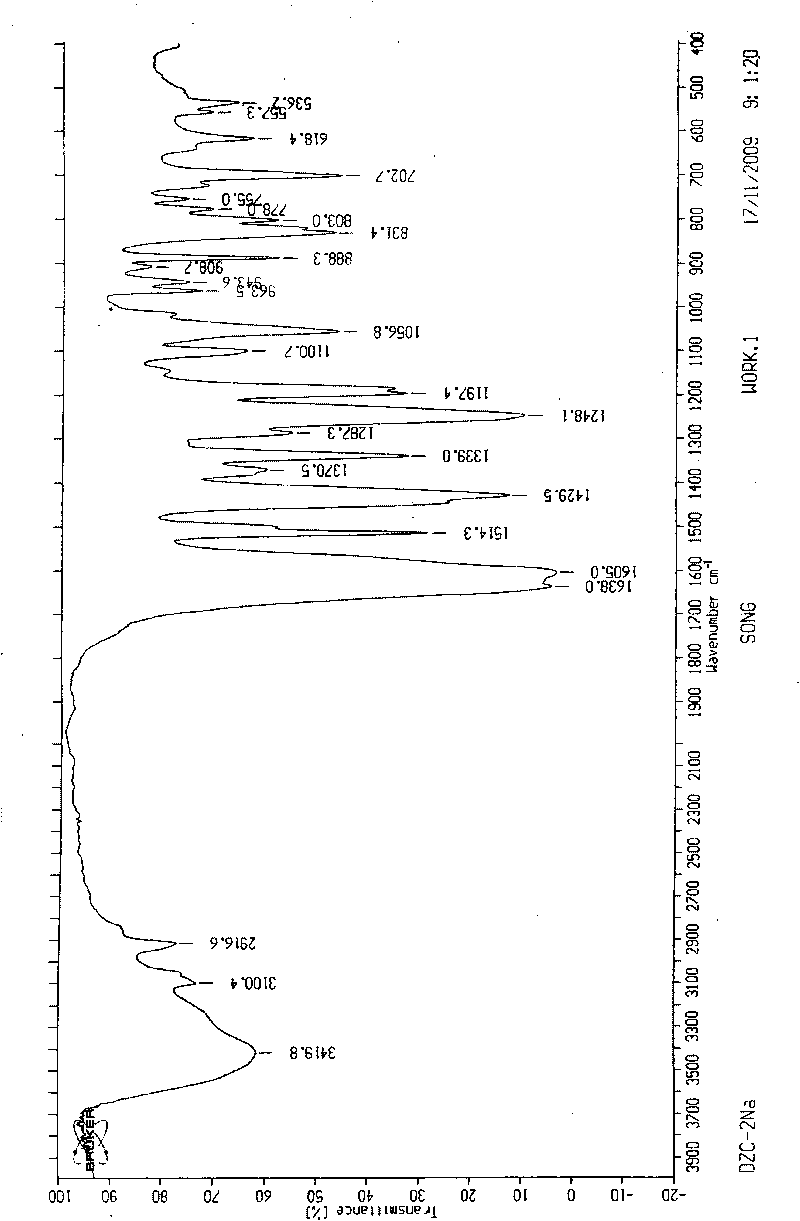
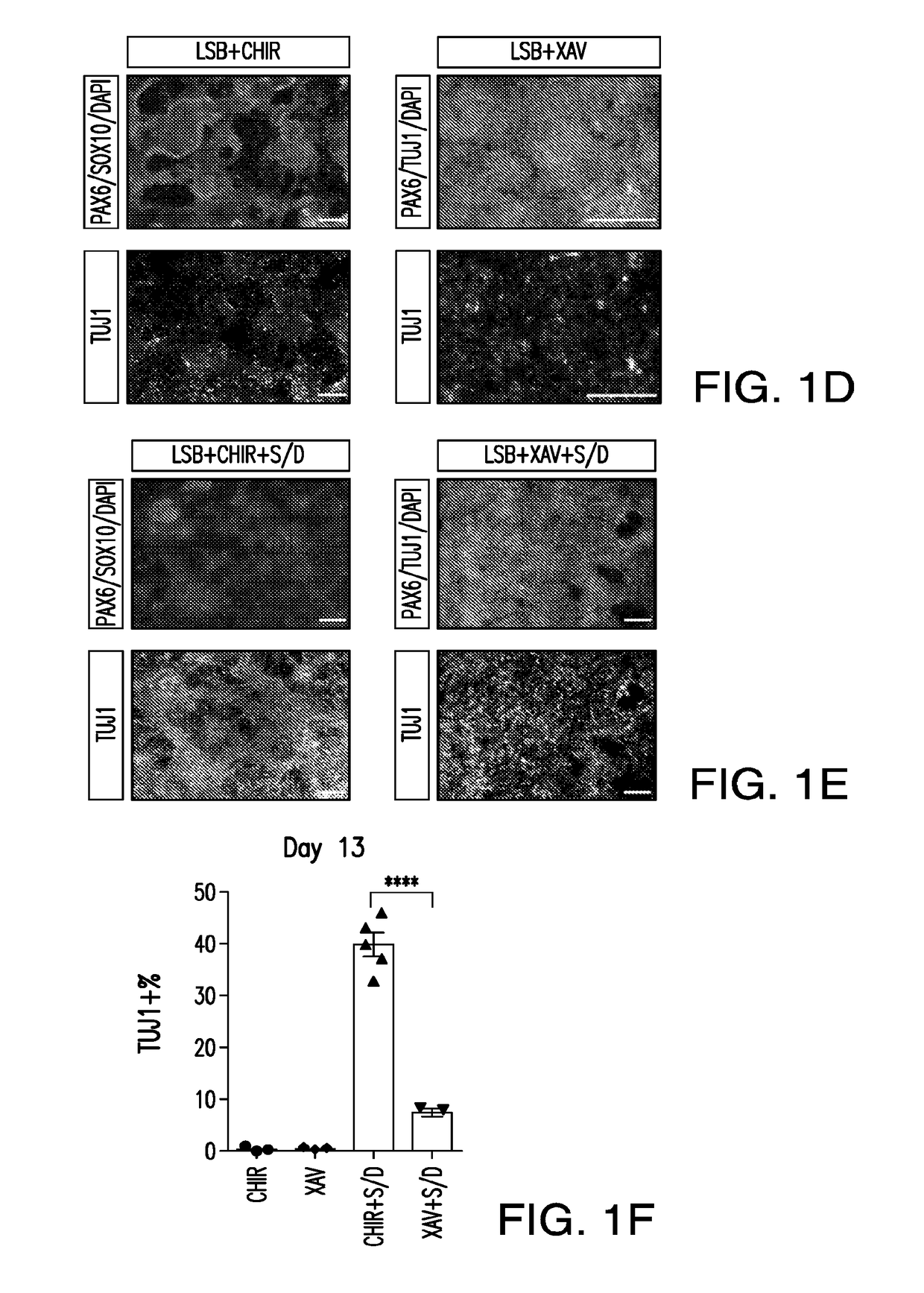
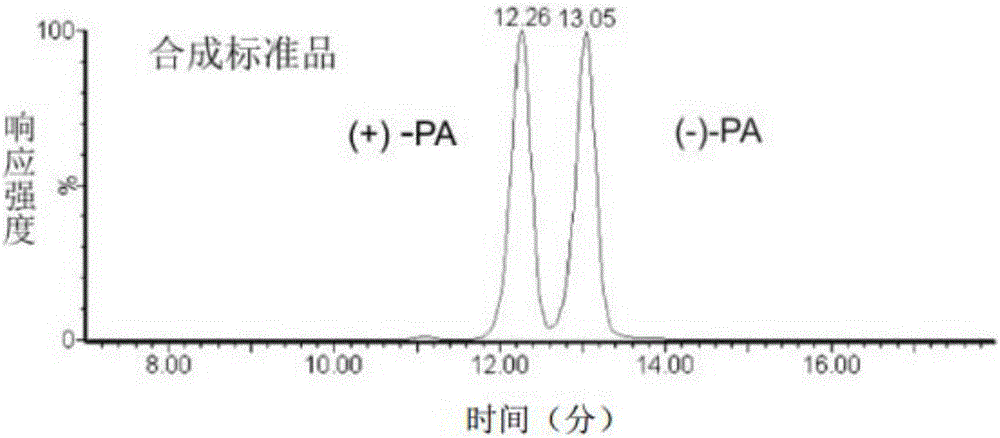
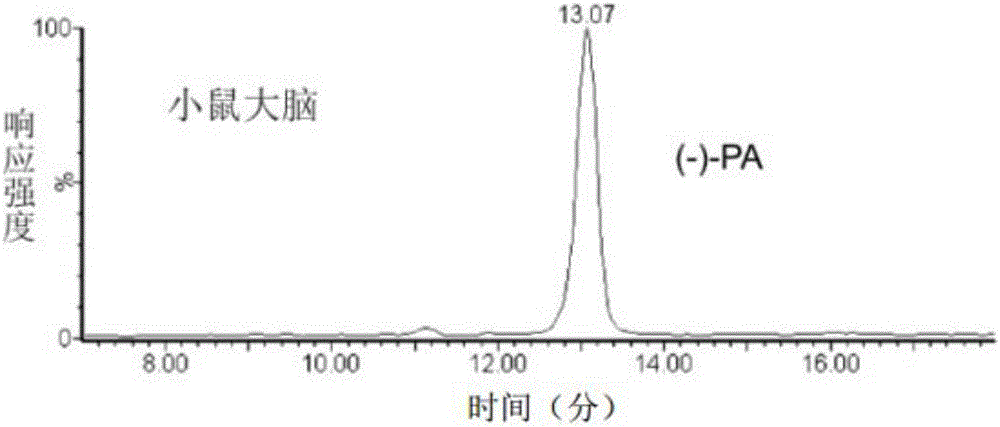
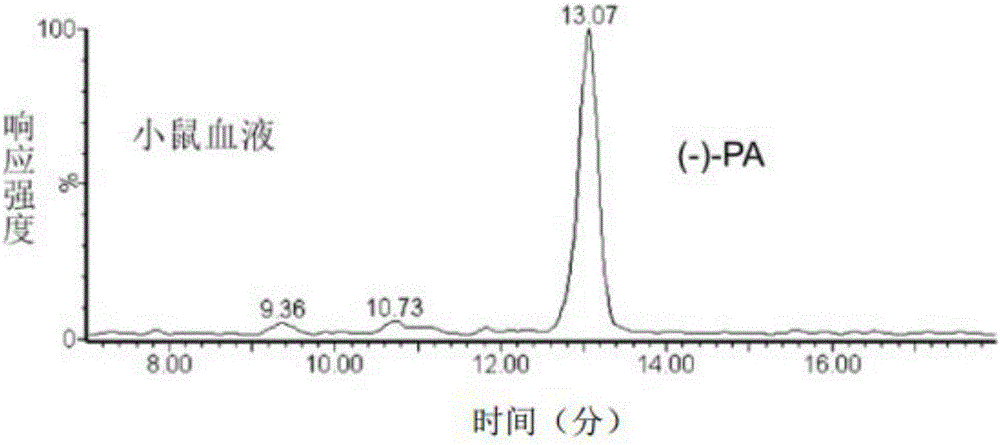
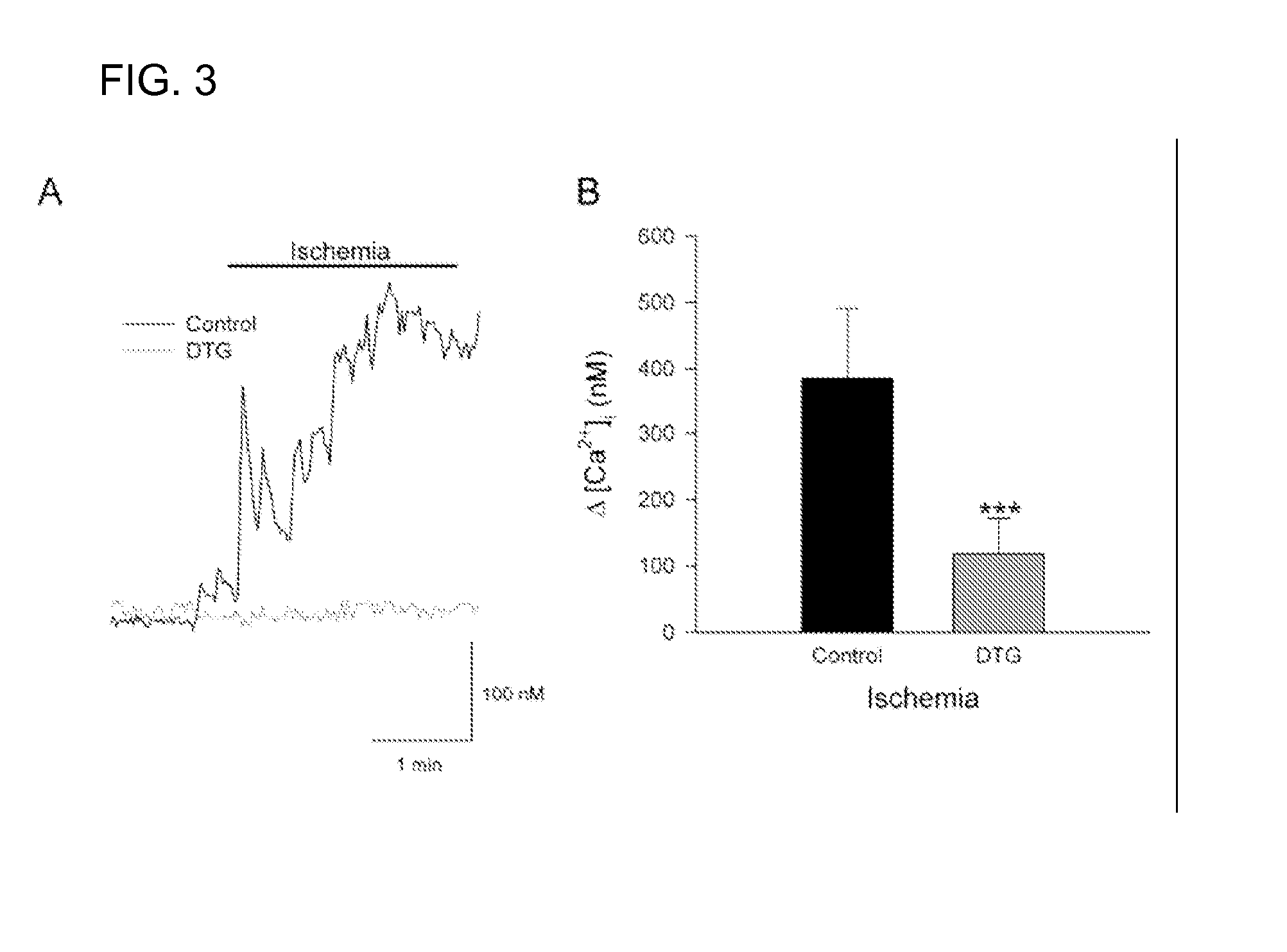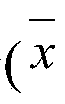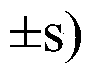Patents
Literature
51 results about "Cortical neurons" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cortical neurons are the cells of the brain's largest region, the two hemispheres of the cerebral cortex. Most of the complex activity of the brain enabling thought, perception, and voluntary movement is connected to the activity of these neurons.
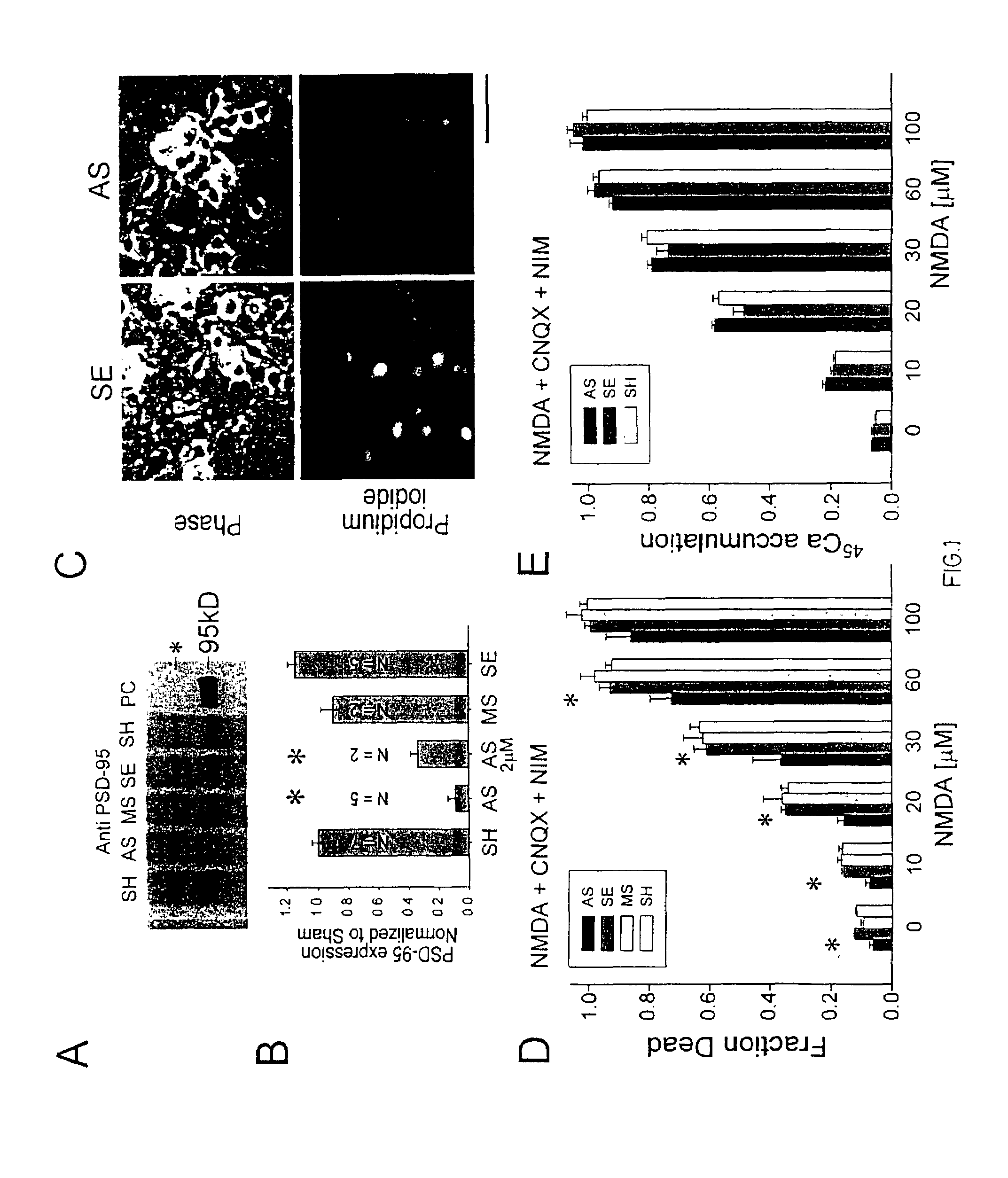
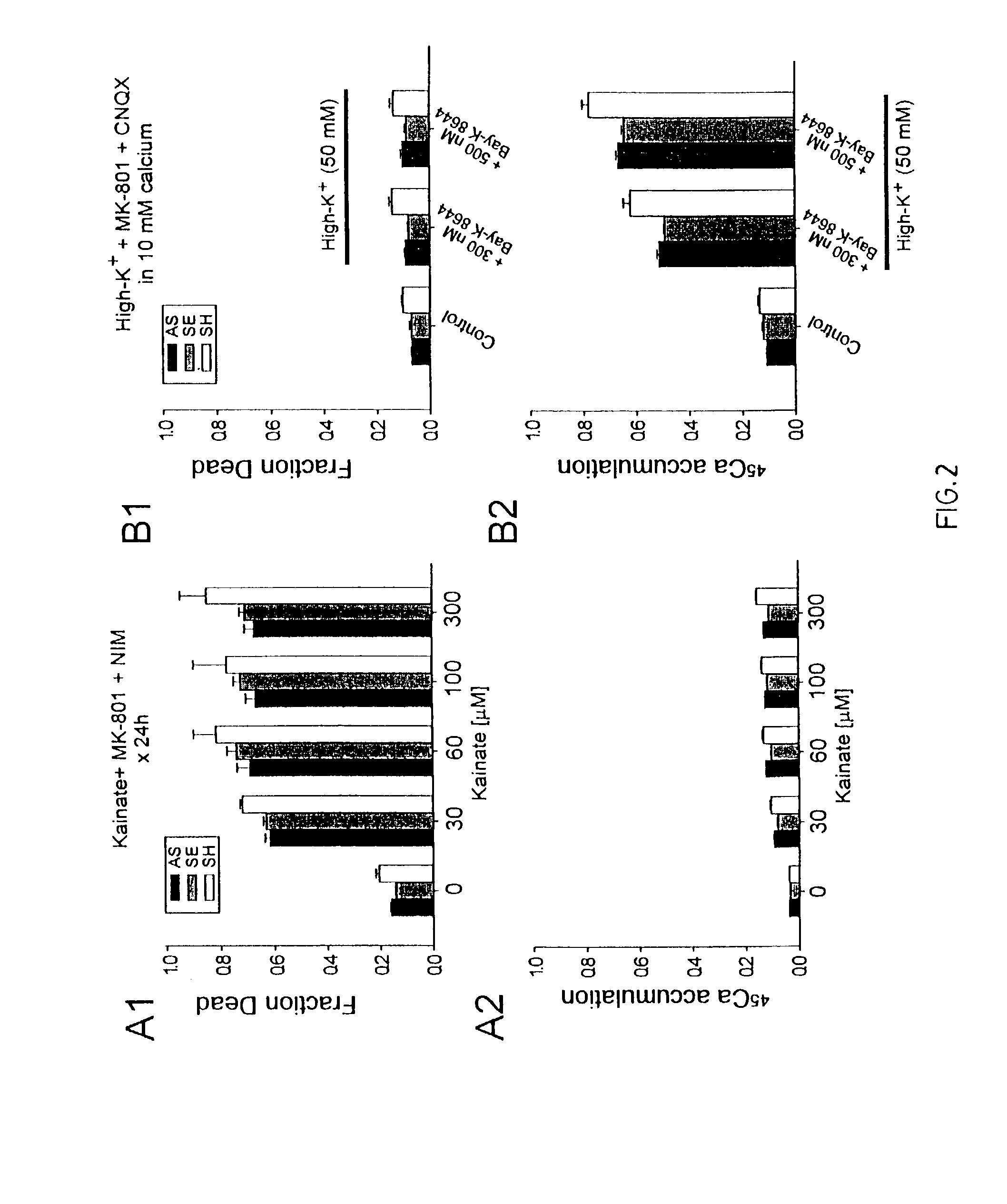
Method of reducing injury to mammalian cells
InactiveUS20050059597A1Attenuated downstream NMDAR signalingReduced infarct volumeNervous disorderCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsNR1 NMDA receptorN methyl D aspartate receptors
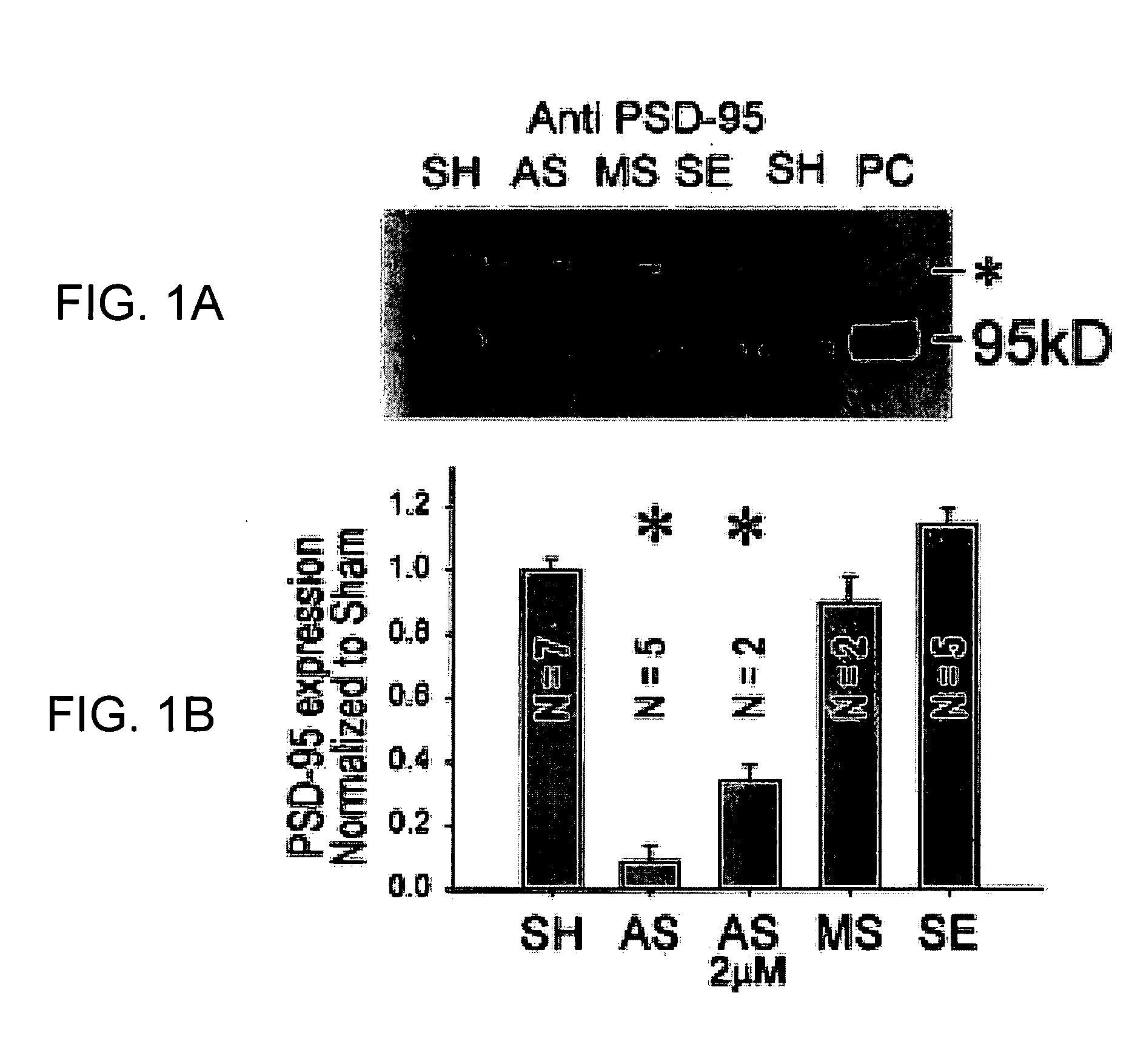
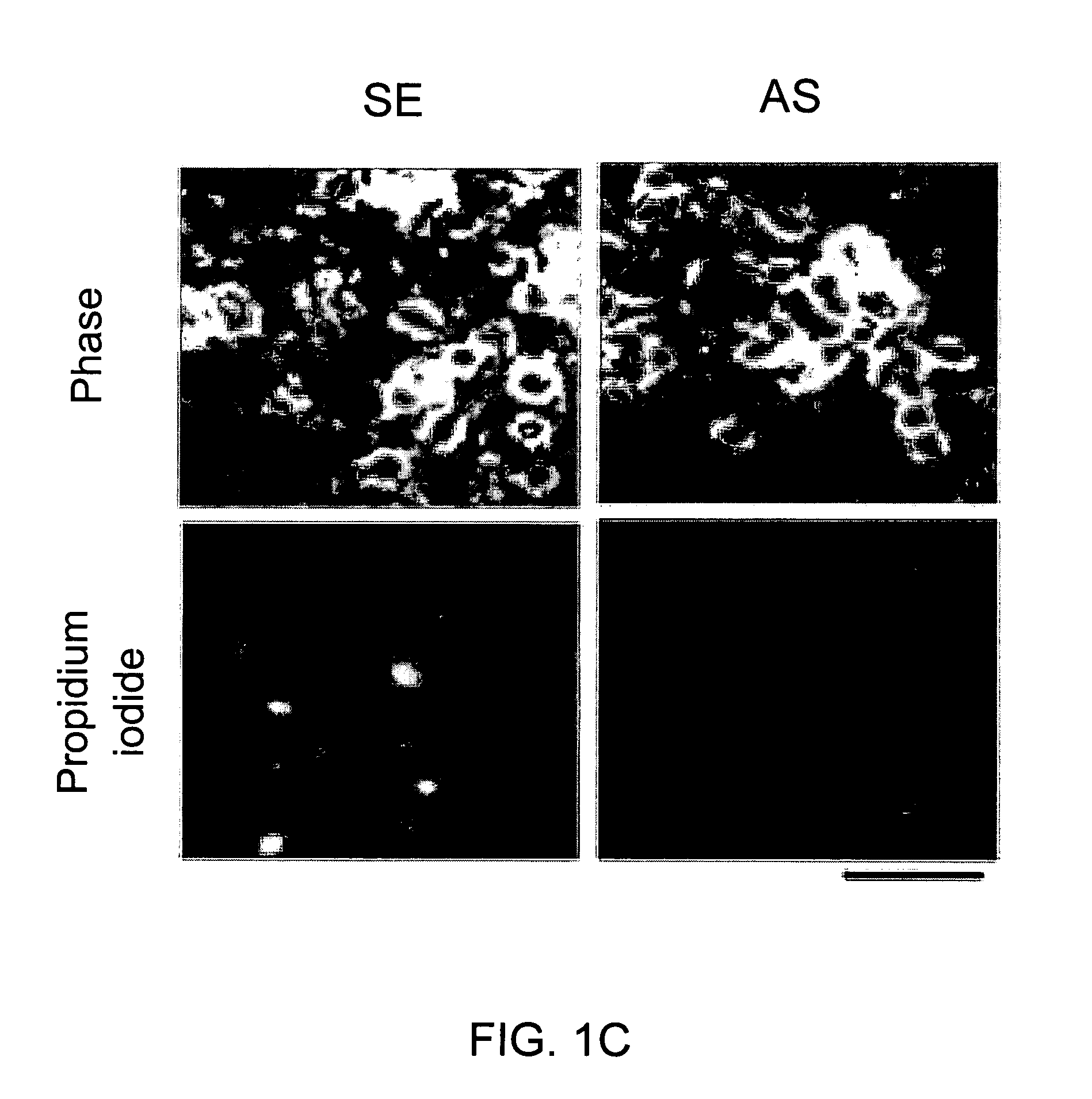
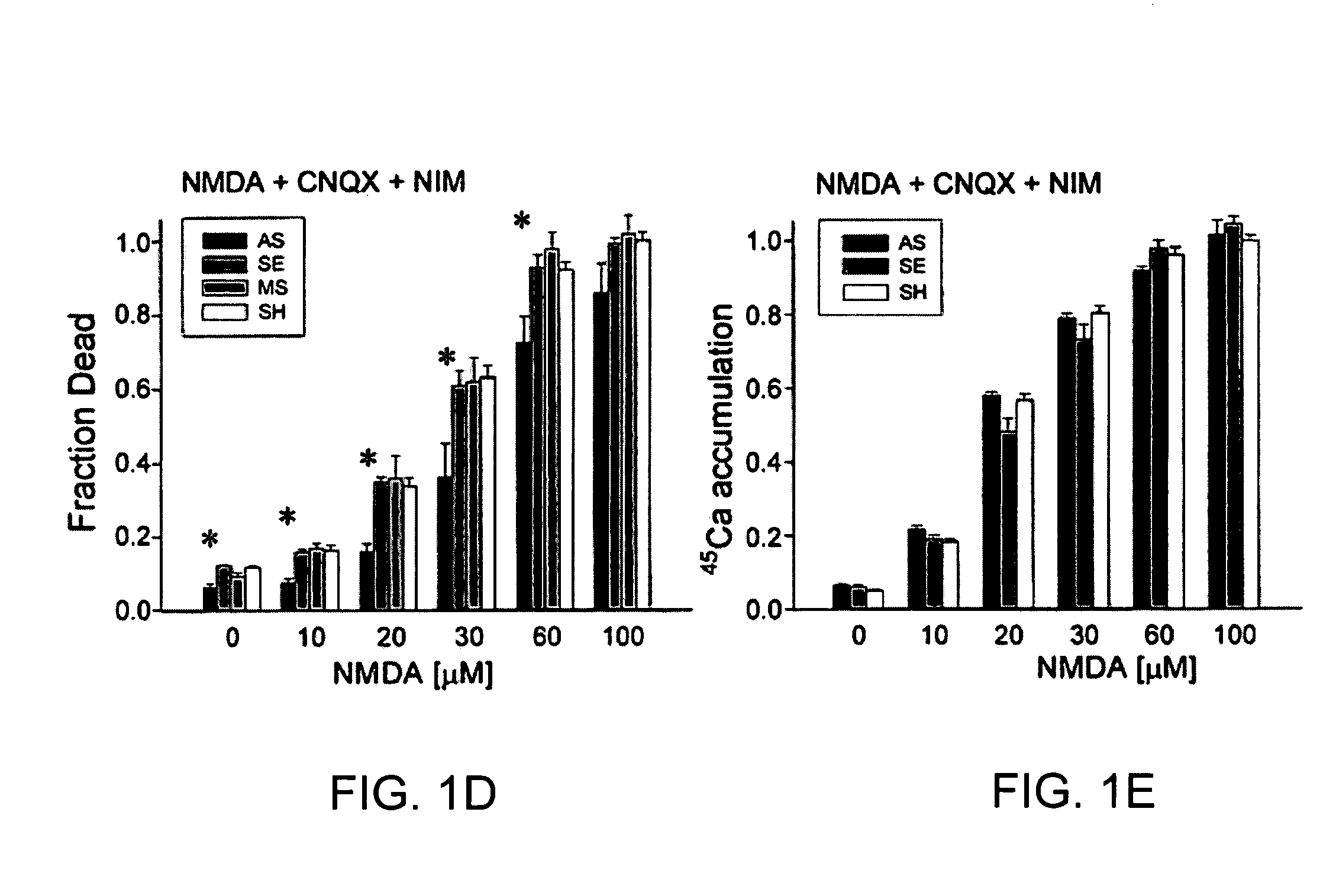
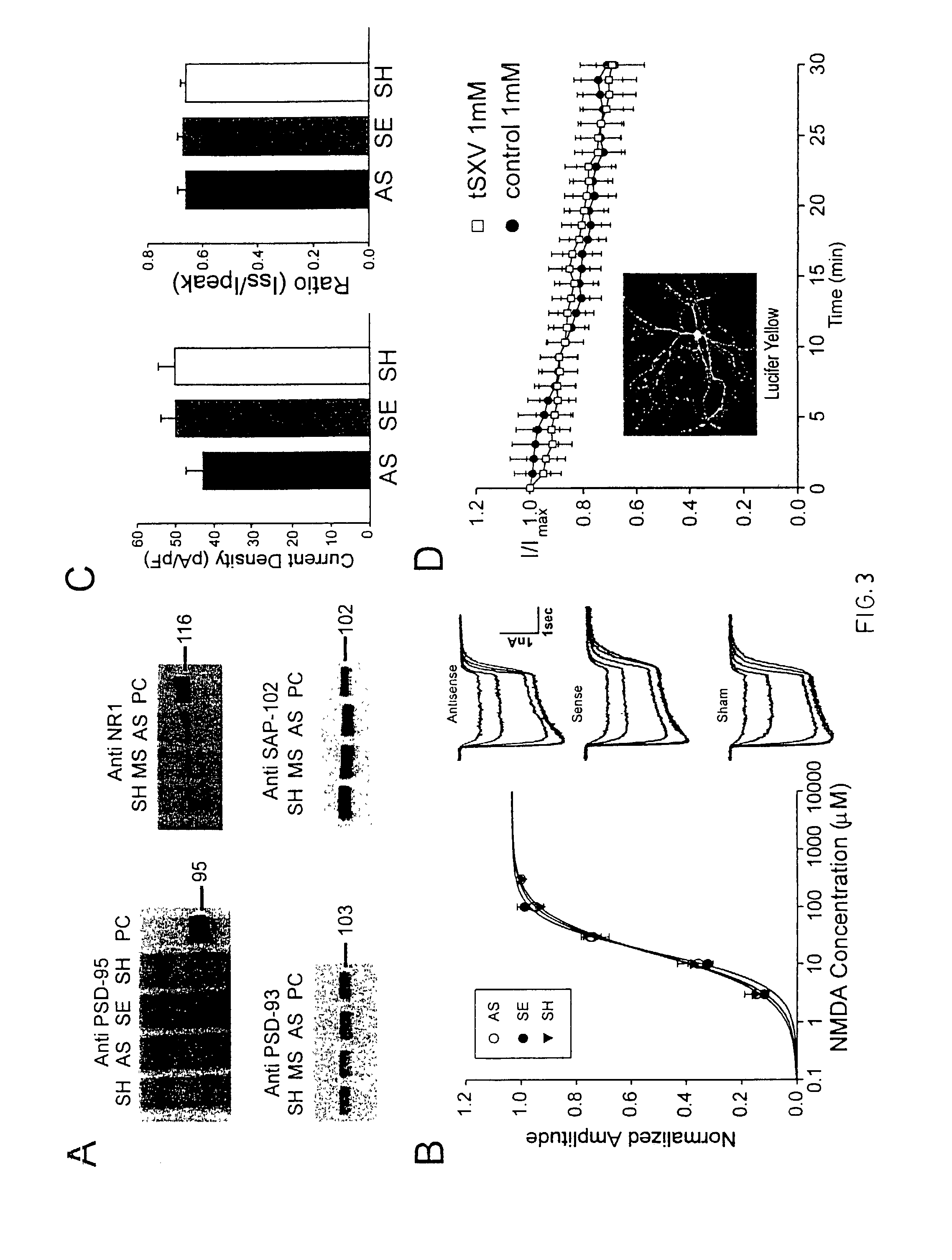
