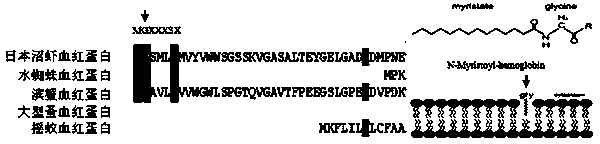Patents
Literature
85 results about "Macrobrachium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Macrobrachium is a genus of freshwater prawns or shrimps characterised by the extreme enlargement of the second pair of pereiopods, at least in the male.
Ecoalimental macrobrachium rosenbergii feed and production method thereof
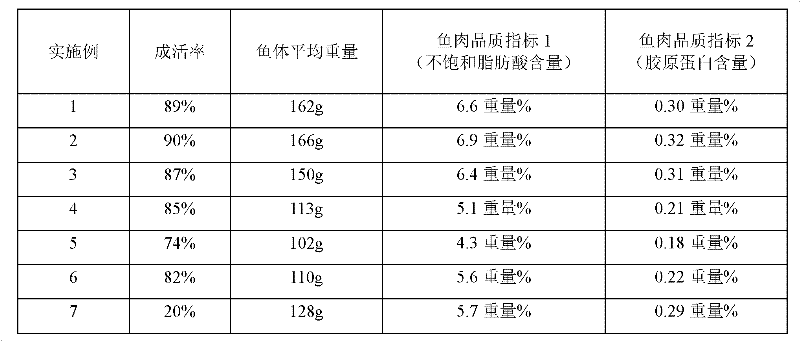
InactiveCN101444266ALower protein contentImprove stabilityFood processingClimate change adaptationMacrobrachiumCompounded preparations
The invention discloses an ecoalimental macrobrachium rosenbergii feed and a production method thereof, belonging to an animal feed production method. The macrobrachium rosenbergii feed comprises fish meal, bean pulp, fermented bean pulp, wheat middling, cuttlefish paste, oil bran, various mineral salt, lycine, fish oil, various vitamins, eclosion hormone, bond, antioxidant, mildew preventive, compound enzyme preparation, microecological preparation 'quick-healing hormone', a Chinese herb sophora flavescens alkaloid compound preparation, and the like. The yield of per mu is 310kg and can be improved by 44kg by using the ecoalimental the macrobrachium rosenbergii feed than common feeds. The effective utilization of the protein and amino acid in the feed by the macrobrachium rosenbergii is improved; the coefficient of the macrobrachium rosenbergii feed bait is 1.57 which is lower by 0.2 than the common feed. The ecoalimental macrobrachium feed reduces the pollution to a breeding environment. The produced matching feed of the macrobrachium rosenbergii can induce the macrobrachium rosenbergii to eat, the growing speed of the macrobrachium rosenbergii is quick, and feed coefficient is low.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES +1
A kind of method of cultivating cuttlefish pond
InactiveCN102283150AMake sure it's palatableImprove survival rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaZooplanktonFlavor
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Industrially breeding method of macrobrachium nipponense
InactiveCN102187837ASolve the problem of asynchronous growthReduce economic lossClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaPrawnWater quality
The invention provides an industrially breeding method of macrobrachium nipponense, comprising the steps of: selection of parent macrobrachium of macrobrachium nipponense, cultivation of fingerlings, treatment of fingerling cultivation water quality, daily cultivation management in the breeding period and the like. By use of the industrially breeding method of macrobrachium nipponense, provided by the invention, the cultured macrobrachium nipponense fingerlings have high survival rate and stable quality. According to the industrially breeding method disclosed by the invention, the problems of low survival rate and unstable quality in the conventional macrobrachium nipponense breeding process can be solved, and the economic loss of the macrobrachium culturists can be reduced.
Owner:高雷
Production process for preparing hot reaction shrimp-taste essence with macrobrachium shells
ActiveCN102132857ARealistic fragranceMellow fragranceFood preparationMaillard reactionFood technology
The invention belongs to the technical field of food, and relates to a production process for preparing hot reaction shrimp-taste essence with pondcrafish shells, which mainly comprises the technical units of macrobrachium shell pretreating unit, a softening unit, an enzymolysis unit, a Maillard reaction unit, a drying unit, a blending unit and the like. The preparation steps are as follows: taking produced macrobrachium byproduct, namely the macrobrachium shells as raw materials, soaking the macrobrachium shells by de-fishy liquid and washing and leaching, crushing into powder after being drying, softening at high temperature, blending by adding water, adding one or more protease for enzymolysis, adding reducing sugar, thiamine and other substances in the enzymolysis liquid, carrying out the Maillard reaction at high temperature for blending, taking the clear liquid for concentration after finishing, and making into power by spray drying, and on the basis, adding natural essence powder or extract to prepare hot reaction shrimp-taste essence with specific odor type. The product shrimp-taste essence is vivid and natural, the meaty taste is mellow, thus being a healthy seasoning product, and being widely applied to production of modern food and traditional seasoning products.
Owner:江苏戚伍水产发展股份有限公司 +1
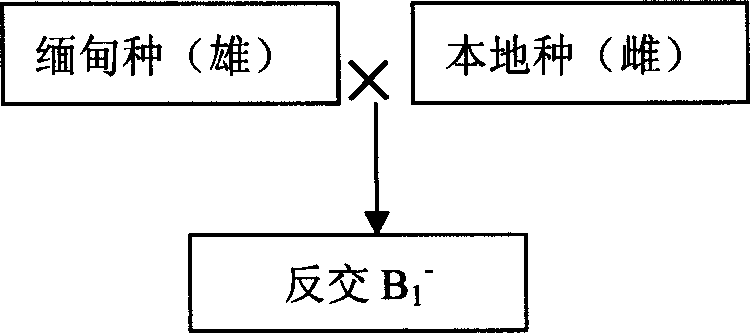
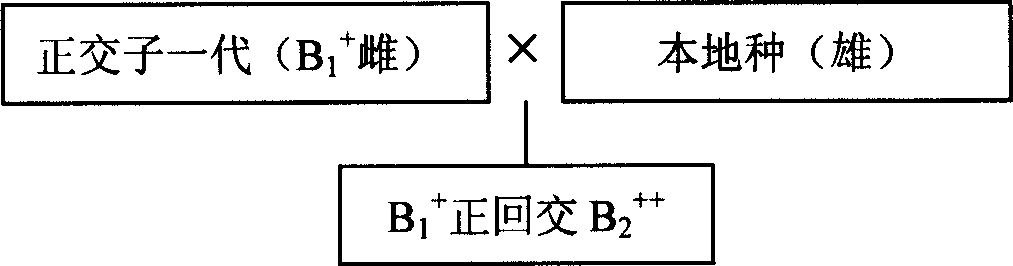
Cross breeding method of Macrobrachium rosenbergu
InactiveCN1762310AGood for survivalGood production traitsAnimal reproductionClimate change adaptationCross cutMacrobrachium rosenbergii
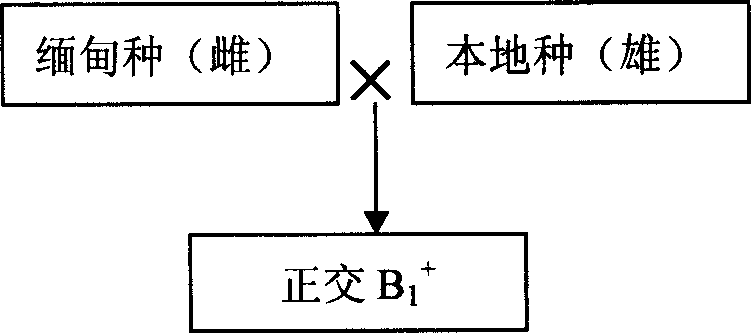
The invention relates to method of crossbreeding the exotic fresh water crayfish, especially to method of crossbreeding the Luo shi swamp shrimp. The invention introduces the distant Luo shi swamp shrimp sprout A, mating the female parent shrimp and male parent shrimp of the distant Luo shi swamp shrimp sprout A with that of native breed and getting the cross cut B1+ and negative cross B1-; mating the cross cut B1+ and negative cross B1- with the native breed and getting the backcross B2++ of B1+, negative back cross B2+- of B1+, negative back cross B2-- of B1- and back cross B2-+ of B1-; breeding the backcross B2++ of B1+, negative back cross B2+- of B1+, negative back cross B2-- of B1- and back cross B2-+ of B1-. The survival rate and seed-accumulating rate of the four kinks of sprout is all good, the composition of water, coarse ash content, coarse protein, coarse fat content, amino acid and aliphatic acid is higher than that of native obviously by applying the technique in this invention, especially the breed-accumulating rate of the cross B2-+ of B1- is increased to 67.25%, the rate of emergence to 94.56%.
