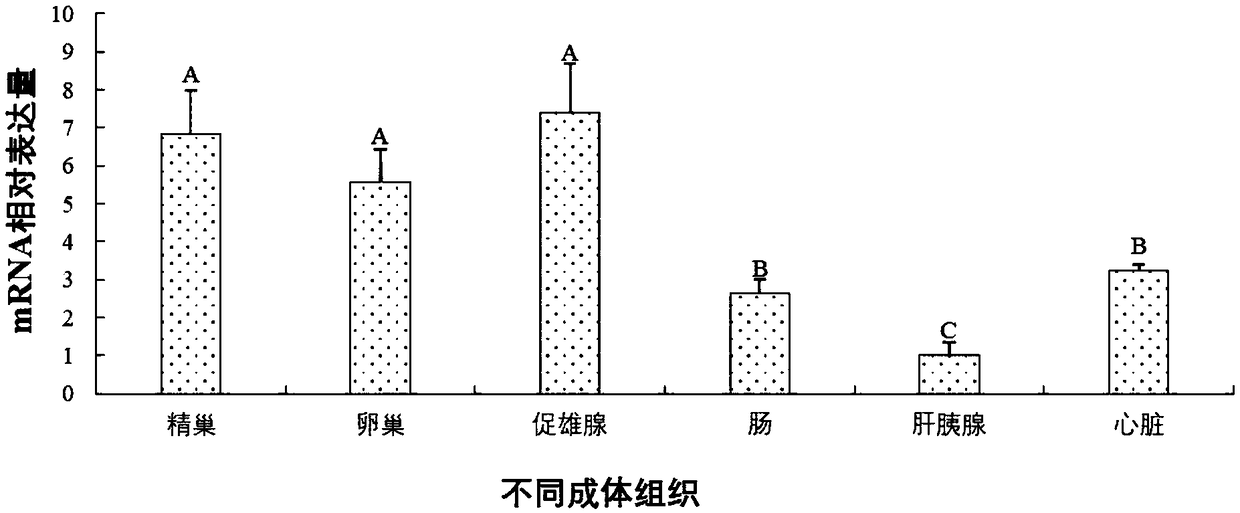
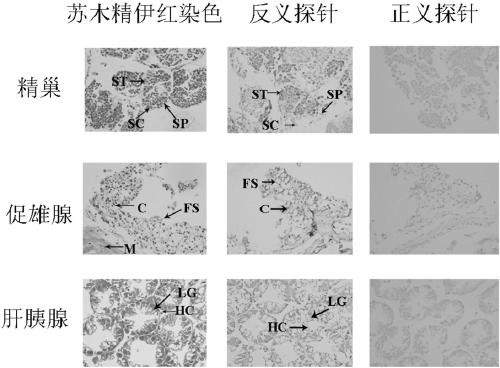
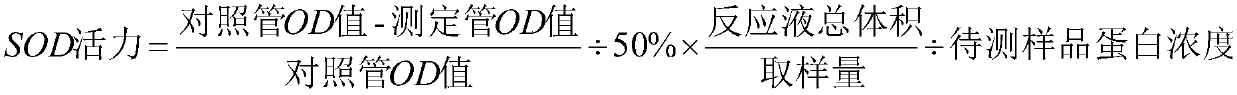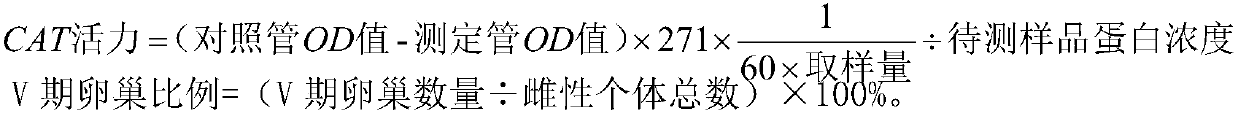Patents
Literature
71 results about "Macrobrachium nipponense" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Macrobrachium nipponense is a species of freshwater shrimp found in Asia that was first described in 1849.
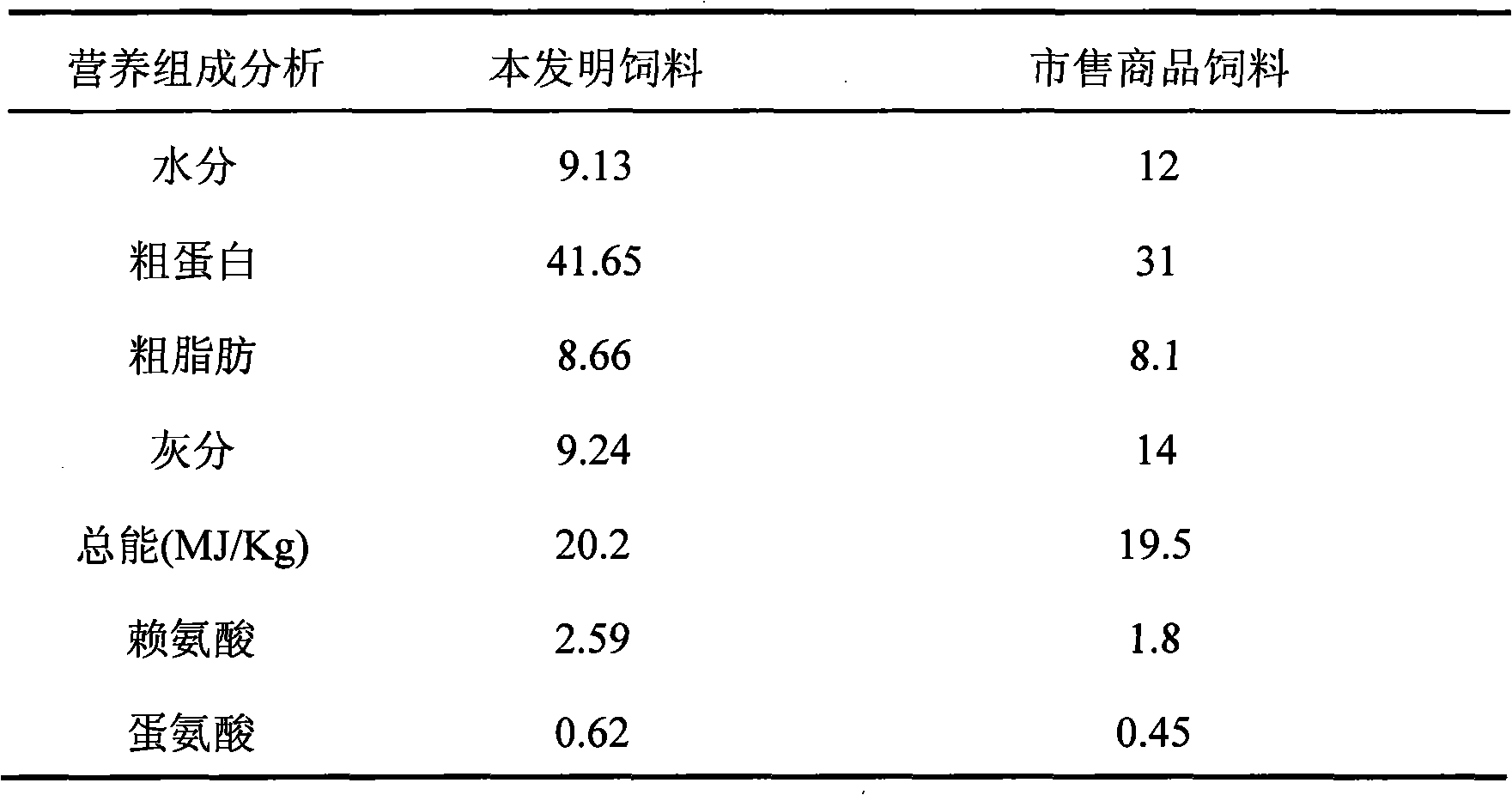
Formula of macrobrachium nipponense feed and method for preparing macrobrachium nipponense compound feed from macrobrachium nipponense feed
InactiveCN101978859AMeeting nutritional needsIncrease food intakeFood processingClimate change adaptationPeanut mealFish oil
The invention relates to a formula of a macrobrachium nipponense feed and a method for preparing a macrobrachium nipponense compound feed from the macrobrachium nipponense feed. The formula of the macrobrachium nipponense feed consists of fish meal, fermented soybean meal, peanut meal, blood powder, yeast, flour, multi-vitamin, multi-mineral, shrimp bran, soybean oil, fish oil, phospholipid oil, squid liver powder and yeast extract. The method for preparing the macrobrachium nipponense compound feed from the macrobrachium nipponense feed comprises the following steps of: weighing according tothe feed formula, stirring and mixing in a stirrer, introducing steam, preparing particles with the particle size of 1 to 1.6mm, dehydrating, cooling, and reducing the temperature of the particles toroom temperature to obtain the macrobrachium nipponense compound feed. The macrobrachium nipponense compound feed is used for feeding macrobrachium nipponense, contributes to meeting the nutritional requirements of the macrobrachium nipponense and improving the food intake of the macrobrachium nipponense, improves feed utilization, increases the yield of the cultured macrobrachium nipponense and reduces culture cost. The macrobrachium nipponense compound feed is applied to the feed used in the culture of the macrobrachium nipponense.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Method for in vitro incubation of macrobrachium nipponense
InactiveCN101720684AOvercoming Biological DifficultiesFill in research gapsClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaBiological propertyShrimp
The invention relates to a method for in vitro incubation of fertilized eggs of macrobrachium nipponense, which is characterized in that the method comprises the steps of selection of parent shrimps, mating and oviposition, treatment of incubation water, egg stripping, egg washing, incubation, daily management and the like. The method for the in vitro incubation of the fertilized eggs of the macrobrachium nipponense solves the problem of biological characteristics that the fertilized eggs depend on parent bodies to be incubated, lays a foundation for genetic operations of the macrobrachium nipponense such as gene transfer, nuclear transplantation and the like, fills the research gap of the field, and has important practical application value.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Industrially breeding method of macrobrachium nipponense
InactiveCN102187837ASolve the problem of asynchronous growthReduce economic lossClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaPrawnWater quality
The invention provides an industrially breeding method of macrobrachium nipponense, comprising the steps of: selection of parent macrobrachium of macrobrachium nipponense, cultivation of fingerlings, treatment of fingerling cultivation water quality, daily cultivation management in the breeding period and the like. By use of the industrially breeding method of macrobrachium nipponense, provided by the invention, the cultured macrobrachium nipponense fingerlings have high survival rate and stable quality. According to the industrially breeding method disclosed by the invention, the problems of low survival rate and unstable quality in the conventional macrobrachium nipponense breeding process can be solved, and the economic loss of the macrobrachium culturists can be reduced.
