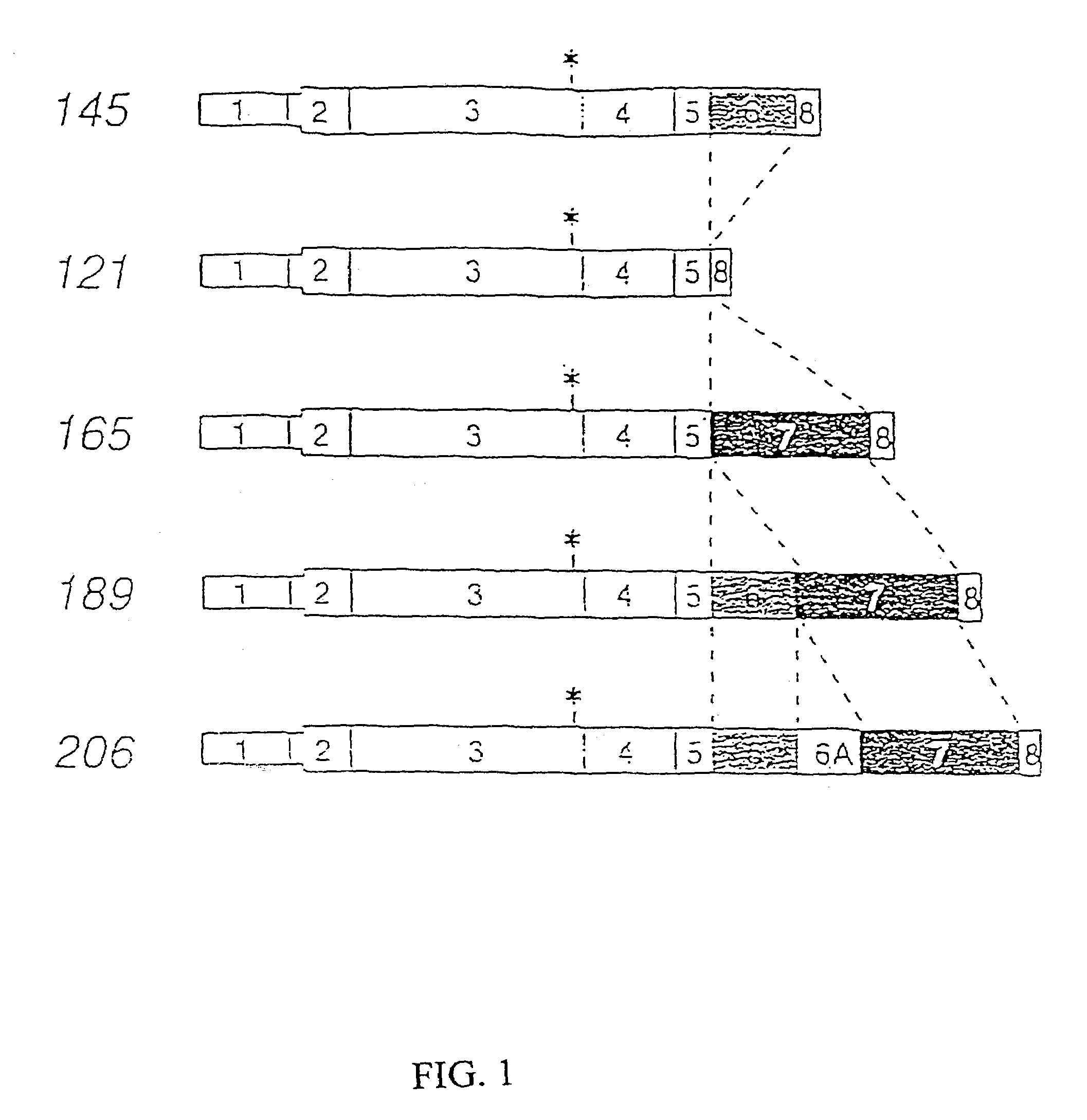
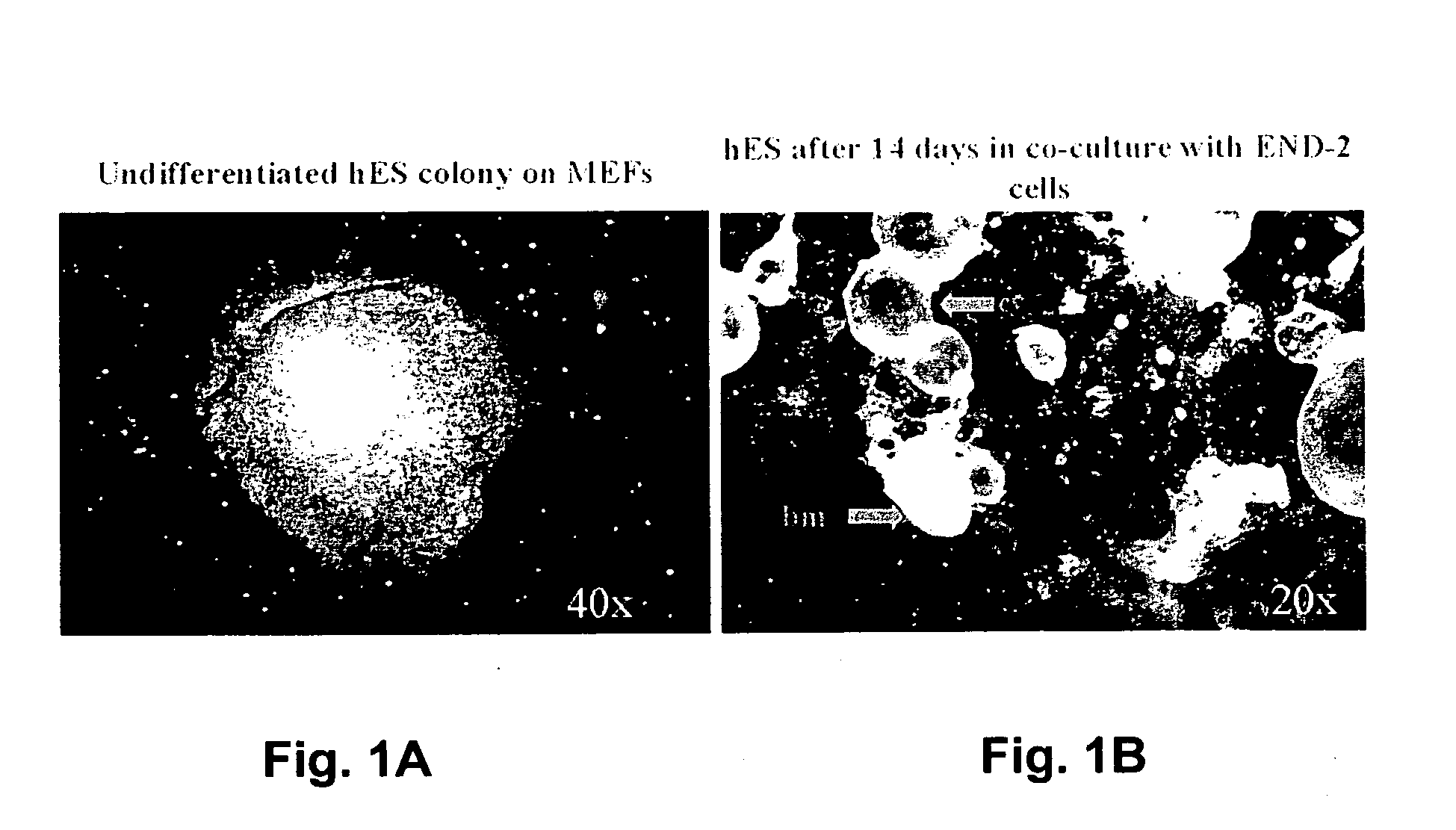
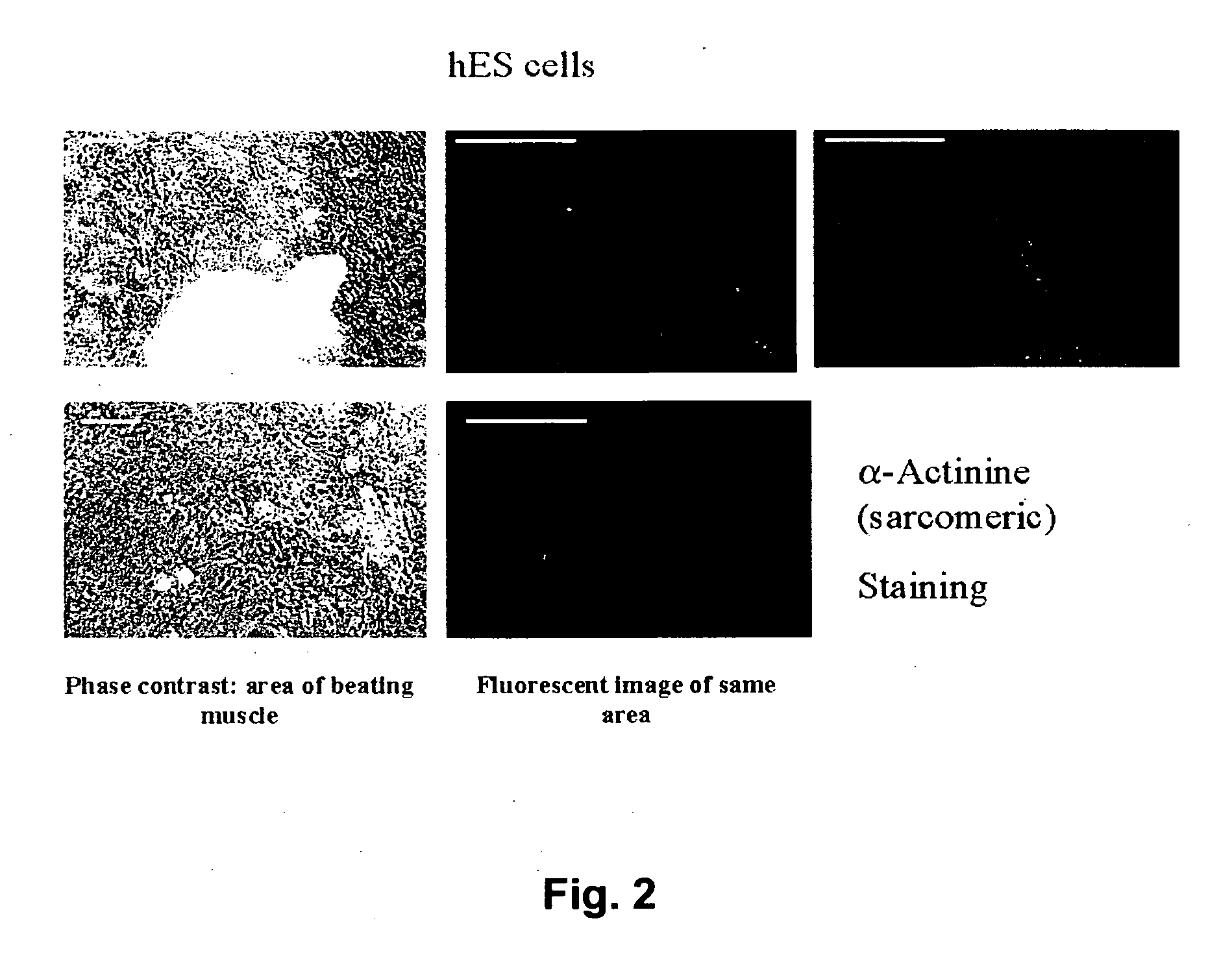
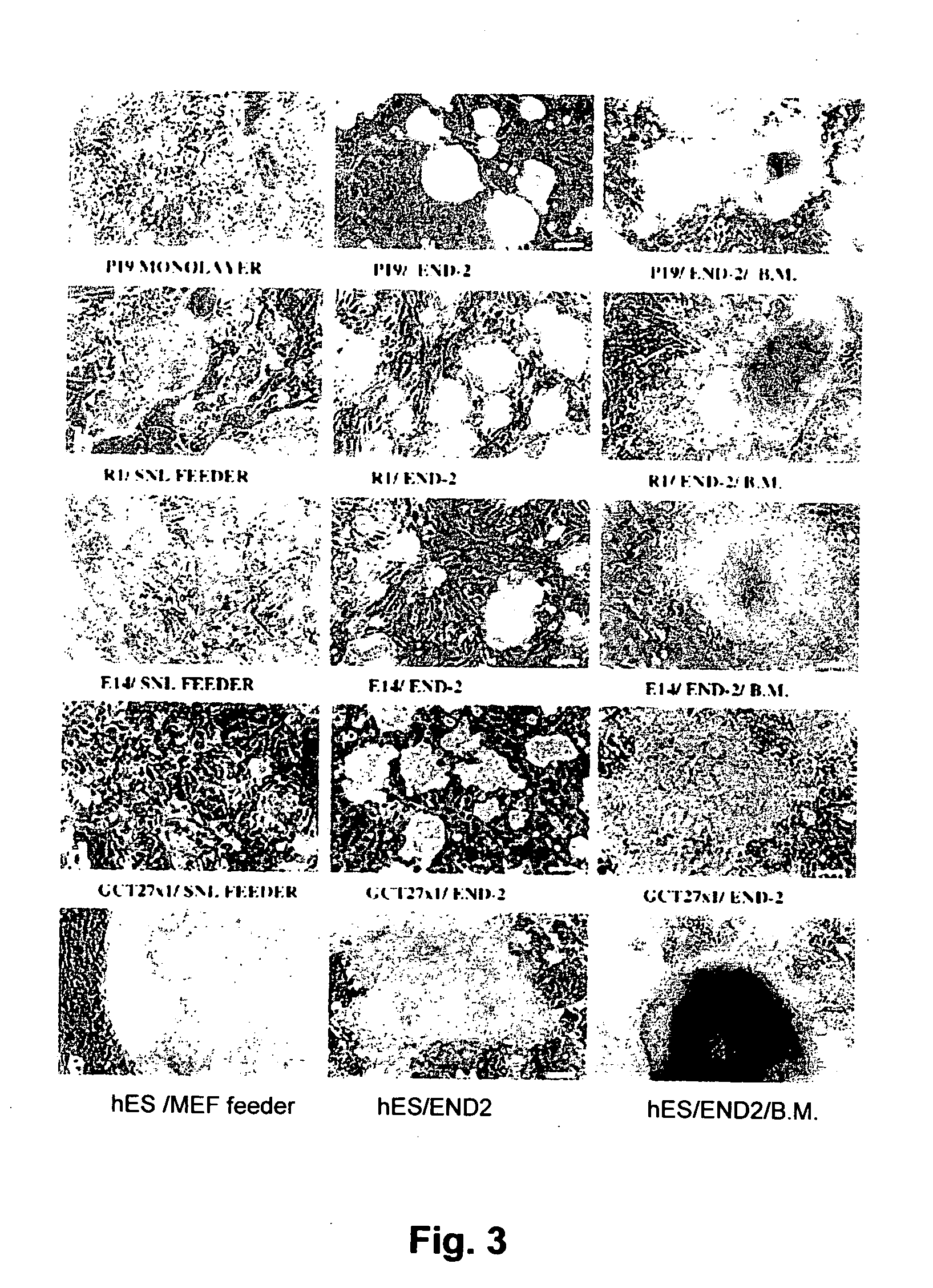
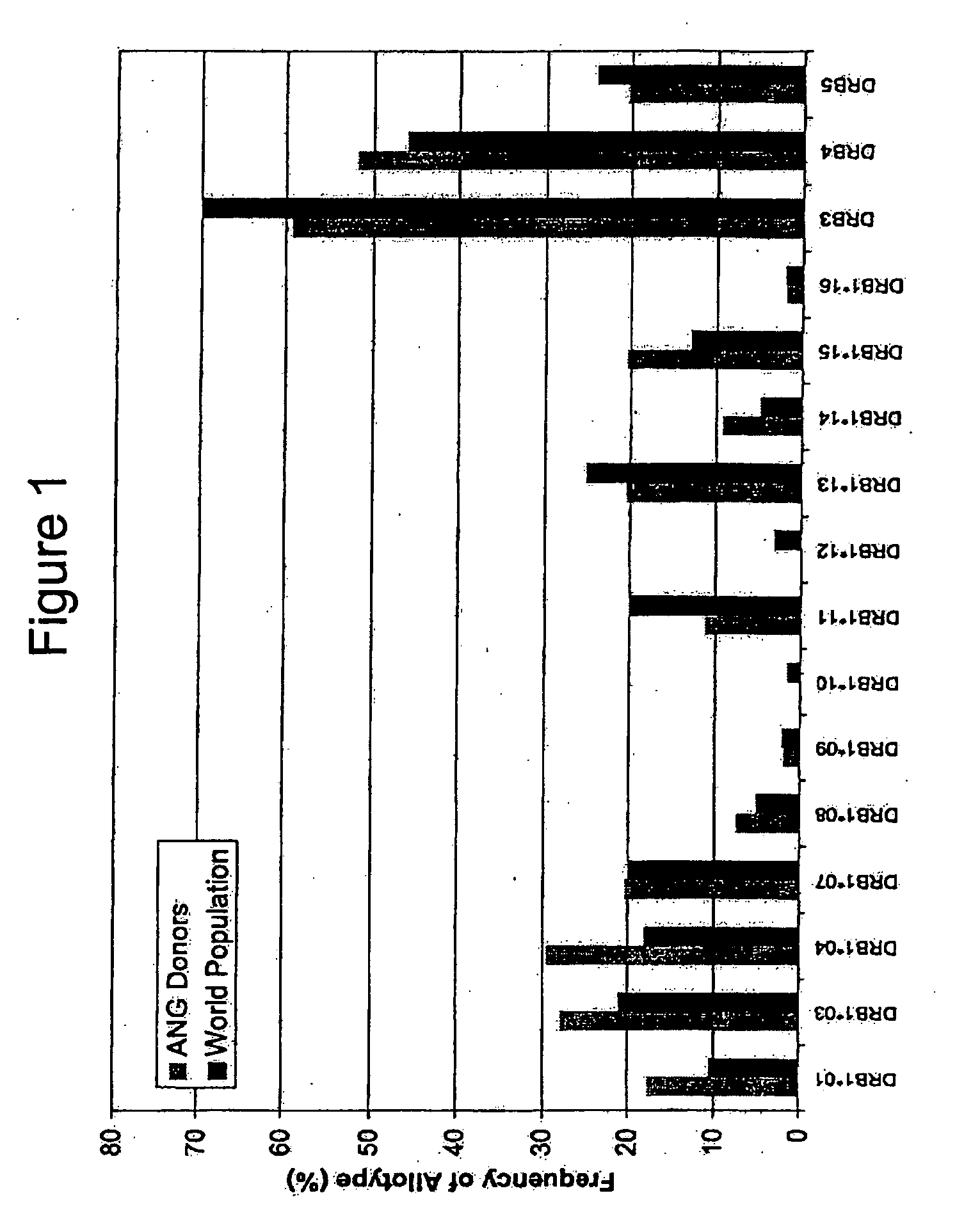
Patents
Literature
1227 results about "Vascular endothelium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Vascular endothelium. The simple squamous epithelial tissue lining the blood vessels. It is a semipermeable barrier between the blood and the vascular smooth muscle, produces vasodilator chemicals, and may inhibit vasoconstrictor substances.