Owner:ZHEJIANG INST OF FRESH WATER FISHERIES
Method for continuously cropping and ecologically breeding macrobrachium nipponensis and hydrilla verticillata
InactiveCN103461240APromote growthMeet growthClimate change adaptationAgricultural fishingSporeEcological environment
The invention discloses a method for continuously cropping and ecologically breeding macrobrachium nipponensis and hydrilla verticillata. The method is used for breeding the macrobrachium nipponensis by means of continuously cropping the macrobrachium nipponensis and the hydrilla verticillata. The method has the advantages that eutrophic substances and harmful substances such as residual feed and feces in ponds can be converted by the hydrilla verticillata owing to a technical mode for ecologically and continuously cropping the macrobrachium nipponensis and the hydrilla verticillata, and a characteristic of strongly inhibiting generation of some algae of the hydrilla verticillata is sufficiently utilized, so that purposes of purifying breeding water and ecologically breeding the macrobrachium nipponensis can be achieved; breeding byproducts such as ammonia nitrogen and nitrite in bottom sediments of the ponds can be consumed by means of planting the hydrilla verticillata, effects of purifying the bottom sediments and maintaining excellent ecological environments of the ponds can be realized, the macrobrachium nipponensis is in the suitable ecological environments of the ponds in total breeding procedures, suitable habitat environments and palatable green feed are provided for growth of the macrobrachium nipponensis by the hydrilla verticillata, the bred macrobrachium nipponensis is high in yield and good in quality, and the price of the macrobrachium nipponensis can be increased; spores and grass seeds of the hydrilla verticillata can be offered for sale, so that an extra economical benefit can be created.
Owner:LIYANG AQUATIC PROD TECH PROMOTION STATION
Enclosure intercultural mode and aquaculture method thereof
ActiveCN103931524ATake advantage ofReduce pollutionClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaFresh waterRiver prawn
The invention discloses an enclosure intercultural mode and an aquaculture method thereof. River crabs in a lake enclosure serve as the main aquaculture variety, and meanwhile, tropical fresh water Macrobrachium rosenbergii, Macrobrachium nipponensis, Odontobutis obscurus and Siniperca chuatsi are intercultured, wherein the Macrobrachium nipponensis, the Odontobutis obscurus and the Siniperca chuatsi are commonly seen in lakes. According to the intercultural mode, feedstuff can be fully utilized, pollution caused by river crab aquaculture is reduced, aquaculture benefits are improved, and the intercultural mode is environmentally friendly and efficient.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV +1
Method for sex induction of hermaphrodite shrimps
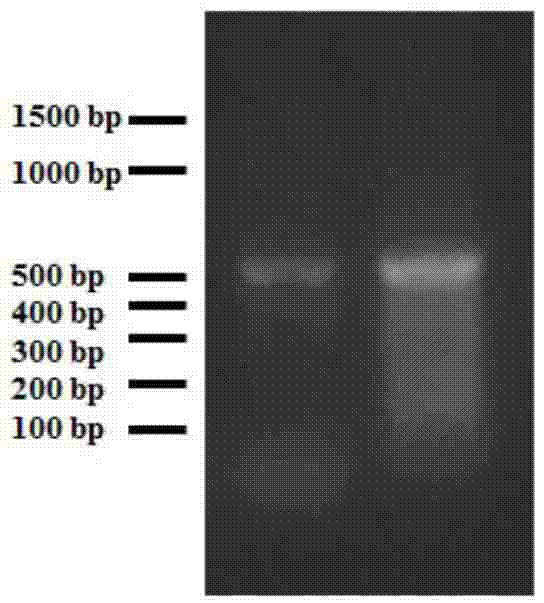
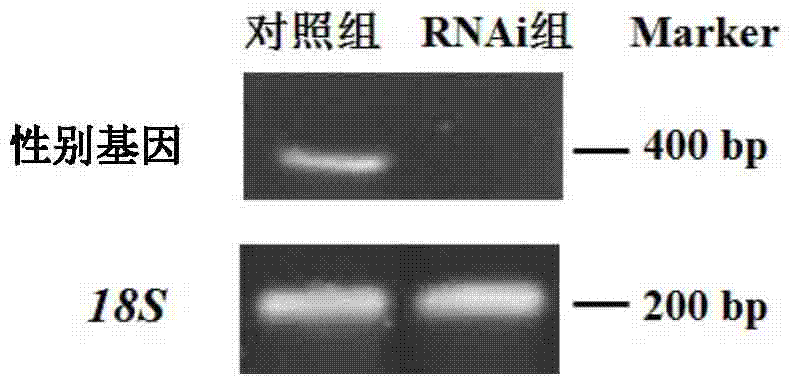
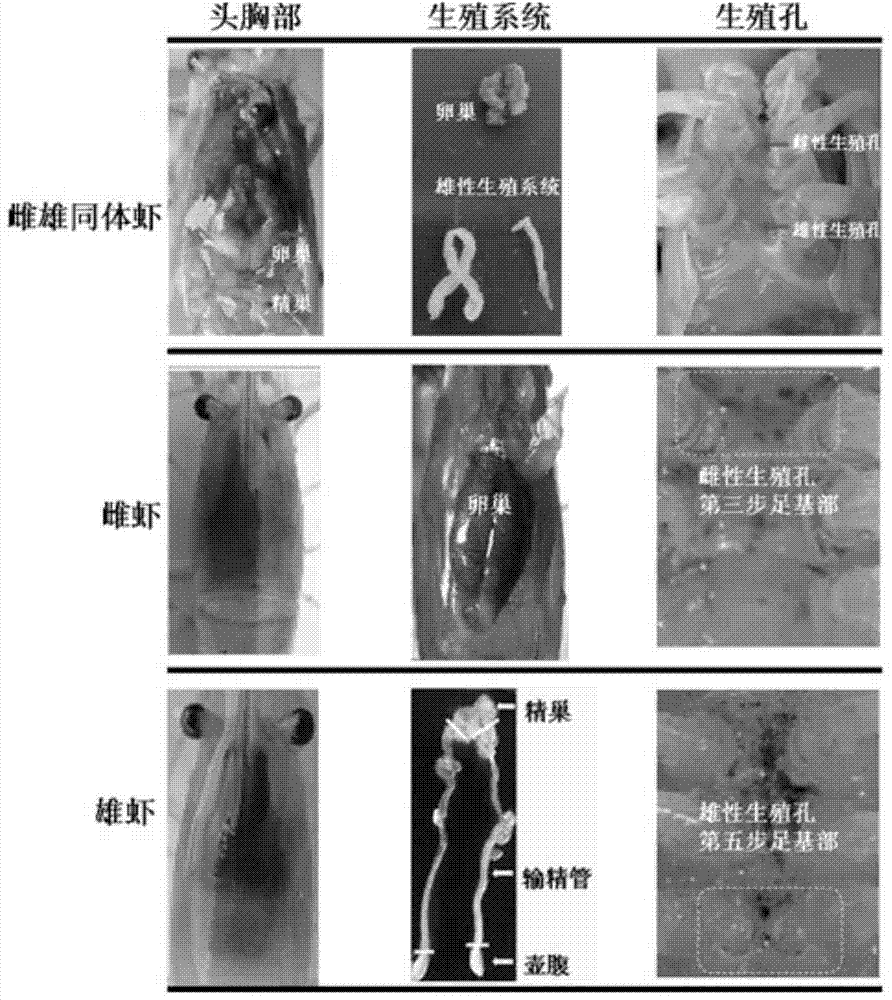
InactiveCN104745628ASex-induced realizationFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionMale reproductive systemGene silencing