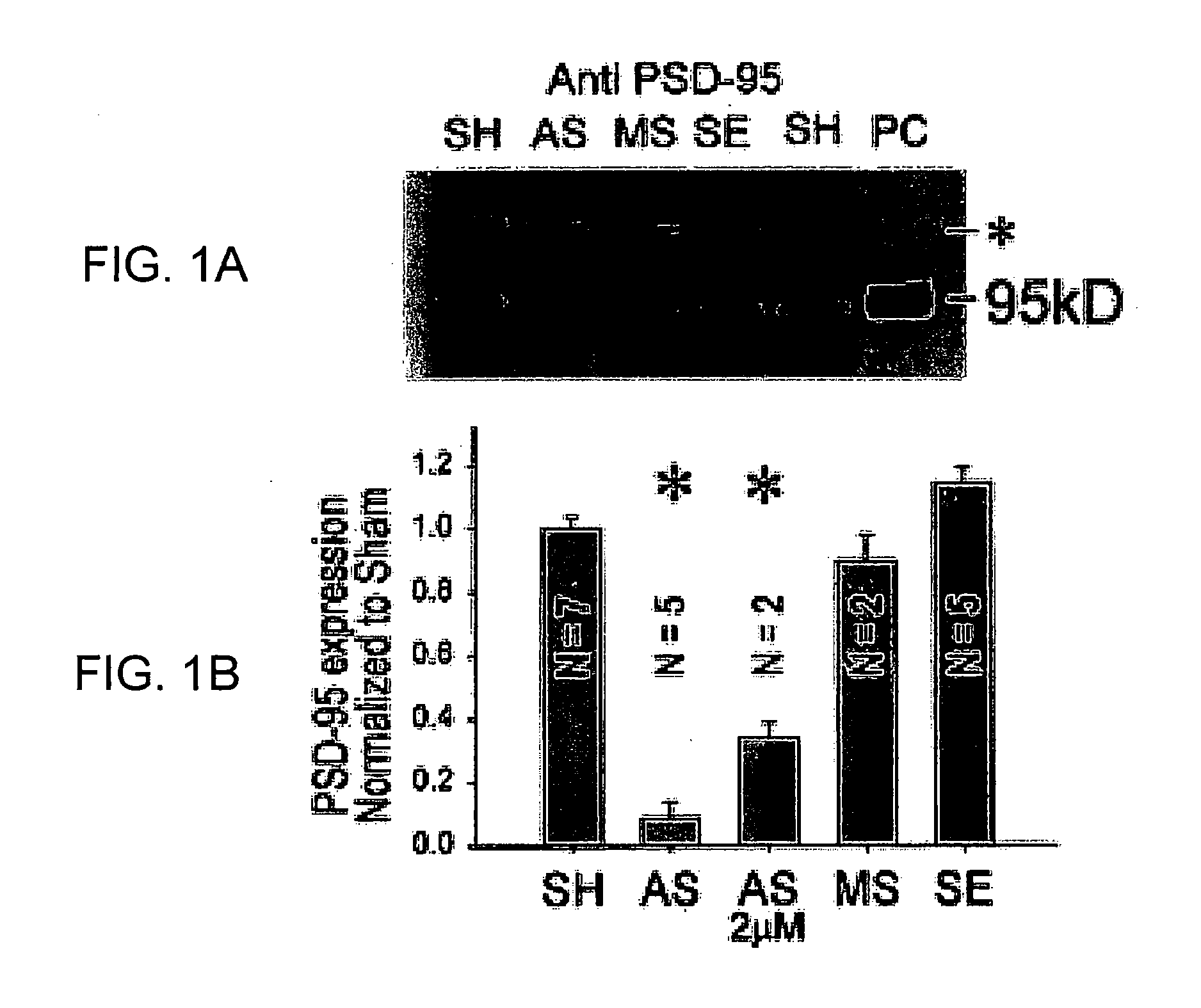
A method of inhibiting the binding between N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors and neuronal proteins in a neuron is disclosed. The method comprises administering to the neuron an effective inhibiting amount of a peptide replacement agent for the NMDA receptor or neuronal protein interaction domain that effect said inhibition of the NMDA receptor—neuronal protein interaction. The method is of value in reducing the damaging effect of injury to mammalian cells. Postsynaptic density-95 protein (PSD-95) couples neuronal N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) to pathways mediating excitotoxicity, ischemic and traumatic brain damage. This coupling was disrupted by transducing neurons with peptides that bind to modular domains on either side of the PSD-95 / NMDAR interaction complex. This treatment attenuated downstream NMDAR signaling without blocking NMDAR activity, protected cultured cortical neurons from excitotoxic insults, dramatically reduced cerebral infarction volume in rats subjected to transient focal cerebral ischemia, and traumatic brain injury (TBI) in rats.
