Patents
Literature
103 results about "Juvenile" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A juvenile is an individual organism that has not yet reached its adult form, sexual maturity or size. Juveniles sometimes look very different from the adult form, particularly in colour. In many organisms the juvenile has a different name from the adult (see also List of animal names).
Sepia lycidas fry breeding method
InactiveCN102823529AFilling up the technology blank of artificial breeding squidImprove survival rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaJuvenileShrimp
The invention relates to a Sepia lycidas fry breeding method, belonging to the field of aquatic fry breeding. The method specifically comprises the following five steps of: fishing of parents, temporary culture of the parents, acquisition of eggs, hatching of the eggs and breeding of fries, wherein sexually mature parent Sepia lycidas are selected and put into a water pond, temperature, salinity and stocking density are controlled, the water quality is kept and alive small fish and shrimps are fed for temporary culture; the parents with eggs are put into egg laying ponds in proportion and fertilized eggs are collected periodically; the eggs of the same batch are put into a hatching pond for hatching; embryos to be hatched soon are collected and put into breeding ponds, the area of each breeding pond is 10-15 square meters, the water temperature is 20-30DEG C, the seawater salinity is 25-35, the stocking density is 200-400 fries per square meter, and the fries are fed for the first time after 6-12 hours from the time when the fries are hatched and get out of embryonic membranes; and after the mantle length of the fries is more than 1.5cm, the fry breeding process is completed and the fries are moved out. The breeding method has the advantages of high survival rate, few diseases, rapid growth, easiness in operation and high success rate, and is suitable for large-scale breeding.
Owner:ZHANJIANG NORMAL UNIV
Reed-fish-shrimp-crab ecological polyculture method for inland soda saline-alkaline reed swamps
InactiveCN103004651ABreeding successIdeal domestication survival rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaPolyculturePrawn
The invention provides a reed-fish-shrimp-crab ecological polyculture method for inland soda saline-alkaline reed swamps, which includes crab acclimation, stocking densities of fries, juvenile shrimps and juvenile crabs, culture management and catch and reed culture. After the method is adopted, the survival rate of acclimated crabs is 81.3 percent; the average stocking densities of river crabs, fishes and shrimps are 2138 river crabs / hm<2>, 510 fishes / hm<2> and 11750 shrimps / hm<2>, the average catch weights of the river crabs, fishes and shrimps are 87.15kg / hm<2>, 233.30kg / hm<2> and 52.88kg / hm<2>, the average catch specifications of the river crabs, fishes and shrimps are 145.2g per crab, 670.6g per fish and 5.3g per shrimp, the average recapture rates of the river crabs, fishes and shrimps are 26.83 percent, 69.45 percent and 83.63 percent, the average density of reed is increased by 9.69 percent, the average yield is increased by 12.47 percent, and the input-output ratio of the experimental area is 1:3.174.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
Giant freshwater juvenile prawn cultivating method
InactiveCN104798706AImprove survival ratePrecise feeding managementClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaJuvenileSocial benefits
The invention discloses a giant freshwater juvenile prawn cultivating method and belongs to the technical field of cultivation of giant freshwater juvenile prawns. Environmental conditions are optimized, a cultivating pond is rational constructed, shrimp seeds are scientifically released and breeding management is precisely performed; the method provides a set of complete method for improving survival rate during cultivation of juvenile prawns. The giant freshwater juvenile prawn cultivating method is simple to operate, low in cost and has remarkable effect, obvious economic benefits and social benefits.
Owner:高邮市阳光特种水产专业合作社
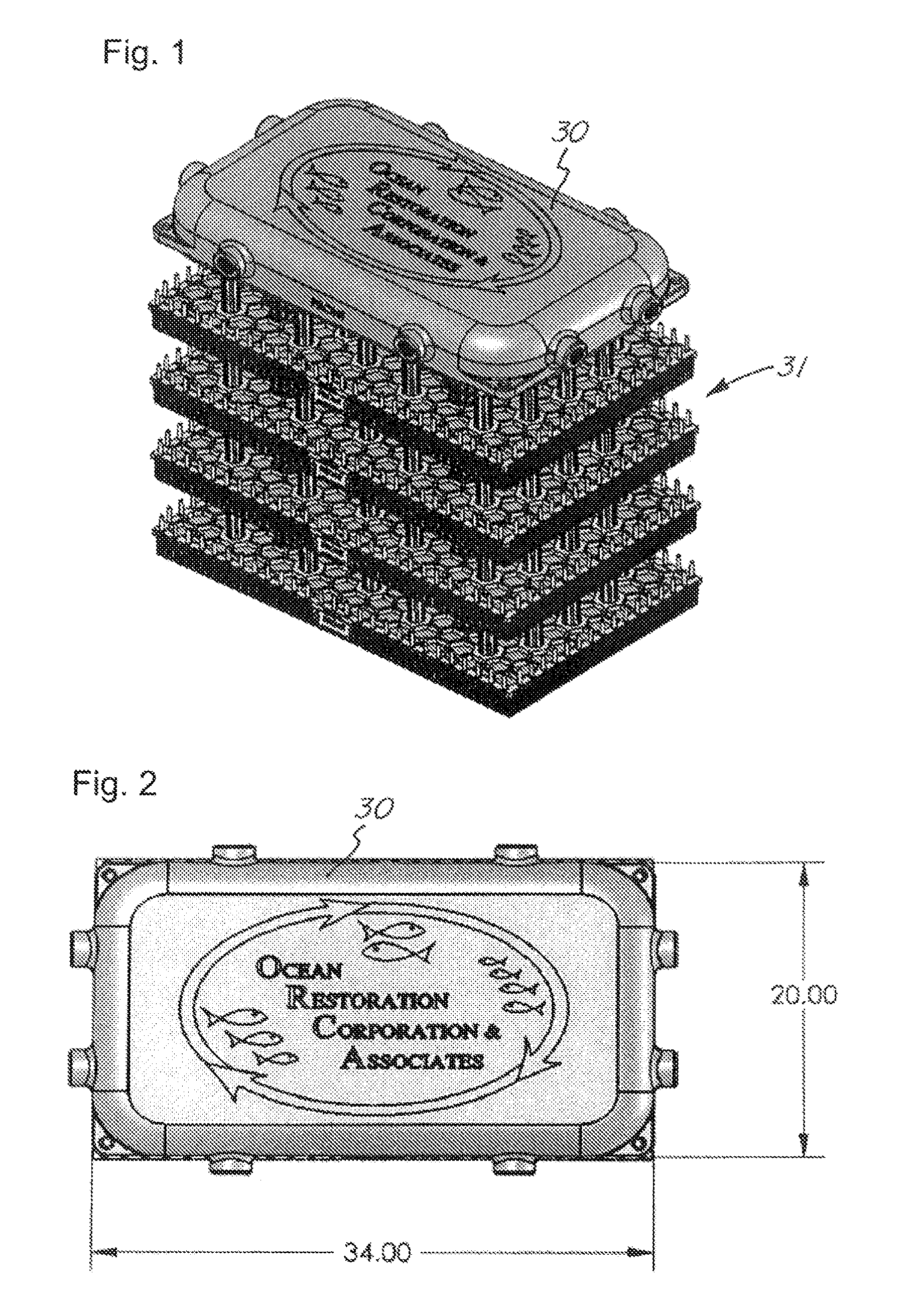
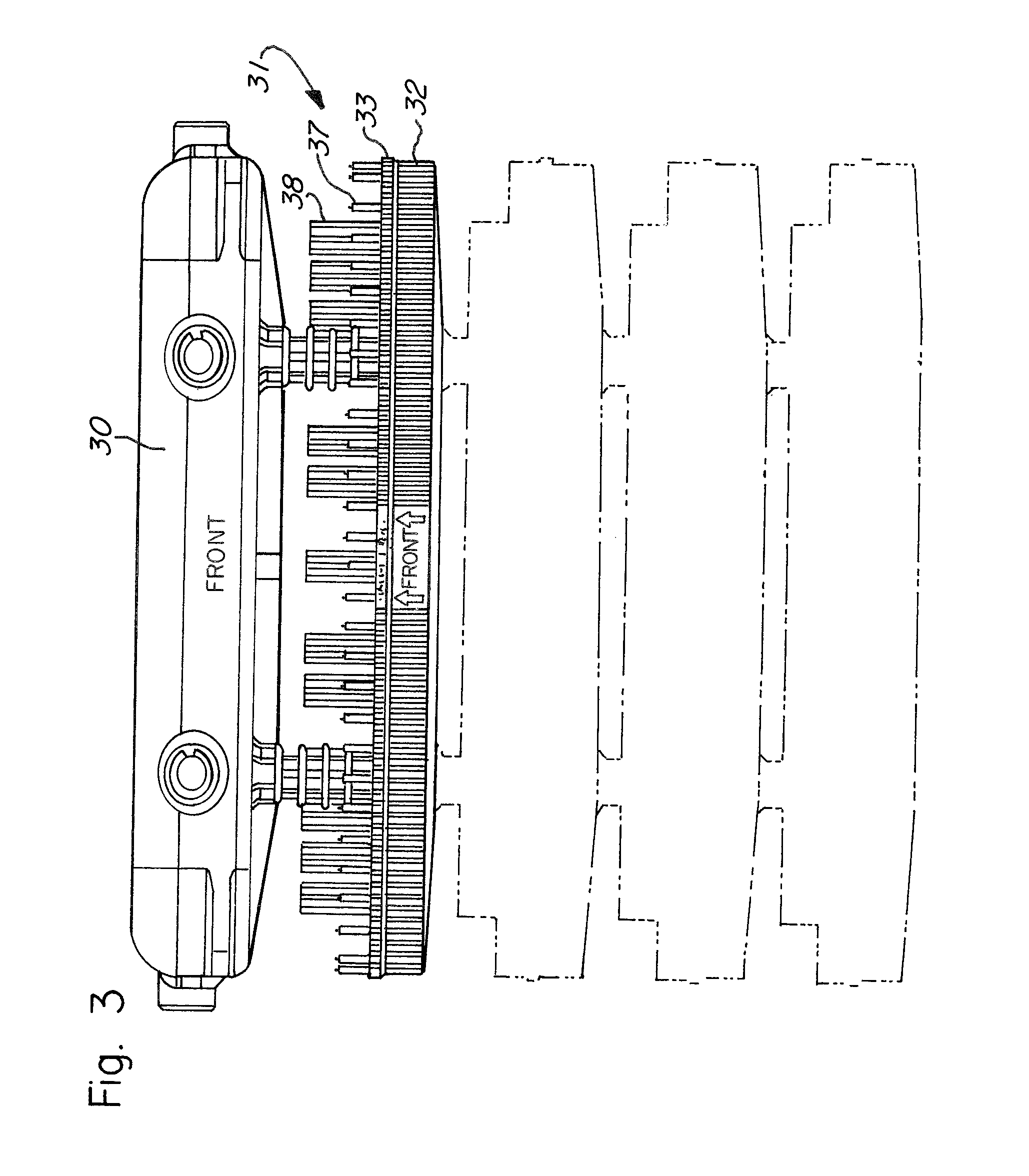
Marine habitat systems
InactiveUS8033250B2Increase diversityEasilyClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaJuvenileMarine habitats
Owner:OCEAN RESTORATION CORP & ASSOCS
Double-harvest-one-year industrialized culture method for octopuses
InactiveCN101984791AStabilize and improve physical fitnessReduce lossesClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaDiseaseHigh concentration
The invention discloses a double-harvest-one-year industrialized culture method for octopuses, which comprises the following steps of: cultivating parent octopuses in a strengthened mode, laying eggs, hatching fertilized eggs, cultivating young bodies, cultivating adults at a controlled temperature and the like. The method can stabilize and improve the physical quality of the parent octopuses, reduce mutual killing, effectively reduce the diseases of the fertilized eggs and improve hatchability. Furthermore, an adopted octopus industrialized cultivator for the fertilized eggs of the octopuses can be conveniently moved, so that cost is low, sterilization and desinsection can be performed by a high concentration medicated bath, the infringement of parasites to the octopus eggs which have relatively long hatching periods can be greatly reduced, and the adopted octopus industrialized cultivator is particularly suitable for hatching the octopus eggs on a large scale. By adopting hidden matters, the energy loss of octopus young bodies caused by swinging can be reduced, and the growth speed of the octopus young bodies can be improved. Male and female octopuses are bred in an isolated mode in the step of cultivating the adults at the controlled temperature, so that the mutual killing and energy loss caused by mating can be avoided, and the weight increment of finished octopuses is facilitated. The double-harvest-one-year industrialized culture method for the octopuses has the advantages of industrialization value, short production period, high hatchability and fewer diseases.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Ecological lotus root and soft-shelled turtle coexistence culture method
InactiveCN104770325AGrowth benefitsPromote growthHorticultureAnimal husbandryLand resourcesWater resources
The invention discloses an ecological lotus root and soft-shelled turtle coexistence culture method, which includes the following steps: (1) preparation of a culture pond: the area of the culture pond is 3 mu to 5 mu, the pond depth is 1.2m to 1.5m, baffles are laid around the pond bank, and after the pond is constructed, the bottom soil is dug loose by 15cm to 20cm deep; a feeding platform and a sunning platform need to be built on the culture pond; (2) planting of lotus roots: in January or February, the lotus roots are planted into the pond bottom, the planting area of the lotus roots is one third to half of the pond area, the water level is slightly low at the budding time of the lotus roots, and as the stems and leaves of the lotus roots flourish gradually, the water level is increased gradually; (3) stocking of juvenile soft-shelled turtles: in May or June, the juvenile soft-shelled turtles are chosen, 650 to 1000 juvenile soft-shelled turtles are stocked per mu, and before being stocked into the pond, the juvenile soft-shelled turtles are disinfected; (4) coexistence culture of the lotus roots and the soft-shelled turtle. The ecological lotus root and soft-shelled turtle coexistence culture method disclosed by the invention is a high-efficiency culture pattern, on one hand, the utilization rate of water resource and land resource and yield can be increased, and on the other hand, a mutual benefit relation is established between aquaculture and vegetable and fruit cultivation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HUZHOU JINLIANHUA ECOLOGY AGRI
Trionyx sinensis juvenile feed table for weighing feeding amounts
PendingCN107821329AEasy to eatEasy to operateSpecial purpose weighing apparatusAnimal husbandryJuvenileAnimal science
The invention relates to the technical field of aquaculture devices, in particular to a trionyx sinensis juvenile feed table for weighing feeding amounts. The trionyx sinensis juvenile feed table comprises a pontoon. The pontoon is used for being arranged at an aquaculture water surface in a floating manner, and a weighing device is arranged above the pontoon; the weighing device comprises a tray,the tray is arranged right above the pontoon and is hung at a lifting hook of an electronic crane scale by lifting wires, and a feed disc is arranged in the tray; the electronic crane scale is arranged at an end of a fixing frame by a suspension wire, the suspension wire is wound in a rolling device arranged at the end of the fixing frame, and the rolling device is used for rolling up and payingoff the suspension wire. The trionyx sinensis juvenile feed table has the advantages that tedious operation steps in existing feeding amount measurement and calculation procedures can be effectively simplified by the trionyx sinensis juvenile feed table, and feeding amount measurement and calculation effects can be effectively quickly and conveniently realized in aquaculture systems.
