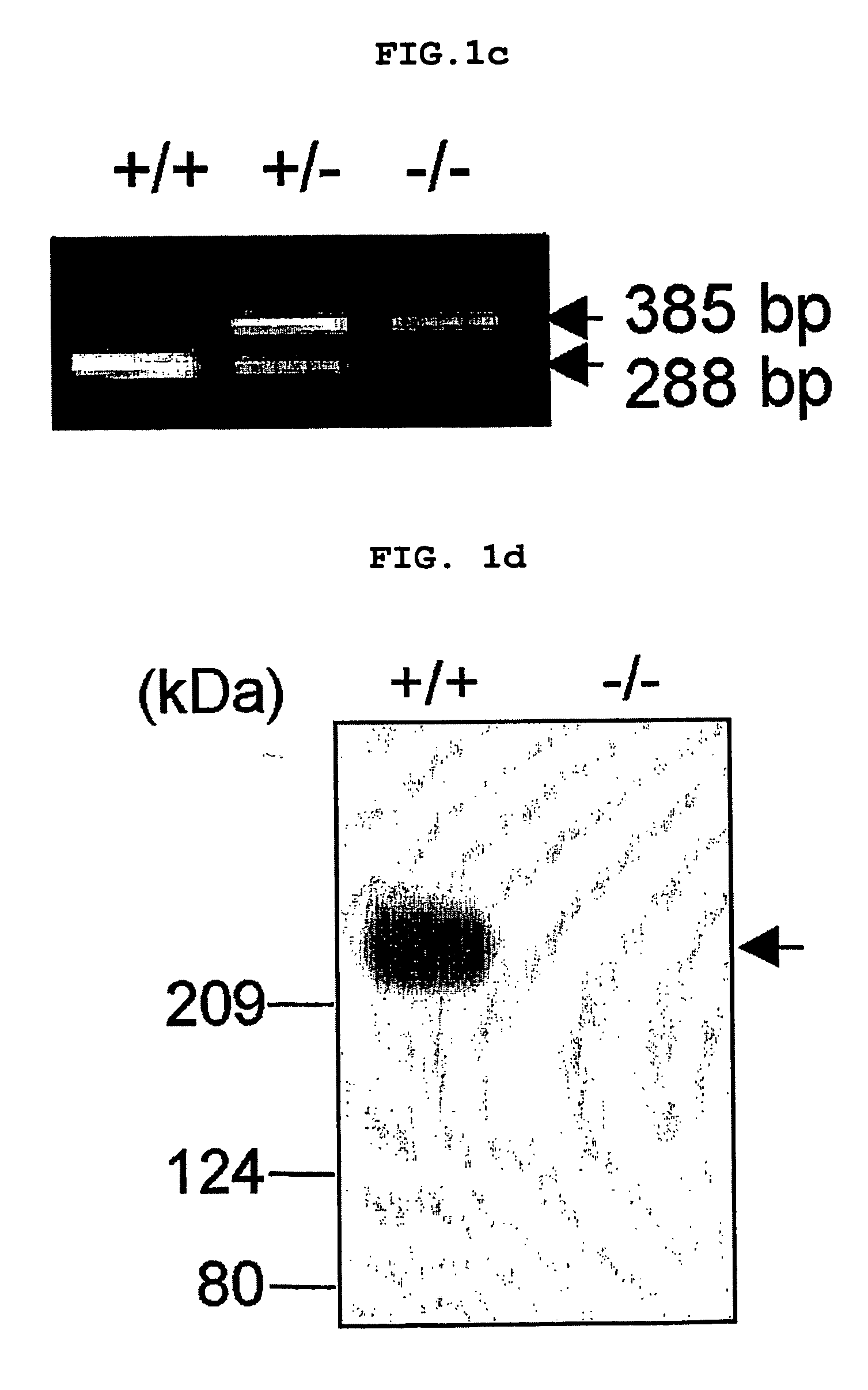
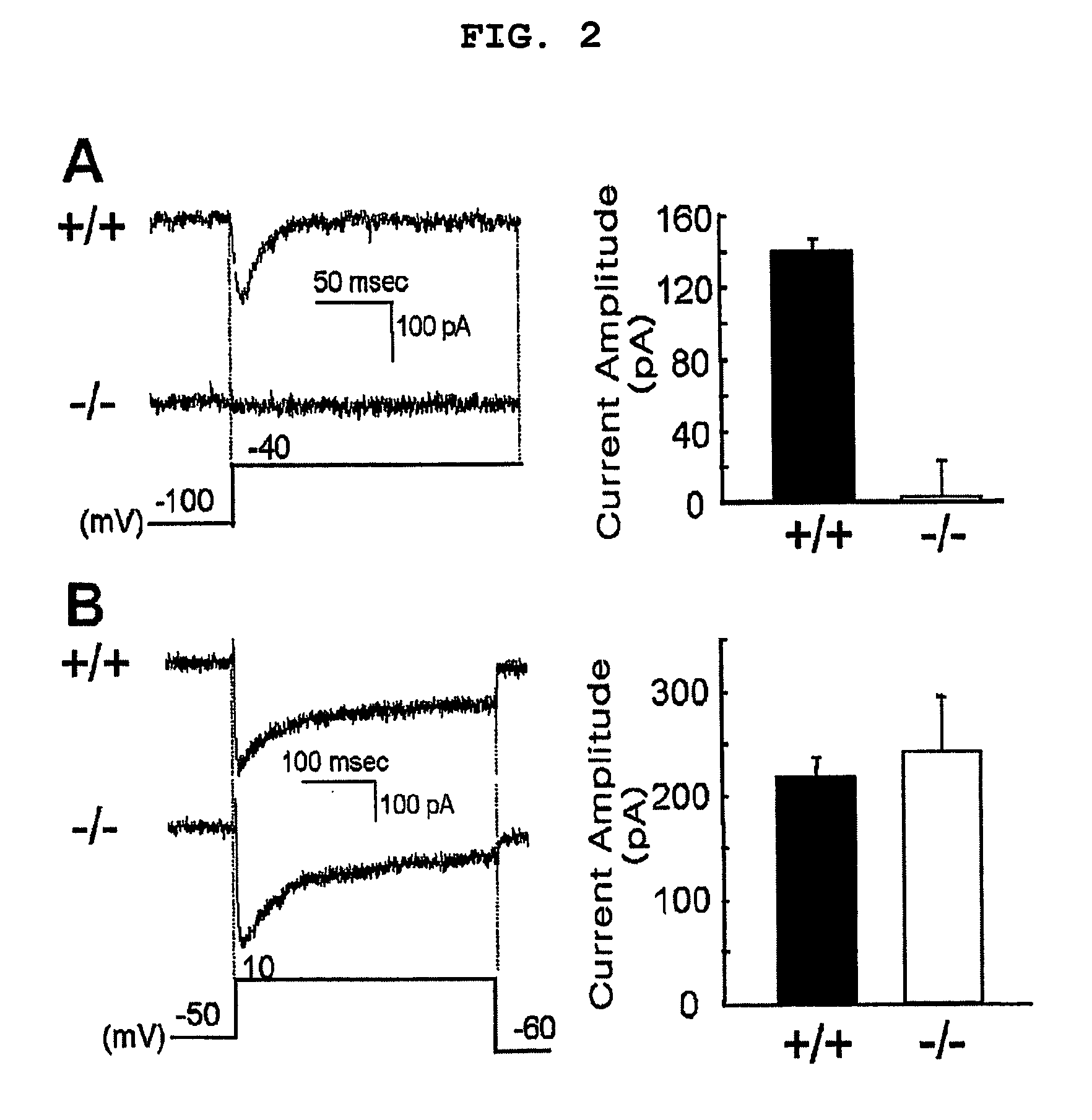
Patents
Literature
288 results about "Knockout animal" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
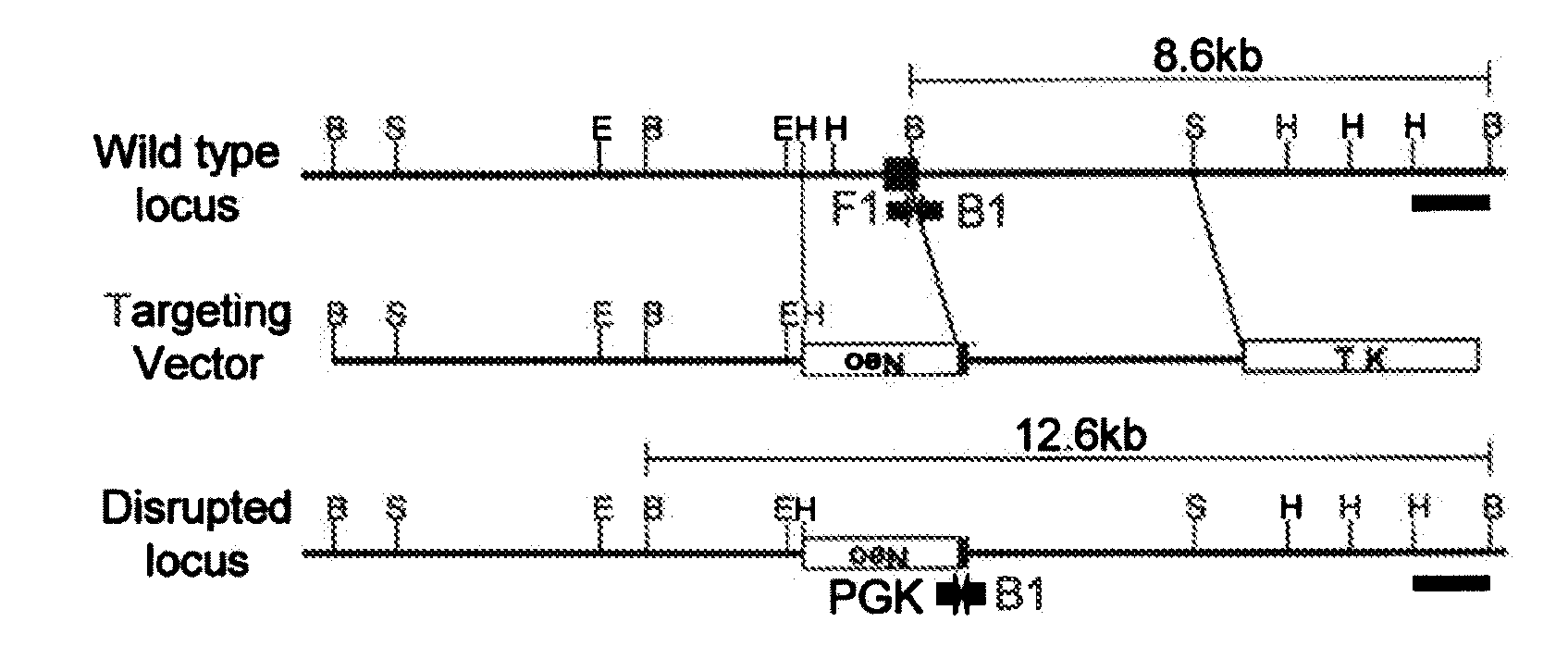
Knockout mouse. A knockout mouse or knock-out mouse is a genetically modified mouse (Mus musculus) in which researchers have inactivated, or "knocked out", an existing gene by replacing it or disrupting it with an artificial piece of DNA.
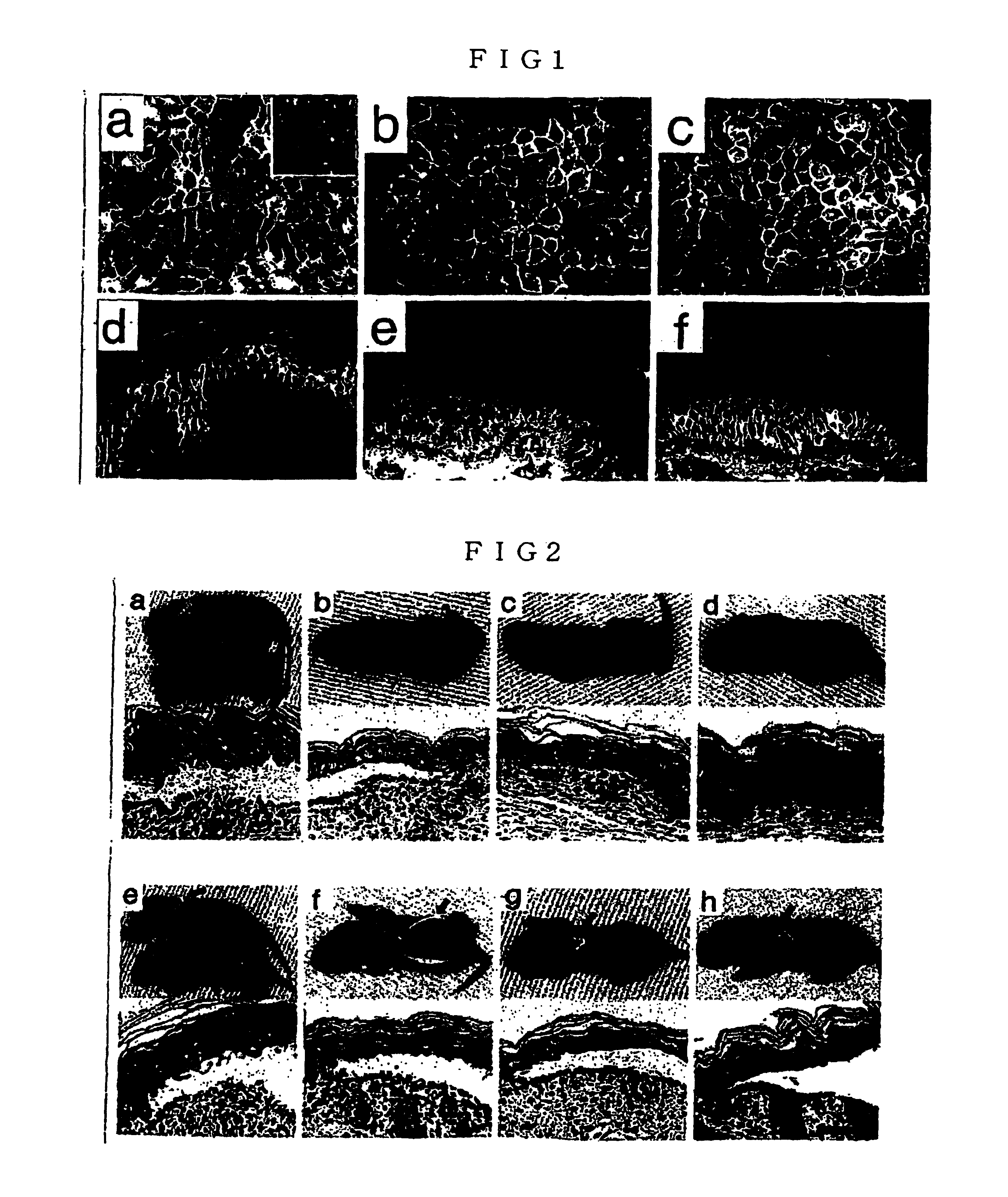
Phospholipase c beta1 (plcbeta1) knockout mice as a model system for testing schizophrenia drugs
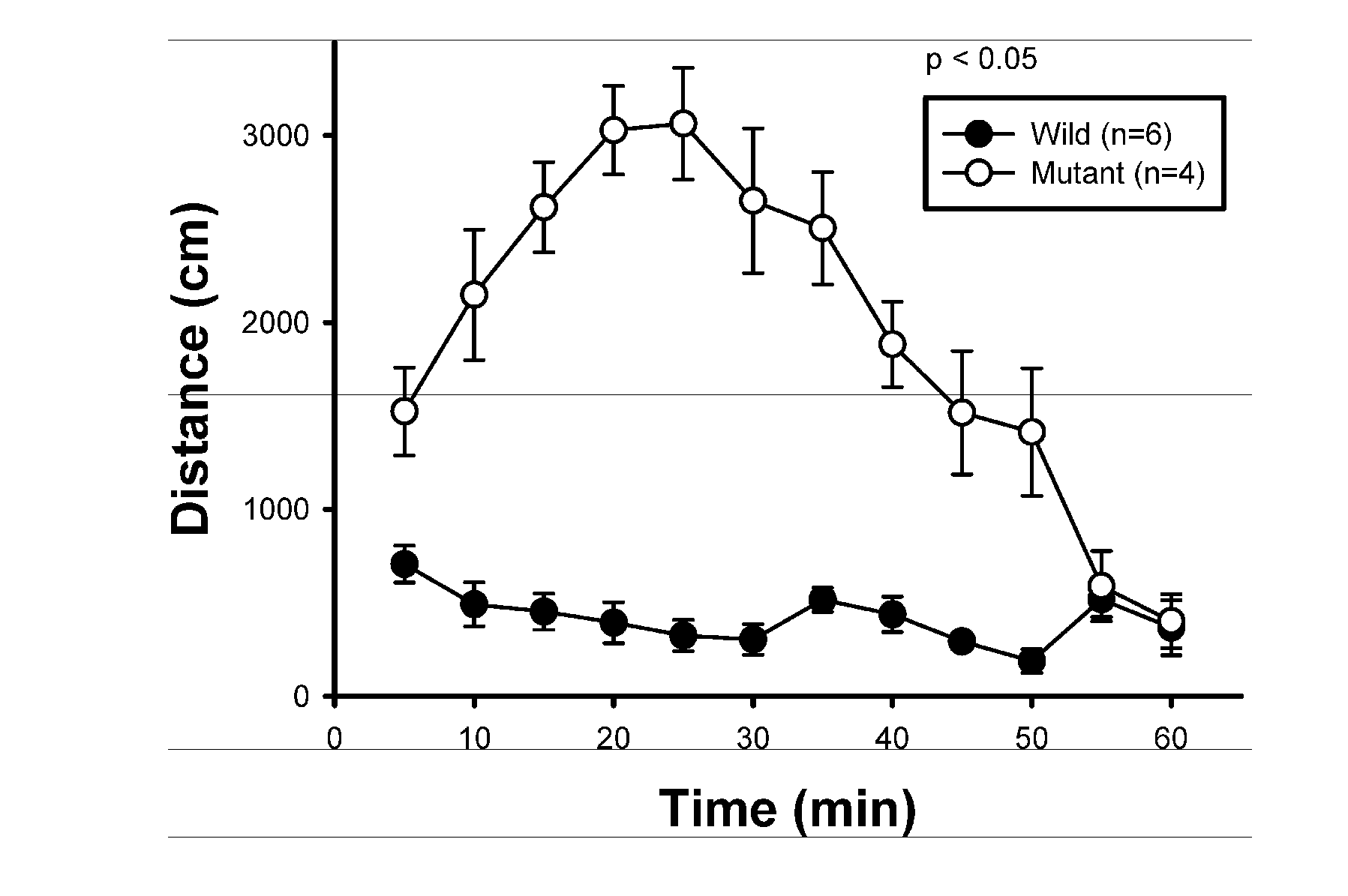
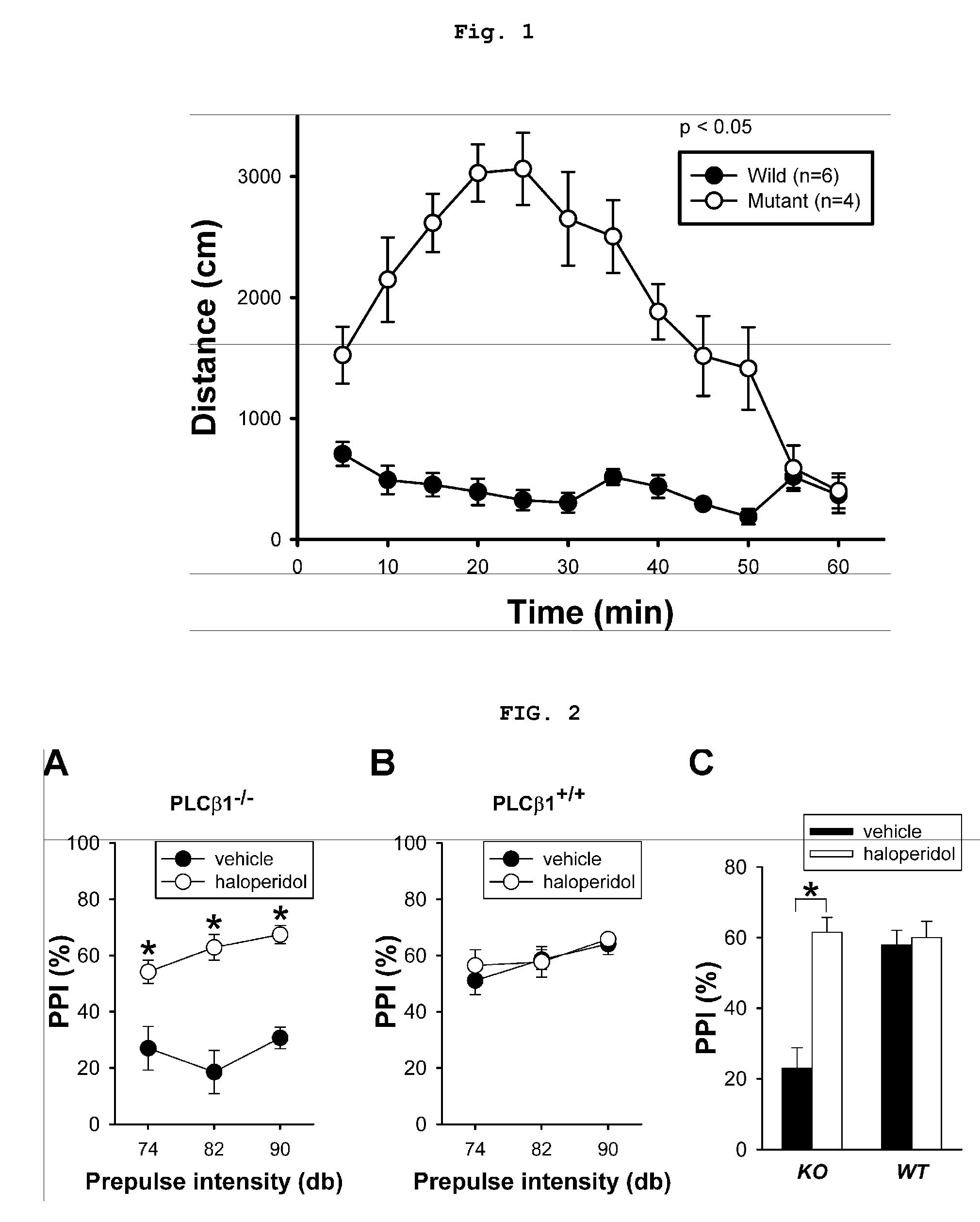
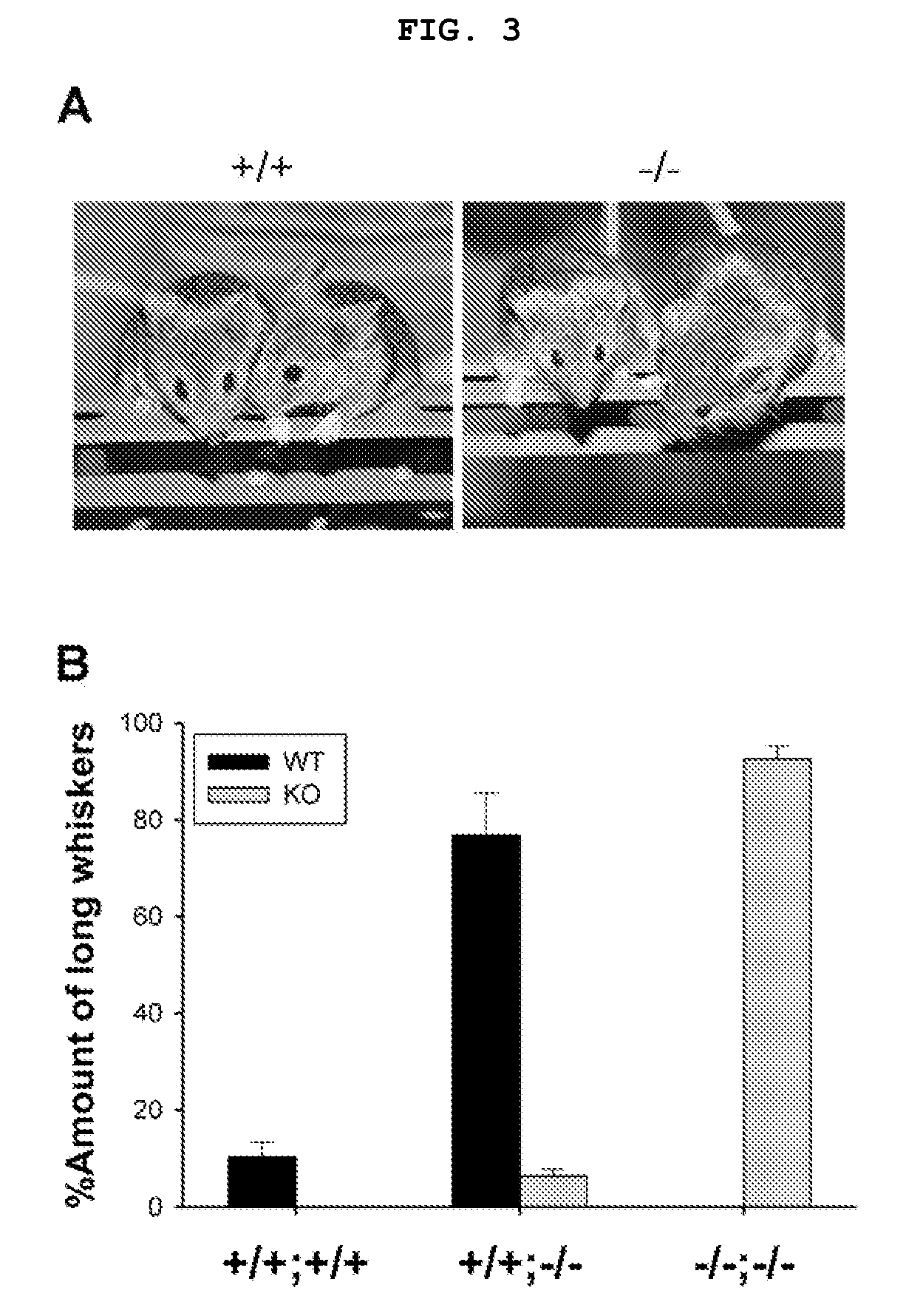
The present invention relates to a method for screening therapeutic drugs of schizophrenia using an animal model of the disease. More specifically, this invention relates to a screening method based on the phospholipase C β1 (PLCβ1) knockout mouse as an animal model of schizophrenia with all the major symptoms of the human disease. This knockout mouse exhibits symptoms similar to human schizophrenia such as locomotor hyperactivity, impaired prepulse inhibition of the startle response, lack of barbering and nesting behaviors, socially subordinate status, impaired learning, and lack of type II theta rhythm which has been implicated in working memory. Thus, the knockout mouse of the present invention can be useful as an animal for screening therapeutic drugs against schizophrenia.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
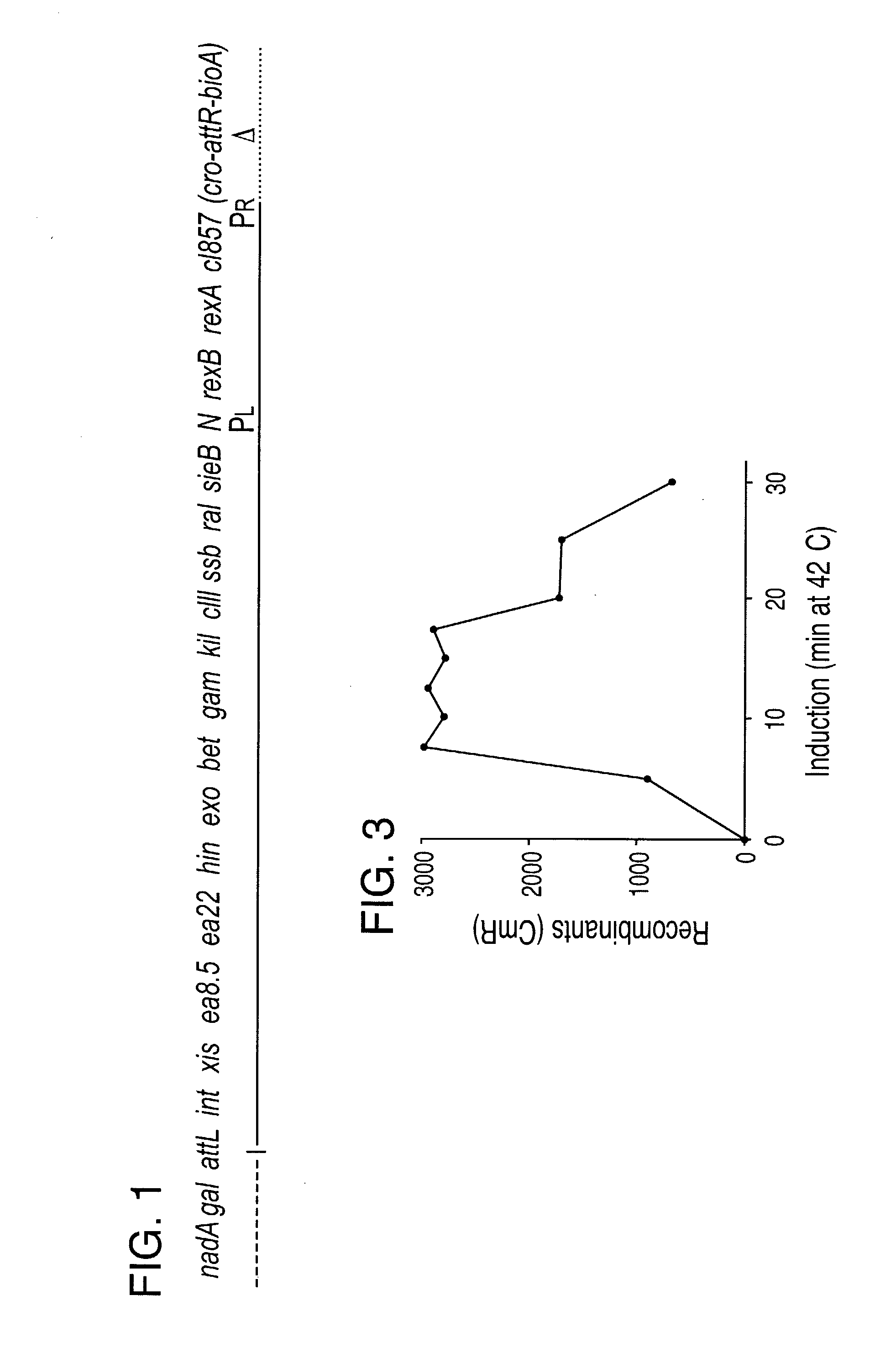
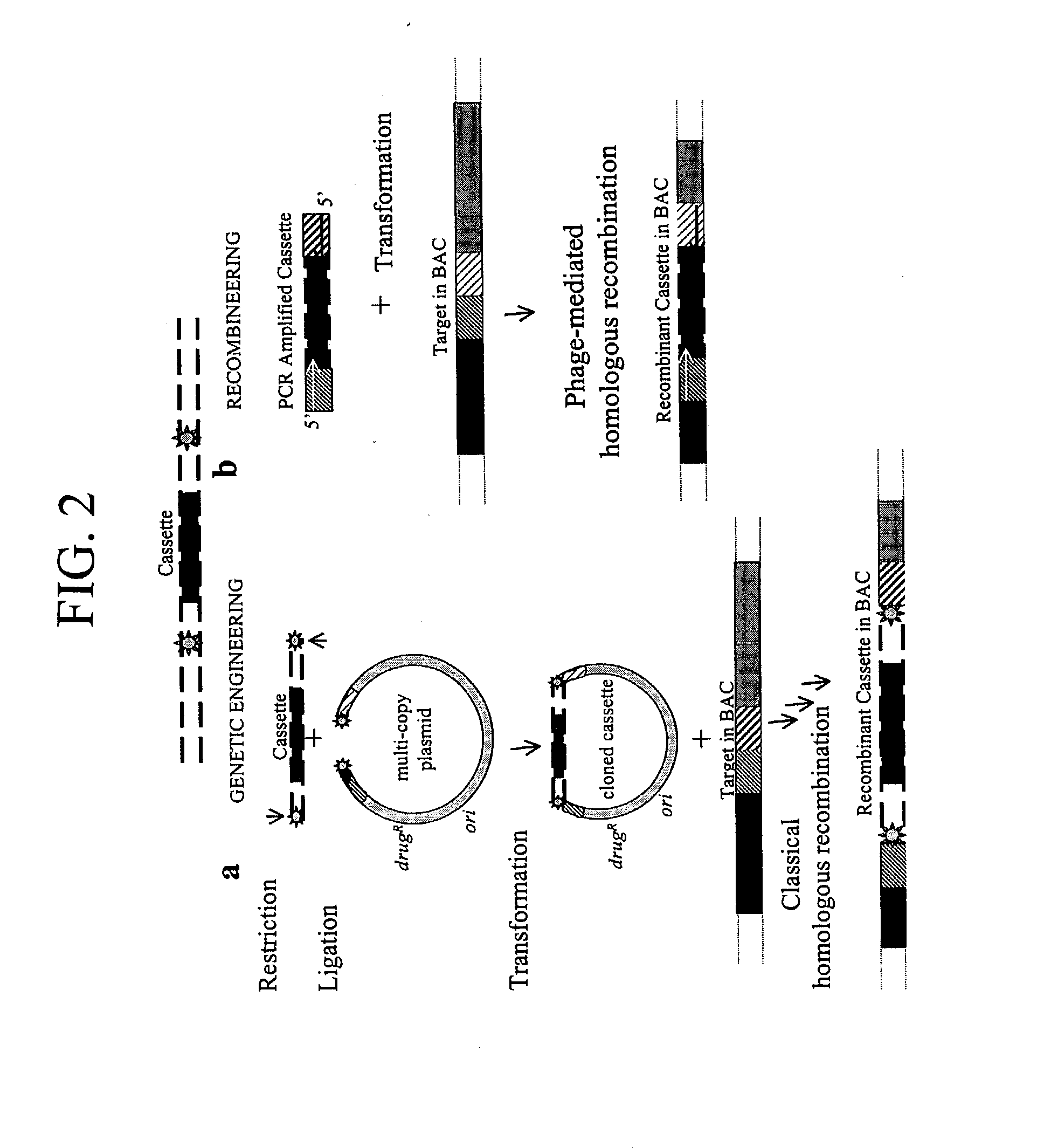
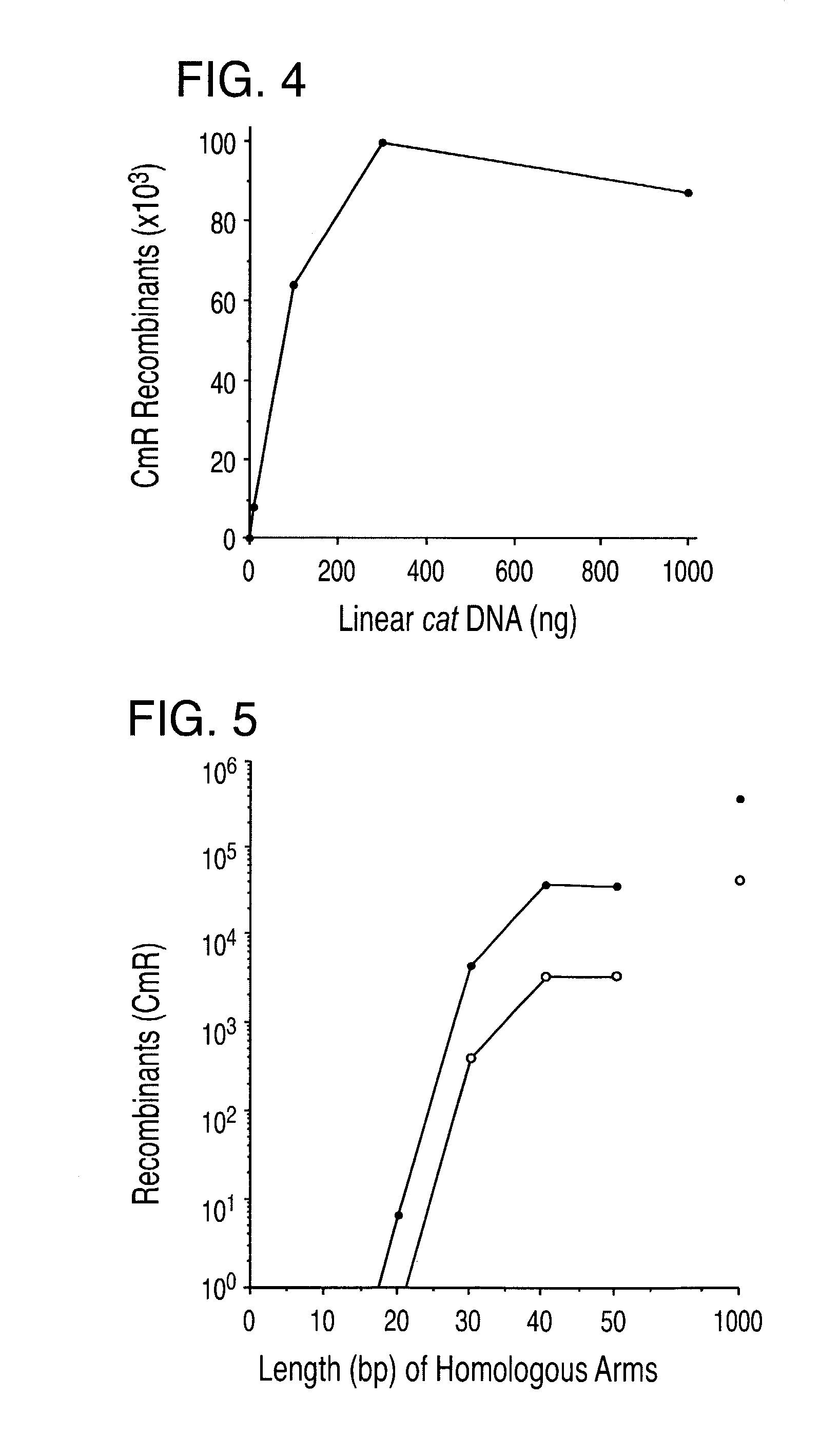
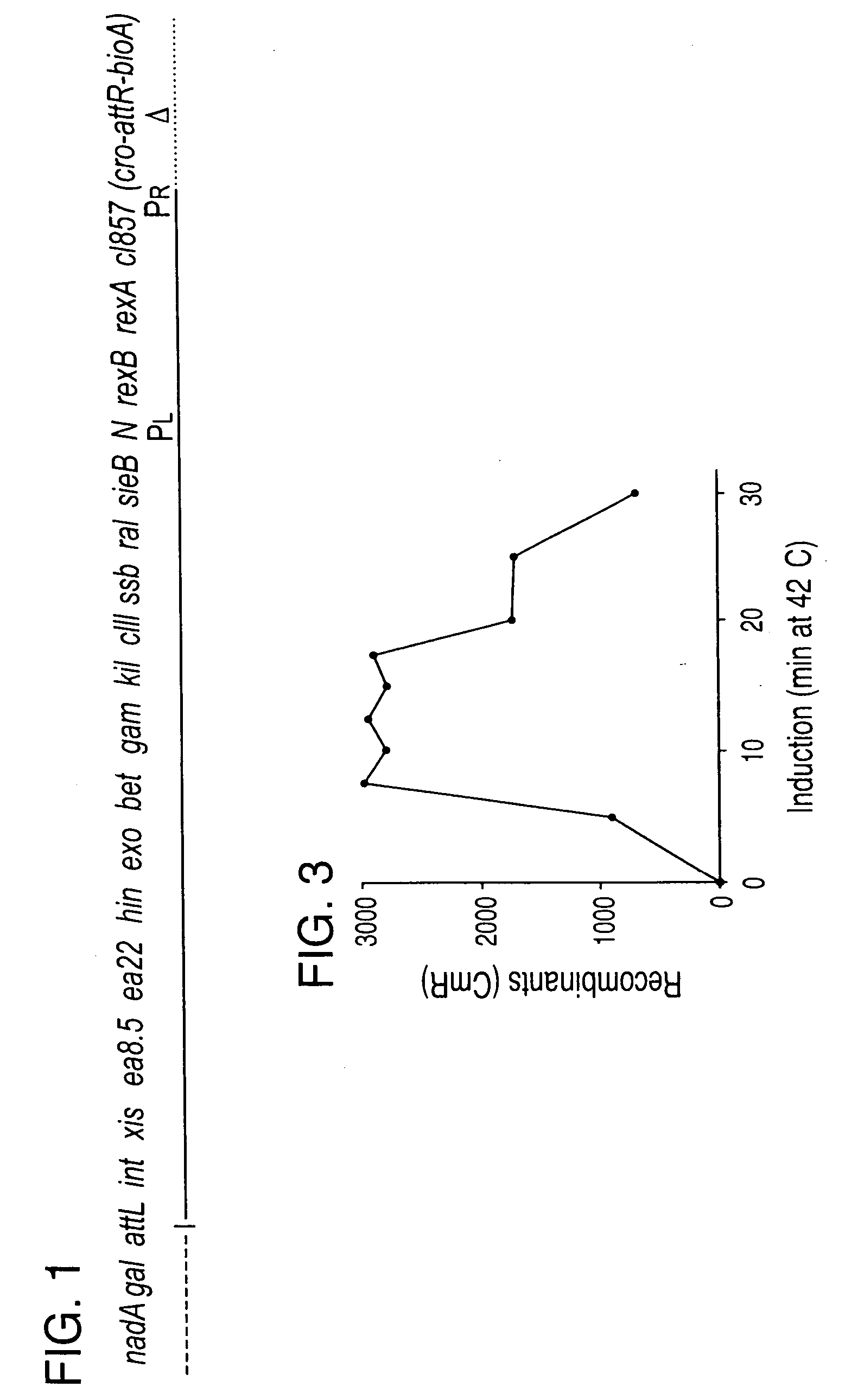
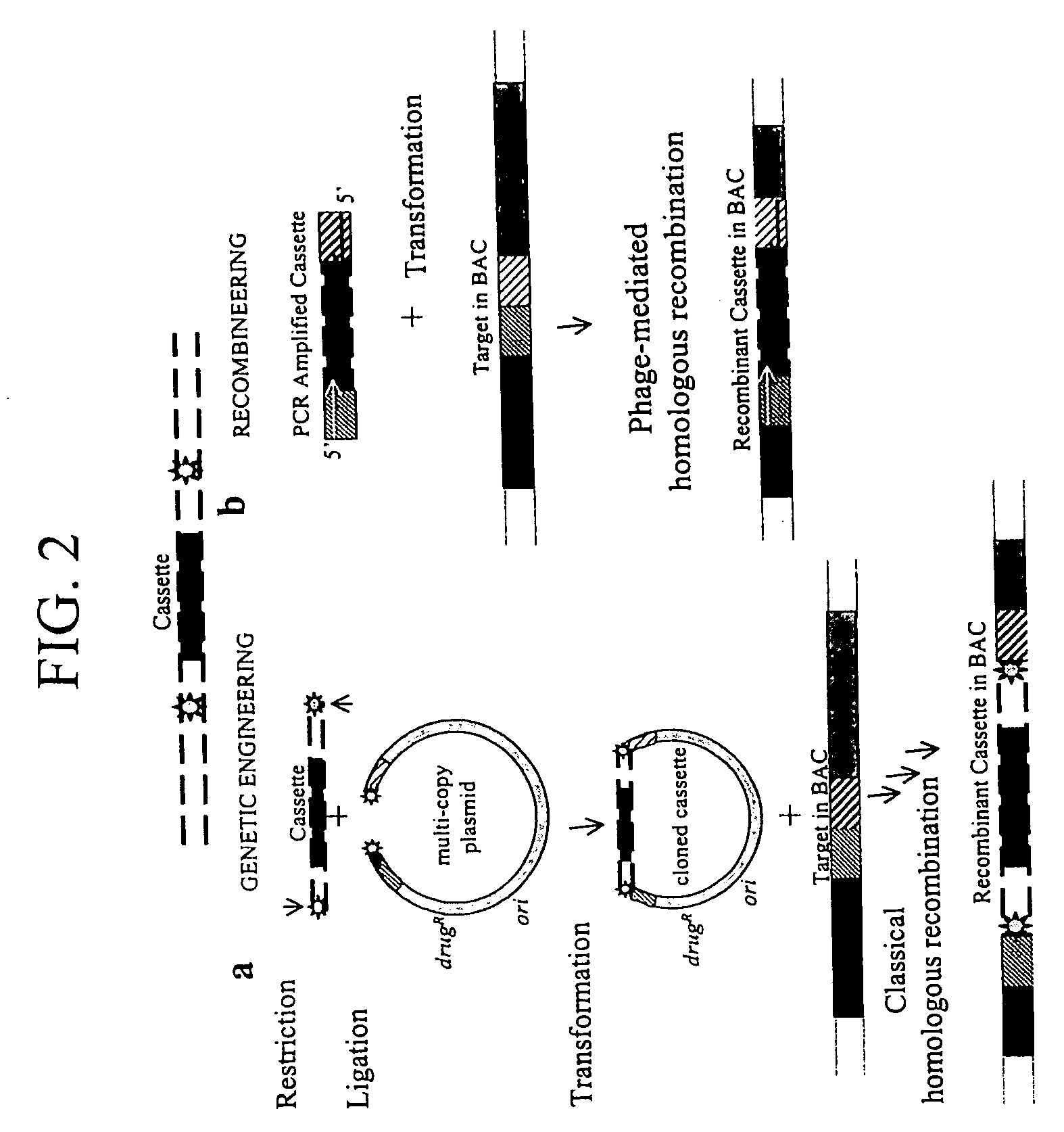
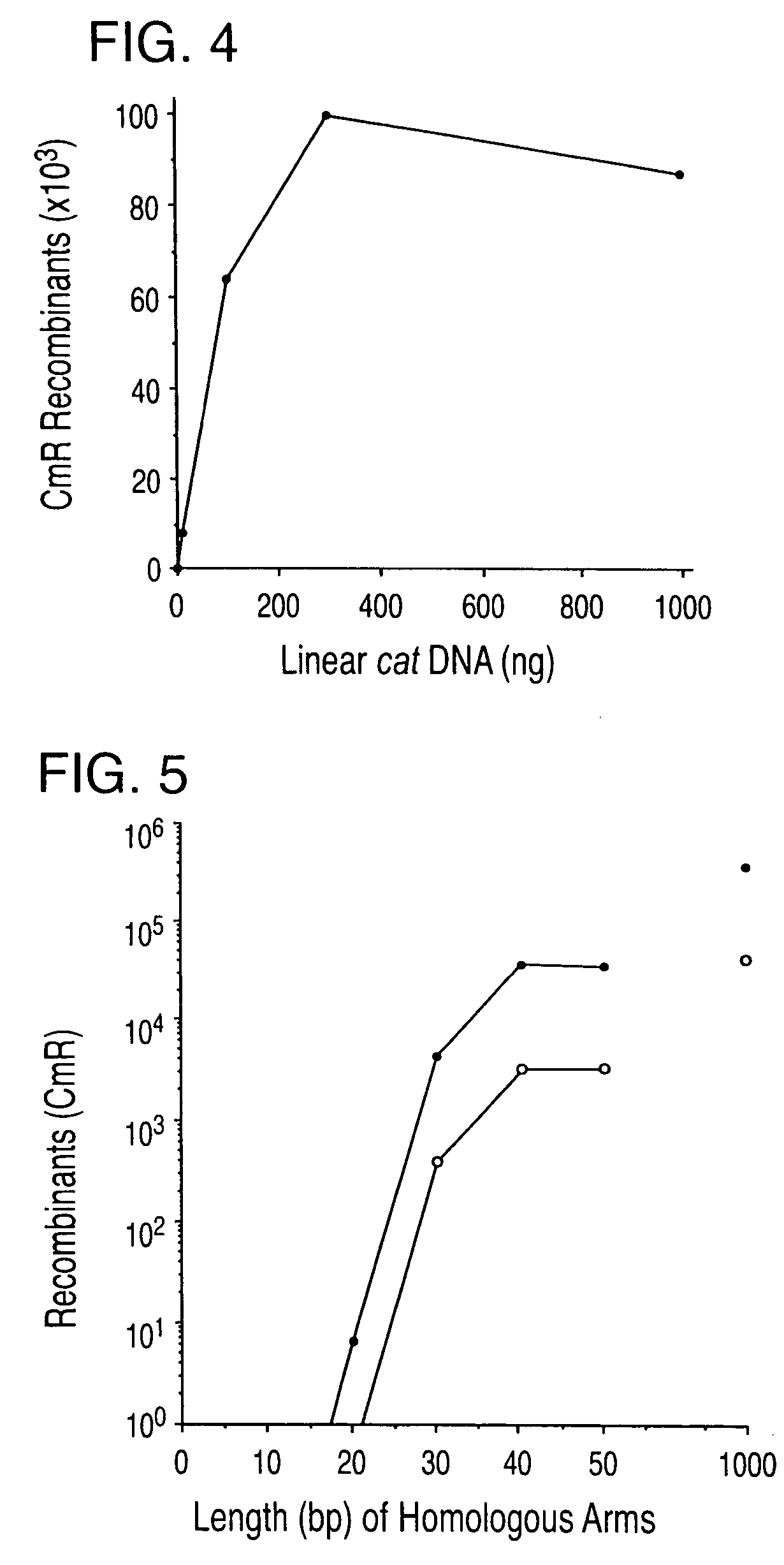
Enhanced homologous recombination mediated by lambda recombination proteins
InactiveUS20030224521A1Reduce chanceNormal EcoRV digestion pattern is restoredFungiBacteriaMammalKnockout animal
Disclosed herein are methods for generating recombinant DNA molecules in cells using homologous recombination mediated by recombinases and similar proteins. The methods promote high efficiency homologous recombination in bacterial cells, and in eukaryotic cells such as mammalian cells. The methods are useful for cloning, the generation of transgenic and knockout