Patents
Literature
1644 results about "Ischemia" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
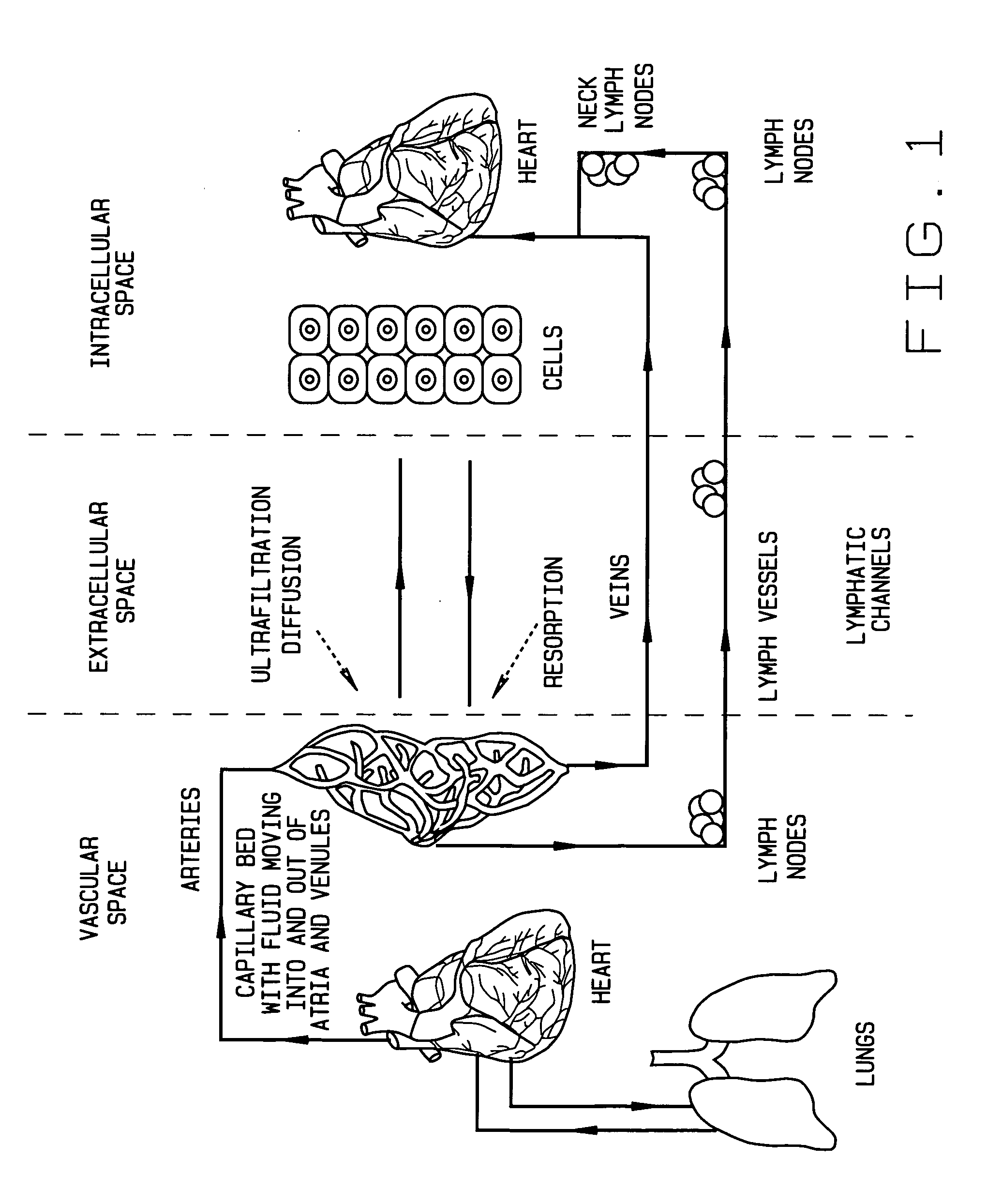
Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to tissues, causing a shortage of oxygen that is needed for cellular metabolism (to keep tissue alive). Ischemia is generally caused by problems with blood vessels, with resultant damage to or dysfunction of tissue. It also means local anemia in a given part of a body sometimes resulting from constriction (such as vasoconstriction, thrombosis or embolism). Ischemia comprises not only insufficiency of oxygen, but also reduced availability of nutrients and inadequate removal of metabolic wastes. Ischemia can be partial (poor perfusion) or total.
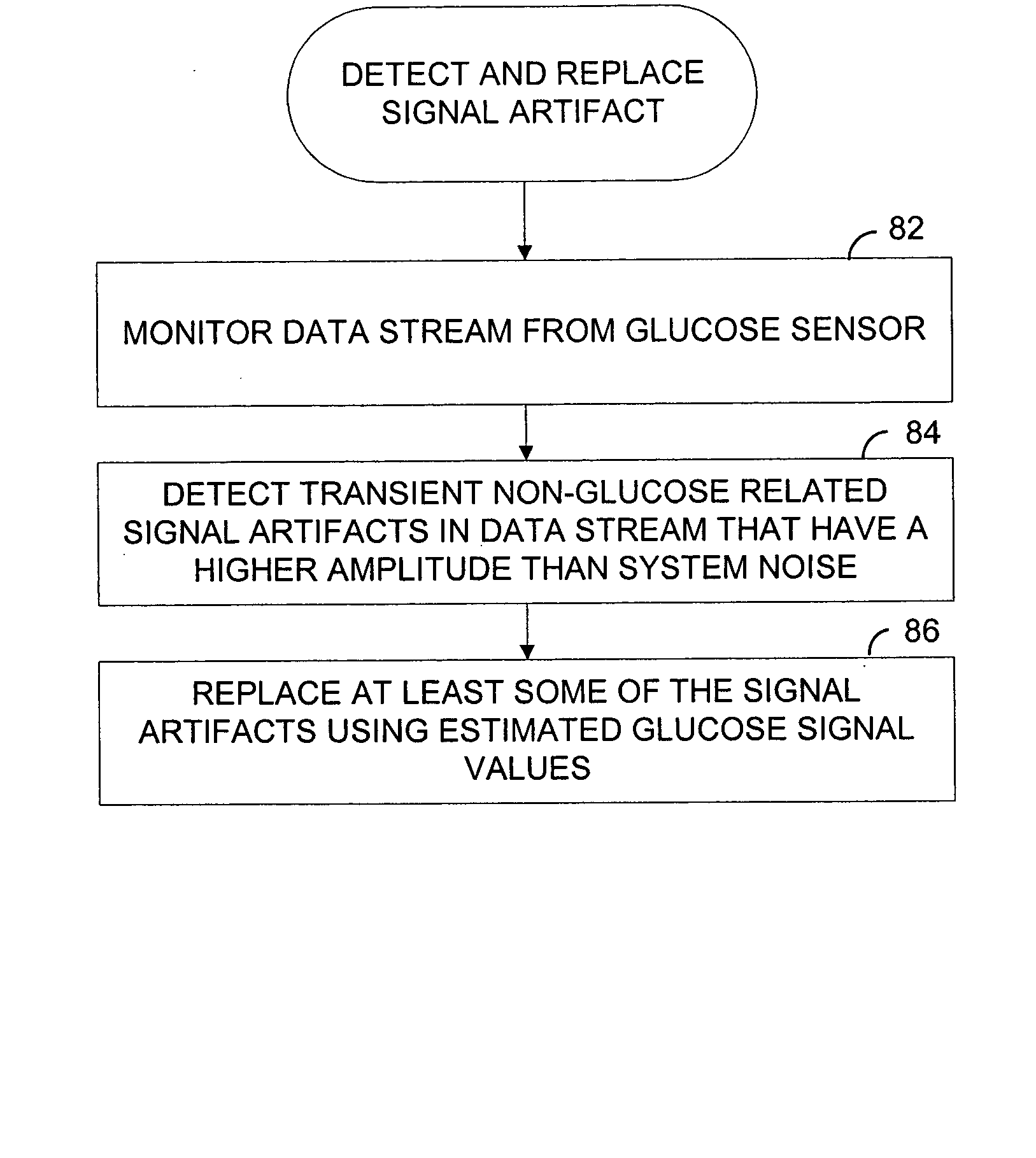
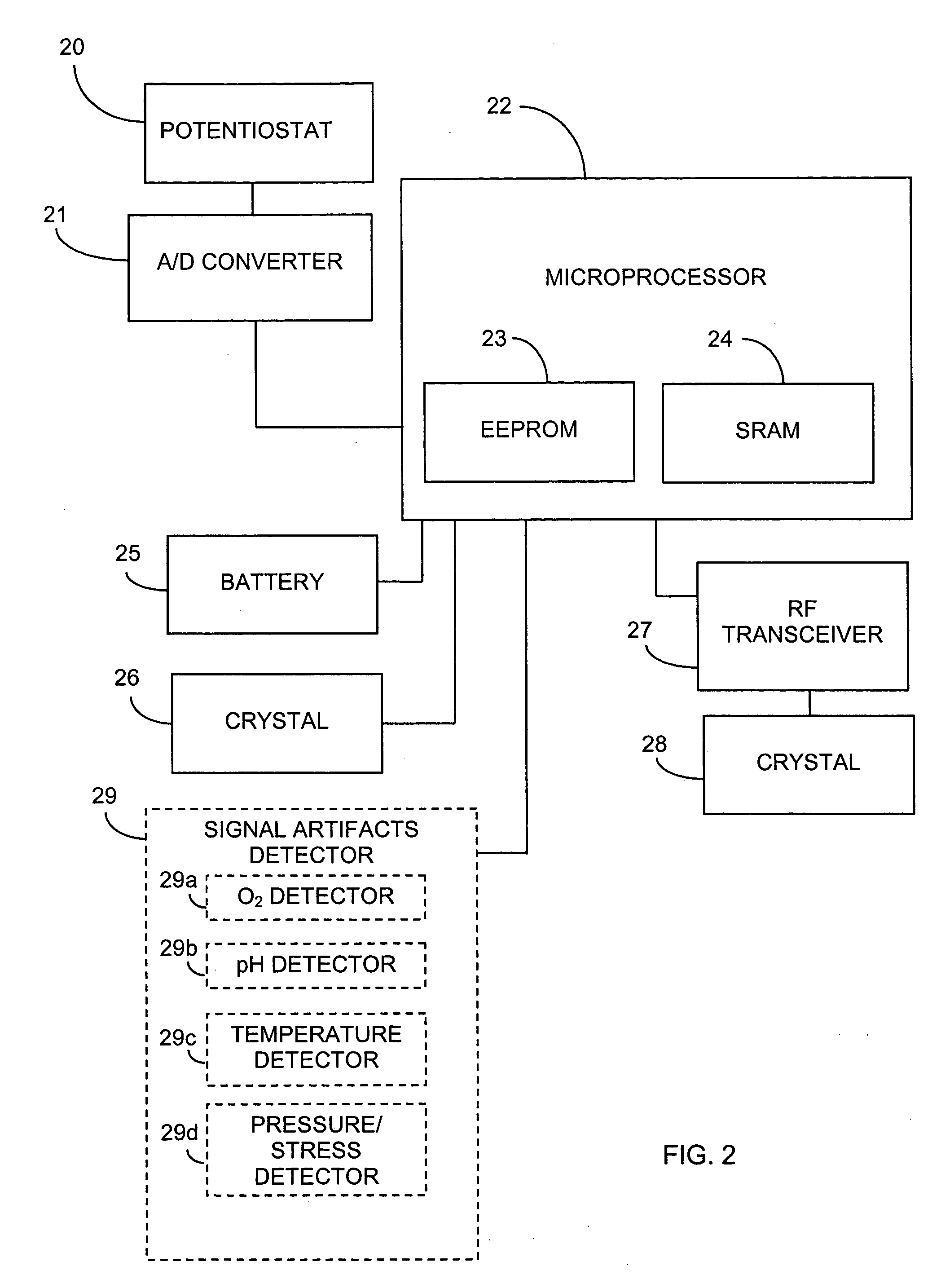
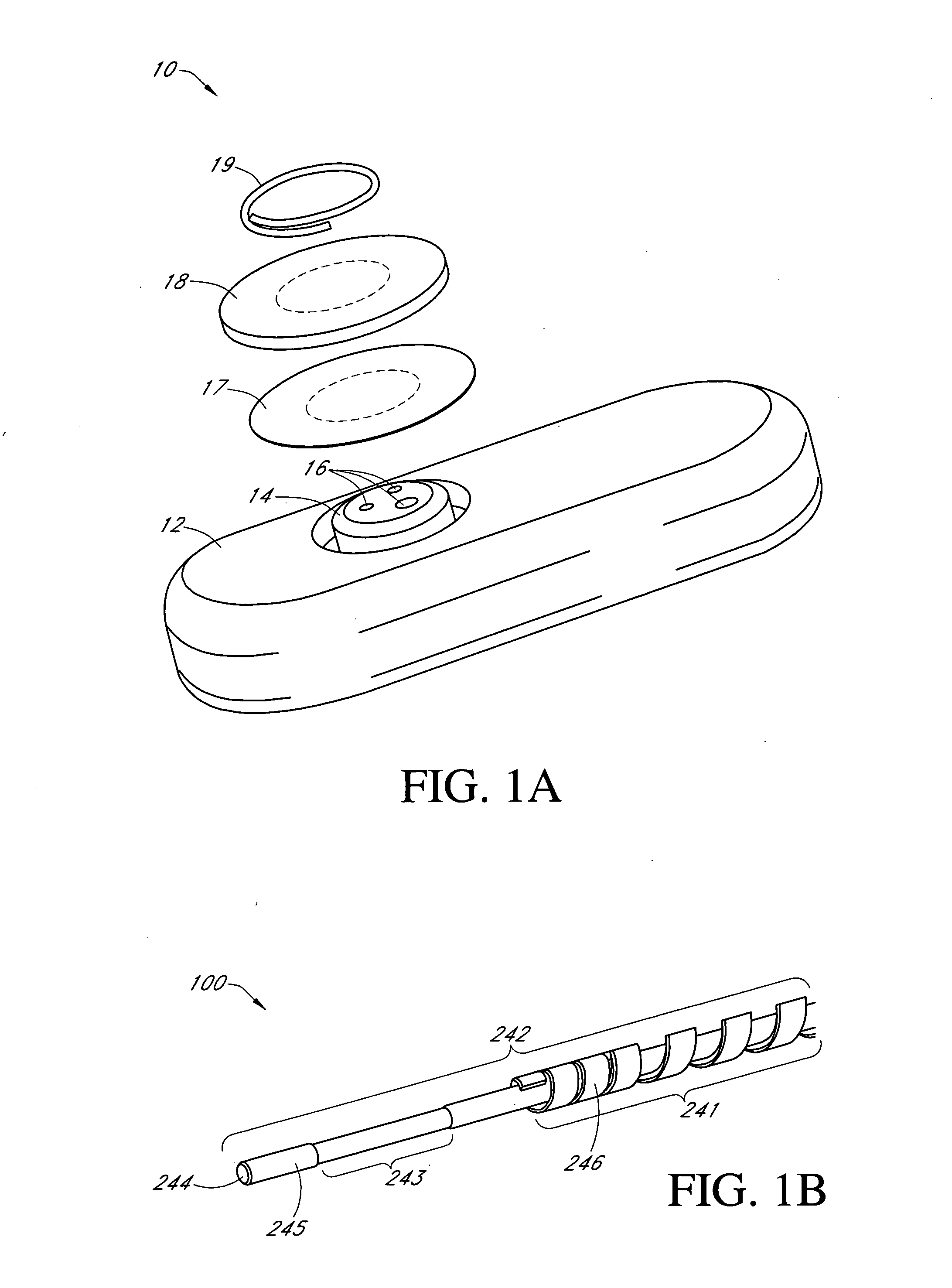
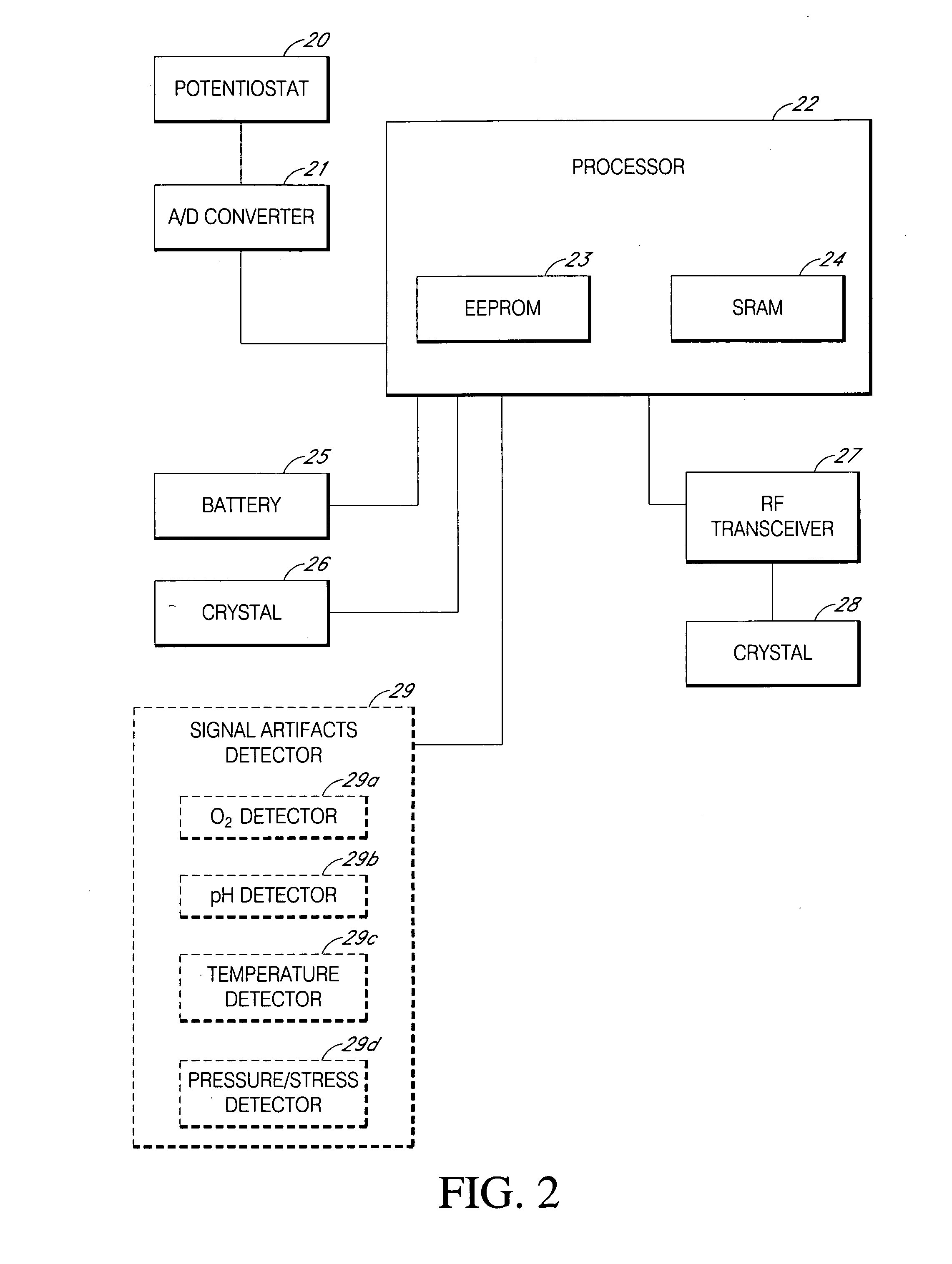
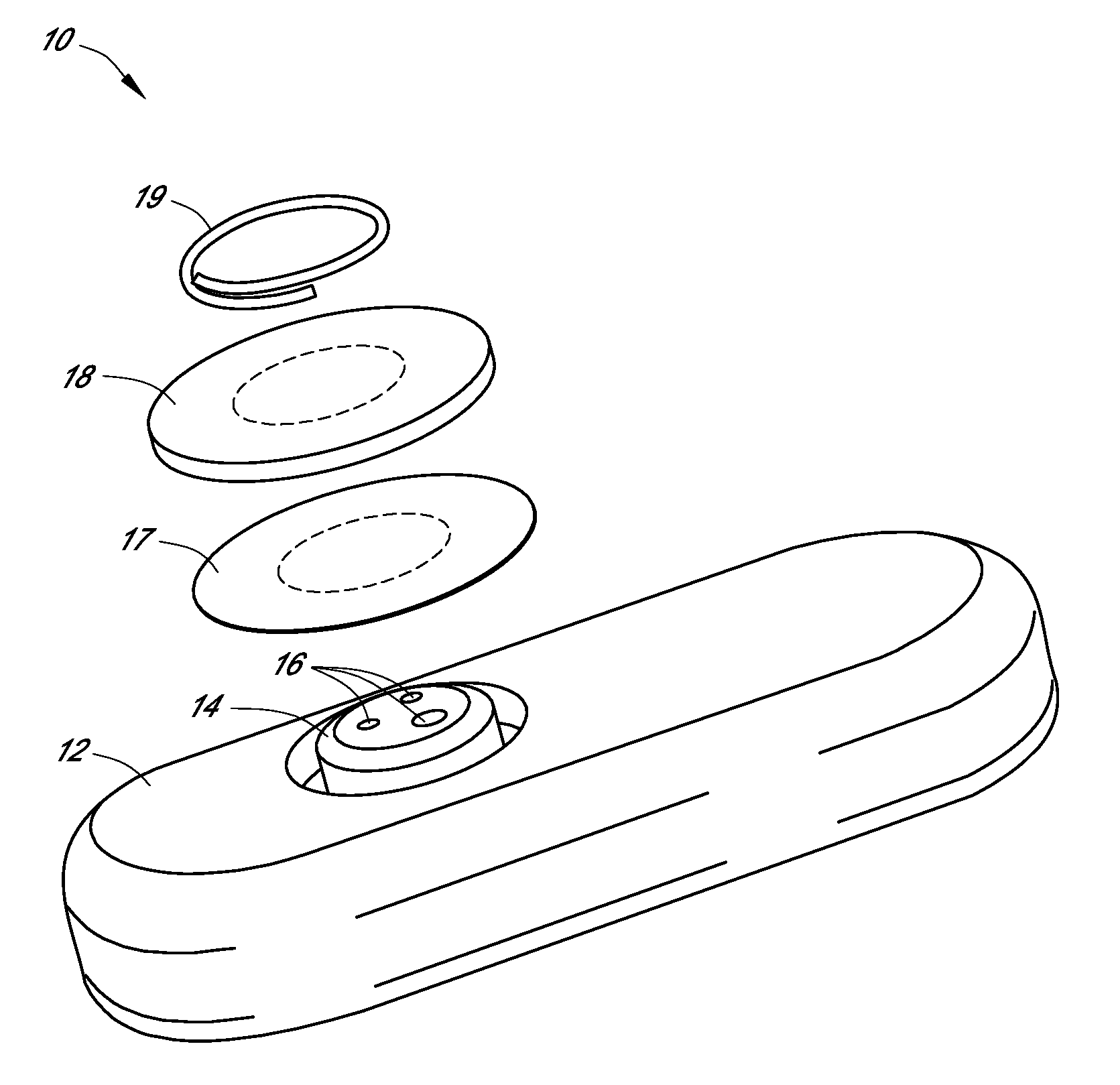
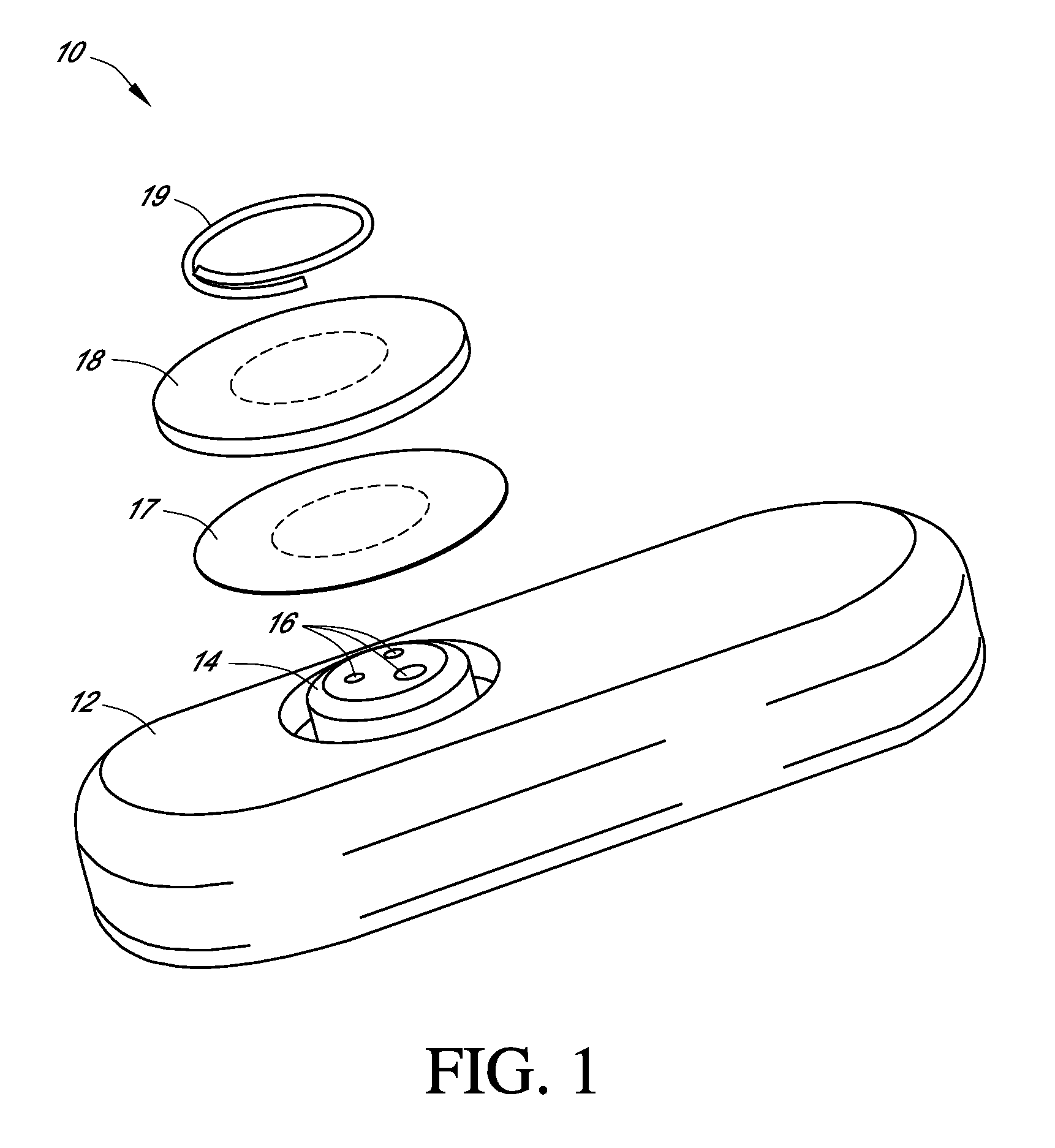
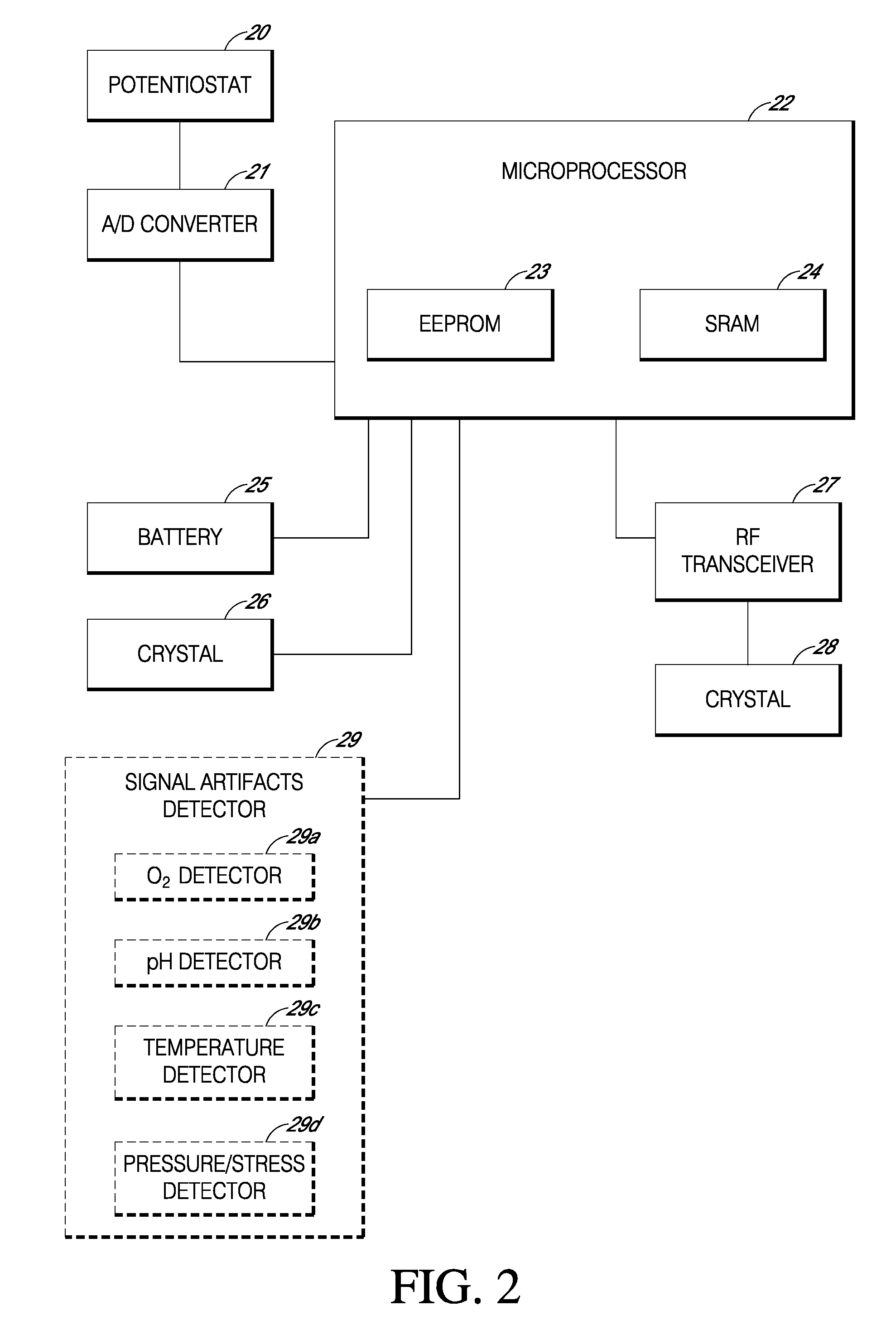
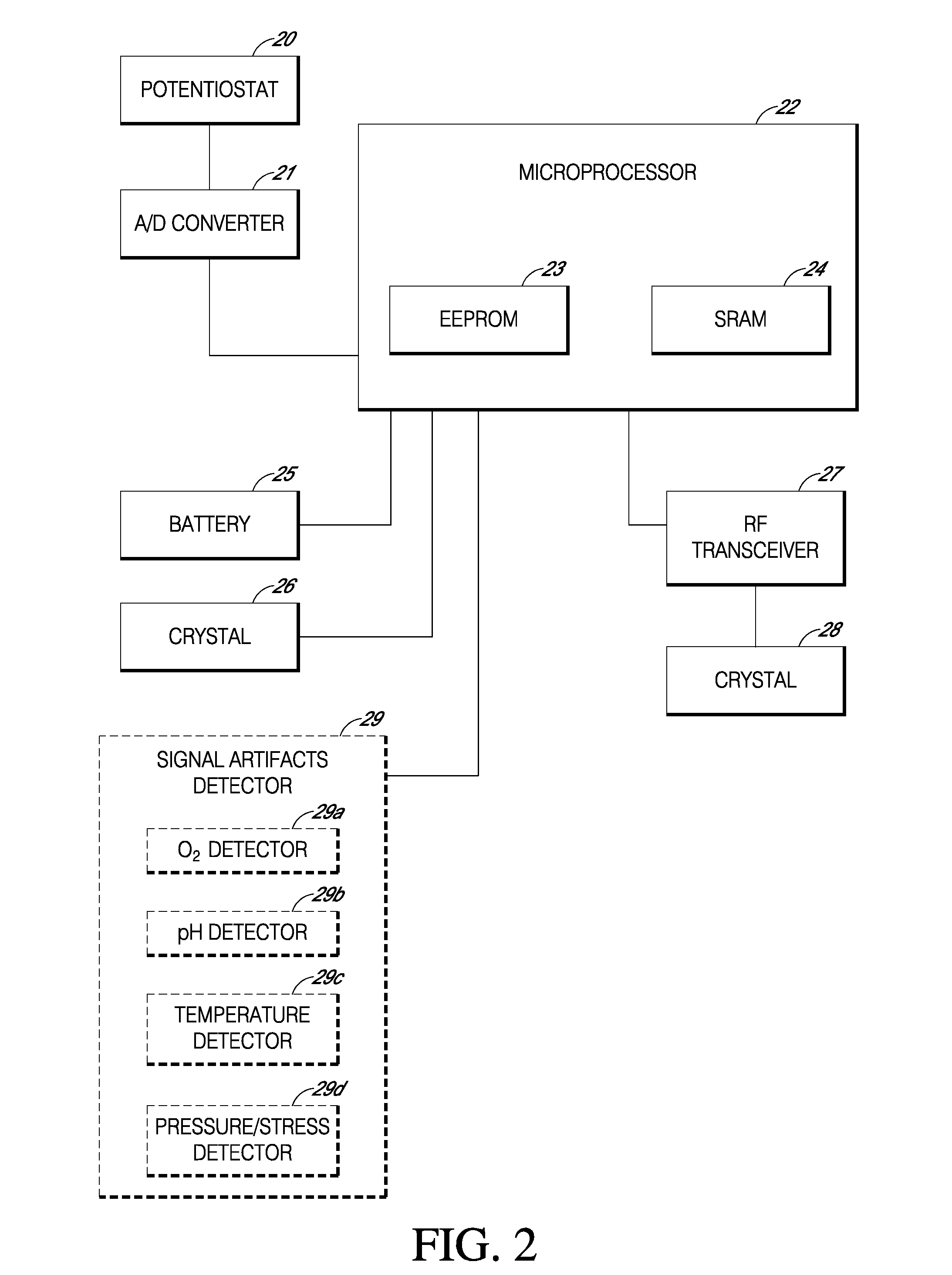
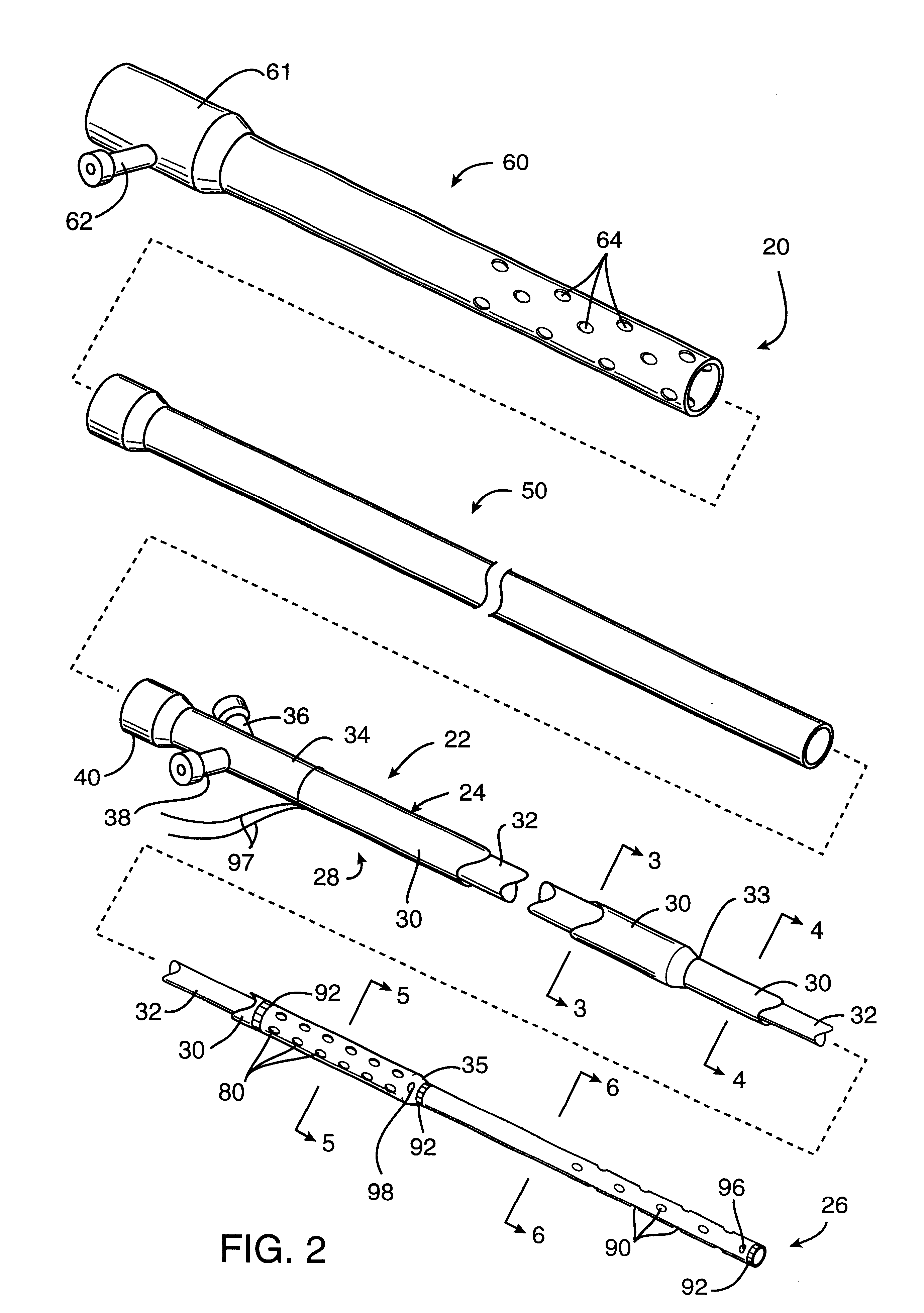
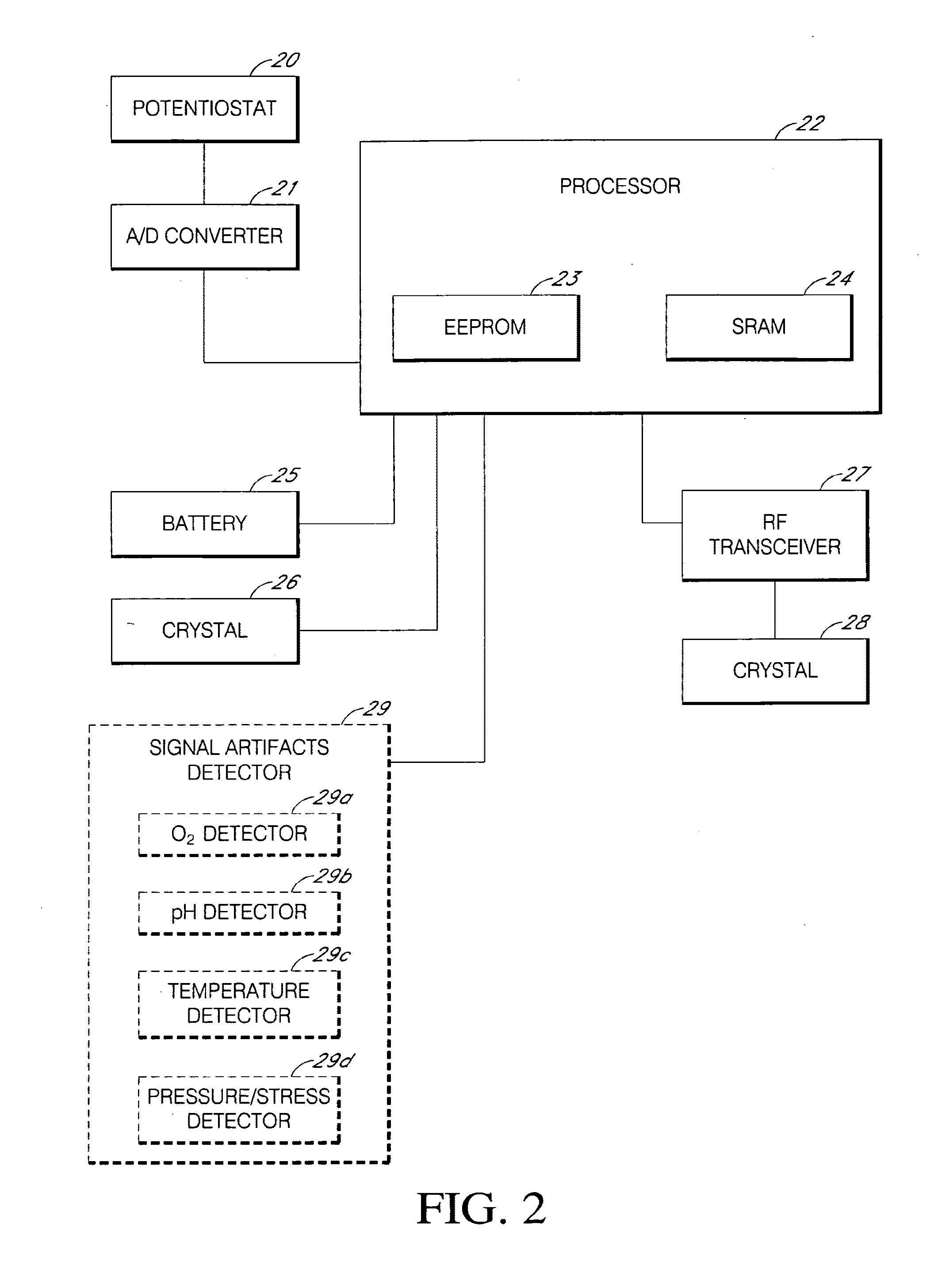
Systems and methods for replacing signal artifacts in a glucose sensor data stream
ActiveUS20050043598A1Accurate detectionAccurate replacementCatheterTemperature sensorsRate limitingData stream
Systems and methods for minimizing or eliminating transient non-glucose related signal noise due to non-glucose rate limiting phenomenon such as ischemia, pH changes, temperatures changes, and the like. The system monitors a data stream from a glucose sensor and detects signal artifacts that have higher amplitude than electronic or diffusion-related system noise. The system replaces some or the entire data stream continually or intermittently including signal estimation methods that particularly address transient signal artifacts. The system is also capable of detecting the severity of the signal artifacts and selectively applying one or more signal estimation algorithm factors responsive to the severity of the signal artifacts, which includes selectively applying distinct sets of parameters to a signal estimation algorithm or selectively applying distinct signal estimation algorithms.
Owner:DEXCOM
Systems and methods for replacing signal artifacts in a glucose sensor data stream
ActiveUS20070032706A1Accurate detectionAvoid adjustmentMedical automated diagnosisCatheterRate limitingData stream