Owner:高雷
High-efficiency ecological cultivation method for macrobrachium nipponense
ActiveCN105165669AEasy feedingPromote growthClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaShrimpOrganic matter
The present invention discloses a high-efficiency ecological cultivation method for macrobrachium nipponense. The method comprises: (1) preparing a shrimp pond; (2) disinfecting the shrimp pond; (3) planting and managing water weeds; (4) stocking and managing postlarvae; (5) carrying out oxygenation water quality management and oxygenation; (6) carrying out feeding management; and (7) catching adult shrimps. According to the present invention, the high-efficiency ecological cultivation method for macrobrachium nipponense is simple and easy in operation, can greatly reduce content of poisonous and harmful organic matters, residual feed and the like by virtue of management methods such as planting water weeds, matching filter-feeding fishes, reducing a mixed feed proportion, reasonably and effectively feeding, controlling water weed density, carrying out oxygenation by virtue of an aerator, and the like, thereby reducing cost investment and keeping water quality freshness. by postponing shrimp postlarvae stocking time and applying quicklime, occurrence of autumn propagated postlarvae can be inhibited; and by leaving an area besides a pond with no water weeds planted, feeding and growing of macrobrachium nipponense can be promoted. The macrobrachium nipponense cultivated by the method is high in yield, good in quality, high in large-size commercial shrimp rate, good in cultivation benefits, so that the health development of macrobrachium nipponense cultivation industry is promoted.
Owner:上海市水产研究所(上海市水产技术推广站)
Method for ecologically breeding macrobrachium nipponensis and Odontobutis obscura in pond by utilizing artificial ecological base
ActiveCN104285851AThe application operation method is simple and practicalGood and stable water qualityFood processingClimate change adaptationMoenkhausiaWater quality
The invention discloses an application method for ecologically breeding macrobrachium nipponensis and Odontobutis obscura in a pond by utilizing an artificial ecological base. The method comprises the following steps of (1) pond selection; (2) forming of pond artificial ecological base layout and biological film; (3) fry stocking; (4) feedstuff feeding; (5) water quality regulation and control and daily management; (6) fishing of grown macrobrachium nipponensis and grown Odontobutis obscura. Compared with the prior art, according to the method, the water quality of the pond can be kept good and stable, water does not need to be replaced in the whole breeding period except in the season with higher water temperature, new water is added to increase the water level, no breeding wastewater is drained, and the ecological benefits are obvious; the biocenosis such as microorganisms and algae on the ecological base can provide the suitable habitat for shrimp seeds and the Odontobutis obscura; the Odontobutis obscura is utilized for catching and feeding on the weak and sick shrimp seeds and autumn seeds bred in august; the breeding disease rate of the macrobrachium nipponensis is reduced; the out-of-pond specification and yield of the grown macrobrachium nipponensis are improved, and the economic benefits are obvious.
Owner:ZHEJIANG INST OF FRESH WATER FISHERIES
Method for sifting macrobrachium nipponensis microsatellite mark with magnetic bead concentration method
InactiveCN101403013APolymorphism richImprove reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementGerm plasmEnrichment methods
The invention provides a method for screening microsatellite markers of Macrobrachium nipponensis by a magnetic beads enrichment method, including the following steps: the extraction of the genomic DNA of the Macrobrachium nipponensis; the hybridization of a probe and a target segment; the enrichment of magnetic beads; positive sequencing clone and the amplification of the genomic DNA according to primers which are related to the flanking sequences of the microsatellite. As the invention combines the magnetic beads enrichment and PRC amplification of bacterial liquid to carry out second-time screening, no isotope is needed. The method has the advantages of safety and high efficiency and low cost, short cycle, high reliability and the like. At the same time, in the enrichment process, the magnetic beads are repeatedly washed for a plurality of times, which can clean and remove microsatellite sequences which are not firmly adhered because of less repetition times. Therefore, the obtained microsatellite sequences are longer and are repeated for more times. The microsatellite sequences which are more frequently repeated are considered to have rich diversity at interspecies and intraspecies and can be widely applied to the diversity identification of germ plasm, the building of genetic maps, and QTL. Therefore, the method is one which screens the microsatellite markers of Macrobrachium nipponensis and can be easily popularized.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
High-yield large-scale breeding method carried out by scientifically utilizing autumn cannon-head macrobrachium nipponense larvae
InactiveCN101946728AIncrease total outputImprove farming efficiencyClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaPrawnAquatic product
The invention discloses a high-yield large-scale breeding method carried out by scientifically utilizing autumn cannon-head macrobrachium nipponense larvae, belonging to the field of aquaculture science. The high-yield large-scale breeding method comprises the following steps of: breeding after macrobrachium nipponense parents in different local water areas are collected in March-April of the current year; starting to fish cannon-head macrobrachium nipponense with larger sizes in batches for sparse breeding in different ponds after female shrimps brood and incubate to generate a large quantity of the larvae in mid-June-July, wherein the cannon-head macrobrachium nipponense sparsely bred in the different ponds start to achieve sexual maturity and brood and incubate autumn larvae in mid-August-September; breeding by utilizing the incubated autumn larvae; and fishing large macrobrachium nipponense and remaining small macrobrachium nipponense during a breeding period, and lasting to about May of the coming year. The invention can effectively carry out the breeding by utilizing the autumn macrobrachium nipponense larvae, and enhances the total output of the macrobrachium nipponense by more than 20 percent, the proportion of large-size macrobrachium nipponense by more than 10 percent and the breeding benefit by more than 15 percent.
Owner:南京市水产科学研究所
Safe overwintering method for macrobrachium nipponense parents
InactiveCN101720706AConducive to survivalReduce lossClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaEconomic benefitsFishery
The invention discloses a safe overwintering method for macrobrachium nipponense parents, which mainly comprises selection of a parent overwintering temporary culture pond, overwintering pretreatment, construction of overwintering conditions, parents matching and density and overwintering feeding management technology and the like. The method is an overwintering method suitable for macrobrachium nipponense biology, ethology and ecology, the method can furthest improve the overwintering survival rate of the macrobrachium nipponense, and the overwintering survival rate can reach over 85 percent. The method reduces the overwintering loss of the macrobrachium nipponense, directly increases the economic benefit, provides reliable assurance for conservation and overwintering of good strains of the macrobrachium nipponense, and is helpful for improving the economic benefit of macrobrachium nipponense culture and promoting healthy and sustainable development of the macrobrachium nipponense breeding industry in China.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Method for amplifying complete sequence of mitochondrial genome of Macrobrachium nipponense
The invention discloses a method for amplifying a complete sequence of a mitochondrial genome of a Macrobrachium nipponense. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting the mitochondrial genome of the Macrobrachium nipponense by a high-salinity precipitation method; amplifying two gene segments, namely cytochrome oxidase I (CO I) and 16S rRNA in the mitochondrial genome of the Macrobrachium nipponense; and performing long polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification on the mitochondrial genome deoxyribose nucleic acid (DNA) of the Macrobrachium nipponense. Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) is a very useful material in the research of molecular genetic evolution. As a mitochondrial gene is not rearranged during cell reduction division and the point mutation rate is high, the method contributes to examining the changes of the gene in a shorter period and comparing the difference among the same genes of different species so as to determine the evolutionarily genetic relationship of the species.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Primer group, marking method and application of EST-SSR (Expressed Sequence Tag-Simple Sequence Repeats) molecular marker of macrobrachium nipponense
InactiveCN103484459AAchieve molecular markersImplement initial applicationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyCrustacean
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biological DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) marking technologies and applications thereof and particularly relates to a sieving method and application of an EST (Expressed Sequence Tag) microsatellite marker (EST-SSR (Simple Sequence Repeats)) of a macrobrachium nipponense as a freshwater economic shelled animal. By using an EST-SSR marking technology, the hereditary feature and group structure of a macrobrachium nipponense breeding group can be researched, the primary application of a molecular marker in macrobrachium nipponense breeding can be realized, and a foundation is laid for carrying out auxiliary molecular marker breeding through constructing a high-density macrobrachium nipponense genetic linkage picture and locating the important economic character of a QTL (Quantitative Trait Locus).
