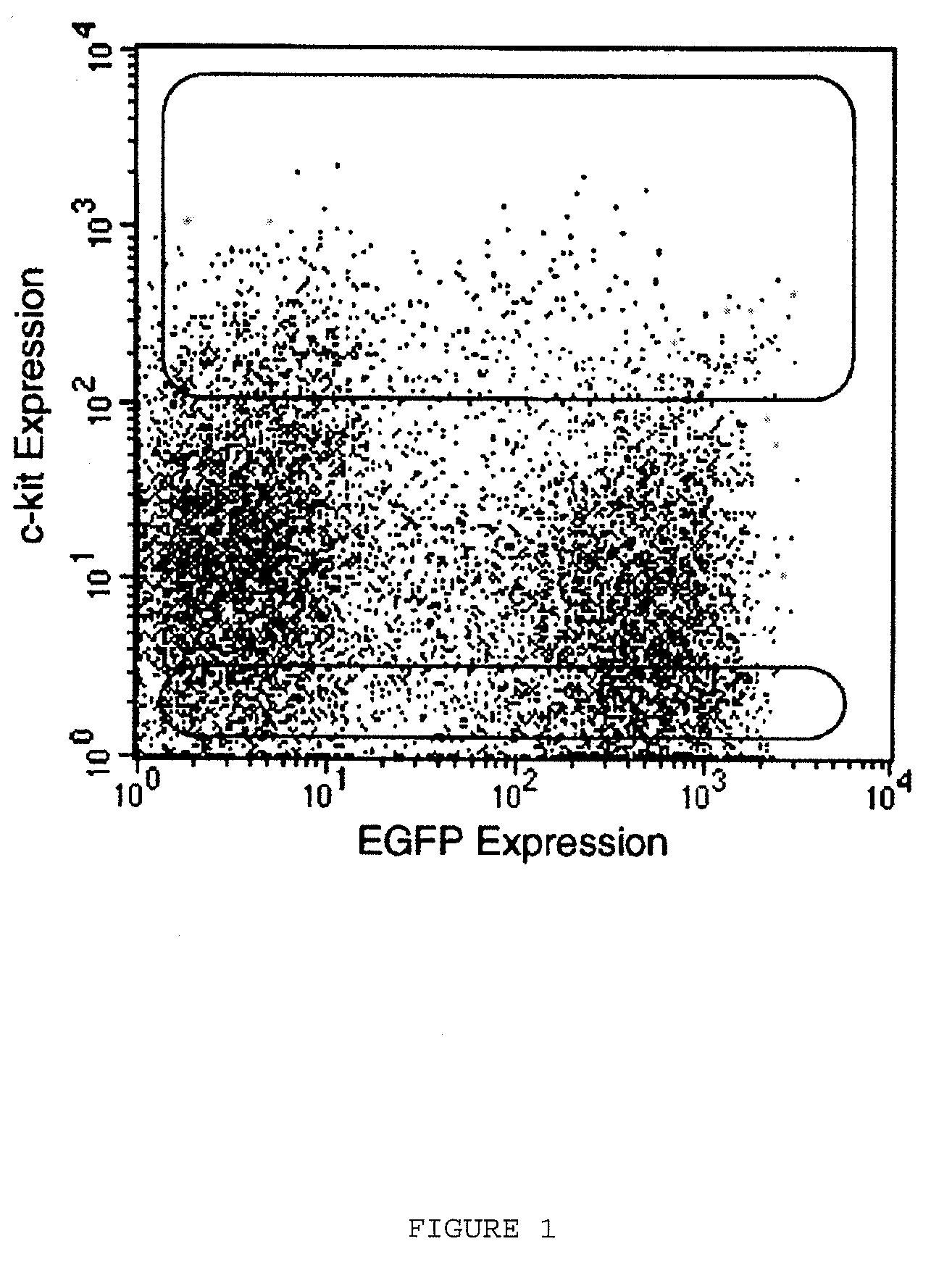
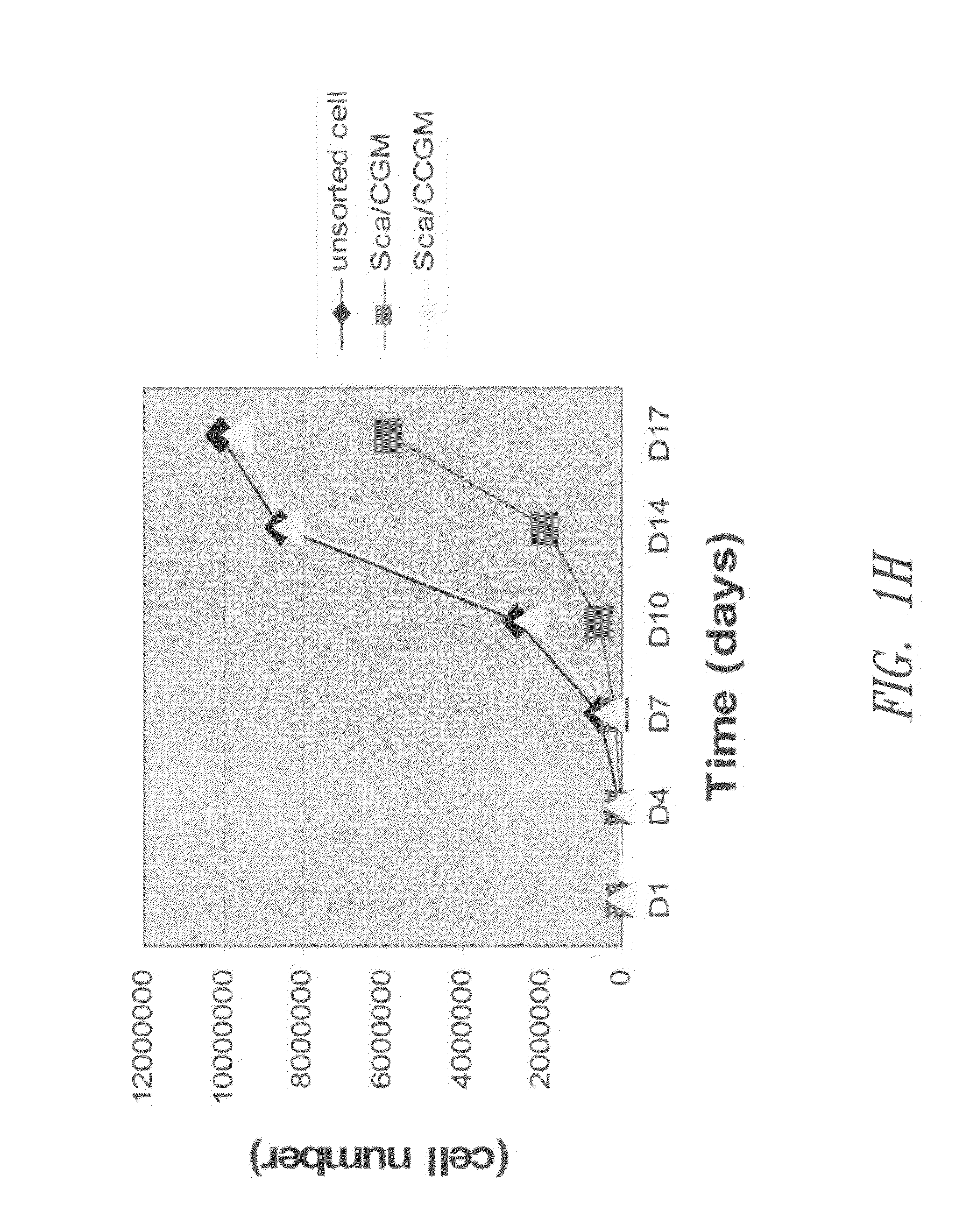
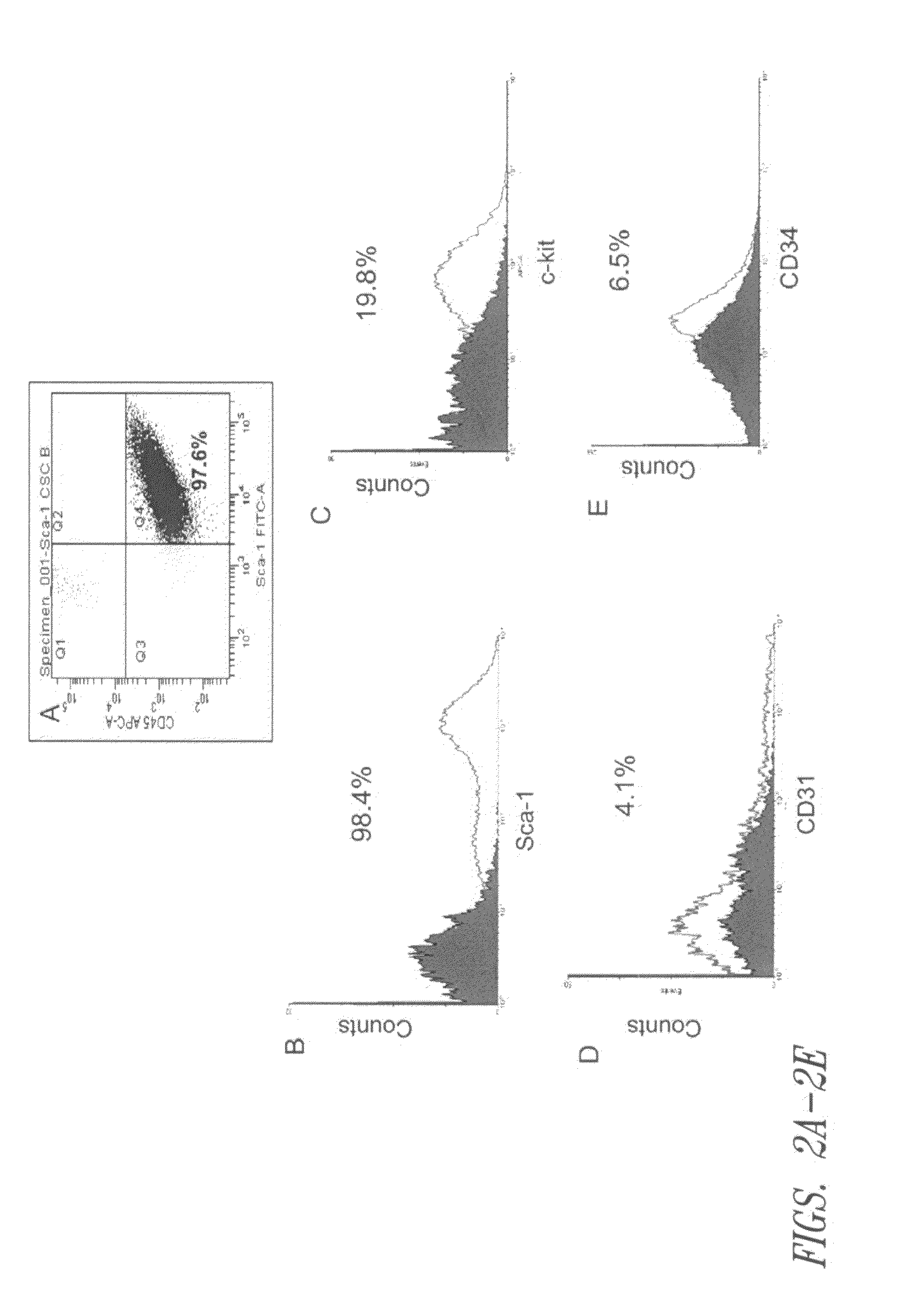
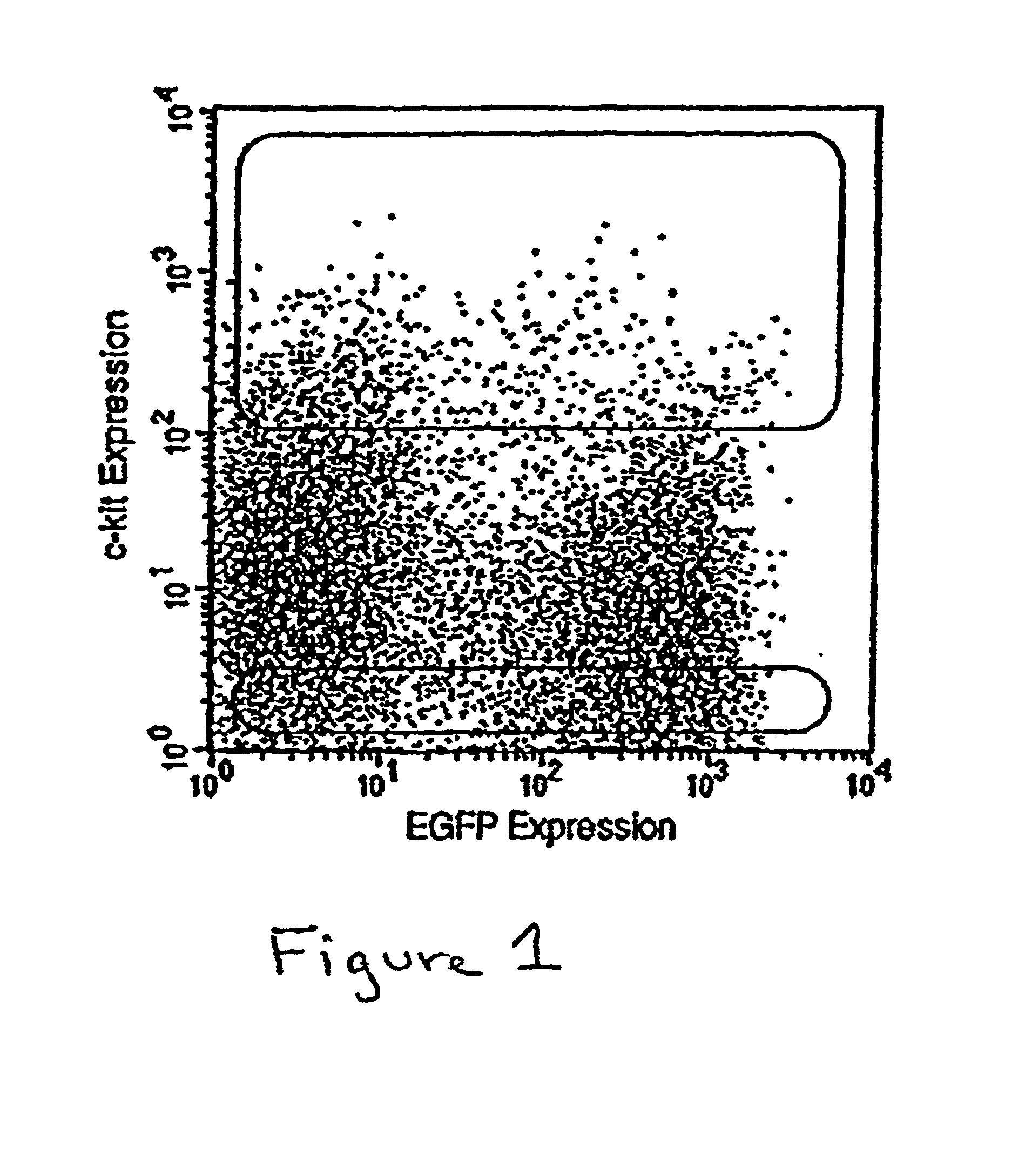
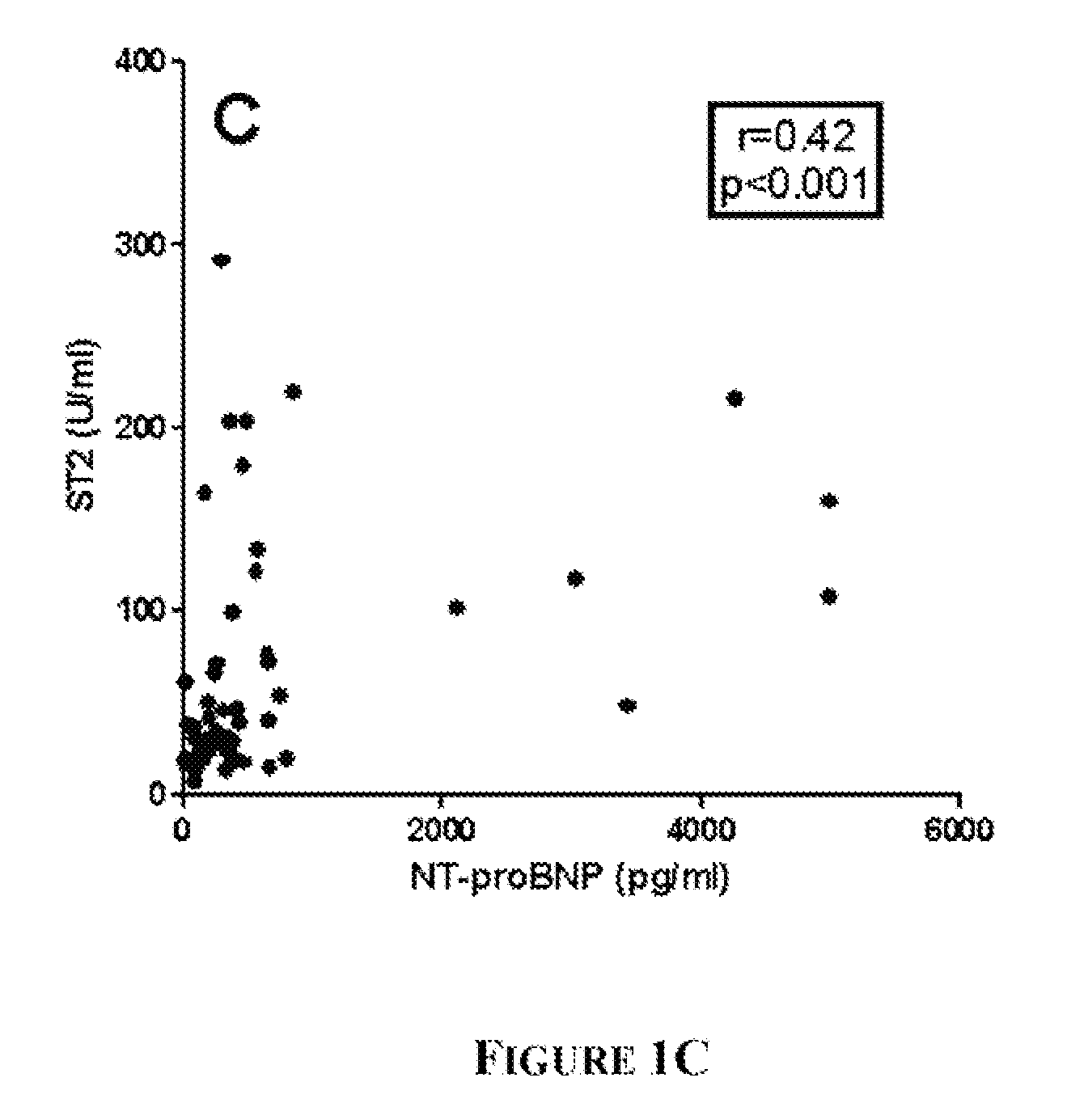
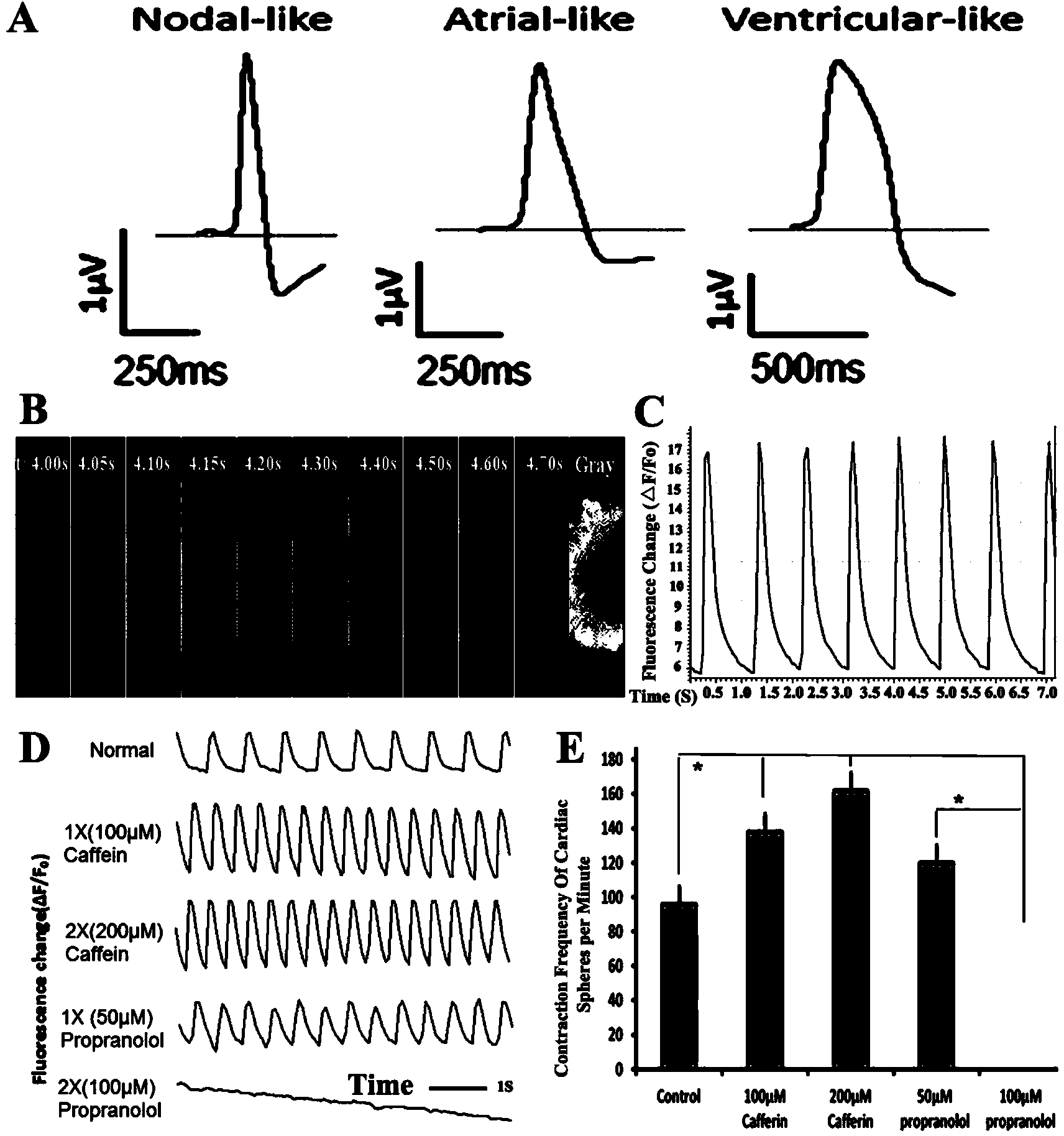
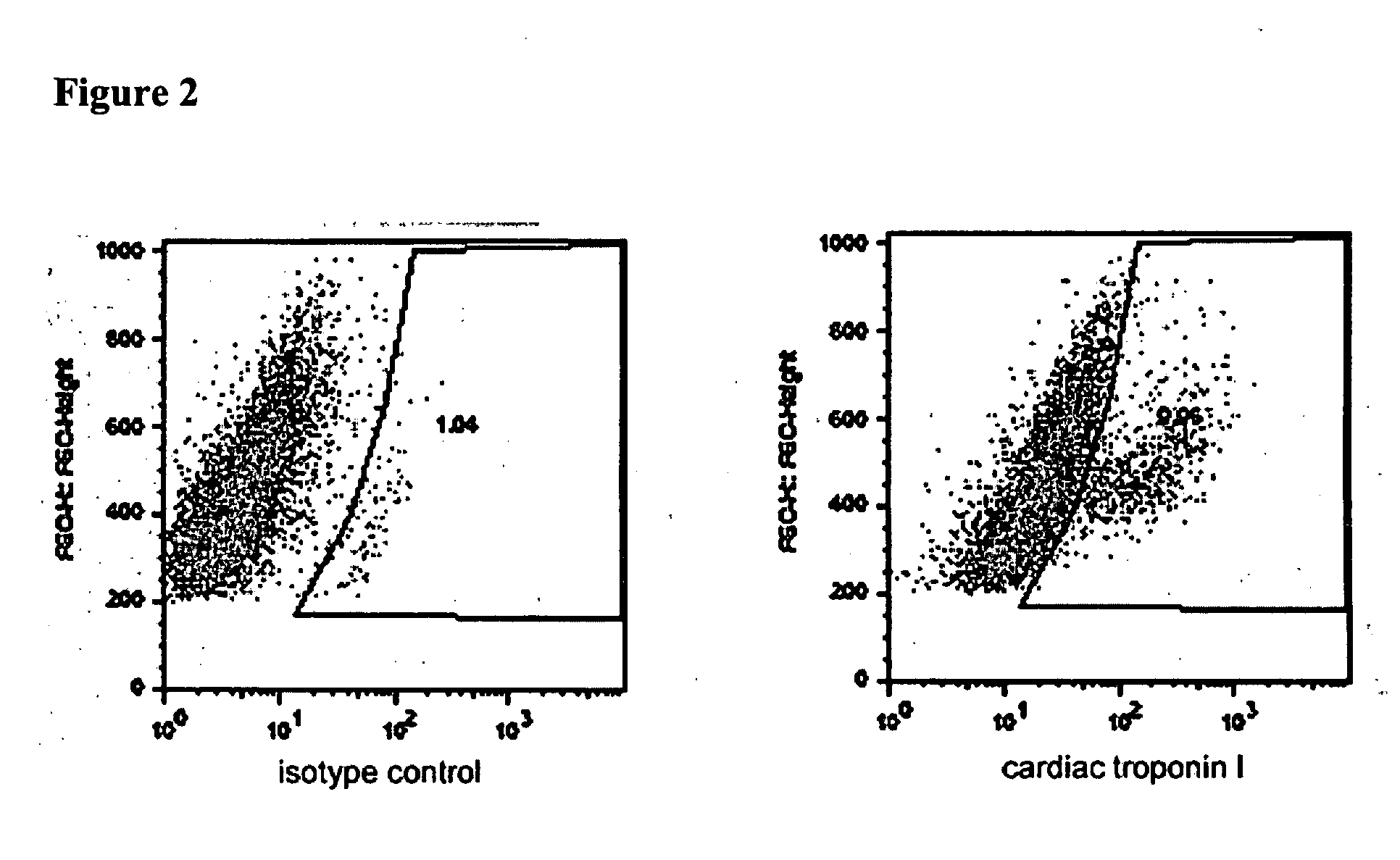
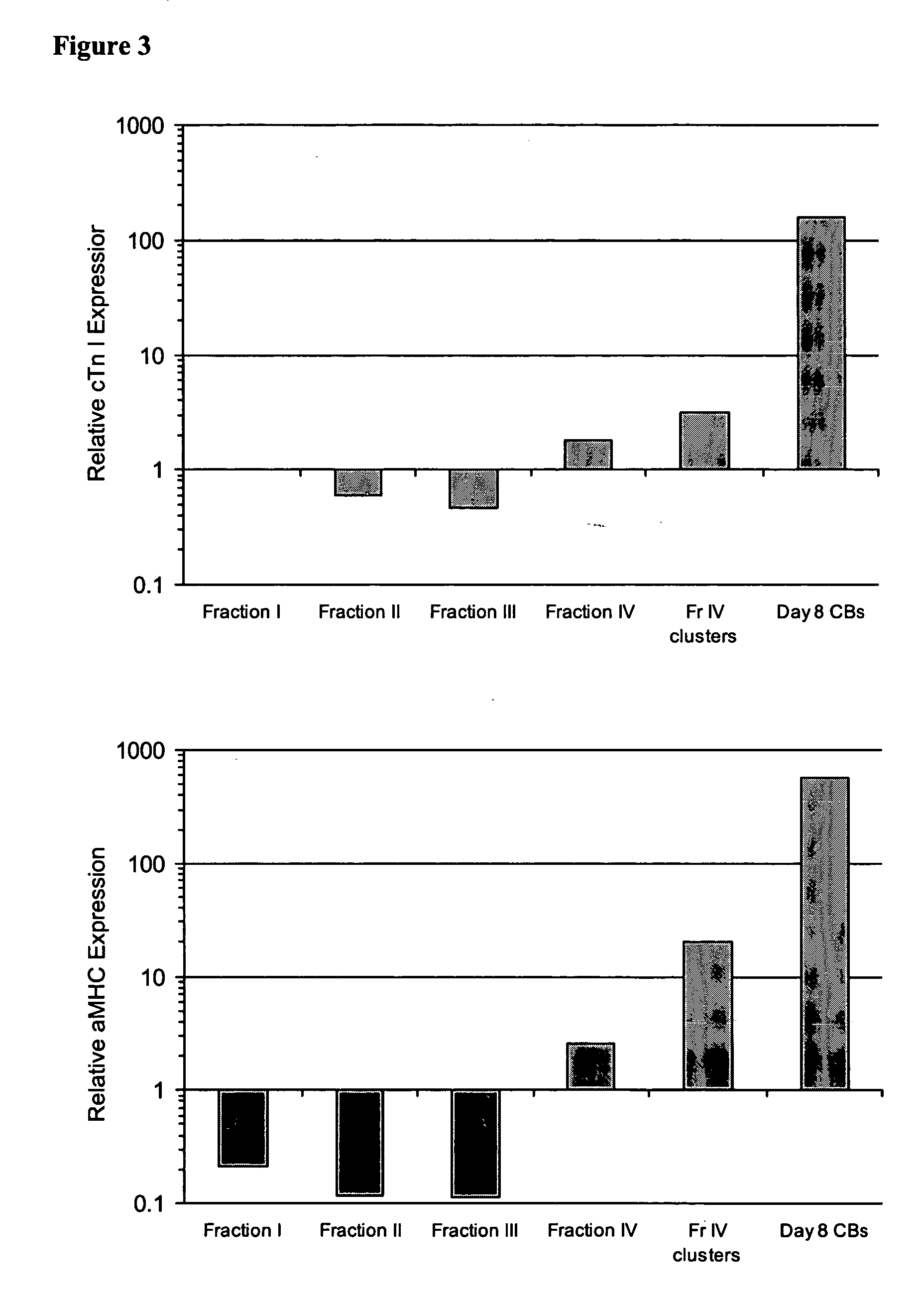
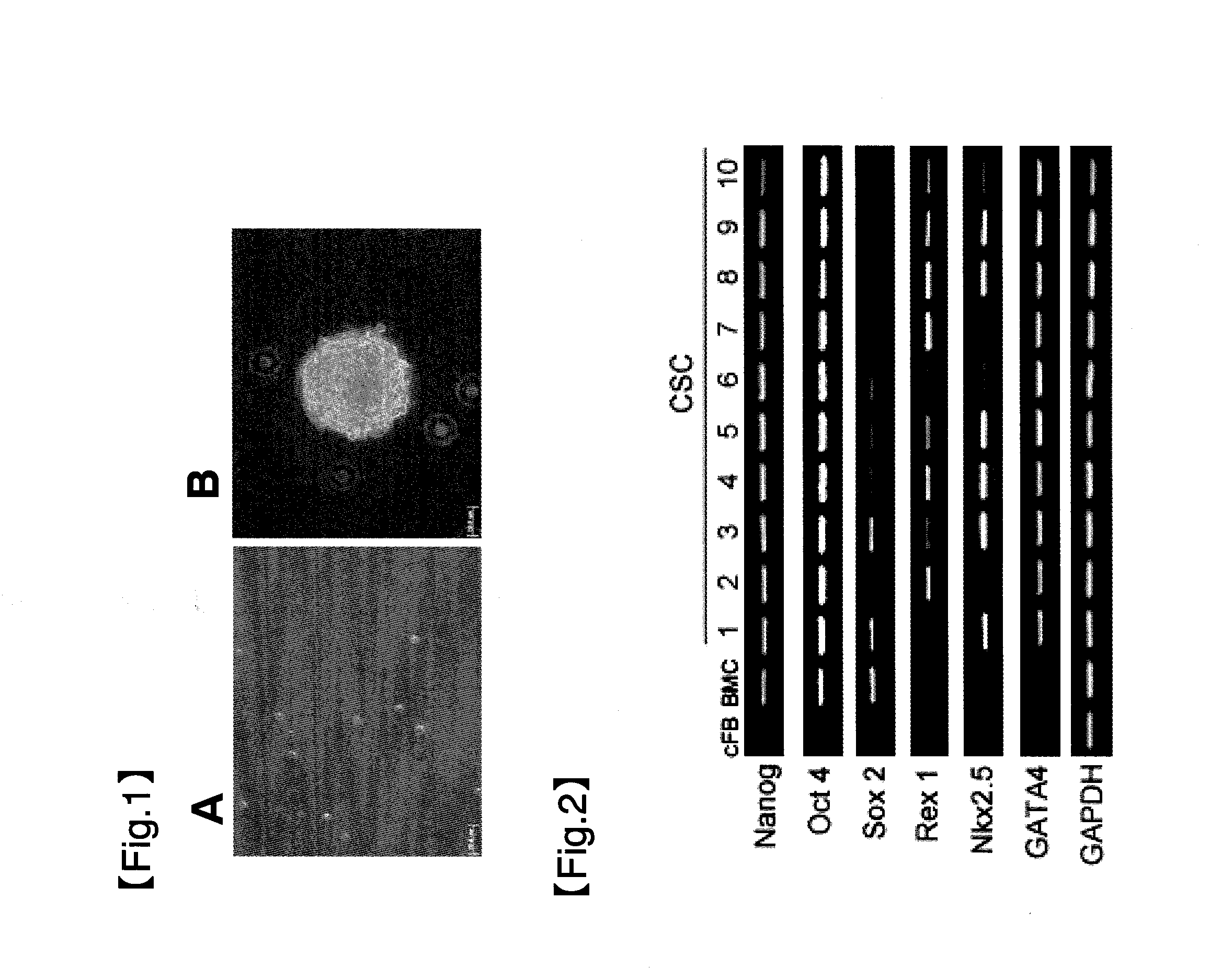
Patents
Literature
1037 results about "Myocardial cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methods and compositions for the repair and/or regeneration of damaged myocardium
InactiveUS20020061587A1Restoring functional integrityRestoring structuralBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsCardiac muscleCytokine
Owner:NEW YORK MEDICAL COLLEGE
Methods and compositions for the repair and/or regeneration of damaged myocardium
InactiveUS20030054973A1Restoring functional integrityRestoring structuralBiocideOrganic active ingredientsCardiac muscleCytokine
Owner:NEW YORK MEDICAL COLLEGE
Methods of imaging and treatment
InactiveUS7329402B2For signal receptionDecreasing background tissue signalTetrapeptide ingredientsEchographic/ultrasound-imaging preparationsThrombusTarget tissue
Novel ultrasound methods comprising administering to a patient a targeted vesicle composition which comprises vesicles comprising a lipid, protein or polymer, encapsulating a gas, in combination with a targeting ligand, and scanning the patient using ultrasound. The scanning may comprise exposing the patient to a first type of ultrasound energy and then interrogating the patient using a second type of ultrasound energy. The targeting ligand preferably targets tissues, cells