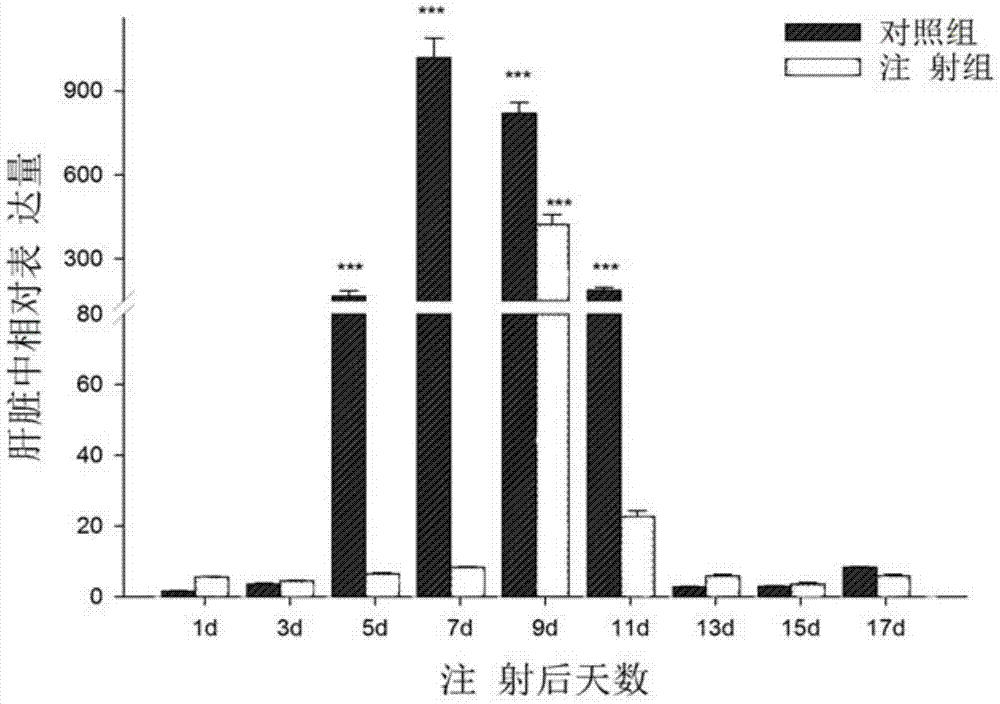
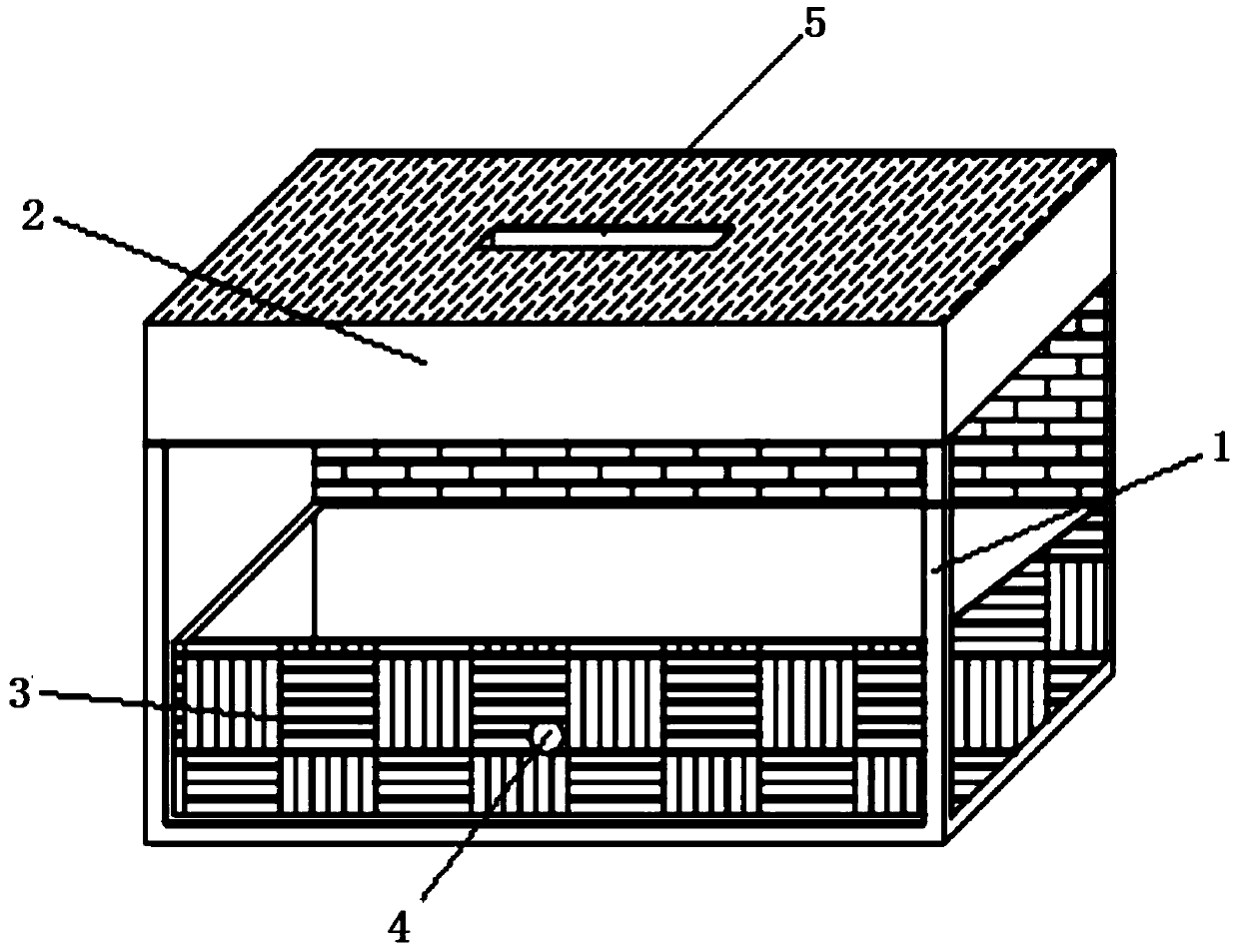
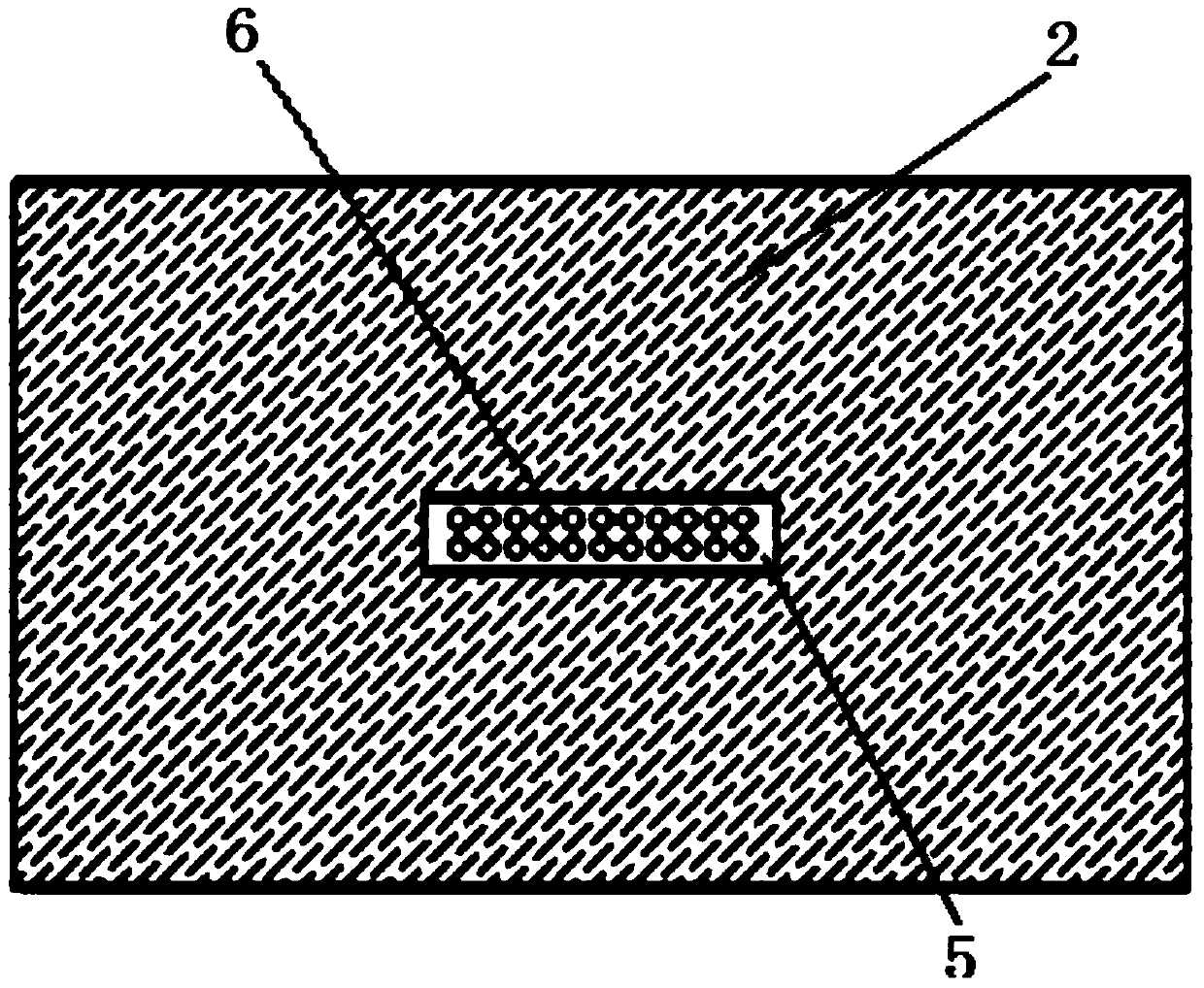
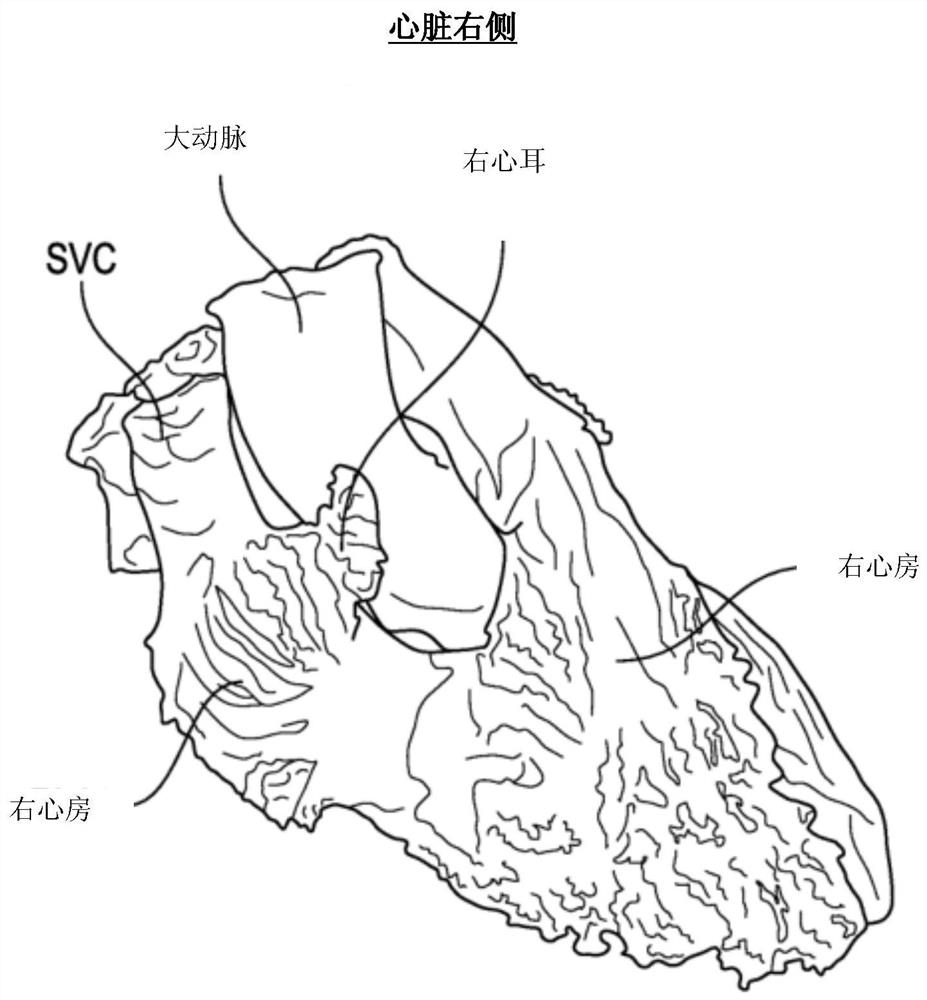
Patents
Literature
56 results about "Pericardial cavity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
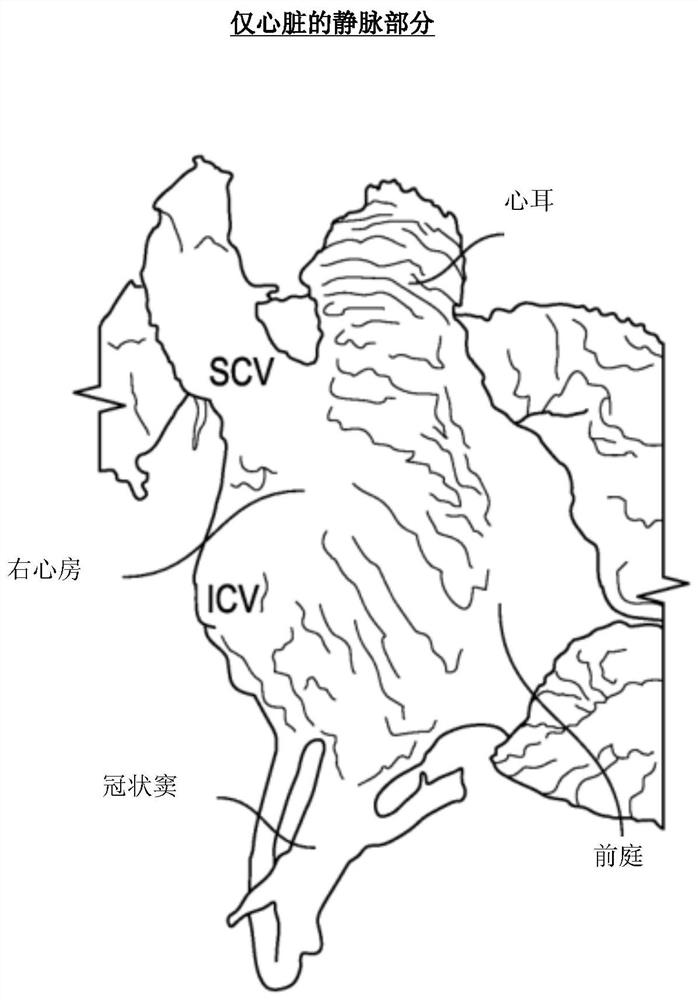
The pericardial cavity is a potential space between the parietal pericardium and visceral layer. It contains a supply of serous fluid. The serous fluid that is found in this space is known as the pericardial fluid.
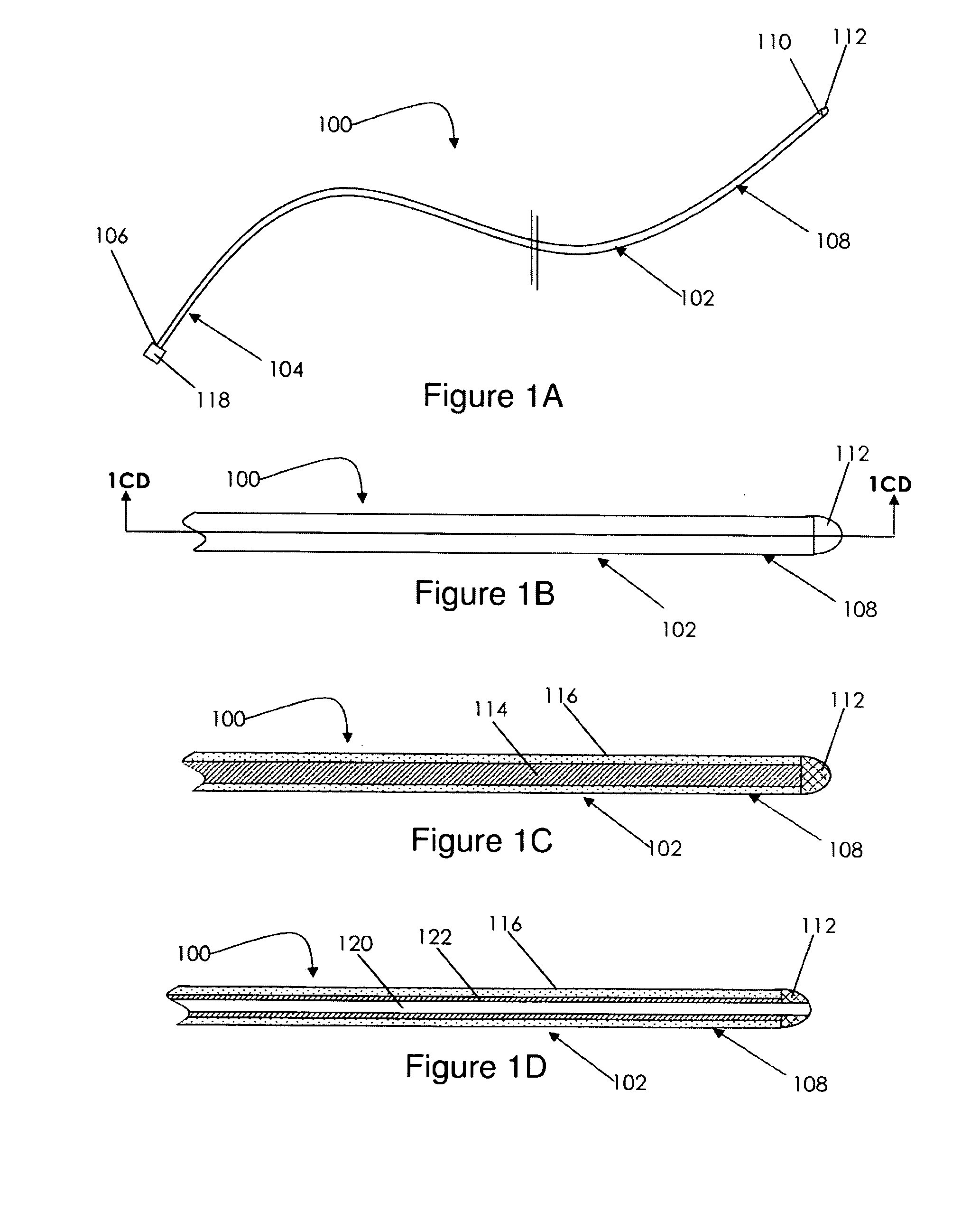
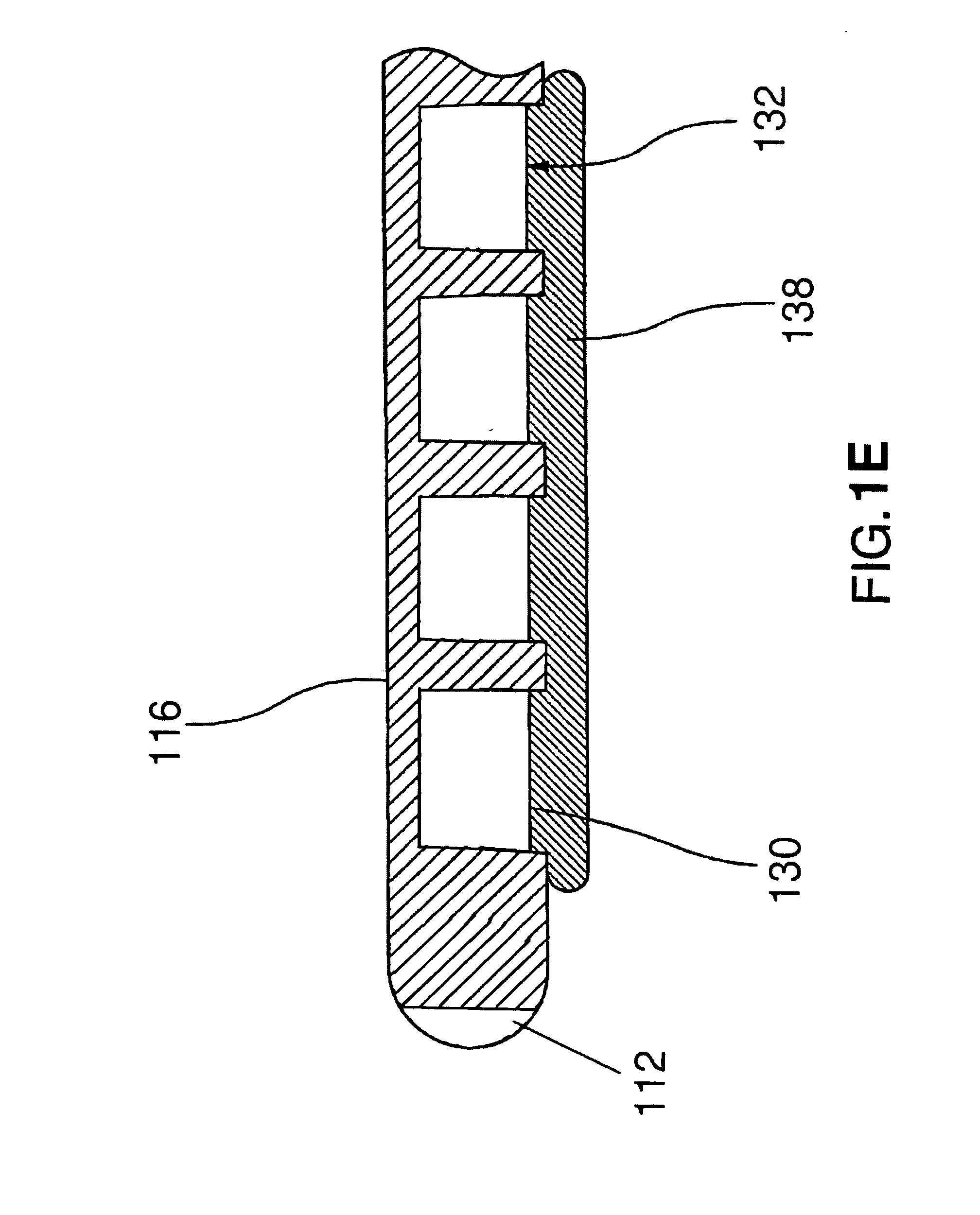
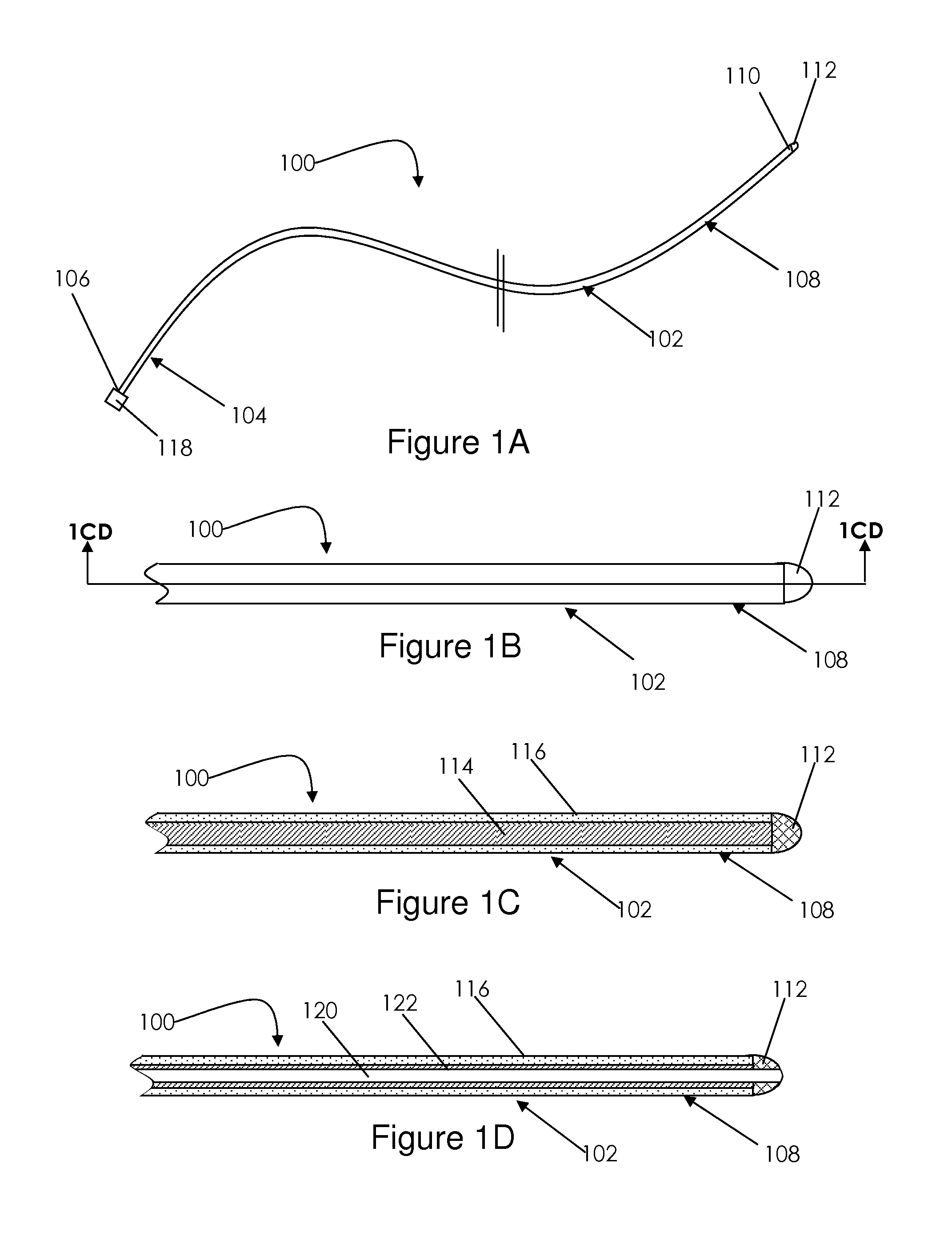
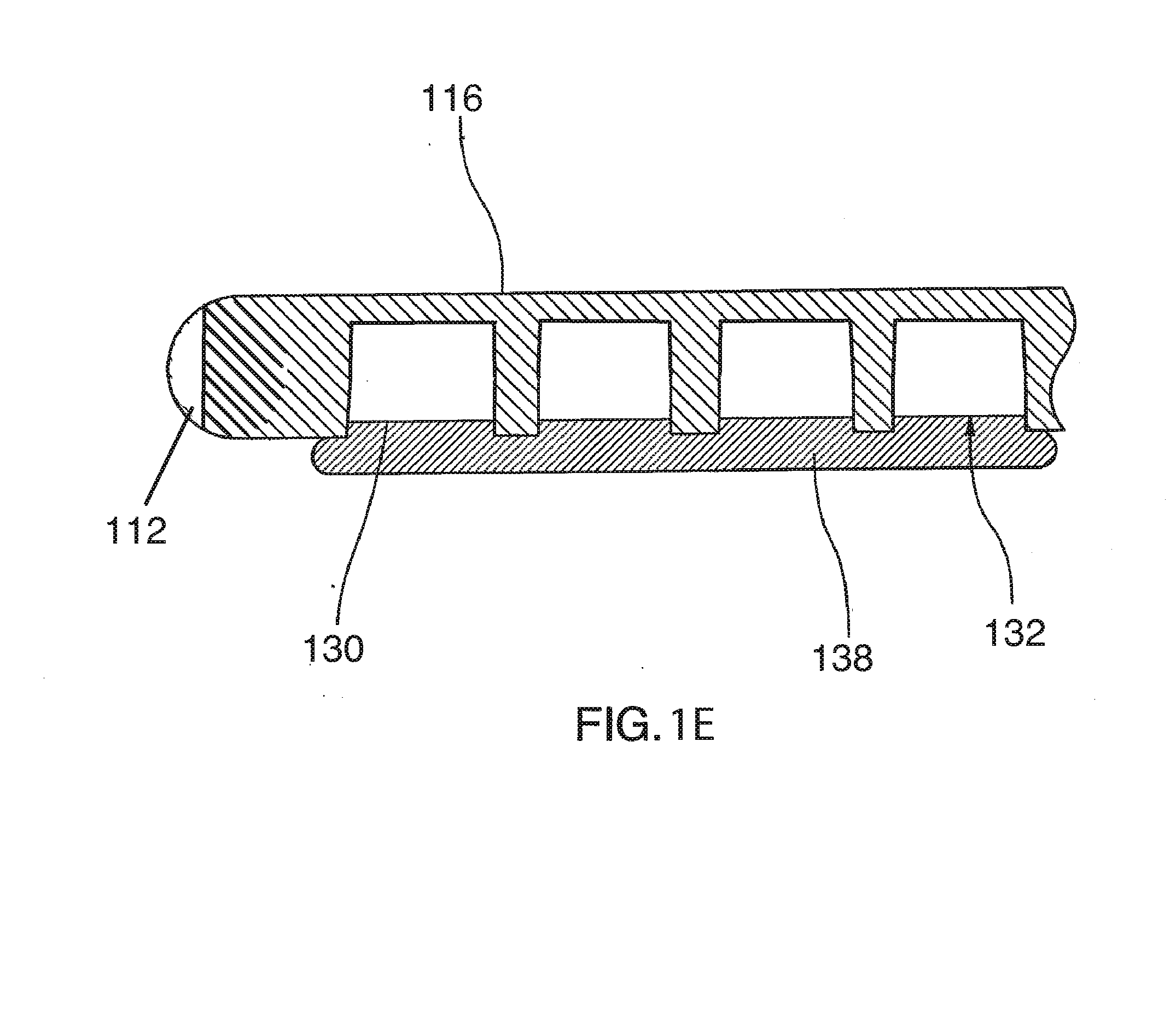
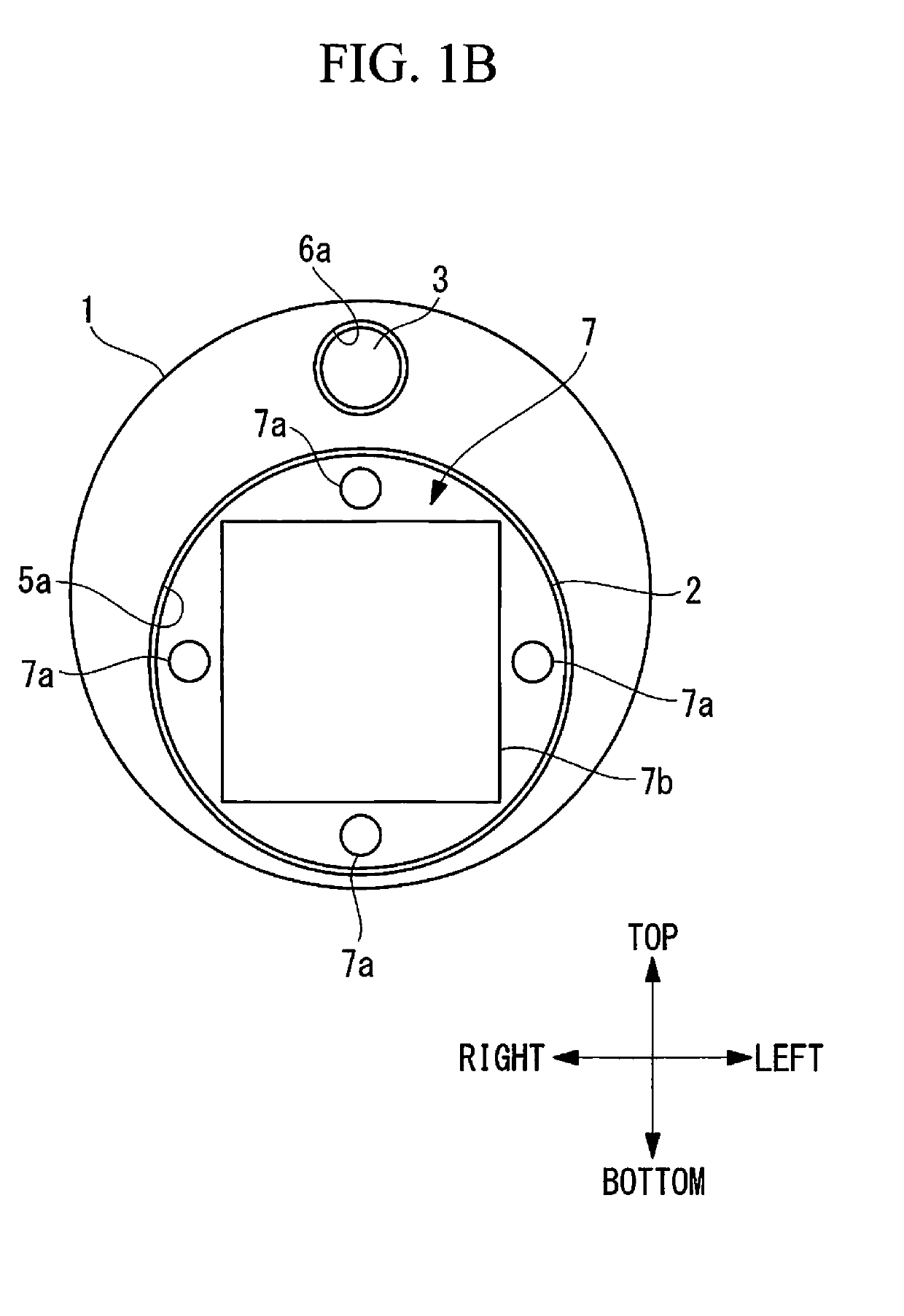
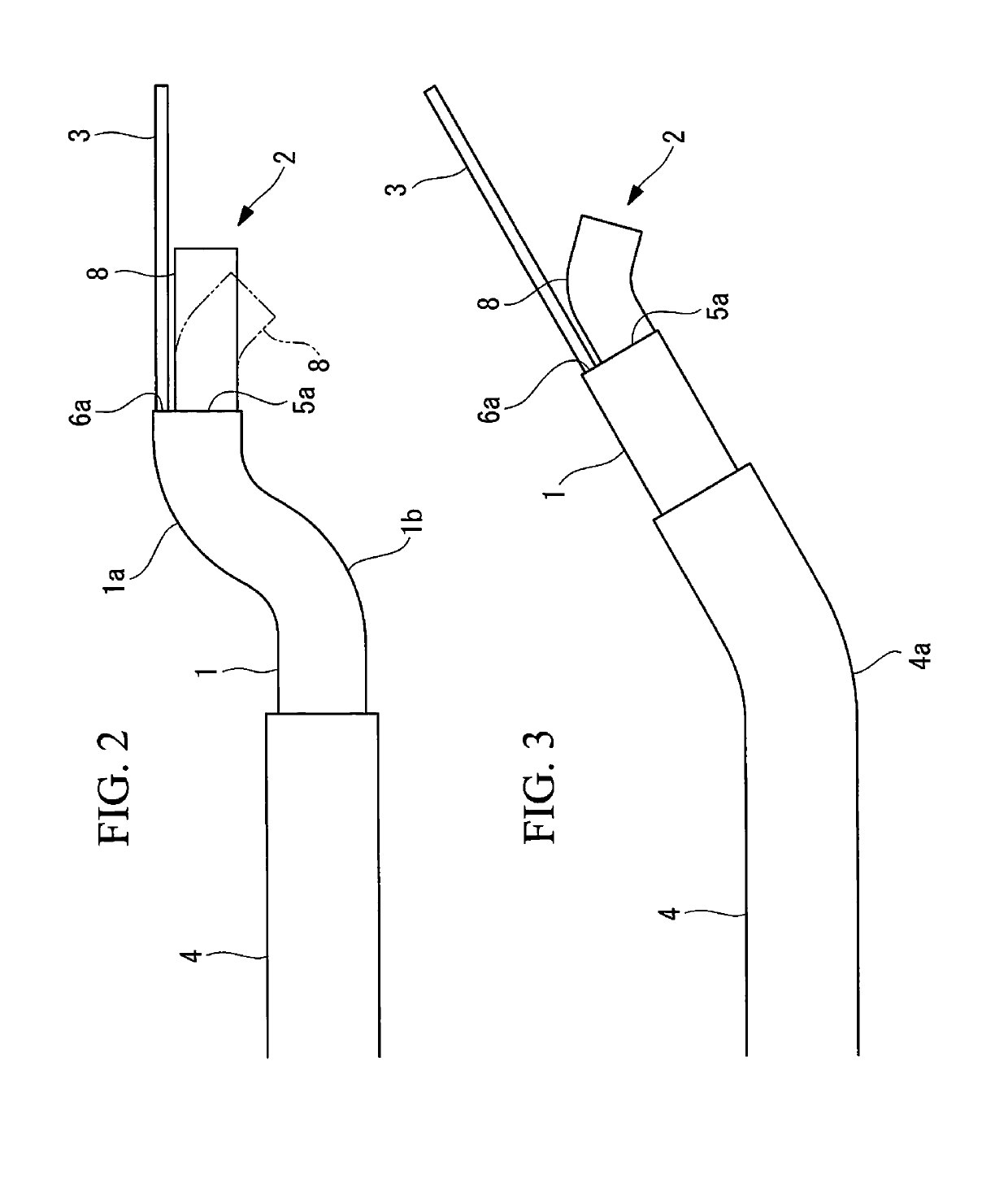
Epicardial mapping and ablation catheter
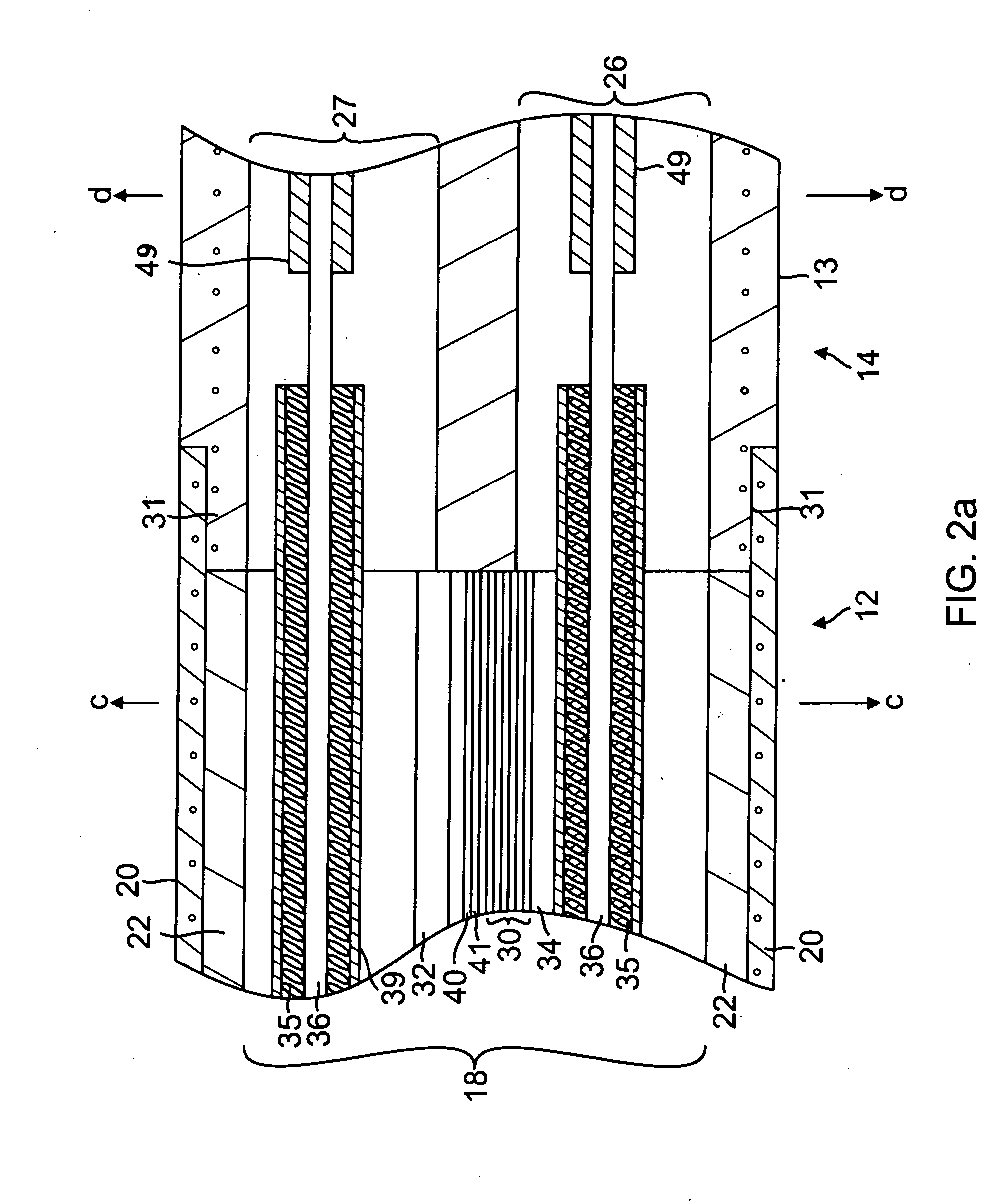
ActiveUS8287532B2Safely maneuverReliable contactBioelectric signal measurementCatheterEpicardial mappingThermocouple Wire
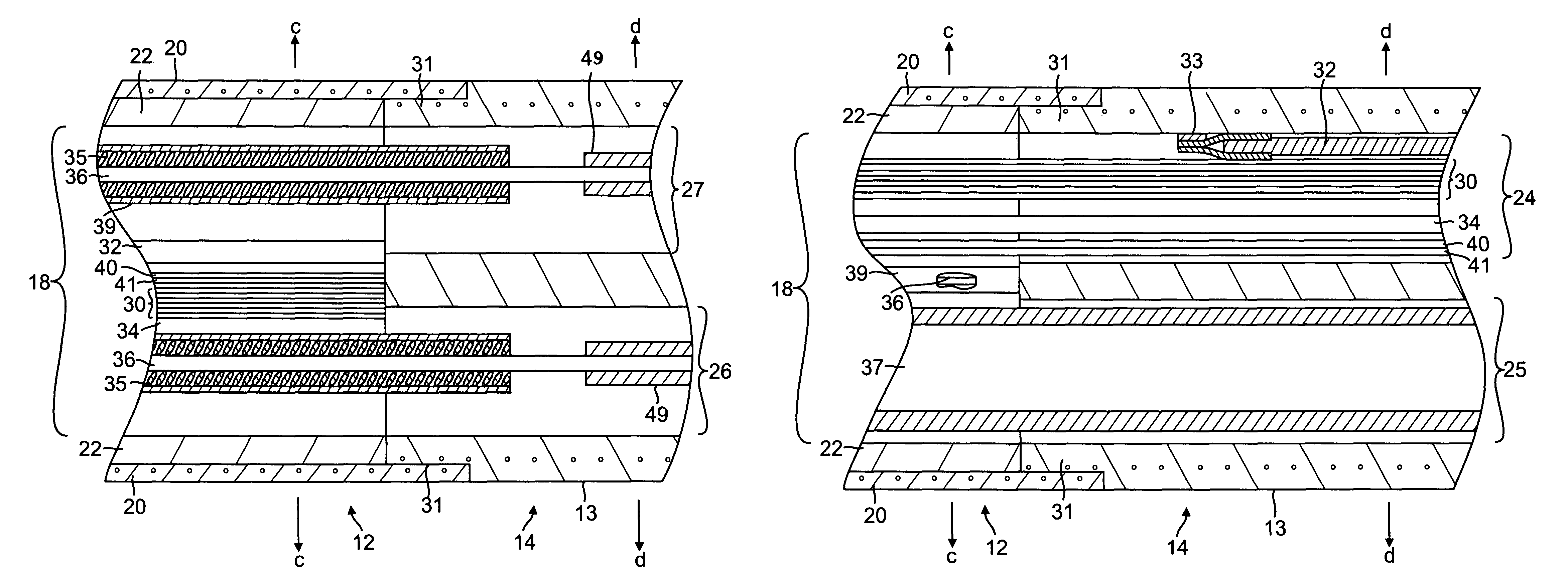
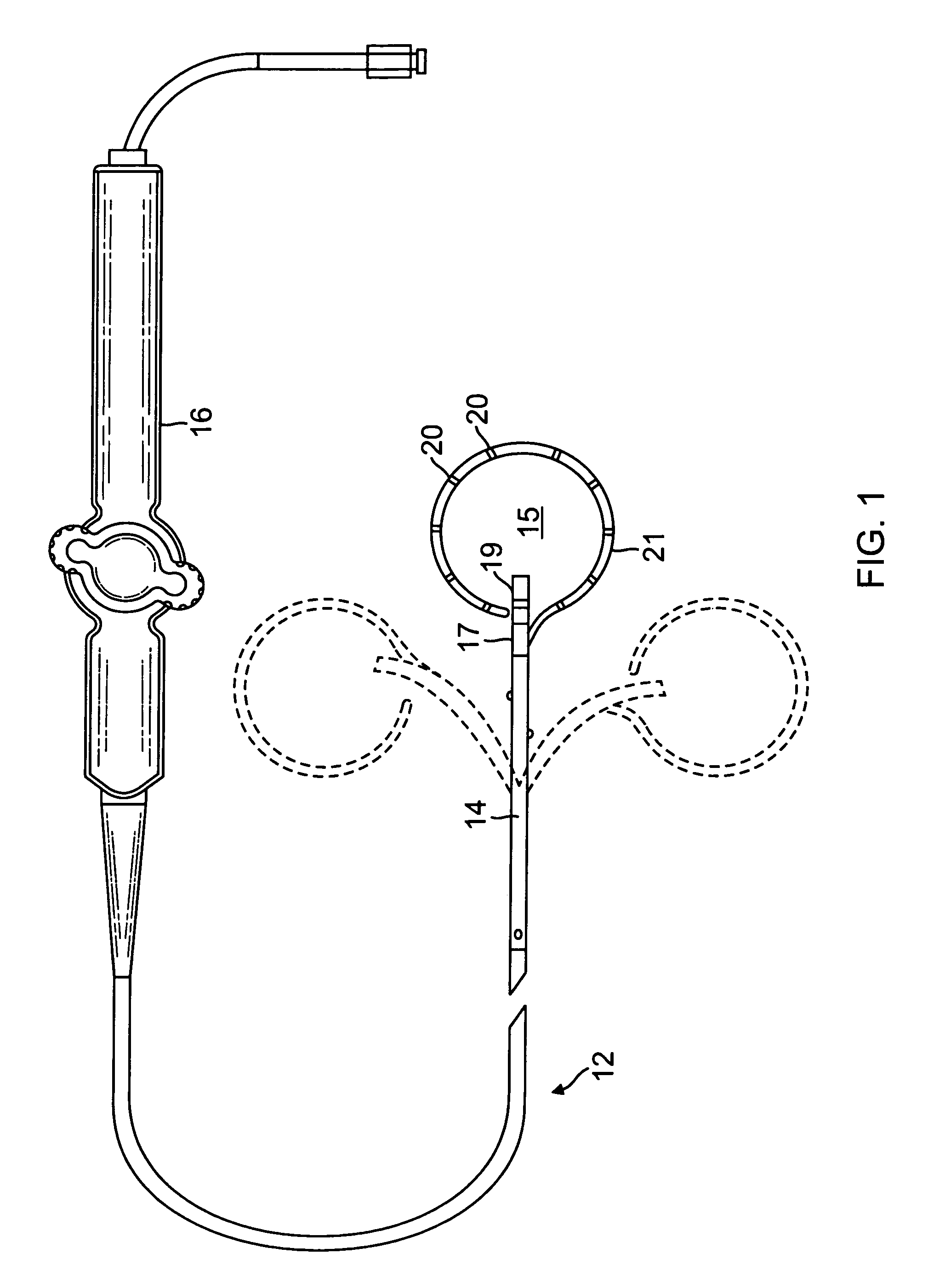