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Macrobrachium nipponense FoxL2 (Forkhead box protein L2) protein as well as coding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN104592378AShortened maturation timeReduce developmentOrganic active ingredientsFermentationPericardial cavityMacrobrachium nipponense
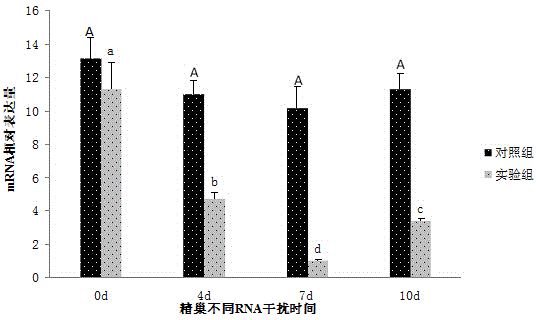
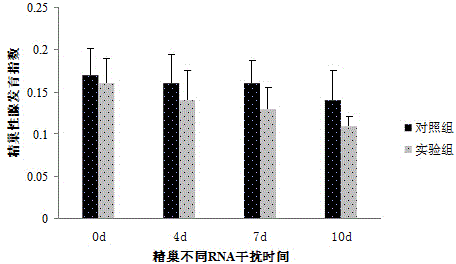
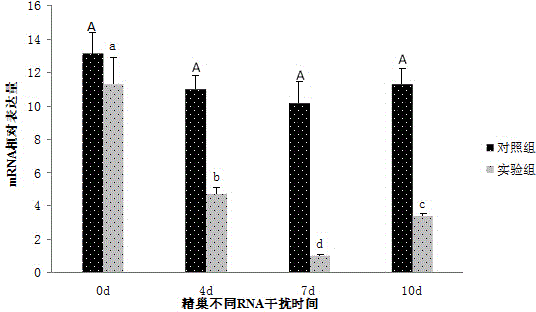
The invention discloses a macrobrachium nipponense FoxL2 (Forkhead box protein L2) protein as well as a coding gene and an application thereof. An FoxL2 gene is cloned from testes or ovaries of the macrobrachium nipponense by using primer groups provided by the invention, dsRNA is prepared by using the FoxL2 gene, after the dsRNA is injected into the pericardial cavity of male or female macrobrachium nipponense, the expression of the FoxL2 gene in the testes or ovaries can be silenced, the development of the testes of the macrobrachium nipponense can be delayed, but the influence on the development of the ovaries of the macrobrachium nipponense is not obvious. Thus, the FoxL2 gene of the macrobrachium nipponense can be used for promoting the development of the testes and has the function against the action of the FoxL2 gene in mammals and fishes. According to the macrobrachium nipponense FoxL2 protein as well as the coding gene and the application thereof, new thinking and effective means are provided for overcoming the sexual precocity phenomenon of the macrobrachium nipponense and breeding good varieties.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Method for breeding macrobrachium nipponense in two seasons
InactiveCN108703094AScientific and reasonable feeding methodsIncrease productionClimate change adaptationWaste water treatment from animal husbandryWater qualityHabit
The invention discloses a method for breeding macrobrachium nipponense in two seasons. The provided method for breeding macrobrachium nipponense is scientific and reasonable, living habits and nutrient demands of macrobrachium nipponense are fully taken into account, organic fertilizer is applied as base fertilizer and can serve as low-release fertilizer, and meanwhile, application of chemical fertilizer is avoided, so that influences of chemicals on young shrimps are reduced; since macrobrachium nipponense is characterized by preferentially eating food matched with their mouth sizes, macrobrachium nipponense is fed with feed matched with different mouth sizes according to different growth stages of macrobrachium nipponense, and therefore the requirement of eating food matched with the mouth sizes is met. By removing silt at regular time, injecting water, conducting oxygenation and carrying out other management methods, the content of toxic harmful organic matter and bait residues canbe effectively reduced, and water is kept clean and healthy. Macrobrachium nipponense bred by means of the method is high in yield and quality.
Owner:桂阳县上梓木水产养殖专业合作社
Mixed-culture method for macrobrachium nipponense and yellow catfishes
InactiveCN107751053AImprove immunityReduce the risk of diseaseFood processingClimate change adaptationAquatic animalWater quality
The present invention proposes a mixed-culture method for macrobrachium nipponense and yellow catfishes. The method comprises the following steps: (1) selecting a pond; (2) disinfecting the pond: putting water with a depth of 0.5-1m into the vacant pond obtained in the step (1), throwing quicklime for disinfection, planting aquatic plants, hanging a decomposed microbial organic fertilizer at the edge of the pond, placing a shielding substance, and adjusting a water temperature, a dissolved-oxygen amount and a pH value of the pond to obtain a cultivation pond; (3) throwing fry and young macrobrachium nipponense; and (4) performing feeding management: from a first week to a seventh week, every day performing feeding for 2 times and throwing boiled primary feed; after an eighth week, performing feeding according to the water temperature, throwing traditional Chinese medicine feed, improving the water quality every 3-5 days, and throwing young grass carp and bellamya quadrata. The culturemethod provided by the present invention fully utilizes culture resources, maintains the water quality, improves the immunity of the yellow catfishes, reduces the morbidity rates of the macrobrachiumnipponense and the yellow catfishes, greatly improves the utilization rate of the feed, and increases the yield of aquatic animals.
Owner:HEFEI KANGQINGYUAN BREEDING CO LTD
In-situ purification and ecological comprehensive utilization method for freshwater aquaculture pond
InactiveCN104756936AImprove qualityReduce sizePisciculture and aquariaFresh water organismFresh water
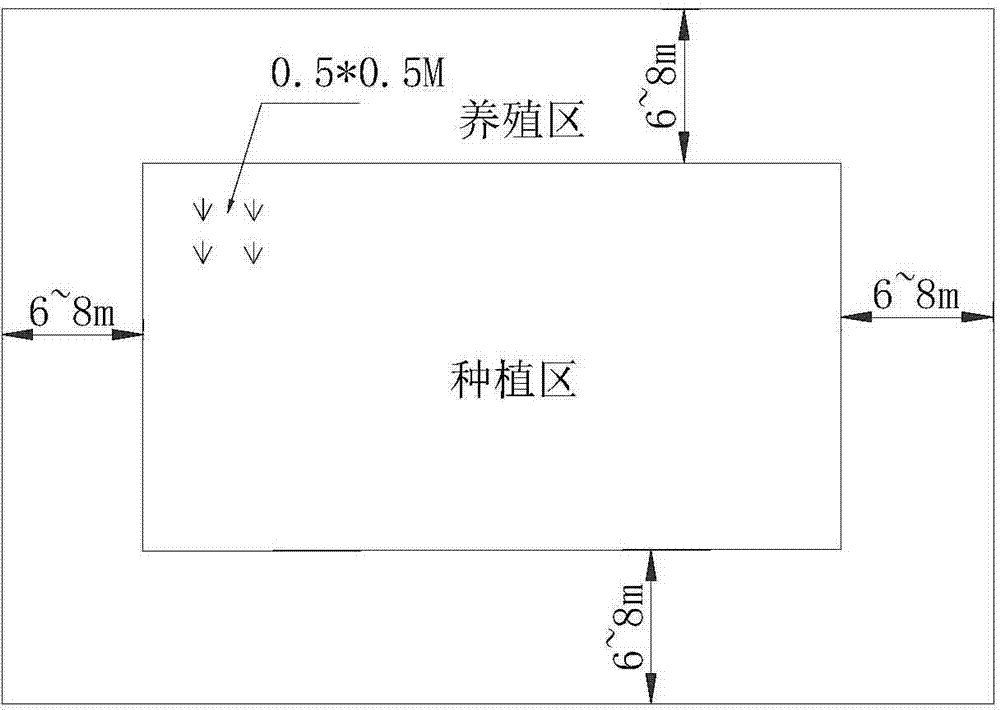
The invention relates to an in-situ purification and ecological comprehensive utilization method for a freshwater aquaculture pond. The in-situ purification and ecological comprehensive utilization method comprises the following steps that 1, dry pond solarization is performed, the pond bottom is flattened, the whole pond is cleaned, and fresh water is filled to keep soil wet after one week; 2, rice is planted, an aquaculture operation zone with the width of 6-8 meters is reserved for the surrounding of the pond and serves as a ground cage setting and feeding zone, bunch planting is conducted on rice seeds in the remaining zone of the pond, the water level can be increased with plant height of the rice after rice seedlings resume growth; 3, macrobrachium nipponense larvae are bred, and the water level of the pond is increased with rice growth; 4, timely using ground cages to catch large macrobrachium nipponense and reserve small macrobrachium nipponense, and listing and selling are performed, and harvesting is performed in a rice ear cutting mode after the rice matures; 5, grass carp stocking is performed after the rice is harvested, the grass carps are utilized to consume rice straws in the pond; 6, all grass carps and remaining macrobrachium nipponense are caught. Compared with an existing pond purifying technology, the in-situ purification and ecological comprehensive utilization method is economic and effective, conforms to environment-friendly trend and can be accepted by farmers.