or receptors, including myocardial cells, endothelial cells, epithelial cells, tumor cells and the glycoprotein GPIIbIIIa receptor. The methods may be used to detect a thrombus, enhancement of an old or echogenic thrombus, low concentrations of vesicles and vesicles targeted to tissues, cells or receptors.
Owner:IMARX PHARM CORP
Method of inducing the differentiation of stem cells into myocardial cells
InactiveUS20070134215A1Efficiently and selectively producedBiocideGenetic material ingredientsCardiac muscleBmp signaling
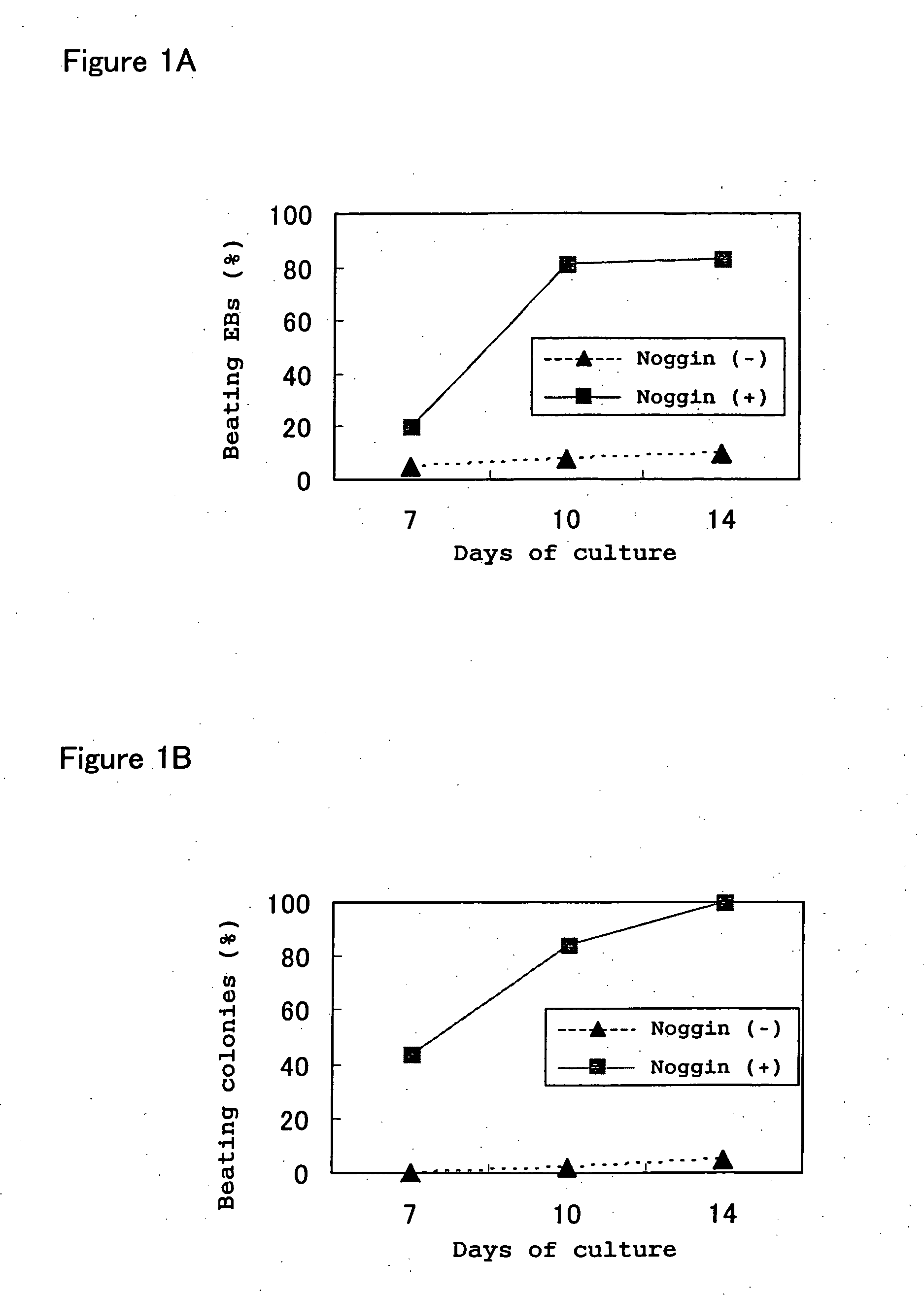
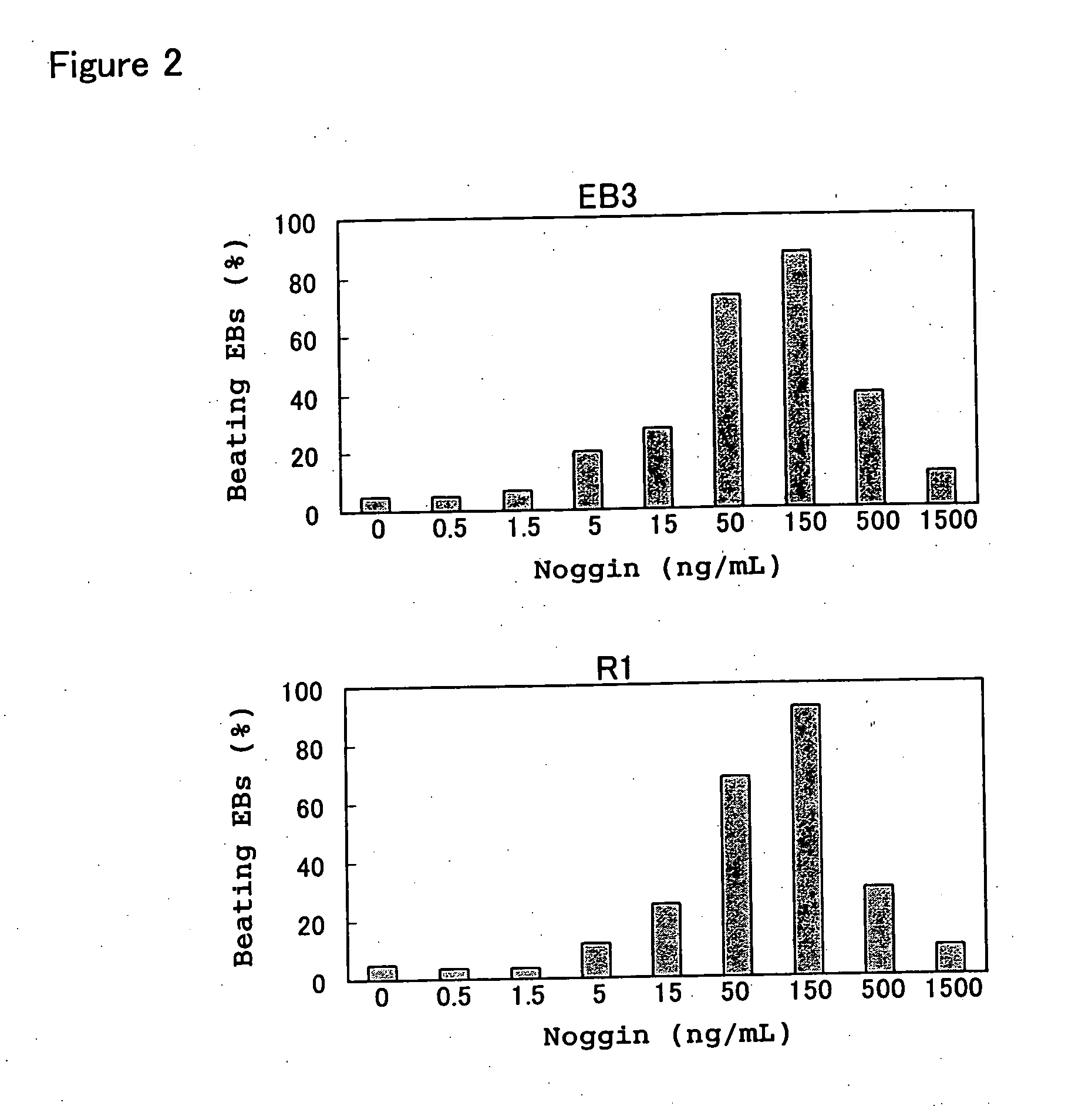
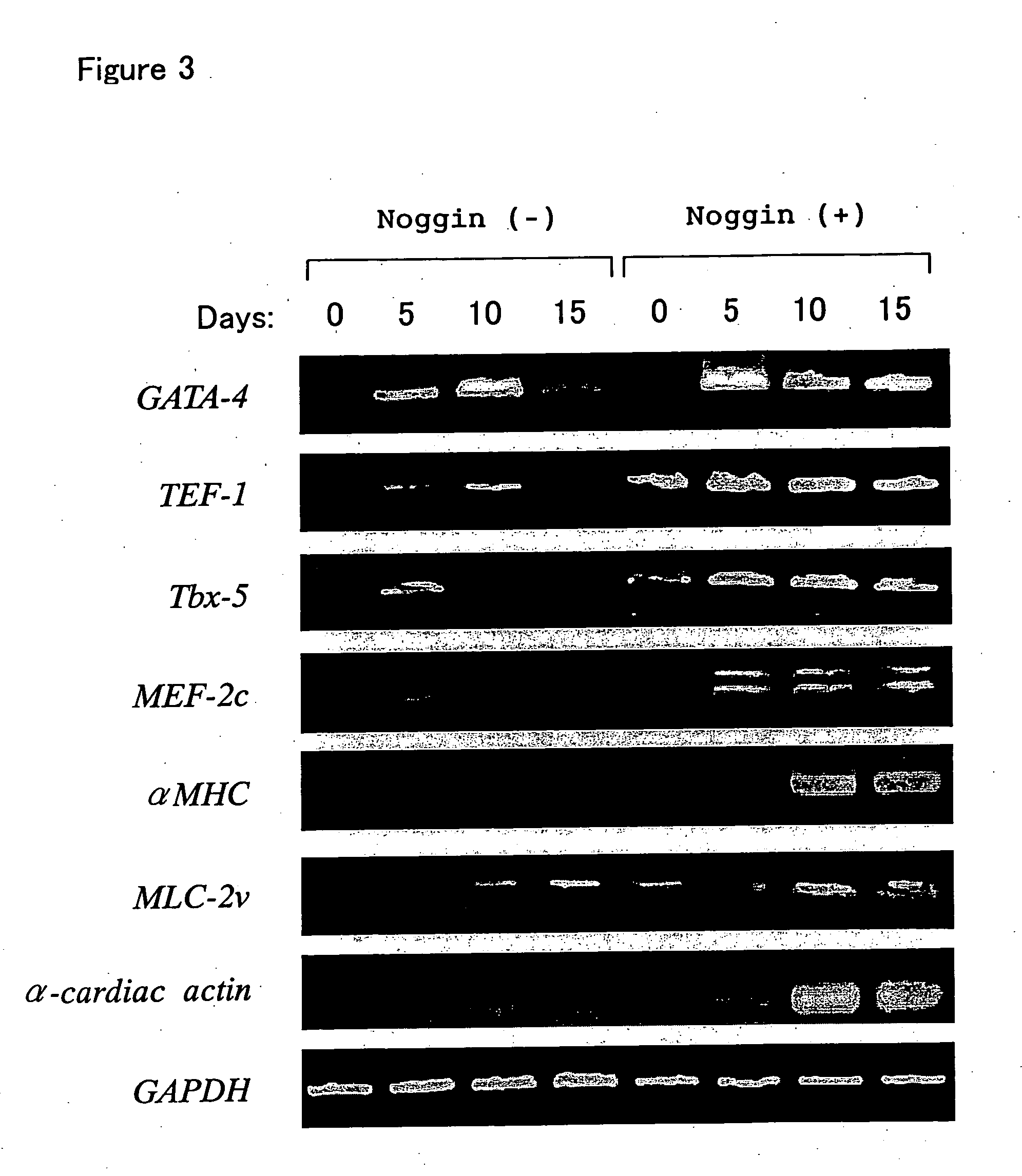
For a method of inducing differentiation of cardiomyocytes from stem cells, a method is provided to induce efficiently and selectively differentiation of cardiomyocytes by such a method in which the stem cells are cultured to induce differentiation into cardiomyocytes in the presence of a substance that inhibits BMP signaling.
Owner:FUKUDA
Methods and compositions for the repair and/or regeneration of damaged myocardium
InactiveUS20060239983A1Restoring functional integrityRestoring structuralBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineCardiac muscle
Owner:NEW YORK MEDICAL COLLEGE
Process for making transplantable cardiomyocytes from human embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS20050054092A1Efficient productionGenetically modified cellsDrug screeningDiseaseHuman cell
