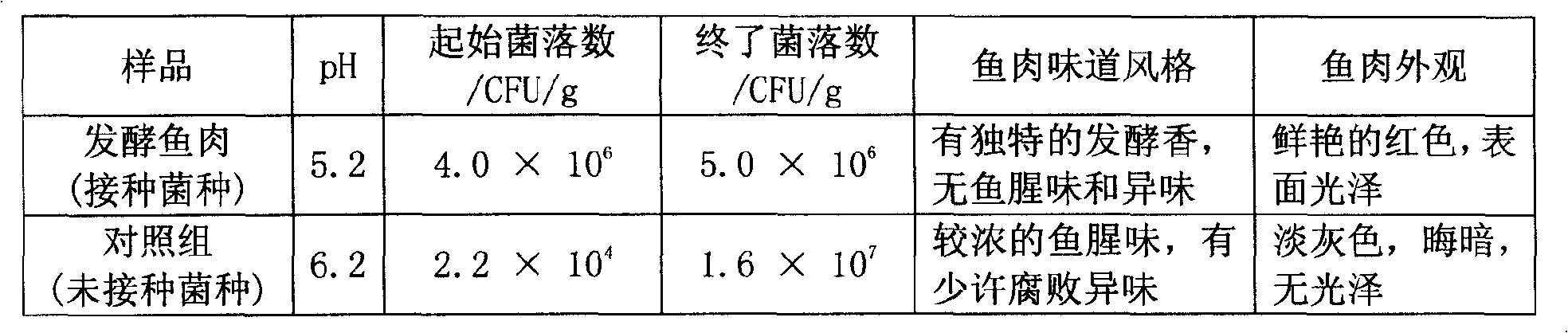
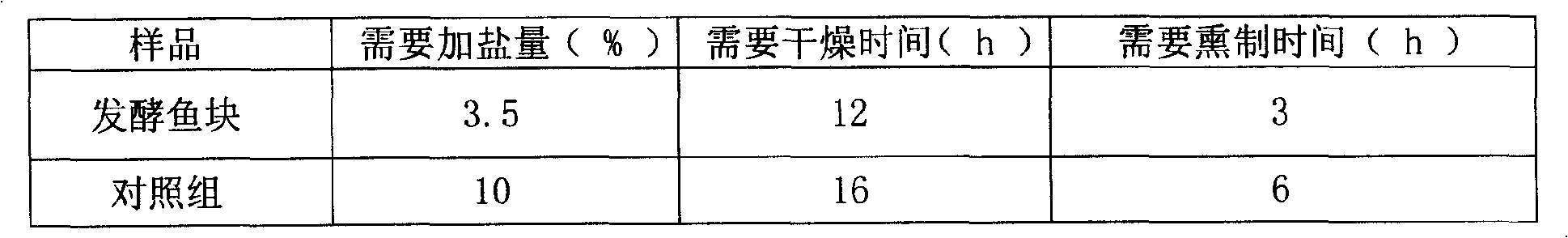
Hongqu fish fermented by mixed bacterium based on lactobacillus and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101491350AIncrease the fragranceImprove gel propertiesMeat/fish preservation using chemicalsFood preparationFresh fishColony count
The invention discloses red yeast fish fermented by mixed strains based on lactic acid bacteria, which is made by using fresh fish blocks as a base material, and inoculating the base material with I-type mixed basic bacteria of which the colony count is 10CFUs per gram of fish and II-type mixed basic bacteria of which the colony count is 10spores per gram of fish, and subjecting the inoculated base material to main processing procedures of pickling, fermentation, drying and fumigation to obtain the finished product. The invention adopts a technical proposal that initial culture of microorganism lactic streptococci, lactobacillus bulgaricus and saccharomyces cerevisiae of a single species of the I-type mixed basic bacteria of which the colony count is 10CFUs per gram of fish and initial culture of monascus of the II-type mixed basic bacteria of which the colony count is 10spores per gram of fish are mixed and inoculate with the fish block base material, and the mixture is subjected to pickling, fermentation, drying fumigating and the like to give the red yeast fish blocks, and the technical proposal overcomes the defects that natural fermentation is uneasy to ensure the sanitation and safety of the product and has high salt content. The red yeast fish is suitable for producing various fermented fish blocks.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
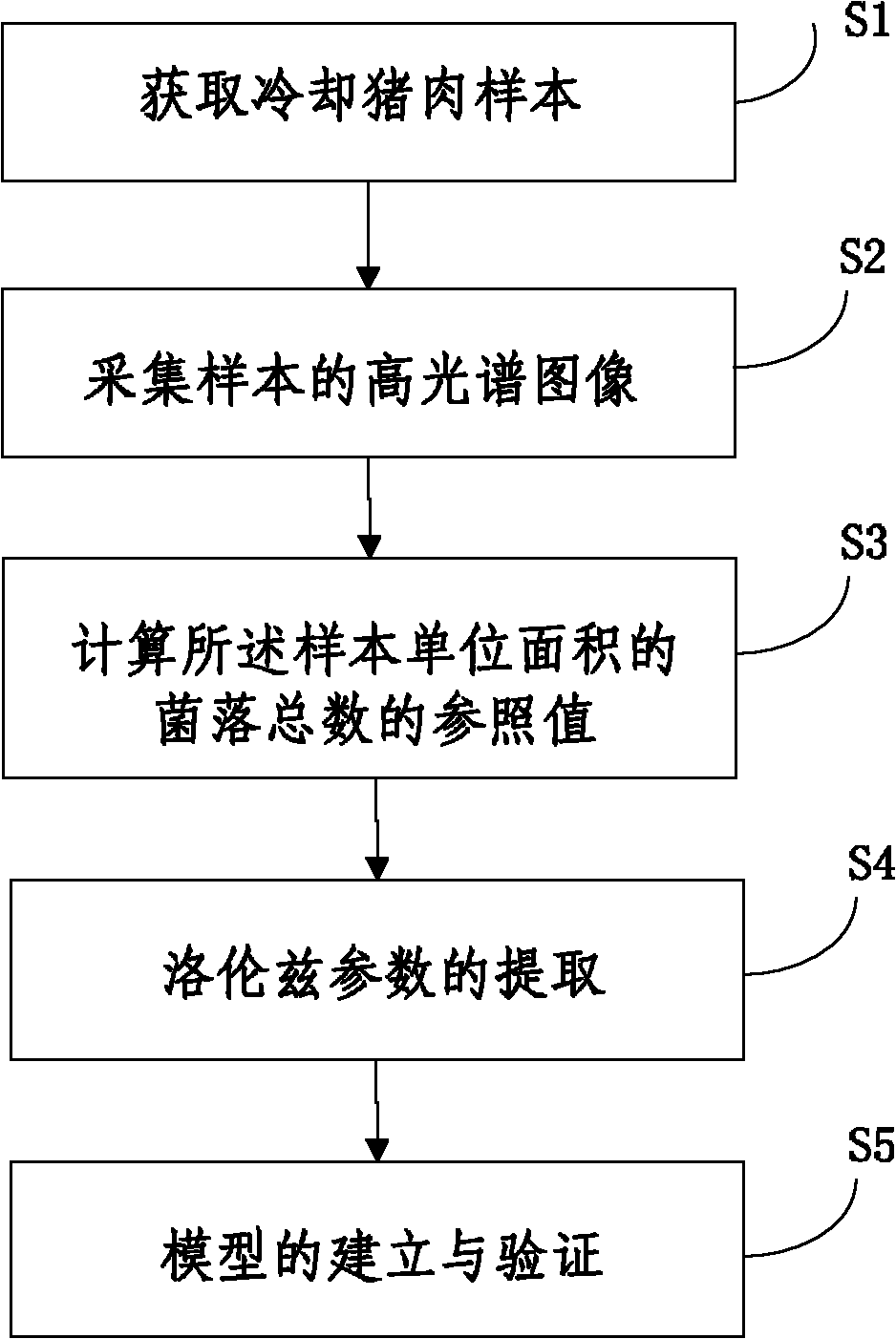
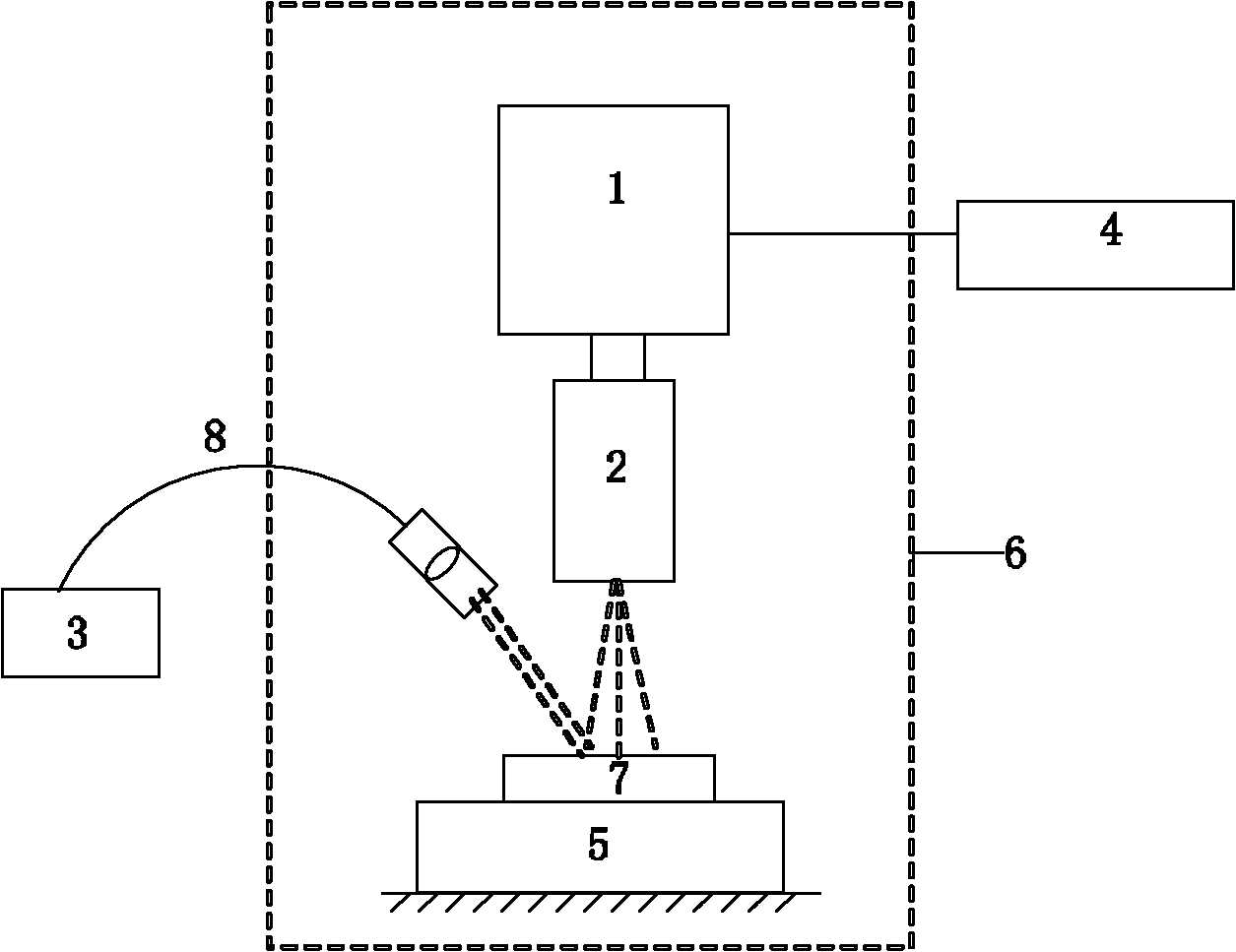
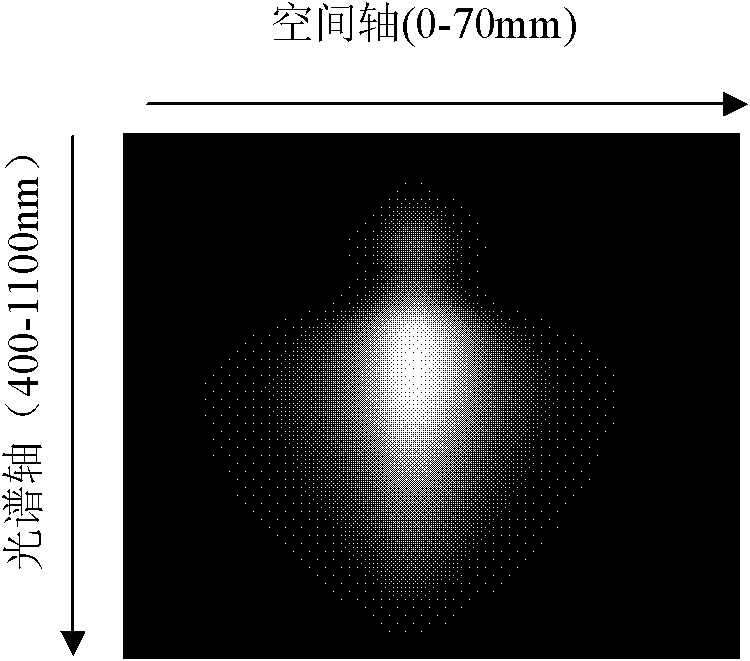
Method for rapidly and nondestructively detecting colony count of chilled meat
InactiveCN102181514AEasy to predictFit closelyMicrobiological testing/measurementMathematical modelColony count
The invention discloses a method for rapidly and nondestructively detecting the colony count of chilled meat, which comprises the following steps of: S1. obtaining a chilled meat sample; S2. collecting a high-spectrum image of the sample; S3. calculating the reference value of the colony count per unit area of the sample; S4. subjecting the high-spectrum image to space decomposition so as to obtain spatial diffusion information of the sample at different wavelengths, wherein the Lorentz parameters of the component information of the representative sample is extracted by utilizing the spatial diffusion information according to a nonlinear regression method; and S5. obtaining the relationship between the Lorentz parameters and the reference value in a certain wavelength range so as to establish a mathematical model of the Lorentz parameters and the colony count of the sample according to a multivariate linear regression method, and predicting the colony count of the chilled meat sample by utilizing the model. By means of the method disclosed by the invention, rapid and nondestructive detection of the colony count of a meat product can be realized.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
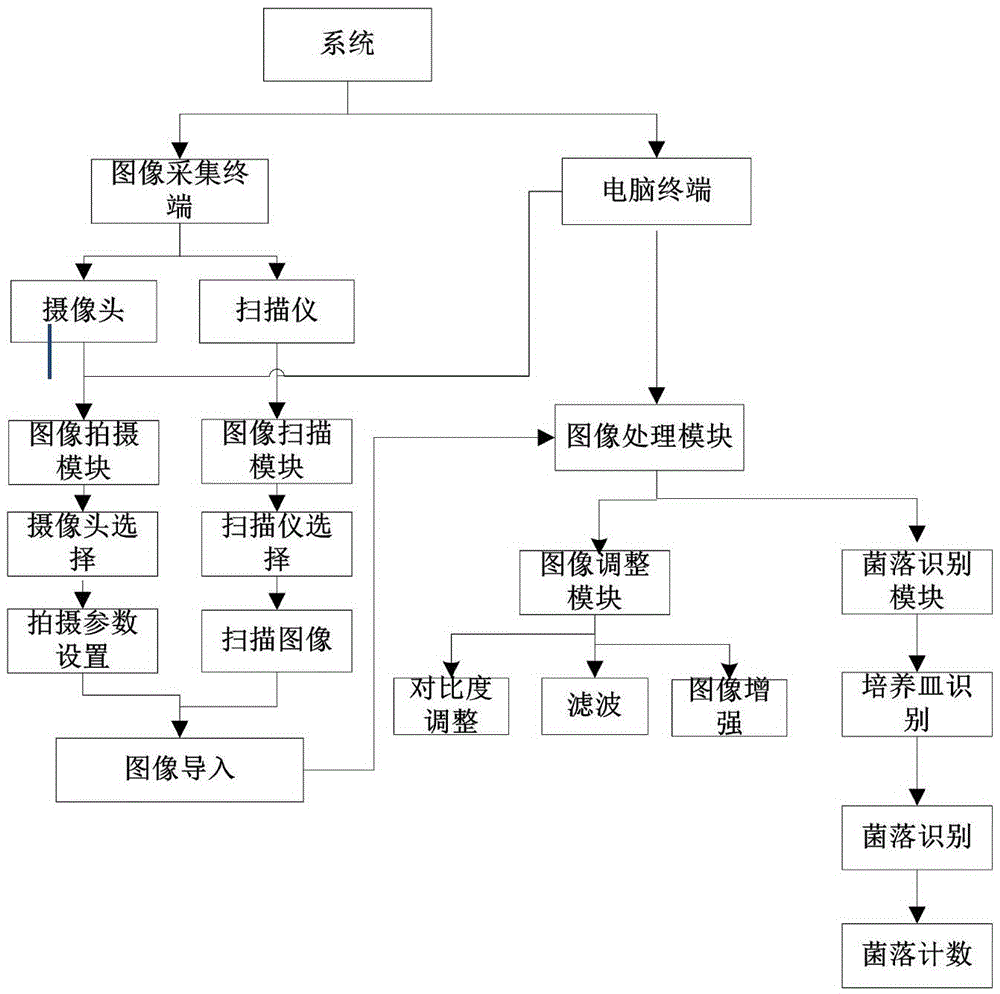
Image acquisition, recognizing and counting method for colonies
InactiveCN105491279AIn line with operating habitsEasy to operateImage enhancementTelevision system detailsColony countDirect control
An image acquisition, recognizing and counting method for colonies comprises the following steps: clicking a colony counting EXE icon to enter an EXE interface; clicking a corresponding image shooting button on the EXE interface; adjusting an image to be operated after the image is opened; recognizing petri dishes in an EXE colony image; and recognizing and counting colonies in the EXE colony image. According to the method, shooting equipment, light sources and certain shooting parameters can be controlled from a terminal directly, so that the operation process and difficulty are simplified. The image acquisition, recognizing and counting method is a method integrating computer processing and image processing, and is higher in simplicity, accuracy and efficiency when being compared with other traditional methods.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Composite bacterial agent for deodorization and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a composite bacterial agent for deodorization and a preparation method thereof; the composite bacterial agent comprises a bacillus group composed of bacillus subtilis, thiobacillus intermedius, bacillus licheniformis, and a yeast group composed of saccharomyces ellipsoideus and nectaromyces sp. The preparation method comprises the following steps: activating the purchased2 groups of microorganism, preparing a bacterial agent with a total colony count of each group of not less than 1*107 / ml by two steps of seed culture and fermenter culture, uniformly distributing the2-group bacterial agents at different areas of fillers in a biological filter tank for deodorization operations, wherein the bacterial agent comprises by weight 30-50% of bacillus groups and 50-70% of yeast groups, and the two groups are not mixed during distribution. The composite bacterial agent for deodorization prepared by the method provided by the invention has the advantages of good deodorization effect and long deodorization period, and the service time is increased by above 30% when compared with that of agents without the addition of the composite bacterial agent.