Owner:HANGZHOU AQUATIC PROD TECH PROMOTION GENERAL STATION
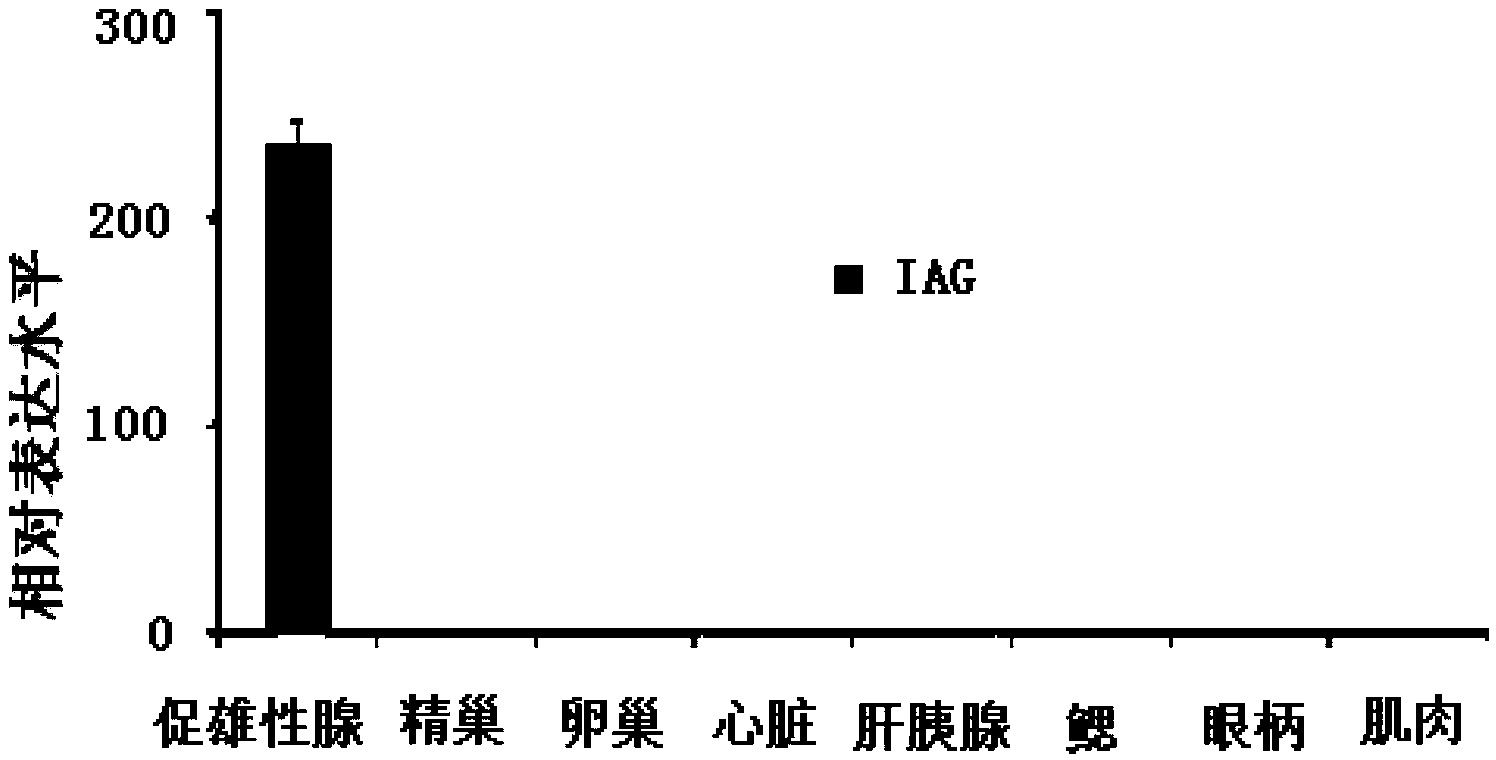
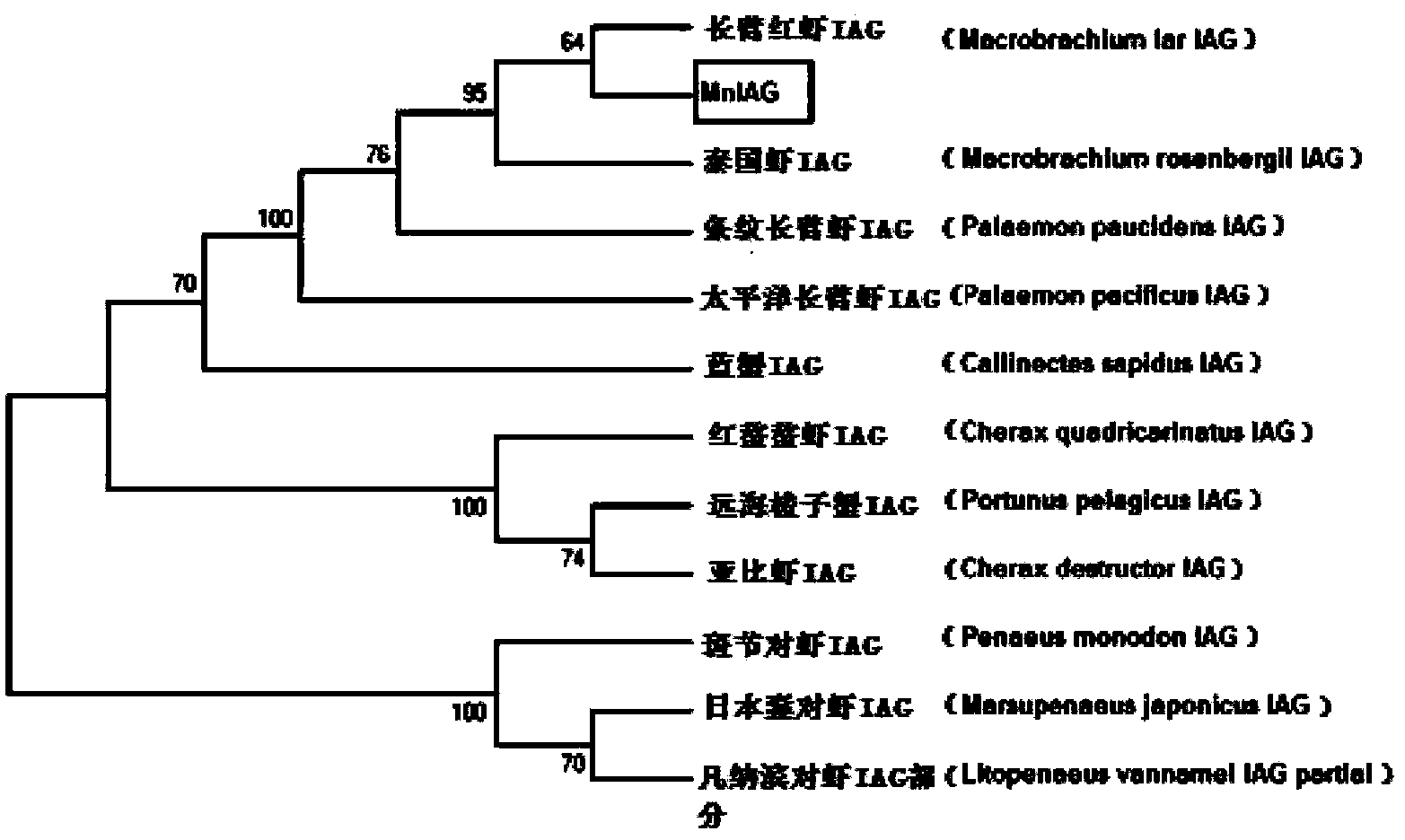
Macrobrachium nipponense MnIAG gene, and amplimer group and amplification method thereof
The invention discloses a Macrobrachium nipponense MnIAG gene, and an amplimer group and an amplification method thereof. The full-length cDNA sequence of the MnIAG gene is cloned from the androgenic gland tissue of Macrobrachium nipponense through utilizing the primer group provided by the invention, and an important basis is established for the function of the Macrobrachium nipponense MnIAG gene, especially the important effect in sex differentiation.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
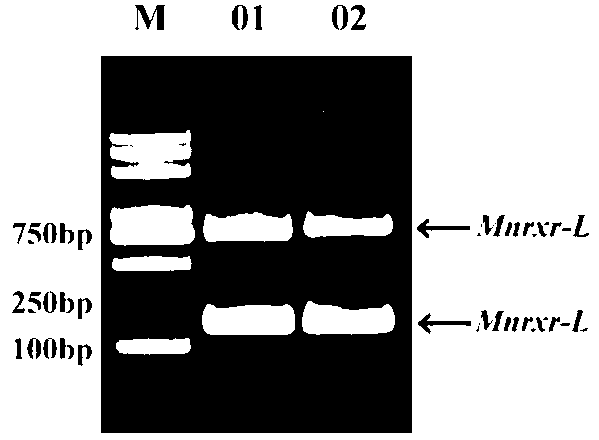
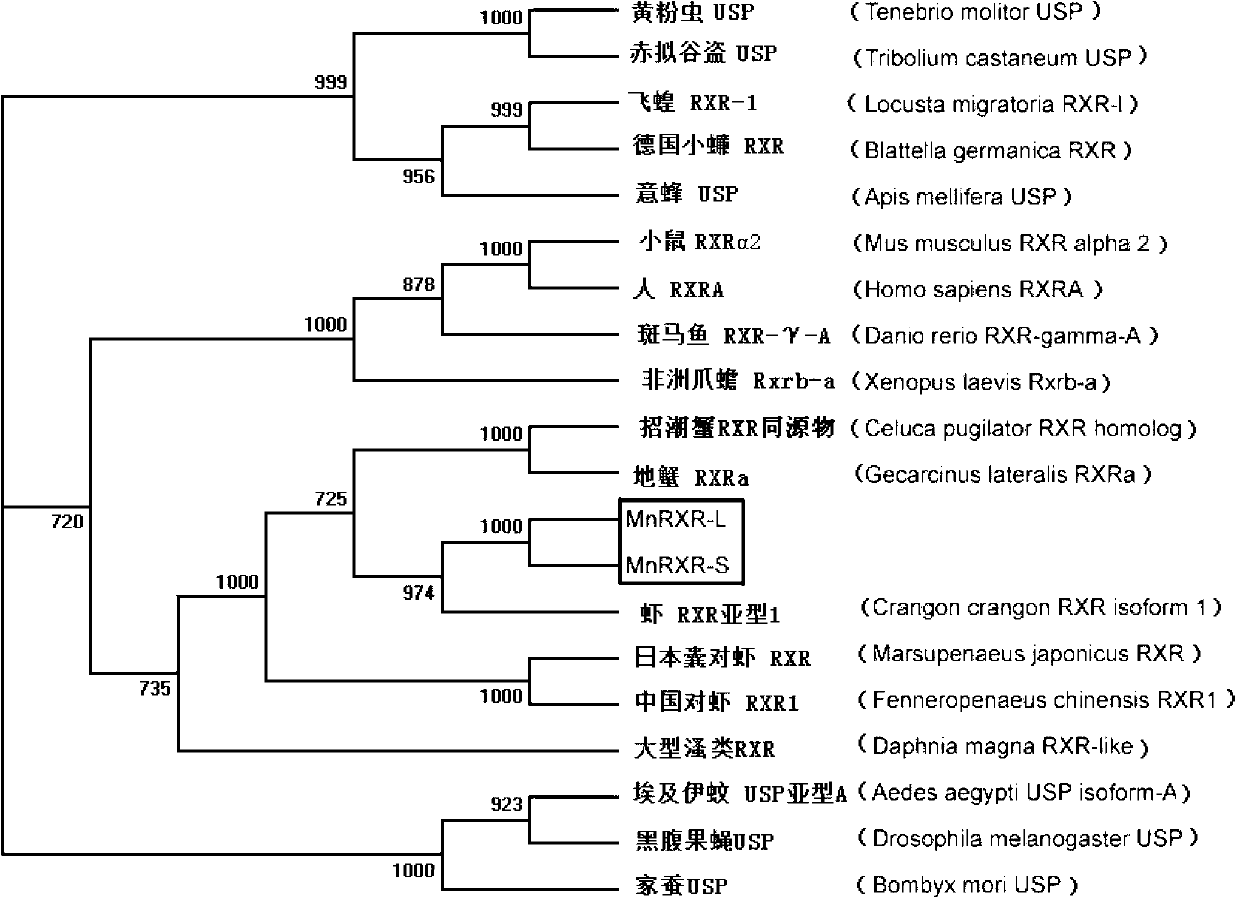
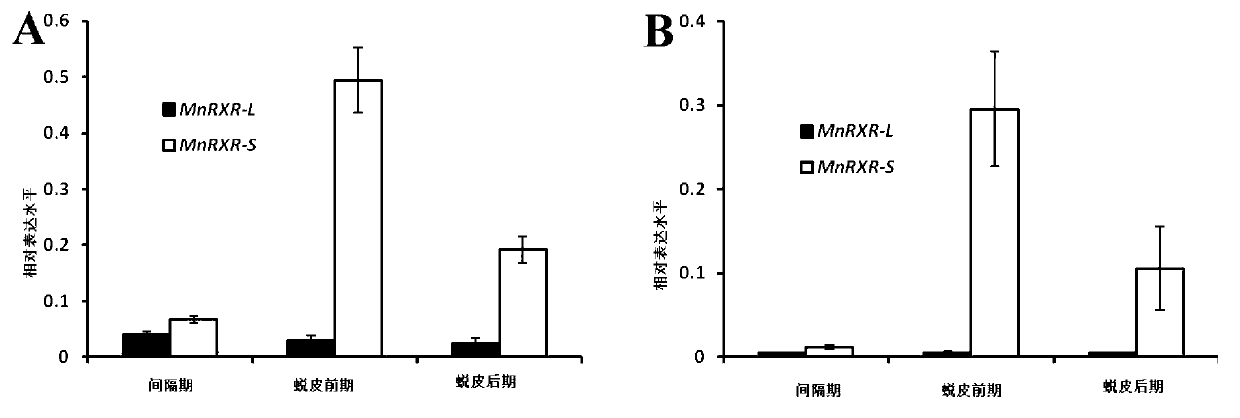
MnRXR gene of macrobrachium nipponensis, and amplification primer group and amplification method thereof
The invention discloses a MnRXR gene of macrobrachium nipponensis, and an amplification primer group and an amplification method thereof. A full-length cDAN sequence of the MnRXR gene is cloned from the hepatopancreas tissue of macrobrachium nipponensis. The gene comprises two variable spliceosomes: MnRXR-L and MnRXR-S. The invention lays an important base for research on functions of the MnRXR gene of macrobrachium nipponensis, in particularon important effects in a moult cycle.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Microsatellite marker applied to growth trait analysis of Macrobrachium nipponense and application thereof
ActiveCN106350606AAmplification results are stableMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMicrosatelliteGenetics
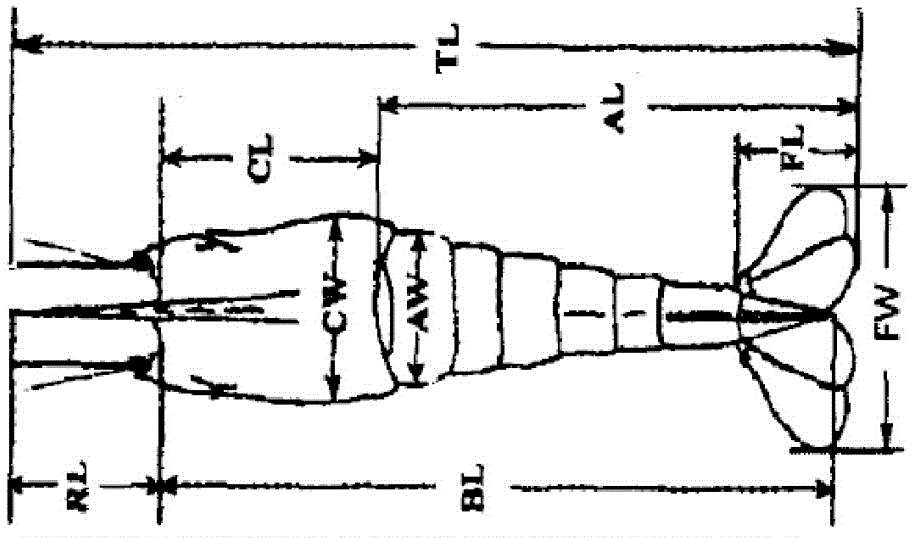
The invention discloses a microsatellite marker applied to growth trait analysis of Macrobrachium nipponense. The microsatellite marker comprises a microsatellite marker GL01 and a microsatellite marker GL02, wherein the microsatellite marker GL01 is correlated with a rostrum length trait; the microsatellite marker GL02 is correlated with a tail fan length trait, a second walking leg length trait and a second walking leg length knuckle trait; the nucleotide sequence of an upstream primer of the microsatellite marker GL01 is shown as SEQ ID NO:1; the nucleotide sequence of a downstream primer of the microsatellite marker GL01 is shown as SEQ ID NO:2; the nucleotide sequence of an upstream primer of the