Owner:NONO INC
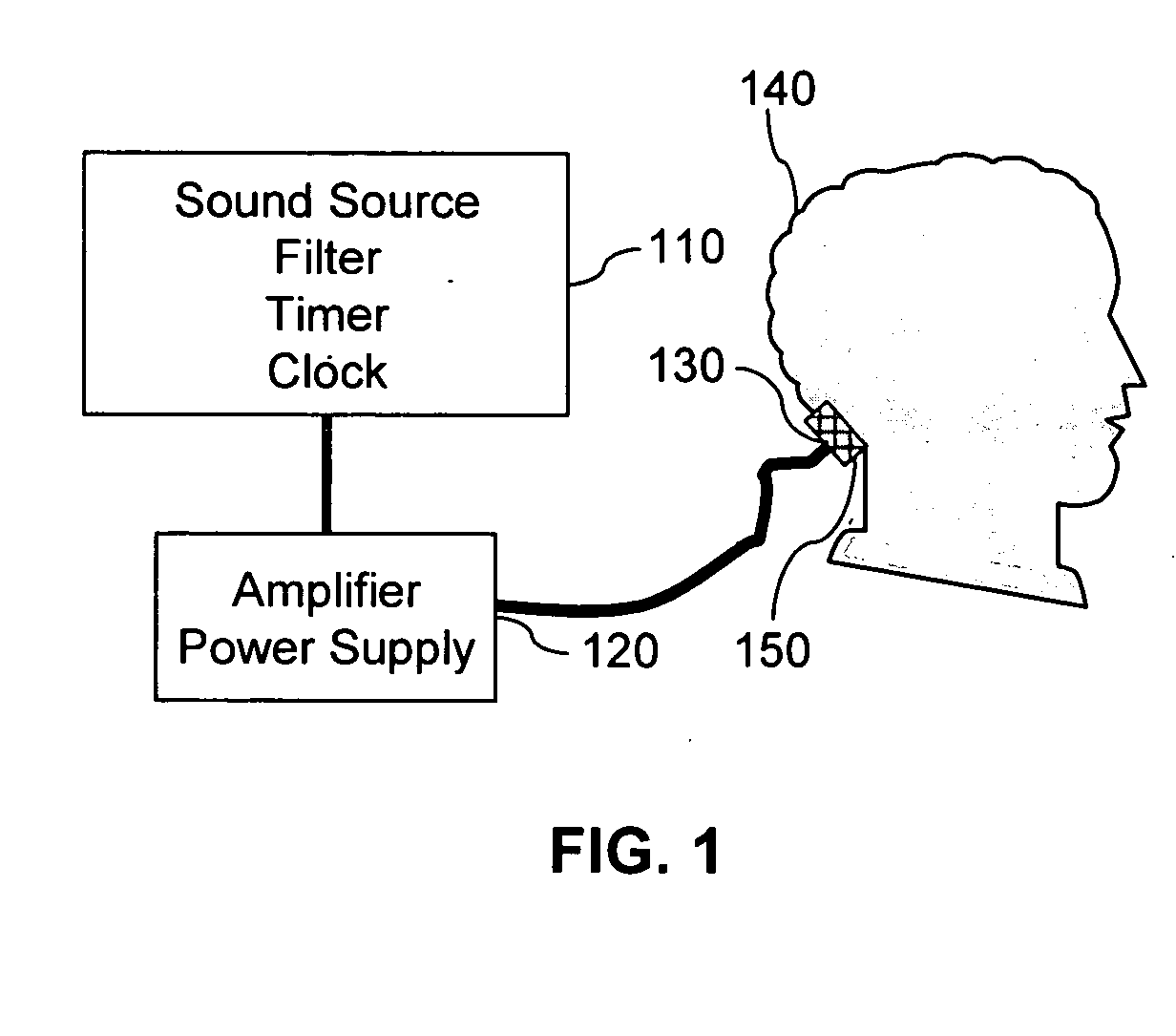
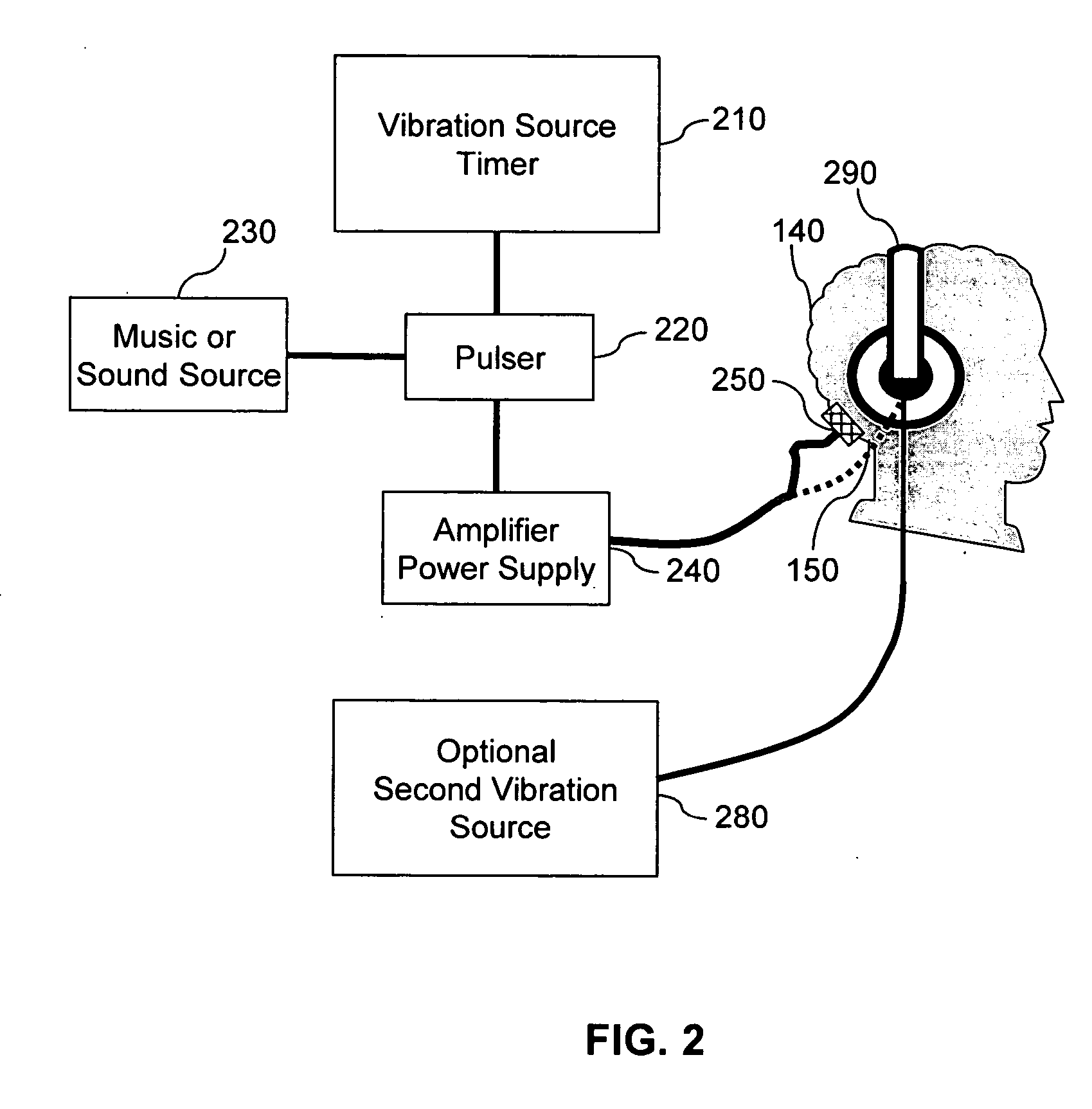
Method and apparatus for improving hearing in patients suffering from hearing loss
InactiveUS20050201574A1Improve hearingHigh sensitivityVibration massageTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsTelecommunications linkSonification
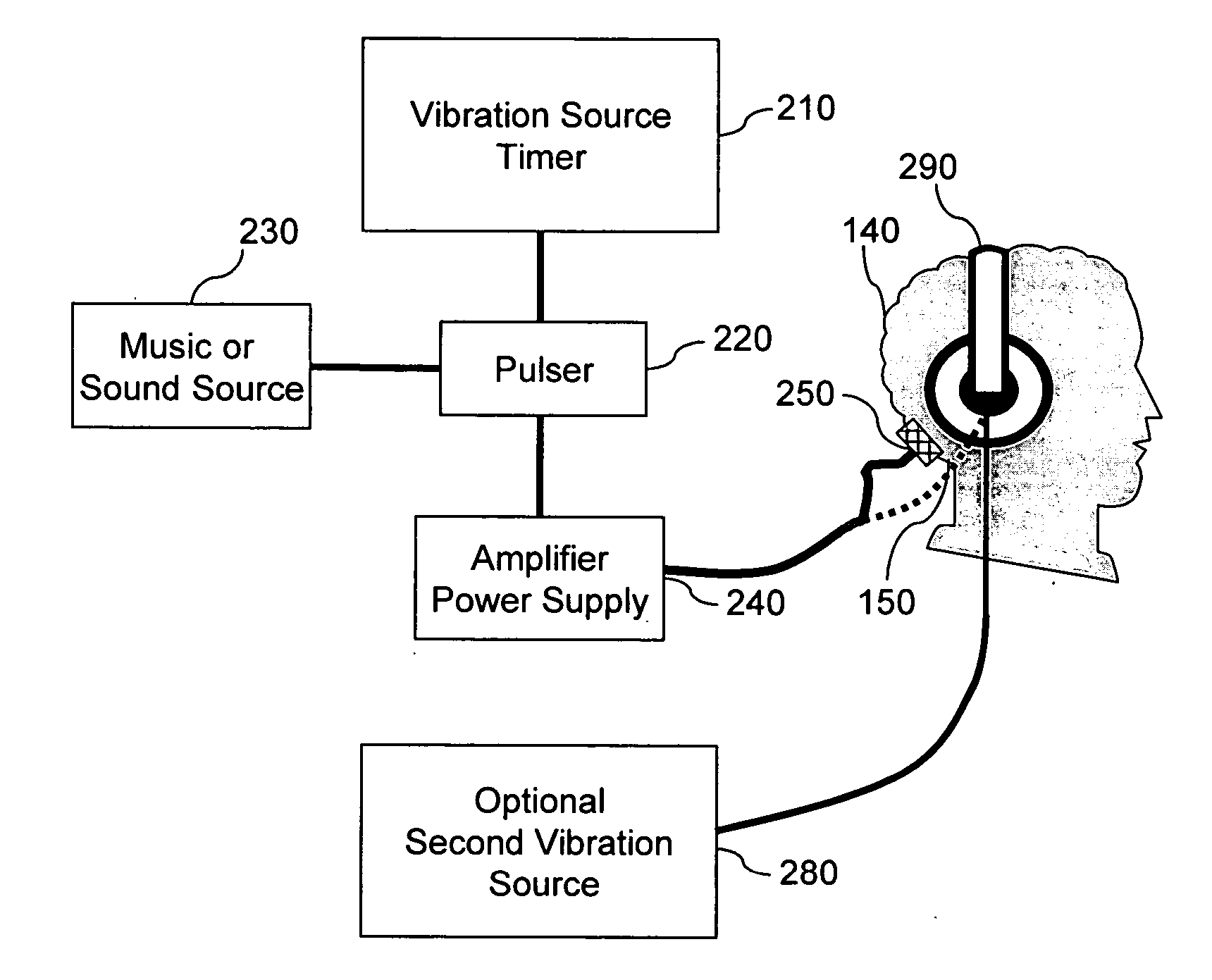
Methods, apparatus and systems for treating sensrineural hearing loss include applying high frequency to ultrasonic frequency vibration stimulus to the head or neck of a patient for a suitable period of time. Hearing and sound discrimination are improved by stimulating the patient's cortices leading to stimulation of cortical neurons to increase sensitivity to high frequency sound. Stimulus signals may be applied by bone conduction via transducers attached to the head or neck, or by airborne conduction via headphones, or by a combination thereof. Stimulus signals may be recorded and may be remotely produced and transmitted via a telecommunications link to a receiver in a remote location. A compact auditory stimulation device includes electronics for storing a personalized stimulus signal, sound generators to produce the stimulus, a microprocessor, and a vibrator, such as headphones. Audiometer functions may be included in the auditory stimulation device to permit testing of the patient's hearing level thresholds.
Owner:SOUND TECHN SYST
Method of reducing injury to mammalian cells
InactiveUS7595297B2Prevent negative consequenceReduce signalingNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsNR1 NMDA receptorN methyl D aspartate receptors
A method of inhibiting the binding between N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors and neuronal proteins in a neuron the method comprising administering to the neuron an effective inhibiting amount of a peptide replacement agent for the NMDA receptor or neuronal protein interaction domain that effect said inhibition of the NMDA receptor neuronal protein. The method is of value in reducing the damaging effect of injury to mammalian cells. Postsynaptic density-95 protein (PSD-95) couples neuronal N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) to pathways mediating excitotoxicity and ischemic brain damage. This coupling was disrupted by transducing neurons with peptides that bind to modular domains on either side of the PSD-95 / NMDAR interaction complex. This treatment attenuated downstream NMDAR signaling without blocking NMDAR activity, protected cultured cortical neurons from excitotoxic insults and dramatically reduced cerebral infarction volume in rats subjected to transient focal cerebral ischemia. The treatment was effective when applied either before, or one hour after, the onset of excitotoxicity in vitro and cerebral ischemia in vivo. This approach prevents negative consequences associated with blocking NMDAR activity and constitutes practical therapy for stroke.
Owner:NONO INC
Treatment with Sigma Receptor Agonists Post-Stroke
InactiveUS20070123556A1Decrease in infarction areaHigh affinityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsHippocampal regionGlial fibrillary acidic protein
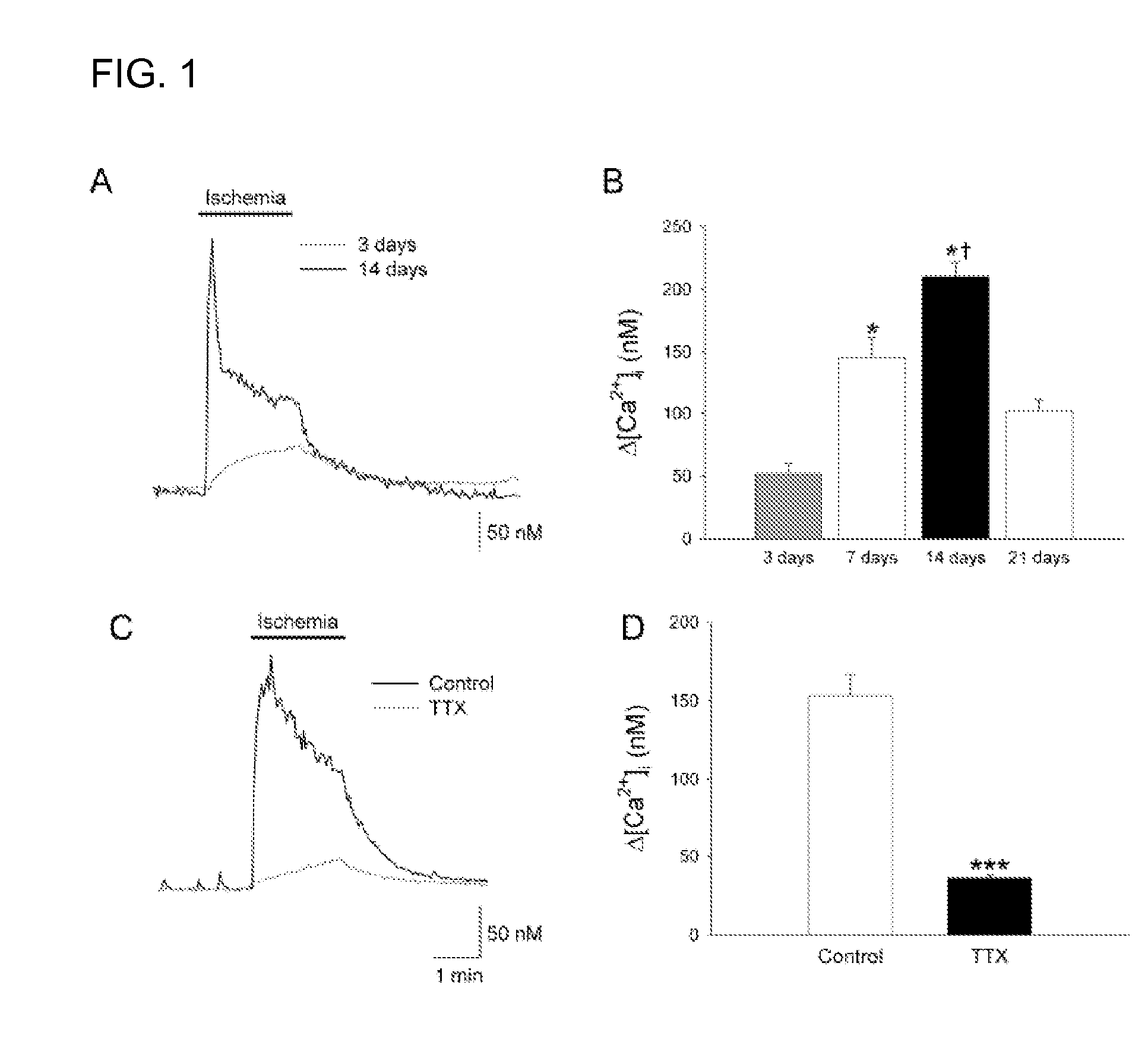
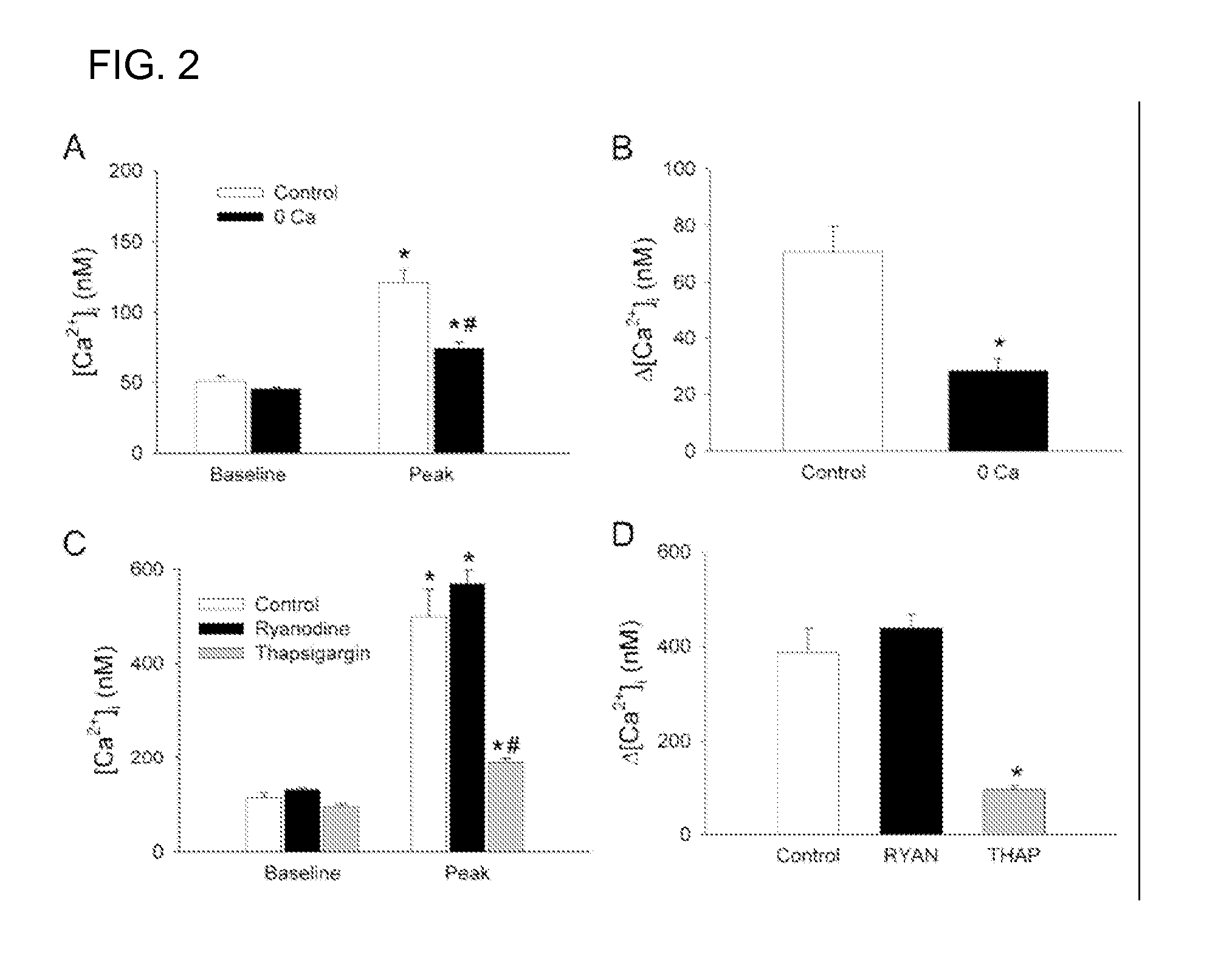
A method of post-stroke treatment at delayed timepoints with sigma receptor agonists. Sigma receptors are promising targets for neuroprotection following ischemia. One of the key components in the demise of neurons following ischemic injury is the disruption of intracellular calcium homeostasis. The sigma receptor agonist, DTG, was shown to depress [Ca2+]i elevations observed in response to ischemia induced by sodium azide and glucose deprivation. Two sigma receptor antagonists, metaphit and BD-1047, were shown to blunt the ability of DTG to inhibit ischemia-evoked increases in [Ca2+]i. DTG inhibition of ischemia-induced increases in [Ca2+]i was mimicked by the sigma-1 receptor-selective agonists, carbetapentane, (+)-pentazocine and PRE-084, but not by the sigma-2 selective agonist, ibogaine, showing that activation of sigma-1 receptors is responsible for the effects. Activation of sigma receptors can ameliorate [Ca2+]i dysregulation associated with ischemia in cortical neurons, providing neuroprotective properties. The effects of 1,3-di-o-tolyguanidine (DTG), a high affinity sigma receptor agonist, as a potential treatment for decreasing infarct area at delayed time points was further examined in rats. DTG treatment significantly reduced infarct area in both cortical / striatal and cortical / hippocampal regions by >80%, relative to control rats. These findings were confirmed by immunohistochemical experiments using the neuronal marker, mouse anti-neuronal nuclei monoclonal antibody (NeuN), which showed that application of DTG significantly increased the number of viable neurons in these regions. Furthermore, DTG blocked the inflammatory response evoked by MCAO, as indicated by decreases in the number of reactive astrocytes and activated microglia / macrophages detected by immunostaining for glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and binding of isolectin IB4, respectively. Thus, the sigma receptor-selective agonist, DTG, can enhance neuronal survival when administered 24 hr after an ischemic stroke. In addition, the efficacy of sigma receptors for stroke treatment at delayed time points is likely the result of combined neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory properties of these receptors.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