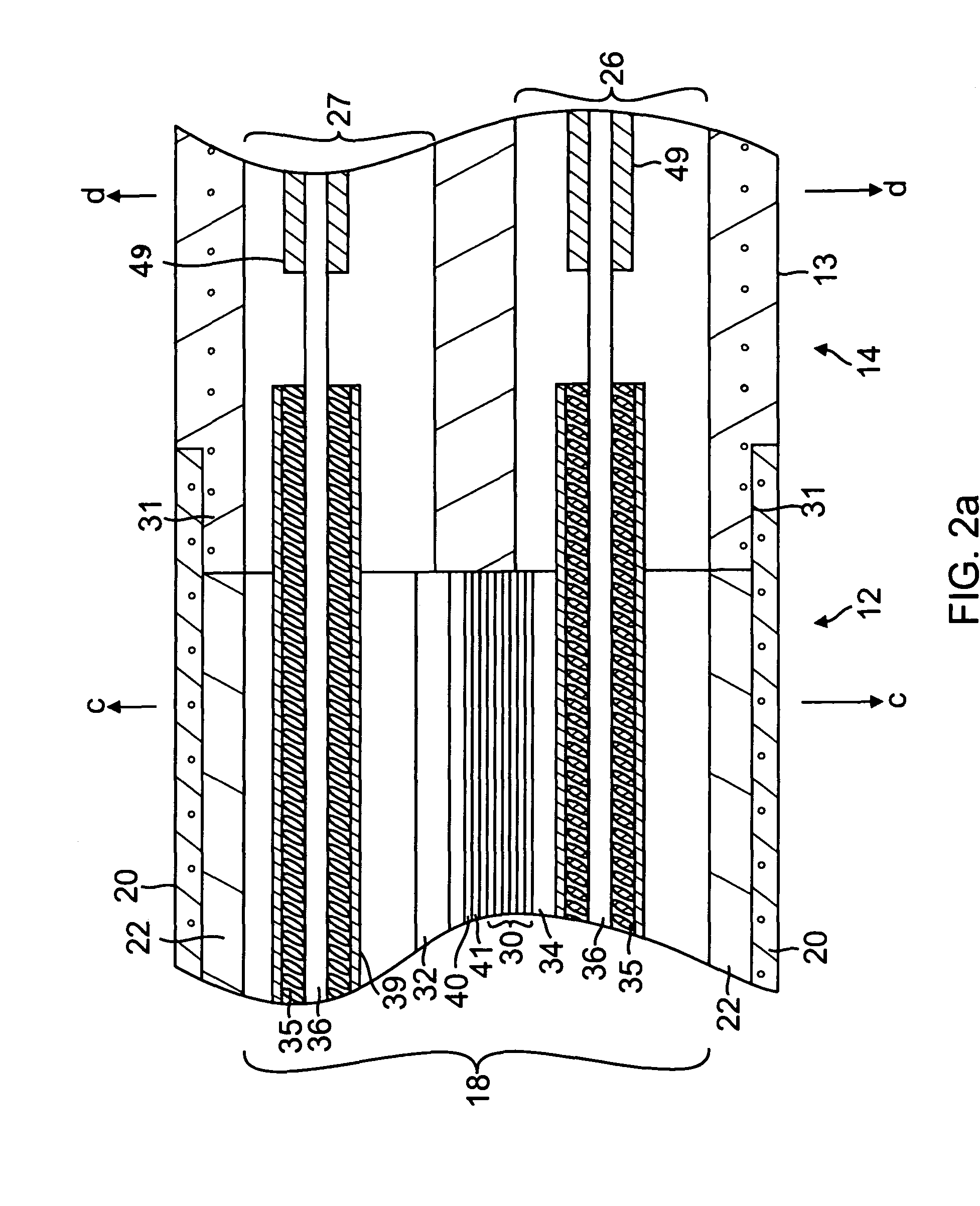
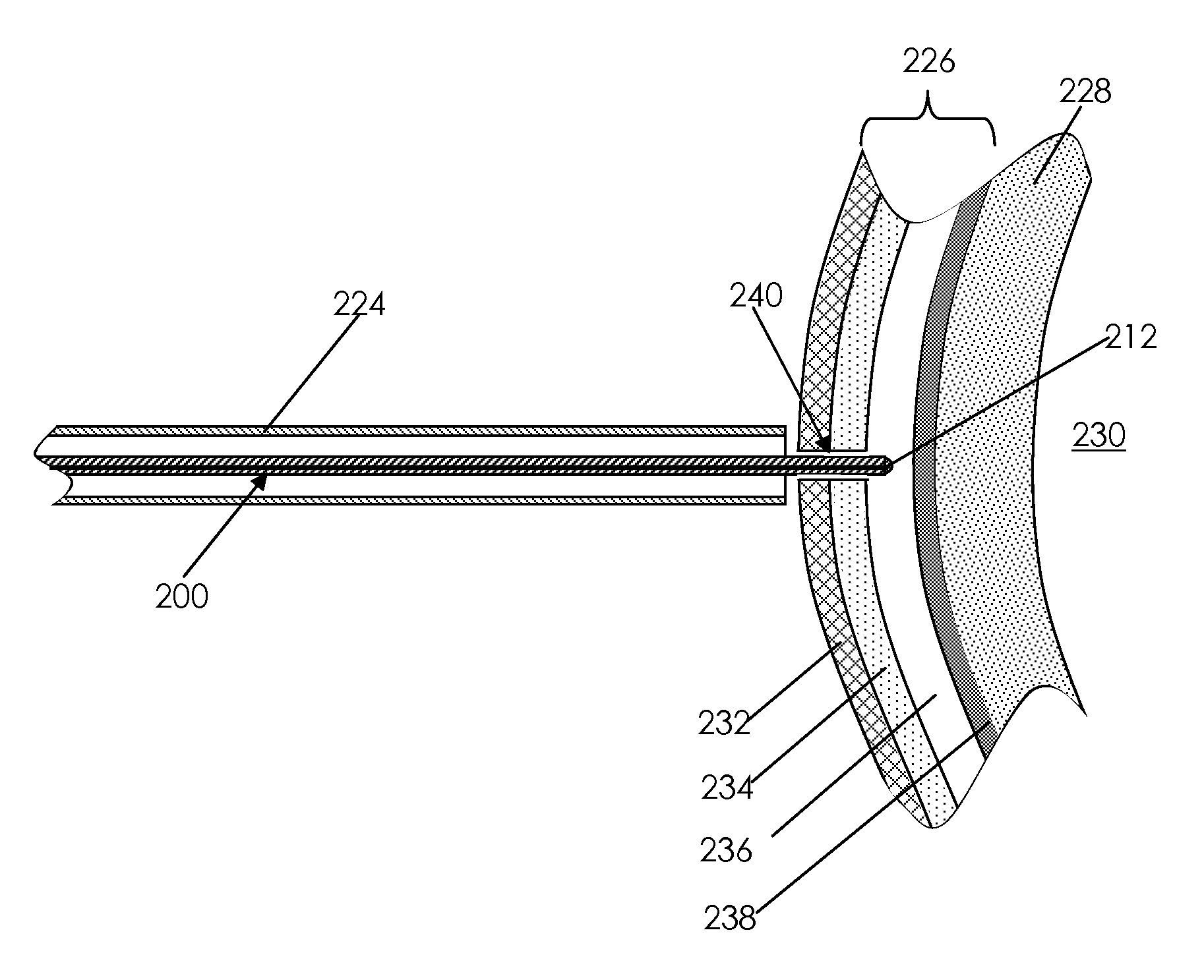
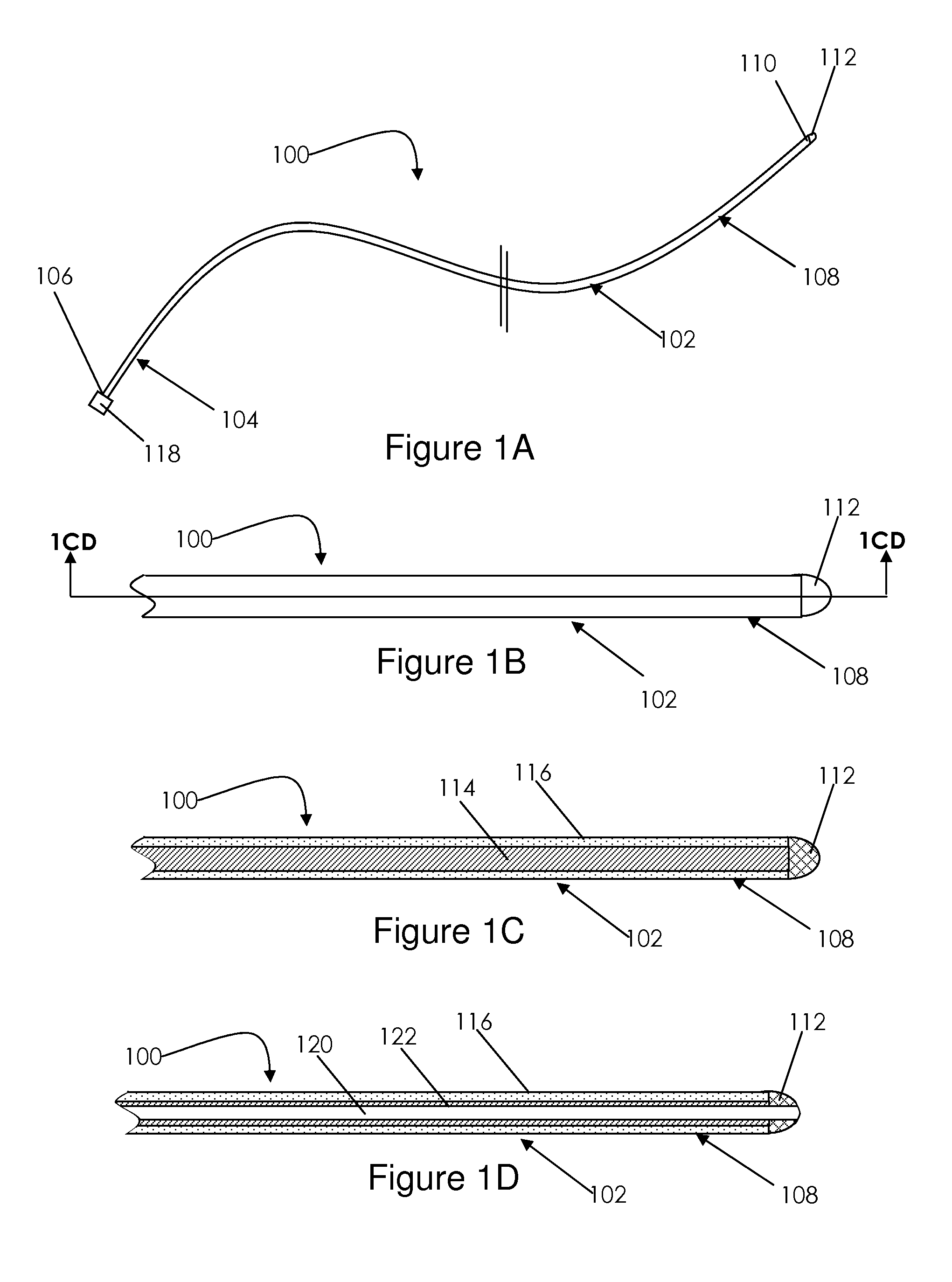
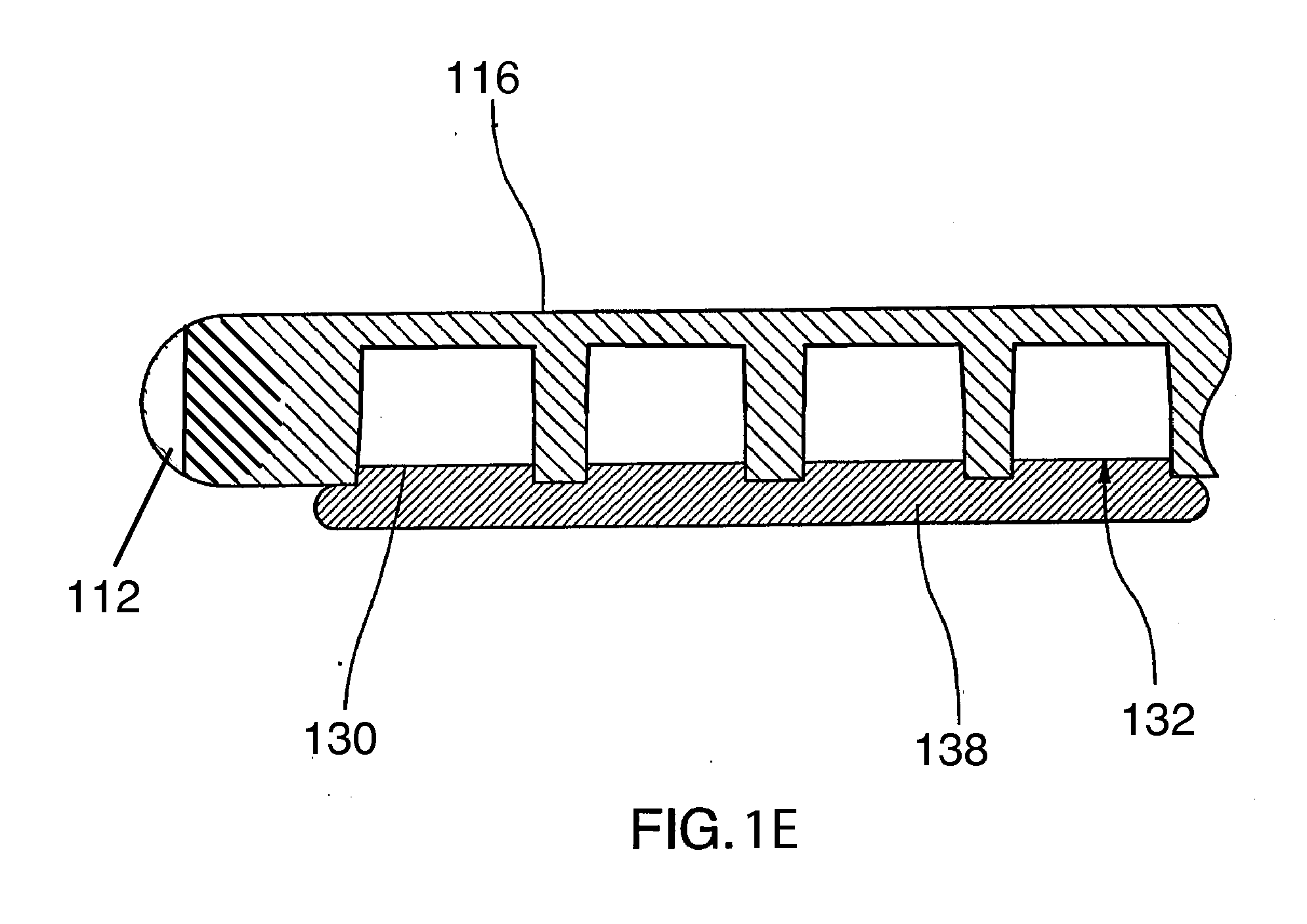
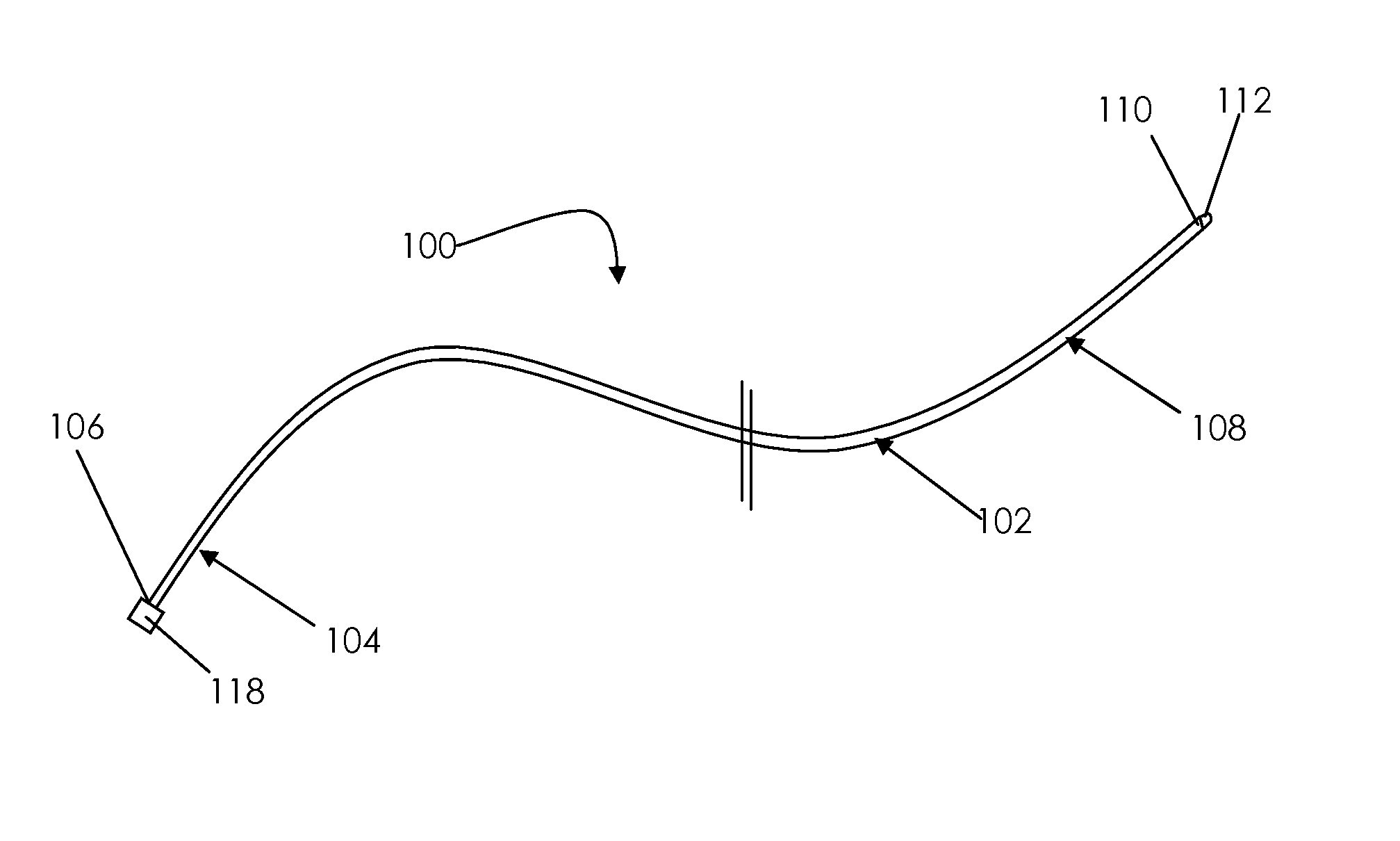
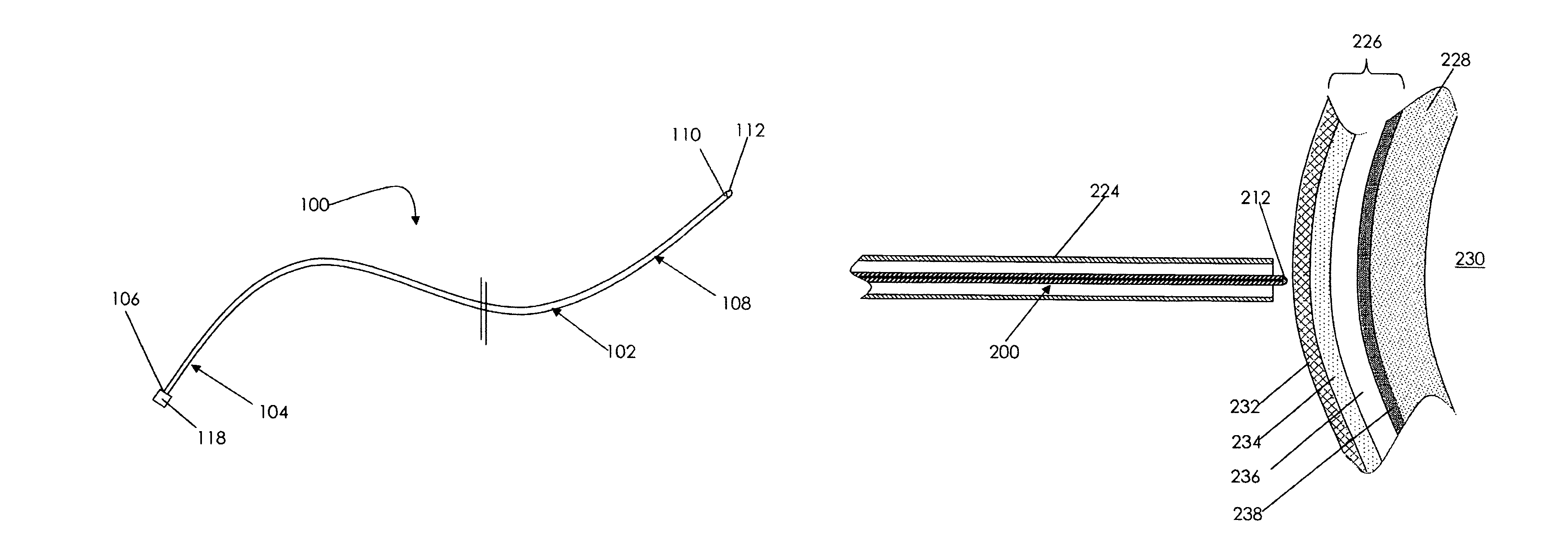
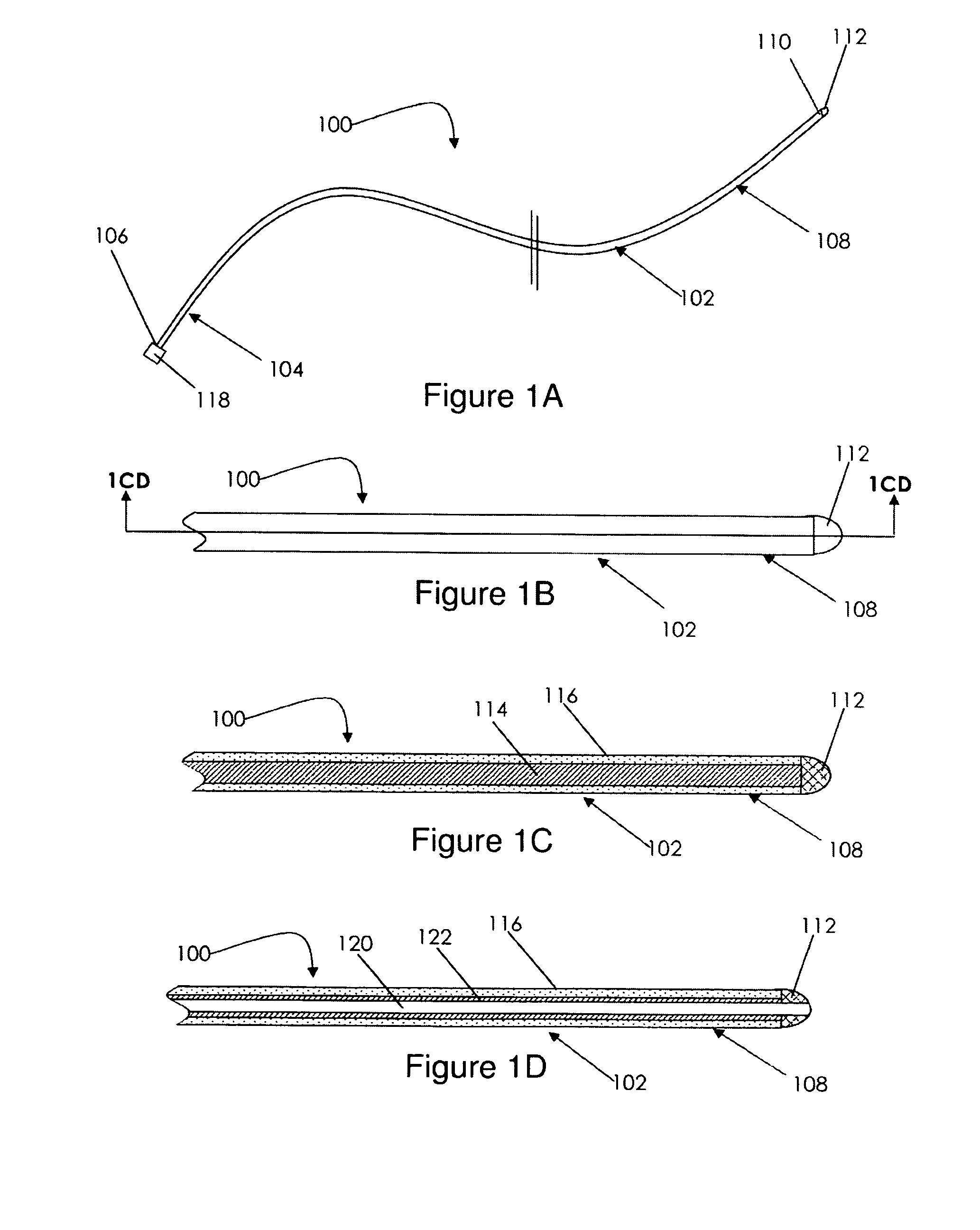
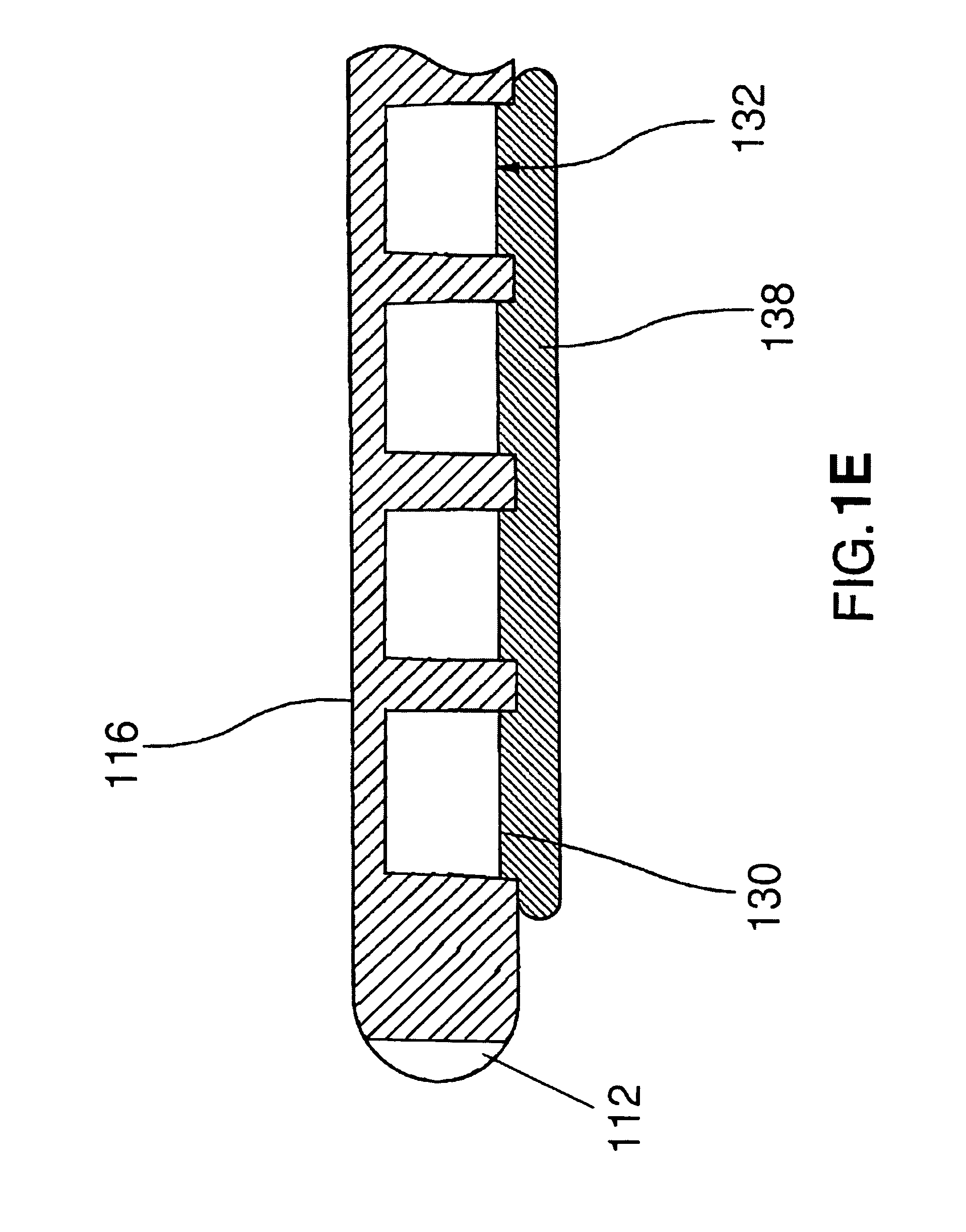
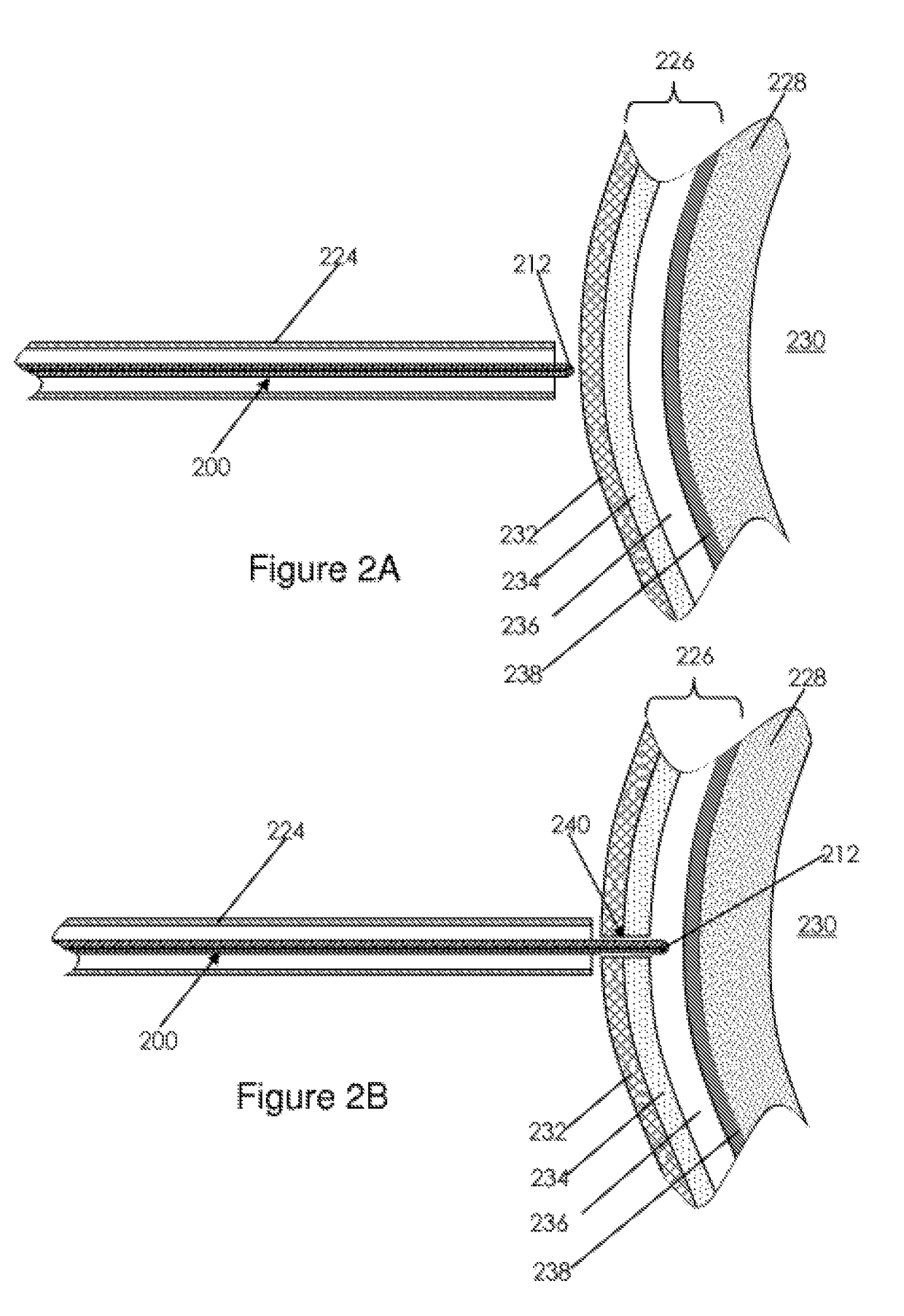
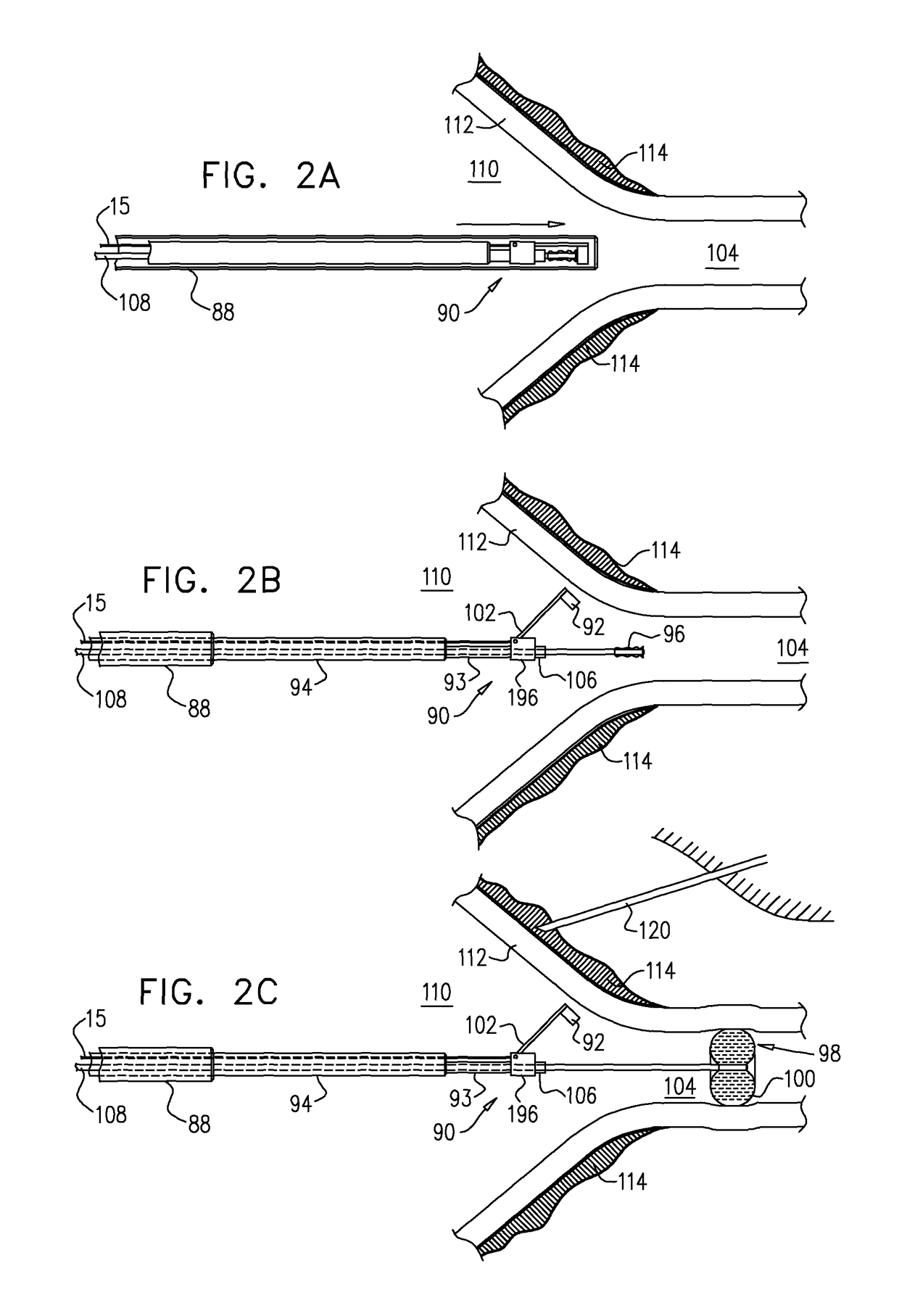
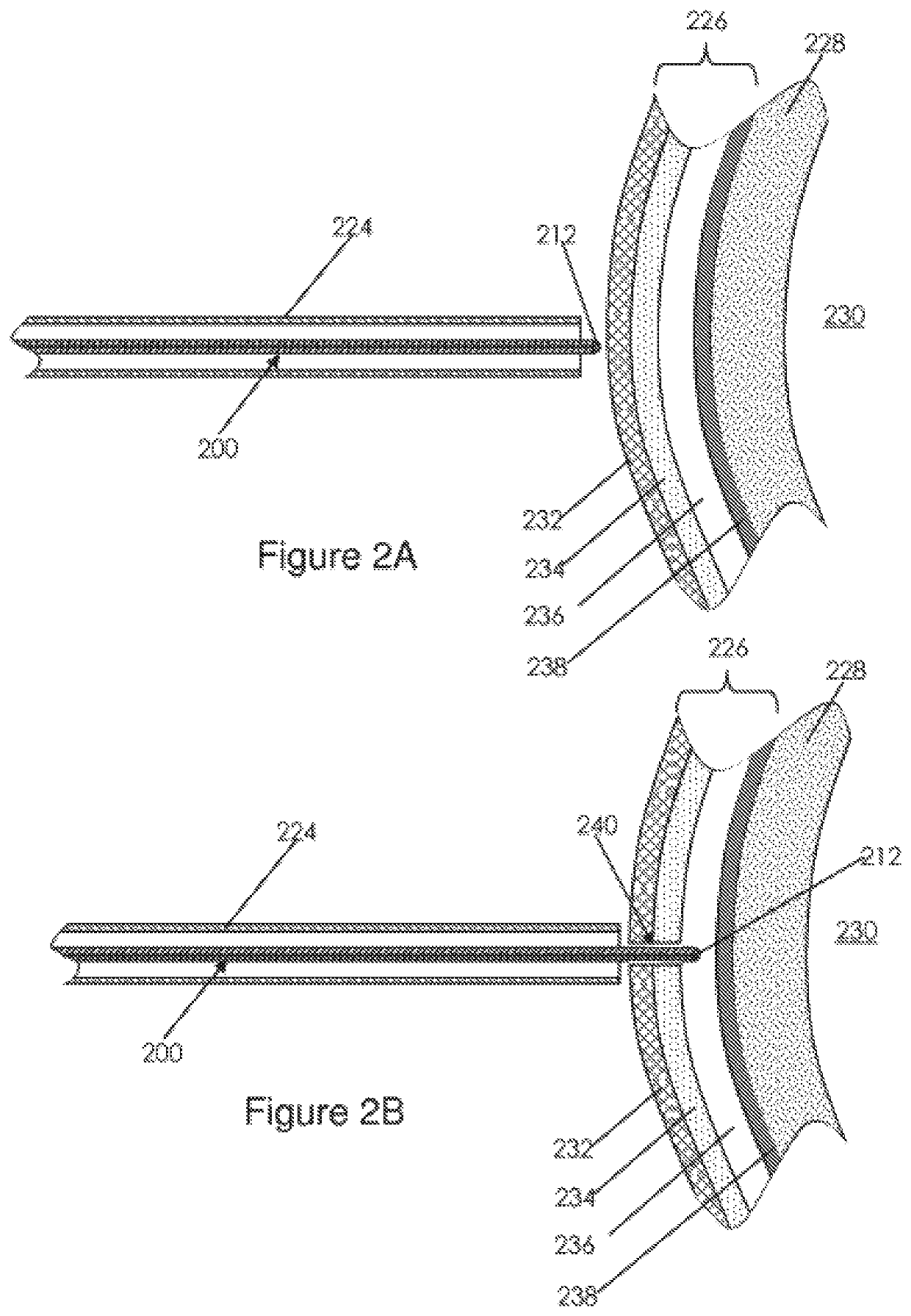
A catheter adapted for mapping and ablating epicardial tissue from the pericardial cavity includes a catheter body and an electrode assembly that has a tip section and a loop member lying generally within a plane, wherein the tip section includes an ablation electrode exposed on one side of the loop member and an insulation member exposed on an opposite side of the loop member. The catheter also includes a intermediate section between the catheter body and the electrode assembly, wherein the intermediate deflects the loop member and the tip section bi-directionally