This invention provides populations human cells of the cardiomyocyte lineage. The cells are obtained by causing cultures of pluripotent stem cells to differentiate in vitro, and then harvesting cells with certain phenotypic features. Differentiated cells bear cell surface and morphologic markers characteristic of cardiomyocytes, and a proportion of them undergo spontaneous periodic contraction. Highly enriched populations of cardiomyocytes and their replicating precursors can be obtained, suitable for use in a variety of applications, such as drug screening and therapy for cardiac disease.
Owner:ASTERIAS BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
Cardiac muscle regeneration using mesenchymal stem cells
InactiveUS7514074B2Increase opportunitiesShorten the timeBiocideGenetic material ingredientsCardiac muscleMesenchymal stem cell
Disclosed is a method for producing cardiomyocytes in vivo by administering to the heart of an individual a cardiomyocyte producing amount of mesenchymal stem cells. These cells can be administered as a liquid injectible or as a preparation of cells in a matrix which is or becomes solid or semi-solid. The cells can be genetically modified to enhance myocardial differentiation and integration. Also disclosed is a method for replacing cells ex vivo in a heart valve for implantation.
Owner:MESOBLAST INT
Cardiac muscle regeneration using mesenchymal stem cells
InactiveUS20050112104A1Shorten the timeEasy to convertBiocideGenetic material ingredientsCardiac muscleMesenchymal stem cell
Disclosed is a method for producing cardiomyocytes in vivo by administering to the heart of an individual a cardiomyocyte producing amount of mesenchymal stem cells. These cells can be administered as a liquid injectible or as a preparation of cells in a matrix which is or becomes solid or semi-solid. The cells can be genetically modified to enhance myocardial differentiation and integration. Also disclosed is a method for replacing cells ex vivo in a heart valve for implantation.
Owner:MESOBLAST INT
Methods and compositions for the repair and/or regeneration of damaged myocardium
InactiveUS20020098167A1Recovery functionRestoring structuralBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsCardiac muscleCytokine
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Induction of pluripotent stem cells into mesodermal lineages
InactiveUS20080038820A1Promotes commitment and survivalGenetic material ingredientsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsProgenitorGerm layer
The present invention provides a method of inducing mesoderm derived cells from pluripotent stem cells. In contrast to methods known in the art that are often designed to replicate in vivo events of mesoderm induction, the present invention provides a unique, yet simple, method whereby pluripotent stem cells are mesodermally primed in the presence of factors that concomitantly inhibit the spontaneous differentiation of endoderm and ectoderm during expansion and suspension steps. Exposure and / or adherence of primed aggregates to a extracellular matrix that promotes the commitment and survival of induced mesoderm progenitors, followed by exposure to various mesoderm associated factors, allows for the subsequent induction of such cells into terminally differentiated lineages, such as cardiomyocytes. End products of this induction system will ultimately provide an unlimited source of mesoderm-derived cell types for therapeutic and pharmacological purposes.