Owner:SHANGHAI MASTECK ENVIRONMENTAL
Preserved meat quality detection method
InactiveCN106290224AGet quality output valueEasy to eatMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopic imageNitrite
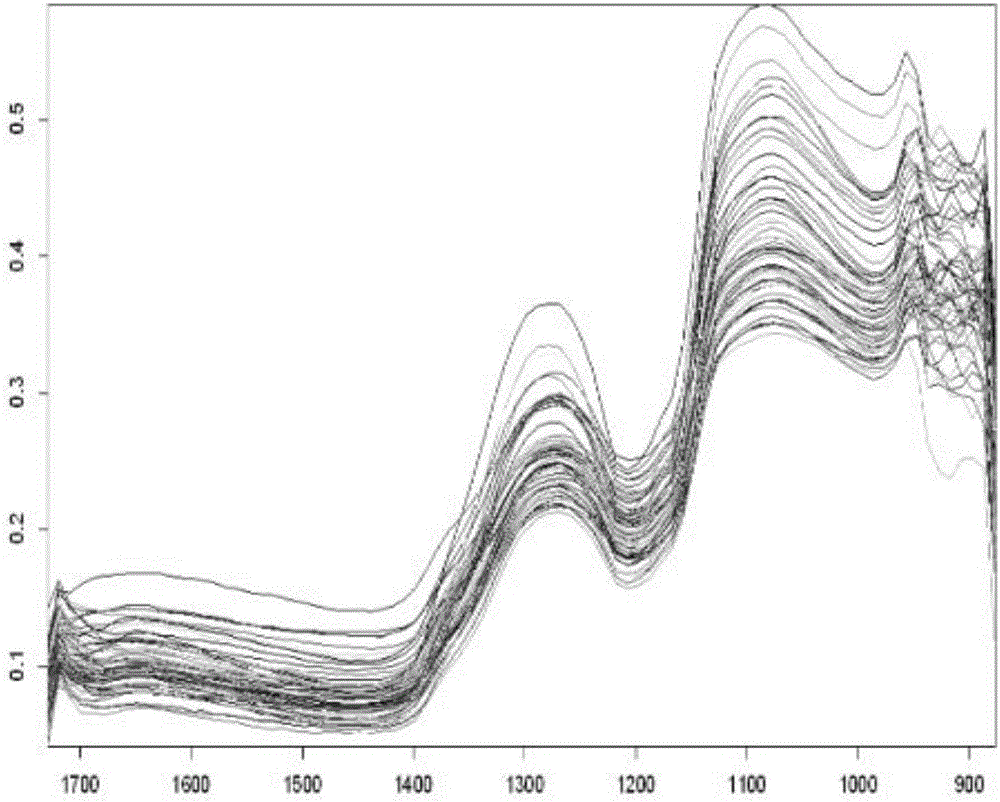
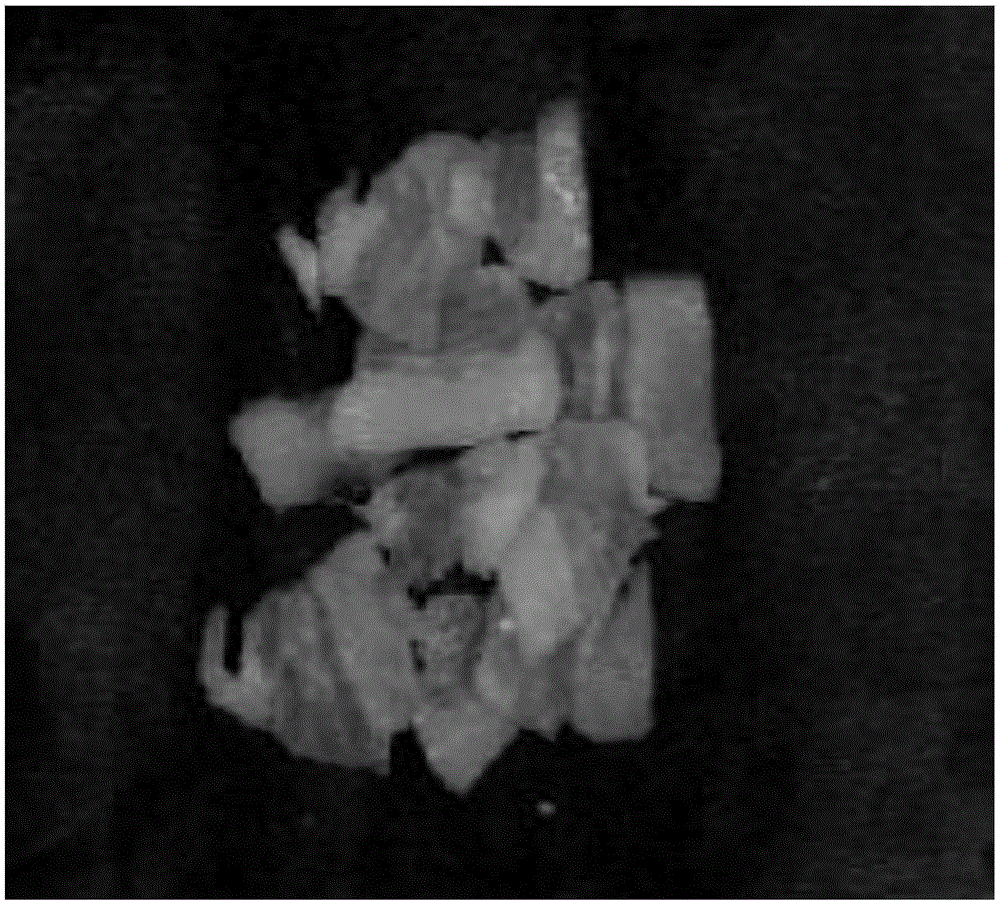
The invention discloses a preserved meat quality detection method. The method includes steps: simultaneously acquiring hyperspectral image characteristic wavelength information and hyperspectral nitrite content spectral information of preserved meat, and acquiring microscopic image information of colony count of the preserved meat to obtain image characteristic wavelength, nitrite content and colony count of the preserved meat; taking the image characteristic wavelength, the nitrite content and the colony count of the preserved meat as input of a radial basis function artificial neural network multi-data fusion predication model to obtain preserved meat quality output values according to a genetic optimization method; judging preserved meat quality according to the preserved meat quality output values, and performing quality grading predication. By adoption of the preserved meat quality detection method, quickness and accuracy in quality detection and grading of the preserved meat can be realized, and whether the preserved meat is safe to eat or not can be identified more conveniently.
Owner:BEIJING TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITY
Quantitative determination and drug allergy determination kits for helicobacter pylori viable bacteria and determination method
InactiveCN103757088ASolve the deficiency of only qualitative detection of Helicobacter pyloriSimple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementUrocaninaseDrug allergy
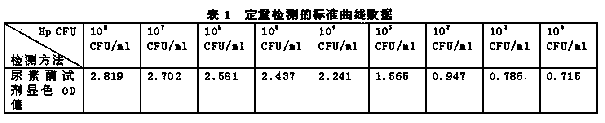
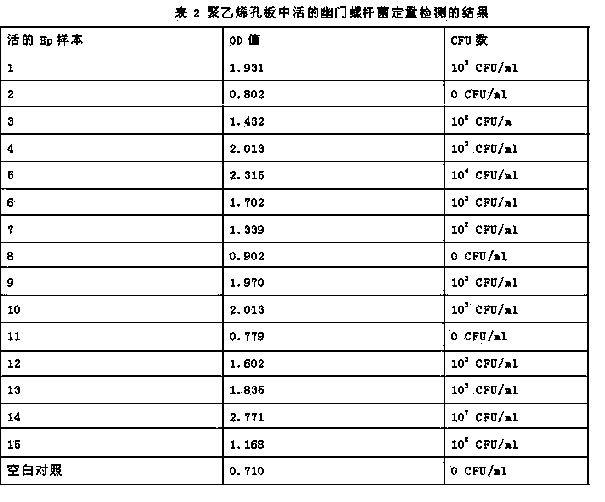
The invention discloses quantitative determination and drug allergy determination kits for helicobacter pylori viable bacteria and a determination method. The method adopts viable helicobacter pylori as a sample to be detected; the property that the viable helicobacter pylori can generate urease is used for rapidly and accurately reading the quantity of the helicobacter pylori by a helicobacter pylori colony counting standard method (CFU / ml, namely the bacterium individual quantity in each ml of bacterium liquid and a colony quantity standard curve); the detection result is accurate and sensitive and has high reliability; the counting difficulty of existing helicobacter pylori clinic microbiological identification, caused by difficult culture and complicated operation, is solved; the drug allergy determination kit and a preparation method, which are expanded by the invention, can be used for carrying out various drug allergy tests at the same time; clinicians can rapidly and conveniently screen suitable anti-helicobacter pylori medicines so that the time and the labor are saved and the cost is saved, so as to provide a beneficial technical solution for clinical scientific treatment.
Owner:SICHUAN VACCINE TECH
Ecological microbial inoculum for remedying oil-polluted soils and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101914444ALarge specific surface areaRestoration of polluted soil ecologyFungiBacteriaEcological environmentCandida tropicalis
The invention relates to an ecological microbial inoculum for remedying oil-polluted soils and a preparation method thereof. The ecological microbial inoculum for remedying oil-polluted soils is a mixed microflora of bacillus subtilis, pseudomonas fluorescens, berea trichosporon asahii and candida tropicalis, which are optimally mixed in a ratio of 1:1:1:1 basically. The invention has the advantages that: after the microbial inoculum is applied to the oil-polluted soils, a micro-ecological dominant microflora can be formed rapidly; and in case that the microbial inoculum in an amount which is 2 to 5 percent based on the weight of surface soils (cultivation layer: about 15 to 20cm) is applied to the oil-polluted soils, the oil removing rate is more than or equal to 75 percent (by using the methylene chloride refluxing extraction / gravimetric method) within three months; and the ecological microbial inoculum has a high effective colony count, a strong adaptability, and an obvious effect on remedying the ecological environments of oil-polluted soils.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV +1
Preparation method of fermentation microbial inoculum for reinforcing and promoting organic fertilizer compost
InactiveCN102796668ALarge specific surface areaPlay deodorizingFungiBio-organic fraction processingBacillus licheniformisSludge
The invention relates to a preparation method of a fermentation microbial inoculum for reinforcing and promoting organic fertilizer compost. The method provided by the invention is characterized in that the microbial inoculum of the invention has compost promotion effects on chicken manure, sludge and garbage, and is complex microorganisms composed of bacillus subtilis, Bacillus licheniformis, Rhodopseudomonas palustris, saccharomyces cerevisiae and candida tropicalis with a ratio of 1:1:1:1:1 basically. The method has the active effects that 0.5-1% of microbial inoculum is added in a compost material (chicken manure, sludge or house refuse), and a micro-ecological dominant microflora can be formed rapidly. According to the invention, the odor of a compost material with water content of 50%-60% can be eliminated on the second day (determination by character description) under normal temperature, and the compost process can be completed in 5-7 days. The fermentation microbial inoculum has a high effective colony count and strong adaptability, and has obvious effects for eliminating the odor and promoting the composting process.