within the same plane. So arranged, the catheter can be safely maneuvered in the pericardial sac and swept in a side to side motion over the epicardium with the ablation electrode reliably facing and making contact with the epicardium. The tip section can include a balloon that is inflatable to push away surrounding pericardial tissue. The catheter may further include an injection needle whose distal end can extend outside of the tip section to puncture epicardial tissue. A lumen in the injection needle allows for delivery to agents directly to the punctured tissue and thermocouple wires can be carried in the lumen for temperature sensing at the treatment site.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
Cardiac electrosurgery
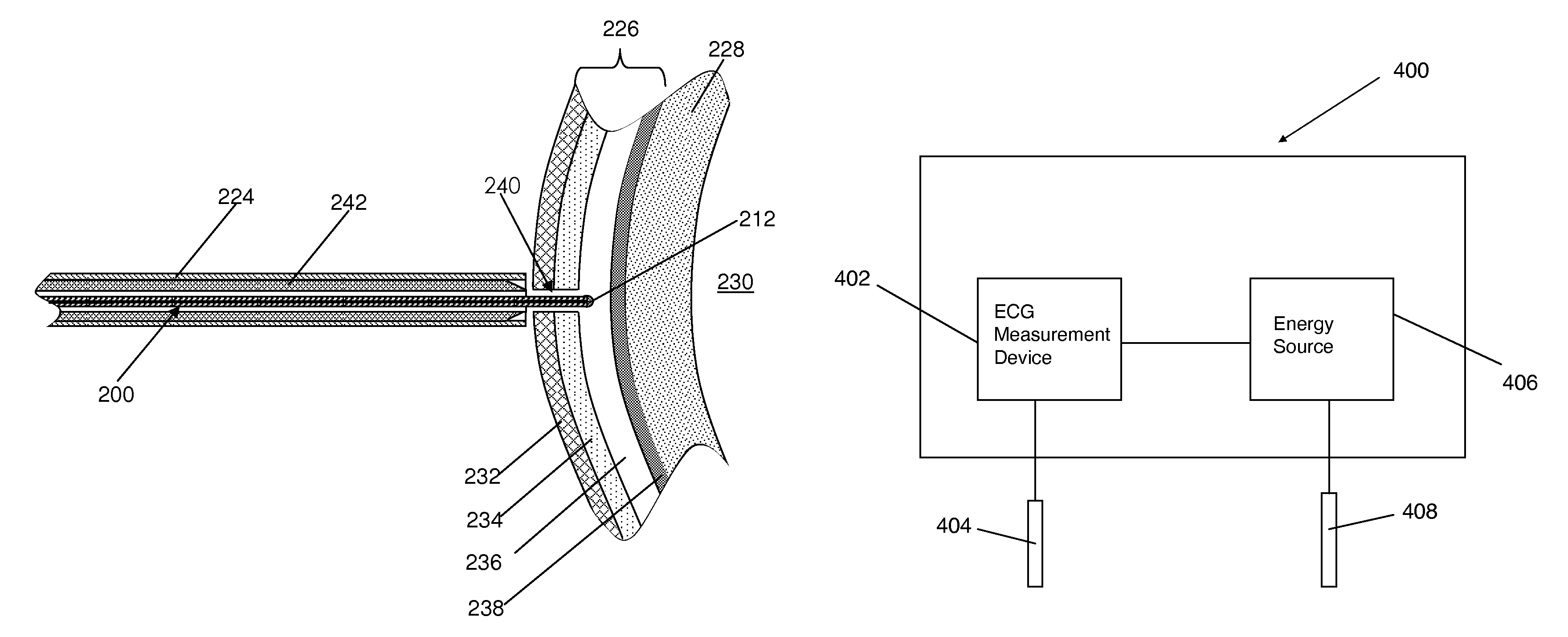
A method of accessing a pericardial cavity of a heart is disclosed, comprising delivering electrical energy to a pericardium in a manner which creates a channel substantially through a parietal pericardium and does not substantially affect myocardial tissue.