Owner:RUDY REIL DIANE ELIZABETH DR +1
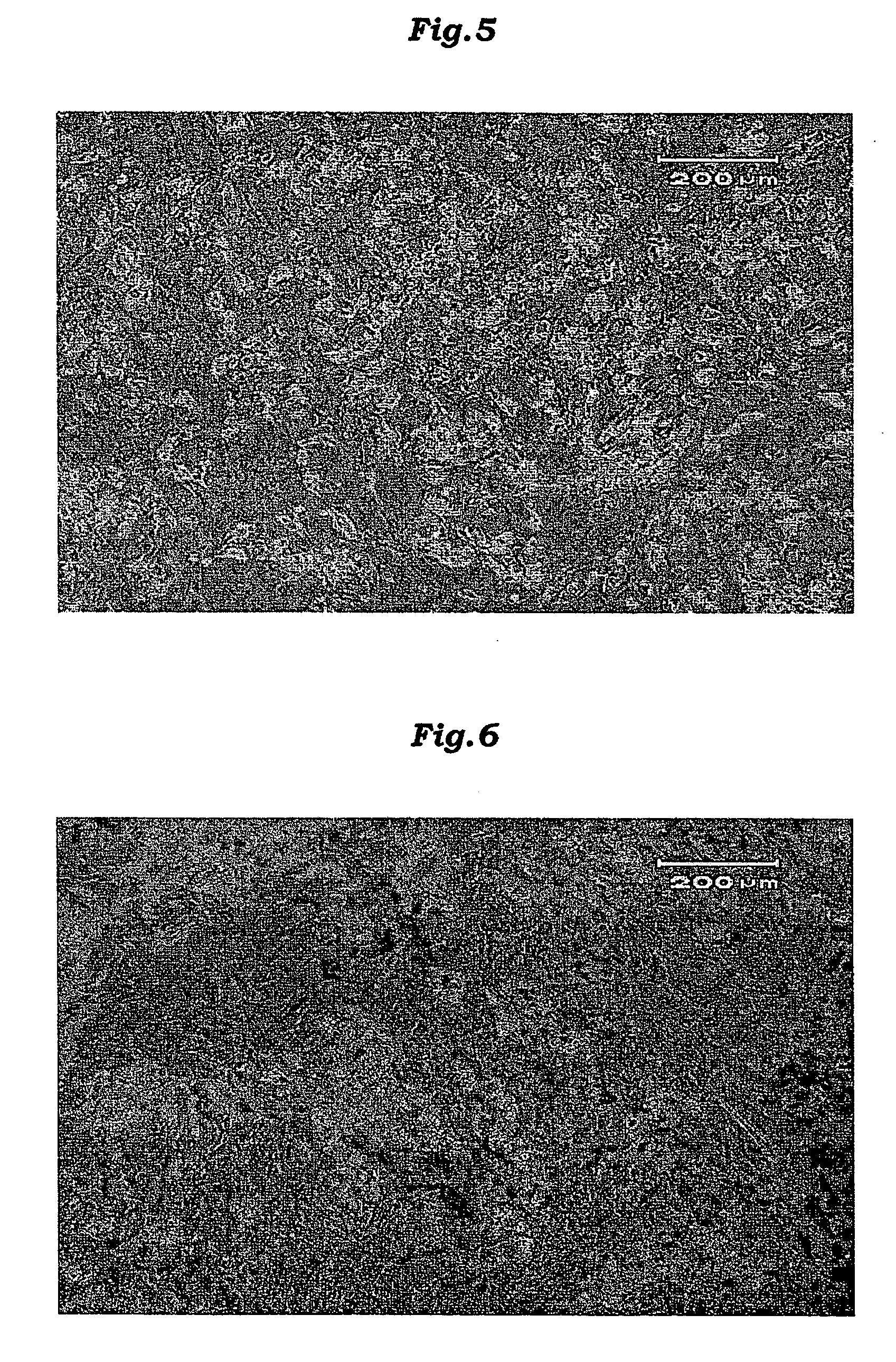
Induction of Myocardial Cell From Mammalian Bone Marrow Cell or Cord Blood-Derived Cell and Fat Tissue
InactiveUS20070212676A1Improve securityEasy to getCell differentiationMicrobiological testing/measurementCord blood stem cellCardiac muscle
This invention provides a method for differentiating mammalian bone marrow cells or cord blood-derived cells into myocardial precursor cells and / or myocardial cells by culturing said bone marrow cells or cord blood-derived cells with cells isolated from mammalian fat tissues or a culture supernatant thereof.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Pluripotent stem cell-hereditary cardiomyopathy cardiac muscle cell and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105039399AWide variety of sourcesLong-term in vitro cultureVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsDiseaseDisease phenotype
The invention belongs to the field of researching and application of biomedicine and particularly relates to human pluripotent stem cell-hereditary cardiomyopathy cardiac muscle cells and a preparation method thereof. The invention provides a human hereditary cardiomyopathy-pluripotent stem cell, which is constructed by means of TALEN or CRISPR / CAS9 genome editing technology. The human hereditary cardiomyopathy cardiac muscle cell can be combined with any scaffold materials to culture various in-vitro human hereditary cardiomyopathy cardiac muscle tissues. The human hereditary cardiomyopathy cardiac muscle cells in the invention have disease phenotypes and electrophysiology change being similar as the cardiac muscle cells of human hereditary cardiomyopathy patients. The human hereditary cardiomyopathy cardiac muscle cells are wide in sources and can be cultured in-vitro for a long time. The invention provides excellent tools and platforms for researching an effective new therapy means and researching an effective corresponding treatment medicine.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
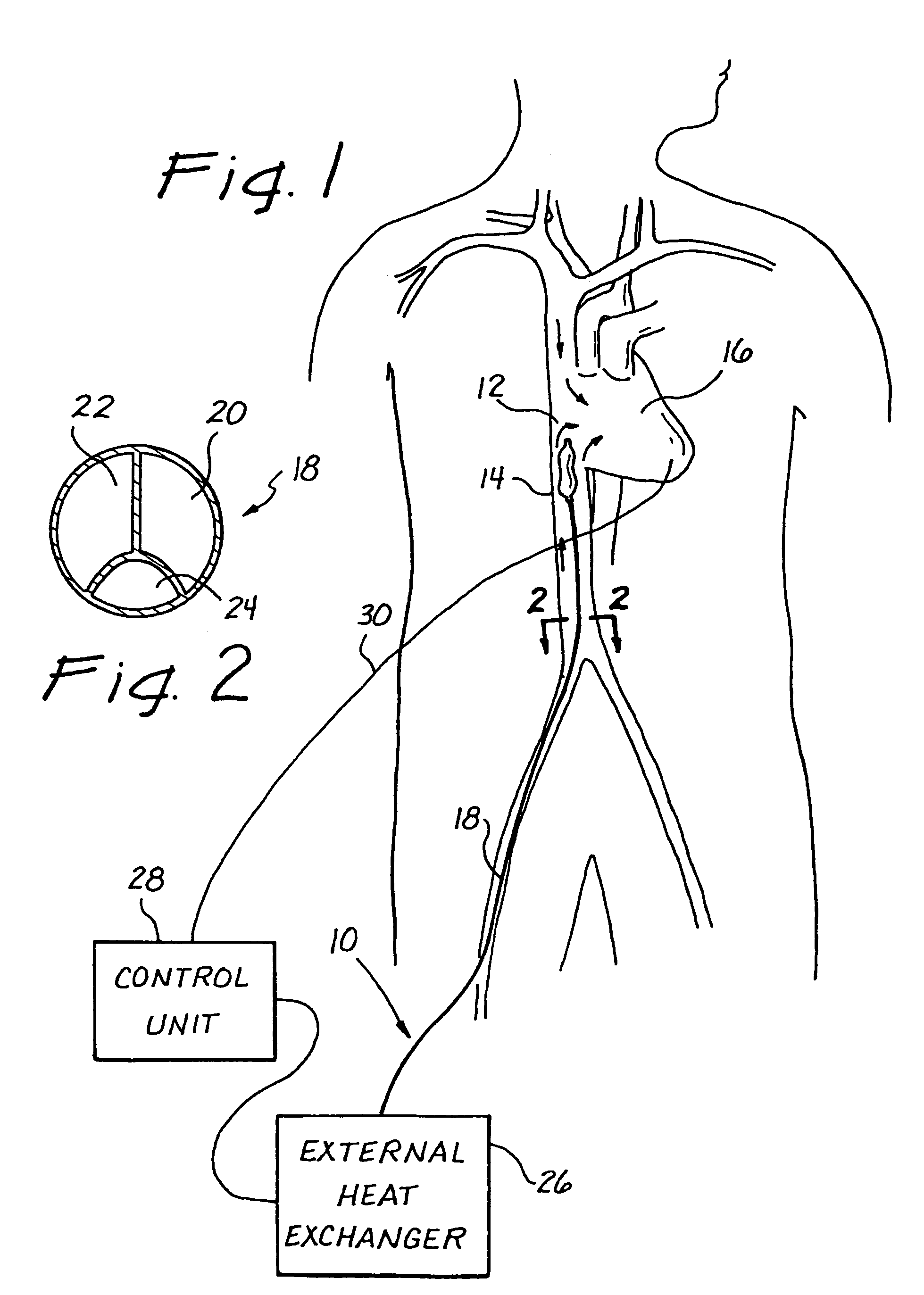
Use of intravascular hypothermia during angioplasty procedures
InactiveUS7510569B2Prevent and deter and minimize and treat other type of damagePrevent and lessen myocardial infarctionStentsCatheterPercutaneous angioplastyIschemic myocardium
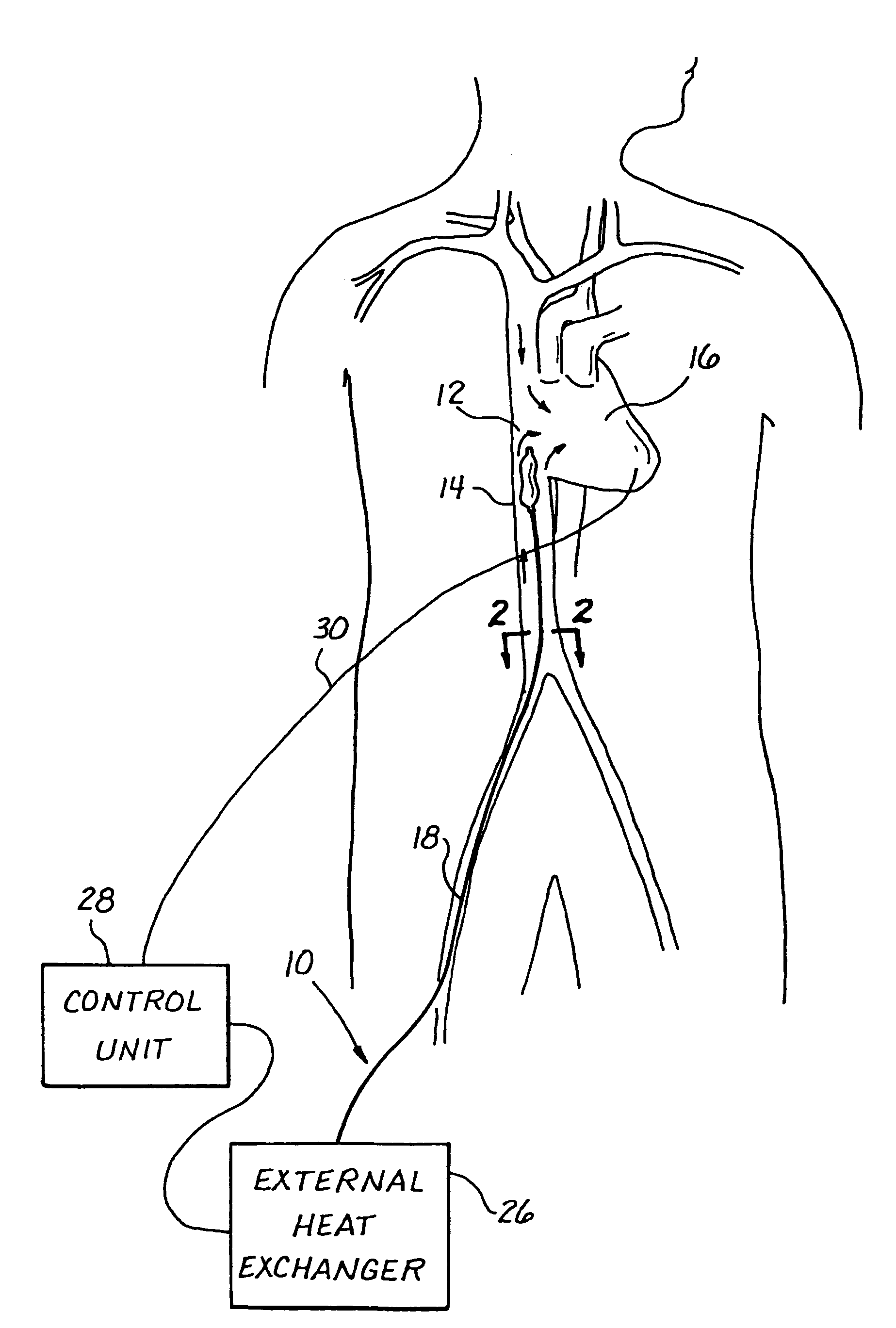
Methods and apparatus for preventing myocardial infarction, or lessening the size / severity of an evolving myocardial infarction, by cooling at least the affected area of the myocardium using an intravascular heat exchange catheter. The heat exchange catheter may be inserted into the vasculature (e.g., a vein) and advanced to a position wherein a heat exchanger on the catheter is located in or near the heart (e.g., within the vena cava near the patient's heart). Thereafter, the heat exchange catheter is used to cool the myocardium (or the entire body of the patient) to a temperature that effectively lessens the metabolic rate and / or oxygen consumption of the ischemic myocardial cells or otherwise protects the ischemic myocardium from undergoing irreversible damage or infarction.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
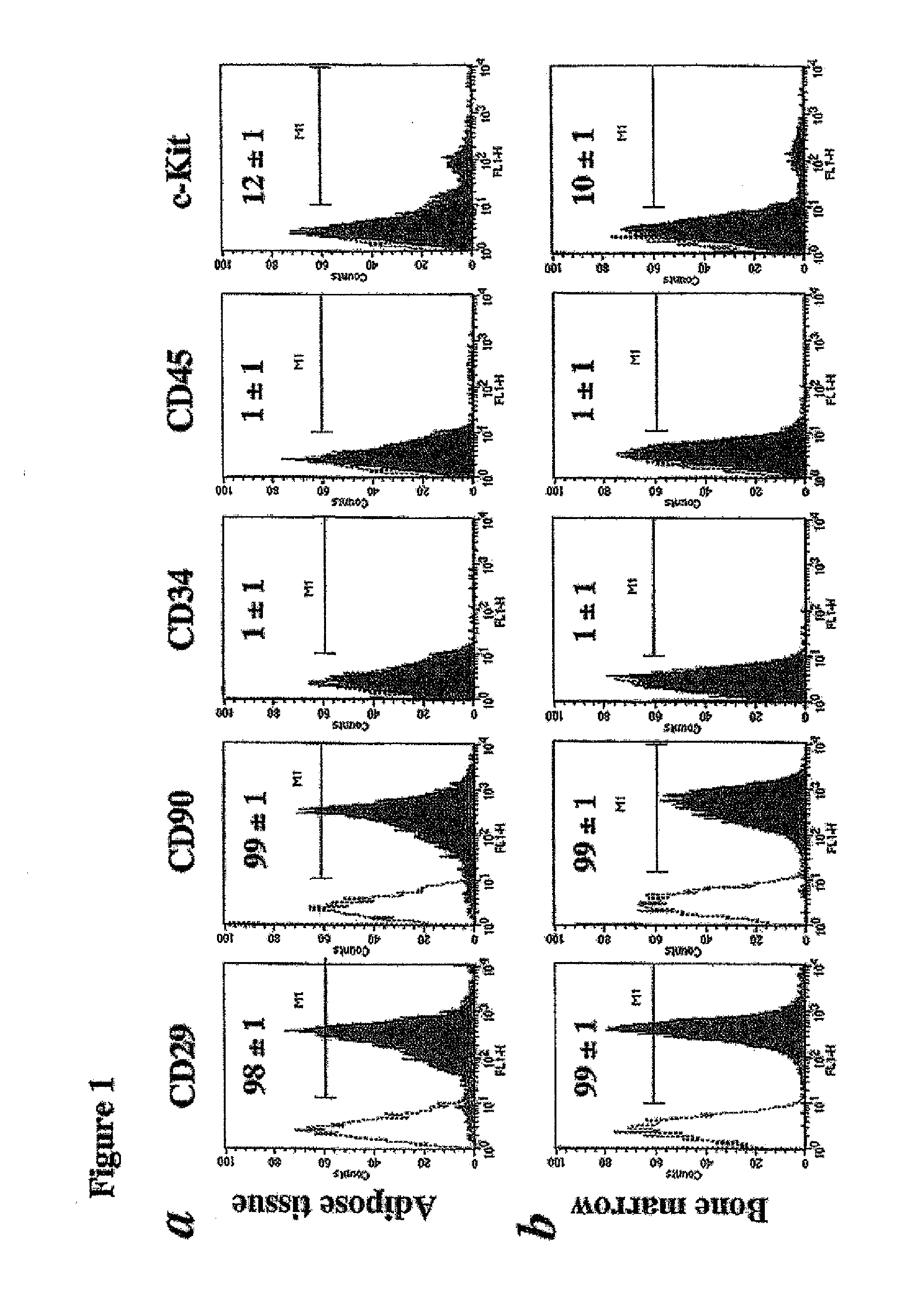
Pluripotent Cells Distributed Ubiquitously In Animal Tissue, Which Proliferate Selectively In Lower-Serum Culture
InactiveUS20070202592A1Lose volumeImprove mass productionArtificial cell constructsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsVascular endotheliumOsteocyte
It is intended to provide a pluripotent cell having the following properties: (1) being contained in a mixed-cell type population obtained by enzymatic treatment of the tissue collected from an animal; (2) being contained in a sedimented cell population obtained by centrifugating the mixed-cell type population of the property (1); (3) selectively proliferating by culturing in a medium containing 2% (v / v) or lower serum and 1 to 100 ng / ml of fibroblast growth factor-2; and (4) being differentiated into cells having the characteristics of adipocytes, osteoblasts, chondrocytes, tendon cells, myocardial cells, myoblasts, neurocytes or vascular endothelial cells by adjusting the culture condition; cells having differentiated from the above cell; and a method of conveniently obtaining the pluripotent cell in a large amount.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD +3
Cell Sheet Containing Mesenchymal Stem Cells
ActiveUS20090053277A1Induce cardiac muscleInduce neovascularizationBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsVascular endotheliumThree vessels
Mesenchymal stem cells are pluripotent cells capable of differentiating into myocardial and vascular endothelial cells. The present invention demonstrates that the mesenchymal stem cell sheet have therapeutic potential for a severely damaged heart due to its pluripotency and in situ self-renewal capability. Mesenchymal stem cells derived from adipose tissue were cultured to prepare a mesenchymal stem cell sheet. Four weeks after induction of myocardial infarction in rats, the mesenchymal stem cell sheet was transplanted to the heart. The mesenchymal stem cell sheet were readily engrafted to the surface of the scarred myocardium, grew gradually in situ, and formed a thick layer (approximately 600 μm) in 4 weeks. The grown transplanted mesenchymal tissue contained newly formed blood vessels, myocardial cells, and undifferentiated mesenchymal cells. The engrafted mesenchymal stem cells inhibited thinning of the myocardial wall in the scar area, and improved cardiac function and survival rate in rats with myocardial infarcts. Thus, mesenchymal stem cell sheet transplantation may represent a novel therapeutic approach for myocardial tissue regeneration.