Systems and methods for minimizing or eliminating transient non-glucose related signal noise due to non-glucose rate limiting phenomenon such as interfering species, ischemia, pH changes, temperatures changes, known or unknown sources of mechanical, electrical and / or biochemical noise, and the like. The system monitors a data stream from a glucose sensor and detects signal artifacts that have higher amplitude than electronic or diffusion-related system noise. The system processes some or the entire data stream continually or intermittently based at least in part on whether the signal artifact event has occurred.
Owner:DEXCOM
Systems and methods for replacing signal artifacts in a glucose sensor data stream
ActiveUS20090124877A1Accurately detect and replaceAvoid adjustmentCatheterTemperature sensorsRate limitingGlucose sensors
Systems and methods for minimizing or eliminating transient non-glucose related signal noise due to non-glucose rate limiting phenomenon such as ischemia, pH changes, temperatures changes, and the like. The system monitors a data stream from a glucose sensor and detects signal artifacts that have higher amplitude than electronic or diffusion-related system noise. The system replaces some or the entire data stream continually or intermittently including signal estimation methods that particularly address transient signal artifacts. The system is also capable of detecting the severity of the signal artifacts and selectively applying one or more signal estimation algorithm factors responsive to the severity of the signal artifacts, which includes selectively applying distinct sets of parameters to a signal estimation algorithm or selectively applying distinct signal estimation algorithms.
Owner:DEXCOM INC
Systems and methods for replacing signal artifacts in a glucose sensor data stream
ActiveUS20090124878A1Accurately detect and replaceAvoid adjustmentCatheterTemperature sensorsRate limitingData stream
Systems and methods for minimizing or eliminating transient non-glucose related signal noise due to non-glucose rate limiting phenomenon such as ischemia, pH changes, temperatures changes, and the like. The system monitors a data stream from a glucose sensor and detects signal artifacts that have higher amplitude than electronic or diffusion-related system noise. The system replaces some or the entire data stream continually or intermittently including signal estimation methods that particularly address transient signal artifacts. The system is also capable of detecting the severity of the signal artifacts and selectively applying one or more signal estimation algorithm factors responsive to the severity of the signal artifacts, which includes selectively applying distinct sets of parameters to a signal estimation algorithm or selectively applying distinct signal estimation algorithms.