Owner:叶城县金秋实业生物肥有限公司
Method for counting colonies
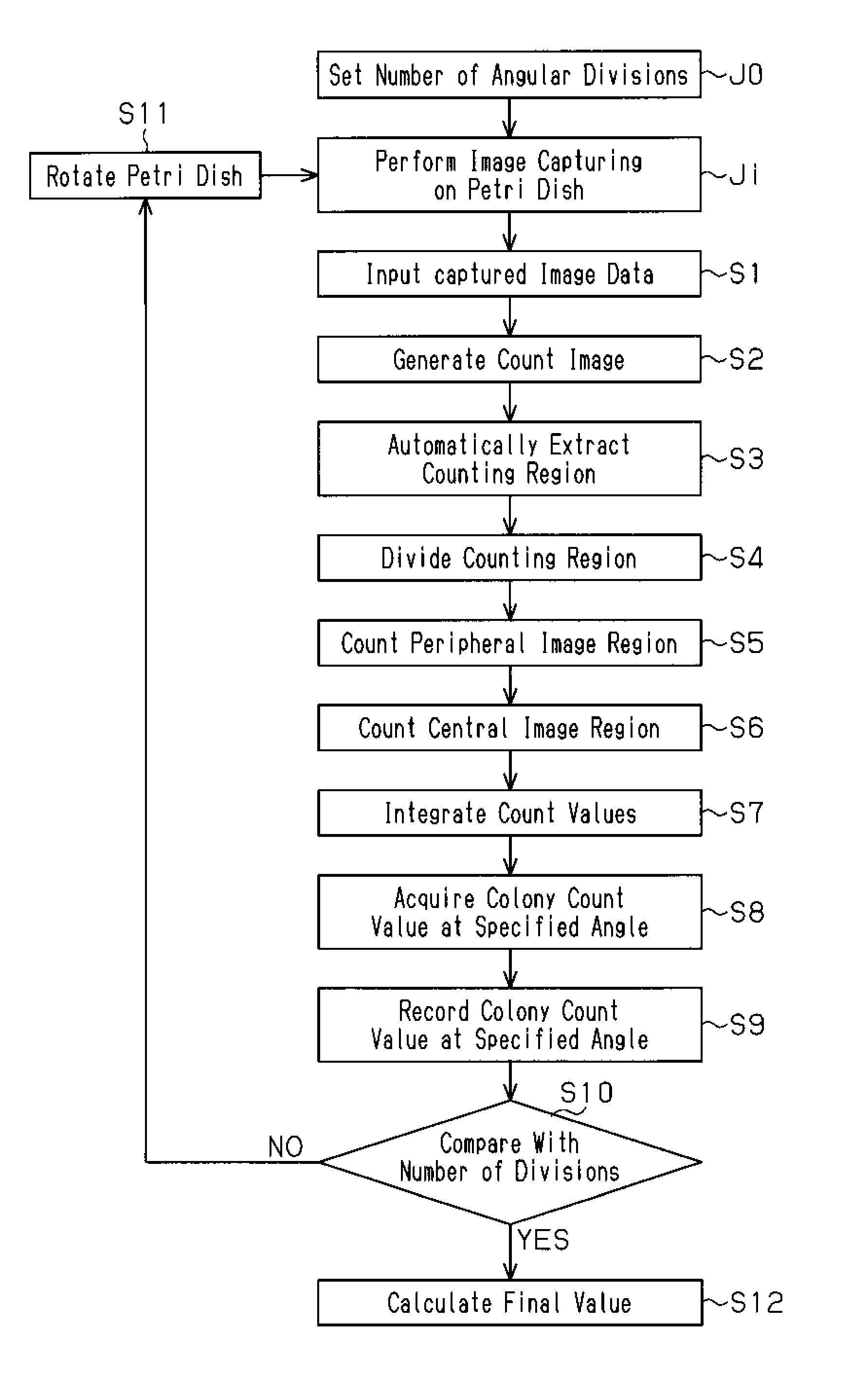
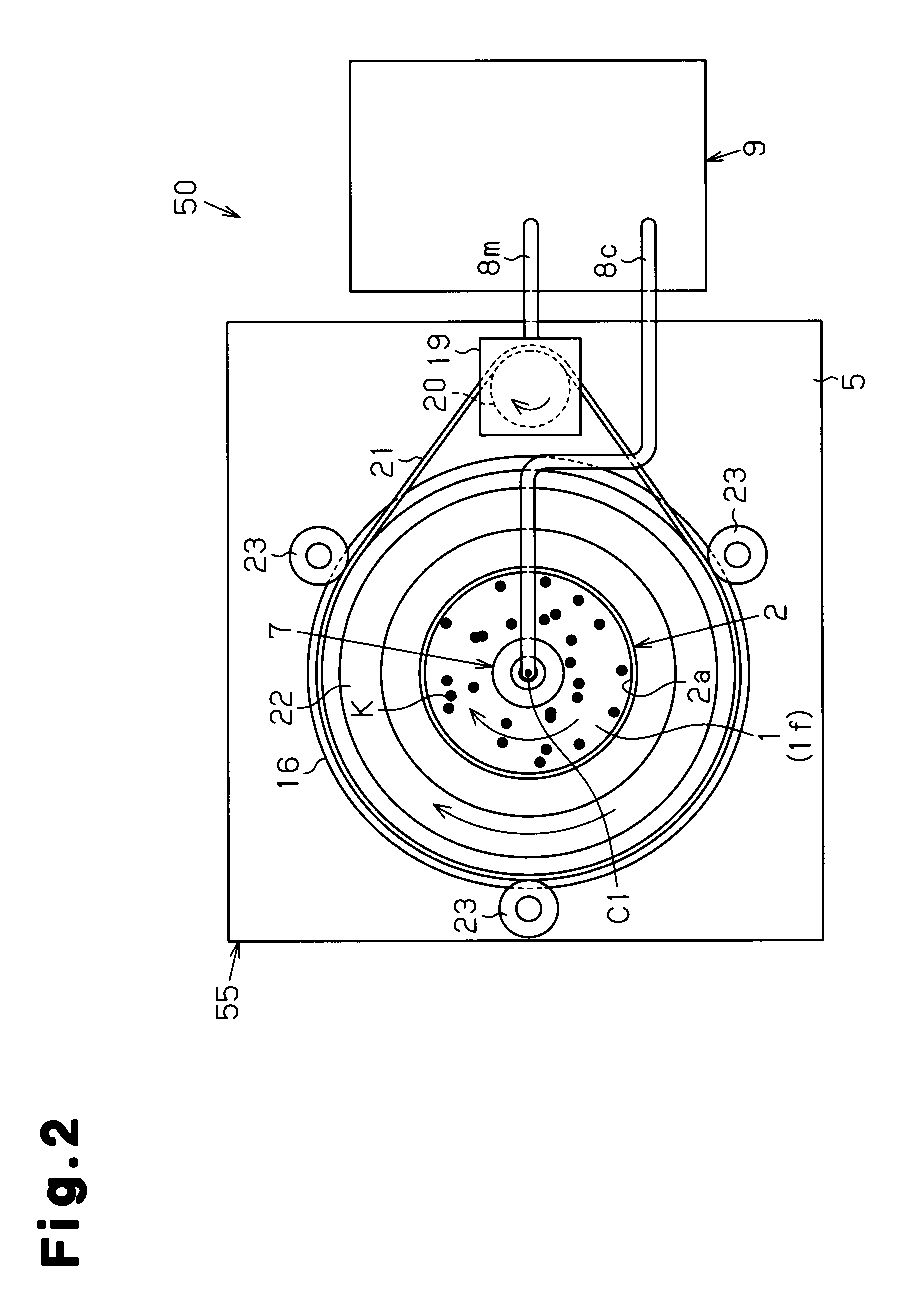
ActiveUS8831326B2Calculation stableEliminate the problemImage enhancementImage analysisColony countComputer science
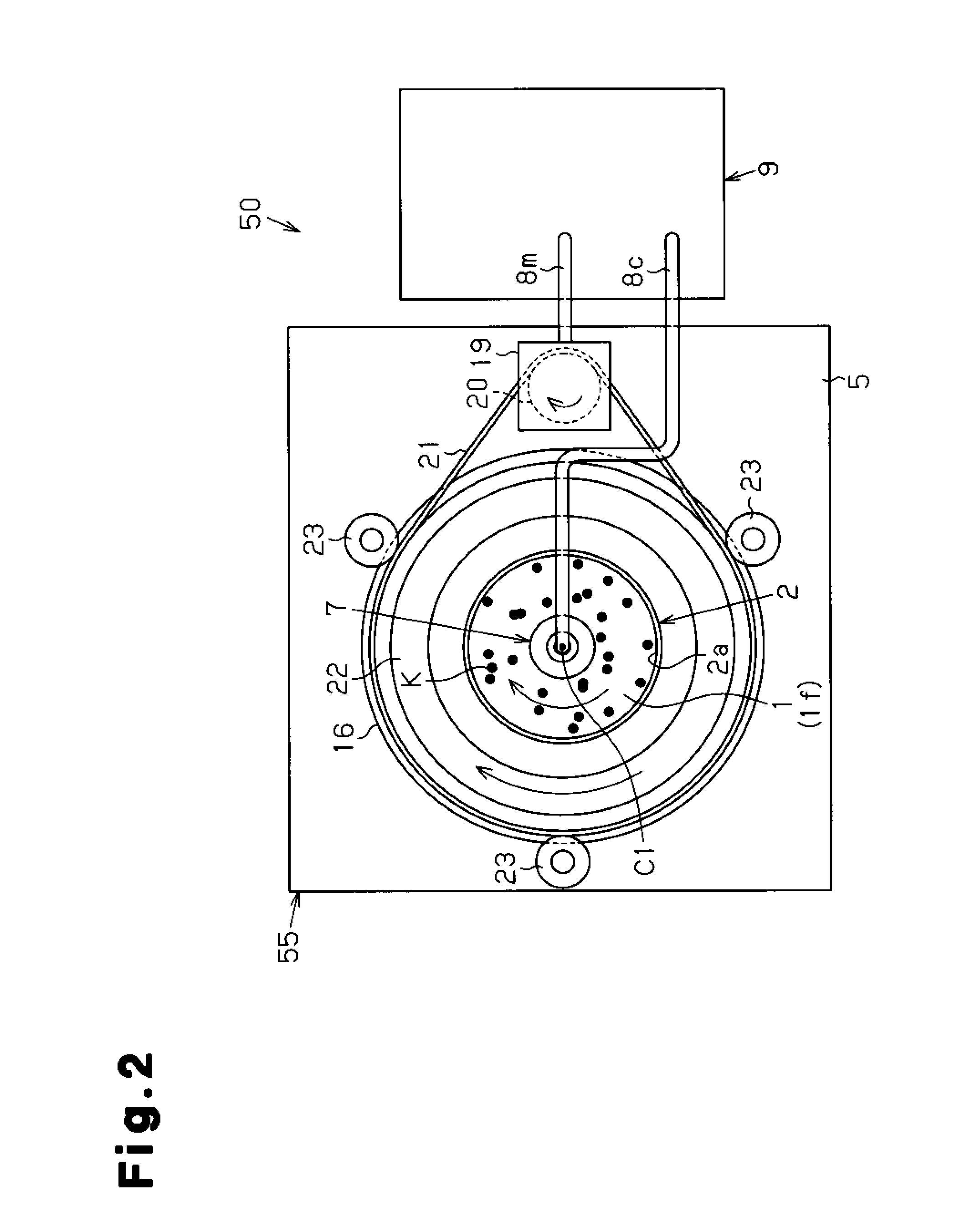
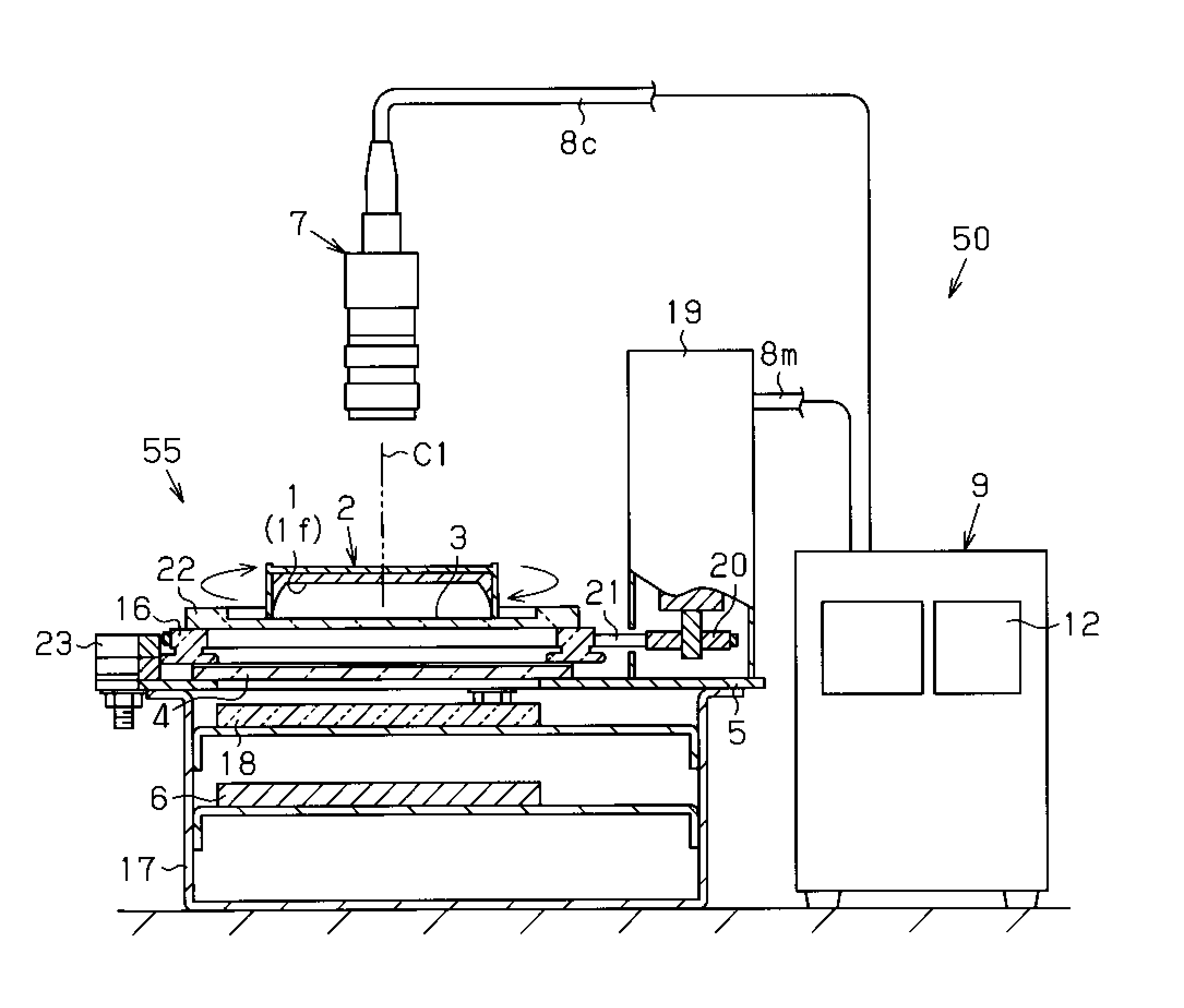
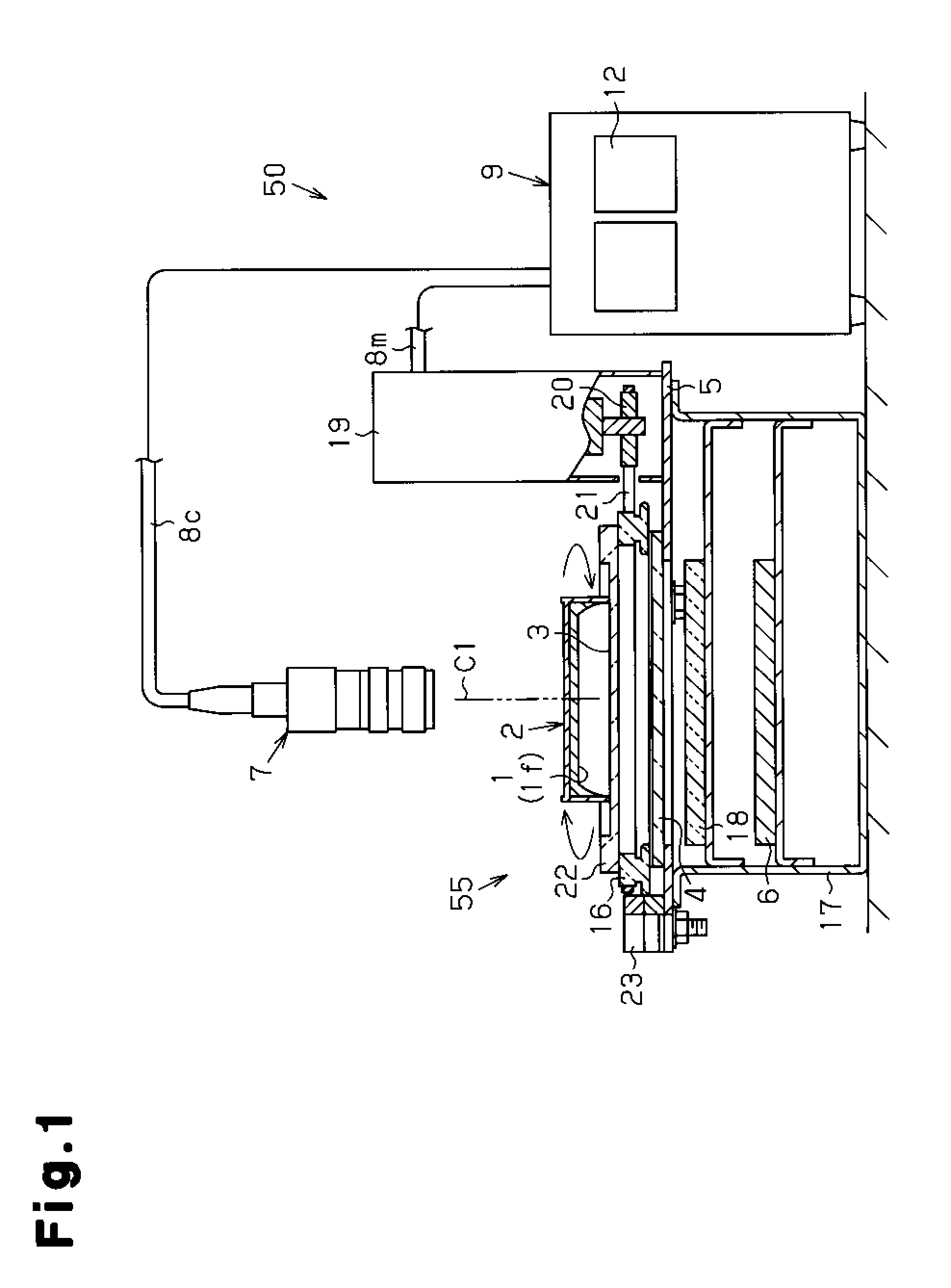
Colonies growing on a culture medium surface may be more accurately counted with reduced variation in the counts obtained by capturing a plurality of images of the entire culture medium surface, wherein successive images are captured following rotation of the culture medium surface relative to the image capture apparatus by n / 360 degrees where n is the number of images to be captured; performing data processing on image data of the entire culture medium surface of the petri dish at each specified angle; and the number of colonies in the petri dish is calculated by performing numerical processing on the number of colonies counted separately at each specified angle.