Owner:ZHEJIANG WANLI UNIV
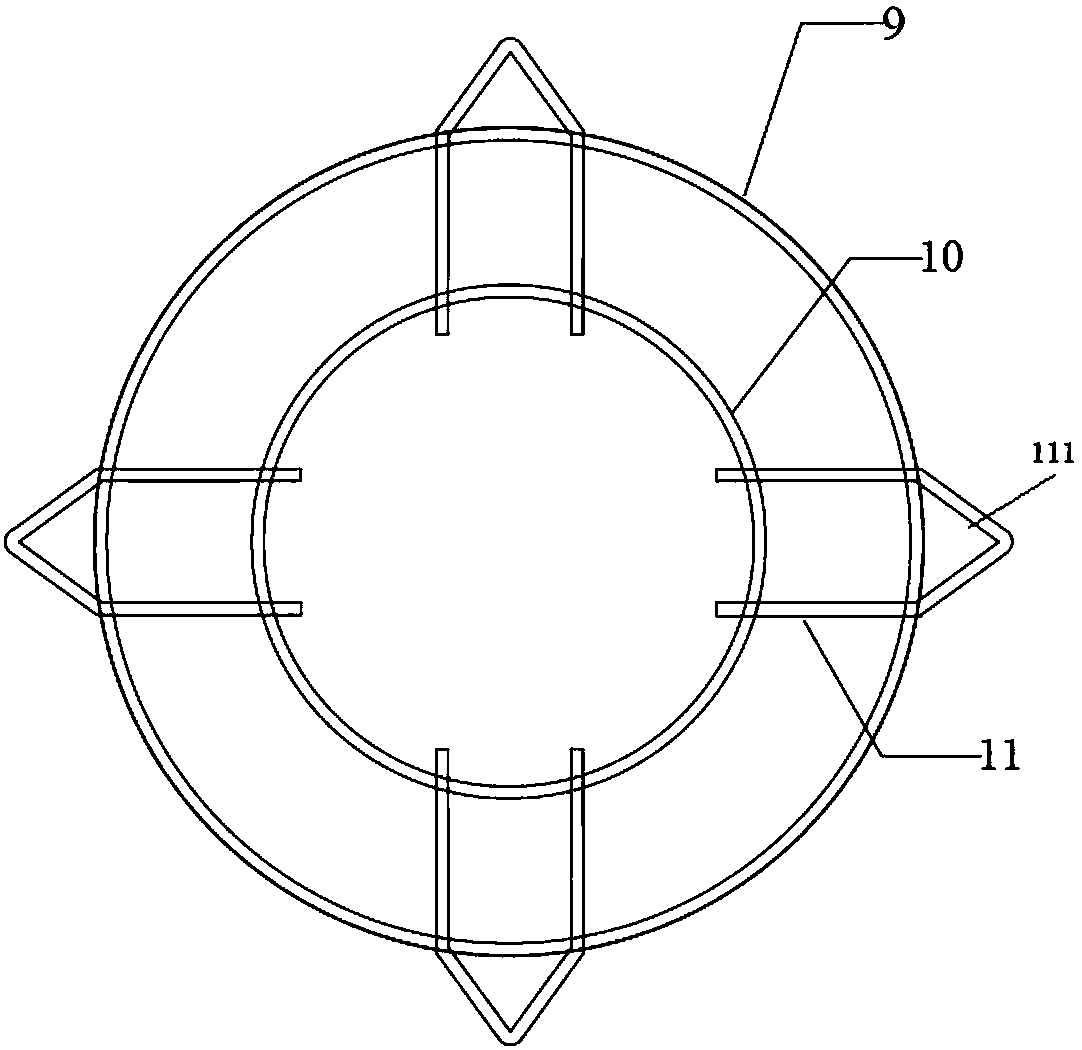
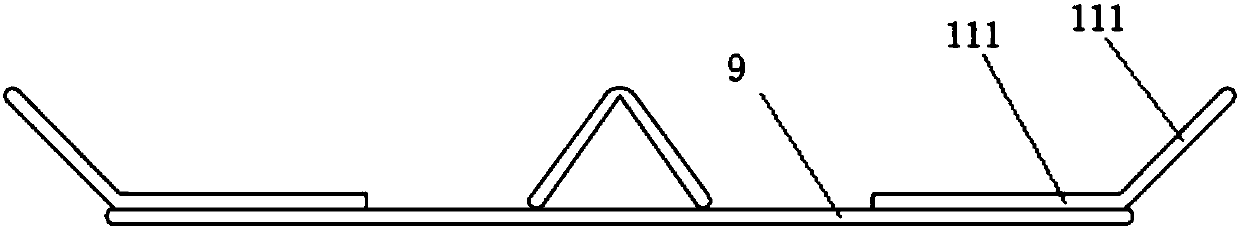
Rice field-based polyculture juvenile crab breeding method
ActiveCN113826569AEasy dischargePrevent escapeClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaJuvenilePolyculture
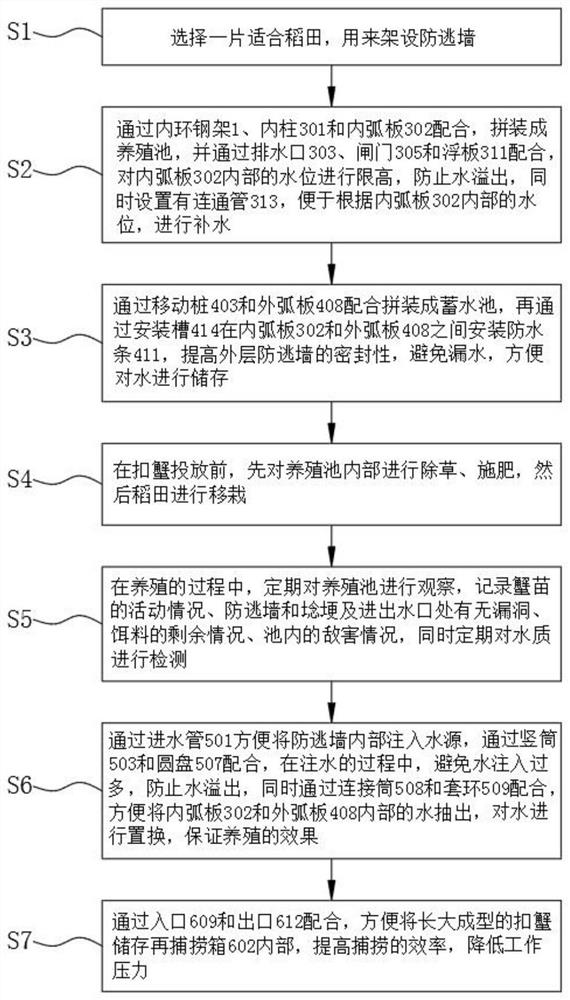
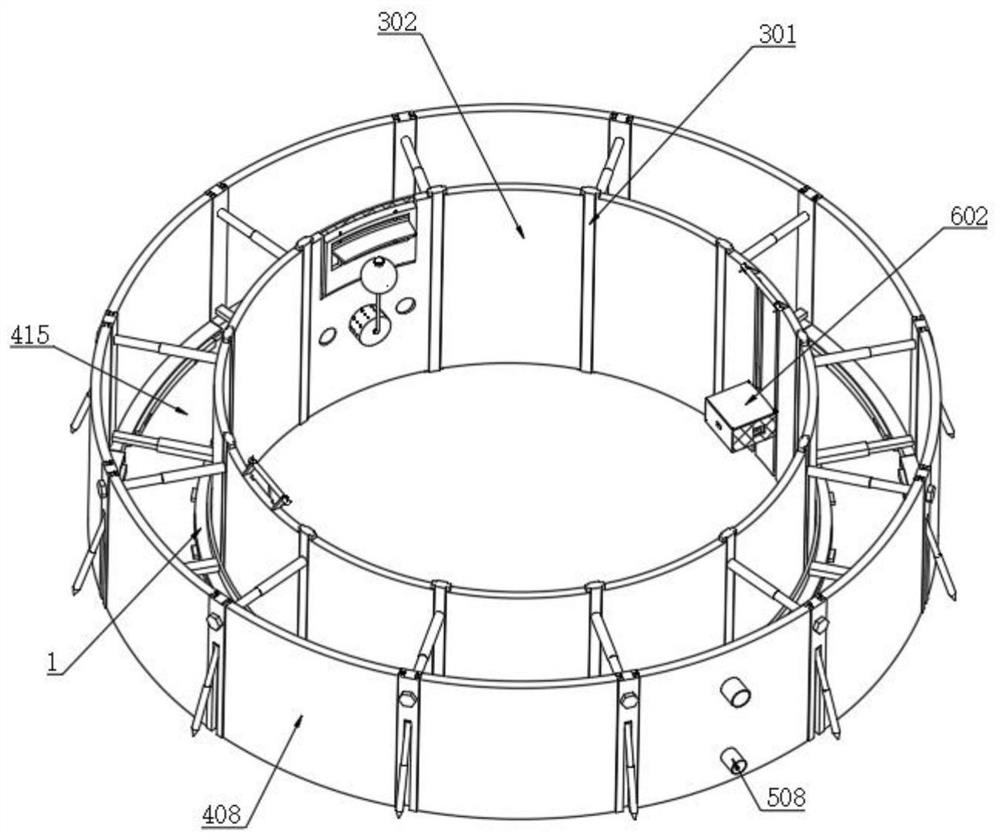
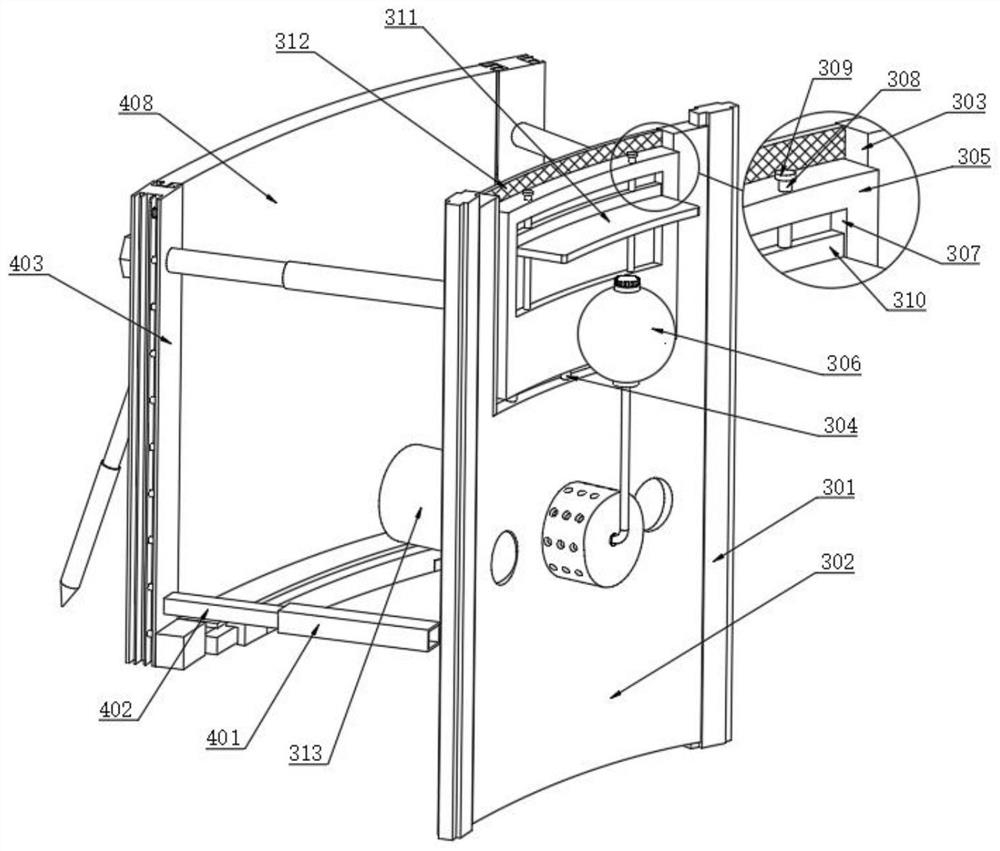
The invention discloses a rice field-based polyculture juvenile crab breeding method. The rice field-based polyculture juvenile crab breeding method comprises the following steps that S1, a suitable rice field is selected for erecting an escape-proof wall; and S2, a culture pond is spliced through cooperation of an inner ring steel frame, inner columns and inner arc plates, and the water level in the inner arc plate is limited to prevent water overflow through cooperation of a water outlet, a gate and a floating plate. Meanwhile, a communicating pipe is arranged, and water replenishment is carried out according to the water level in the inner arc plates; the rice field-based polyculture juvenile crab breeding method is scientific and reasonable in structure and safe and convenient to use, the inner ring steel frame is matched with the inner columns, the inner arc plates are assembled into the culture pond, when rainfall in the rainy season is large, the water level in the inner arc plates rises to push floating plates, the gate is driven to ascend through cooperation of a lifting plate and an adjusting rod, sealing of a water outlet is relieved, water in the inner arc plates is conveniently drained, the water level in the inner arc plates is prevented from being too high, juvenile crabs are prevented from climbing out of the inner arc plates, death of the juvenile crabs is reduced, and loss is reduced.