Owner:DEXCOM INC
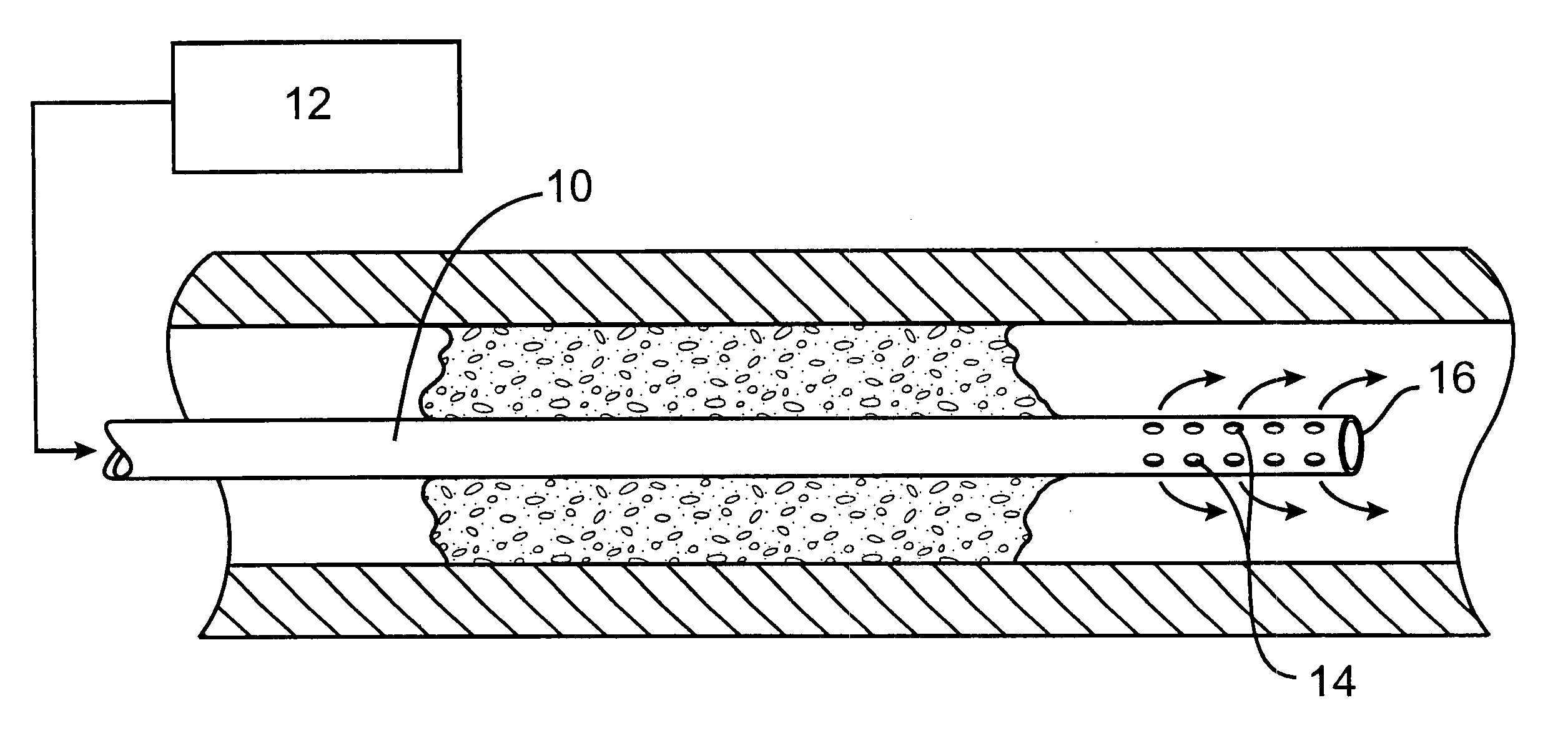
Sensors for detecting substances indicative of stroke, ischemia, or myocardial infarction
ActiveUS20060079740A1Thickness minimizationTransport of glucose to the sensor is not altered over timeStentsCatheterMetaboliteCitrulline
A sensor is disclosed, for implantation within a blood vessel to monitor a substance in or property of blood. In one embodiment, the sensor detects nitric oxide or a nitric oxide metabolite. In another embodiment, other substances such as glutamate, aspartate, arginine, citrulline, acetylcholine, calcium, potassium, or dopamine are monitored. The sensor may be attached to a support structure such as a stent, guidewire, or catheter. In a further embodiment, a catheter is disclosed that extracts patient fluid to a sensor outside the body for monitoring a substance or property of the patient fluid. Methods are also disclosed.
Owner:SILVER JAMES H +1
Systems for heart treatment
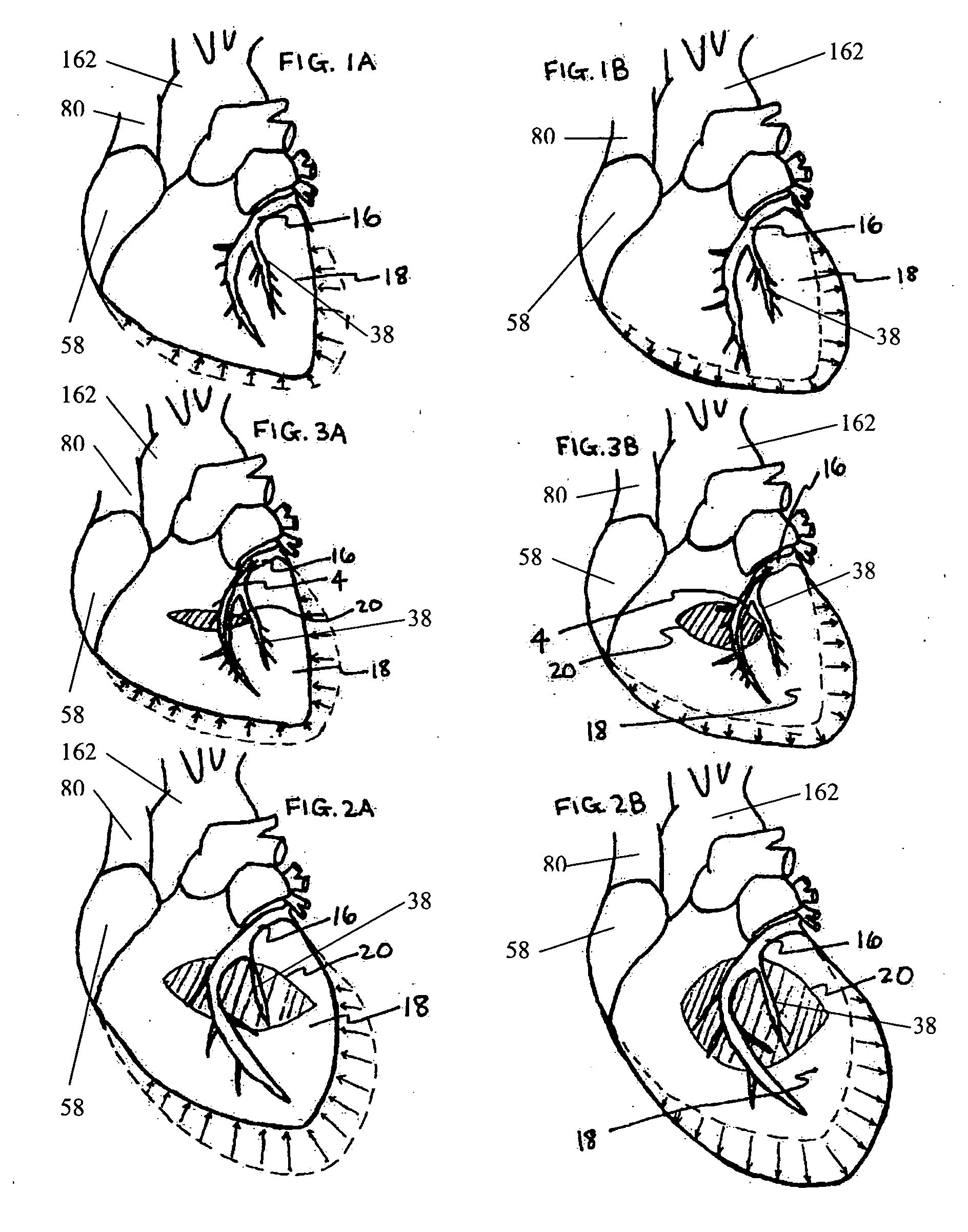
InactiveUS20050197694A1Reduce stressReduce/limit volumeSuture equipmentsElectrotherapyLeft ventricular sizeTherapeutic treatment
Described are devices and methods for treating degenerative, congestive heart disease and related valvular dysfunction. Percutaneous and minimally invasive surgical tensioning structures offer devices that mitigate changes in the ventricular structure (i.e., remodeling) and deterioration of global left ventricular performance related to tissue damage precipitating from ischemia, acute myocardial infarction (AMI) or other abnormalities. These tensioning structures can be implanted within various major coronary blood-carrying conduit structures (arteries, veins and branching vessels), into or through myocardium, or into engagement with other anatomic structures that impact cardiac output to provide tensile support to the heart muscle wall which resists diastolic filling pressure while simultaneously providing a compressive force to the muscle wall to limit, compensate or provide therapeutic treatment for congestive heart failure and / or to reverse the remodeling that produces an enlarged heart.
