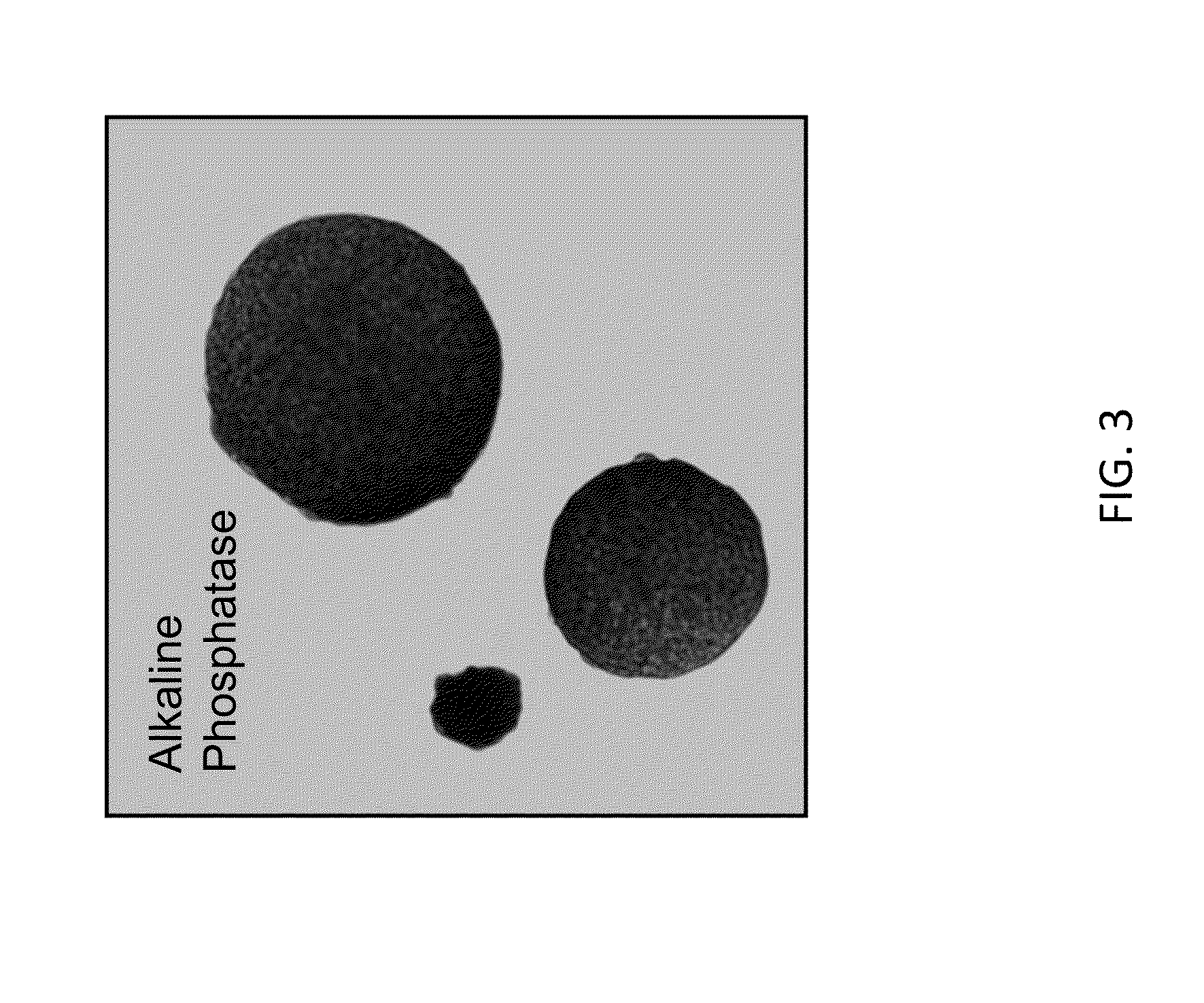
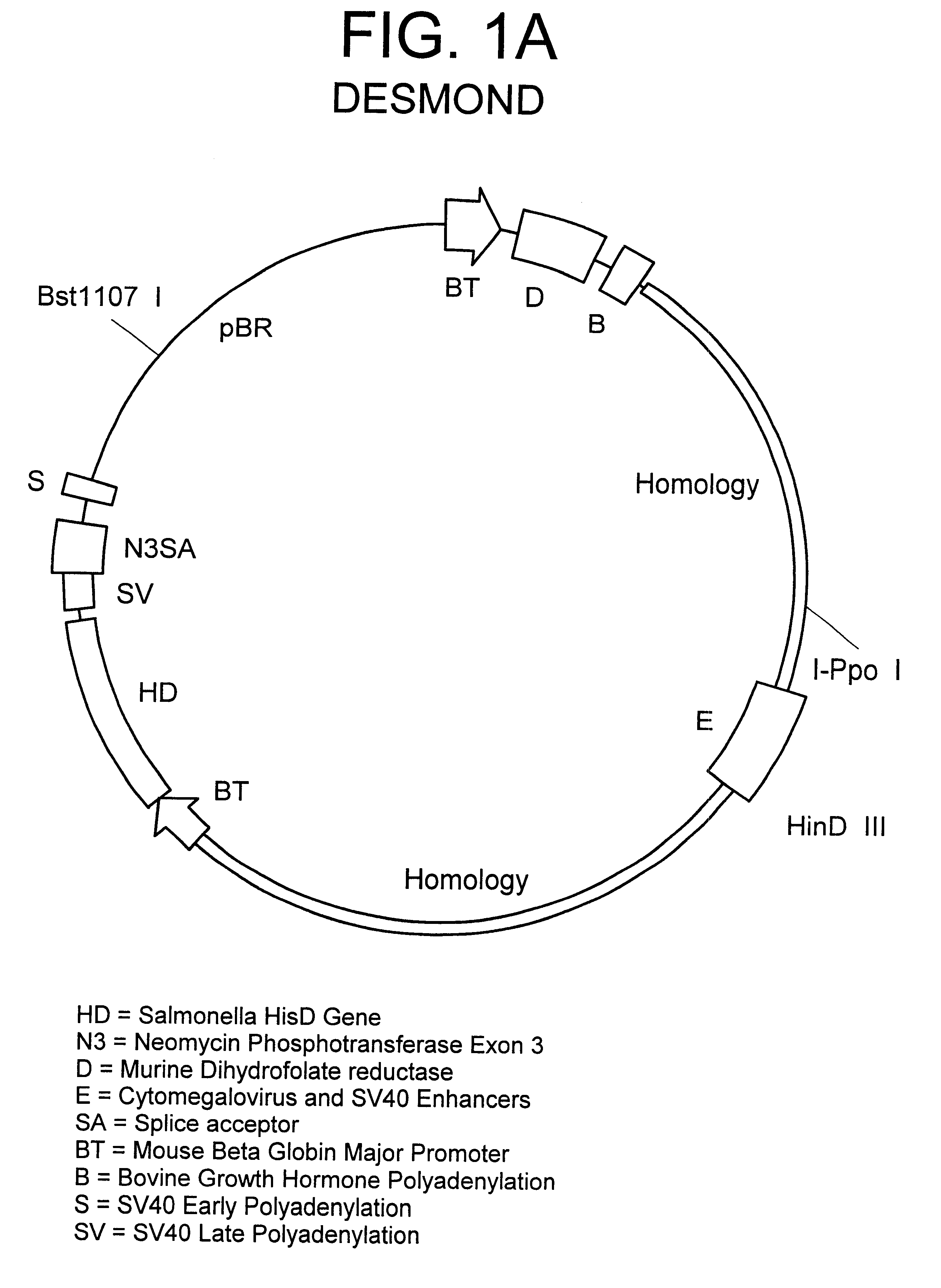
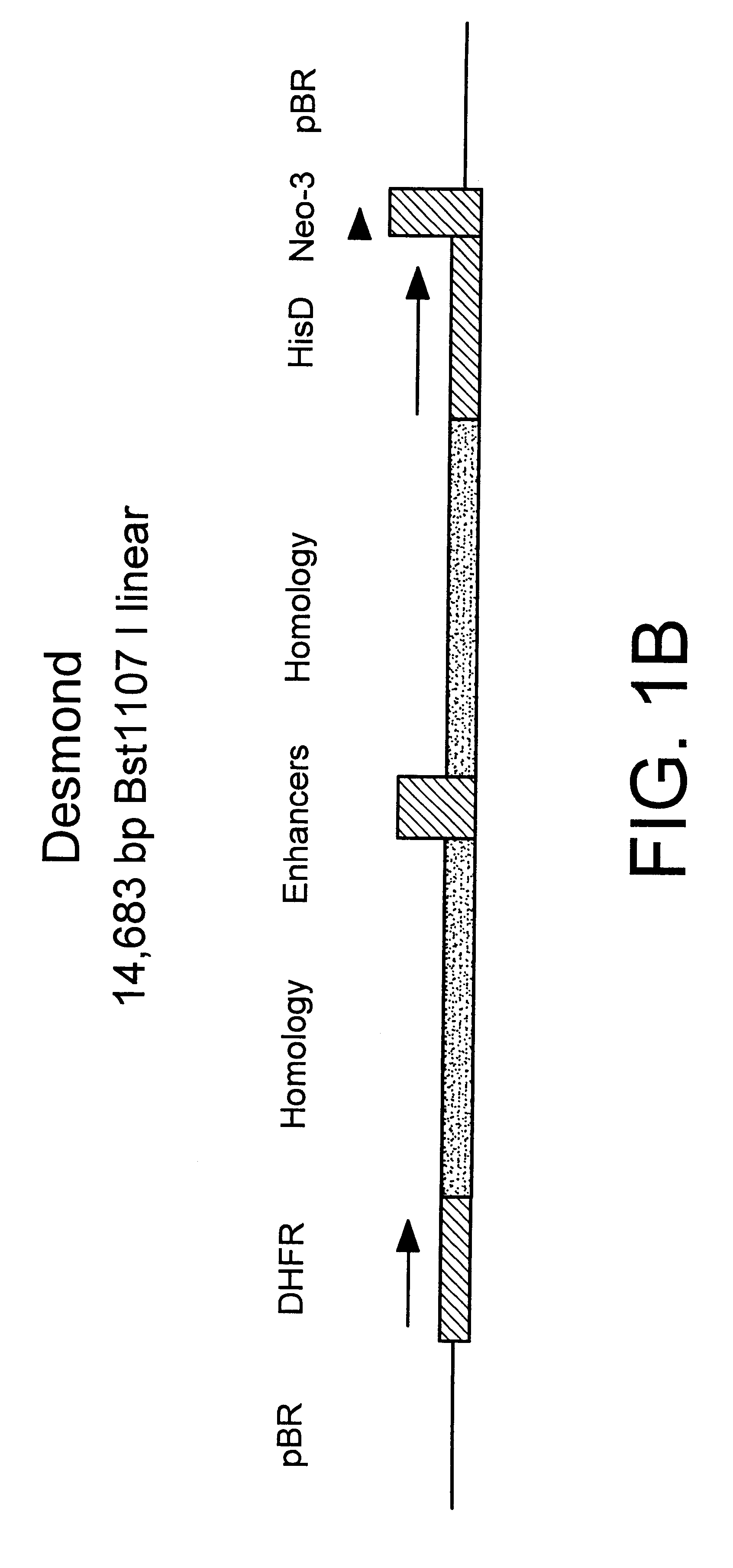
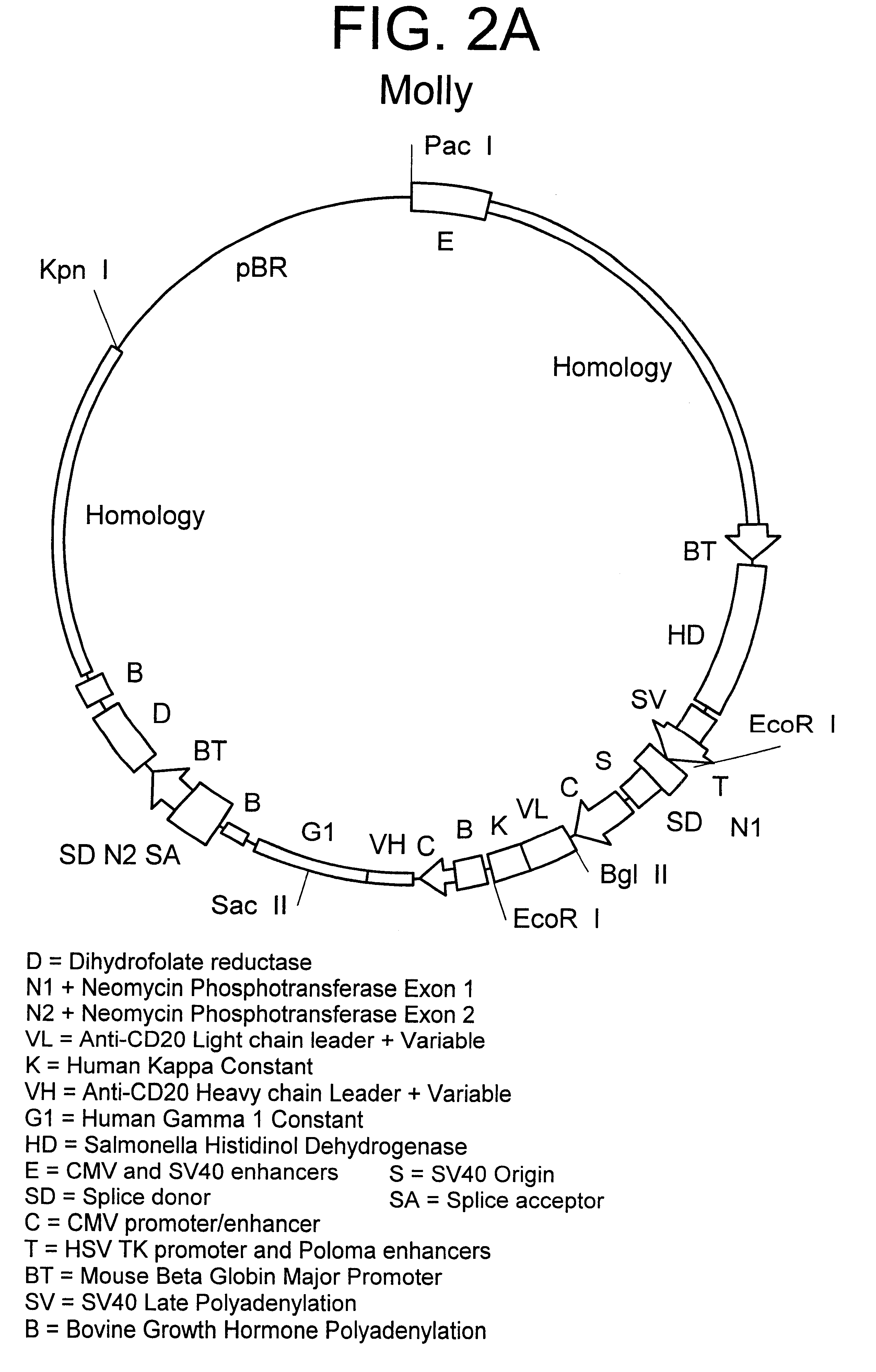
Patents
Literature
3564results about "Stable introduction of DNA" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methods of modifying eukaryotic cells
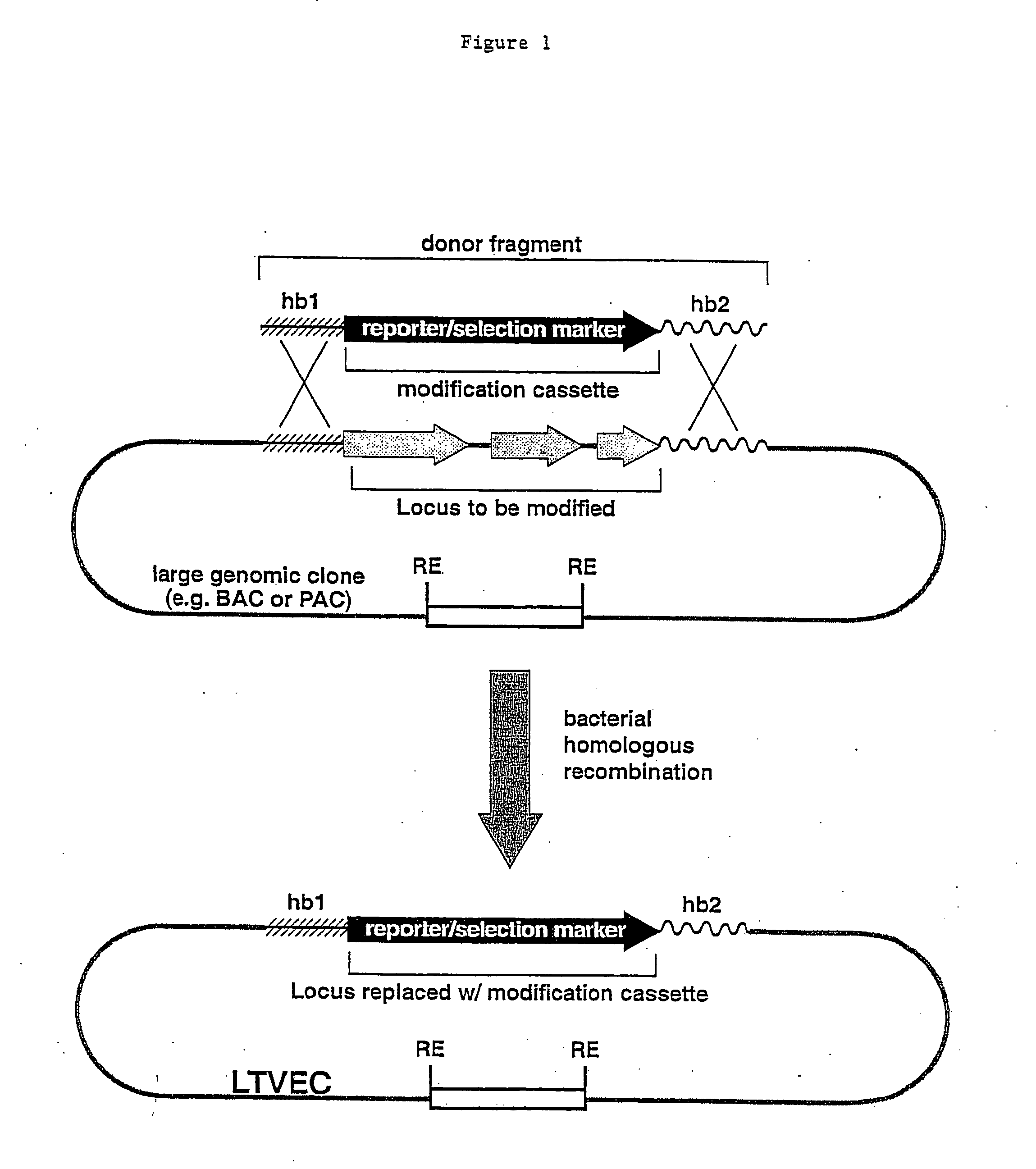
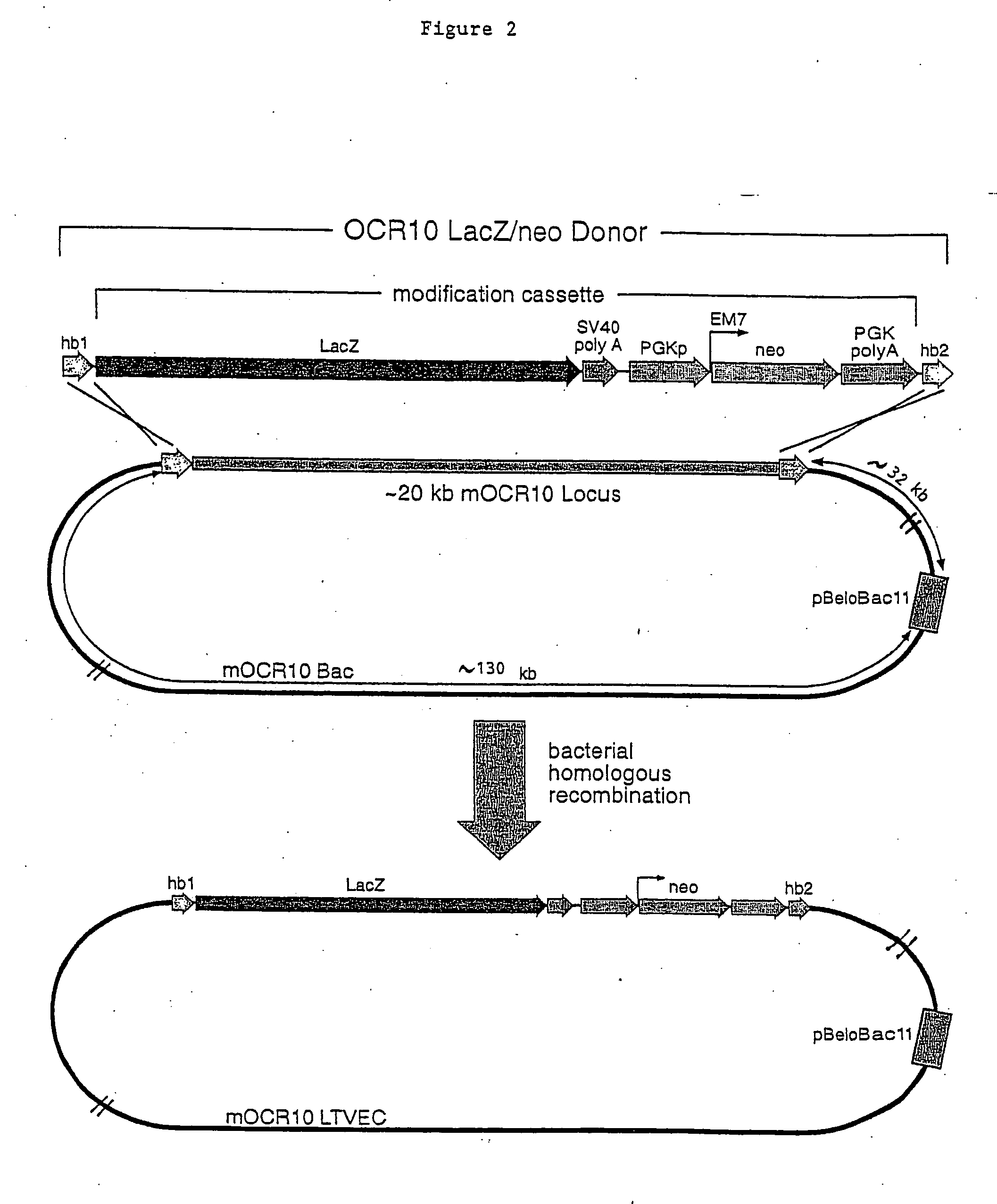
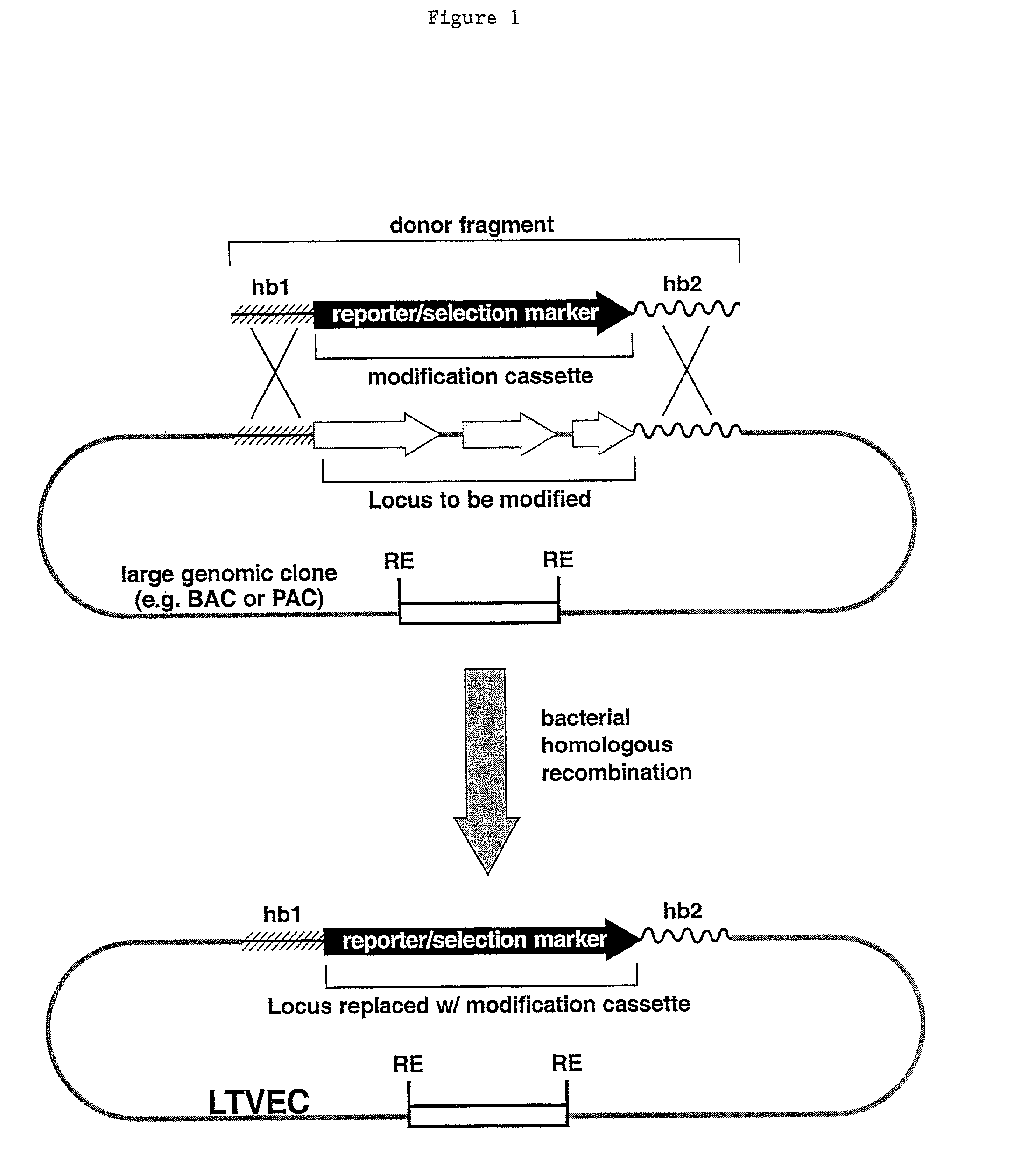
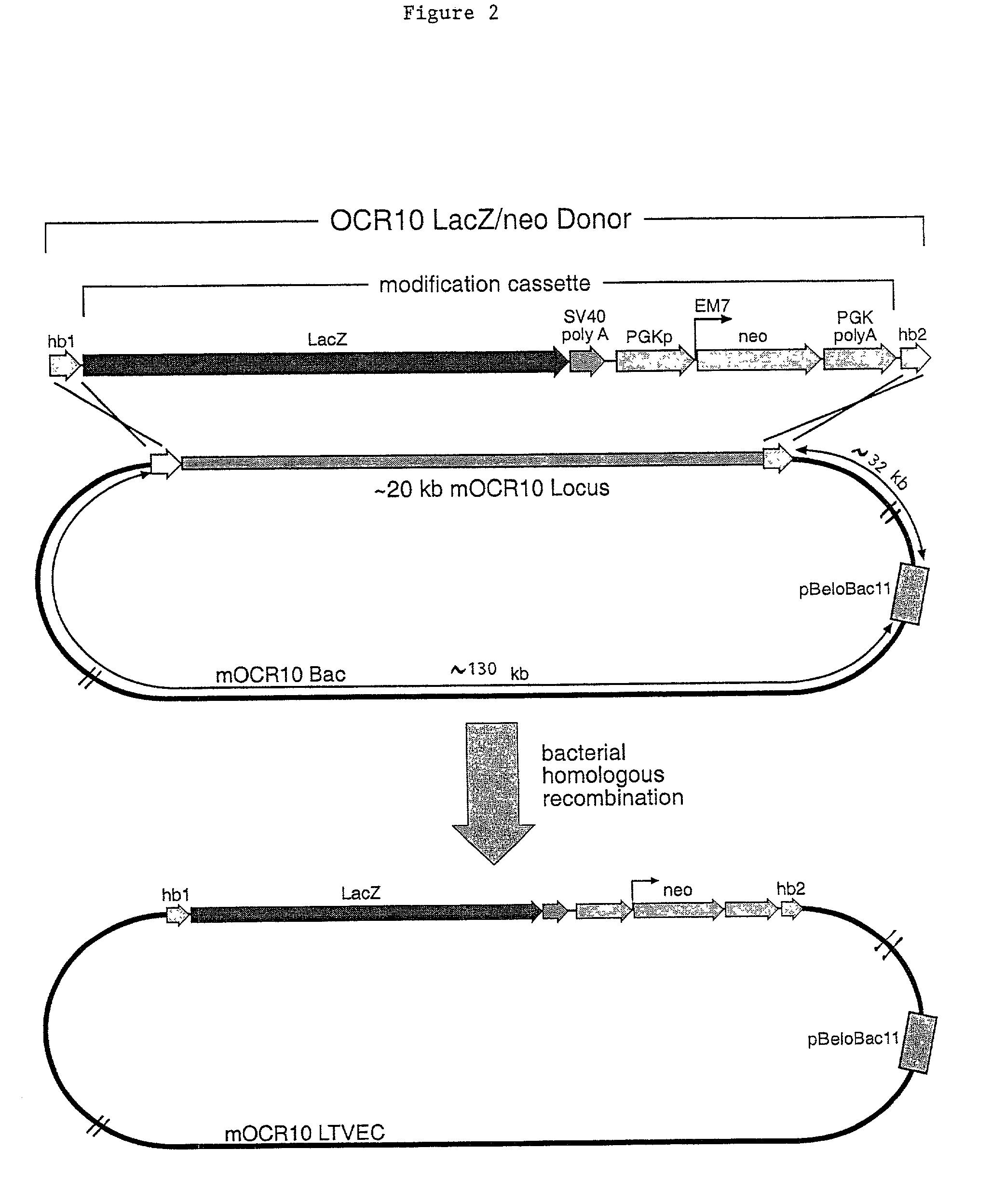
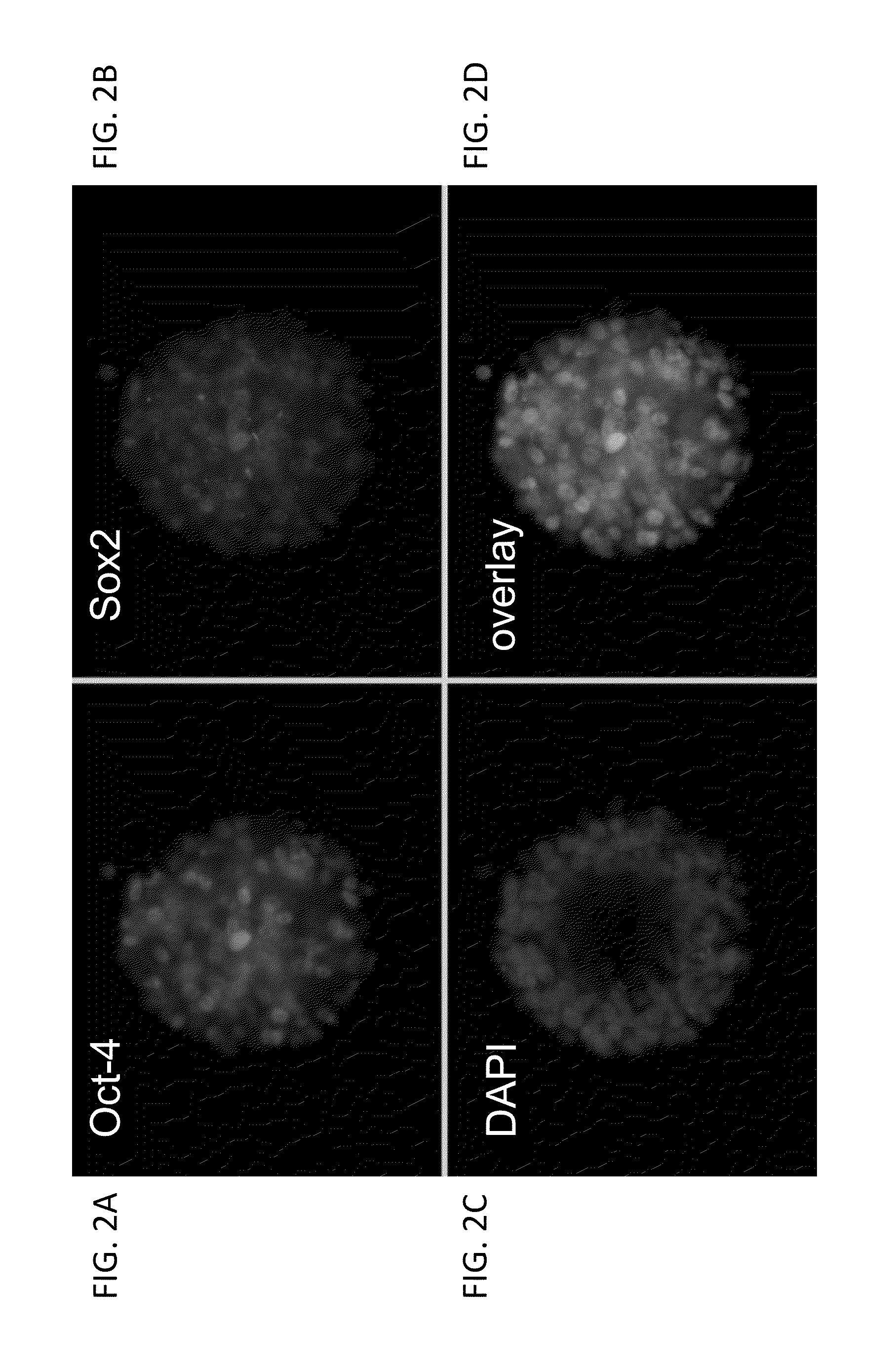
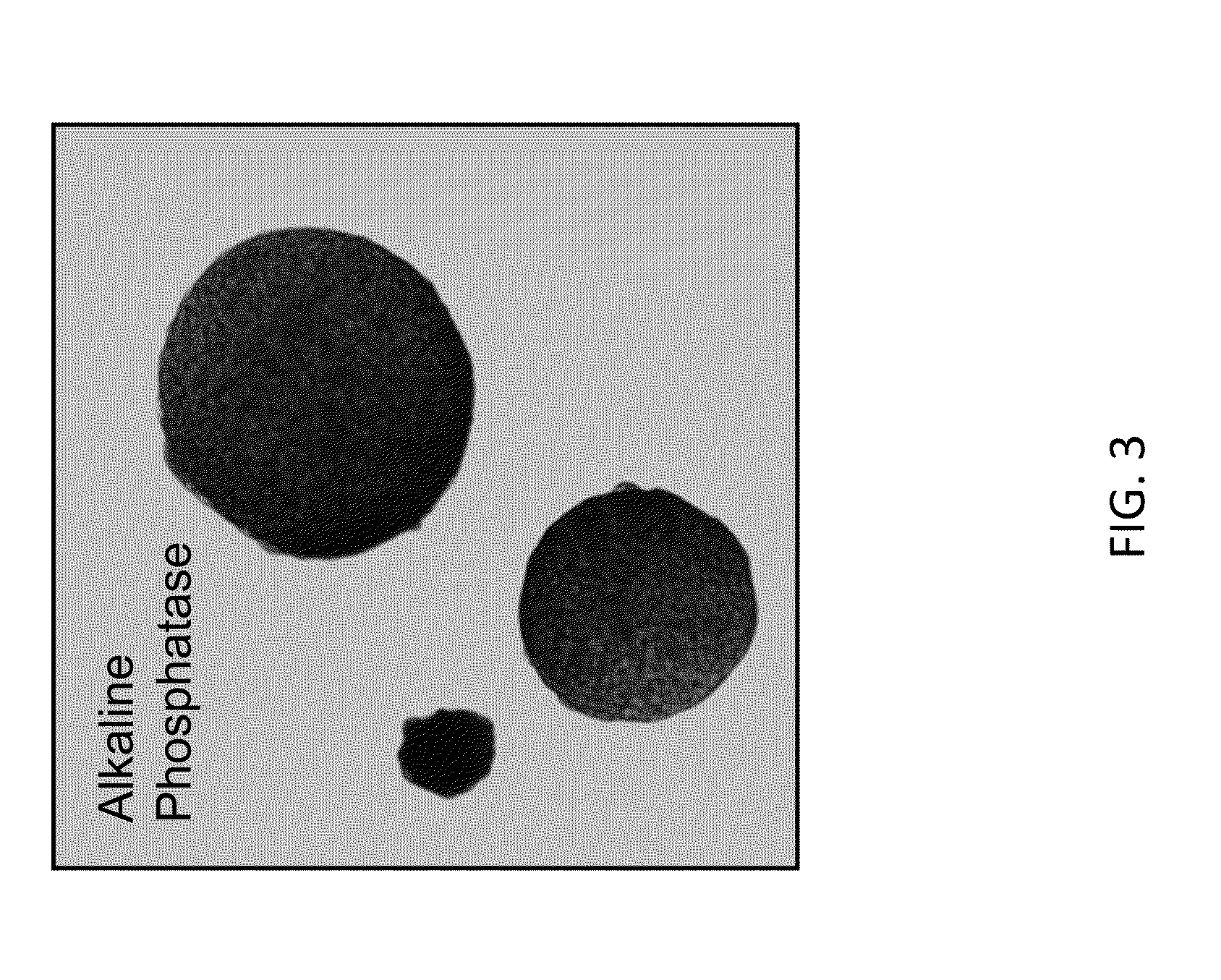
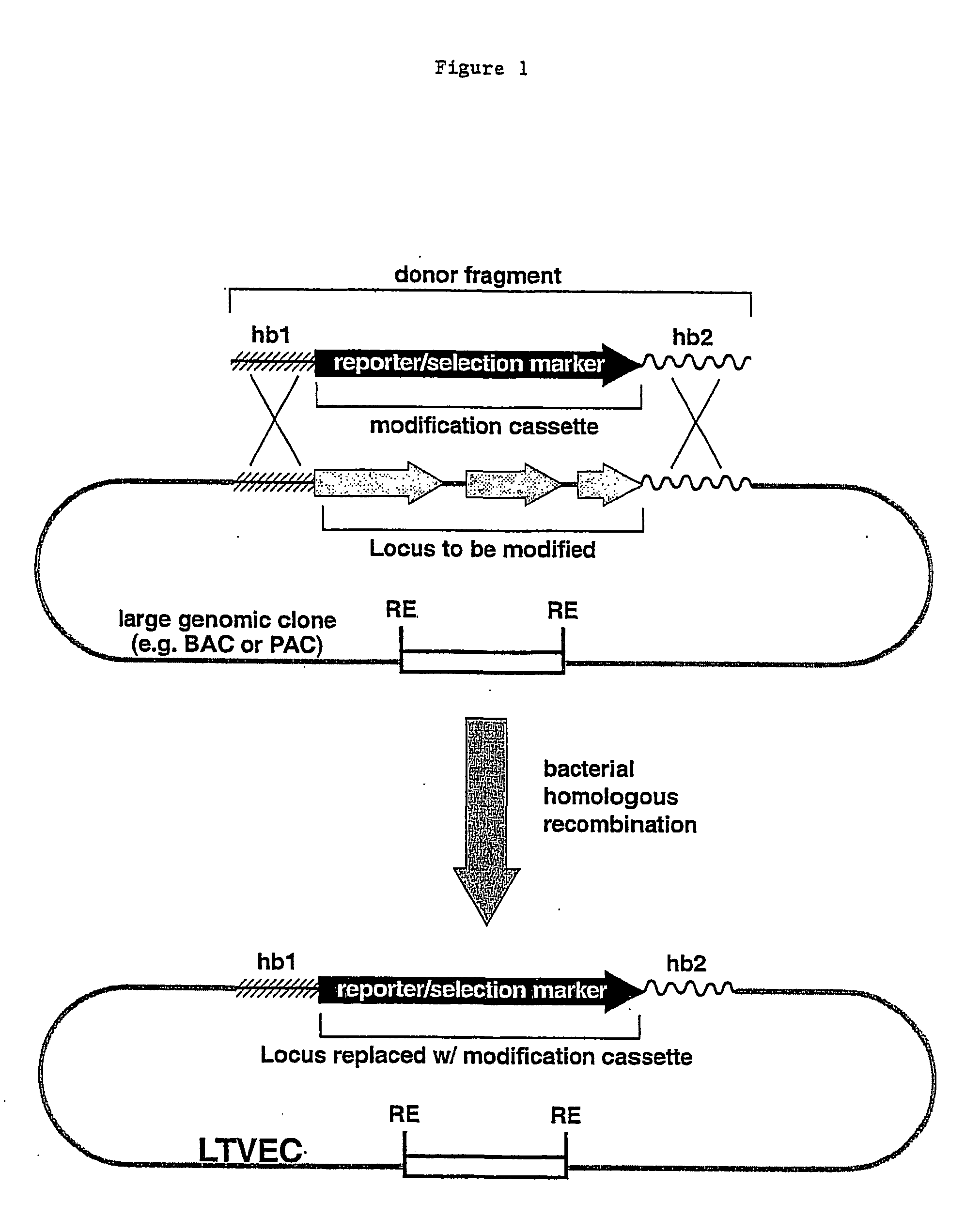
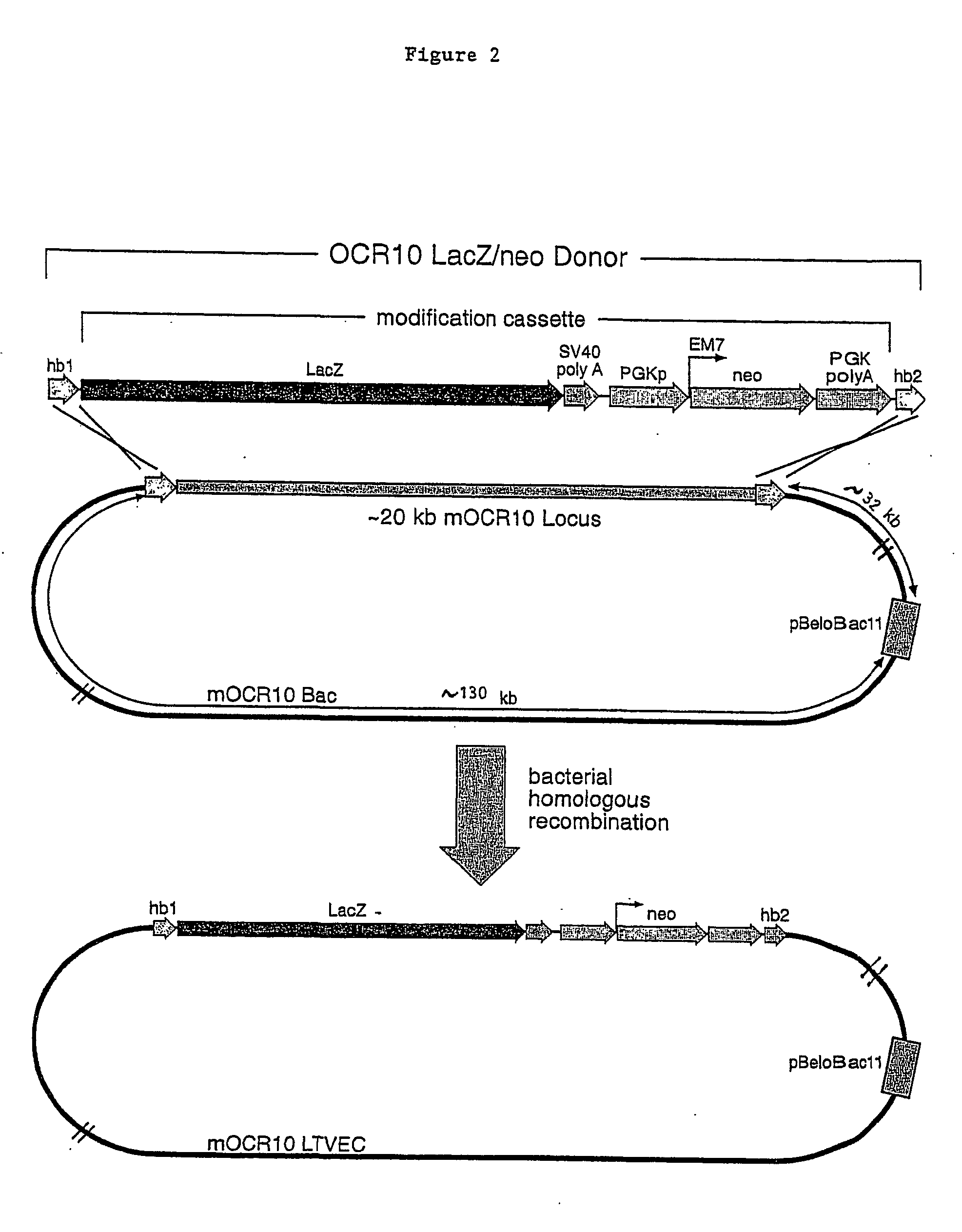
A method for engineering and utilizing large DNA vectors to target, via homologous recombination, and modify, in any desirable fashion, endogenous genes and chromosomal loci in eukaryotic cells. These large DNA targeting vectors for eukaryotic cells, termed LTVECs, are derived from fragments of cloned genomic DNA larger than those typically used by other approaches intended to perform homologous targeting in eukaryotic cells. Also provided is a rapid and