Owner:H&L MEDICAL CORP
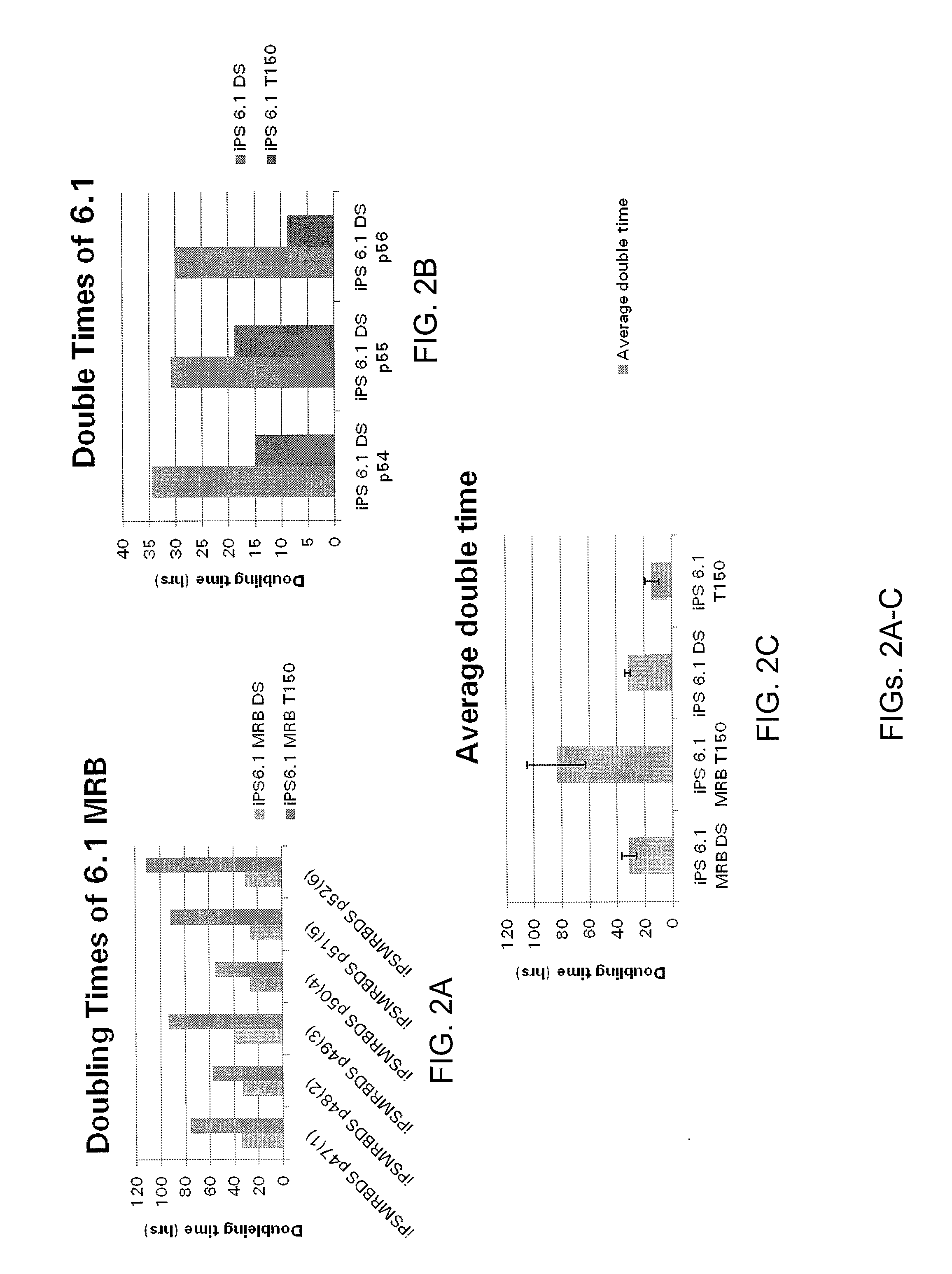
Cardiomyocyte production
ActiveUS20110097799A1Enhanced signalPromote differentiationCell dissociation methodsSugar derivativesCardiac muscleCulture mediums
Methods and composition for the production of cardiomyocytes from differentiation of pluripotent stem cells are provided. For example, in certain aspects methods including differentiating pluripotent stem cells in a large volume of suspension culture in the presence of ROCK inhibitors are described. In further aspects, methods for differentiation of stem cells into cardiomyocytes that overcome variability between different stem cell clones and different batch of culture medium are provided.
Owner:FUJIFILM CELLULAR DYNAMICS INC
Differentiation of human embryonic stem cells to cardiomyocytes
InactiveUS20070161107A1Improve compatibilityPromote differentiationArtificial cell constructsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCardiac muscleCo culturing
A method for inducing cardiomyocyte differentiation of a hES cell, the method comprising co-culturing the hES cell with a cell excreting at least one cardiomyocyte differentiation inducing factor or with an extracellular medium therefrom, under conditions that induce differentiation, cells and cell populations so produced, and uses of the cells.
Owner:MUMMERY CHRISTINE LINDSAY +2
Methods and compositions for the repair and/or regeneration of damaged myocardium
InactiveUS20090143296A1Recovery functionRestoring structuralPeptide/protein ingredientsMuscular disorderMedicineCardiac muscle
Owner:NEW YORK MEDICAL COLLEGE
Enriched stem cell and progenitor cell populations, and methods of producing and using such populations
InactiveUS8017389B2BiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementIschemic heartFirst myocardial infarction
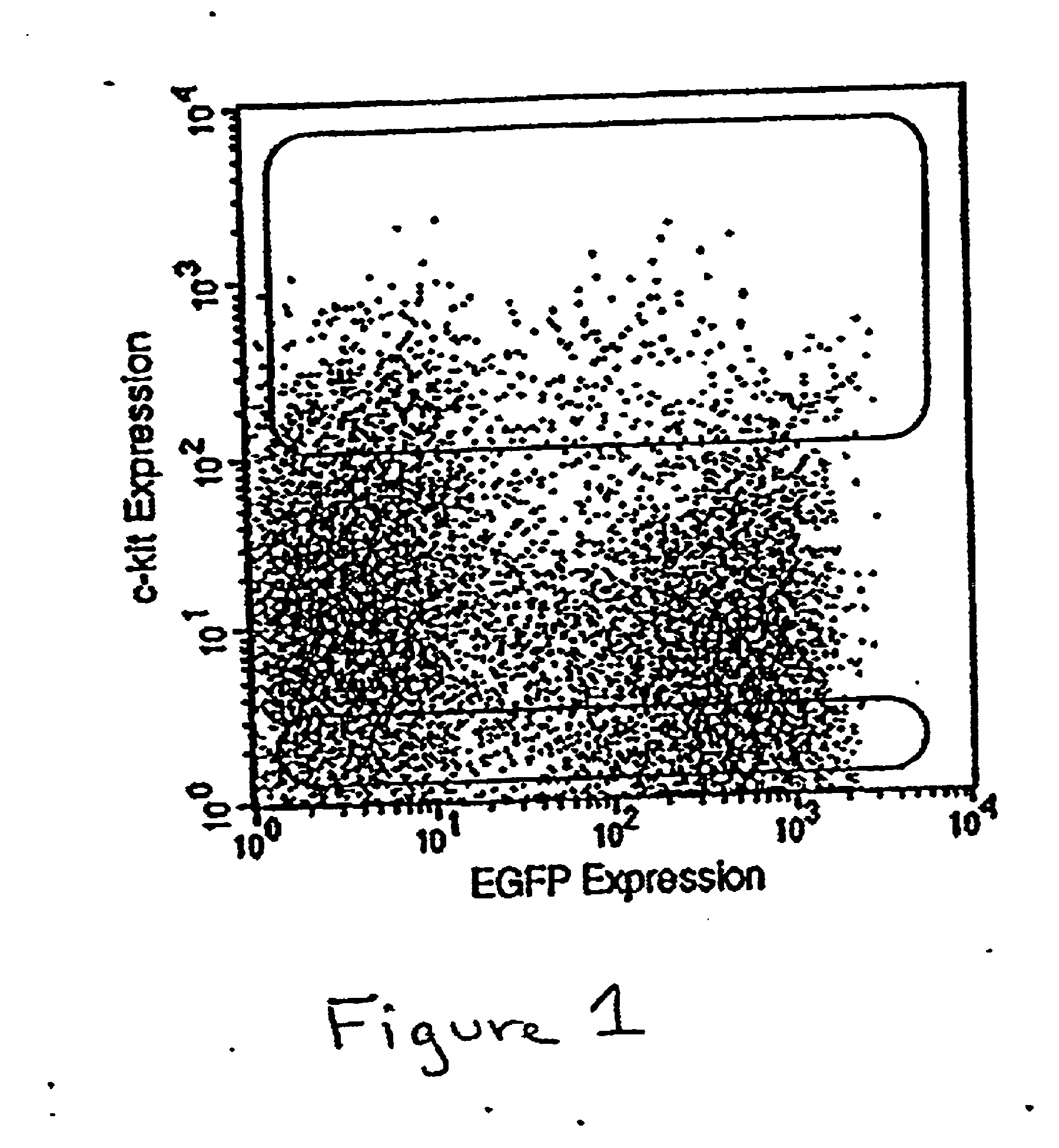
The present invention provides a novel method to isolate and expand pure progenitor / stem cells from a primary tissue explant, which produces a population enriched in multipotent functional progenitor / stem cells free of contaminating fibroblasts and other cell types. Cardiac progenitor / stem cells isolated by this method maintain their self-renewal and clonogenic character in vitro and differentiate into normal cells in myocardium, including cardiomyocytes, endothelial cells, and smooth muscle cells, after transplantation into ischemic hearts. The present invention also includes substantially pure populations of multipotent progenitor / stem cells, e.g., cardiac progenitor / stem cells, and their use to treat and prevent diseases and injuries, including those resulting from myocardial infarction.