Compositions for targeting the vasculature of solid tumors
InactiveUS6051230AEffectively compete for bindingReduce TEC-4 or TEC-11 bindingHybrid immunoglobulinsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenCell Surface Antigens
The present invention relates generally to methods and compositions for targeting the vasculature of solid tumors using immunological- and growth factor-based reagents. In particular aspects, antibodies carrying diagnostic or therapeutic agents are targeted to the vasculature of solid tumor masses through recognition of tumor vasculature-associated antigens, such as, for example, through endoglin binding, or through the specific induction of endothelial cell surface antigens on vascular endothelial cells in solid tumors.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
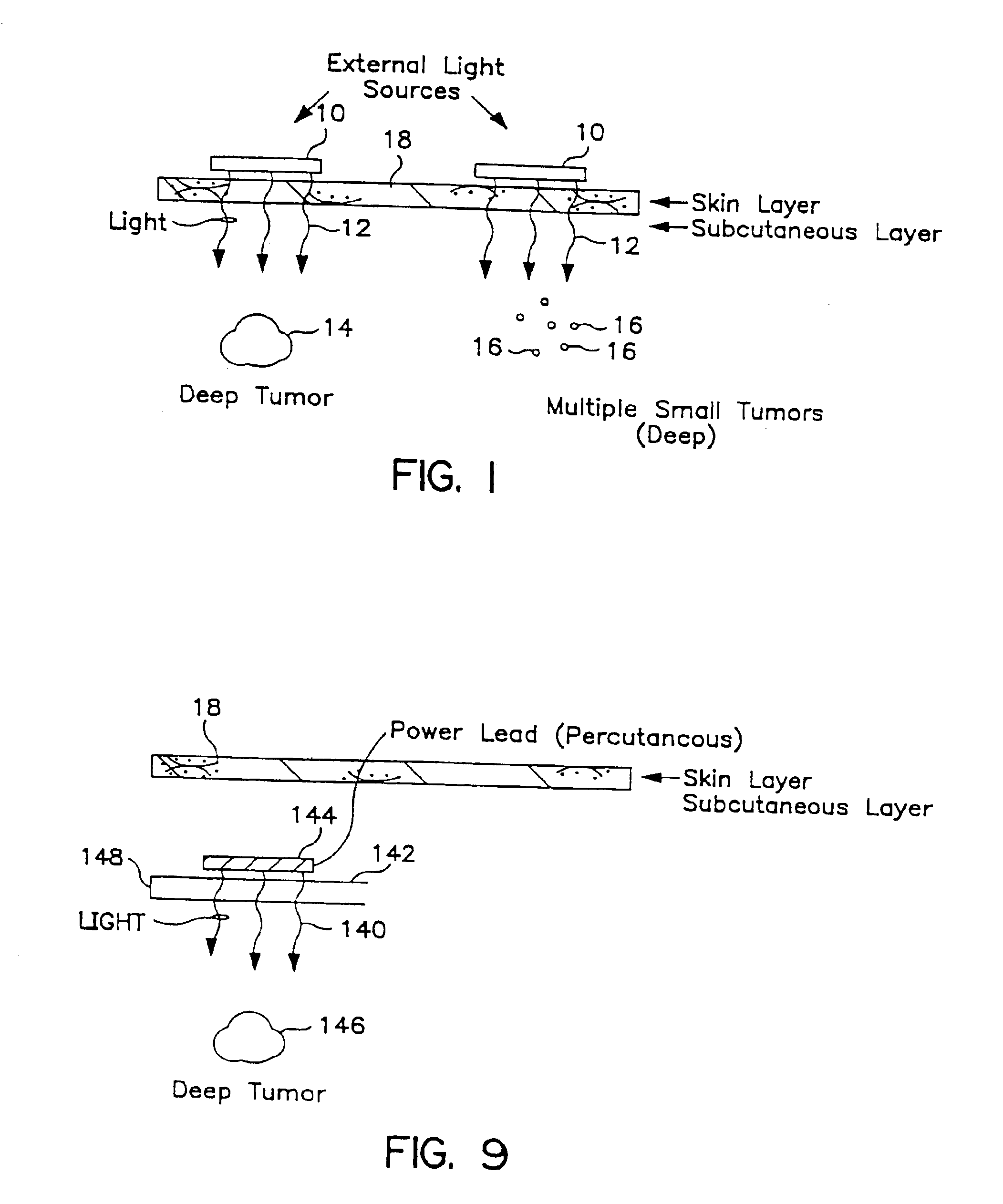
Transcutaneous photodynamic treatment of targeted cells
The present invention is drawn to methods and compounds for photodynamic therapy (PDT) of a target tissue or compositions in a mammalian subject, using a light source that preferably transmits light to a treatment site transcutaneously. The method provides for administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a targeted substance, which is either a targeted photosensitizing agent, or a photosensitizing agent delivery system, or a targeted prodrug. This targeted substance preferably selectively binds to the target tissue. Light at a wavelength or waveband corresponding to that which is absorbed by the targeted substance is then administered. The light intensity is relatively low, but a high total fluence is employed to ensure the activation of the targeted photosensitizing agent or targeted prodrug product. Transcutaneous PDT is useful in the treatment of specifically selected target tissues, such as vascular endothelial tissue, the abnormal vascular walls of tumors, solid tumors of the head and neck, tumors of the gastrointestinal tract, tumors of the liver, tumors of the breast, tumors of the prostate, tumors of the lung, nonsolid tumors, malignant cells of the hematopoietic and lymphoid tissue and other lesions in the vascular system or bone marrow, and tissue or cells related to autoimmune and inflammatory disease.
Owner:LIGHT SCI ONCOLOGY
Treatment and diagnosis of cancer
InactiveUS7163680B2Effective diagnosisEffective treatmentBiological material analysisNanomedicineAntigenVascular endothelium
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Temporary vascular filters
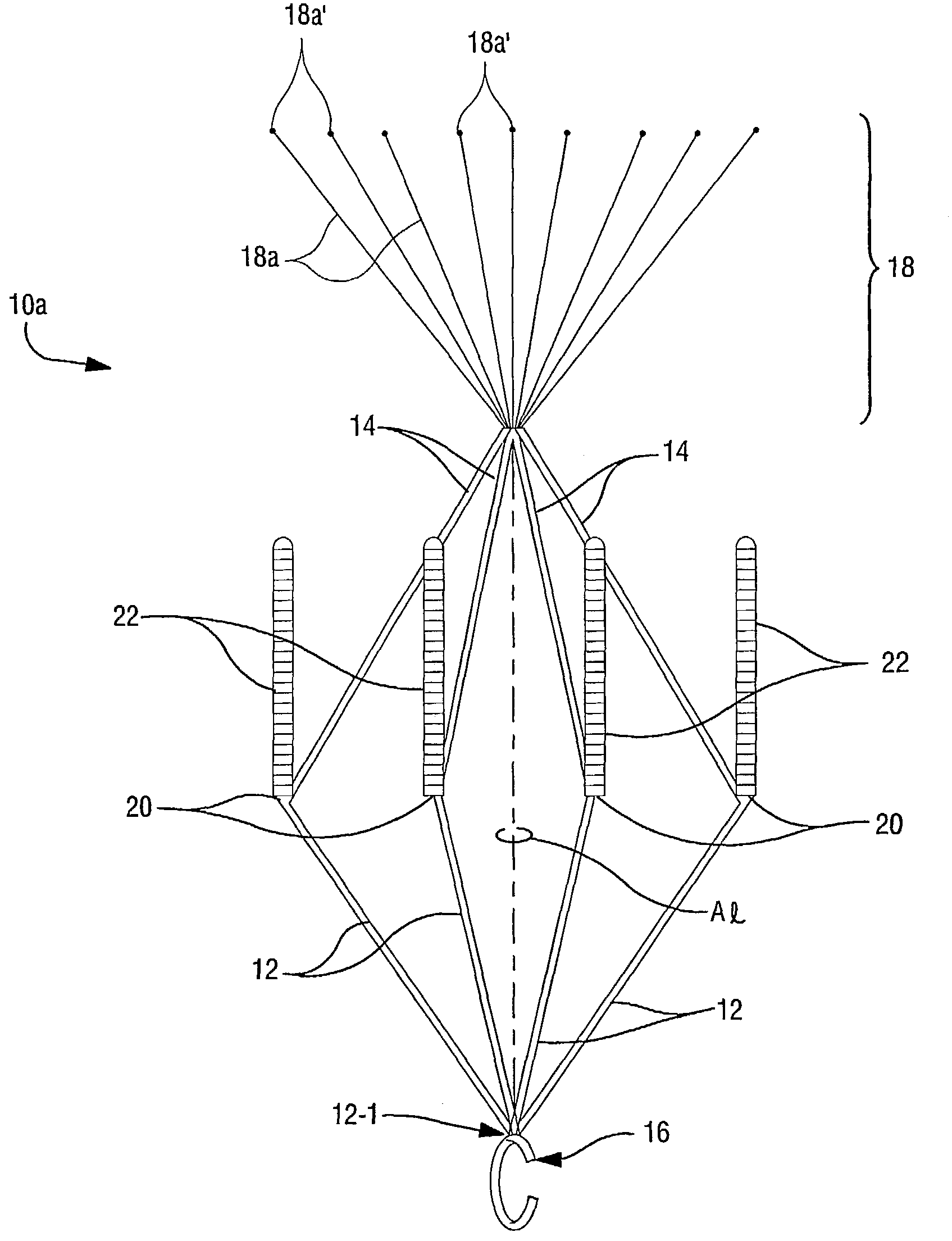
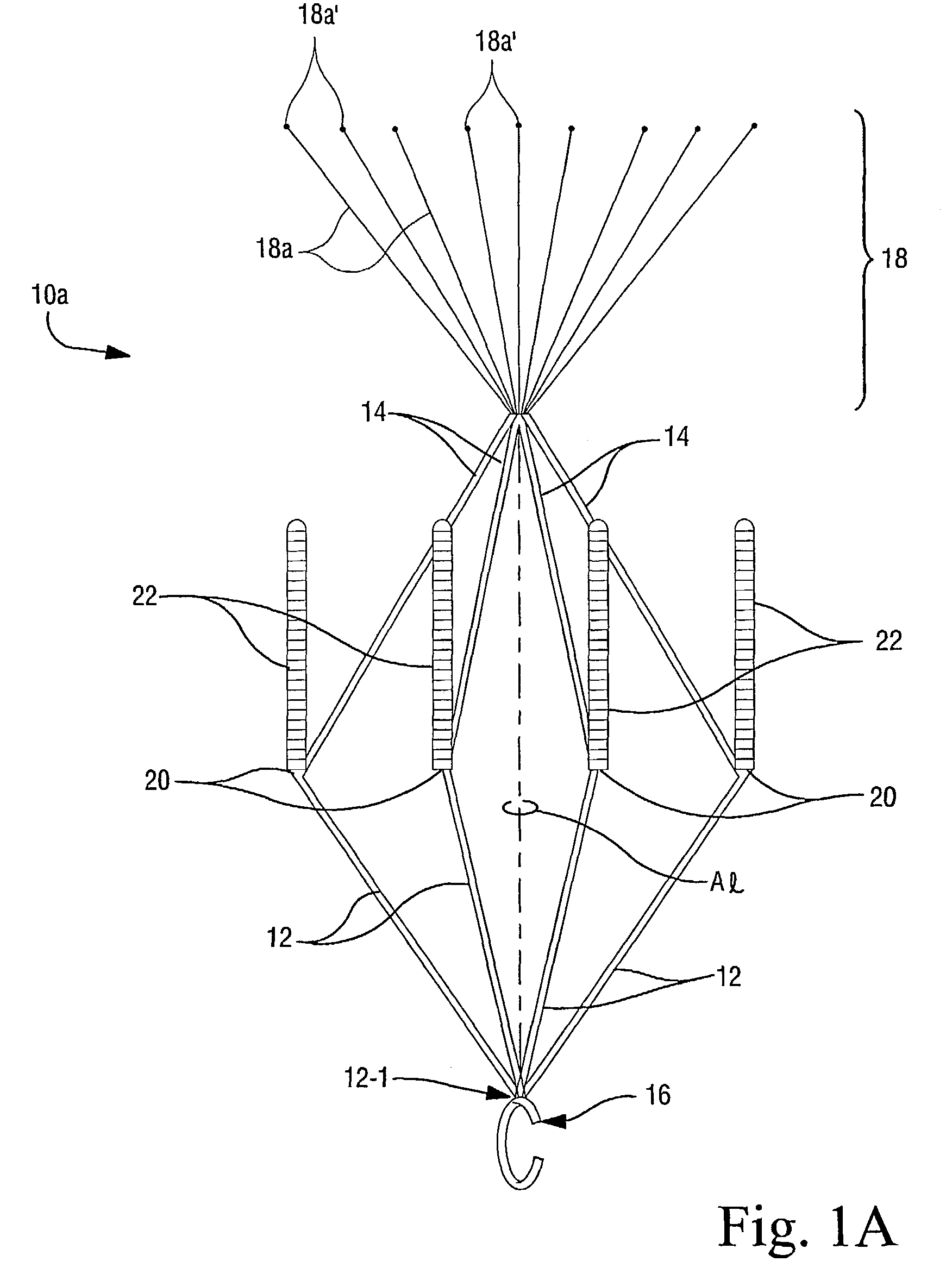
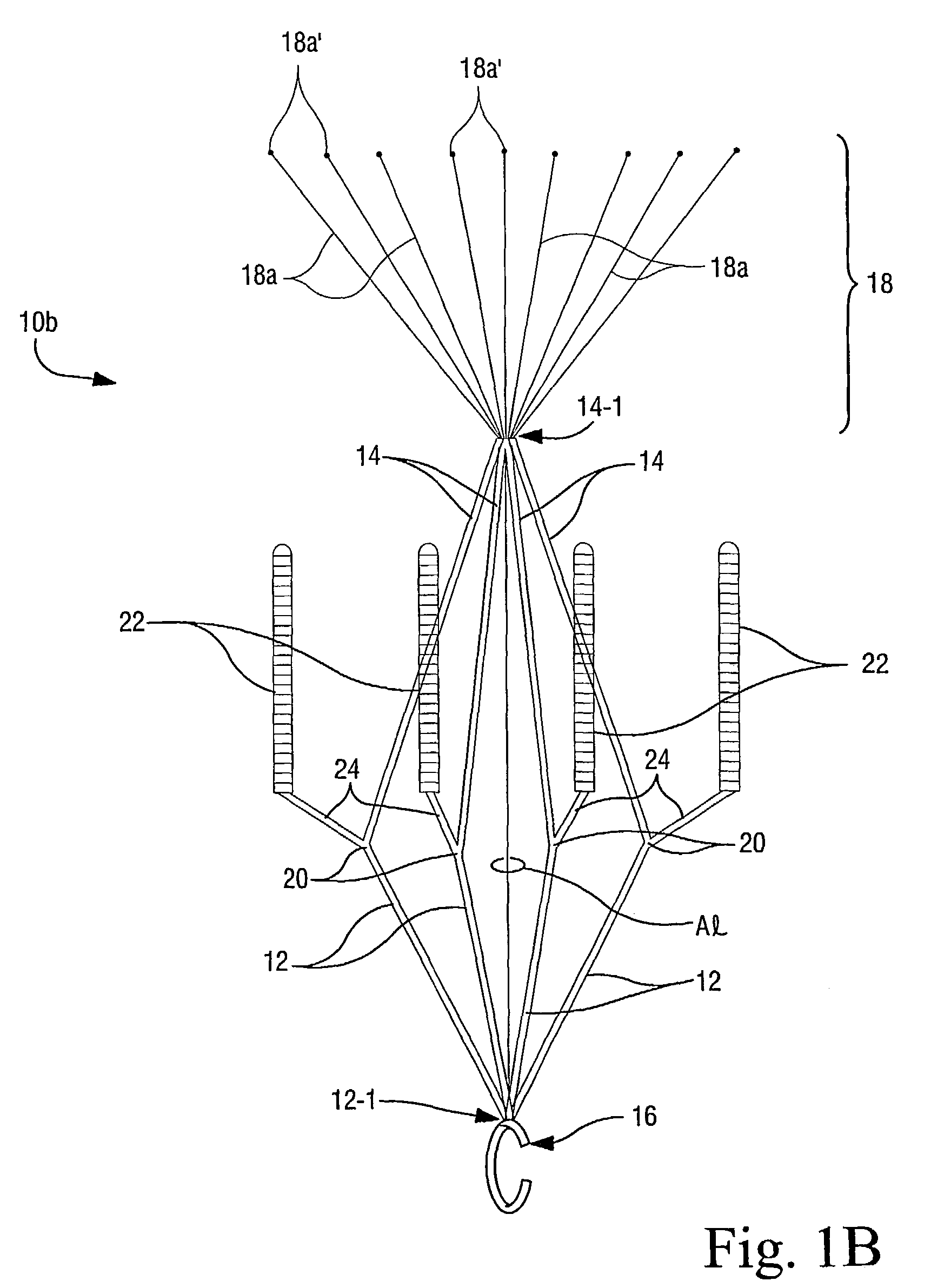
InactiveUS7147649B2Easily and safely removableEasily and safely removedStentsSurgeryVascular filterVascular endothelium
Blood filters (10a, 10b) sized and configured to be positioned within a vascular vessel include a plurality of anchoring arms (22) having a removable sleeve (22-2) for temporarily anchoring the blood filter to a vessel wall. In especially preferred embodiments, the removable sleeve (22-2) is formed of bioabsorbable material. When the filter (10a, 10b) is deployed, it is this removable sleeve (22-2) which comes into contact with the inner tissue wall of the patient's blood vessel (typically the inferior vena cava). When it is desired to remove the filter, endothelization of the sleeve (22-2) has typically occurred but since the sleeves are a removable (separable) component part of the anchoring arms (22), the entire filter device (10a, 10b) can be retrieved thereby leaving the endothelized sleeves (22-2) remaining in place on the interior wall of the patient's vascular vesse. However, such sleeves (22-2) will be absorbed over time (preferably by means of hydrolysis) since they are formed of a bioabsorbable polymeric material. In such a manner, the filters (10a, 10b) of the present invention allow relatively easy retrieval while minimizing (if not preventing entirely) harm to the vascular endothelium.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
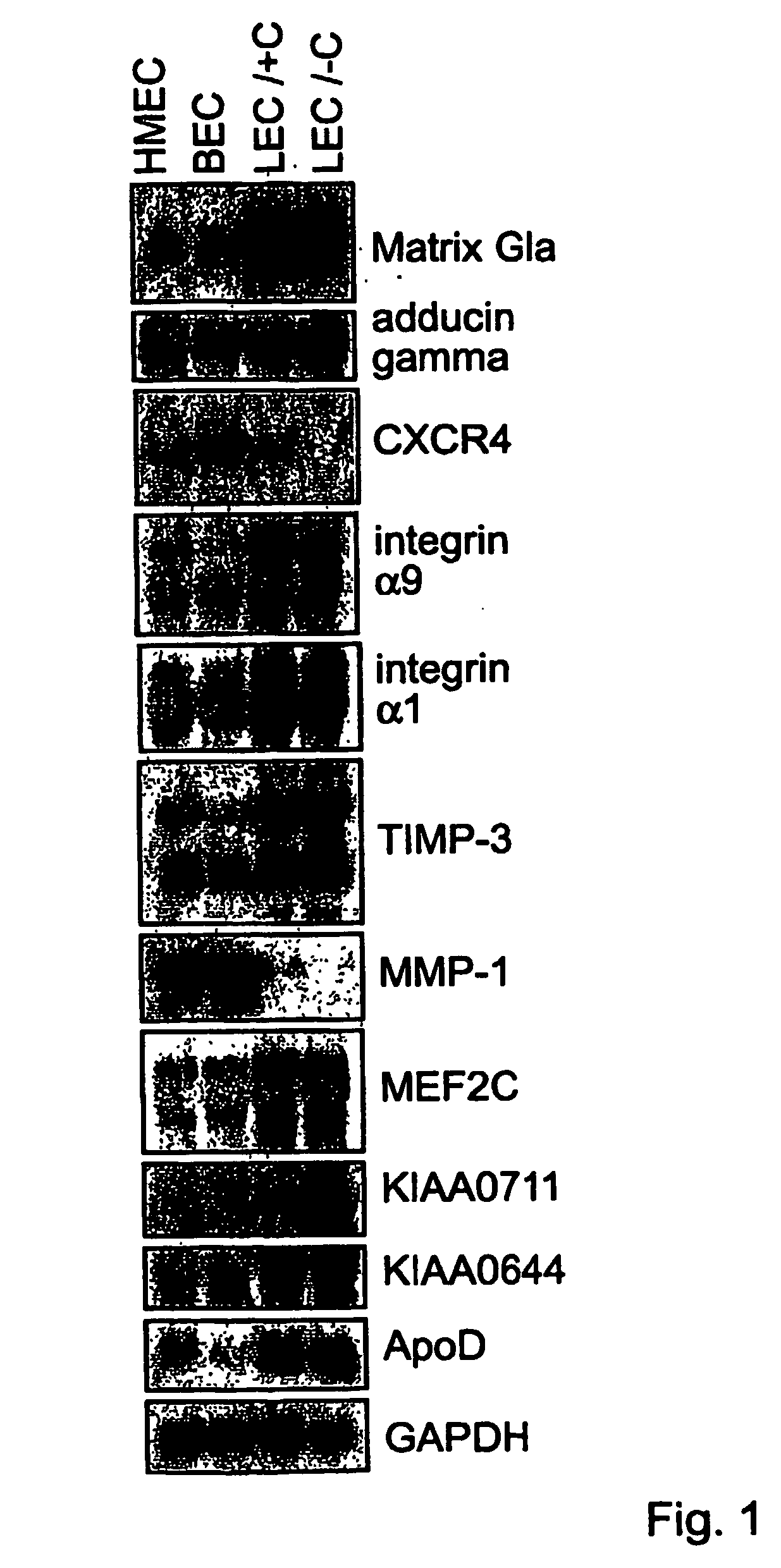
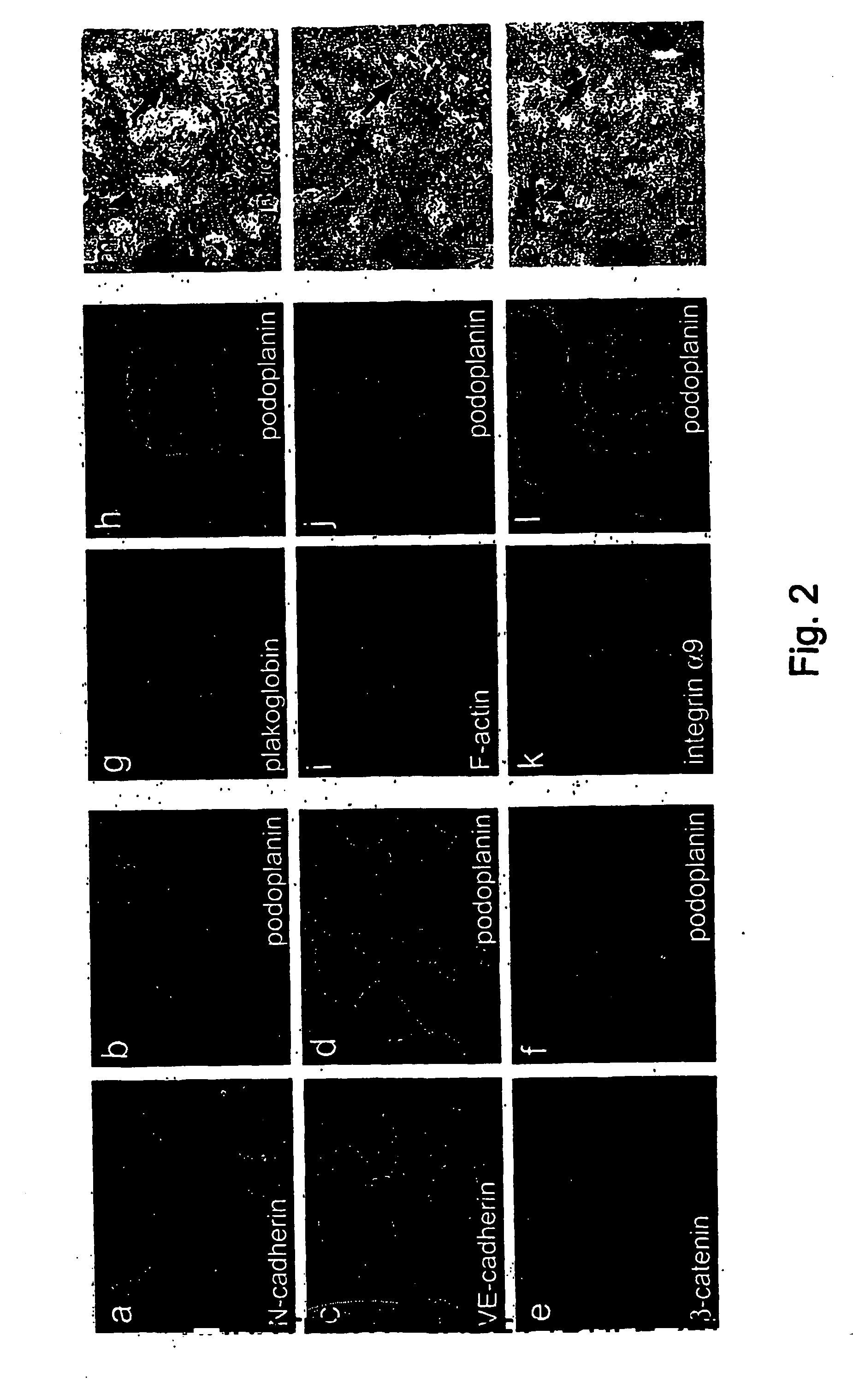
Lymphatic and blood endothelial cell genes
The invention provides polynucleotides and genes that are differentially expressed in lymphatic versus blood vascular endothelial cells. These genes are useful for treating diseases involving lymphatic vessels, such as lymphedema, various inflammatory diseases, and cancer metastasis via the lymphatic system.