Owner:BOSTON SCI MEDICAL DEVICE LTD
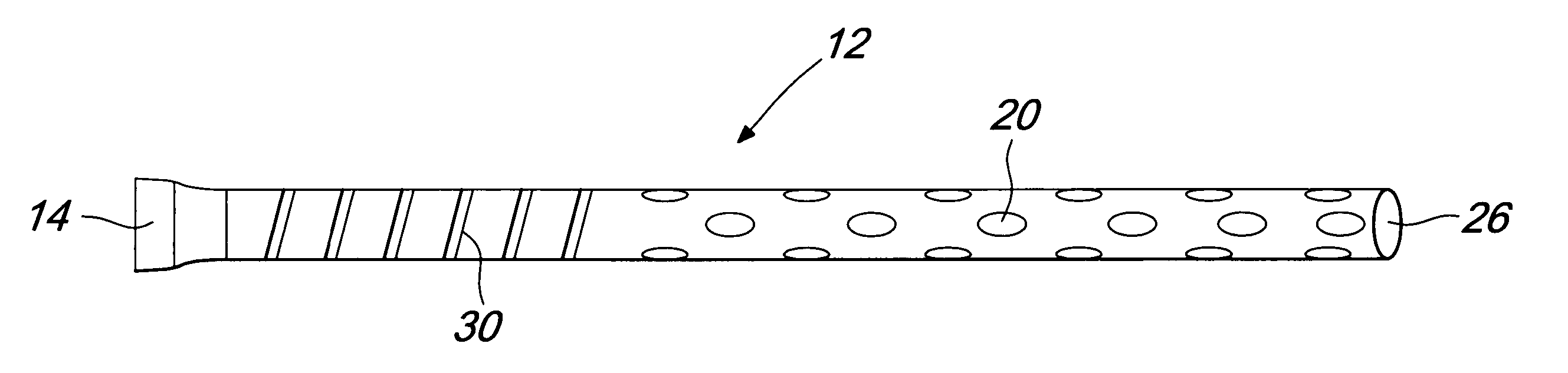
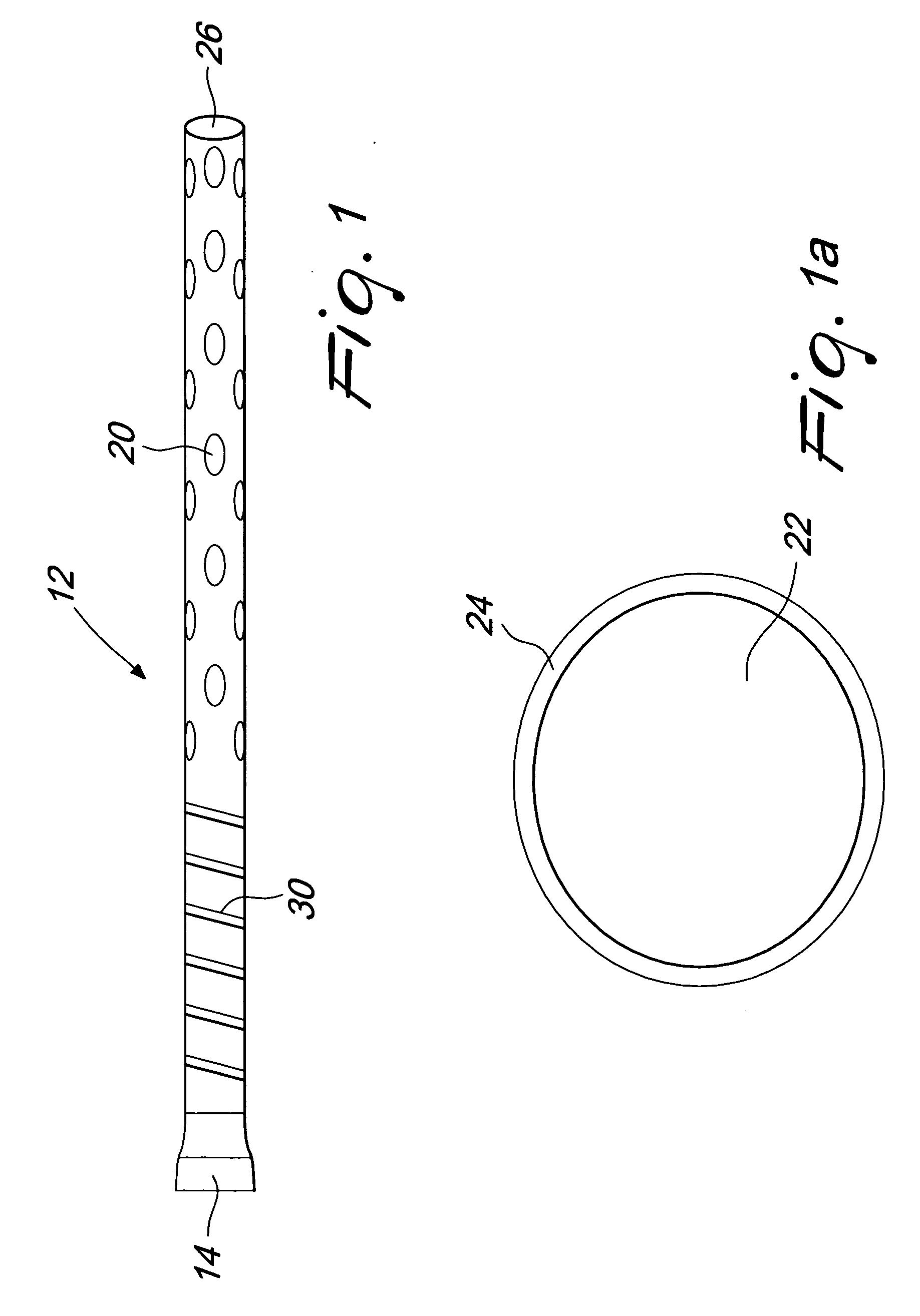
Method and apparatus for delayed pericardial drainage
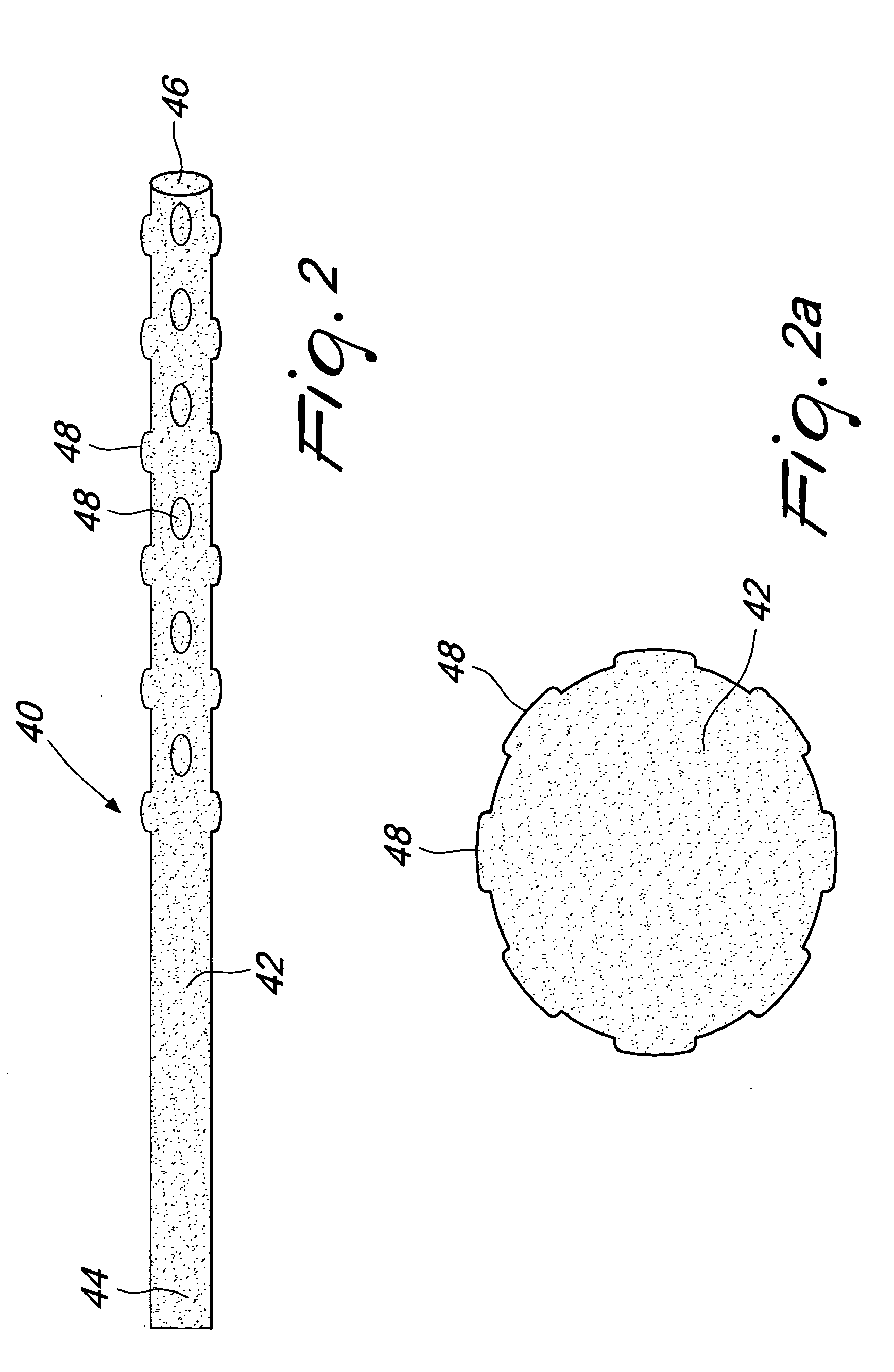
Device for placement in the thoracic cavity of a patient. The device is a cannula, tube or catheter for pericardial drainage and serves as a conduit for drainage of excessive fluid in the pericardial cavity to a receptacle outside the body. The device is placed in the pericardial cavity at the time of surgery and is used for drainage of fluid collection that is formed at a later stage when all other drainage tubes have been already removed or are clogged by organic material. The device incorporates a system for preventing that any clog or material might close all fenestrations that are present in the tube at a plurality of sites.
Owner:MEDICAL INSTR
Apparatus and method for accessing an intrapericardial space
A medical device is disclosed herein that is configured to engage and penetrate a pericardial sac. The device includes an outer tubular body, an inner tubular body, and a helical tissue engagement member. The outer tubular body includes a proximal end, a distal end and a lumen extending between the ends. The inner tubular body includes a proximal end and a distal end. The inner tubular body is located in the lumen of the outer tubular body. The proximal end of the inner tubular body is operably coupled to the proximal end of the outer tubular body. The distal end of the inner tubular body is extendable out of the distal end of the outer tubular body. The helical tissue engagement member is displaceable from a first position to a second position, the first position being in the lumen of the outer tubular body recessed relative to the distal end of the outer tubular body, and the second position extending out of the distal end of the outer tubular body. The helical tissue engagement member is also rotatable relative to the outer tubular body.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Cardiac Electrosurgery
ActiveUS20130046305A1Surgical needlesSurgical instruments for heatingElectrosurgeryPericardial cavity
Devices and methods are disclosed for providing access to the pericardial cavity while reducing risk of myocardial damage. The methods include maintaining the positions of a puncture device and of a portion of a parietal pericardium relative to one other while delivering energy from the puncture device to create a channel through the pericardium. Additional embodiments disclosed include delivering a pulse or pulses of energy to the parietal pericardium and attempting to advance the puncture device through the parietal pericardium between deliveries of energy pulses.
Owner:BOSTON SCI MEDICAL DEVICE LTD
Cardiac Electrosurgery
ActiveUS20140228841A1Easy accessDiagnosticsSurgical needlesElectrical resistance and conductancePericardium tissue
Devices and methods are disclosed for providing access to the pericardial cavity while reducing risk of myocardial damage. One method includes advancing a puncture device towards a heart, the puncture device including an energy delivery device; measuring an electrical impedance at the energy delivery device; delivering energy from the energy delivery device to at least partially puncture a pericardium; and repeating one or more of the above steps, if necessary, until the energy delivery device is located at least partially within the pericardial cavity. Some embodiments of the method include using supplemental means of monitoring, including measuring voltage to plot an ECG, medical imaging and using contrast fluid, using tactile feedback, and aspirating fluid.
Owner:BOSTON SCI MEDICAL DEVICE LTD
Epicardial mapping and ablation catheter
ActiveUS20120130366A1Safely maneuverReliable contactBioelectric signal measurementCatheterEpicardial mappingThermocouple Wire
A catheter adapted for mapping and ablating epicardial tissue from the pericardial cavity includes a catheter body and an electrode assembly that has a tip section and a loop member lying generally within a plane, wherein the tip section includes an ablation electrode exposed on one side of the loop member and an insulation member exposed on an opposite side of the loop member. The catheter also includes a intermediate section between the catheter body and the electrode assembly, wherein the intermediate deflects the loop member and the tip section bi-directionally within the same plane. So arranged, the catheter can be safely maneuvered in the pericardial sac and swept in a side to side motion over the epicardium with the ablation electrode reliably facing and making contact with the epicardium. The tip section can include a balloon that is inflatable to push away surrounding pericardial tissue. The catheter may further include an injection needle whose distal end can extend outside of the tip section to puncture epicardial tissue. A lumen in the injection needle allows for delivery to agents directly to the punctured tissue and thermocouple wires can be carried in the lumen for temperature sensing at the treatment site.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