The invention aims to provide a method for sex induction of hermaphrodite shrimps. According to the method, a target gene in macrobrachium is silenced by using an RNA interference technology to realize sex induction of macrobrachium rosenbergii, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the target gene is SEQ ID NO:1. By virtue of the induction technology provided by the invention, a macrobrachium individual has sex reversion and becomes hermaphrodite macrobrachium rosenbergii, and the developments of a female reproductive system and a male reproductive system are realized in the body of the hermaphrodite macrobrachium rosenbergii, so that a set of effective macrobrachium rosenbergii sex induction technology is established. Meanwhile, by using the hermaphrodite shrimps cultured by the method provided by the invention, a good scientific research material and an animal sample can be provided for sex determination, sex differentiation and researches on reproduction and fertilization of shrimps and crabs.
Owner:ZHEJIANG WANLI UNIV
Method for ecologically breeding macrobrachium nipponensis and Odontobutis obscura in pond by utilizing artificial ecological base
ActiveCN104285851AThe application operation method is simple and practicalGood and stable water qualityFood processingClimate change adaptationMoenkhausiaWater quality
The invention discloses an application method for ecologically breeding macrobrachium nipponensis and Odontobutis obscura in a pond by utilizing an artificial ecological base. The method comprises the following steps of (1) pond selection; (2) forming of pond artificial ecological base layout and biological film; (3) fry stocking; (4) feedstuff feeding; (5) water quality regulation and control and daily management; (6) fishing of grown macrobrachium nipponensis and grown Odontobutis obscura. Compared with the prior art, according to the method, the water quality of the pond can be kept good and stable, water does not need to be replaced in the whole breeding period except in the season with higher water temperature, new water is added to increase the water level, no breeding wastewater is drained, and the ecological benefits are obvious; the biocenosis such as microorganisms and algae on the ecological base can provide the suitable habitat for shrimp seeds and the Odontobutis obscura; the Odontobutis obscura is utilized for catching and feeding on the weak and sick shrimp seeds and autumn seeds bred in august; the breeding disease rate of the macrobrachium nipponensis is reduced; the out-of-pond specification and yield of the grown macrobrachium nipponensis are improved, and the economic benefits are obvious.
Owner:ZHEJIANG INST OF FRESH WATER FISHERIES
Method for breeding loach in macrobrachium pond in mixed mode
InactiveCN104542368AAvoid enteringImprove obesityClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffDiseaseEcological environment
The invention provides a method for breeding loach in a macrobrachium pond in a mixed mode, and belongs to the field of aquaculture. The method includes the following steps of breeding pool selection, disinfection, fertilizer applying, water plant culture, young loach throwing, young macrobrachium throwing and feeding. By means of the omnivory characteristic of loach, excessive bred young macrobranchium and sick and weak macrobranchium are eaten as bait, and therefore the self-breeding amount of macrobranchium is controlled, and the specifications of macrobranchium coming into the market are large. Meanwhile, loach frequently gets into mud to move, and therefore the bottom mud can be loosened, the decomposition of ammonia nitrogen and nitrite in a water body and organic matters in the bottom soil is promoted, the self-cleaning and repair capacity of the breeding water body is enhanced, diseases are reduced, water is basically not changed in the whole breeding process, and the ecological environment is effectively maintained while the aquatic product quality is improved.