Owner:VEGENICS PTY LTD
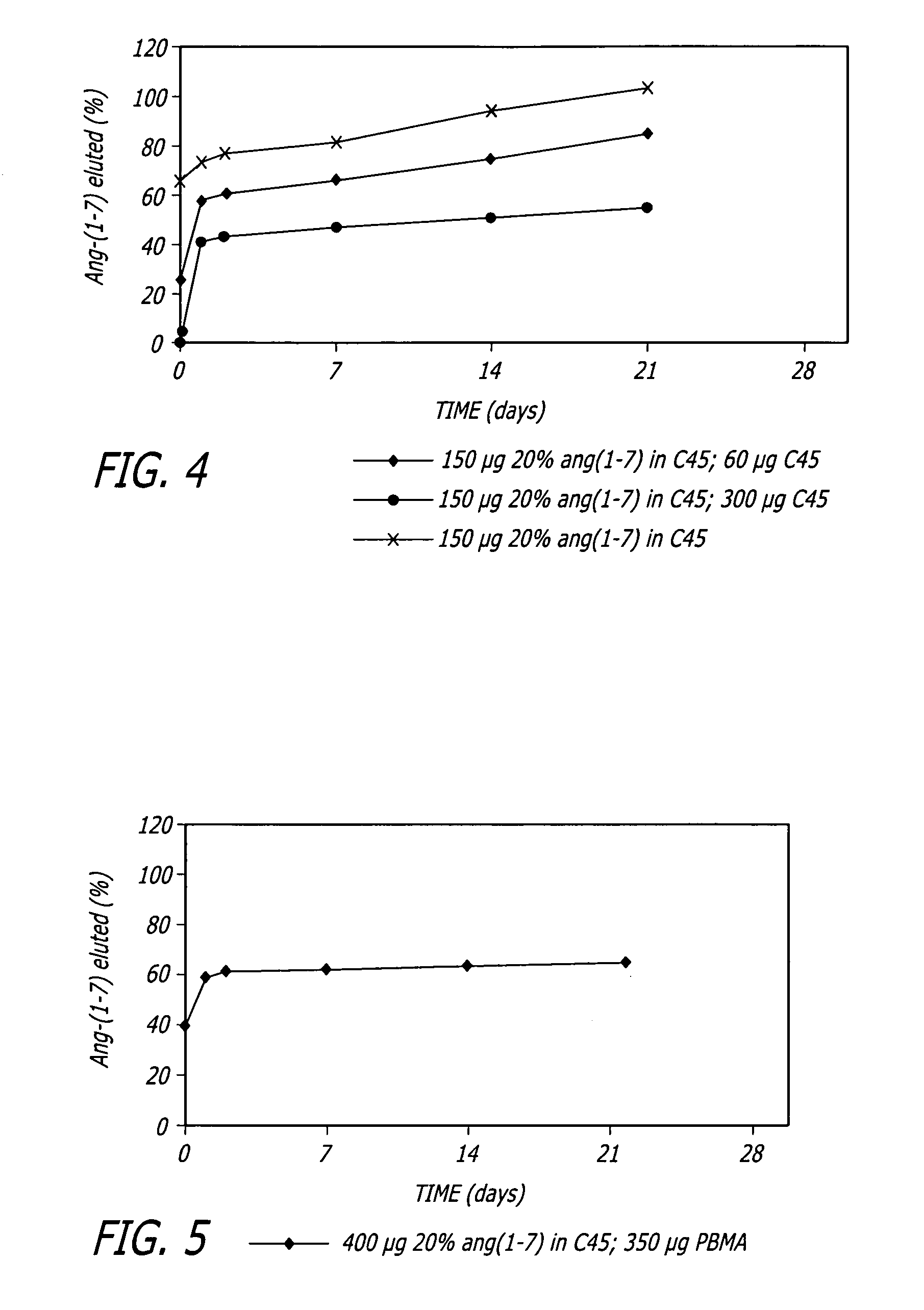
Angiotensin-(1-7) eluting polymer-coated medical device to reduce restenosis and improve endothelial cell function
InactiveUS7176261B2Function increasePrevent restenosisAngiotensinsPeptide/protein ingredientsVascular endotheliumPercent Diameter Stenosis
Medical devices with polymer coatings designed to control the release of angiotensin-(1-7) receptor agonists from medical devices are disclosed. The present application also discloses providing vascular stents with angiotensin-(1-7) receptor agonist-containing controlled-release coatings. Methods for treating or inhibiting post-stent implantation restenosis as well as improving vascular endothelial function in patients are also provided.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
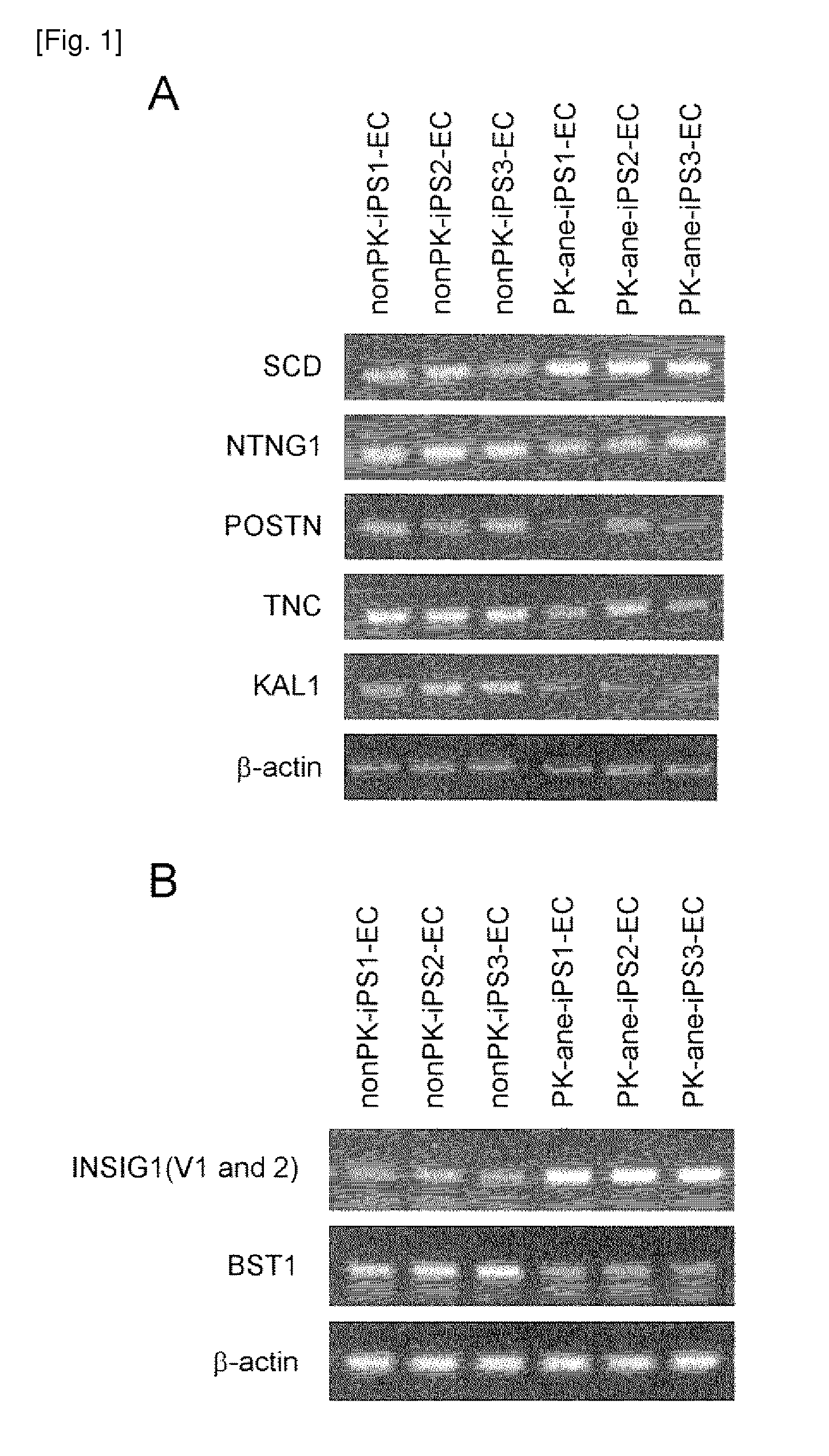
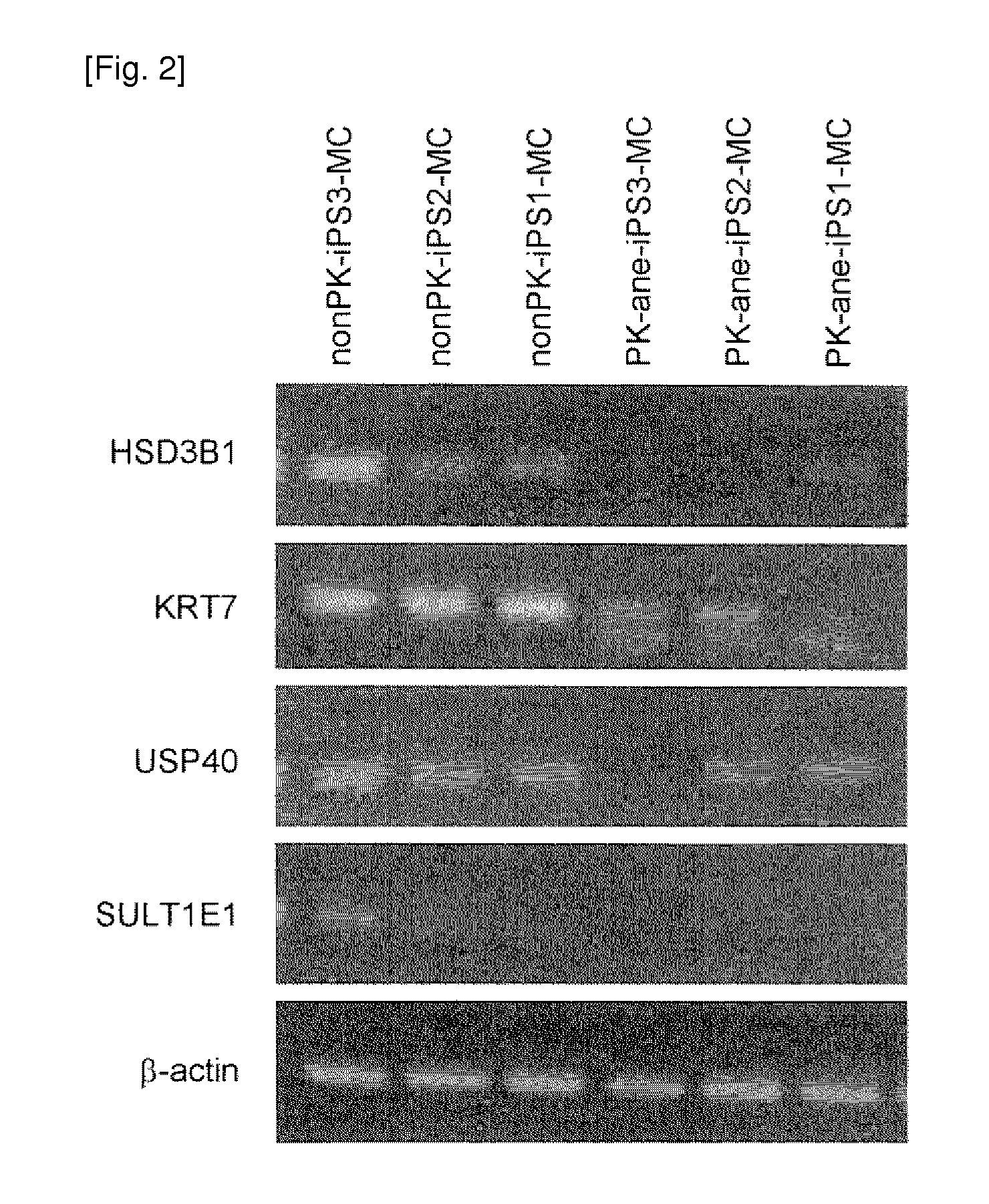
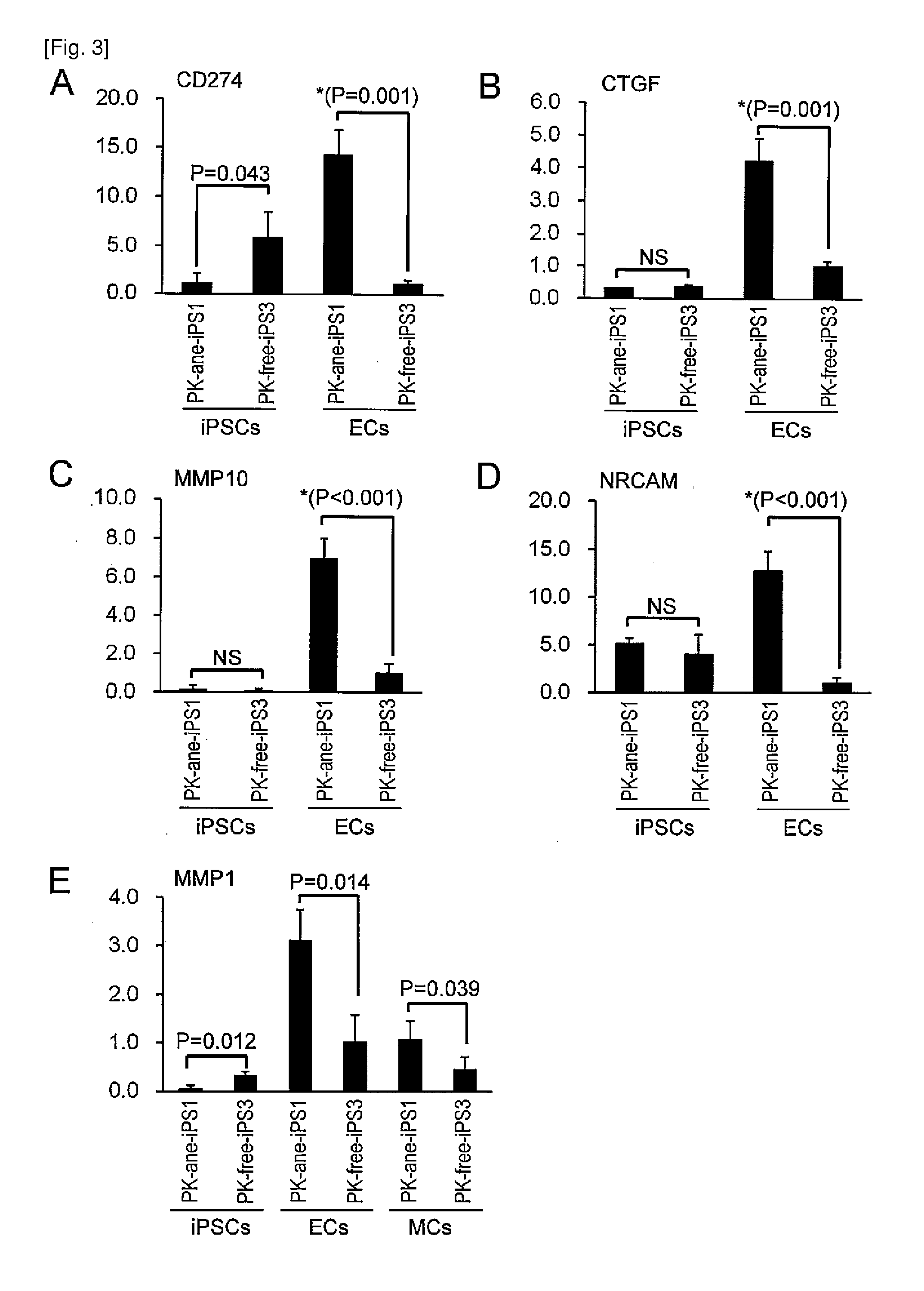
Method of examining polycystic kidney disease and method of screening for therapeutic agent of the disease
The present invention provides a method of examining polycystic kidney disease or a complication of polycystic kidney disease using a gene(s) selected from the group consisting of NTNG1, POSTN, TNC, KAL1, BST1, ACAT2, INSIG1, SCD, HSD3B1, KRT7, USP40, SULT1E1, BMP6, CD274, CTGF, E2F7, EDN1, FAM43A, FRMD3, MMP10, MYEOV, NR2F1, NRCAM, PDCK1, PLXNA2, SLC30A3, SNAI1, SPOCD1, MMP1, TFPI2, HMGA2, KRTAP4-7, KRTAP4-8, KRTAP4-9, MYPN, RPPH1, and SIAE, and a method of screening for a therapeutic agent or a preventive agent therefore, and further vascular endothelial cells or vascular mural cells obtained via differentiation induction from iPS cells formed from a somatic cell of a subject suffered from polycystic kidney disease and having cerebral aneurysm as a complication.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Multipotent stem cells derived from placenta tissue and cellular therapeutic agents comprising the same
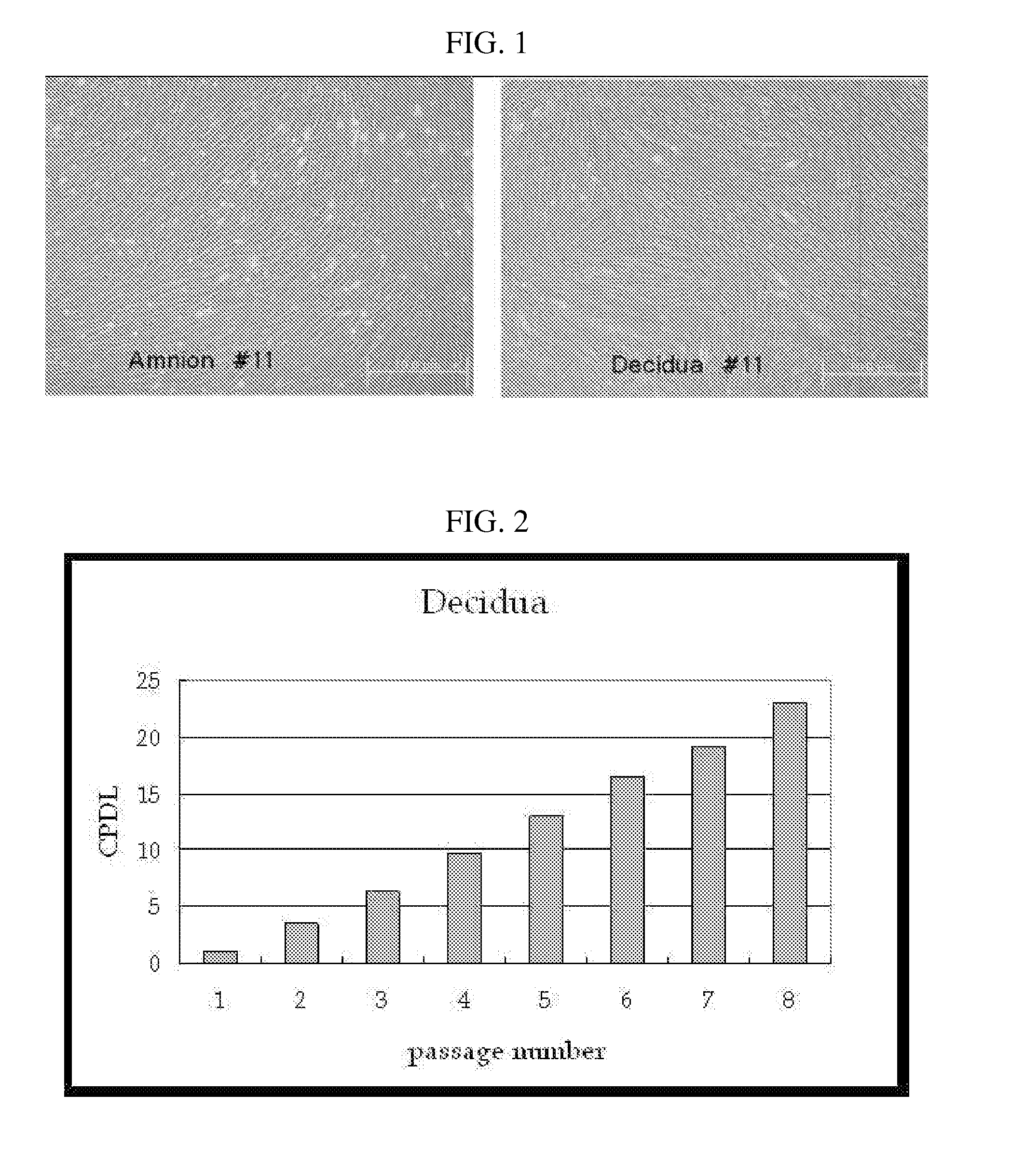
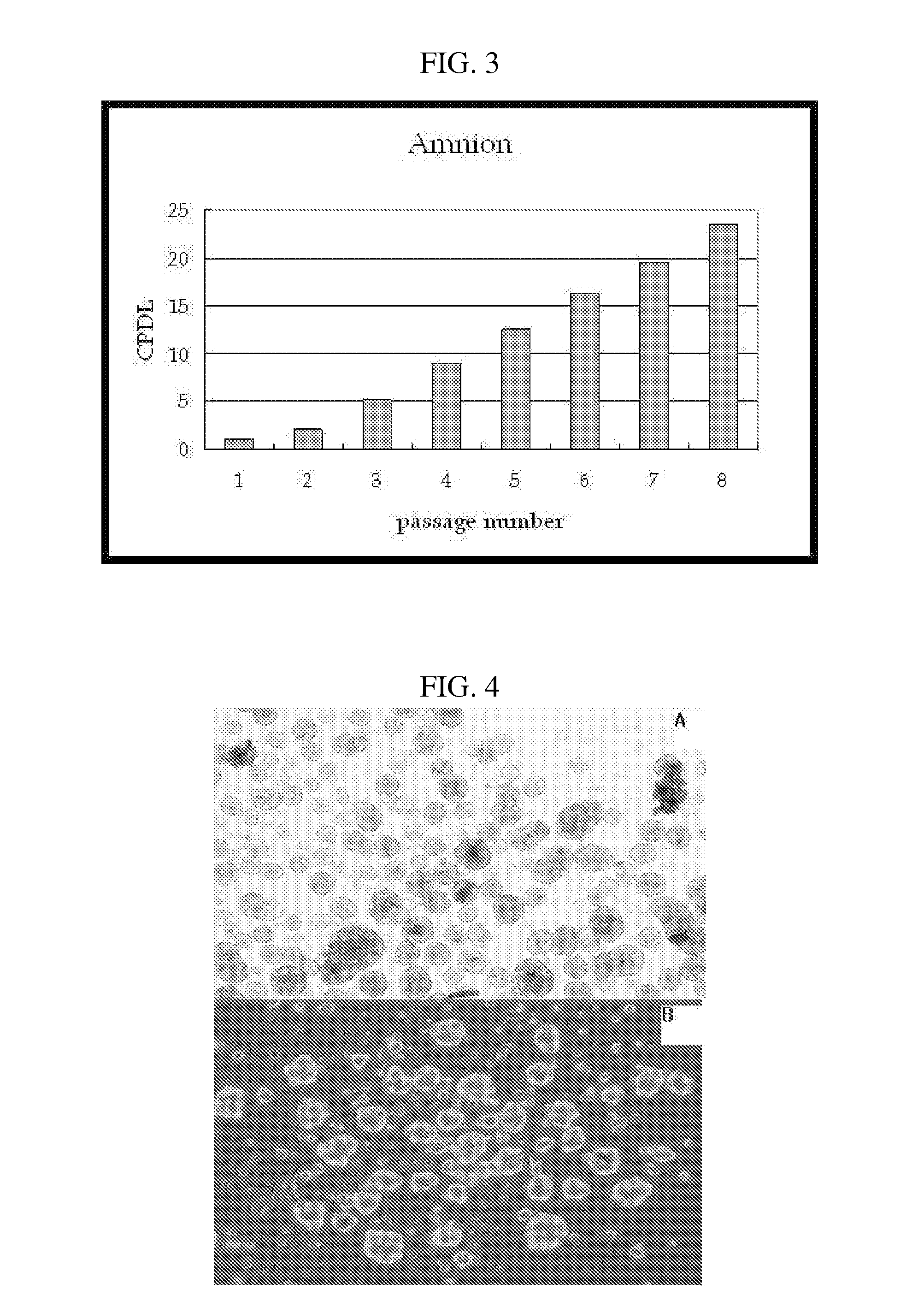
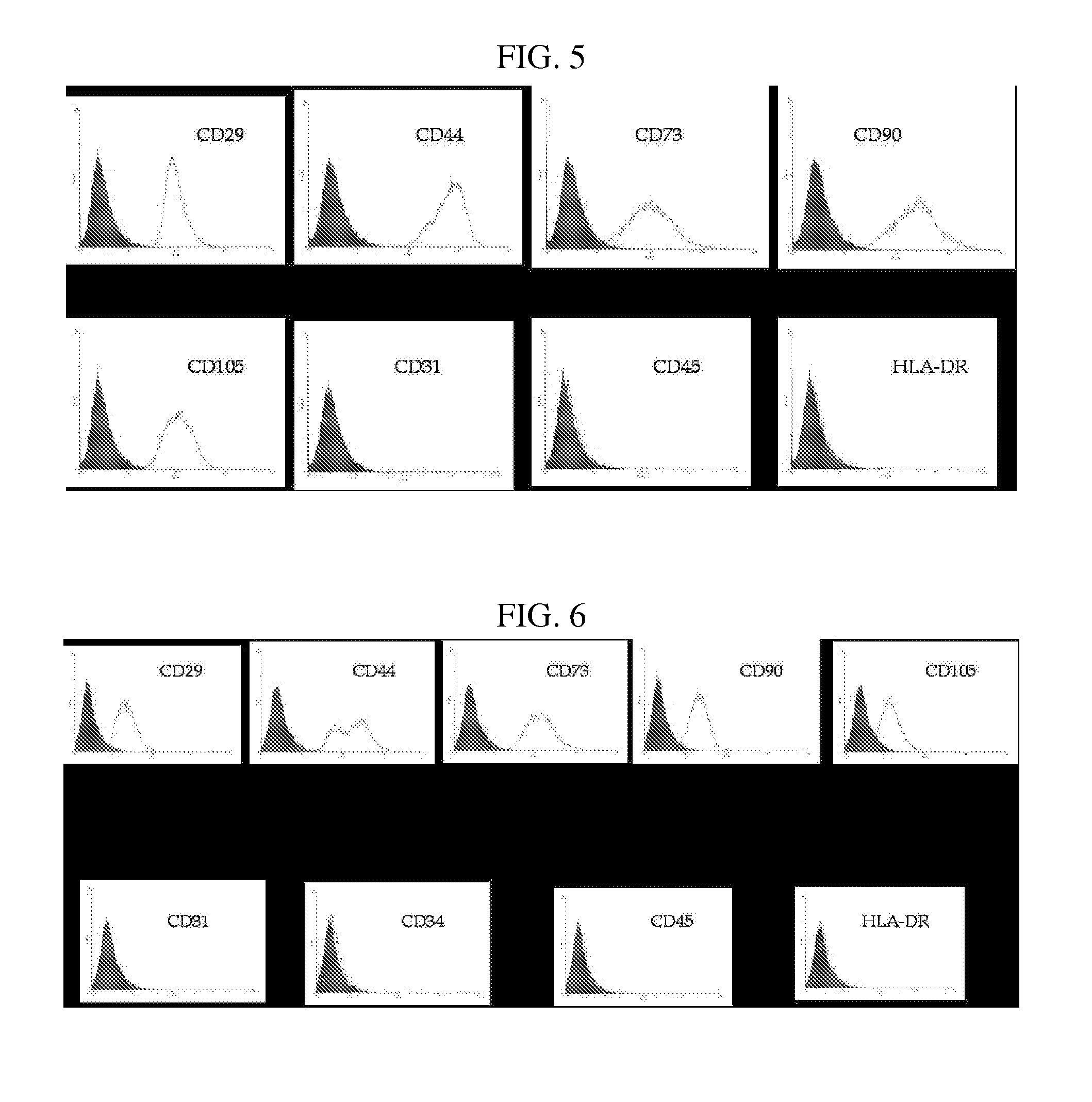
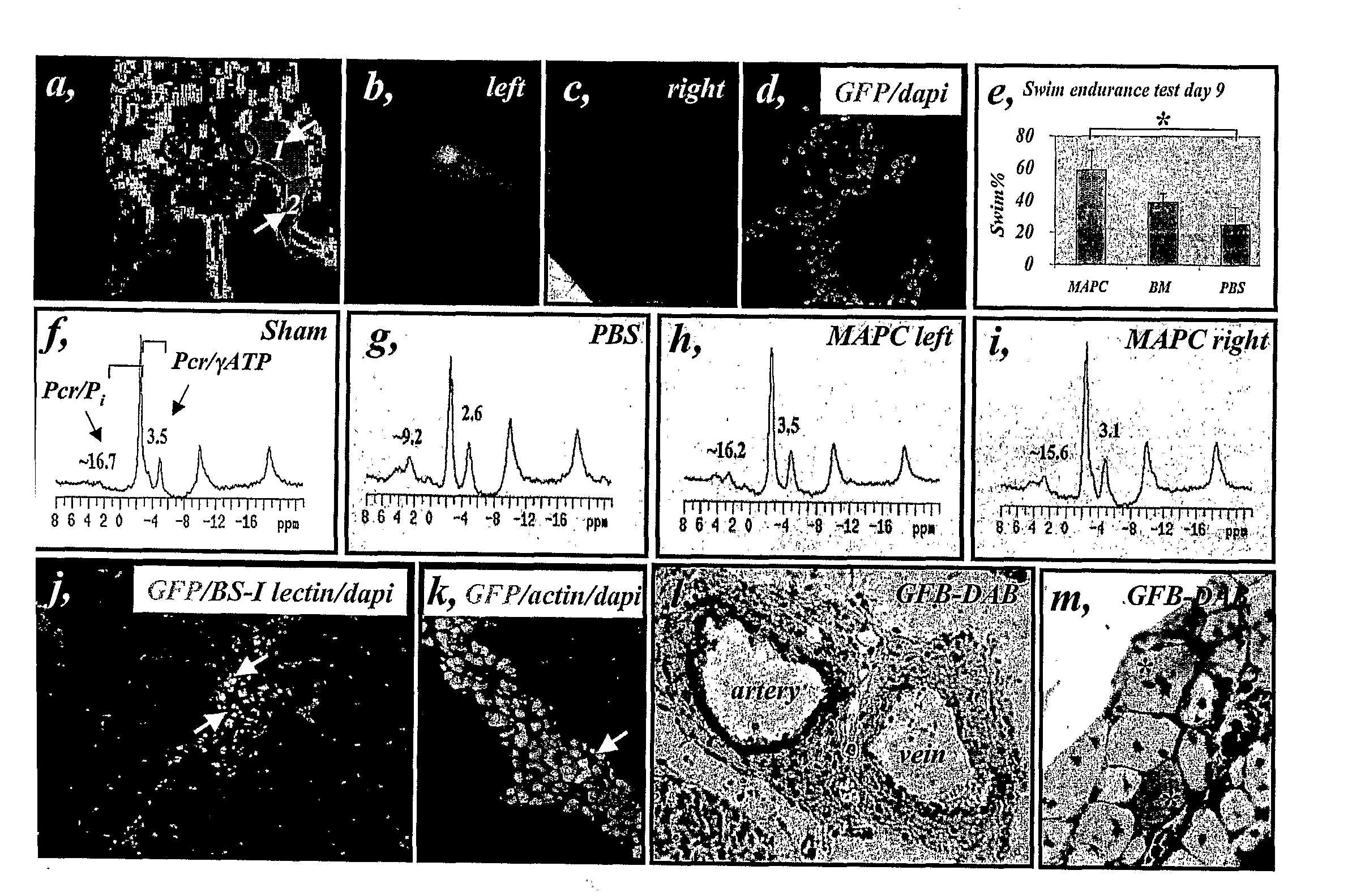
InactiveUS20070243172A1Negative immunological responseBiocideArtificial cell constructsGerm layerDisease
The present invention relates to placenta tissue-derived multipotent stem cells and cell therapeutic agents containing the same. More specifically, to a method for producing placenta stem cells having the following characteristics, the method comprising culturing amnion, chorion, decidua or placenta tissue in a medium containing collagenase and bFGF and collecting the cultured cells: (a) showing a positive immunological response to CD29, CD44, CD73, CD90 and CD105, and showing a negative immunological response to CD31, CD34, CD45 and HLA-DR; (b) showing a positive immunological response to Oct4 and SSEA4; (c) growing attached to plastic, showing a round-shaped or spindle-shaped morphology, and forming spheres in an SFM medium so as to be able to be maintained in an undifferentiated state for a long period of time; and (d) having the ability to differentiate into mesoderm-, endoderm- and ectoderm-derived cells. Also the present invention