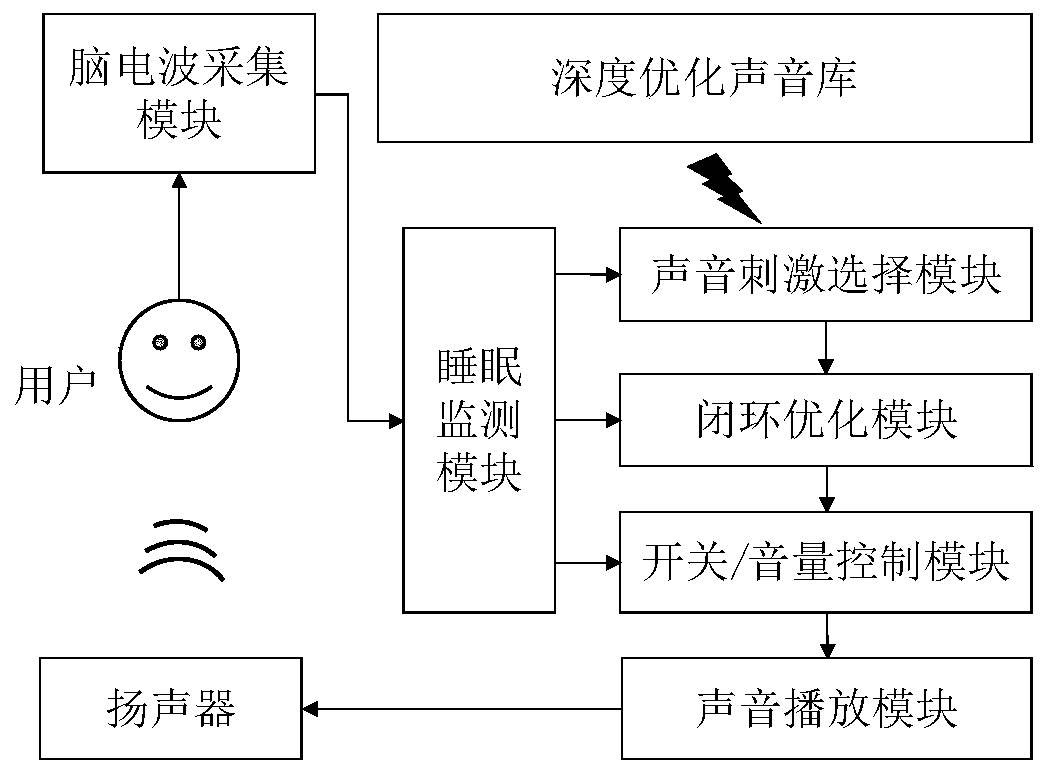
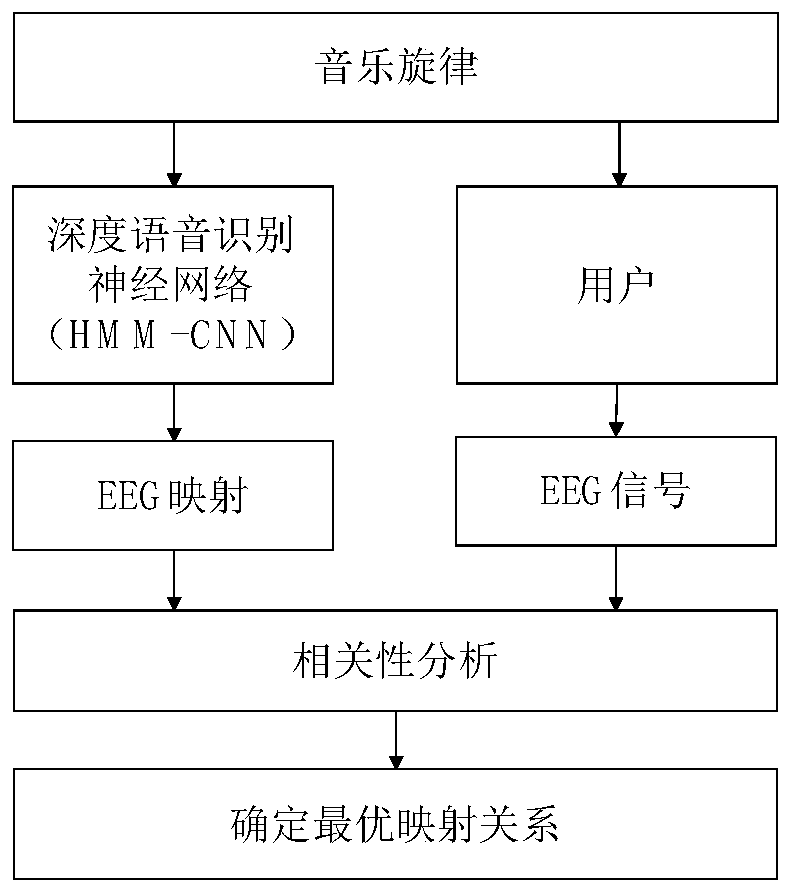
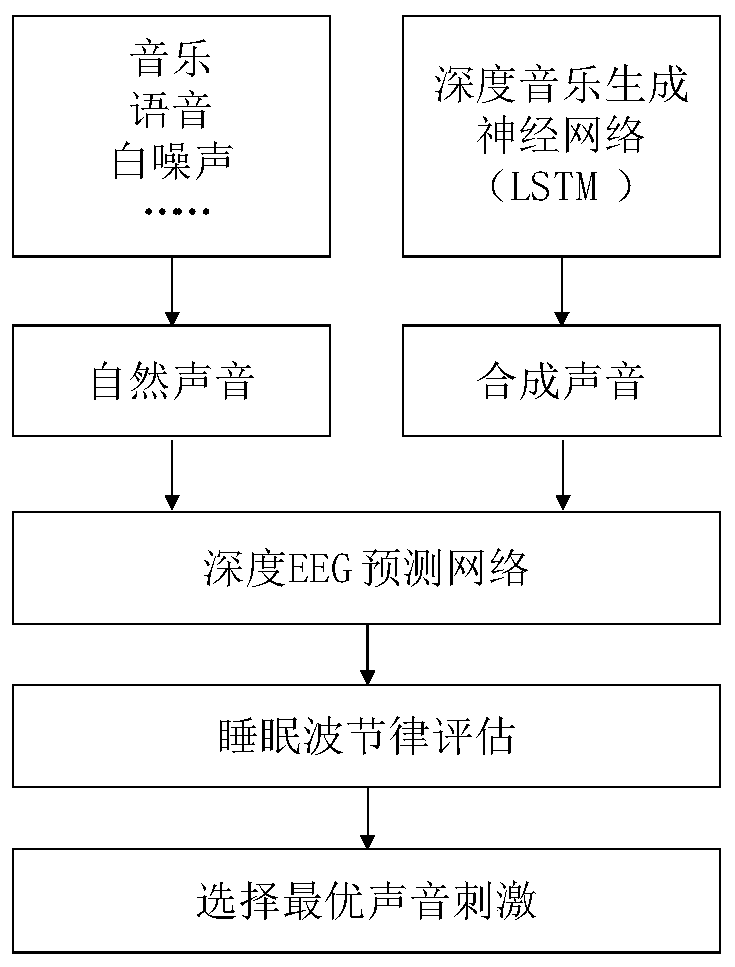
Deep sound stimulation system and method for sleep regulation
ActiveCN110841169AImprove sleep qualityEfficient large-scale testingDiagnostics using spectroscopyMedical devicesInformation processingNerve network
The invention relates to a system and method using a deep neural network to select and optimize sound stimulation so as to regulate and improve human body sleep quality. The deep neural network can represents the external stimulation (images, sounds and the like) information processing of human brain cortical neurons. By inputting massive sound stimulation into the deep neural network, the sound mode capable of optimizing the model estimated sleep brain waves can be found, the sound mode is applied to a real human body, and the strength of corresponding sleep waves of the human body in different sleep stages is enhanced through closed loop optimization so as to regulate sleep. The system and method is mainly used to solve the technical problem of how to use the deep neural network to select and optimize the used sound stimulation to improve the sleep quality to the maximum extent when the sound stimulation (music, voices, natural sounds, white / colored noise and the like) is used to assist human body sleep.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Application of Li2WO4 in preparing medicine
InactiveCN101036669AInhibitory activityInhibit hyperphosphorylationNervous disorderInorganic active ingredientsCortical neuronsProtein C
The invention discloses an application of tungstate lithium for preparing a medicine, in particular an application for preparing drug for treating neurodegenerative disease, neuropathy caused by diabetes, and cerebral ischemia including cerebral dysfunction. Both of activity of anion and cation of the tungstate lithium can perform synergistic reaction to inhibit activity of a GSK-3 much better. By inhibiting activity of a GSK-3 alpha, generation of the A beta is reduced to decrease SP; by inhibiting activity of a GSK-3 beta, hyperphosphorylation of tau protein is inhibitted to reduce NFT. Thereby, survival and wound repair of neurocyte are promoted even in a state of ischemia and anoxia to improve learning and memory dysfunction by increasing content of BDNF in cortical neurons.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
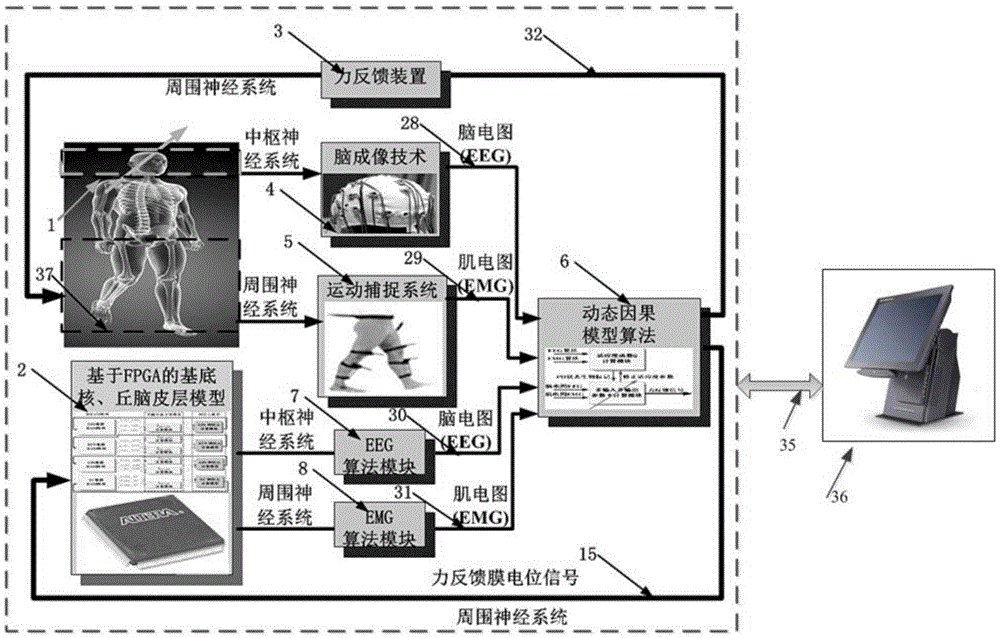
Dyskinesia non-intrusive rehabilitative closed-loop brain-computer integrated system based on FPGA
InactiveCN105653873AAchieve outputReduce treatment riskMedical simulationHealth-index calculationClosed loopCortical neurons
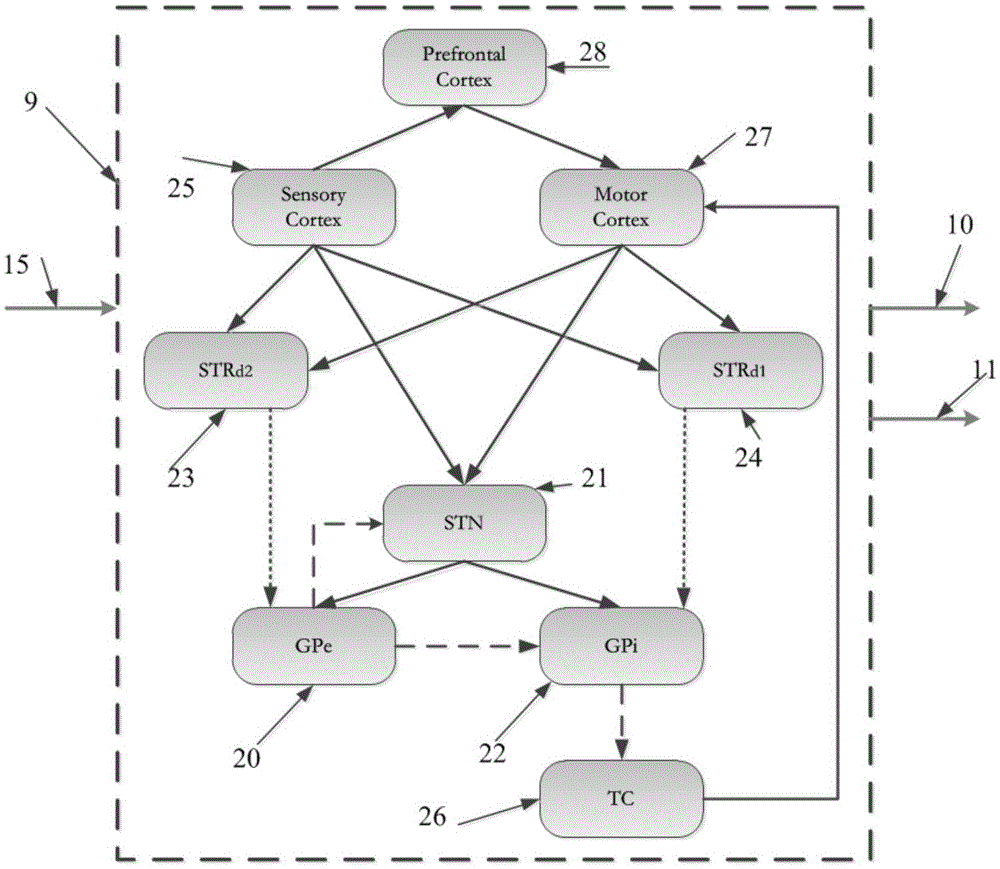
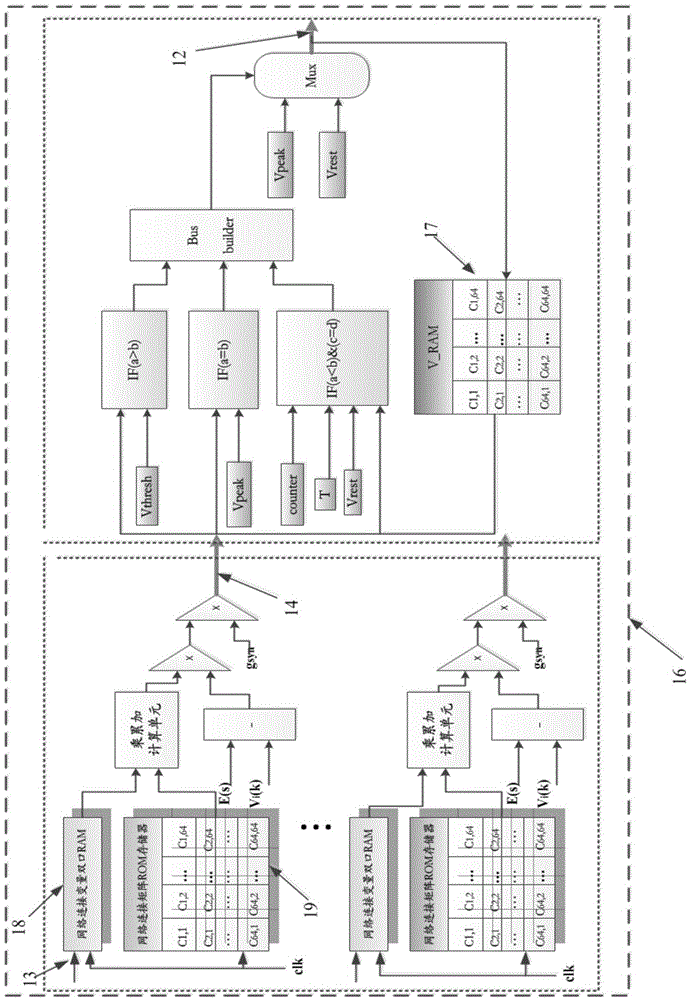
The invention provides a dyskinesia non-intrusive rehabilitative closed-loop brain-computer integrated system based on an FPGA. The FPGA is used as a control core of the system, nuclei basales and thalamic-cortical prosthesis hardware model is set up, data obtained through calculation of a self-adaptation control algorithm based on the FPGA is used as input to control model parameter setting and force feedback and adjustment until an expected control result is achieved, the self-adaptation control algorithm based on the dynamic causal model is realized, force feedback signals are output, and therefore rehabilitation of patients with the dyskinesia nervous system diseases is achieved. Rehabilitation of the patients with dyskinesia nervous system diseases is achieved, and the complex nuclei basales and thalamic-cortical neuron network and the self-adaptation control algorithm of the dynamic causal model are modeled. The platform provides the effective theoretical basis and technical support for rehabilitation of the dyskinesia nervous system diseases and has important practical value in research on control and treatment on nerve diseases such as Parkinson's disease, epilepsia and alzheimer's disease.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Application of tekaning (Chinese character) in preparation of mitochondrial injury protective agent
InactiveCN103877094AAvoid damagePromote autophagyNervous disorderFood preparationDiseaseSignalling molecules
The invention discloses application of a compound tekaning (Chinese character) with a structure in a formula (I) in the specification in preparation of a mitochondrial injury protective agent. In addition, the invention also discloses the mitochondrial injury protective agent of which the effective component is the compound tekaning with the structure in the formula (I). The application fully proves that the compound tekaning, and drugs, drinks or health products containing effective components of the compound tekaning can be used for effectively promoting expression of mitochondrial autophagy key signal molecules, and enhancing mitochondrial autophagy to inhibit the mitochondrial injury, so as to effectively clear mitochondrial dysfunction existing in cortical neuron, especially, dopaminergic neurons of the brain of which the mitochondrial mass is relatively low. Thus, the dopaminergic neuron is protected to play the roles of relieving parkinson's disease and the like and treating a nerve disease.