Owner:北大荒集团黑龙江八五六农场有限公司
Catadromous migration salmon breeding method for migratory salmon
InactiveCN111771776AQuality improvementConditions are highly controllableClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaZooidJuvenile
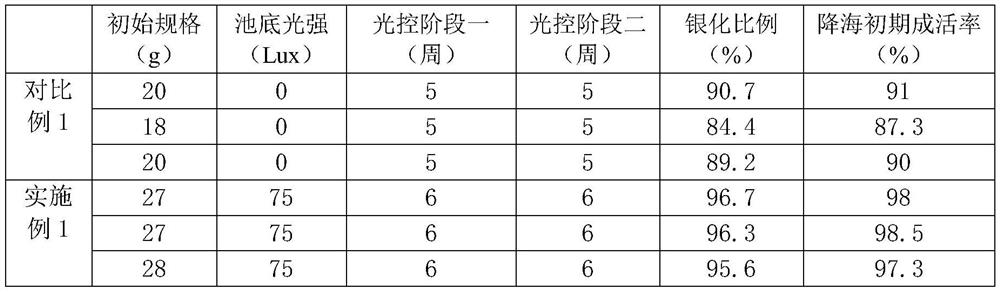
The invention belongs to the technical field of aquaculture, and relates to a catadromous migration salmon breeding method for migratory salmon. The method specifically comprises the following steps:(1) selection of juvenile salmons, wherein the average sampling weight is at least 25g, and the proportion of individuals smaller than 25g is not higher than 10%; (2) during the catadromous migrationperiod, adding an underwater light source at the bottom of the culture pond to ensure that the illumination intensity in the water body at the bottom of the pond is not lower than 20Lux; (3) cultivation in a catadromous migration stage, wherein a light control strategy is as follows: firstly, a light cycle strategy (LD12: 12) of 12 hours of illumination every day and 12 hours of darkness is adopted for 6 weeks, and then the light cycle strategy is converted into 24 hours of illumination every day (LD24: 0) and lasts for 6 weeks as well; and (4) completing the catadromous migration stage. According to the method, the weight of the catadromous migration juvenile salmon is controlled, light rays are controlled, and the form and physiological indexes of the catadromous migration stage are monitored. The catadromous migration rate can be increased by at least 4.9%, the survival rate after s catadromous migration is increased by at least 6.3%, and large-scale cultivation of catadromous migration salmons under the industrialized condition can be achieved.
Owner:国信东方(烟台)循环水养殖科技有限公司 +1
Bait domestication method for juvenile hippocampus
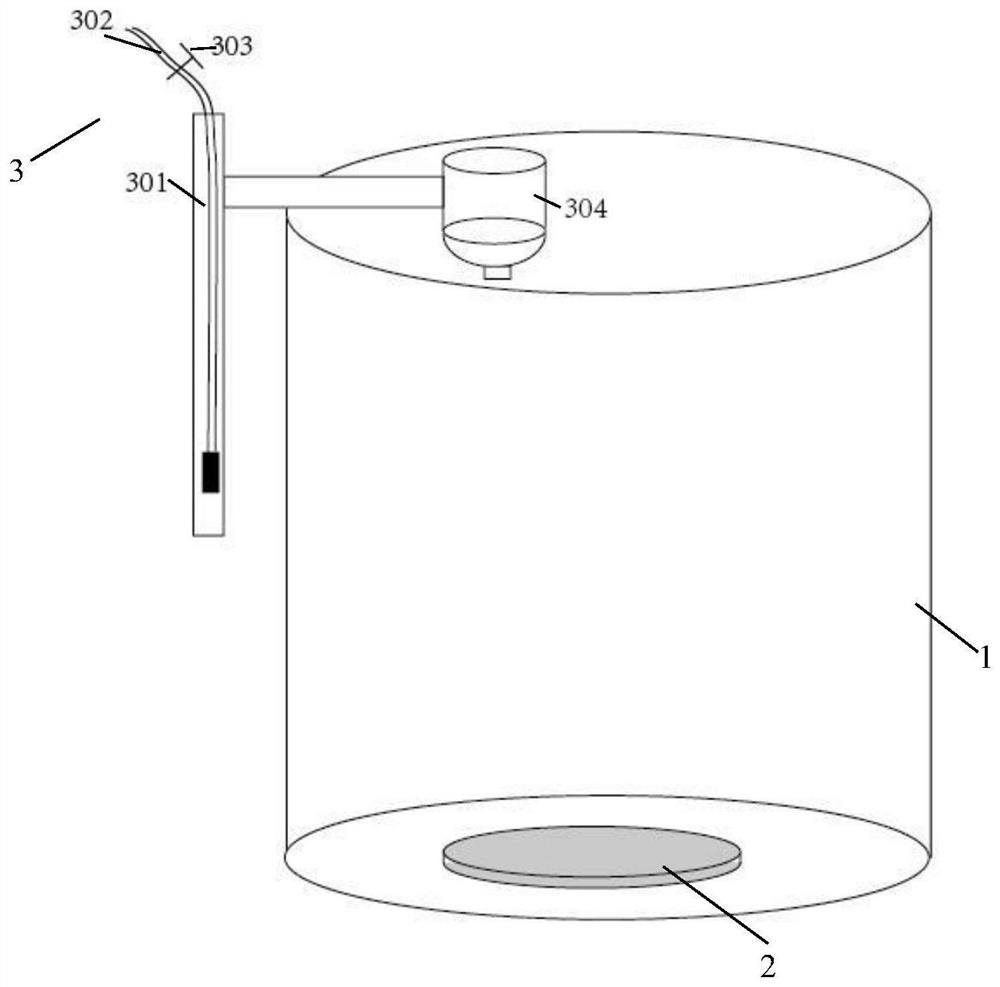
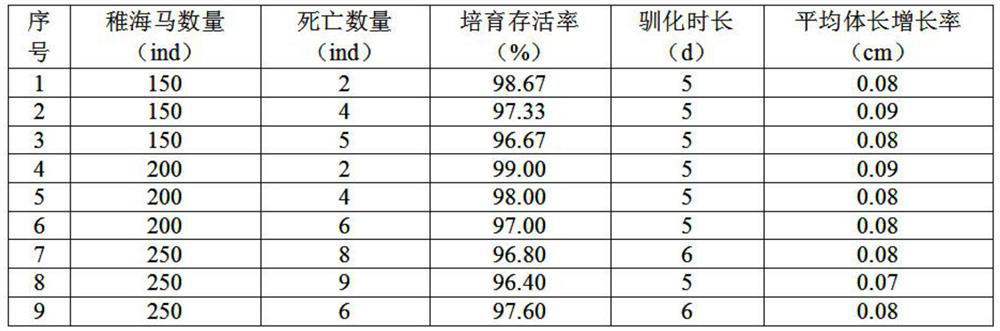
PendingCN114128647AQuick domesticationAvoid the problem of unstable supplyClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaOpossumJuvenile
The invention provides a bait domestication method for young sea horses. The bait domestication method comprises the four steps of preparation of a breeding pond, ecological construction of a domestication pond, installation of domestication equipment and management in the domestication period. 5 days before the juvenile sea horses enter the culture pond, the culture pond is prepared, a culture net cage and a bait table are placed, scatophagus argus and horseshoe shells are put into the culture pond, and 0.3-0.5 ppm of shrimp slices are poured into the culture pond every day until the water body is tawny. After the breeding ecology is constructed, feeding the young sea horses three times a day according to the standard that 200 young sea horses are fed into each breeding net cage, feeding the young sea horses in a satiation mode, and thoroughly cleaning a bait table 1.5 h after feeding each time. And domesticating for about 5 days until the hippocampus can actively eat opossum shrimps on the bait platform, and after domestication is finished, transferring the hippocampus into a culture pond for culture. According to the method for domesticating the ecological sea horse bait, an ecological breeding system is constructed, the breeding water body is stable, the domestication efficiency is high, water is saved, and the labor cost is reduced.