relates to placenta stem cells obtained using the production method. The inventive multipotent stem cells have the ability to differentiate into muscle cells, vascular endothelial cells, osteogenic cells, nerve cells, satellite cells, fat cells, cartilage-forming cells, osteogenic cells, or insuline-secreting pancreatic β-cells, and thus are effective for the treatment of muscular diseases, osteoporosis, osteoarthritis, nervous diseases, diabetes and the like, and are useful for the formation of breast tissue.
Owner:RNL BIO
Vascular/Lymphatic Endothelial Cells
Owner:PROYECTO DE BIOMEDICINA CIMA +1
Noninvasive vascular therapy
InactiveUS20020127230A1Significant cytotoxicityMinor side effectsOrganic active ingredientsElectrotherapyDiseaseAutoimmune disease
The present invention is drawn to methods and compounds for transcutaneous photodynamic therapy ("PDT") of a target tissue or compositions in a mammalian subject, which includes administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of a photosensitizing agent or a photosensitizing agent delivery system or a prodrug where the photosensitizing agent or photosensitizing agent delivery system or prodrug selectively binds to the target tissue; and irradiating at least a portion of the subject with light at a wavelength absorbed by the photosensitizing agent or if prodrug, by a prodrug product thereof where the light is provided by a light source, and where the irradiation is at low fluence rate that results in the activation of the photosensitizing agent or prodrug product. These methods of transcutaneous PDT are useful in the treatment of specifically selected target tissues, such as: vascular endothelial tissue abnormal vascular wall of tumors; tumors of the head and neck; tumors of the gastrointestinal tract; tumors of the liver; tumors of the esophopharyngeal; tumors of the lung; lymphoid tissue; lesions in the vascular system; hone marrow and tissue related to autoimmune disease.
Owner:LIGHT SCI ONCOLOGY
Treatment of eclampsia and preeclampsia
InactiveUS7030083B2Prevention and reduction of endothelial cell injuryPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsVascular endotheliumAngiogenesis Factor
The invention concerns the prevention and treatment of endothelial injury and the injury of tissues containing injured blood vessels by administration of angiogenic factors, such as vascular endothelial cell growth factor (VEGF).
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Methods of inducing differentiation of stem cells
InactiveUS20050227353A1Induced differentiationMicroorganismsMicroorganism based processesVascular endotheliumTherapeutic intent
The present invention relates to methods of inducing differentiation of stem cells. In particular, the invention relates to methods of inducing differentiation of embryonic stem cells into muscle cells or vascular endothelial cells. The invention also includes cells, cell lines, testing models and culture systems used in the methods of the present invention and differentiated cells produced therefrom. The present invention also provides methods of using the differentiated cells of the present invention for therapeutic purposes.