Owner:何蓉蓉
Functional astrocytes and cortical neurons from induced pluripotent stem cells and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS10494602B1Promote differentiationCulture processNervous system cellsProgenitorCortical neurons
Human pluripotent stem cells are differentiated in vitro into human cortical spheroids (hCS), which contain astrocytes, as well as cortical progenitors and neurons for use in analysis, screening programs, and the like.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
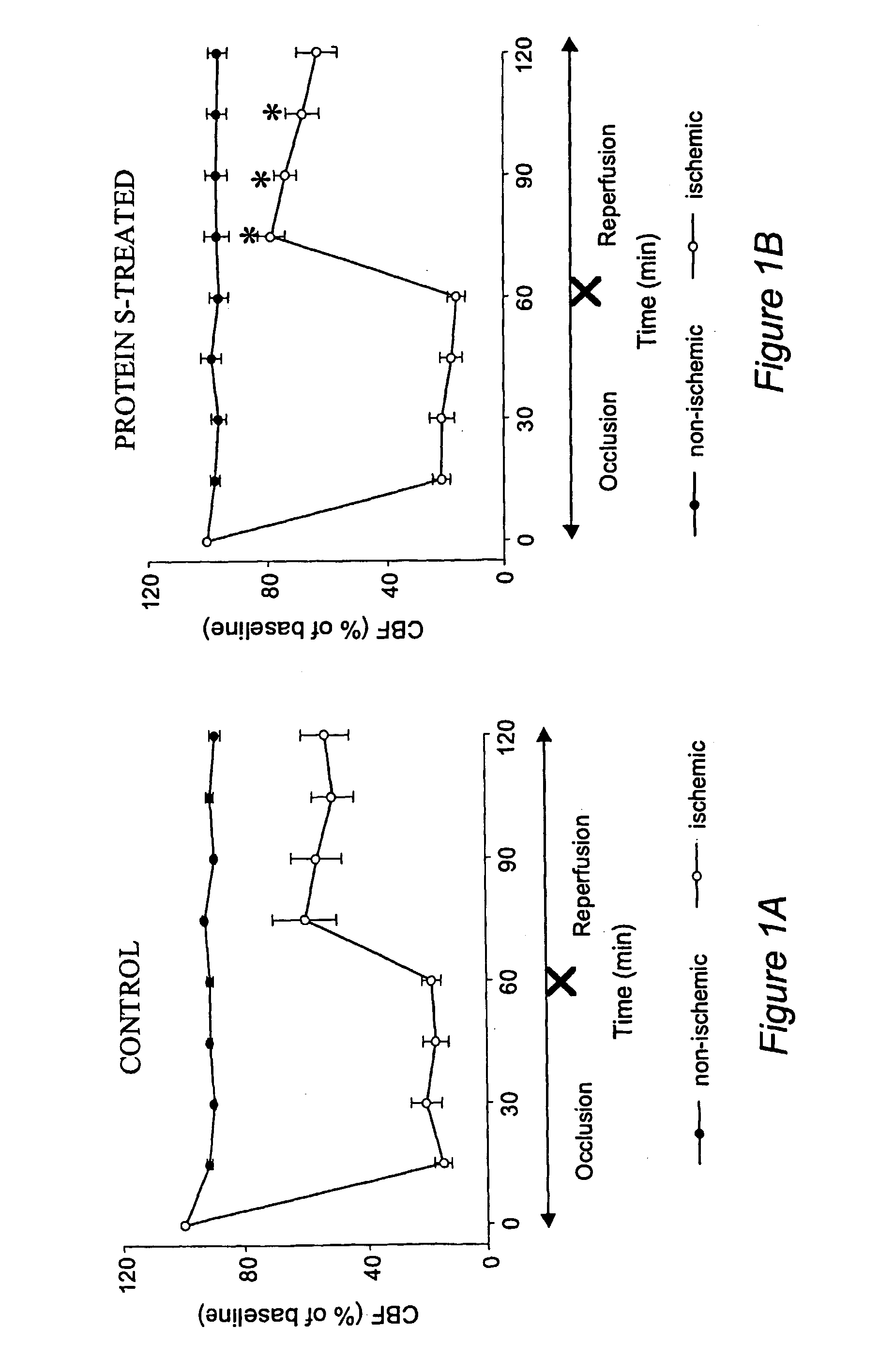
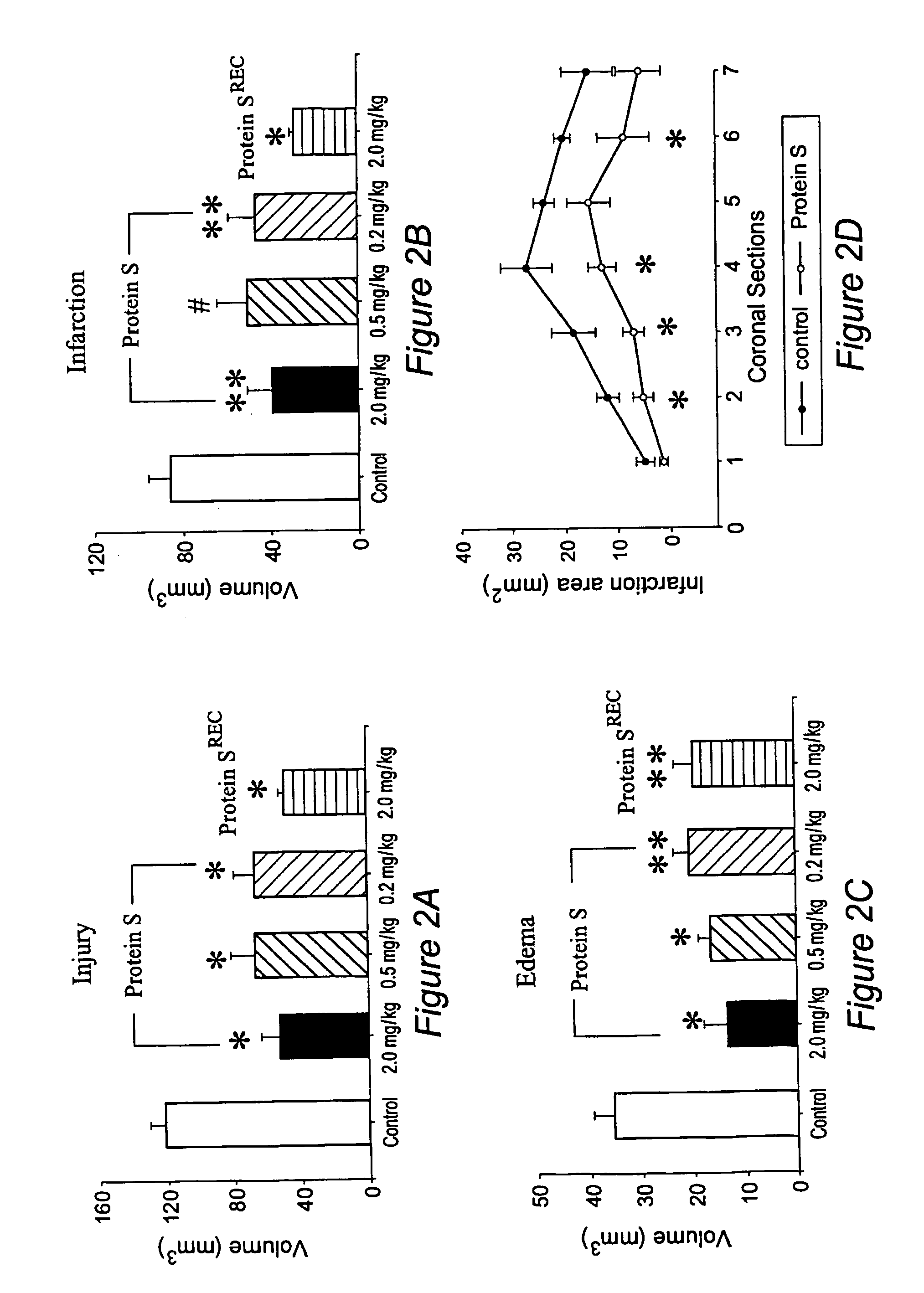
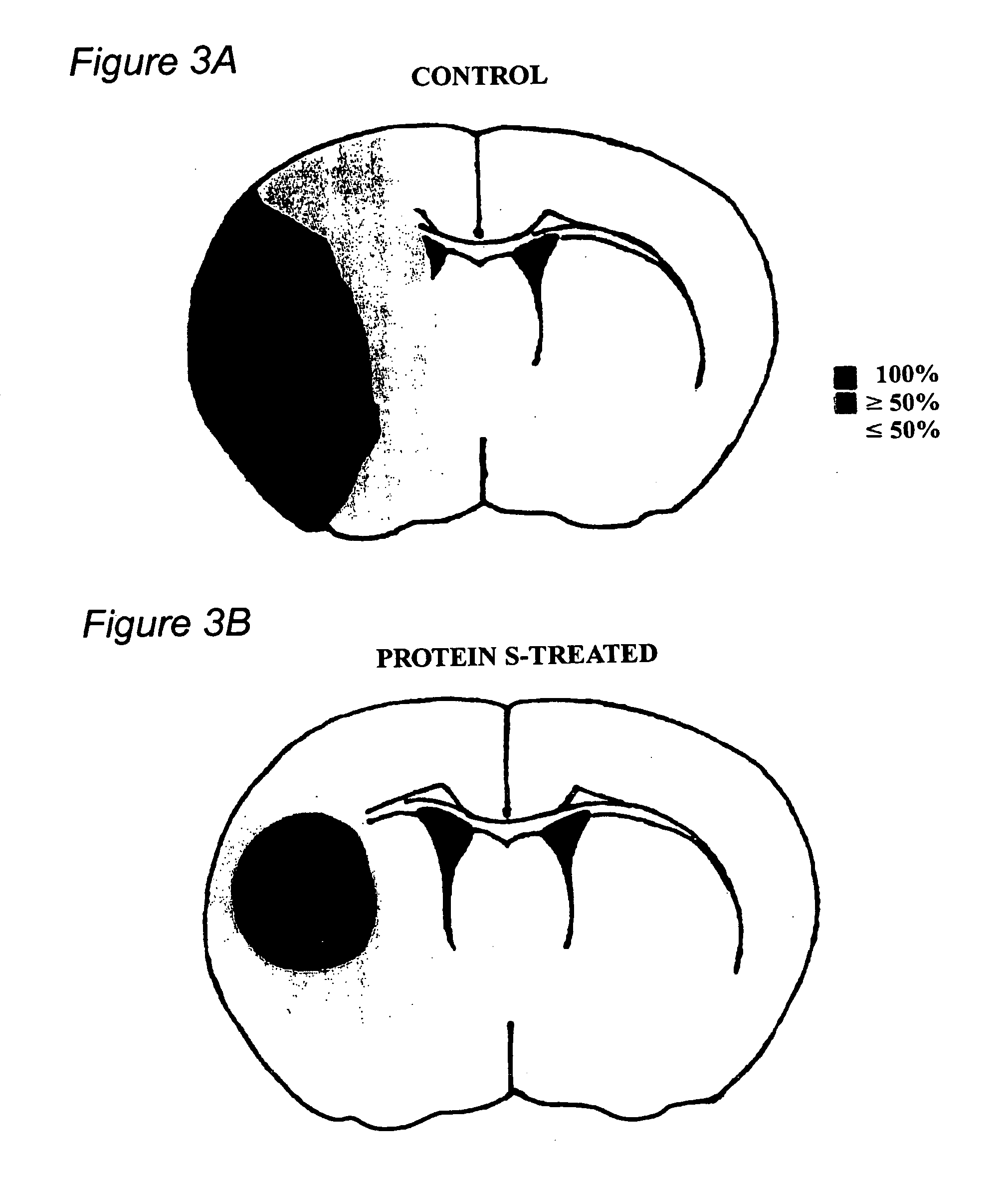
Protein s protects the nervous system from injury
InactiveUS20060052281A1Improve protectionPrevention of cell injuryCompound screeningNervous disorderNervous systemApoptosis
Protein S is a significant neuroprotectant when administered after focal ischemic stroke and prevents hypoxic / re-oxygenation injury. Purified human plasma-derived or recombinant protein S improves motor neurological function after stroke, and reduced brain infarction and edema. Protein S also enhances post-ischemic reperfusion and reduced brain fibrin and neutrophil deposition. Cortical neurons are protected from hypoxia / re-oxygenation-induced apoptosis. Thus, protein S and variants thereof are prototypes of a class of agents for preventing injury of the nervous system. In particular, a disease or other pathological condition (e.g., stroke) may be treated with such agents having one or more protein S activities (e.g., anti-thrombotic and anti-inflammatory activities, direct cellular neuronal protective effects) although the latter activities are not be required.
Owner:ZZ BIOTECH LLC +2
Application of cholest-4-ene-3,6-dione in preparing drug for treating or preventing neuron injury
The invention discloses an application of cholest-4-ene-3,6-dione in preparing a drug for treating or preventing neuron injury. Cholest-4-ene-3,6-dione can relieve hippocampus neuron oxidative stressinjury caused by glutamic acid, cerebellar granule neuron apoptosis injury caused by potassium deprivation and cortical neuron and cerebellar granule neuron oxidative stress injury caused by glutamicacid, also has a function of remarkably reducing infarct volume in an MACO (middle cerebral artery occlusion) model of a stroke rat and has the potential of a neuroprotective agent used for being developed into multiple acting mechanisms. Neurodegenerative diseases such as the Parkinson's disease, the Alzheimer's disease, the tau protein disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and the like as wellas cerebral stroke, cerebral injury and spinal cord injury are all caused by neuron injury, and neuron injury is further aggravated. Cholest-4-ene-3,6-dione has a protection function on neuron injuryand has potential functions in drugs for treating or preventing neuron injury.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Construction method of in-vitro model for simulating mesenchymal stem cell transplantation
InactiveCN102994450AAvoid interferencePrecise determinantsNervous system cellsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsUltrastructureScanning electron microscope
The invention discloses a construction method of an in-vitro model for simulating mesenchymal stem cell transplantation, which comprises the following steps of: (1) selecting in-vitro neonatal rat cortical neurons; (2) selecting in-vitro rat mesenchymal stem cells; (3) pre-processing the in-vitro rat mesenchymal stem cells, and inoculating in the neonatal rat cortical neurons for co-culture; and (4) after the co-culture, treating the rat mesenchymal stem cells and the neonatal rat cortical neurons by a light microscope, a fluorescence microscope, an atomic force microscope and a scanning electron microscope; and determining an in-vitro model for simulating mesenchymal stem cell transplantation and a growth tendency, an interaction and formation of a synapsis-like structure between the cortical neurons and the mesenchymal stem cells on an ultrastructure. The construction method disclosed by the invention provides a simplified in-vitro model for the mesenchymal stem cell transplantation; meanwhile, the synapsis-like structure formed in the model provides an in-vitro evidence of a structure integration mechanism for the mesenchymal stem cell injury mechanism.
Owner:姜晓丹 +1
Kudzu-vine root daidzein-7, 4'-dioxo acetic acid compound and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101759680AGood water solubilityImprove bioavailabilityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDaidzeinCortical neurons
The invention belongs to the field of medical technology and relates to a kudzu-vine root daidzein-7, 4'-dioxo acetic acid compound and a preparation method thereof; the compound has the following formula, wherein R1 and R2 can be the same of different and are chosen from H, metal ions, organic cations, basic amino acid cations, C1-C10 alkyl group independently; R3 and R4 can be the same or different and are independently chosen from H or C1-C10 alkyl group; the kudzu-vine root daidzein-7, 4'-dioxo acetic acid compound, and a carrier or excipient which can be acceptable medically are combined to form medicine composite; the compound and the medicine composite has the advantages of cerebral ischemia resistance, oxygen-poor resistance, myocardial ischemia resistance, antagonistic dysmnesia resistance, platelet aggregation resistance and thrombopoiesis resistance and protecting rat cortical neuron damage caused by oxygen deficit.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
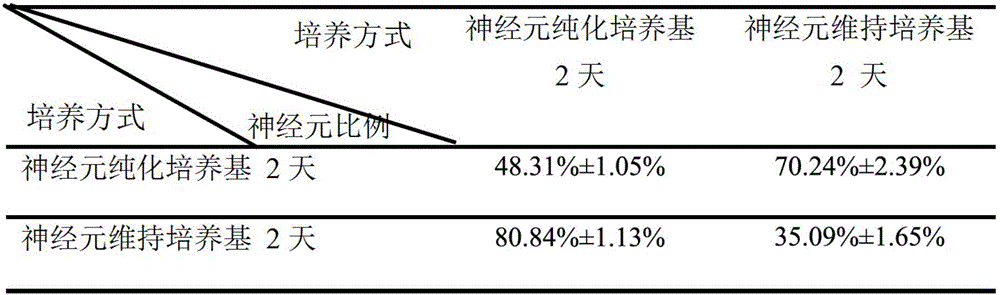
Primary culture method in serum-free medium for fetal rat cortical neurons
The invention discloses a primary culture method in a serum-free medium for fetal rat cortical neurons. According to the method, an insulin-transferrin-sodium selenite serum-free medium is used to culture the fetal rat cortical neurons, and neuron-specific enolase is used for dyeing to identify the fetal rat cortical neurons. According to the primary culture method in a serum-free medium for the fetal rat cortical neurons, dissociated culture model of Wistar fetal rat cortical in vivo is established by using a serum-free culture method, and morphologic observation of the cultured neurons is carried out, establishing a foundation for relative researches in future.
Owner:SUZHOU HEALTH COLLEGE
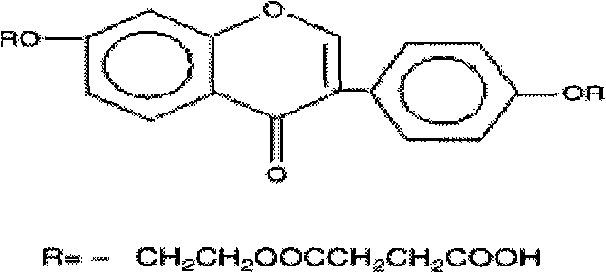
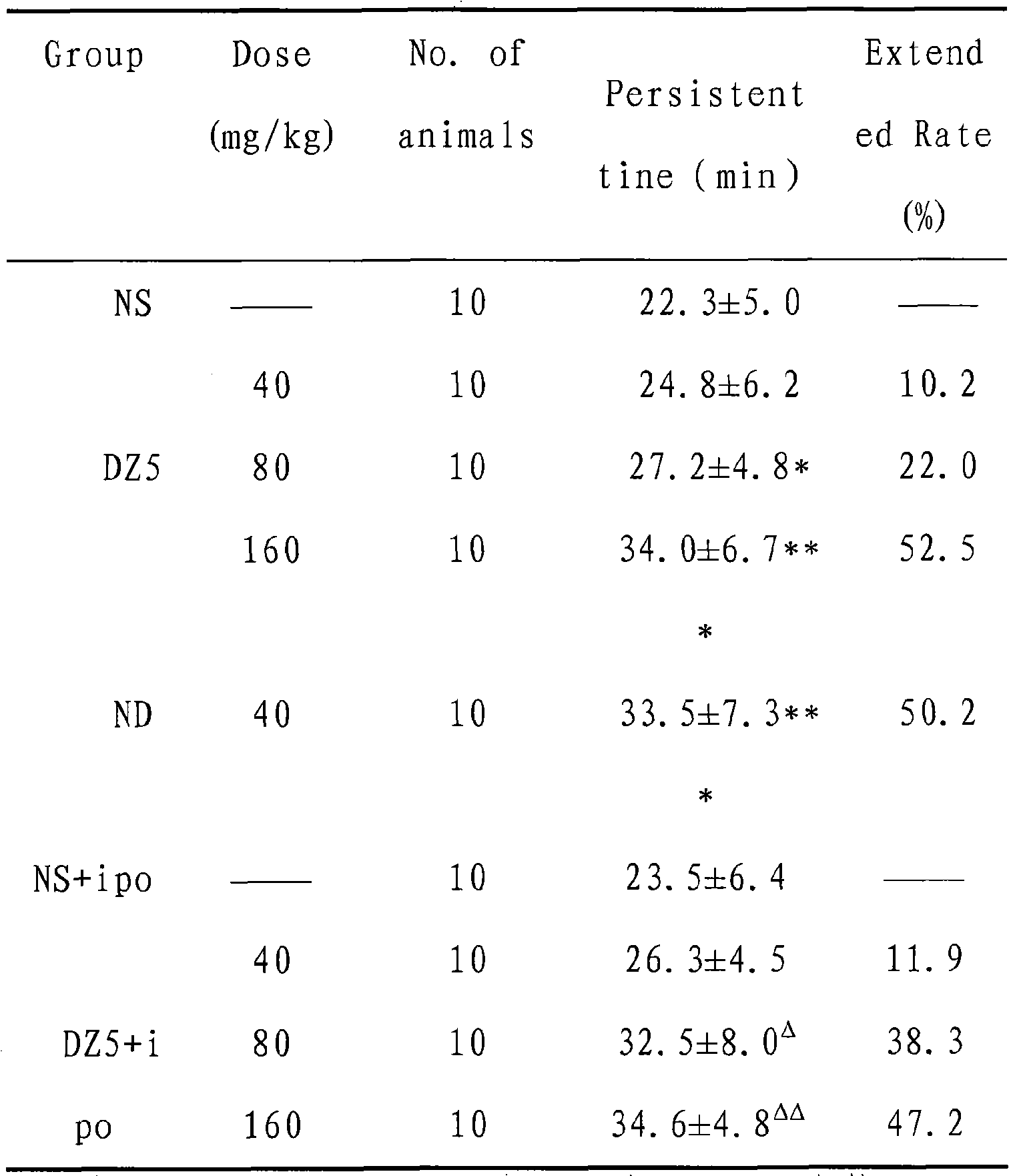
7,4'-di(mono succinate)o-ethoxy-daidzein and novel medical uses thereof
InactiveCN101255149AImprove pharmacological activitySmall side effectsOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDaidzeinPituitrin
The invention discloses new pharmaceutical uses of 7, 4'- di(mono succinate) oxyethoxypropyl daidzein. Pharmacological activity research is carried out to DZ5 by an experimental model for mice under atmospheric hypoxia tolerance, an experimental model for mice acute cerebral ischemia, an experimental model for bilateral common carotid arteries and vagus nerve ligation, an experimental model for mice KCN poisoning, an experimental model for mice NaNO2 poisoning and experimental model for learning and remembering, an action model for rat cortical neuron damage caused by anoxia of DZ5, an effect model for rat myocardial ischemia caused by hypophysin, an experimental model for vitro anti platelet aggregation, an experimental model for vivo anti platelet aggregation, and an effect model for arterial thrombosis in rabbits. Proved by the result, DZ5 has the functions of anti-cerebral ischemia and anoxia, anti-myocardial ischemia and anoxia, antagonistic memory disorders, anti-platelet aggregation and thrombosis, and protection of rat cortical neuron damage caused by anoxia. DZ5 can be mixed with a pharmacologically acceptable carrier or excipient to prepare medicine compositions.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
Method of Reducing Injury to Mammalian Cells
InactiveUS20090281037A1Prevent negative consequenceReduce signalingNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsNR1 NMDA receptorN methyl D aspartate receptors
A method of inhibiting the binding between N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors and neuronal proteins in a neuron is disclosed. The method comprises administering to the neuron an effective inhibiting amount of a peptide replacement agent for the NMDA receptor or neuronal protein interaction domain that effect said inhibition of the NMDA receptor-neuronal protein interaction. The method is of value in reducing the damaging effect of injury to mammalian cells. Postsynaptic density-95 protein (PSD-95) couples neuronal N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARS) to pathways mediating excitotoxicity, ischemic and traumatic brain damage. This coupling was disrupted by transducing neurons with peptides that bind to modular domains on either side of the PSD-95 / NMDAR interaction complex. This treatment attenuated downstream NMDAR signaling without blocking NMDAR activity, protected cultured cortical neurons from excitotoxic insults, dramatically reduced cerebral infarction volume in rats subjected to transient focal cerebral ischemia, and traumatic brain injury (TBI) in rats.
Owner:NONO INC
Differentiation of cortical neurons from human pluripotent stem cells
The presently disclosed subject matter provides for in vitro methods of inducing differentiation of human stem cells into cortical neurons, and cortical neurons generated by such methods. The presently disclosed subject matter also provides for uses of such cortical neurons for treating neurodegenerative CNS disorders.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
A neuroprotective agent
ActiveCN106377520AReduce calcium influxProtection from glutamate toxicityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderChemical compoundCortical neurons
The invention relates to a neuroprotective agent. The neuroprotective agent comprises a chemical compound having a structure formula shown as follows. The chemical compound having the structure formula can reduce cell calcium influx through a glutamate receptor invertibility inhibiting function, thus protecting cortical neurons from excitatory toxicity initiated by glutamic acid. The neuroprotective agent is extremely effective.