Owner:TONGXIANG ZHOUQUAN XIANGXI AQUATIC PROFESSIONAL COOP
Fishing tool for macrobrachium nipponensis seeds and using method for fishing tool
The invention discloses a fishing tool for macrobrachium nipponensis seeds. The fishing tool comprises a net cage, an expelling net and an intercepting net, wherein the net cage consists of a cage frame and a mesh, one end of the net cage is provided with an opening, and the expelling net and the intercepting net are respectively arranged on two opposite sides of the opening of the net cage. By skillfully combining the expelling net, the intercepting net and the net cage, the fishing tool for the macrobrachium nipponensis seeds has a simple structure and low cost; when the fishing tool is used, the conventional expelling, intercepting, spreading and fishing methods are effectively combined; the whole fishing process is operated in water, so the fished objects are not hurt; and the fishing tool effectively reduces the death rate of the fished objects, can realize full-pool fishing at one time, has high fishing efficiency and low labor intensity, and is favorable for large-scale fishing.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Method for sifting macrobrachium nipponensis microsatellite mark with magnetic bead concentration method
InactiveCN101403013APolymorphism richImprove reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementGerm plasmEnrichment methods
The invention provides a method for screening microsatellite markers of Macrobrachium nipponensis by a magnetic beads enrichment method, including the following steps: the extraction of the genomic DNA of the Macrobrachium nipponensis; the hybridization of a probe and a target segment; the enrichment of magnetic beads; positive sequencing clone and the amplification of the genomic DNA according to primers which are related to the flanking sequences of the microsatellite. As the invention combines the magnetic beads enrichment and PRC amplification of bacterial liquid to carry out second-time screening, no isotope is needed. The method has the advantages of safety and high efficiency and low cost, short cycle, high reliability and the like. At the same time, in the enrichment process, the magnetic beads are repeatedly washed for a plurality of times, which can clean and remove microsatellite sequences which are not firmly adhered because of less repetition times. Therefore, the obtained microsatellite sequences are longer and are repeated for more times. The microsatellite sequences which are more frequently repeated are considered to have rich diversity at interspecies and intraspecies and can be widely applied to the diversity identification of germ plasm, the building of genetic maps, and QTL. Therefore, the method is one which screens the microsatellite markers of Macrobrachium nipponensis and can be easily popularized.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Ecological symbiosis breeding method for macrobrachium nipponensis and water fennel based on floating bed cultivation technology
InactiveCN105210940AGuaranteed high qualityEnsure safetyClimate change adaptationAgricultural fishingWater qualityHabitat
The invention discloses an ecological symbiosis breeding method for macrobrachium nipponensis and water fennel based on a floating bed cultivation technology. A pond is internally provided with a floating bed. The floating bed comprises a rectangular frame, a mesh plate, a lining net, and plant fixing devices. The mesh plate is arranged on the enclosed region of the rectangular frame and is connected with the rectangular frame. The lining net is arranged under the mesh plate and a gap is between the mesh plate and the lining net. The mesh plate is provided with planting holes. The plant fixing devices are clamped in the planting holes. The lining net is provided with blocking holes. The water fennel is planted on mesh plate, and the macrobrachium nipponensis is cultivated in water under the mesh plate. Through the floating bed to cultivate the water fennel, cultivation water is purified for a long time, and a habitat which is suitable for the macrobrachium nipponensis is provided. Through harvesting the water fennel at proper time, possibility of polluting the water again is prevented, and after picking of the water fennel, the water fennel can be converted to high economic output.
Owner:SUZHOU YANGCHENG LAKE XIAOJING SHRIMP & CRAB PRODN & SALES PROFESSIONAL COOP +1
Preparation of fermented material in bait bio-bed for main culturing of macrobrachium nipponensis and auxiliary culturing of Penaeus vannamei Boone and application method thereof
InactiveCN103815194APromote growthReduce intensityFood processingClimate change adaptationOxygen tankAdditive ingredient
The invention relates to preparation of a fermented material in a bait bio-bed for main culturing of macrobrachium nipponensis and auxiliary culturing of Penaeus vannamei Boone and an application method thereof. According to the method, a probiotic-fermented batch is poured into a pond, and a bait bio-bed with the fermented material as the main component is constructed at the bottom of the pond after rotary tillage. The fermented material in the bait bio-bed can directly be eaten by shrimps, and benthonic animals and aquatic plants such as Tubificidae, chironomidae larvae, spiral shell, waterweed and the like can be cultivated in the shrimp habitat to be used as the bait of macrobrachium nipponensis and Penaeus vannamei Boone. Food and habitat completion intensity can be reduced; survival rate and cultivation size of Penaeus vannamei Boone can be raised; and it is beneficial to raise culturing output and benifit of shrimps. To guarantee high propagation capability of demersal food organisms in the bait bio-bed in summer, dual oxygen supply of an oxygen tank and a micropore aerator is adopted. The oxygen tank and the micropore aerator are connected and are started regularly in stages every night in summer.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Mixed feed capable of improving antioxidant performance of macrobrachium nipponensis
InactiveCN103141694AIncrease economic lossEnhance antioxidant functionAnimal feeding stuffAntioxidantCholesterol
The invention discloses a mixed feed capable of improving antioxidant performance of macrobrachium nipponensis. The mixed feed comprises the following components by weight percent: 65-80% of protein source raw material, 3-8% of fat source raw material, 8-13% of starch, 0.1-0.7% of cholesterol, 0.1-0.7% of choline chloride, 0.8-2% of monocalcium phosphate, 1.5-3% of vitamin B complex, 2-4% of composite mineral substance, 2-4% of food calling condiment, 0.1% of salt, 3-6% of an adhesive, and 0.05-0.2% of an antioxidant. The mixed feed has complete nutrition and good taste, is environment-friendly and high efficient, and can strengthen the antioxidant performance of the macrobrachium nipponensis.
Owner:YANCHENG INST OF TECH
Preparation of fermented material in bait bio-bed for main culturing of procambarus clarkii and auxiliary culturing of river crab and application method thereof
InactiveCN103815195AExtended exponential growth phaseIncrease dissolved oxygenFood processingClimate change adaptationProcambarus clarkiiOrganism
The invention relates to preparation of a fermented material in a bait bio-bed for main culturing of procambarus clarkii and auxiliary culturing of river crab and an application method thereof. According to the method, a probiotic-fermented batch is poured into a pond, and a bait bio-bed with the fermented material as the main component is constructed at the bottom of the pond after rotary tillage. The fermented material in the bait bio-bed can directly be eaten by shrimps and crabs, and benthonic animals and aquatic plants such as Tubificidae, chironomidae larvae, spiral shell, waterweed and the like also can be cultivated in the shrimp and crab habitat to be used as the bait of procambarus clarkii and river crabs. Thus, food and habitat competition intensity can be reduced, and survival rate of river crabs can be raised. By dual oxygen supply of an oxygen tank and a micropore aerator in the bait bio-bed in summer, it is beneficial to raise culturing efficiency of demersal food organisms. The cultivated natural bait can be used to provide extra nutrition sources for the growth of macrobrachium nipponensis, and it is beneficial to raise culturing output and benefit of macrobrachium nipponensis.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Macrobrachium nipponensis disease-resistant Chinese herbal medicine fodder and processing method thereof
InactiveCN104905012AMeet the nutritional needs of growthImprove survival rateAnimal feeding stuffFish oilMonocalcium phosphate
The invention provides macrobrachium nipponensis disease-resistant Chinese herbal medicine fodder and a processing method of the macrobrachium nipponensis disease-resistant Chinese herbal medicine fodder. The macrobrachium nipponensis disease-resistant Chinese herbal medicine fodder comprises, by weight, 60-70 parts of bone meal, 10-12 parts of bean pulp, 5-8 parts of earthworm powder, 1-5 parts of wheatmeal, 2-5 parts of beer yeast, 1-2 parts of soybean oil, 0.5-1 part of monocalcium phosphate, 0.1-0.2 part of echinacea, 0.2-0.3 part of aloe, 1-2 parts of artemisia apiacea, 0.05-0.1 part of berberine, 0.05-0.08 part of eucommia ulmoides powder, 0.5-1 part of multi vitamins, 1-2 parts of fish oil, 1-2 parts of shell powder, 2-6 parts of silkworm chrysalis and 0.5-1 part of organic trace element premix. The macrobrachium nipponensis disease-resistant Chinese herbal medicine fodder is good in palatability, easy to assimilate and capable of promoting growth of fish and shrimps and enhancing the immunity.