Owner:EXTENSIA MEDICAL
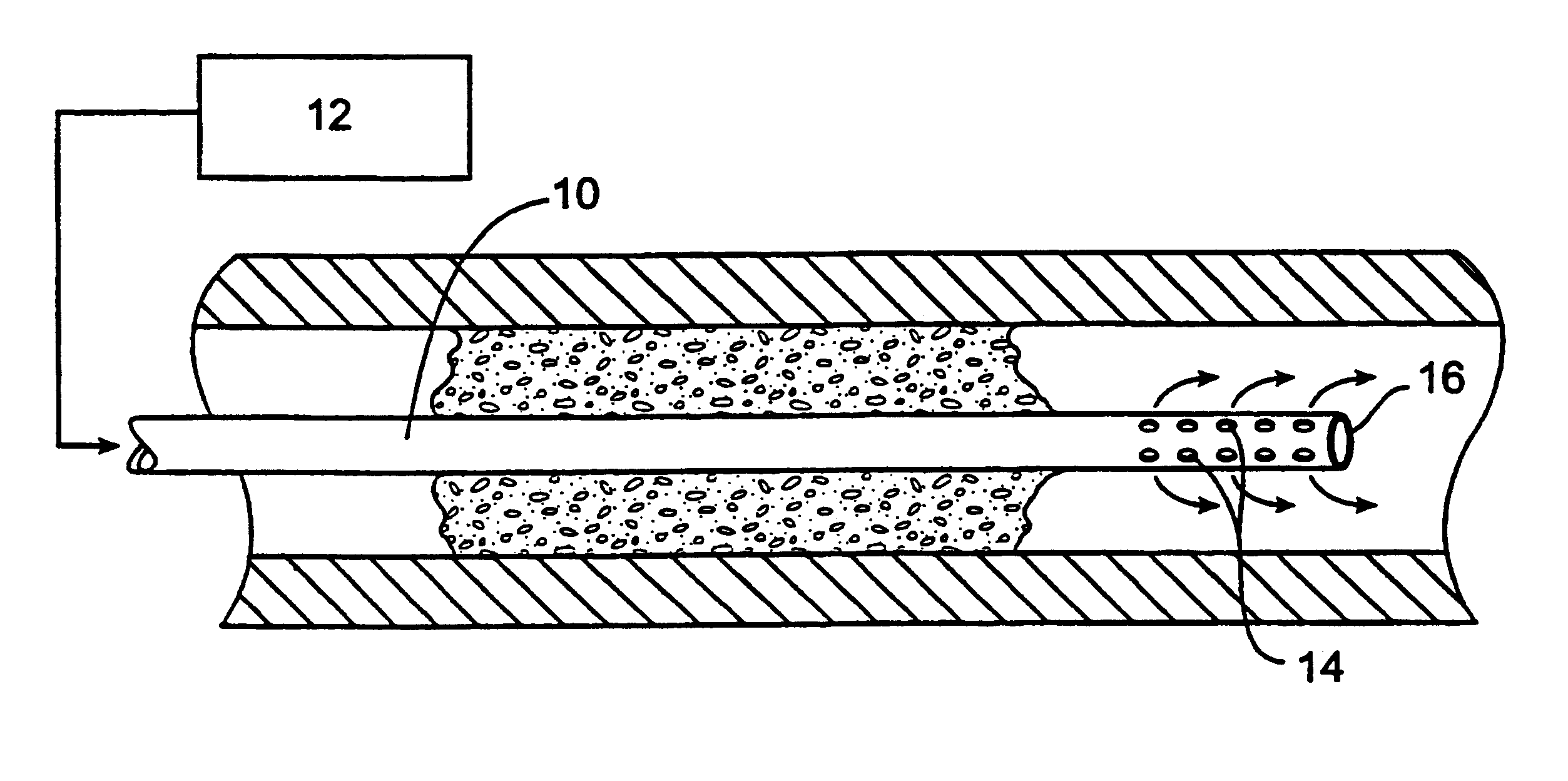
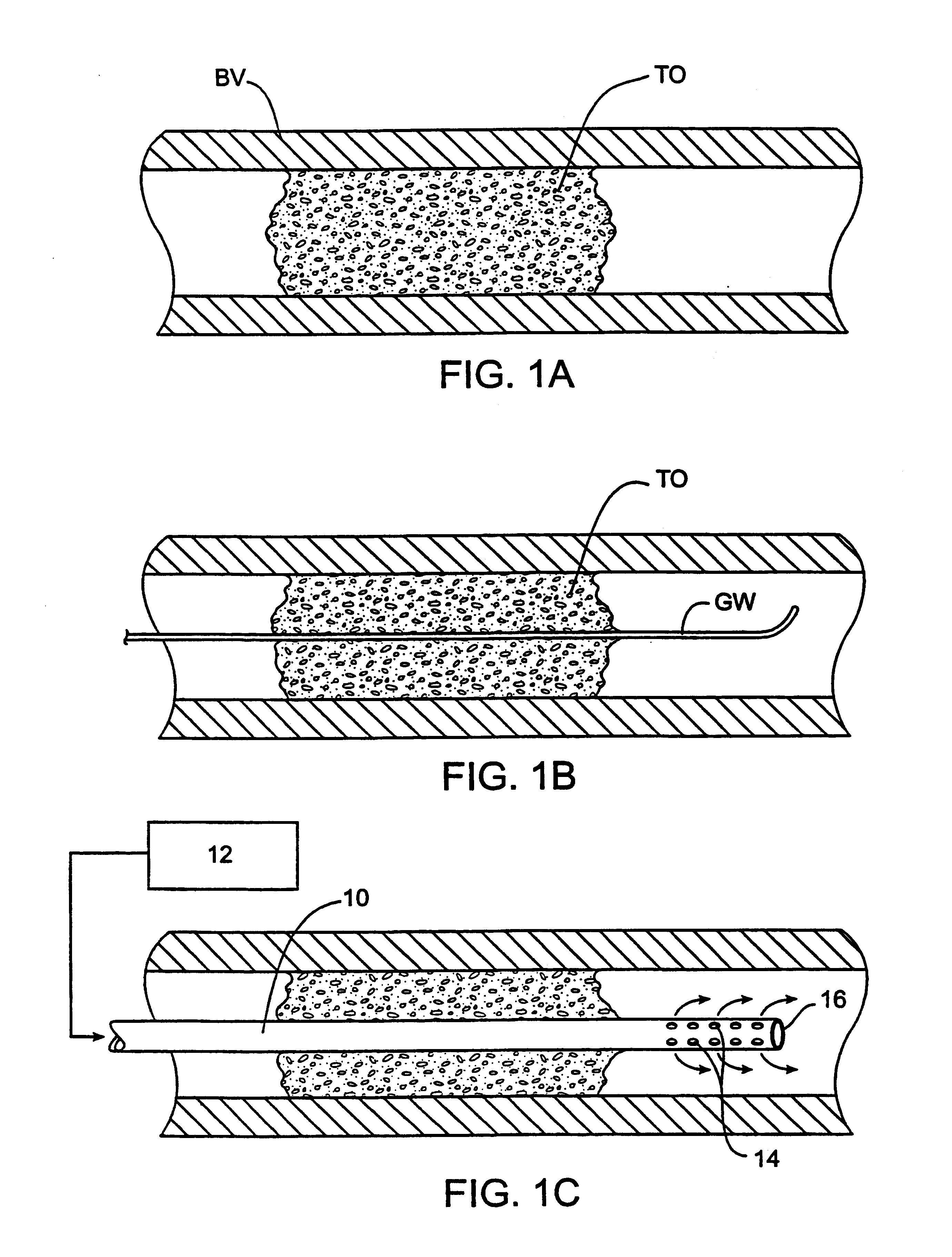
Methods and systems for treating ischemia
InactiveUS6295990B1Promote dissolution and removalMinimize and prevent ischemiaStentsBalloon catheterControl mannerDecreased mean arterial pressure
Methods for treating total and partial occlusions employ a perfusion conduit which is penetrated through the occlusive material. Oxygenated blood or other medium is then perfused through the conduit in a controlled manner, preferably at a controlled pressure below the arterial pressure, to maintain oxygenation and relieve ischemia in tissue distal to the occlusion. In another aspect, interventional devices, such as stents or balloon catheters, are passed through the perfusion catheter to remove obstructions. Optionally, the occlusion may be treated while perfusion is maintained, typically by introducing a thrombolytic or other agent into the occlusive material using the perfusion conduit or by employing mechanical means to remove the obstruction. Such methods are particularly suitable for treating acute stroke to prevent damage to the cerebral tissue.
Owner:SALIENT INTERVENTIONAL SYST
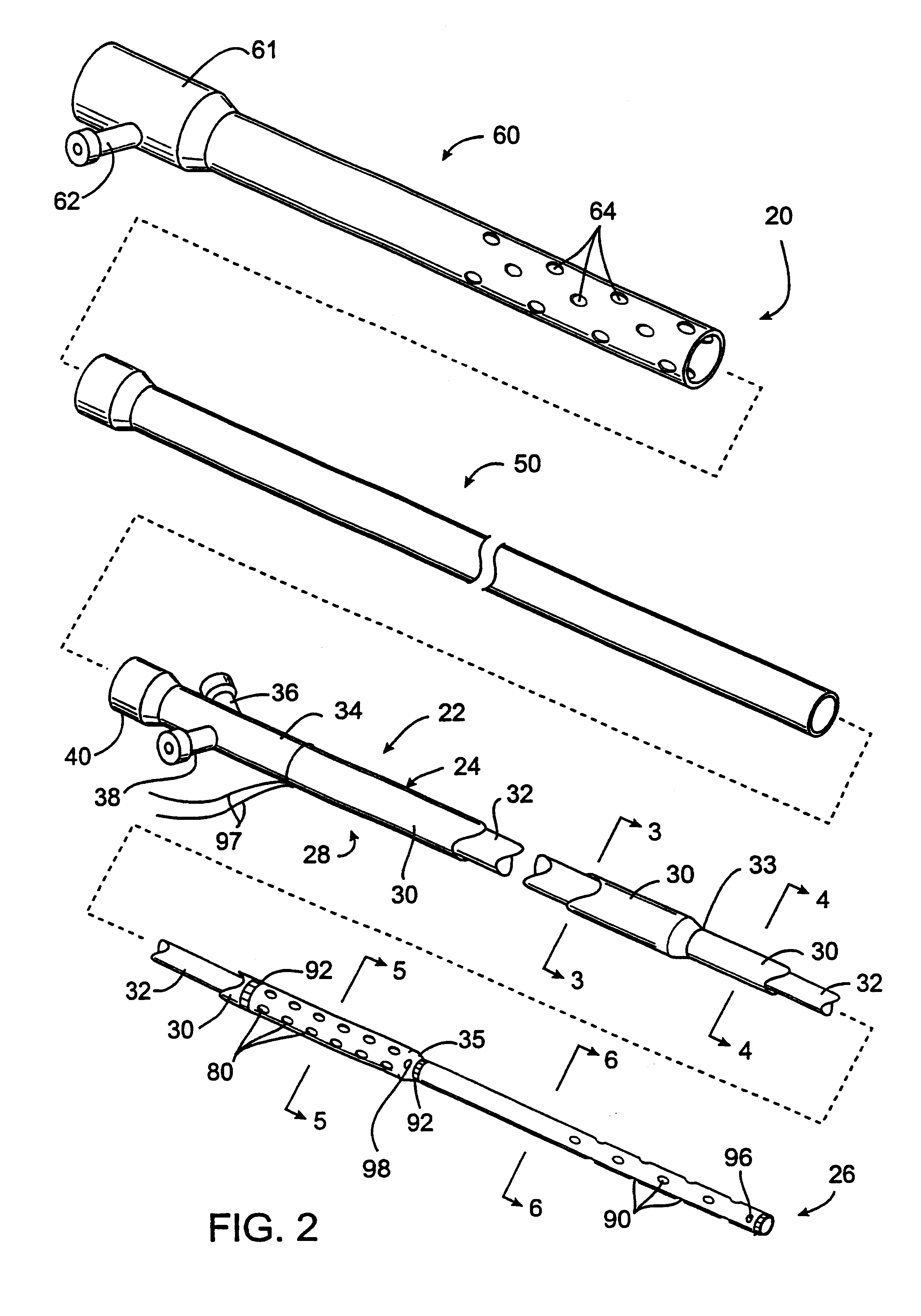
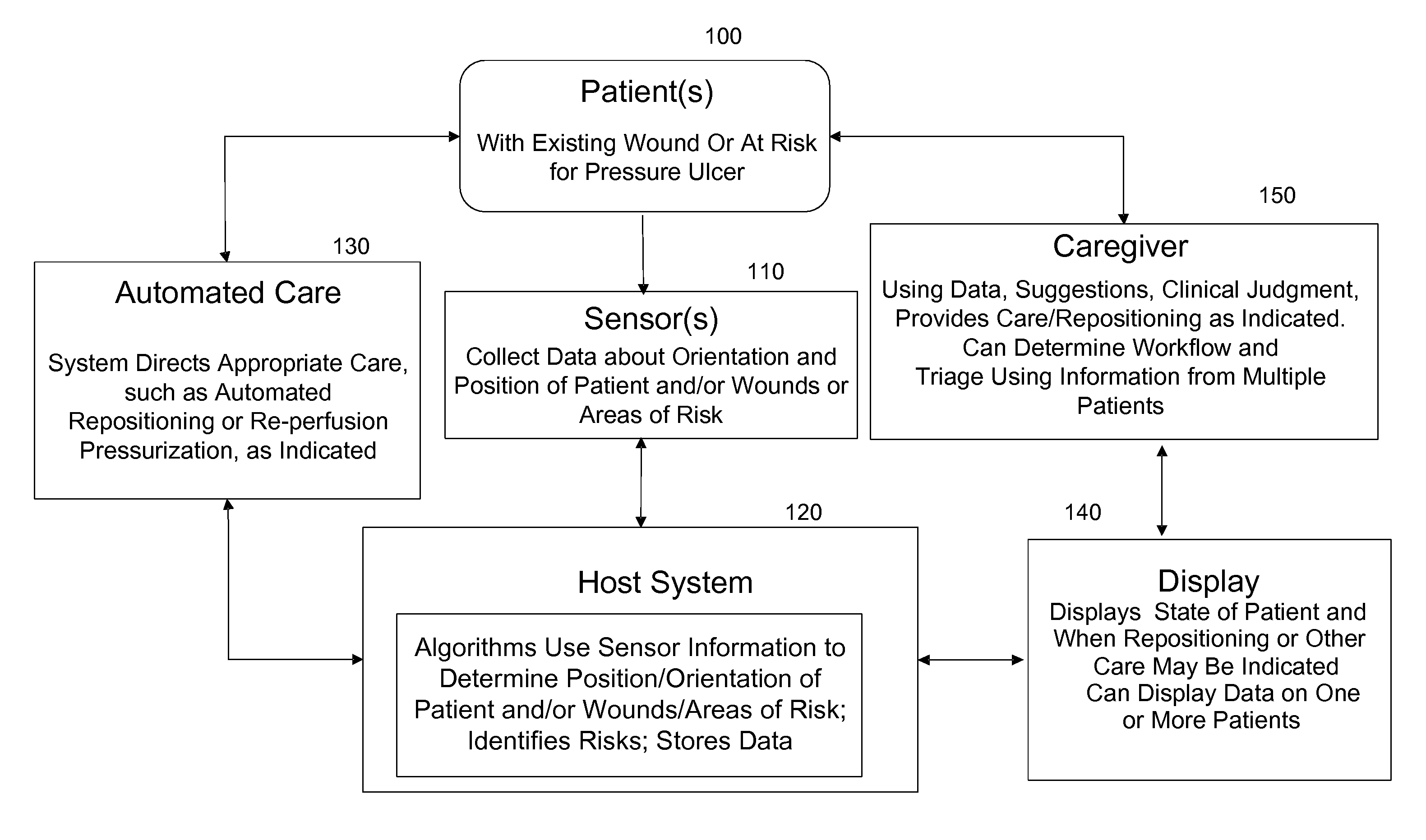
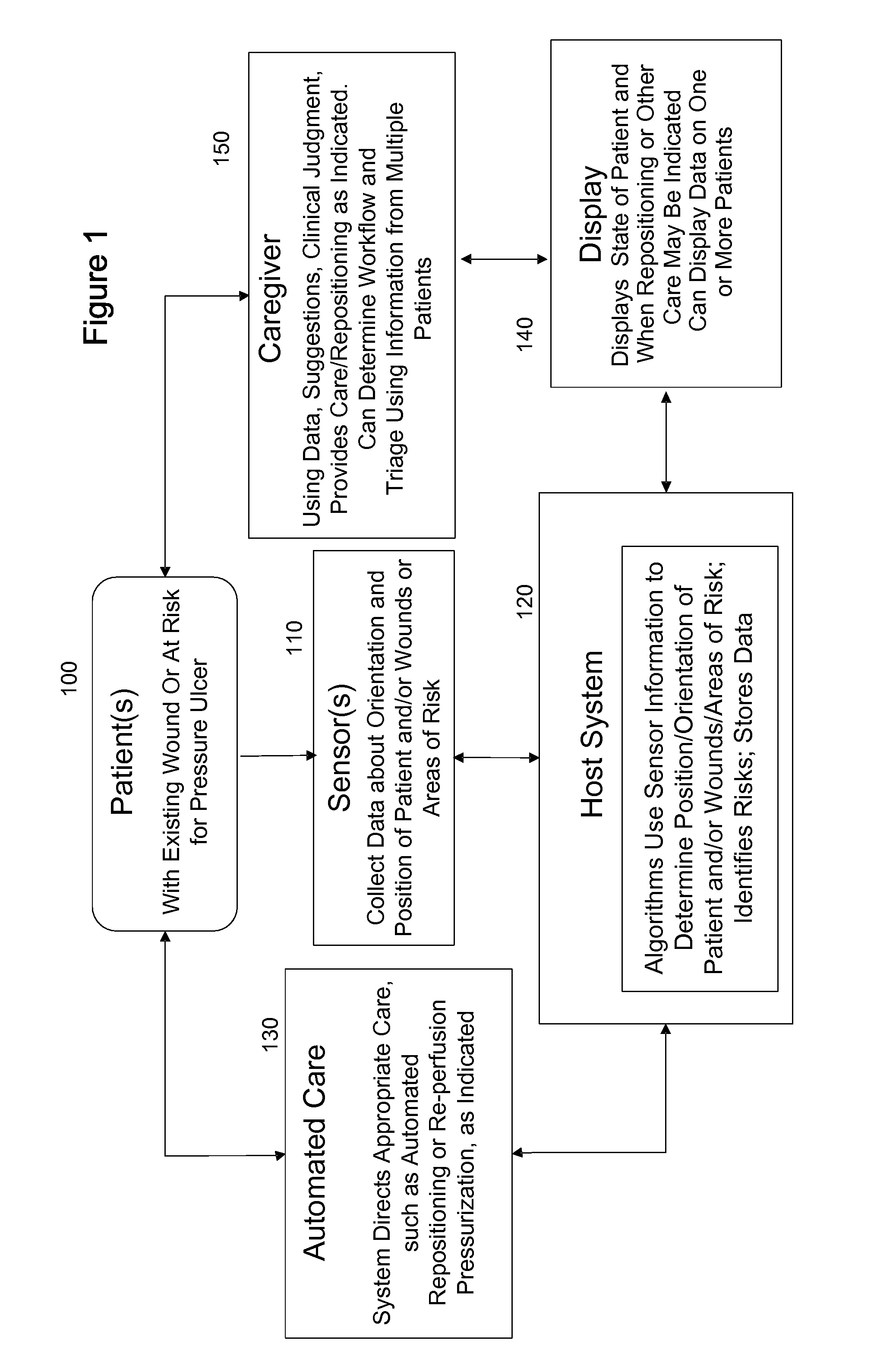
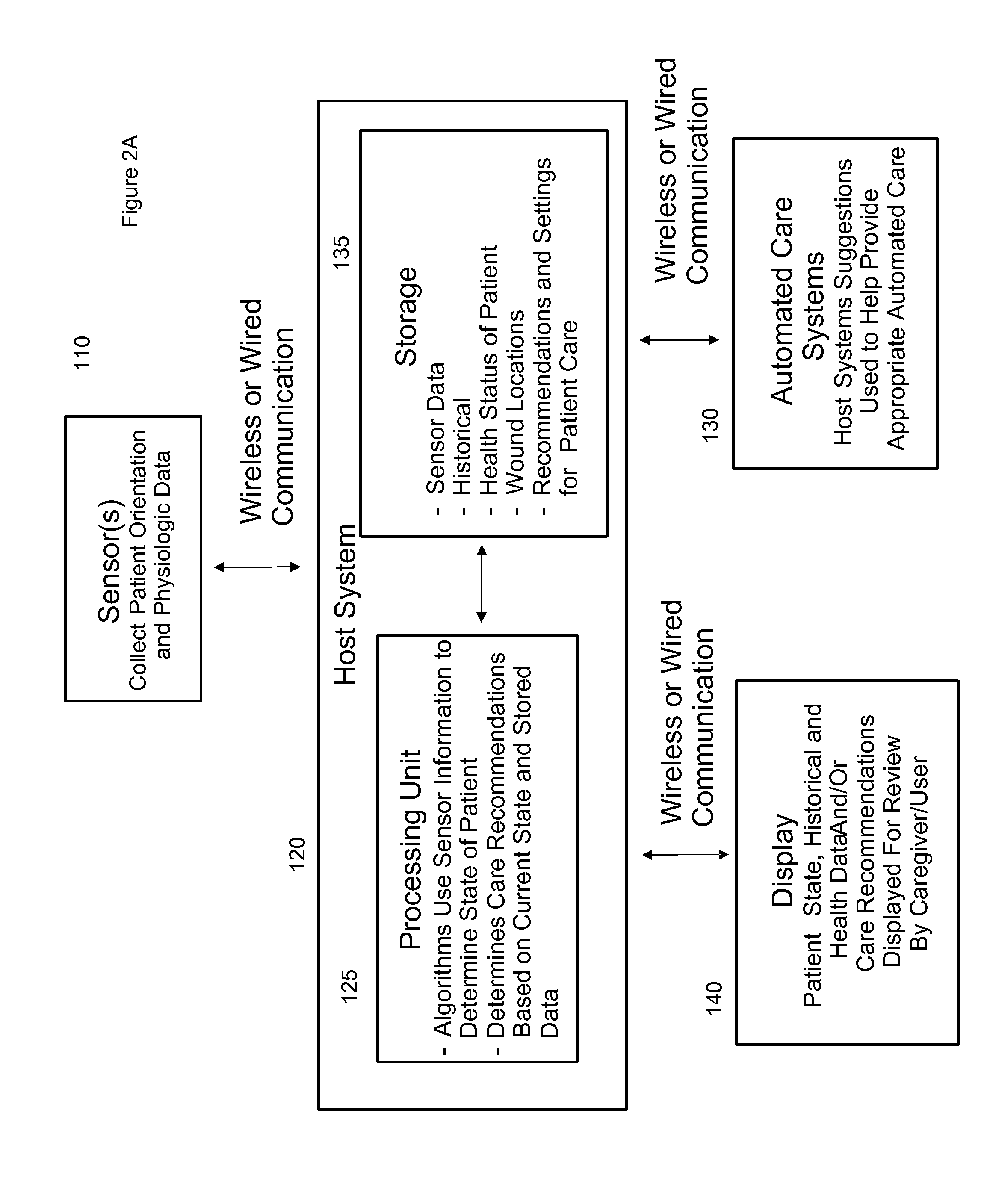
Systems, devices and methods for preventing, detecting and treating pressure-induced ischemia, pressure ulcers, and other conditions
ActiveUS20110263950A1Minimize and eliminate physical contactPromote blood circulationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesOperating chairsAccelerometerPatient characteristics
A system for monitoring medical conditions including pressure ulcers, pressure-induced ischemia and related medical conditions comprises at least one sensor adapted to detect one or more patient characteristic including at least position, orientation, temperature, acceleration, moisture, resistance, stress, heart rate, respiration rate, and blood oxygenation, a host for processing the data received from the sensors together with historical patient data to develop an assessment of patient condition and suggested course of treatment. In some embodiments, the system can further include a support surface having one or more sensors incorporated therein either in addition to sensors affixed to the patient or as an alternative thereof. The support surface is, in some embodiments, capable of responding to commands from the host for assisting in implementing a course of action for patient treatment. The sensor can include bi-axial or tri-axial accelerometers, as well as resistive, inductive, capactive, magnetic and other sensing devices, depending on whether the sensor is located on the patient or the support surface, and for what purpose.
Owner:LEAF HEALTHCARE
Systems for heart treatment
InactiveUS7144363B2Reduce stressReduce/limit volumeSuture equipmentsHeart valvesLeft ventricular sizeTherapeutic treatment
Owner:BAY INNOVATION GROUP
Sensors for detecting substances indicative of stroke, ischemia, infection or inflammation
ActiveUS20080176271A1Thickness minimizationTransport of glucose to the sensor is not altered over timeStentsMicrobiological testing/measurementMetaboliteNitric oxide
A system is disclosed that extracts bodily fluid to a reaction chamber for monitoring a substance or property of the patient fluid. In one embodiment, a pump is used to advance the sample of bodily fluid through a filter to produce a filtrate. Another pump advances filtrate into the reaction chamber, while another pump advances reactant into the reaction chamber. A sensor in communication with the reaction chamber determines a concentration of nitric oxide or one of its metabolic products. Methods are also disclosed.
Owner:SILVER JAMES H
Systems for heart treatment
InactiveUS20050197692A1Decreasing wall stressReinforce wallSuture equipmentsElectrotherapyLeft ventricular sizeTherapeutic treatment