convenient method of detecting eukaryotic cells in which the LTVEC has correctly targeted and modified the desired endogenous gene(s) or chromosomal locus (loci) as well as the use of these cells to generate organisms bearing the genetic modification.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
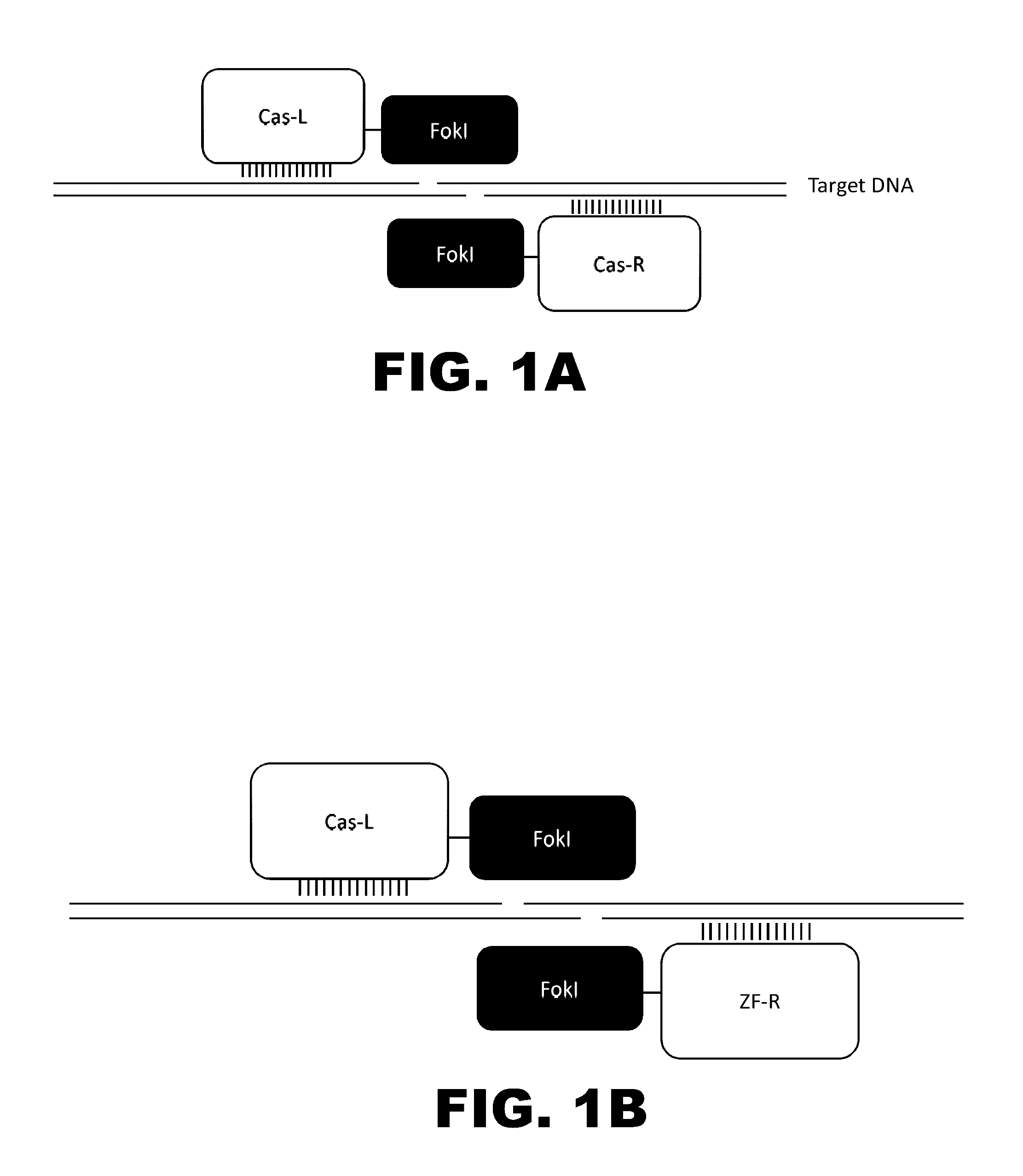
Use of chimeric nucleases to stimulate gene targeting
ActiveUS20050026157A1Ameliorate genetic disorderIncrease productionAntibacterial agentsFusion with DNA-binding domainGene targetsGenetic Change
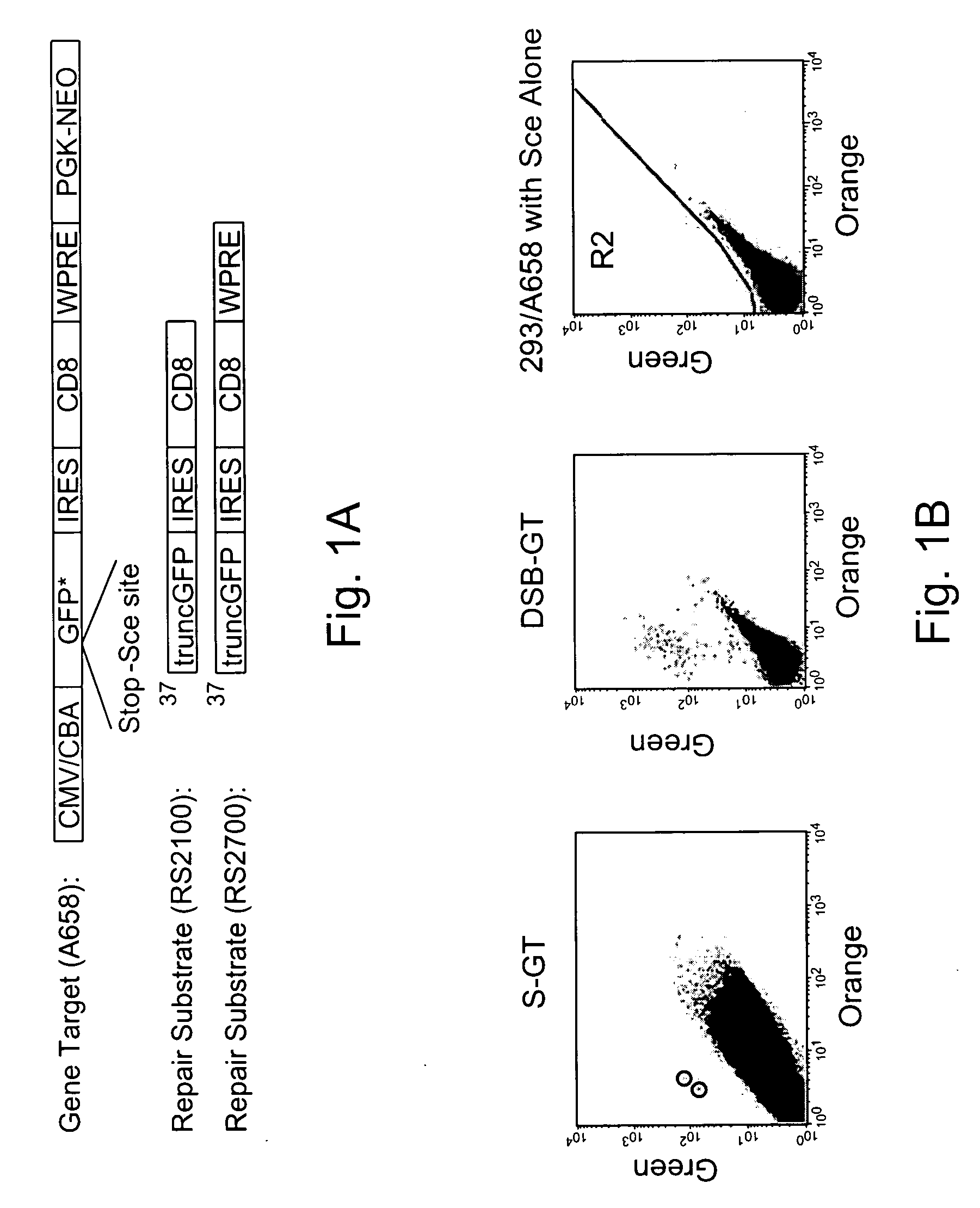
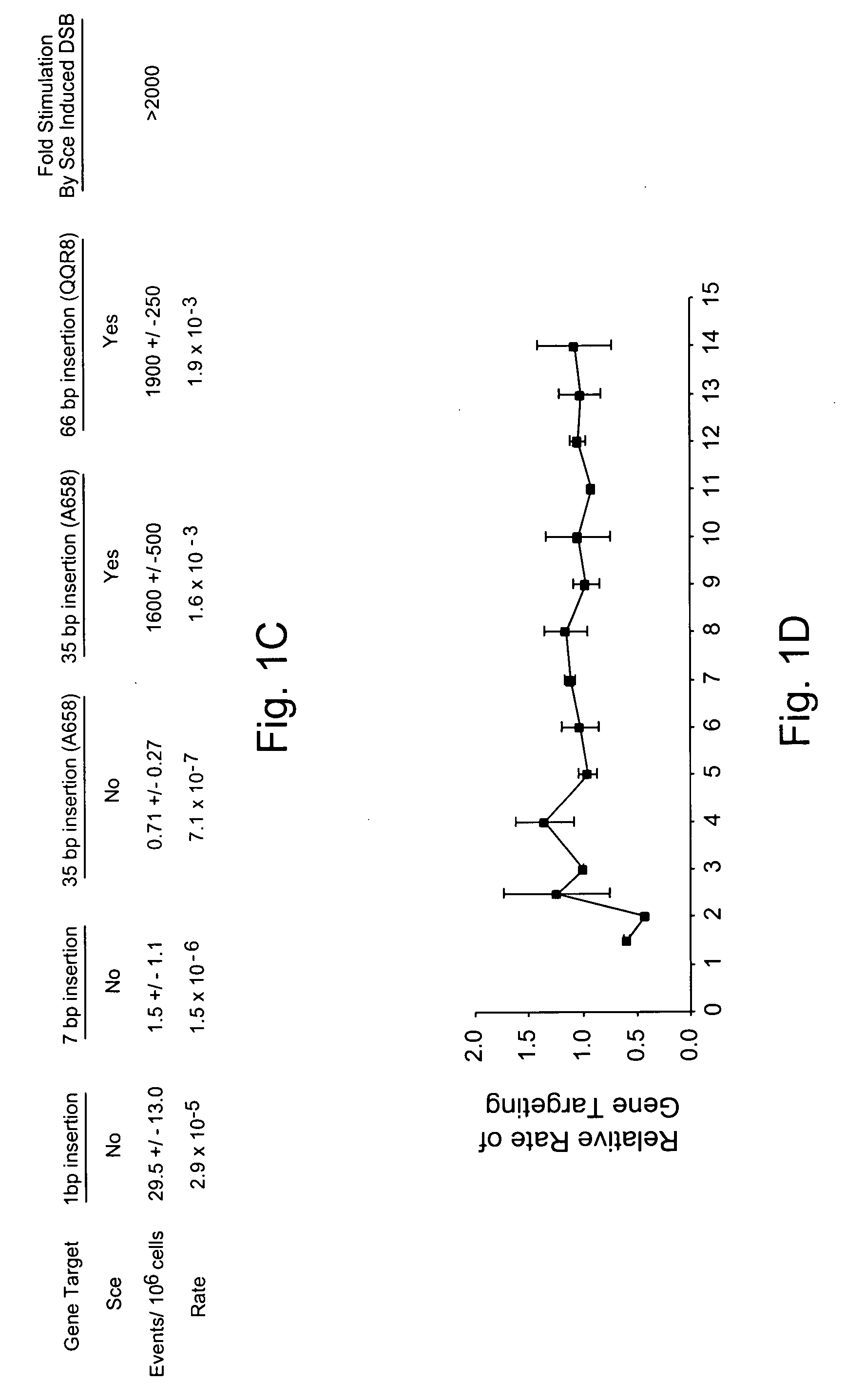
Gene targeting is a technique to introduce genetic change into one or more specific locations in the genome of a cell. For example, gene targeting can introduce genetic change by modifying, repairing, attenuating or inactivating a target gene or other chromosomal DNA. In one aspect, this disclosure relates to methods and compositions for gene targeting with high efficiency in a cell. This disclosure also relates to methods of treating or preventing a genetic disease in an individual in need thereof. Further disclosed are chimeric nucleases and vectors encoding chimeric nucleases.