Electrosurgical Pericardial Puncture
ActiveUS20160058504A1Facilitate ultrasound imagingOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgical needlesUltrasound imagingPericardial cavity
Devices and methods for providing access to the pericardial cavity while reducing risk of myocardial damage. One method includes advancing a distal end of a puncture device towards the heart from a subxiphoid region of a patient wherein the distal end of the puncture device is atraumatic and comprises an energy delivery device; positioning the energy delivery device at a target site on a pericardium of the heart using ultrasound for imaging; and delivering energy from the energy delivery device to a tissue of the target site to create a channel to the pericardial cavity. The method may include repeating one or more of the above steps until the energy delivery device is located within the pericardial cavity. Some embodiments of the method include using supplemental means of monitoring, including medical imaging and using contrast fluid.
Owner:BOSTON SCI MEDICAL DEVICE LTD
Cardiac electrosurgery
A method of accessing a pericardial cavity of a heart is disclosed, comprising delivering electrical energy to a pericardium in a manner which creates a channel substantially through a parietal pericardium and does not substantially affect myocardial tissue.
Owner:BOSTON SCI MEDICAL DEVICE LTD
Cardiac electrosurgery
Devices and methods are disclosed for providing access to the pericardial cavity while reducing risk of myocardial damage. One method includes advancing a puncture device towards a heart, the puncture device including an energy delivery device; measuring an electrical impedance at the energy delivery device; delivering energy from the energy delivery device to at least partially puncture a pericardium; and repeating one or more of the above steps, if necessary, until the energy delivery device is located at least partially within the pericardial cavity. Some embodiments of the method include using supplemental means of monitoring, including measuring voltage to plot an ECG, medical imaging and using contrast fluid, using tactile feedback, and aspirating fluid.
Owner:BOSTON SCI MEDICAL DEVICE LTD
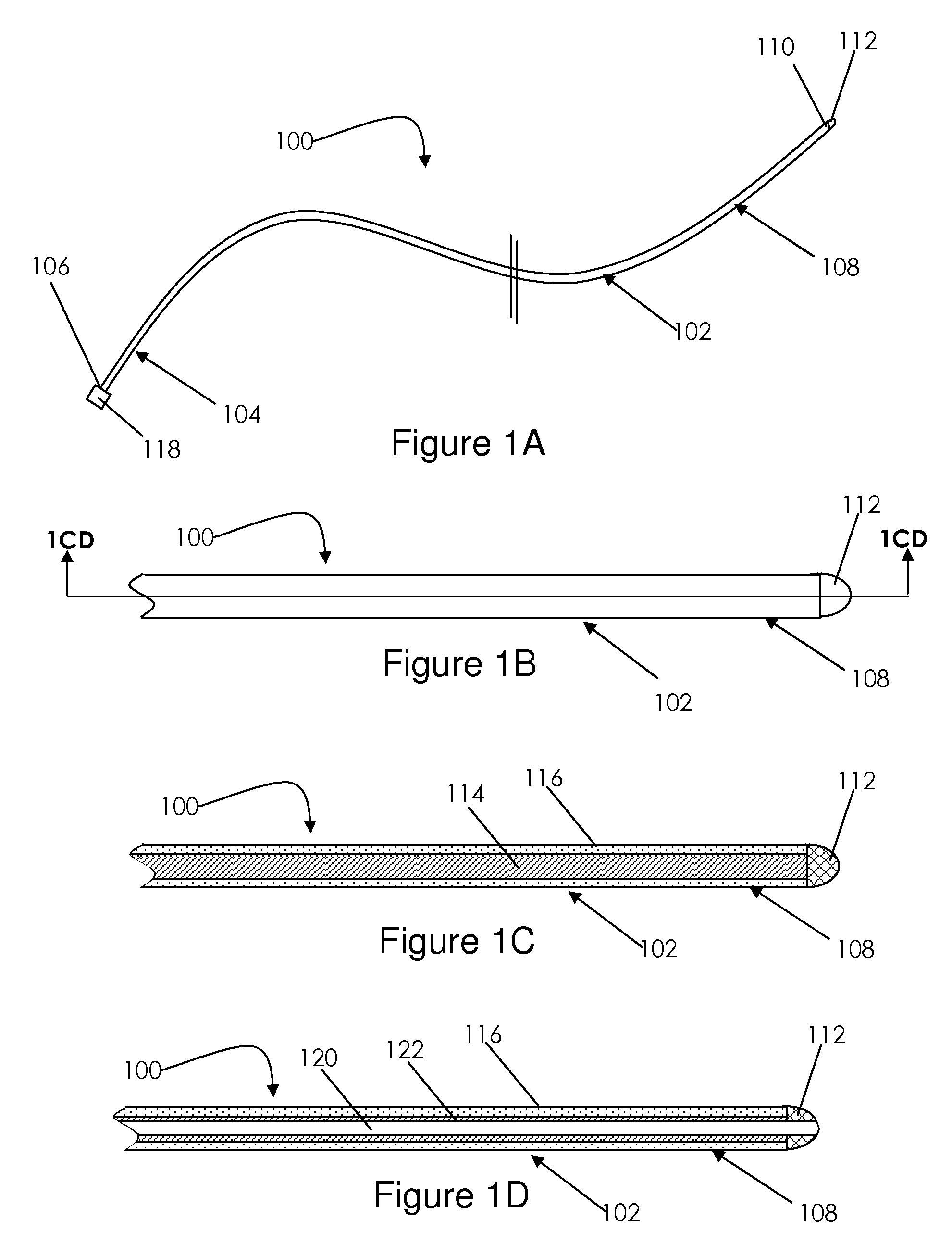
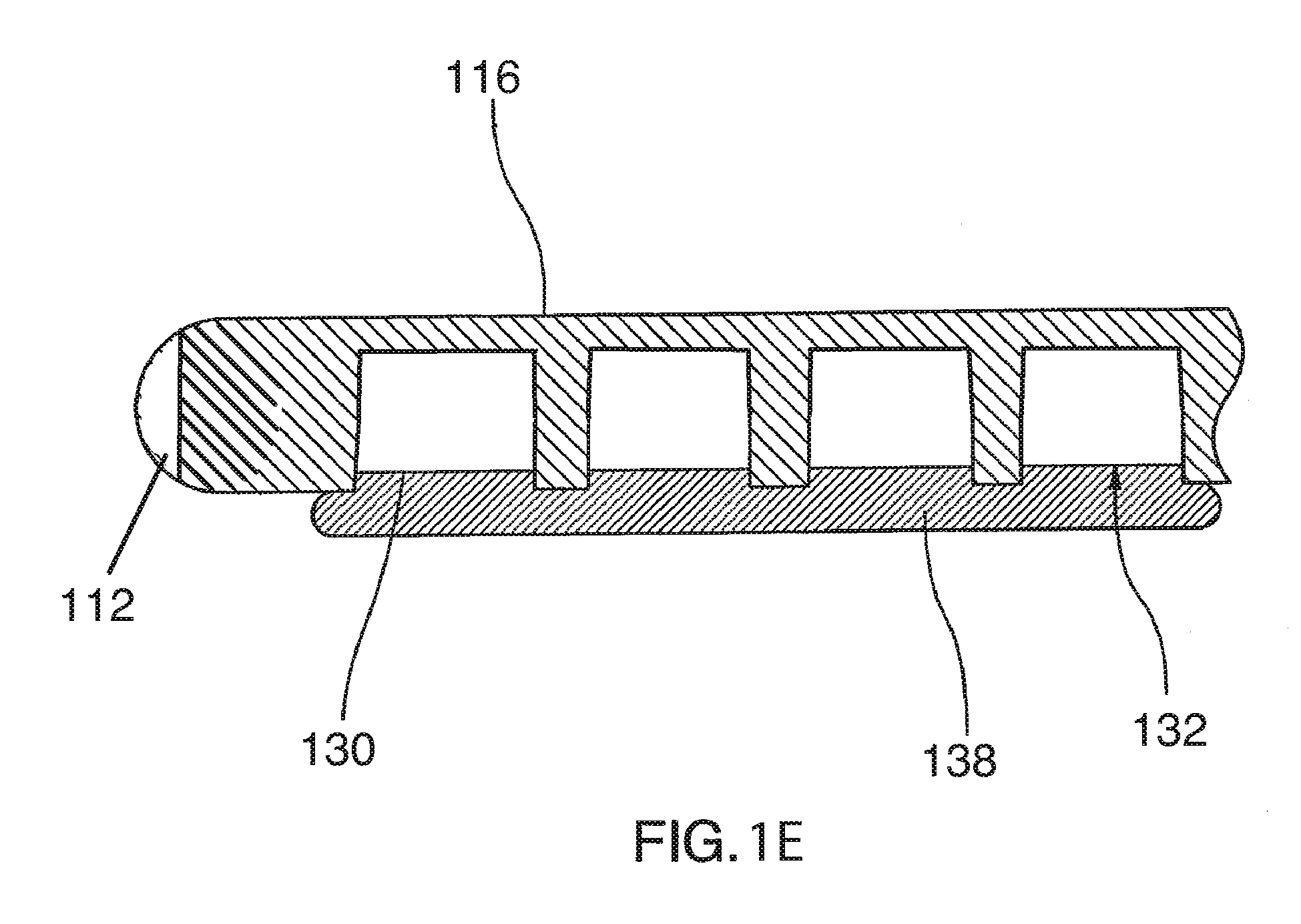
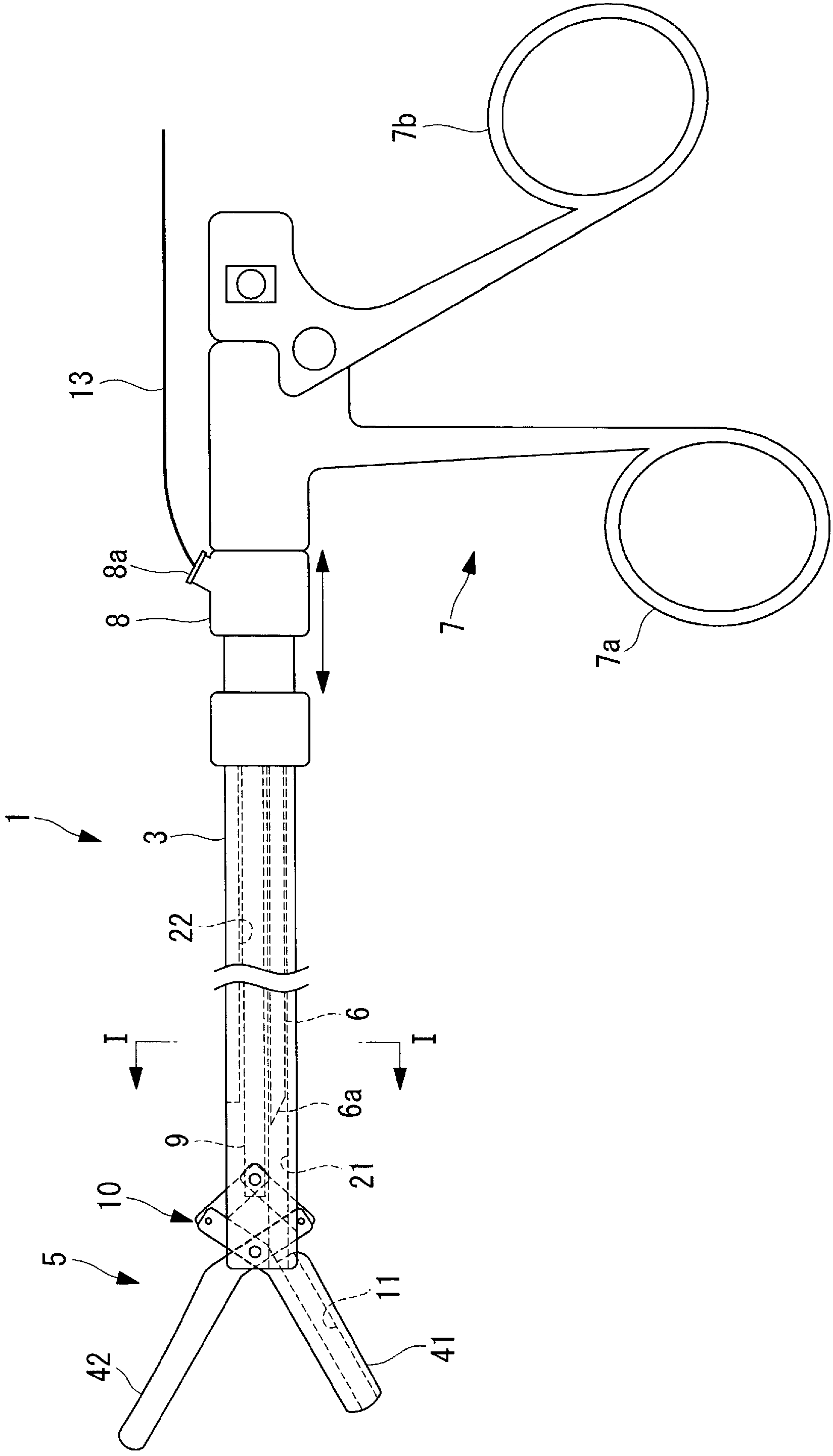
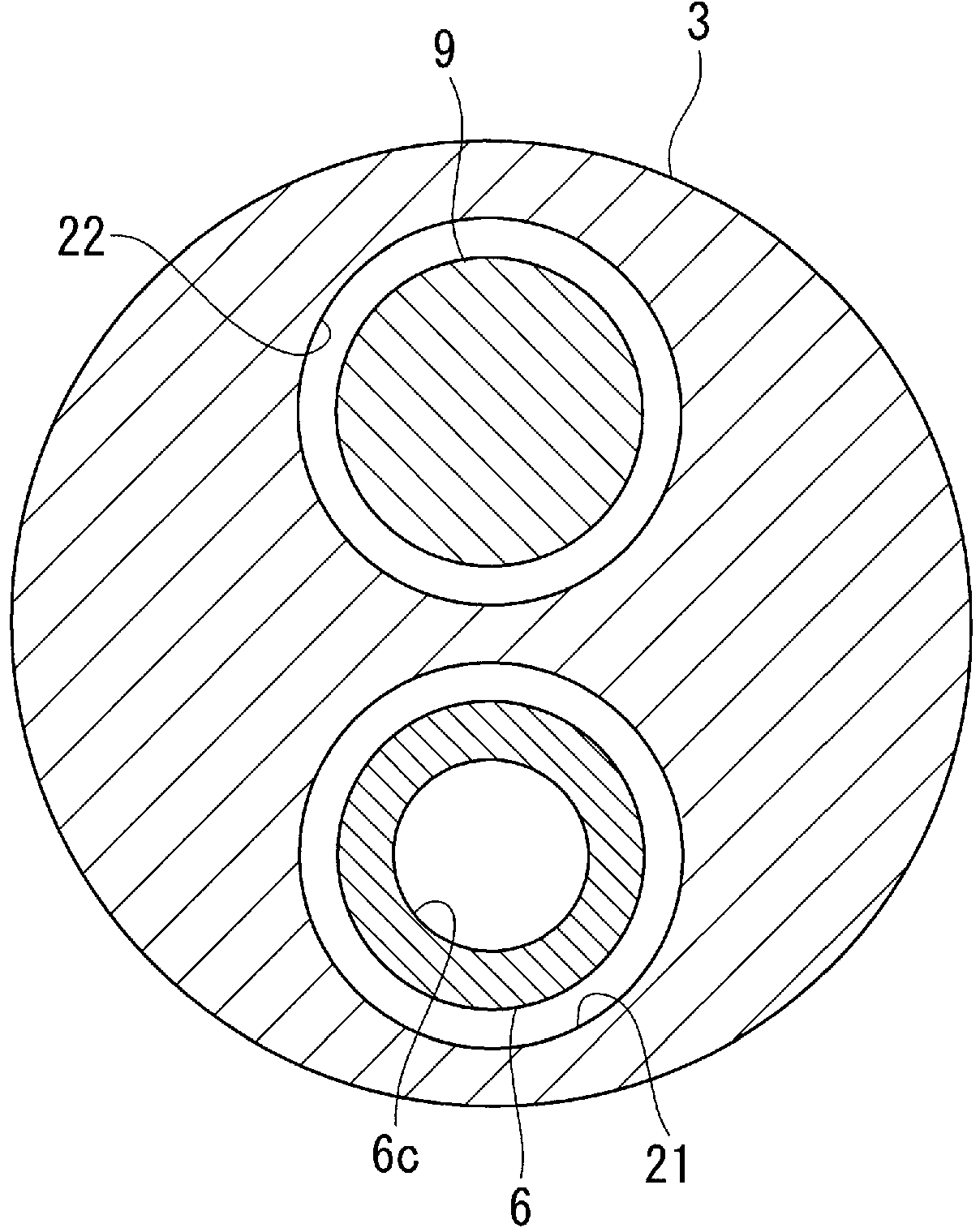
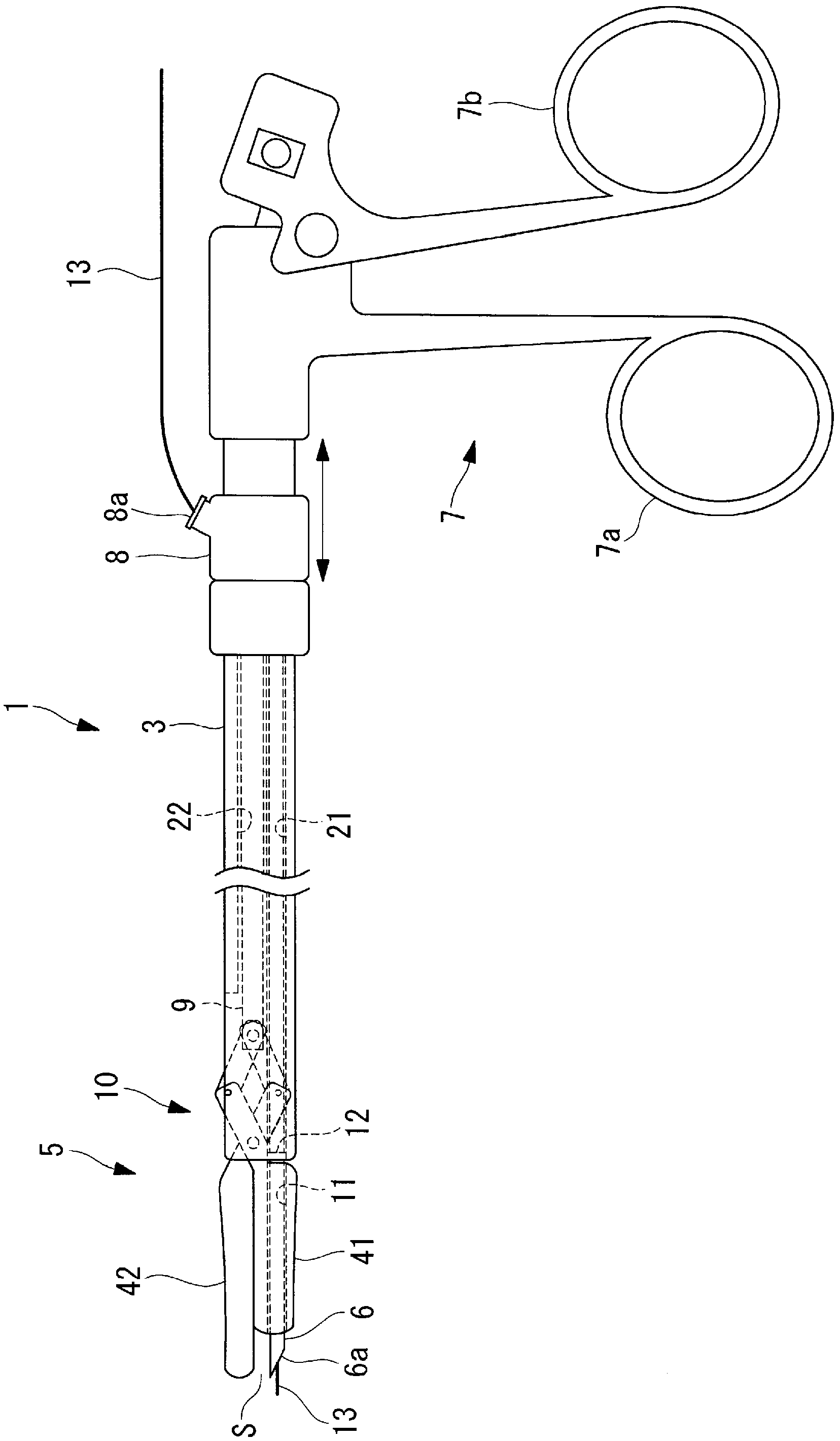
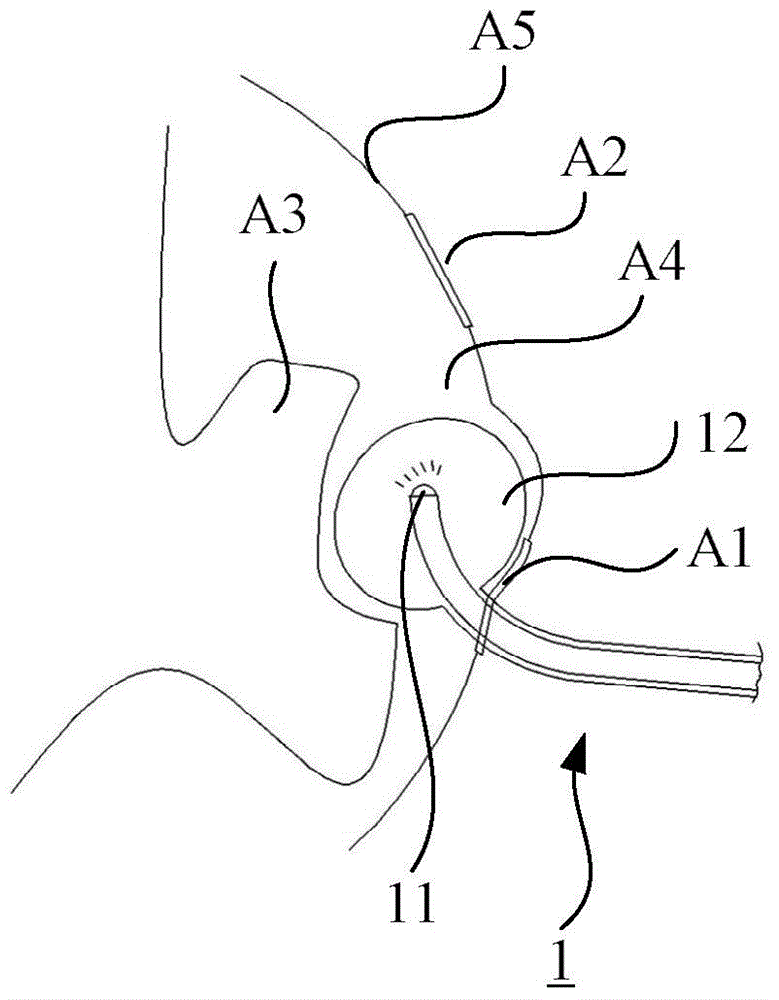
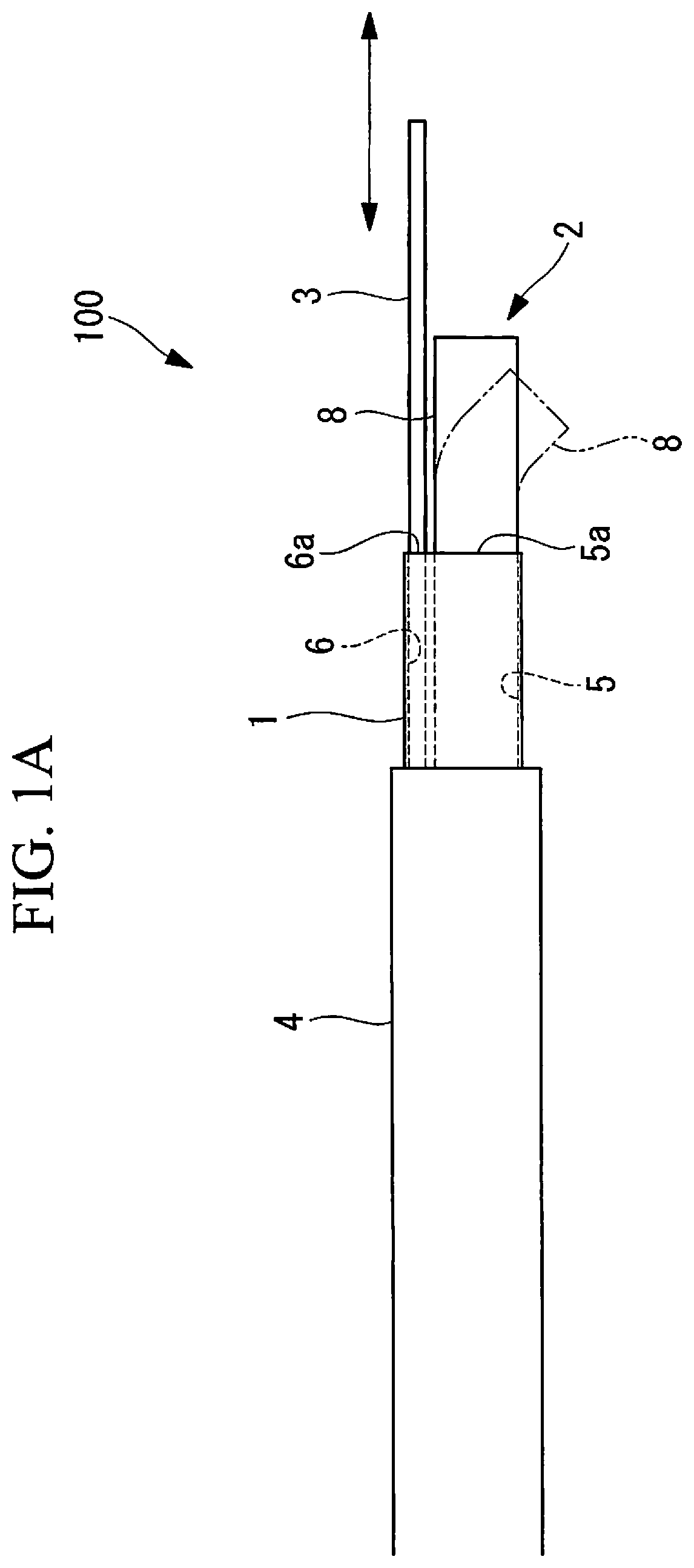
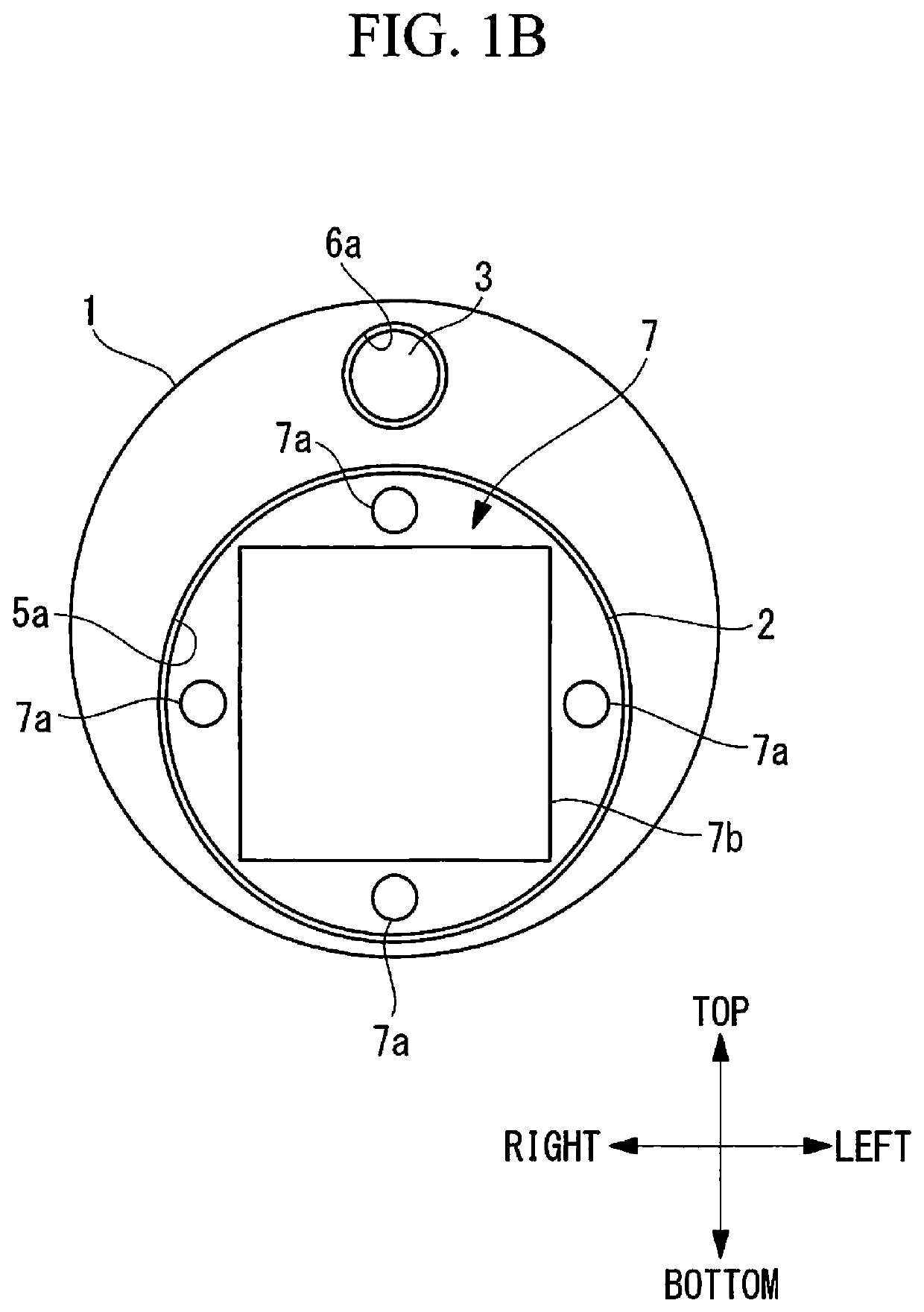
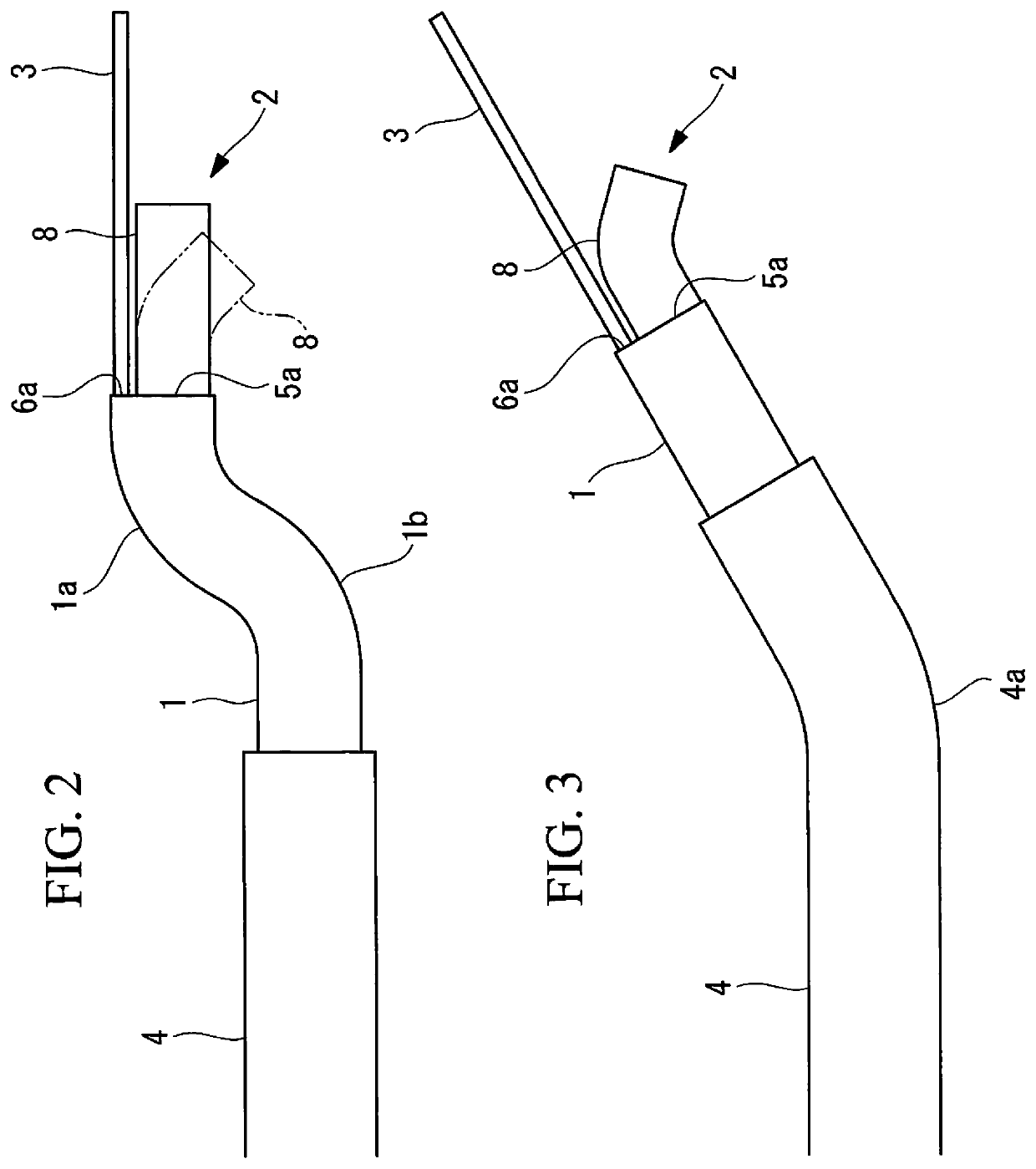
Treatment tool
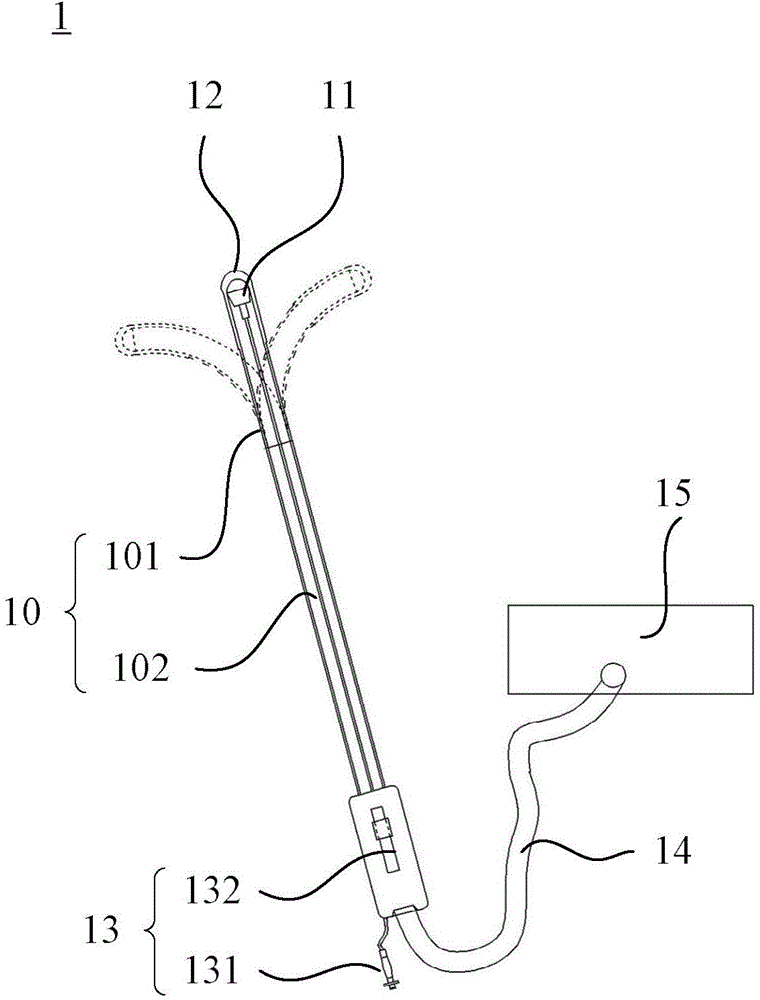
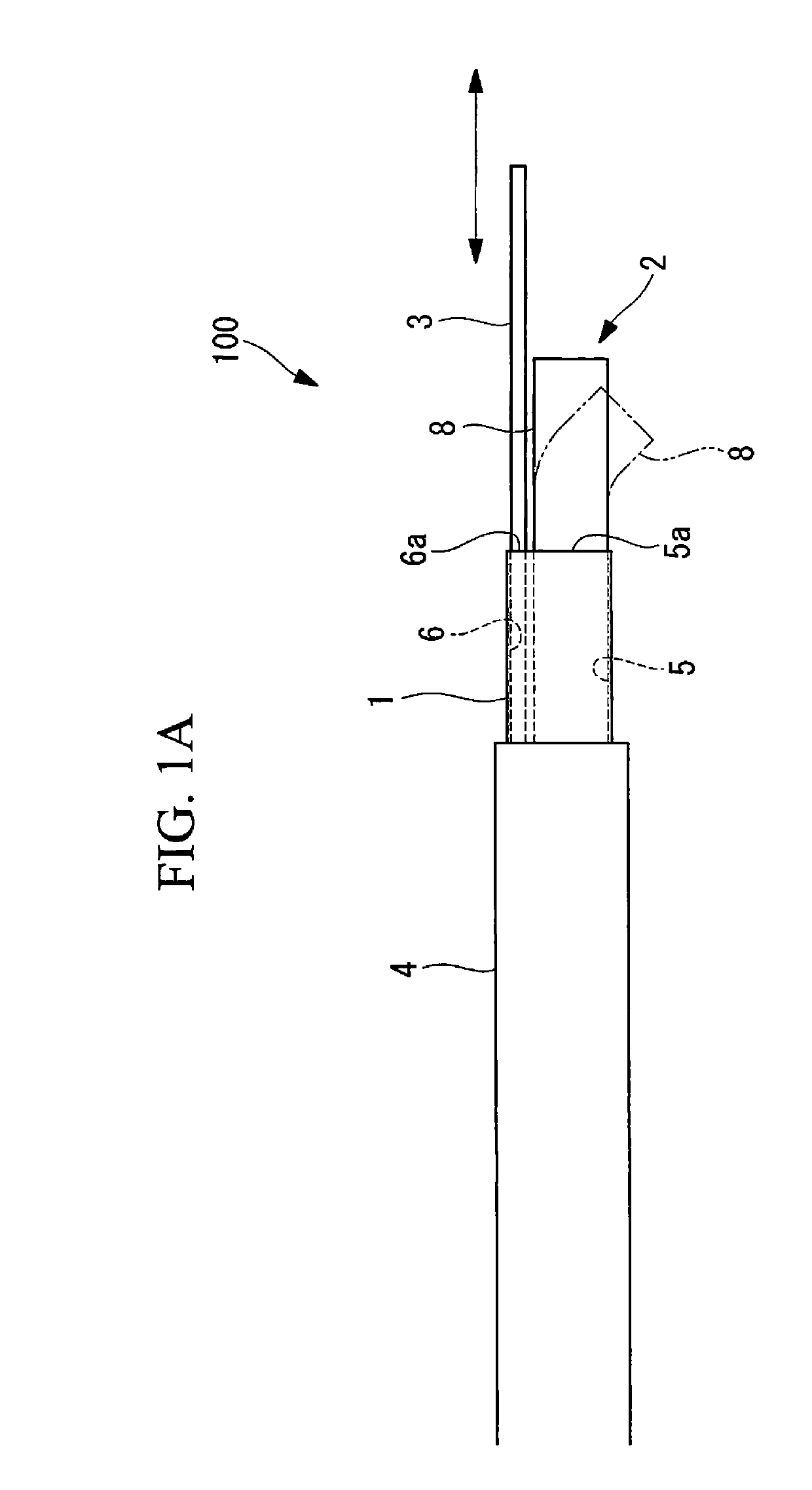
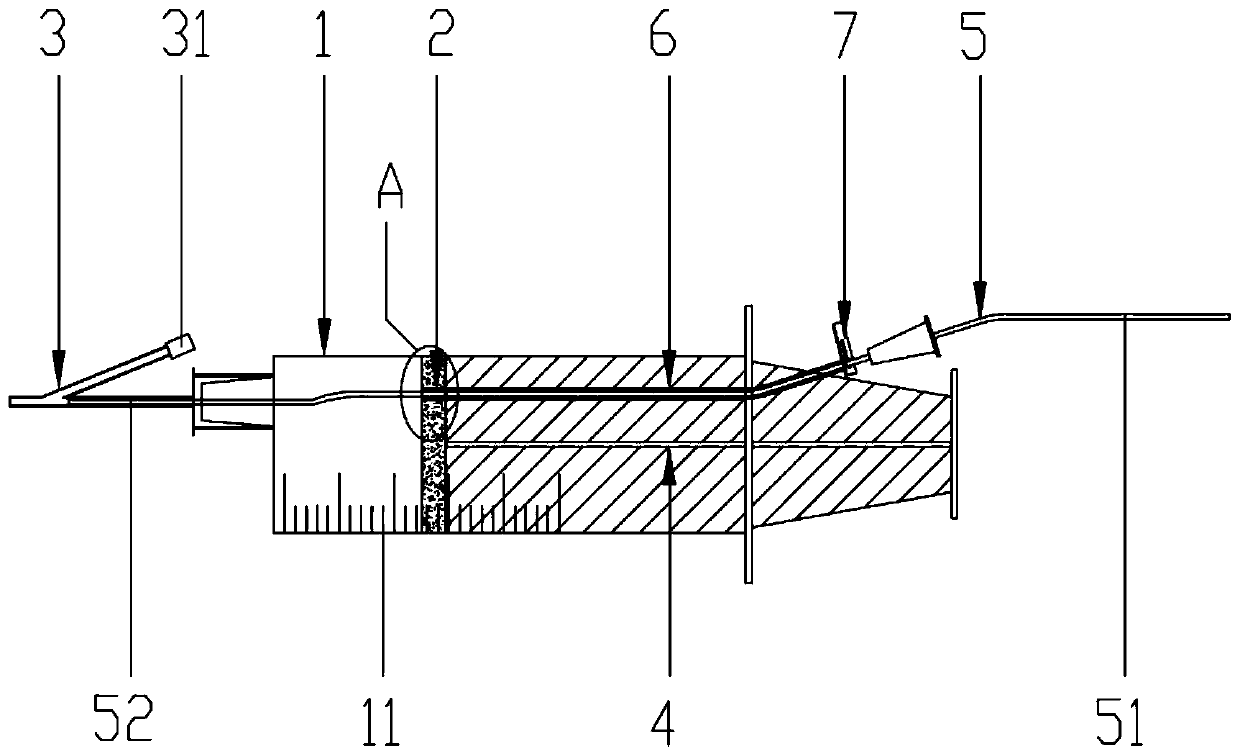
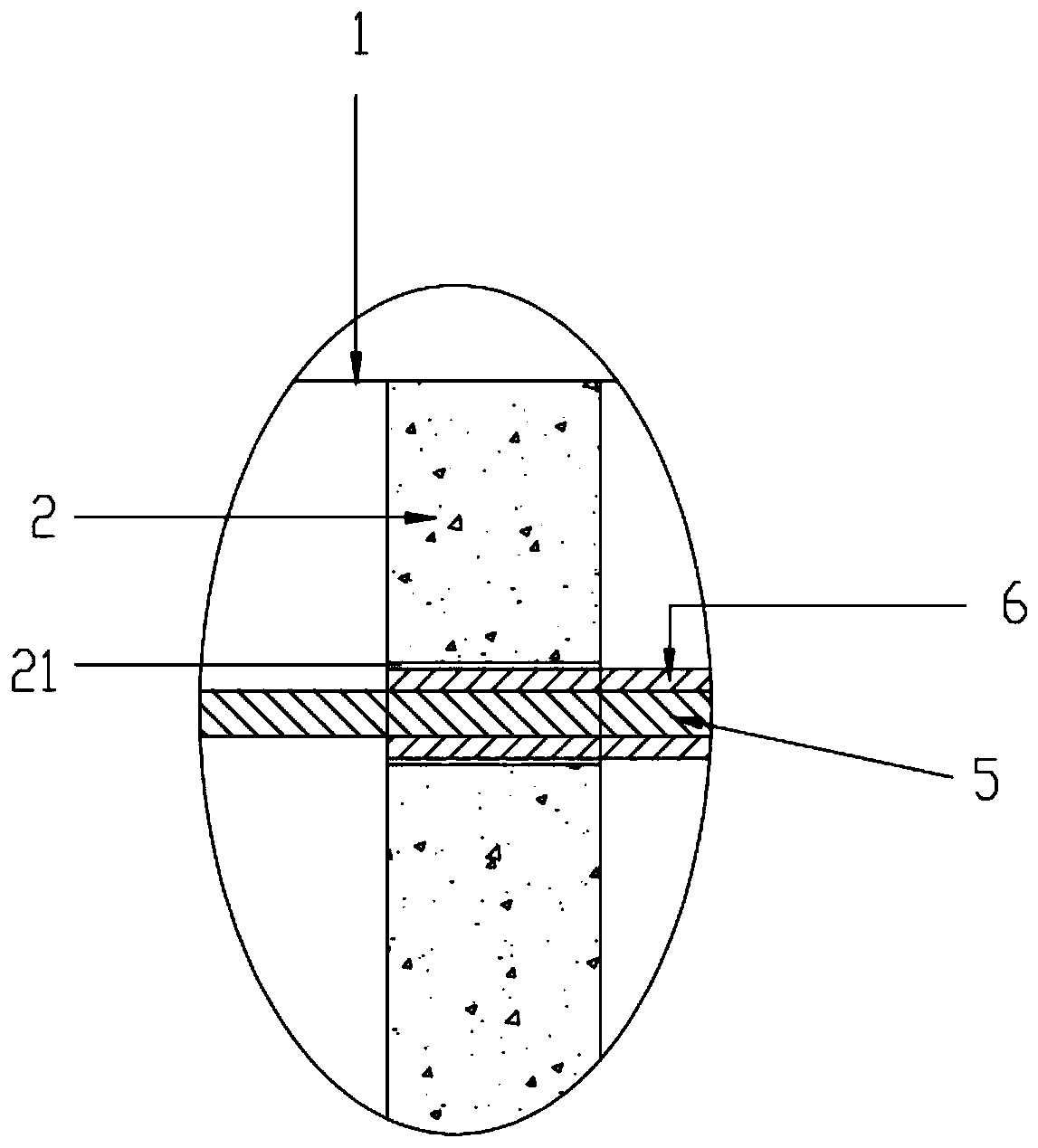
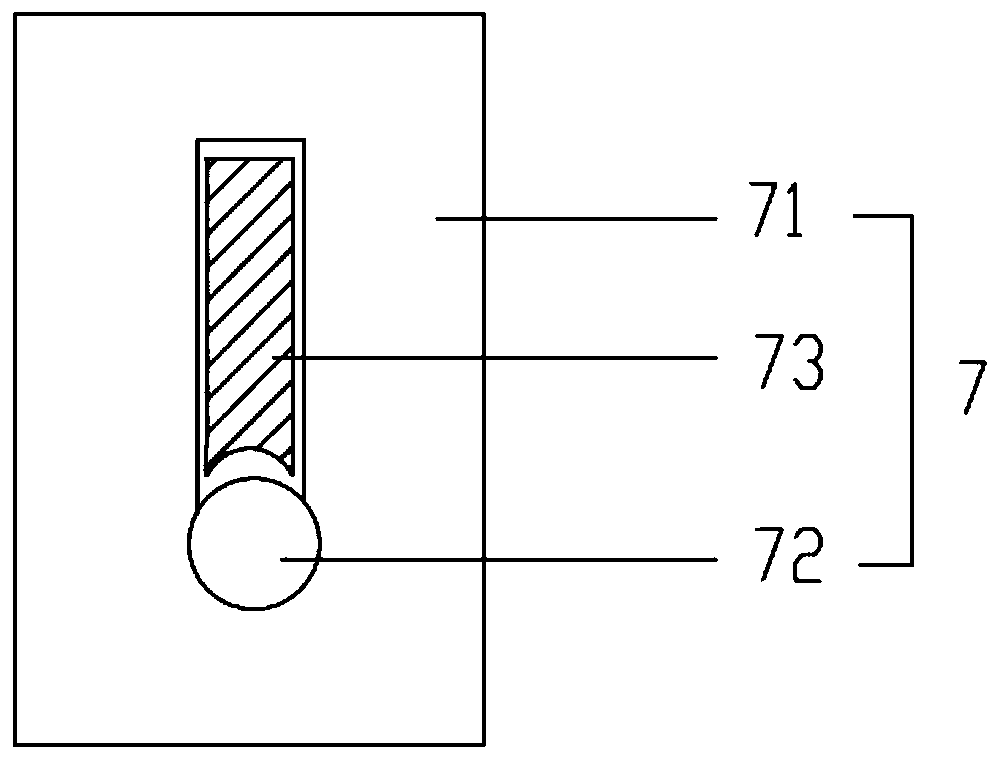
In order to introduce a guide wire into the pericardial cavity while preventing the tip of the guide wire from contacting the heart, provided is a treatment tool (1) provided with: an elongated insertion section (3) having a channel (21) that opens at the tip surface and is formed in the lengthwise direction; a forceps section (5) provided to the tip of the insertion section (3) and having a pair of grasping parts (41,42) that can open and close; and a puncture needle (6) housed movably within the channel (21) and wherein a through hole into which the guide wire (13) can be inserted is formed in the lengthwise direction to the needle tip surface (6a). One of the grasping parts (41) is provided with the tip thereof able to be disposed at a position offset towards the base with respect to the tip of the other grasping part (42). The puncture needle (6) is provided in a manner so as to be able to emerge and recede from the opening at the tip surface of the insertion section (3) into the space (S) formed between the tips of the pair of grasping parts (41, 42) having an offset disposition.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
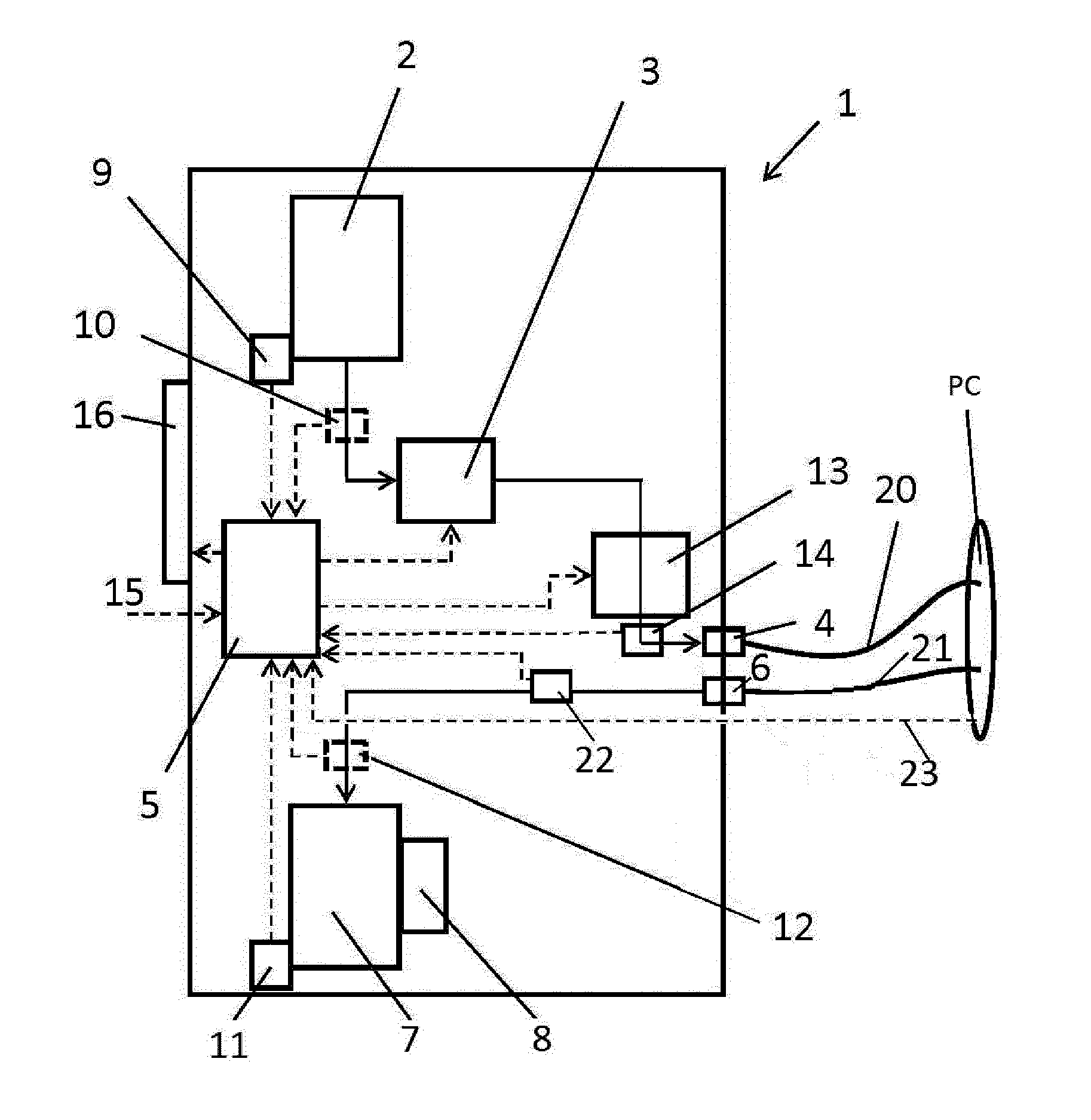
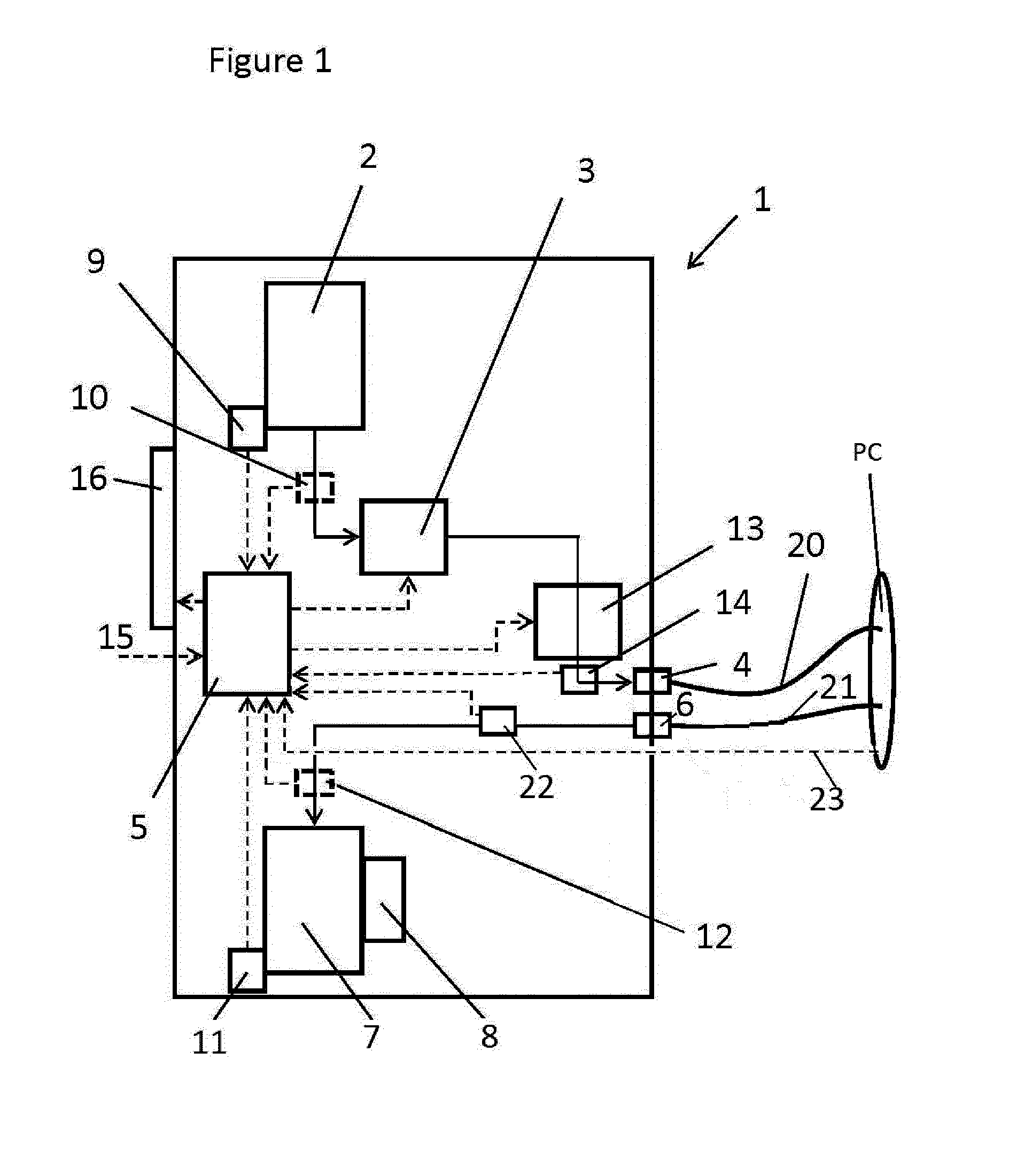
System for flushing a pericardial cavity
ActiveUS20160331888A1Enlarged cavityExpedite evacuationEnemata/irrigatorsMedical devicesControl signalMultiple sensor