Described are devices and methods for treating degenerative, congestive heart disease and related valvular dysfunction. Percutaneous and minimally invasive surgical tensioning structures offer devices that mitigate changes in the ventricular structure (i.e., remodeling) and deterioration of global left ventricular performance related to tissue damage precipitating from ischemia, acute myocardial infarction (AMI) or other abnormalities. These tensioning structures can be implanted within various major coronary blood-carrying conduit structures (arteries, veins and branching vessels), into or through myocardium, or into engagement with other anatomic structures that impact cardiac output to provide tensile support to the heart muscle wall which resists diastolic filling pressure while simultaneously providing a compressive force to the muscle wall to limit, compensate or provide therapeutic treatment for congestive heart failure and / or to reverse the remodeling that produces an enlarged heart.
Owner:EXTENSIA MEDICAL
Methods for the treatment and diagnosis of cardiovascular disease
InactiveUS6156500AImprove throughputBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsClinical trialPercent Diameter Stenosis
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for the treatment and diagnosis of cardiovascular disease, including, but not limited to, atherosclerosis, ischemia / reperfusion, hypertension, restenosis, and arterial inflammation. Specifically, the present invention identifies and describes genes which are differentially expressed in cardiovascular disease states, relative to their expression in normal, or non-cardiovascular disease states, and / or in response to manipulations relevant to cardiovascular disease. Further, the present invention identifies and describes genes via the ability of their gene products to interact with gene products involved in cardiovascular disease. Still further, the present invention provides methods for the identification and therapeutic use of compounds as treatments of cardiovascular disease. Moreover, the present invention provides methods for the diagnostic monitoring of patients undergoing clinical evaluation for the treatment of cardiovascular disease, and for monitoring the efficacy of compounds in clinical trials. Additionally, the present invention describes methods for the diagnostic evaluation and prognosis of various cardiovascular diseases, and for the identification of subjects exhibiting a predisposition to such conditions.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC +1
Cerebral perfusion augmentation
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Methods and systems for treating ischemia
Methods for treating total and partial occlusions employ a perfusion conduit which is penetrated through the occlusive material. Oxygenated blood or other medium is then perfused through the conduit to maintain oxygenation and relieve ischemia in tissue distal to the occlusion. Optionally, the occlusion may be treated while perfusion is maintained, typically by introducing a thrombolytic or other agent into the occlusive material using the perfusion conduit. Such methods are particularly suitable for treating acute stroke to prevent irreversible damage to the cerebral tissue.
Owner:SALIENT INTERVENTIONAL SYST
Cardioelectromagnetic treatment
ActiveUS20050080459A1ElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsImplanted deviceHeart/circulation
A method of treatment or prophylaxis of a disease state or a condition ameliorated or prevented by electromagnetic field application. A person having or susceptible to such disease state or condition is subjected to electromagnetic fields having a frequency between zero and about 200 Hertz. The diseased state or condition may include diseased heart valves, an enlarged heart, circulatory blockage, coronary insufficiencies, and ischemia. The treatment may be administered non-invasively or invasively. An implantable device for invasively administering the treatment may include at least one component emitting electromagnetic fields having a frequency between zero and about 200 Hertz. The component may include at least one inductor.
Owner:JACOBSON RESONANCE ENTERPRISES
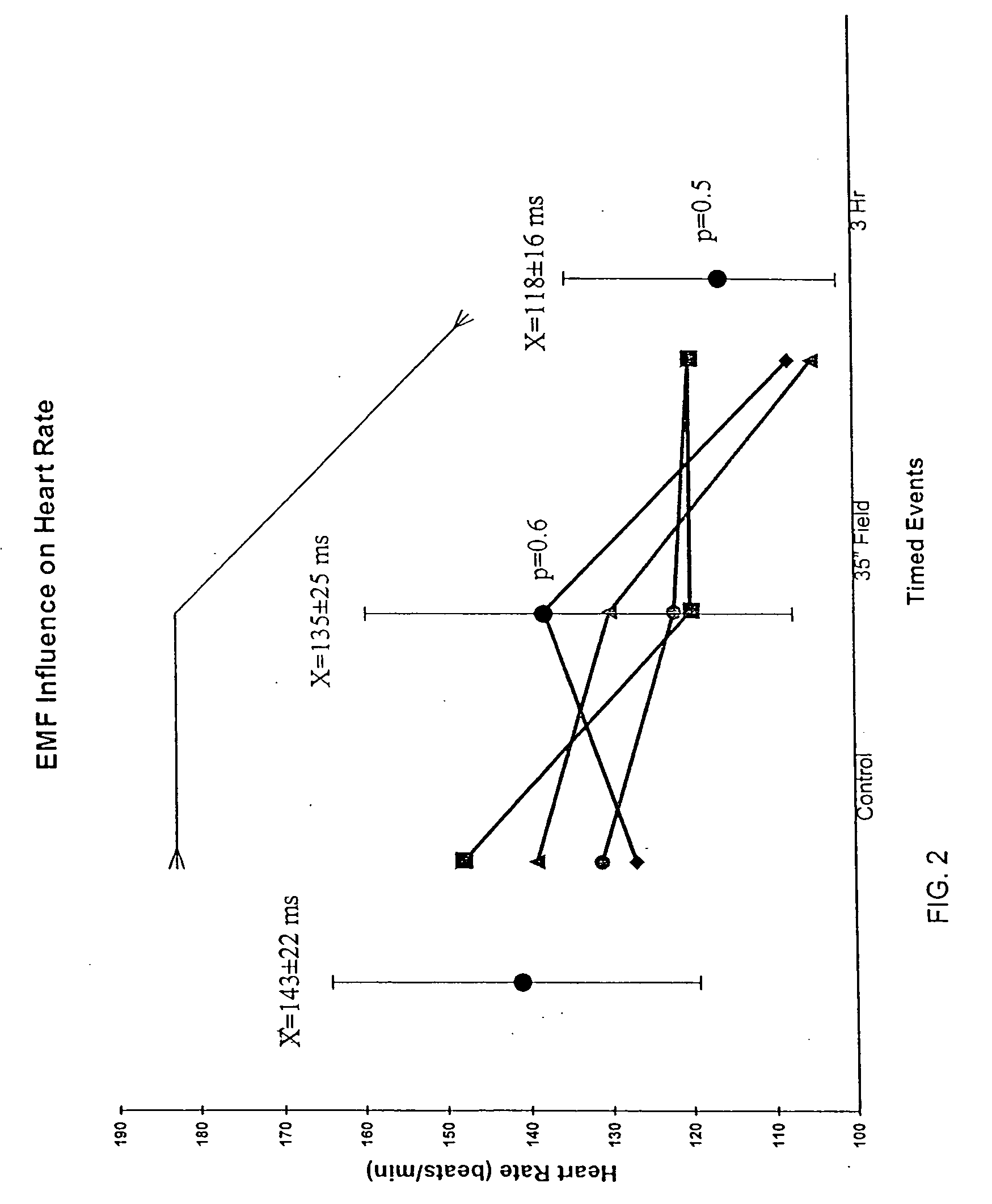
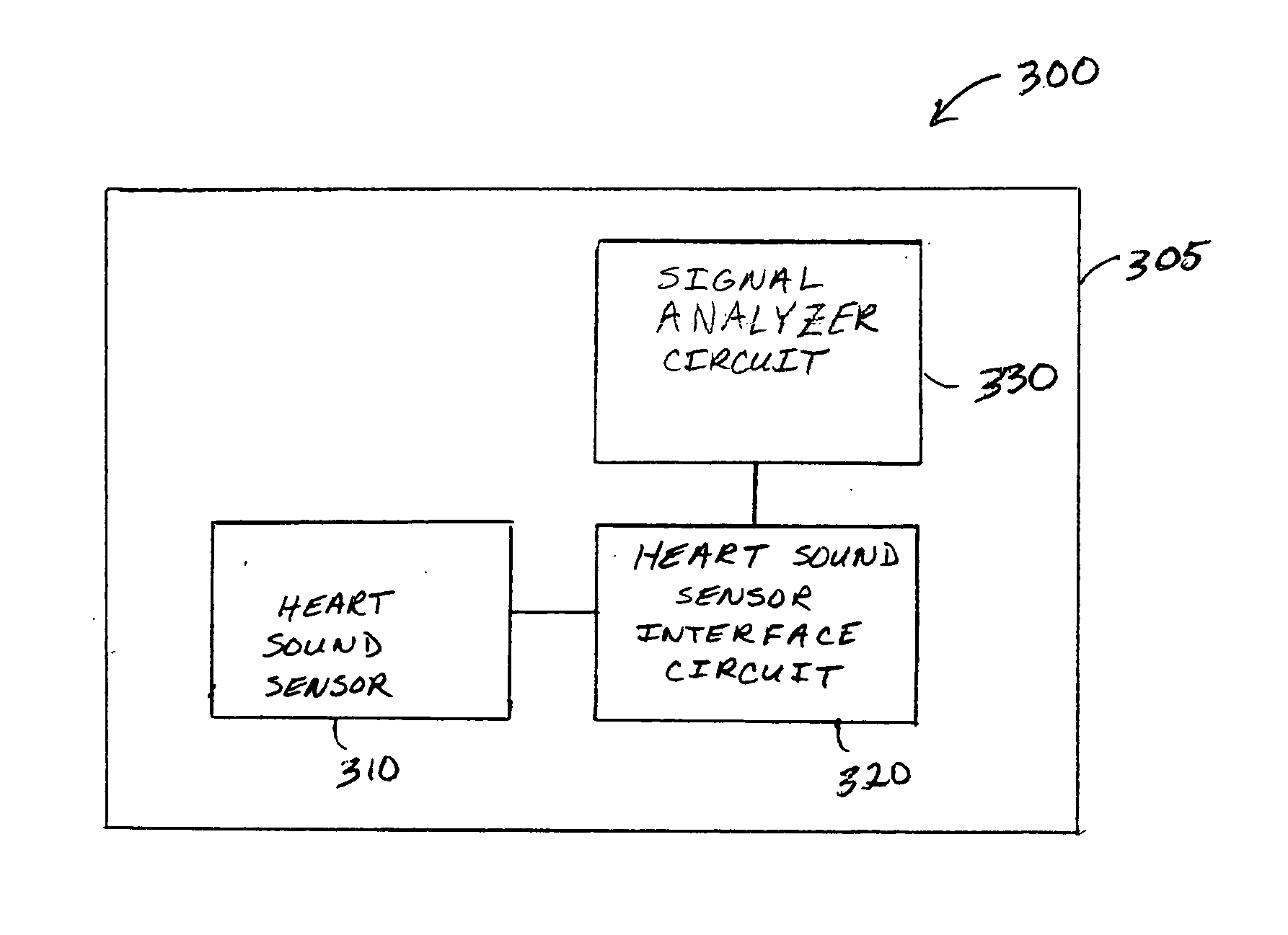
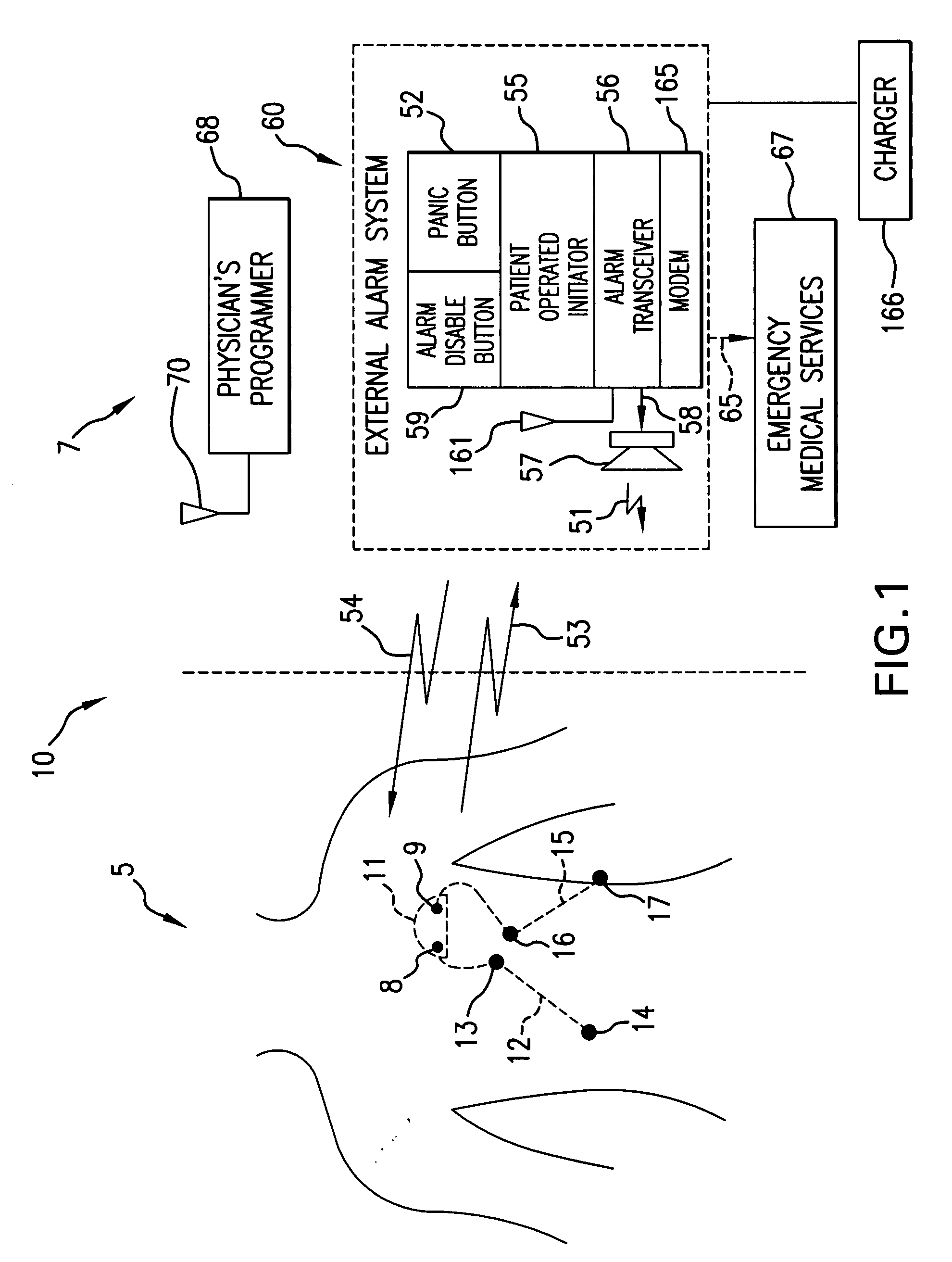
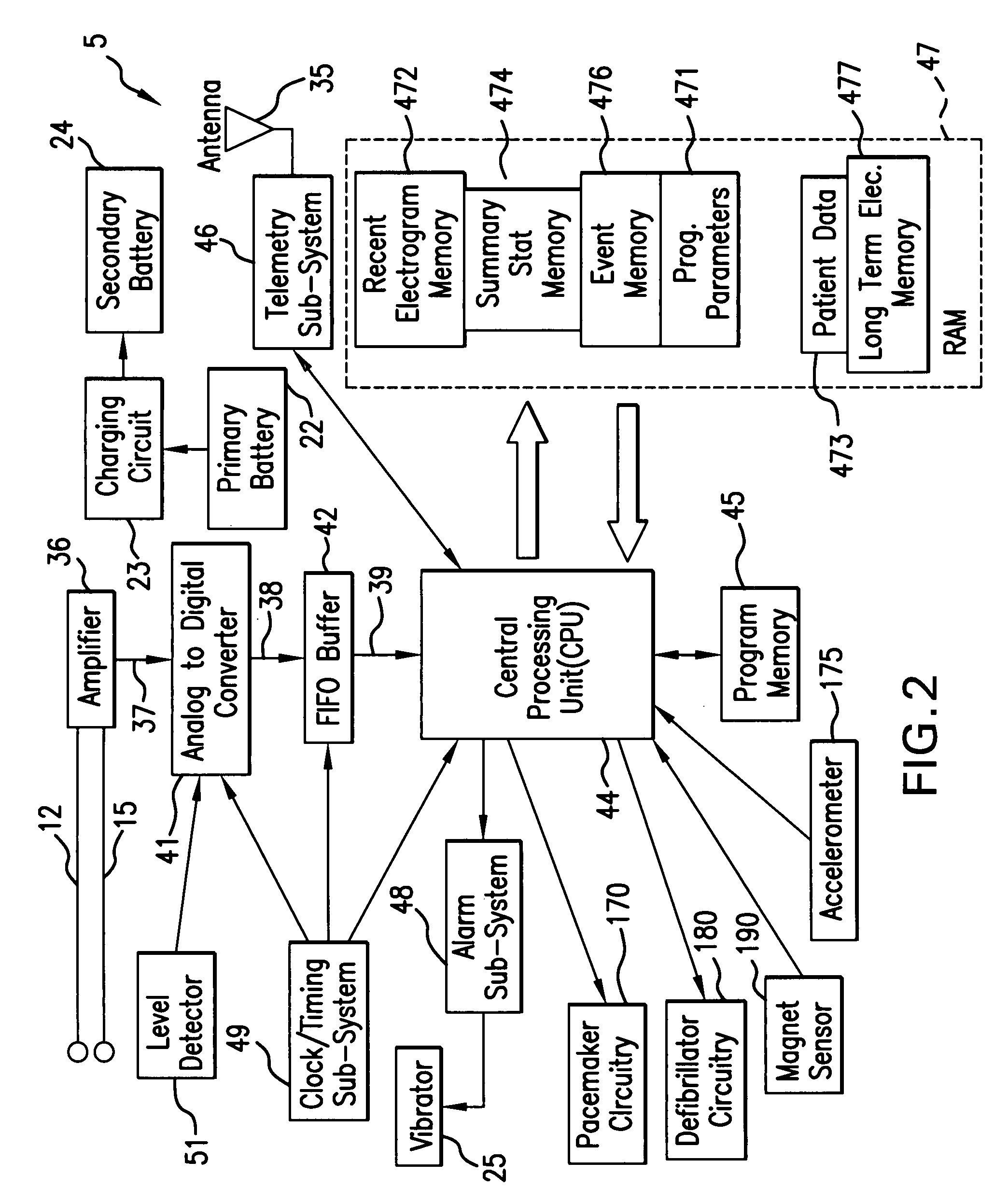
Ischemia detection using a heart sound sensor