Owner:ES CELL INT
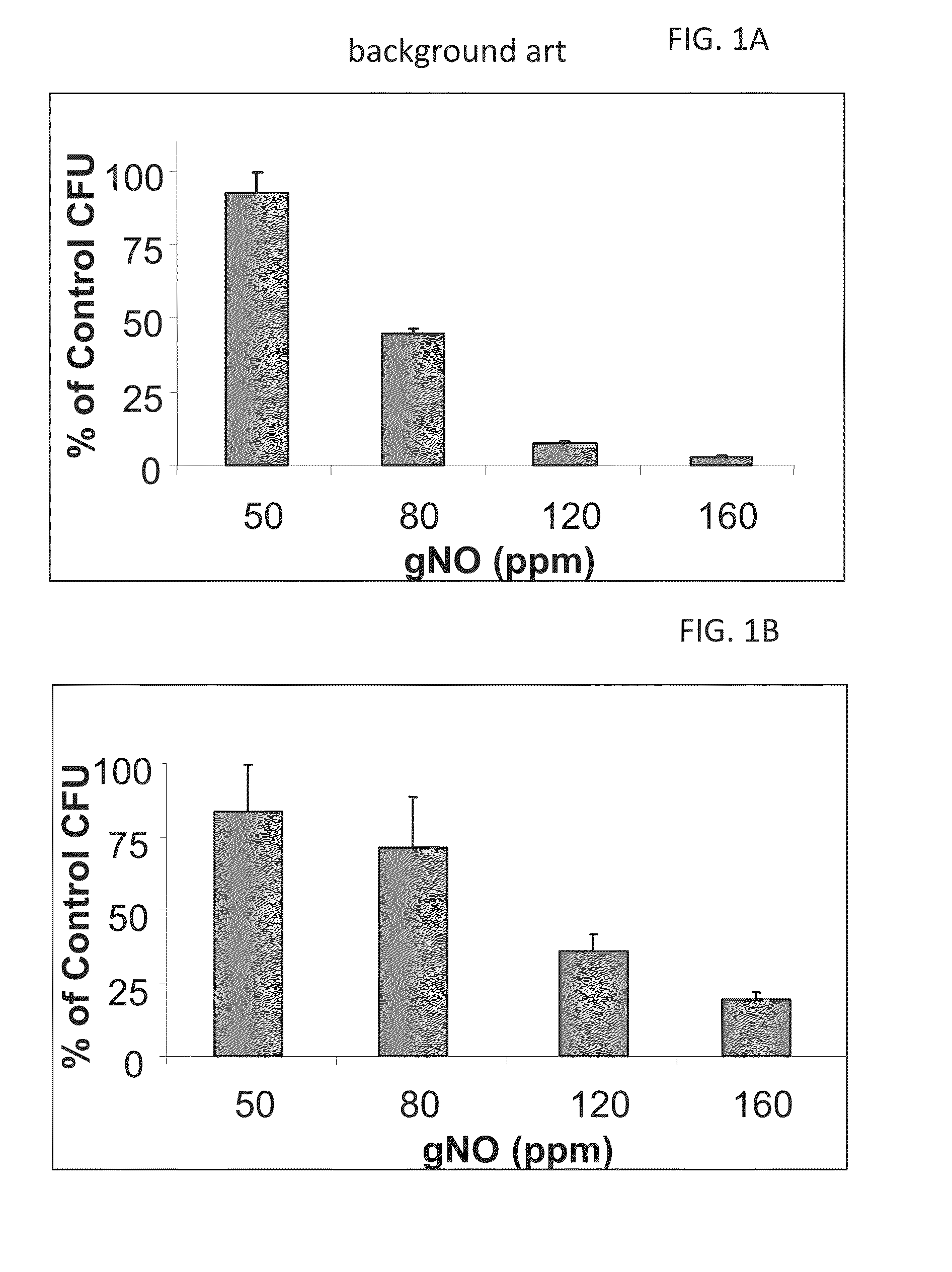
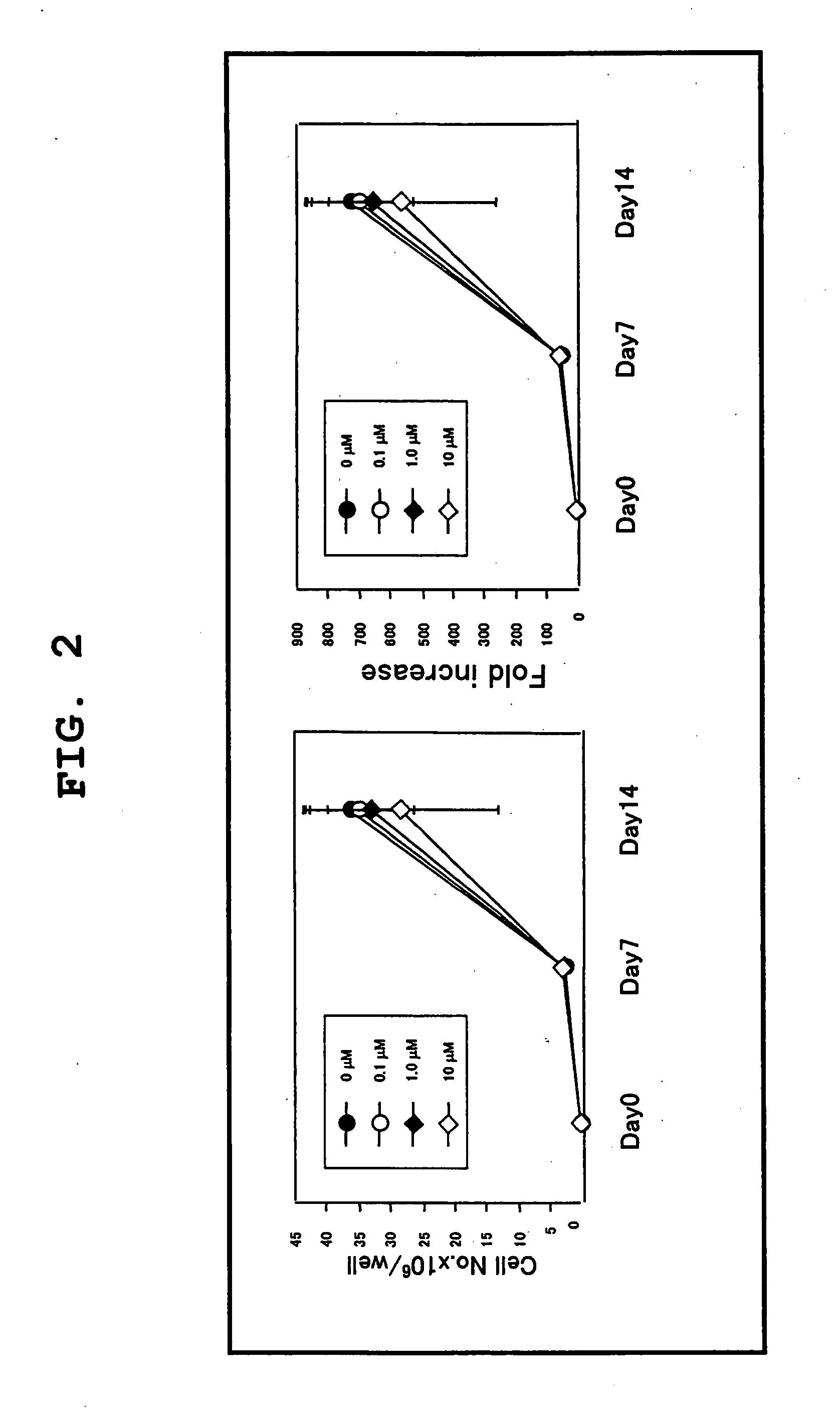
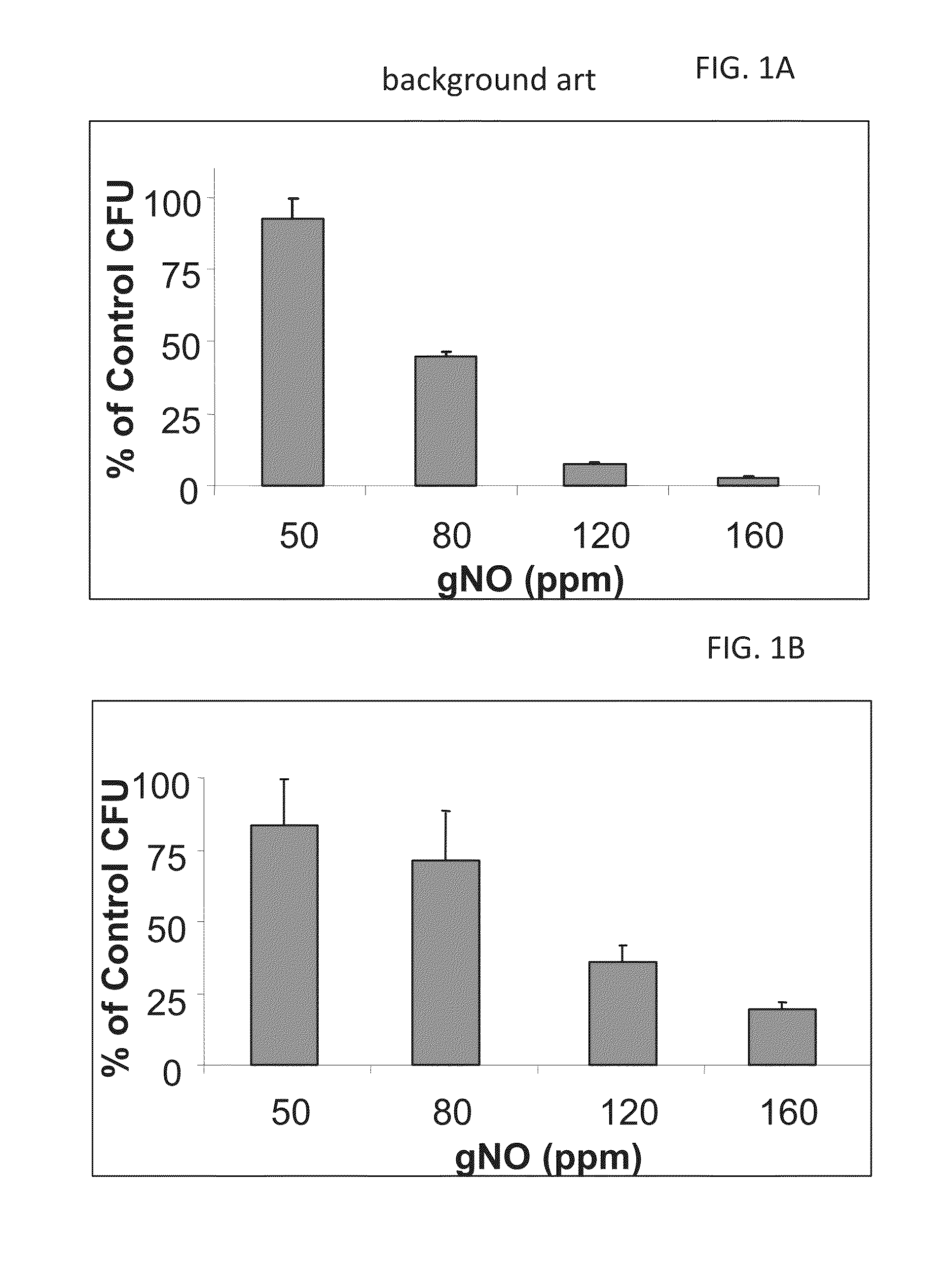
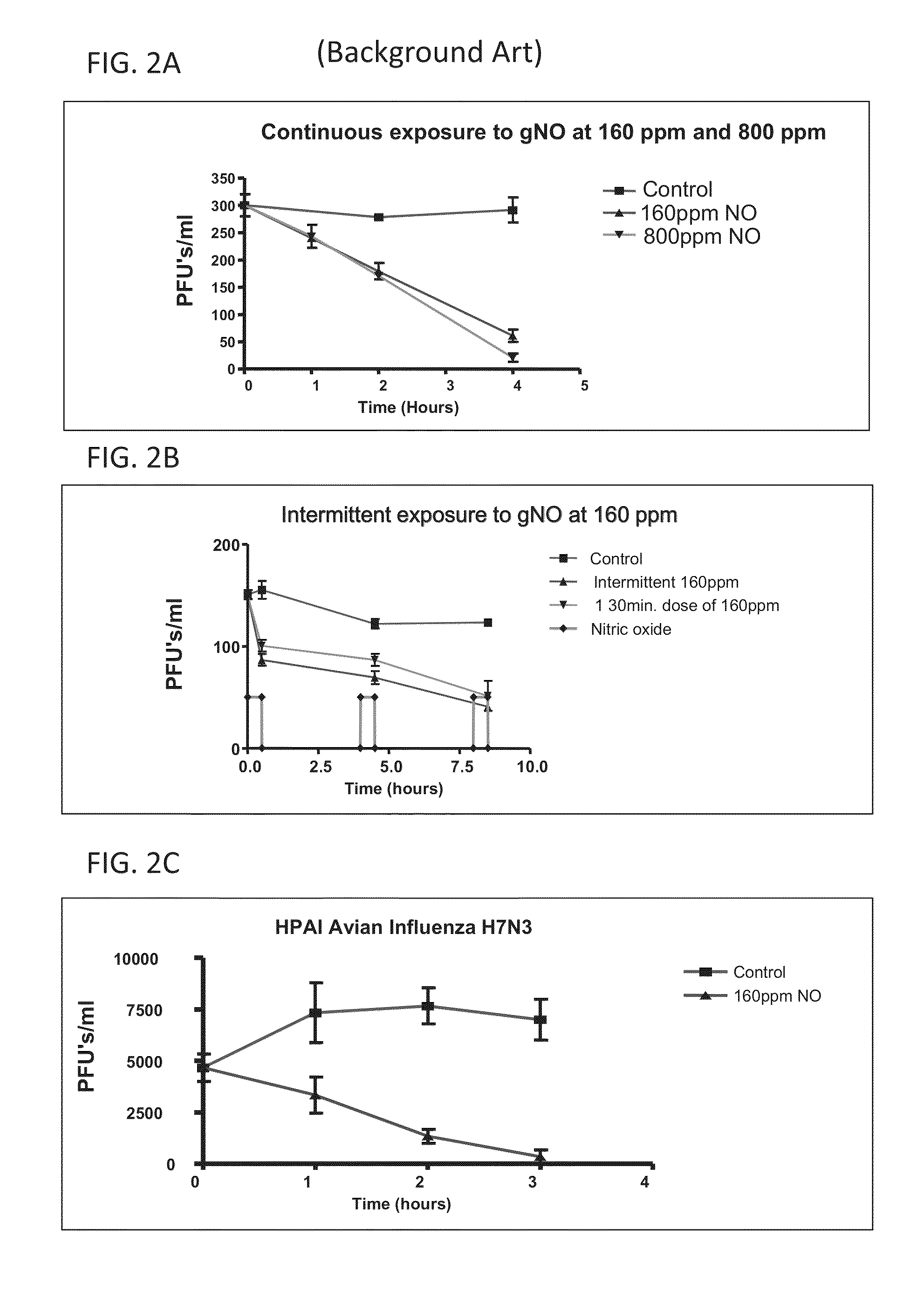
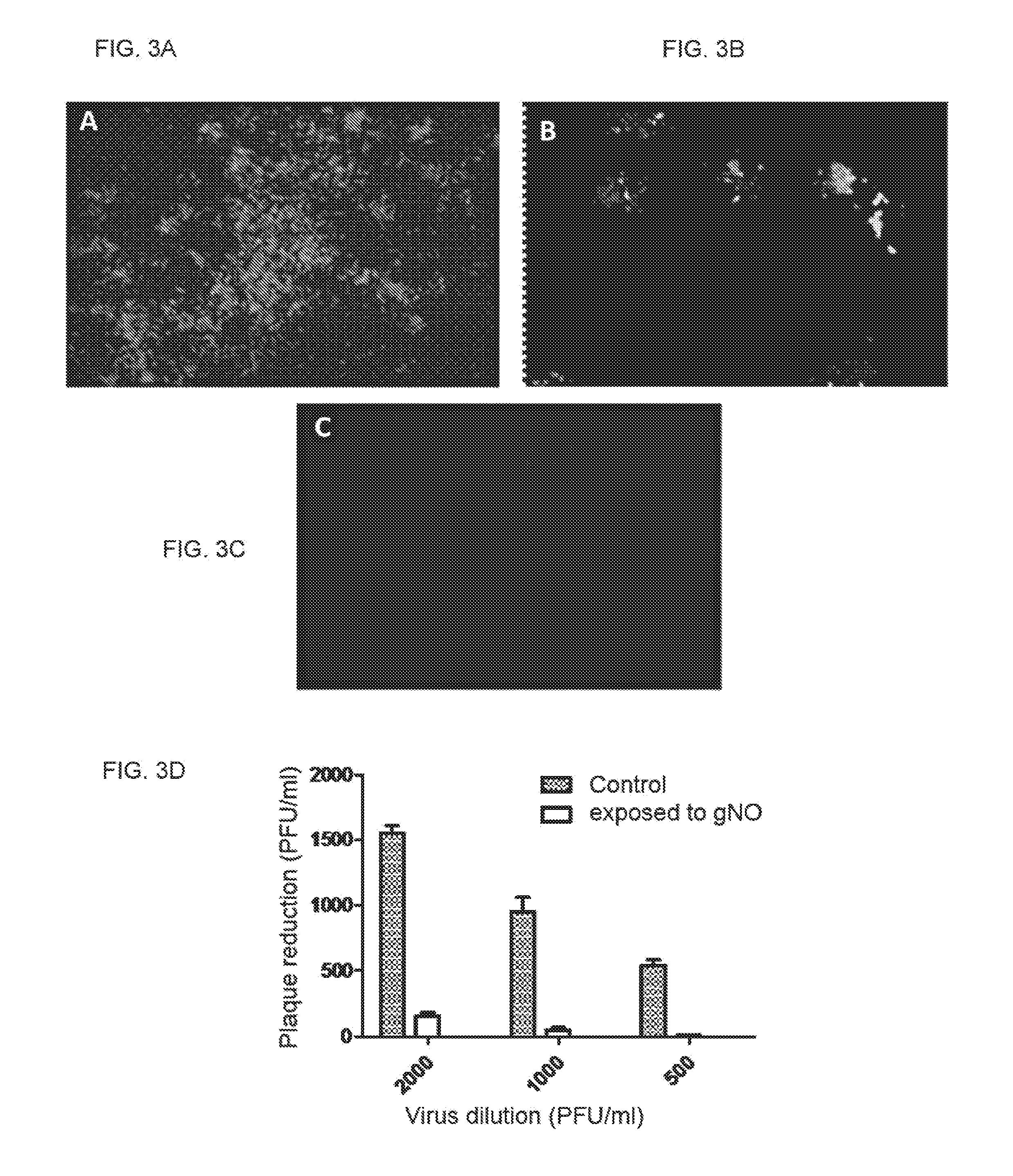
Inhalation of nitric oxide for treating respiratory diseases
InactiveUS20150034084A1Effected safelyRespiratorsInorganic active ingredientsLiver and kidneyVascular endothelium
A method of treating a human subject which is effected by intermittent inhalation of gaseous nitric oxide at a concentration of at least 160 ppm is disclosed. The method can be utilized for treating a human subject suffering from, or prone to suffer from, a disease or disorder that is manifested in the respiratory tract, or from a disease or disorder that can be treated via the respiratory tract. The disclosed method can be effected while monitoring one or more of on-site and off-site parameters such as vital signs, methemoglobin levels, pulmonary function parameters, blood chemistry and hematological parameters, blood coagulation parameters, inflammatory marker levels, liver and kidney function parameters and vascular endothelial activation parameters, such that no substantial deviation from a baseline in seen in one or more of the monitored parameters.
Owner:ADVANCED INHILATION THERAPIES AIT LTD
Method and composition for preventing pain in sickle cell patients
InactiveUS20080112955A1Avoid painPrevent and reduce frequencyBiocideCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsP-selectinPreventing pain
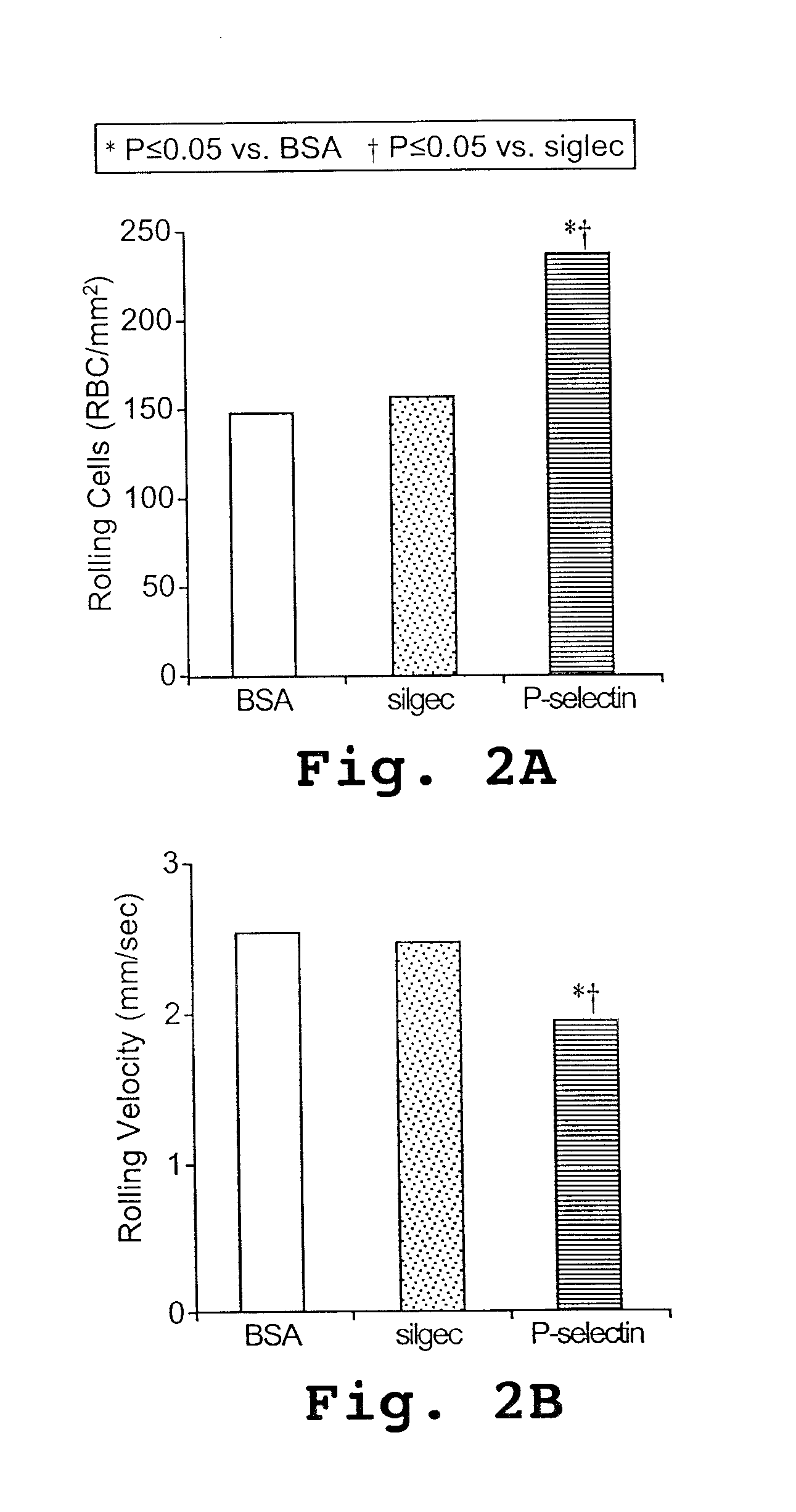
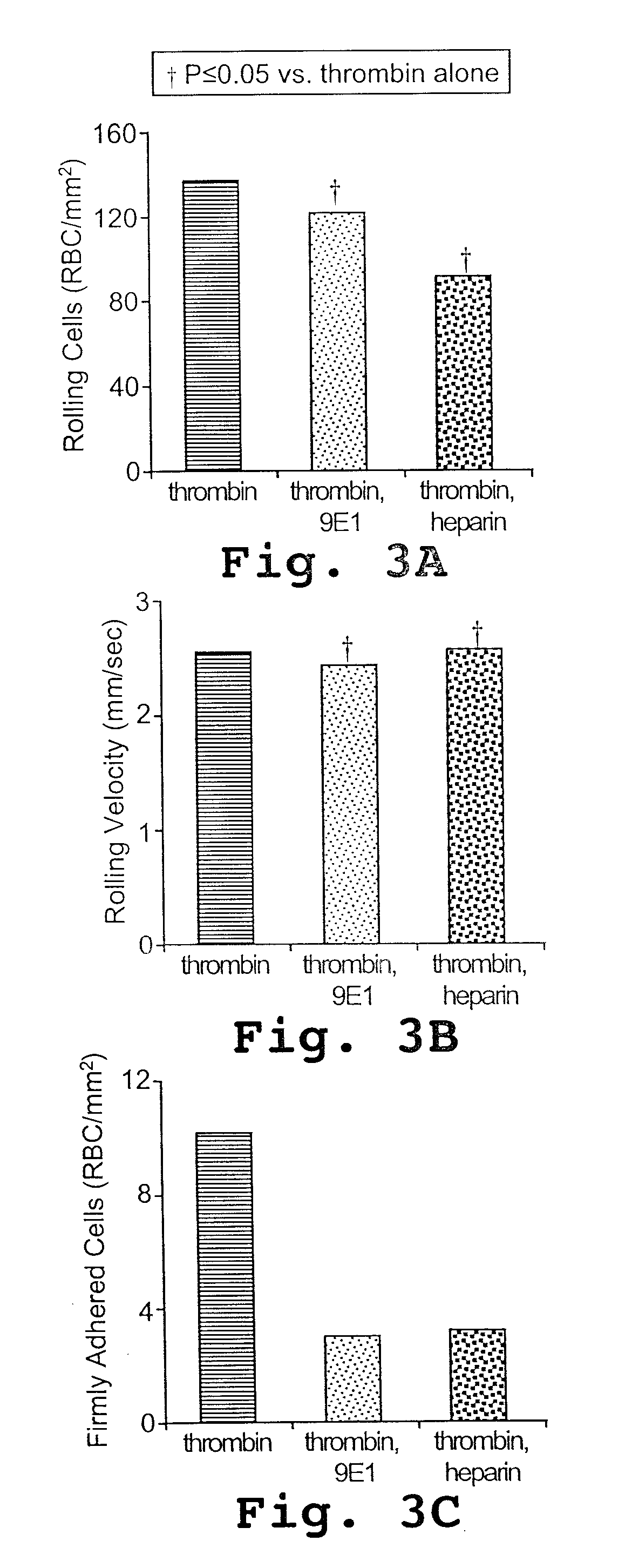
A method of preventing pain in a sickle cell patient is disclosed. The method includes orally administering to the patient, an amount of an active agent effective on oral administration to inhibit binding of the patient's sickle erythrocytes to P-selectin on the patient's vascular endothelium. The inhibition may be evidenced in a number of ways. The active agent administration inhibits the adhesion of sickle erythrocytes to vascular endothelium in the patient, thereby preventing patient pain associated with vascular occlusion. Also disclosed are compositions useful in practicing the method.
