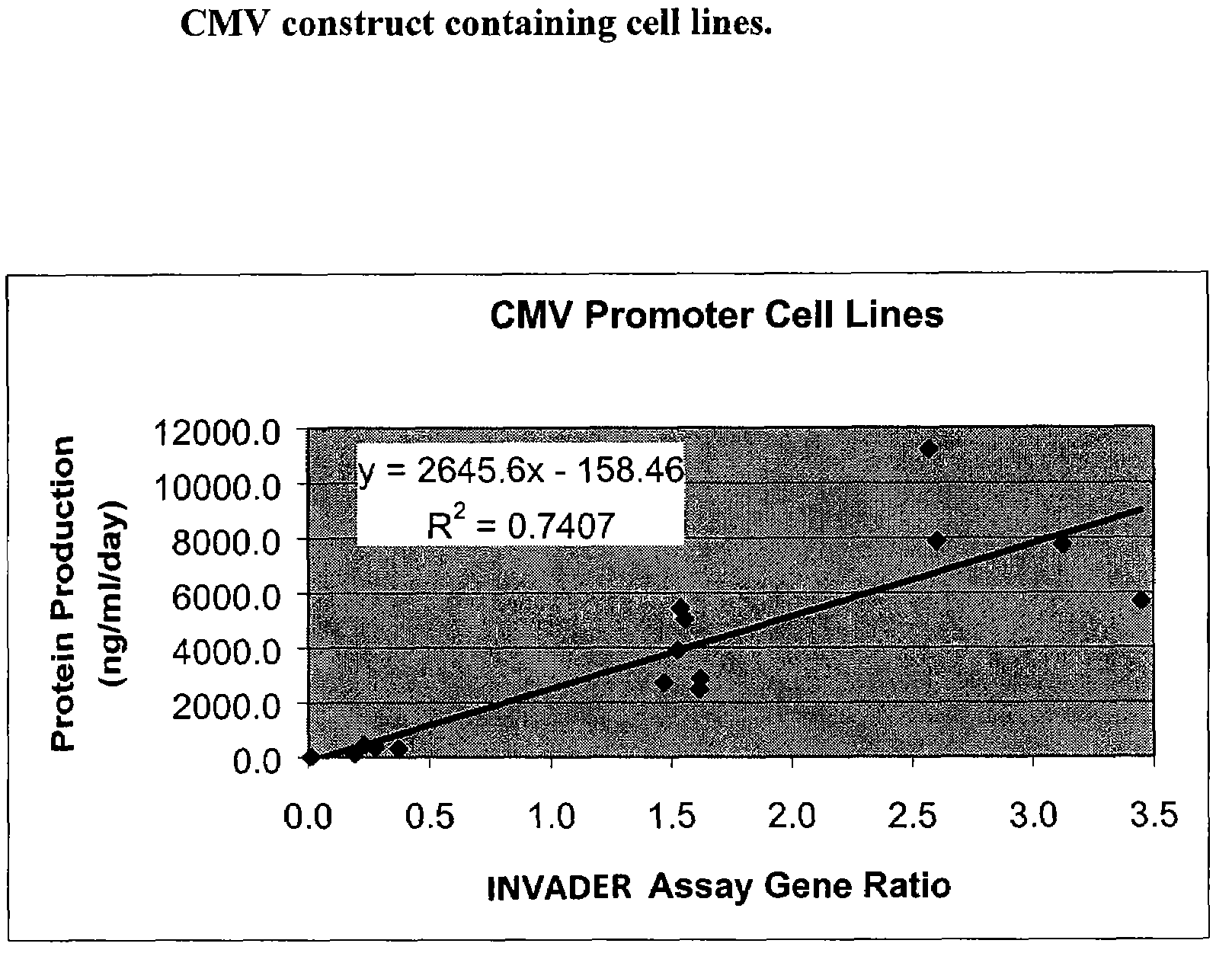
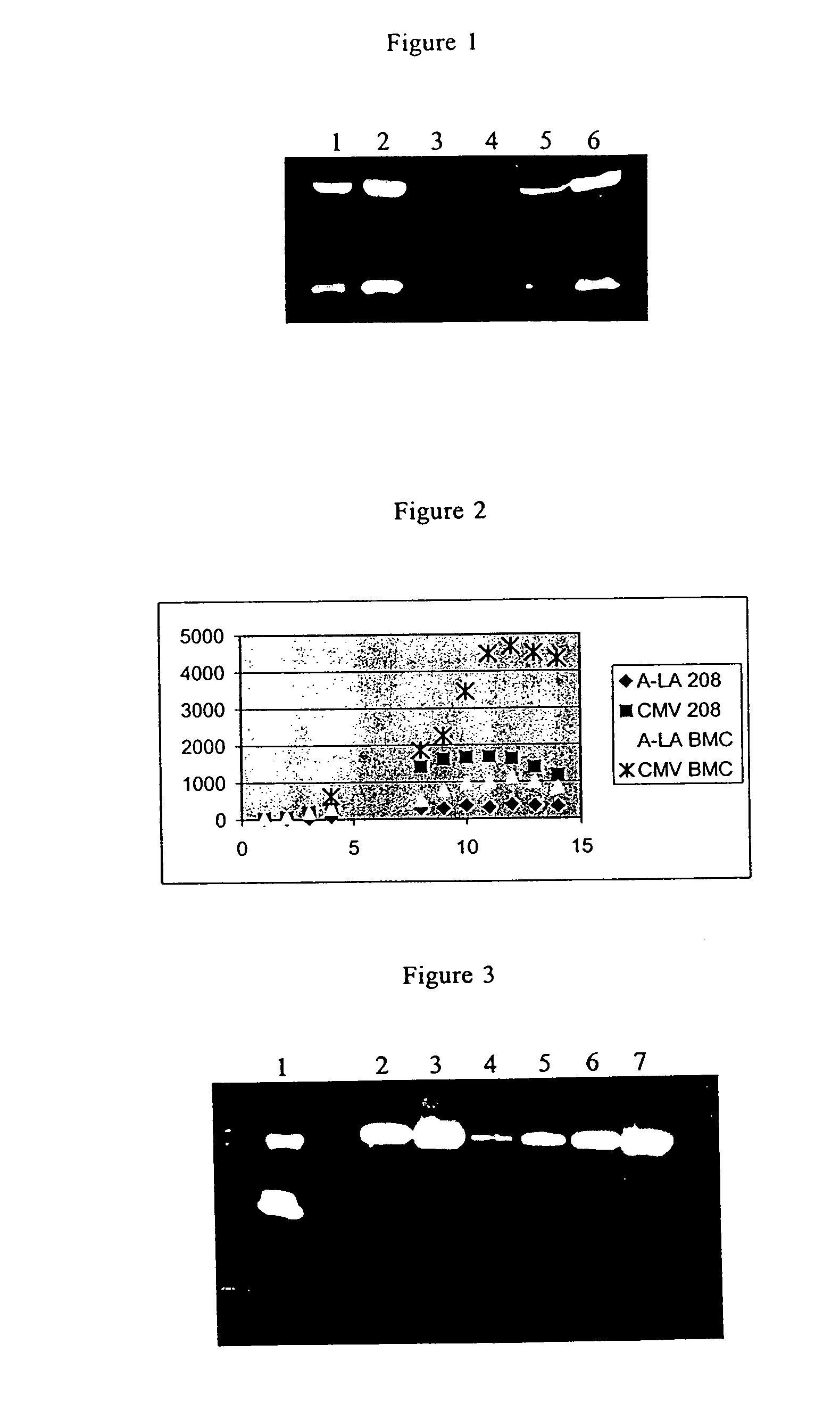
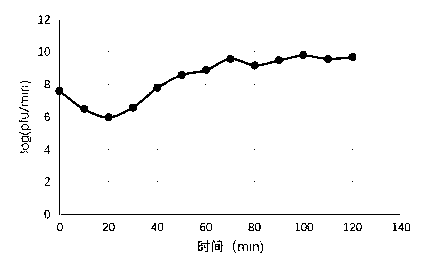
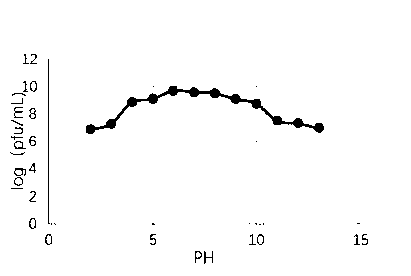
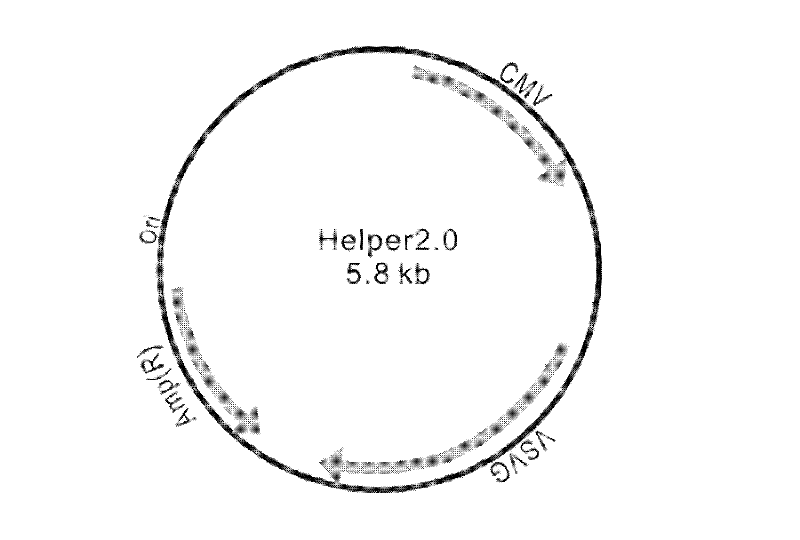
Patents
Literature
54 results about "Multiplicity of infection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
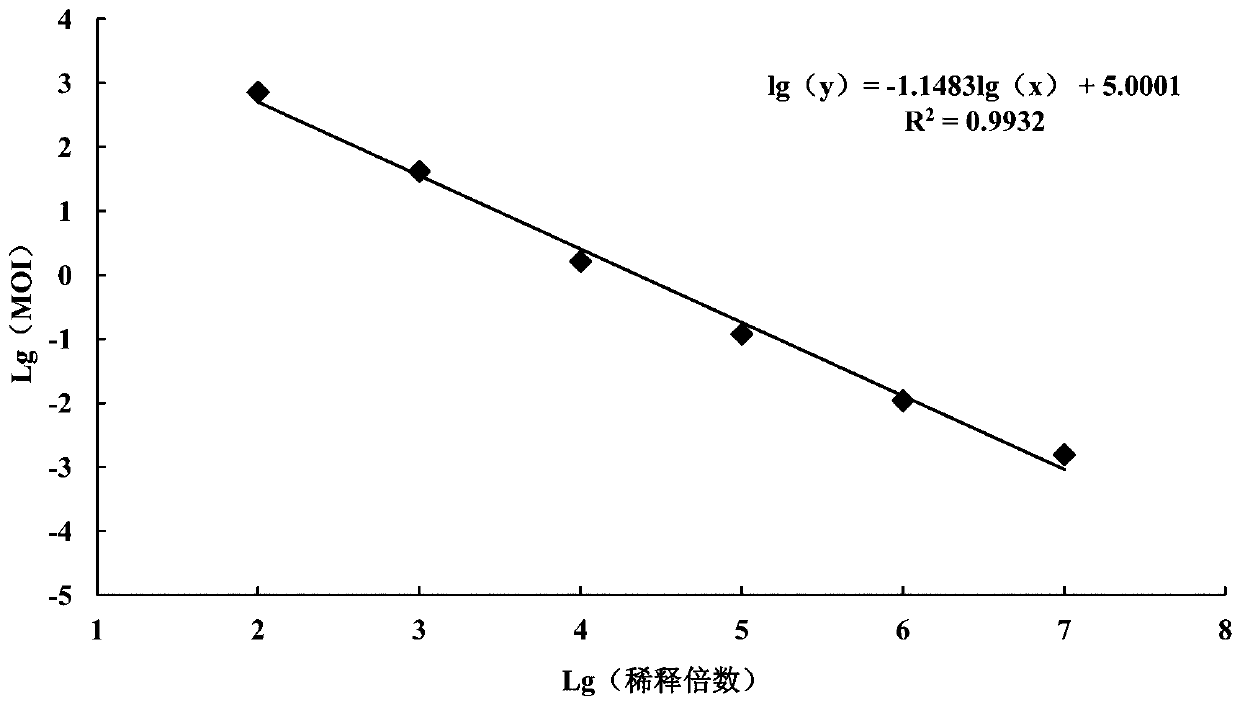
In microbiology, the multiplicity of infection or MOI is the ratio of agents (e.g. phage or more generally virus, bacteria) to infection targets (e.g. cell). For example, when referring to a group of cells inoculated with virus particles, the multiplicity of infection or MOI is the ratio of the number of virus particles to the number of target cells present in a defined space.