animals, and gene replacement. The methods are also useful for subcloning large DNA fragments without the need for restriction enzymes. The methods are also useful for repairing single or multiple base mutations to wild type or creating specific mutations in the genome. Also disclosed are bacterial strains and vectors which are useful for high-efficiency homologous recombination.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +1
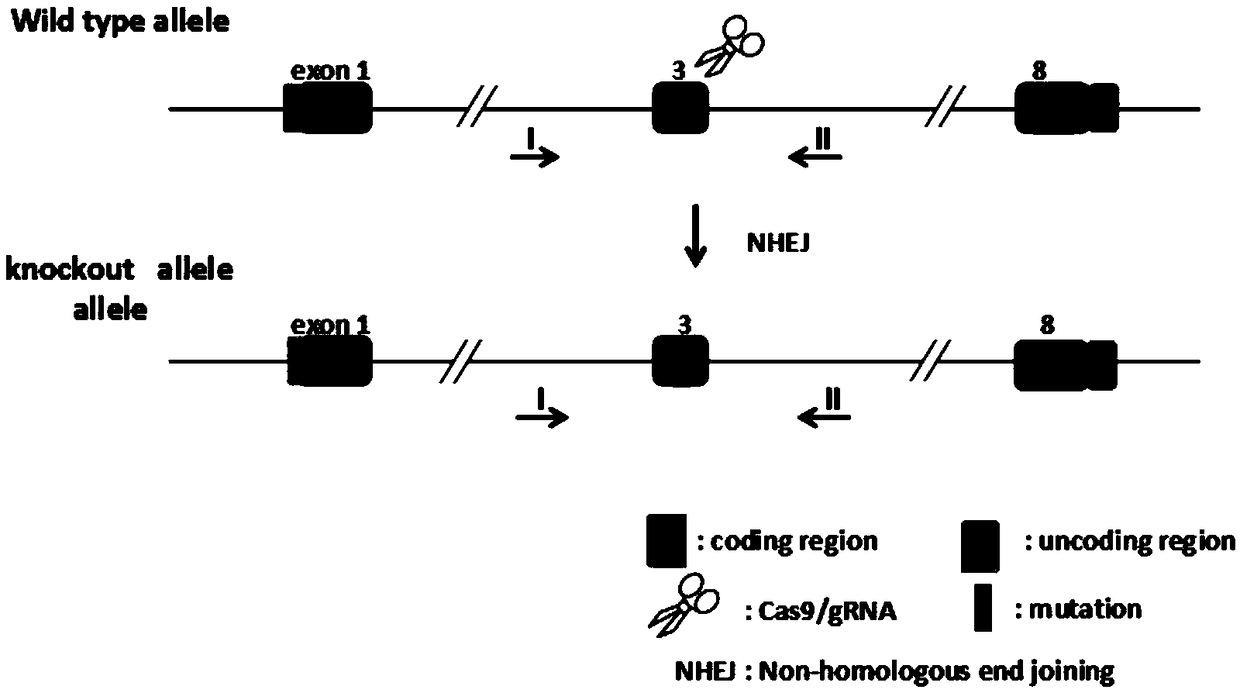
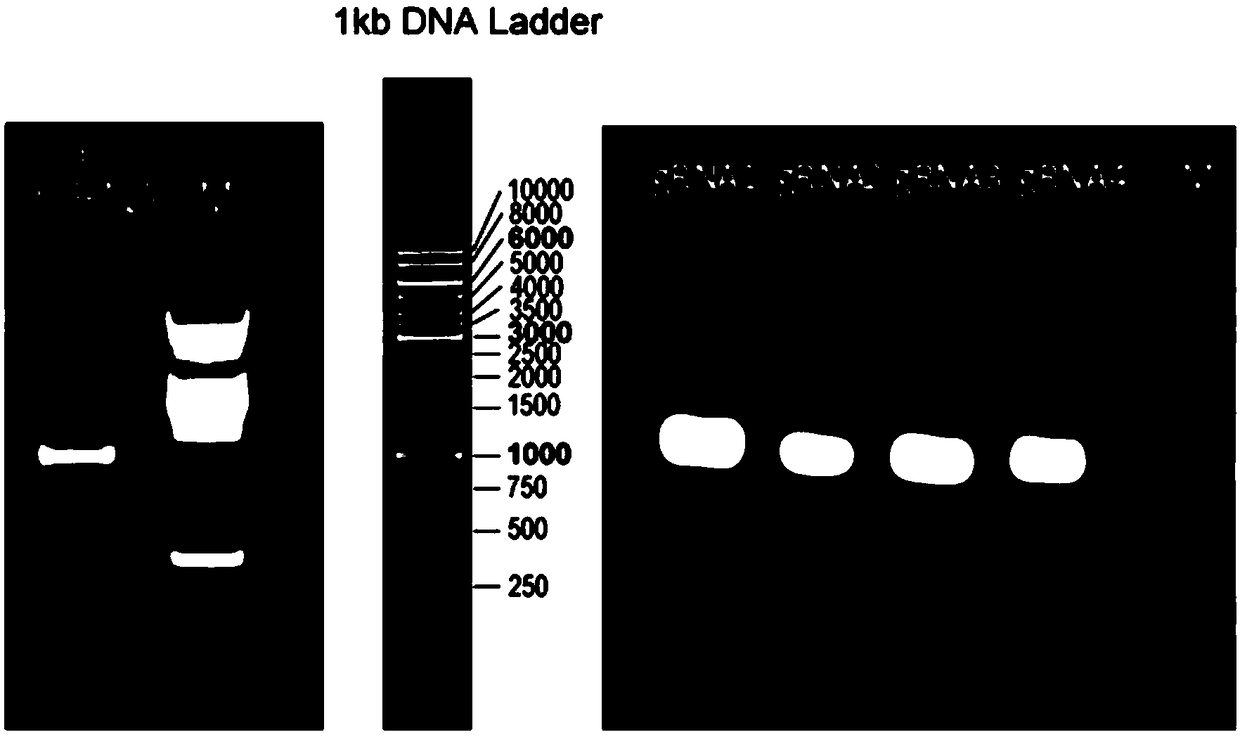
Construction method and application of Ifit3-eKO1 gene knockout mouse animal model
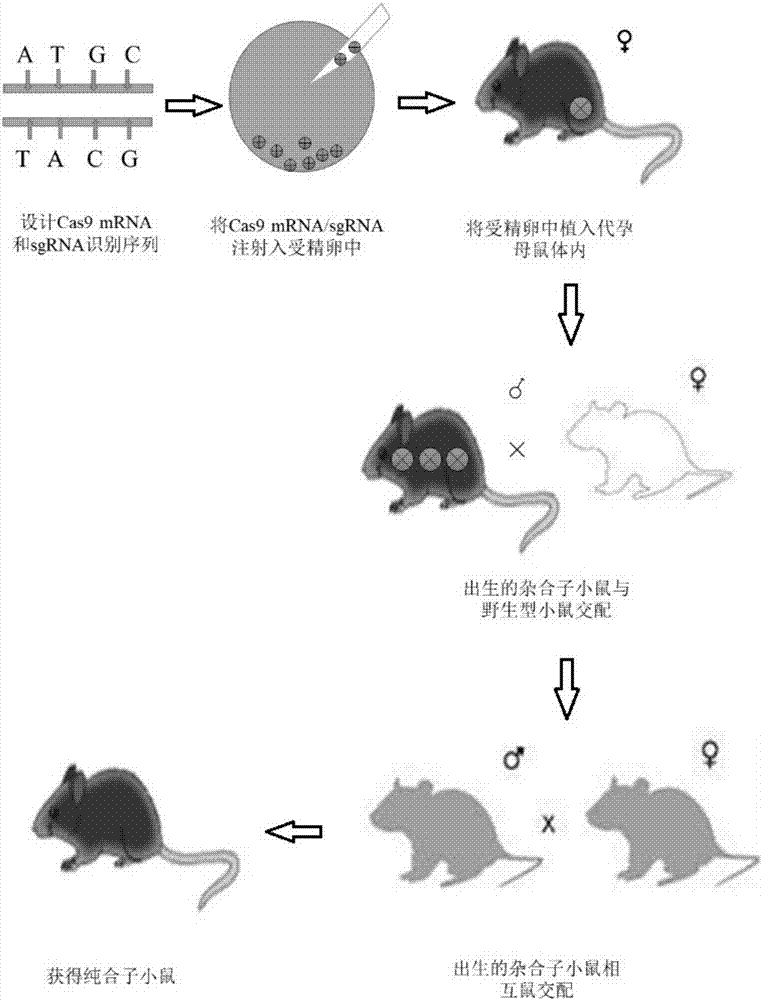
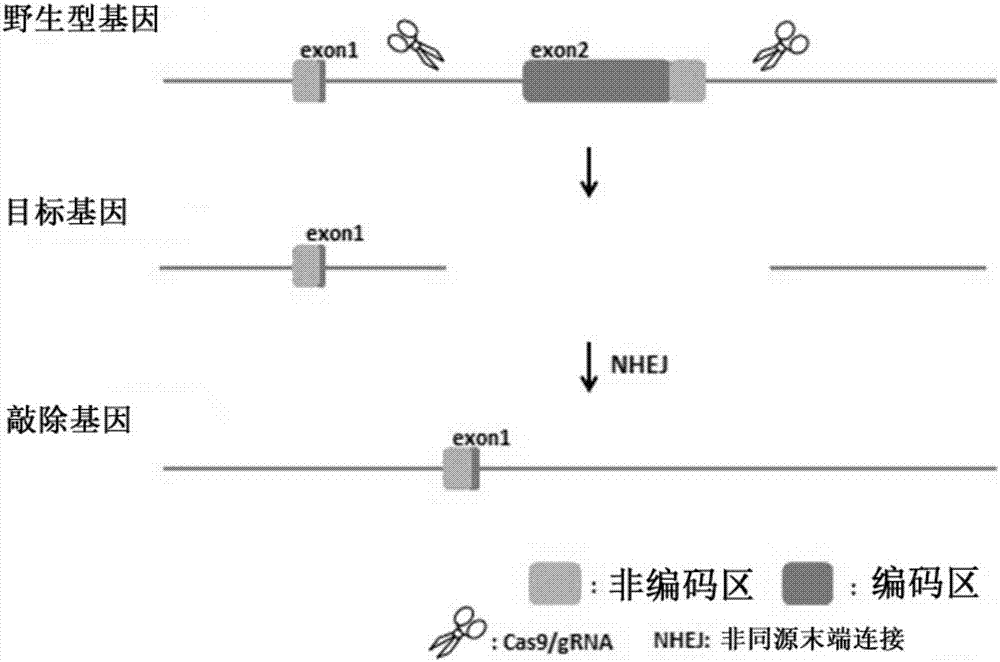
The invention relates to a method of constructing an Ifit3-eKO1 gene knockout mouse animal model and belongs to the biotechnical field. The method comprises the following steps: S1, determining specific target sites sgRNA1 and sgRNA2 of a to-be-knocked out gene of an Ifit3-eKO1 mouse, and performing in vitro transcription with Cas9 nuclease to mRNA; and S2, micro-injecting active sgRNA and Cas9RNA into an oosperm of the mouse to obtain the Ifit3-eKO1 gene knockout mouse. The method has the advantages that by using the CRISPR / Cas9 gene knockout technology, the Ifit3-eKO1 gene knockout mouse animal model is constructed for the first time, thereby providing a convenient, reliable and economical animal model for researching action of Ifit3 in tumorigenesis and development.
Owner:SHANGHAI TONGJI HOSPITAL
Construction method for Sqstm1 whole-genome knockout mouse animal model and application
The invention discloses a construction method for a Sqstm1 whole-genome knockout mouse animal model and application. The mouse animal model is a mouse of which the Sqstm1 gene is knocked out. On the basis of a CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) / Cas9 gene knockout technology, the Sqstm1 gene knockout mouse model is constructed. The construction method comprises the following steps: S1: designing sgRNA (Ribonucleic Acid) and Cas9 RNA, carrying out in vitro transcription to obtain mRNA, carrying out microinjection on the sgRNA and the Cas9 RNA with activity into amouse oosperm, to obtain the Sqtm1 gene knockout mouse; S2: identifying the Sqtm1 gene knockout mouse animal model. On the basis of the CRISPR / Cas9 gene knockout technology, the Sqstm1 gene knockout mouse animal model is constructed for the first time, and a convenient, reliable and economic animal model is provided for researching a relationship between Sqstm1 and diseases including autophagy, tumors and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI TONGJI HOSPITAL