Owner:EAST CHINA SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Efficient cultivation system and method for mudflat economic shellfish juvenile mollusks
ActiveCN113317244AConvenient orientation trainingQuality improvementClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaJuvenileZoology
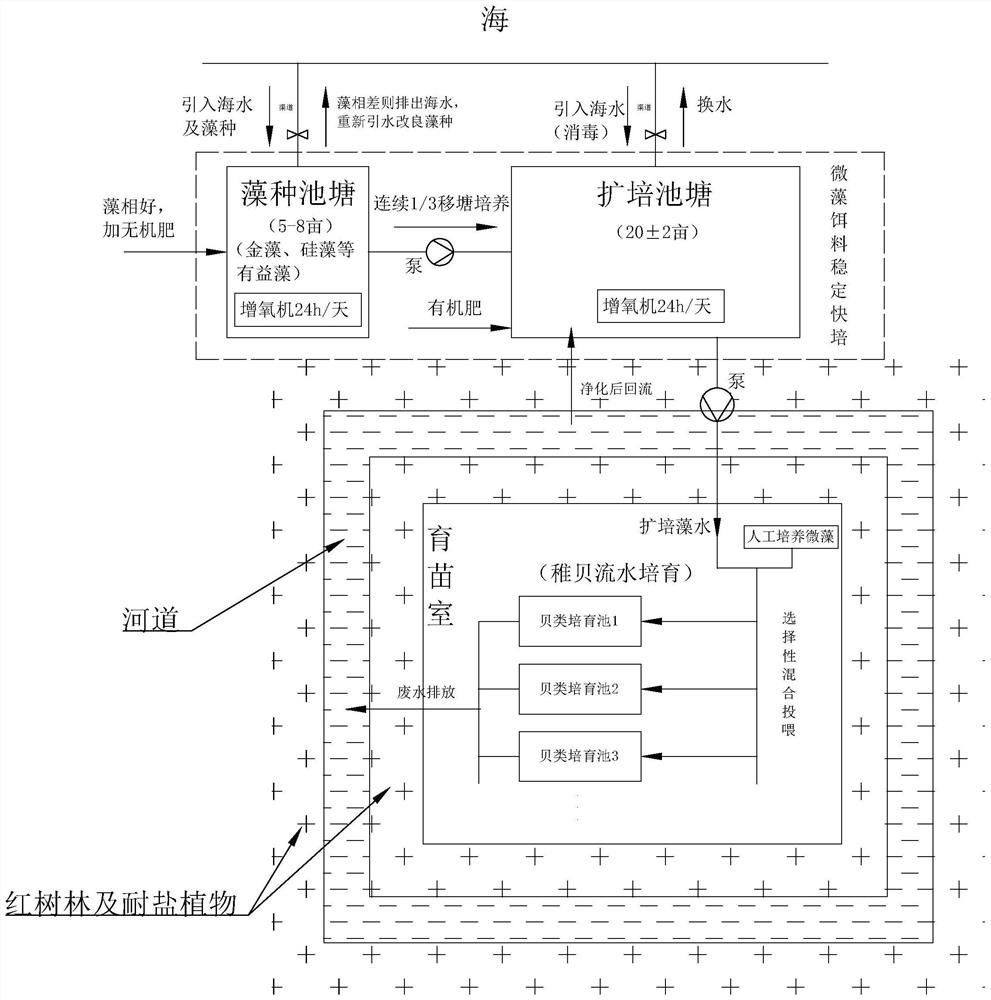
The invention discloses an efficient cultivation system and method for mudflat economic shellfish juvenile mollusks. A 5-8 mu algae species pond and a 20+ / -2 mu algae enlarged culture pond is constructed, seawater and algae species therein are introduced, and algal facies of the seawater in the algae species pond is observed, thereby facilitating disinfection treatment and fertilization of the seawater in the pond. After microscopically detecting the algal facies, proper algal facies are selected, directional enlarged culture on high-quality algae is conducted, water is fertilized to quickly breed the algae to a certain scale, 1 / 3 of seawater reaching the specified enlarged culture concentration in the algae species pond is introduced into the enlarged culture pond for enlarged culture, water is added again to reach the enlarged culture density, pond moving operation is repeated for continuous culture, and finally, water in the enlarged culture pond is led into a seedling raising chamber for juvenile mollusk running water circulation feeding culture, so as to promote growth and development of shellfish. According to the method disclosed by the invention, about 10 billion seedlings with the specification of 1,600,000 / kg can be cultured in the seedling raising chamber with the culture scale of 4-5,000 square meters, so that the culture cost is saved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MARICULTURE RES INST
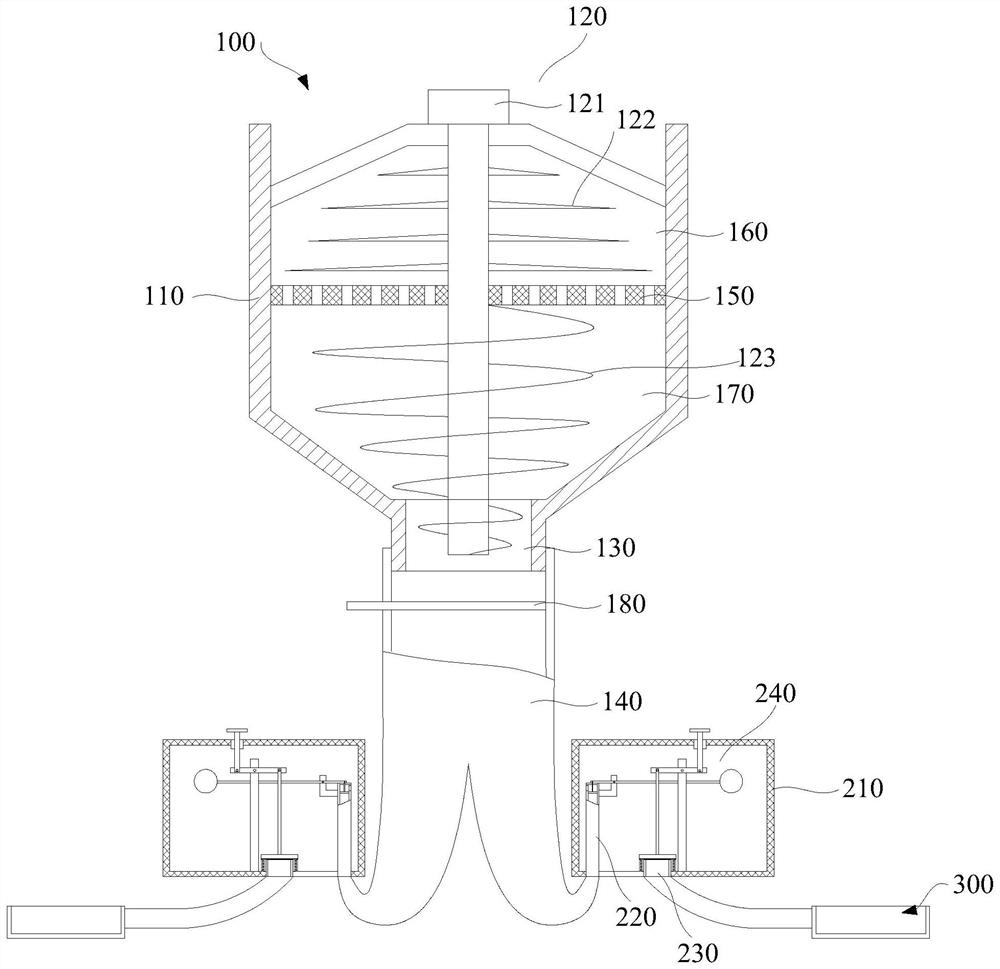
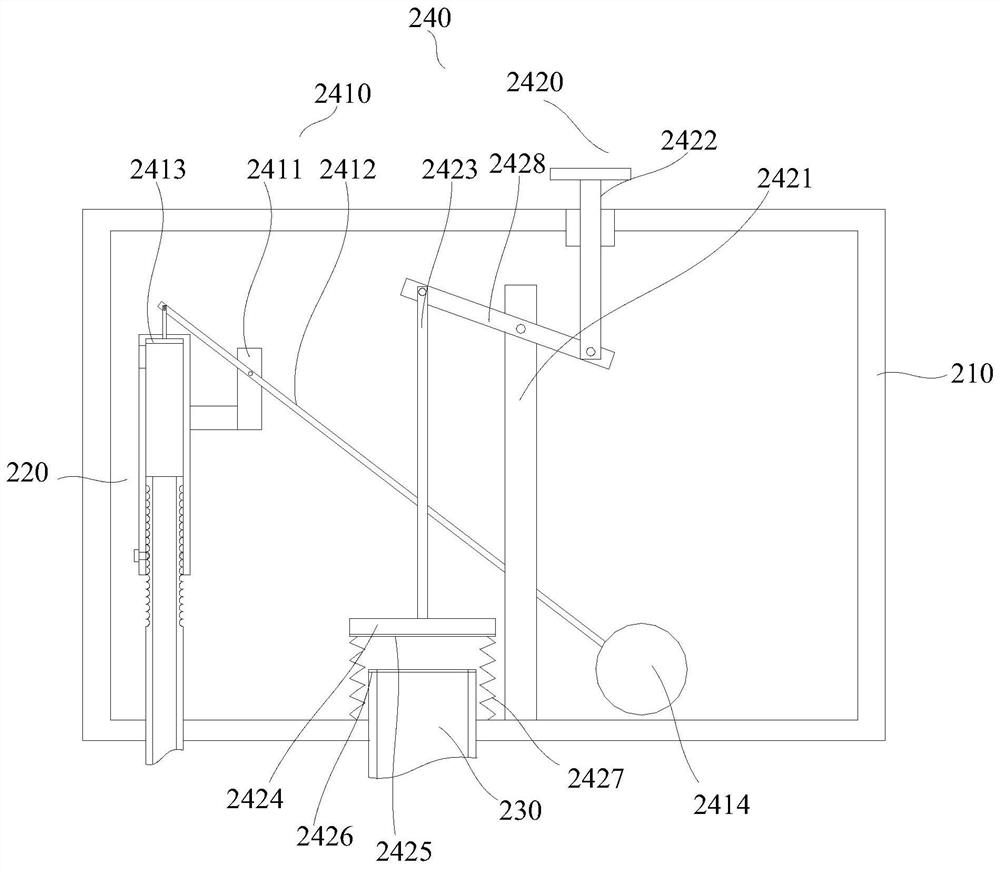
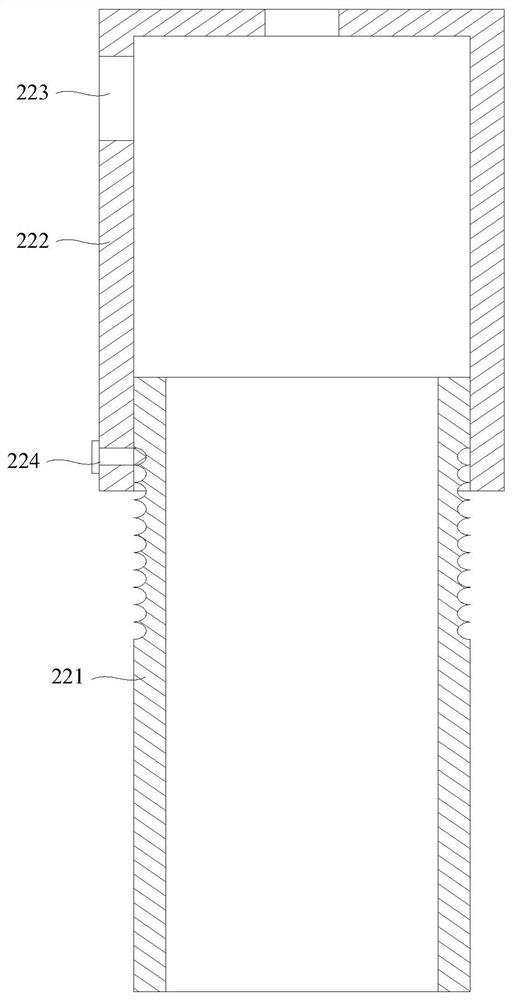
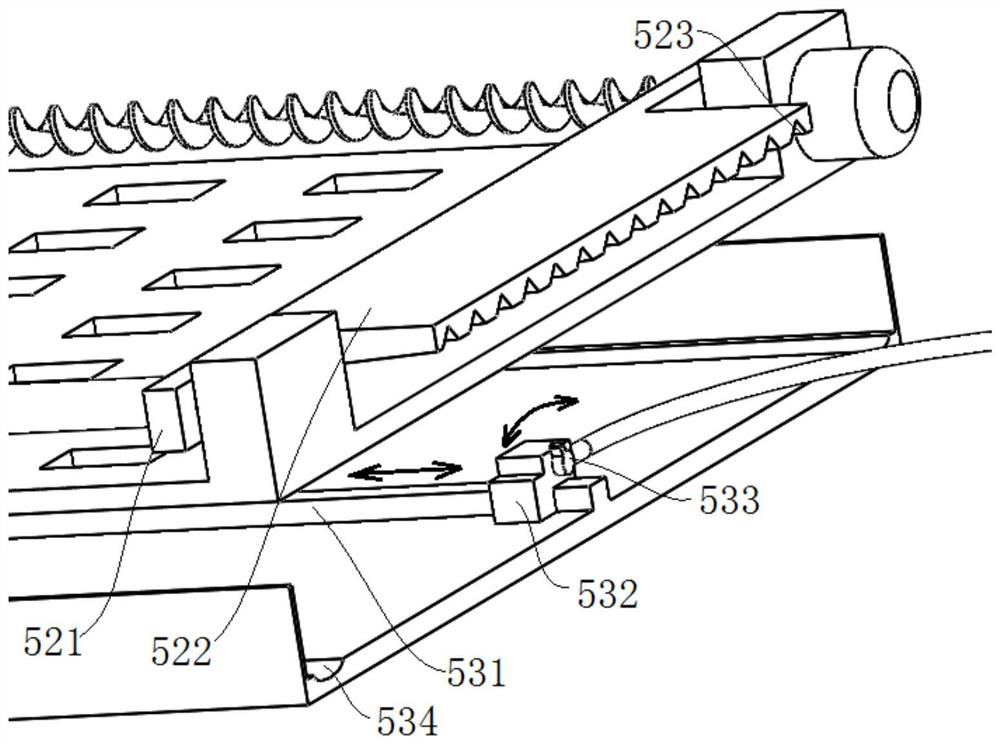
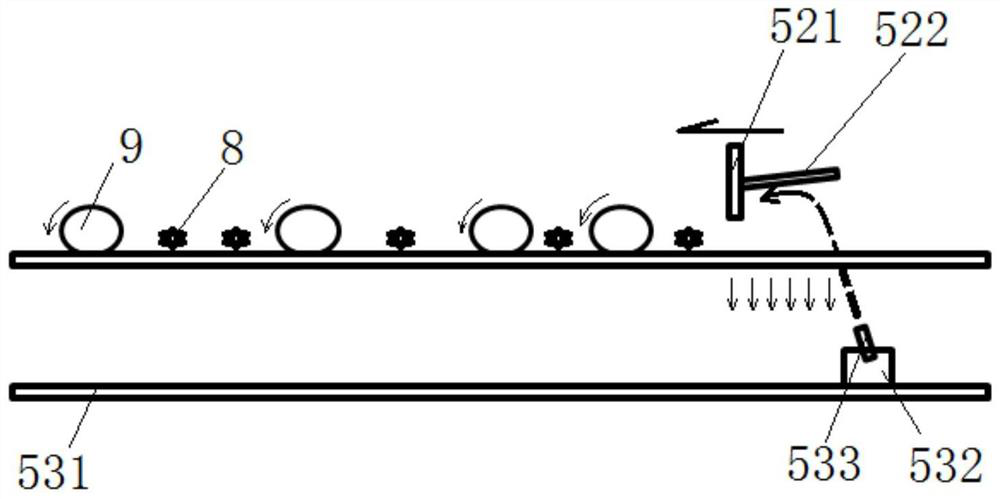
Juvenile crab collecting device
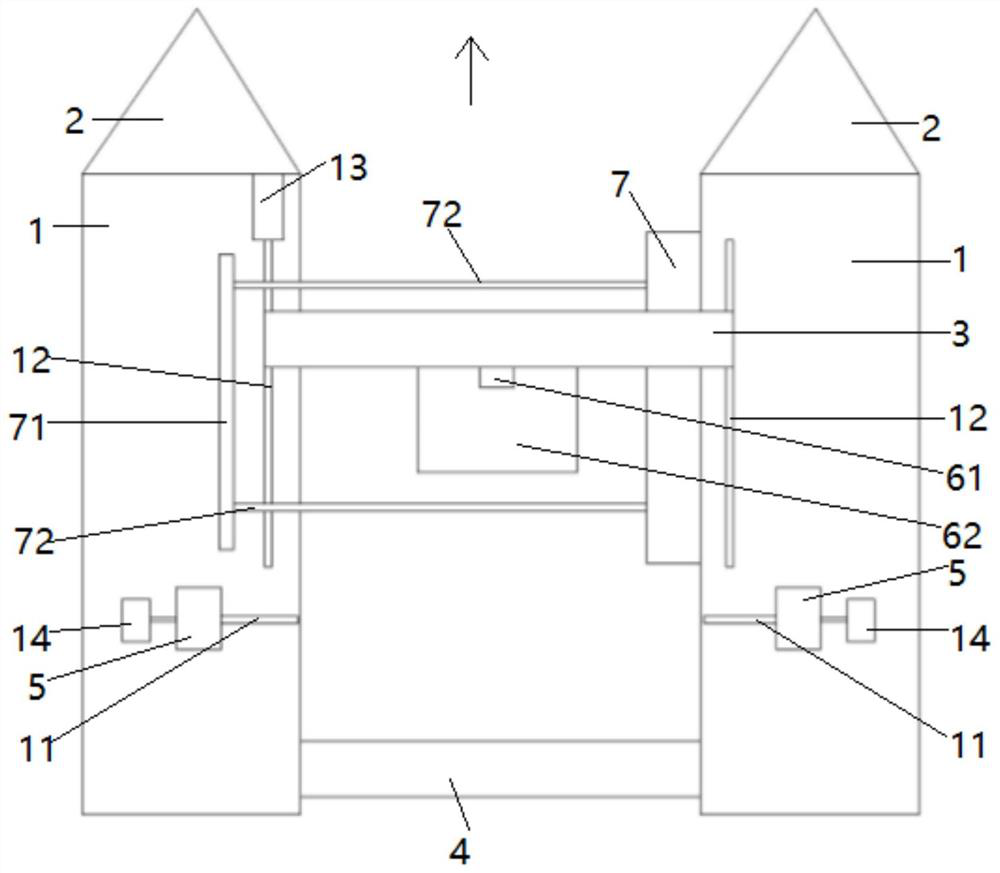
InactiveCN111670869AImprove collection efficiencyDoes not affect normal growthWaterborne vesselsPisciculture and aquariaJuvenileFishery
The invention discloses a juvenile crab collecting device. The juvenile crab collecting device comprises two strip-shaped buoy plates, triangular guide plates arranged at the front part of the buoy plates, a front connecting plate arranged between the front parts of the two buoy plates, a rear connecting plate arranged between the rear parts of the two buoy plates, transverse sliding grooves arranged on the upper surfaces of the buoy plates, support columns slidably connected with the transverse sliding grooves, transverse bars arranged at the upper ends of the support columns, vertical cylinders arranged on the transverse bars, clamping plate structures arranged on telescopic rods of the vertical cylinders and longitudinal sliding grooves arranged on the upper surfaces of the buoy plates.The collecting device has the characteristics that juvenile crab collecting efficiency is high, labor intensity is effectively reduced, and normal growth of Elodea nuttallii cannot be affected.
Owner:杭州林迪德瑞科技有限公司
Novel soilless breeding method of leeches
InactiveCN105746437AEasy to fish and feedNo need to adjust water temperatureAnimal husbandryAquatic animalPlankton
The invention relates to a new method for breeding leeches through fresh water soilless net cages and belongs to the technical field of aquatic animal breeding.Top openings of the net cages are closed, the net cages are fixed to a fresh water supporting object, a certain distance is kept among the net cages, 100-500 artificial bred juveniles with the average body weight being 10 mg are thrown for each net cage bottom face area of 0.5m<2>, after the average body weight of the juveniles is larger than 500 mg, the juveniles are transferred to nets to be bred continuously, or 20-200 wild juveniles with the average body weight being 0.5-4 g are throw for each net cage bottom area of 0.5 m<2>; during breeding, main food is thrown according to the amount which is 20 times of the body weight of the leeches, the food is updated periodically, and after being bred for 60-120 days, the leeches are directly poured out and harvested.The average weight of the leeches exceeds 20 g, and the size meets the use standard of the medicinal leeches.The method is easy to operate, lands are not occupied, the food resource includes natural planktons except snails, the net openings are closed to prevent natural enemies, and the method saves cost and is high in economic benefit.
Owner:MUDANJIANG YOUBO PHARMA CO LTD
Temperature-controllable scylla paramamosain juvenile crab intermediate breeding device and method
InactiveCN111513017AMonitor temperature in real timeImprove qualityClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaJuvenileZooid
The invention discloses a temperature-controllable scylla paramamosain juvenile crab intermediate breeding device and a method. A measuring device is arranged on the left side of a breeding pond, a temperature control house is arranged on the right side of the breeding pond, and aeration equipment is arranged on the outer part of the left side of the breeding pond; a first water pipe and a first water pump are connected to the left side of the bottom of a device body, a third water pipe is connected to the outside of a water outlet of the first water pump, the rear end of the third water pipeis connected to a reservoir, a water outlet of the reservoir is fixedly connected with a filter, a second water pump is fixedly connected to the rear end of the filter, a second water pipe is fixedlyconnected to the outside of a water outlet of the second water pump, the second water pipe is connected to the temperature control house, and a through hole is formed in the bottom left side of the temperature control house to connect to the breeding pond; and the breeding pond is internally provided with a leakage plate, a filter sponge I, a zigzag net clothing and a shelter from bottom to top. The temperature and salinity can be monitored in real time and the temperature of the water body is maintained, fights between individual juvenile crab are prevented, circulating water and the aerationequipment are arranged, the survival rate of scylla paramamosain juvenile crab can be improved, and the growth and development of scylla paramamosain juvenile crab are promoted.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Methods of identifying point mutations in a genome that affect the risk for or the age of appearance of disease