Preparation method of NK (Natural Killer) cells
InactiveCN107904204AClear ingredientsImprove securityCulture processBlood/immune system cellsNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory ReceptorsMicrobiology
The invention discloses a preparation method of NK (Natural Killer) cells. The preparation of the NK cells is prepared through the steps of coating a culture bottle, collecting peripheral blood, separating mononuclear cells, inoculating, amplifying and harvesting the cells. A serum free culture medium provided by the invention has clear components and high safety; after the mononuclear cells are cultured and activated by the culture medium, the amplification capability is strong; after being cultured for 15 to 18 days, the mononuclear cells are amplified for 160 to 200 times; after the cells are detected by a flow cytometer, the content of the NK cells of CD3<->CD56<+> is 65 to 70 percent and the content of T cells of an NK sample of CD3<+>CD56<+> is 5 to 15 percent; the content of NK andNKT cells exceeds 75 percent and the killing activity on K526 reaches 85 percent or above when the multiplicity of infection is 20 to 1; furthermore, an amplification method is simple and efficient and large-scale production is facilitated.
Owner:GENESIS STEMCELL REGENERATIVE MEDICINE ENG CO LTD
Host Cells Containing Multiple Integrating Vectors
InactiveUS20080286779A1Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsVirus peptidesHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsLentivirus
The present invention relates to the production of proteins in host cells, and more particularly to host cells containing multiple integrated copies of an integrating vector. Suitable integrating vectors for use in the present invention include retrovirus vectors, lentivirus vectors, transposon vectors, and adeno-associated virus vectors. Methods are provided in which the host cells are prepared by using the integrating vectors at a high multiplicity of infection. The host cells are useful for producing pharmaceutical proteins, variants of proteins for use in screening assays, and for direct use in high throughput screening.
Owner:CATALENT PHARMA SOLUTIONS INC
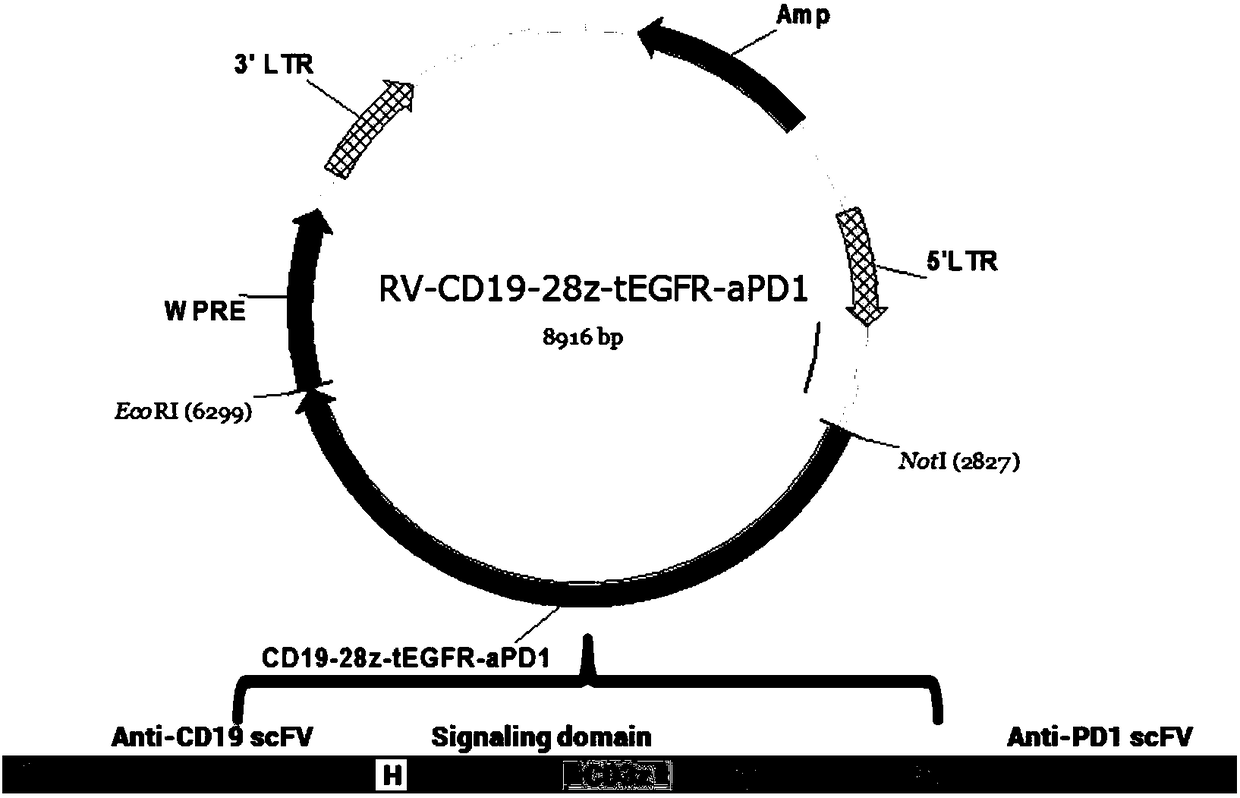
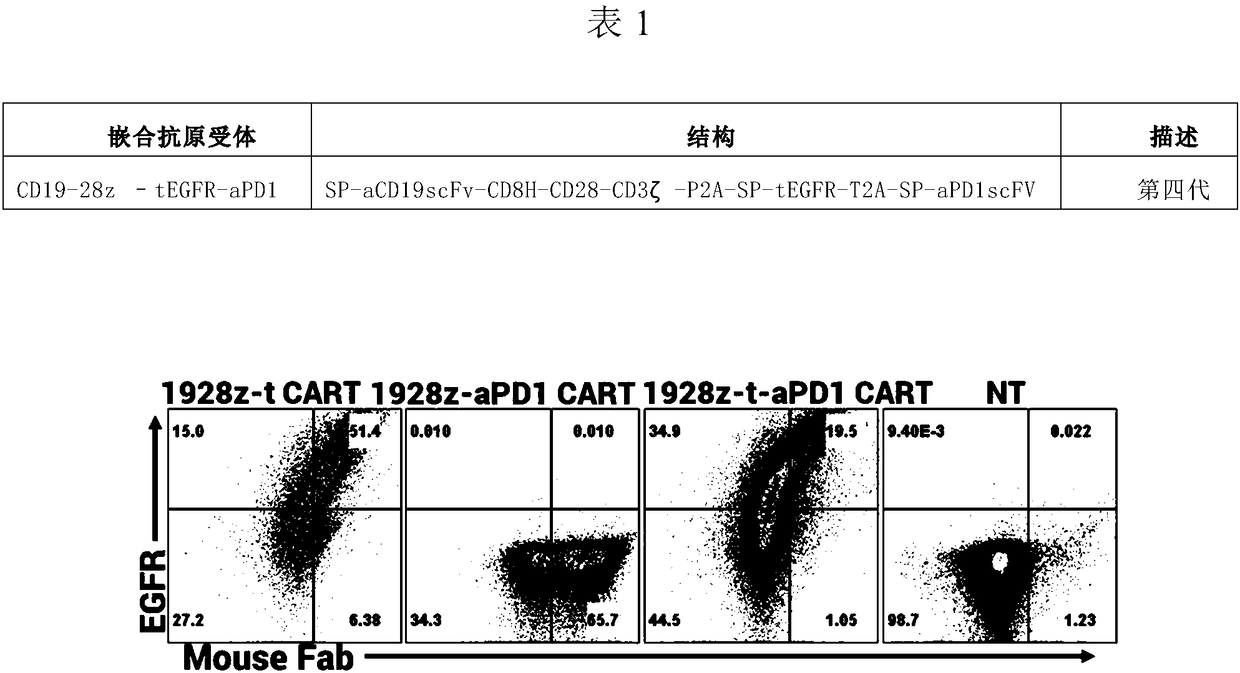
CD19 targeted chimeric antigen receptor, method of dual-modifying same, and application of the CD19 targeted chimeric antigen receptor
ActiveCN108330133APolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilySingle-Chain AntibodiesPolynucleotide
The invention relates to a CD19 targeted chimeric antigen receptor and an application thereof, and particularly provides a polynucleotide sequence, which is selected from: (1) a polynucleotide sequence which contains, in a successively connected manner, an encoding sequence of anti-CD19 single-chain antibody, an encoding sequence of human CD8[alpha] hinge zone, an encoding sequence of human CD28 transmembrane zone, an encoding sequence of human CD28 intracellular zone, an encoding sequence of human CD3 [zeta] intracellular zone, and optionally, a fraction, which contains an extracellular domain III and an extracellular domain IV of EGFR, and an encoding sequence of anti-human PD1 sequence fraction; and (2) a complementary sequence of the polynucleotide sequence (1). The invention also provides related fusion proteins, a carrier containing the encoding sequences, and applications of the fusion proteins, encoding sequences and carrier. The CAR-T cell has strong killing effect on specifictumor cells, and can reach more than 90% in killing efficiency on the specific tumor cells under the multiplicity of infection of 1:2. The CAR-T cell can secrete the PD1 antibody and has regulation effect on immunosuppression micro-environments.
Owner:HRAIN BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Host cells containing multiple integrating vectors
The present invention relates to the production of proteins in host cells, and more particularly to host cells containing multiple integrated copies of an integrating vector. Suitable integrating vectors for use in the present invention include retrovirus vectors, lentivirus vectors, transposon vectors, and adeno-associated virus vectors. Methods are provided in which the host cells are prepared by using the integrating vectors at a high multiplicity of infection. The host cells are useful for producing pharmaceutical proteins, variants of proteins for use in screening assays, and for direct use in high throughput screening.
Owner:CATALENT USA WOODSTOCK INC +3
Lytic salmonella phage and separation method thereof
InactiveCN108118033AStock solution titer is highActiveMicroorganism based processesBacteriophagesBiological propertySalmonella Phage
The invention relates to a lytic salmonella phage and a separation method thereof. The phage has a tadpole-shaped form, has the head in an icosahedral cubical symmetry manner and has a telescopic tail. The phage is subjected to biological characteristic study. After multiplication of the phage separated in the invention, the fluid titer of the phage is high, the titer of the phage in the inventionis more than or equal to 10<9>pfu / mL, the phages have a certain activities under different infection multiplicity conditions, and the titer of the phage at a temperature of 30-60 DEG C is basically invariable. The biological characteristic study on the phage separated in the invention provides theoretical guiding significance for further research and development of novel antibacterial drugs.
Owner:QINGDAO RUNDA BIOTECH
Classical swine fever virus vaccine and production method thereof
InactiveCN101926991AHigh poison priceExpand production scaleInactivation/attenuationMicroorganism based processesCulture fluidFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a method for preparing a classical swine fever (CSF) vaccine by using a cell microcarrier suspension culture system, which comprises the following steps of: (1) inoculating cells for preparing the vaccine to a carrier tank containing culture solution and a microcarrier, and uniformly mixing the cells and the microcarrier to make the cells attached to the microcarrier; (2) when the concentration after cell proliferation is 5 to 40 times of the initial inoculation concentration, inoculating CSF virus (lapinized virus) to the cells according to multiplicity of infection (M.O.I.) of the virus of 0.01-1 and reproducing the virus; and (3) mixing prepared virus liquid, adding an appropriate freeze-drying protective agent, fully and uniformly mixing, quantitatively packaging, and freeze-drying to obtain the CSF vaccine. The CSF vaccine produced by the method has the advantages of high density of cultured cells, continuous culture, high yield of the virus, high immune effect, high safety, complete immune protection on attack of violent CSF, and the like.
Owner:PU LIKE BIO ENG
Hog fever virus csfv E2 protein ligand epitope polypeptide and application thereof
ActiveCN102268079AAvoid infectionReduce infection ratePeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementClassical swine fever virus CSFVViral Receptor
The invention relates to a (classical swine fever virus) CSFV E2 protein ligand epitope peptide and application thereof. The peptide has an amino acid sequence of VHASDERLGPMPCRPKEIGSSAGPVRKTSCTFNYAKTGKNKYYEPRDSYF and a molecular weight of 5.73kDa. With the PK-15 cell as the target cell, and by means of infection and harvest of the CSFV, TCID50 and the MOI (multiplicity of infection) of the CSFV can be determined. A binding test of a synthetic peptide and the target cell, a virus blocking test and a test for the peptide to block the CSFV from infecting the target cell shows that the screened specific binding target cell can inhibit the virus from infecting the ligand epitope peptide, and ligand epitope of the CSFV is positioned accurately. The peptide SE24 of the invention can inhibit the CSFV from infecting the PK-15 cell, and with the increase of the peptide concentration, the infection rate of the PK-15 cell is reduced. When the peptide concentration is 0.2mmol / L, the CSFV can be completely inhibited from infecting the PK-15 cell. The ligand epitope peptide of the invention provides the theoretical basis for a further study of the virus ligand epitope from the aspect of interactions between virus ligands and virus receptors.