Global nav1.7 knockout mice and uses
InactiveUS20120185956A1Robust behaviorPrevents painful responseCompounds screening/testingAnimal feeding stuffKnockout animalMyeloma cell
A viable global NaV1.7− / − knockout mouse is disclosed, and a breeding colony of global NaV1.7− / − knockout mice. Also disclosed are an isolated mouse gamete that does not encode a functional NaV1.7− / −, produced by the NaV1.7− / − knockout mouse; an isolated NaV1.7− / − mouse cell, or a progeny cell thereof, isolated from the NaV1.7− / − knockout mouse; and a primary cell culture or a secondary cell line and a tissue or organ explant or culture thereof derived from the NaV1.7− / − knockout mouse. Disclosed also are a hybridoma, wherein the hybridoma was originally formed from the fusion of the isolated NaV1.7− / − mouse cell mouse cell and a myeloma cell, and a method of making an antibody. Also disclosed are assays useful for screening prospective NaV1.7 inhibitors and dose ranging a test NaV17 inhibitor compound, which were validated using the NaV1.7− / − knockout mouse.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Method for constructing mouse model for conditional knockout of CCR5 gene of endothelial cell
ActiveCN107858373ALow densityIntegrity breachStable introduction of DNAAnimals/human peptidesKnockout animalHIV receptor
The invention discloses a method for constructing a mouse model for conditional knockout of CCR5 gene of endothelial cell. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, obtaining a CCR5loxp / loxp mouse, and mating with a Tie-2-cre / ERT2 mouse, so as to obtain heterozygous mice with specific knockout of CCR5 gene of the endothelial cell; mutually mating the heterozygous mice, so as to obtain homozygous mice with specific knockout of CCR5 gene out of the endothelial cell. The constructing method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the mouse with conditional knockout of endothelial cell gene is constructed via the CRISPR / Cas9 system, the mutation is led into the mouse by a cell specificity method, the missing of the CCR5 target gene occurs at the certain tissue organ of the test animal, the controllability of mechanism study is furthest realized, and the disadvantages that different tissues or cells are not distinguished, and target genes in all tissues or cells of themouse body are all removed in the conventional gene knockout technique is overcome.