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Systems for in vivo site-directed mutagenesis using oligonucleotides
InactiveUS20040171154A1Large deletionImprove applicabilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHeterologousSite-directed mutagenesis
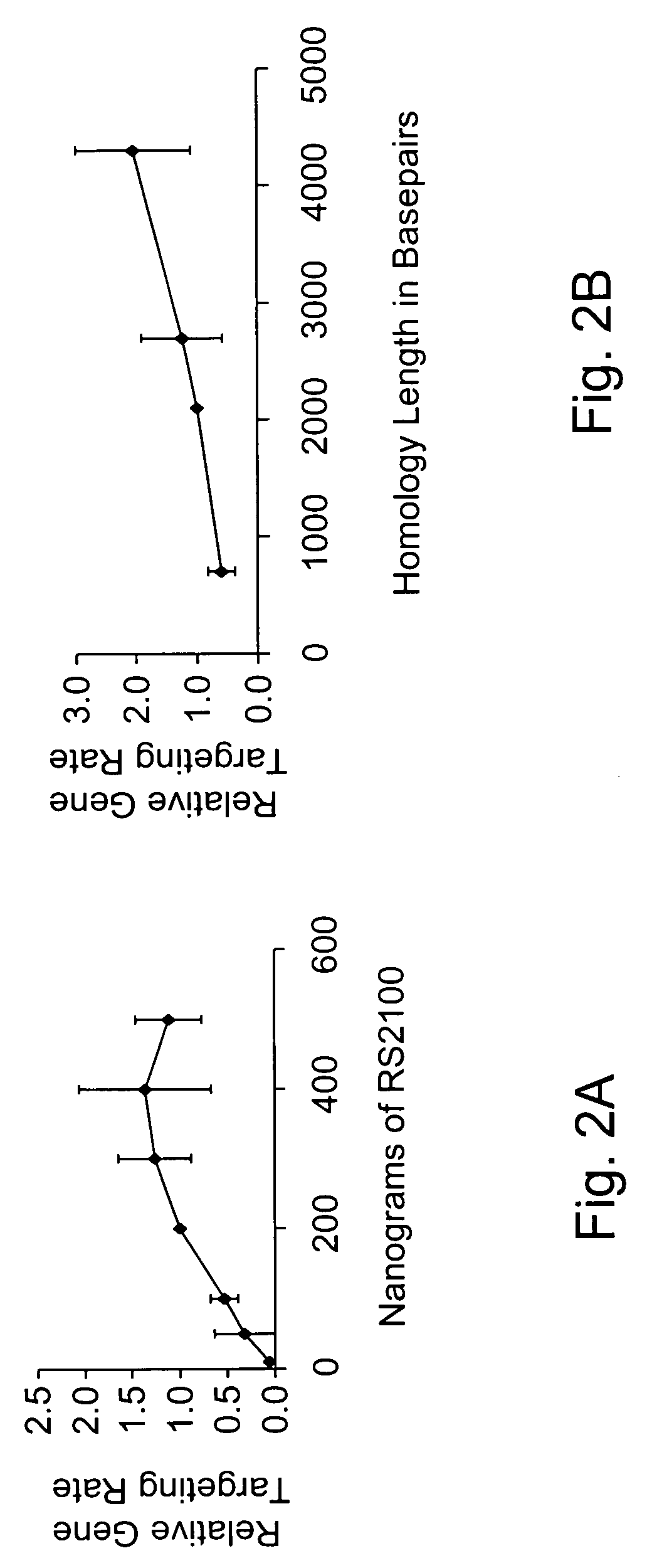
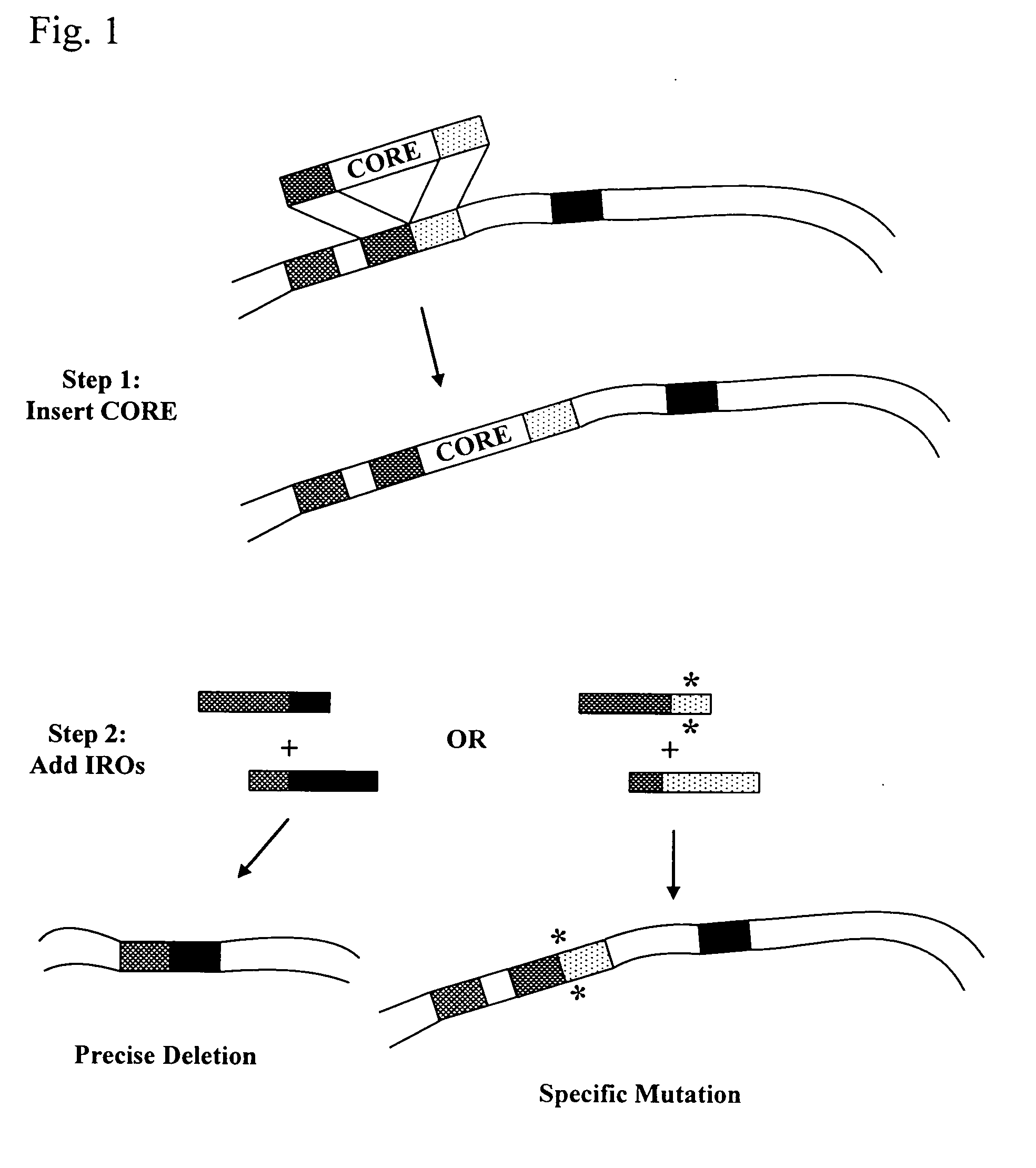
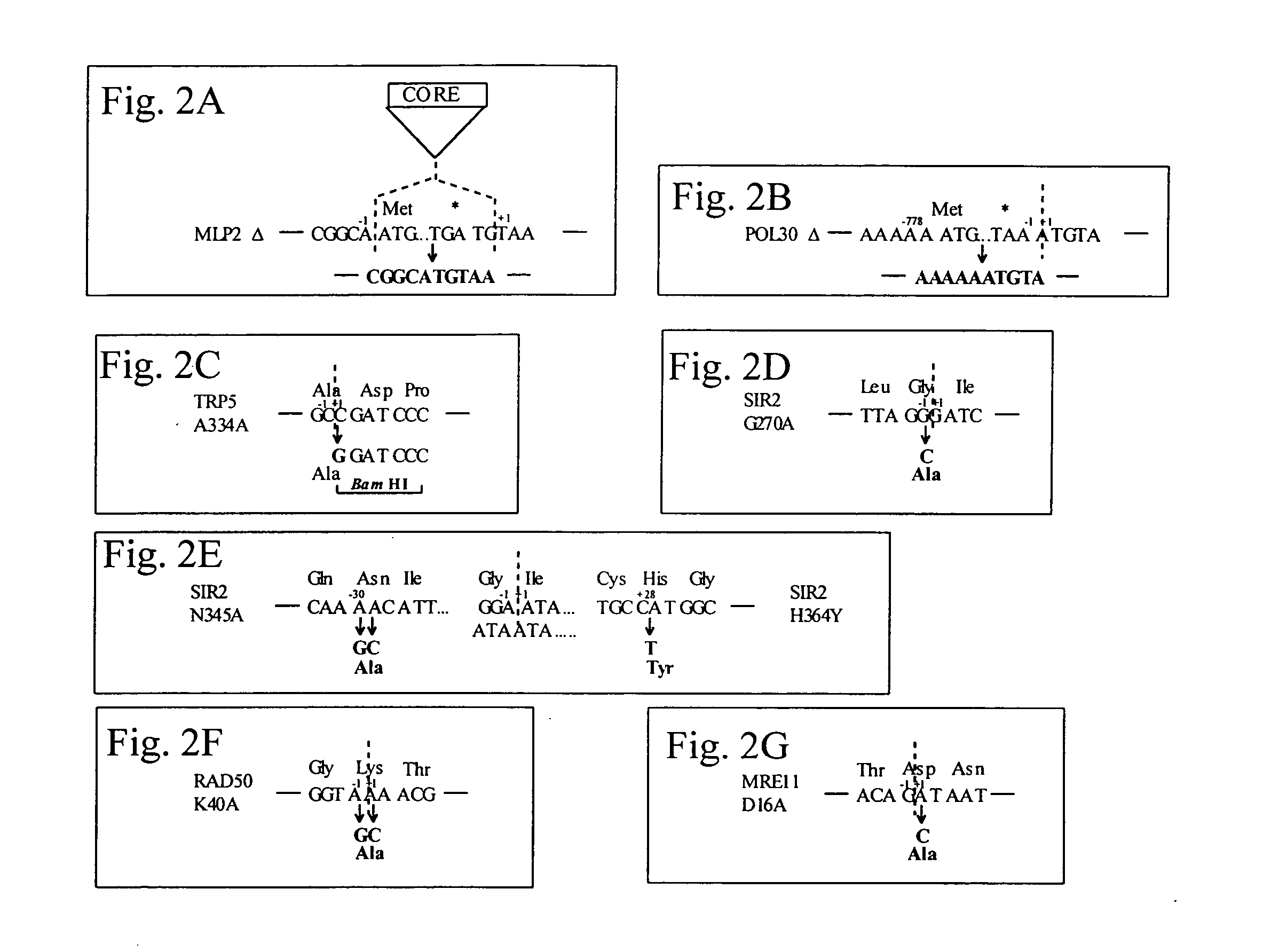
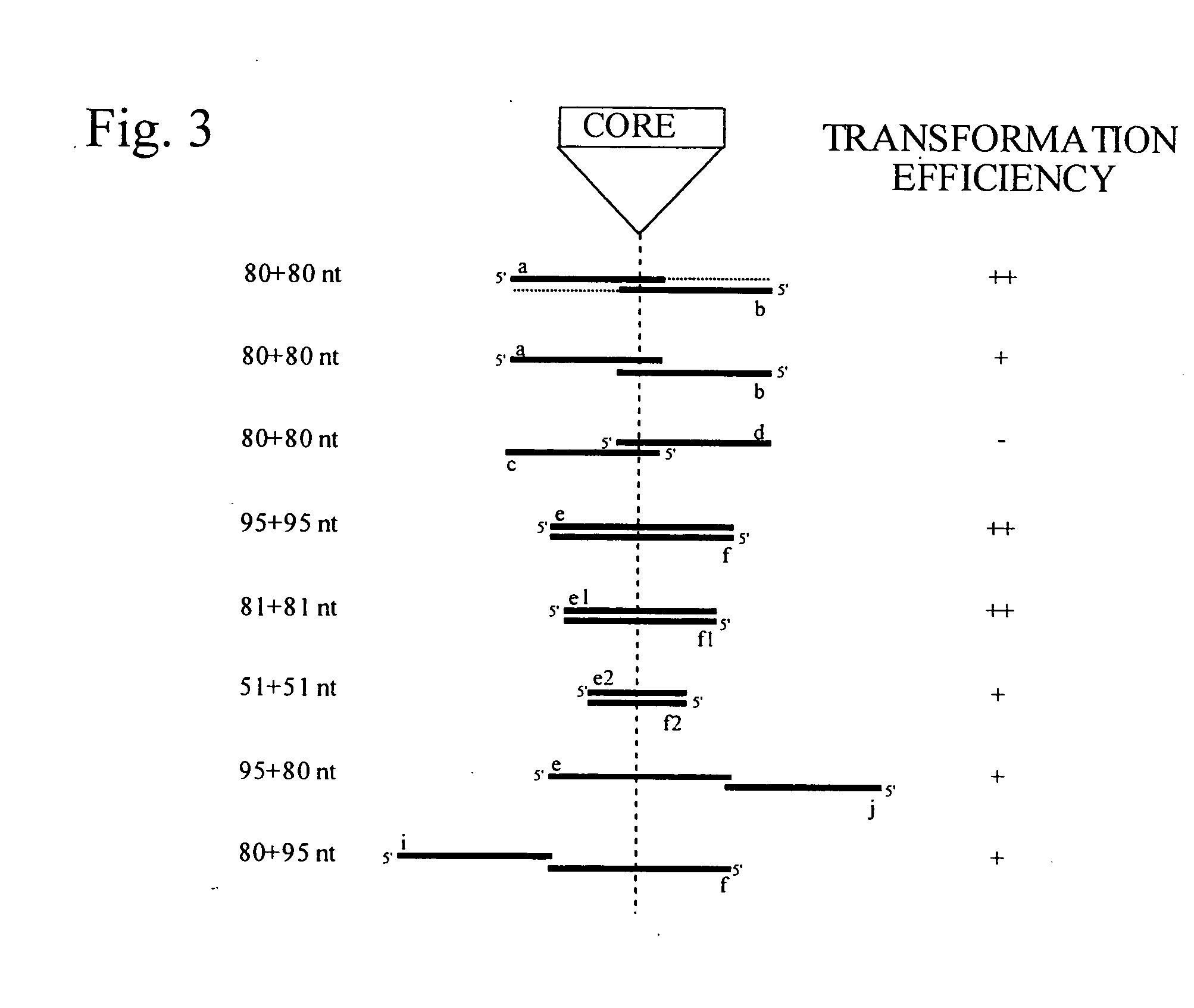
This disclosure provides several methods to generate nucleic acid mutations in vivo, for instance in such a way that no heterologous sequence is retained after the mutagenesis is complete. The methods employ integrative recombinant oligonucleotides (IROs). Specific examples of the described mutagenesis methods enable site-specific point mutations, deletions, and insertions. Also provided are methods that enable multiple rounds of mutation and random mutagenesis in a localized region. The described methods are applicable to any organism that has a homologous recombination system.