Owner:N TECH +2
Method for treating liquid dung in pig farms
InactiveCN105152416AReduce CODGood processing effectWaste water treatment from animal husbandryMultistage water/sewage treatmentPig farmsUltrafiltration
Owner:周智 +3
Method for Counting Colonies
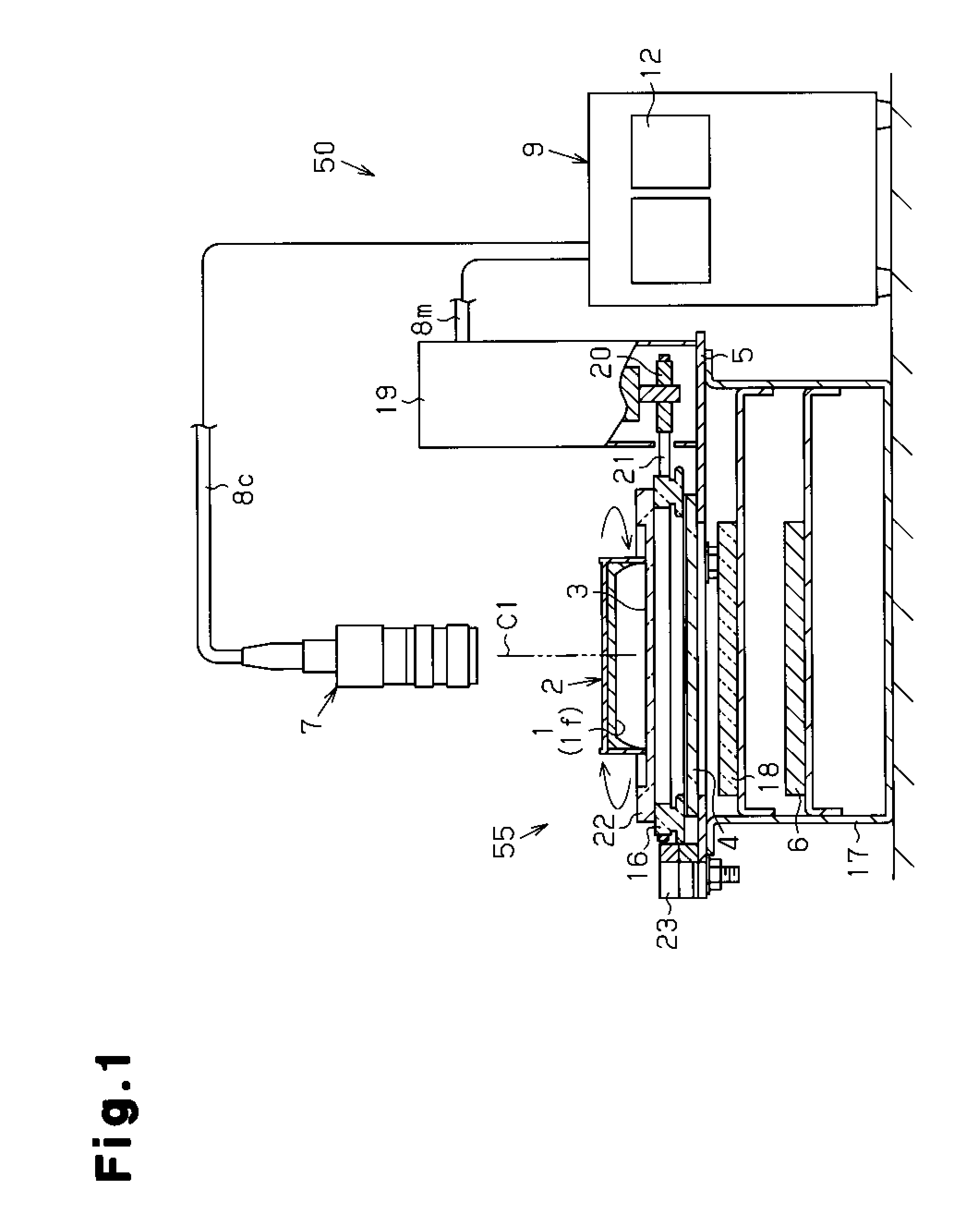
ActiveUS20100166271A1Stable data calculationEliminate the problemImage enhancementImage analysisCcd cameraColony count
Problem to be Solved There is provided a colony counting method capable of obtaining highly reliable and stable colony count values with easy and simple means by eliminating the variation in colony count due to image capturing conditions when the number of colonies is counted by performing data processing on an image obtained by image capturing means performing image capturing on a petri dish.Solution When the number of colonies is counted by performing image capturing and data processing on microbial colonies developed in a culture medium 1 in a petri dish 2 by a CCD camera 7 (image capturing means) provided in an extension direction of a rotational axis C1, which is set near a center of the culture medium surface if of the petri dish, the petri dish is rotated around the rotational axis by a specified angle obtained by dividing one rotation of the petri dish by a predetermined number, and image data of the entire culture medium surface of the petri dish is acquired for each rotation by a specified angle; the number of colonies at each specified angle is counted separately by performing data processing on image data of the entire culture medium surface of the petri dish at the specified angle; and the number of colonies in the petri dish is calculated by performing numerical processing on the number of colonies counted separately at each specified angle.
Owner:N TECH +2
Method for exploring indicator bacteria by utilizing n-butyl alcohol oxidizing bacteria as oil-gas microorganism
InactiveCN102002519AImprove reliabilityShort training periodMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismDistilled water
The invention relates to a method for exploring indicator bacteria by utilizing n-butyl alcohol oxidizing bacteria as oil-gas microorganism, comprising the following steps of: carrying out block process on a soil sample; coating the soil sample in the hydrocarbon oxidizing bacteria medium by utilizing a spread-plate method in an aseptic operating room; and putting the hydrocarbon oxidizing bacteria medium in a static incubator to cultivate the hydrocarbon oxidizing bacteria, wherein the n-butyl alcohol is used as the unique carbon and energy source of hydrocarbon oxidizing bacteria medium, the cultivating parameter is set as 30 DEG C, 5 days form a cultivating period, and the needed soil sample is air dried rapidly, then dissolved in distilled water and put in a shaking table to activate for use. The method has the advantages of shortening the cultivating period to 5 days, simplifying the whole experiment operating process, enhancing the safety, accurately obtaining the quantity of the needed objective colony by utilizing the medium with n-butyl alcohol as the unique carbon source, and enhancing the reliability of the colony count data through reducing the cultivating time.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
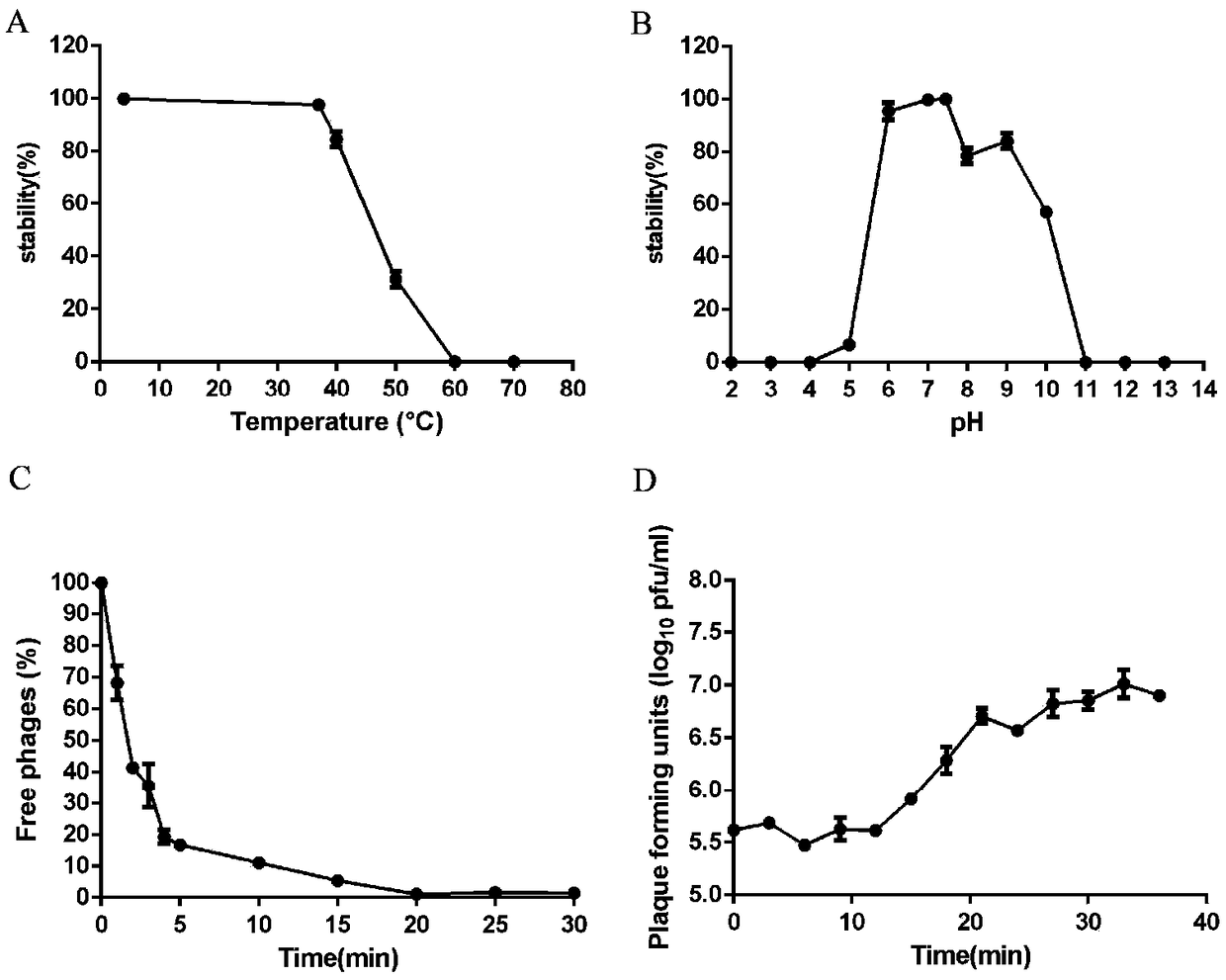
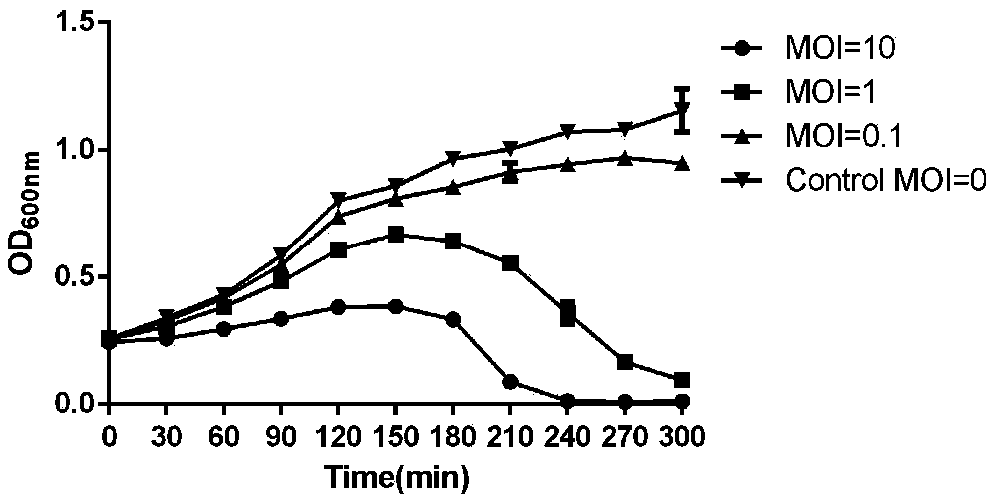
Staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage and application
ActiveCN109082414AEffectively eliminateGood bodyAntibacterial agentsViral/bacteriophage medical ingredientsBacteroidesStaphylococcus cohnii