Owner:SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY OF CHINA
Application of heterophyllin B in improving memory and/or preventing Alzheimer's disease
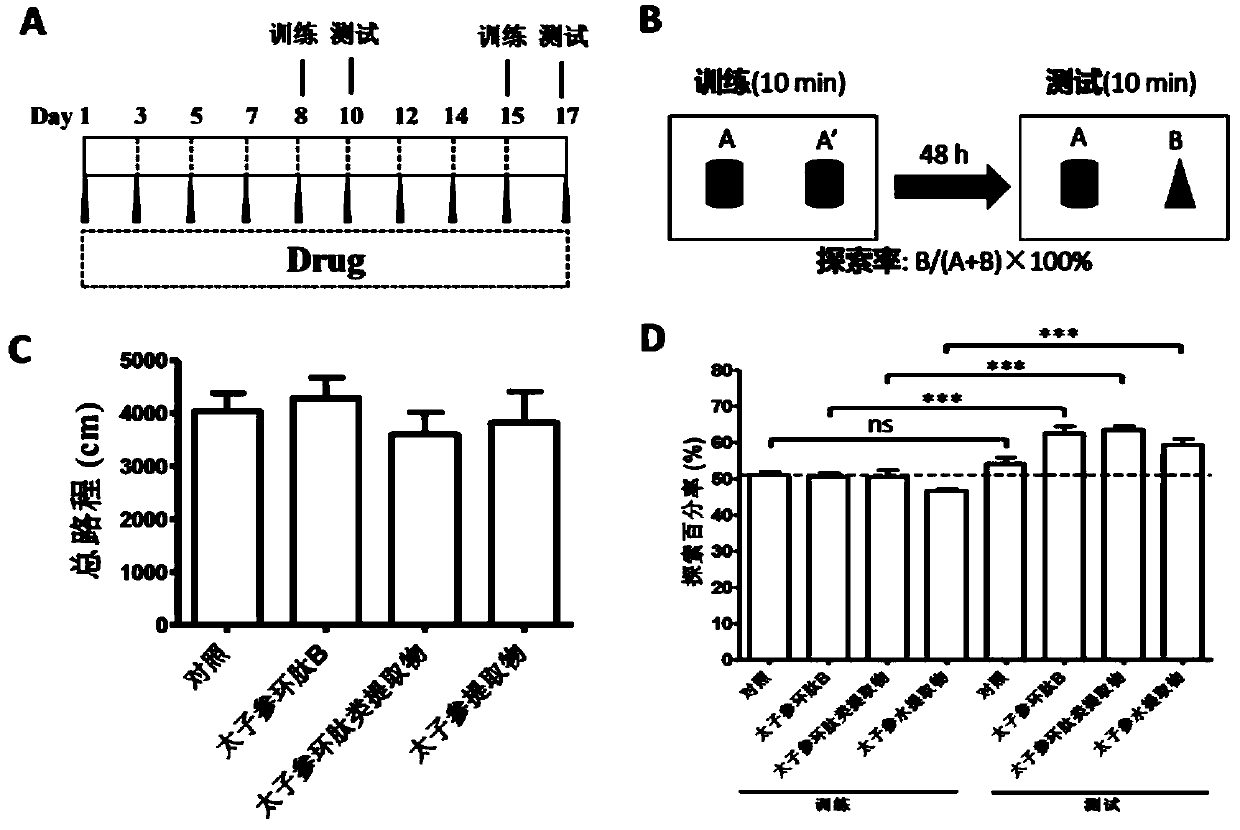
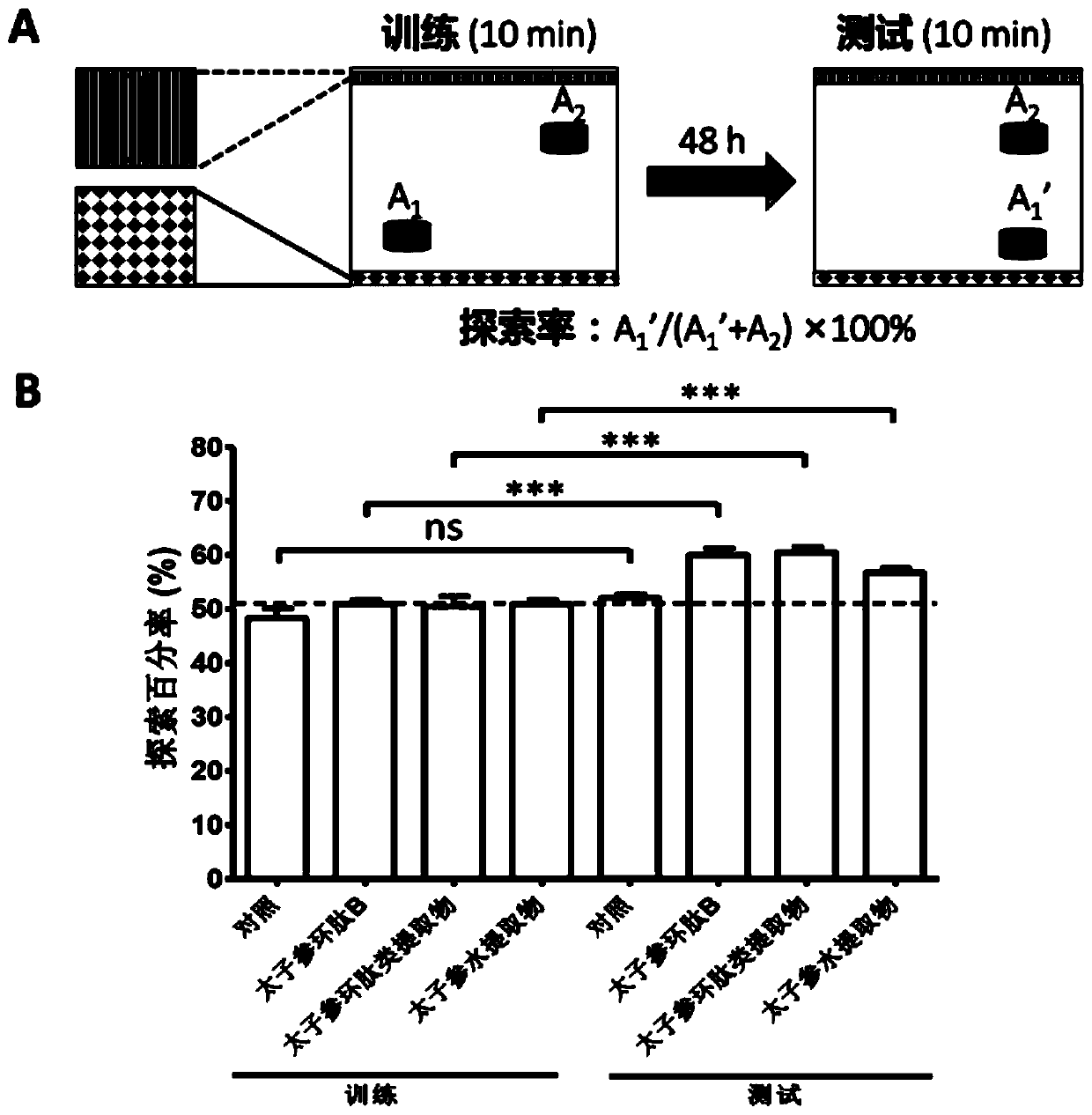
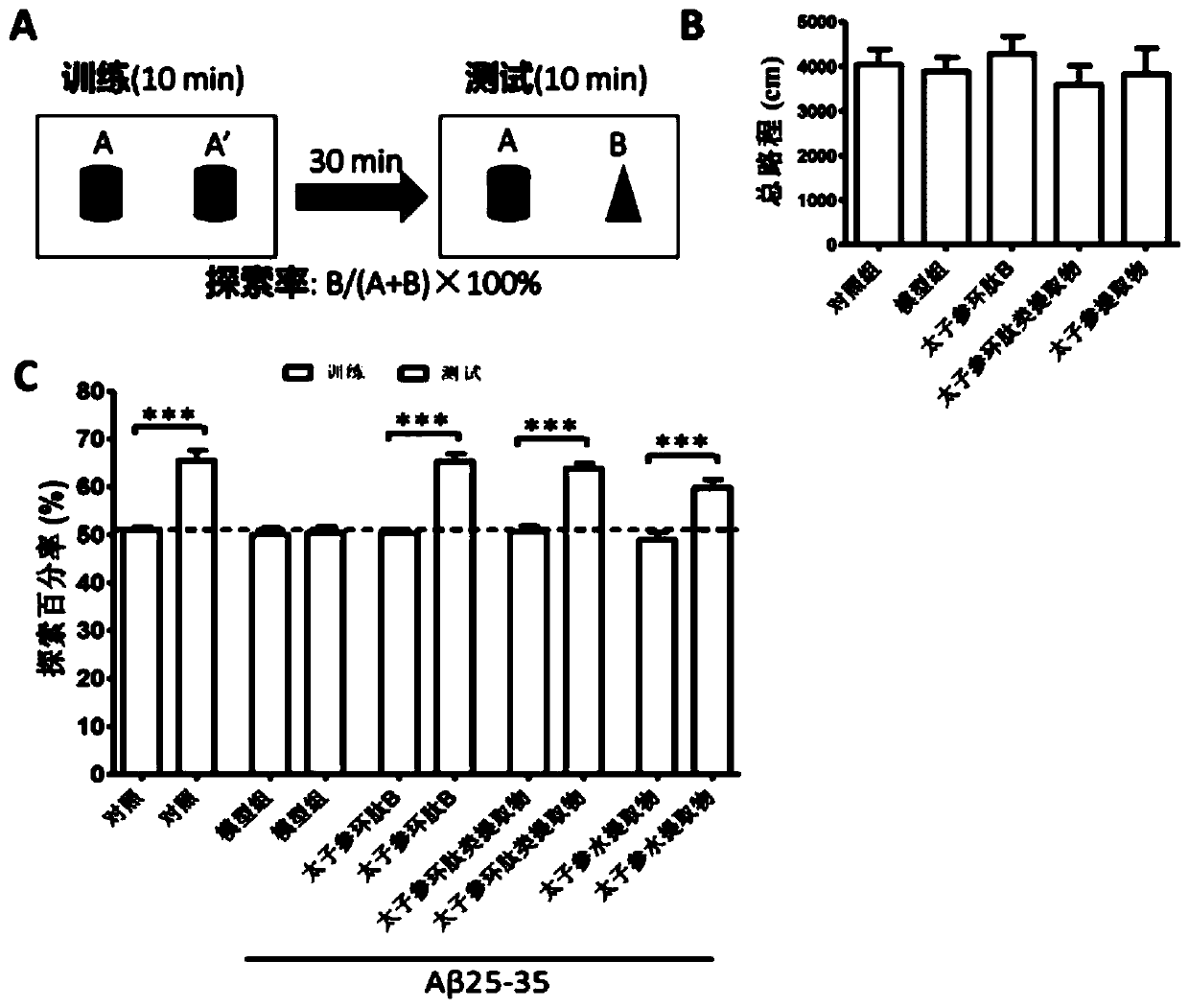
ActiveCN110237232AImprove memory impairmentEnhance cognitive memoryNervous disorderCyclic peptide ingredientsCortical neuronsCerebral cortex
The invention discloses application of heterophyllin B in improving memory and / or preventing the Alzheimer's disease, particularly discloses the memory enhancement function of a radix pseudostellariae aqueous extract, radix pseudostellariae cyclopeptide extract and heterophyllin B for normal mice and the amelioration function on learning and memory dysfunction of dementia mice by injecting Abeta1-42 to the paracele, and discusses the action mechanism of the heterophyllin B. Results show that the radix pseudostellariae aqueous extract, the radix pseudostellariae cyclopeptide extract and the heterophyllin B can significantly enhance the cognitive memory ability of the normal mice and ameliorate the memory impairment of the dementia model mice, the regeneration of cerebral cortex neurites is promoted, and cortical neuron loss and neurite atrophy which are induced by Abeta are prevented; results prompt that the heterophyllin B, a radix pseudostellariae solution and a cyclopeptide extract may reconstruct the neural circuit network by promoting the regeneration of the neurites to play the memory improvement role, and the heterophyllin B can be used for preparing drugs or health foods for preventing and treating the Alzheimer's disease.
Owner:GUANGDONG OCEAN UNIVERSITY
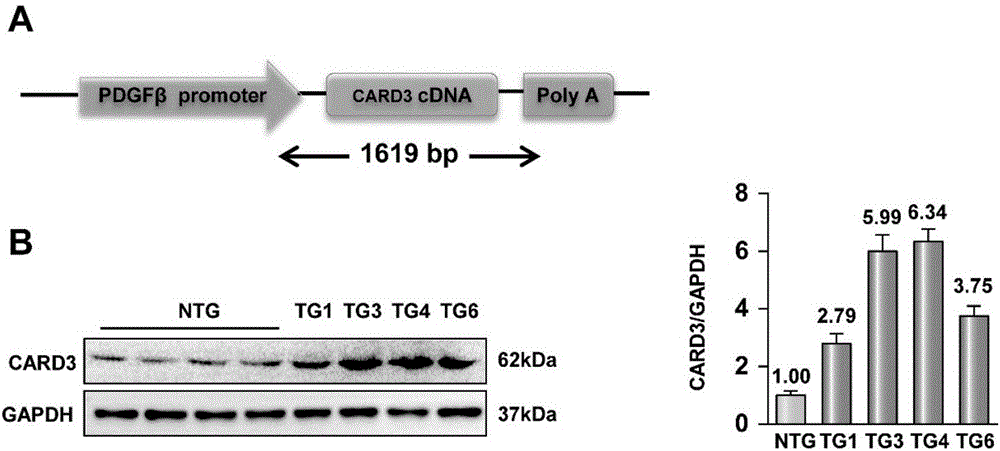
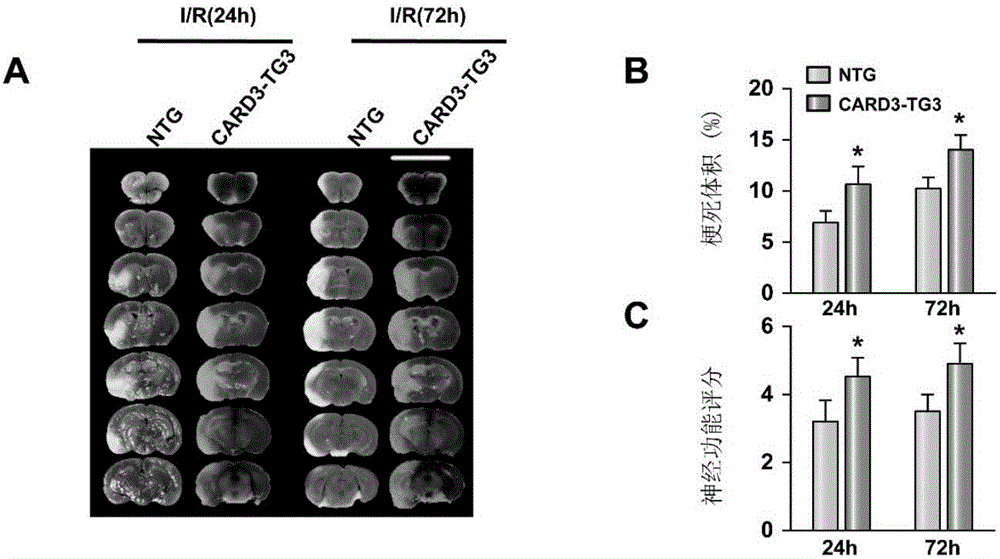
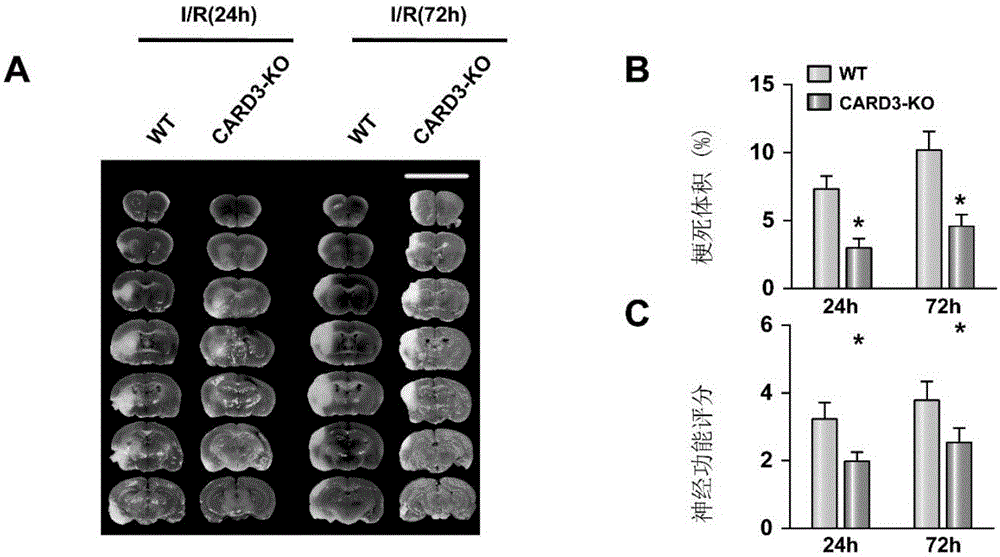
Caspase activation and recruitment domain 3 (CARD3) and application of inhibitor of CARD3 to cerebral stroke diseases
InactiveCN106771198AExacerbation of stroke diseaseCompound screeningOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseKnockout animal
The invention provides a Caspase activation and recruitment domain 3 (CARD3) and application of an inhibitor of the CARD3 to cerebral stroke diseases and belongs to the field of functions and application of genes. On one hand, an in-vitro cell experiment shows that adenovirus-mediated CARD3 interference can reduce injuries caused by anoxia / reoxygenation of primary cortical neuron cells and neuron cell apoptosis is inhibited; on the other hand, neuron-specific CARD3 knockout mice and neuron-specific CARD3 transgenic mice are used as experiment objects and a middle cerebral artery ischemia reperfusion model is used for researching; a result shows that the CARD3 has a neurological deterioration function and can aggravate and promote the development of cerebral stroke; theoretical basis and clinical foundation are provided for new targets and new strategies for research, prevention, alleviation and / or treatment of the cerebral stroke diseases.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
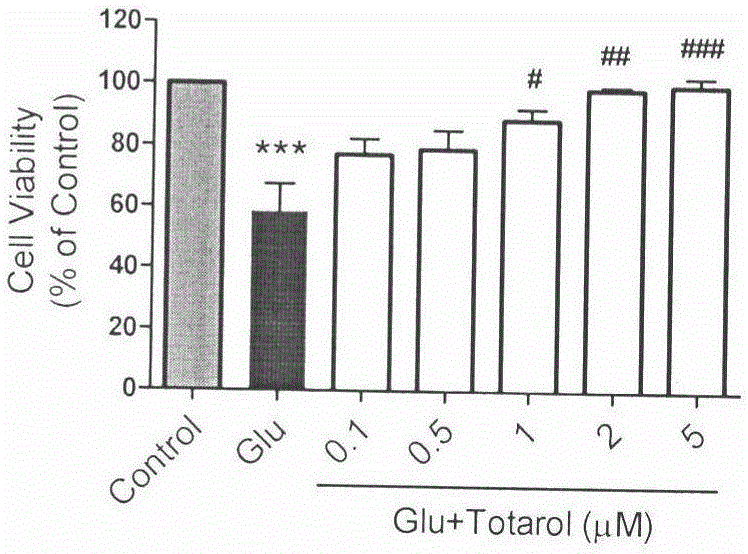
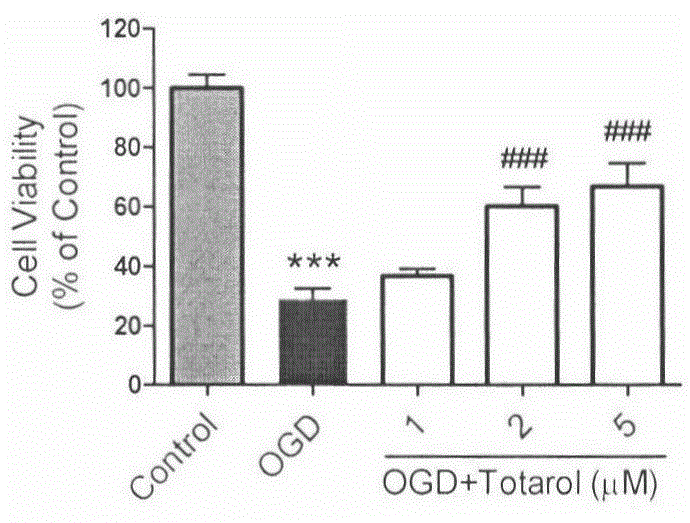
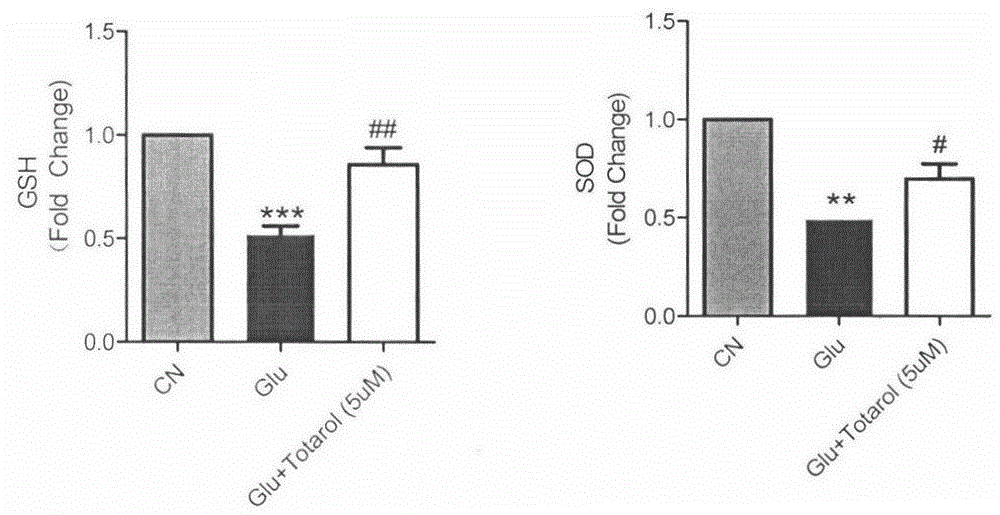
Application of totarol to preparation of drug for preventing and treating ischemic cerebral apoplexy
InactiveCN105055380AHydroxy compound active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderCortical neuronsHypoglycemia
The invention belongs to the field of pharmaceuticals and relates to application of totarol serving as a natural product extracted from podocarpus totara to preparation of a drug for preventing and treating ischemic cerebral apoplexy. A result obtained by researching glutamic acid of rat cortex neurons, a hypoxia and hypoglycemia model and a rat middle cerebral artery occlusion experimental model shows that the totarol can be used for reducing neurotoxicity caused by glutamic acid, reducing neuron injury caused by hypoxia and hypoglycemia, improving the activity of glutathione peroxidase in cortical neurons and brain tissues and the activity of superoxide dismutase, reducing the volume of cerebral ischemia infarct caused after cerebral apoplexy and improving the scores of neurological behaviors. The result proves that the totarol has a remarkable neuroprotective effect for ischemic brain tissues and can be used for preparing a drug for preventing and treating ischemic cerebral apoplexy.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Corticogenesis of human pluripotent cells
This invention relates to in vitro methods for the induction of corticogenesis in human pluripotent cells, such as iPS cells, by culturing the cells under conditions which stimulate retinoid signalling and inhibit TGFss superfamily signalling. This may be useful in production of cortical neurons, in particular patient- specific cortical neurons; the modelling of juvenile and adult-onset neurological diseases; and the development of therapeutics.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE ENTERPRISE LTD