InactiveUS20080057496A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingGeneticsDeleterious mutation
The invention relates to a method for identifying inherited point mutations in a targeted region of the genome in a large population of individuals and determining which inherited point mutations are deleterious, harmful or beneficial. Deleterious mutations are identified directly by a method of recognition using the set of point mutations observed in a large population of juveniles. Harmful mutations are identified by comparison of the set of point mutation observed in a large set of juveniles and a large set of aged individuals of the same population. Beneficial mutations are similarly identified.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Automatic juvenile shellfish dispensing device
ActiveCN111109169AExquisite designReasonable layoutClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaJuvenileEngineering
Owner:DALIAN OCEAN UNIV
Micro-running-water net cage culture method of juvenile crabs for large-scale river crab culture
ActiveCN112021225AFast growthRealize nurturingClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaJuvenileWater net
The invention relates to the technical field of river crab culture, and discloses a micro-running-water net cage culture method of juvenile crabs for large-scale river crab culture. The micro-running-water net cage culture method comprises the following steps: 1, the juvenile crabs are put into a culture device; 2, water is continuously introduced into the culture device, so that the water in theculture device keeps flowing; 3, daily scientific culture management is conducted on the juvenile crabs in the culture device; and 4, after the juvenile crabs are cultivated and formed, the juvenile crabs are taken out of the culture device to be stocked. The micro-running-water net cage culture method of the juvenile crabs for large-scale river crab culture is simple and convenient to operate, the labor intensity of workers is effectively reduced, deposited sludge can be prevented from influencing the water quality of water in a water tank, and the safety of juvenile crab culture is effectively improved.
Owner:当涂县乌溪蟹苗养殖有限公司
Application of a non-destructive sampling method for Chinese mitten crab
ActiveCN108432675BEasy to collectGuaranteed normal hatchingMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationJuvenileVelvet crab
The invention discloses a non-destructive sampling method and application of living body of Chinese mitten crab. By sampling the fertilized eggs of the ovipositous parents of the Chinese mitten crab, the DNA and RNA thereof are extracted to detect related pathogens, and the parents not containing the detection target pathogen are tested. SPF megalopa of Eriocheir sinensis was obtained by isolation cultivation and artificial propagation. The method has the following advantages: the sampling does not damage the mother body, ensures the normal egg hatching of the parent crab, and the obtained megalopa of the Chinese mitten crab does not carry specific pathogens. The present invention solves the problem of non-destructive live sampling in SPF seedling cultivation of Chinese mitten crab, provides a simple and feasible way for SPF seedling cultivation of Chinese mitten crab, and is expected to cultivate SPF healthy seedlings and improve the economic benefits of Chinese mitten crab cultivation .
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Scientific releasing method of juvenile tylorrhynchus heterochaetus
InactiveCN110637761AThe implementation method is simpleEasy to operatePisciculture and aquariaJuvenileMedicine
The invention relates to a scientific releasing method of juvenile tylorrhynchus heterochaetus. The scientific releasing method of the juvenile tylorrhynchus heterochaetus comprises the following steps: (1) releasing site selection; (2) source and specification of released juvenile tylorrhynchus heterochaetus; (3) health examination of the released juvenile tylorrhynchus heterochaetus; (4) releasing time selection; (5) counting of the released juvenile tylorrhynchus heterochaetus; (6) transportation and releasing of the released juvenile tylorrhynchus heterochaetus; (7) effect evaluation of the released juvenile tylorrhynchus heterochaetus. The method accords with the biological and physiological ecological habits of the released juvenile tylorrhynchus heterochaetus; the operation method is simple, reasonable and scientific; the population quantity of the tylorrhynchus heterochaetus is restored effectively; and the method exerts greater economic, social and ecological benefits.
Owner:福建省洋泽海洋生物科技有限公司
Method for increasing in-vitro culture hatching rate of macrobrachium rosenbergii embryos
ActiveCN111304145AImprove hatchabilityImprove survival rateCell dissociation methodsInvertebrate cellsJuvenileAnimal science
The invention relates to a method for increasing the in-vitro culture hatching rate of macrobrachium rosenbergii embryos. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing adult shrimp breedingwater; (2) preparing a parental shrimp feed; (2) breeding parental shrimps of macrobrachium rosenbergii; (4) preparing an egg washing liquid; (5) implementing an in-vitro method of embryos; and (6) implementing a hatching mode. By adopting the method provided by the invention, fertilized embryos of the macrobrachium rosenbergii are subjected to in-vitro hatching, defects caused by direct broodinghatching of mother shrimps can be reduced, the hatching rate of in-vitro culture of the macrobrachium rosenbergii can be increased, the survival rate of membrane rupture larvae of the macrobrachium rosenbergii can be increased, and a good application technique can be provided for the industry.