Owner:XINXIANG UNIV
Multiple-virus-obtaining process for proliferating porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus by Marc (rhesus monkey kidney cell)-145 cell cultured by microcarriers
InactiveCN103555674AIncrease profitReduce manufacturing costMicroorganism based processesViruses/bacteriophagesInfective DoseRespiratory syndrome virus
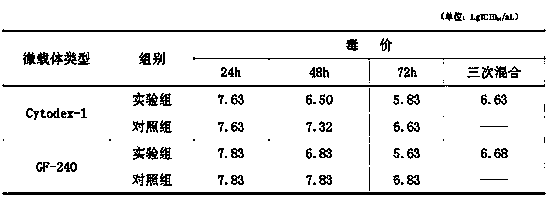
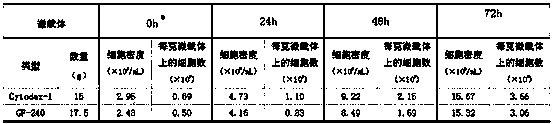
The invention discloses a multiple-virus-obtaining process for proliferating a porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS) virus by a Marc (rhesus monkey kidney cell)-145 cell cultured by microcarriers. The multiple-virus-obtaining process comprises the following steps: culturing the Marc-145 cell by using two microcarriers of 2-10 g / L of Cytodex-1 or GF-240; inoculating PRRS virus liquids by using 0.01-0.1 of M.O.I (Multiplicity Of Infection); separating the PRRS virus liquids into a contrast group and an experimental group; sampling and measuring TCID50 (Tissue Culture Infective Dose) at 24 hours, 48 hours and 72 hours after viruses are inoculated in the contrast group; and respectively obtaining a virus supernate every 24-28 hours after viruses are inoculated in the experimental group, and then supplementing a maintenance medium to the virus supernate for continuous culturing to obtain the virus liquids twice or three times. The multiple-virus-obtaining process for proliferating the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus by the Marc-145 cell cultured by the microcarriers, which is disclosed by the invention, has the beneficial effects that the qualified virus liquid obtained in a multiple-virus-obtaining manner when the Marc-145 cell is used for proliferating the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus under microcarrier culture conditions is more than twice of that obtained in a normal virus-obtaining manner, the utilization rate of the microcarriers and seed cells is increased and the production cost of vaccines is reduced.
Owner:乔自林 +2
Production method for recombinant human fibroblast growth factor-18 and application of growth factor-18
InactiveCN105200085AHigh expressionHigh yieldPeptide/protein ingredientsSkeletal disorderViral vectorProtein C
The invention relates to a production method for recombinant human fibroblast growth factor-18 protein. The production method comprises the following steps: 1, expressing the fibroblast growth factor-18 protein in insect cells by using an insect baculovirus vector expression system, specifically comprising 1) obtaining recombinant baculovirus Bacmid-FGF18 (fibroblast growth factor-18), wherein the FGF18 gene is a fibroblast growth factor-18 gene and has a base sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, and 2) infecting the insect cells with the Bacmid-FGF18 recombinant baculovirus with MOI (Multiplicity of Infection) of 1 to 32, and then culturing the infected insect cells for 12 to 96 hours at the temperature of 25 to 29 DEG C to harvest cell fluid; and 2, purifying the cell fluid harvested in the step 1 to obtain the human fibroblast growth factor-18 protein. The invention also discloses application of the human fibroblast growth factor-18 protein in treating bone diseases and alopecia.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV +1
Staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage and application
ActiveCN109082414AEffectively eliminateGood bodyAntibacterial agentsViral/bacteriophage medical ingredientsBacteroidesStaphylococcus cohnii
The invention discloses staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage and application. The staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage and the application have the advantages that staphylococcus aureus can be specifically effectively eliminated by the staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage, excellent in-vivo and in-vitro antibacterial effects can be realized by the staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage for medicine-resistant staphylococcus aureus, experimental foundations can be provided to clinically developing preparations for preventing and treating medicine-resistant staphylococcus aureus infection, and the staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage has great clinical application potential; the skin abscess average areas of nude mice of bacteriophage treatment groups are 47.32 mm<2> in skin abscess models when MOI(multiplicity of infection) is equal to 10, and the average bacterium load is 3.553*10<7> CFU / g; the skin abscess average areas of nude mice of MRSA (methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus) infection groups are 150.4 mm<2>, and the average bacterium load is 2.284*10<8> CFU / g; the skin abscess areas of the mice of the bacteriophage treatment groups are smaller than the skin abscess areas of the mice of the MRSA infection groups, the colony count of the mice of the bacteriophage treatment groups is lower than the colony count of the mice of the MRSA infection groups, and the difference of the skin abscess areas and the colony count has statistical significance.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Host cells containing multiple integrating vectors
InactiveUS20050100952A1Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsVirus peptidesLentivirusHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
The present invention relates to the production of proteins in host cells, and more particularly to host cells containing multiple integrated copies of an integrating vector. Suitable integrating vectors for use in the present invention include retrovirus vectors, lentivirus vectors, transposon vectors, and adeno-associated virus vectors. Methods are provided in which the host cells are prepared by using the integrating vectors at a high multiplicity of infection. The host cells are useful for producing pharmaceutical proteins, variants of proteins for use in screening assays, and for direct use in high throughput screening.
Owner:CATALENT USA WOODSTOCK INC +3
Construction and identification of over-expression lentivirus vector of rat GSK-3 beta (Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 beta) target gene
InactiveCN102212535AExpression stable and long-termUnderstanding PathogenesisMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingDiseaseWestern blot
The invention discloses construction of an over-expression lentivirus vector of a rat GSK-3 beta (Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 beta) target gene, comprising the following steps of: tagging the GSK-3 beta target gene by using a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) method; performing directional exchange on the GSK-3 beta target gene and an enzyme-cutting linear vector to obtain a product; converting the product into bacterial competent cells; performing bacterial colony PCR identification on grown clones; and sequencing positive clones identified by the PCR. The invention further discloses identification of the over-expression lentivirus vector of the rat GSK-3 beta target gene, comprising the following steps of: transfecting rat WB-F344 (Western Blot F344) cells by the target gene over-expression lentivirus vector, a vacuolating virus vector and physiological saline; after achieving optimal infection multiplicity, observing expression of fluorescent protein; and detecting the expression condition by adopting Western Blot. According to the construction and identification disclosed by the invention, action mechanisms of the GSK-3 beta in organisms and related diseases thereof can be known deeply; pathogenesis of the diseases can be known better; and a foundation for future clinical application can be laid.
Owner:单云峰
Method for producing porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome viruses
ActiveCN101748101AReduce generationDoes not affect multiplication rateRecovery/purificationAntigenCytopathic effect
The invention discloses a method for producing and harvesting porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome viruses (PRRSV), which comprises the following steps: culturing Marc-145 cells in a spinner bottle; after the cells grow into a monolayer, removing a growth-promoting media; inoculating the PRRSV according to 0.01 infection multiplicity (MOI: multiplicity of infection); absorbing for 1 hour at a temperature of 37 DEG C; adding DMEM serving as a maintenance media to carry out expanding propagation of viruses; arranging the spinner bottle on a rotary machine of a 37 DEG C thermostatic chamber to carry out rotation culture for 72 to 84 hours; and when 75 to 80 percent of cytopathic effect occurs, directly collecting the supernatant to obtain the PRRSV. The invention reduces allergen in the rough antigens and improves the vaccine quality. And the time that the Marc-145 cells have CPE is consilient with that before the process is improved, but the virus harvesting time is shortened.
Owner:WENS FOOD GRP CO LTD
Proliferation method of siniperca chuatsi infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus (ISKNV)
ActiveCN104694483AIncrease contentPromote proliferationMicroorganism based processesViruses/bacteriophagesRenal necrosisNecrovirus
The invention discloses a proliferation method of a siniperca chuatsi infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus (ISKNV). According to the proliferation method, synchronous virus inoculation is adopted, the virus and a siniperca chuatsi brain tissue cell line (CPB) are in a suspended state, and the mutual contact surface area between the virus and the siniperca chuatsi brain tissue cell line is large so that the virus enters cells through more space receptors; and the virus infects the cells while the cells differentiate and proliferate, thus obtaining the high content ISKNV. After the CPB is cultured for 30 hours to 60 hours, the CPB is transferred to 5%-8% v / v of fetal calf serum culture medium, and the ISKNV is synchronously inoculated at the MOI (Multiplicity of Infection) value of 0.85-2.3, thus obtaining a low-cost ISKNV proliferation method. After the CPB is cultured for 20 hours to 40 hours, the CPB is transferred to 8%-10% v / v of fetal calf serum culture medium, and the ISKNV is synchronously inoculated at the MOI (Multiplicity of Infection) value of 30-45, thus obtaining a short ISKNV proliferation method. Cultivation methods can be selected according to existing conditions. The proliferation method provides theoretical basis for production of low-cost viruses.
Owner:PEARL RIVER FISHERY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Antiapoptosis high expression hVEGF165 (human Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor 165) cell model and building method thereof
InactiveCN102329777AApoptotic ratio decreasedResolve poorly transfected cellsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsViruses/bacteriophagesDiseaseApoptosis
The invention relates to an antiapoptosis high expression hVEGF165 (human Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor 165) cell model and a building method thereof. The cell model takes BMSCs (Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cells) as transfection cells and coexpresses a recombinant adenovirus with double genes hBCL-2 and hVEGF165. The building method of the cell model comprises the following steps of: 1) separating and purifying rat BMSCs to obtain massive purified BMSCs with good vitality; 2) transfecting the BMSCs by the recombinant adenovirus, building the cell model built by the BMSCs transfected for 72 hours by adopting a multiplicity of infection (MOI) is equal to 400. The application characteristics are as follows: 1) the cell model is used for treating diseases such as myocardial infarction and the like; and 2) the cell model is used for being transplanted into a receptor organ. Compared with common BMSCs, the transfection recombinant adenovirus BMSCs provided by the invention has the advantages that cell apoptosis ratio is obviously reduced, service life is prolonged, the hVEGF165 can be efficiently expressed, the cell model can be conveniently transplanted to the receptor organ, and effect for treating diseases can be improved, thus the cell model and the building method thereof which are provided by the invention have wide application prospect.