Owner:HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES DEPT OF THE GOVERNMENT OF THE US SEC THE
Methods of modifying eukaryotic cells
A method for engineering and utilizing large DNA vectors to target, via homologous recombination, and modify, in any desirable fashion, endogenous genes and chromosomal loci in eukaryotic cells. These large DNA targeting vectors for eukaryotic cells, termed LTVECs, are derived from fragments of cloned genomic DNA larger than those typically used by other approaches intended to perform homologous targeting in eukaryotic cells. Also provided is a rapid and convenient method of detecting eukaryotic cells in which the LTVEC has correctly targeted and modified the desired endogenous gene(s) or chromosomal locus (loci) as well as the use of these cells to generate organisms bearing the genetic modification.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Methods and Compositions for the Targeted Modification of a Genome
Compositions and methods are provided for modifying a genomic locus of interest in a eukaryotic cell, a mammalian cell, a human cell or a non-human mammalian cell using a large targeting vector (LTVEC) comprising various endogenous or exogenous nucleic acid sequences as described herein. Further methods combine the use of the LTVEC with a CRISPR / Cas system. Compositions and methods for generating a genetically modified non-human animal comprising one or more targeted genetic modifications in their germline are also provided.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Method for integrating genes at specific sites in mammalian cells via homologous recombination and vectors for accomplishing the same
InactiveUS6413777B1Reduce in quantityImprove the level ofPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsMammalReactive site
A method for achieving site specific integration of a desired DNA at a target site in a mammalian cell via homologous recombination is described. This method provides for the reproducible selection of cell lines wherein a desired DNA is integrated at a predetermined transcriptionally active site previously marked with a marker plasmid. The method is particularly suitable for the production of mammalian cell lines which secrete mammalian proteins at high levels, in particular immunoglobulins. Novel vectors and vector combinations for use in the subject cloning method are also provided.
Owner:BIOGEN INC
Expression of heterologous proteins
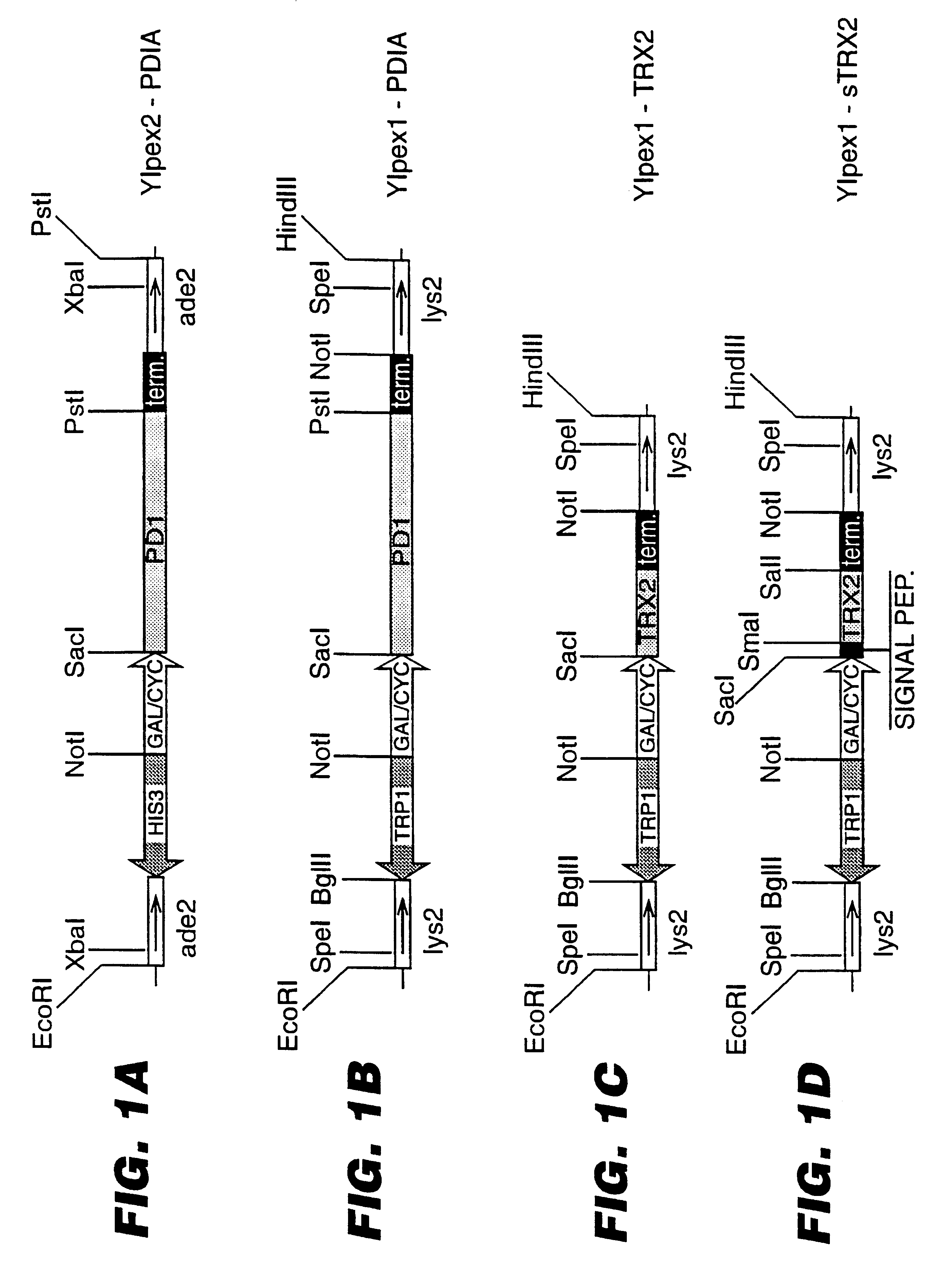