Owner:SHANDONG KEYUAN PHARMA
Construction method and application of immunodeficient mouse animal model
InactiveCN107460196AImprove the level ofPromote basic researchCompounds screening/testingGenetically modified cellsKnockout animalWilms' tumor
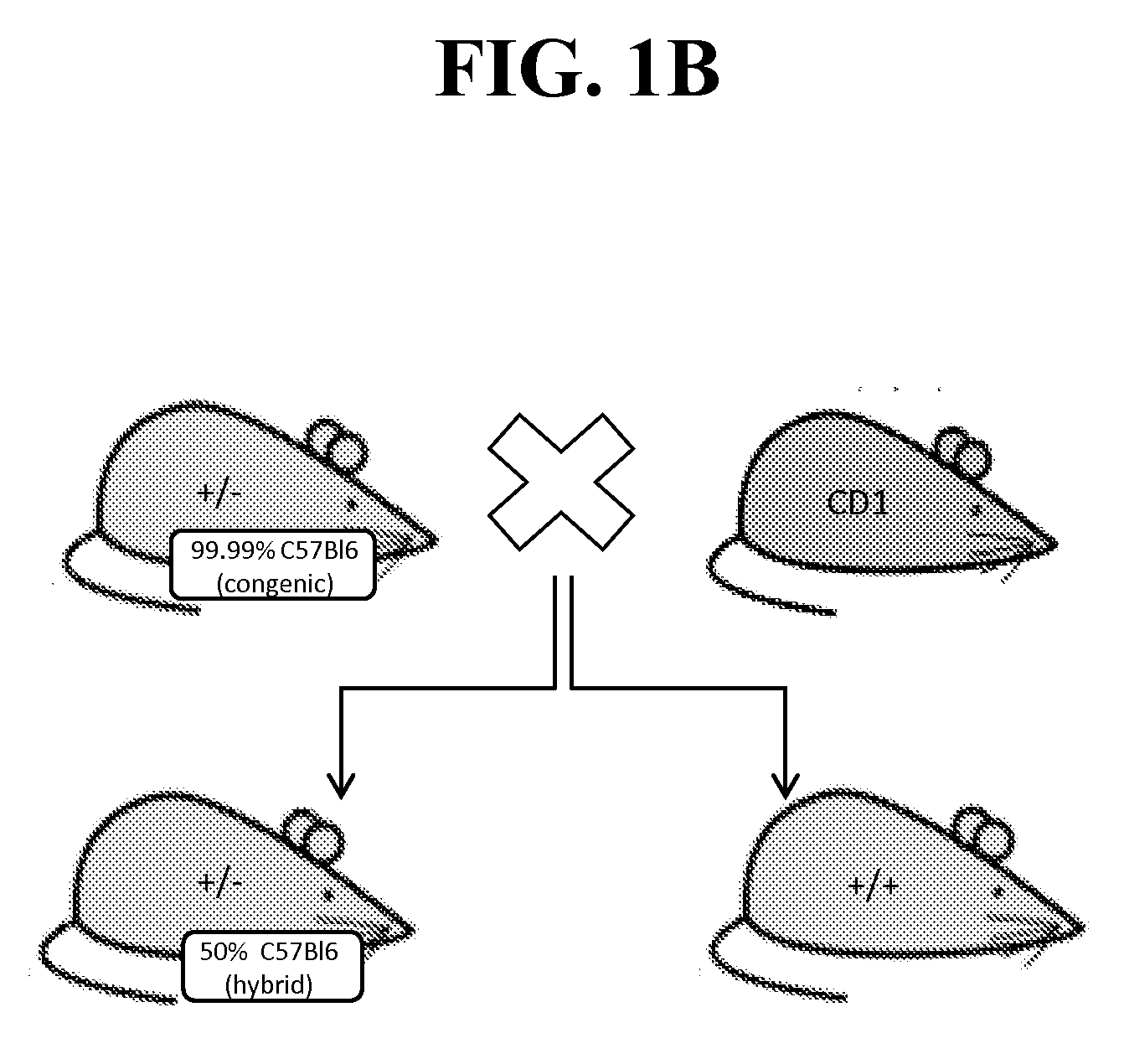
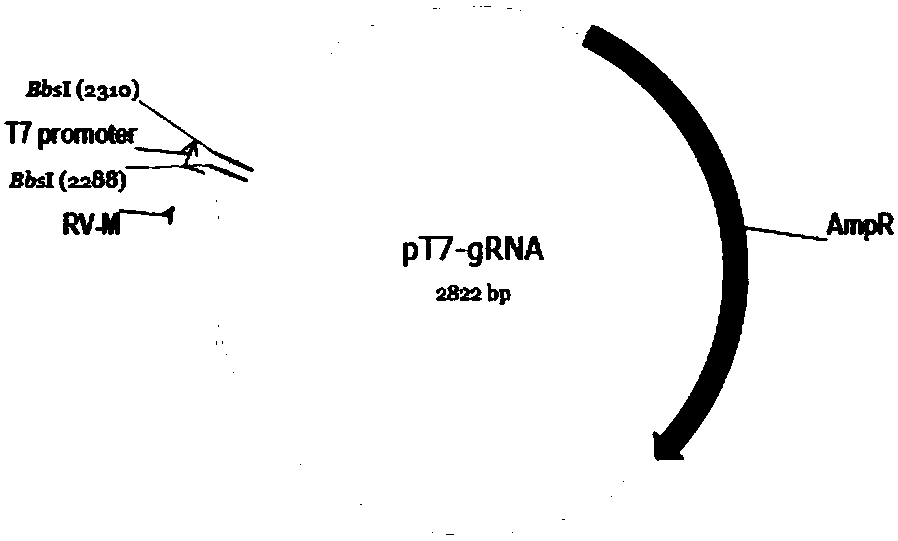
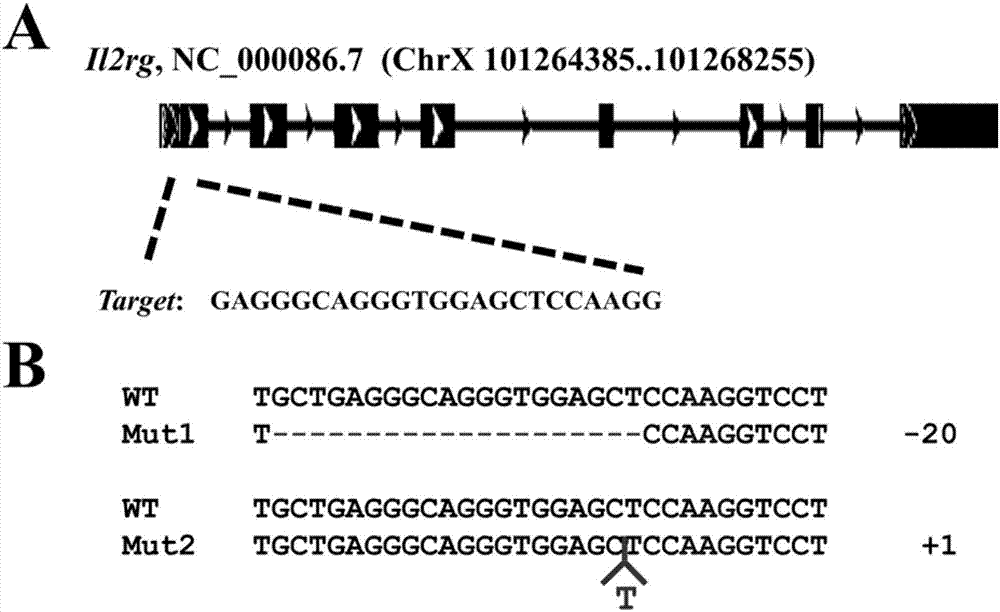
The invention relates to a construction method and application of an immunodeficient mouse animal model, belonging to the field of animal gene engineering and genetic modification. Il2rg gene knockout mice can be obtained by using a CRISPR / Cas9 technology; the Il2rg gene knockout mice have an immunodeficient phenotype. The construction method can be widely applied to multiple fields such as humanized animal models as well as stem cell and tumor research.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
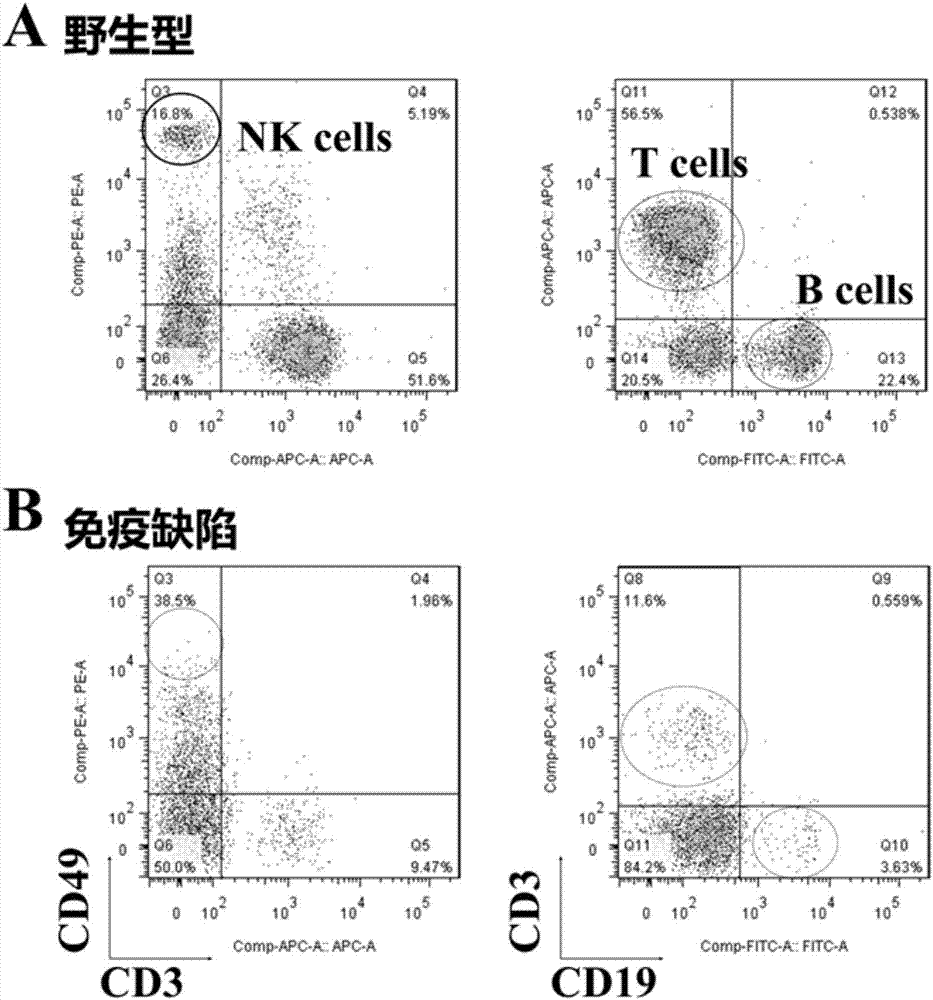
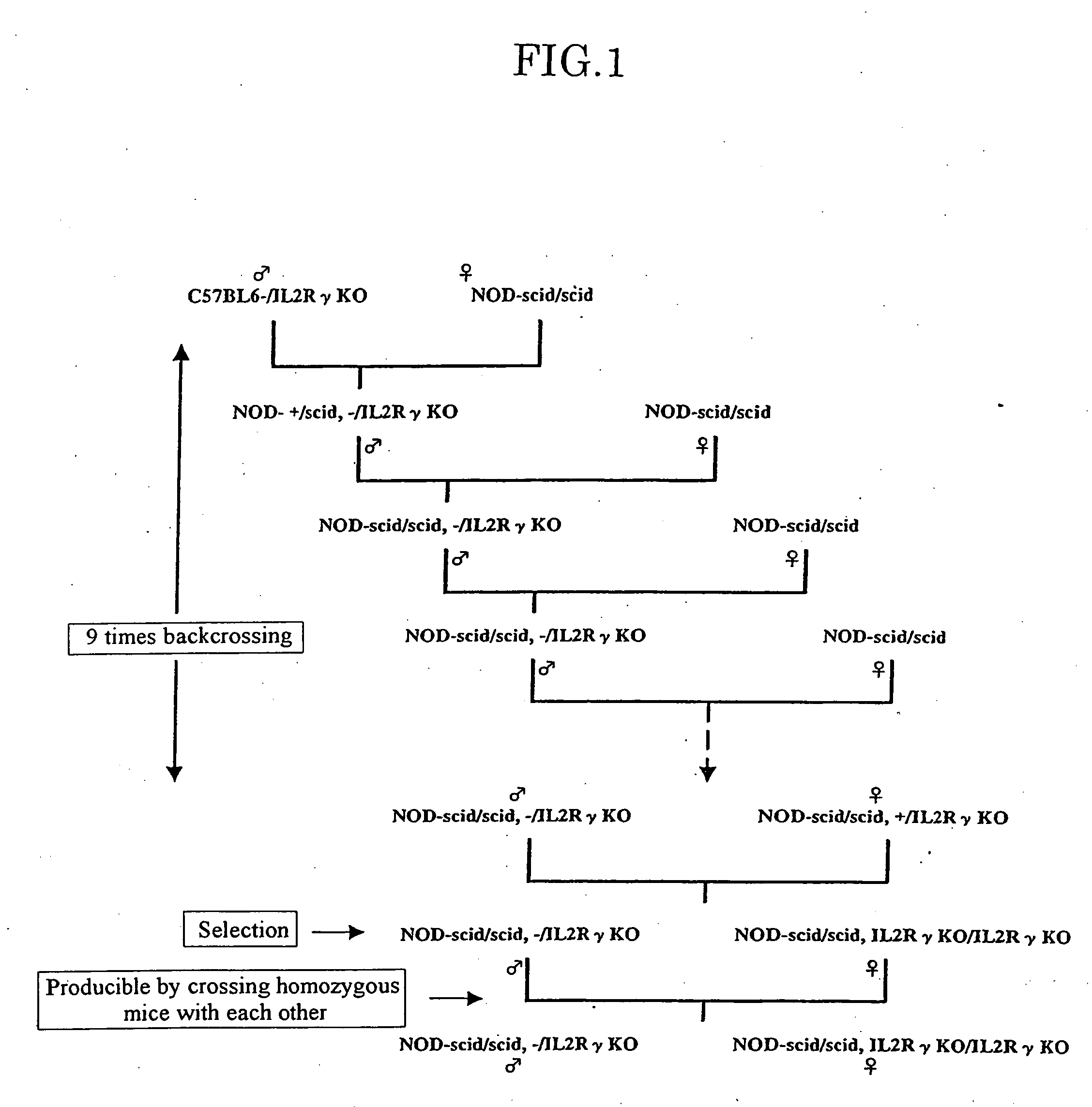
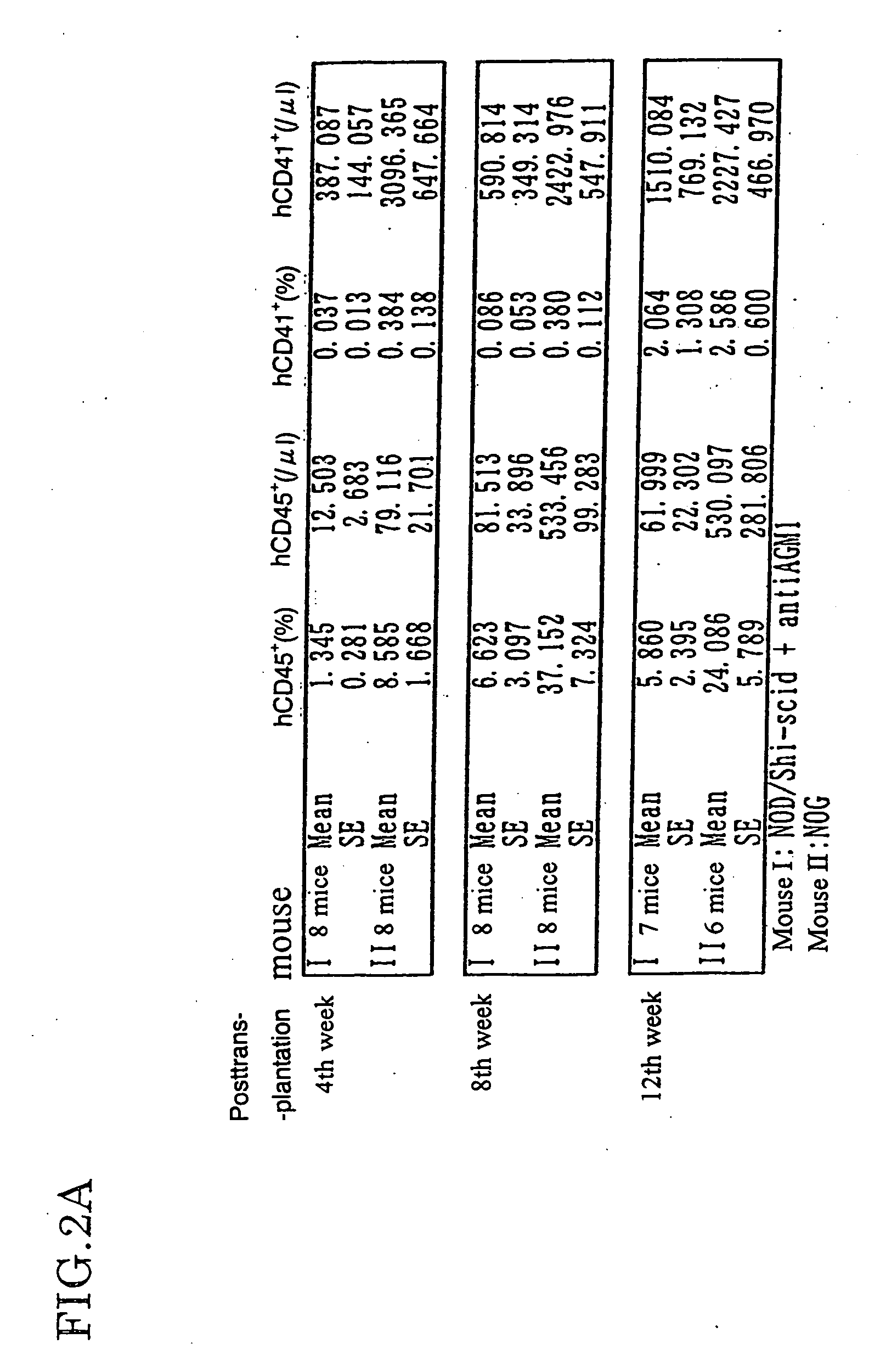
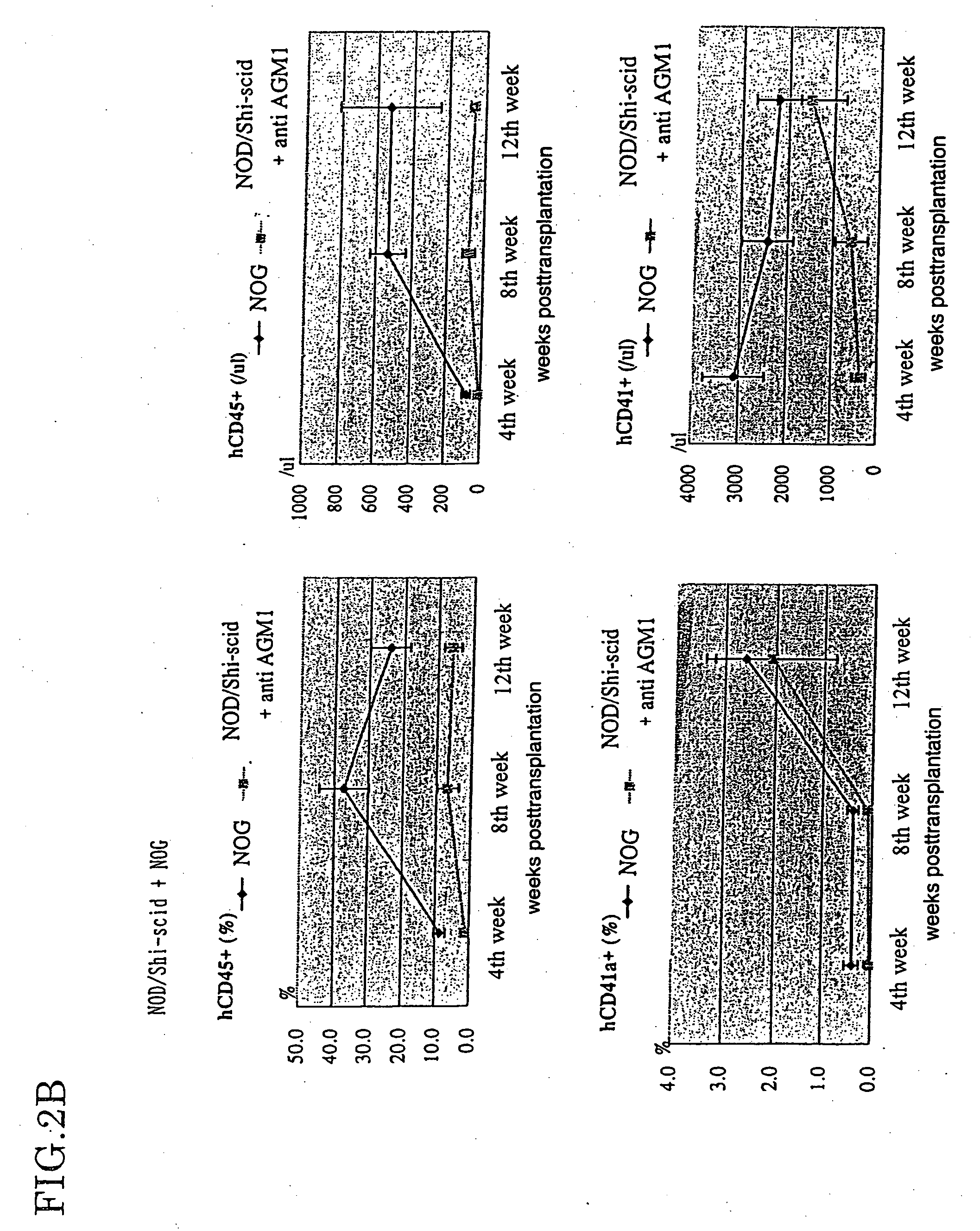
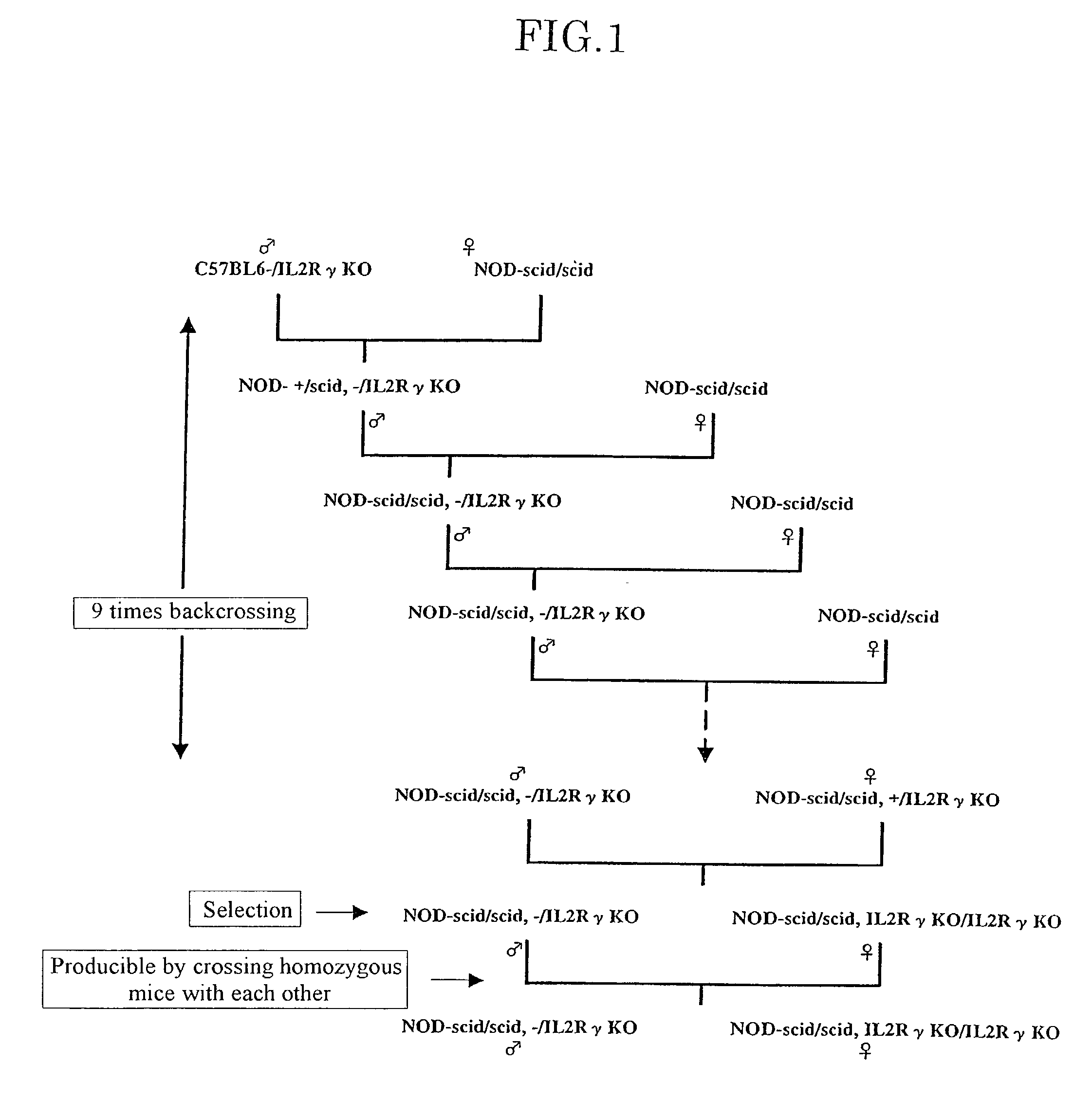
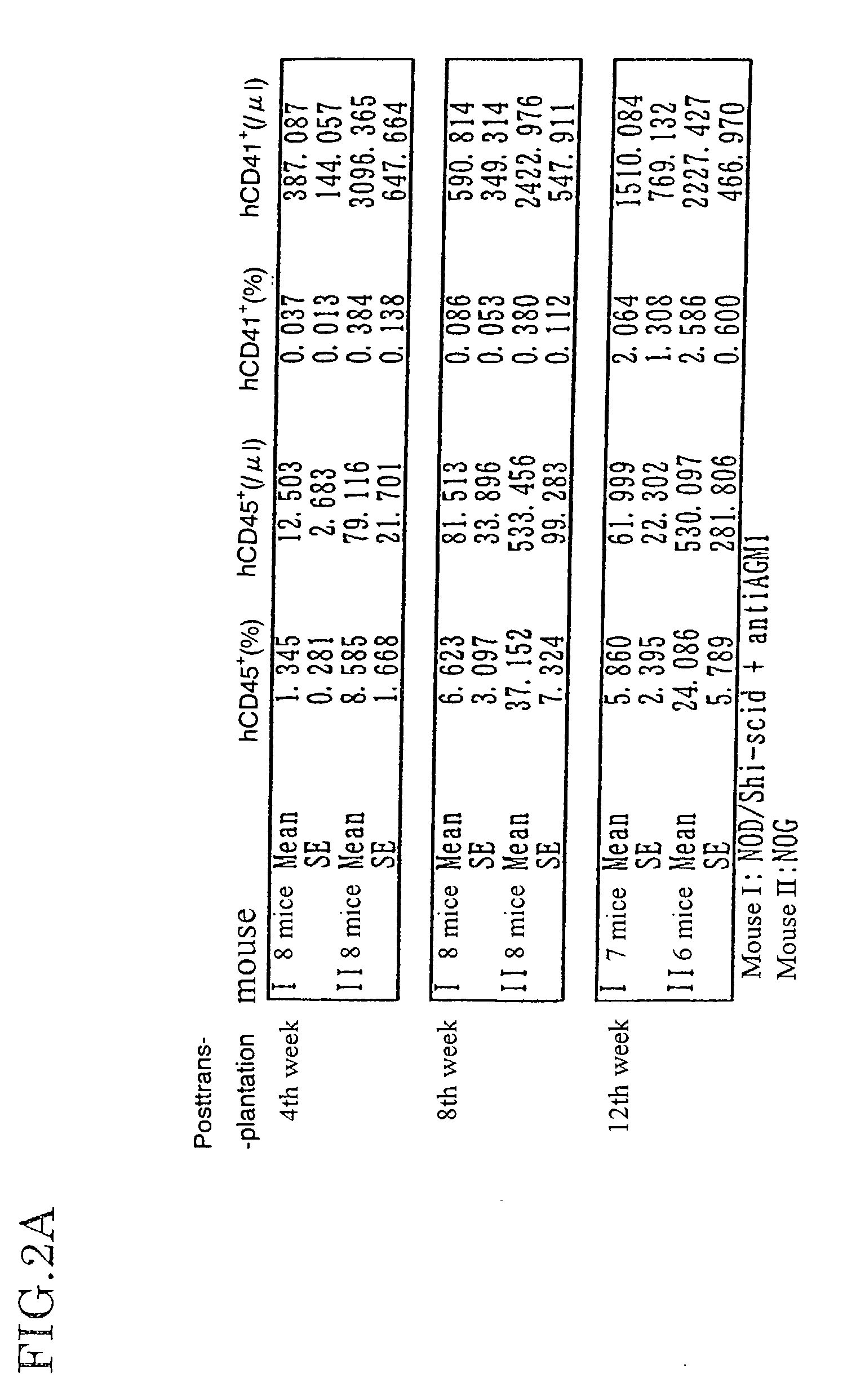
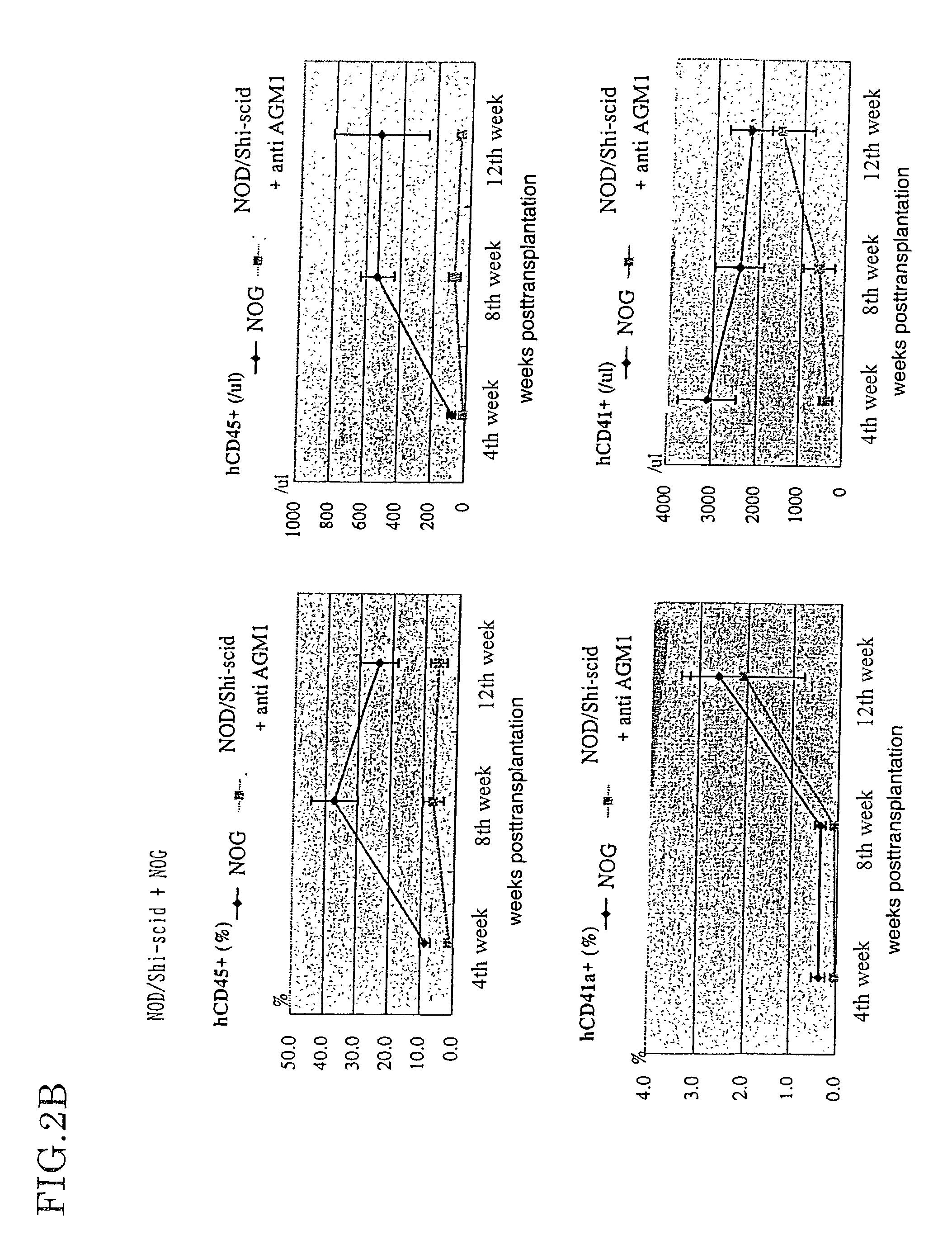
Method of producing a mouse suitable for engraftment, differentiation and proliferation of heterologous cells, mouse produced by this method and use of the mouse
InactiveUS20070011753A1Excellent heterologous cell engraftment capacityImmunoglobulins against animals/humansArtificially induced pluripotent cellsHeterologousAbnormal tissue growth
The present invention provides an immunodeficient mouse (NOG mouse) suitable for engraftment, differentiation and proliferation of heterologous cells, and a method of producing such a mouse. This mouse is obtained by backcrossing a C.B-17-scid mouse with an NOD / Shi mouse, and further backcrossing an interleukin 2-receptor γ-chain gene-knockout mouse with the thus backcrossed mouse. It is usable for producing a human antibody and establishing a stem cell assay system, a tumor model and a virus-infection model.