A system comprising an implantable medical device (IMD) includes an implantable heart sound sensor to produce an electrical signal representative of at least one heart sound. The heart sound is associated with mechanical activity of a patient's heart. Additionally, the IMD includes a heart sound sensor interface circuit coupled to the heart sound sensor to produce a heart sound signal, and a signal analyzer circuit coupled to the heart sound sensor interface circuit. The signal analyzer circuit measures a baseline heart sound signal, and deems that an ischemic event has occurred using, among other things, a measured subsequent change in the heart sound signal from the established baseline heart sound signal.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
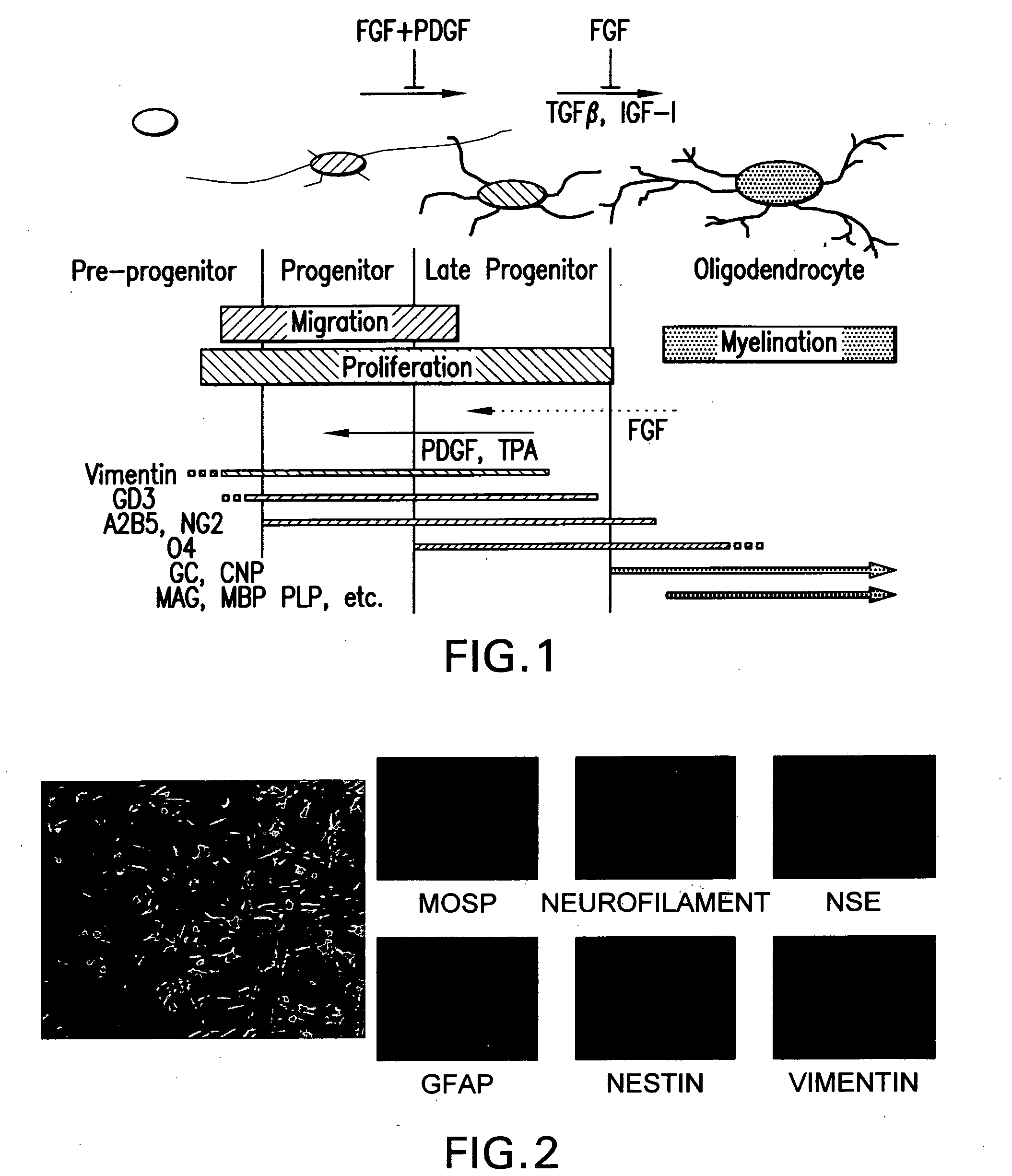
Production of oligodendrocytes from placenta-derived stem cells
The present invention provides methods and compositions for the production of glial cells and oligodendrocytes from placenta stem cells. The invention further provides for the use of these glia and oligodendrocytes in the treatment of, and intervention in, for example, trauma, ischemia and degenerative disorders of the central nervous system (CNS), particularly in the treatment of demyelinating diseases such as multiple sclerosis.
Owner:CELULARITY INC
Materials, methods, and devices for treatment of arthropathies and spondylopathies
Novel modalities are introduced to treat joint and cartilage ischemia and related pathologies to improve outcome in the treatment of arthropathies and spondylopathies. The invention includes compositions, materials or devices which will improve oxygen, substrate and nutrient delivery to joint tissues and modalities to decrease the degradation of joint tissues by inflammatory and other destructive processes.
Owner:LEVIN BRUCE
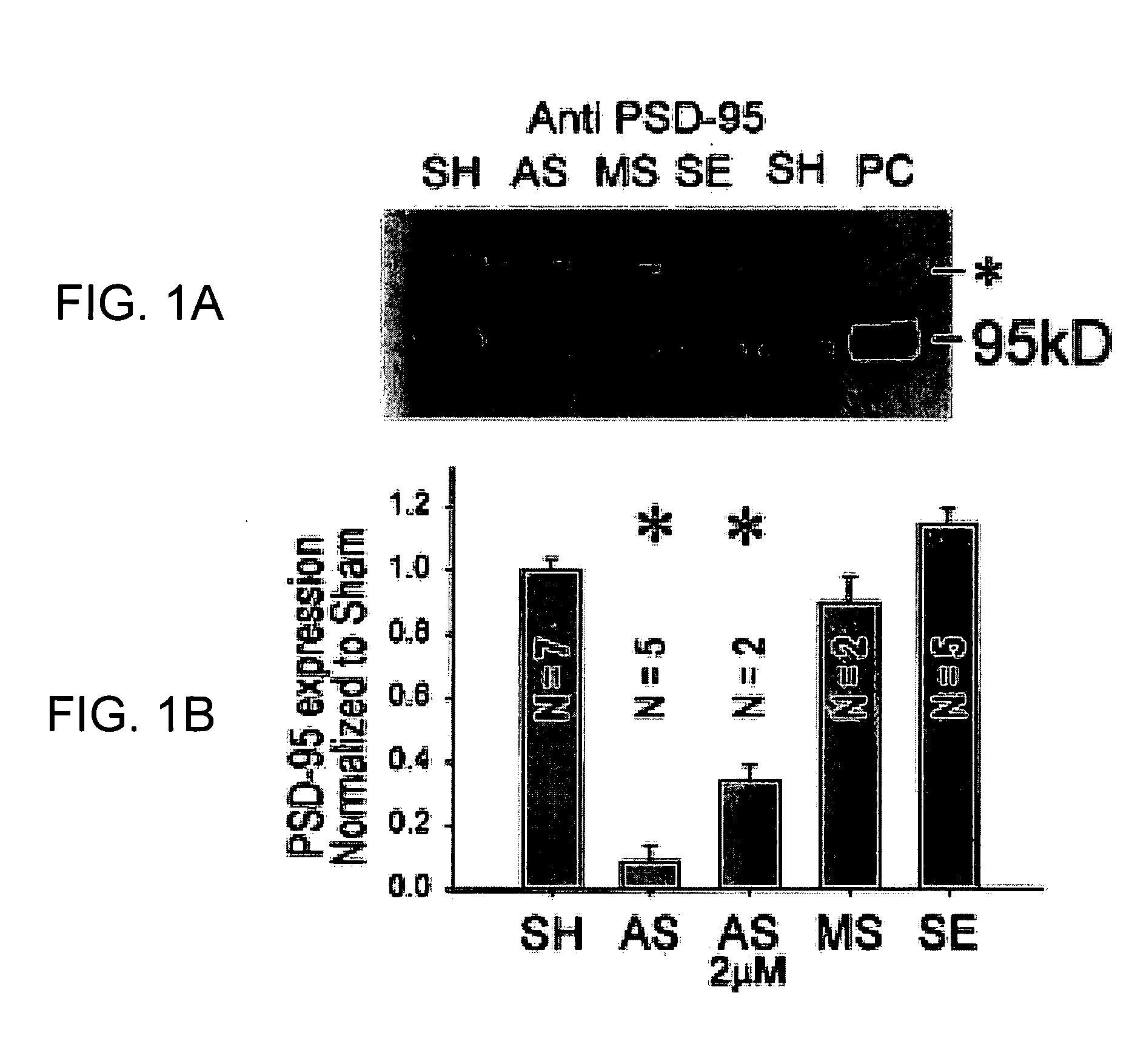
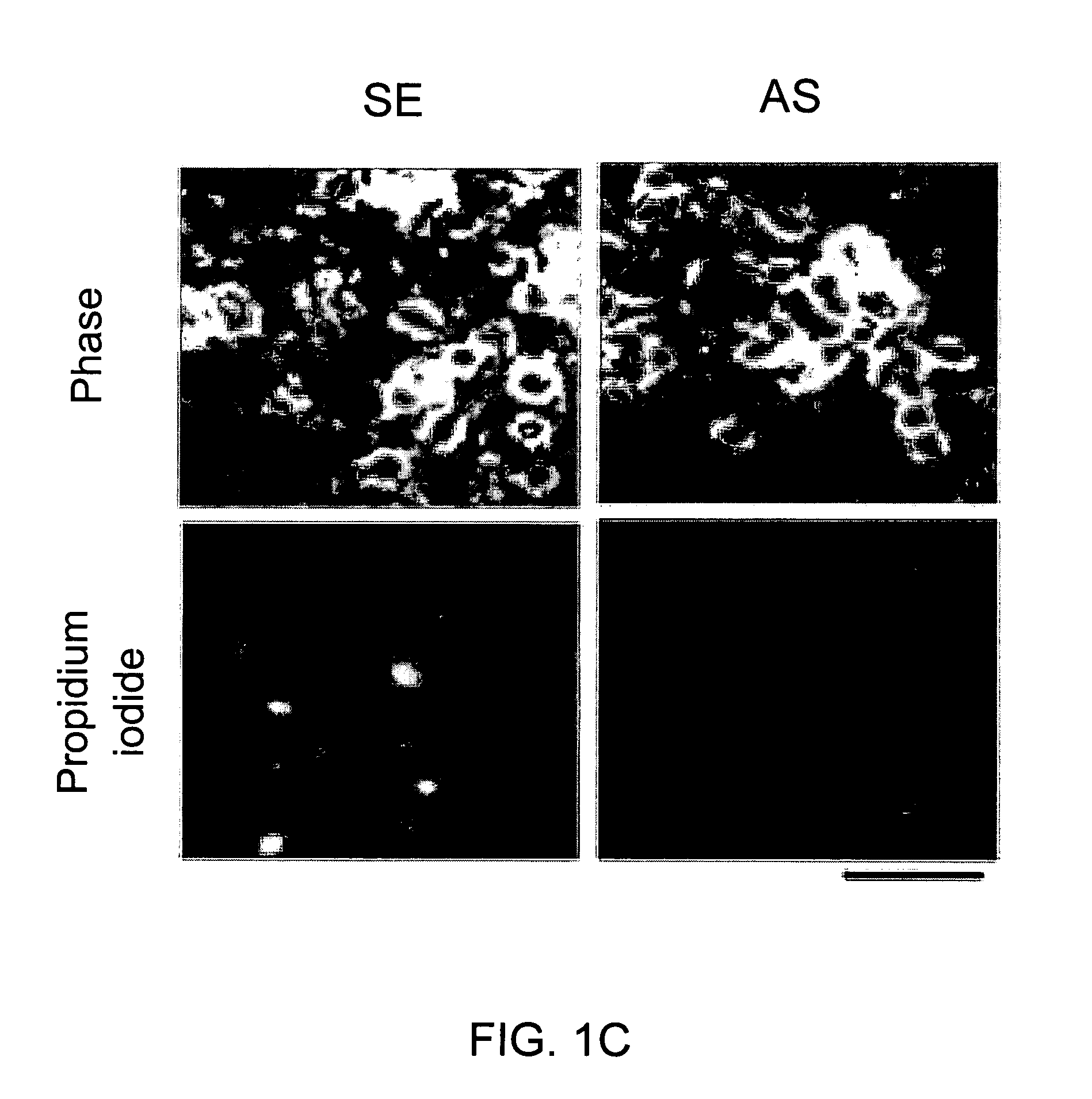
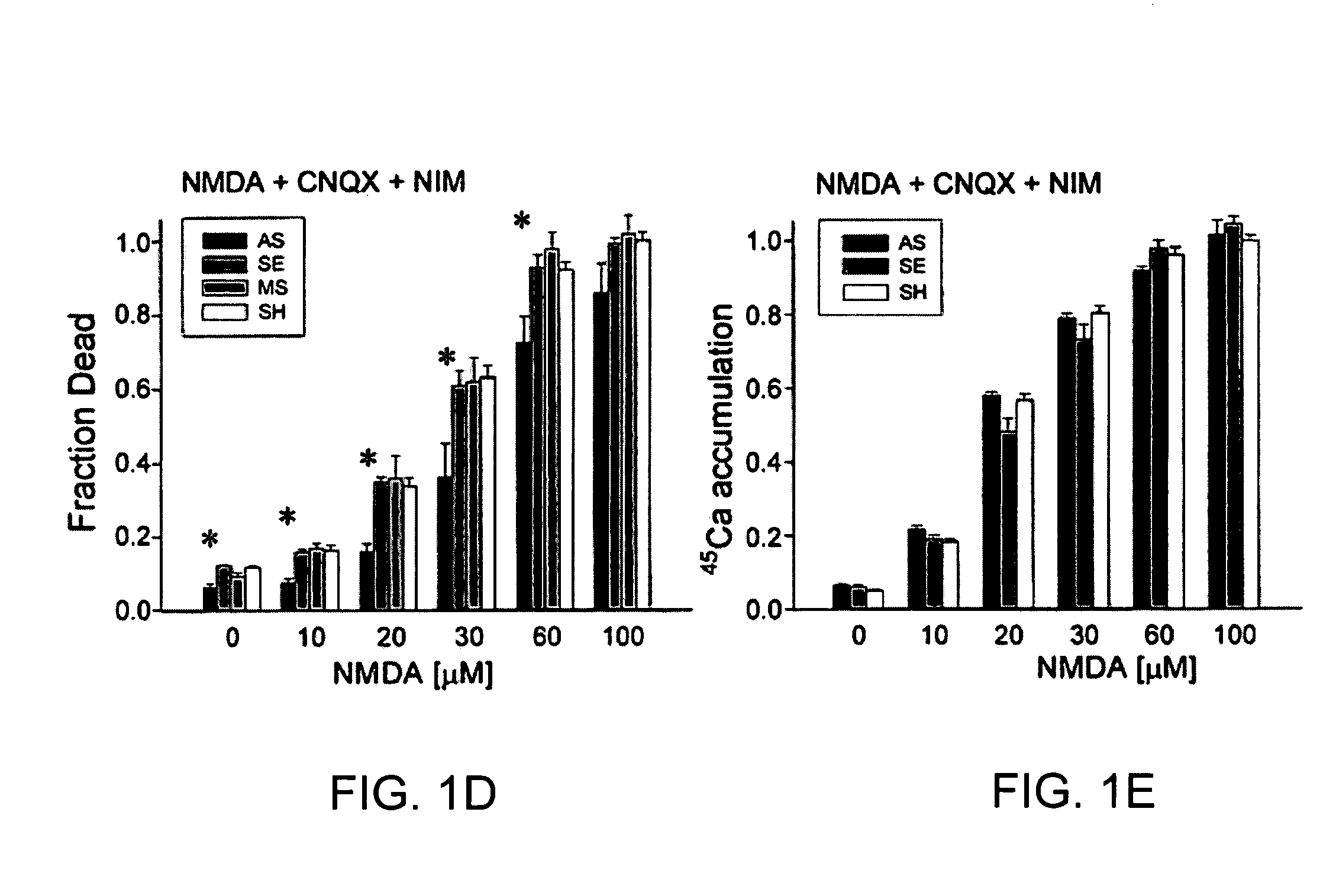
Method of reducing injury to mammalian cells
InactiveUS20050059597A1Attenuated downstream NMDAR signalingReduced infarct volumeNervous disorderCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsNR1 NMDA receptorN methyl D aspartate receptors
A method of inhibiting the binding between N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors and neuronal proteins in a neuron is disclosed. The method comprises administering to the neuron an effective inhibiting amount of a peptide replacement agent for the NMDA receptor or neuronal protein interaction domain that effect said inhibition of the NMDA receptor—neuronal protein interaction. The method is of value in reducing the damaging effect of injury to mammalian cells. Postsynaptic density-95 protein (PSD-95) couples neuronal N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) to pathways mediating excitotoxicity, ischemic and traumatic brain damage. This coupling was disrupted by transducing neurons with peptides that bind to modular domains on either side of the PSD-95 / NMDAR interaction complex. This treatment attenuated downstream NMDAR signaling without blocking NMDAR activity, protected cultured cortical neurons from excitotoxic insults, dramatically reduced cerebral infarction volume in rats subjected to transient focal cerebral ischemia, and traumatic brain injury (TBI) in rats.
Owner:NONO INC
Arrhythmia discrimination using electrocardiograms sensed from multiple implanted electrodes
Cardiac monitoring and / or stimulation methods and systems provide for monitoring, diagnosing, defibrillation and pacing therapies, or a combination of these capabilities, including cardiac systems incorporating or cooperating with neuro-stimulating devices, drug pumps, or other therapies. Embodiments of the present invention relate generally to implantable medical devices employing automated cardiac activation sequence monitoring and / or tracking for arrhythmia discrimination. Embodiments of the invention are directed to devices and methods involving sensing a plurality of composite cardiac signals using a plurality of implantable electrodes. A source separation is performed using the sensed plurality of composite cardiac signals and the separation produces one or more cardiac signal vectors associated with one or more cardiac activation sequences that is indicative of ischemia. A change of the one or more cardiac signal vectors is detected using the one or more cardiac signal vectors. Cardiac arrhythmias are discriminated using the one or more cardiac signal vectors.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Methods and systems for treating ischemia
