Screening system for anti-Singapore grouper iridovirus (SGIV) drug
A screening method and drug technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, biomaterial analysis, microbial measurement/inspection, etc., can solve problems such as complex process and complex analysis, and achieve simple screening methods and optimized cell activity culture conditions Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
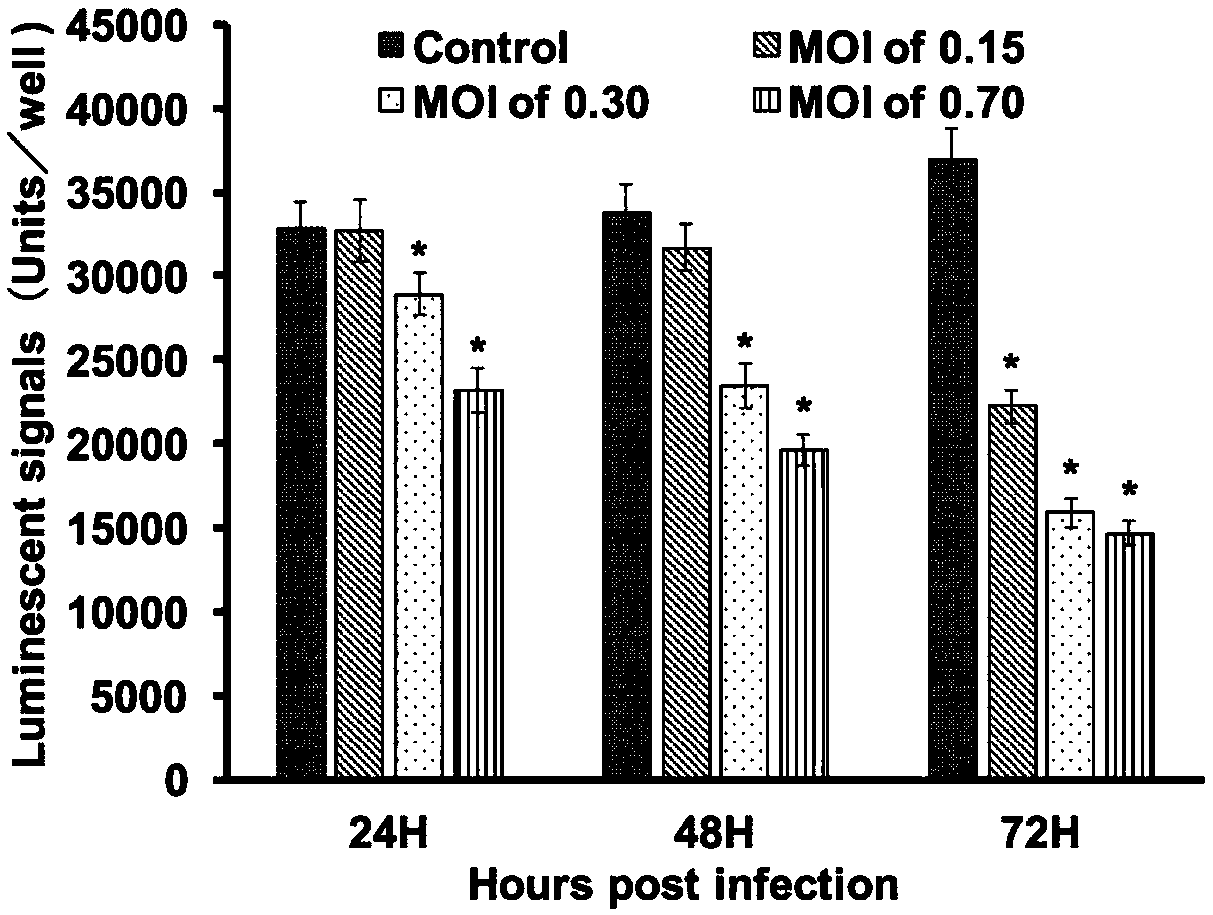
[0030] Example 1 Quantification of CPE caused by SGIV infection, determination of multiplicity of infection and infection time
[0031] ZEB cells were plated on 96-well plates and infected with SGIV at different multiplicity of infection (0.15, 0.3 and 0.7). After 24, 48 and 72 hours of infection, the CPE induced by SGIV infection was detected with the CellTiter-Glo Luminescent Cell Viability kit. The results showed that after 24, 48 and 72 h, the fluorescence signal (equivalent to cell viability) of ZEB cells at MOIs of 0.3 and 0.7 was significantly reduced compared with cells not infected with virus. However, the cell viability of cells with a multiplicity of infection of 0.15 did not decrease significantly at 24 and 48 hours after infection ( figure 1 ). The results demonstrate that SGIV infection-induced CPE can be quantified.