microsatellite marker GL02 is shown as SEQ ID NO:3; the nucleotide sequence of a downstream primer of the microsatellite marker GL02 is shown as SEQ ID NO:4. Meanwhile, the invention further discloses an application of the microsatellite marker to growth trait analysis of the Macrobrachium nipponense. The primers of the microsatellite marker have the characteristic of stable PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification result, and the microsatellite markers can be applied to growth trait analysis of the Macrobrachium nipponense and can be used for assisting in molecular marker breeding of the Macrobrachium nipponense.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY
Chinese-western compound pharmaceutical composition for treatment of bacterial gill-rot disease in Macrobrachium nipponense
InactiveCN103417746AEffective treatmentLow toxicityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseMedicine
The invention discloses Chinese-western compound pharmaceutical composition for the treatment of bacterial gill-rot disease in Macrobrachium nipponense. The composition is characterized by comprising, by weight, 25-40 parts of Chinese rhubarb, 15-25 parts of indigowoad leaf, 10-20 parts of gallnut, 10-20 parts of baical skullcap root, 10-20 parts of corktree bark, 5-10 parts of coptis root, and 5-10 parts of Enrofloxacin powder. The effective content of the Enrofloxacin powder is 10%. The composition has the advantages that body immunity and bacterial infection resistance in Macrobrachium nipponense can be improved; bacterial gill-rot disease in Macrobrachium nipponense can be effectively treated with the composition; a preparation method of the composition is simple; the composition is safe and convenient to use, low in applicant cost, and suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:YANCHENG INST OF TECH
Bionic water grass
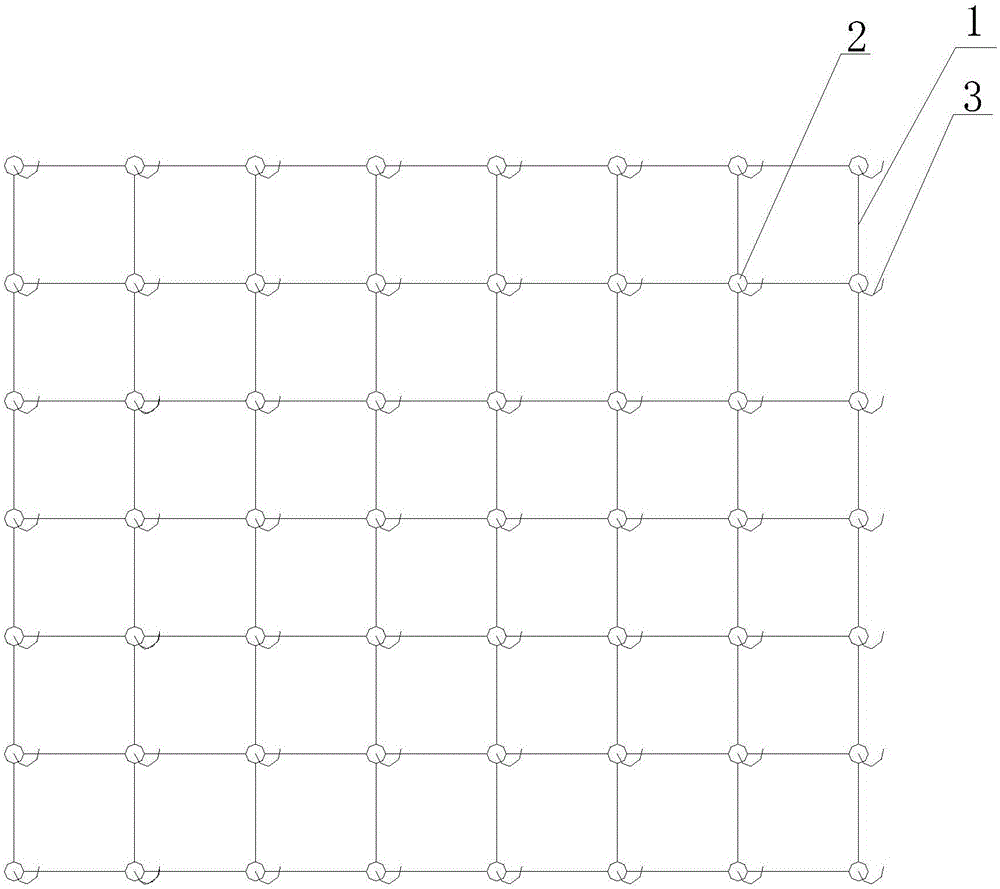
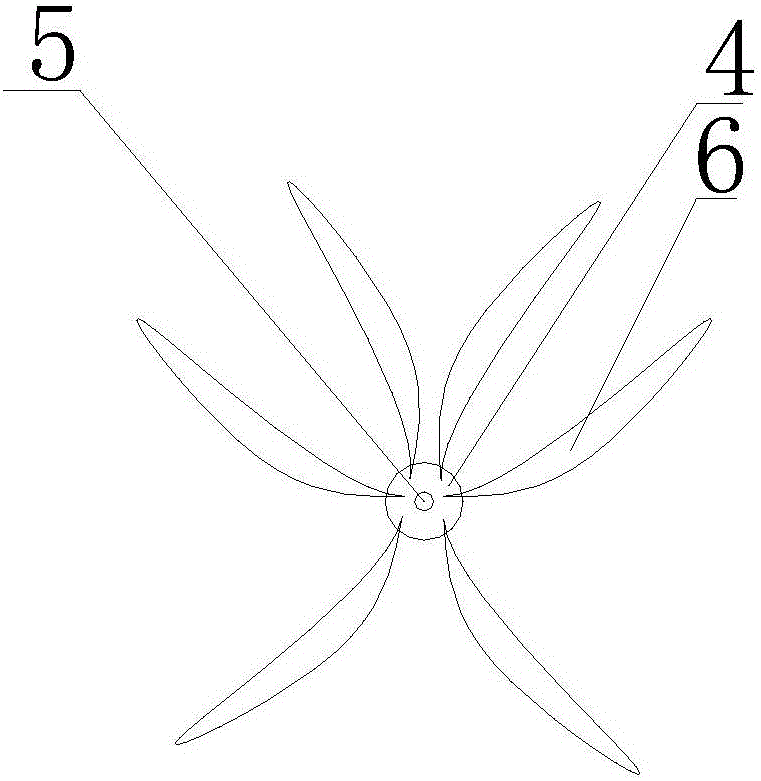
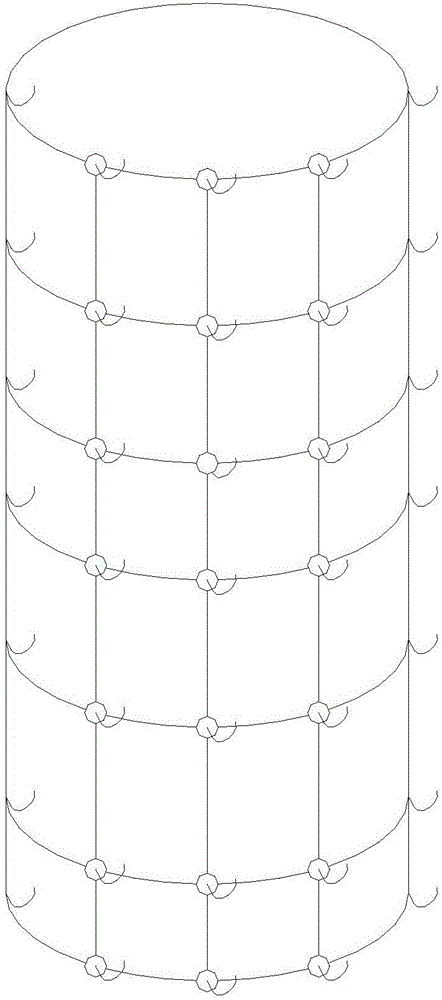
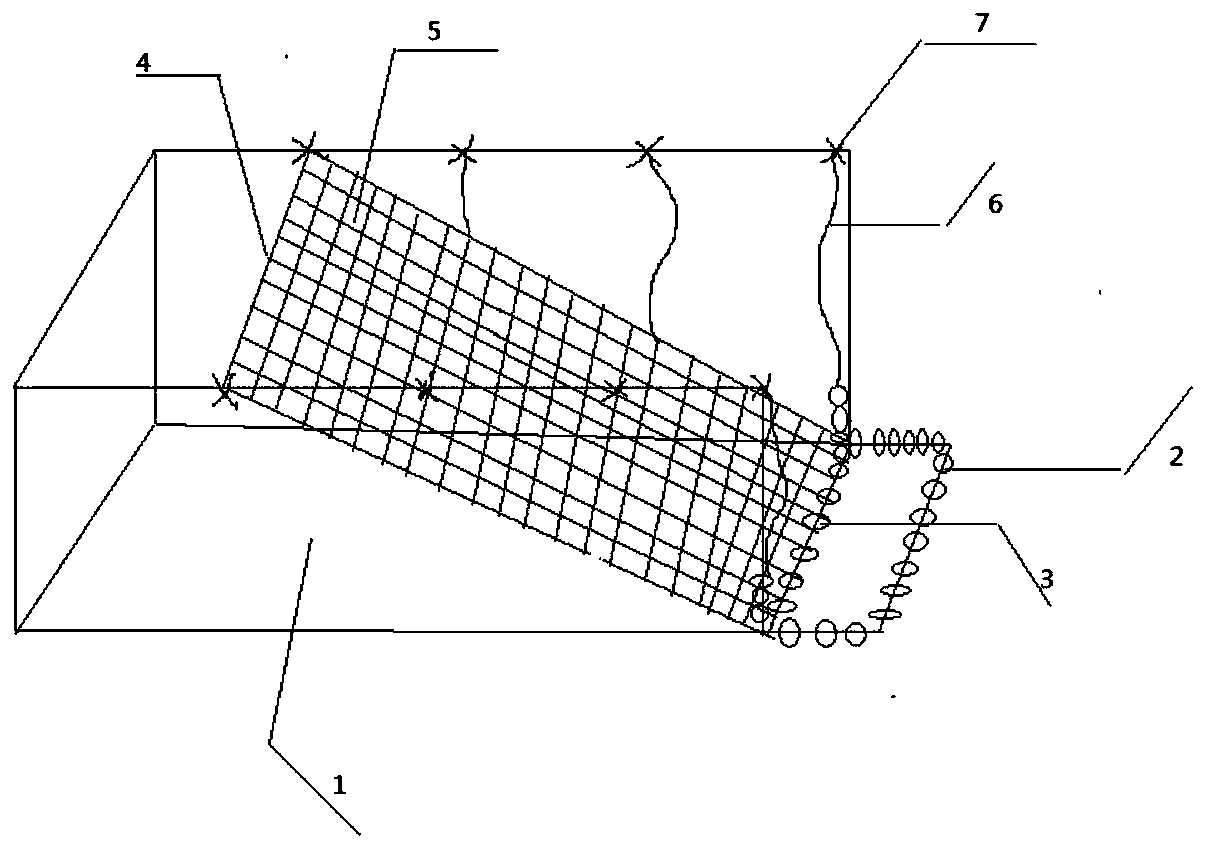
ActiveCN105766733AEasy to clean and disinfectAvoid stressClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaPrawnEngineering
The invention provides an artificial sheltering bionic water grass for increasing the breeding rate of macrobrachium nipponense. A main body of the bionic water grass is formed by combining grid structures, bases are arranged at four corners of each grid structure, hooks are further arranged on the bases, the adjacent grid structures are connected through the hooks and the bases, and the main body is further connected with bionic grass bundles through the hooks. The bionic water grass adopting the structure can allow the macrobrachium nipponense to avoid predators and to settle and inhabit at all stages, the survival rate of parents, larvae and postlarva of the macrobrachium nipponense in all periods and at all stages can be increased, the final breeding rate of the macrobrachium nipponense is further increased, and accordingly, the actual yield of young shrimps during artificial breeding is increased. Besides, the bionic water grass further can be used for artificial breeding of commercial prawns, the space utilization rate of a water body is increased, the application water range is wide, the feeding amount of the macrobrachium nipponense per unit water body can be increased, and the yield is further increased.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Macrobrachium nipponensis indoor feeding and breeding method
ActiveCN104737948AGuaranteed long-term survivalGuaranteed normal reproductionClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaPrawnShrimp culture
The invention discloses a macrobrachium nipponensis indoor feeding and breeding method. The method includes the following steps: constructing a simulation ecological system, placing macrobrachium nipponensis into the simulation ecological system, feeding the macrobrachium nipponensis one time each day, and changing water one time every one week; selecting berried shrimps from the macrobrachium nipponensis to serve as parent shrimps which are placed into cultivation jars to be fed, and placing one berried shrimp into each jar; after larvae break away from the parent shrimps, placing the parent shrimps back into the simulation ecological system to be fed continuously, and placing the larvae into juvenile prawn cultivation jars for cultivation; after the zoaea larvae are just hatched, feeding the zoaea larvae two times each day, and feeding the zoaea larvae one time after the zoaea larvae get into the larva stage. According to the macrobrachium nipponensis indoor feeding and breeding method, the operability is high, frequent water changing and manual management are not needed, it can be guaranteed that the macrobrachium nipponensis can live and conduct breeding in a room for a long time, and a guarantee is provided for the smooth development of medicine environment safety assessment.