Owner:ITO MAMORU +9
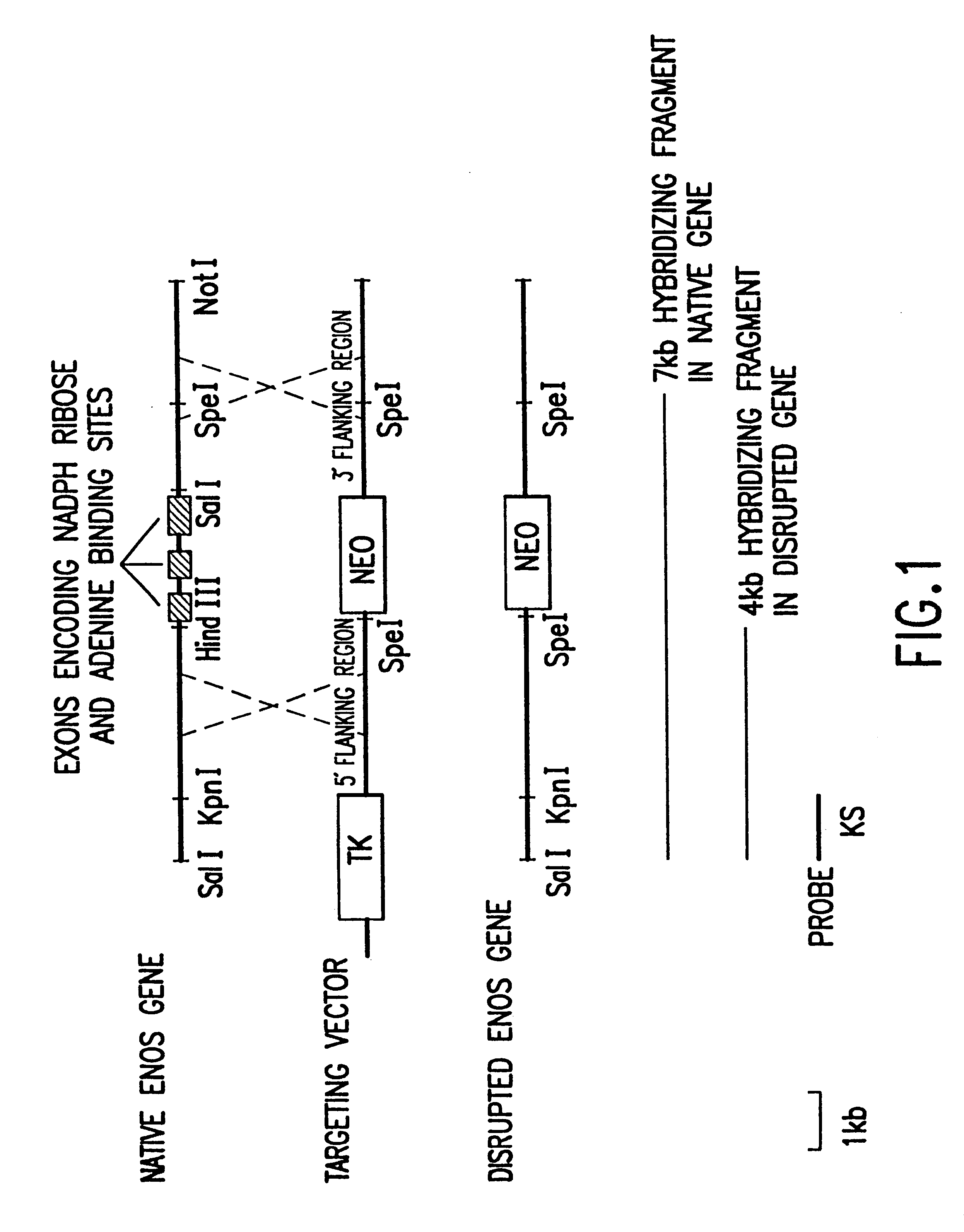
Endothelial NOS knockout mice and methods of use
This invention relates to transgenic non-human animals comprising a disrupted endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene. These animals exhibit abnormal wound-healing properties and hypertension. This invention also relates to methods of using the transgenic animals to screen for compounds having a potential therapeutic utility for vascular endothelial disorders, such as hypertension, cerebral ischemia or stroke, atherosclerosis and wound-healing activities. Moreover, this invention also relates to methods of treating a patient suffering from hypertension and wound-healing abnormalities with the compounds identified using the transgenic animals, and methods of making the transgenic animals. A method of treating a wound using nitroglycerin is also provided.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
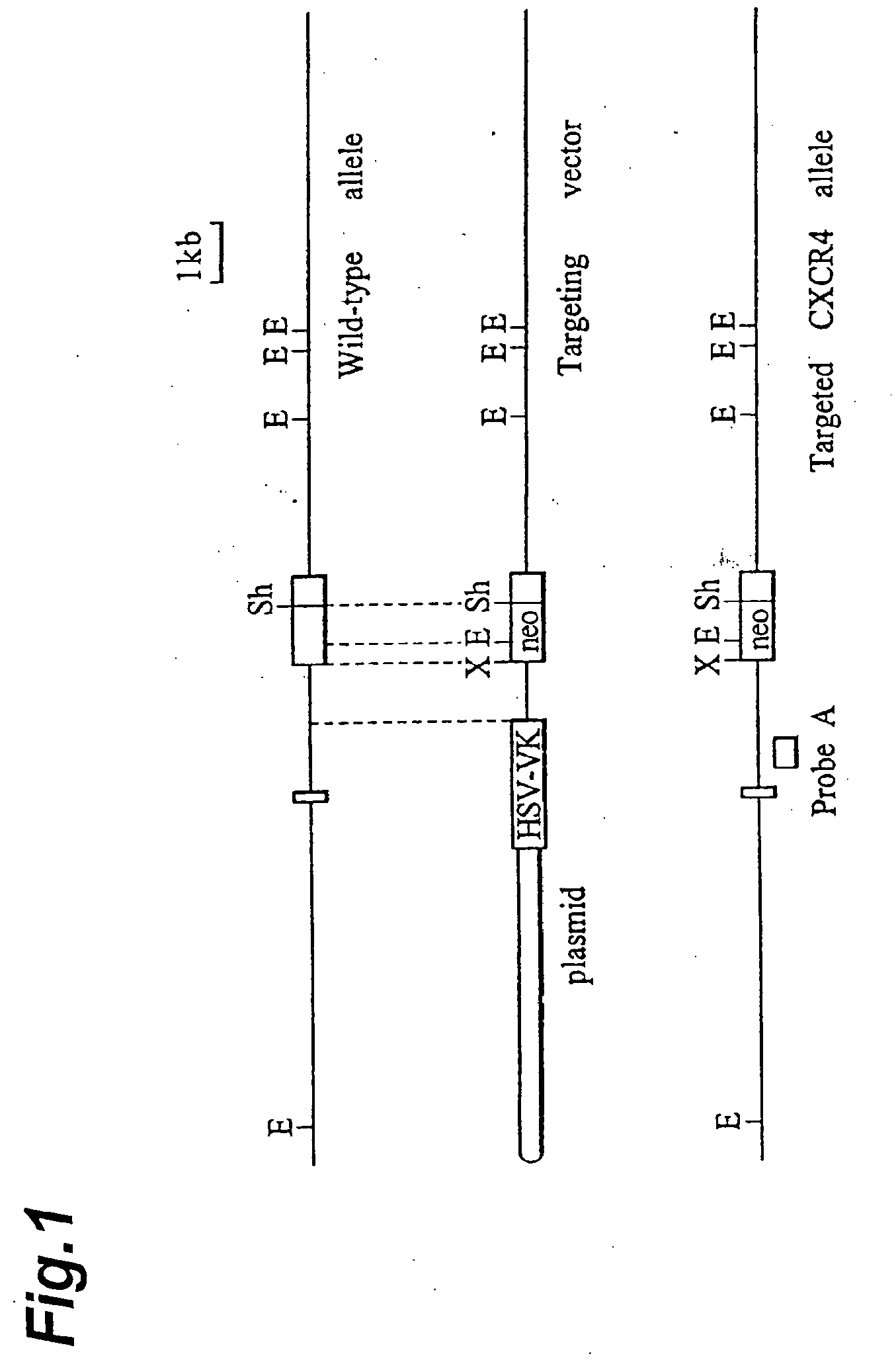
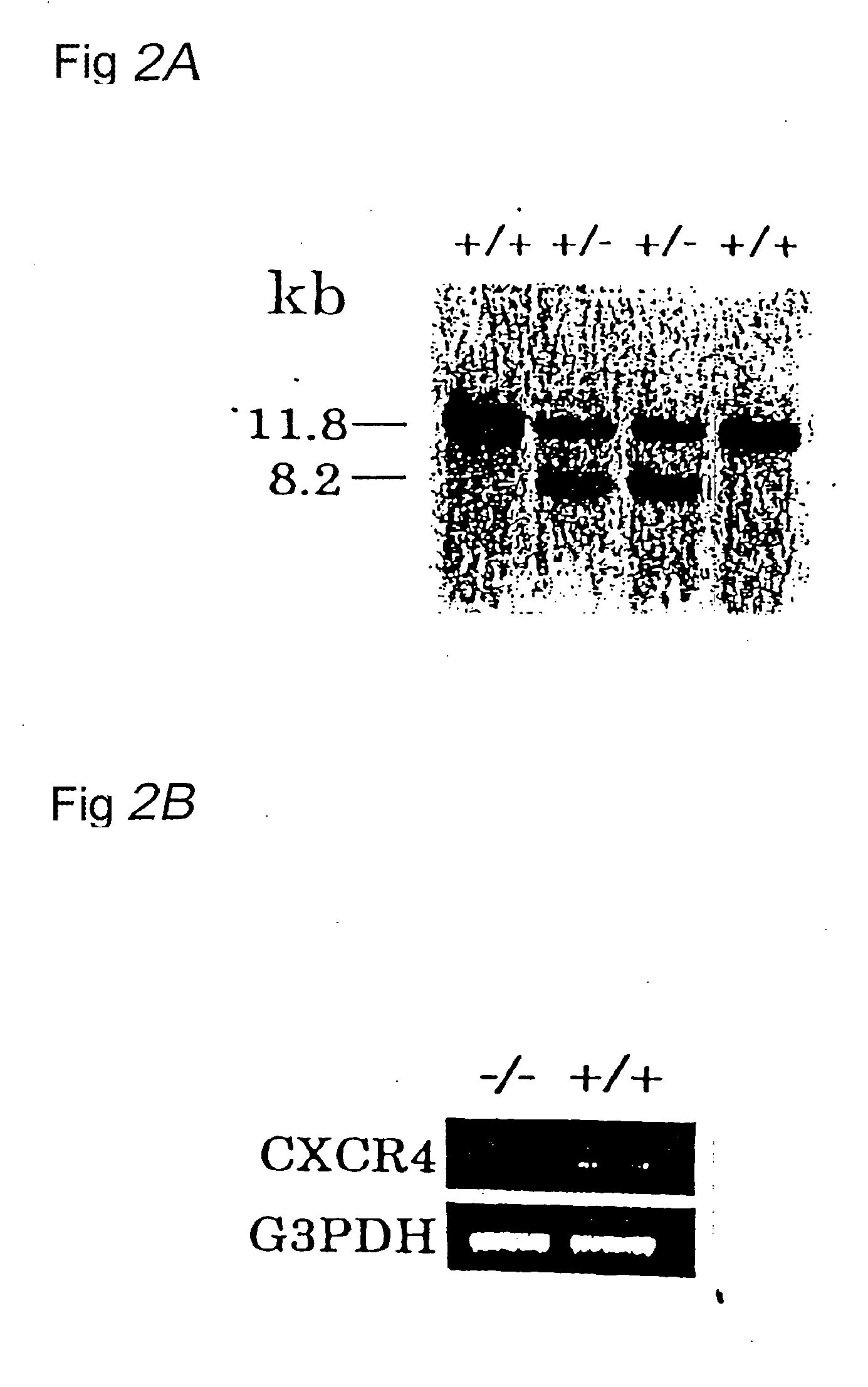
Vascularization Inhibitors
InactiveUS20130236889A1Increased vascularizationPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementCXCR4Knockout animal
This invention provides a therapeutic agent for inhibiting neovascularization, a therapeutic agent for a solid cancer, a therapeutic agent for a disease pathologically caused by neovascularization, and a therapeutic agent for repairing a tissue comprising as the effective ingredient, a substance that potentiates the action of CXCR4.Based on the finding that vascularization is suppressed in CXCR4 knockout mice, it becomes possible to prepare a therapeutic agent for suppressing vascularization, a therapeutic agent for a solid cancer, a therapeutic agent for a disease pathologically caused by neovascularization, each of which comprises as the effective ingredient, a substance that inhibits the action of CXCR4, as well as to prepare a therapeutic agent for repairing a tissue comprising as the effective ingredient, a substance that potentiates the action of CXCR4. Methods for treatment are made possible that use these therapeutic agents.
Owner:KISHIMOTO TADAMITSU +2
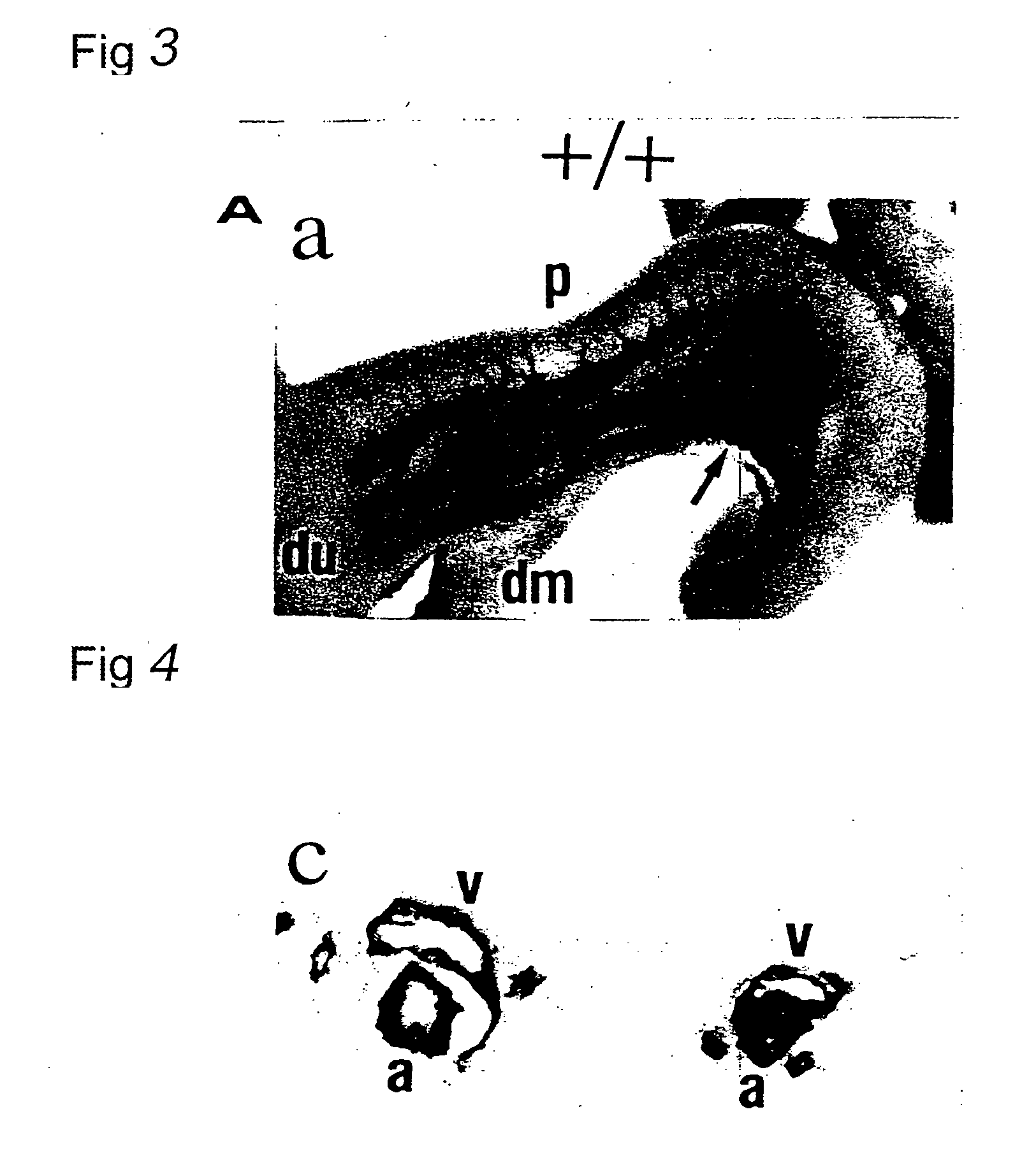
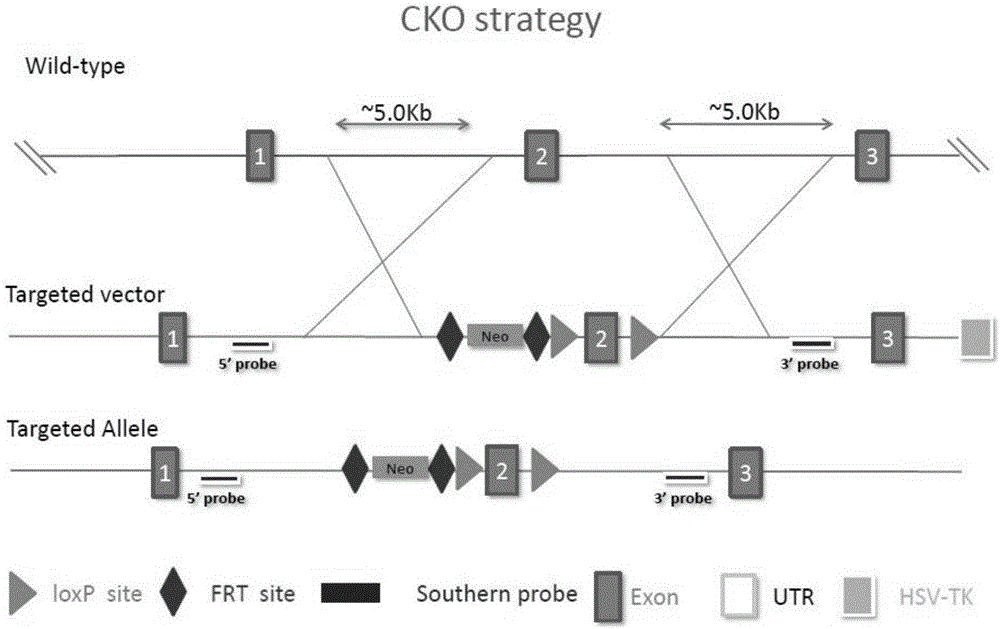
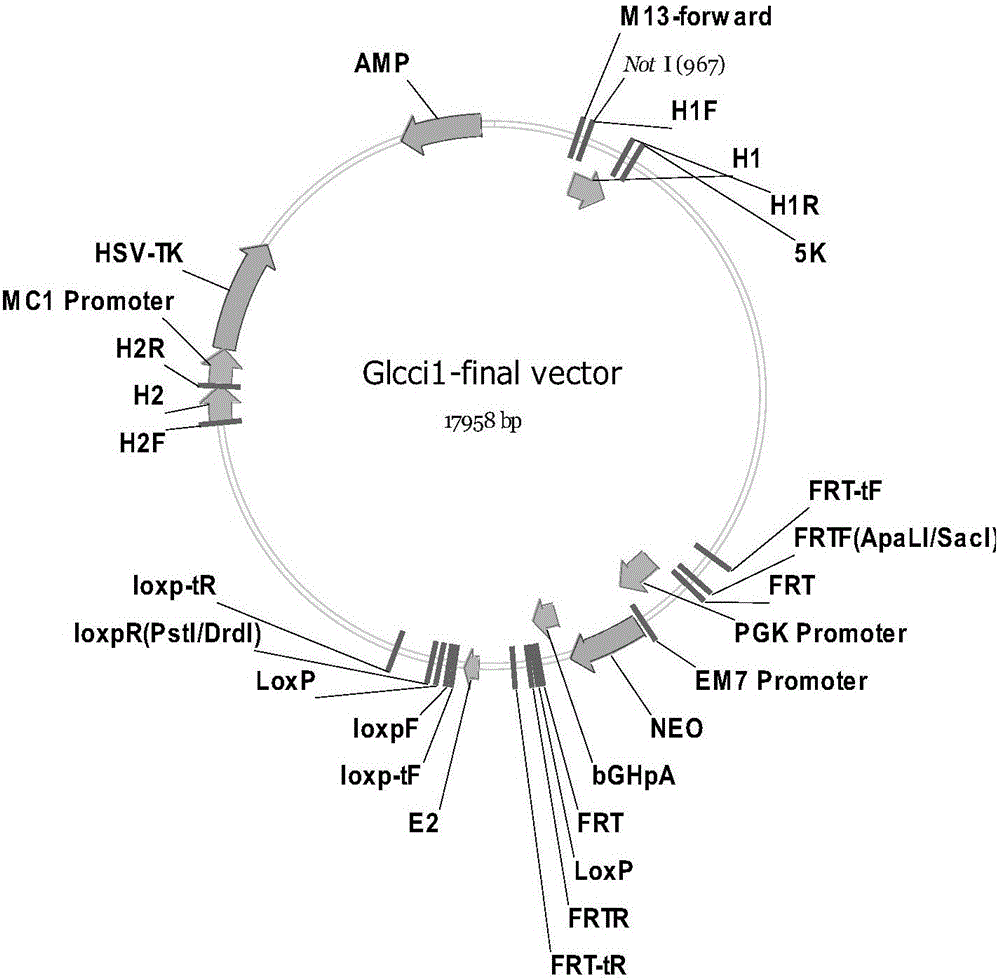
Cre-LoxP condition-based GLCCI1 gene knockout mouse model constructing kit and constructing method
The invention discloses a Cre-LoxP condition-based GLCCI1 gene knockout mouse model constructing kit, and a targeting vector and a constructing method of the above mouse model. A loxP sequence is respectively arranged at two ends of a target sequence of GLCCI1 by using a Cre / loxP principle to obtain a flox mouse, the flox mouse and a mouse with a systematic knockout Cre line are mated to obtain a systematic GLCCI1 gene knockout mouse line, and the obtained GLCCI1 gene knockout mouse is applied to the function researches of the GLCCI1 gene and proteins.