Owner:TRF PHARMA
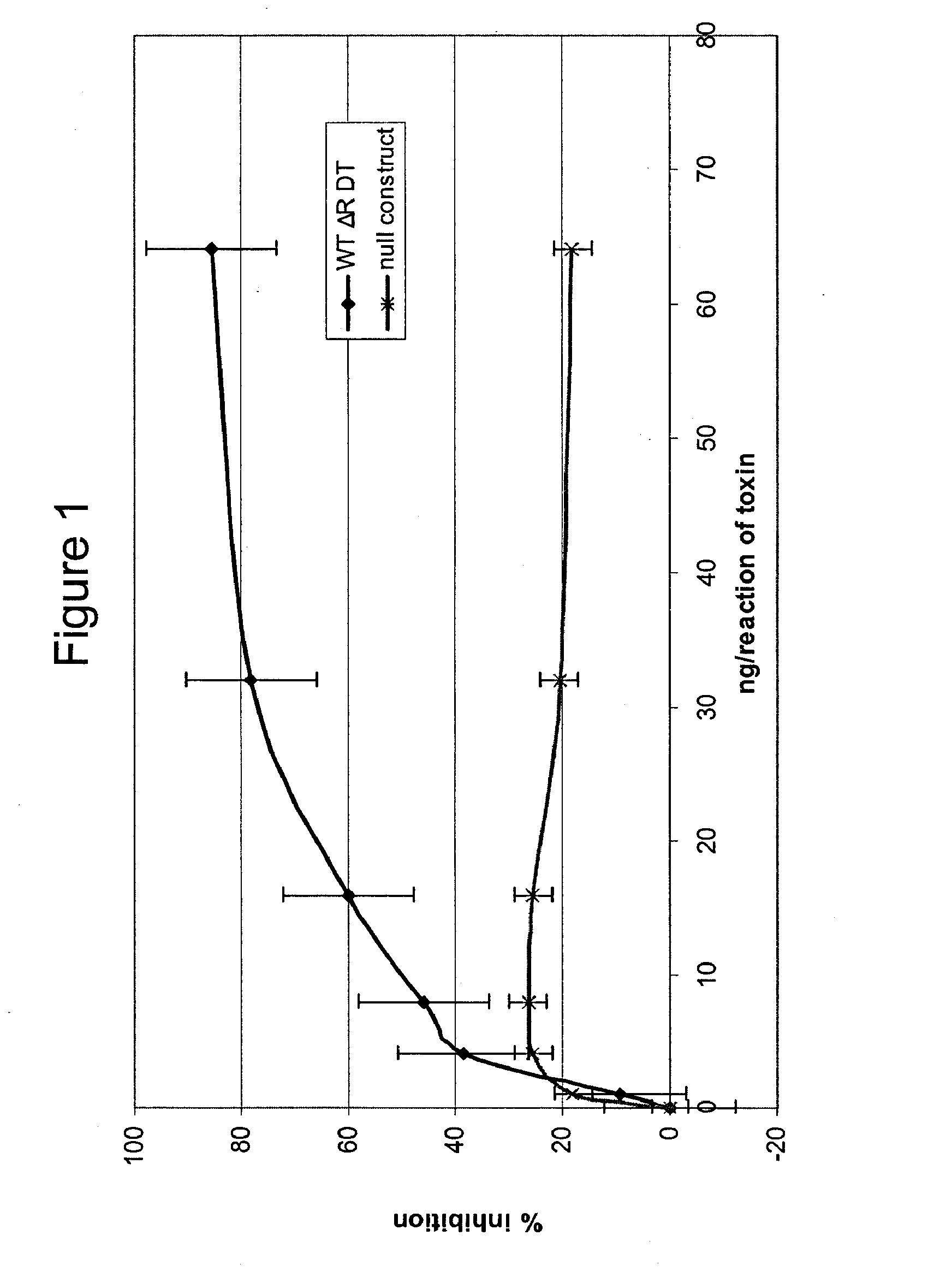
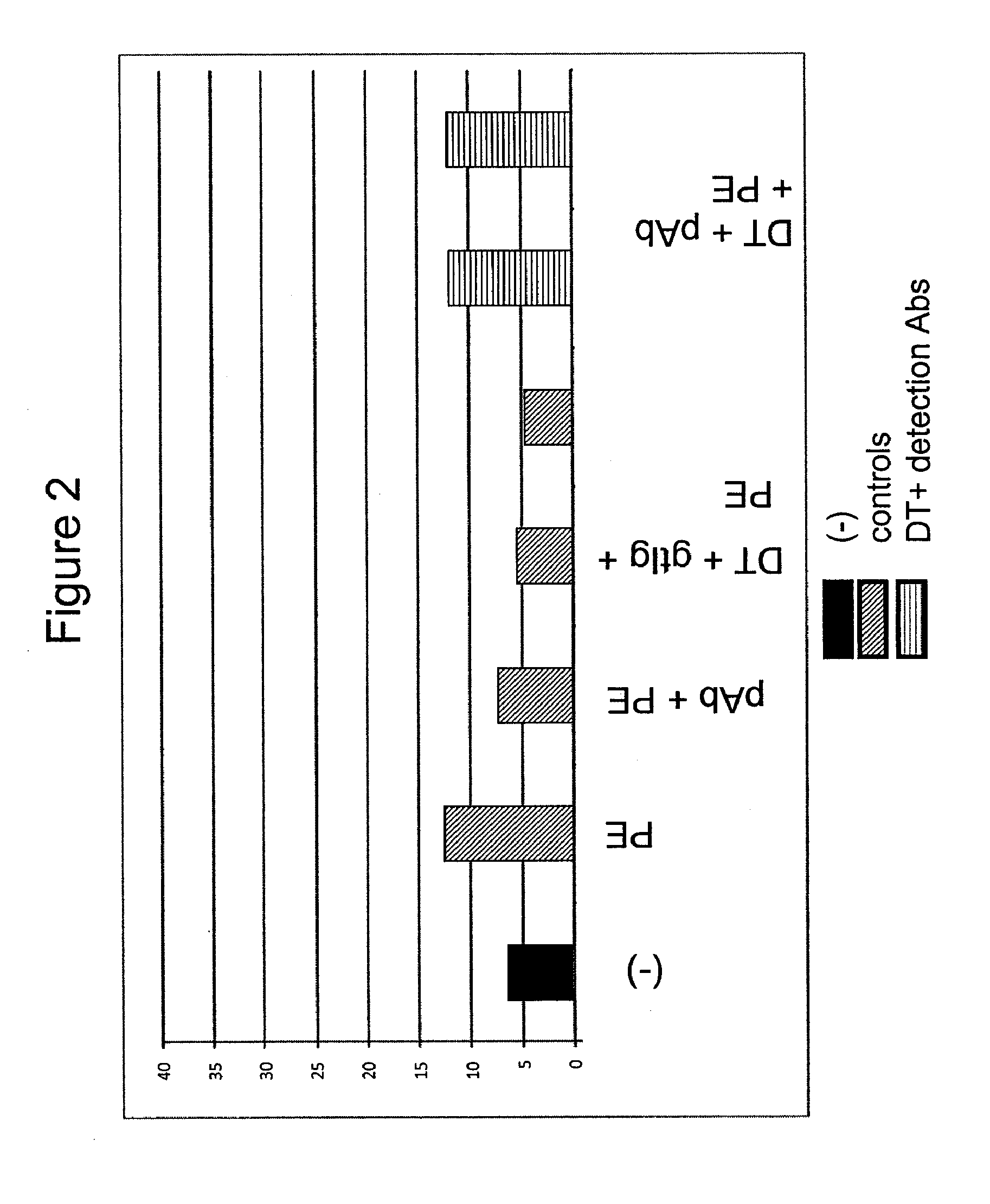
Modified diphtheria toxins
InactiveUS20090010966A1High anticancer activityReduced binding activityBacterial antigen ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseCell binding
The present application relates to compositions of modified diphtheria toxin and fusion proteins containing modified diphtheria toxin that reduce binding to vascular endothelium or vascular endothelial cells, and therefore, reduce the incidence of Vascular Leak Syndrome, as well as methods of making the compositions. The present application also relates to a polypeptide toxophore from a modified diphtheria toxin, where the modification is at least one amino acid residue at the amino acid residues 6-8, 28-30 or 289-291 of an unmodified native diphtheria toxin. Also described are fusion proteins which contain a modified diphtheria toxin and a non-diphtheria toxin fragment which contains a cell binding portion. The modified diphtheria toxins described can be used for the treatment of a malignant disease or a non-malignant disease.
Owner:ANGELICA THERAPEUTICS
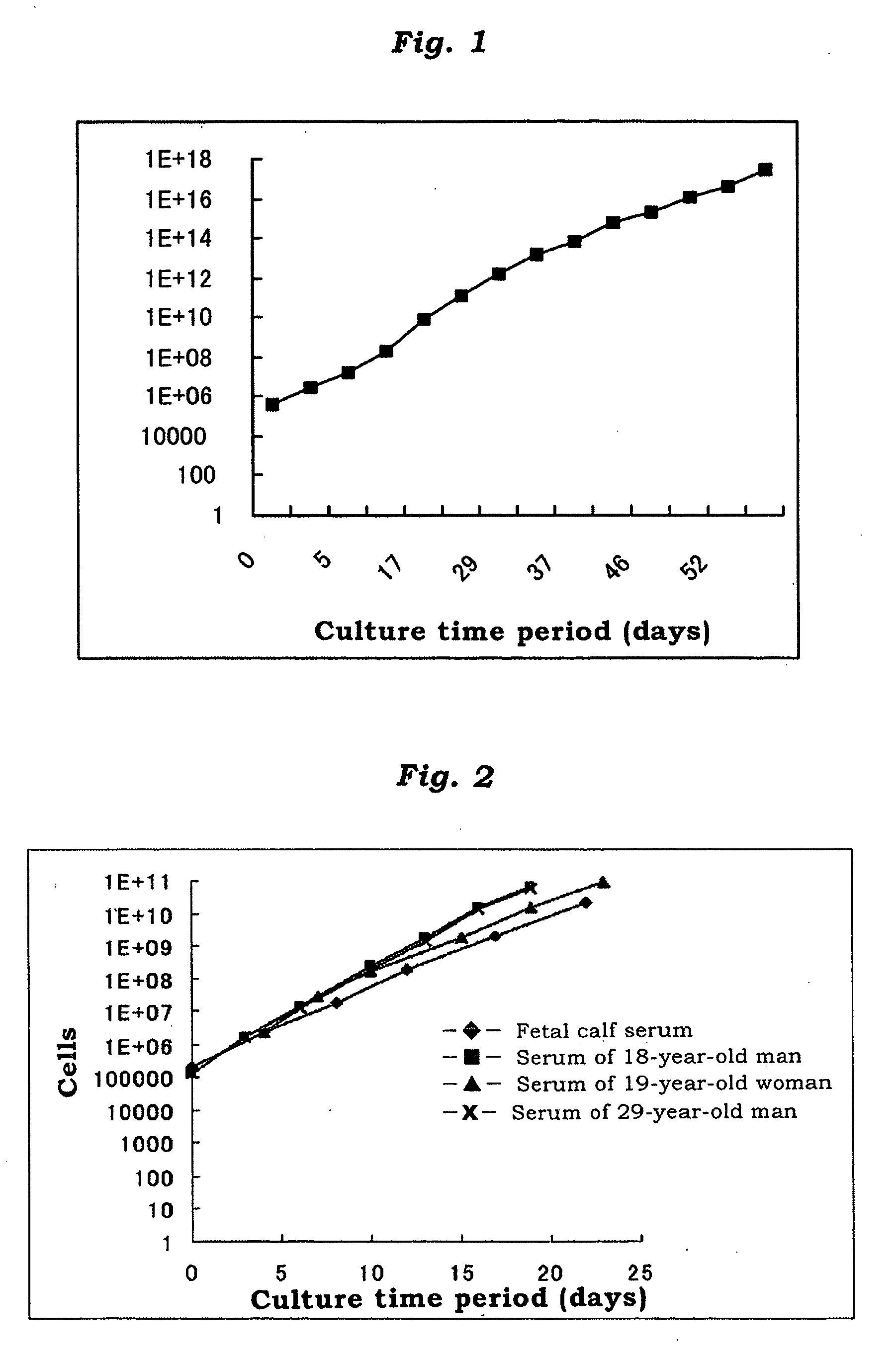
Pluripotent Cells Distributed Ubiquitously In Animal Tissue, Which Proliferate Selectively In Lower-Serum Culture
InactiveUS20070202592A1Lose volumeImprove mass productionArtificial cell constructsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsVascular endotheliumOsteocyte
It is intended to provide a pluripotent cell having the following properties: (1) being contained in a mixed-cell type population obtained by enzymatic treatment of the tissue collected from an animal; (2) being contained in a sedimented cell population obtained by centrifugating the mixed-cell type population of the property (1); (3) selectively proliferating by culturing in a medium containing 2% (v / v) or lower serum and 1 to 100 ng / ml of fibroblast growth factor-2; and (4) being differentiated into cells having the characteristics of adipocytes, osteoblasts, chondrocytes, tendon cells, myocardial cells, myoblasts, neurocytes or vascular endothelial cells by adjusting the culture condition; cells having differentiated from the above cell; and a method of conveniently obtaining the pluripotent cell in a large amount.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD +3
Cell Sheet Containing Mesenchymal Stem Cells
ActiveUS20090053277A1Induce cardiac muscleInduce neovascularizationBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsVascular endotheliumThree vessels
Mesenchymal stem cells are pluripotent cells capable of differentiating into myocardial and vascular endothelial cells. The present invention demonstrates that the mesenchymal stem cell sheet have therapeutic potential for a severely damaged heart due to its pluripotency and in situ self-renewal capability. Mesenchymal stem cells derived from adipose tissue were cultured to prepare a mesenchymal stem cell sheet. Four weeks after induction of myocardial infarction in rats, the mesenchymal stem cell sheet was transplanted to the heart. The mesenchymal stem cell sheet were readily engrafted to the surface of the scarred myocardium, grew gradually in situ, and formed a thick layer (approximately 600 μm) in 4 weeks. The grown transplanted mesenchymal tissue contained newly formed blood vessels, myocardial cells, and undifferentiated mesenchymal cells. The engrafted mesenchymal stem cells inhibited thinning of the myocardial wall in the scar area, and improved cardiac function and survival rate in rats with myocardial infarcts. Thus, mesenchymal stem cell sheet transplantation may represent a novel therapeutic approach for myocardial tissue regeneration.