The invention discloses staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage and application. The staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage and the application have the advantages that staphylococcus aureus can be specifically effectively eliminated by the staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage, excellent in-vivo and in-vitro antibacterial effects can be realized by the staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage for medicine-resistant staphylococcus aureus, experimental foundations can be provided to clinically developing preparations for preventing and treating medicine-resistant staphylococcus aureus infection, and the staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage has great clinical application potential; the skin abscess average areas of nude mice of bacteriophage treatment groups are 47.32 mm<2> in skin abscess models when MOI(multiplicity of infection) is equal to 10, and the average bacterium load is 3.553*10<7> CFU / g; the skin abscess average areas of nude mice of MRSA (methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus) infection groups are 150.4 mm<2>, and the average bacterium load is 2.284*10<8> CFU / g; the skin abscess areas of the mice of the bacteriophage treatment groups are smaller than the skin abscess areas of the mice of the MRSA infection groups, the colony count of the mice of the bacteriophage treatment groups is lower than the colony count of the mice of the MRSA infection groups, and the difference of the skin abscess areas and the colony count has statistical significance.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
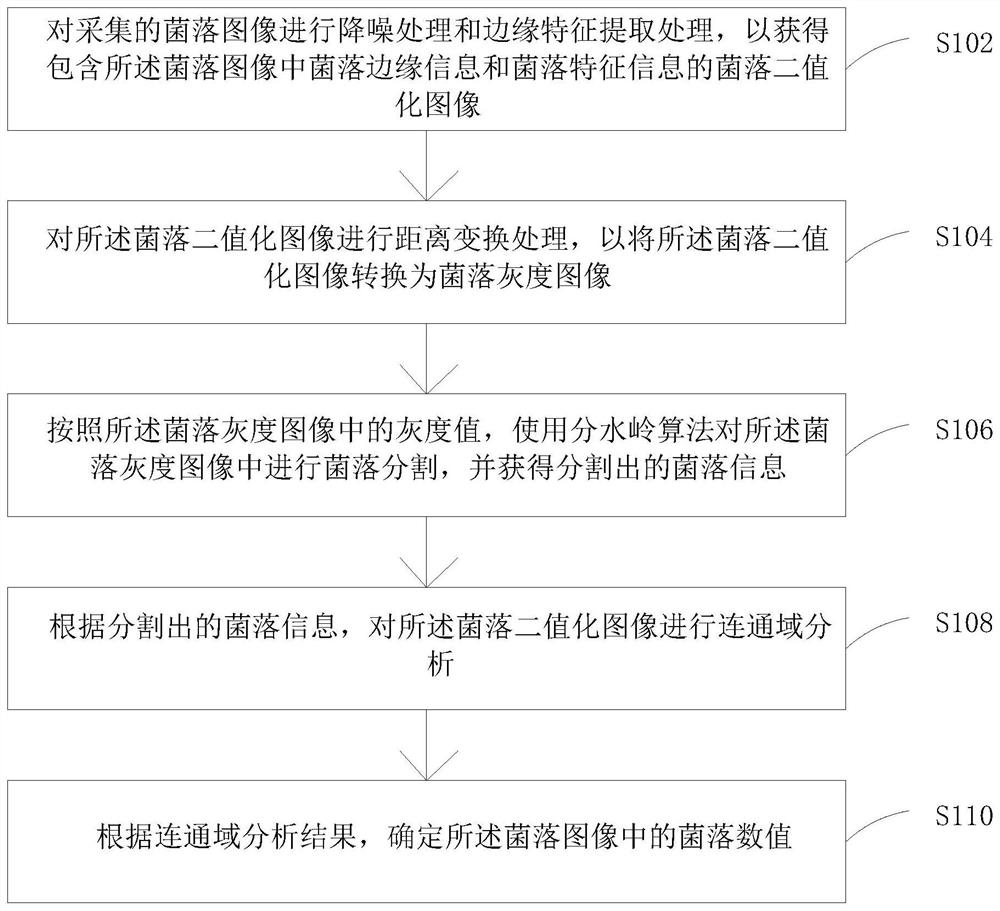
Bacterial colony counting method and device and computer storage medium
PendingCN112614062ASolve unclear edges and glued bordersSolve the problem of easy overlapImage enhancementImage analysisFeature extractionGray level
The embodiment of the invention provides a bacterial colony counting method and device and a computer storage medium. The bacterial colony counting method comprises the following steps: performing noise reduction processing and edge feature extraction processing on an acquired bacterial colony image to obtain a bacterial colony binary image containing bacterial colony edge information and bacterial colony feature information in the bacterial colony image; carrying out distance transformation processing on the bacterial colony binarization image to convert the bacterial colony binarization image into a bacterial colony gray level image, wherein the gray level value of the bacterial colony edge indicated by bacterial colony edge information in the bacterial colony gray level image is smaller than the gray level value of the interior of the bacterial colony indicated by bacterial colony feature information; according to the gray value in the bacterial colony gray image, carrying out bacterial colony segmentation on the bacterial colony gray image by using a watershed algorithm, and obtaining segmented bacterial colony information; carrying out connected domain analysis on the bacterial colony binarization image according to the segmented bacterial colony information; and determining a bacterial colony numerical value in the bacterial colony image according to a connected domain analysis result. The method is more accurate in counting.
Owner:北京陆桥技术股份有限公司
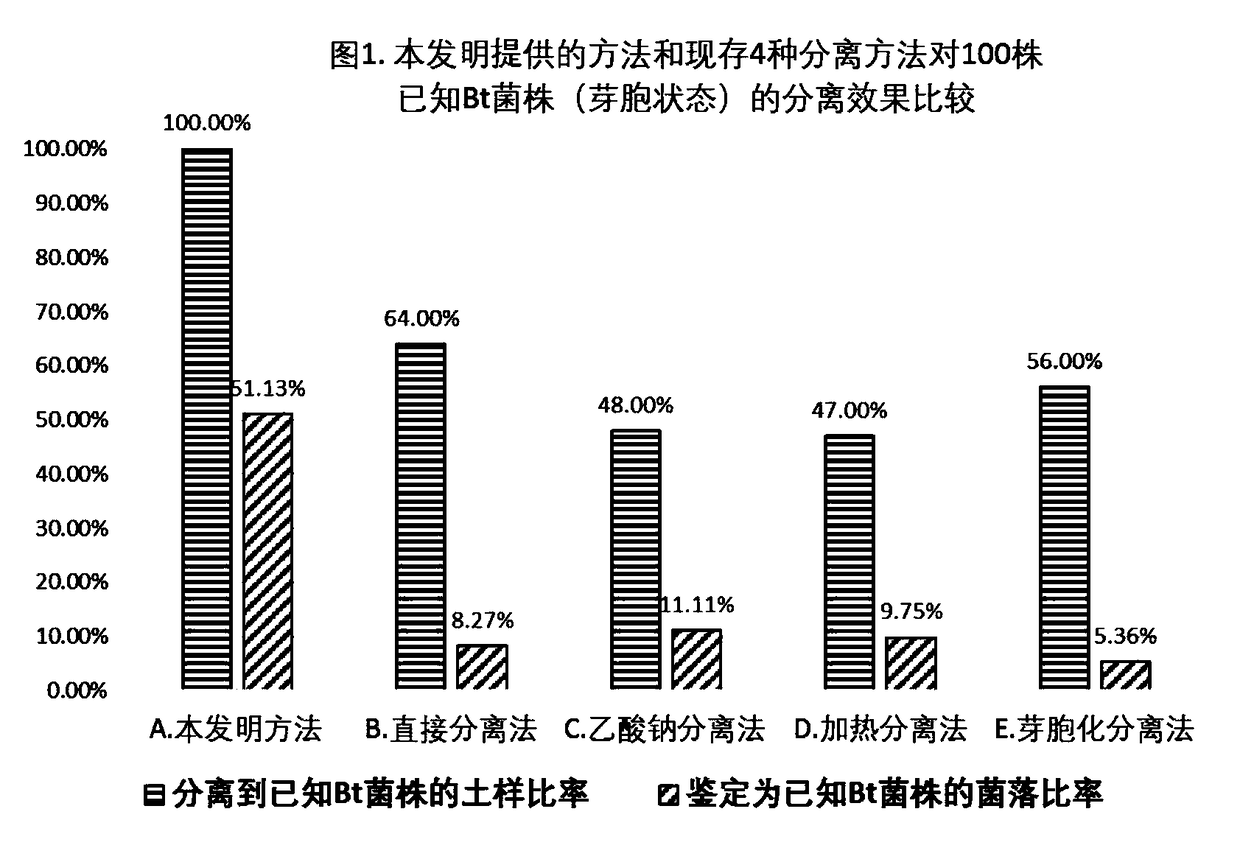
Method for high throughput screening and separation of bacillus thuringiensis and application
ActiveCN108611296AIncrease biomassEfficient separationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacillus thuringiensisHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
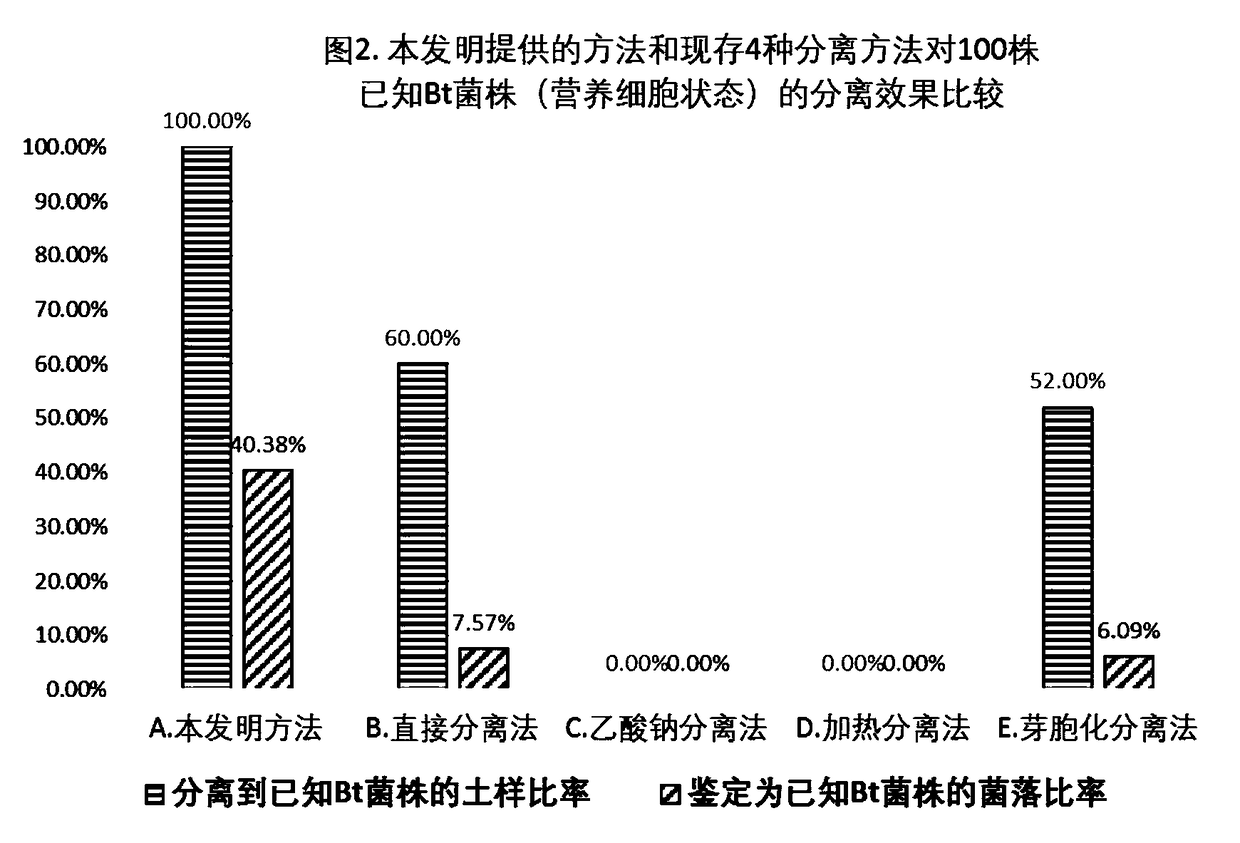
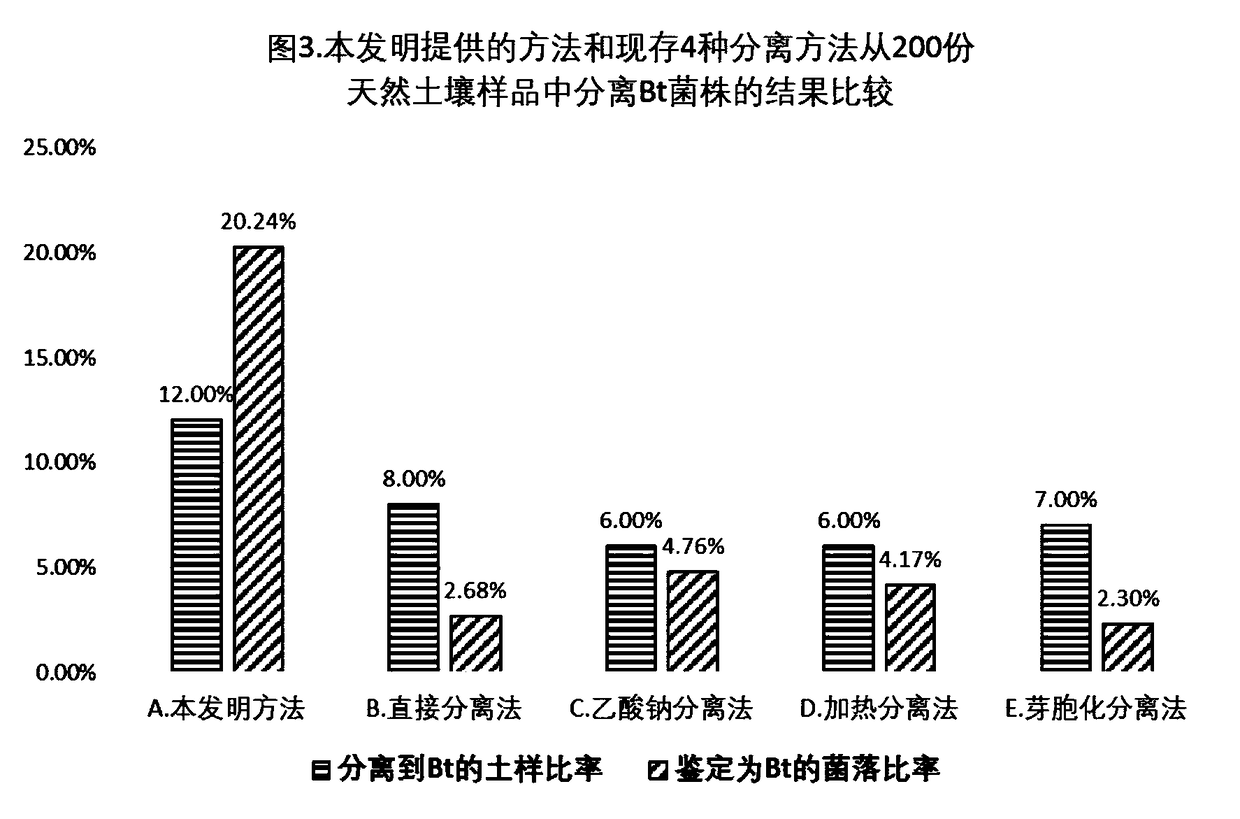
The invention belongs to the field of microbiology and discloses a method for high throughput screening and separation of bacillus thuringiensis (Bt for short) and application. The method is characterized in that absolute biomass and relative proportion of Bt cells in a sample are greatly improved by selective culture of continuous three-step different strategies; colony counts needing to be picked for transfer culture and microscopic examination are reduced, separating efficiency is greatly improved and greater convenience in operation is realized; meanwhile, the needed sample quantity is reduced and high-throughput operation can be realized; the method is particularly suitable for separating Bt strains from samples with small sample amount or samples with small Bt biomass.