[0032] Determination of virus infection time and multiplicity of infection (MOI): ZEB cells were spread to 96-well plates at a density of 5000 / ...
Embodiment 2
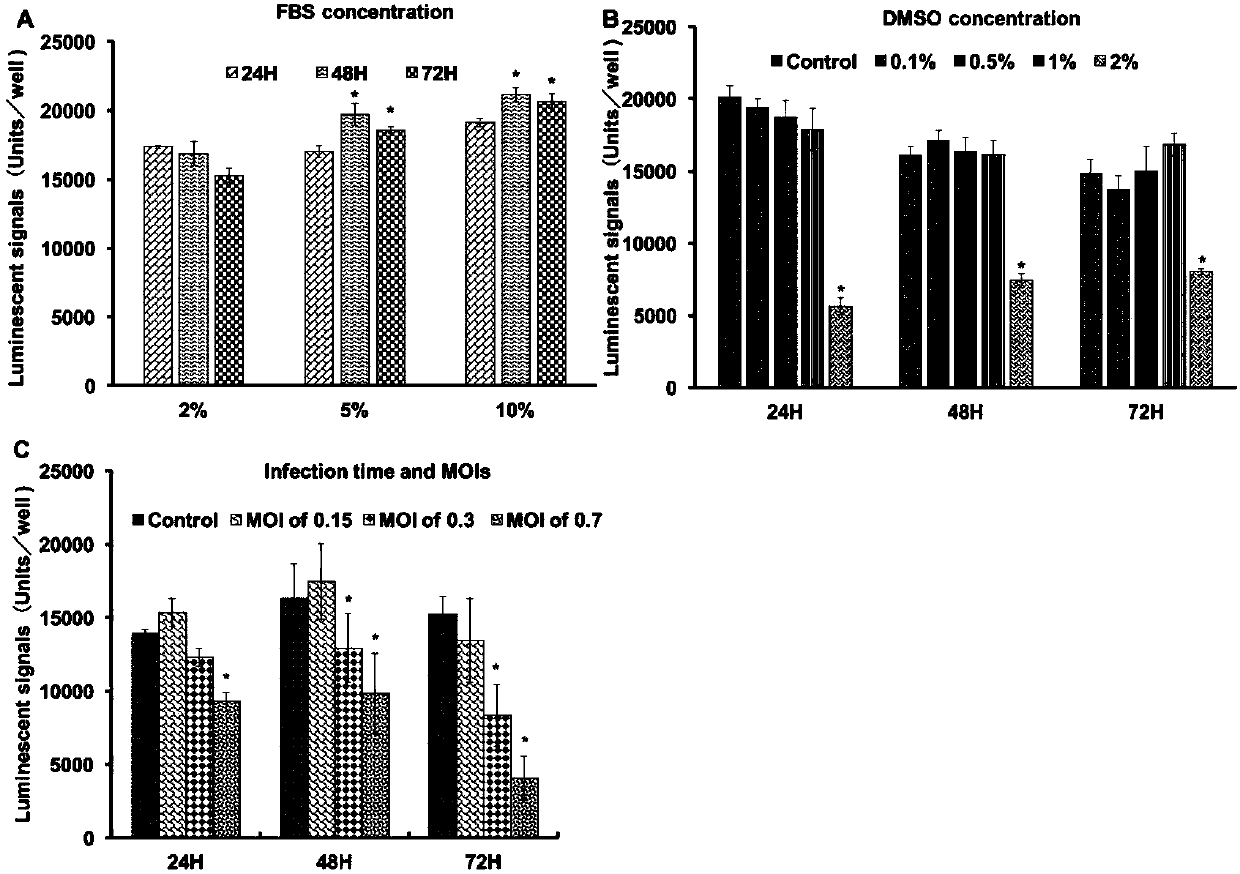
[0034] Example 2 Optimization of CPE-based cell culture conditions
[0035] Determination of serum concentration: ZEB cells were transferred to a 96-well plate at a density of 5000 / well, and cultured with DMEM medium containing different serum concentrations (2%, 5%, 10%). Cell viability was tested with CellTiter-Glo kit 24, 48, and 72 hours after passage. The experiment was repeated three times, and the obtained experimental data was the average of 8 parallel sample data.