Owner:H&L MEDICAL CORP
Apparatus and method for maintaining and/or restoring viability of organs
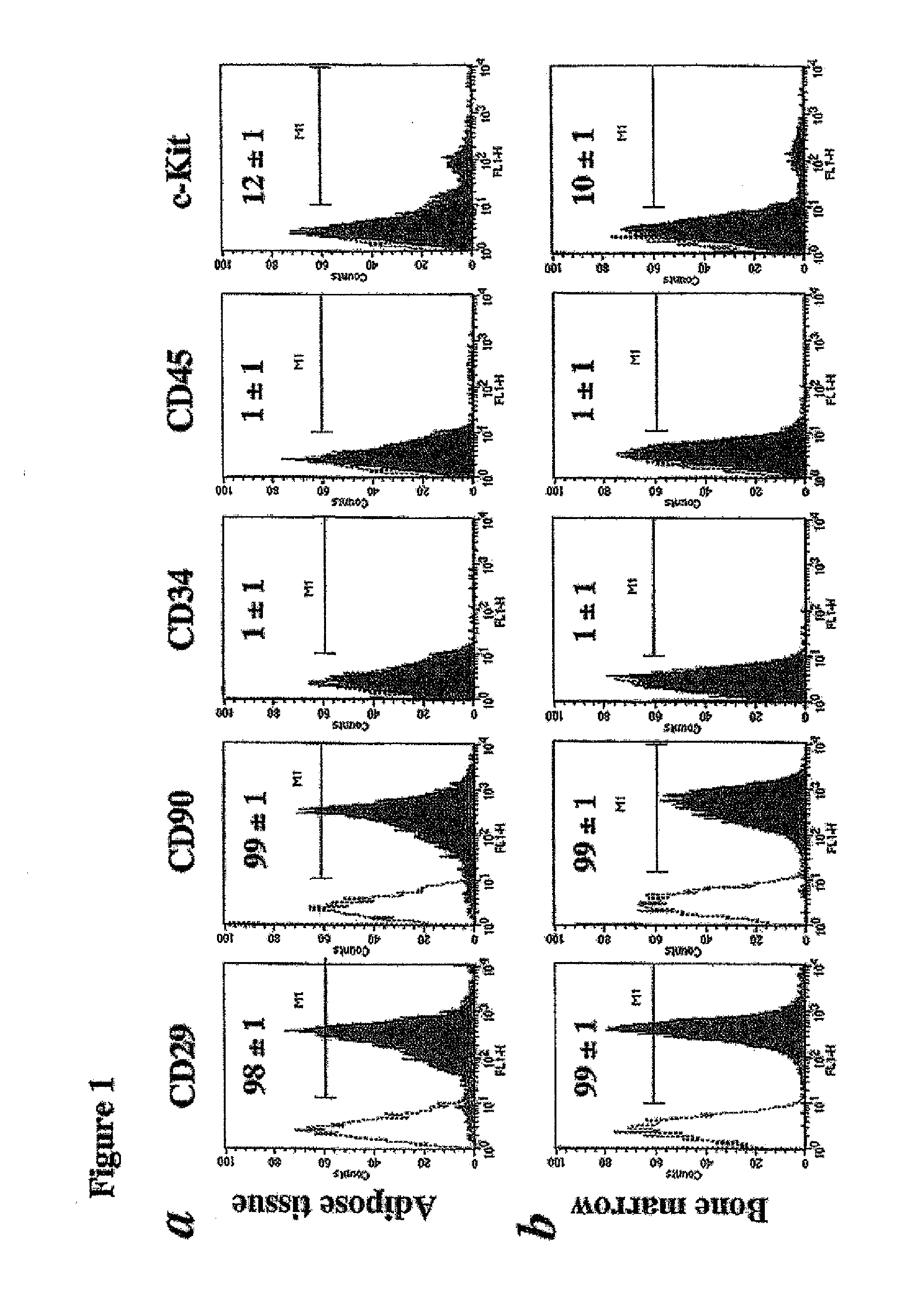
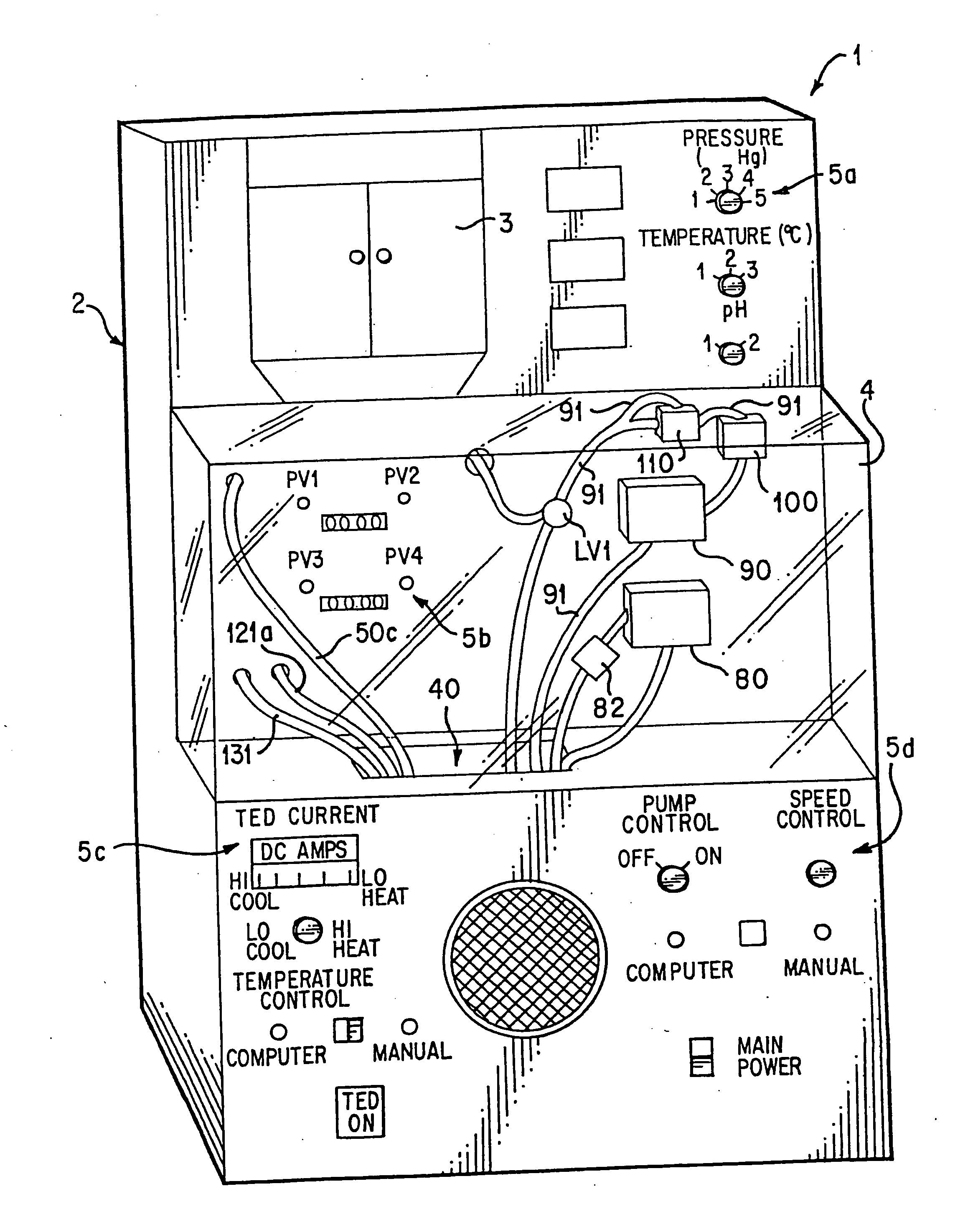
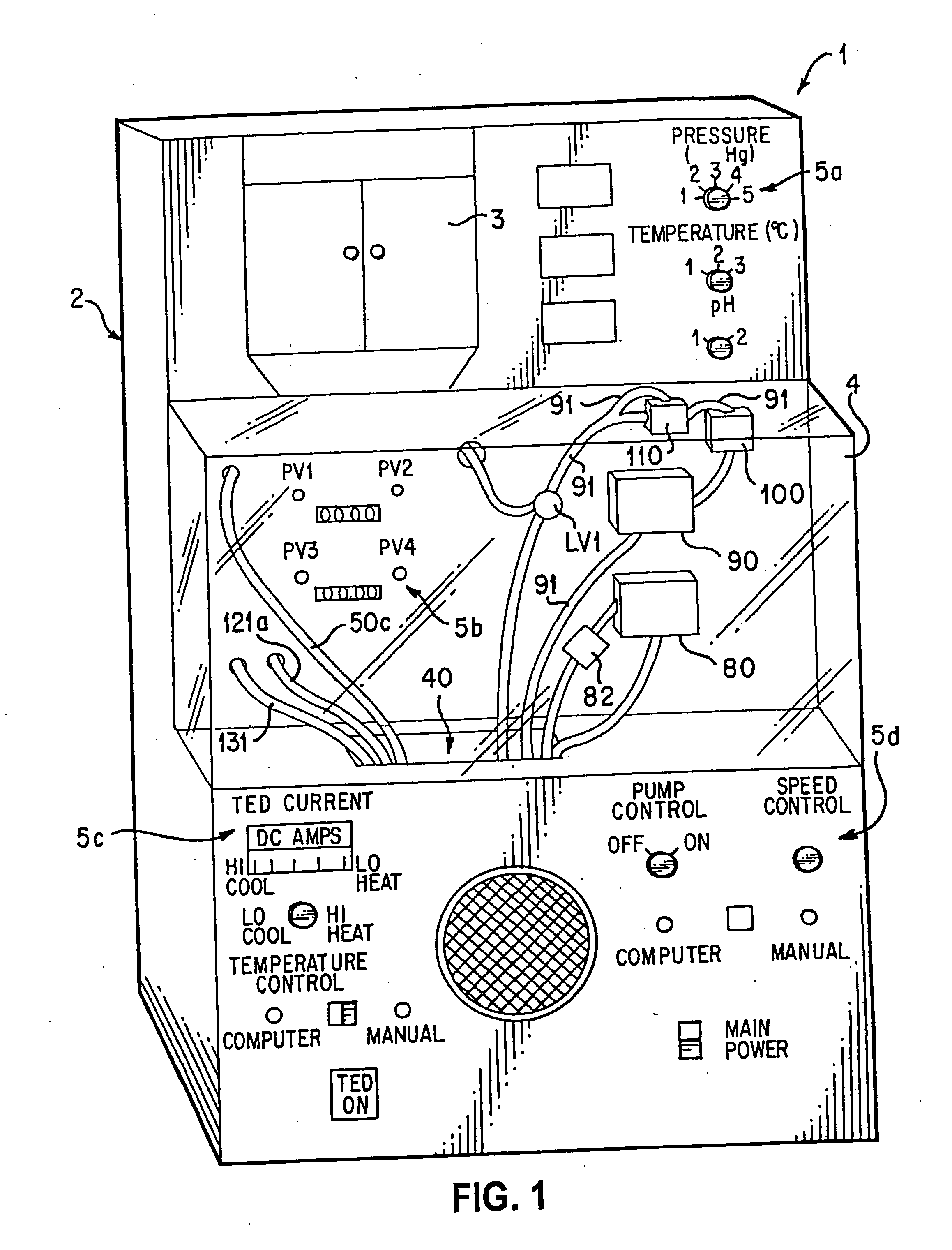
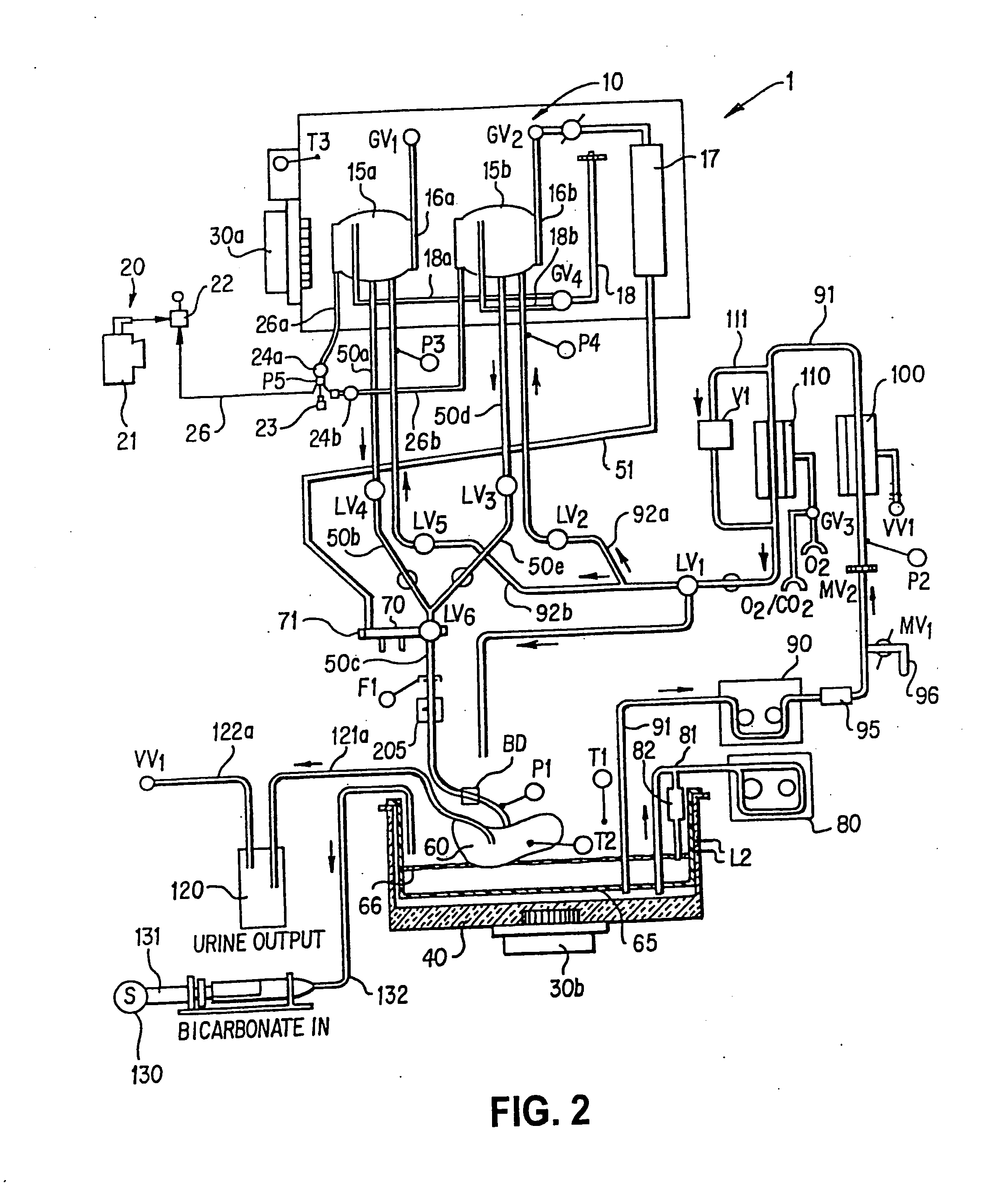
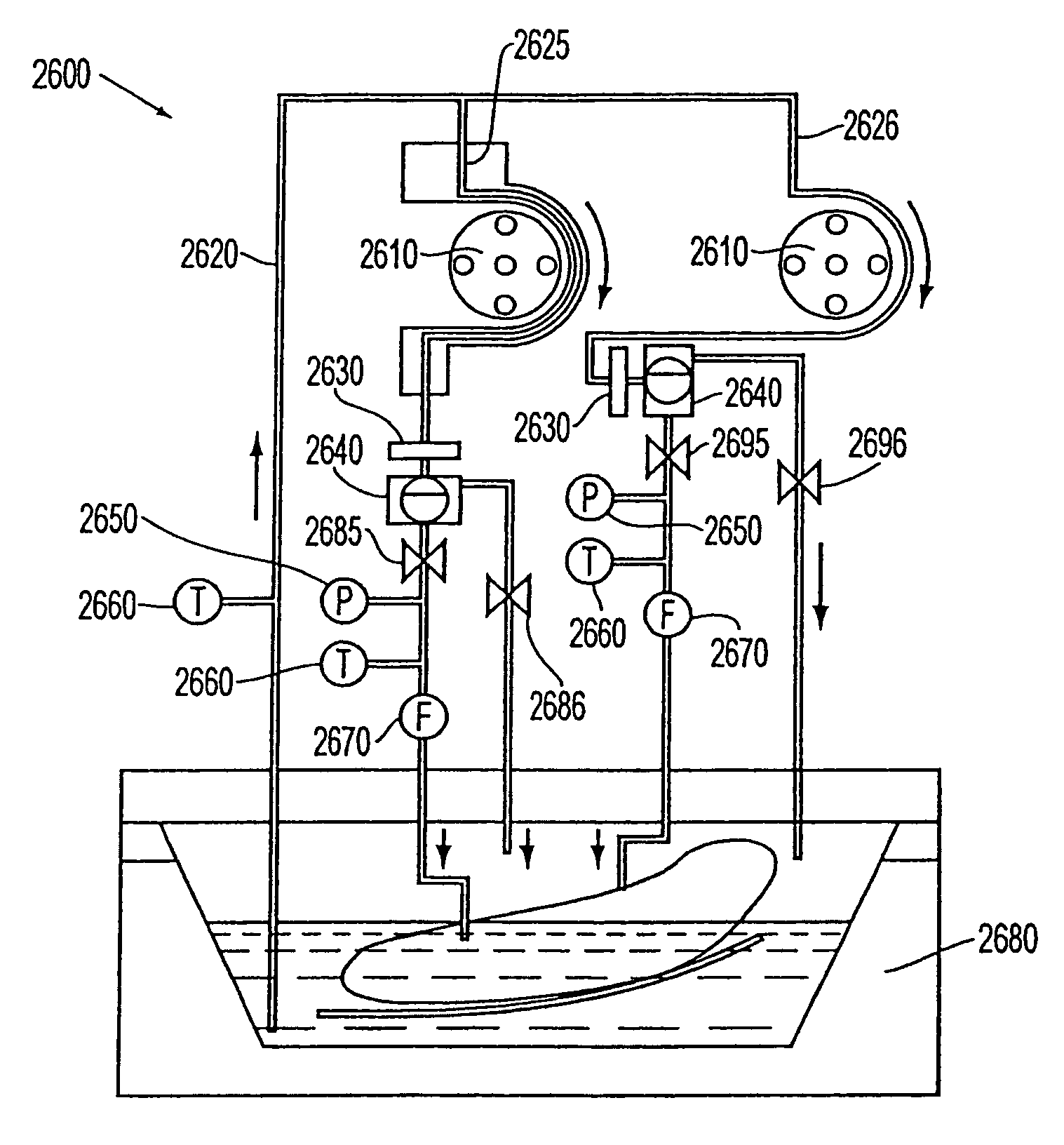
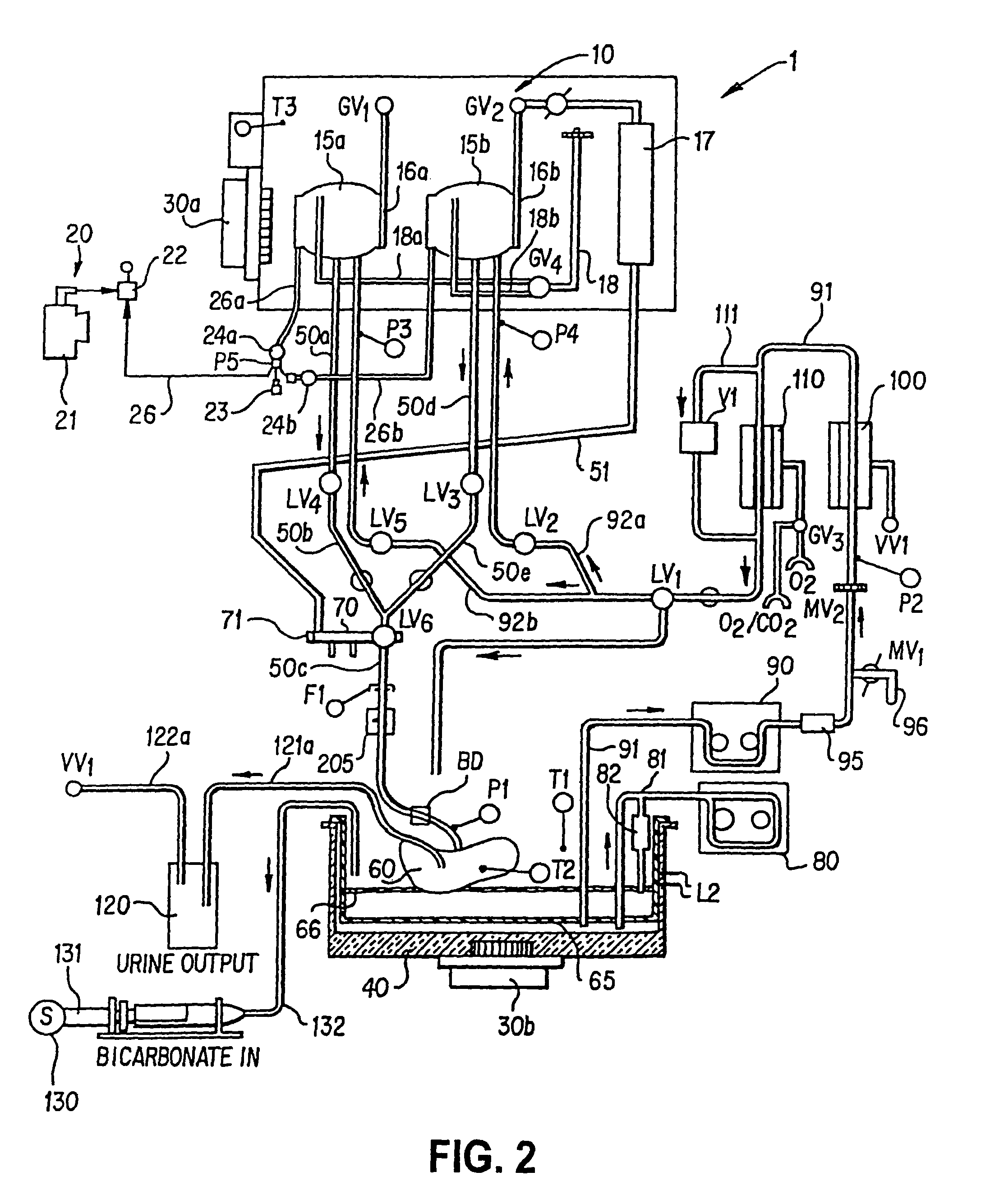
InactiveUS20110183310A1Prevent overpressureEliminating overpressurization prevents and/orBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAutomatic controlOrgan Viability
An organ perfusion apparatus and method monitor, sustain and / or restore viability of organs and preserve organs for storage and / or transport. Other apparatus include an organ transporter, an organ cassette and an organ diagnostic device. The method includes perfusing the organ at hypothermic and / or normothermic temperatures, preferably after hypothermic organ flushing for organ transport and / or storage. The method can be practiced with prior or subsequent static or perfusion hypothermic exposure of the organ. Organ viability is restored by restoring high energy nucleotide (e.g., ATP) levels by perfusing the organ with a medical fluid, such as an oxygenated cross-linked hemoglobin-based bicarbonate medical fluid, at normothermic temperatures. In perfusion, organ perfusion pressure is preferably controlled in response to a sensor disposed in an end of tubing placed in the organ, by a pneumatically pressurized medical fluid reservoir, providing perfusion pressure fine tuning, overpressurization prevention and emergency flow cut-off. In the hypothermic mode, the organ is perfused with a medical fluid, preferably a simple crystalloid solution containing antioxidants, intermittently or in slow continuous flow. The medical fluid may be fed into the organ from an intermediary tank having a low pressure head to avoid organ overpressurization. Preventing overpressurization prevents or reduces damage to vascular endothelial lining and to organ tissue in general. Viability of the organ may be automatically monitored, preferably by monitoring characteristics of the medical fluid perfusate. The perfusion process can be automatically controlled using a control program.