Method for detecting cortical neuron axonal growth guidance and application thereof
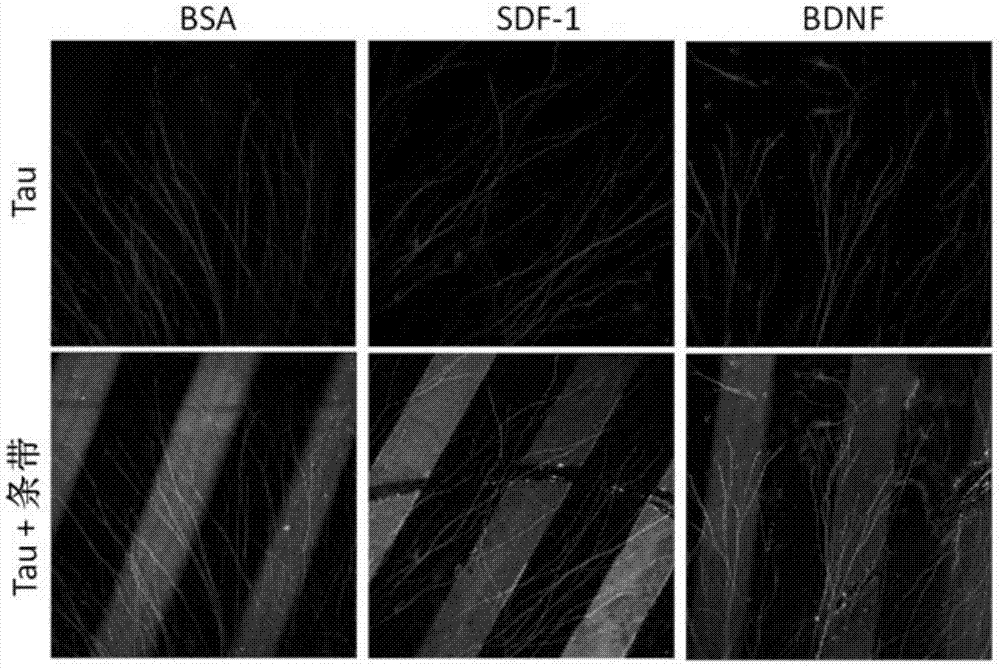
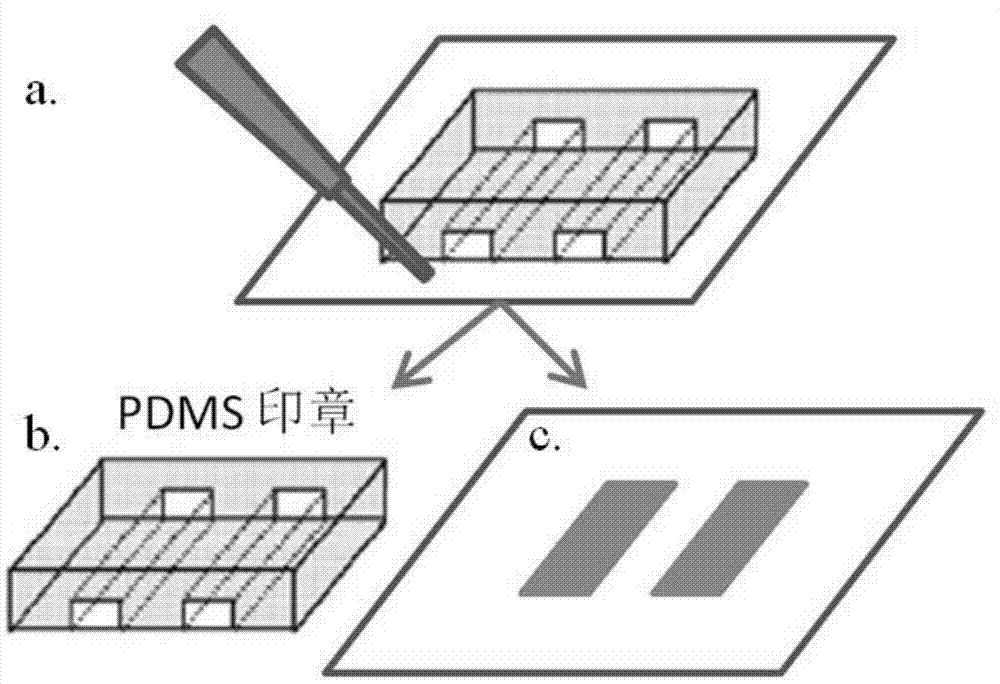
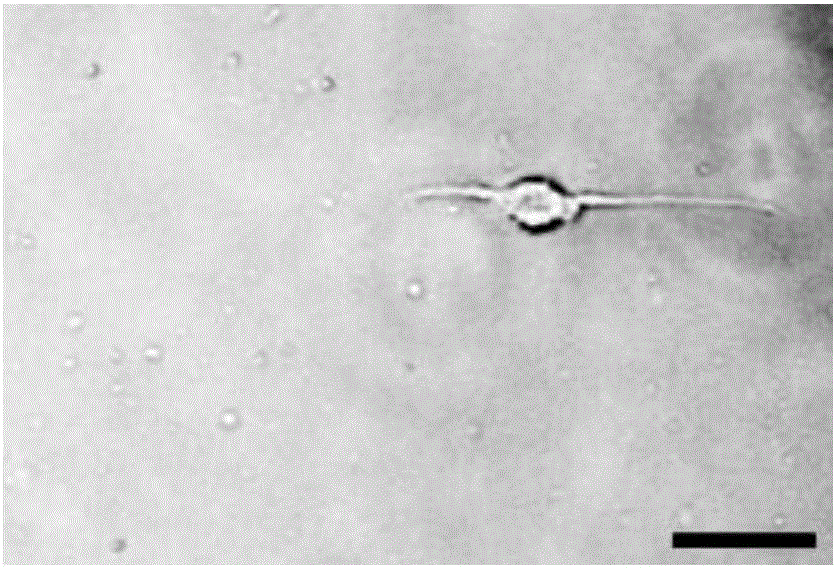
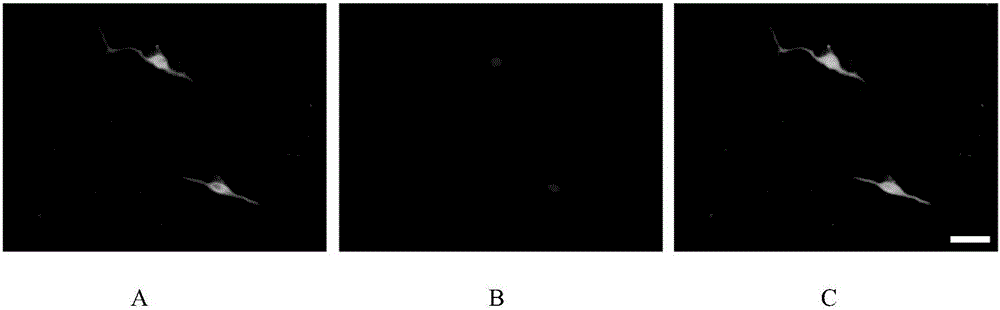
The invention relates to a method for detecting cortical neuron axonal growth guidance. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a stamp with a microscopy channel on a mold through polydimentylsiloxane, buckling the stamp on a glass slide for coating poly-L-lysine, adding a solution containing guidance factors and fluorescent molecules from one side of the channel so as to form parallel stripes with equal intervals after entering ducts; and performing neuron cultivation on the glass slide coated with the fluorescent stripe, observing whether newborn axon enters the stripe containing the guidance factors, and computing proportion of the newborn axon and the stripe, statistically analyzing. The method disclosed by the invention is not only in favor of understanding the forming mechanism of the neural circuit in a brain, but also has potential treatment value to the axonal degeneration and axonal injury diseases. On the basis of the method for detecting the cortical neuron axonal growth guidance, a disease model is established, the specificity expression of the secretion factor in the brain in the time and the space is simulated through exogenously giving cell secretion factor, the functional reconstruction of the neutron is induced, and the experimental basis is established for clinical translational medicine for treating above diseases.
Owner:SHANGHAI TENTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Naked mole rat cortical neuron culture method
ActiveCN105695411AGood conditionHigh activityCulture processNervous system cellsBiological propertyFunctional activity
The invention relates to the technical field of cell biology and in particular relates to a separation, purification and culture method of naked mole rat cortical neurons. The cortical neurons are separated from cerebral cortices of newly-born naked mole rats and are purified and cultured by comprehensively utilizing a plurality of types of culture mediums, and a reasonable culture method applicable to poikilothermal rodent mammal naked mole rat cortical neurons is explored. The method provided by the invention can be used for simply, conveniently, efficiently and economically obtaining a lot of naked mole rat cortical neurons with normal functional activity, and cells can still keep biological characteristics under an in-vivo state in an in-vitro environment through culture under a low-oxygen condition, so that special physiological functions of the naked mole rat cortical neurons can be conveniently and directly researched in a pure in-vitro cell culture model, and furthermore, an important theoretical basis is provided for exploring a biological mechanism and applying the biological mechanism to clinically relative fields.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Application of sambucus chinensis extract in preparing medicine for treating brain blood circulation disturbance
InactiveCN105380984AAvoid damageHigh activityNervous disorderCardiovascular disorderBrain sectionCortical neurons
The invention discloses application of a sambucus chinensis extract in preparing a medicine for treating brain blood circulation disturbance. The brain blood circulation disturbance refers to cerebral apoplexy. The sambucus chinensis extract is capable of reducing neurotoxicity caused by glutamic acid, reducing cortical neuron damage caused by oxygen-glucose deprivation, increasing the activity of glutathione peroxidase and superoxide disumtase in cortical neuronal cells and brain tissues and reducing the volume of cerebral ischemia infarction after cerebral apoplexy.
Owner:赵利锋
Application of magnolia odoratissma alkyl diol in preparation of composition having nerve restoration function
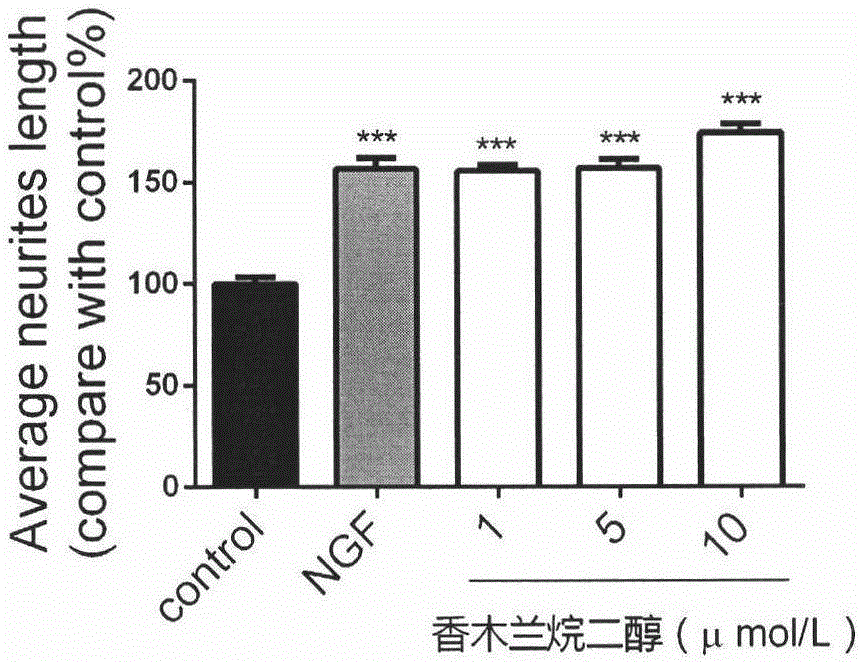
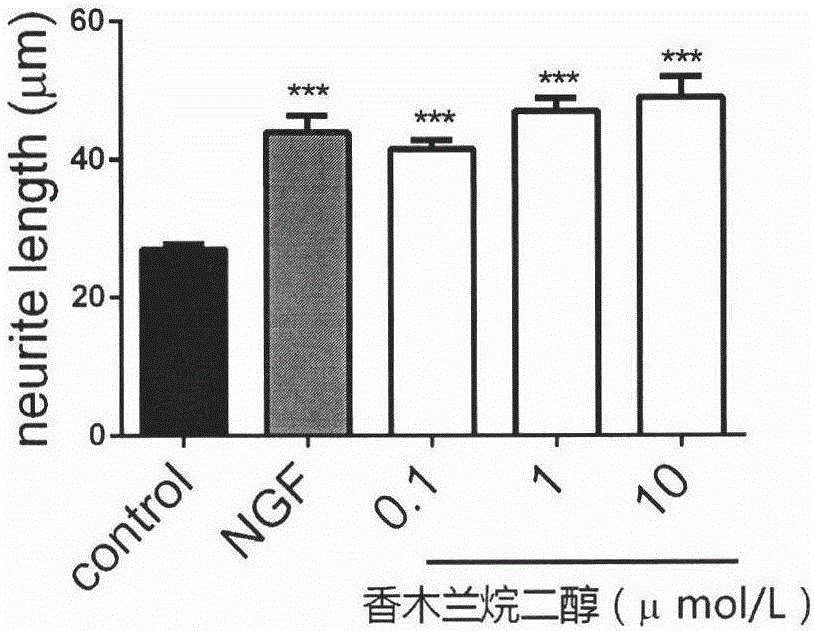
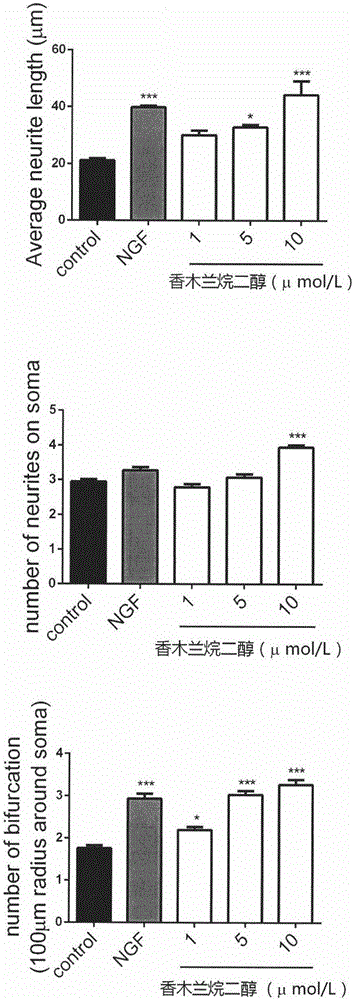
InactiveCN106265608ADiscovery of function that promotes nerve regenerationVitality has no effectNervous disorderHydroxy compound active ingredientsDiolCortical neurons
The invention relates to magnolia odoratissma alkyl diol which promotes regeneration of a nerve cell system and nerve cell axons, can promote increase of low-concentration induced PC-12 cell differentiation amount, obvious increased of the cell axon amount, obvious increase of axon length, obvious increase of neuroma mother cell N1E-115 axon length and prolonging and regeneration of fetal rat primary cortical neuron axons.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Compound, compositions and methods for preventing neurodegeneration in acute and chronic injuries in central nervous system