Owner:江西省农业科学院农业应用微生物研究所
Dairy cow early-stage mastitis monitoring method
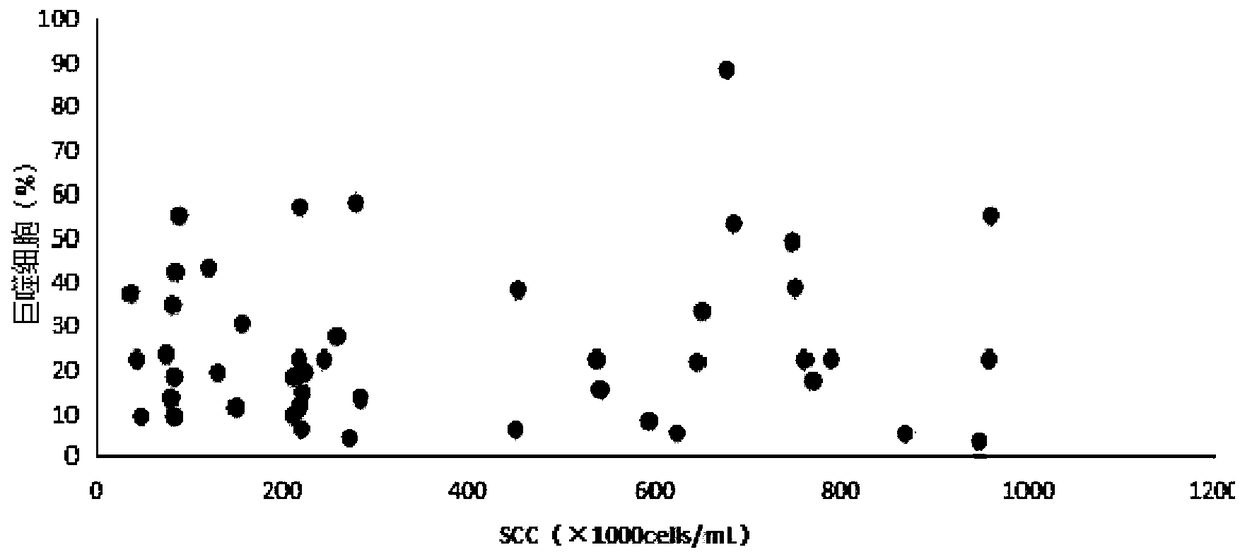
The invention provides a dairy cow early-stage mastitis monitoring method. The method includes following steps: (1), performing SCC count detection on milk; (2), performing pathogenic microorganism identification of the milk: colony count and bacteriological identification; (3), performing somatic cell typing detection; (4), identifying protein differential expression level and function of the milk: protein concentration measuring, protein quantifying and analysis protein differential expression level and function identification. By detecting differentiation degree of immune cells in cow's milk somatic cells and identifying expression level and function of mycoprotein in the milk, the method is conducive to timely finding early-stage mastitis and pathogen types inducing early-stage inflammation to make full preparation for timely prevention and targeted treatment of dairy cow mastitis.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF AGRI +1
Fermented milk sampling infectious microbe detection device for production
PendingCN113637567AReduce stepsEasy to detectBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiotechnologyMixed culture
The invention discloses a fermented milk sampling infectious microbe detection device for production. The device comprises a base and a mounting plate fixed on the base, the mounting plate is provided with a liquid strain mixing part and a gas strain culture part, the mounting plate is provided with a constant temperature box for culturing a strain culture mixed solution at a constant temperature, the mounting plate is provided with a detection part used for observing the number of infectious microbe colonies, the liquid strain mixing part is used for mixing fermented milk liquid and a culture solution, the mixed culture mixed solution is subjected to constant-temperature culture in a constant-temperature box, and the gas strain culture part is used for performing constant-temperature culture on a mixed solution of gas and the culture solution, and the detection part is used for observing the colony count of the liquid strain mixed solution and the gas strain mixed solution, observing whether bacterial contamination exists or not and judging the bacterial type. The device can perform pretreatment and detection on a sample, the whole process is continuous, sampling detection of infectious microbe by experimenters is greatly facilitated, and efficiency is high.
Owner:ANHUI XIQIANG DAIRY GROUP
Escherichia coli dynamic growth monitoring method
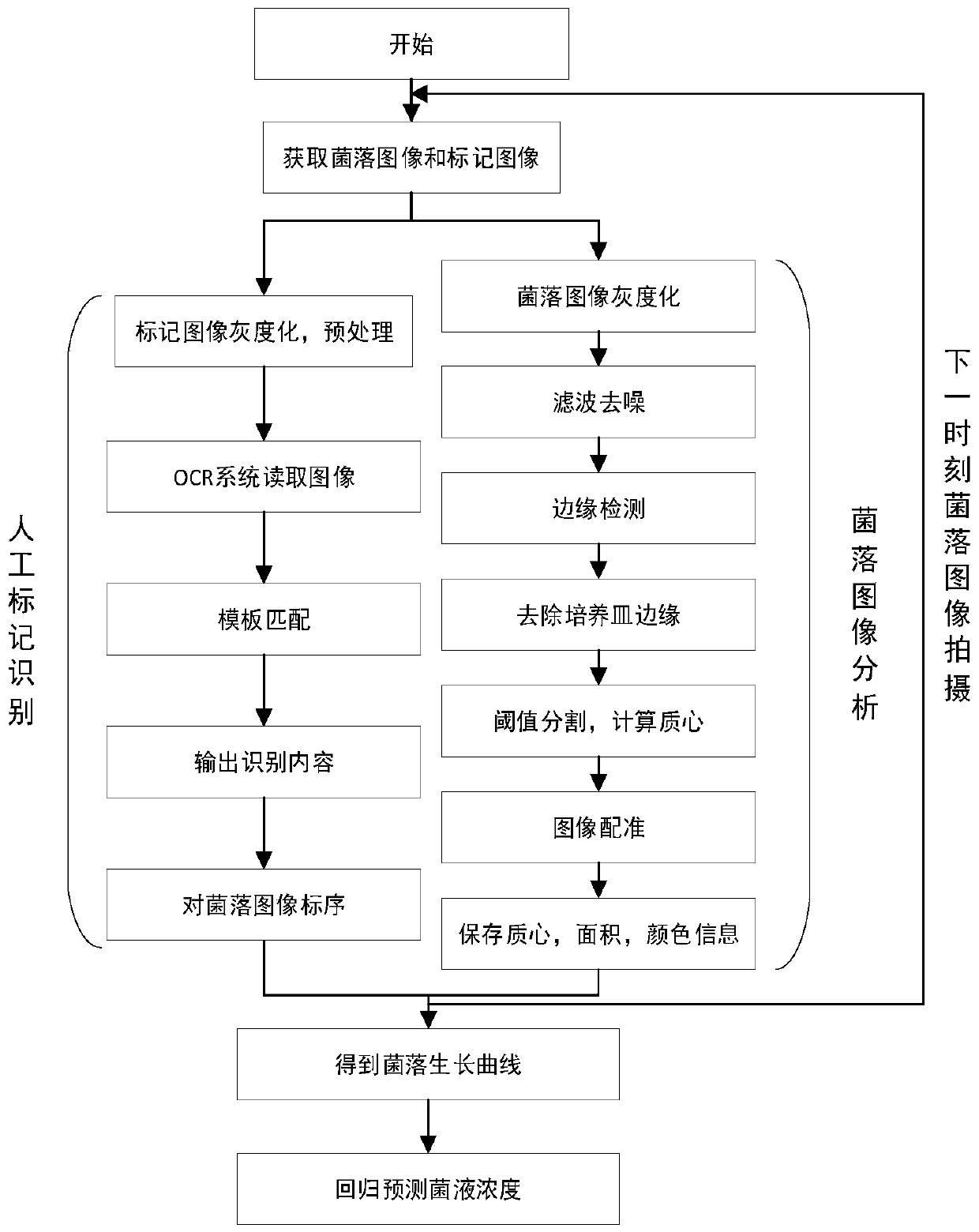
ActiveCN111368643AFacilitate dynamic growth informationUniform lightImage analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementEscherichia coliPetri dish
The invention discloses an escherichia coli dynamic growth monitoring method, and provides a method for realizing registration of an escherichia coli colony image and a previous moment image, which comprises the following steps: enabling the angles of the two images to be consistent, obtaining the centroid position of each colony, and further quickly obtaining the number of colonies in a culture dish; each bacterial colony can be positioned, the size and color information of each bacterial colony at the growth moment is counted, the growth speed is calculated according to the culture time, thegrowth stage of each bacterial colony at each time node is judged, and then a growth curve is obtained; according to the method, a regression model is used for predicting the bacterial liquid concentration according to two variable values of bacterial colony delay period time and growth rate in a logarithmic phase, the bacterial liquid concentration is compared with the concentration obtained bya traditional counting method, and error samples in the experiment process are screened out; based on the characteristics of bacterial colony growth, the regression model is established to accuratelypredict the concentration of the escherichia coli liquid, and compared with the traditional counting method which is easily interfered by the external environment, the method is more accurate, and thereliability of the obtained data is higher.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Method for inspecting microbial limit of nifuratel and nysfungin vaginal soft capsules
InactiveCN108315384AAvoid false negativesImprove medication safetyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismYeast
The invention belongs to the technical field of drug detection, and particularly relates to a method for inspecting microbial limit of nifuratel and nysfungin vaginal soft capsules. The method comprises the following steps: preparing bacterial liquid; preparing a test solution; measuring a total quantity of aerobic bacteria, molds and yeasts; determining that a ratio of a value of the quantity ofbacteria in a test group minus the quantity of bacteria in a test sample group to the quantity of bacteria in a bacterial liquid group is qualified in a range of 0.5-2; inspecting control bacteria. The sample treatment adopted in the invention can better eliminate nifuratel, reduces bacteriostasis, has simple operation process and low pollution probability, prevents samples from false negative during inspection, and improves medication safety of patients.
Owner:BEIJING JINCHENG TAIER PHARMA CO LTD
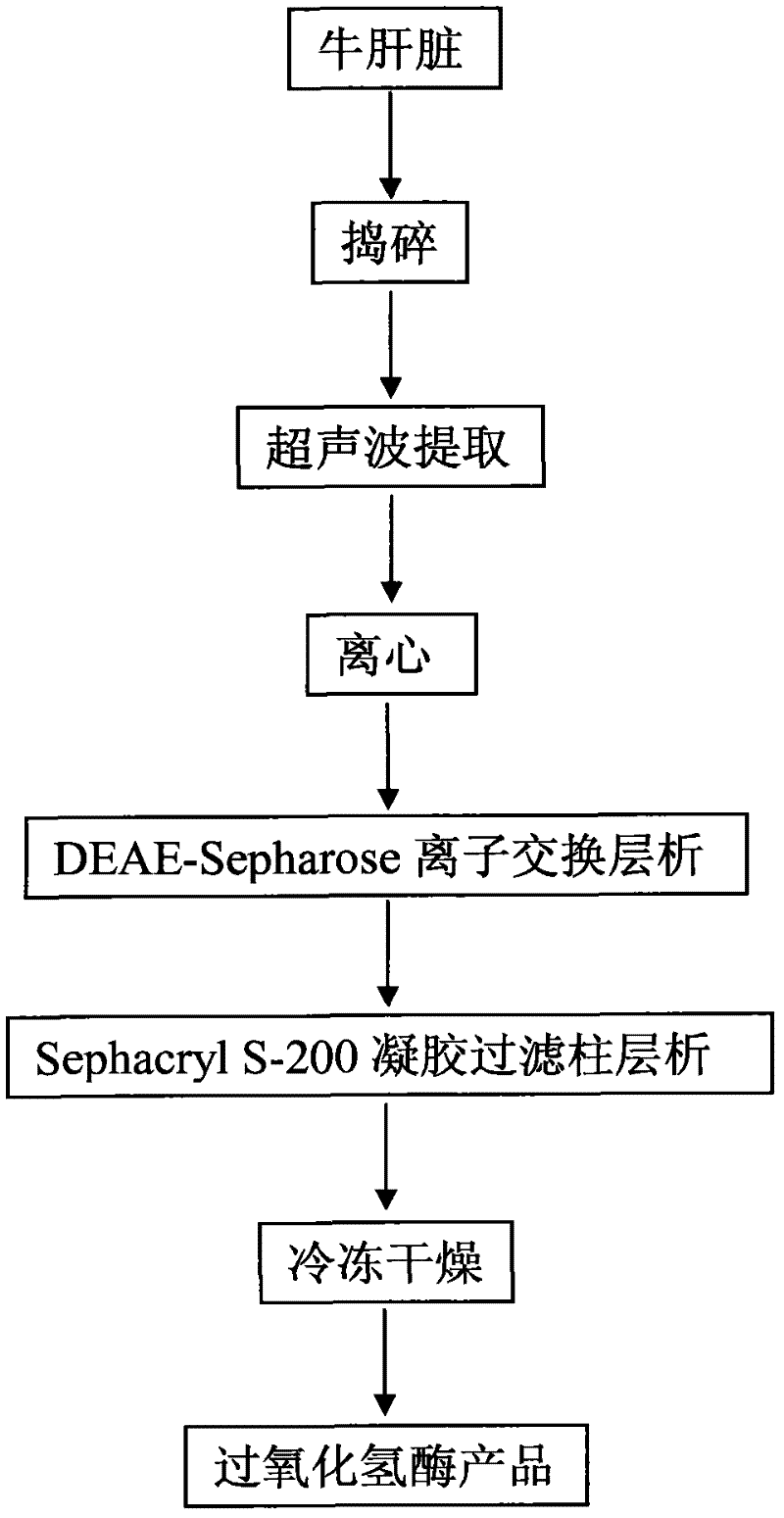
Method for preparing catalase by using bovine livers
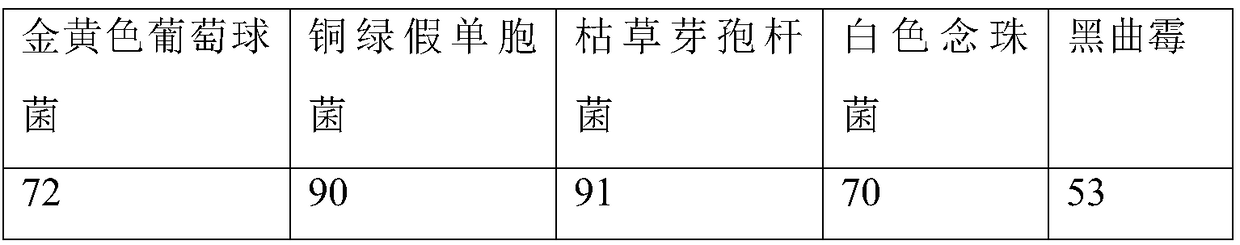
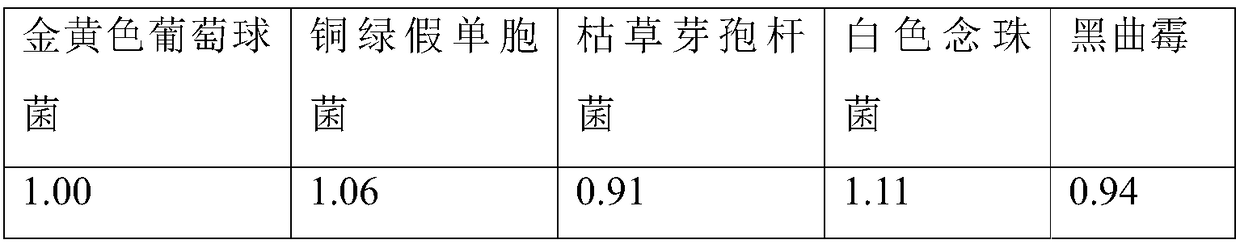
The invention provides a method for preparing catalase by using bovine livers, wherein fresh bovine livers are used as raw materials and subjected to chopping and homogenization, and a catalase product with high enzyme activity is obtained by means of processes such as ultrasonic extraction, ion exchange chromatography, gel filtration chromatography and freeze drying. The method of the invention solves the problems of complex production process, heavy pollution, high production cost and low product yield of the prior art in preparing the product. The catalase prepared by the method of the invention has an enzyme activity of 6000 U / mg and a colony count of less than or equal to 1000 cells / ml, and is suitable to be widely used in the fields of food, paper making and textile industry.