Owner:THE SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Recombinant rabies virus carrying deoptimized M gene and two G genes
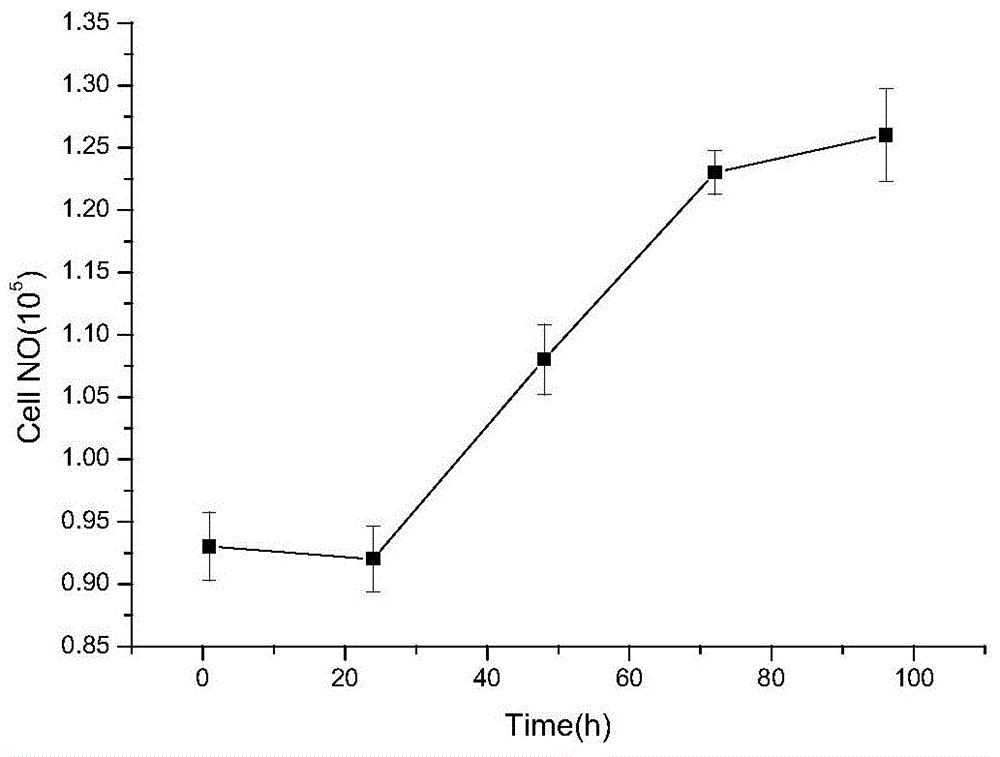
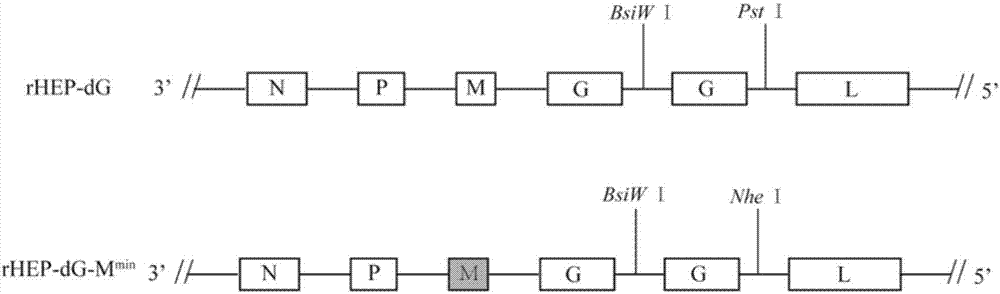
ActiveCN107201371AHigh viral titerLow costSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsRabies virus strainRecombinant virus vaccine
The invention discloses a recombinant rabies virus carrying a deoptimized M gene and two G genes. Firstly, a reading frame part of the M gene is deoptimized, wherein the sequence after deoptimization is as shown in SEQ ID NO.2; secondly, a rabies virus HEP-Flury strain is taken as a skeleton, an M gene in the HEP-Flury is replaced by the deoptimized M gene, and an additional rabies virus G gene is inserted to obtain recombinant rabies virus pHEP-dG-Mmin plasmid carrying the deoptimized M gene and two G genes; finally, rescuing and screening are conducted to obtain a recombinant rabies virus strain rHEP-dG-Mmin. The recombinant virus has higher virus titer, and the cost of canine vaccine can be reduced. Under the condition of multiplicity of infection, G protein with higher level can be expressed, virus replication and transcription of each structural gene are increased, and the recombinant virus has the potential of serving as a rabies vaccine candidate strain.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for producing parvovirus having high infectivity titer
ActiveUS20150299668A1Overcome negative influenceRecovery/purificationSsDNA virusesDouble-timeMicrobiology
A method for stably and easily producing a parvovirus having a high infectivity titer is provided. The problem is solved by a method for producing a parvovirus having an infectivity titer as high as 108 TCID50 / mL or more in a culture supernatant, comprising the steps of inoculating a seed virus of the parvovirus into a culture substrate comprising host cells having a cell density of 1 / 500 to 1 / 20 of the cell density of the host cells confluently grown and a medium at a multiplicity of infection of 0.0001 to 0.1, culturing for a period of 5 to 11 times the doubling time of the host cells, and recovering a culture supernatant.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI MEDICAL CO LTD
Dual-target chimeric antigen receptor and use thereof
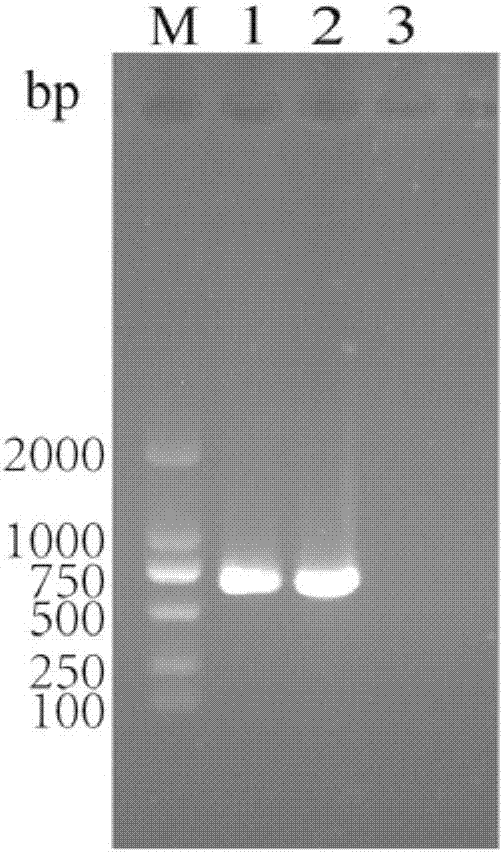
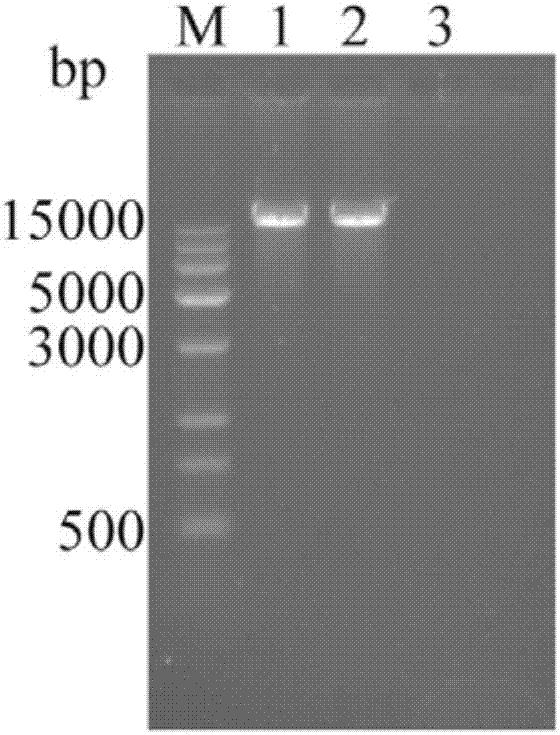
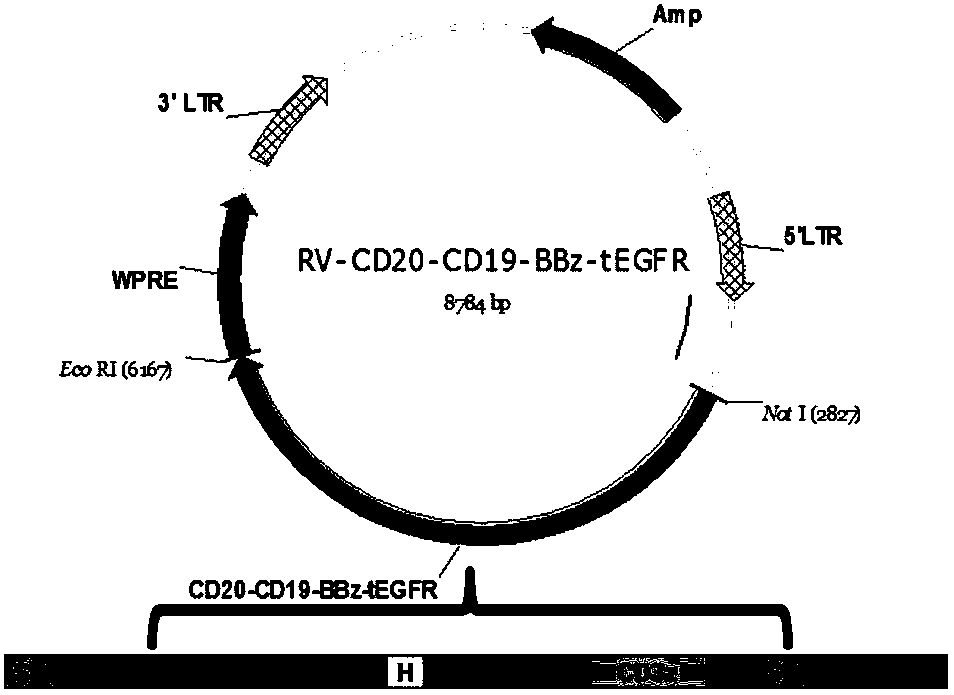
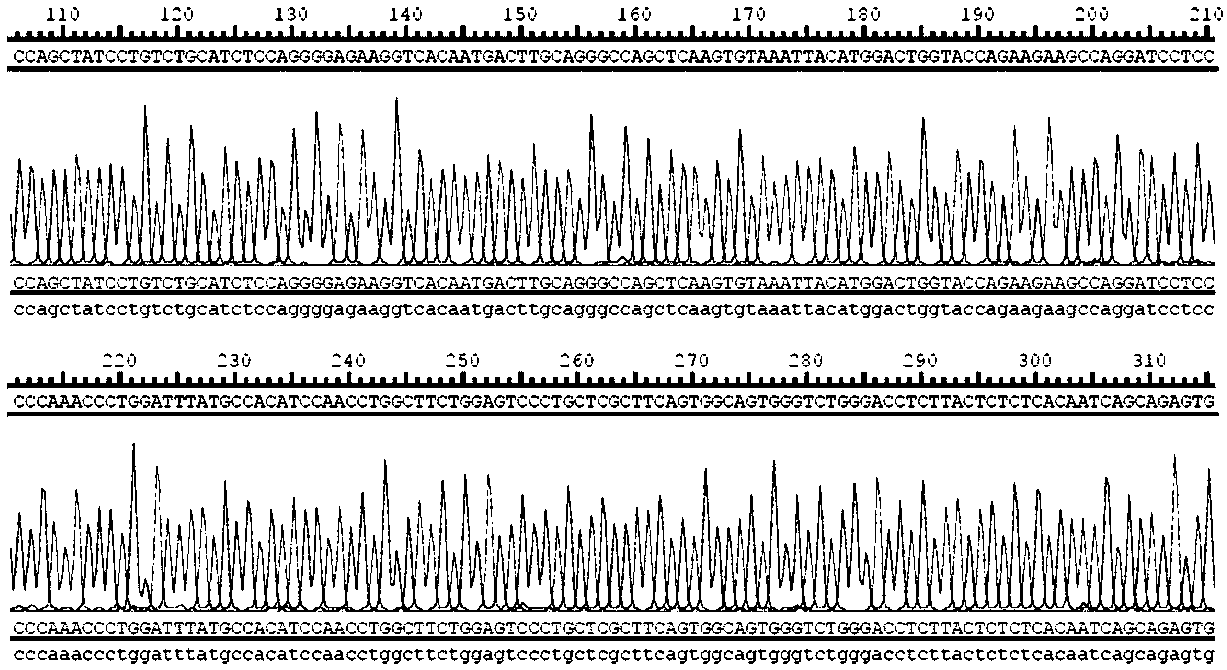
PendingCN109423495AShorten the timeImprove conversion efficiencyAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMammal material medical ingredientsCD20Single-Chain Antibodies
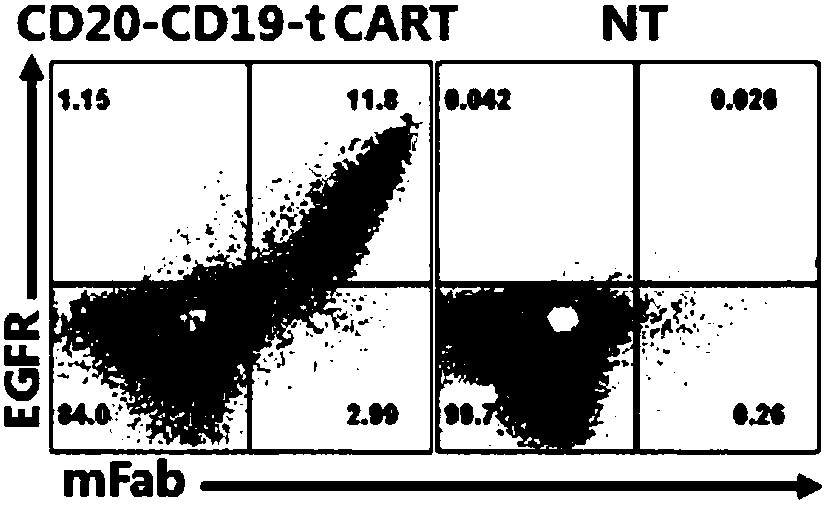
The present invention relates to a dual-target chimeric antigen receptor that targets CD19 and CD20 and use thereof. In particular, the present invention provides a polynucleotide sequence selected from the group consisting of: (1) a polynucleotide sequence including coding sequences of anti-CD20 and anti-CD19 single-chain antibodies, a coding sequence of a human IgG4 hinge region, a coding sequence of a human CD28 transmembrane region, a coding sequence of a human 41BB intracellular region, a coding sequence of a human CD3[Zeta] intracellular region, and an optional coding sequence of an EGFRfragment including extracellular domains III and IV; and (2) a sequence complementary with the sequence (1). The invention also provides related fusion protein, vectors comprising the coding sequences, and use of the fusion protein, the coding sequences and the vectors. A CD20-CD19-BBz-tEGFR CAR-T cell prepared has strong killing function on specific tumor cells, high CD107a expression and IFN[gamma] secretion are achieved, and even when the multiplicity of infection is 5:1, the target cell killing efficiency reaches about 60%.