Owner:SICHUAN GUOFENG ZHONGKE BIOTECH
Sterilizing organic-inorganic spherical special fertilizer for aquaculture
The invention discloses a sterilizing organic-inorganic spherical special fertilizer for aquaculture. The special fertilizer overcomes the problems of a single function, incapacity of meeting growth and development demands of fish and the like of conventional fertilizers. The special fertilizer is characterized in that the special fertilizer is prepared from organic fertilizer, inorganic fertilizer, zeolite powder, trace element amino acid chelate, compound sodium nitrophenolate, em probiotics, etc. through mixing and granulation. A preparation method for the special fertilizer comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing the organic fertilizer with other raw materials; then conveying the obtained mixture to a granulator for granulation; delivering the granulated material to a dryer for drying, wherein heat of the dryer is supplied by combustion of coal; subjecting the dried material to cooling and screening; and packaging the obtained finished product with a particle size of 1.5 to 3 mm and warehousing the product. The special fertilizer is applicable to culture of grass carp, crucian carp, carp, silver carp, bighead carp, catfish, tilapia, colossoma brachypomum, saltwater fish, soft-shelled turtle, mandarin fish, eel, river crab, prawn, white prawn, freshwater shrimp, Ma shrimp, macrobrachium, lobster, loach, swamp eel, sea cucumber, abalone, pearl, mussel, Sinonovacula constricta, oyster, green lipped mussel, clam, Tegillarca granosa, shellfish, laver, sea-tangle, etc.
Owner:湖北丰益肥业有限公司
Special organic fertilizer for meinong muskmelons and preparation method of special organic fertilizer
InactiveCN104725159AImprove water retentionImprove fat retentionBio-organic fraction processingAnimal corpse fertilisersBiotechnologyMicrobial agent
The invention discloses a special organic fertilizer for meinong muskmelons. The special organic fertilizer is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 10-15 parts of peanut cakes, 30-50 parts of pig manure, 12-16 parts of sesame seed cakes, 6-8 parts of cotton seed hulls, 4-6 parts of potassium fulvate, 5-6 parts of weathered coal, 4-5 parts of JT microbial agent, 5-8 parts of ammonium nitrate, 6-10 parts of ammonium phosphate, 3-5 parts of sweet potato stems, 6-7 parts of furfural residues, 4-5 parts of pine needle leaf powder, 4-5 parts of macrobrachium shells, 6-8 parts of potato starch, 4-5 parts of sodium sulfate, 30-40 parts of a soil conditioner and a proper amount of water. The fertilizer disclosed by the invention is prepared from a great number of organic matters serving as main raw materials so as to restore oil, maintain ecological capacity and enhance the water retaining, fertilizer retaining and fertilizer making functions of soil; meanwhile, all the raw materials are reasonably proportioned, so that all the components can more sufficiently take effects, and furthermore the fertilizer effect is higher; and the aims of reducing the product cost and increasing the economic incomes of fruit farmers because the raw materials are cheap and available are achieved on the premise of ensuring the fertilizer effect.
Owner:MAANSHAN QUANRUN AGRI SCI & TECH
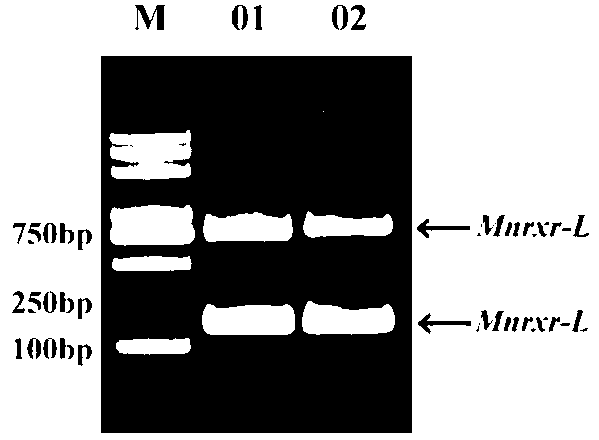
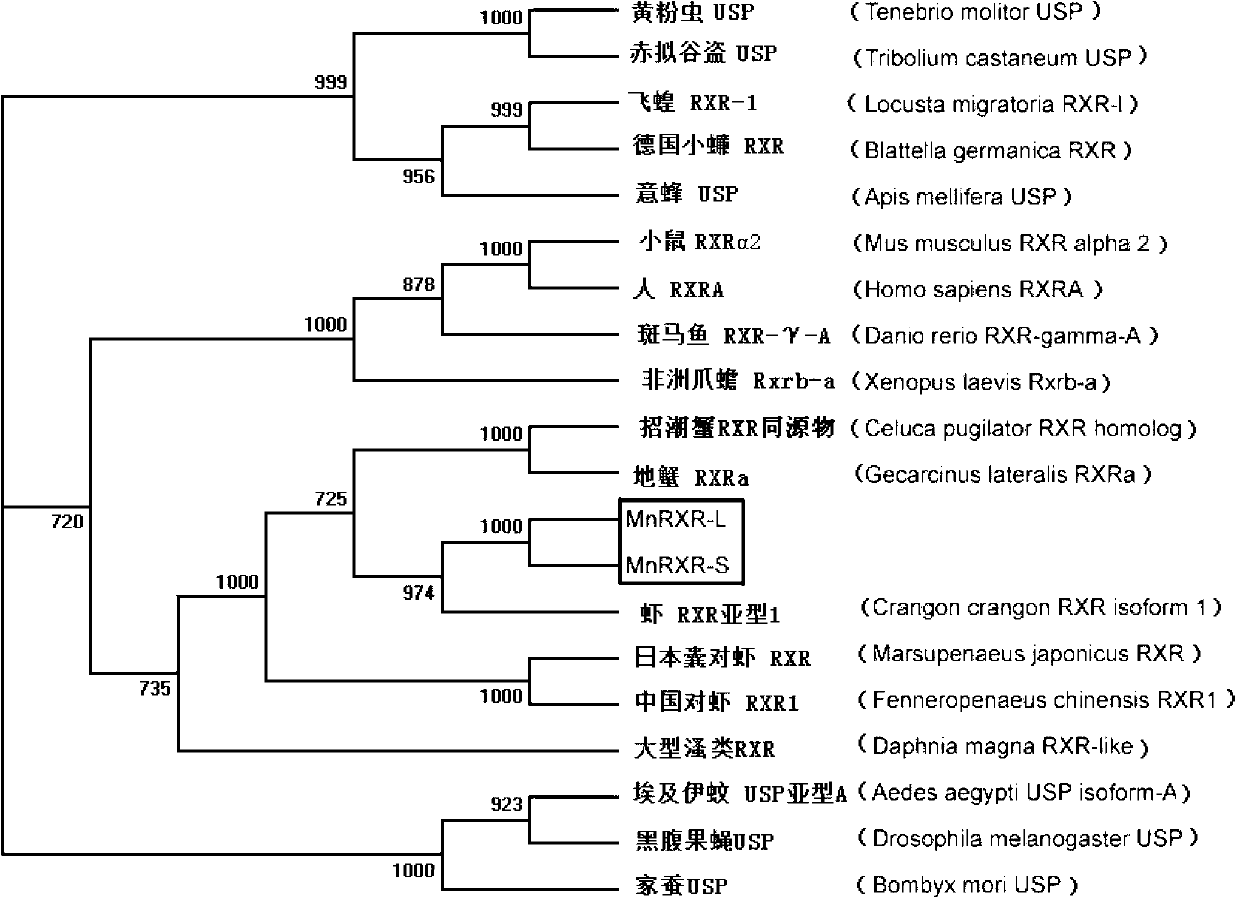
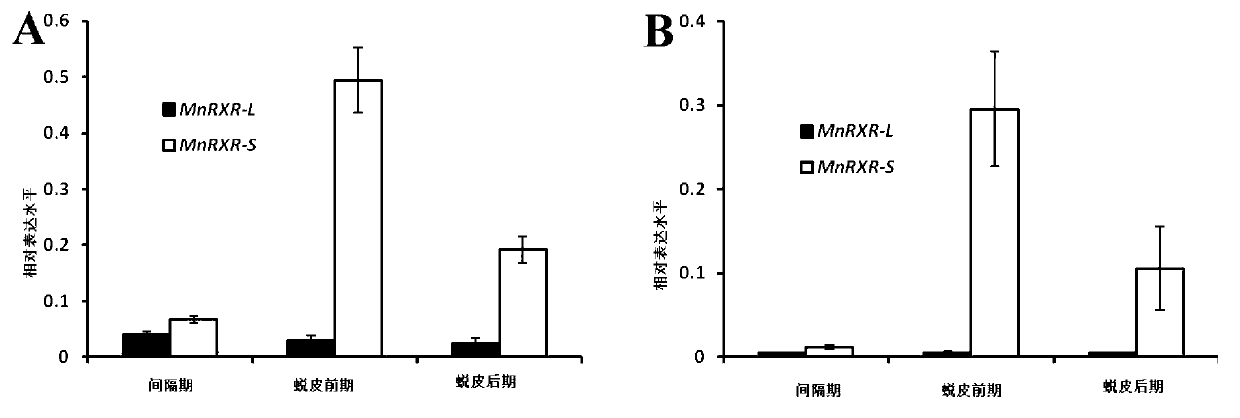
MnRXR gene of macrobrachium nipponensis, and amplification primer group and amplification method thereof
The invention discloses a MnRXR gene of macrobrachium nipponensis, and an amplification primer group and an amplification method thereof. A full-length cDAN sequence of the MnRXR gene is cloned from the hepatopancreas tissue of macrobrachium nipponensis. The gene comprises two variable spliceosomes: MnRXR-L and MnRXR-S. The invention lays an important base for research on functions of the MnRXR gene of macrobrachium nipponensis, in particularon important effects in a moult cycle.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Method for extracting macrobrachium spermatophore through pulse electric shock method and macrobrachium intraspecific crossbreeding method
InactiveCN105532537AFast, efficient and safe extractionIncrease success rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaElectricityPrawn
The invention discloses a method for extracting macrobrachium spermatophore through a pulse electric shock method and a macrobrachium intraspecific crossbreeding method. The methods comprise the steps that two pulse electrode tips are put on the portions close to the rear sides of two fifth paraeiopod bases, a connecting lead between the two electrode tips is parallel to the junction loop line of the cephalothorax and the abdomen of male macrobrachium, the electrode tips are basically perpendicular to the abdomen surface of the male macrobrachium, a pulse power switch is gently clicked once or twice, and the male macrobrachium is simulated through pulse electricity; a person pays close attention to spermatophore discharging holes formed in the inner sides of the fifth paraeiopod bases, takes down the spermatophore as soon as finding the spermatophore with ophthalmological tweezers and rapidly stick the spermatophore to the portions between the fourth paraeiopod bases and the fifth paraeiopod bases of congener female macrobrachium which just finishes reproductive uncoating, and the female macrobrachium conducts oviposition and incubation by itself. According to the method for extracting the macrobrachium spermatophore through the pulse electric shock method and the macrobrachium intraspecific crossbreeding method, the spermatophore can be extracted from the male macrobrachium rapidly, effectively and safely, the pulse electricity is adopted to extract the spermatophore, the male macrobrachium is not damaged, and compared with stimulation through an ordinary alternating current, the extracting success rate, the transplanting success rate and the fertilization rate are all obviously increased.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Freshwater prawn transvaalensis method
InactiveCN1463596AGood for healthExcellent New Variety of ShrimpClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaAquaculture industryPrawn
The artificial crossbreeding process of pond caray features the paired culture of female and male parent caray of different varieties, promoting estrus by artificial means, taking out the sperm atophore of male caray and attaching it to between the fourth and the fifth walking legs of female caray, alone culturing of the female caray to complete spawning and hatching and to obtain hybrid caray fry. The present invention provides one feasible way for breeding hybrid pond caray and it expects to breed excellent new variety of shrimp.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Method for improving in vitro hatching rate of fertilized eggs of macrobrachium nipponense
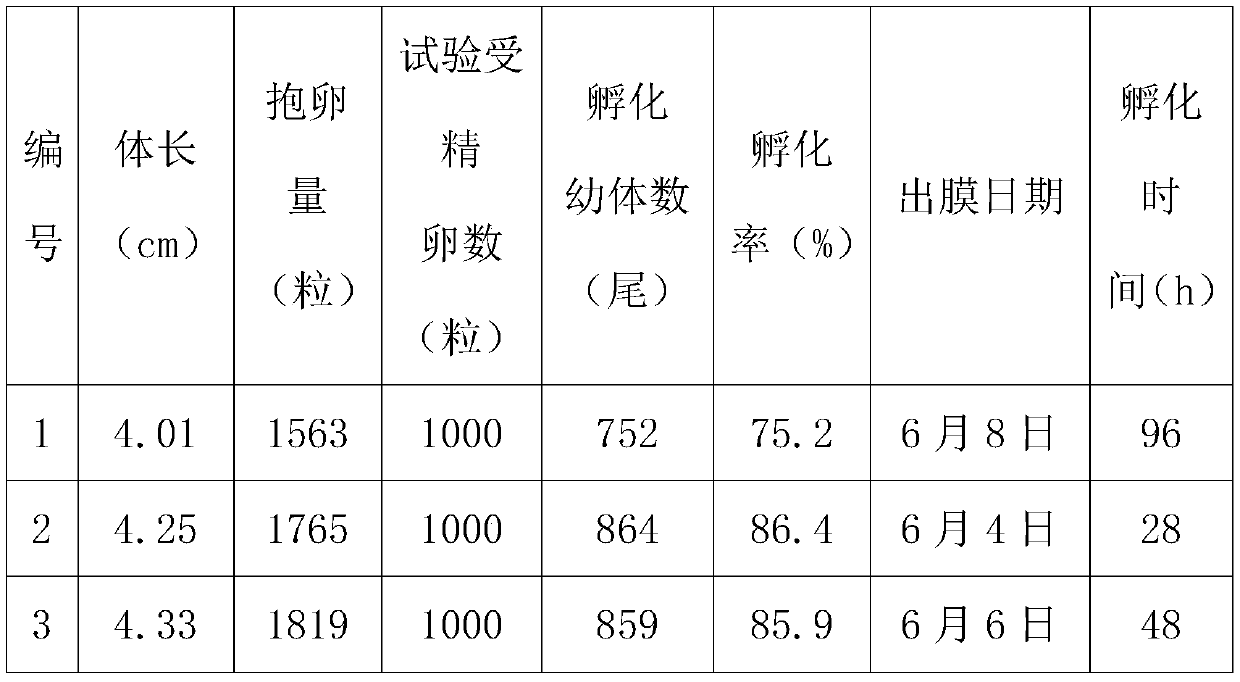
ActiveCN110250056AImprove survival rateReduced susceptibility to SaprolegniasisClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaFertilizerMacrobrachium
The invention discloses a method for improving the in vitro hatching rate of fertilized eggs of macrobrachium nipponense. The method comprises the following steps that 1, macrobrachium is selected, wherein the length of the macrobrachium body carrying eggs is greater than 4 cm, and the egg holding volume is 1,500 grains or above; 2, the macrobrachium is cultured, wherein plastic water grass is placed in a culture pond for the macrobrachium to inhabit, culture water is changed every 2 days, and the water exchange amount is 1 / 3 of the total water volume; 3, the fertilized eggs are separated, wherein the fertilized eggs are the fertilizer eggs obtained when the macrobrachium carrying the eggs is cultured until two black eye points appear in the eggs; 4, hatching is conducted; 5, hatching management is conducted. According to the method for improving the in vitro hatching rate of the fertilized eggs of the macrobrachium nipponense, the in vitro hatching cycle of the fertilized eggs can be effectively shortened, cumbersome operation in the hatching process can be reduced, the convenience of management in the hatching process can be increased, and the phenomenon that the fertilized eggs are infected with water mold after leaving the body and in the hatching process can be effectively avoided, so that the in vitro hatching rate of the fertilized eggs of the macrobrachium is effectively improved.
Owner:HUAIYIN TEACHERS COLLEGE
Macrobrachium nipponensis indoor feeding and breeding method
ActiveCN104737948AGuaranteed long-term survivalGuaranteed normal reproductionClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaPrawnShrimp culture