Owner:HUNAN PLANT PROTECTION INST
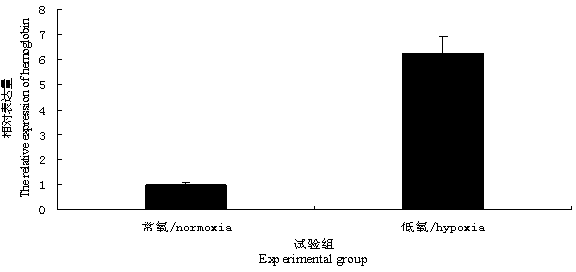
Hemoglobin gene of macrobrachium nipponensis, cloning method of hemoglobin gene, and preparation method of recombinant protein
InactiveCN104073501AOxygen-carrying functionImprove antibacterial propertiesAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsOpen reading frameMacrobrachium nipponense
The invention discloses hemoglobin gene of macrobrachium nipponensis, a clone method of the hemoglobin gene, and a preparation method of recombinant protein. The hemoglobin gene of macrobrachium nipponensis is cloned through an expressed sequence tag technology and 3'and 5' rapid amplification cDNA end (RACE), wherein the overall length of the cDNA is 1201bp, the gene has a 579bp open reading frame and encodes 193 amino acids, 5' noncoding region is 199bp and 3' noncoding region is 420bp, and the gene has polyadenylic acid tailing signal and polyadenylic acid tail. The gene plays an important role in immune defense of macrobrachium nipponensis. The hemoglobin gene of macrobrachium nipponensis is obtained by in vitro recombination expression; the recombinant protein not only can carry oxygen, but also has bacteriostasis, thereby providing theoretical basis for disease control and gene-assisted breeding of macrobrachium nipponensis,and development of feed additives for macrobrachium nipponensis.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
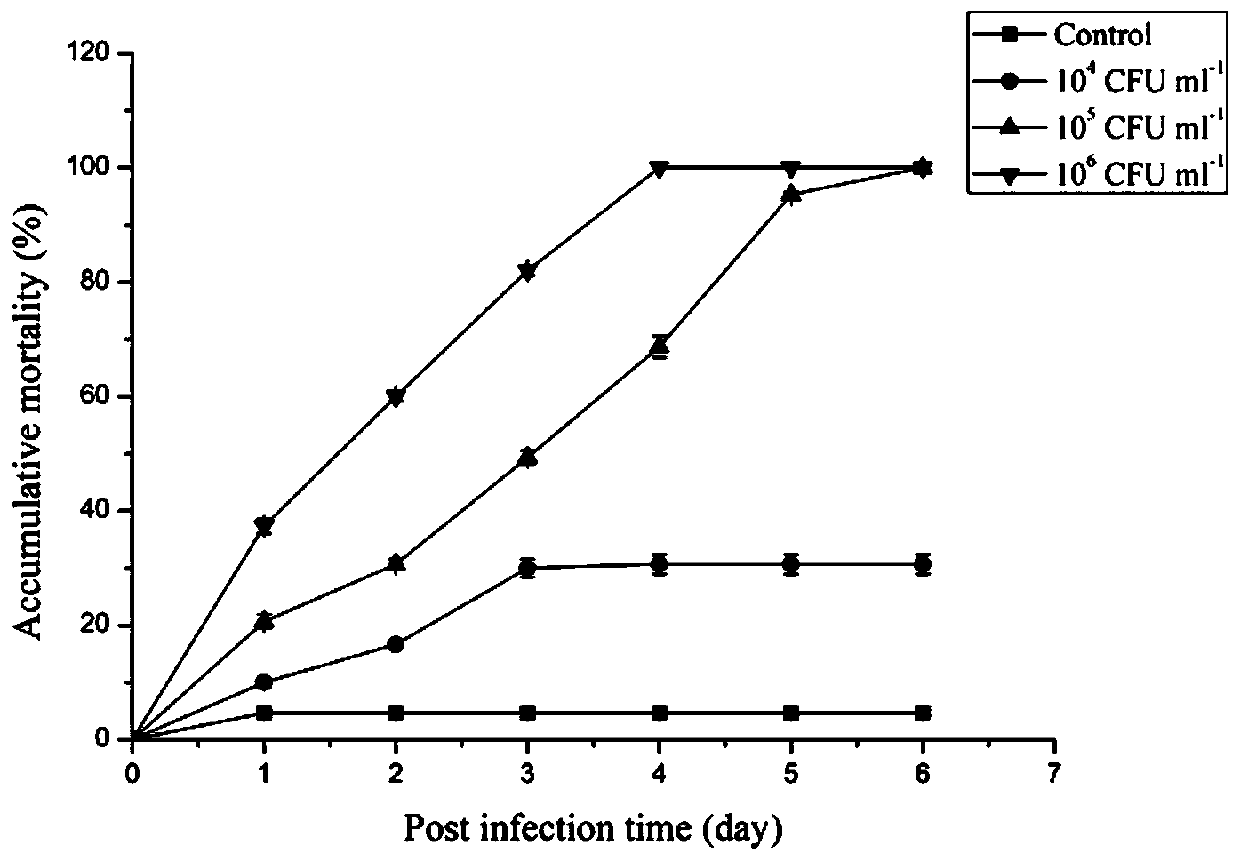
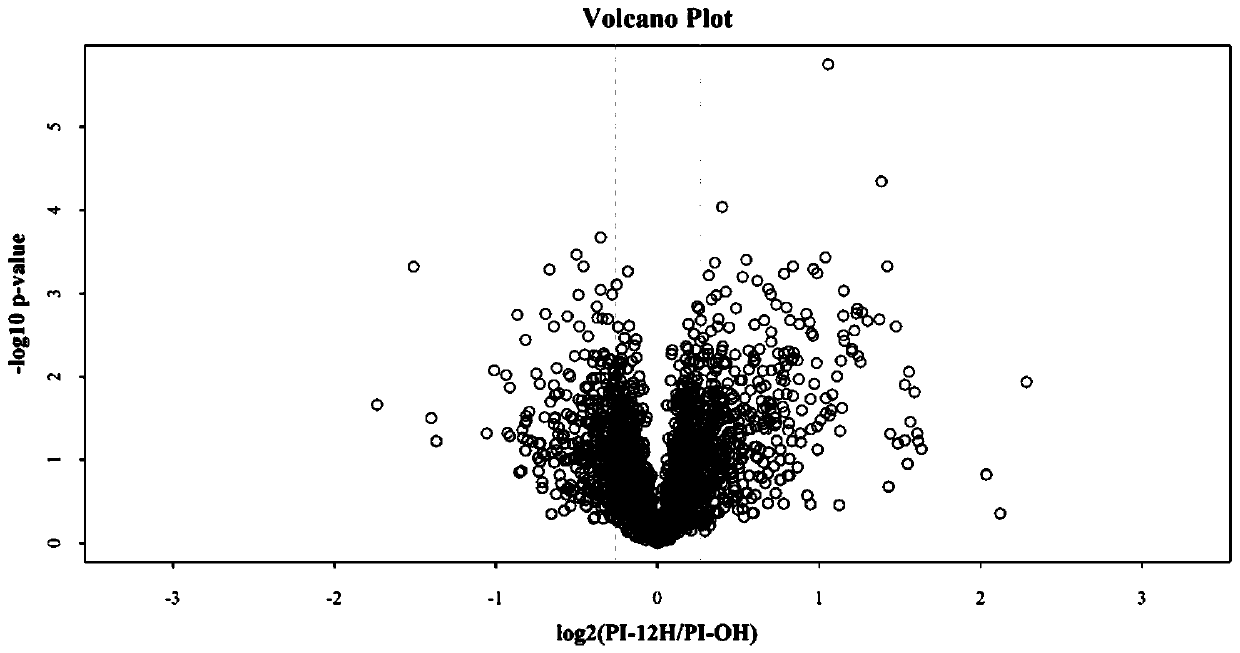
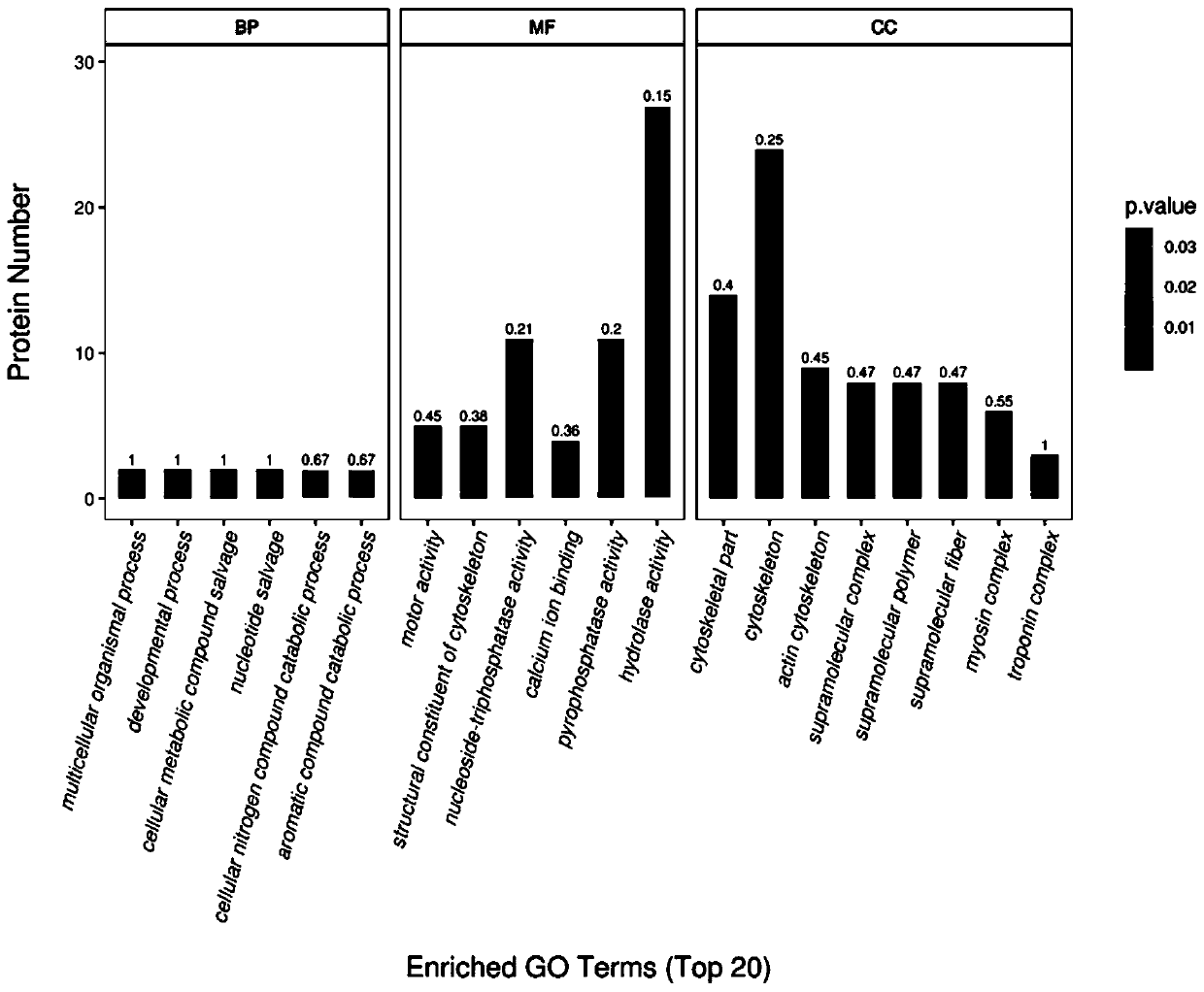
Method for analyzing aeromonas hydrophila infected macrobrachium nipponense blood cell differential expression protein based on proteomics quantitative technology
ActiveCN111272889AEnrich protein dataComponent separationBiological testingSAA proteinChromatographic separation
The invention belongs to the technical field of freshwater aquaculture, and relates to a method for analyzing aeromonas hydrophila infected macrobrachium nipponense hemocyte differential expression protein based on a proteomics quantitative technology. The method comprises the following steps of (1) extracting the hemolymph of macrobrachium nipponense infected with aeromonas hydrophila, separatingthe blood cells, and cracking the cells to extract protein; (2) carrying out trypsin enzymolysis on the protein obtained in the step (2), and carrying out iTRAQ labeling on an enzymolysis peptide fragment; (3) carrying out purification, liquid chromatographic separation and mass spectrometric analysis on the peptide fragment marked in the step (3); and (4) carrying out protein identification, quantitative analysis and bioinformatics analysis on the mass spectrum analysis result obtained in the step (3), and analyzing to obtain differentially expressed protein. The invention is based on the rapid proteomics research of the infected macrobrachium nipponense by iTRAQ, and provides a reference for further researching the effect of immune-related proteins.