Owner:HRAIN BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Screening system for anti-Singapore grouper iridovirus (SGIV) drug
InactiveCN107794291ACell Viability Culture Condition OptimizationHigh-precision detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisCytopathic effectScreening method
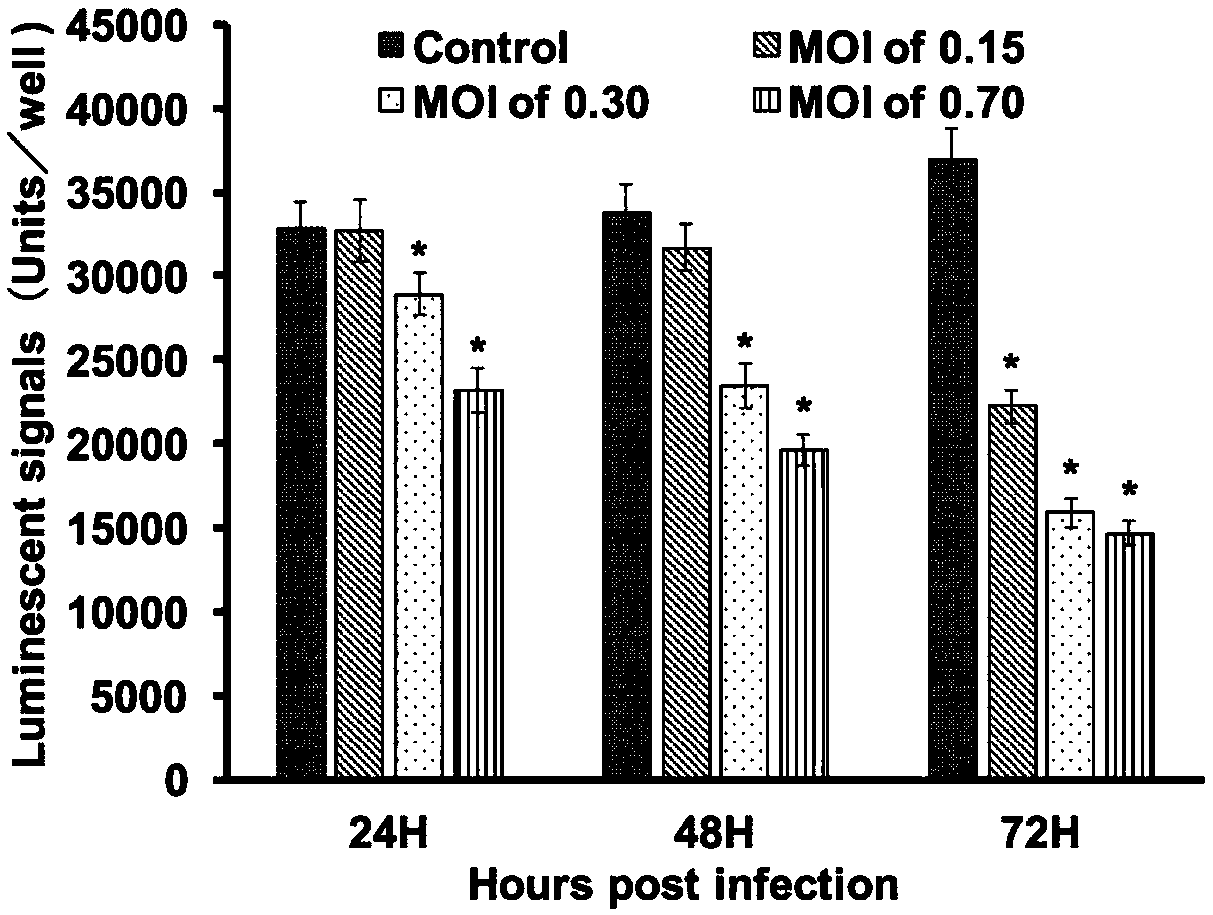
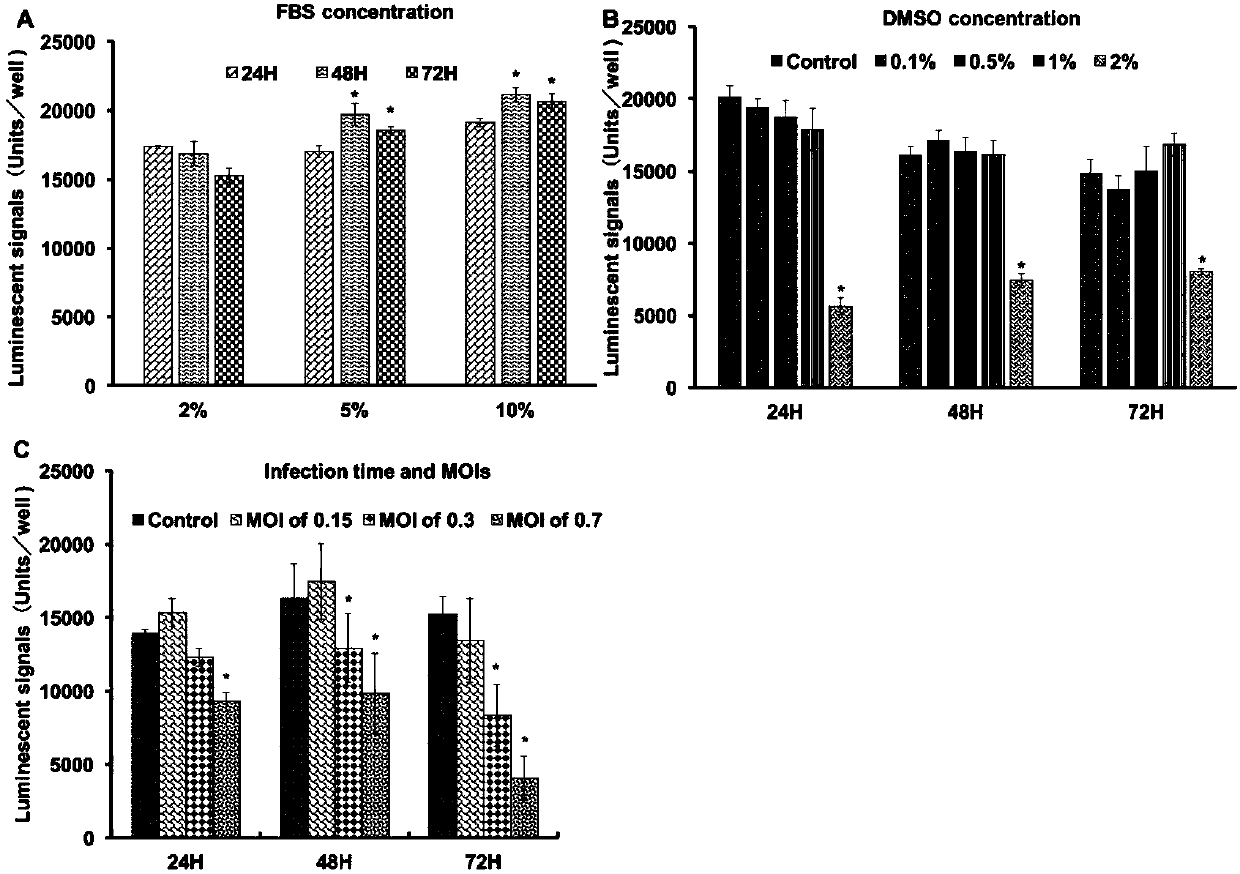
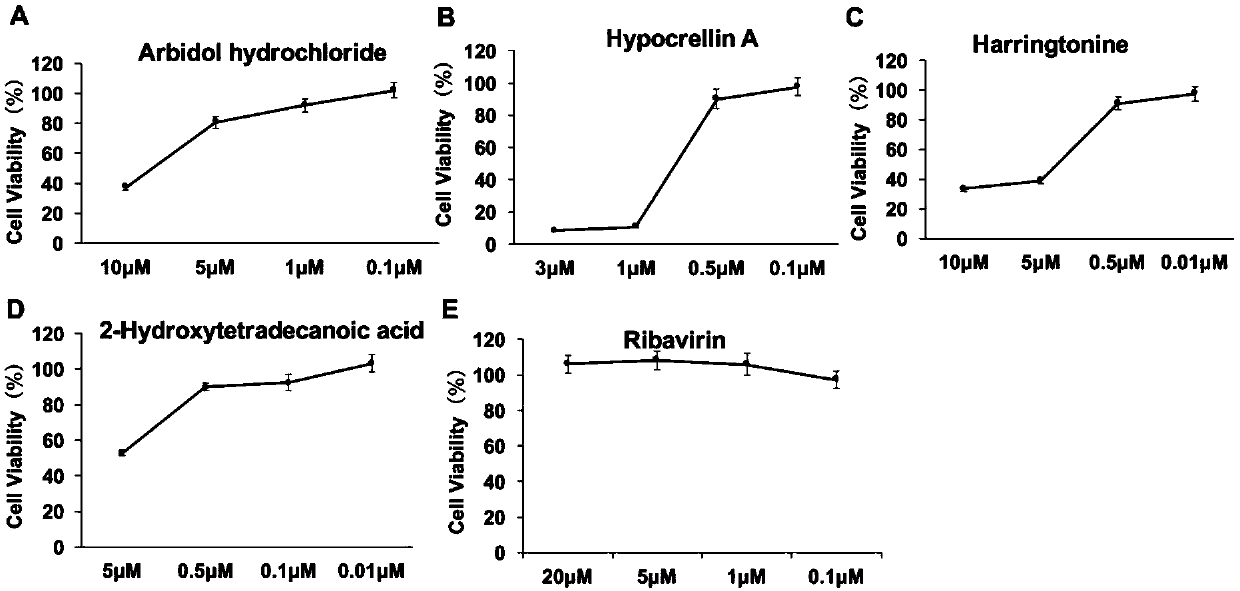
The invention provides a cell screening system for anti-SGIV drug screening based on cell activity analysis, comprising: serum concentration of 5%, when DMSO needs to be added as a solvent, the DMSO concentration is not higher than 1%, the multiplicity of infection of the virus is 0.3, and the virus The infection time is 48h. The invention also provides an optimization method of a cell screening system for screening anti-SGIV drugs and a drug screening method. The advantage of the method of the present invention is that the cytopathic effect (CPE) caused by quantitative SGIV infection can be quantified for the first time, the cell screening system for anti-SGIV drug screening is optimized, and a simple screening method is established using this system, using ddPCR for The detection of screening results is accurate and fast.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Method for improving in-vitro expression of cytochrome P450 enzyme family
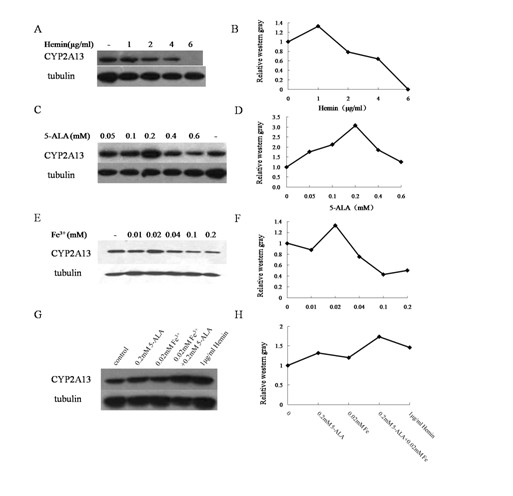
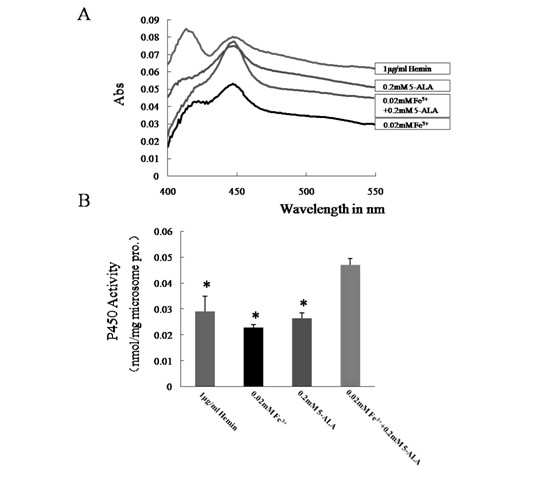
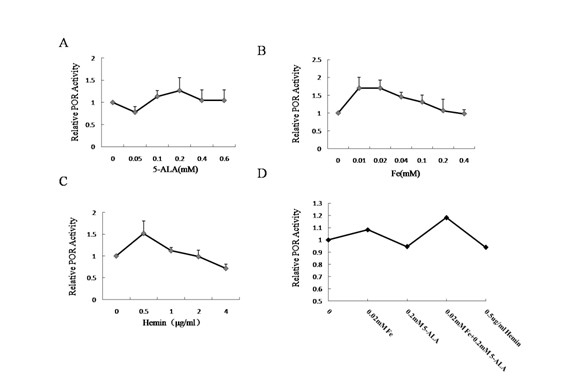
InactiveCN102094000AImprove expression levelHigh activityMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyP450 oxidoreductaseHemin
The invention relates to cytochrome P450 enzymes, in particular to a method for improving the in-vitro expression of a cytochrome P450 enzyme family. The method for improving the in-vitro expression of the cytochrome P450 enzyme family is characterized in that a cofactor in step D is any one of the following components: (1) Hemin with the concentration of between 0.5 and 6mu g / ml; (2) 5-ALA at the concentration of between 0.05 and 0.6mM; (3) Fe<3+> at the concentration of between 0.01 and 0.4mM; and (4) a mixture of the 5-ALA at the concentration of between 0.05 and 0.6mM and the Fe<3+> at the concentration of between 0.01 and 0.4mM. System optimization is performed on cytochrome P450 (CYP) protein, P450 oxidoreductase (POR) protein and coexpression conditions thereof for the first time, and the result shows that the expression levels of the proteins and the activities thereof are highest when the Fe<3+> at the concentration of 0.02mM and the 5-ALA at the concentration of 0.2mM are synchronously given to treat cells. When the multiplicity of infection (MOI) of CYP is 5pfu / cell and the MOI of POR is 2pfu / cell, the coexpression efficiency of the CYP and the POR is highest.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Detection method for slow virus infected cell
InactiveCN102367476AConvenient imaging diagnosisGood treatment effectMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisInfected cell
The invention discloses a detection method for a slow virus infected cell. The method comprises the steps of: synthesizing a single stranded random oligonucleotide library, and infecting an HEK293 cell with MOI (multiplicity of infection)=5; incubating the random oligonucleotide library with a target molecule together for 1h at a temperature of 4DEG C, then washing the monolayer of the cell with PBS (phosphate buffer solution); conducting enzymatic hydrolysis to gain a cell which is resuspended in 0.5ml of H2O at a temperature for 5min so as to release a combined oligonucleotide ligand candidate molecule, generating a new subordinated library through PCR (polymerase chain reaction) or RT-PCR (reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction), then carrying out combination with the target molecule for a second round screening, repeating the circulation for several times so as to screen out a nucleic acid ligand able to be specifically bound with the target molecule, marking the nucleic acid ligand with Cy5, and incubating the nucleic acid ligand with the slow virus infected HEK293 cell together, performing flow cytometry analysis after washing, cloning the identified nucleic acid ligand to a vector for sequence analysis. The method of the invention can detect a slow virus infected human tissue cell rapidly, simply and effectively, and also can be used for detection of other virus infection or the generation processes of other diseases.