Owner:KECK GRADUATE INST A UNIV OF THE STATE OF CALIFORNIA
Methods and compositions for the repair and/or regeneration of damaged myocardium
InactiveUS7862810B2Recovery functionRestoring structuralBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineCardiac muscle
Owner:NEW YORK MEDICAL COLLEGE
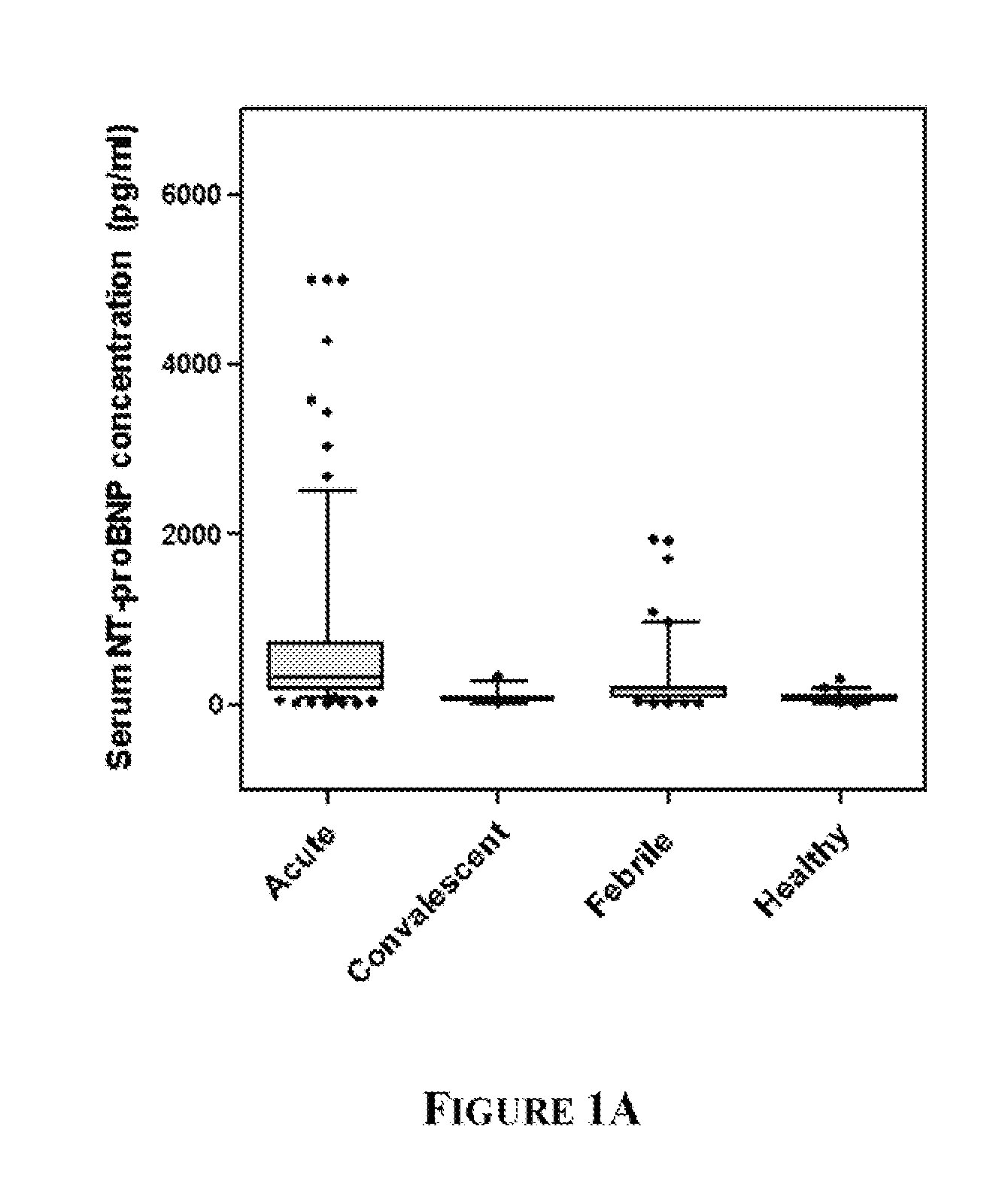
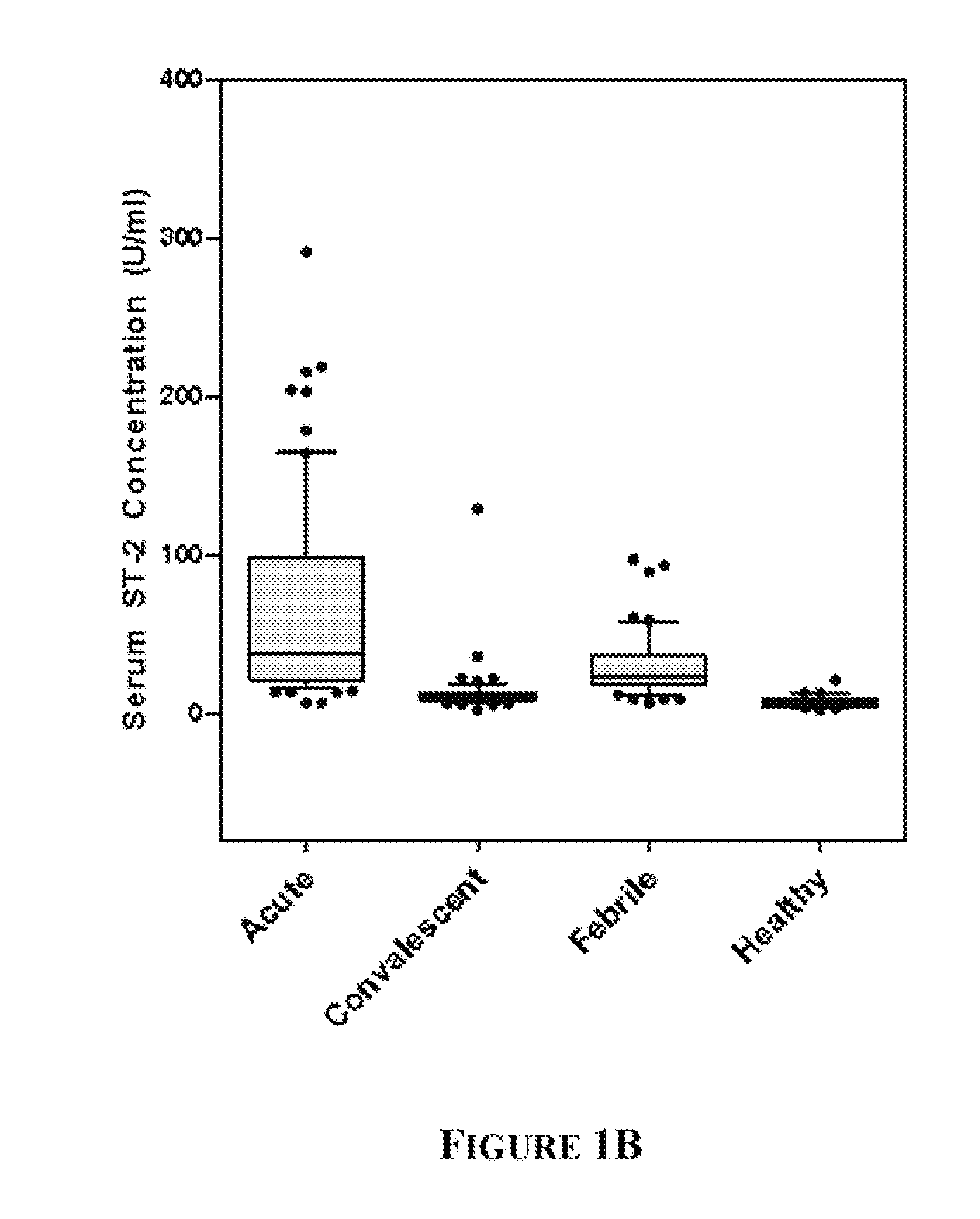
Protein Biomarkers and Methods for Diagnosing Kawasaki Disease
InactiveUS20110189698A1Improve diagnostic accuracyComponent separationDisease diagnosisKawasaki diseaseBiology
A method, kit and device for diagnosing Kawasaki Disease are provided. The invention provides detecting an expression level of at least two Kawasaki Disease diagnostic biomarkers in a biological sample from a patient with a capture agent and diagnosing the patient as having Kawasaki Disease when the expression levels of the at least two diagnostic biomarkers in the patient biological sample are higher than the normal expression levels of the same biomarkers in a biological sample from a control subject. The first Kawasaki Disease diagnostic biomarker disclosed in the present invention is a cardiomyocyte biomarker, and the second Kawasaki Disease diagnostic biomarker is an inflammatory biomarker. The invention further provides detecting an expression level of a third biomarker, interferon type-I biomarker, in the patient biological sample with a capture agent and diagnosing the patient as having Kawasaki Disease when the expression level of interferon type-I biomarker is lower than the expression level in a control subject.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Cardiac wall tension relief with cell loss management
InactiveUS20050095268A1Reduce loss rateDecreasing wall stressElectrotherapyPeptide/protein ingredientsCardiac wallCardiac muscle
Method and apparatus are disclosed for treating congestive heart failure. The method includes relieving wall stress on a diseased heart by an amount to decrease a rate of myocardial cell loss. Further, the method includes pharmacologically encouraging a myocardial cell gain. Cell gain may be encouraged by cell replication, cell recruitment or inhibition of cell death. Further embodiments of the method include a passive cardiac constraint selected to reduce wall stress on the heart. An apparatus of the present invention includes a passive cardiac constraint and a pharmacological agent to encourage cell gain.
Owner:ACORN CARDIOVASCULAR
Method of providing a dynamic cellular cardiac support
The present invention provides a method for repairing damaged myocardium. The method comprises using a combination of cellular cardiomyoplasty and electrostimulation for myogenic predifferentiation of stem cells and to synchronize the contractions of the transplanted cells with the cardiac cells. The method comprises the steps of obtaining stem or myogenic cells from a donor, culturing and electrostimulating the isolated cells in vitro, and implanting the cells into the damaged myocardium.
Owner:BIOHEART
Targeted compositions for diagnostic and therapeutic use
InactiveUS7452551B1Echographic/ultrasound-imaging preparationsDiagnostic recording/measuringTherapeutic ultrasoundTarget tissue
Novel targeted compositions which may be used for diagnostic and therapeutic use. The compositions may comprise lipid, protein or polymer gas-filled vesicles which further comprise novel compounds of the general formula L-P-T, wherein L comprises a hydrophobic compound, P comprises a hydrophilic polymer, and T comprises a targeting ligand which targets tissues, cells or receptors, including myocardial cells, endothelial cells, epithelial cells, tumor cells and the glycoprotein GPIIbIIIa receptor. The compositions can be used in conjunction with diagnostic imaging, such as ultrasound, as well as therapeutic applications, such as therapeutic ultrasound.
Owner:CEREVAST MEDICAL
Method for directionally differentiating multipotential stem cell in vitro into myocardial cell
ActiveCN104293730AMany connectionsDecreased frequency of calcium wavesVertebrate cellsArtificial cell constructsGerm layerHeart development
The invention provides a method for directionally differentiating a multipotential stem cell in vitro into a myocardial cell and provides a culture medium for establishing myocardial cell differentiation by means of induction in vitro under a three-dimensional suspension condition. The culture medium comprises a differential medium for induced differentiation of a multipotential stem cell into a precursor cell of mesoblast, a differential medium for differentiating the precursor cell of mesoblast into the myocardial cell and a long-term maintaining culture medium of the myocardial cell. The method provided by the invention is simple and reliable, low in cost, stable and efficient and high in safety. By adopting a suspension culture system, high-quality myocardial cells can be industrially produced without any subsequent screening and purifying steps, can be directly used for application demands of scientific research of heart development, cell therapy of heart diseases, transplanting due to cardiac trauma and drug screening, and has inestimable scientific, social and economical benefits.
Owner:昆明圆梦生命科学研究院有限公司
Pulse multipolar ablation catheter for hearts
ActiveCN111388085AEffective ablationAvoid damageSurgical navigation systemsSurgical instruments for heatingMedical equipmentCatheter
The invention relates to the field of medical equipment, in particular to a pulse multipolar ablation catheter for hearts. The pulse multipolar ablation catheter for hearts comprises an electrode assembly, a tube body and a handle, wherein the electrode assembly is connected to the tail end of the tube body, the handle is connected to the proximal end of the tube body, and the electrode assembly includes an even number of electrode arms which are evenly arranged in a ring shape; and electrodes are arranged on the electrode arms, every two adjacent electrodes are used for generating high-pressure energy pulse trains which have the same pulse width, equal field strength but opposite polarity, and the generated high-pressure energy pulse trains are applied to cardiomyocytes. A multipolar array is formed by the electrodes which are arranged on the electrode arms so as to form an annular ablation zone, the tissue cells can be ablated more effectively, the operation time is shortened greatly, and the ablation efficiency is improved greatly; and ablation is carried out through adoption of the high-pressure energy pulse trains, and targeted tissue can be ablated selectively, so that damageto the tissue cells is reduced, and the incidence of complications is reduced.