[0036] Cell culture medium with high FBS content may cause excessive cell proliferation and reduce cell viability. The optimal concentration of FBS can be determined by detecting the effect of FBS concentration on the activity of ZEB cells. Analysis showed that ZEB cells were inoculated into DMEM medium containing 5% and 10% FBS, and the fluorescent signals at 48h and 72h after inoculation were stronger than those at 24h after inoculation. However, when ZEB cells were cultured with DMEM medium containin...
Embodiment 3
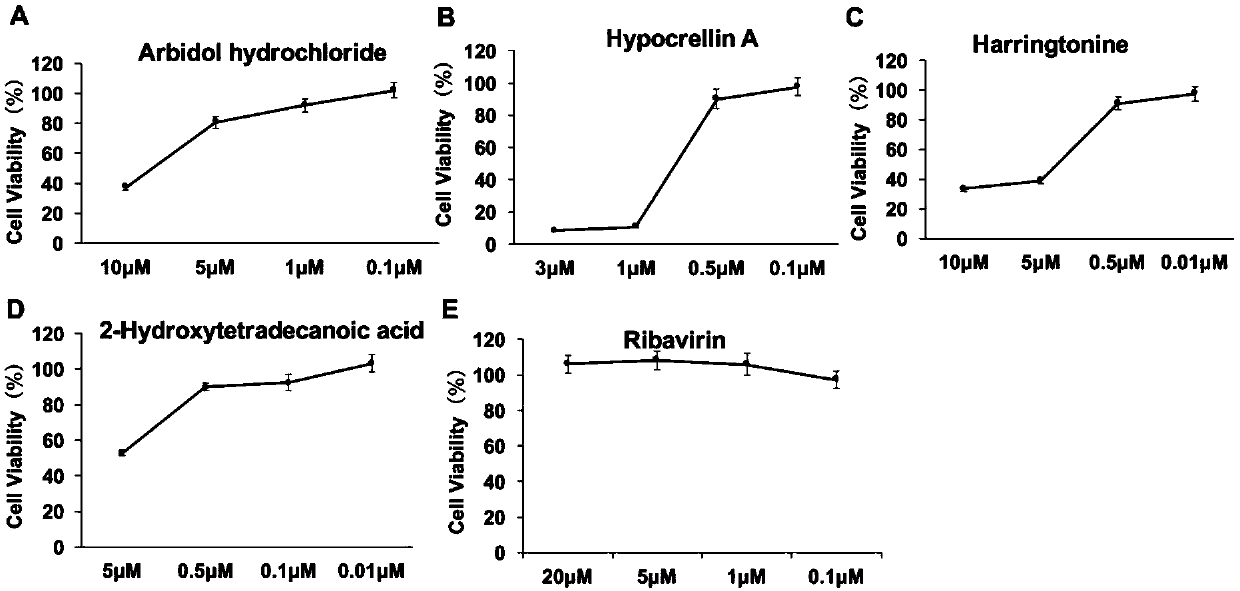
[0039] Example 3 Addition of screened drugs and screening of drugs by cell activity
[0040]Drugs to be screened were: ribavirin, arbidol hydrochloride and hydroxytetradecanoic acid purchased from Sigma (St.Louis, MO). Hypocretin A and harringtonine were purchased from Abcam (Cambridge, UK). Harringtonine was dissolved in DMSO to a concentration of 9.4×10 3 μM. Hypocretin A was dissolved in DMSO at a concentration of 1.83 × 10 3 μM. Hydroxytetradecanoic acid (20.4×10 3 μM), Arbidol hydrochloride (1×10 3 μM), ribavirin (40.95×10 3 μM) were dissolved in DMSO and stored at -20°C.
[0041] The ZEB cells were spread to 96 wells at a density of 5000 / well, and pre-treated with different concentrations of ribavirin, arbidol hydrochloride, hydroxytetradecanoic acid, hypocretin A or harringtonine at 28°C. Incubate for 24h. In the presence of the above compounds, SGIV (MOI=0.3) was added to the pretreated and untreated cells, and after incubation at 28°C for 48h, the fluorescenc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com