Owner:TAIHU RUIJING BIO TECH
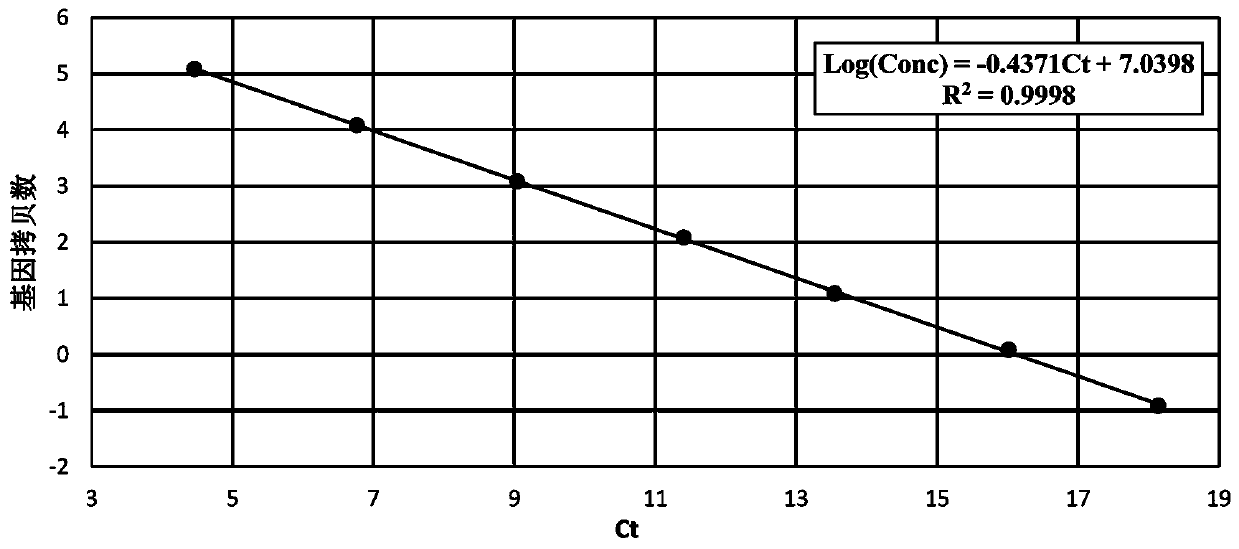
Absolute quantitative PCR method for rapidly determining titer of ascoviruses
ActiveCN111235309ALower requirementShort timeMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesMedicinePcr method
The invention relates to an absolute quantitative PCR method for rapidly determining the titer of ascoviruses. The absolute quantitative PCR method comprises the following steps: ultrasonically crushing a to-be-detected sample containing the ascoviruses, carrying out diluting and filtering, allowing the ascoviruses to infect cells in a logarithmic phase for 1 hour, collecting a cell suspension, calculating the number of the cells, and extracting total DNA; carrying out qPCR detection on the DNA, and drawing a standard curve of absolute quantitative PCR detection by taking a pGEM-T vector containing the fragment of the DNA as a standard substance; calculating the copy number of a virus genome contained in each sample according to the Ct value of each sample; and according to an infection complex number formula, calculating the average number of virus particles infecting each cell, namely the ratio of the number of viruses to the number of the cells during infection so as to calculate the titer of the viruses. The absolute quantitative PCR method provided by the invention is used for measuring the titer of the ascoviruses; the detection time is only 4-6 hours when the concentration of a sample is 1 * 10<2> to 1 * 10<11> virus gene copy / mL, so the consumed time is short; compared with a traditional virus titer detection method, the absolute quantitative PCR method provided by theinvention has simple and rapid operation, is accurate, greatly improves the detection efficiency of the titer of the ascoviruses, and is especially applicable to rapid determination of the titer of the ascoviruses.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
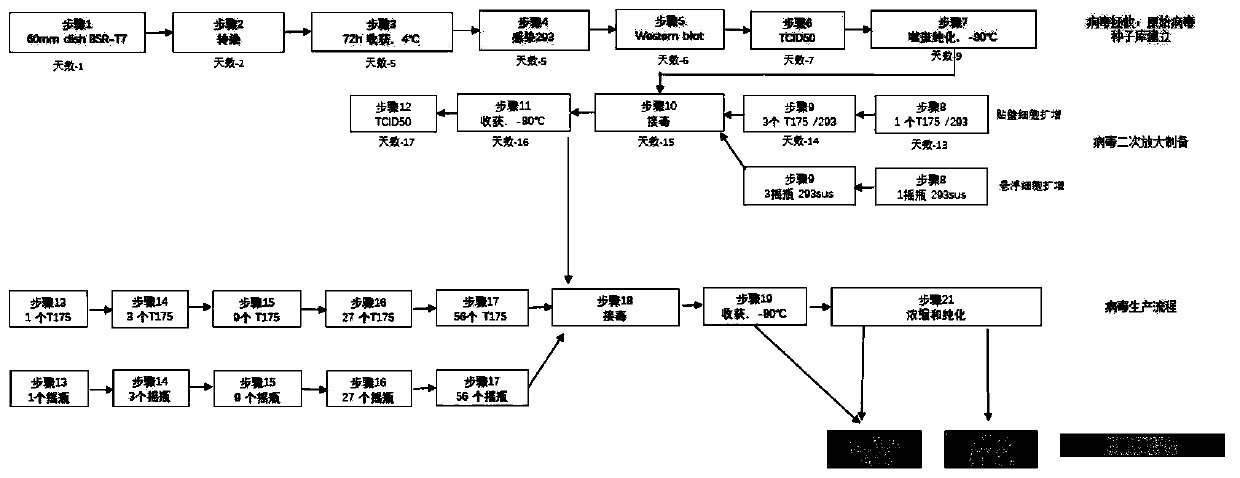
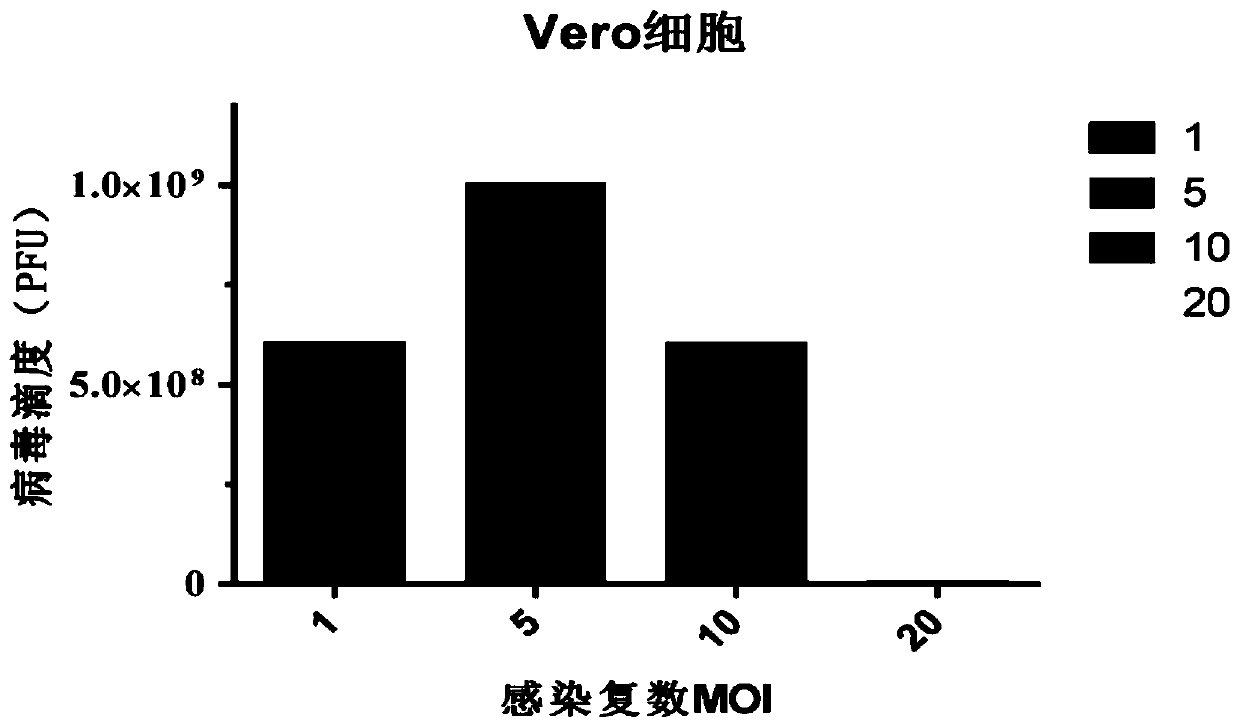
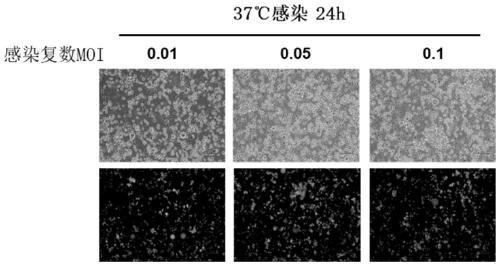
Method for preparing oncolytic virus by using 293 cells
InactiveCN110305850ALow costHigh yieldSsRNA viruses negative-senseMicroorganism based processesHigh cellHarvest time
The invention discloses a method for preparing an oncolytic virus by using 293 adherent cells and 293sus suspension cells. The method utilizes adherent or suspension 293 cells to prepare oncolytic virus, and utilizes 293 adherent cells to optimize the optimal conditions for virus amplification and production, wherein, the optimal conditions comprise multiplicity of infection (MOI), a virus weak solution, a serum concentration during virus amplification, a virus harvest time, and a virus amplification temperature; further, a method for preparing the oncolytic virus by optimizing 293sus suspension cells includes optimizing the multiplicity of infection (MOI), the virus harvest time, and the like, and the single cell production amount reaches E4 power. Further, when the high cell density expansion is carried out, the virus yield can reach 4E10 pfu / mL. Both 293 cells can produce the high-titer virus efficiently and stably, which provides technical support for the large-scale production ofsubsequent viruses.