The invention provides a flushing system (1) configured to flush the pericardial cavity (PC) of a patient, wherein the system comprises: an infusion liquid outlet (4) to connect a first tube(20) having an infusion liquid lumen to guide a flow of infusion liquid from the system to the pericardial cavity, and an effusion liquid inlet (6) to connect to a second tube (21) having an effusion liquid lumen to guide the effusion liquid flow from the pericardial cavity to the system, a flow rate control system to control the flow rate of the infusion liquid flow at the infusion liquid outlet (4) on the basis of multiple sensor signals, wherein the flow rate control system comprises: a control unit (5) to provide a control signal on the basis of the sensor signals, and a pump device (3) to pump infusion liquid to the infusion liquid outlet (4) at an infusion liquid flow rate, wherein the infusion liquid flow rate is adjustable by the control signal of the control unit (5) and wherein the sensor signals registered by the control unit (5) comprise: an infusion liquid signal representative for the infusion liquid flow to the pericardial cavity, an effusion liquid signal representative for the effusion liquid flow rate from the pericardial cavity, a blood volume signal generated by a hematocrit sensor (12) representative for a blood loss flow rate in the effusion liquid from the pericardial cavity, and a pressure control signal representative for the pressure in the pericardial cavity generated by a pressure sensor positioned inside or in connection with the first tube (20), the second tube (21) or the pericardial cavity. The invention also provides a method of monitoring the blood loss volume or flow rate from the pericardium based on multiple sensor signals as well as, a method of treatment of postoperative cardiac patients in order to reduce the risk of cardiac tamponade, reduce post-operative blood loss and reduce the accumulation of blood and clots in the pericardial cavity, wherein the pericardial cavity of the patient is flushed with a flushing system according to the invention.
Owner:ACADEMISCH MEDISCH CENT BIJ DE UNIV VAN
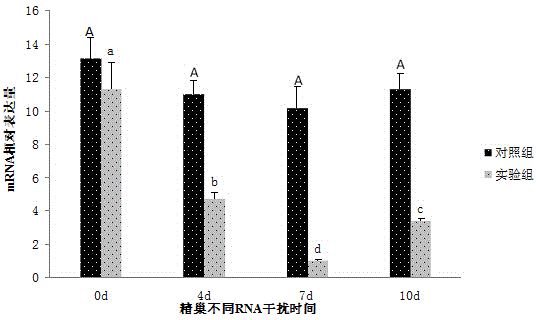
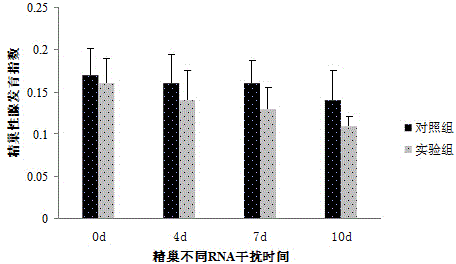
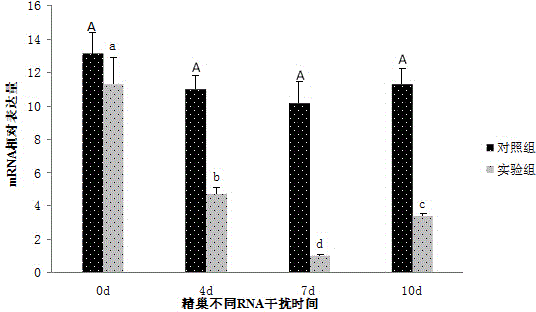
Macrobrachium nipponense FoxL2 (Forkhead box protein L2) protein as well as coding gene and application thereof
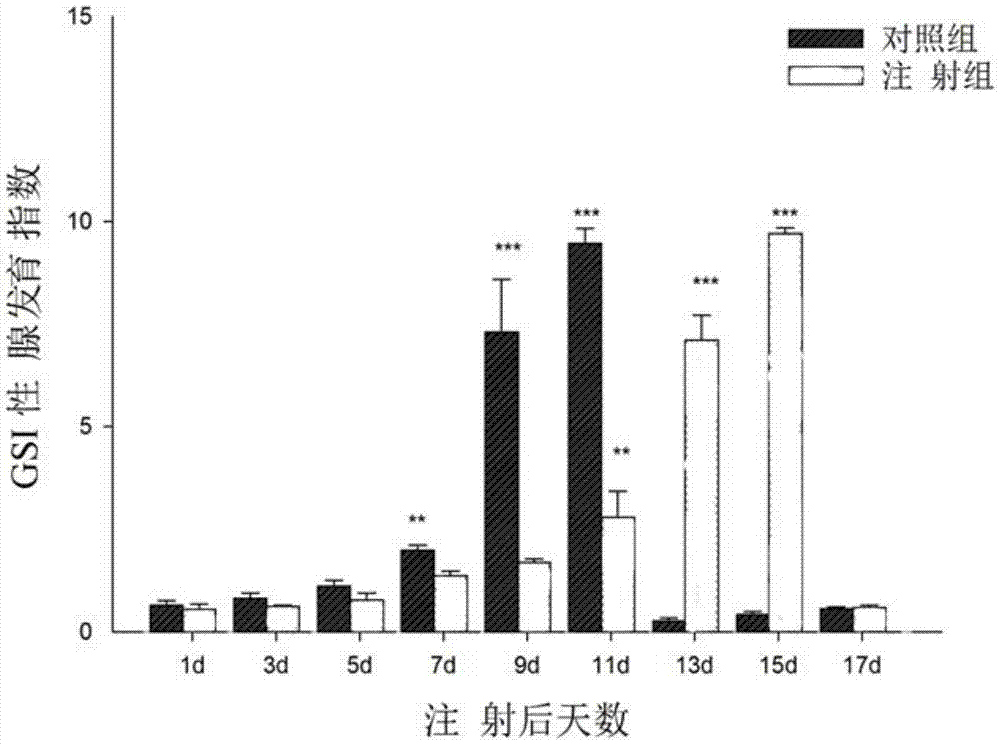
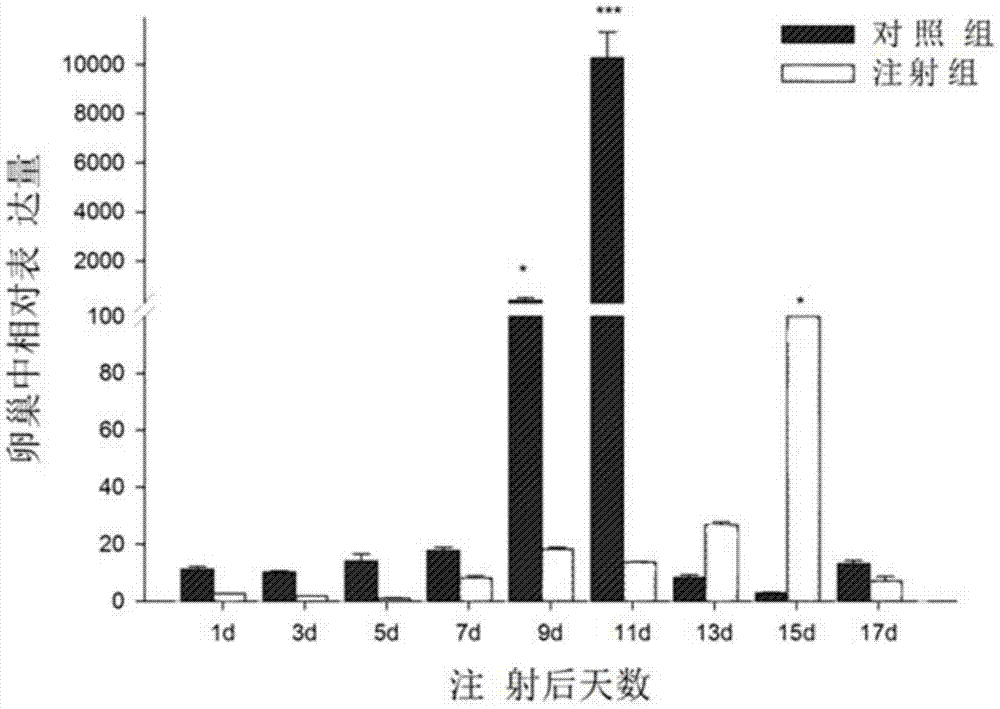
InactiveCN104592378AShortened maturation timeReduce developmentOrganic active ingredientsFermentationPericardial cavityMacrobrachium nipponense
The invention discloses a macrobrachium nipponense FoxL2 (Forkhead box protein L2) protein as well as a coding gene and an application thereof. An FoxL2 gene is cloned from testes or ovaries of the macrobrachium nipponense by using primer groups provided by the invention, dsRNA is prepared by using the FoxL2 gene, after the dsRNA is injected into the pericardial cavity of male or female macrobrachium nipponense, the expression of the FoxL2 gene in the testes or ovaries can be silenced, the development of the testes of the macrobrachium nipponense can be delayed, but the influence on the development of the ovaries of the macrobrachium nipponense is not obvious. Thus, the FoxL2 gene of the macrobrachium nipponense can be used for promoting the development of the testes and has the function against the action of the FoxL2 gene in mammals and fishes. According to the macrobrachium nipponense FoxL2 protein as well as the coding gene and the application thereof, new thinking and effective means are provided for overcoming the sexual precocity phenomenon of the macrobrachium nipponense and breeding good varieties.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
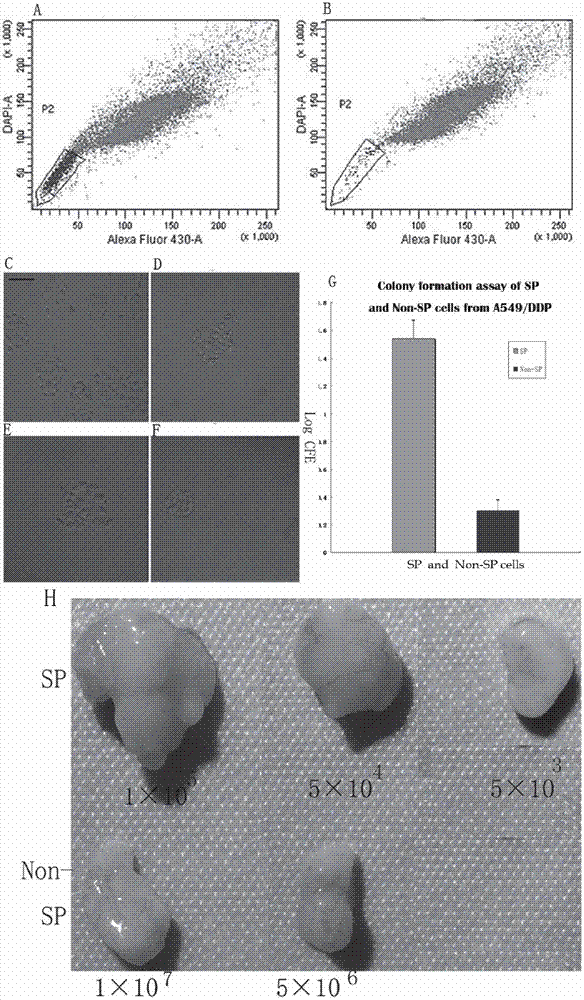
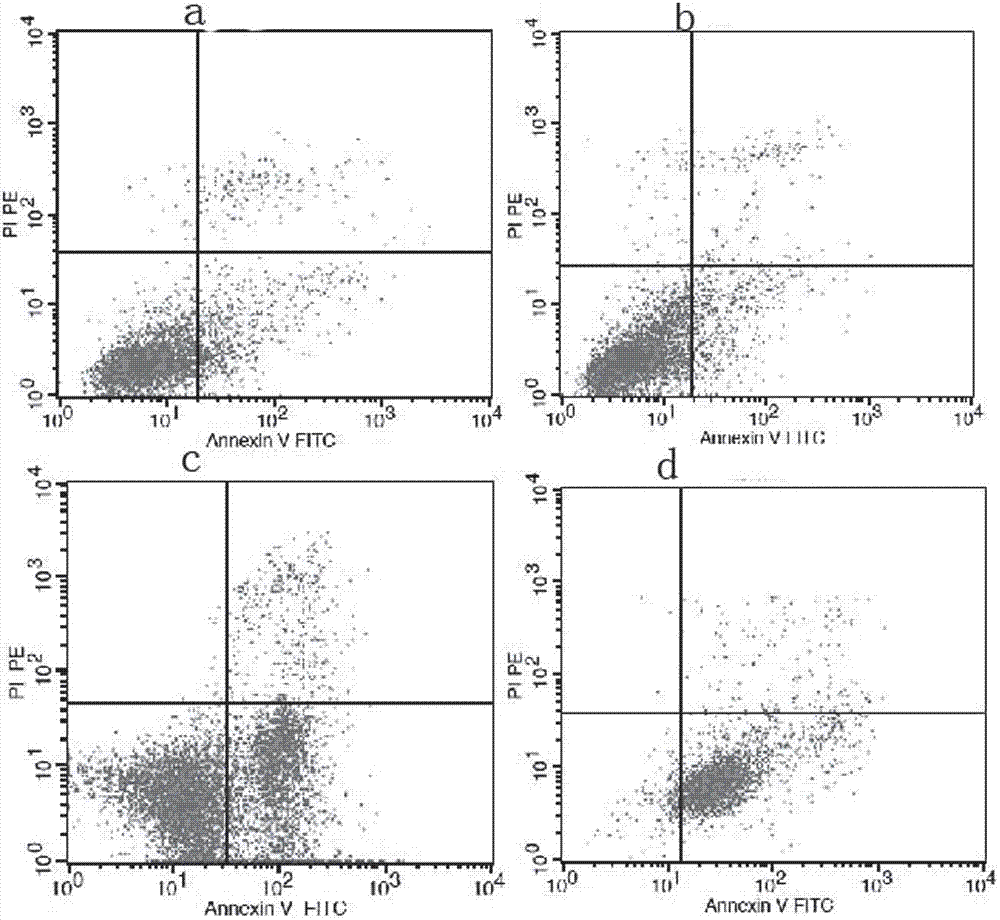
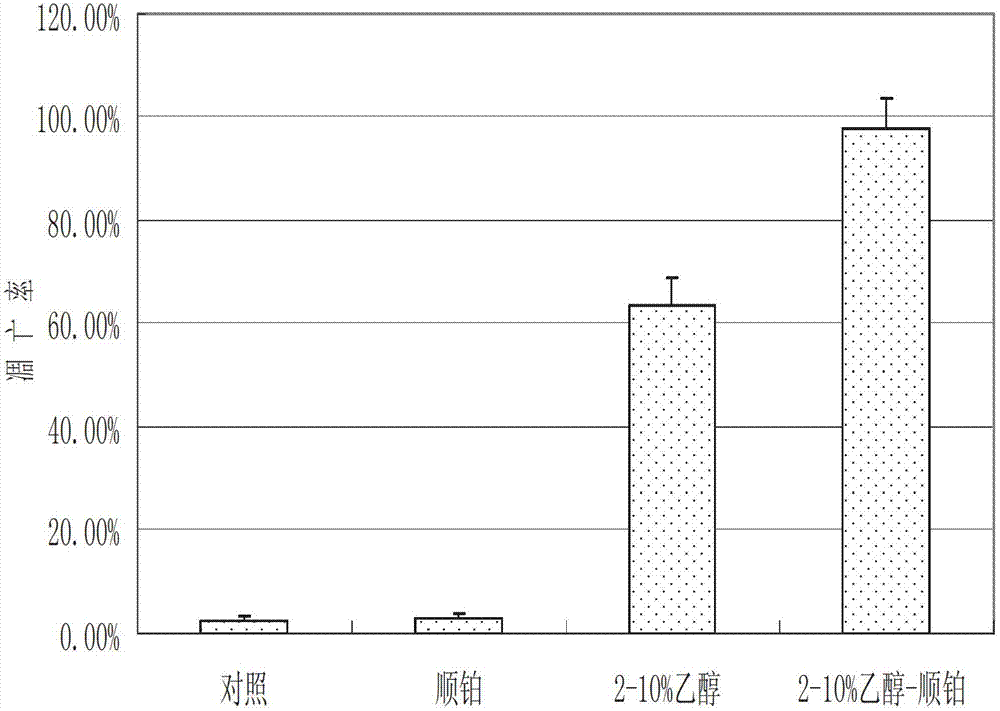
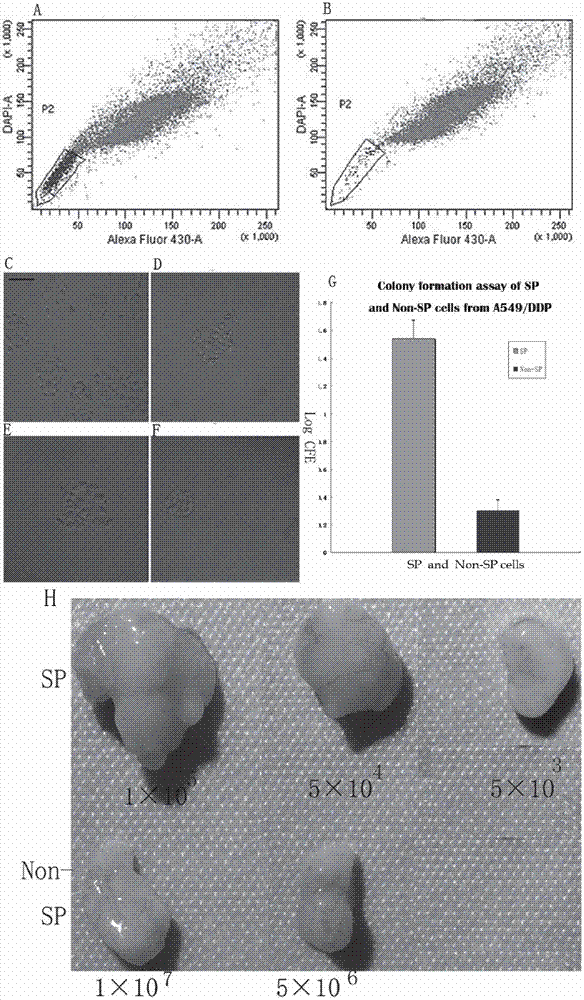
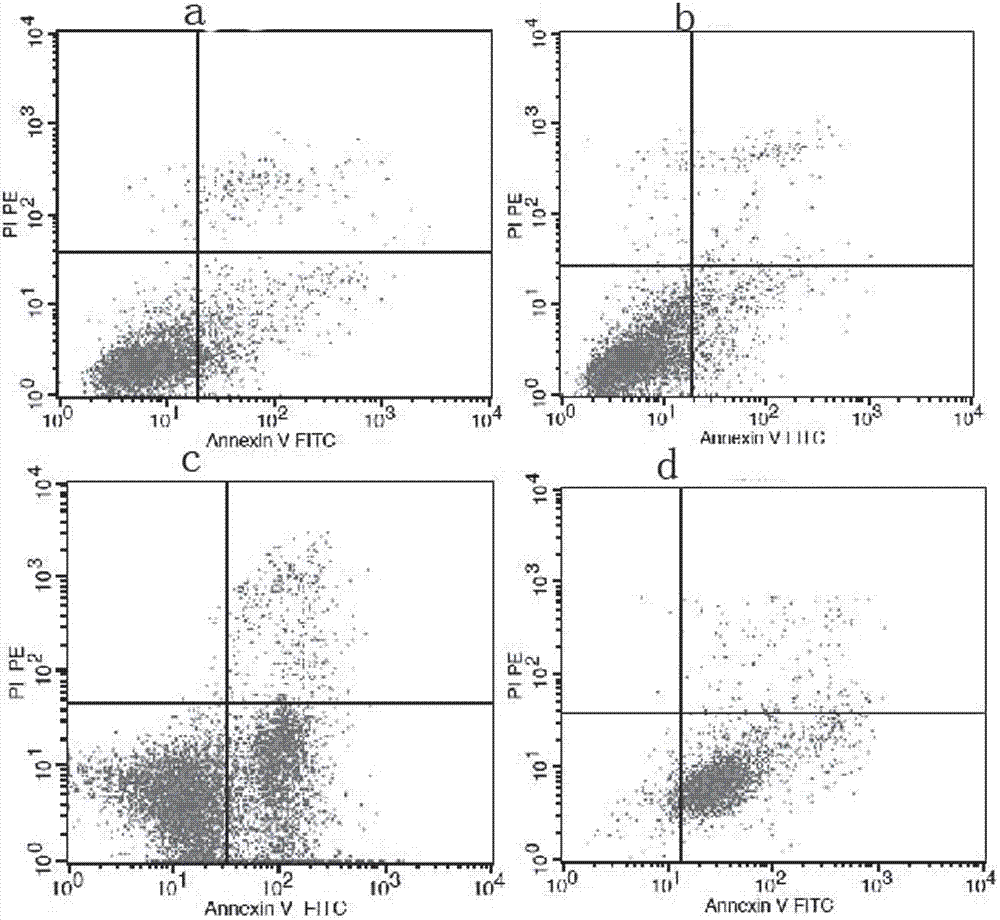
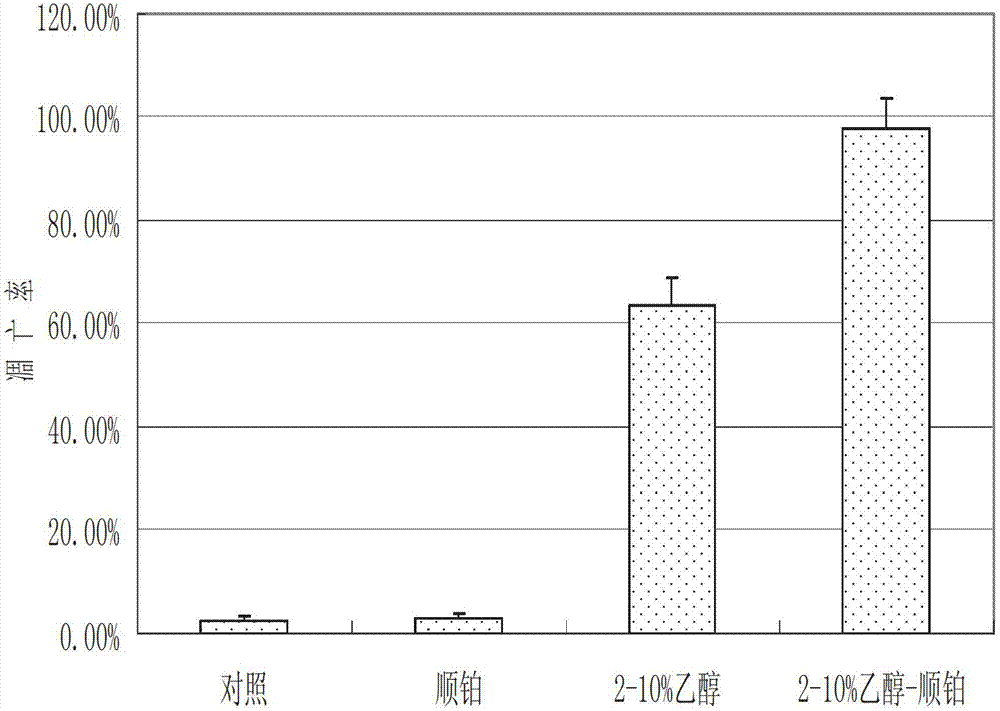
Cancer therapeutic medicine capable of killing medicine-resistant tumor cells and tumor stem cells in chemicotherapy
InactiveCN102772429AEfficient killingProlong survival timeAntibacterial agentsHeavy metal active ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthLymphatic Spread
The invention discloses a cancer therapeutic medicine capable of killing medicine-resistant tumor cells and tumor stem cells in chemicotherapy and an application thereof. The medicine is characterized by comprising the following components: the liquid medicine in every 100 milliliters contains 2-10ml of absolute ethyl alcohol, 40-50mg of cis-platinum complexes and 90-98ml of sterile water. The medicine is mainly used for local injection of tumors or intravesical therapy of chest, abdomen, pericardial cavity malignant effusion or aerosol inhalation therapy of lung tumors, and is suitable for the therapy of various solid tumors such as lung cancer, liver cancer, pancreatic cancer, ovarian cancer, cervical cancer, mammary cancer, retroperitoneal tumor or retroperitoneal lymph node metastasis, cardia cancer, gastrointestinal malignant cancer, soft tissue sarcoma, glioma and head and neck neoplasm and the medicine-resistant or medicine-sensitive tumor therapy with chest, abdomen, pericardial cavity malignant effusion.