Owner:LIFELINE SCI
Blood brain barrier permeation peptides
InactiveUS20060039859A1Enough timeIn-vivo radioactive preparationsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsVascular endotheliumTarget peptide
Novel blood-brain barrier permeant amyloid-targeting peptides and peptide conjugates are described. The peptide conjugates include a radioisotope or other label in a stable complex that translocates across brain capillary endothelial cell monolayers. The labeled peptide conjugate binds to amyloid plaques (Aβ) associated with Alzheimer's disease, and is useful for the targeted delivery of therapeutic and diagnostic molecules into the brain.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
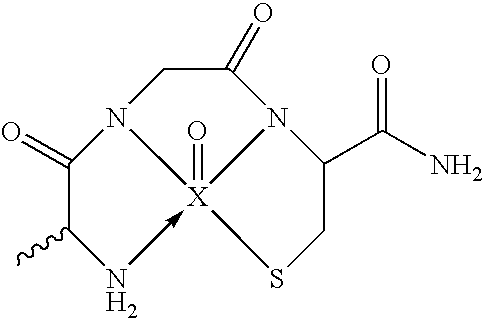
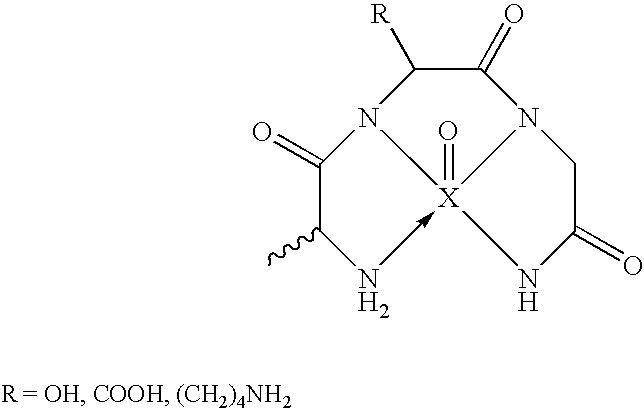
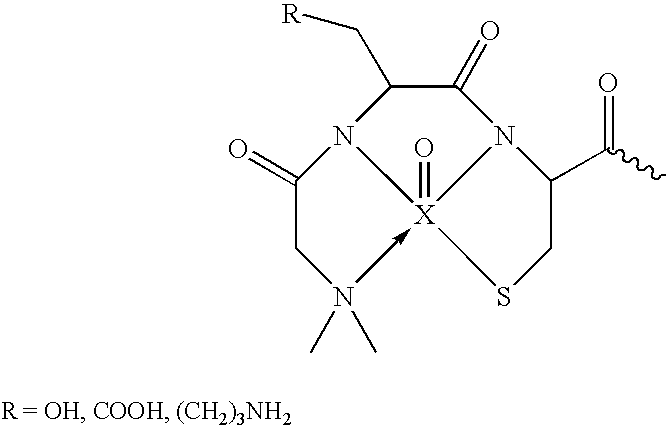
Endothelial NOS knockout mice and methods of use
This invention relates to transgenic non-human animals comprising a disrupted endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene. These animals exhibit abnormal wound-healing properties and hypertension. This invention also relates to methods of using the transgenic animals to screen for compounds having a potential therapeutic utility for vascular endothelial disorders, such as hypertension, cerebral ischemia or stroke, atherosclerosis and wound-healing activities. Moreover, this invention also relates to methods of treating a patient suffering from hypertension and wound-healing abnormalities with the compounds identified using the transgenic animals, and methods of making the transgenic animals. A method of treating a wound using nitroglycerin is also provided.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Preparation method of essence containing human mesenchymal stem cell factors
InactiveCN106344493APromote growthPromote proliferationCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsFreeze-dryingVascular endothelium
The invention discloses a preparation method of an essence containing human mesenchymal stem cell factors. The preparation method of the essence containing the human mesenchymal stem cell factors comprises the steps: preparation of freeze-dried powder of the human mesenchymal stem cell factors, preparation of a solvent and mixing. The preparation method obtains a high-purity and high-activity stem cell active factor concentrated solution by a cryoconcentration technique and the concentrated solution is freeze-dried to obtainfreeze-dried powder at low temperature in vacuum, so that the factor activity can be kept for a long time; and the solvent contains multiple skin nourishing and moisturizing components and a stem cell lysis solution, can well dissolve the cell factor freeze-dried powder and keeps the cell factor activity. The stem cell essence disclosed by the invention contains vascular endothelial cell growth factors, platelet derived growth factors, epidermal growth factors and other components, can promote skin regeneration, can play roles in moisturizing, tendering, whitening and repairing the skin, and has good application prospects in fields of medical beauty treatment, health protection and the like.
Owner:GENESIS STEMCELL REGENERATIVE MEDICINE ENG CO LTD
Methods and compositions for the treatment of fibrotic conditions & impaired lung function & to enhance lymphocyte production
InactiveUS20030008816A1Improve complianceFunction increaseAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsCell adhesionPulmonary compliance
The present invention provides methods and compositions to treat fibrotic conditions, to increase lymphocyte production in vivo, and to improve and / or normalize lung function, pulmonary compliance, blood oxygenation, and blood pH to inhibit inflammatory processes to stimulate or inhibit pro-inflammatory and immune cells, and to inhibit migration of vascular endothelial cells. The invention contemplates the administration of human uteroglobin, native or recombinant, as a means of achieving these ends. Specifically, it has been found that uteroglobin inhibits cell adhesion to fibronectin, increases lymphocyte production in vivo, and improves and / or normalizes lung function, pulmonary compliance, blood oxygenation, and blood pH, and inhibits inflammatory process. In addition it has been found that uteroglobin can stimulate or inhibit pro-inflammatory and immune cells and inhibitor migration of vascular endothelial cells.
Owner:CC10 SWEDEN +4
Injectable microfoam containing a sclerosing agent
Injectable microfoam for sclerotcraphy. The sclerotherapy of varices is based on the injection of liquid substances capable of suppressing them. The present invention relates to the preparation of sclerosing substances in the form of a microfoam. The microfoam is prepared with sclerosing agents, and is then injected in the vein to be treated, so that the microfoam displaces the blood contained in the vein and provides for the contact of the sclerosing agent with the vascular endothelium, with a predetermined known concentration and during a controllable time.
Owner:BTG INT LTD
Method for Amplification of Endothelial Progenitor Cell in Vitro
ActiveUS20080166327A1Function increaseImprove heart functionBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsInterleukin 6Fms-Like Tyrosine Kinase 3
The present invention provides a method for expanding an endothelial progenitor cell in vitro. More particularly, the present invention provides a method for culturing a hemangioblast comprising incubating a hemangioblast in a serum-free culture medium containing one or more factors selected from the group consisting of stem cell growth factor, interleukin-6, FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 and thrombopoietin, and a vascular endothelial cell produced by the method; and a serum-free culture medium containing one or more factors selected from the group consisting of stem cell growth factor, interleukin-6, FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 and thrombopoietin, and a kit for the preparation of the serum-free culture medium and the like.
Owner:STEMMED +1
Inhalation of nitric oxide for treating respiratory diseases
A method of treating a human subject which is effected by intermittent inhalation of gaseous nitric oxide at a concentration of at least 160 ppm is disclosed. The method can be utilized for treating a human subject suffering from, or prone to suffer from, a disease or disorder that is manifested in the respiratory tract, or from a disease or disorder that can be treated via the respiratory tract. The disclosed method can be effected while monitoring one or more of on-site and off-site parameters such as vital signs, methemoglobin levels, pulmonary function parameters, blood chemistry and hematological parameters, blood coagulation parameters, inflammatory marker levels, liver and kidney function parameters and vascular endothelial activation parameters, such that no substantial deviation from a baseline in seen in one or more of the monitored parameters.
Owner:ADVANCED INHILATION THERAPIES AIT LTD
Materials and methods involving hybrid vascular endothelial growth factor DNAs and proteins
InactiveUS6965010B2Improve purification effectExtended half-lifeOrganic active ingredientsFungiNucleotideVascular endothelium
The present invention provides polypeptides that bind cellular receptors for vascular endothelial growth factor polypeptides; polynucleotides encoding such polypeptides; compositions comprising the polypeptides and polynucleotides; and methods and uses involving the foregoing. Some polypeptides of the invention exhibit unique receptor binding profiles compared to known, naturally occurring vascular endothelial growth factors.
Owner:VEGENICS PTY LTD
Modified toxins
ActiveUS20090041797A1Low immunogenicityPeptide/protein ingredientsBacteria peptidesDiseaseVascular endothelium
Owner:ANGELICA THERAPEUTICS
Inhalation of nitric oxide for treating respiratory diseases
InactiveUS20160022731A1Effected safelyBiocideInorganic active ingredientsLiver and kidneyVascular endothelium
A method of treating a human subject which is effected by intermittent inhalation of gaseous nitric oxide at a concentration of at least 160 ppm is disclosed. The method can be utilized for treating a human subject suffering from, or prone to suffer from, a disease or disorder that is manifested in the respiratory tract, or from a disease or disorder that can be treated via the respiratory tract. The disclosed method can be effected while monitoring one or more of on-site and off-site parameters such as vital signs, methemoglobin levels, pulmonary function parameters, blood chemistry and hematological parameters, blood coagulation parameters, inflammatory marker levels, liver and kidney function parameters and vascular endothelial activation parameters, such that no substantial deviation from a baseline in seen in one or more of the monitored parameters.
Owner:ADVANCED INHILATION THERAPIES AIT LTD
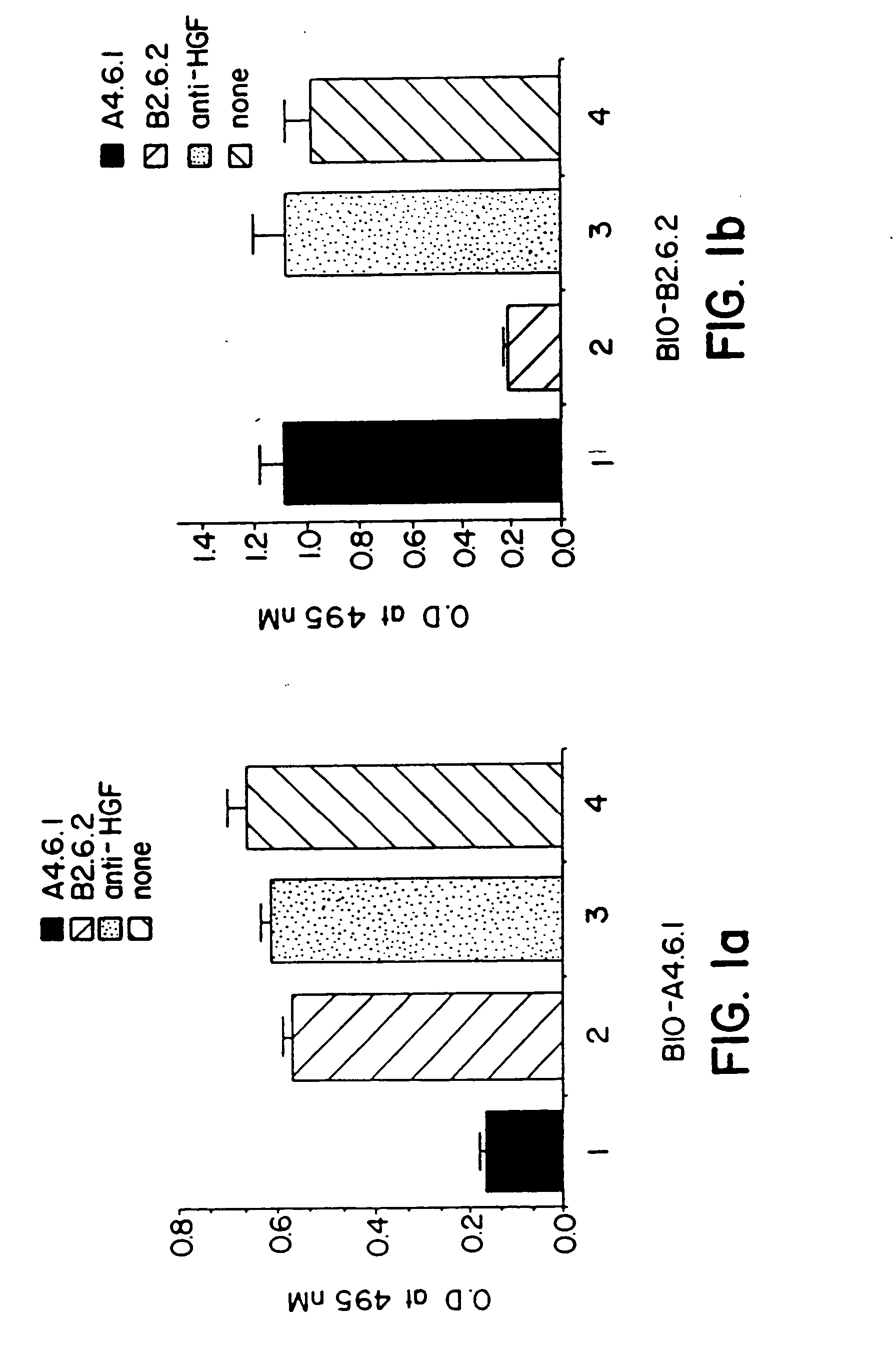
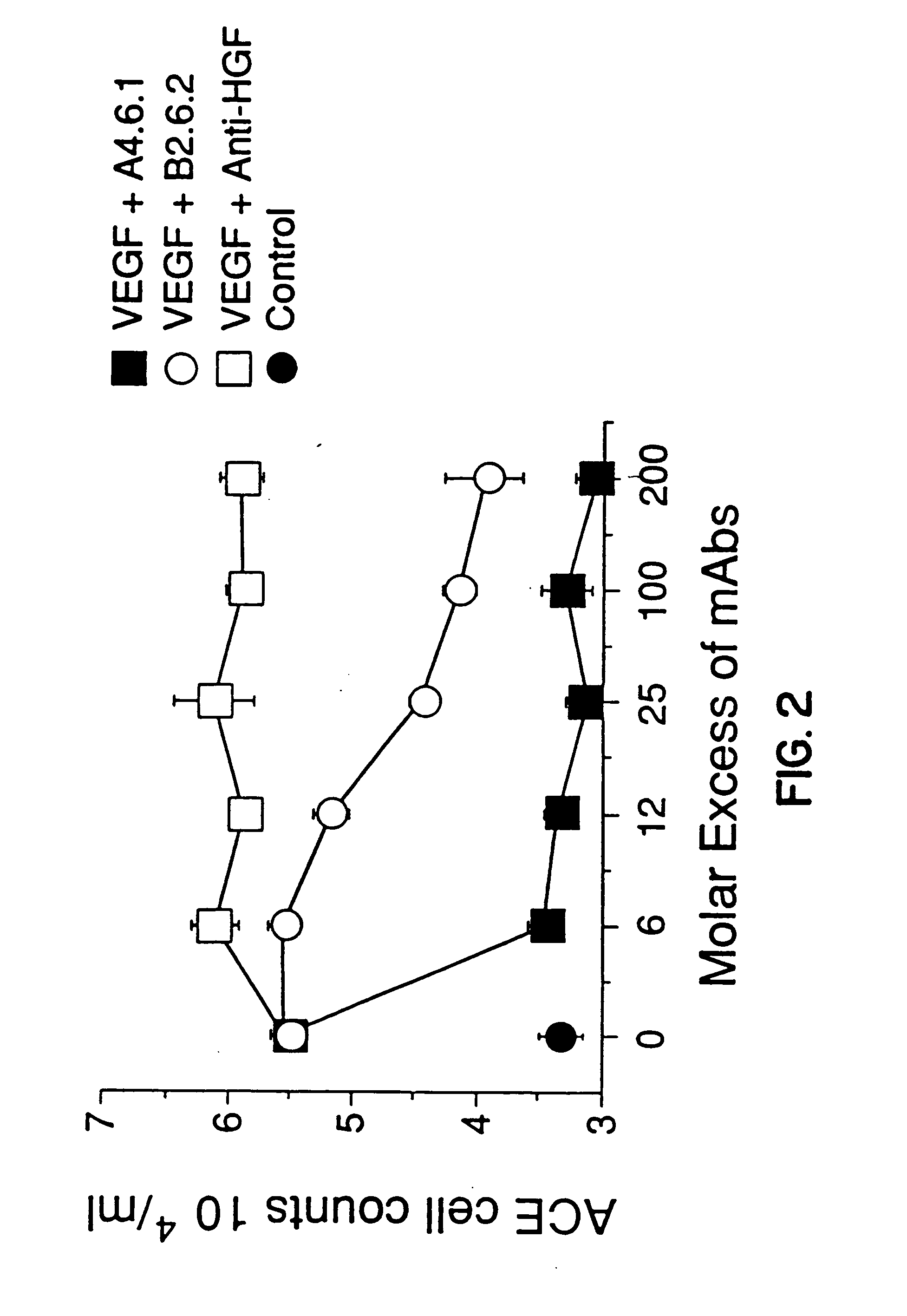
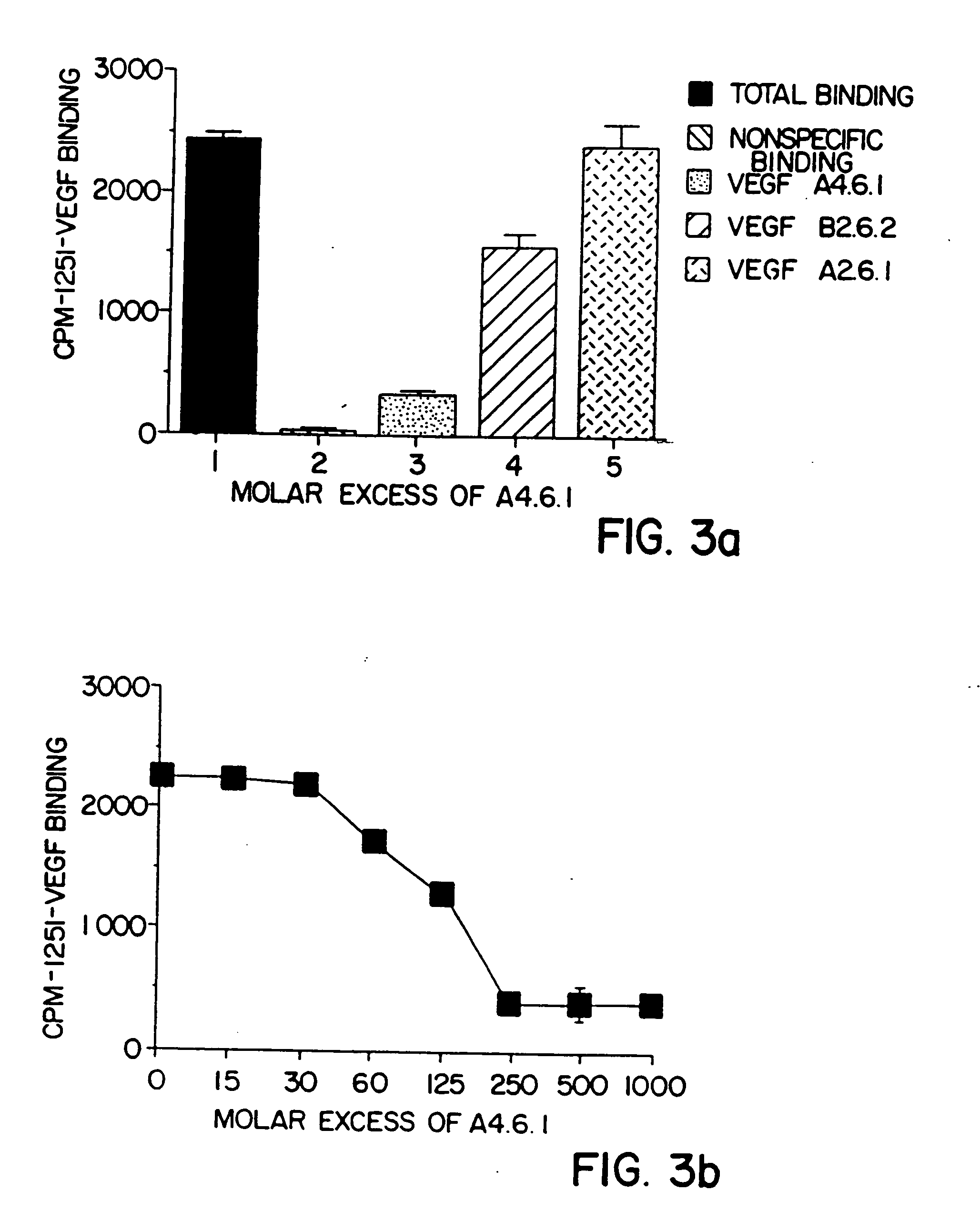
Vascular endothelial cell growth factor antagonists and uses thereof
The present invention provides vascular endothelial cell growth factor (VEGF) antagonists and methods of using VEGF antagonists. VEGF antagonists contemplated by the invention include VEGF antibodies and VEGF receptor fusion proteins. Methods of treating edema and stroke using VEGF antagonists are also provided.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Apparatus and method for maintaining and/or restoring viability of organs
InactiveUS8323954B2Prevent overpressureEliminating overpressurization prevents and/orBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAutomatic controlOrgan Viability
An organ perfusion apparatus and method monitor, sustain and / or restore viability of organs and preserve organs for storage and / or transport. Other apparatus include an organ transporter, an organ cassette and an organ diagnostic device. The method includes perfusing the organ at hypothermic and / or normothermic temperatures, preferably after hypothermic organ flushing for organ transport and / or storage. The method can be practiced with prior or subsequent static or perfusion hypothermic exposure of the organ. Organ viability is restored by restoring high energy nucleotide (e.g., ATP) levels by perfusing the organ with a medical fluid, such as an oxygenated cross-linked hemoglobin-based bicarbonate medical fluid, at normothermic temperatures. In perfusion, organ perfusion pressure is preferably controlled in response to a sensor disposed in an end of tubing placed in the organ, by a pneumatically pressurized medical fluid reservoir, providing perfusion pressure fine tuning, overpressurization prevention and emergency flow cut-off. In the hypothermic mode, the organ is perfused with a medical fluid, preferably a simple crystalloid solution containing antioxidants, intermittently or in slow continuous flow. The medical fluid may be fed into the organ from an intermediary tank having a low pressure head to avoid organ overpressurization. Preventing overpressurization prevents or reduces damage to vascular endothelial lining and to organ tissue in general. Viability of the organ may be automatically monitored, preferably by monitoring characteristics of the medical fluid perfusate. The perfusion process can be automatically controlled using a control program.
Owner:LIFELINE SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com