Owner:FANTASIA BIOPHARMA ZHEJIANG CO LTD
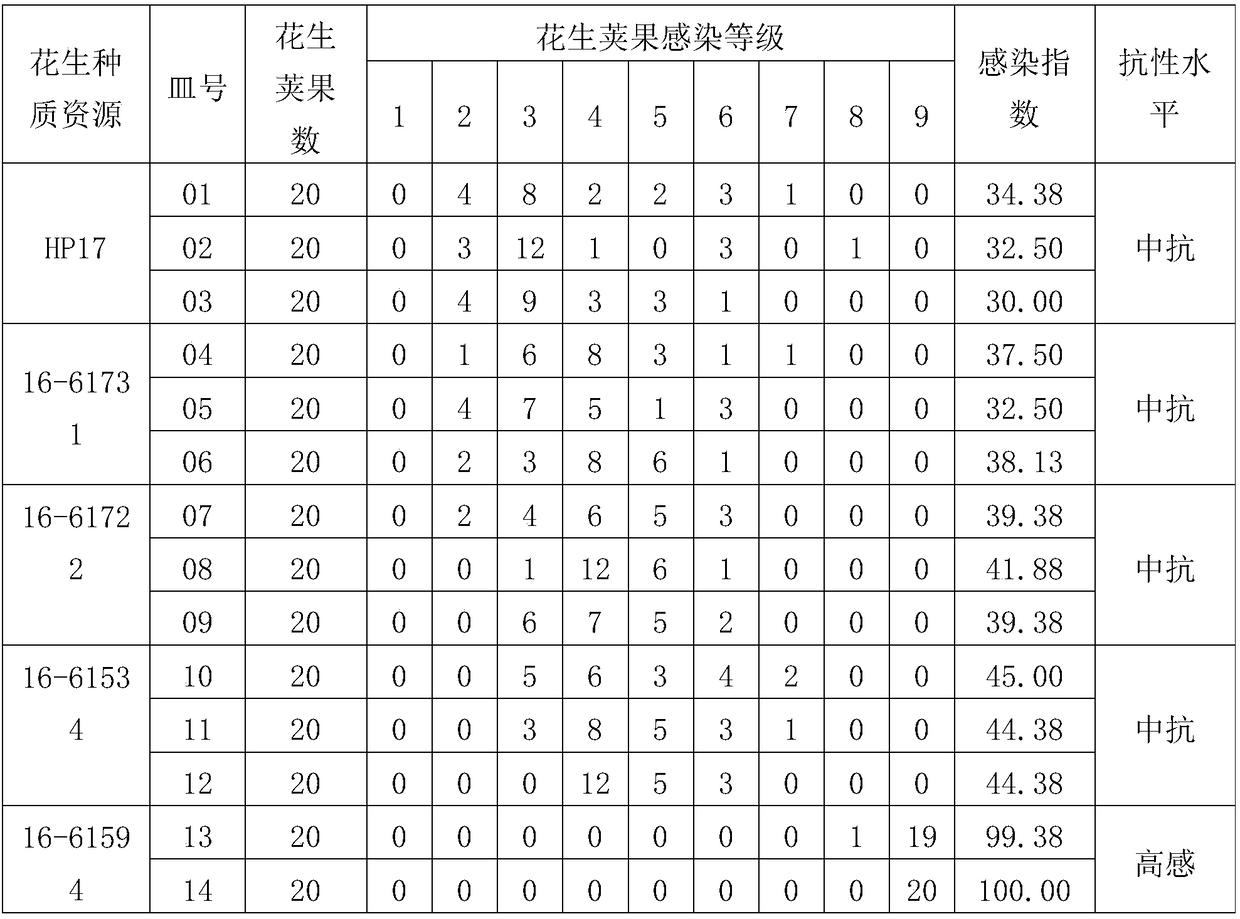
Indoor identification method for resistance of peanut pods to Aspergillus flavus infection and application of indoor identification method
PendingCN109001385AEfficient identificationAccurate identificationTesting foodAgricultural scienceMultiplicity of infection
The invention relates to an indoor identification method for resistance of peanut pods to Aspergillus flavus infection and an application of the indoor identification method to screening of peanut germplasm resources with resistance to Aspergillus flavus infection. The indoor identification method for resistance of the peanut pods to Aspergillus flavus infection is characterized by comprising thefollowing steps: (1) selecting an Aspergillus flavus strain; (2) selecting, sterilizing and rehydrating the peanut pods; (3) inoculating the peanut pods with Aspergillus flavus: healthy peanut pods are inoculated with an Aspergillus flavus spore suspension; (4) performing culture: dark culture is performed in an incubator for 7 days after inoculation; (5) classifying the cultured peanut pods according to infection degree; (6) calculating the Aspergillus flavus MOI (multiplicity of infection) of the peanut pods; (7) evaluating resistance levels. The method is simple to operate, easy to implement, can identify resistance of the peanut pods to Aspergillus flavus infection efficiently and accurately in a batch manner and is suitable for batch screening of the peanut germplasm resources with resistance to Aspergillus flavus infection. The foundation is laid for researching the resistance mechanism of the peanut pods to Aspergillus flavus infection and breeding peanut varieties with resistance to Aspergillus flavus infection.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
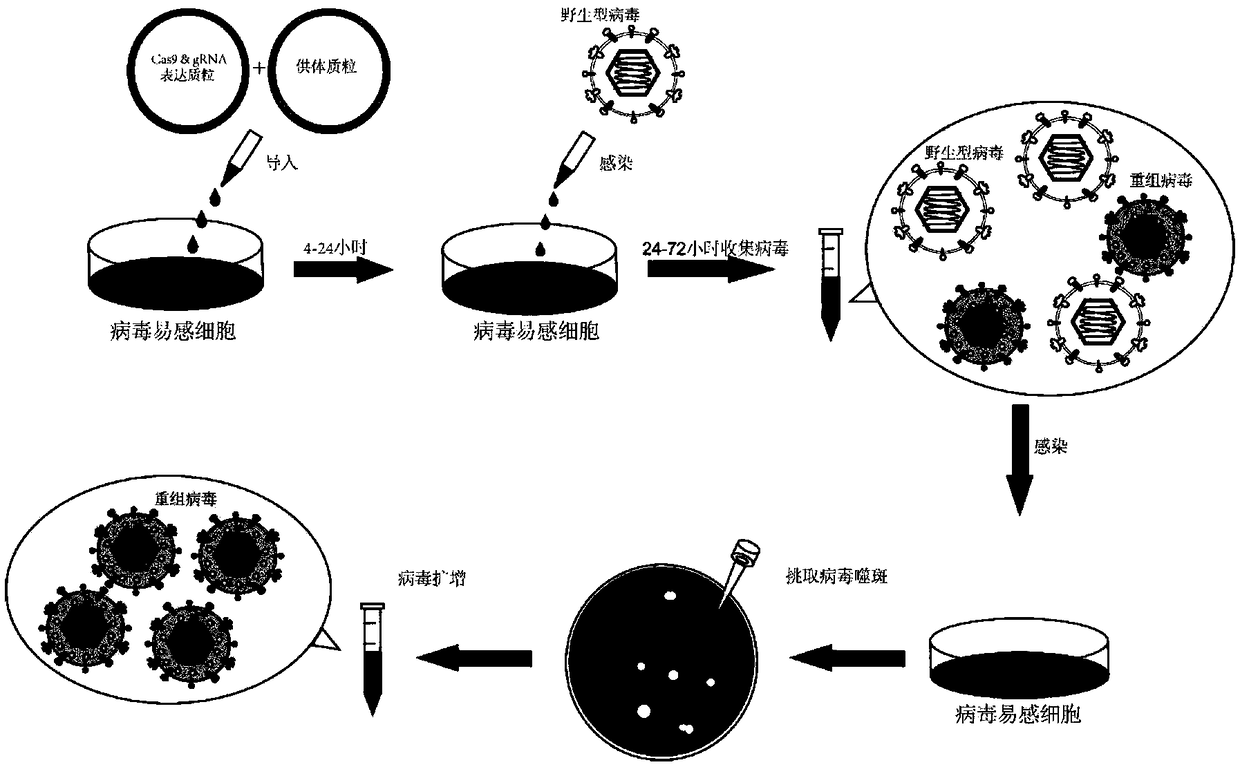
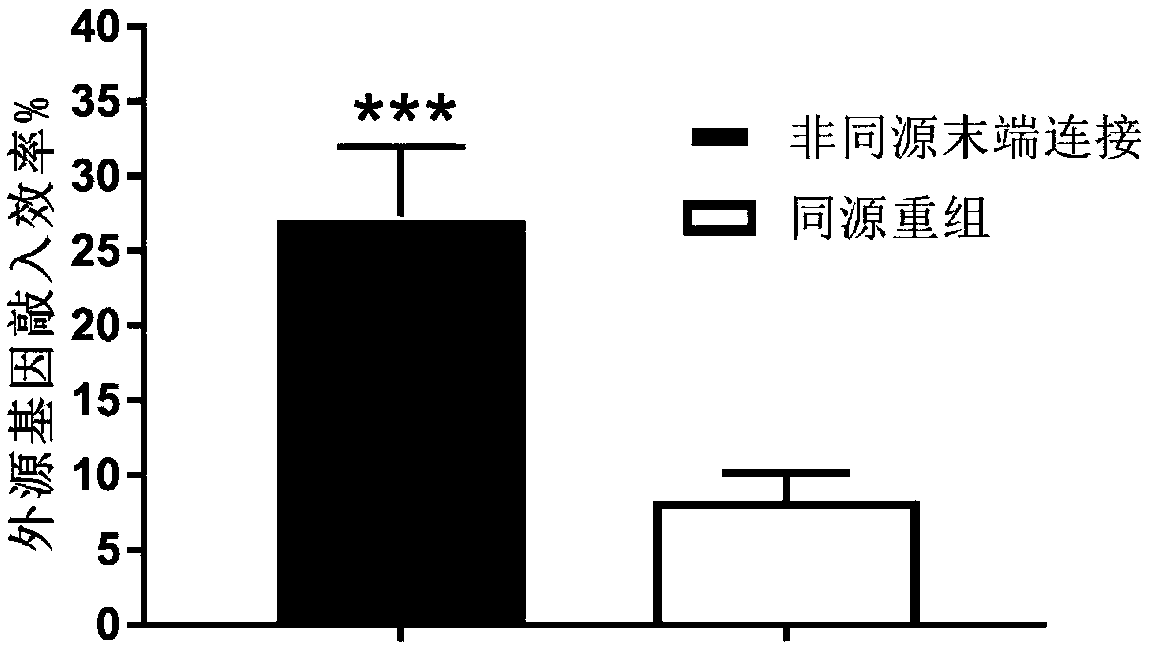
Method for inserting exogenous fragments into DNA virus genome in efficient, fixed-point and directional manner
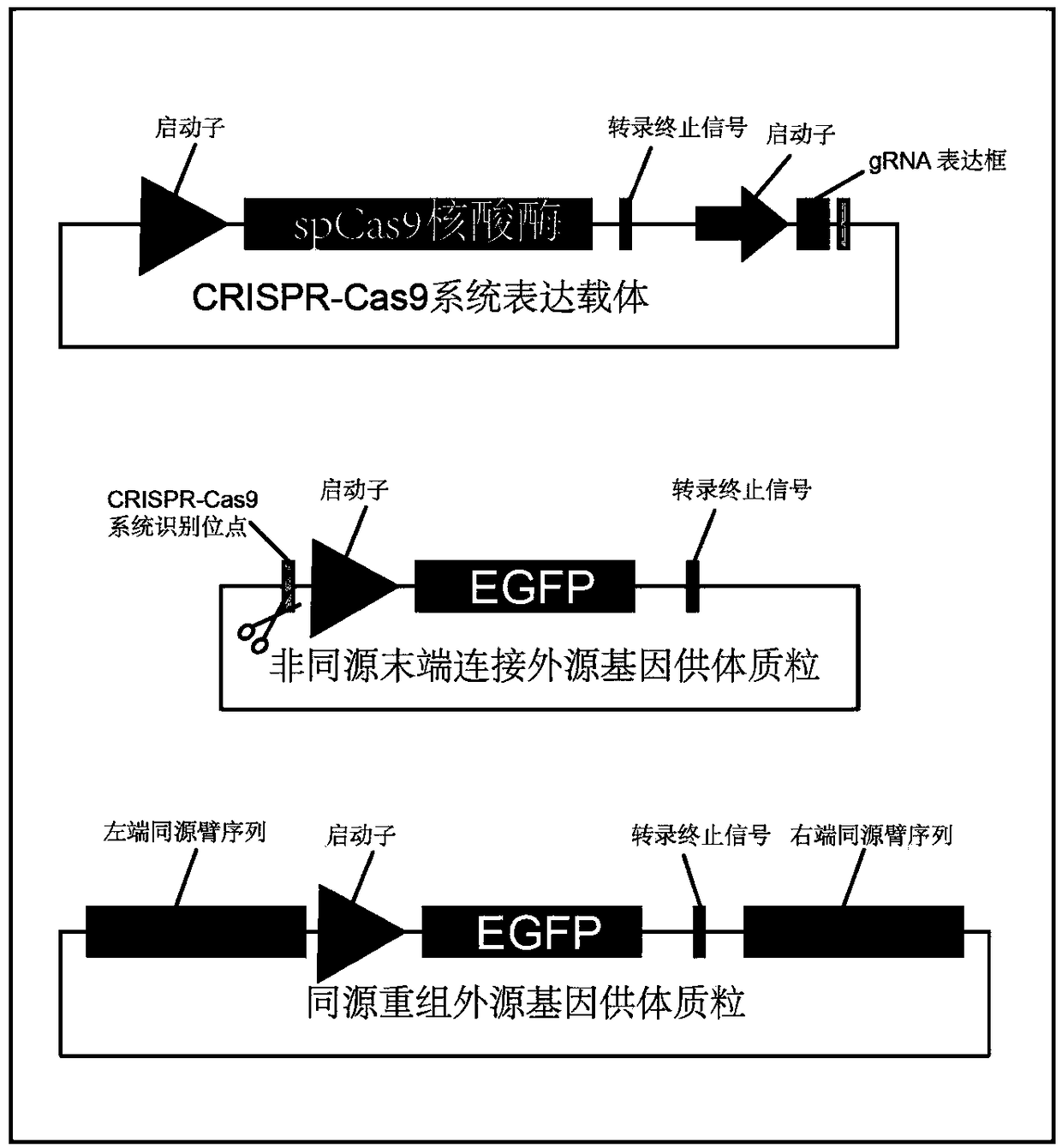
InactiveCN108913684AImprove efficiencyReduce workloadHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAInfection timeRecombinant virus
The invention belongs to the technical field of virus gene recombination, and particularly relates to a method for inserting exogenous DNA fragments into a specific large DNA virus genome in a fixed-point, directional and efficient manner by utilizing a non-homologous recombination mechanism. The method comprises the following steps of 1) designing and constructing a CRISPR-Cas9 (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats and CRISPR-associated protein 9) system for a specific cleavage site of the DNA virus genome; 2) designing and constructing an exogenous gene donor carrying one or more same cleavage sites; 3) introducing an expression vector of the CRISPR-Cas9 system and the exogenous gene donor into a specific cell according to a certain proportion and sequence; 4) aftera period of time, according to virus characteristics, selecting a proper infection time point and multiplicity of infection, and infecting the cell with viruses; 5) selecting an optimized time point to collect progeny recombinant viruses generated after virus infection; and 6) separating, screening and identifying target recombinant progeny DNA viruses. By means of the method, the recombination efficiency of inserting an exogenous gene into the DNA virus genome in a fixed-point and directional manner can be remarkably improved, so that the construction and screening time of the recombinant viruses can be shortened.