Owner:TIBET TIANCHENG AGRI ANIMAL HUSBANDRY IND
Preparation method of high-activity microencapsulated lactic acid bacteria starter
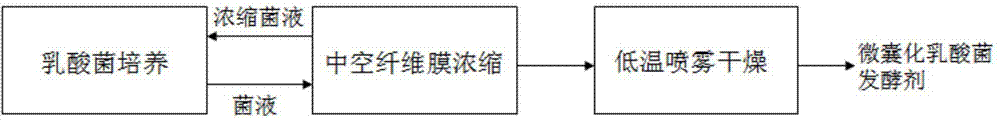
The invention discloses a preparation method of a high-activity microencapsulated lactic acid bacteria starter. The preparation method comprises the following steps: inoculating lactic acid bacteria to a culture medium to be cultured; filtering the bacterial liquid with a hollow fiber membrane, and concentrating to form a concentrated bacterial liquid; injecting a fresh culture medium into the concentrated bacterial liquid to be cultured; filtering the prepared bacterial liquid with the hollow fiber membrane and concentrating for 2-3 times to obtain a concentrated bacterial liquid with a unit colony count up to 1,011 cfu / ml above; adding gelatin, sucrose and whey protein into the concentrated bacterial liquid as wall materials; carrying out spray drying to obtain the microencapsulated lactic acid bacteria starter. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, the hollow fiber membrane is combined with a bioreactor to carry out high-density culture and concentration of the lactic acid bacteria, so as to implement online continuous filtration, concentration and culture and avoid pollution due to thallus transfer; the coupled spray drying at a low temperature is carried out to effectively protect the concentrated high-density bacteria, so as to obtain the lactic acid bacteria starter with a unit viable count up to 1*10<11>-1*10<12> cfu / ml.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
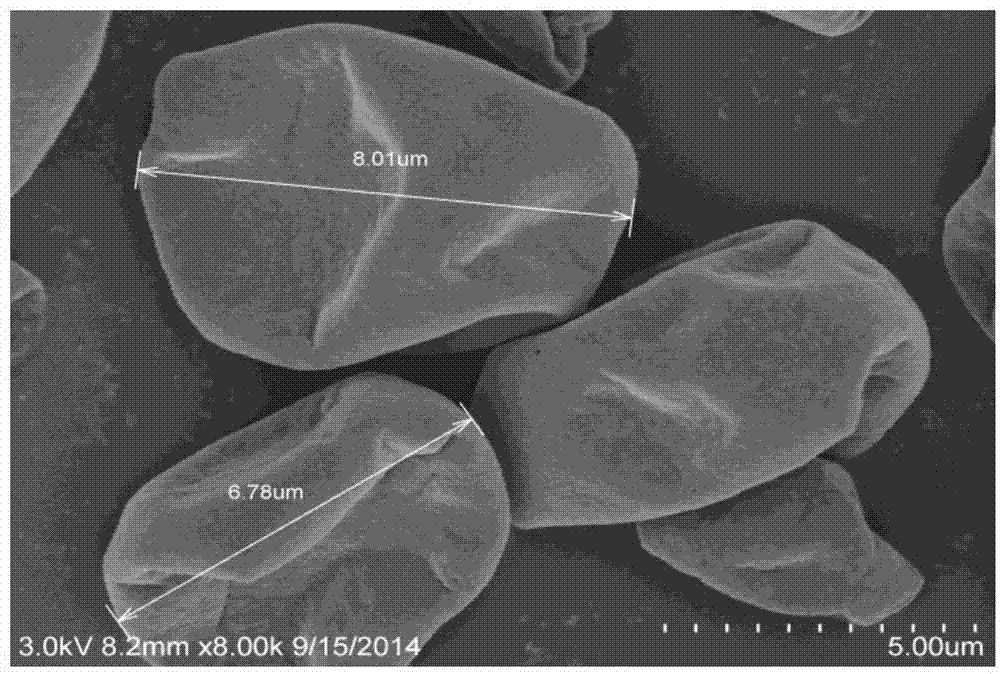
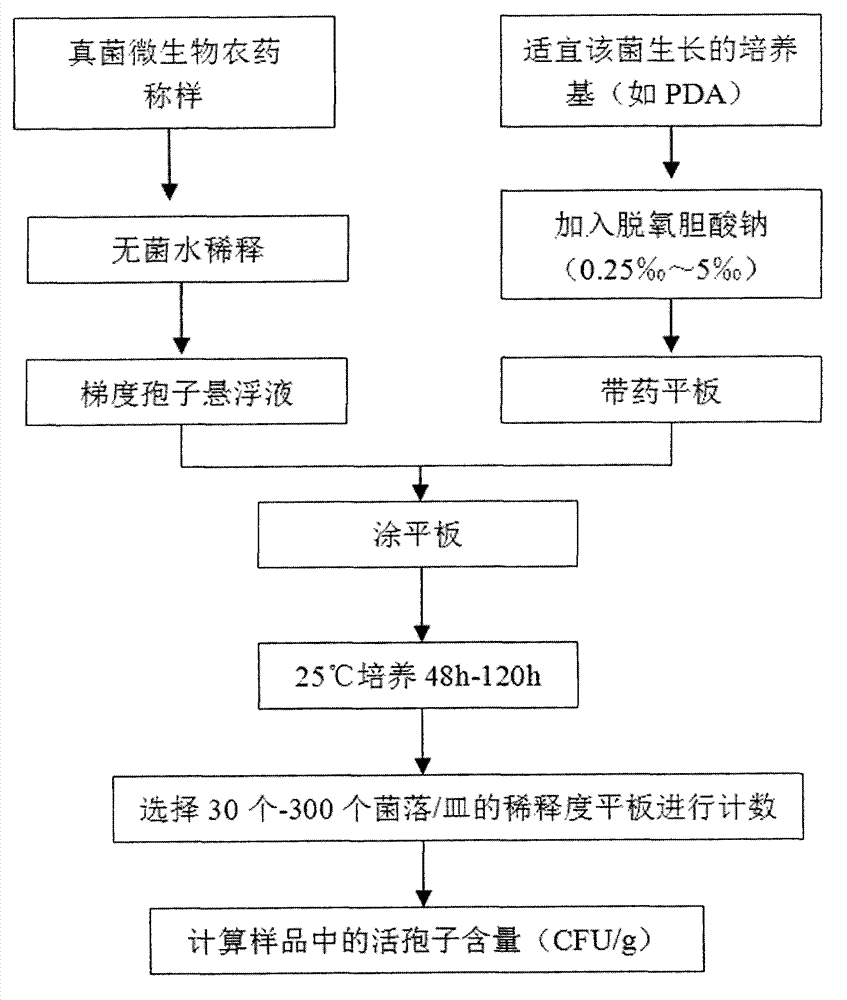
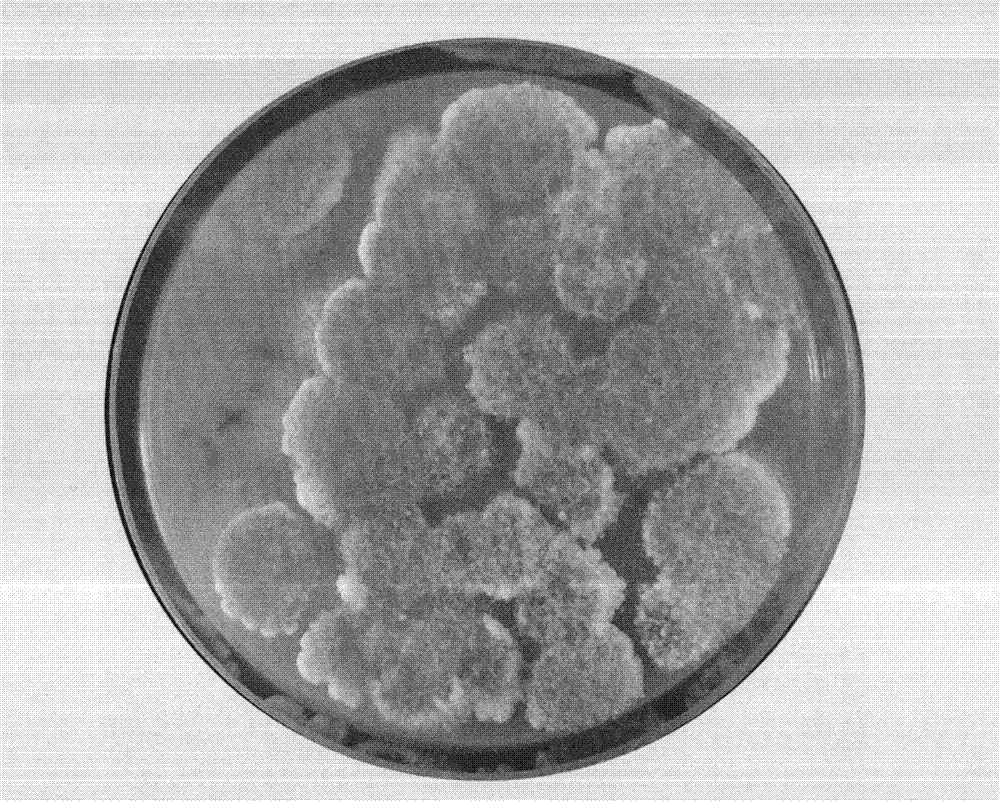
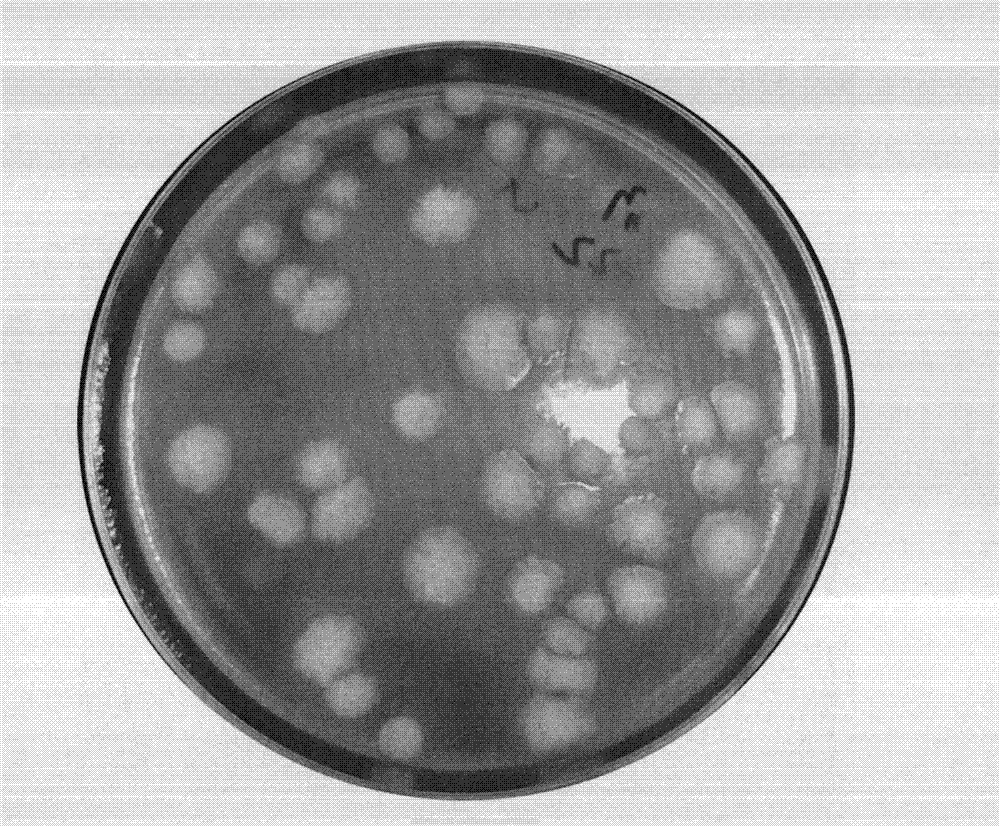
Method for measuring content of live spores in fungal microbial pesticide quickly
InactiveCN102899386ADoes not inhibit germinationDoes not suppress extensionMicrobiological testing/measurementPolyethylene glycolColony count
The invention discloses a method for measuring the content of live spores in a fungal microbial pesticide quickly. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) adding 0.25 to 5 weight percent of sodium deoxycholate into a fungal culture medium, and preparing flat plates; (2) soaking fungal microbial pesticide samples in sterilization water containing Tween 20 or polyethylene glycol octylphenol ether, and shaking; (3) diluting in a multiple gradient mode, coating the samples of different dilutability on the flat plate respectively and uniformly, and culturing at room temperature for 48 to 120 hours; (4) counting colony counts, wherein the flat plates on which the colony counts are 30 to 300 are effectively-counted flat plates; and (5) counting the content of the live spores, namely C is equal to T*N*10, wherein in a formula, C is the content of the fungal pesticide live spores, the unit is colony forming unit (CFU) / gram, T is dilution times corresponding to the counted flat plates, and N is average colony counts on a plurality of effectively-counted flat plates of the same dilution times. By the method, the content of the live spores of the fungal microbial pesticide can be measured simply, conveniently and quickly, and the detection accuracy is high.