Owner:TIANJIN AGRICULTURE COLLEGE
A method for ecologically cultivating third-stage larvae in salt marsh wetland underground brackish water
ActiveCN108124803BRealize nurturingClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaJuvenileBrackish water
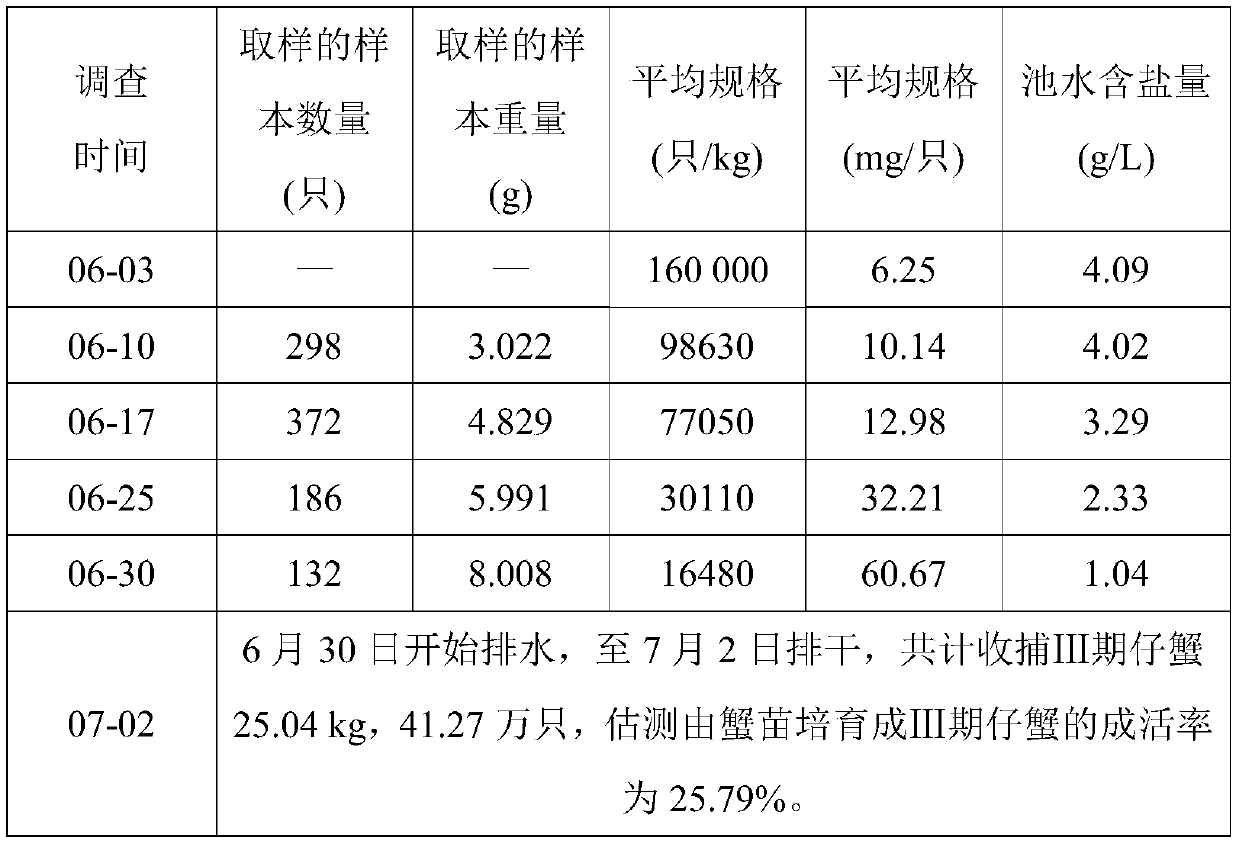
The invention provides a method for ecologically breeding III-stage juvenile crabs through salt marsh wetland underground brackish water, and relates to a method for salt-breeding the III-stage juvenile crabs. The method aims at solving the technical problem that breeding of the III-stage juvenile crabs cannot be achieved in inland fresh water regions currently. The method includes the steps of 1,selection of the place of a breeding pool; 2, digging of a slope-shaped annular groove; 3, establishment of a water source; 4, cultivating of high-quality palatable bait; 5, juvenile crab releasing;6, feed supplementing; 7, water supplementing. The method aims at developing and utilizing salt marsh wetland underground brackish water resources to ecologically breed the III-stage juvenile crabs, creating advantages for breeding one-year-old juvenile crabs and achieving the purpose of self-feed or partial self-feed of one-year-old juvenile crabs in the large-scale commercial crab breeding industry. After 28 days of breeding by means of the method for ecologically breeding the III-stage juvenile crabs through the salt marsh wetland underground brackish water, the average specification of theIII-stage juvenile crabs bred from juvenile crabs can reach 60.67 mg, and the survival rate reaches 25.79%. The method is applied to breeding the III-stage juvenile crabs.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
Compound immunoenhancer for larvae and juvenile of tilapia
InactiveCN101627801BImprove the body's immunityHigh activityAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsPhosphoric Acid EstersJuvenile
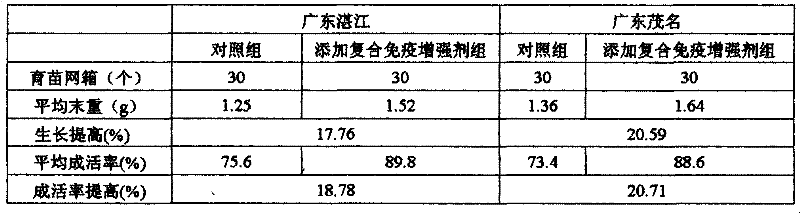
The invention relates to a feed additive, especially a compound immunoenhancer for larvae and juvenile of tilapia, which is characterized in that the components and weight percent (%) are as below: 20-30% of beta-glucan, 5-10% of ginsenoside, 10-20% of seaweed polysaccharides, 5-10% of phospholipids, 20-30% of vitamin C-2-polyphosphate ester, vitamin E 10-15, 5-10% of digestive enzyme and 5-10% of citric acid. The invention has the following advantages of: (1) obviously enhancing the immunity of the larvae and juvenile of the tilapia and increasing the survival rate; (2) obviously improving the activities and growth speed of the larvae and juvenile of the tilapia; (3) the compound immunoenhancer being used as a feed additive in the feed of the larvae and juvenile of the tilapia, with additive dosage of only 0.2-0.3%; (4) having no adverse effect on the feed palatability; and (5) the raw material of the invention being stable, the cost being low and the production technology being simple.
Owner:GUANGDONG OCEAN UNIVERSITY
Eriocheir sinensis juvenile crab density measuring method at Yangtze estuary
InactiveCN103162733ASimple structureThe sampling operation process is simple and feasibleWater resource protectionMeasurement devicesCurrent meterNose
The invention discloses an eriocheir sinensis juvenile crab density measuring method at Yangtze estuary. A push net type eriocheir sinensis juvenile crab gathering device is prepared for the eriocheir sinensis juvenile crab density measuring method at Yangtze estuary. The eriocheir sinensis juvenile crab density measuring method at Yangtze estuary is characterized in that the push net type eriocheir sinensis juvenile crab gathering device is composed of a push rod, a connecting rod, a gathering box, a fixing rod, a net bag, a cone-shaped net, a current meter, a dipsey, a float and a fishing wire. The push net type eriocheir sinensis juvenile crab gathering device utilizes that the pushing rod is fixed on the front portion of a nose of a juvenile crab sampling ship in a suspending manner, the juvenile crab sampling ship pushes the gathering device to go forward at a uniform velocity, and the current meter records flow velocity of water relative to a ship body, and records sampling time and the amount of the gathered juvenile crabs; the juvenile crab density is calculated through an equation of p= S / (T*V*1.2), wherein S stands for the amount of the gathered juvenile crabs, a unit is one; T is the sampling time, the unit is hour; V is the flow velocity of water relative to the ship body, the unit is meter per hour, 1.2 is the area of gathering box net opening, and the unit is square meter. The eriocheir sinensis juvenile crab density measuring method at Yangtze estuary can provide basis for protecting juvenile crab habitats and recovering ecology at Yangtze estuary.