InactiveUS6435189B1Promote dissolution and removalMinimize and prevent ischemiaStentsBalloon catheterControl mannerDecreased mean arterial pressure
Methods for treating total and partial occlusions employ a perfusion conduit which is penetrated through the occlusive material. Oxygenated blood or other medium is then perfused through the conduit in a controlled manner, preferably at a controlled pressure below the arterial pressure, to maintain oxygenation and relieve ischemia in tissue distal to the occlusion. In another aspect, interventional devices, such as stents or balloon catheters, are passed through the perfusion catheter to remove obstructions. Optionally, the occlusion may be treated while perfusion is maintained, typically by introducing a thrombolytic or other agent into the occlusive material using the perfusion conduit or by employing mechanical means to remove the obstruction. Such methods are particularly suitable for treating acute stroke to prevent damage to the cerebral tissue.
Owner:SALIENT INTERVENTIONAL SYST
Embolectomy catheters and methods for treating stroke and other small vessel thromboembolic disorders
InactiveUS7691121B2Prevent and minimize severityEasy extractionStentsDilatorsThrombosis embolismThromboembolic disorder
Embolectomy catheters, rapid exchange microcatheters, systems and methods for removing clots or other obstructive matter (e.g., thrombus, thromboemboli, embolic fragments of atherosclerotic plaque, foreign objects, etc.) from blood vessels. This invention is particularly useable for percutaneous removal of thromboemboli or other obstructive matter from small blood vessels of the brain, during an evolving stroke or period of cerebral ischemia. In some embodiments, the embolectomy catheters of this invention are advanceable with or over a guidewire which has been pre-inserted through or around the clot. Also, in some embodiments, the embolectomy catheters include clot removal devices which are deployable from the catheter after the catheter has been advanced at least partially through the clot. The clot removal device may included a deployable wire nest that is designed to prevent a blood clot from passing therethrough. The delivery catheter may include telescoping inner and outer tubes, with the clot removal device being radially constrained by the outer tube. Retraction of the outer tube removes the constraint on the clot removal device and permits it to expand to its deployed configuration. An infusion guidewire is particularly useful in conjunction with the embolectomy catheter, and permits infusion of medicaments or visualization fluids distal to the clot.
Owner:MICROVENTION INC
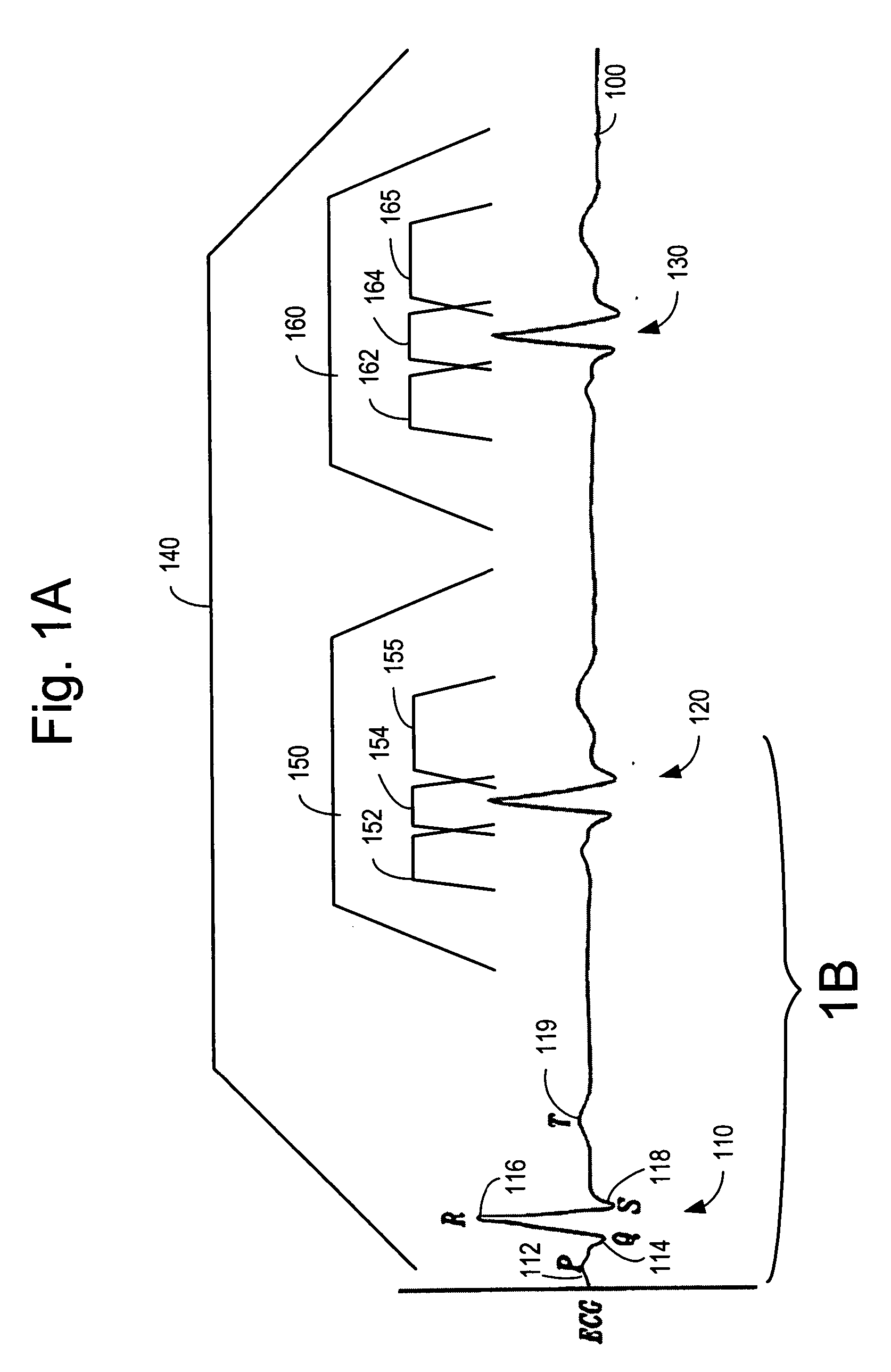
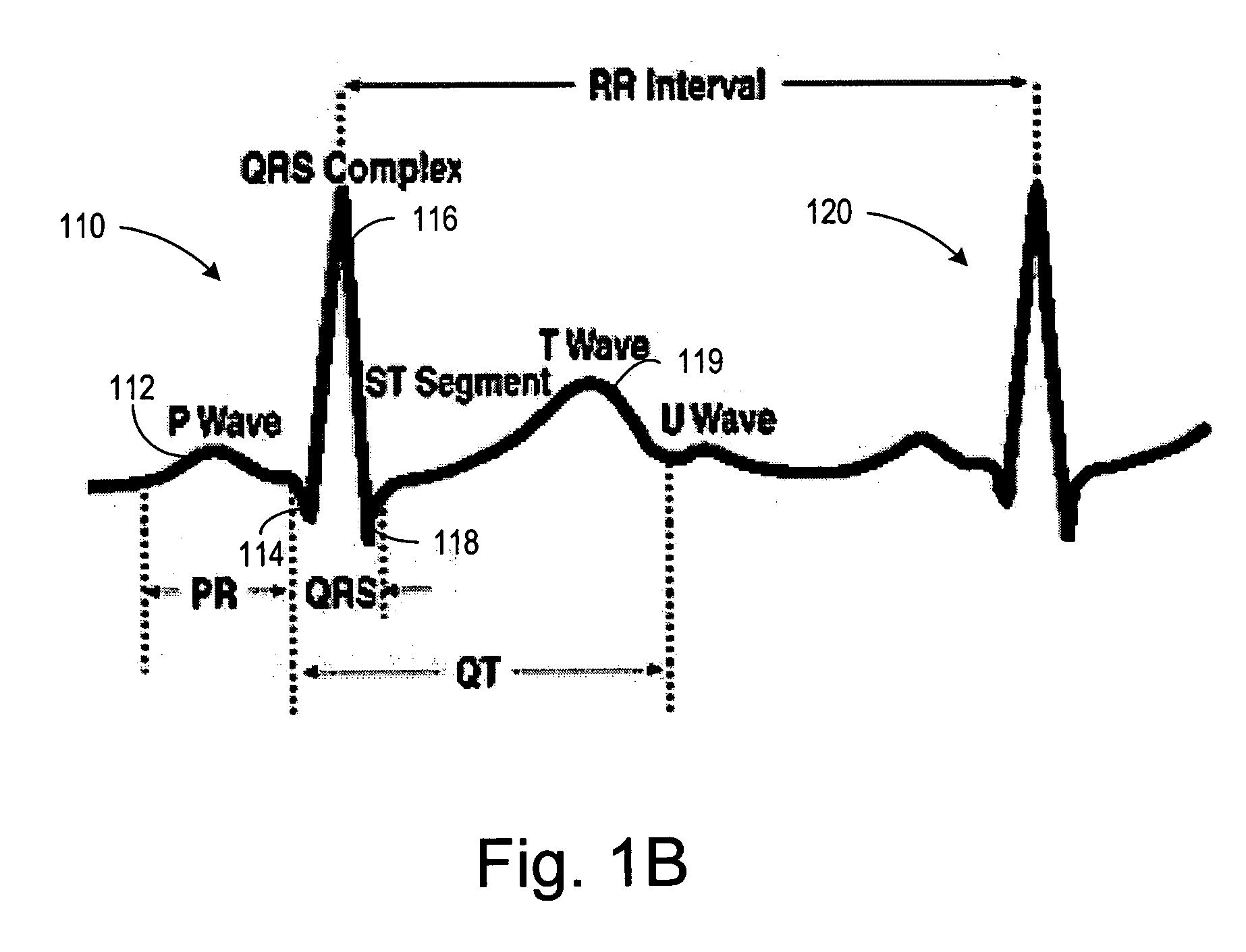
Heart disease detection patch
InactiveUS20060030782A1Inexpensive and simple to useSuitable for self-administrationElectrocardiographySensorsFibrillationNon invasive
The invention provides a disposable sensor patch for the non-invasive detection of heart disease. The patch is placed on a person's chest area for automatic analysis of ECG. The heart condition is indicated via an indicator integrated within the patch. The patch is inexpensive and simple for self-administration. In one embodiment, the status of the heart is indicated via multiple LEDs. The detection and indication typically occurs, within 24 hours or sooner if a condition is readily identifiable. The patch is thin, flexible, and incorporates a battery, ECG amplifier, and a processor for analyzing ECG waveform and indicating the heart condition. A software algorithm searches for a cardiac abnormality such as arrhythmia, bradycardia, tachycardia, fibrillation, mycocardial infarction, ischemia, long-QT syndrome, blocks, late potentials, and premature contractions. In another embodiment, results and relevant ECG data are stored in memory for later retrieval.
