Bionic water grass
A technology of bionic aquatic plants and bionic grasses, applied in the field of bionic aquatic plants in artificial shelters, can solve the problems of difficulty in stably breeding high-quality shrimp seedlings, low reproductive success rate, and low yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
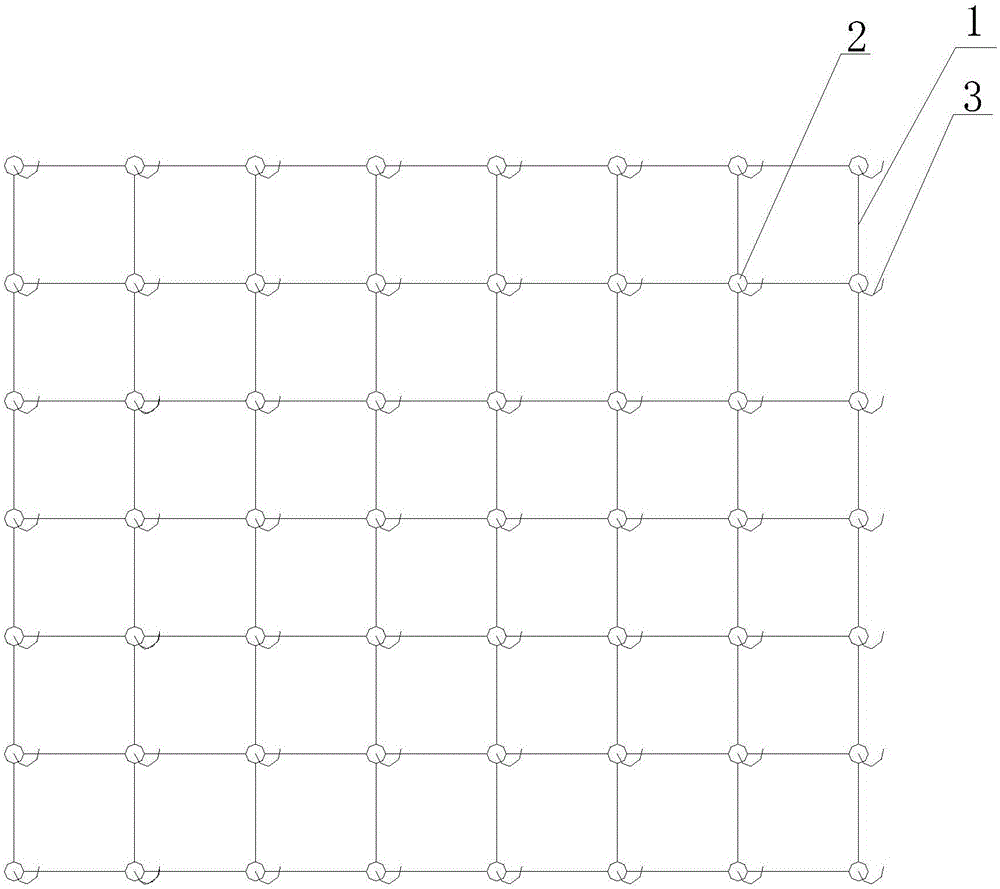
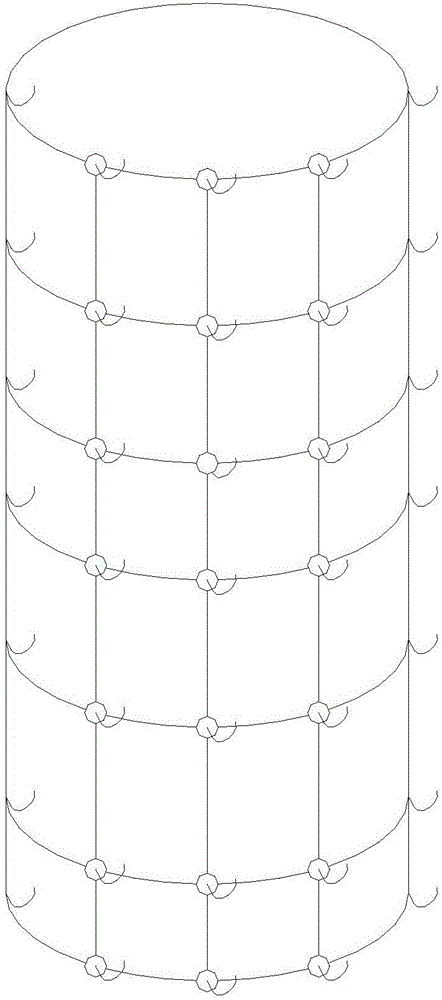
[0020] A bionic aquatic plant, the main body of the bionic aquatic plant is composed of a grid structure 1, the four corners of the grid structure 1 are provided with a base 2, and the base 2 is also provided with a hook 3, and the adjacent nets The grid structure is connected through the base 2, and the bionic grass bundle is also connected to the main body, and the bionic grass bundle is connected to the main body through the hook 3;
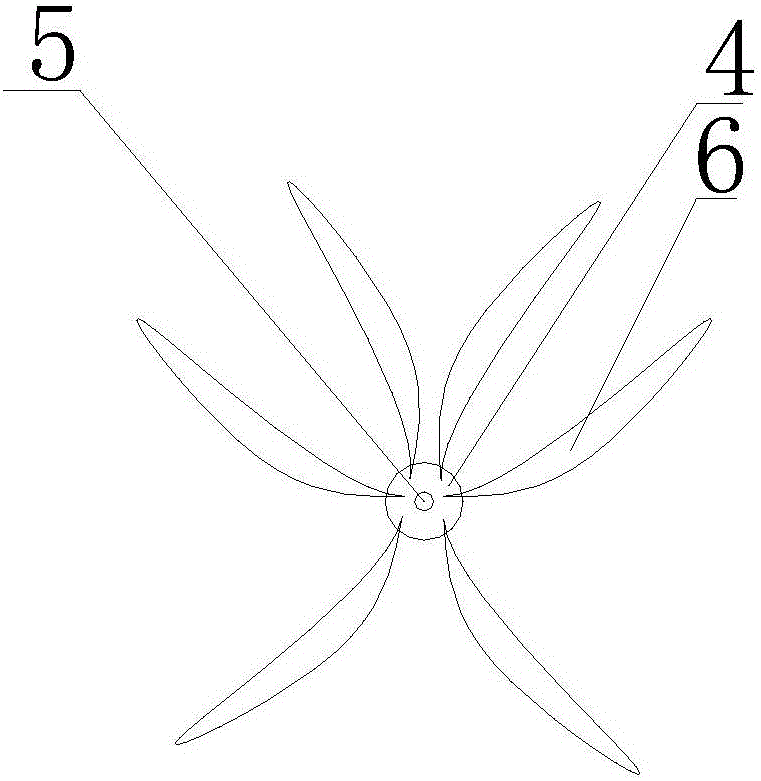
[0021] The biomimetic grass bundle includes a grass blade base 4 on which a bionic grass blade 6 is connected, and a through hole 5 is arranged in the center of the grass blade base 4 .
[0022] Each hook on the main body is connected with bionic grass bundles at intervals.
[0023] The entire bionic aquatic plant is made of non-toxic plastic and is green as a whole.
Embodiment 2
[0025] A bionic aquatic plant, the main body of the bionic aquatic plant is composed of a grid structure 1, the four corners of the grid structure 1 are provided with a base 2, and the base 2 is also provided with a hook 3, and the adjacent nets The grid structure is connected through the base 2, and the bionic grass bundle is also connected to the main body, and the bionic grass bundle is connected to the main body through the hook 3;
[0026] The biomimetic grass bundle includes a grass blade base 4 on which a bionic grass blade 6 is connected, and a through hole 5 is arranged in the center of the grass blade base 4 .
[0027] Each hook on the main body is connected with a bundle of bionic grass.
[0028] The whole bionic aquatic plant is made of non-toxic rubber, and the whole is brown.
Embodiment 3
[0030] A bionic aquatic plant, the main body of the bionic aquatic plant is composed of a grid structure 1, the four corners of the grid structure 1 are provided with a base 2, and the base 2 is also provided with a hook 3, and the adjacent nets The grid structure is connected through the base 2, and the bionic grass bundle is also connected to the main body, and the bionic grass bundle is connected to the main body through the hook 3;
[0031] The biomimetic grass bundle includes a grass blade base 4 on which a bionic grass blade 6 is connected, and a through hole 5 is arranged in the center of the grass blade base 4 .
[0032] Each hook on the main body is connected with bundles of bionic grass at intervals;
[0033] The bottom of the main body is connected with a supporting seat through a hook, so as to keep the whole main body upright in the water.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com