Owner:EAST CHINA SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Breeding method of freshwater crabs under laboratory conditions
InactiveCN111264430AGuaranteed reproductive capacityGuaranteed survival rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaJuvenileExperimental laboratory
The invention is a breeding method of freshwater crabs under laboratory conditions. Each seed breeding crab has a weight of 30-50 g and a healthy and complete body, and the method comprises the steps:disinfecting the seed crabs with a potassium permanganate aqueous solution, performing cleaning, putting 3 male crabs and 6-9 female crabs into a breeding box with a water pool with water of a depthof 5 cm, connecting the breeding box with an aquarium filter system, maintaining water circulation, arranging a wood board which is higher than the water pool and applied to activity and inhabitancy in the breeding box of the freshwater crabs, placing a wooden nest, controlling the room temperature at 21-26 DEG C and light intensity at 80-120 Lx, performing illumination for 12 hours, breeding theplaced seed crabs in the breeding box for about 15 days, centralizing the female crabs with egg-attached pleopod in another breeding box, and hatching the larvae so as to ensure the fertility of the female crabs and the survival rate of young crabs. Artificial and efficient reproduction of experimental crabs can be achieved under laboratory conditions.
Owner:KUNMING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
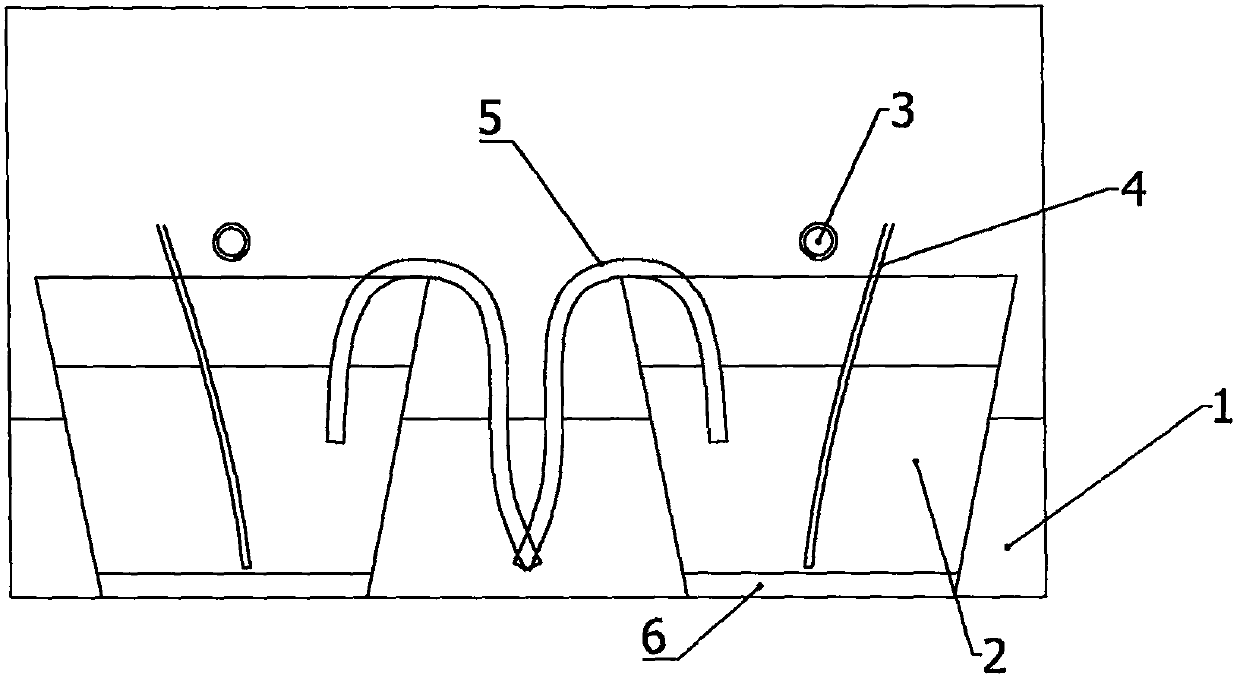
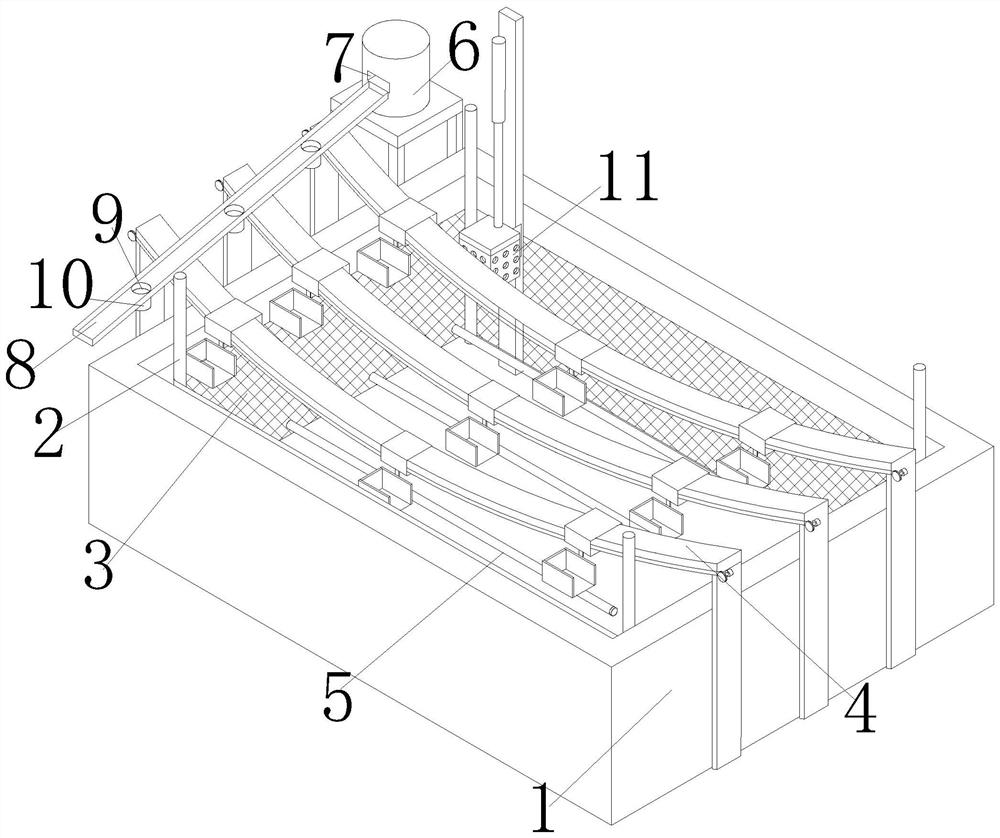
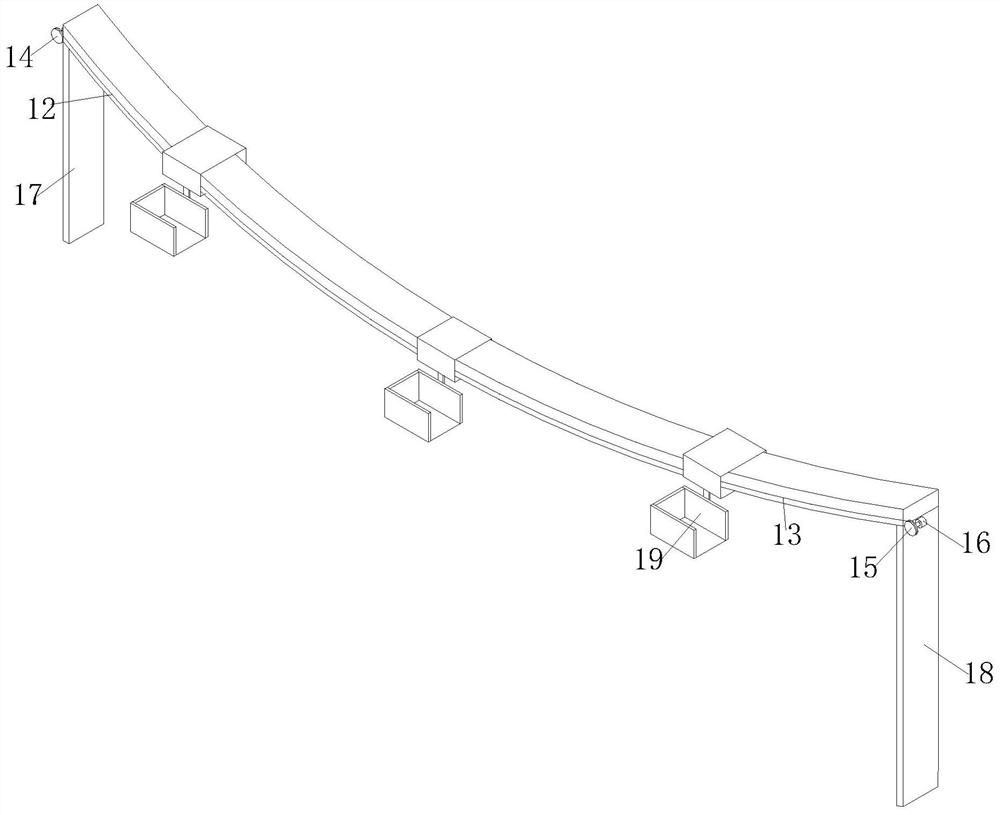
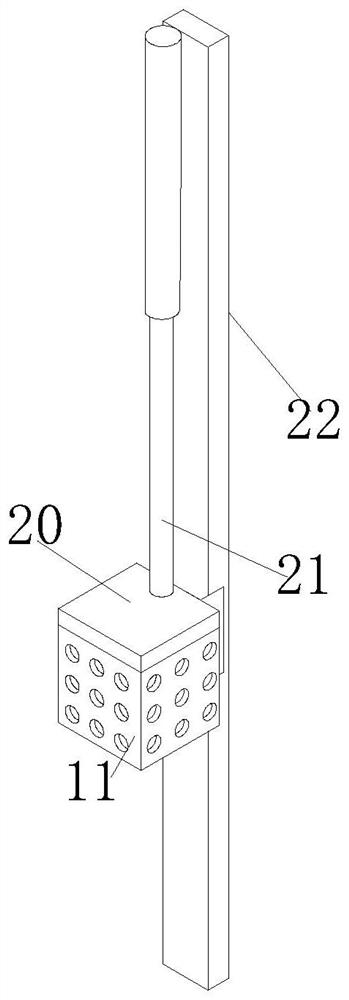
Juvenile crab collection system for crab culture pond
The invention discloses a juvenile crab collection system for a crab culture pond. The juvenile crab collection system comprises two strip-type buoy plates, triangular guide plates arranged at front parts of the buoy plates, a front connecting plate arranged between the front parts of the two buoy plates, a back connecting plate arranged between back parts of the two buoy plates, transverse sliding grooves formed in upper surfaces of the buoy plates and support columns slidably connected with the transverse sliding grooves; the juvenile crab collection system further comprises a left air cylinder and a right air cylinder arranged on the upper surface of the back connecting plate and two vertical traction rods; and the lower ends of the two vertical traction rods are connected with a cutting structure. The juvenile crab collection system has the characteristics that the juvenile crab collection efficiency is high, the labor intensity is effectively reduced and normal growth of elodea nuttallii is not affected.
Owner:重庆蓝宏生猪养殖有限公司
An ecological circulation type poultry breeding system and breeding method thereof
Owner:湖北民大农牧发展有限公司
Method for evaluating eye stimulation of infant cosmetics by using zebra fish
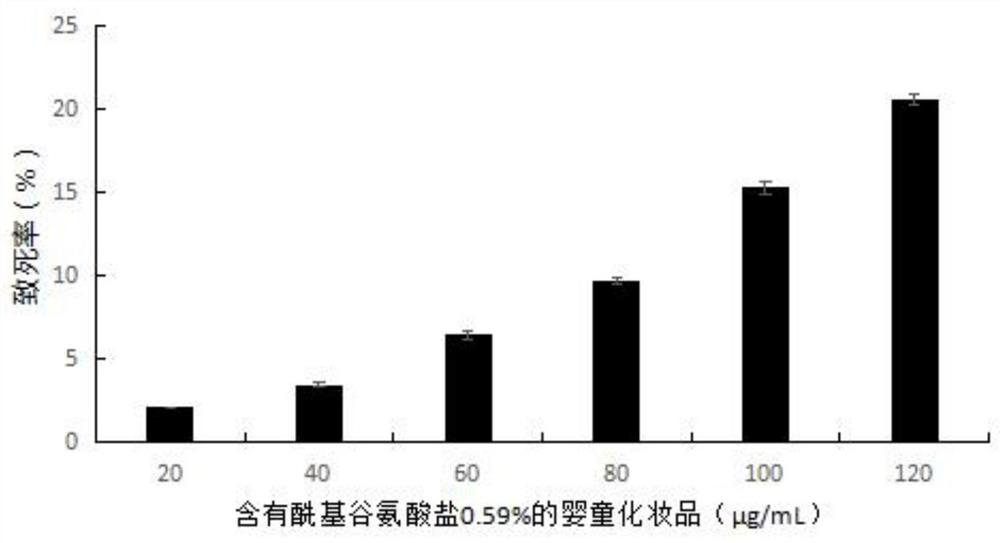
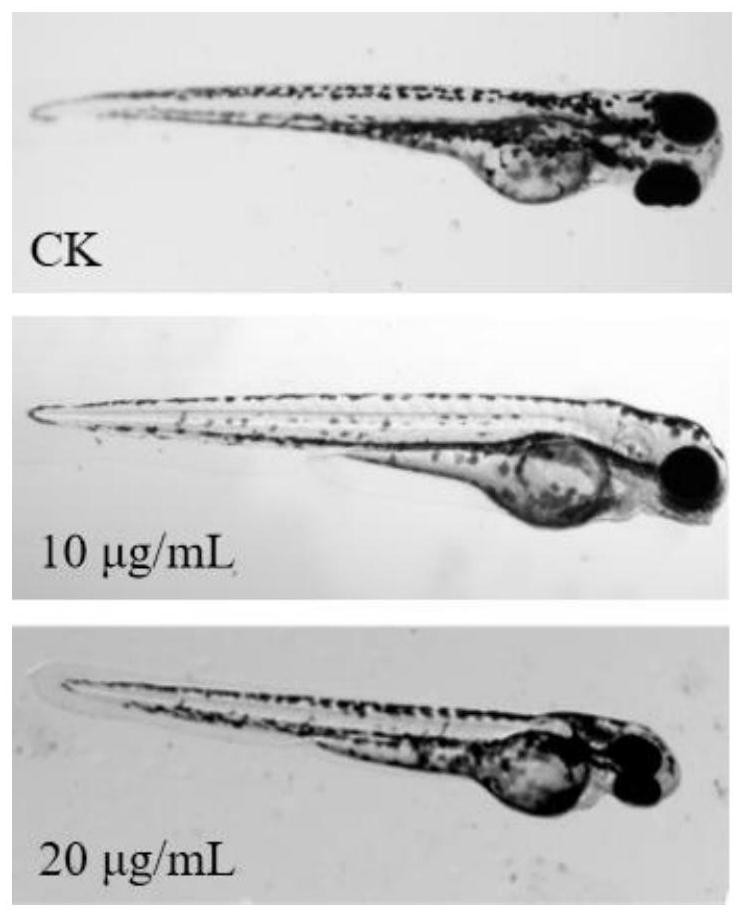
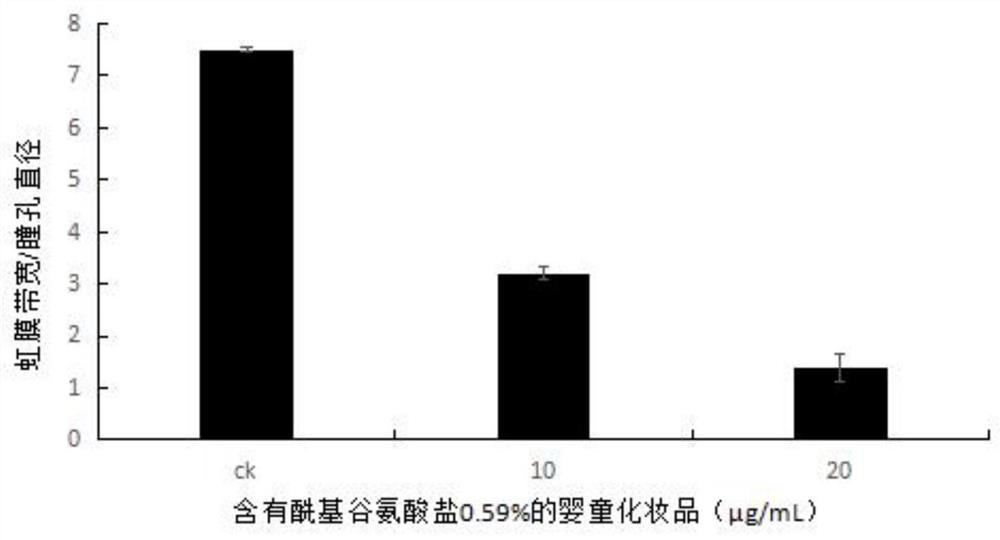
The invention provides a method for evaluating eye stimulation of cosmetics for infants and children by using zebra fish. The method comprises the following steps: exposing zebrafish embryos developed for 3 days in an embryo culture solution containing baby cosmetics, and culturing the embryo at a specific temperature and in a periodic light and dark environment by adopting a semi-static culture method; and when the zebrafish embryos develop for 6 days, evaluating the eye stimulation of juvenile zebrafish, response ability to light stimulation and variation conditions of genes related to eye development. The model organism zebra fish used in the method has the advantages that the breeding cycle is short, the dosage of used medicine is small, the genetic level is similar to that of human beings, the size is small, embryos are transparent and micromanipulation is convenient. In addition, the visual system of the zebra fish is very similar to that of other vertebrates including the human beings, so that the zebra fish eyes can serve as a good visual model, and meanwhile, zebra fish embryos which are just bred and developed are selected as models, and evaluation on infant cosmetics is more representative.