Owner:XIANGYA HOSPITAL CENT SOUTH UNIV
Enhanced homologous recombination mediated by lambda recombination proteins
InactiveUS20040092016A1Reduce chanceNormal EcoRV digestion pattern is restoredBacteriaStable introduction of DNAMammalKnockout animal
Disclosed herein are methods for generating recombinant DNA molecules in cells using homologous recombination mediated by recombinases and similar proteins. The methods promote high efficiency homologous recombination in bacterial cells, and in eukaryotic cells such as mammalian cells. The methods are useful for cloning, the generation of transgenic and knockout animals, and gene replacement. The methods are also useful for subcloning large DNA fragments without the need for restriction enzymes. The methods are also useful for repairing single or multiple base mutations to wild type or creating specific mutations in the genome. Also disclosed are bacterial strains and vectors which are useful for high-efficiency homologous recombination.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Method of resistance of epilepsy by suppressing the function of alpha 1g protein
InactiveUS20060025397A1Suppressing functionResisting epilepsyOrganic active ingredientsHeavy metal active ingredientsKnockout animalSuppressor
The disclosure concerns a method for resistance of epilepsy by suppressing the function of alpha 1 G protein of T-type calcium channels, use of suppressor of alpha 1 G protein for prevention or treatment for epilepsy, knockout mice resisting epilepsy by disrupting alpha 1 G subunit of T-type calcium channel, and preparation method thereof. In addition, suppressing alpha 1 G protein of T-type calcium channels does not occur epilepsy, and alpha 1 G-deficient mice are useful to study of mechanism related to epilepsy.
Owner:POHANG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Method of producing a mouse suitable for the engraftment, differentiation and proliferation of heterologous cells, mouse produced by this method and use of the mouse
InactiveUS7145055B2Excellent heterologous cell engraftment capacityImmunoglobulins against animals/humansMutant preparationAbnormal tissue growthHeterologous
The present invention provides an immunodeficient mouse (NOG mouse) suitable for engraftment, differentiation and proliferation of heterologous cells, and a method of producing such a mouse. This mouse is obtained by backcrossing a C.B-17-scid mouse with an NOD / Shi mouse, and further backcrossing an interleukin 2-receptor γ-chain gene-knockout mouse with the thus backcrossed mouse. It is usable for producing a human antibody and establishing a stem cell assay system, a tumor model and a virus-infection model.
Owner:CENT INST FOR EXPERIMENTAL ANIMALS
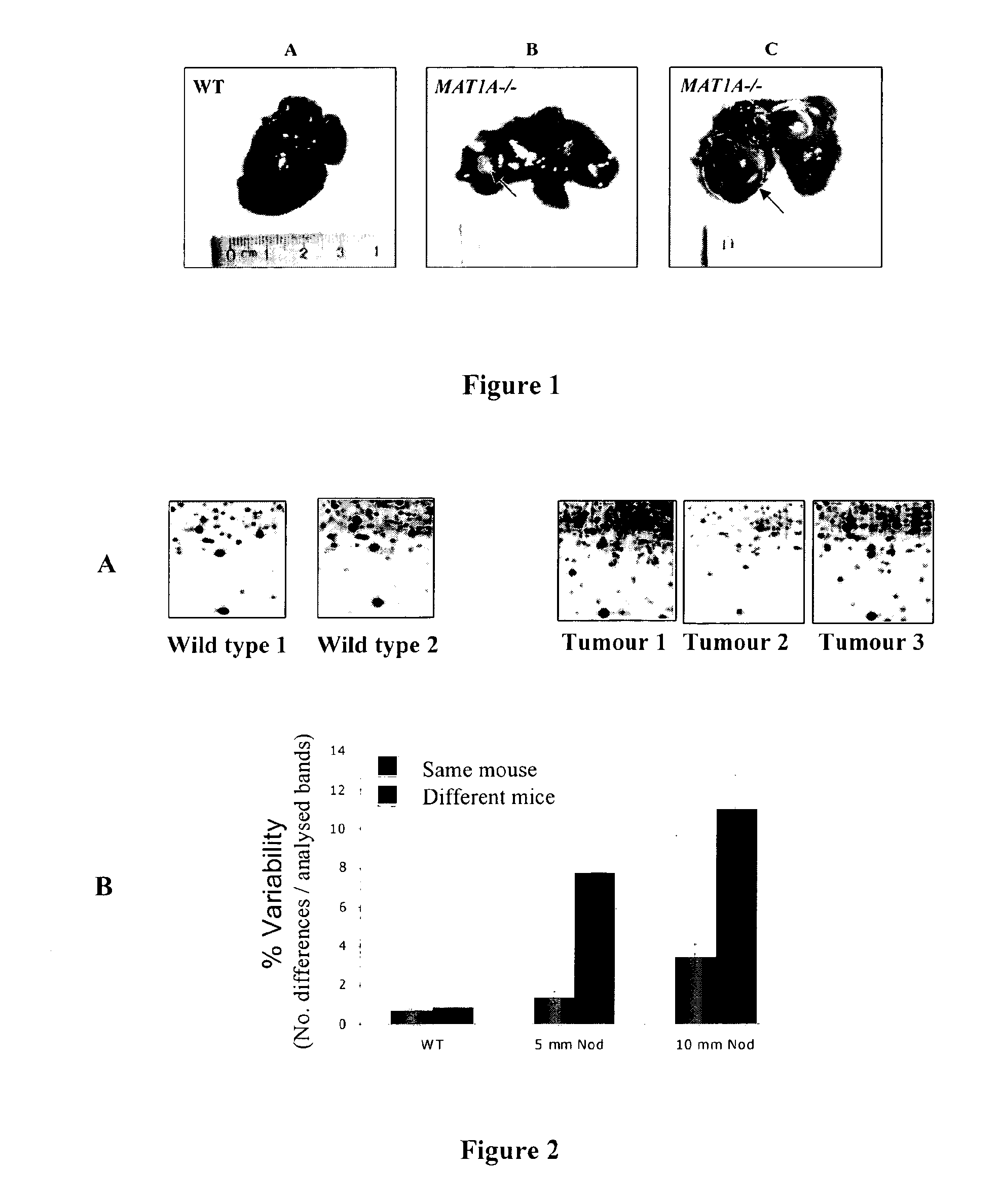
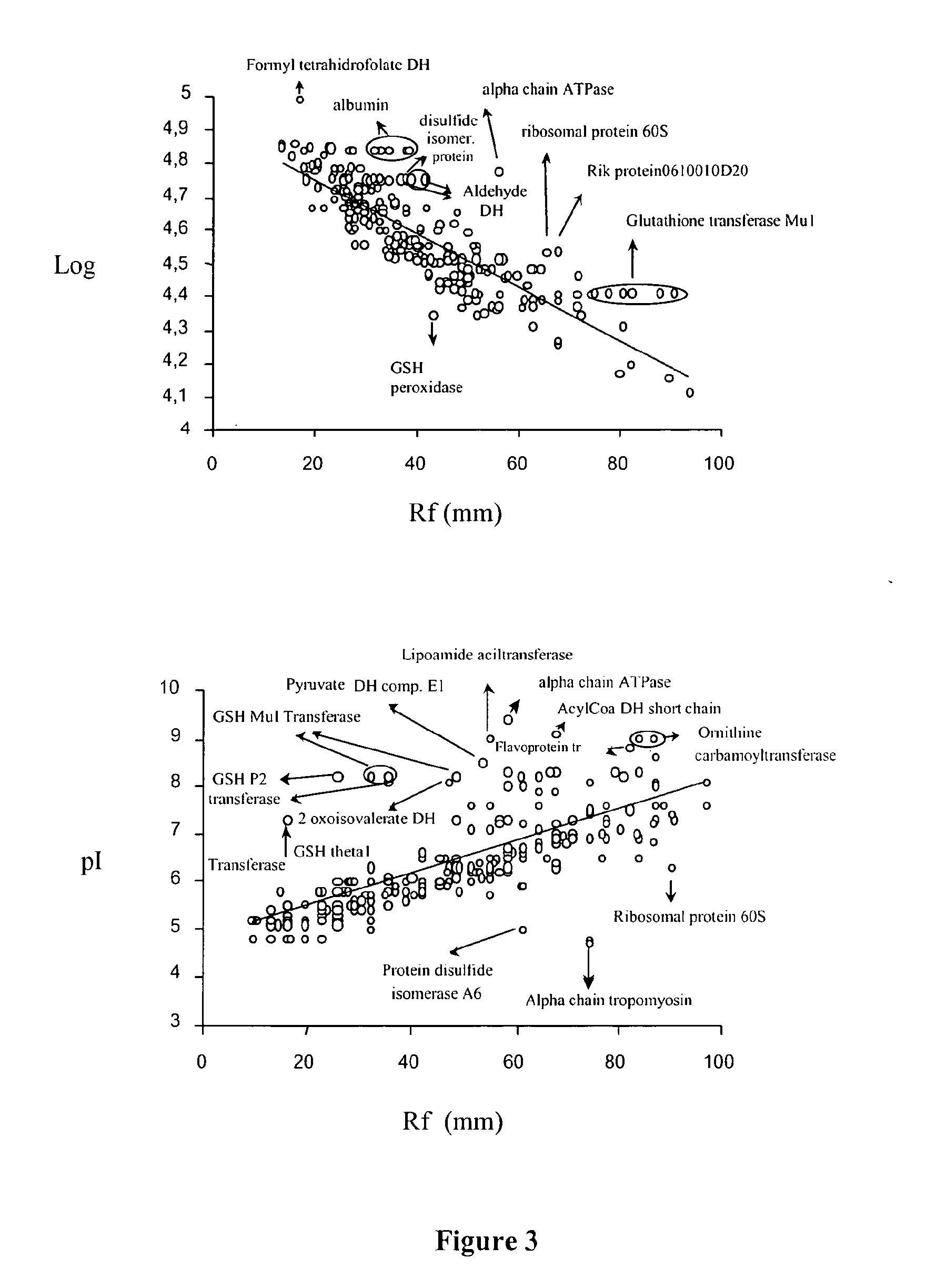
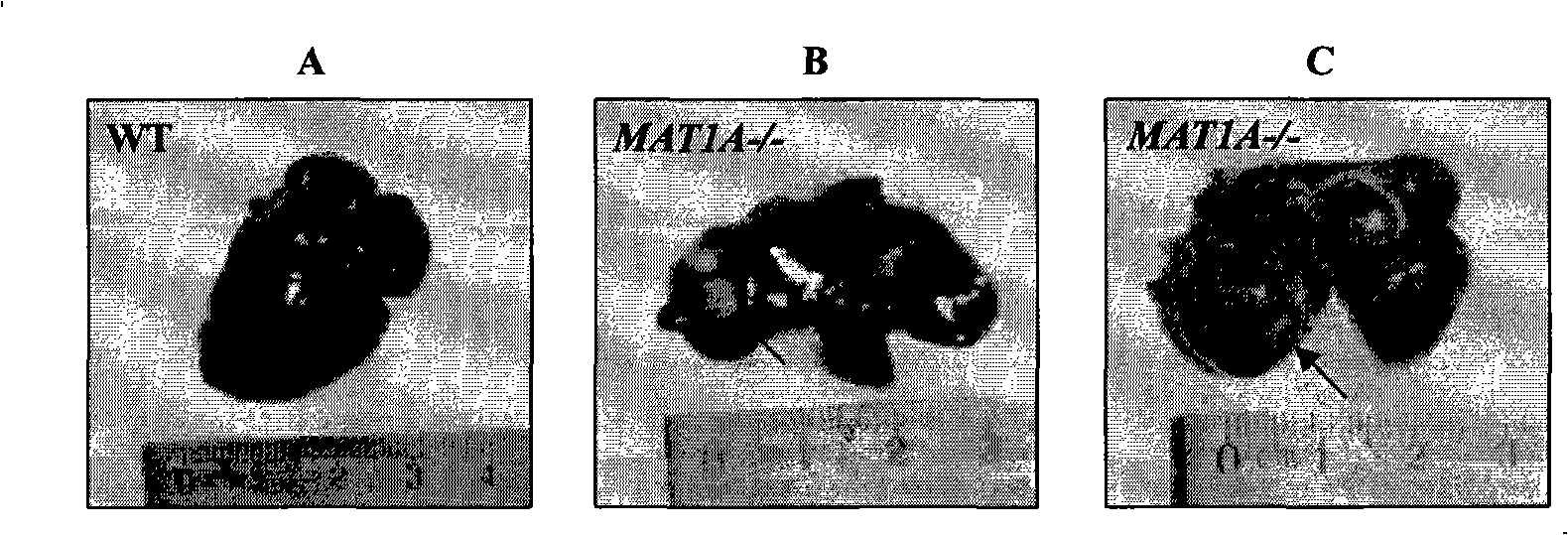
Molecular markers of hepatocellular carcinoma and their applications
InactiveUS20090181379A1Precise definitionFacilitate prognosisCompound screeningApoptosis detectionEtiologyProteomics methods
By means of a proteomic approach, the markers of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in the liver of a knockout mouse (MAT1A− / −) have been identified for the MAT1A gene (deficient in the synthesis of S-adenosylmethionine). 27 proteins have been detected the expression thereof is altered in, at least, 50% of the analysed tumours. Amongst them, 13 proteins have been validated in biopsies of patients with HCC of different etiology, and 7 of them have been validated in biopsies of patients with liver cirrhosis, a stage prior to the development of HCC, which makes it possible to differentiate between prior stages of the disease and even between different etiologies (viral and alcoholic). Having a panel of markers available may contribute to more accurately defining the alterations associated with the development of HCC and thus facilitate prognosis and diagnosis of this disease.
Owner:PROYECTO DE BIOMEDICINA CIMA
Transgenic mouse whose genome comprises a homozygous disruption of its α1G gene, a method of preparing the same and use thereof
InactiveUS7626076B2Compounds screening/testingCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsNervous systemKnockout animal
The disclosure concerns a method for resistance of epilepsy by suppressing the function of alpha 1G protein of T-type calcium channels, use of suppressor of alpha 1G protein for prevention or treatment for epilepsy, knockout mice resisting epilepsy by disrupting alpha 1G subunit of T-type calcium channel, and preparation method thereof. The α1G-knockout transgenic mouse can be used for investigating the relationship between diseases particularly neuropathy or psychopathy and the function of α1G T-type calcium channel via various behavioral tests since α1G subunit is mainly expression in central nervous system (CNS) and pheripheral nervous system (PNS). Further, the α1G-knockout transgenic mouse can be used for screening antileptic agents.
Owner:ORIENTBIO
Methods and animal model for analyzing age-related macular degeneration
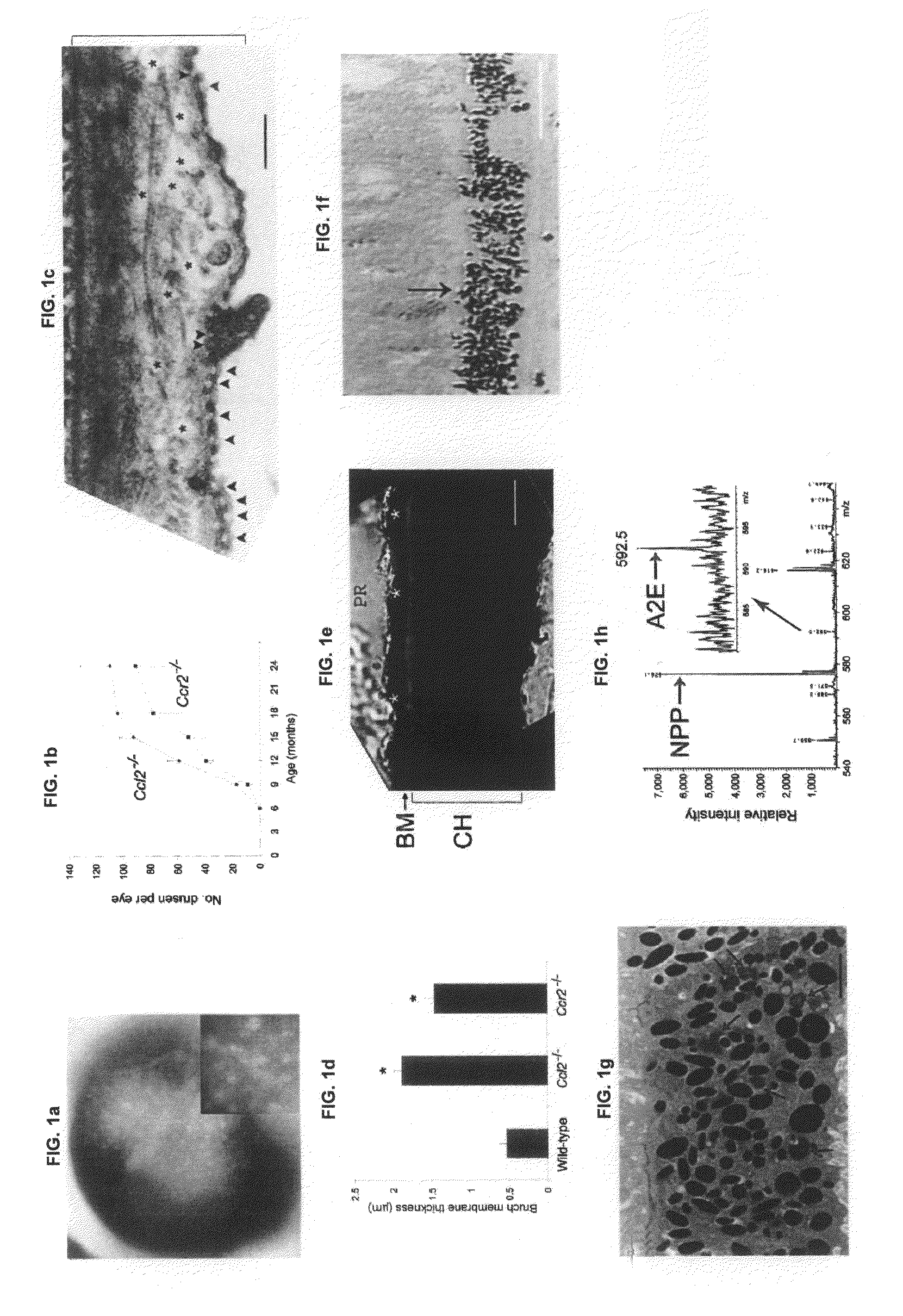
InactiveUS7595430B2Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsMicrobiological testing/measurementCCL2Knockout animal
Methods for testing candidate drugs for treatment of age-related macular degeneration are provided. Ccl2-deficient, and Ccr2-deficient mice are used to determine the effect of candidate drugs and treatments on development of age-related macular degeneration. Also provided is a Ccl2-deficient, Ccr2-deficient dual knockout mouse, which is a useful animal model for age-related macular degeneration.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
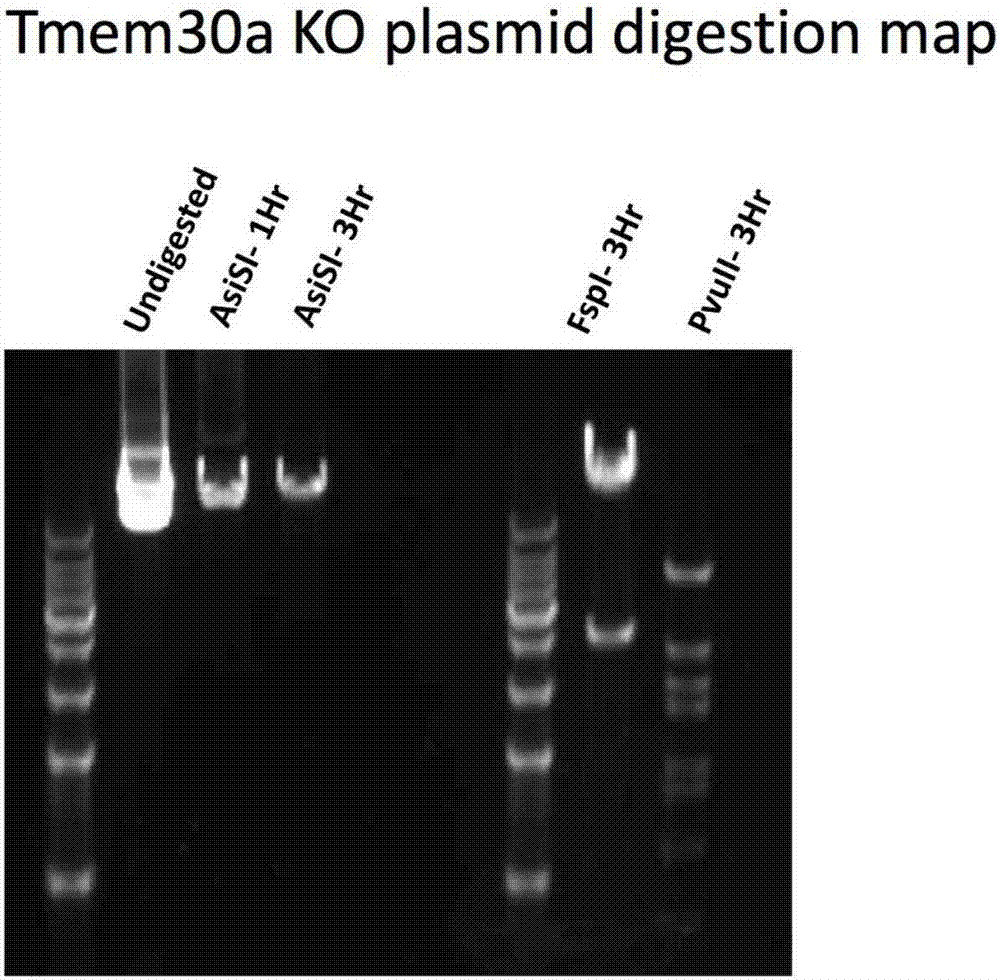
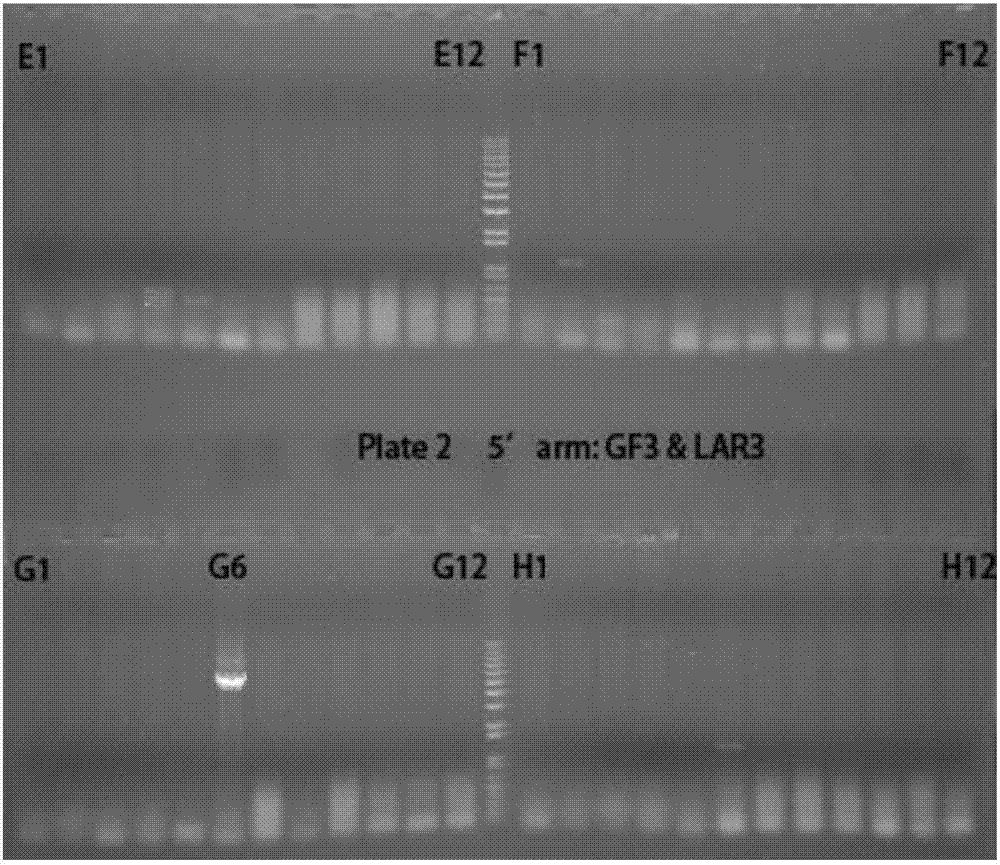
Construction method for mouse model with conditionally deleted Tmem30a genes and with pancreatic beta cells and application
The invention discloses a construction method for a mouse model with conditionally deleted Tmem30a genes and with pancreatic beta cells and an application. The construction method comprises the following steps: constructing a conditionally deleted Tmem30a gene homozygote mouse, wherein the two ends of one or more exon of the Tmem30a genes are inserted into homonymous arrayed loxP locus; mating the mouse with pancreatic beta cell specific transgenic mouse Ins2-Cre, thereby acquiring the mouse model with conditionally deleted Tmem30a genes and with pancreatic beta cells. The mouse with conditionally deleted Tmem30a genes and with pancreatic beta cells shows glucose intolerance and poor insulin sensitivity. The mouse model can be used as a diabetes research model.