The invention discloses a macrobrachium nipponensis indoor feeding and breeding method. The method includes the following steps: constructing a simulation ecological system, placing macrobrachium nipponensis into the simulation ecological system, feeding the macrobrachium nipponensis one time each day, and changing water one time every one week; selecting berried shrimps from the macrobrachium nipponensis to serve as parent shrimps which are placed into cultivation jars to be fed, and placing one berried shrimp into each jar; after larvae break away from the parent shrimps, placing the parent shrimps back into the simulation ecological system to be fed continuously, and placing the larvae into juvenile prawn cultivation jars for cultivation; after the zoaea larvae are just hatched, feeding the zoaea larvae two times each day, and feeding the zoaea larvae one time after the zoaea larvae get into the larva stage. According to the macrobrachium nipponensis indoor feeding and breeding method, the operability is high, frequent water changing and manual management are not needed, it can be guaranteed that the macrobrachium nipponensis can live and conduct breeding in a room for a long time, and a guarantee is provided for the smooth development of medicine environment safety assessment.
Owner:HUNAN PLANT PROTECTION INST
Hemoglobin gene of macrobrachium nipponensis, cloning method of hemoglobin gene, and preparation method of recombinant protein
InactiveCN104073501AOxygen-carrying functionImprove antibacterial propertiesAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsOpen reading frameMacrobrachium nipponense
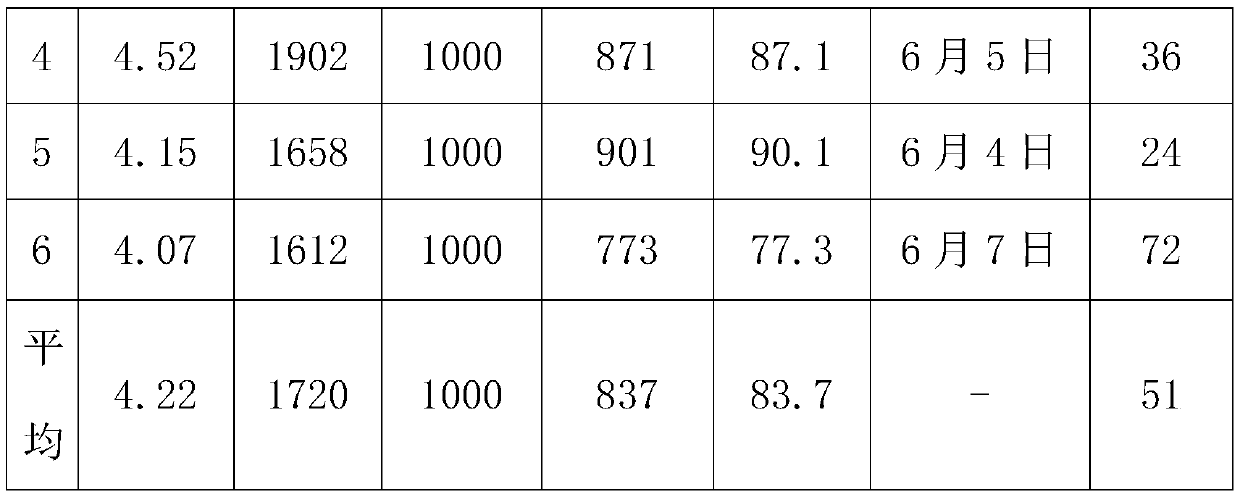
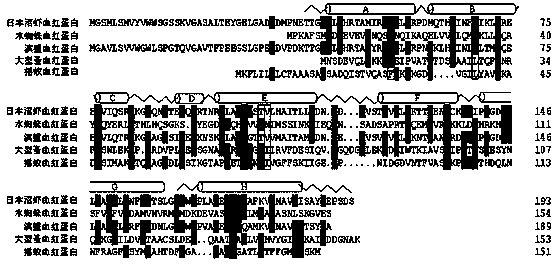
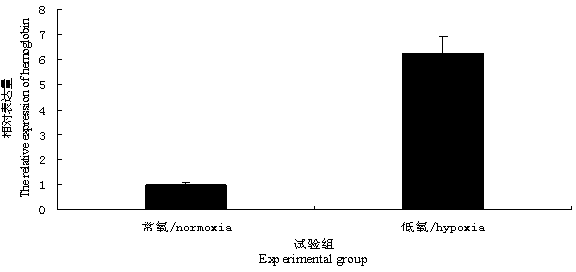
The invention discloses hemoglobin gene of macrobrachium nipponensis, a clone method of the hemoglobin gene, and a preparation method of recombinant protein. The hemoglobin gene of macrobrachium nipponensis is cloned through an expressed sequence tag technology and 3'and 5' rapid amplification cDNA end (RACE), wherein the overall length of the cDNA is 1201bp, the gene has a 579bp open reading frame and encodes 193 amino acids, 5' noncoding region is 199bp and 3' noncoding region is 420bp, and the gene has polyadenylic acid tailing signal and polyadenylic acid tail. The gene plays an important role in immune defense of macrobrachium nipponensis. The hemoglobin gene of macrobrachium nipponensis is obtained by in vitro recombination expression; the recombinant protein not only can carry oxygen, but also has bacteriostasis, thereby providing theoretical basis for disease control and gene-assisted breeding of macrobrachium nipponensis,and development of feed additives for macrobrachium nipponensis.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Methods for preparing and applying fermented feed for food organism bed for mainly breeding macrobrachium nipponensis and intercropping river crab
InactiveCN103798546AReduce intensityPromote growthFood processingClimate change adaptationOrganismFood competition
The invention relates to methods for preparing and applying a fermented feed for a food organism bed for mainly breeding macrobrachium nipponensis and intercropping river crabs. According to the preparing method, a batch mixture which is fermented by using probiotics is fed to a pond, and through rotary tillage, a 'food organism bed' which takes the fermented feed as a main component is established at the bottom of the pond, the fermented feed in the 'food organism bed' can be directly taken by shrimps and crabs, and at the same time, benthonic animals and aquatic plants such as water earthworm, chironomidae larvae, spiral shells and aquatic plants which can be used as a feed for the macrobrachium nipponensis and the river crabs can be cultivated on a habitat area of the shrimps and the crabs, so that the intensity of food competition habitat area competition is alleviated, the survival rate of the intercropped river crabs is increased, and the improvement of the breeding yield and the benefits of the shrimps and the crabs are facilitated. To ensure that a high propagation capability of demersal food organisms in the 'food organism bed' is stilled maintained in summer, oxygen cylinders and micropore aerators are adopted for double-oxygen supply, and the oxygen cylinders are coupled with micropore aeration tubes and are switched on at regular time in different periods each night in summer.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Macrobrachium nipponensis cement pool intensive artificial hatching method
InactiveCN105010184AImprove survival ratePhysically fitClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaPrawnSeedling
The invention provides a macrobrachium nipponensis cement pool intensive artificial hatching method, and relates to the field of macrobrachium nipponensis culture technology. The method comprises the following steps: 1, using an indoor cement pool, before putting young macrobrachium nipponensis, scrubbing clean the cement pool firstly, then adding water, carrying out disinfection, emptying the water in the pool every one day, refilling the pool with new water, filtering the new water by use of an 80-mesh screen mesh when the pool is refilled with the new water, and when the water temperature in the pool rises to more than 20 DEG C, preferentially putting egg-carrying macrobrachium nipponensis which have similar growth degrees and are about to mature into a net cage in the cement pool for hatching, wherein the putting density of the macrobrachium nipponensis is 3000-5000 per pool; and 2, after juveniles of the macrobrachium nipponensis are hatched, trapping the juveniles to a scope of a water surface by use of light, dragging the juveniles out by use of the dense-mesh net case, concentrating the juveniles at one corner of the net cage, and then scooping the juveniles out by use of utensils. The method provided by the invention can realize intensive hatching in an indoor environment, the hatching conditions are conveniently controlled, the hatching rate in unit area is high, the hatched young macrobrachium nipponensis has good physique, the survival rate is high, and the catching is convenient.
Owner:HUAIYUAN KONGJINHU AGRI DEV
Large-scale culture method for Macrobrachium
InactiveCN107094678AGrow fastExpand farming methodsClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaShrimpMacrobrachium
The invention relates to a large-scale culture method for Macrobrachium. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) site arrangement and management; (2) early-stage management; and (3) culture management. By changing the Macrobrachium culture method, the site improvement and feeding distribution increase the growth speed of Macrobrachium; and the sectionalized management of culture can save the culture resources more efficiently, increases the large-scale culture modes of Macrobrachium, efficiently increases the growth speed of Macrobrachium, and prevents the pathogen transmission of shrimps.
Owner:安徽省鑫旺农业开发有限公司
Japanese pondcrayfish reovirus gene diagnosis reagent kit
InactiveCN101509044AQuick checkSensitive detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesRNA extractionPositive control
The invention discloses a macrobrachium nipponensis reovirus gene diagnosis kit, and relates to a virogene diagnosis kit. The kit comprises the following reagents: reagent A is tissue homogenate buffer solution which is Tris-NaCl-EDTA buffer solution; reagent B is RNA extracting solution which is Trizol liquid; reagent C is macrobrachium nipponensis reovirus RNA reverse transcription reaction liquid which contains special primer MnRV-325R; reagent D is PCR reaction liquid that contains special primer MnRV 325R and MnRV 325F; reagent E liquid is positive control which is an MnRV positive DNA template. The kit can be used for rapidly, sensitively and exactly testing whether young macrobrachium nipponensis, shrimp, grown shrimp and parent shrimp carry the macrobrachium nipponensis reovirus or not.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Feed additive capable of improving antioxidant function and reproductive performance of macrobrachium nipponensis
InactiveCN109645258AEnhance antioxidant functionImprove antioxidant capacityClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffYolkDisease
The invention relates to a feed additive capable of improving the antioxidant function and reproductive performance of macrobrachium nipponensis. The feed additive is prepared from, by weight, 15-27 parts of radix isatidis, 17-25 parts of astragalus polysaccharides, 4-8 parts of flos lonicerae, 4-8 parts of fructus rosae laevigatae, 4-13 parts of radix et rhizoma rhei, 8-15 parts of rhizoma calami, 7-15 parts of shrimp shell meal, 4-9 parts of shell powder and 16-22 parts of yolk immunoglobulin. The feed additive has the advantages that 2-8% of the feed additive is stirred in basic feed of which the protein content is 37.4%, when the water temperature rises to 10 DEG C in March, feeding is started, feeding is carried out twice each day, continuous feeding is carried out for 1 month, thereby being capable of not only improving the growth speed of macrobrachium nipponensis and the antioxidant function of the hepatopancreas, but also promoting the development of the ovary of female shrimps; the problems that a macrobrachium nipponensis female parent is slow in growth speed, low in disease resistance and slow in ovary development in the traditional macrobrachium nipponensis breeding process are solved, the additive amount is low, and the preparation method is simple.
Owner:YANCHENG INST OF TECH
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com