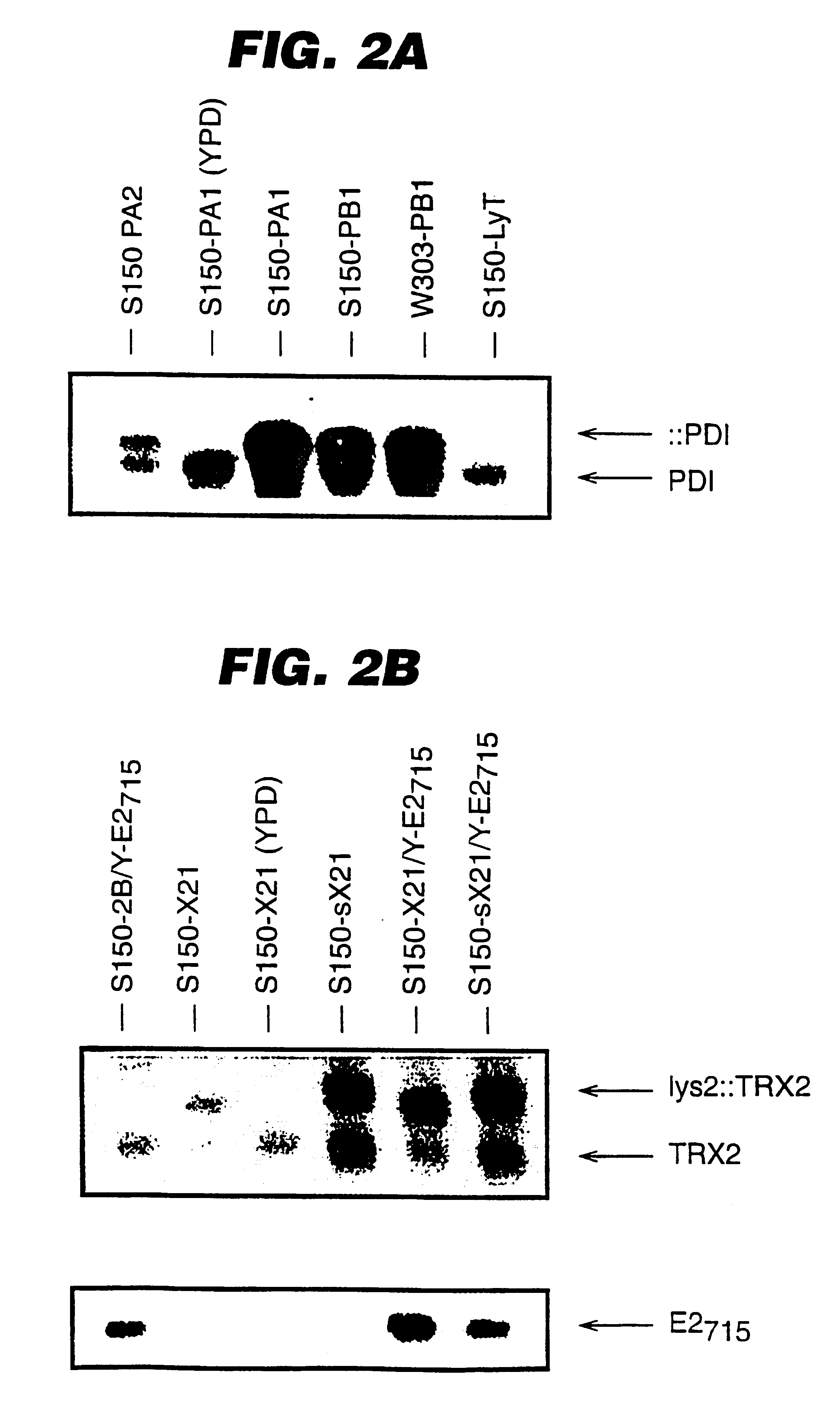
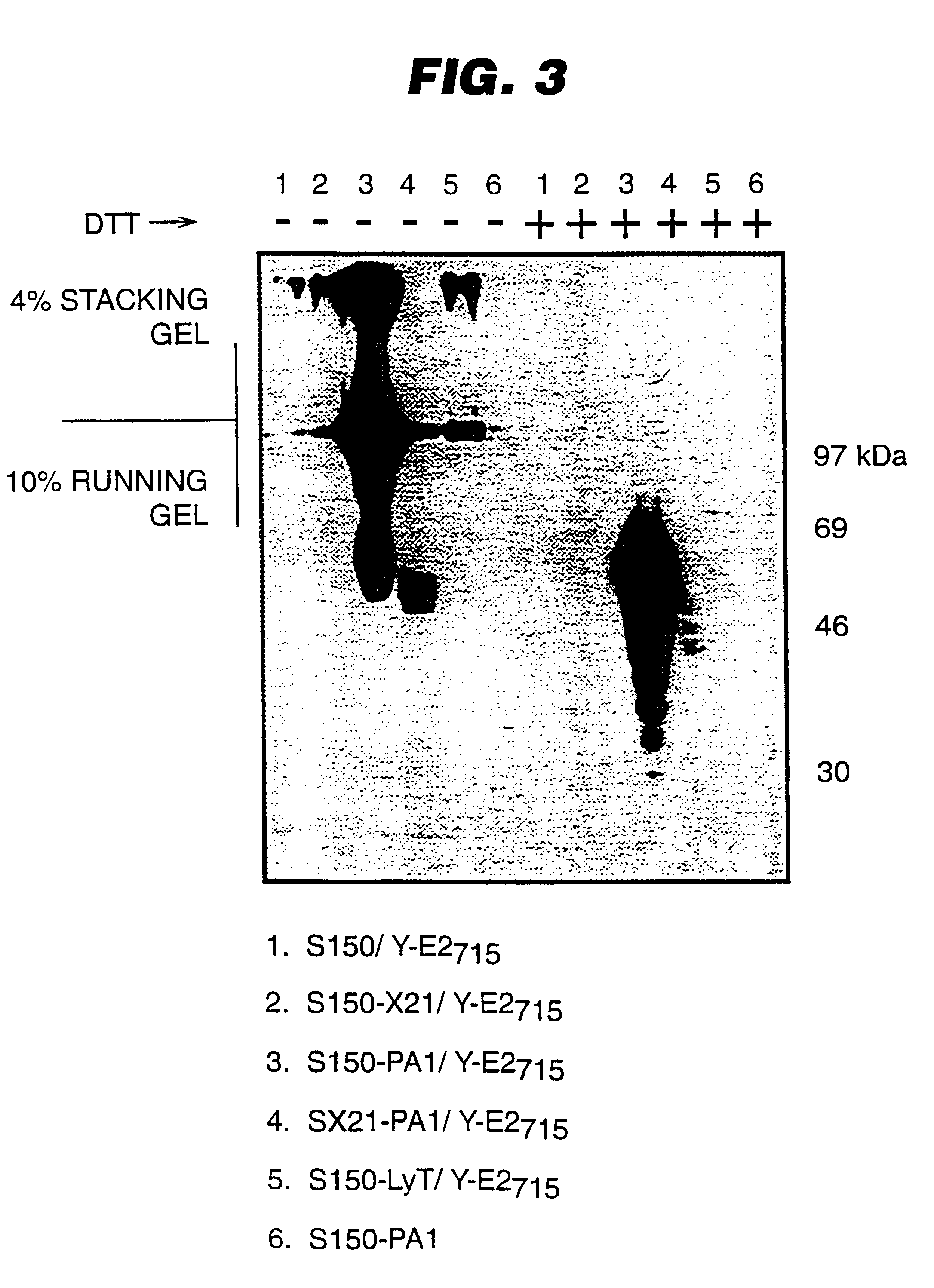
An expression system which provides heterologous proteins expressed by a non-native host organism but which have native-protein-like biological activity and / or structure. Disclosed are vectors, expression hosts and methods for expressing the heterologous proteins. The expression system involves co-expression of protein factor(s) which is / are capable of catalyzing disulphide bond formation and desired heterologous protein(s). The expression system is presented using yeast cells as the preferred host, protein disulphide isomerase (PDI) and thioredoxin (TRX) as the preferred examples of the protein factors and HCV-E2715 envelope glycoprotein and human FIGF as the preferred examples of the heterologous proteins.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
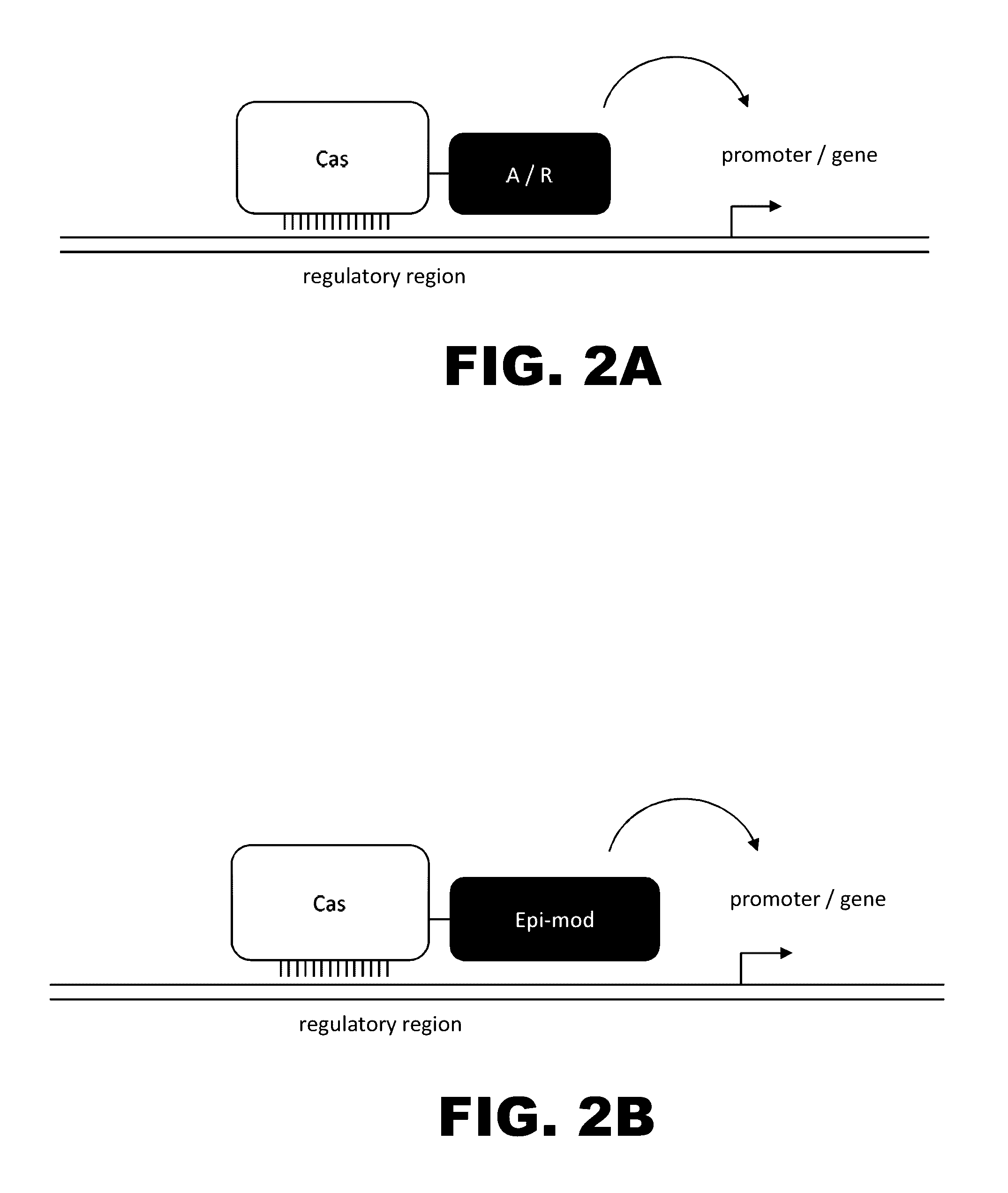
Crispr-based genome modification and regulation
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
Methods of in vivo engineering of large sequences using multiple crispr/cas selections of recombineering events
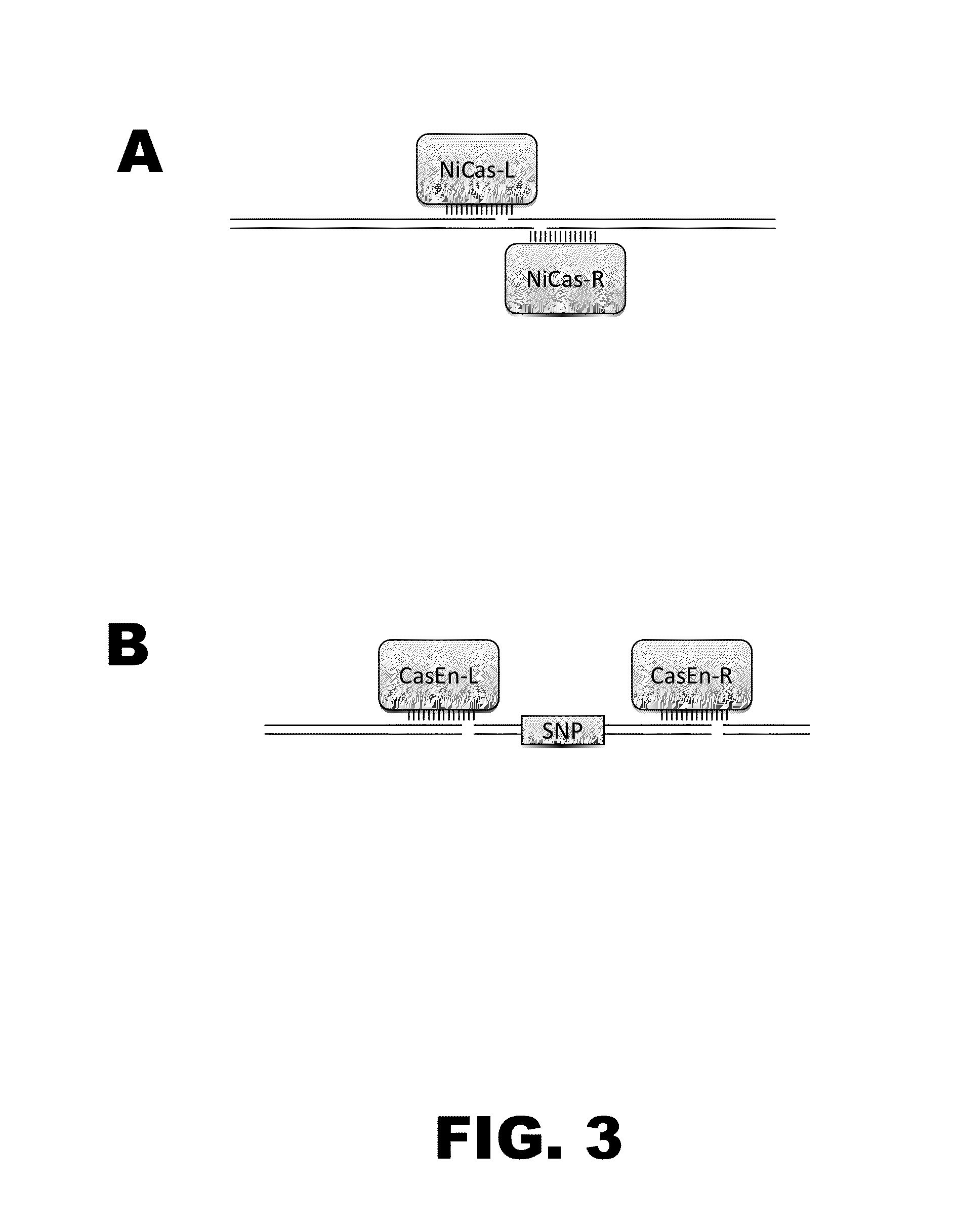
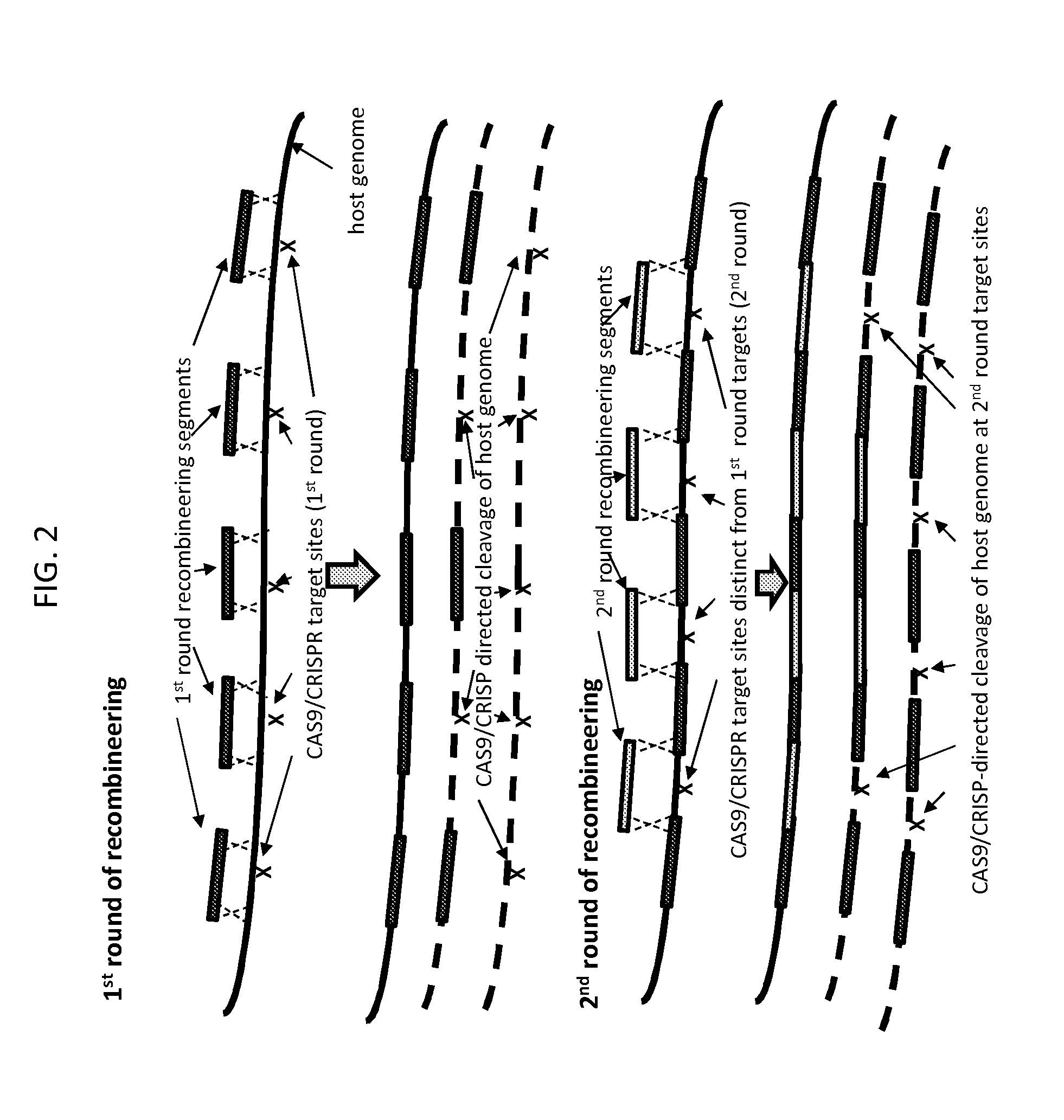
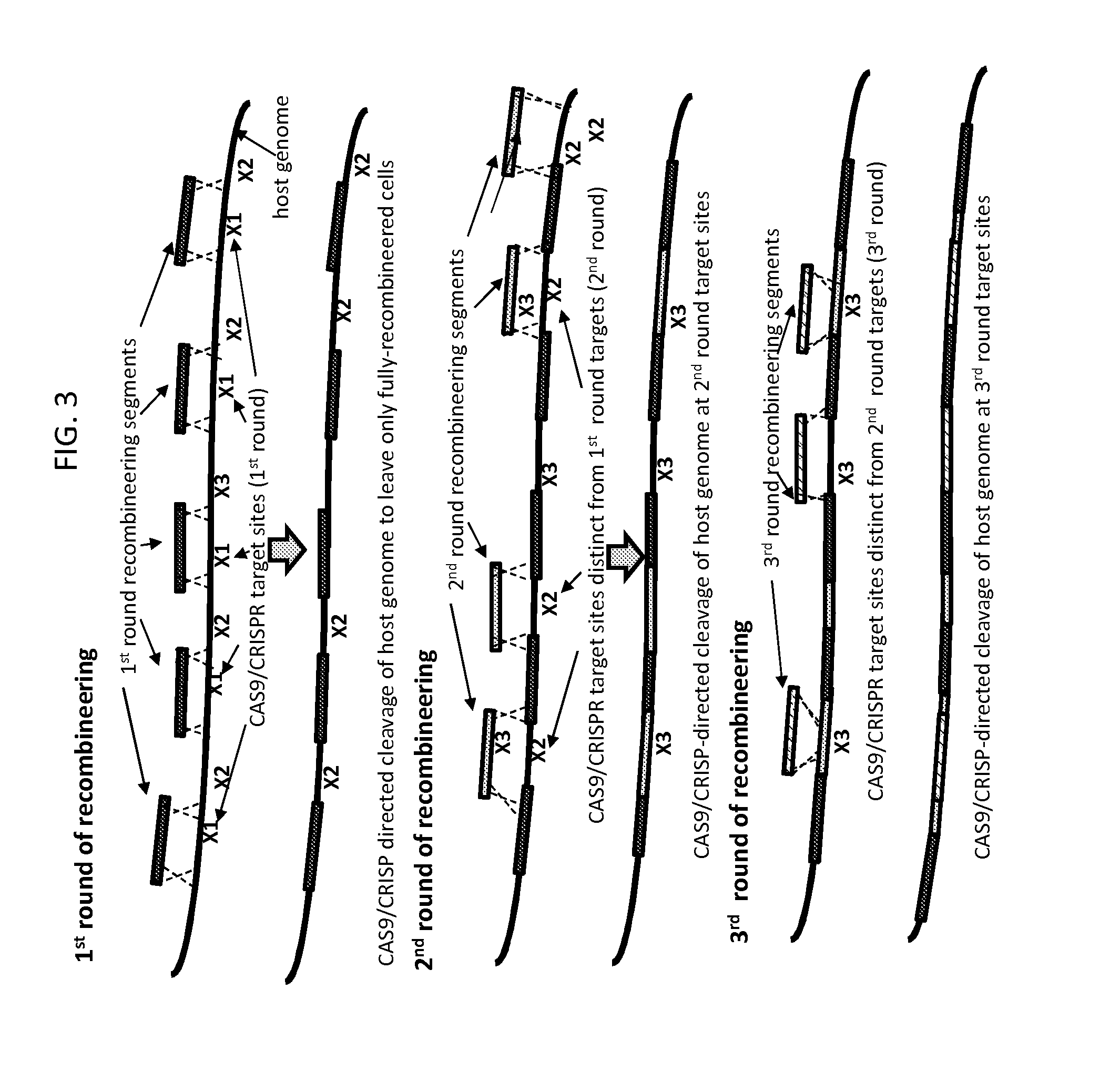
ActiveUS20160024529A1Eliminate generationMinimize the numberBacteriaHydrolasesIn vivoHost cell filopodium
The present invention provides a method for making a large nucleic acid having a defined sequence in vivo. The method combines recombineering techniques with a CRISPR / Cas system to permit multiple insertions of defined sequences into a target nucleic acid at one time, double stranded cleavage of target nucleic acids in which the defined sequences were not successfully inserted, and selection of successful recombinant cells. The method further includes repeating the process one or more times, using a successful recombinant from one round as the host cell for the next round.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
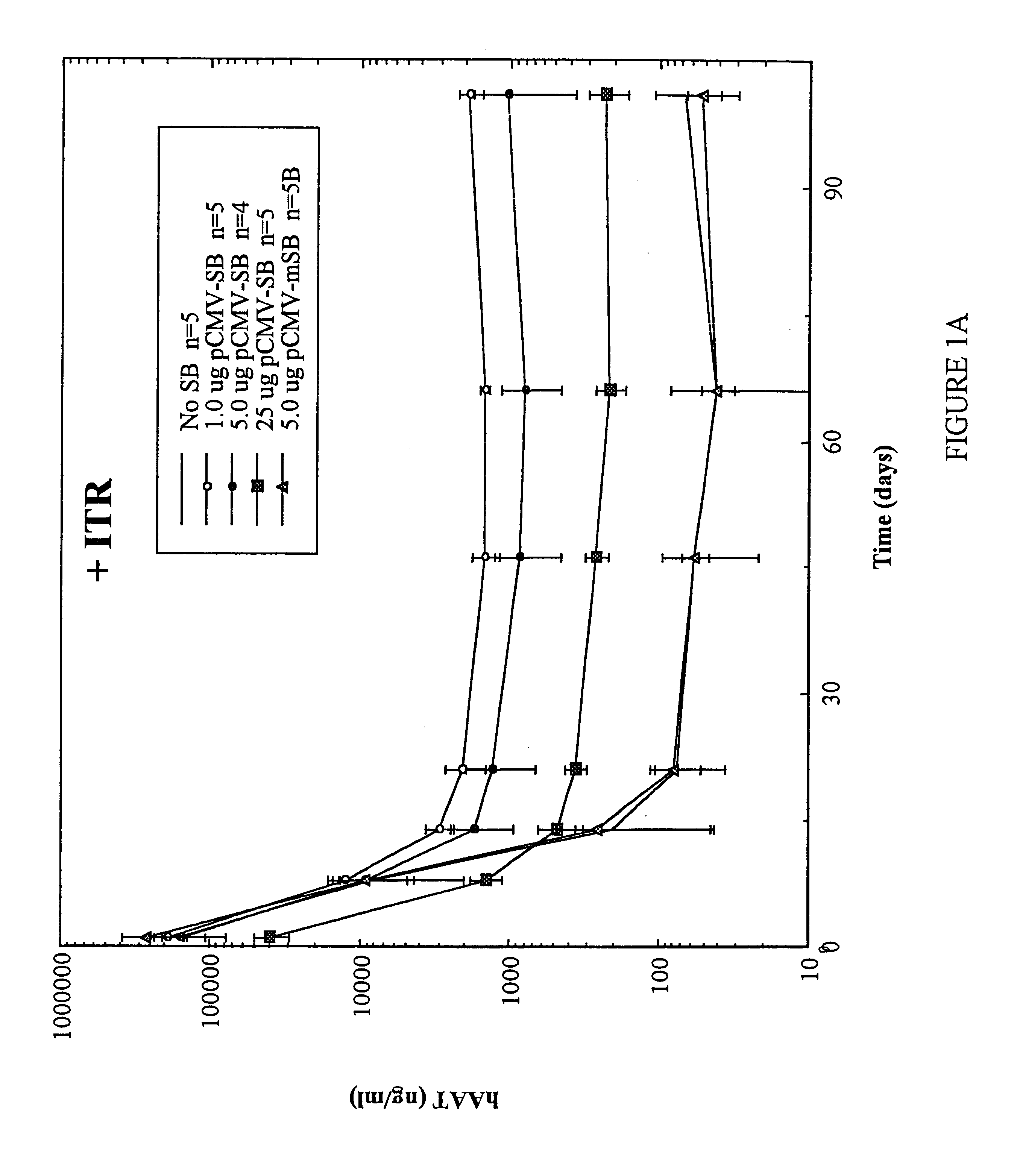
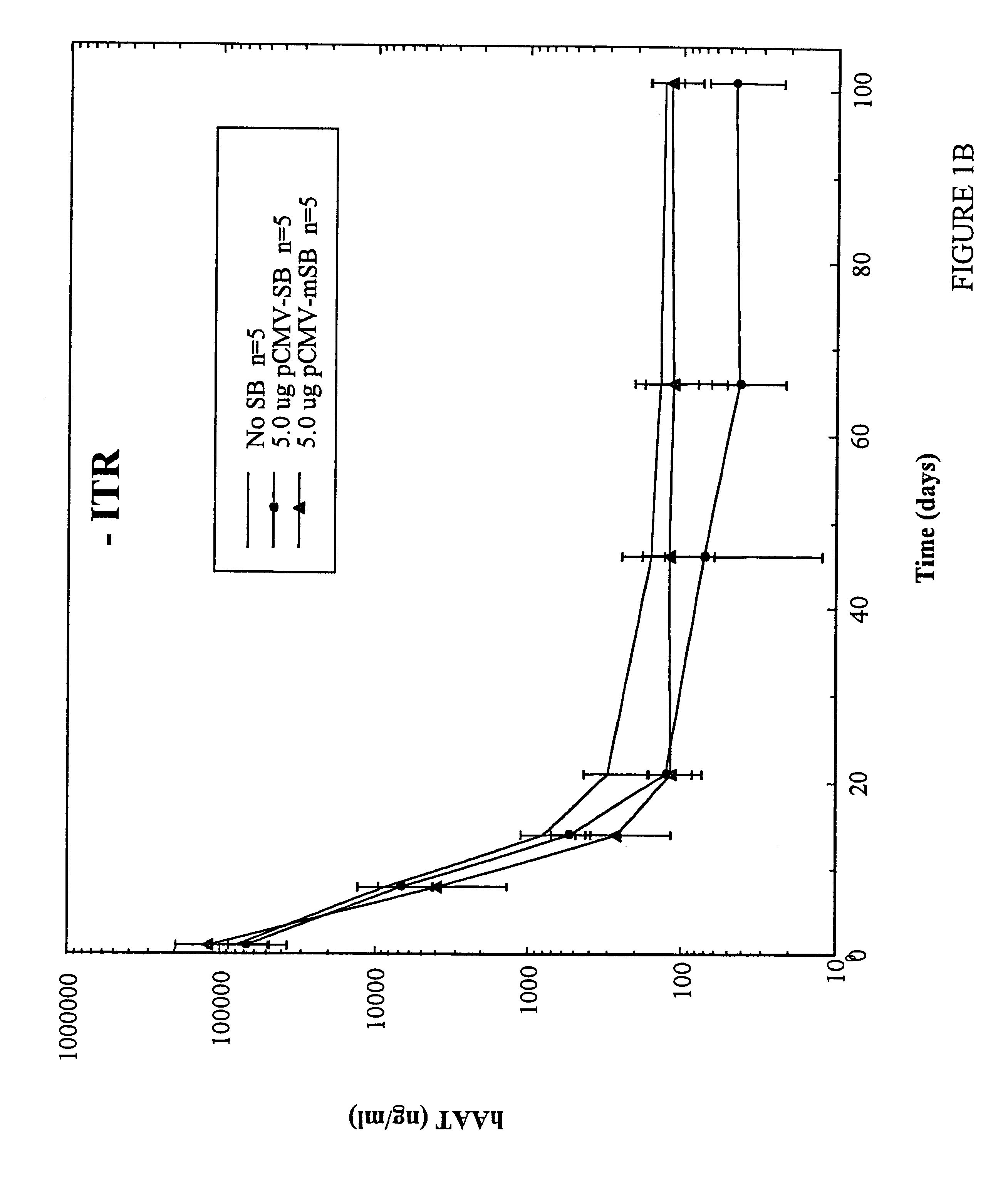
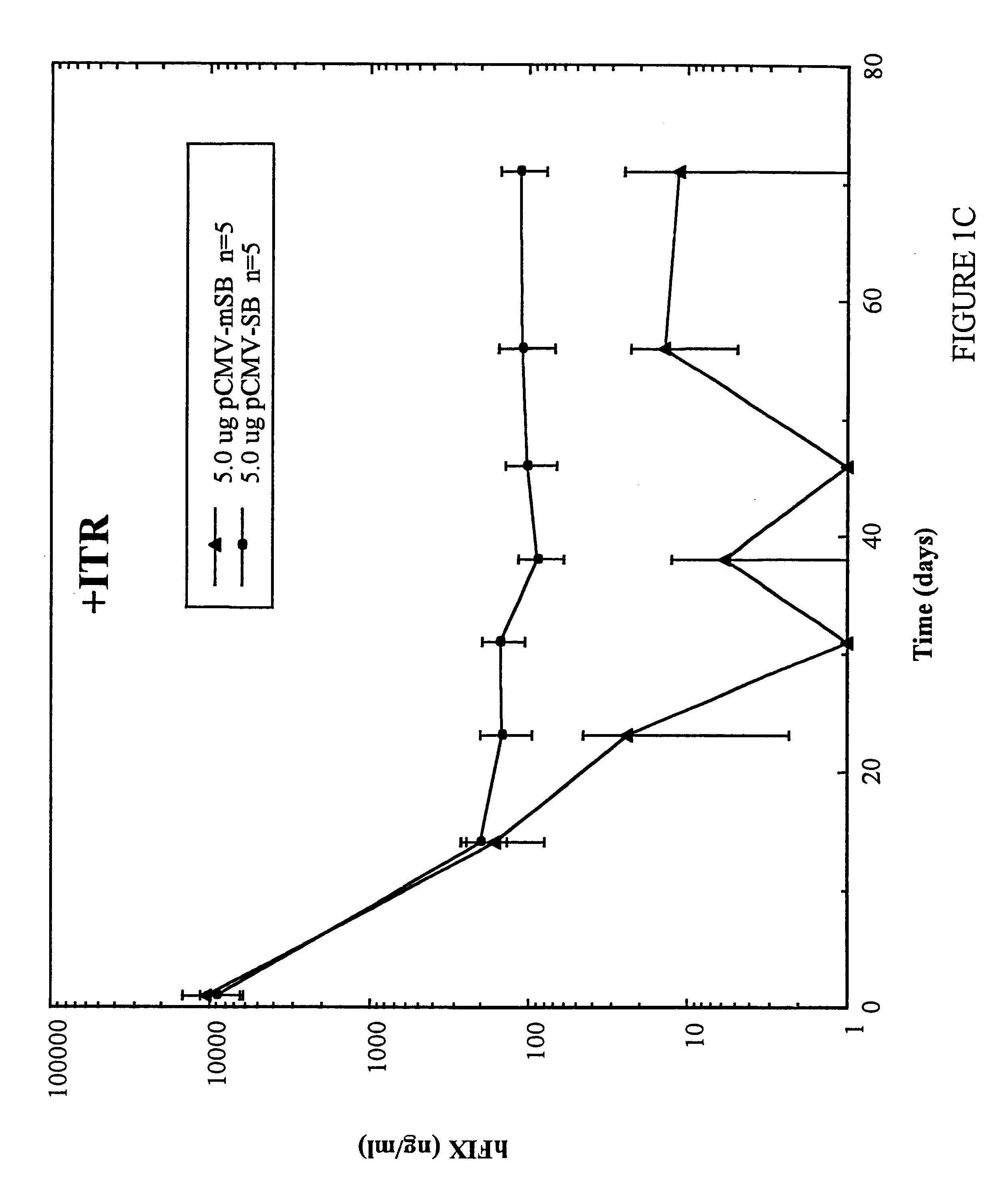
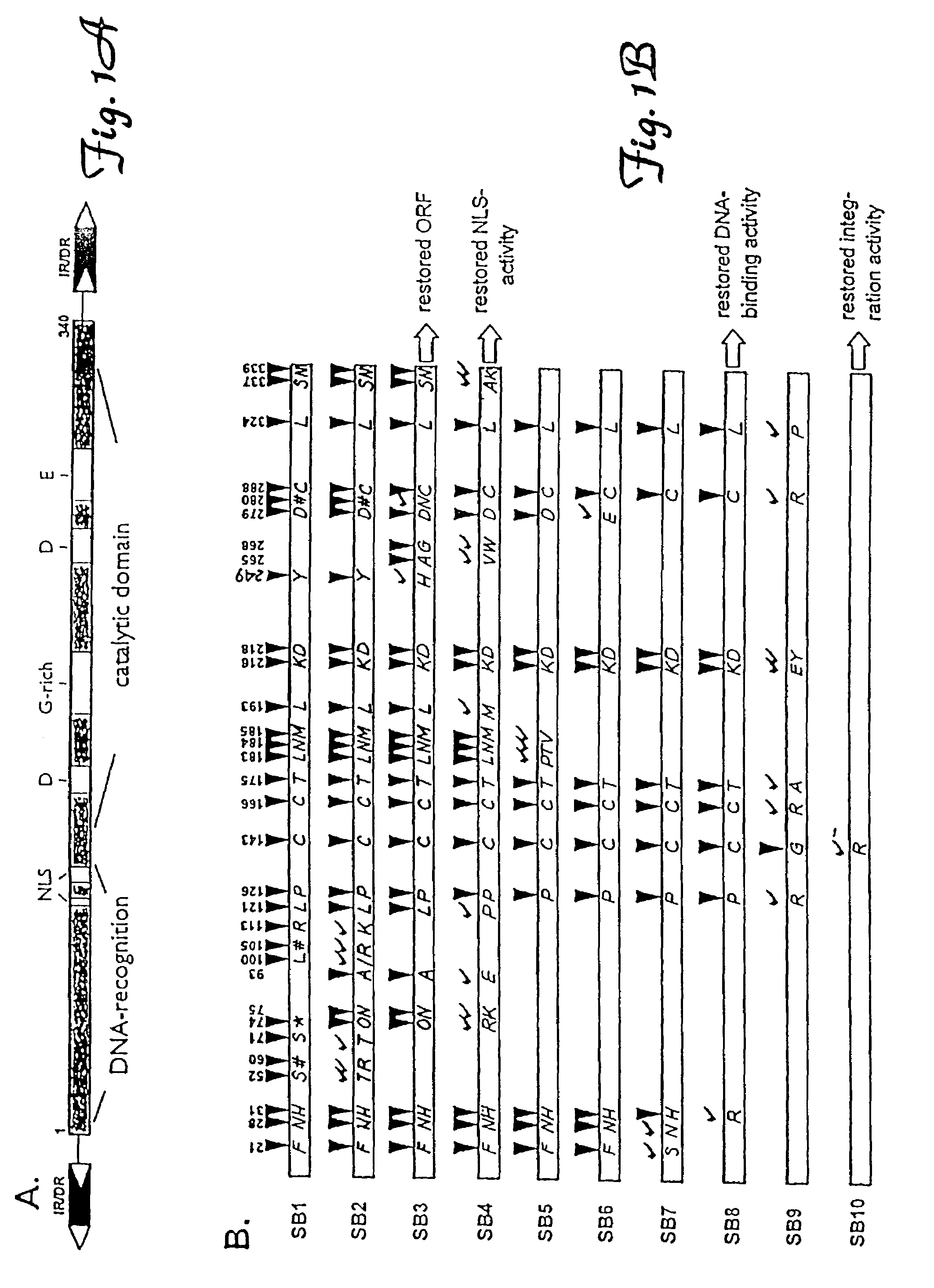
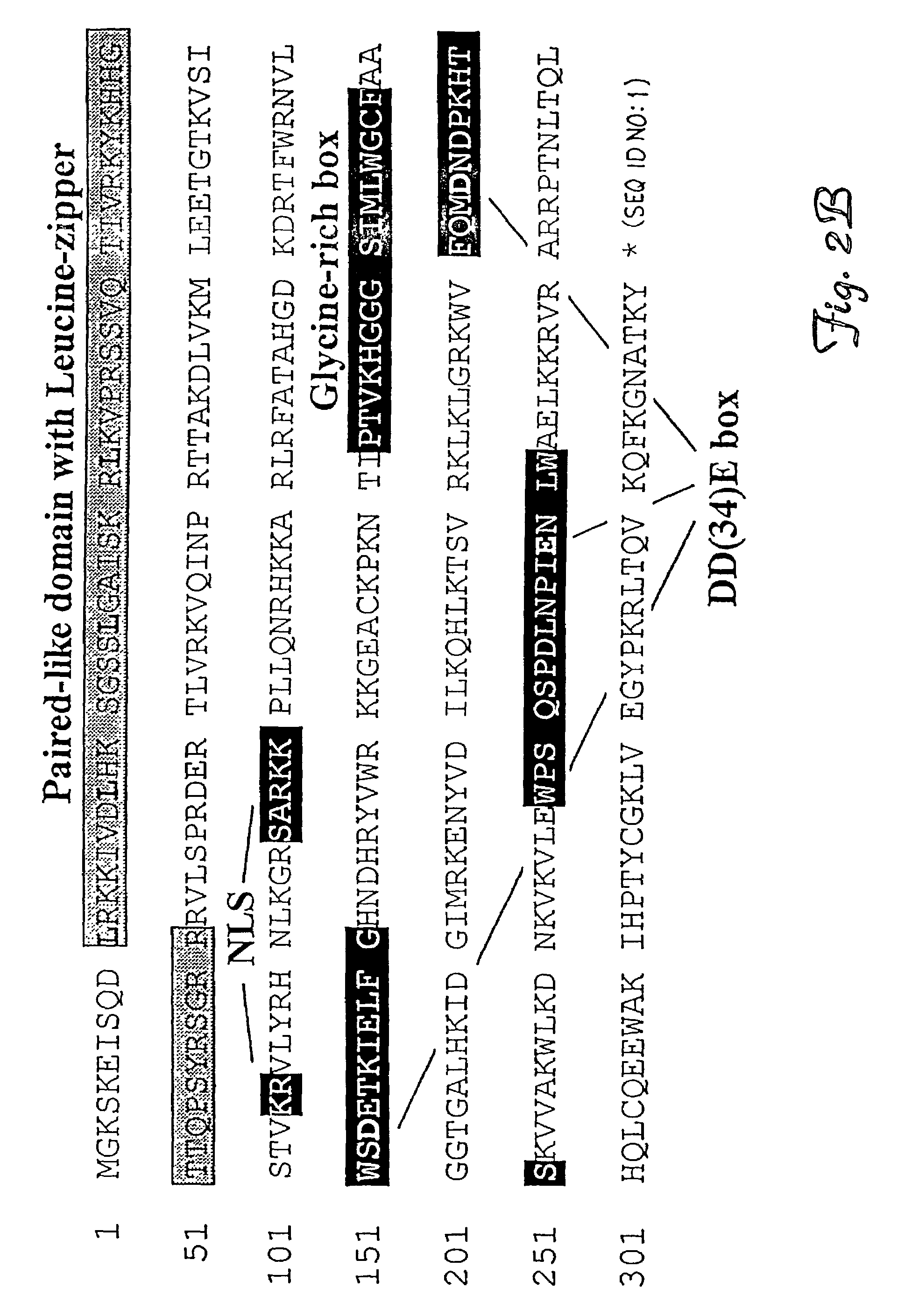
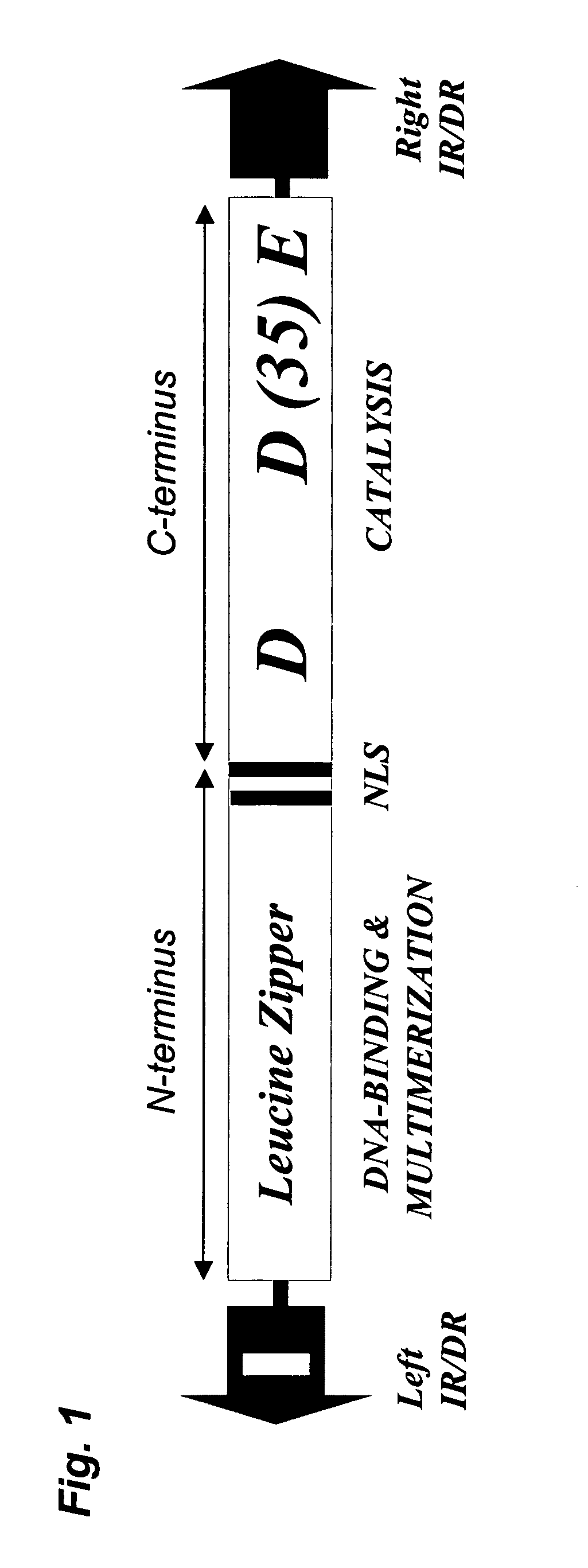
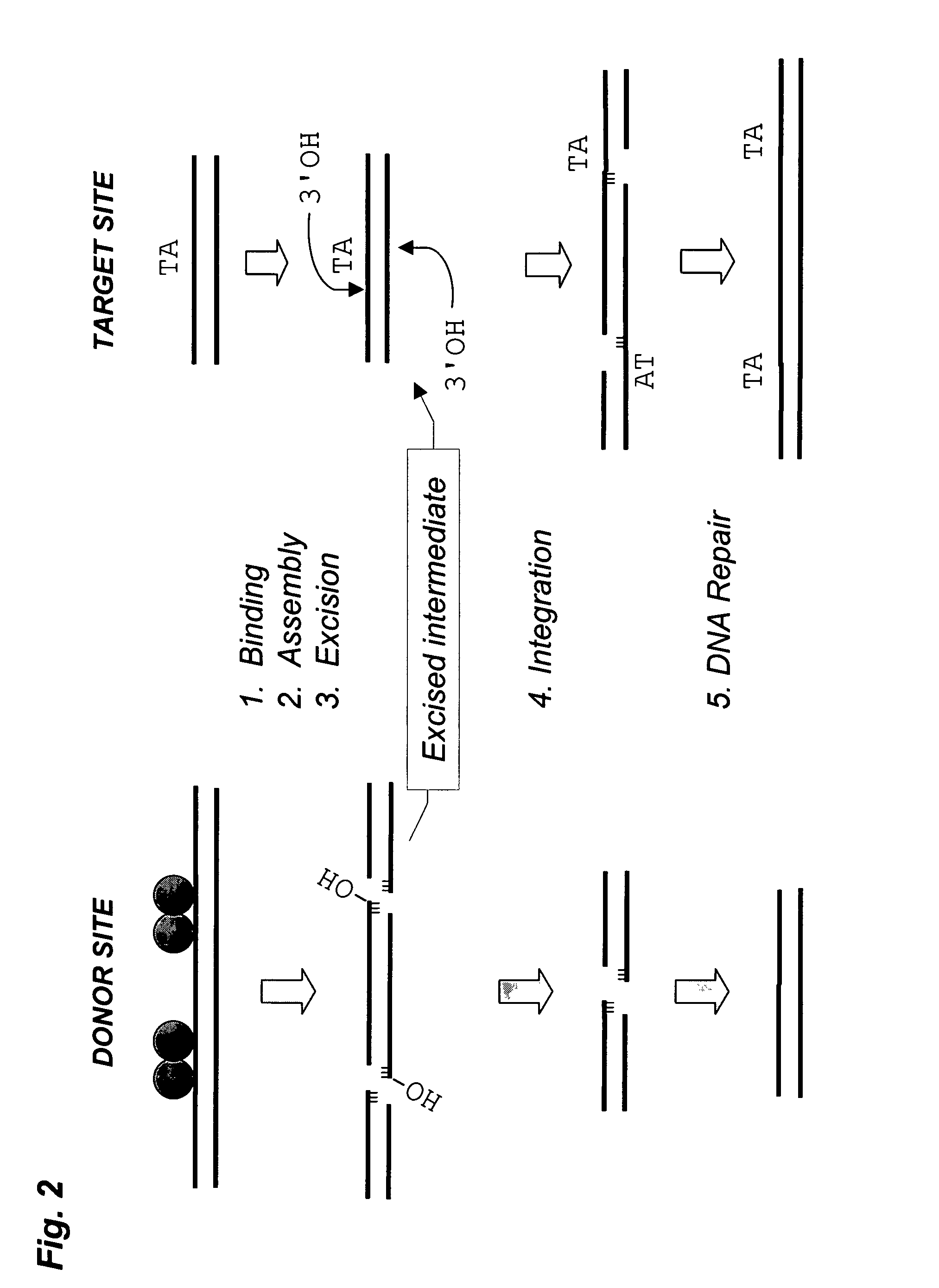
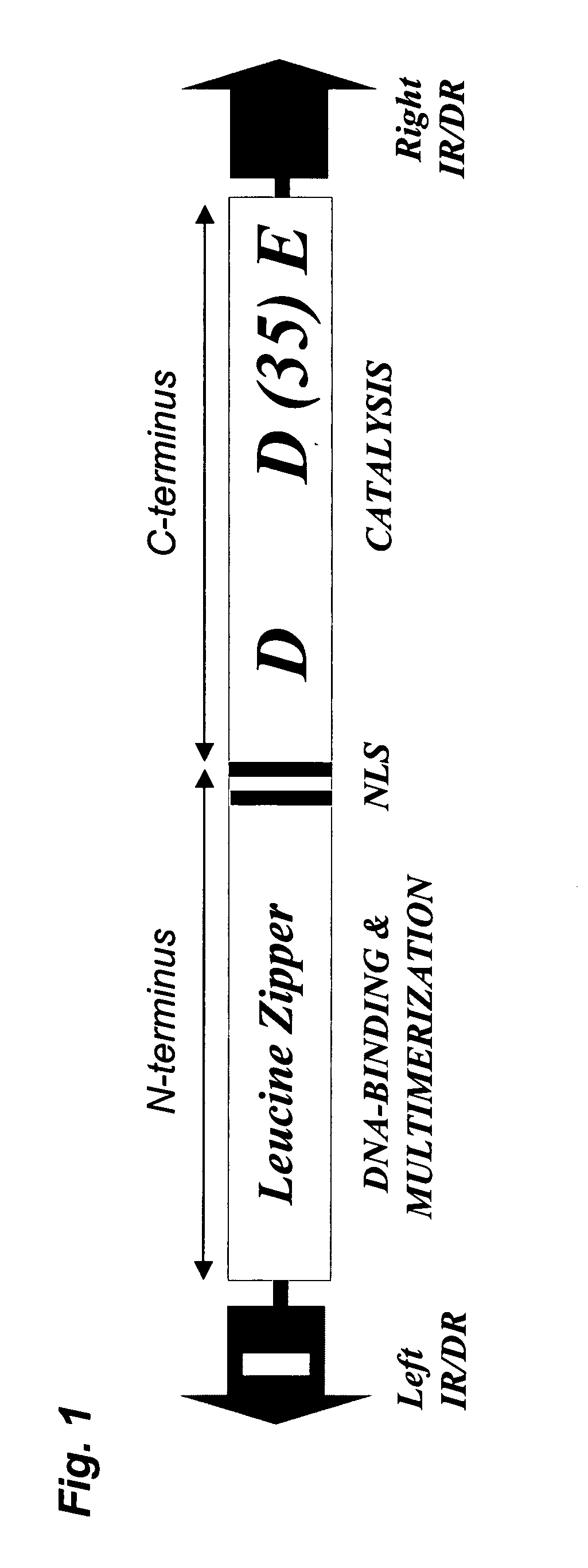
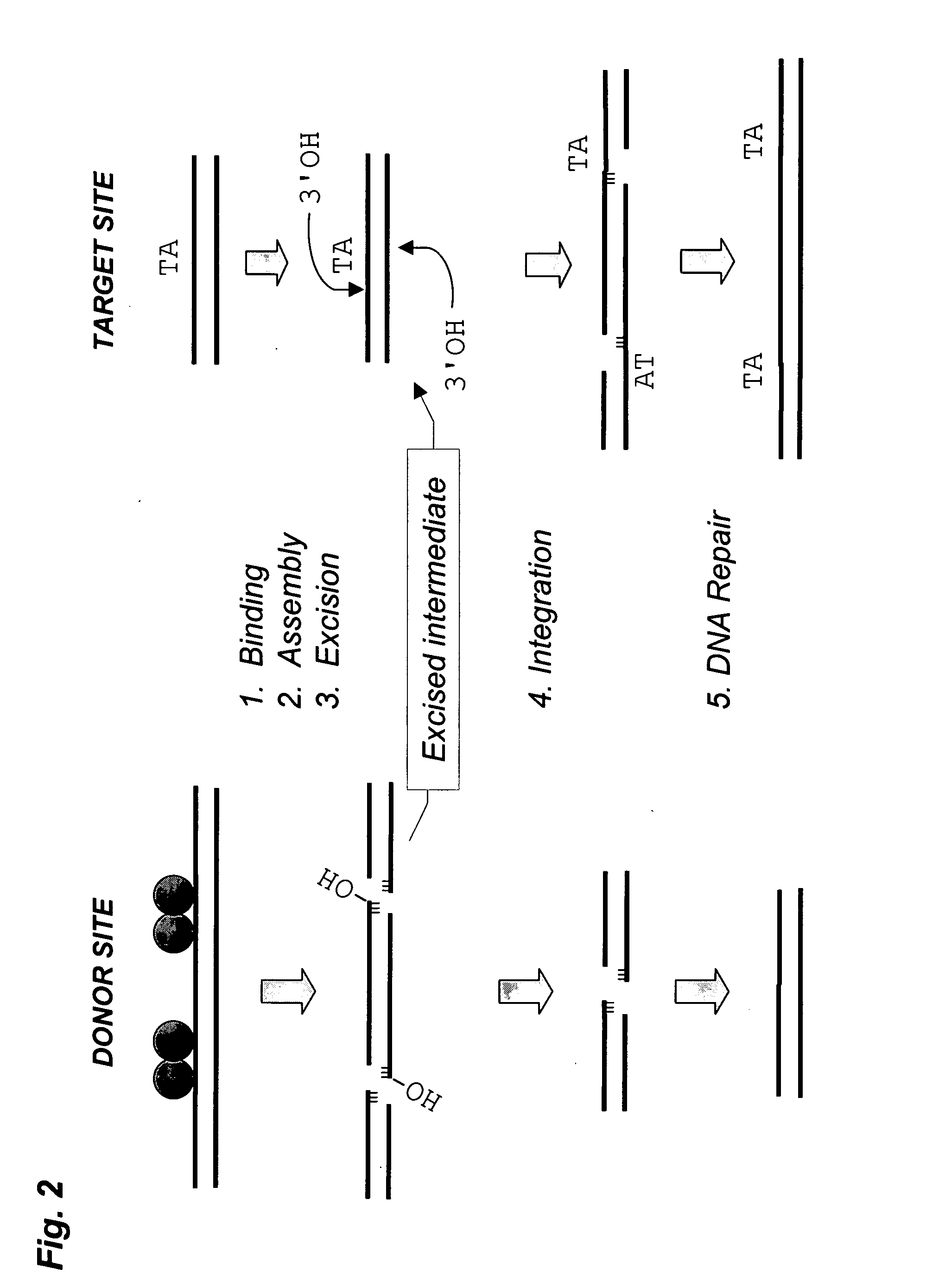
Methods of in vivo gene transfer using a sleeping beauty transposon system