Owner:牛旗 +1
Electrosurgical Pericaridial Puncture
ActiveUS20190008588A1Organ movement/changes detectionSurgical needlesParietal PericardiumCardiac muscle
Devices and methods for providing access to the pericardial cavity while reducing risk of myocardial damage. One method includes using an apparatus to apply pressure to a parietal pericardium, retracting the apparatus, and puncturing the parietal pericardium by delivering electrical energy using a puncture device. Another method includes moving a portion of parietal pericardium away from a surface of myocardium of the heart and puncturing the parietal pericardium by delivering electrical energy using a puncture device. The methods may include a step of confirming that the puncture device is at least partially within the parietal cavity by injecting or aspirating fluid through a lumen in the puncture device or measuring the pressure or electrical impedance at the distal end of the puncture device.
Owner:BOSTON SCI MEDICAL DEVICE LTD
Fish real-time ECG miniature collecting method, device and system
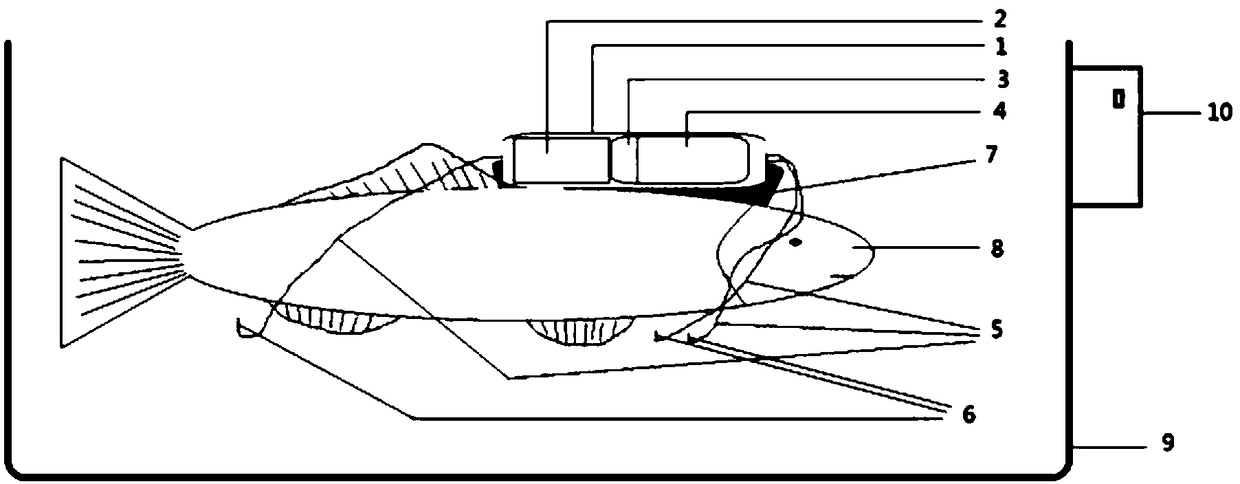
ActiveCN109044343AEasy to carryContinuous acquisitionSensorsTelemetric patient monitoringEcg signalPericardial cavity
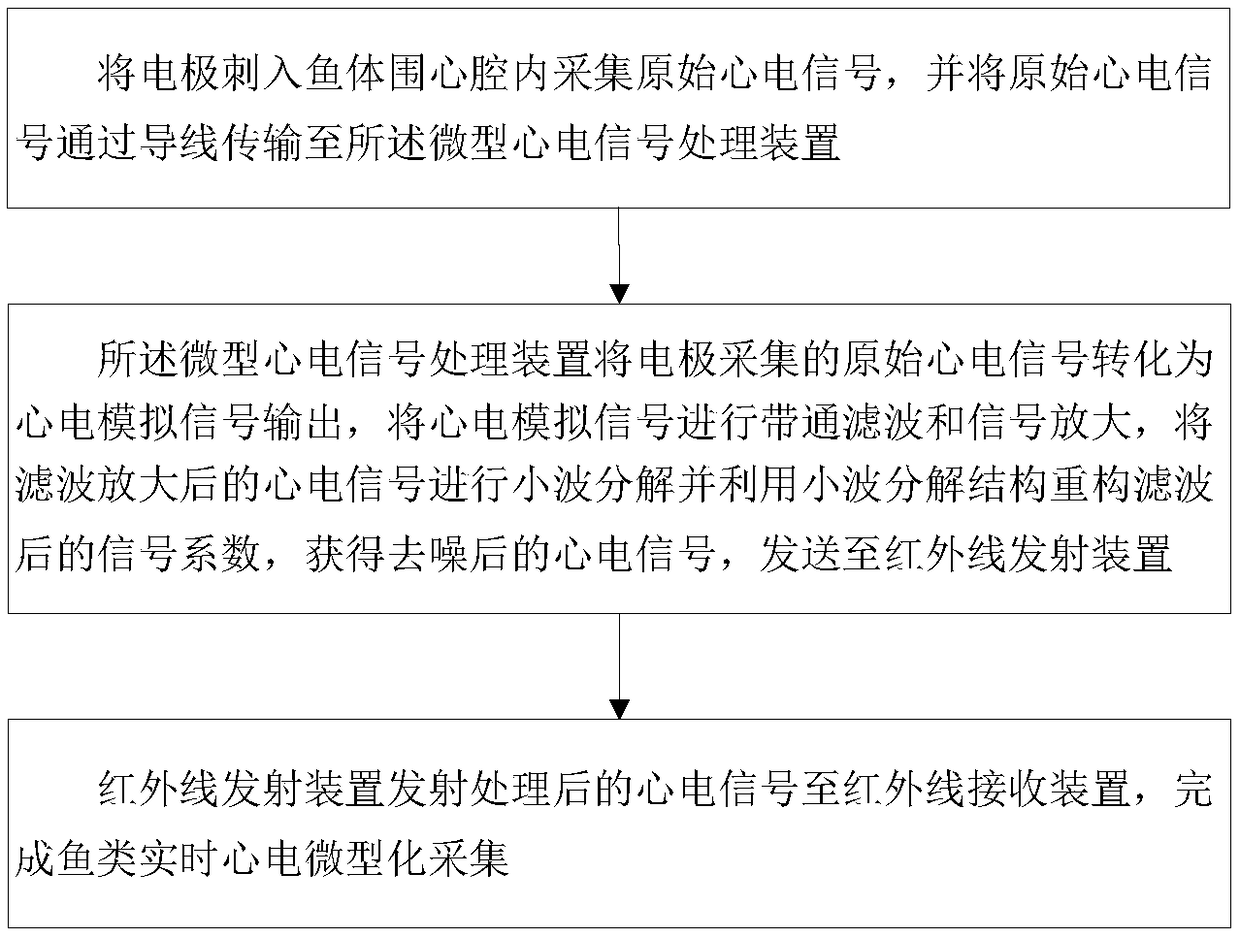
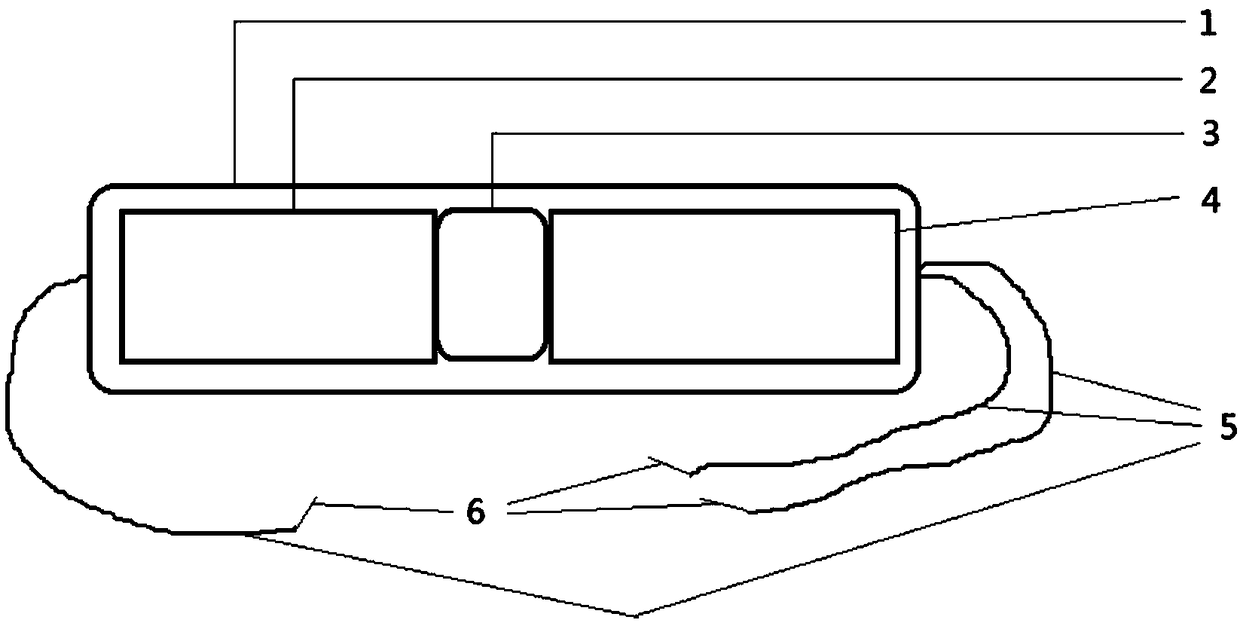
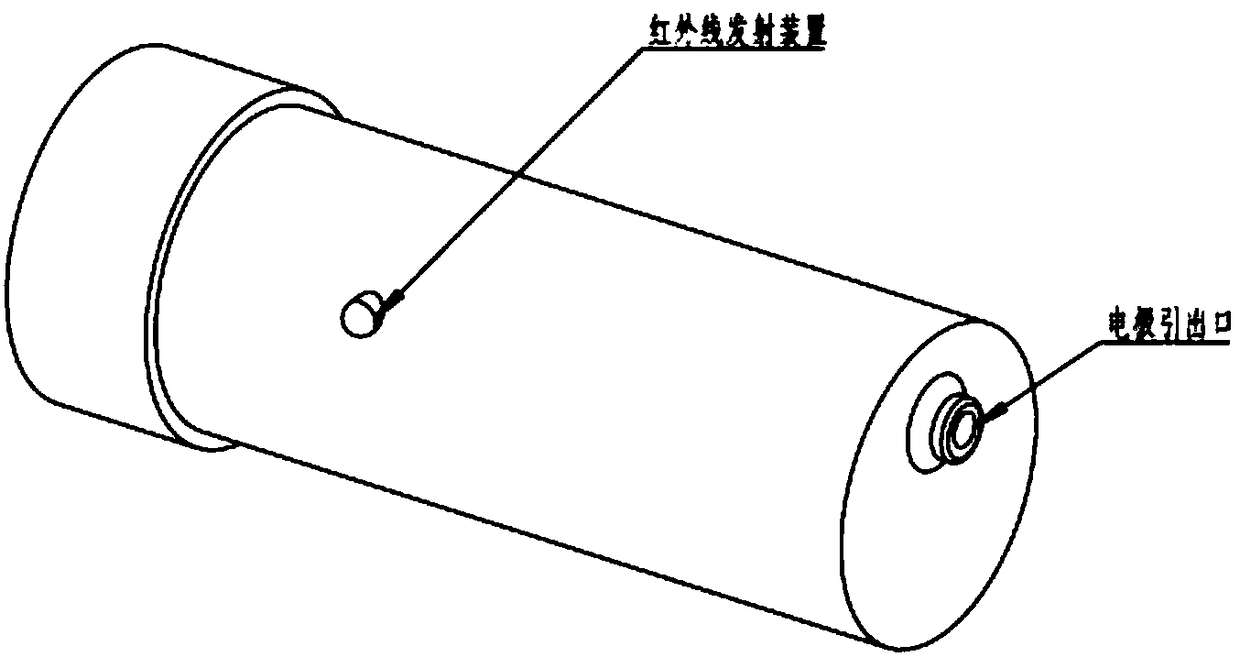
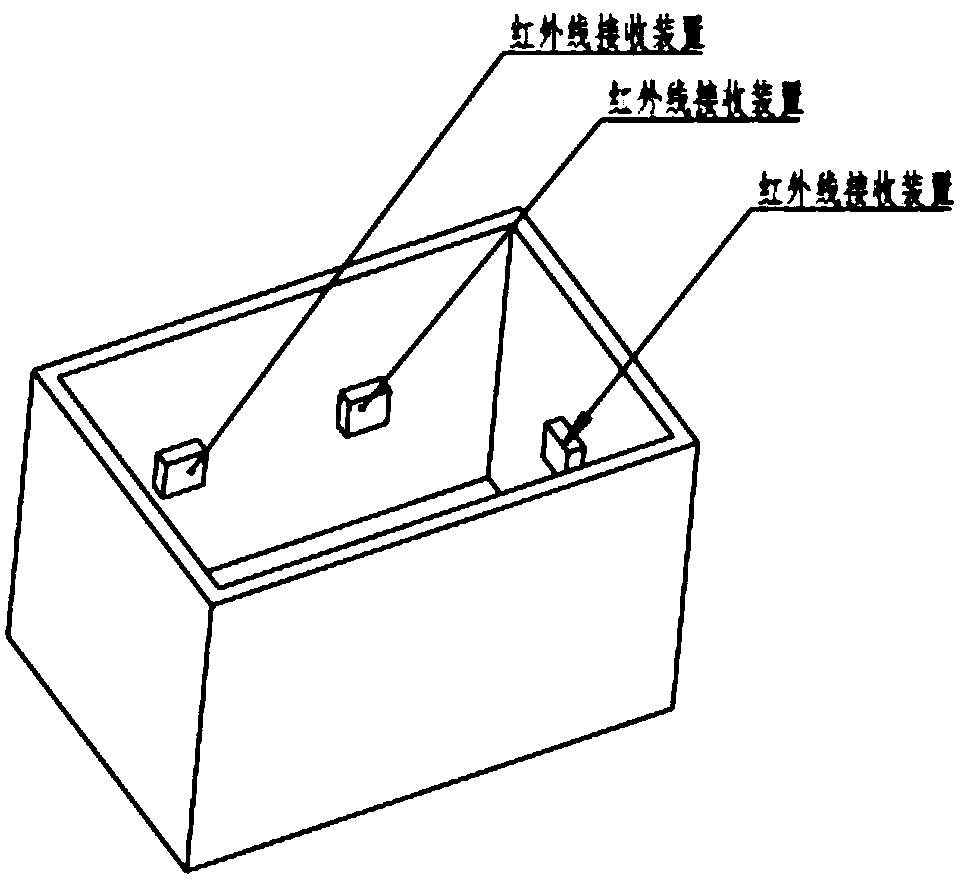
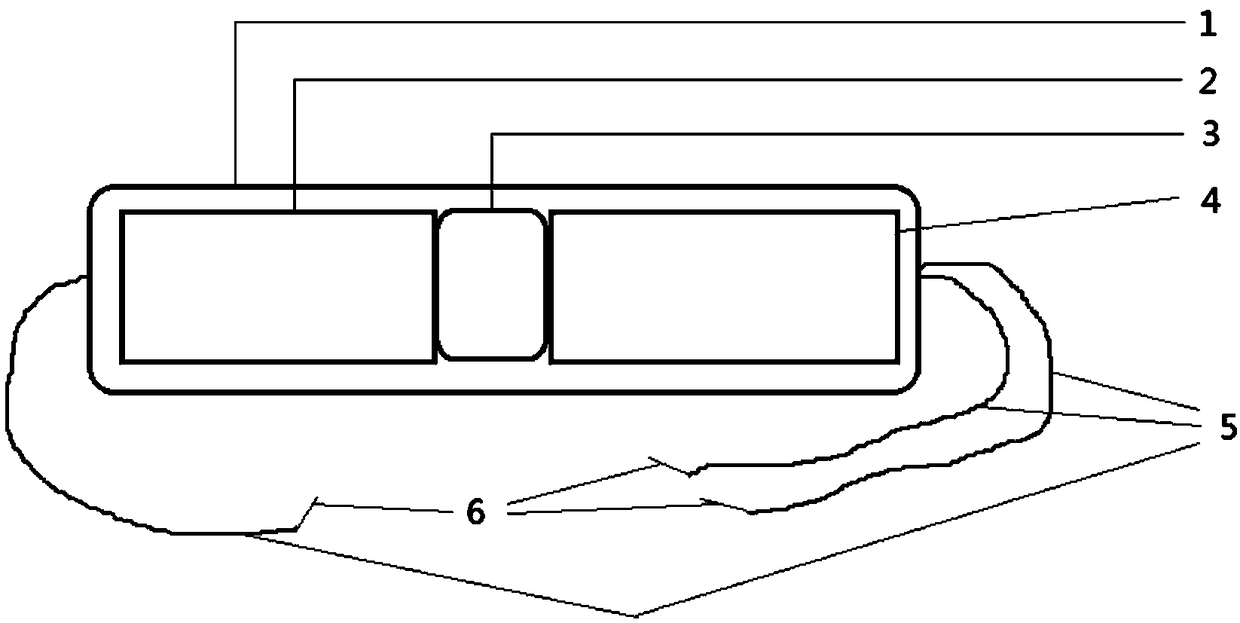
The invention discloses a fish real-time ECG miniature collecting method, device and system. The device comprises a waterproof shell. The waterproof shell comprises a waterproof shell body and a waterproof cover in sealing connection with the waterproof shell body. A miniature ECG signal processing device, and a storage device and a battery which are connected with the miniature ECG signal processing device are fixedly placed in the waterproof shell body. The miniature ECG signal processing device is connected with an electrode through a wire. An electrode lead-out opening is formed in the bottom end of the waterproof shell. The electrode pierces in a pericardial cavity of a fish body to collect original ECG signals and transmits the ECG signals to the miniature ECG signal processing device through the wire to be processed. A through hole for placing an infrared signal transmitting device is formed in the side face of the waterproof shell. The transmitting end of the infrared signal transmitting device is in sealing connection with the through hole. The infrared signal transmitting device is connected with the battery and the miniature ECG signal processing device and transmits theprocessed ECG signals to an infrared signal receiving device matched with the infrared signal transmitting device so that fish real-time ECG signal collection can be completed.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Fish electrocardiogram real-time acquisition system, and method and system for water environment monitoring
ActiveCN109222959AEasy to carryWill not bear weightDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEcg signalData acquisition
The invention discloses a fish electrocardiogram real-time acquisition system and a method and a system for water environment monitoring. The system comprises a fish electrocardiogram real-time acquisition device and an infrared signal receiving device. The fish electrocardiogram real-time collecting device is installed on the fish body through a carrier which fits the fish shape, and the carrierrealizes the state that the gravity and buoyancy of the carrier and the fish electrocardiogram real-time collecting device are equal. The fish electrocardiogram real-time acquisition device comprisesa waterproof shell, a miniature electrocardiogram signal processing device fixedly arranged in the waterproof shell, a storage device and a battery connected with the miniature electrocardiogram signal processing device, wherein the miniature electrocardiogram signal processing device is connected with an electrode through a conductor, and the electrode is pierced into the fish body pericardial cavity to collect the original electrocardiogram signal. The infrared signal transmitting device is respectively connected with a battery and a miniature electrocardiogram signal processing device, andthe processed electrocardiogram signal is transmitted to the infrared signal receiving device cooperated with the infrared signal transmitting device to complete the real-time electrocardiogram signalacquisition of fish.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Cell feeding method for treating heart disease
InactiveCN104922155AGuaranteed biological activityGood initial retentionMammal material medical ingredientsCardiovascular disorderTherapeutic effectHeart disease
The invention discloses a cell feeding method for treating heart disease. The method comprises the following steps: a, culturing treatment cells; b, preparing a suspension of the treatment cells and a culture medium; and c, placing the suspension into pericardial cavity. The method has advantages as follows: it can be ensured that the treatment cells simultaneously have better initial retention rate, in vivo survival rate and cell utilization rate, bioactivity of the treatment cells after transplantation can be well maintained, and cell treatment effect on heart disease can be further enhanced.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN MEMORIAL HOSPITAL SUN YAT SEN UNIV +1
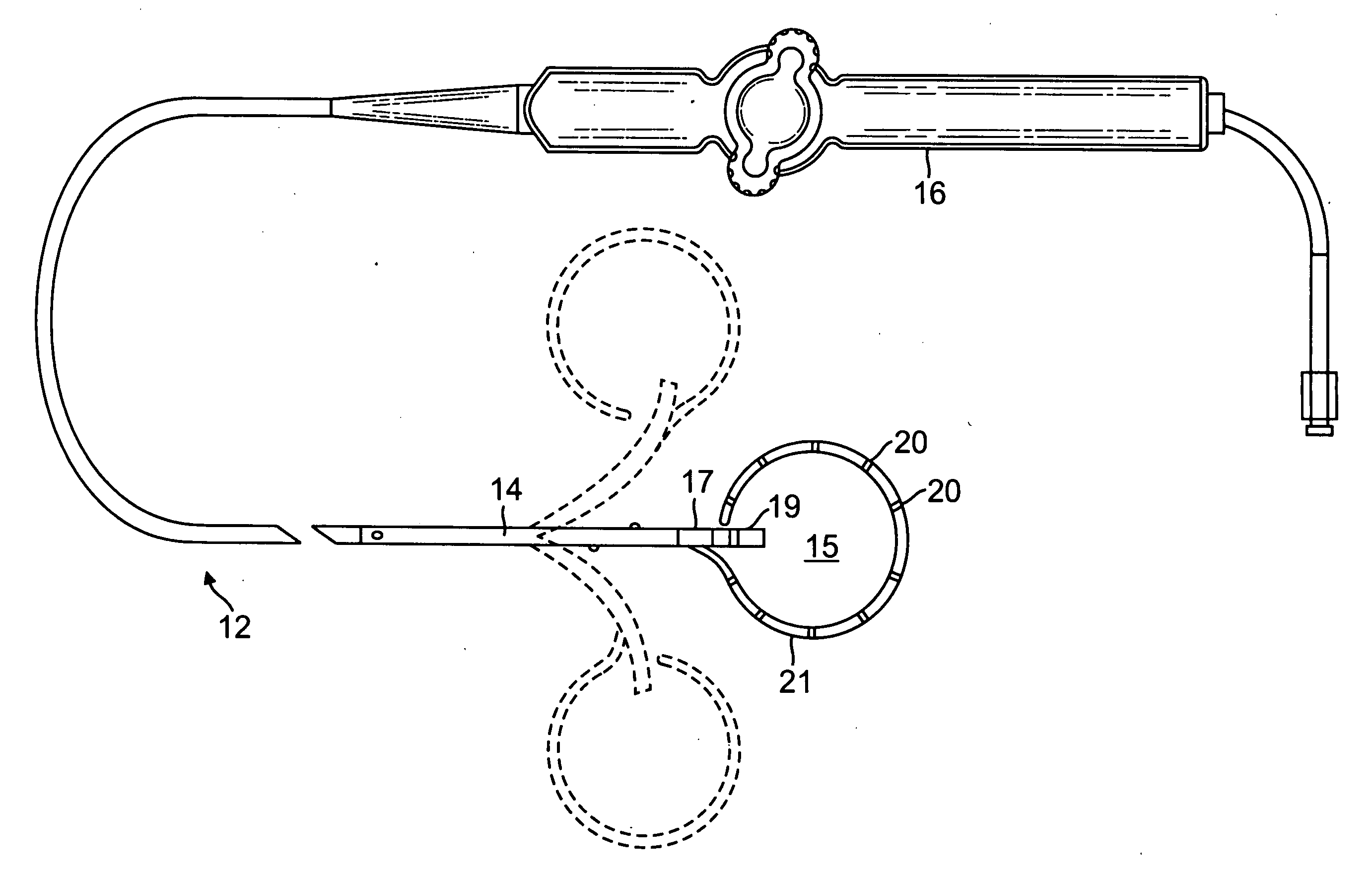
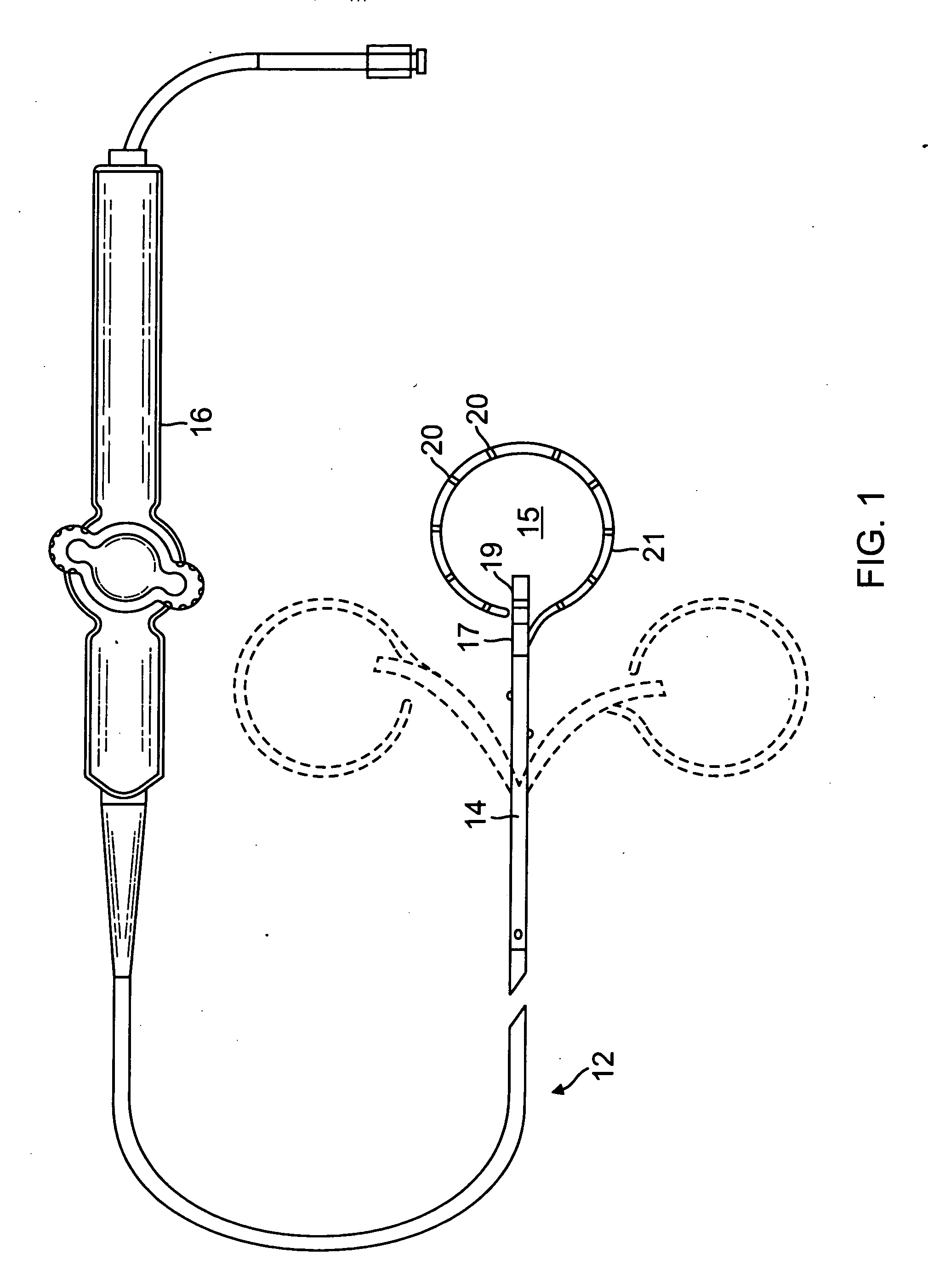
Pericardium endoscope, lasso device and heart left aurcle closing system
The invention provides a pericardium endoscope, a lasso device and a heart left aurcle closing system which are simple in instrumental design, low in cost, and low in operating requirement. Particularly, when left aurcle closing operating is carried out, the pericardium endoscope enters a pericardial cavity through pericardiopuncture. After an expanding saccule is inflated and expanded, observing is carried out, and the position of the left aurcle is confirmed. A clamping device also enters the pericardial cavity through the pericardiopuncture. The pericardium endoscope is utilized to obtain an observing image, clamping is carried out on the left aurcle, and the left aurcle is fixed. After clamping is fixed, the lasso structure is sleeved with the clamping device, enters the pericardial cavity and is sleeved with the left aurcle. An operating handle controls the lasso structure to be fastened and to be separated from a lasso guiding pipe, and closing / blocking operating of the left aurcle can be completed.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICROPORT EP MEDTECH CO LTD
Reflectance-facilitated ultrasound treatment and monitoring
InactiveUS9707414B2High energyFacilitate ablationUltrasound therapyElectrocardiographyTransducerPericardial cavity
Apparatus comprising a reflection-facilitation element, which is disposed in the pericardial cavity of a subject and on a first side of a tissue of the subject. The reflection-facilitation element comprises an inflatable member, having a first side and a second side, and configured to be inflated while disposed in the pericardial cavity, and a plurality of electrodes, comprising at least a first electrode and a second electrode, the first electrode being disposed on the first side of the inflatable member. The apparatus further comprises an ultrasound transducer placed on a second side of the tissue of the subject, and configured to apply ultrasound energy to the tissue of the subject such that at least a portion of the energy reaches the inflatable member. The inflatable member reflects at least a portion of the ultrasound energy that reaches the inflatable member.