Owner:INST OF MEDICAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Application of CD3xB7H3 bispecific antibody in directional killing of human bladder cancer cells
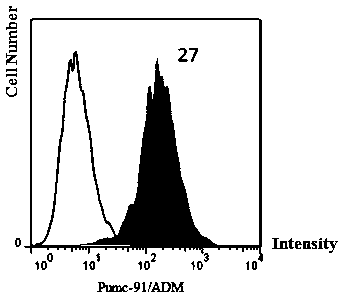
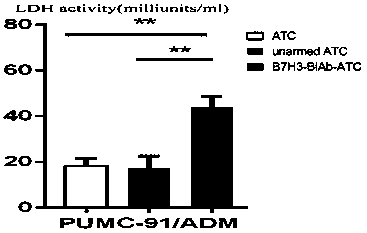
InactiveCN109971711AMammal material medical ingredientsBlood/immune system cellsCancer cellTumor necrosis factor alpha
The invention aims to provide an application of coupling CD3xB7H3 bispecific antibody in directional killing of human bladder cancer cells, and particularly, the coupling CD3xB7H3 bispecific antibodycan enhance the killing effect of activated T cells (ATC) on human bladder cancer cells and provides a new immunotherapy target for targeted therapy of drug resistance of bladder cancer. The researchof the invention proves that B7H3 is highly expressed in human bladder cancer cells; and compared with ATC which is not coupled with the CD3xB7H3 bispecific antibody, the ATC which is combined with the CD3xB7H3 bispecific antibody has enhanced capability of directionally killing the human bladder cancer cells, and has obvious cytotoxic activity on the human bladder cancer cells. When ATC combinedwith the CD3xB7H3 bispecific antibody and tumor cells are co-cultured at the multiplicity of infection of 10:1, the killing effect is significantly increased. Meanwhile, the ATC combined with the CD3xB7H3 bispecific antibody has increased level of secreting interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha).
Owner:张曼
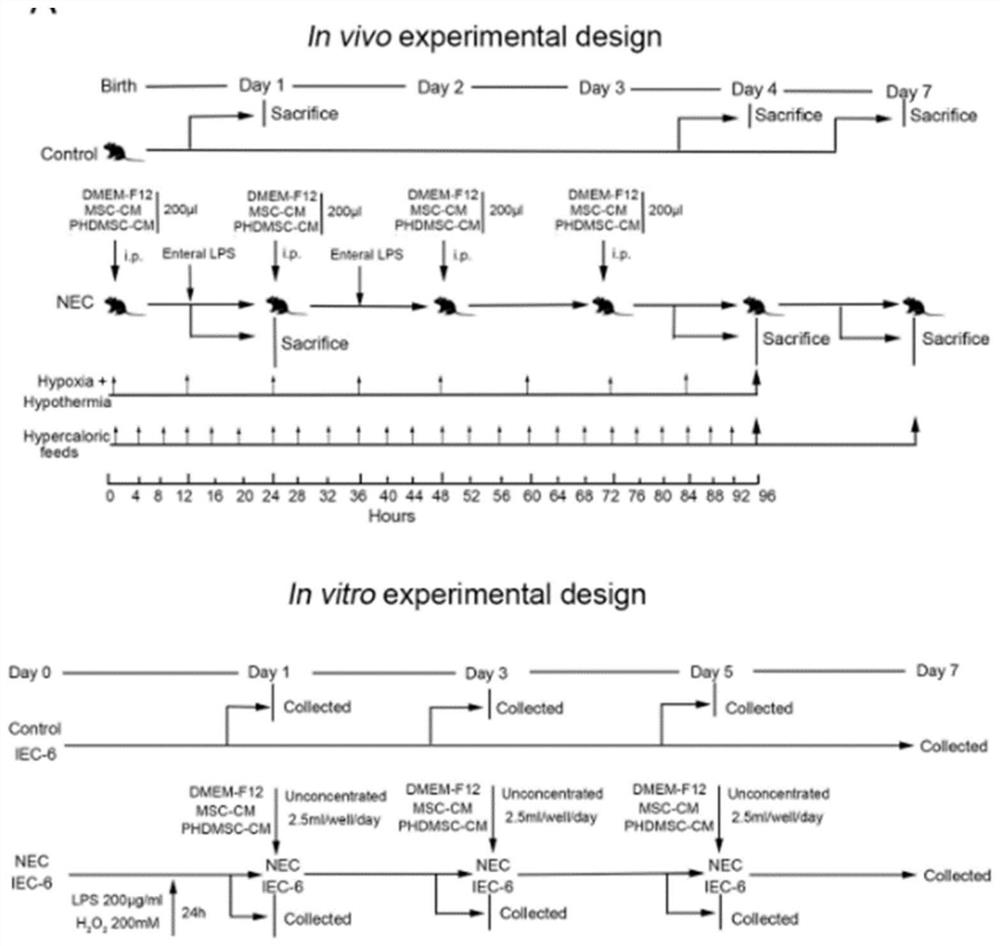
Method for preparing BM-MSCs conditioned medium, conditioned medium and application
PendingCN112410303AExpression mechanisms that enhance paracrine actionGood restorativeDigestive systemSkeletal/connective tissue cellsTransfer vectorCulture mediums
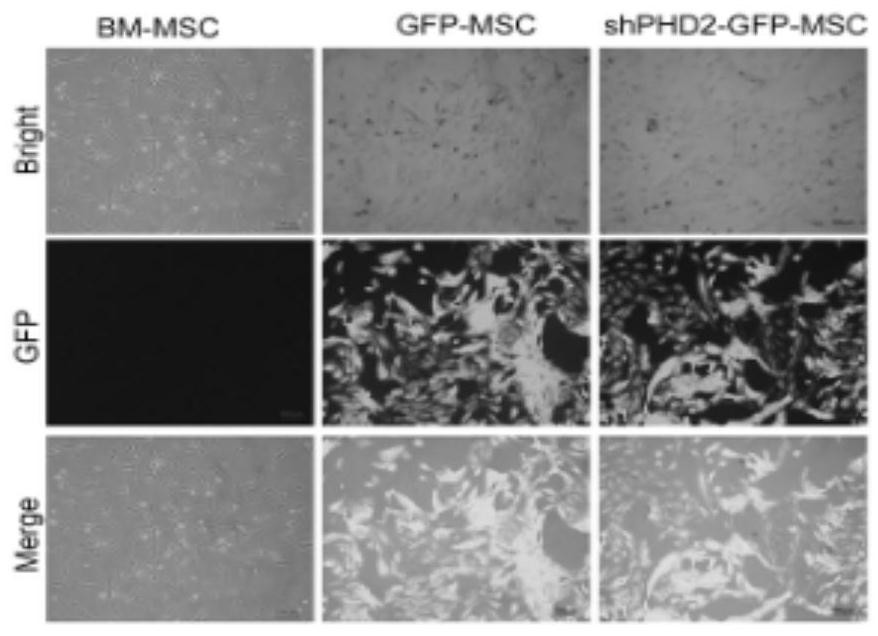
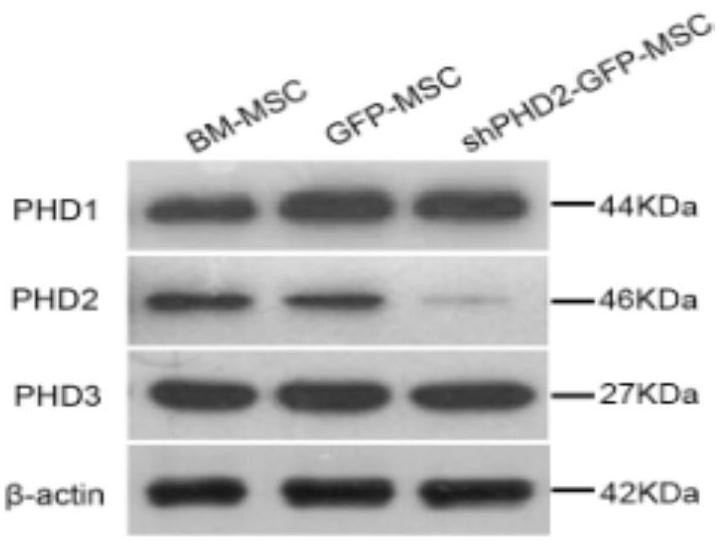
The invention provides a method for preparing a BM-MSCs conditioned culture medium, the conditioned culture medium and application. The method comprises the following steps of (1) constructing PHD2. shRNA on a lentiviral gene transfer vector pGCSIL-GFP; (2) under the condition that the multiplicity of infection(MOI) is 10, transfecting the BM-MSCs by using a lentivirus containing shPHD2-GFP; (3) determining stably transfected BM-MSCs by detecting GFP fluorescence and PHD2 protein expression, carrying out cell sorting and enrichment, and then culturing the BM-MSCs in a new serum-free basic culture medium for 48 hours to obtain a basic conditioned culture medium containing paracrine substances efficiently expressed by BM-MSCs; and (4) performing ultrafiltration concentration on the basic conditioned culture medium by 50 times, controlling the molecular weight cut-off to be 5kDa to obtain a concentrated conditioned culture medium, and then storing the obtained conditioned culture medium at minus 20 DEG C. In the basic conditioned culture medium obtained in the step (3), 1mL of non-concentrated conditioned culture solution is equivalent to the secretion volume of 1.5-2.5 * 10 <5> BM-MSCs. The conditioned culture medium prepared by the invention can enhance the paracrine effect of the BM-MSCs.
Owner:GUANGDONG GENERAL HOSPITAL
Method for producing parvovirus having high infectivity titer
ActiveUS9809800B2Overcome negative influenceSsDNA virusesForeign genetic material cellsDouble-timeMicrobiology
Owner:ASAHI KASEI MEDICAL CO LTD
Compound doxycycline hydrochloride soluble powder and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101653419AOvercoming a lack of appetiteQuick curePowder deliveryTetracycline active ingredientsRed blood cellDoxycycline hydrochloride
The invention discloses a compound doxycycline hydrochloride soluble powder and a preparation method thereof, and aims to provide the compound doxycycline hydrochloride soluble powder which has a quick response to treatment of the multiplicity of infection of eperythrozoon suis and toxoplasma, has high cure rate, treats both symptoms and root causes, can improve the recovery rate of pigs and is convenient to use, and the preparation method which has a simple process and is easy to implement. The powder comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 2 to 20 percent of doxycycline hydrochloride, 5 to 20 percent of sulfathiazole sodium, 2 to 10 percent of taurine, and the balance of anhydrous dextrose. The compound doxycycline hydrochloride soluble powder is a compound preparation of the combination of three medicaments, wherein the doxycycline hydrochloride kills eperythrozoon; the sulfathiazole sodium kills the toxoplasma; the taurine is antithermic and antiphlogistic; andthe three components are blended together reasonably. Thus, the compound doxycycline hydrochloride soluble powder has a quick response to the multiplicity of infection of the eperythrozoon suis and the toxoplasma, is effective and efficient, treats both symptoms and root causes, and can reduce the losses of raisers.
Owner:TIANJIN SHENGJI GRP CO LTD
Method for preparing newcastle disease inactivated vaccine, and product and application thereof
InactiveCN104689312ASave training spaceSmall batch-to-batch varianceViral antigen ingredientsAntiviralsDrugTiter
The invention discloses a method for preparing a newcastle disease inactivated vaccine, and a product and application thereof, belonging to the field of preparation and application of newcastle disease inactivated vaccines. The method for preparing the newcastle disease inactivated vaccine disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps of: (1), culturing animal cells by utilizing a cell factory; (2), inoculating newcastle disease virus, and proliferating the virus in the cell factory; and (3), harvesting the virus to prepare the inactivated vaccine. According to the invention, proliferation conditions of the newcastle disease virus in the cell factory including cell density, virus infection multiplicity, TPCK-pancreatin concentration and virus culture time are optimized; the newcastle disease virus cultured by the method disclosed by the invention has high titer, so that immune production requirements can be satisfied; the process is steady, so that the newcastle disease inactivated vaccine can be produced in a large scale; the newcastle disease inactivated vaccine prepared by the method disclosed by the invention is safe to chickens; 100% immunoprotection to attack of the newcastle disease virus can be realized; and thus, the newcastle disease inactivated vaccine can be used for preparing a medicine or a reagent for preventing or treating newcastle diseases.
Owner:JILIN ZHENGYE BIOLOGICAL PROD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com