Owner:成都基康医药科技有限公司
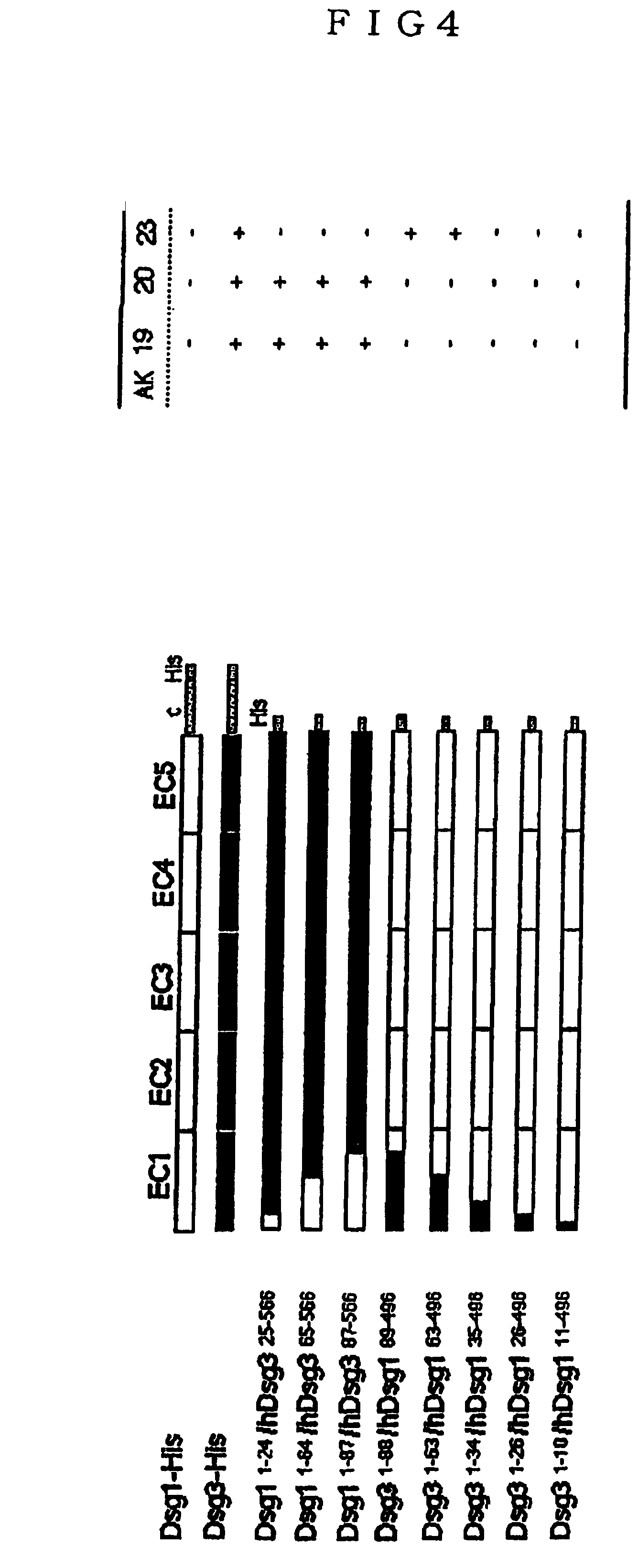
Pemphigus monoclonal antibody
The present invention provides a monoclonal antibody having a pathogenic activity that can induce pemphigus lesion, a peptide specifically recognized by the monoclonal antibody and useful as a therapeutic drug for pemphigus autoimmune disease, etc. As anti-mouse Dsg3 antibody-producing cells are present in the splenocytes of pemphigus vulgaris mouse model constructed by using autoantigen knockout mouse, cell fusion was conducted with the splenocytes of said mouse model and mouse myeloma cells using polyethyleneglycol, hybridomas were constructed, and monoclonal antibodies against Dsg3 were constructed. Among them, a monoclonal antibody having a pathological activity that can induce pemphigus lesions was screened, the base sequence and amino acid sequence in its variable region (heavy chain, light chain) was determined, and the specific epitope part was identified.
Owner:KEIO UNIV
Molecular markers of hepatocellular carcinoma and their applications
InactiveCN101313220AAccurate Prognosis SystemCompound screeningApoptosis detectionEtiologyProteomics methods
Owner:PROYECTO DE BIOMEDICINA CIMA
Fatty-liver-related liver cancer model building method based on knockout mice
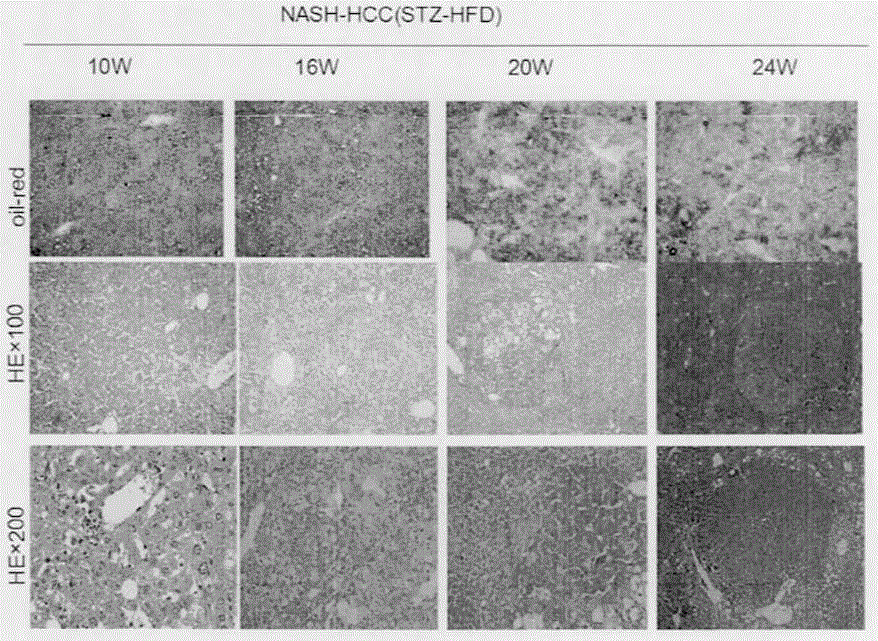
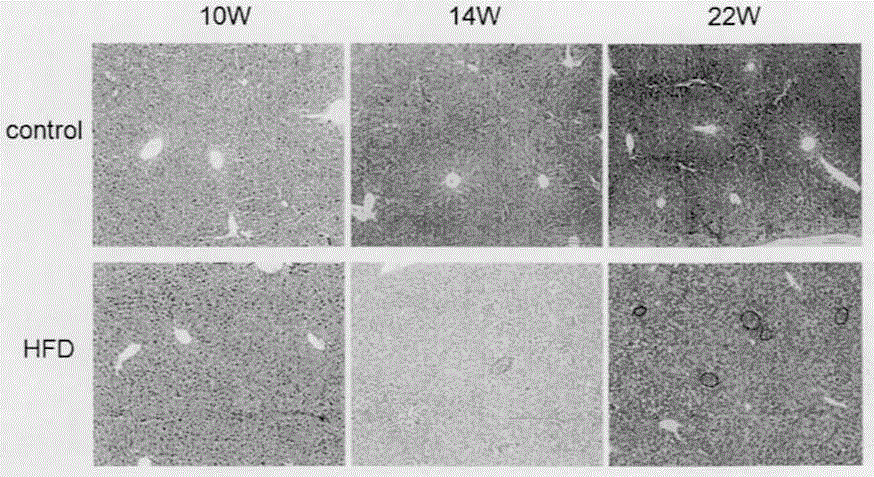
ActiveCN105052830AIncrease incidenceMicrobiological testing/measurementAnimal husbandryKnockout animalGenotype
The invention relates to a fatty-liver-related liver cancer model building method based on knockout mice. The method is characterized in that APOE- / - and LDLR- / - knockout mice including female mice and male mice are selected, the female mice and the male mice are matched in number, and double knockout mice are obtained; a primer is designed, and the genotypes in mice are identified through a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) system; the PCR (polymerase chain reaction) system comprises an ApoE gene identification PCR conditions and LDLR gene identification PCR conditions; the double knockout mice are pregnant, and suckling mice are obtained; streptozotocin is injected to the suckling mice, the suckling mice begin a high-fat diet after ablactation, and finally the suckling mice surfer from liver cancer; it is identified that the suckling mice begin the high-fat diet after ablactation, fatty liver occurs six weeks later, NASH occurs 8-10 weeks later, dysplastic nodule occurs 13-16 weeks later, and the liver cancer occurs 18-24 weeks later. The occurrence rate of the liver cancer is about 100% 24 weeks later. The time when pure-gene APOE- / - and LDLR- / - knockout mice suffer from NASH and HCC due to the high-fat diet is advanced by 24-30 weeks, and the occurrence rate is high.
Owner:施军平
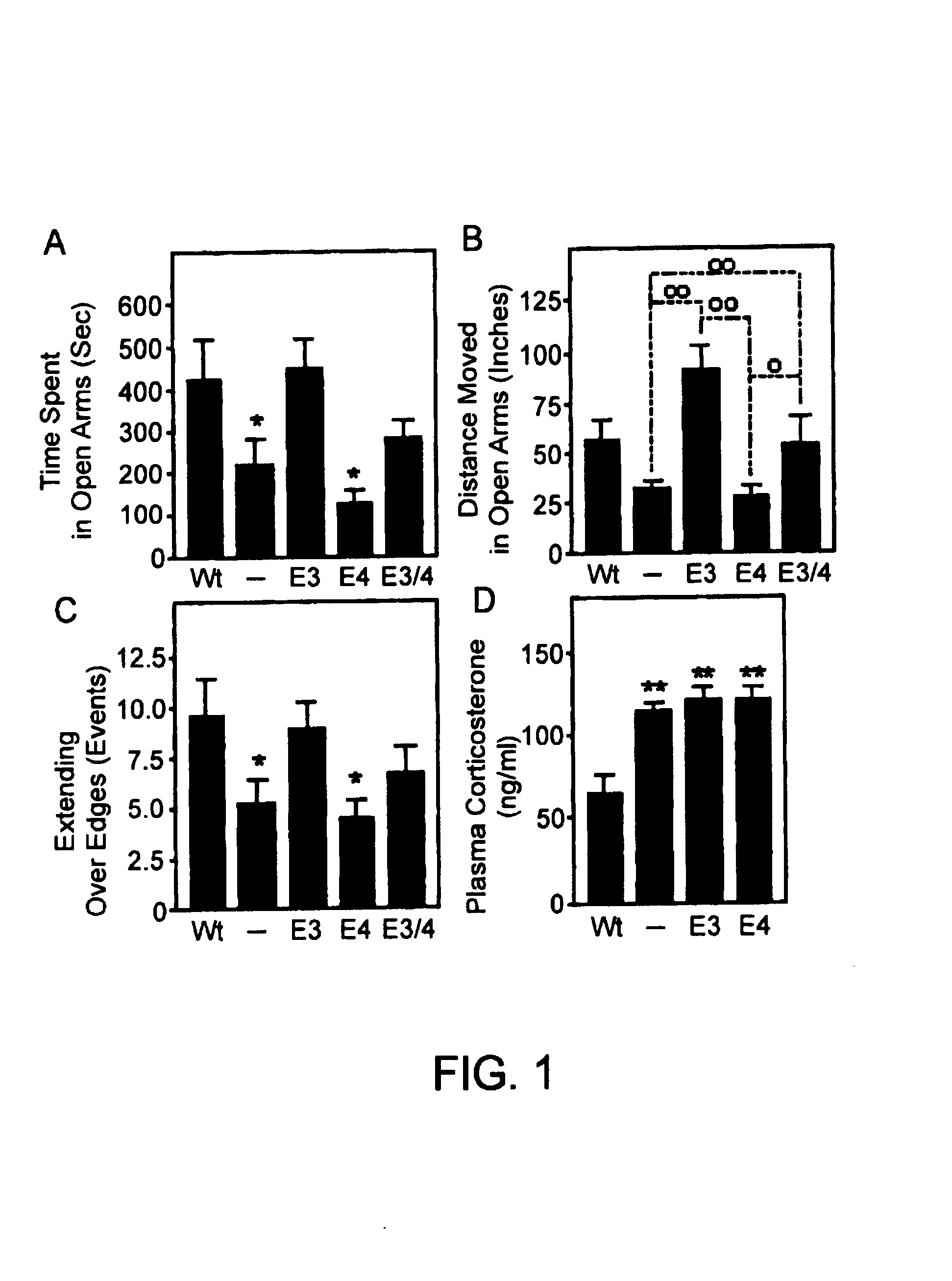
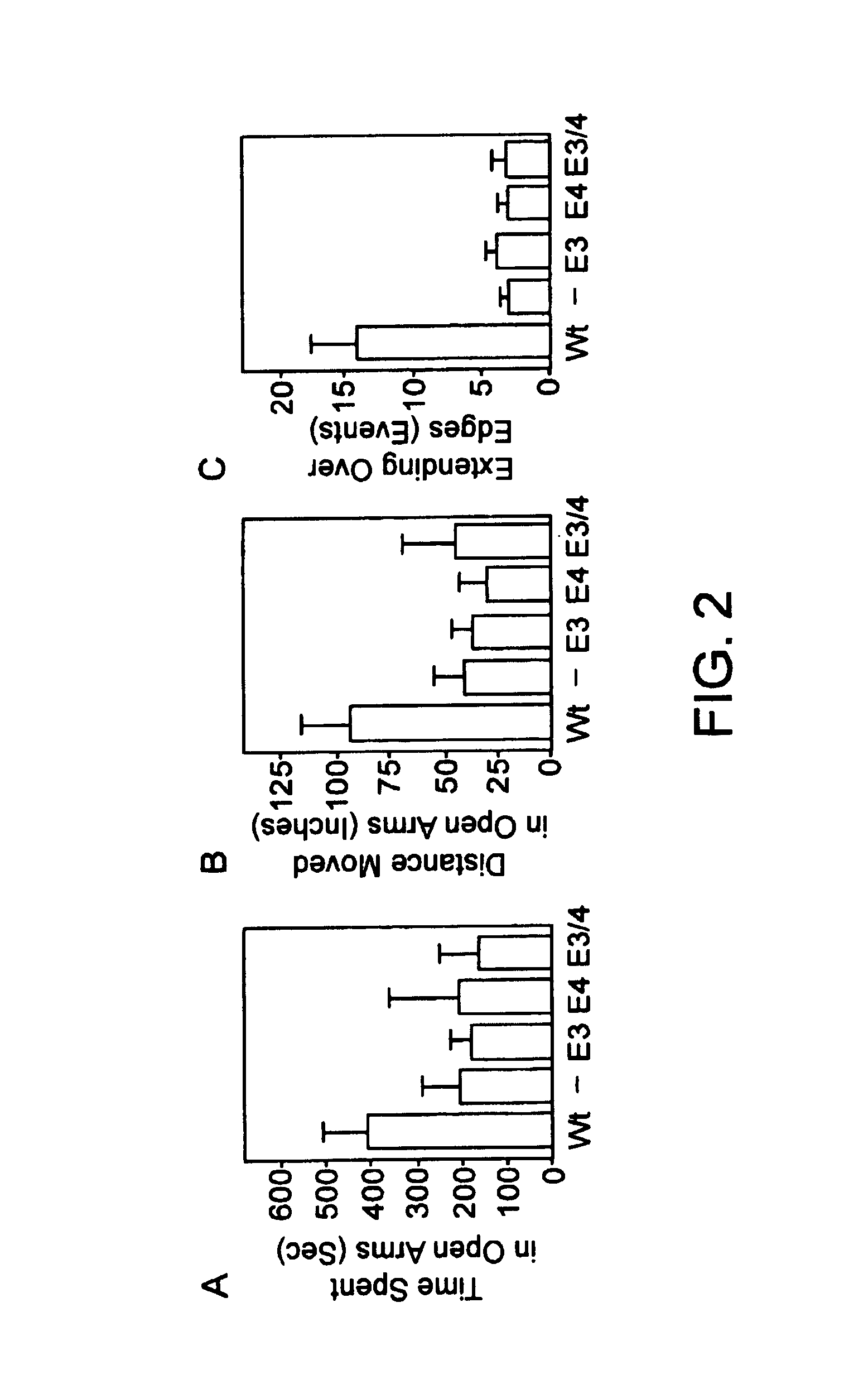
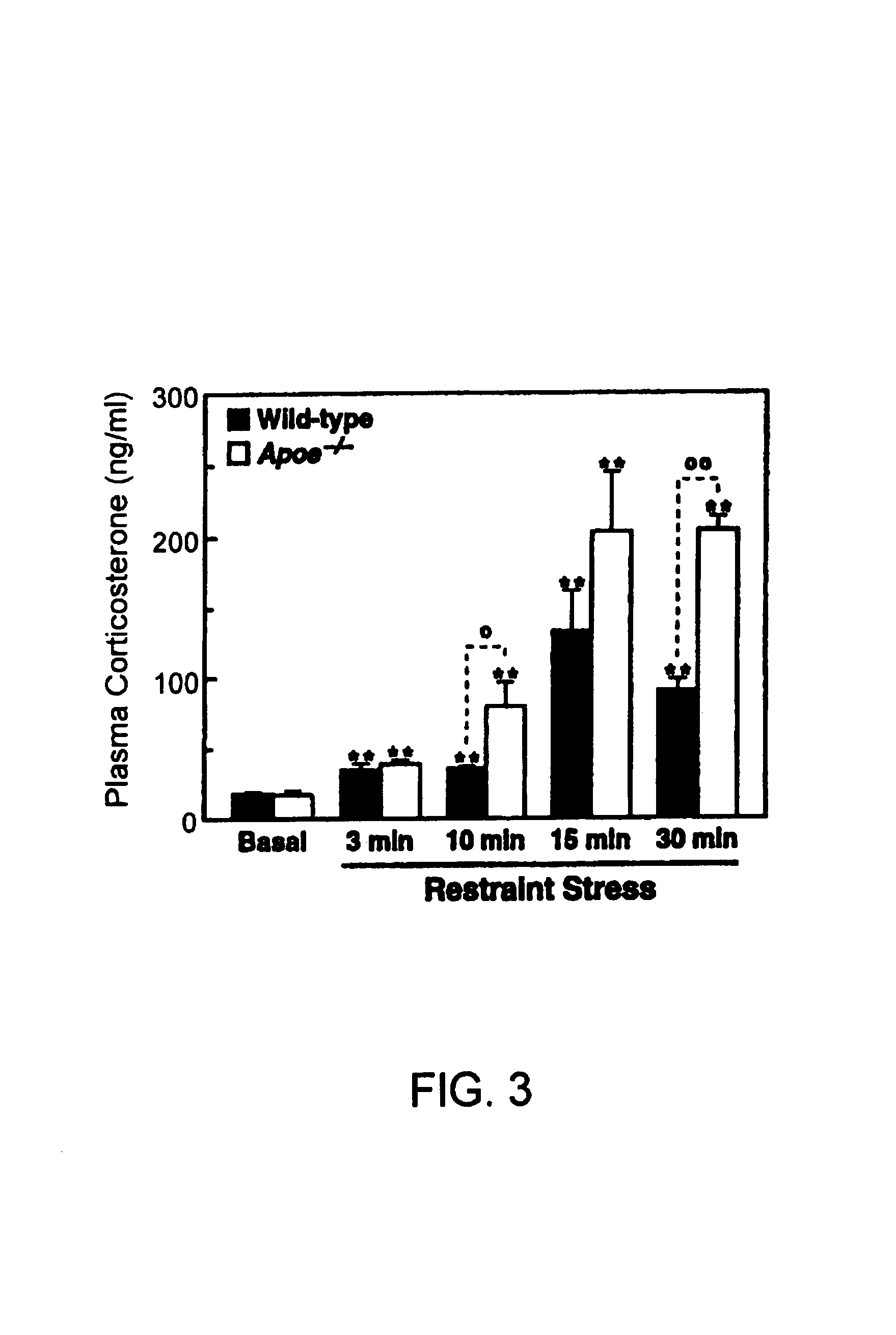
Method of screening a compound for anxiolytic activity in an Apolipoprotein e knockout animal
InactiveUS6982361B1Peptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsStress inducedApolipoprotein e4
Methods and compositions for use in treating anxiety are provided. In the subject methods, an effective amount of an agent having ApoE3 activity is administered to a host suffering from an anxiety, e.g. excessive anxiety, unwanted anxiety, an anxiety disorder, etc. Also provided are methods and compositions for modulating adrenal steroidogenesis and / or release, particularly stress induced adrenal steroidogenesis and / or release, and the hippocampal-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. In these methods, an effective amount of an ApoE activity modulating agent, e.g. an ApoE agonist or antagonist, is administered to the host.