Owner:RAINBOW MEDICAL LTD
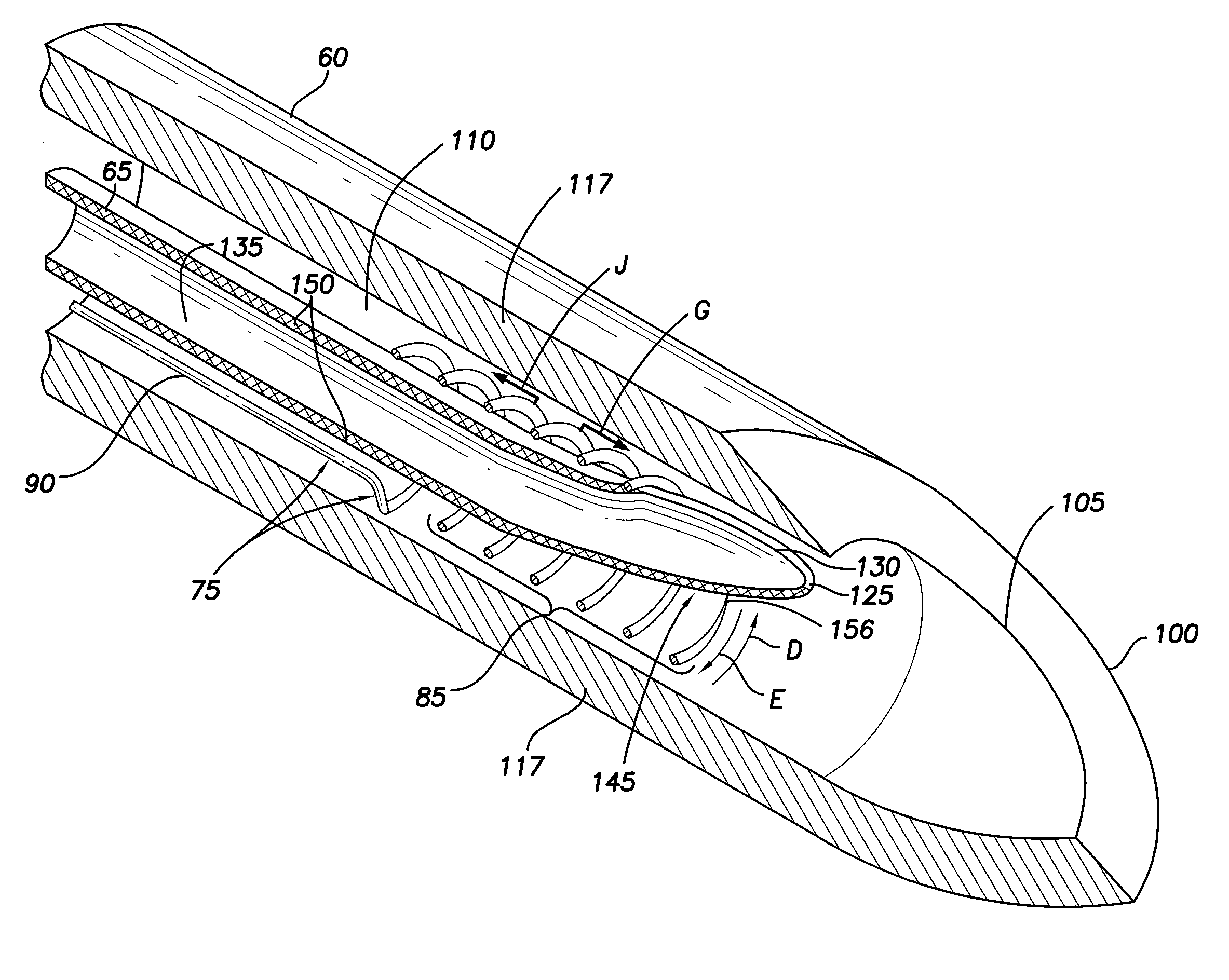
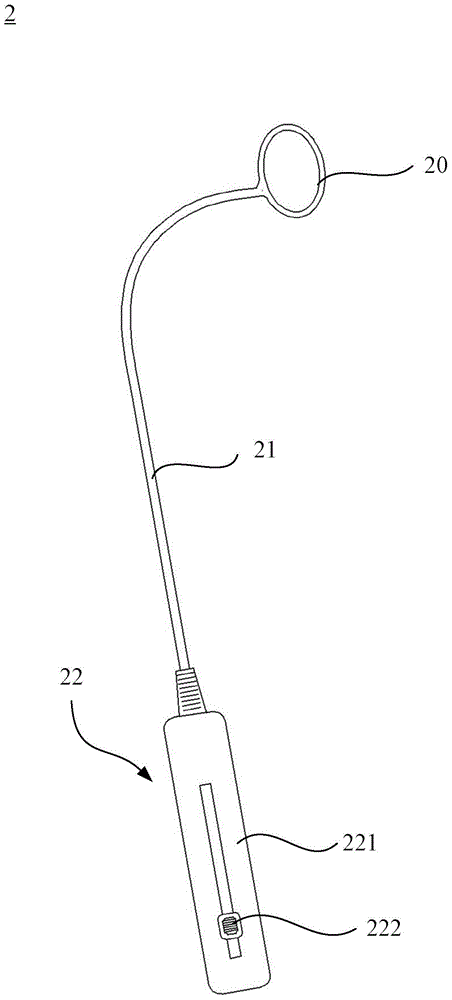
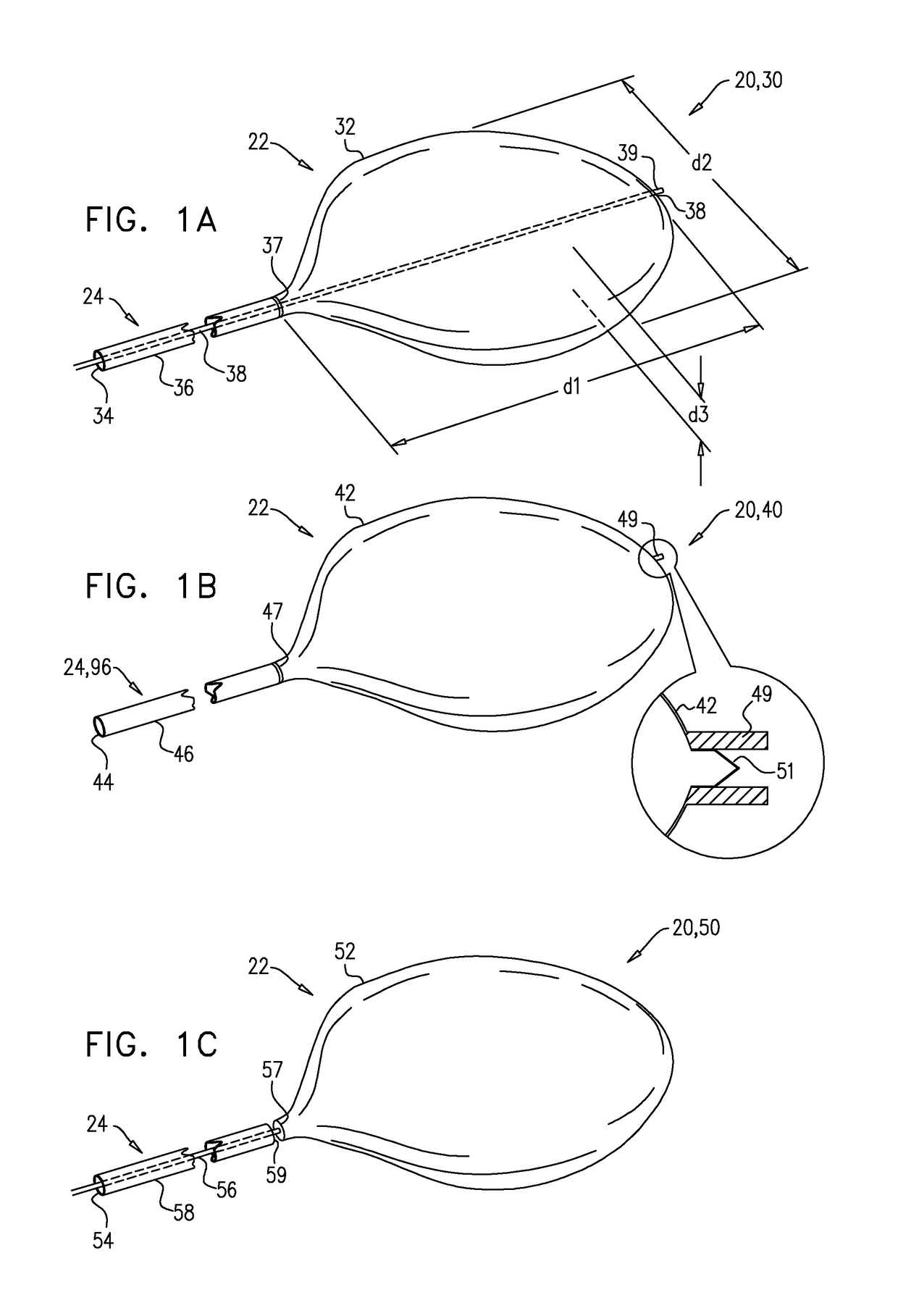
Pericardial access devices and methods
Described here are devices, systems, and methods for accessing the pericardial space through the pericardium. The access devices may include a plurality of elongate members having lumens that may be advanced together through the body to the pericardium. The elongate members may have different lengths and may be slideably positioned one within the lumen of another. At least one of the elongate members may comprise a distal tip configured to pierce tissue. In some instances, the access devices may also comprise a locking member to constrain the position of one elongate member relative to another.
Owner:SENTREHEART
Preparation of lipoic acid-loaded nano material and application of lipoic acid-loaded nano material in acute myocardial infarction disease
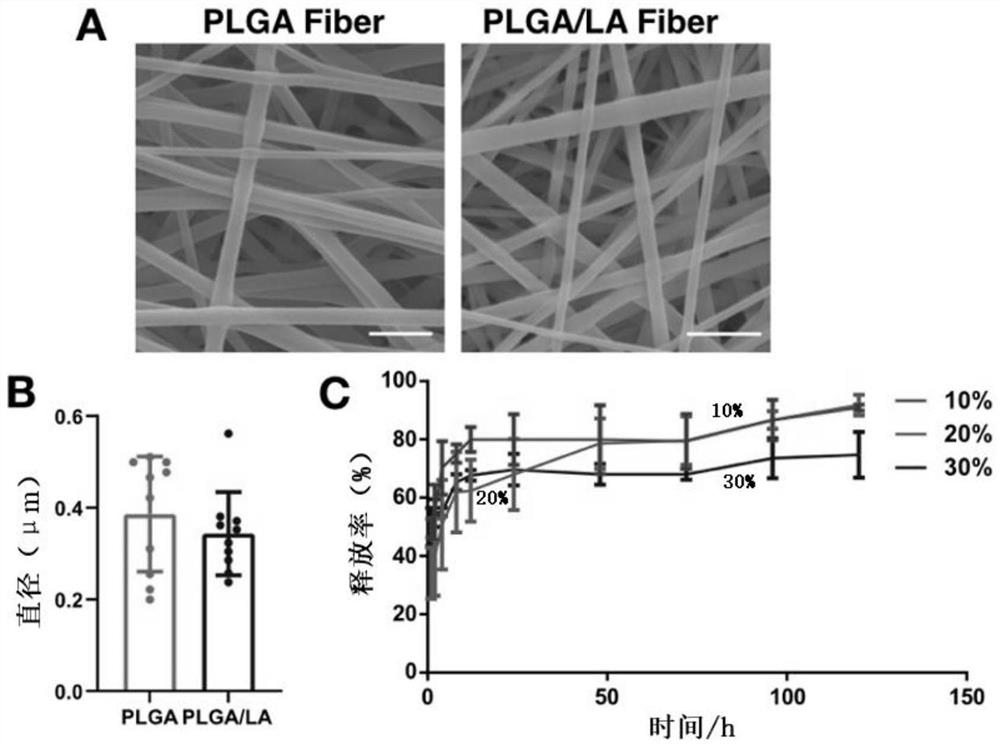
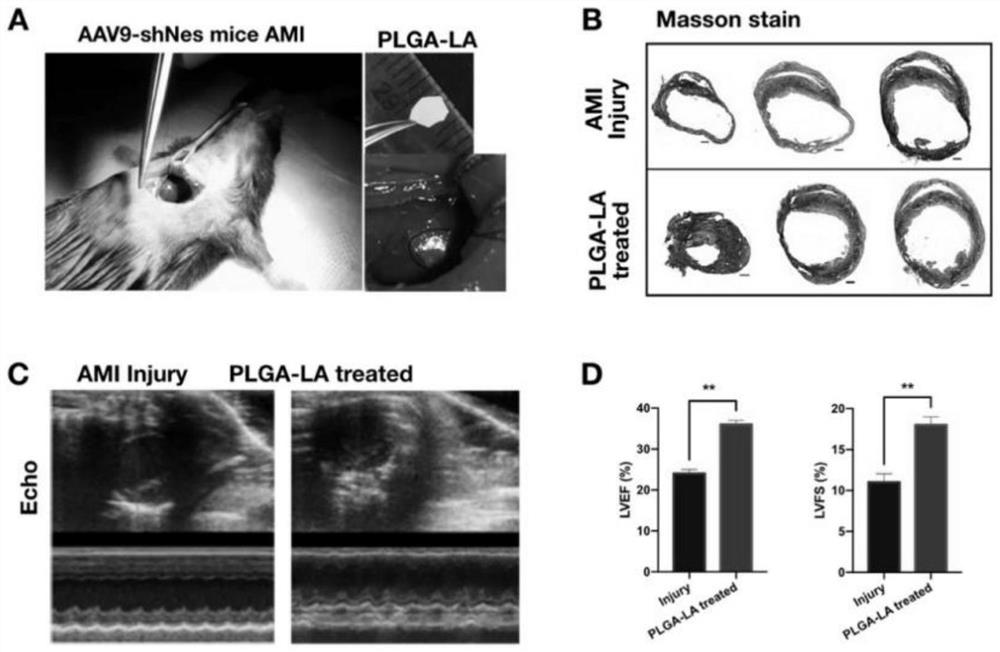
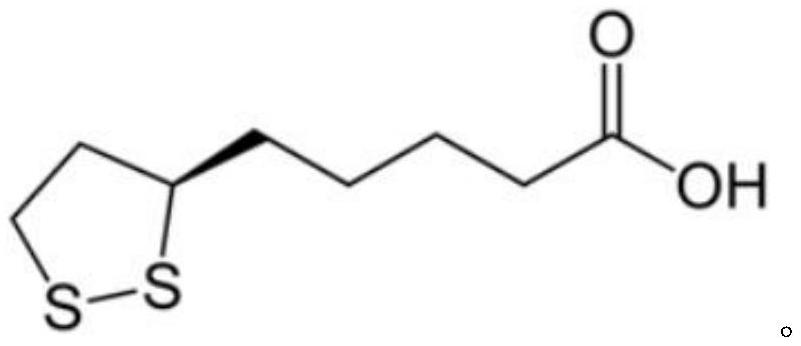
ActiveCN114652702AHigh drug loadingHigh encapsulation efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsElectro-spinningDiseaseAntioxidative stress
The invention belongs to the technical field of biochemical medicines, and particularly relates to preparation of a lipoic acid-loaded nano-material and application of the lipoic acid-loaded nano-material in acute myocardial infarction diseases. An electrospinning technology is adopted, and a multi-layer lipoic acid-loaded PLGA nano-film material is synthesized by taking PLGA which is degraded at a controllable speed as a raw material to load lipoic acid; the nano-film material has better drug loading capacity and encapsulation efficiency, and also has a better drug release effect in a PBS (Phosphate Buffer Solution), so that the drug can be quickly and continuously released locally in a myocardial infarction area, and a good anti-oxidative stress treatment effect is achieved; when being applied to myocardial infarction treatment (namely being placed on the surface of myocardial infarction heart tissue in a pericardial cavity) as a cardiac functional patch, the medicine can improve ventricular remodeling, improve the cardiac function level, effectively relieve myocardial cell oxidative stress injury and improve the treatment effect of acute myocardial infarction.
Owner:THE THIRD AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SUN YAT SEN UNIV
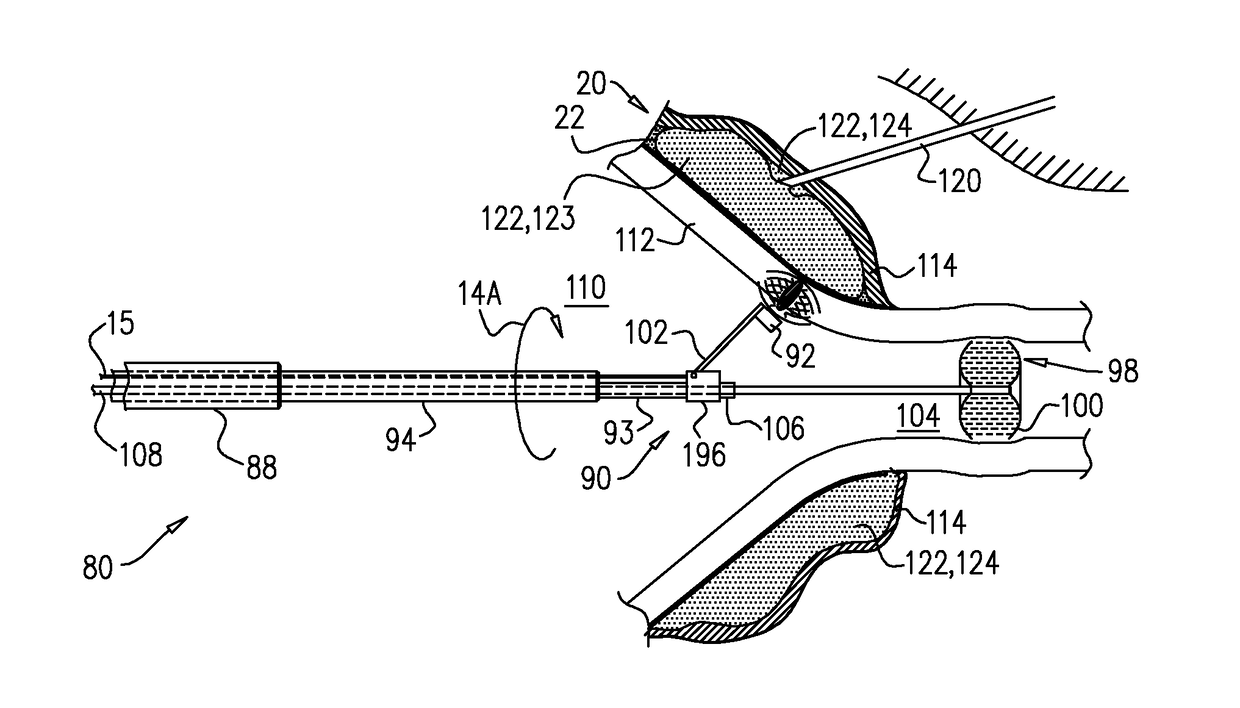
Pericardial-cavity observing method
A pericardial-cavity observing method including: a step of inserting an endoscope sheath and an endoscope into a space between the heart and the pericardium; a step of disposing a protruding portion closer to the pericardium than an optical member is so that an angle that is formed between a centerline that passes through a center of the protruding portion and a center of the optical member and a tangent of the pericardium that passes through a foot of a perpendicular line drawn, from the center of the optical member of the endoscope, to the pericardium sagging down from the protruding portion toward the heart becomes greater than an angle formed between the centerline and an external common tangent of the protruding portion and the optical member; and a step of observing the heart by means of the endoscope.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Electrosurgical Pericardial Puncture
Devices and methods for providing access to the pericardial cavity while reducing risk of myocardial damage. One method comprises the steps of: (a) advancing a puncture device towards a heart, the puncture device including an energy delivery device at a distal end of the puncture device; (b) delivering a single pulse of a pulsed energy through the energy delivery device to a parietal pericardium of the heart to create a void relatively close to the energy delivery device while maintaining the distal end of the puncture device in a substantially stationary position relative to the parietal pericardium; (c) advancing the puncture device a short distance into the void; (d) checking if the puncture device has accessed the pericardial cavity by measuring pressure on the distal end of the puncture device; and (e) repeating steps (b), (c), and (d), if necessary, until the energy delivery device is located at least partially within the pericardial cavity. The methods may include a step of confirming that the puncture device is at least partially within the parietal cavity by injecting or aspirating fluid through a lumen in the puncture device or measuring the pressure or electrical impedance at the distal end of the puncture device.
Owner:BAYLIS MEDICAL
Pericardiopuncture device
PendingCN109730754AAvoid punctureSimple and fast operationSurgical needlesTrocarParietal PericardiumPericardial cavity
The invention relates to the technical field of clinical puncture, in particular to a pericardiopuncture device. The device comprises a needle pushing device, a sliding piece, a puncture needle, a guiding wire, a guiding wire sleeve and a clamp, the sliding piece reciprocately slides along the wall body in the length direction of the needle pushing device, and the puncture needle is detachably connected with the needle pushing device; the guiding wire sleeve is fixedly connected with the sliding piece; the guiding wire penetrates through the puncture needle and the guiding wire sleeve; the clamp is connected with the guiding wire sleeve and used for controlling sliding of the guiding wire; the guiding wire slides in the puncture needle and the guiding wire sleeve; the guiding wire is pressed to be an arc shape under the effects of the sliding piece and the puncture needle to form certain tension, when the puncture needle carrying the guiding wire enters into the parietal pericardium, under the condition of the internal and external pressure difference of the pericardial cavity, the guiding wire is bounced into the pericardial cavity, and the effect of protecting the needle point isachieved; it is avoided that the sharp needle point punctures the coronary artery and the heart, then hydrops is extracted to complete the operation, and the pericardiopuncture method is safe, simplein operation and easy to master.
Owner:黄飞雄
Cancer therapeutic medicine capable of killing medicine-resistant tumor cells and tumor stem cells in chemicotherapy
InactiveCN102772429BEfficient killingProlong survival timeAntibacterial agentsHeavy metal active ingredientsHead and neck tumorsTumor therapy
The invention discloses a cancer therapeutic medicine capable of killing medicine-resistant tumor cells and tumor stem cells in chemicotherapy and an application thereof. The medicine is characterized by comprising the following components: the liquid medicine in every 100 milliliters contains 2-10ml of absolute ethyl alcohol, 40-50mg of cis-platinum complexes and 90-98ml of sterile water. The medicine is mainly used for local injection of tumors or intravesical therapy of chest, abdomen, pericardial cavity malignant effusion or aerosol inhalation therapy of lung tumors, and is suitable for the therapy of various solid tumors such as lung cancer, liver cancer, pancreatic cancer, ovarian cancer, cervical cancer, mammary cancer, retroperitoneal tumor or retroperitoneal lymph node metastasis, cardia cancer, gastrointestinal malignant cancer, soft tissue sarcoma, glioma and head and neck neoplasm and the medicine-resistant or medicine-sensitive tumor therapy with chest, abdomen, pericardial cavity malignant effusion.
Owner:牛旗 +1
Pericardial-cavity observing method
A pericardial-cavity observing method including: a step of inserting an endoscope sheath and an endoscope into a space between the heart and the pericardium; a step of disposing a protruding portion closer to the pericardium than an optical member is so that an angle that is formed between a centerline that passes through a center of the protruding portion and a center of the optical member and a tangent of the pericardium that passes through a foot of a perpendicular line drawn, from the center of the optical member of the endoscope, to the pericardium sagging down from the protruding portion toward the heart becomes greater than an angle formed between the centerline and an external common tangent of the protruding portion and the optical member; and a step of observing the heart by means of the endoscope.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Green shrimp vitellogenin vg gene, encoded protein and its application
InactiveCN104193814BShortened maturation timeMicroinjection basedFermentationVitellogeninsFull length cdna
The invention discloses a freshwater shrimp vitellogenin Vg gene, an encoding protein and an application of the freshwater shrimp vitellogenin Vg gene. The full-length cDNA sequence of the Vg gene is cloned from hepatopancreas of the freshwater shrimp by a primer group provided by the invention, and the expression of a vitellogenin gene in the ovary and the liver can be silenced after the dsRNA of the gene is injected to the pericardial cavity of a female freshwater shrimp, so that the ovary development of the freshwater shrimp is remarkably delayed. The invention provides a new thought and an effective means for solving the sexual precocity phenomenon of the freshwater shrimp and culturing good varieties.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
A kind of efficient extraction method of hemolymph of bivalve mollusk
ActiveCN105476646BIncrease expansionHigh purityAnimal fetteringBlood sampling devicesAlcoholHemolymph
The invention relates to a method for efficiently extracting hemolymph of bivalve. The method includes the following steps that a, seawater on the surface of the bivalve is completely absorbed through cotton balls, the surface of the bivalve is wiped with ethyl alcohol to be sterilized, and seawater on the surface of the bivalve is completely sucked up through cotton balls; b, the bivalve which is completely wiped is placed in a groove of an extracting device, the adductor muscle of the bivalve is ripped open, a shell is open, and two shells are flatly open and erected in the groove; c, after pelecypod of the bivalve and the portion below a water pipe are cushioned with cotton balls, an outer sleeve membrane above a pericardial cavity is slightly shifted away through tweezers, and the pericardial cavity is completely exposed; d, a gun head of a liquid moving device is cut, meanwhile, the pelecypod of the bivalve is stimulated, and hemolymph is fast sucked with the liquid moving device when the heart beats and the pericardial cavity swells. The method has the advantages that the method is easy to operate, the total amount of the extracted hemolymph of the bivalve can be effectively increased, the purity of the hemolymph is improved, and the operating environment can be kept clean in the operating process.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
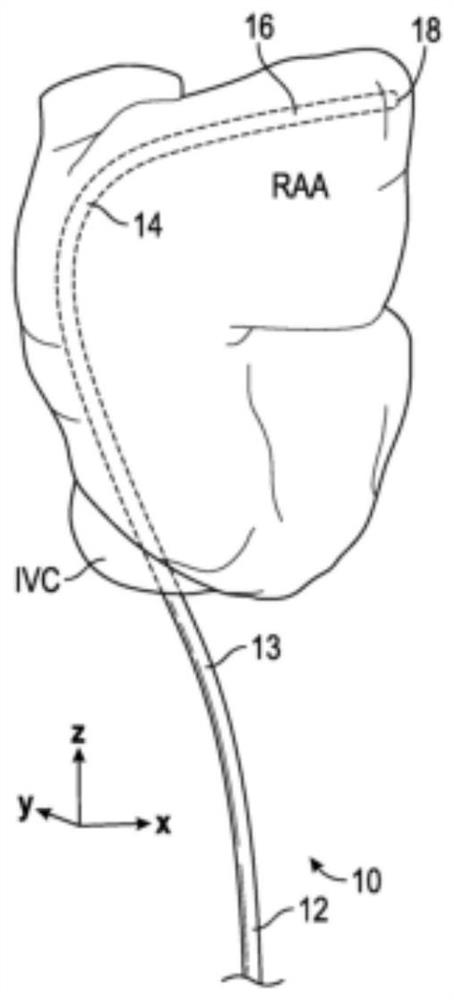
Three-dimensional Right Atrial Appendage Curved Catheter
Disclosed herein is a delivery catheter having a three-dimensional curvature that facilitates access to the RAA from the inferior vena cava, positioning the distal end of the catheter so that the puncture site within the RAA is approximately parallel to the plane of the pericardial cavity, orienting the puncture device to avoid Orientation of the right coronary artery, aorta, pulmonary artery, and other structures to prevent "bystander" injury to these structures and provide sufficient rigidity to penetrate the wall of the RAA into the pericardial cavity.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com