Owner:CARDIOVU
Segmented pneumatic pad for regulating pressure upon parts of the body during usage
InactiveUS20050154336A1Accommodatable for travelSimple designStuffed mattressesPneumatic massageAfter treatmentBody contact
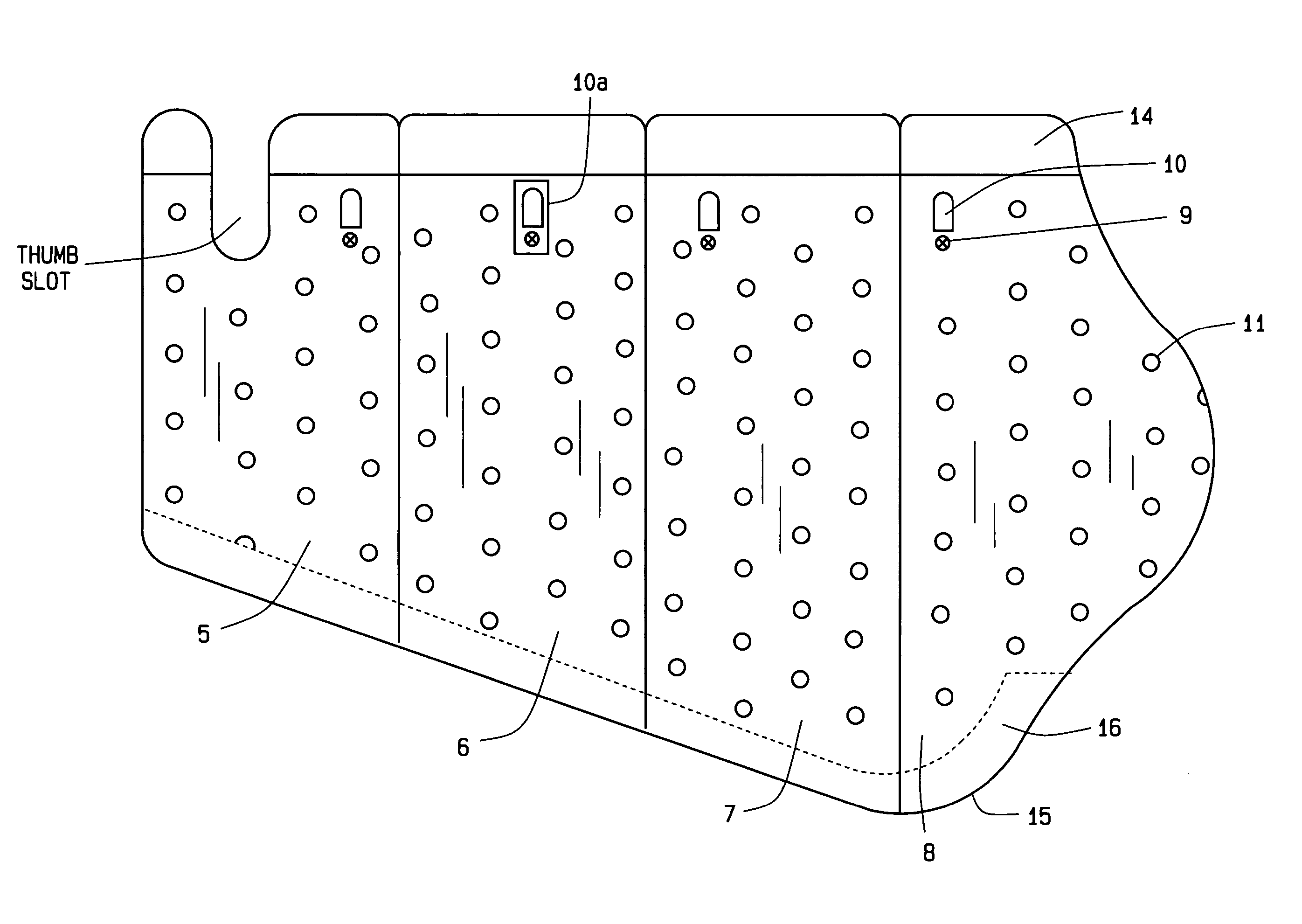
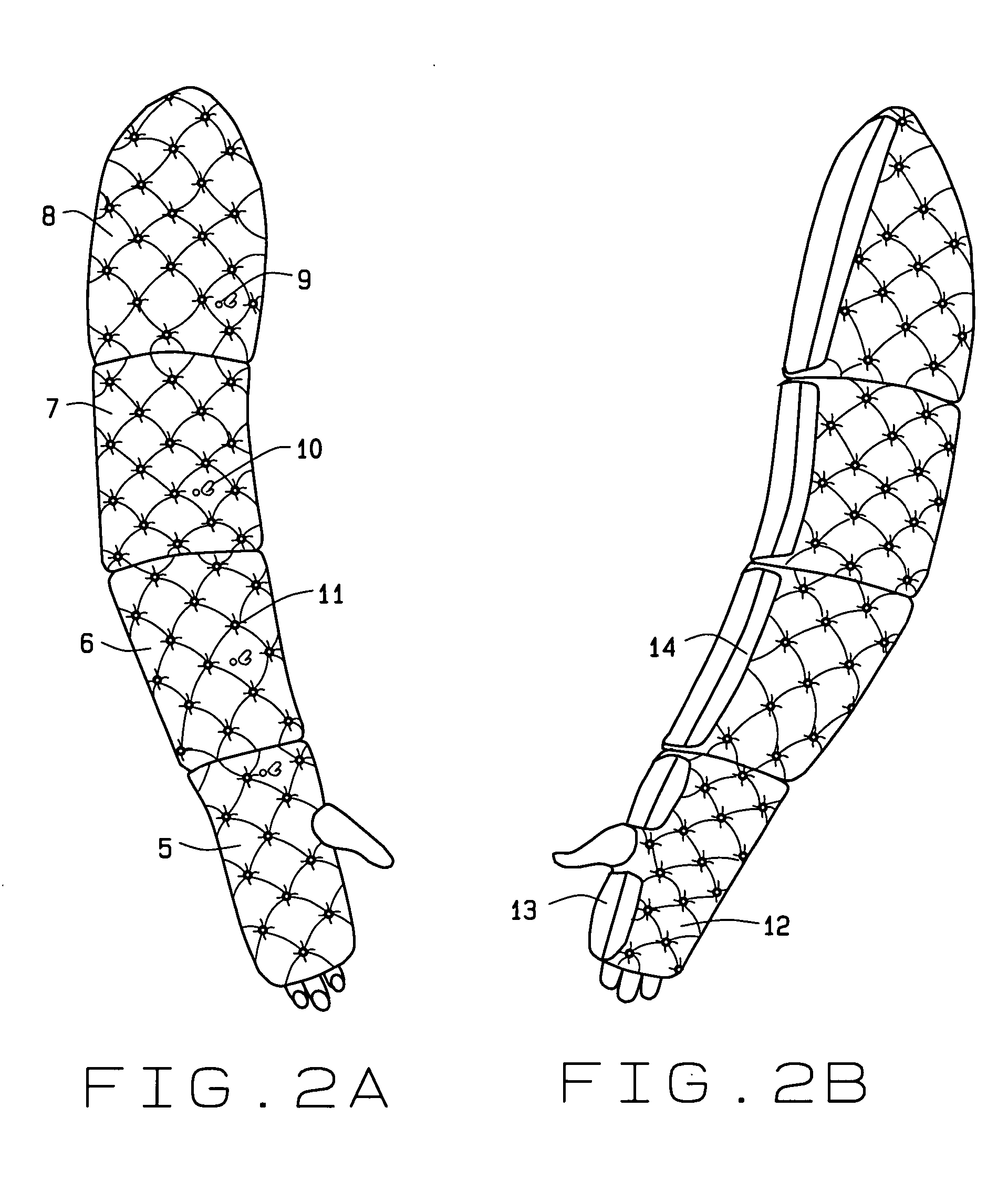
A compression garment for selective application for treatment of lymphedema and prevention of local ischemia of tissues at various locations of the body. The garment includes a pair or series of layers of hermetically sealed material, that can capture pressurized air, when applied therein, and is formed through the patterned sealing of the layers of the garment together, at select locations, to form air pockets that can selectively apply isolated points of pressure to the patient's affected area, without disrupting normal vascular and lymphatic functioning. The garment is design cut, for application to various segments of the body, and applies encompassing pressure over the entire affected area, and includes valves that can allow for the injection of measurable air, to the desired pressure points, or its deflation, after treatment. The compression device of this invention may also be formed as a segmented pad or mat, into which pneumatic pressurized air may be applied, at various segments, so as to regulate the amount of pressure applied to the surface of the body that is in contact with the pad or mat of this invention.
Owner:KLOECKER RICHARD J +2
Ultrasound Apparatus and Method to Treat an Ischemic Stroke
InactiveUS20080262350A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyTransducerIschemic stroke
Owner:CEREVAST THERAPEUTICS
Methods and systems for treating ischemia
InactiveUS6436087B1Promote dissolution and removalMinimize and prevent ischemiaStentsBalloon catheterControl mannerThrombus
Methods for treating total and partial occlusions employ a perfusion conduit which is penetrated through the occlusive material. Oxygenated blood or other medium is then perfused through the conduit in a controlled manner, preferably at a controlled pressure below the arterial pressure, to maintain oxygenation and relieve ischemia in tissue distal to the occlusion. In another aspect, interventional devices, such as stents or balloon catheters, are passed through the perfusion catheter to remove obstructions. Optionally, the occlusion may be treated while perfusion is maintained, typically by introducing a thrombolytic or other agent into the occlusive material using the perfusion conduit or by employing mechanical means to remove the obstruction. Such methods are particularly suitable for treating acute stroke to prevent damage to the cerebral tissue.
Owner:SALIENT INTERVENTIONAL SYST
Systems and methods for replacing signal artifacts in a glucose sensor data stream
ActiveUS20120203467A1Accurate detectionAvoid adjustmentMedical automated diagnosisCatheterRate limitingDiffusion
Systems and methods for minimizing or eliminating transient non-glucose related signal noise due to non-glucose rate limiting phenomenon such as interfering species, ischemia, pH changes, temperatures changes, known or unknown sources of mechanical, electrical and / or biochemical noise, and the like. The system monitors a data stream from a glucose sensor and detects signal artifacts that have higher amplitude than electronic or diffusion-related system noise. The system processes some or the entire data stream continually or intermittently based at least in part on whether the signal artifact event has occurred.
Owner:DEXCOM INC
Extraction process of tanshin general phenolic acid and its prepn and use
InactiveCN1384090ASimple processSimple regenerationPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsSalvia miltiorrhizaVascular disease
The present invention relates to extraction process of total tanshin phenolic acid, the preparation process and application of its preparation. The total tanshin phenolic acid and its preparation mayuse in preparing medicine for preventing and treating cardiac and cerebral vascular diseases, senile dementia and hypomnesia caused by cerebral ischemia. The total tanshin phonelic acid prepared based on the process of the present invention has rich active components of tanshin and obvious pharmacological effect, stable performance and les stoxicity and is safety and reliable.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA AN INST OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI +1
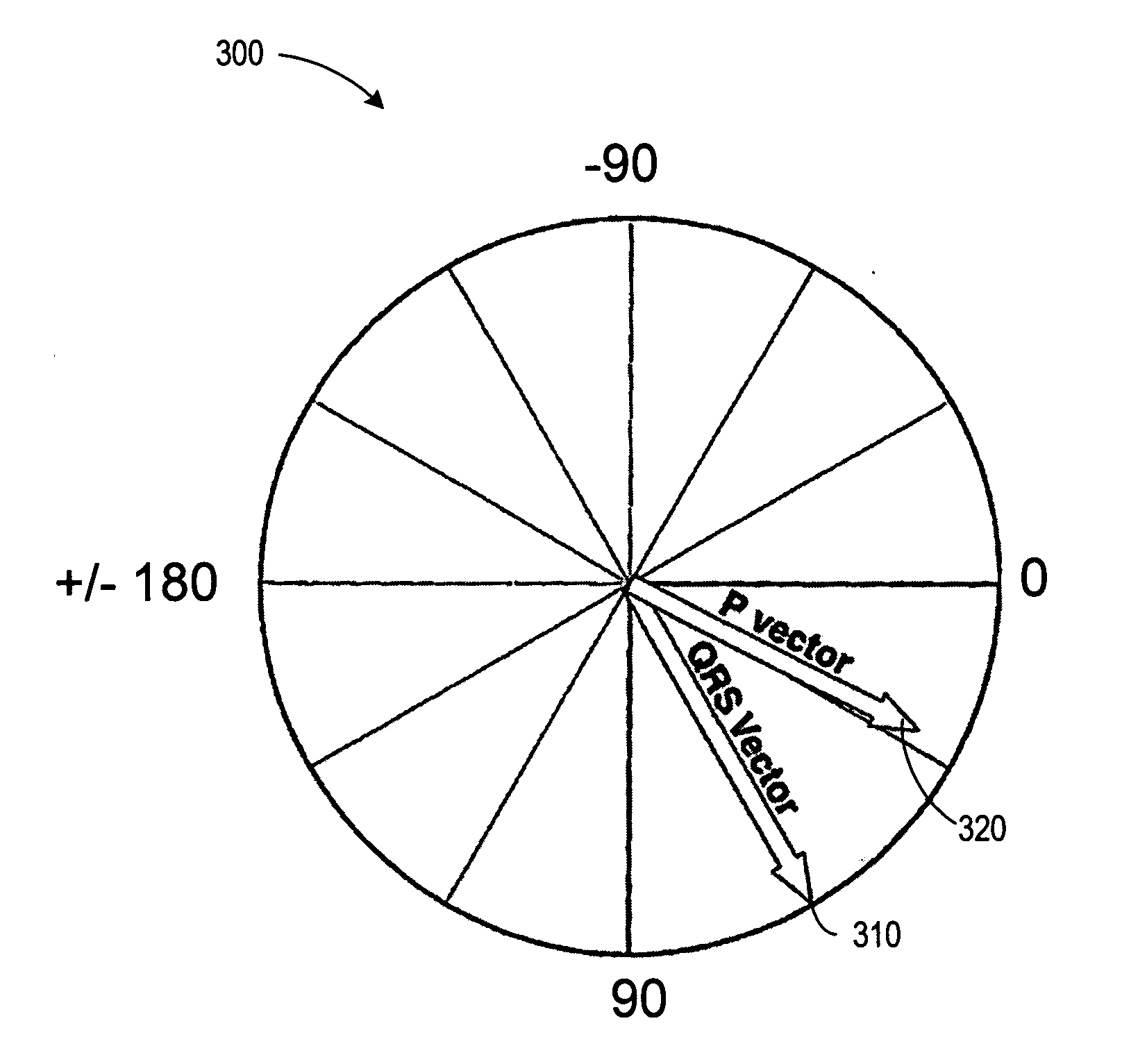
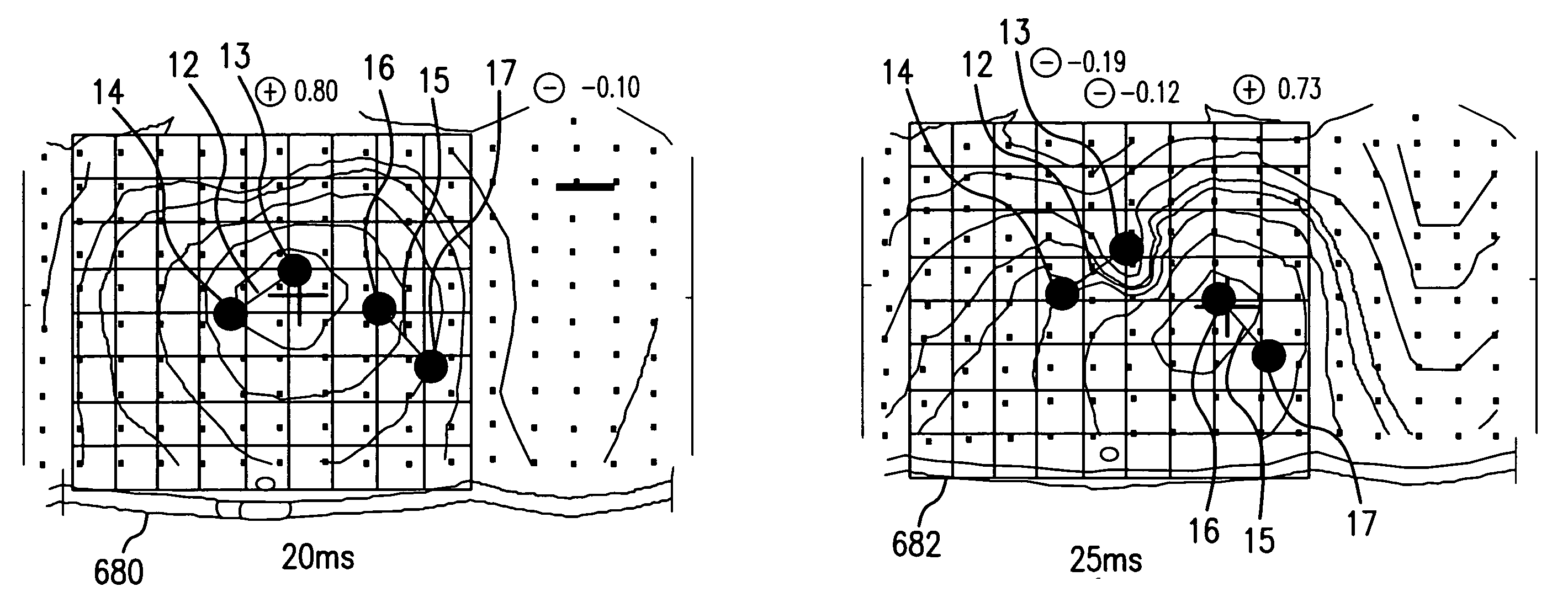
System and methods for detecting ischemia with a limited extracardiac lead set
Disclosed is a system for detecting pathophysiological cardiac conditions from a reduced number of extracardiac leads. A right side lead measures the electrical signal between the middle superior chest region over the heart and inferior right torso position. A left side lead measures the electrical signal between the left precordial chest region and an inferior left lateral or posterior torso position. The lead montage is preferably chosen so that, regardless of patient position (e.g. supine, upright), negative ST segments and / or T waves are used to detect right coronary or left circumflex ischemia. Also, in these positions, reduced slope of the final deflection in the QRS can be used to detect these types of ischemia. To detect transmural ischemia, the system examines changes in QRS slopes, ST segment, T wave and the difference between the J point and the PQ potentials. In addition, for transmural ischemia associated with the left anterior descending artery, a proxy for the propagation time across the front of the heart is examined by comparing QRS features of the right side lead with QRS features of the left side lead. Histogram profiles, trends, and statistical summaries, especially running averages, of all of the above mentioned features, corrected for heart rate, are maintained.
Owner:ANGEL MEDICAL SYST
System and methods for sliding-scale cardiac event detection
A system for the detection of cardiac events occurring in a human patient is provided. At least two electrodes are included in the system for obtaining an electrical signal from a patient's heart. An electrical signal processor is electrically coupled to the electrodes for processing the electrical signal. The system determines the presence of a cardiovascular condition by applying a sliding scale rule to heart signal feature values. When the cardiovascular condition is ischemia, the ST segment may be analyzed. A sliding scale is applied to ST segment shifts such that when the magnitudes of ST segment shifts are relatively small, a larger number of beats is required to detect ischemia compared to the case when the magnitudes of ST shifts are large.
Owner:ANGEL MEDICAL SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com