InactiveUS6613752B2Observed effectPromote cloningBiocideHydrolasesSleeping Beauty transposon systemMulticellular organism
Methods and compositions for introducing a nucleic acid into the genome of at least one cell of a multicellular organism are provided. In the subject methods, a Sleeping Beauty transposon that includes the nucleic acid is administered to the multicellular organism along with a source of a Sleeping Beauty transposase activity. Administration of the transposon and transposase results in integration of the transposon, as well as the nucleic acid present therein, into the genome of at least one cell of the multicellular organism The subject methods find use in a variety of different applications, including the in vivo transfer of genes for use in, among other applications, gene therapy applications.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
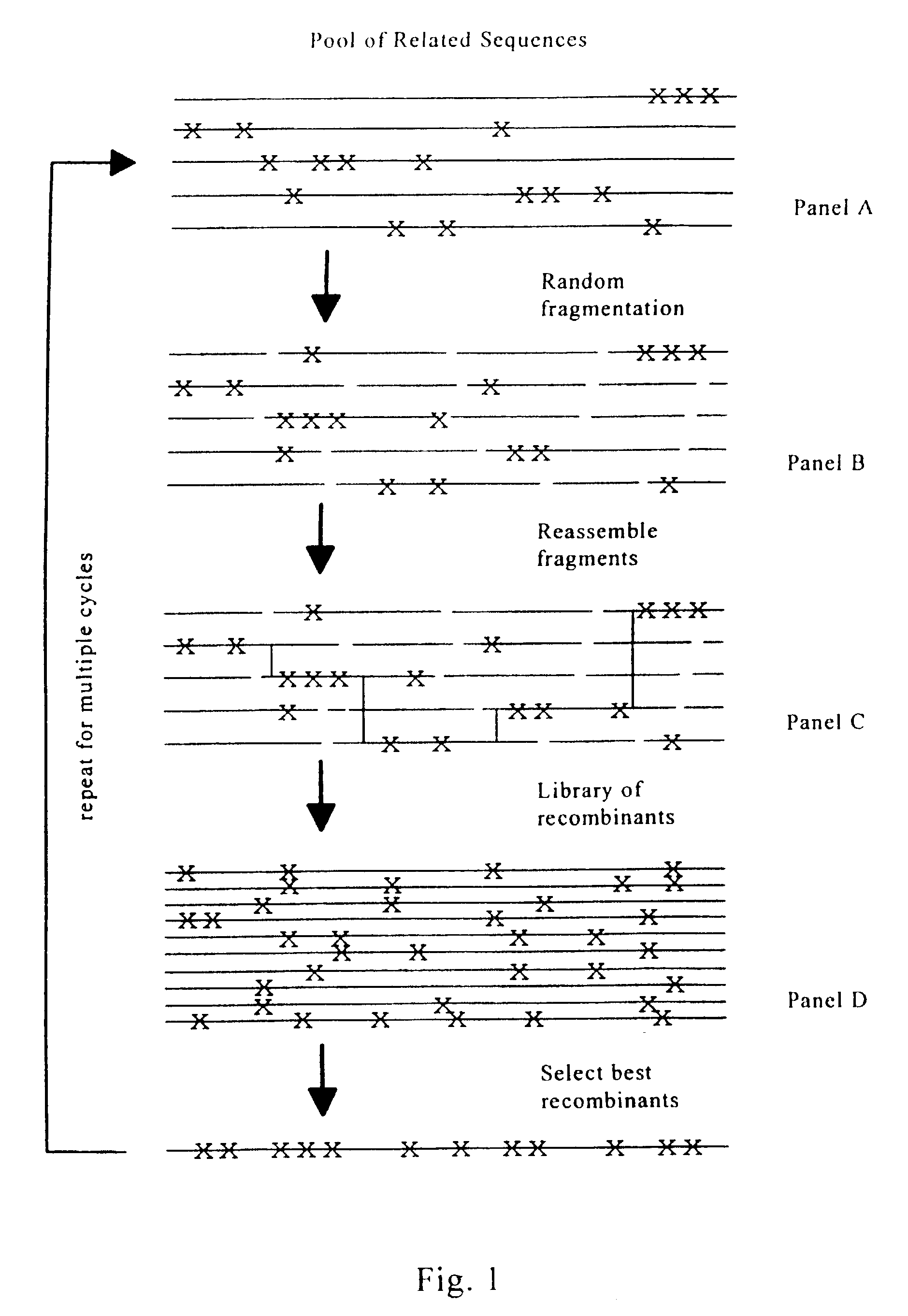
Evolution of whole cells and organisms by recursive sequence recombination
InactiveUS7148054B2Increase diversityFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementMetaboliteSecondary metabolite
The invention provides methods employing iterative cycles of recombination and selection / screening for evolution of whole cells and organisms toward acquisition of desired properties Examples of such properties include enhanced recombinogenicity, genome copy number, and capacity for expression and / or secretion of proteins and secondary metabolites.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Human antibodies derived from immunized xenomice
Antibodies with fully human variable regions against a specific antigen can be prepared by administering the antigen to a transgenic animal which has been modified to produce such antibodies in response to antigenic challenge, but whose endogenous loci have been disabled. Various subsequent manipulations can be performed to obtain either antibodies per se or analogs thereof.
Owner:KUCHERLAPATI RAJU +4
P element derived vector and methods for its use
Novel P element derived vectors and methods for their use to insert an exogenous nucleic acid into the genome of a target cell are provided. The subject vectors have a pair of P element transposase recognized insertion sites, e.g. 31 base pair inverted repeats, flanking at least two transcriptionally active genes. In practicing the subject methods, a vector of the subject invention is introduced into the target cell under conditions sufficient for transposition to occur. The subject methods find use in a variety of applications in which the insertion of an exogenous nucleic acid into the genome of a target cell is desired, e.g. include research, synthesis and therapeutic applications.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Methods and compositions for the targeted modification of a genome