Owner:JINING UNIV
Net cage and method for rapidly separating parents and seeds of macrobrachium nipponense
PendingCN109937944AEasy to separateRapid lesion dissectionPisciculture and aquariaMacrobrachium nipponenseFishing
The invention discloses a net cage and a method for rapidly separating parents and seeds of macrobrachium nipponense. The net cage comprises a seed collection net cage, and a quadrilateral parent collection net cage arranged in the seed collection net cage. The four sides of the parent collection net cage intersect with four surfaces of the seed collection net cage, and the parent collection net cage is movably connected with the seed collection net cage. The net cage and the method have the advantages that rapid low-damage separation of the parents and the seeds of the macrobrachium nipponense can be realized in a seed fishing process of the macrobrachium nipponense in summer, and the re-capture rate of the parents can reach more than 90%; the separated parents can be used for centralizedbreeding again or can be sold on the market, and accordingly, the breeding benefits of the macrobrachium nipponense are increased.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Metabolism regulating and body detoxification promoting feather hydrolyzed powder feed for macrobrachium nipponense culture and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106721586AImprove conversion rateImprove palatabilityFood processingClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyFeed conversion ratio
The present invention discloses a metabolism regulating and body detoxification promoting feather hydrolyzed powder feed for macrobrachium nipponense culture and a preparation method thereof. The feed can regulate the metabolism of the macrobrachium nipponense, accelerate the discharge of the harmful waste, promote the detoxification of toxins, inhibit and reduce the toxicity of heavy metal ions, improve the nutrition of the macrobrachium nipponense meat, promote the digestion and utilization of the macrobrachium nipponense to nutrients, improve feed conversion rate, improve immune function, reduce morbidity and improve gastrointestinal health.
Owner:汪敏节
Medicine, feed and method for preventing fighting and self-disability of cultured macrobrachium nipponense
PendingCN112056457AImprove survival rateAvoid enteringOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemBiotechnologyTryptophan
The present invention provides a medicine, a feed and a method for preventing fighting and self-disability of cultured macrobrachium nipponense. 0.5%-1% by mass of the medicine is added into a basic daily ration, and feeding is conducted twice everyday in the morning and evening; residual baits are fished out 1 hour after the feeding; in cloudy and rainy days, feeding is conducted once or not; avoiding pipes are arranged at positions, where no grass is planted, in breeding areas and the three-dimensional avoiding positions are provided for the macrobrachium nipponense; and the medicine comprises 30-40 g of spina date seeds, 30-40 g of platycladi seeds, 8-20 g of L-tryptophan, 2-5 g of dimethyl-beta-propiothetin (DMPT), 2-5 g of plant essential oil and 0.5-1.0 g of ferulic acid. The methodrelieves fighting and self-disability states of the macrobrachium nipponense, improves a survival rate of the macrobrachium nipponense in a breeding process, and is easy and convenient to operate andlow in cost.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
GEM gene of Macrobrachium nipponense and encoding protein and application thereof
ActiveCN109207482ASignificant economySignificant application prospectsFermentationGenetic engineeringShrimpFull length cdna
A GEM gene of Macrobrachium nipponense and an encoding protein and application thereof are disclosed. That full-length cDNA sequence of the GEM gene is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. A protein encoded by theGEM gene of Macrobrachium nipponense has an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 2. As compared with that prior art, the gene has the following advantage: (1) the important role of the GEM gene ofthe green shrimp in the male differentiation and development process of the green shrimp provides a theoretical basis and a train of thought for the research on the male differentiation and the development mechanism of the green shrimp; 2) that Macrobrachium nipponense GEM gene of the invention can regulate the immune response mechanism of the Macrobrachium nipponense; 3) that Macrobrachium nipponense GEM gene of the invention can be use in the selection and breeding of an all-male population of Macrobrachium nipponense, and has remarkable economic value and application prospect in the procesof culturing Macrobrachium nipponense.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Feed additive capable of improving antioxidant function and reproductive performance of macrobrachium nipponensis
InactiveCN109645258AEnhance antioxidant functionImprove antioxidant capacityClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffYolkDisease
The invention relates to a feed additive capable of improving the antioxidant function and reproductive performance of macrobrachium nipponensis. The feed additive is prepared from, by weight, 15-27 parts of radix isatidis, 17-25 parts of astragalus polysaccharides, 4-8 parts of flos lonicerae, 4-8 parts of fructus rosae laevigatae, 4-13 parts of radix et rhizoma rhei, 8-15 parts of rhizoma calami, 7-15 parts of shrimp shell meal, 4-9 parts of shell powder and 16-22 parts of yolk immunoglobulin. The feed additive has the advantages that 2-8% of the feed additive is stirred in basic feed of which the protein content is 37.4%, when the water temperature rises to 10 DEG C in March, feeding is started, feeding is carried out twice each day, continuous feeding is carried out for 1 month, thereby being capable of not only improving the growth speed of macrobrachium nipponensis and the antioxidant function of the hepatopancreas, but also promoting the development of the ovary of female shrimps; the problems that a macrobrachium nipponensis female parent is slow in growth speed, low in disease resistance and slow in ovary development in the traditional macrobrachium nipponensis breeding process are solved, the additive amount is low, and the preparation method is simple.
Owner:YANCHENG INST OF TECH
Feed for improving the of Macrobrachium nipponense and a production method of feed
InactiveCN104905071AMeet the nutritional needs of growthImprove survival rateAnimal feeding stuffAnimal scienceFish oil
The invention provides a feed for improving the yield of Macrobrachium nipponense and a production method of the feed. The feed comprises the following raw materials in part by weight: 40-50 parts of bone meal, 10-12 parts of soybean meal, 5-8 parts of blood powder, 1-5 parts of rice bran, 1-5 parts of wheat flour, 2-5 parts of beer yeast, 1-2 parts of soybean oil, 0.5-1 part of calcium dihydrogenphosphate, 1-2 parts of peanut meal, 2-3 parts of phosphatide oil, 0.5-1 part of vitamins, 1-2 parts of fish oil, 1-2 parts of shell powder, 2-6 parts of silkworm pupa and 0.5-1 part of organic trace elements premix. The feed is good in palatability and easy to digest and absorb, can promote the growth of fish and shrimps, and can improve the immunity.
Owner:SICHUAN GUOFENG ZHONGKE BIOTECH
A kind of method of Macrobrachium japonicus hatching in vitro
InactiveCN101720684BOvercoming Biological DifficultiesFill in research gapsClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaBiological propertyPrawn
The invention relates to a method for in vitro incubation of fertilized eggs of macrobrachium nipponense, which is characterized in that the method comprises the steps of selection of parent shrimps, mating and oviposition, treatment of incubation water, egg stripping, egg washing, incubation, daily management and the like. The method for the in vitro incubation of the fertilized eggs of the macrobrachium nipponense solves the problem of biological characteristics that the fertilized eggs depend on parent bodies to be incubated, lays a foundation for genetic operations of the macrobrachium nipponense such as gene transfer, nuclear transplantation and the like, fills the research gap of the field, and has important practical application value.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Macrobrachium nipponense high-yield culture method
InactiveCN109463331AIncrease dissolved oxygen contentLow densityWater treatment parameter controlClimate change adaptationShrimpOxygen content
The invention discloses a macrobrachium nipponense high-yield culture method. The method comprises the following steps that 1, a pond is built, wherein the area of the pond is 1,500-3,500 m<2>, and the depth is 1-2 m; 2, the pond is disinfected, wherein the pond is cleaned with quick lime, the quick lime dosage is 7.5-20 kg / 100 m<2>, after cleaning and drying, exposure to the sun is conducted for20-30 days to use, water plants are tied into ricks to be laid at the bottom of the pond every 2 m, and water plants are planted around the pond; 3, shrimp fry stocking is conducted, wherein 12,000,000-18,000,000 shrimp fry are subjected to stocking per mu, stocking is conducted in a cloudy day or in the morning, and the stocking time is from February to March in spring and from June to July in summer; 4, feed feeding is conducted, wherein the daily feeding amount is 4-8% of shrimp weight, the feeding location is fixed to the pond side shallows, and feeding is conduced twice daily at 8:00-9:00in the morning and 18:00-19:00 in the evening; 5, water quality management is conducted, wherein the water quality is fresh, dissolved oxygen is high, the transparency is 30 cm or above, probiotics is applied, and pond water environment is improved; an impeller aerator is equipped, and the pond water dissolved oxygen content is kept at 5 mg / L or above. Accordingly, the process is simple, industrialization is easy to achieve, and the method is suitable for application and popularization.
Owner:YANCHENG INST OF TECH
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com