Owner:FROG PRINCE (FUJIAN) BABY & CHILD CARE PROD CO LTD +1
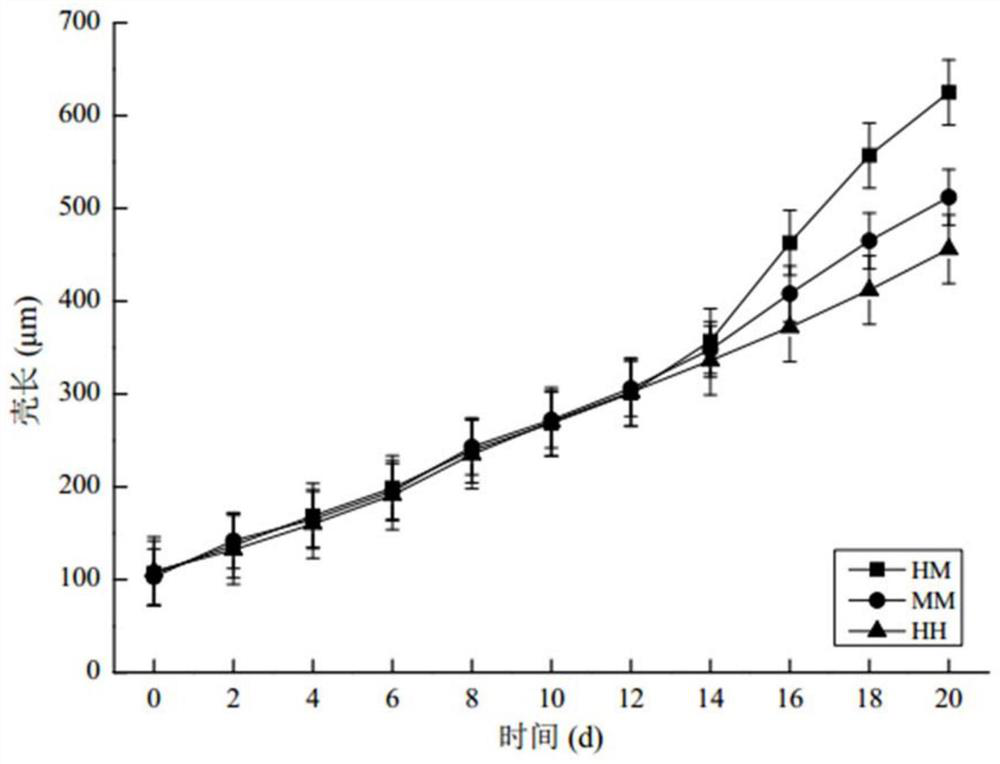
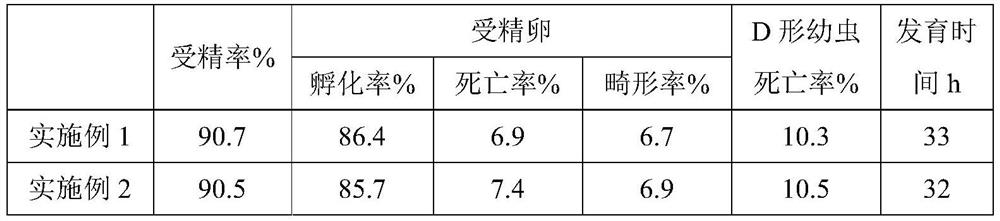
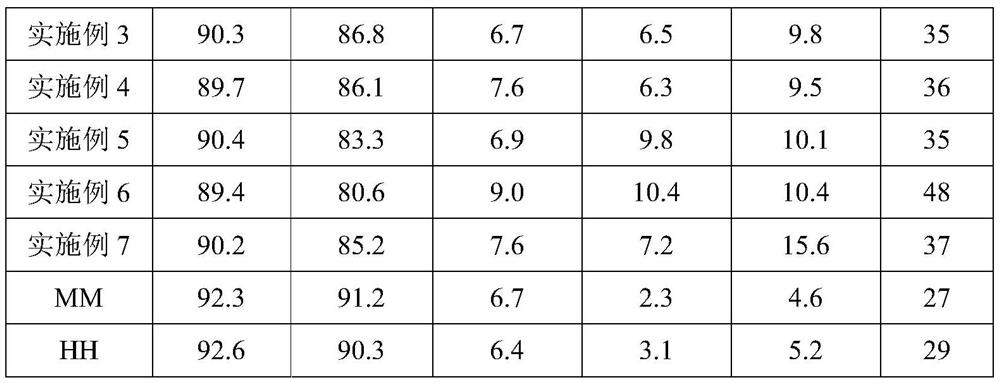
Hybrid seed production method of Chlamys grandis and Bay scallop
ActiveCN110432194BHigh affinityImprove the barrier phenomenonClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaJuvenileAnimal science
The invention provides a method for hybrid seed production of Chlamys grandis and Bay scallop, which belongs to the technical field of hybrid breeding, comprising: selecting and temporarily raising the parents of the above-mentioned scallops, artificially inducing labor on the above-mentioned parents, and then collecting mature eggs and sperm for artificial Fertilization, and, the process of hatching the above-mentioned fertilized eggs; in the above-mentioned hatching process of fertilized eggs, after the D-shaped larvae are cultivated, the D-shaped larvae are subjected to a stress intervention process in an extreme environment, and then the offspring spat are cultivated. The hybrid seed production method provided by the invention has a high fertilization rate, and the hatching process is optimized to improve hatching efficiency and save production costs; it can reduce the adhesion and bacterial contamination rate of fertilized eggs, reduce the mortality rate and deformity rate of fertilized eggs, and avoid It eliminates the asynchronous development of hybrid fertilized eggs, improves the survival rate and hatching rate of fertilized eggs; it can enhance the anti-stress ability of D-shaped larvae, overcome the phenomenon of high mortality of hybrid larvae, and increase the survival rate of hybrid offspring.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
A kind of temporary raising method for juvenile shellfish in selected family line
ActiveCN107494356BReduce mistakesSave human effortClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaJuvenileZoology
The invention relates to a label control method in an indoor intermediate breeding stage in a tidal shellfish family breeding process, in particular to a breeding family juvenile mollusk intermediate temporary rearing method. The problems that in the prior art, the survival rate of juvenile mollusks is low, the cultivation cost is high, and the breeding operation difficulty is high are solved. A plurality of groups of culturing barrels are arranged in a culturing pond, growth conditions of the various culturing barrels are the same, and the breeding cost can be reduced; and moreover, the method is simple, the survival rate is high, and the method is suitable for breeding a plurality of families, and meets requirements of development of the large-scale shellfish family breeding industry.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MARICULTURE RES INST
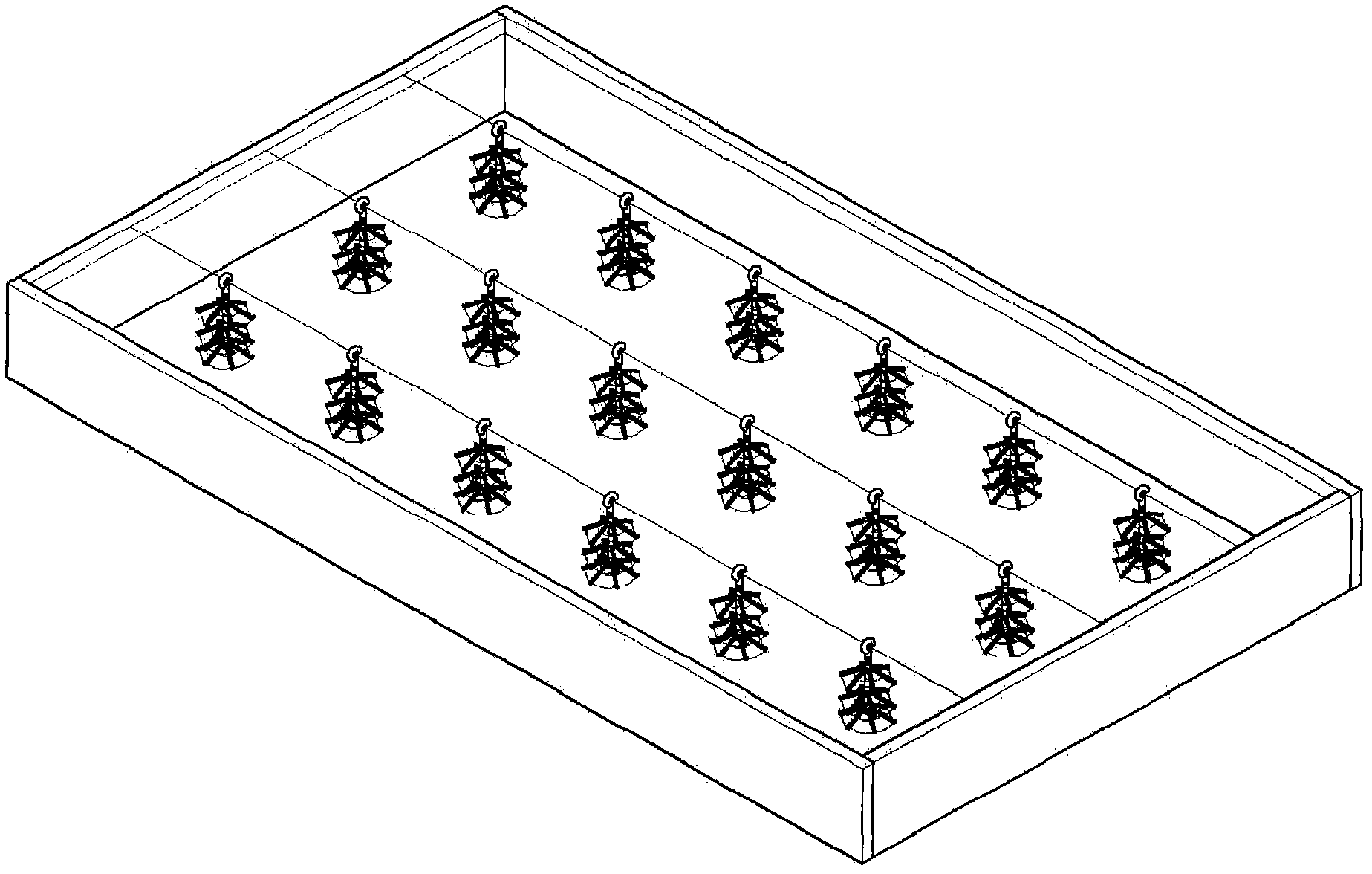
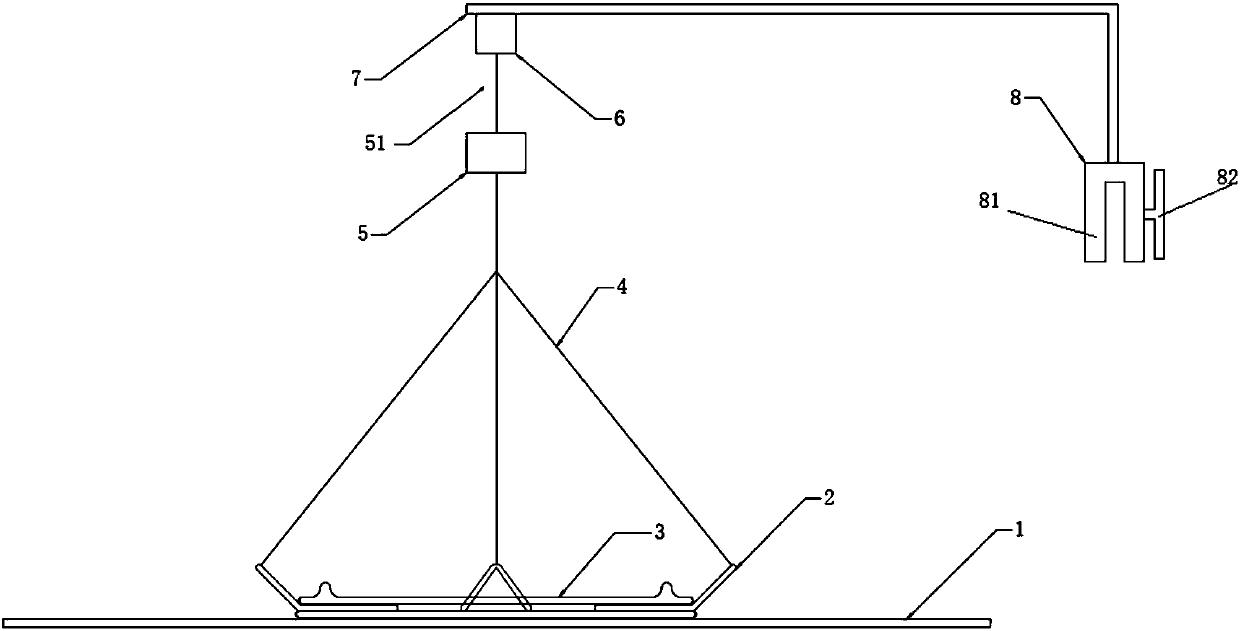
Mitten crab ecological breeding system
PendingCN112931373ARealize automatic feedingAffect the survival rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaJuvenileFishery
The invention provides a mitten crab ecological breeding system which comprises a breeding pond; a plurality of hoses for conveying oxygen are laid at the bottom of the breeding pond; one end of each hose is connected with a piston through a buckle; a plurality of oxygen outlets are formed in the end face of each hose; the other end of each hose is connected with an aerator through an oxygen supply pipe; a plurality of feeding boxes are arranged in the breeding pond; the feeding boxes are connected with a guide rail through sliding blocks; the bottoms of the two ends of the guide rail are fixedly connected with a left support and a right support respectively; the end faces of the two ends of the sliding blocks are connected with a left rotating wheel and a right rotating wheel through a left cable and a right cable respectively; the left rotating wheel and the right rotating wheel pass through a left motor and a right motor respectively; a placing box is arranged at one side of the guide rail; and the placing box is connected with a second guide rail through a sliding block. By arranging the guide rail, automatic feeding of cultured fishes is achieved; and by arranging the placing box, juvenile crabs can be adaptively placed when placed, and the situation that the juvenile crabs have problems when directly placed, and then the survival rate of the juvenile crabs is affected is prevented.
Owner:安徽益丰生态农业开发有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com