Compositions and methods are provided for modifying a genomic locus of interest in a eukaryotic cell, a mammalian cell, a human cell or a non-human mammalian cell using a large targeting vector (LTVEC) comprising various endogenous or exogenous nucleic acid sequences as described herein. Further methods combine the use of the LTVEC with a CRISPR / Cas system. Compositions and methods for generating a genetically modified non-human animal comprising one or more targeted genetic modifications in their germline are also provided.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Methods of modifying eukaryotic cells
A method for engineering and utilizing large DNA vectors to target, via homologous recombination, and modify, in any desirable fashion, endogenous genes and chromosomal loci in eukaryotic cells. These large DNA targeting vectors for eukaryotic cells, termed LTVECs, are derived from fragments of cloned genomic DNA larger than those typically used by other approaches intended to perform homologous targeting in eukaryotic cells. Also provided is a rapid and convenient method of detecting eukaryotic cells in which the LTVEC has correctly targeted and modified the desired endogenous genes(s) or chromosomal locus (loci) as well as the use of these cells to generate organisms bearing the genetic modification.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
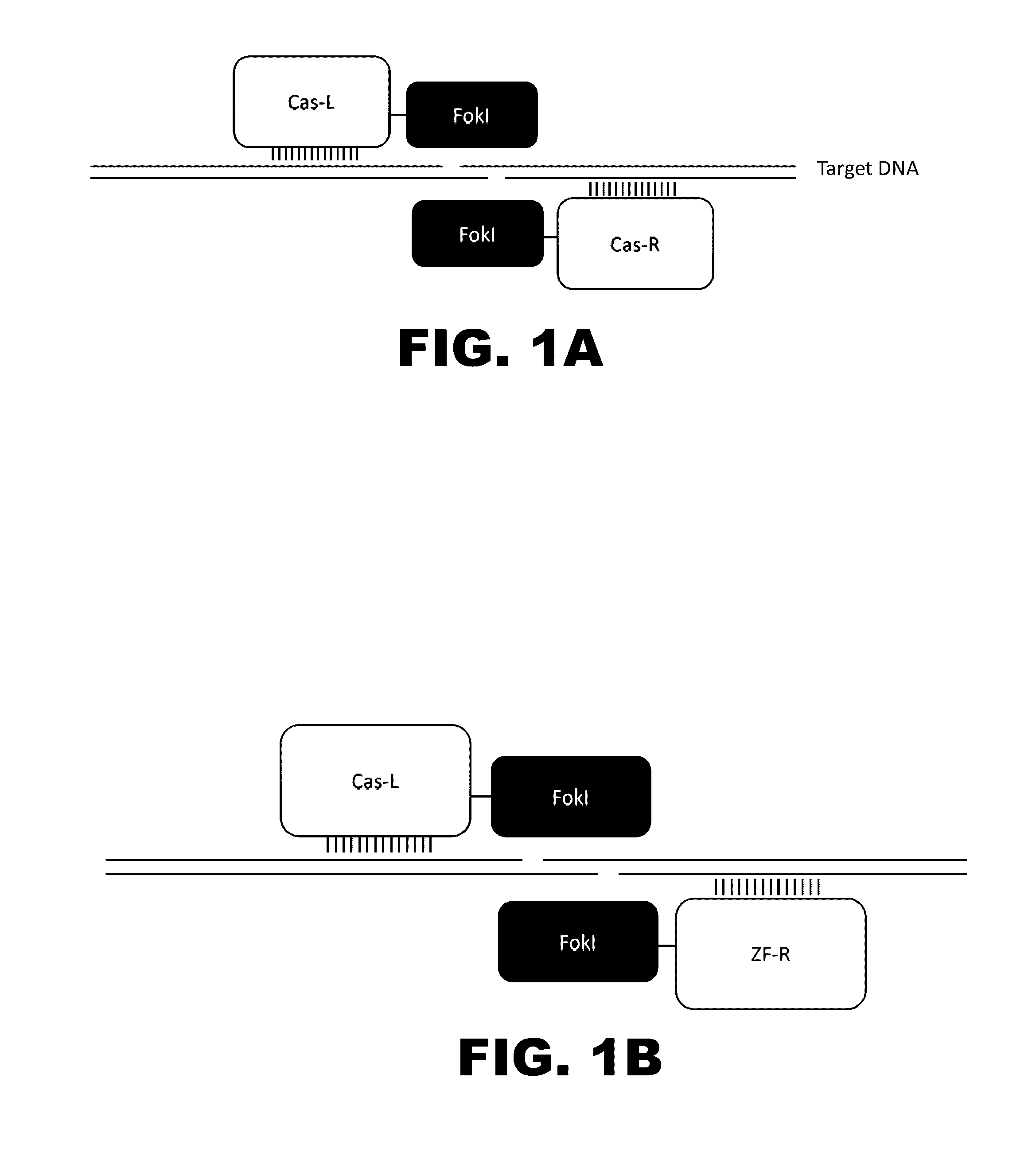
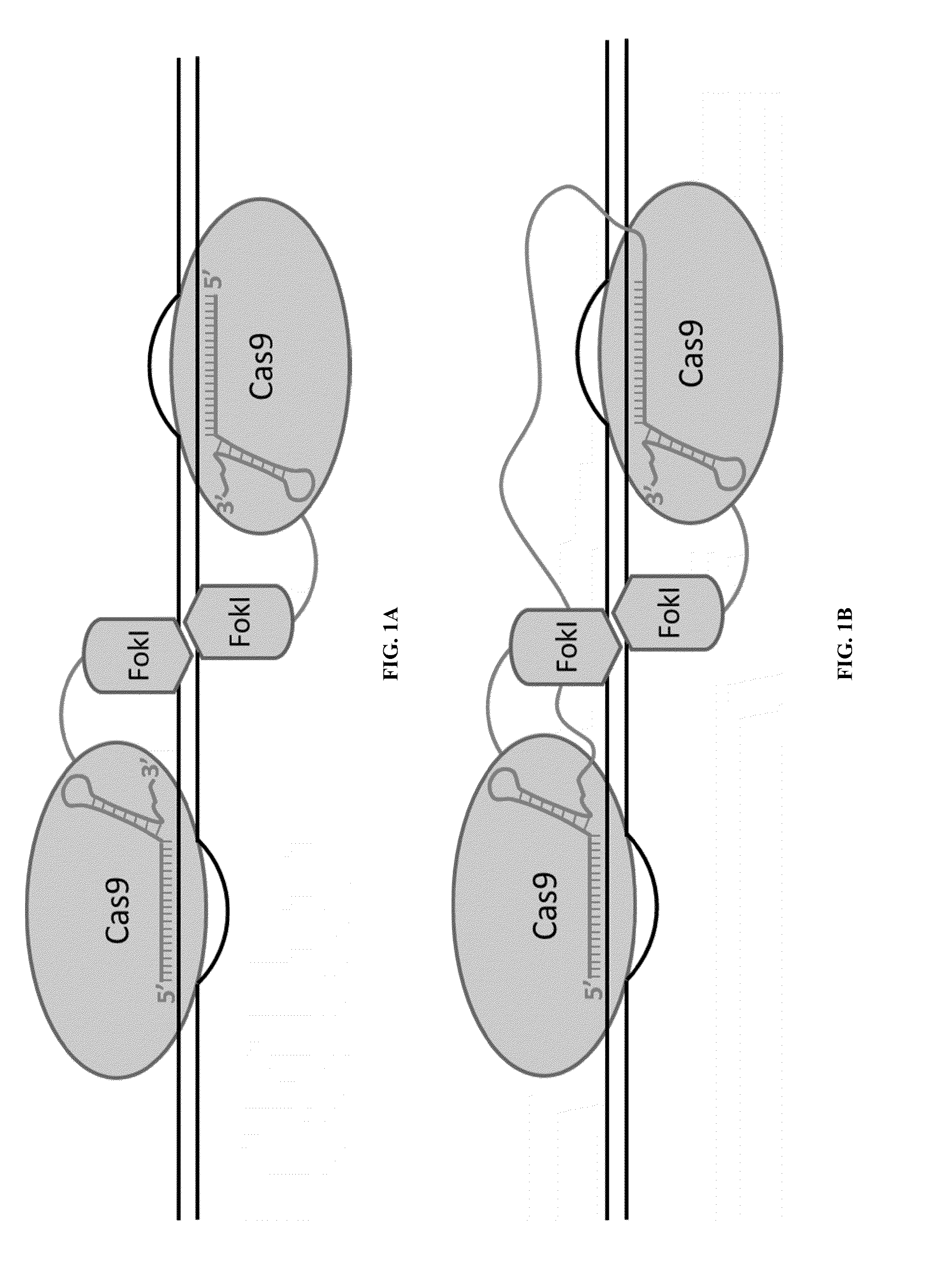
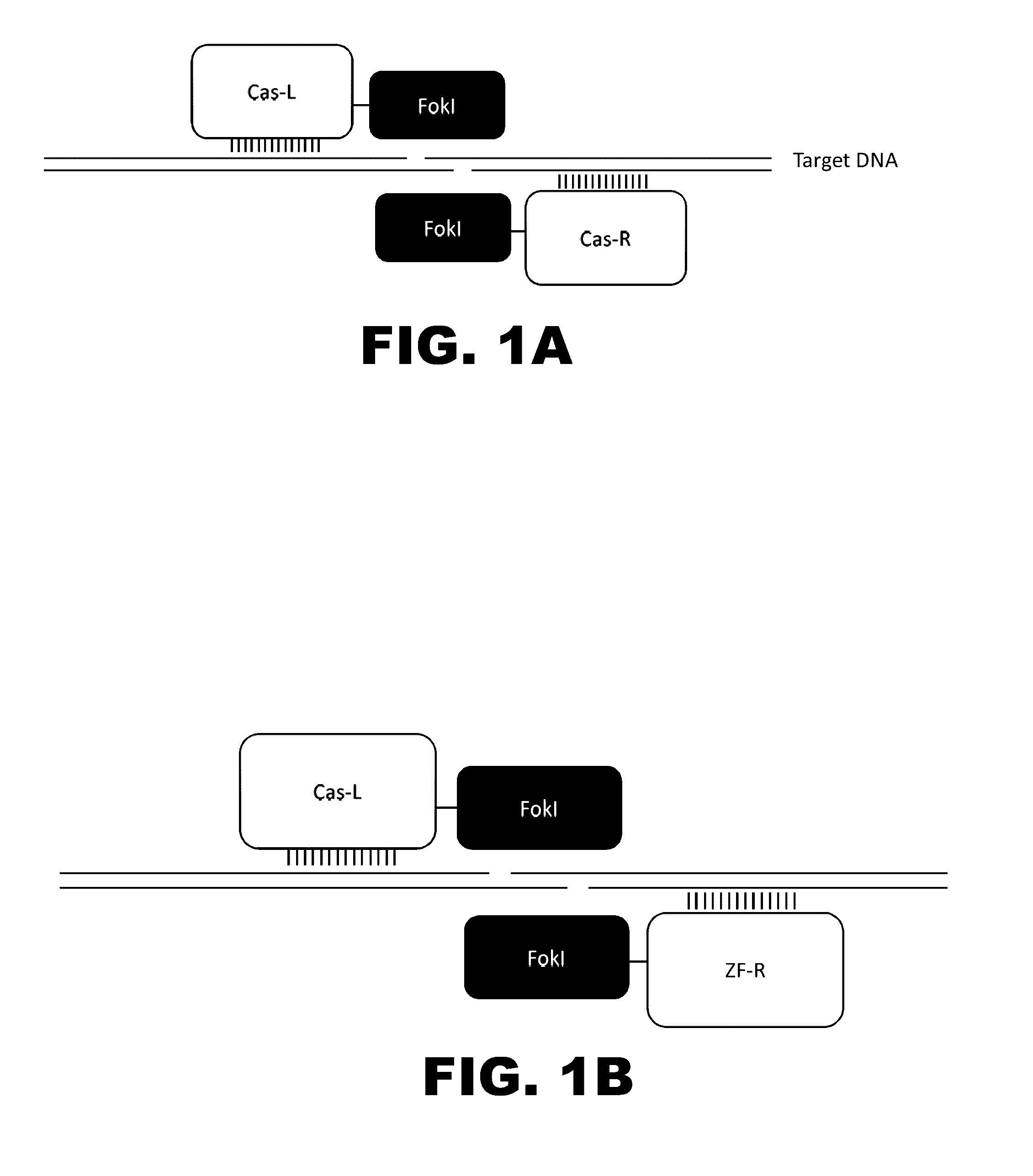
Cas9-recombinase fusion proteins and uses thereof
ActiveUS20150071898A1Strong specificityReduce the possibilityFusion with DNA-binding domainBacteriaSite-specific recombinationResearch setting
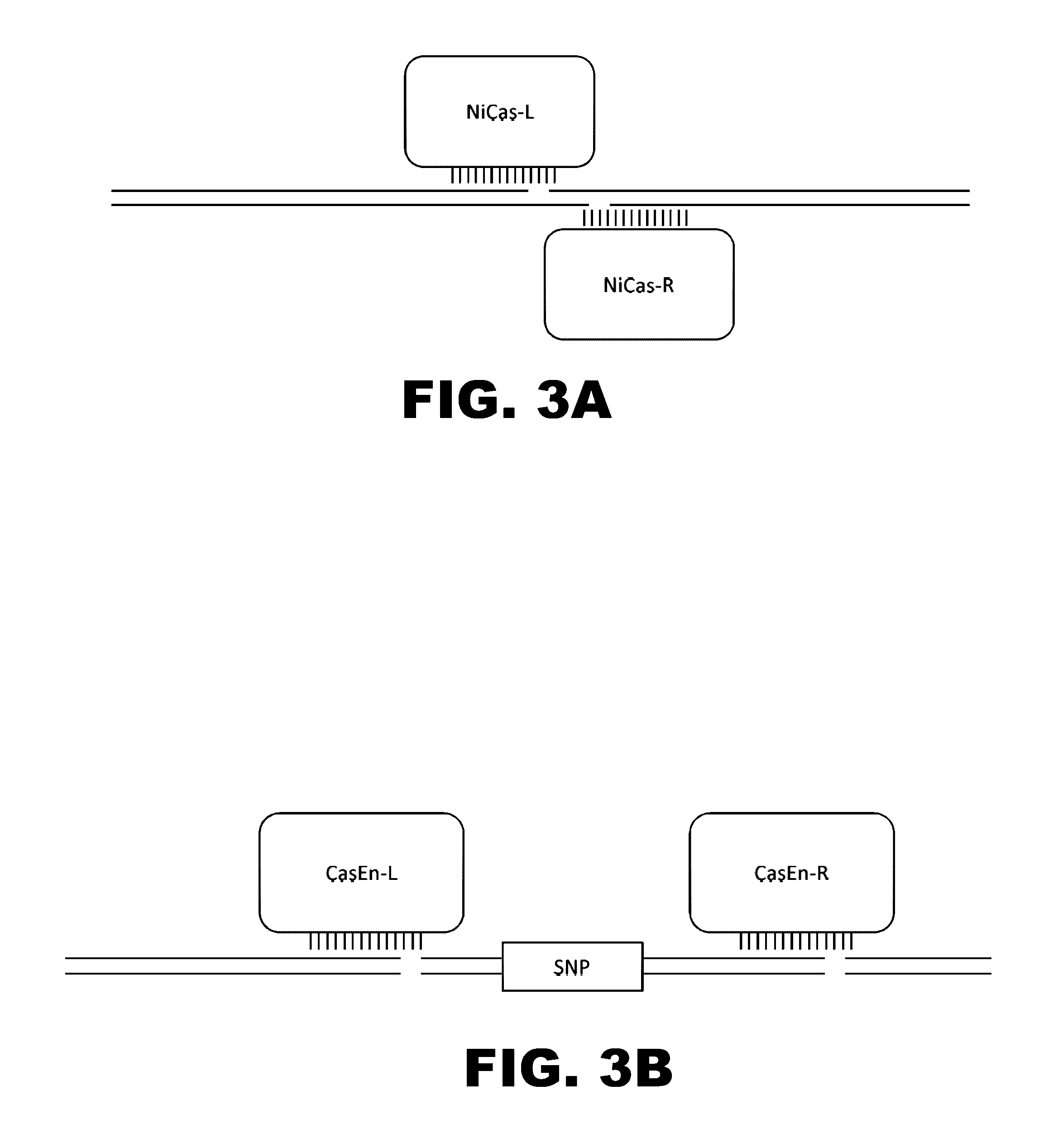
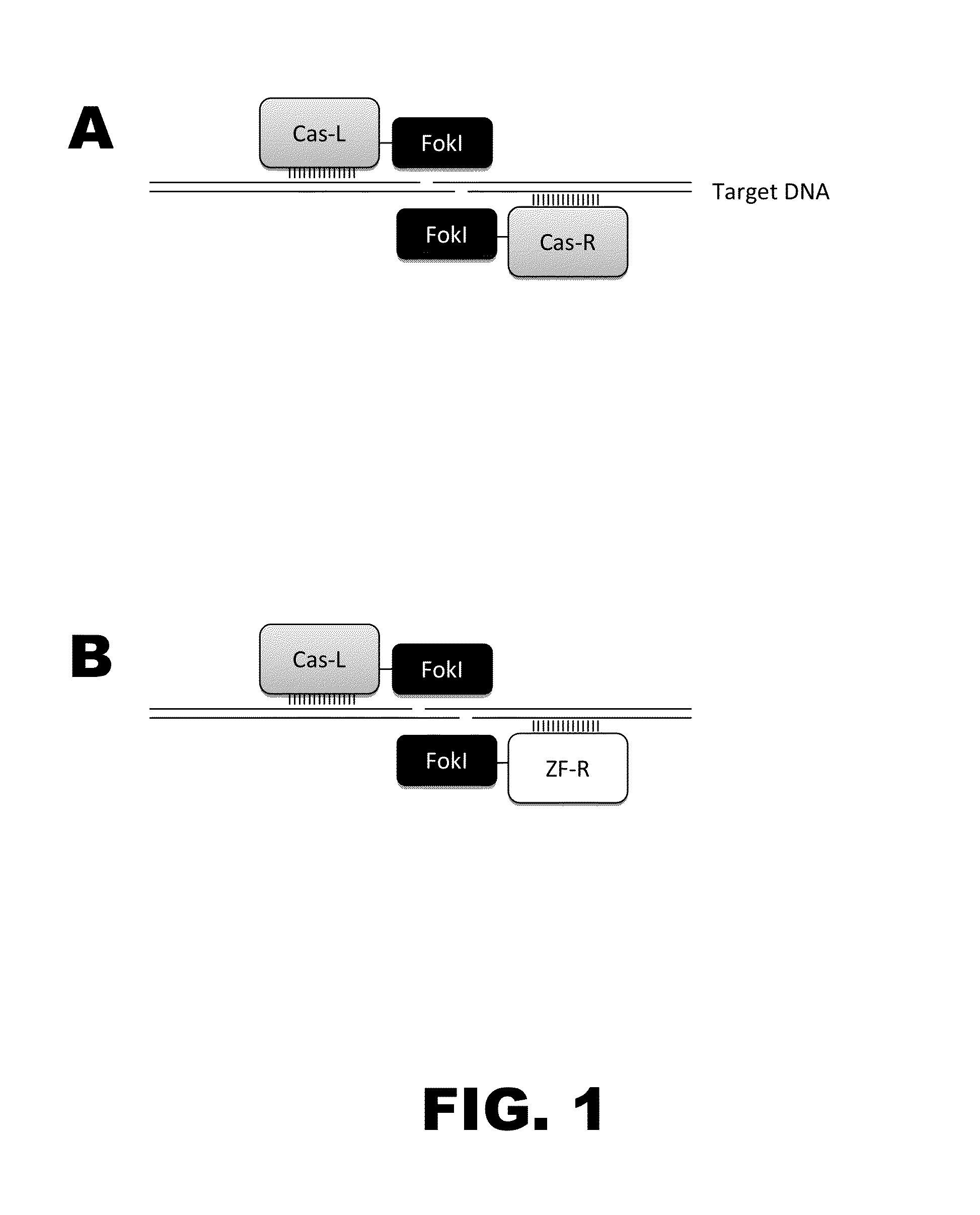
Some aspects of this disclosure provide compositions, methods, and kits for improving the specificity of RNA-programmable endonucleases, such as Cas9. Also provided are variants of Cas9, e.g., Cas9 dimers and fusion proteins, engineered to have improved specificity for cleaving nucleic acid targets. Also provided are compositions, methods, and kits for site-specific recombination, using Cas9 fusion proteins (e.g., nuclease-inactivated Cas9 fused to a recombinase catalytic domain). Such Cas9 variants are useful in clinical and research settings involving site-specific modification of DNA, for example, genomic modifications.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Nucleic acid transfer vector for the introduction of nucleic acid into the DNA of a cell