Defibrillator output stage with H bridge circuit and diphase sawtooth square wave defibrillation high-voltage discharge method
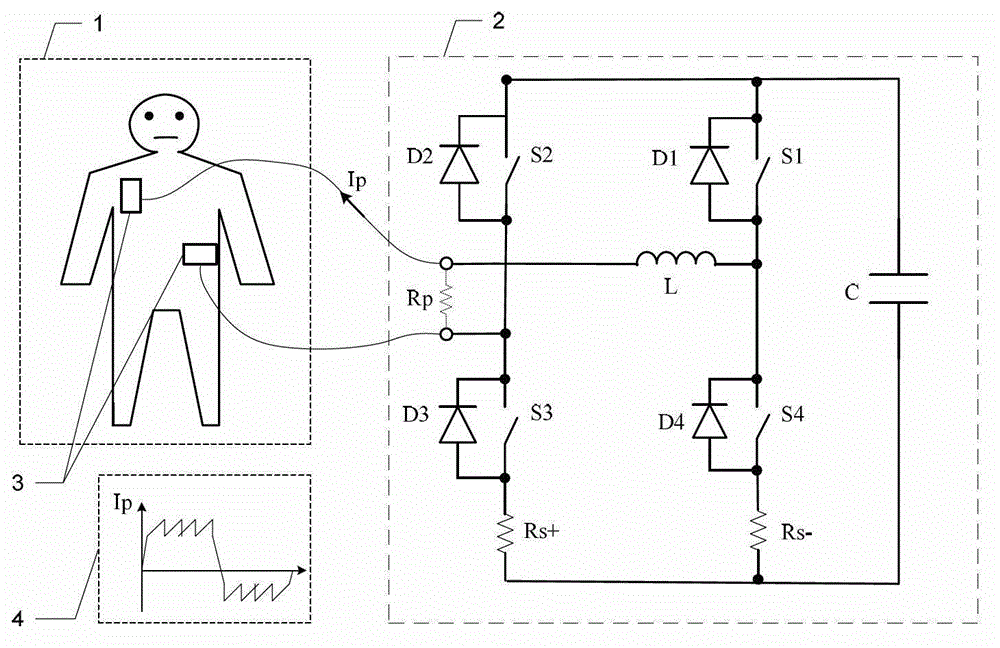
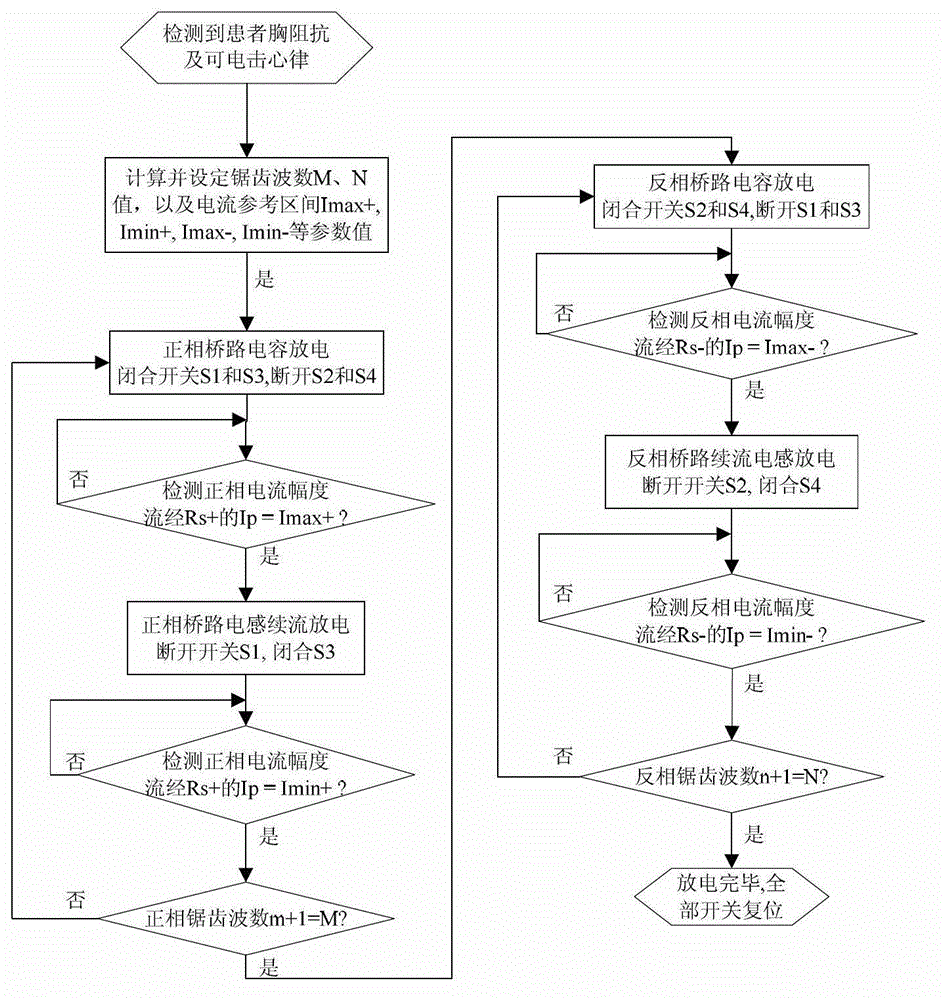
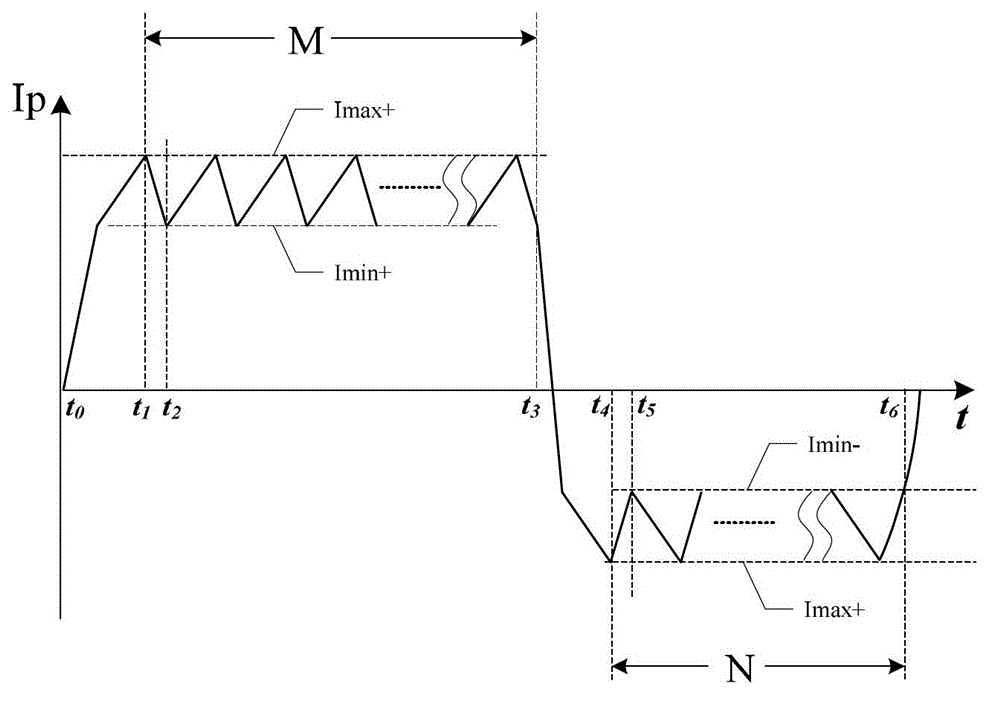
ActiveCN102974039ARescue in timeIncrease success rateHeart defibrillatorsCurrent sensorHigh pressure
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical electronics and particularly relates to an output stage circuit for a cardiac defibrillator and a diphase sawtooth square wave high-voltage discharge method based on the output stage circuit. The output stage circuit consists of an energy storage capacitor, an inductance coil, a semiconductor diode, a current sensor and four control switches, wherein the four control switches form an H bridge type discharge circuit. According to the high-voltage discharge method, electrical energy in the energy storage capacitor conducts a rapid high-voltage shock discharge on a patient in a diphase sawtooth wave pulse form through a defibrillation electrode so as to terminate ventricular fibrillation in a body, and conduct a timely rescue for the patient via the defibrillator output stage with the H bridge circuit according to a preset switch combination of the bridge circuit and a control strategy. The high-voltage defibrillation discharge in a diphase sawtooth square wave form provides the patient with the individual and accurately controlled defibrillation electrical energy, the success rate of the synchronization defibrillation of myocardial cells throughout a ventricle is increased, and injuries to myocardia in a high-voltage defibrillation process are reduced.
Owner:久心医疗科技(苏州)有限公司
Differentiation of primate pluripotent stem cells to cardiomyocyte-lineage cells
ActiveUS20070010012A1Culture processArtificial cell constructsInduced pluripotent stem cellCardiac muscle
The present application describes the new methods for the differentiation of primate pluripotent stem cells into cardiomyocyte-lineage cells. The methods utilize sequential culturing of the primate pluripotent stem cells in certain growth factors to produce cardiomyocyte-lineage cells. In certain embodiments of the invention, the population of cells produced by the sequential culturing is further enriched for cardiomyocyte-lineage cells so as to produce a higher percentage of those cells.
Owner:ASTERIAS BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
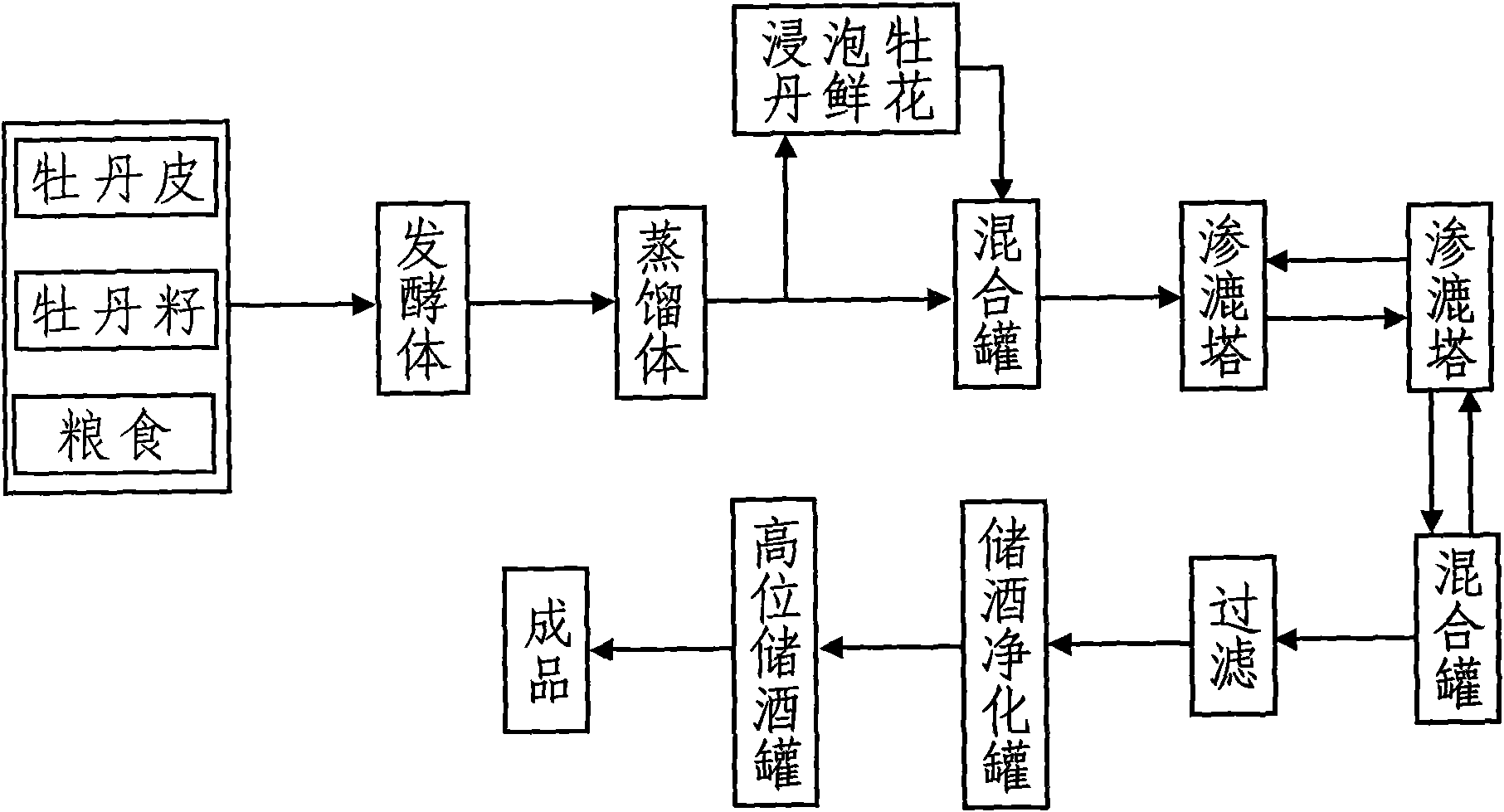
Peony liqueur and production process thereof
InactiveCN101643695AGreat tasteSignificant anti-atherosclerosisAlcoholic beverage preparationNutritive valuesFood flavor
The invention discloses liqueur, relates to peony liqueur and a production process thereof and belongs to prepared liqueur. The method comprises the following steps: fermenting crops, such as sorghum,corn, wheat, rice or peas, and the like with a mixture of peony bark and peony seeds in a weight ratio of 100: (1-4); adding and soaking fresh peonies or star anise, dried tangerine peel, fennel, Chinese wolfberry, and the like in the prepared peony puree wine; and adding food flavor to obtain the peony liqueur, wherein the fresh peonies are added in an amount of 1-3 percent of the peony puree wine by weight; and the star anise, the dried tangerine peel, the fennel and the Chinese wolfberry are added in an amount of 0.5-2 percent of the peony puree wine by weight. The peony liqueur integratesthe functions of nourishment, healthcare and food adornment, has favorable mouthfeel and strong peony fragrance and uses the peonies with extremely high nutritive value and health value as raw materials to not only expand the use value of peony plants, but also achieve the remarkable efficacy for resisting atherosclerosis, protecting myocardial cells and the immune system, activating the blood, regulating the menstruation, obstructing the meridian and nourishing the five viscera, thereby benefiting the body, lengthening the life and suiting for long-term drinking.
Owner:郝凤英 +1
Preparation for treating heart disease used in cell therapy
ActiveUS20100303909A1Improve survivalSufficient degreeBiocidePowder deliveryInduced pluripotent stem cellCardiac muscle
An object of the present invention is to establish a cell transplantation method which can markedly improve the survival of grafted pluripotent stem cells and the efficiency of cardiomyocyte regeneration in cell therapy using pluripotent stem cells derived from heart tissue and can treat heart disease further effectively. Specifically, according to the present invention, enhancement in the survival of grafted pluripotent stem cells and significant improvement in the efficiency of cardiomyocyte regeneration are achieved by using, in combination, pluripotent stem cells derived from heart tissue and a hydrogel containing a basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) in cell therapy for heart disease.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com