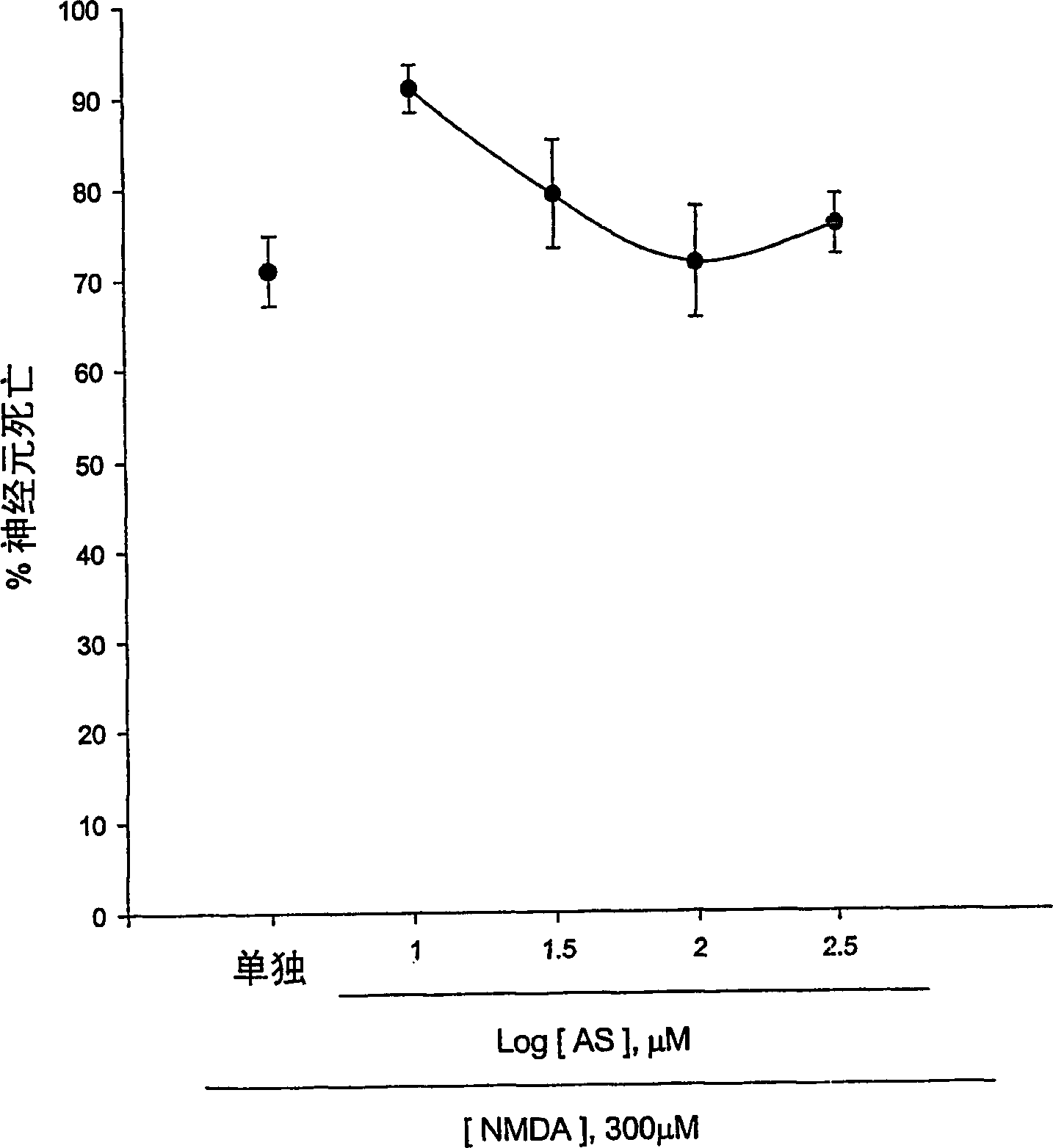
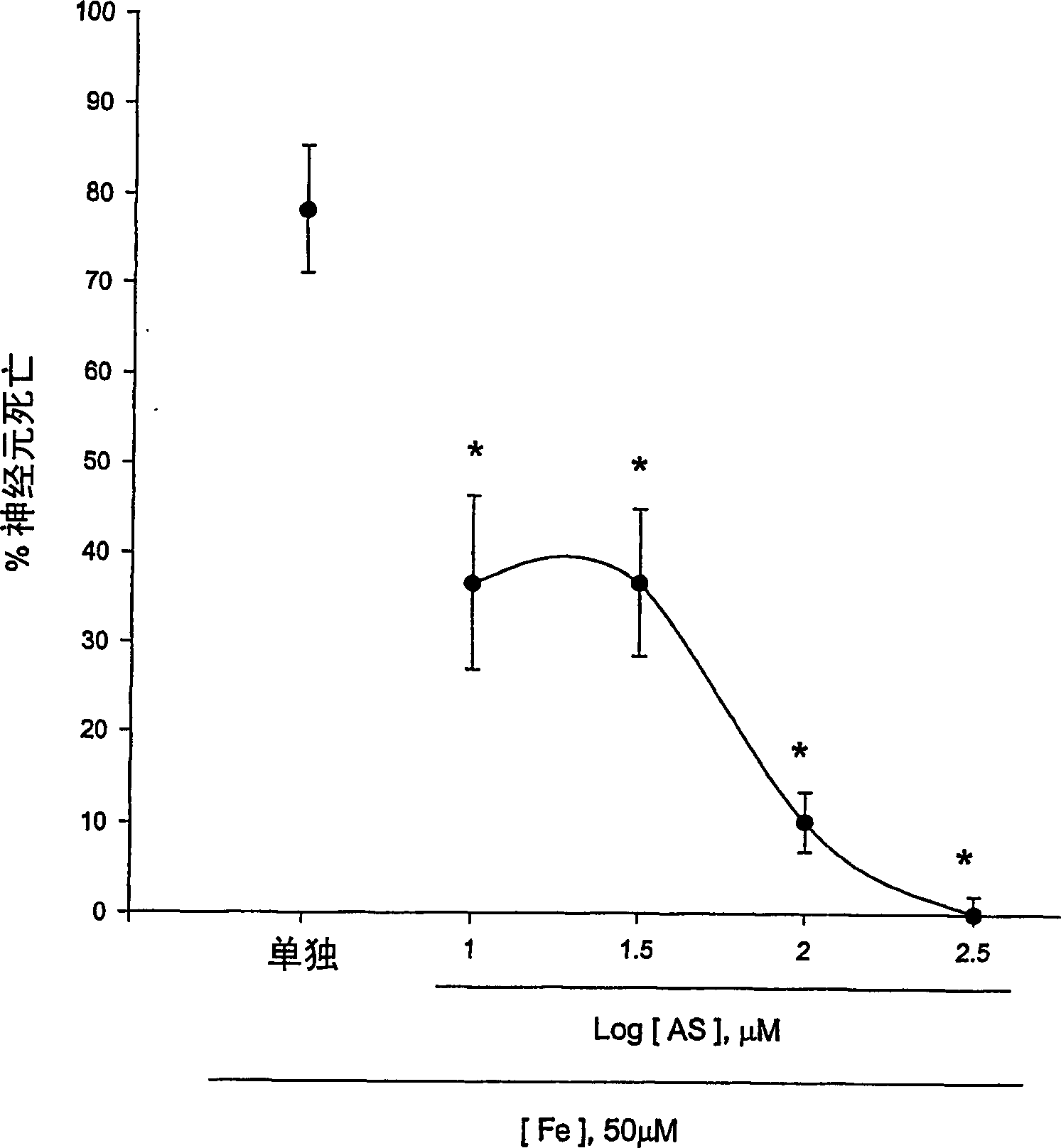
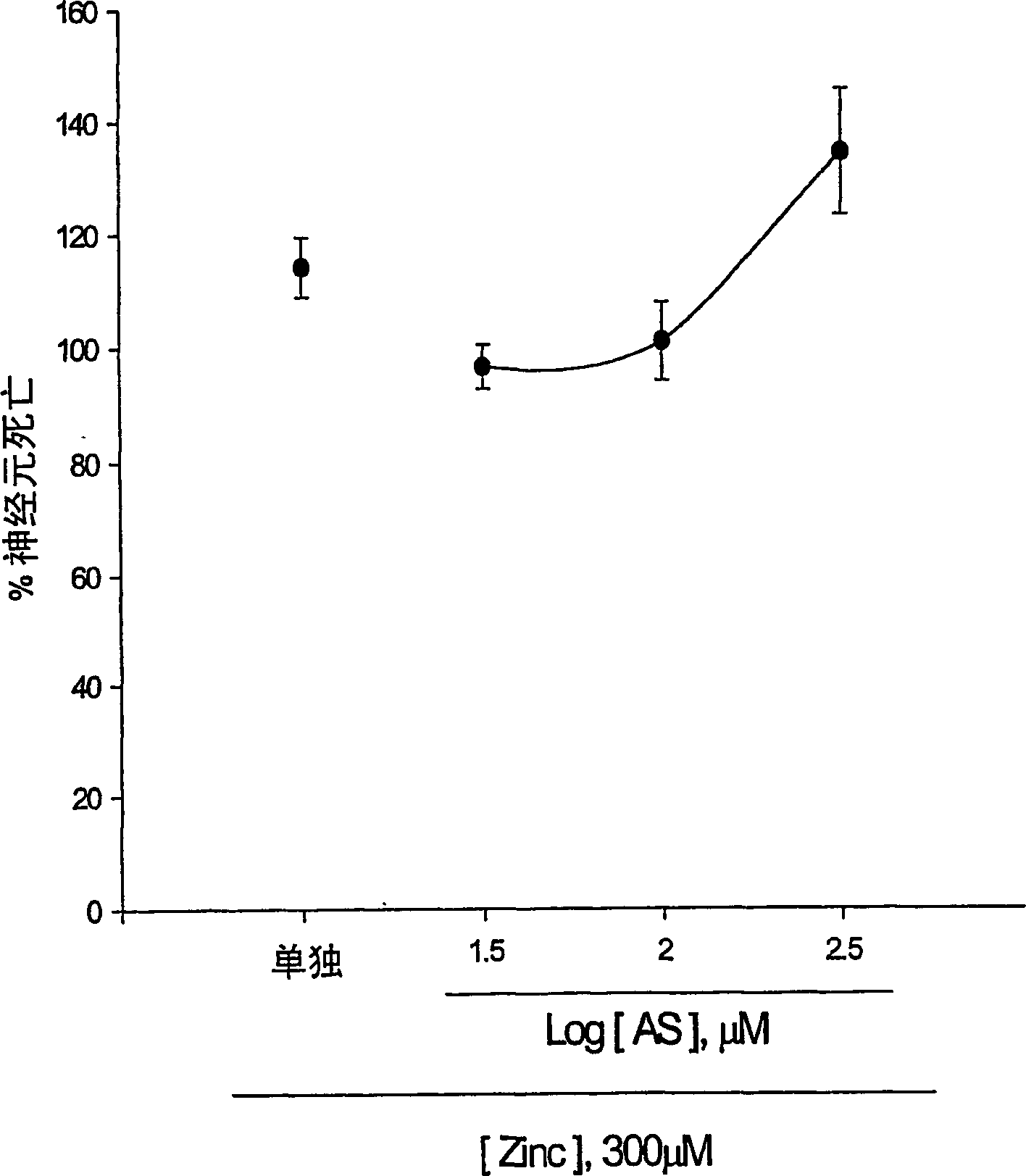
The present invention provides a compositions and methods for prevention and prophylaxis of neurological diseases accompanied by neuronal death. The invention includes synthesis of 5-benzylamino salicylic acid (BAS) and its derivatives. BAS and its derivatives protect cortical neurons from toxic insults by N-methyl-D-aspartate, Zn2+, and reactive oxygen species. Thus, the present invention provides compositions and methods for treating stroke, traumatic brain and spinal cord injury, epilepsy, and neurodegenerative diseases that are accompanied by severe neuronal loss via excitotoxicity, Zn2+ neurotoxicity, and free radical neurotoxicity.
Owner:GNT PHARMA
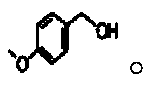
Application of 4-methoxybenzyl alcohol in preparation of neuroprotective drugs
InactiveCN105213357ASuppress generationInhibit apoptosisOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderNeuron morphologyCortical neurons
The invention discloses application of 4-methoxybenzyl alcohol in preparation of neuroprotective drugs. 4-methoxybenzyl alcohol may reduce injury of primary cortical neurons OGD / Rep of fetal rats and neuron morphological structure injury and increase survival rate of OGD / Rep injured cortex; the release of OGD / Rep injured cortical neuron NO is reduced, activity of SOD (superoxide dismutase) in cells is improved, generation of MDA (methane dicarboxylic aldehyde) is inhibited, apoptosis of nerve cells may be inhibited through significant up-regulation of Bcl-2 protein expression and down-regulation of Bax protein and Caspase-3 protein expression, neuroprotective effect is good, neuroprotective drugs may be produced, and nerve injury is reduced; in addition, the 4-methoxybenzyl alcohol may promote synapse growth of nerve cells, up-regulate synapse growth related proteins, promote repair of the nerve cells and treat nerve injury.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Methods and compositions for modulating axonal outgrowth of central nervous system neurons
InactiveUS7172871B1Sustained deliveryCompound screeningNervous disorderNervous systemRetinal ganglion
Methods and compositions for modulating the axonal outgrowth of central nervous system neurons are provided. Methods for stimulating the axonal outgrowth of central nervous system neurons following an injury (e.g., stroke, Traumatic Brain Injury, cerebral aneurism, spinal cord injury and the like) and methods for inhibiting the axonal outgrowth of central nervous system neurons in conditions such as epilepsy, e.g., posttraumatic epilepsy, and neuropathic pain syndrome, are also provided. These methods generally involve contacting the central nervous system neurons with a compound that modulates the activity of N-kinase, or analog thereof. The methods and compositions are particularly useful for modulating the axonal outgrowth of mammalian central nervous system neurons, such as mammalian cortical neurons or retinal ganglion cells. Pharmaceutical and packaged formulations that include the compounds of the invention that modulate the activity of N-kinase are also provided.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Transgenic model of alzheimer's disease
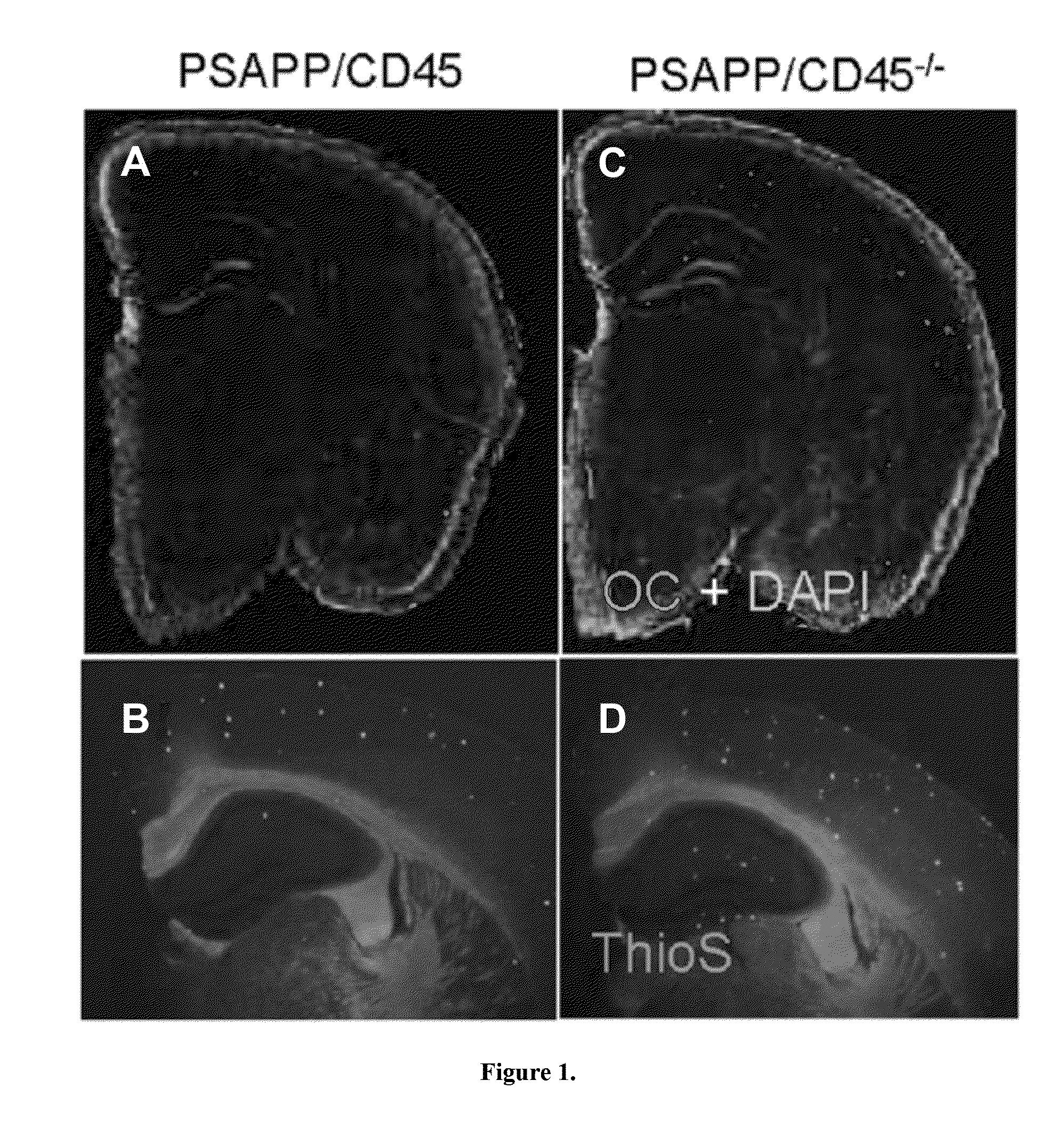
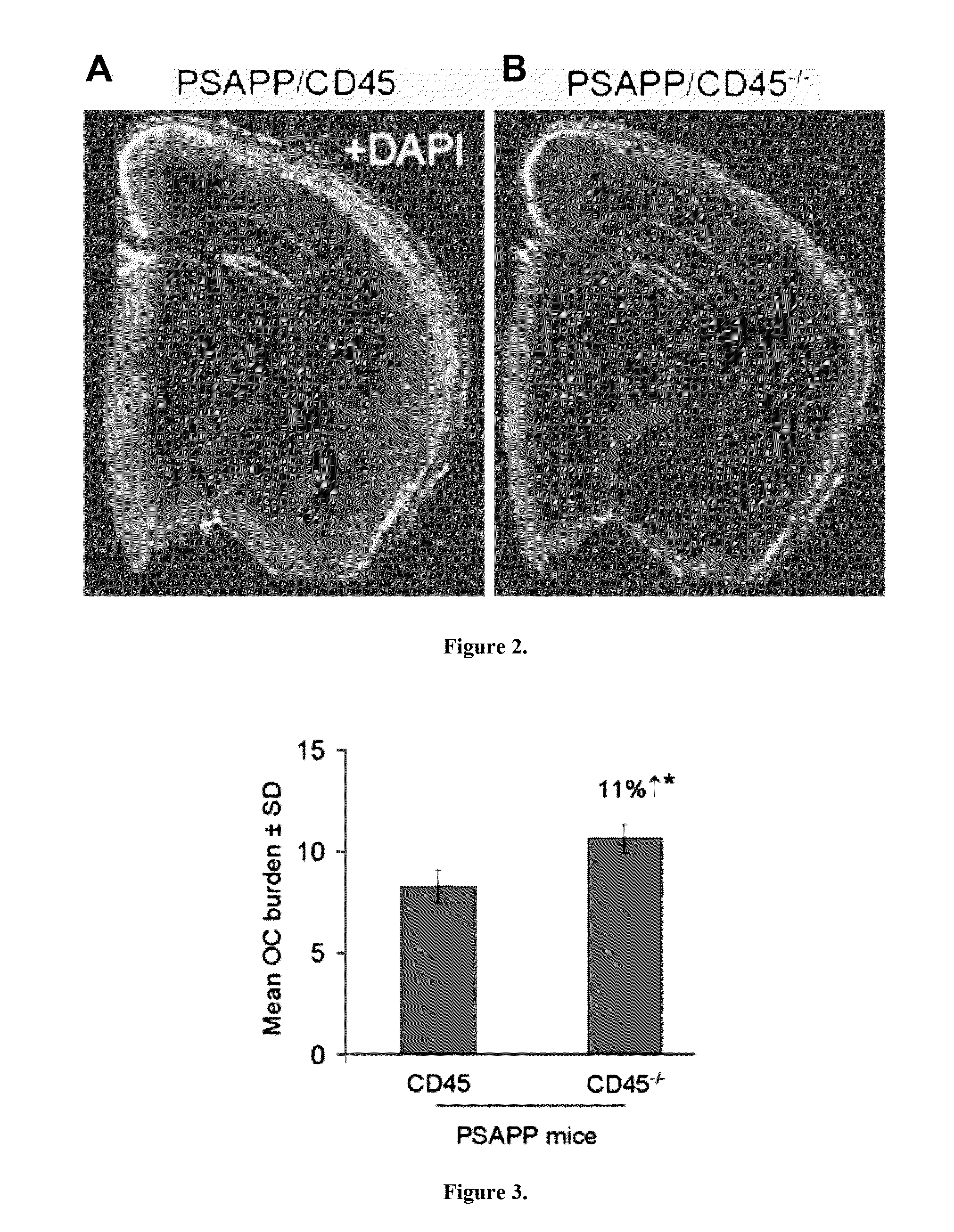
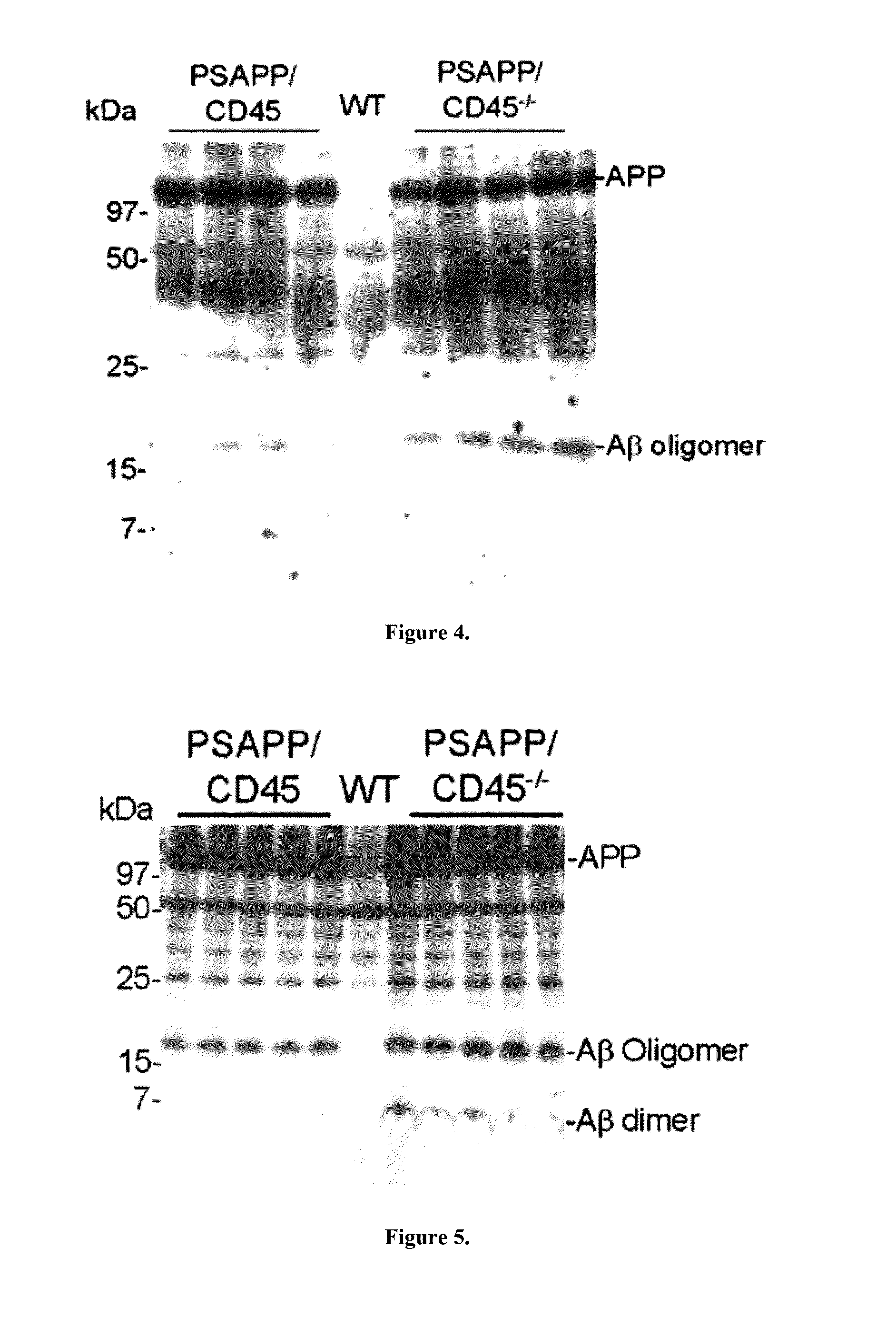
InactiveUS20130291135A1Improve the level ofImpaired amyloid clearanceGenetic engineeringFermentationAβ oligomersMicroglial cell activation
Evidence indicates dysregulation. of the immunoregulatory molecule CD45 occurs in Alzheimer's disease (AD). Transgenic mice overproducing amyloid-β peptide (Aβ) and deficient in CD45 (PSAPP / CD45− / −) recapitulate AD neuropathology. Increased cerebral intracellular and extracellular soluble oligomeric and insoluble Aβ, decreased plasma soluble Aβ increased microglial neurotoxic cytokines TNF-α and IL-1β, and neuronal loss were found in PSAPP / CD45− / − mice compared with CD45-sufficient PSAPP littermates. After CD45 ablation, in vitro and in vivo studies demonstrate a microglial phenotype whereby microglia phagocytose less Aβ but display proinflammatory properties. This microglial activation occurs with elevated Aβ oligomers and neural injury and loss as determined by decreased ratio of anti-apoptotic Bcl-xL to proapoptotic Bax, increased activated caspase-3, mitochondrial dysfunction, and loss of cortical neurons in PSAPP / CD45− / − mice. These data show that deficiency in CD45 activity leads to brain accumulation of neurotoxic Aβ oligomers and validate CD45-mediated microglial clearance of oligomeric Aβ as a novel AD therapeutic target.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com