Owner:THE J DAVID GLADSTONE INST A TESTAMENTARY TRUST ESTABLISHED UNDER THE WILL OF J DAVID GLADS
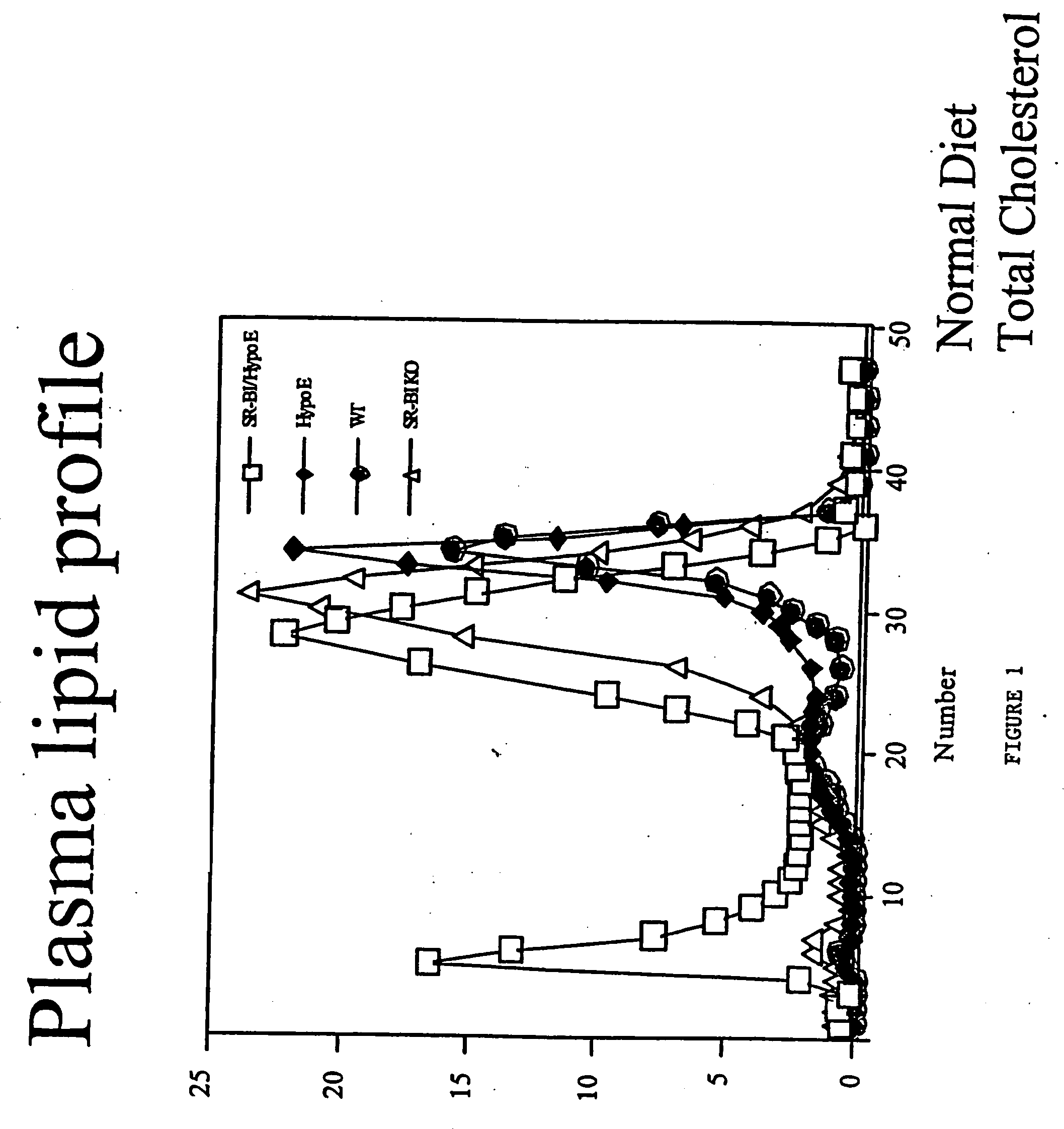
Inducible heart attack animal model
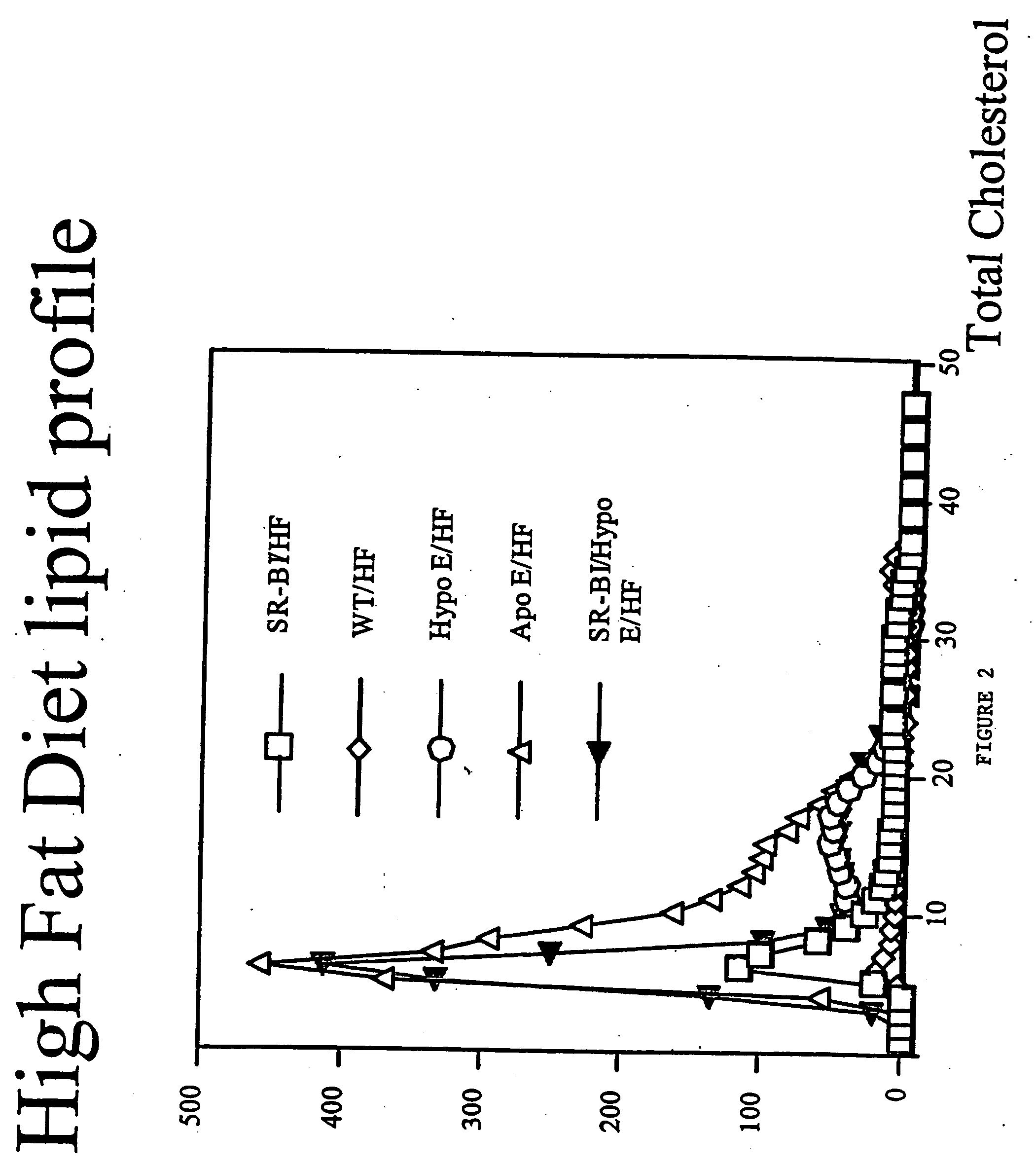
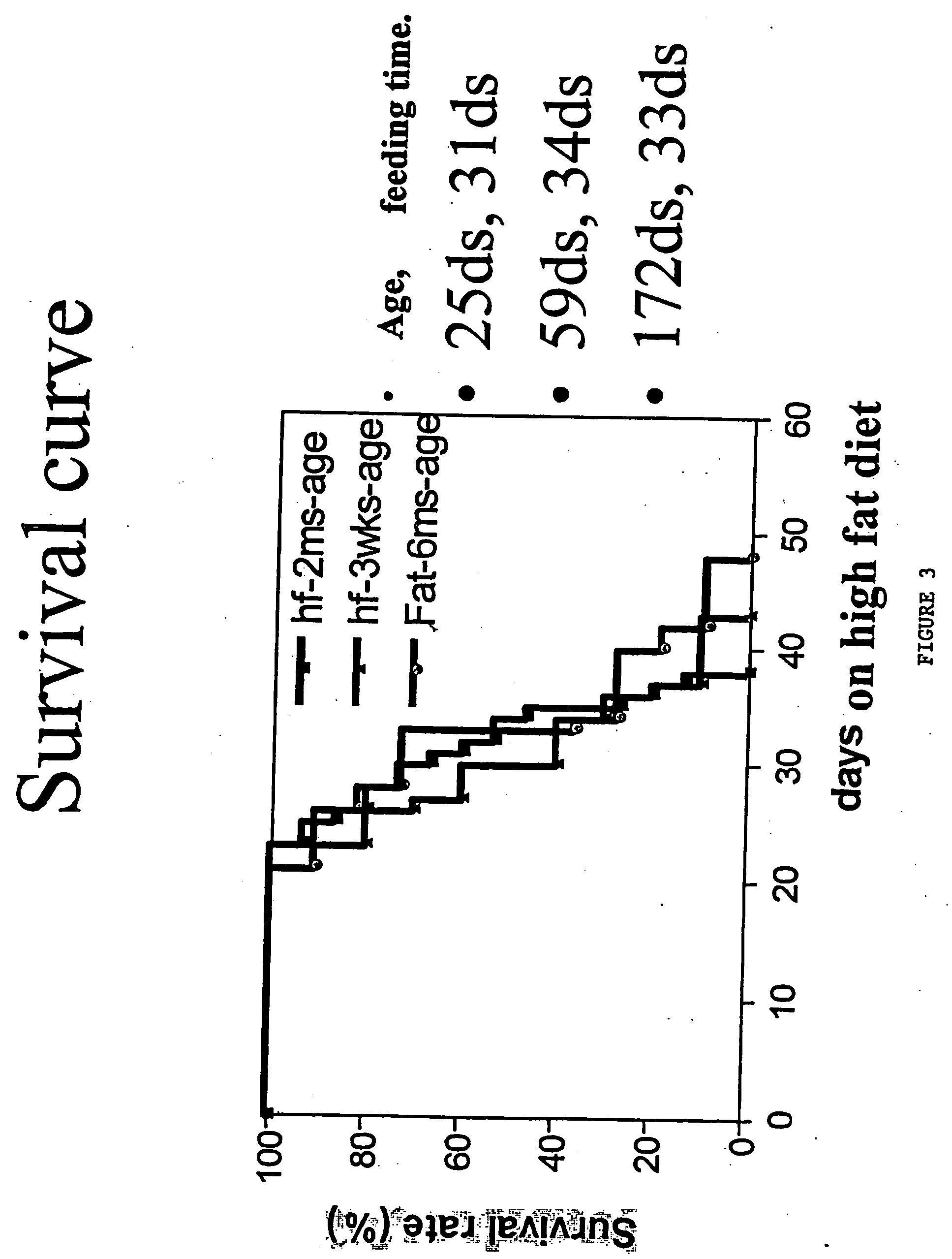
An animal model of coronary heart disease has been developed where myocardial infarct can be induced by altering the animal's diet. In all embodiments, this animal model is a result of reduced activity of scavenger receptor class BI (SR-BI) and apolipoprotein E (ApoE). In a preferred embodiment, the model is a result of crossbreeding two transgenic mouse lines: a knockout of SR-BI (SR-BI− / −) and an impaired ApoE expressor (hypoE). The impaired ApoE gene results in only 2-5% expression of ApoE and a reduction in cholesterol homeostasis. Resulting animals are predisposed to hypercholesterolemia but can live longer than a year on a normal low fat diet. Serum plasma levels can be significantly elevated by changing the animal's diet to one containing high levels of fat and cholesterol. Within a month on a high fat, high cholesterol diet, animals develop atherosclerosis and myocardial infarction occurs. Survival depends on the nature of the diet and the conditions of animal husbandry and can typically be around 20-30 days after administration of the modified diet depending on the specific conditions. Housing the animals alone or in groups significantly affects survival of these animals on a high fat diet. Analysis of B- and T-cell deficient SR-BI / ApoE / RAG2 triple knockout mice established that B- and T-lymphocytes do not play a key role in the pathophysiology of the SR-BI ApoE dKO model of human disease. These animal models can be used to study mechanisms and progression of CHD as a function of diet, treatment with drugs to be screened for efficacy or undesirable side effects, and social environmental effects.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Methods and animal model for analyzing age-related macular degeneration
ActiveUS20090260091A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsMicrobiological testing/measurementCCL2Knockout animal
Methods for testing candidate drugs for treatment of age-related macular degeneration are provided. Ccl2-deficient, and Ccr2-deficient mice are used to determine the effect of candidate drugs and treatments on development of age-related macular degeneration. Also provided is a Ccl2-deficient, Ccr2-deficient dual knockout mouse, which is a useful animal model for age-related macular degeneration.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
Transgenic mouse whose genome comprises a homozygous disruption of its alpha1G gene, a method of preparing the same and use thereof
InactiveUS20080201787A1Suppressing functionResisting epilepsyCompounds screening/testingCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsNervous systemKnockout animal
The disclosure concerns a method for resistance of epilepsy by suppressing the function of alpha 1G protein of T-type calcium channels, use of suppressor of alpha 1G protein for prevention or treatment for epilepsy, knockout mice resisting epilepsy by disrupting alpha 1G subunit of T-type calcium channel, and preparation method thereof. The α1G-knockout transgenic mouse can be used for investigating the relationship between diseases particularly neuropathy or psychopathy and the function of α1G T-type calcium channel via various behavioral tests since α1G subunit is mainly expression in central nervous system (CNS) and pheripheral nervous system (PNS). Further, the α1G-knockout transgenic mouse can be used for screening antileptic agents.
Owner:ORIENTBIO
Nav1.7-related assays
InactiveUS20130115171A1Robust behaviorPrevents painful responseCompounds screening/testingAntiendomysial antibodiesAssay
A viable global NaV1.7− / − knockout mouse is disclosed, and a breeding colony of global NaV1.7− / − knockout mice. Also disclosed are an isolated mouse gamete that does not encode a functional NaV1.7, produced by the NaV1.7− / − knockout mouse; an isolated NaV1.7− / − mouse cell, or a progeny cell thereof, isolated from the NaV1.7− / − knockout mouse; and a primary cell culture or a secondary cell line and a tissue or organ explant or culture thereof derived from the NaV1.7− / − knockout mouse. Disclosed also are a hybridoma, wherein the hybridoma was originally formed from the fusion of the isolated NaV1.7− / − mouse cell mouse cell and a myeloma cell, and a method of making an antibody. Also disclosed are assays useful for screening prospective NaV1.7 inhibitors and dose ranging a test NaV1.7 inhibitor compound, which were validated using the NaV1.7− / − knockout mouse.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Application of human YTHDF1 (Youth-Tech-Health Domain Family Member 1) gene
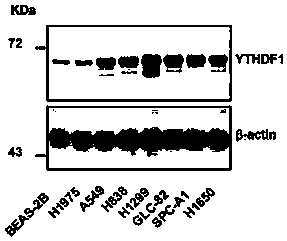
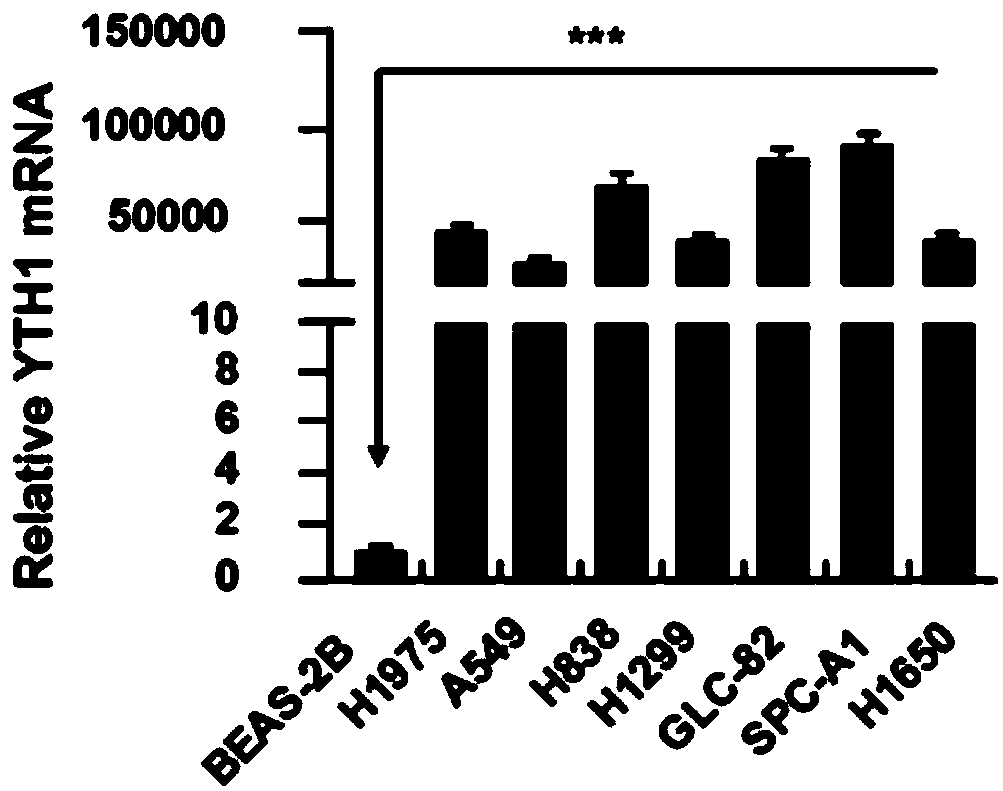
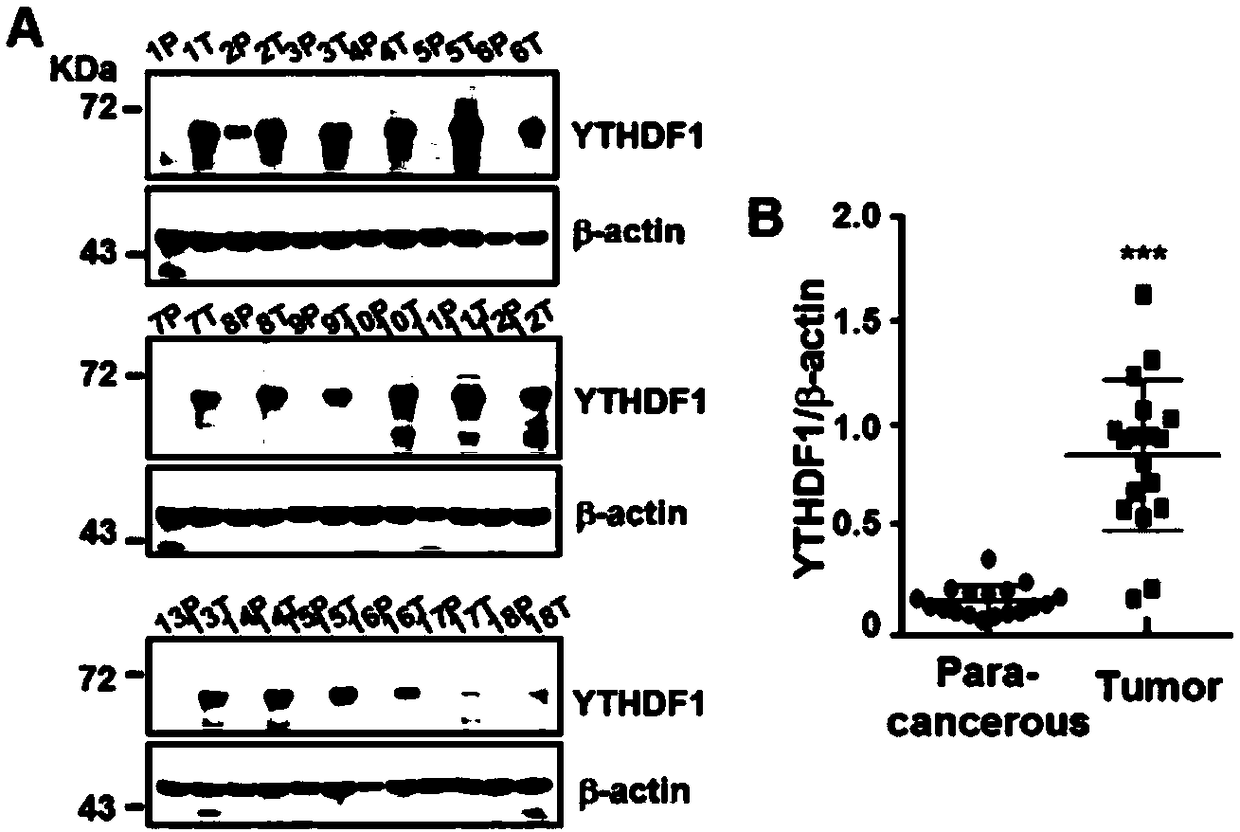
ActiveCN109337980APrevent proliferationPromote apoptosisOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementCancer cellKnockout animal
The invention discloses novel application of a human YTHDF1 (Youth-Tech-Health Domain Family Member 1) gene, that is, a human YTHDF1 gene expression amount detection reagent is applied to preparationof lung cancer clinical diagnosis reagents, a human YTHDF1 gene is applied to preparation of lung cancer medicines, compared with normal pulmonary epithelial cells, the YTHDF1 gene is highly expressed in lung cancer cells, RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) designed according to the YTHDF1 gene is capable of interfering slow viruses, inhibiting expression of YTHDF1, remarkably inhibiting proliferation of thelung cancer cells, retarding tumor cell division at a G0 / G1 phase and promoting cell apoptosis, inhibiting formation of nude mouse transplanted tumour, and furthermore the purpose of treating lung cancer can be achieved; YTHDF1 gene knockout mouse tumor formation capability detection shows that cell proliferation is remarkably inhibited, and cell apoptosis is remarkably increased; the results show that the YTHDF1 gene can be used as a target for lung cancer treatment, and wide prospects are provided for development of lung cancer treatment medicines based on YTHDF1 genes in future.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Process For Producing Multipotential Stem Cell Origination In Testoid Cell
InactiveUS20070202590A1Artificial cell constructsCell culture active agentsKnockout animalNeurotrophic factors
The present invention provides a method of producing pluripotent stem cells, which comprises culturing testis cells using a medium containing glial cell derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) or an equivalent thereto to obtain pluripotent stem cells. The medium can further contain leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF), epidermal growth factor (EGF), basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) and the like. Using the production method of the present invention, it is possible to produce pluripotent stem cells, which have conventionally been only obtainable from fertilized eggs, embryos and the like, from a postnatal individual. Using the pluripotent stem cells, it is possible to construct diverse tissues having histocompatibility for autotransplantation, and the pluripotent stem cells are useful in medical fields such as regeneration medicine and gene therapy. Also, the pluripotent stem cells are useful in the field of biotechnology because they can be used to prepare transgenic animals, knockout animals and the like.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
UTEROGLOBIN IN THE TREATMENT OF IgA MEDIATED AUTOIMMUNE DISORDERS
InactiveUS20090029908A1Avoid developmentInhibition formationNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsProper treatmentKnockout animal
Uteroglobin has been discovered to prevent IgA mediated diseases, such as IgA nephropathy, by preventing the deposition of IgA-Fibronectin immunocomplexes in tissues such as the renal glomeruli. The invention therefore includes methods of treating such diseases by administering therapeutically effective amounts of uteroglobin (and variants or mimetics) to prevent or improve the IgA mediated condition. Transgenic uteroglobin knockout animals, and animals in which uteroglobin-protein expression is reduced by antisense technology, also provide systems for studying IgA mediated diseases, and screening for appropriate treatments.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Molecular marker for diagnosing atherosclerosis and application of marker
PendingCN110205375AThe method is simple and reliableMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisDiseaseResearch Object
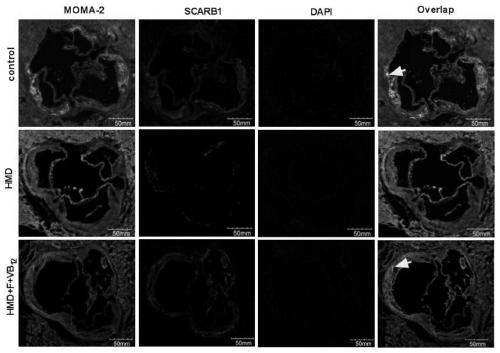
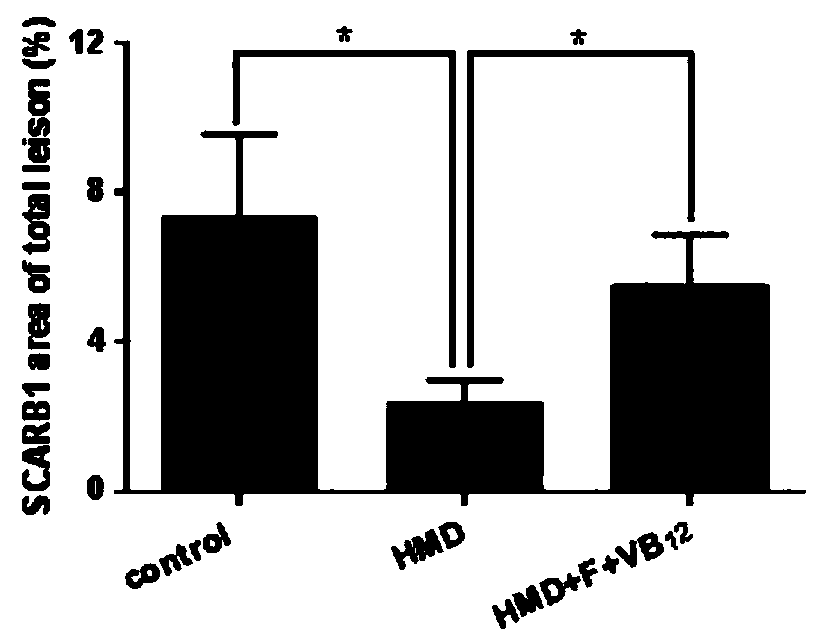
The invention discloses a molecular marker for diagnosing atherosclerosis and an application of the marker, belongs to the technical field of biological engineering and relates to an application of areagent for detecting the expression level of SCRAB1 in blood vessel samples to preparation of products for diagnosing the atherosclerosis, and A sequence of the SCRAB1 is as shown in SEQ: ID: NO: 1.ApoE knockout mice and THP-1 source foam cells serve as research objects, RNA (ribonucleic acid) of tissues or cells is extracted, expression change of the gene SCRAB1 related to AS lipid is observed,cellular level validation is implemented, and a deposition specificity diagnosis method of the AS lipid comprising the SCRAB1 is built. The method is simple and reliable, materials are conveniently taken, sensitivity and specificity of the method are highly consistent with those of imaging diagnosis and gross specimen staining, and the method has high application values in early diagnosis and prognosis evaluation of AS diseases.
Owner:NINGXIA MEDICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com