Owner:农业部农药检定所
Micro-ecological bacterial preparation for killing soil nematodes and its preparation method
InactiveCN101099492ALarge specific surface areaPromote growthBiocideNematocidesMicroorganismEcological environment
The present invention relates to a microecological germicide preparation for killing soil eelworm and its preparation method. Said microecological germicide preparation for killing soil eelworm is made up by using (by wt%) 60%-80%, of bacillus megatherium and 20%-40% of streptolin through a certain preparation process. The soil eelworm-killing rate can be up to 100% and the soil grub-killing rate can be up to above 95%.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
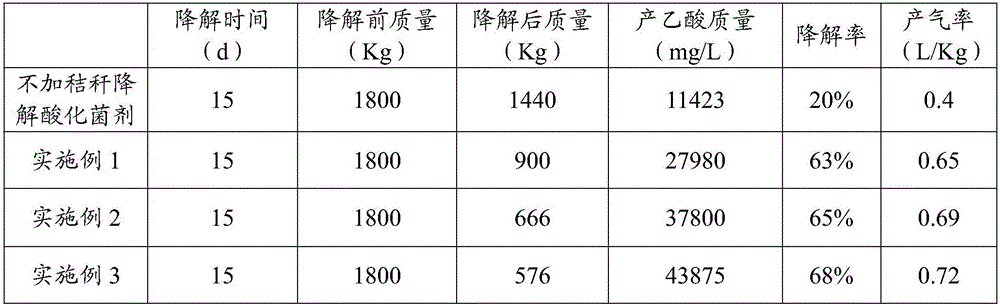
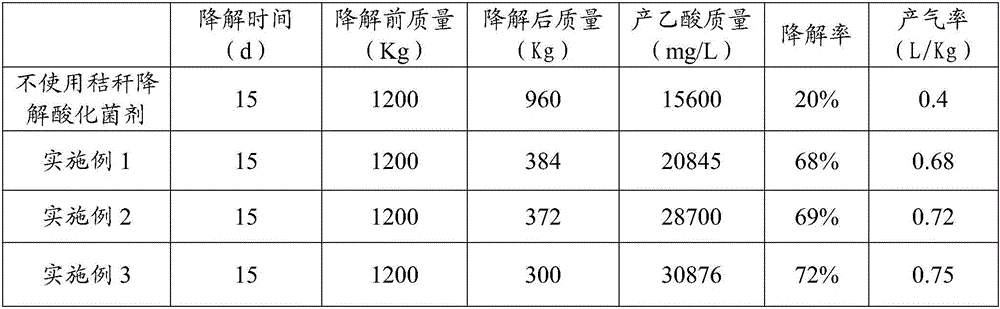
Straw low temperature degradation acidification microbial agent and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106350504AQuick breakdownAccurate measurementMicroorganism based processesWaste based fuelAcetic acidMicrobial agent
The invention discloses a straw low temperature degradation acidification microbial agent. The straw low temperature degradation acidification microbial agent contains a bacterial strain and an adsorption carrier, wherein the bacterial strain contains aminobacterium mobile sp, clostridium cellulolyticum, clostridium xylanolyticum and bacillus cereus, wherein the colony count of aminobacterium mobile sp is 33-36, the colony count of clostridium cellulolyticum is 33-36, the colony count of clostridium xylanolyticum is 18-25, and the colony count of bacillus cereus is 5-15; the adsorption carrier is prepared by mixing medical stones and straw powder; and the ratio of the total number of effective live bacteria to the mass of the absorption carrier in the straw low temperature degradation acidification microbial agent is 1*10<5>-1*10<6>: 1g of adsorption carrier. The straw low temperature degradation acidification microbial agent can quickly decompose celluloses and hemicelluloses at a low temperature and degrade the celluloses and the hemicelluloses into acetic acid, thereby increasing biogas production efficiency. In addition, the invention also provides a preparation method and application of the straw low temperature degradation acidification microbial agent.
Owner:YANBIAN UNIV
Preparation method and application of bacillus subtilis for feed
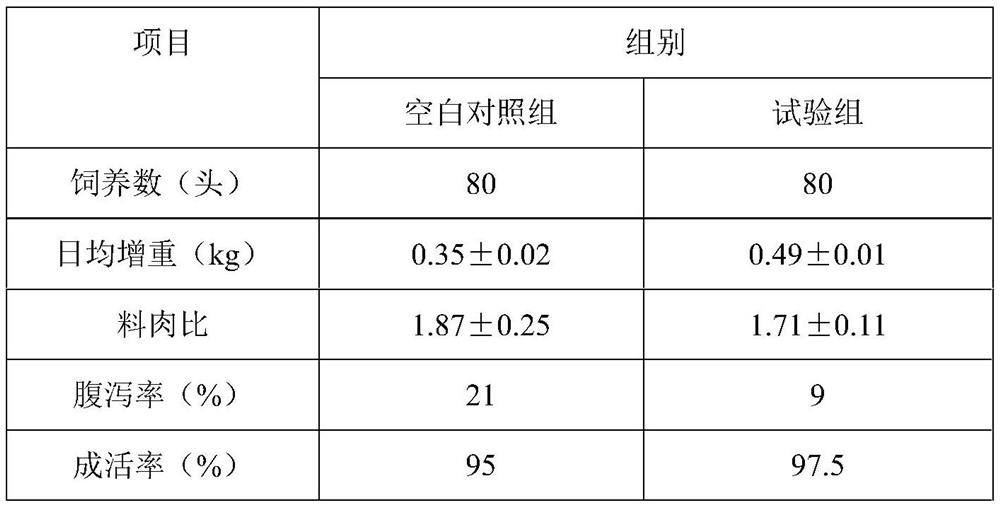
PendingCN113773996AGrow fastShort fermentation cycleBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of bacillus subtilis for feed. The bacillus subtilis is subjected to high-density liquid-state fermentation and then treated, a protective agent is added, and freeze drying is performed to prepare a microbial inoculum serving as a feed additive. In the fermentation process of the strain, the inoculum size of a seed solution is 2-10% (V / V), the strain is inoculated into a fermentation culture medium, the temperature is 25-42 DEG C, fermentation is carried out for 20-48 hours, and the colony count is 5.8*10<10> cfu / g. The fermentation culture medium comprises molasses, corn flour, bean dregs and the like, so that the production cost is remarkably reduced. Compared with a traditional fermentation technology, the colony count of fermentation production is obviously increased, the fermentation period is short, and safety and environment friendliness are achieved; meanwhile, coarse raw materials such as the bean dregs and the molasses are adopted for fermentation production; the bacillus subtilis can be used as the feed additive and has the obvious effects of improving the intestinal environment of livestock and poultry, enhancing animal immunity and promoting animal growth; and the production wastes such as the bean dregs are turned into wealth, so that the recycling of waste resources is realized, the pollution of the waste materials to the environment is reduced, and the production cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH +1
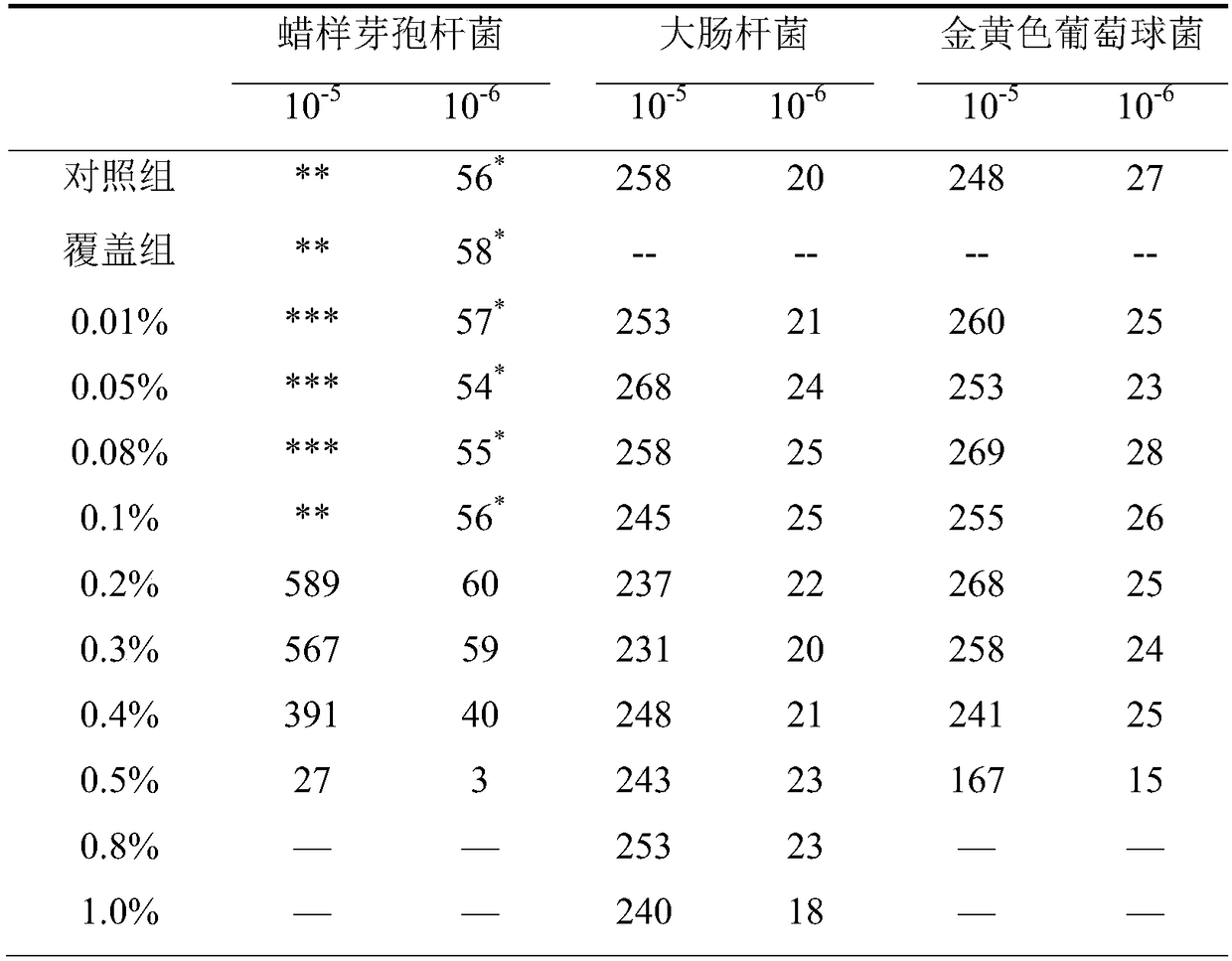
Application of TCC to prevention of colony diffuse growth in colony count determination
The invention provides application of TCC to prevention of colony diffuse growth in colony count determination. The method includes: taking Bacillus cereus, Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureusof appropriate dilution, adding 0.01%, 0.05%, 0.08%, 0.1%, 0.2%, 0.3%, 0.4%, 0.5%, 0.8%, and 1.0% TTC aqueous solution plate count agar, at the same time taking count agar without TTC as control, andobserving the growth condition of bacteria. In colony count determination, if a sample possibly contains Bacillus colonies growing diffusely on an agar medium surface, TTC with a concentration of 0.2%-0.3% can be added to the agar to prevent incalculability situation caused by diffusion of colonies.
Owner:德清县食品药品检验所
Method for measuring bacterial colonies of bacillus thuringiensis in refuse compost
InactiveCN102533934AEfficient use ofReduce wasteMicrobiological testing/measurementBacillus thuringiensisAureobasidium sp.
The invention discloses a method for measuring bacterial colonies of bacillus thuringiensis in refuse compost. According to the method, the average number of bacterial colonies in the same dilution is calculated firstly, if the size of sheet-shaped lawns is less than half that of a panel and the distribution of the other half of bacterial colonies is even, then the number of the bacterial colonies of the whole panel can be expressed by multiplying half the number of the bacterial colonies by 2, then the average number of the bacterial in the dilution is calculated, the bacterial colonies with the average number of the bacterial colonies between 30 and 300 are selected, and when the average number of the bacterial colonies in only one dilution accords with the range, the total number of the microorganism bacterial colonies of a sample is expressed by multiplying the average number of the bacterial colonies by the dilution factor. Experimental results show that the bacterial colonies formed on a culture medium are round, white and non-transparent, are smooth in edges, and are positive by gram stain; observed under a microscope, the bacteria are in oval rhabditiform and bacterial spores are oval; and bromophenol blue and sarranine dye liquor are used for conducting parasporal crystal dye, red bacteria, colourless bacteria spores and blue parasporal crystals are observed under the microscope, therefore, the bacteria are preliminarily evaluated as bacillus thuringiensis.
Owner:TIANJIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for decontaminating dehydrated garlic products
InactiveCN108567098AReduce the amount of bacteriaSolve slow salesMagnetic separationFood dryingElectrolysisColony count
The invention discloses a method for decontaminating dehydrated garlic products. The method for manufacturing the dehydrated garlic products includes steps of soaking and disinfecting selected garlicin acidic electrolytic water with the pH (potential of hydrogen) value of 2-4 for 5-15 min and then cleaning the garlic by the aid of pure water; placing the garlic in ozone water, carrying out cooling treatment on the garlic for 5-10 minutes and splitting the garlic; secondarily treating split raw materials by the aid of ozone water for 20-40 minutes; draining raw materials treated by the aid ofthe ozone water, then carrying out stepped temperature control drying on the raw materials, in other words, drying the raw materials at the temperatures of 110-120 DEG C for 1-2 hours, gradually reducing the temperatures until the temperatures reach 60-80 DEG C, and continuing to dry the raw materials until the moisture contents of the raw materials are reduced and reach 5-8%. The method has the advantages that the quantity of germs carried by the garlic can be reduced by 60%-67%, late sterilization can be omitted, the sterilization intensity of the method is far lower than the sterilization intensity of conventional processing technologies, dehydrated garlic which is subjected to contamination treatment by the aid of the method is little in color and nutritional component change, but thetotal colony count of the dehydrated garlic can be obviously reduced and reaches high standards, and the problem of dull sale due to the fact that the total colony count of existing garlic products exceeds standards can be effectively solved by the aid of the method.
Owner:徐州农丰生物化工有限公司
Colony count card and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN111607633AReduce usageImprove work efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementProcess engineeringColony count
The invention discloses a colony count card and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of rapid microbial detection. Dry powder of various components of a culture medium is utilized, a certain amount of corresponding indicator is added according to different target microorganisms to prepare a microorganism test piece; a series of tedious preparation work such as traditional culture medium preparation high-pressure steam sterilization and plate pouring is omitted, the manufacturing process is simple, the product is stable and convenient to take and use, professional operators and expensive instruments are not needed, and the working efficiency of microbiological detection personnel can be greatly improved; a proper amount of specific enzyme chromogenic indicator isadopted, so that the chromogenic effect and the result accuracy are ensured; the use amount of the culture medium is small, and the detection cost can be greatly reduced.
Owner:北京华益精点生物技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com