InactiveUS7148203B2Sugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsNucleic acid sequencingTransfer vector
This invention relates to a system for introducing nucleic acid into the DNA of a cell. The system includes the use of a member of the SB family of transposases (SB) or nucleic acid encoding the transposase and a nucleic acid fragment that includes a nucleic acid sequence with flanking inverted repeats. The transposase recognizes at least a portion of an inverted repeats and incorporates the nucleic acid sequence into the DNA. Methods for use of this system are discussed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
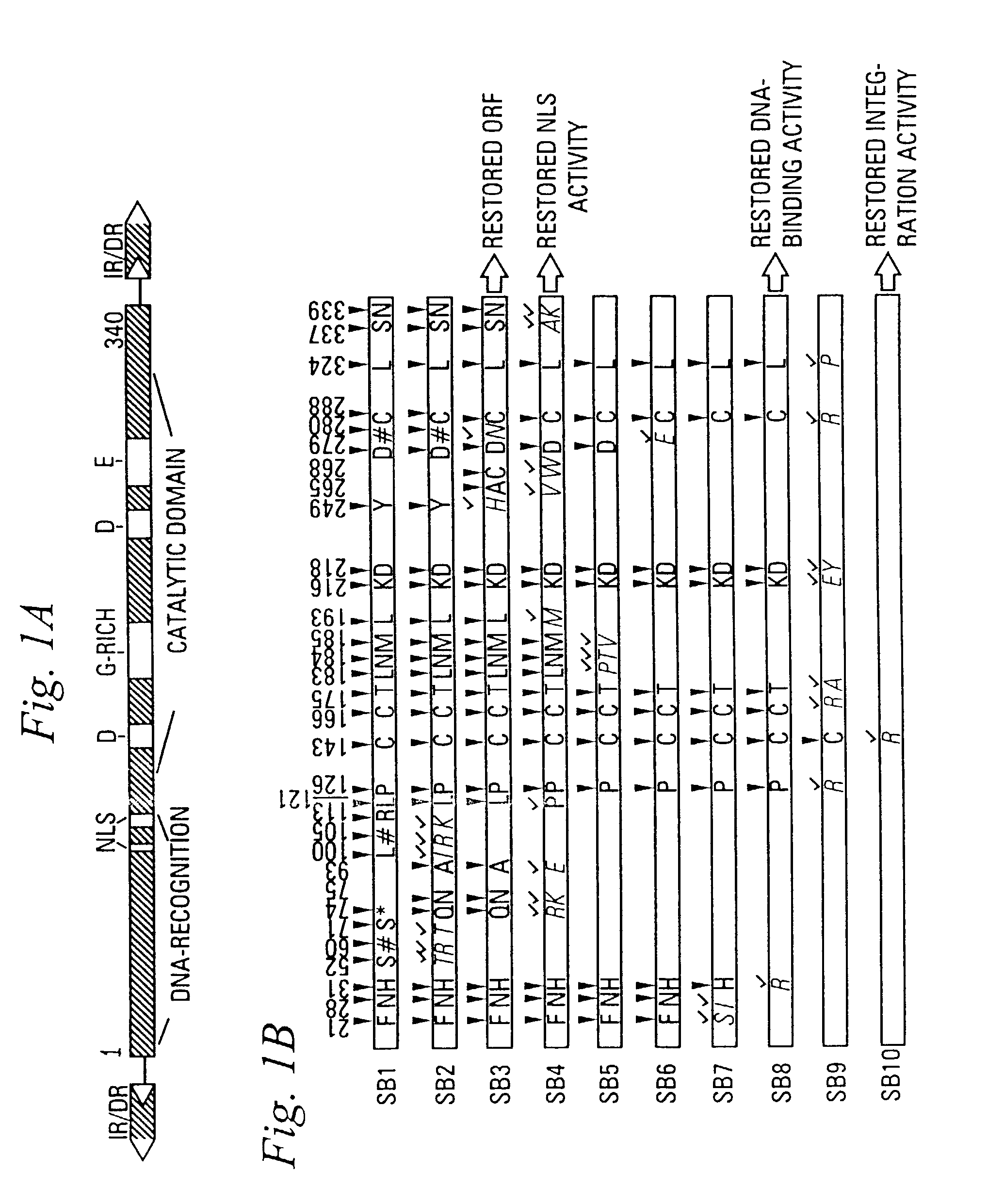
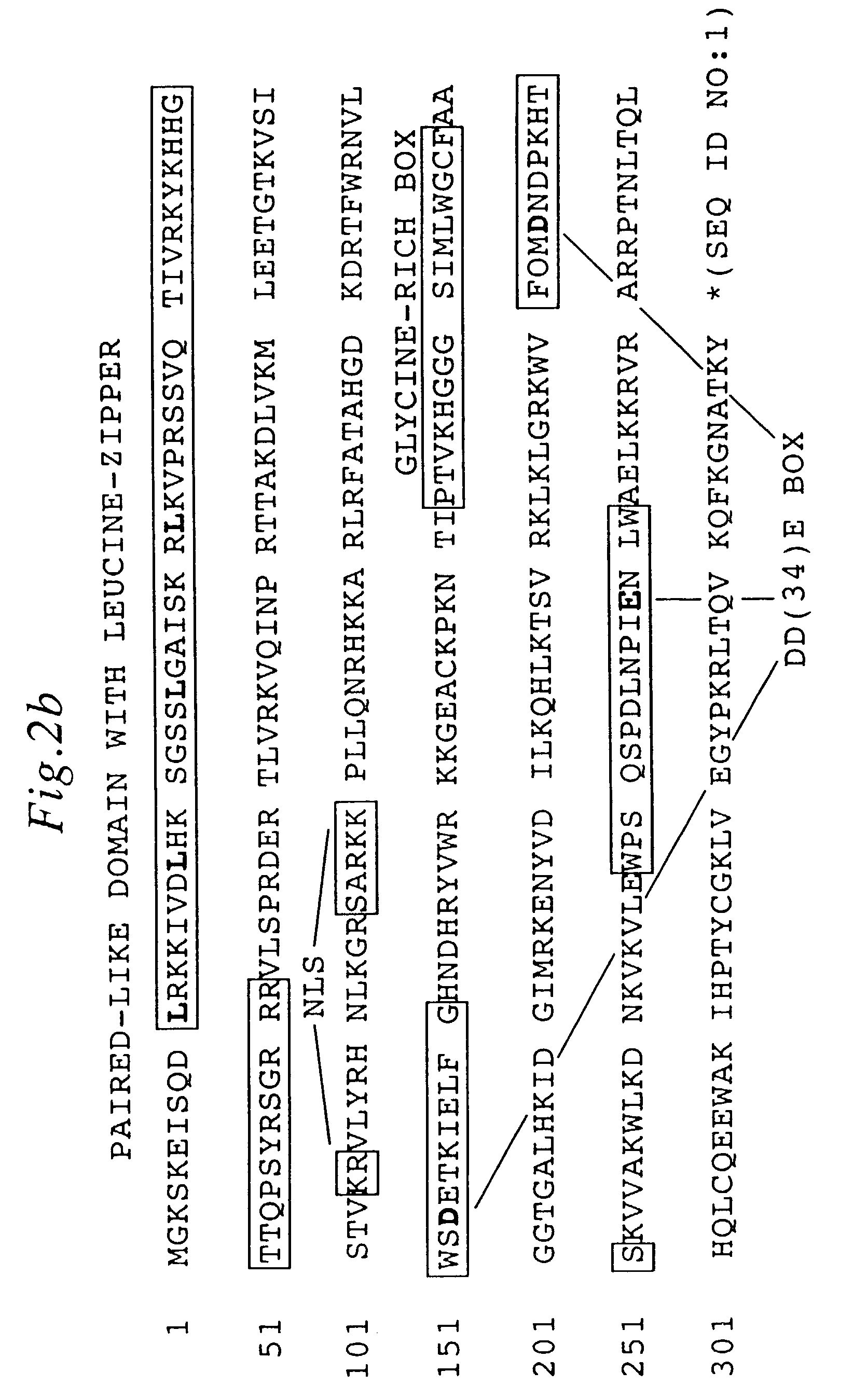
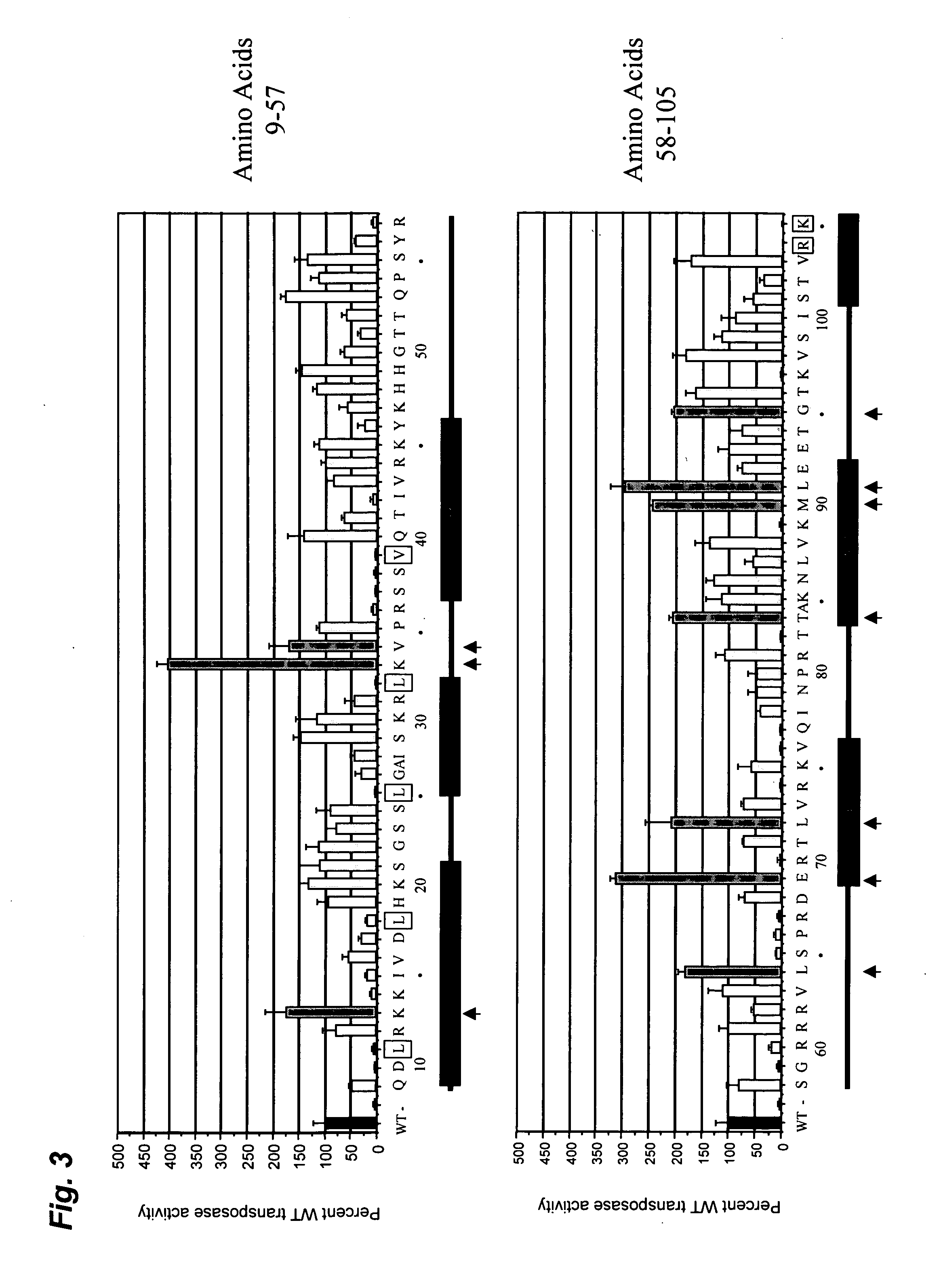
Enhanced sleeping beauty transposon system and methods for using the same
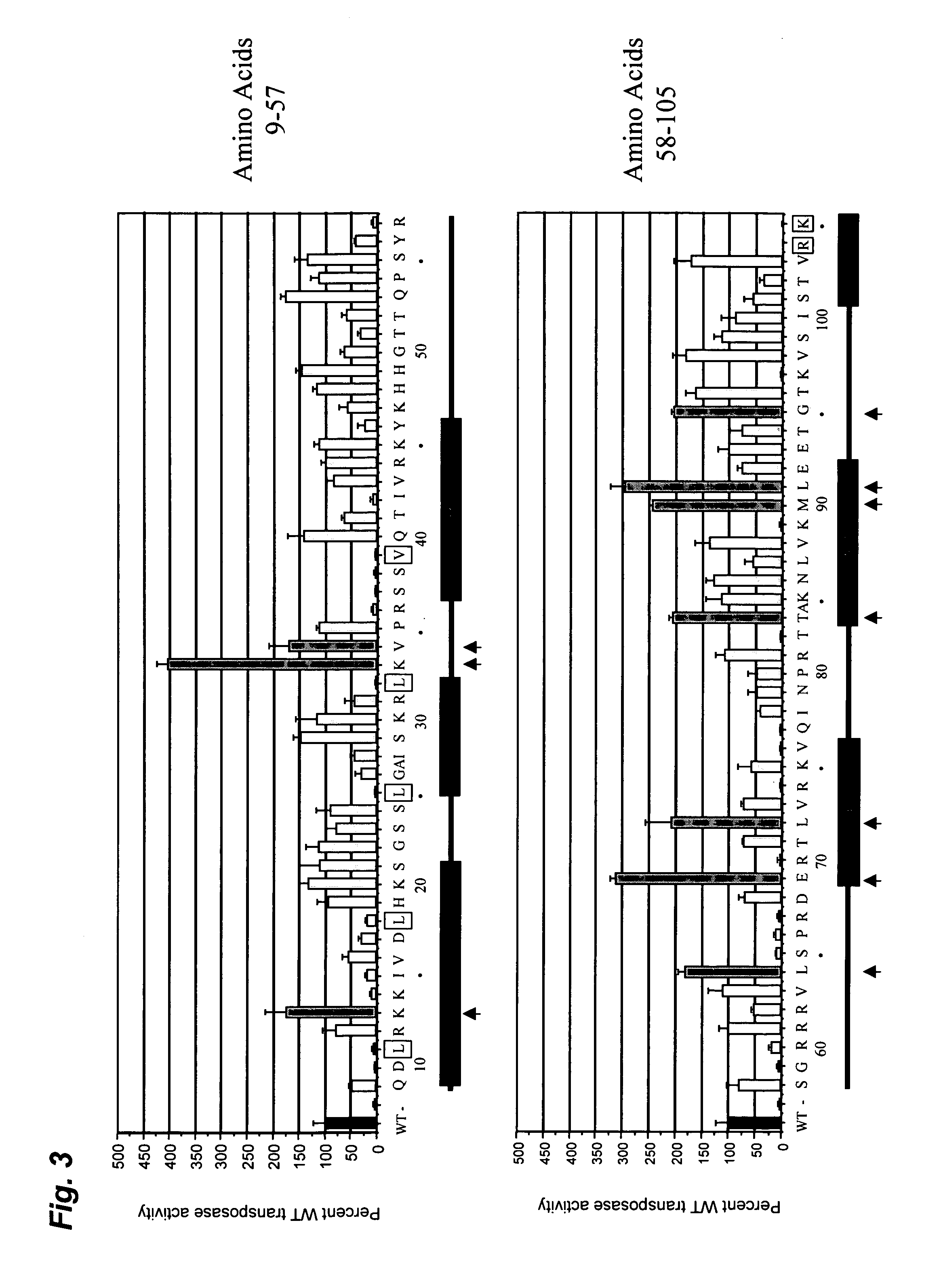
Methods and compositions for introducing a nucleic acid into the genome of a cell are provided. In the subject methods, a Sleeping Beauty transposon that includes the nucleic acid is introduced into the cell along with a source of a mutant Sleeping Beauty transposase that provides for enhanced integration as compared to the wild-type Sleeping Beauty transposase having an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:01. Introduction of the mutant Sleeping Beauty Transposase and transposon results in integration of the nucleic acid into the cell genome. Also provided are mutant transposases and transposons, as well as systems and kits thereof, that find use in practicing the subject methods. The subject methods and compositions find use in a variety of different applications.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Nucleic acid transfer vector for the introduction of nucleic acid into the DNA of a cell
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Crispr-based genome modification and regulation
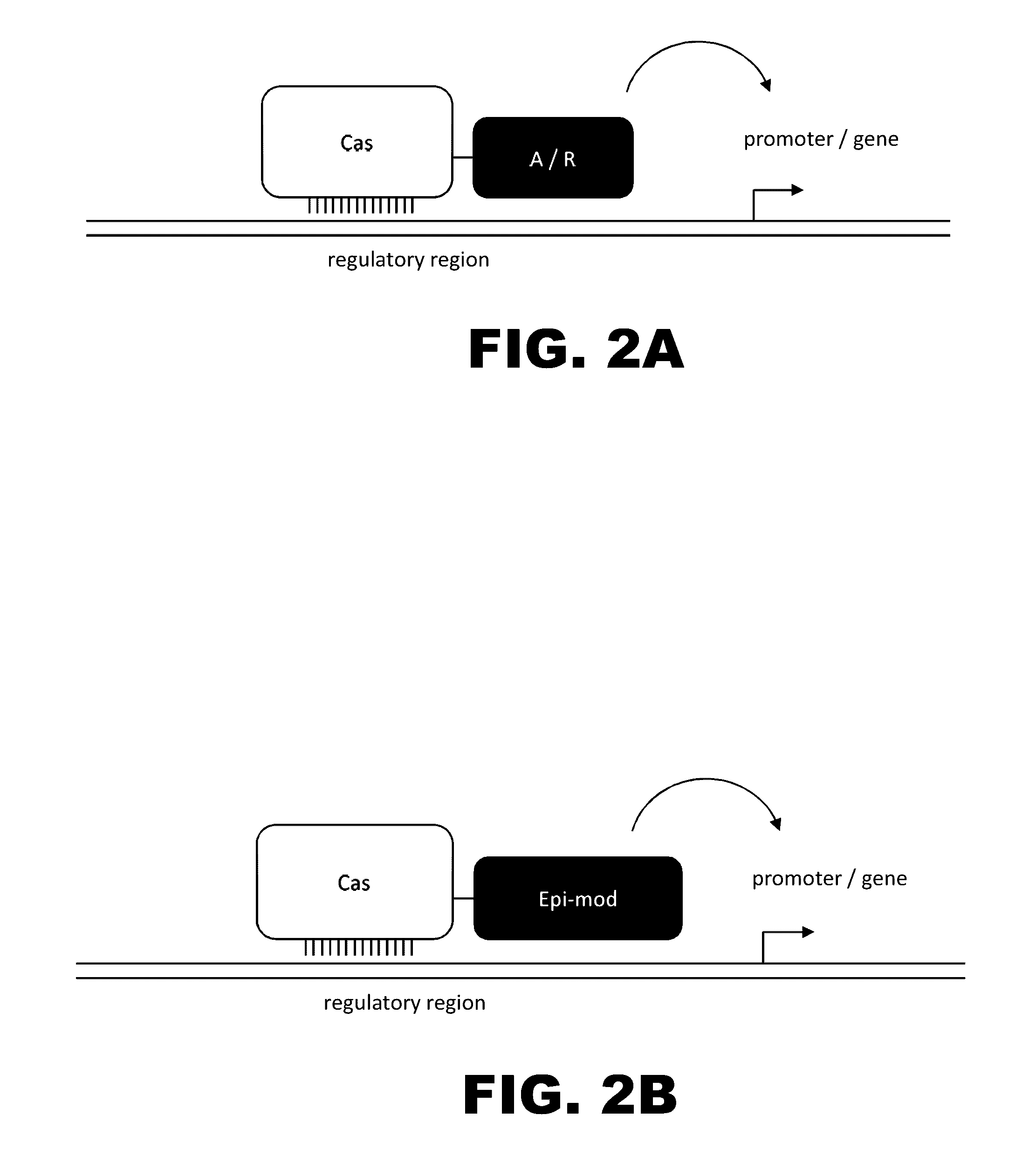
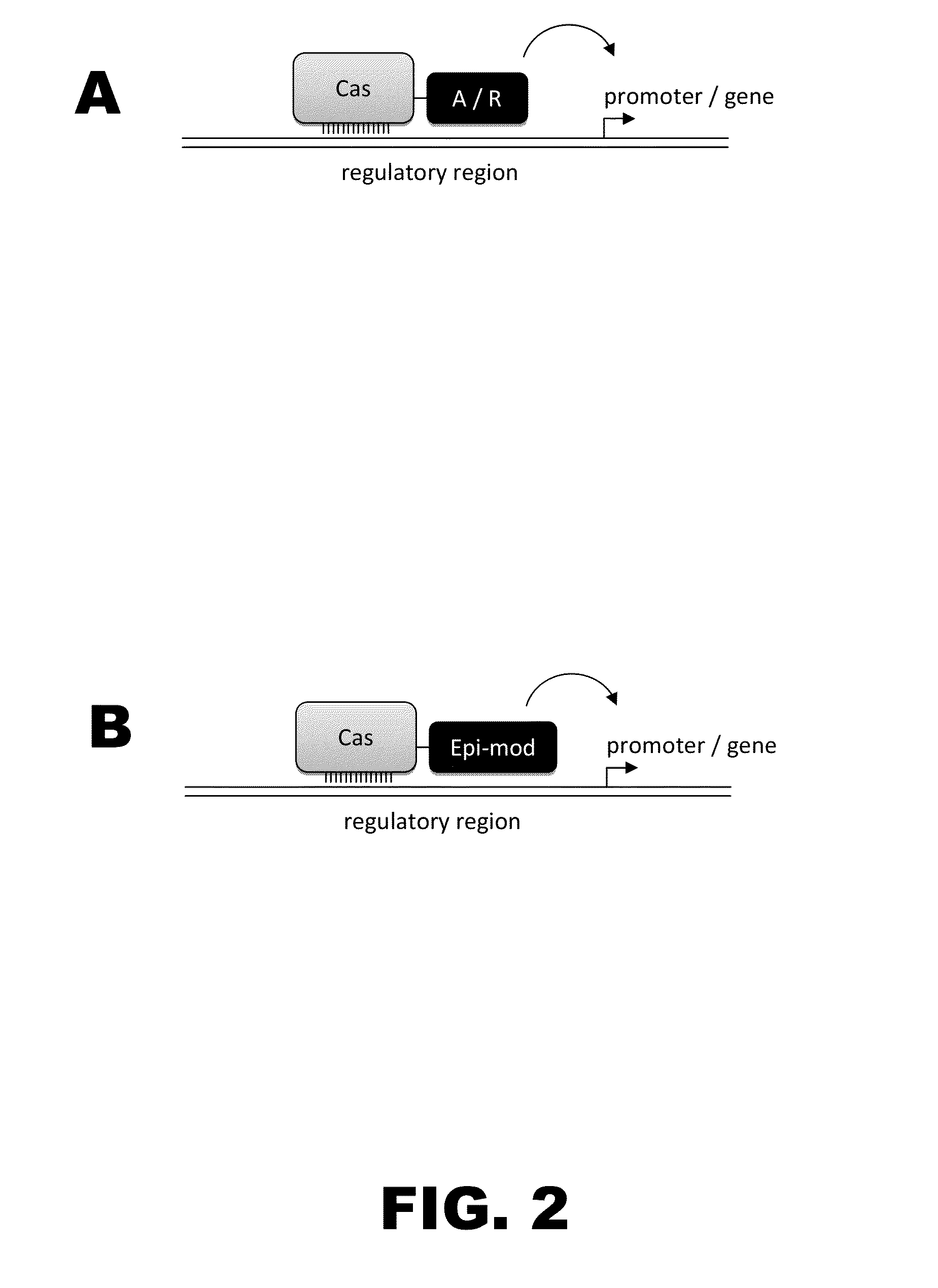
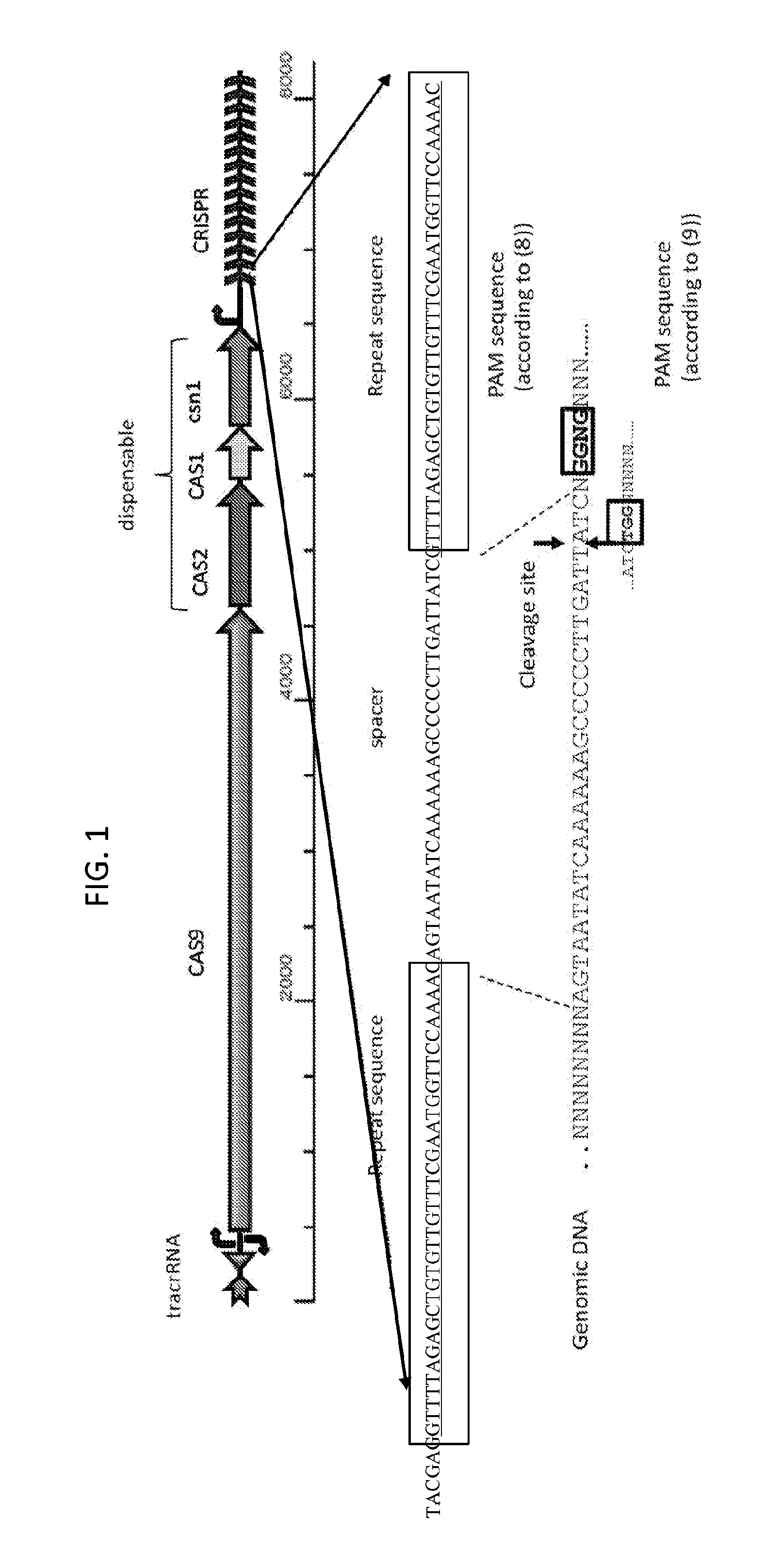
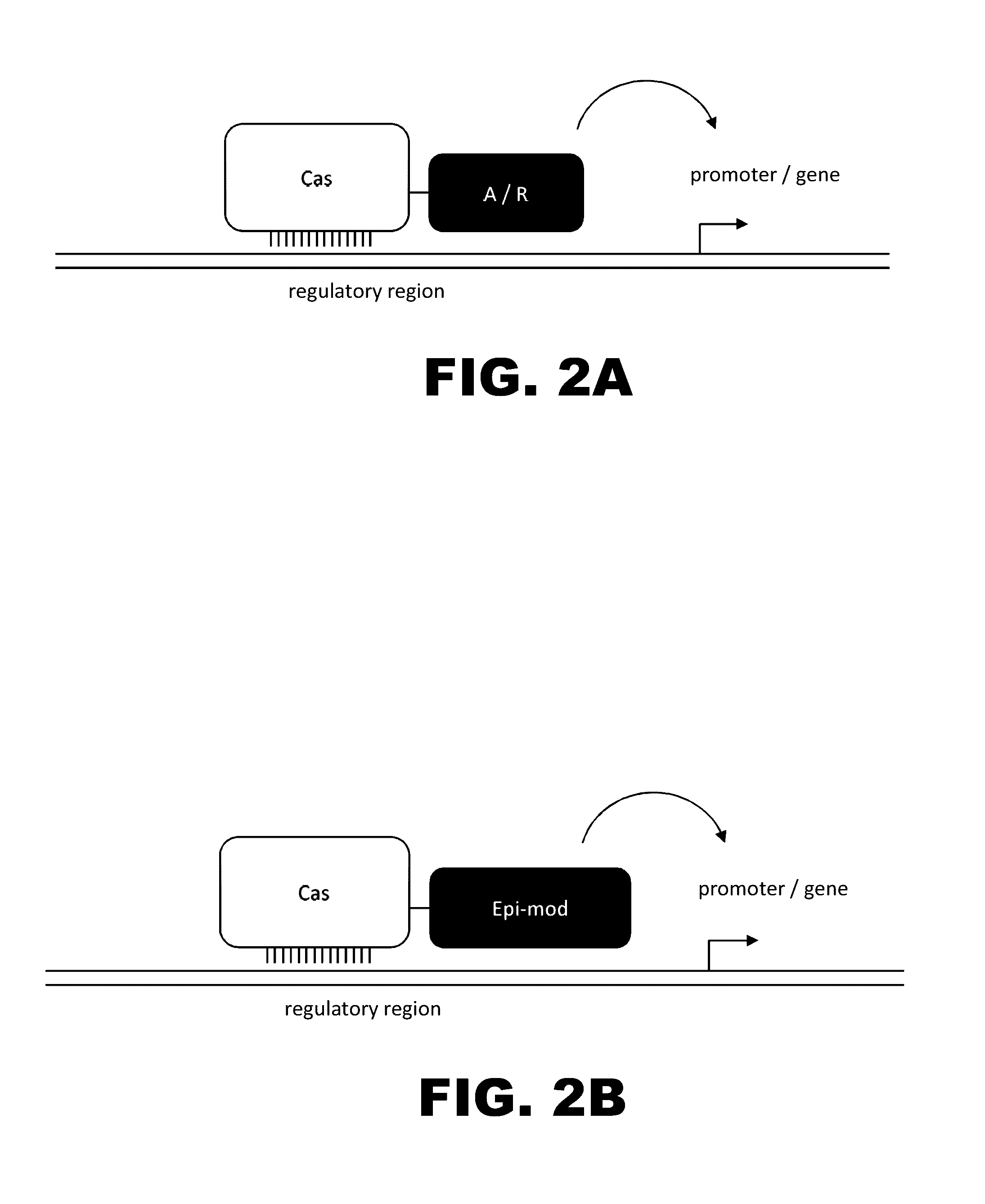
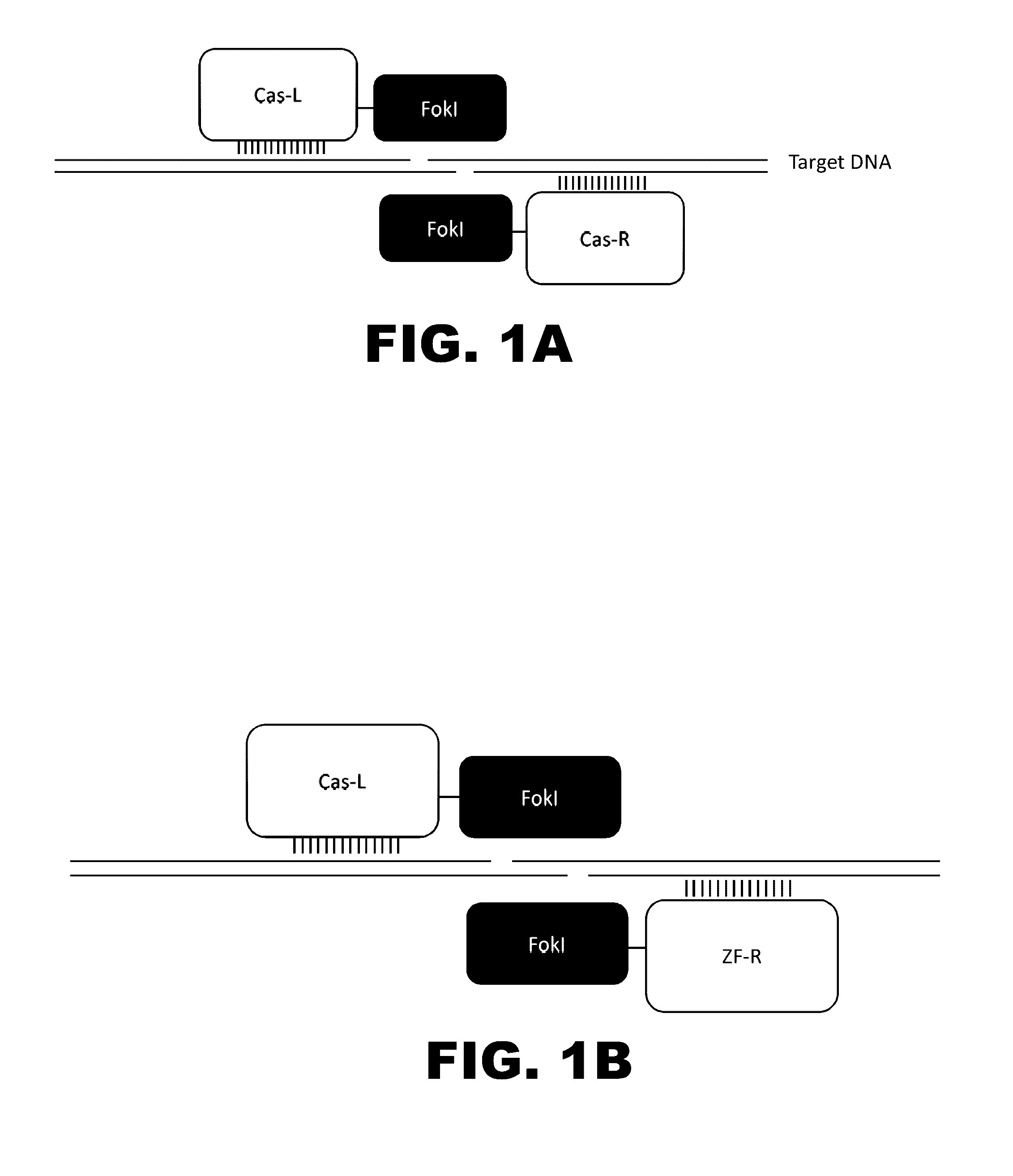
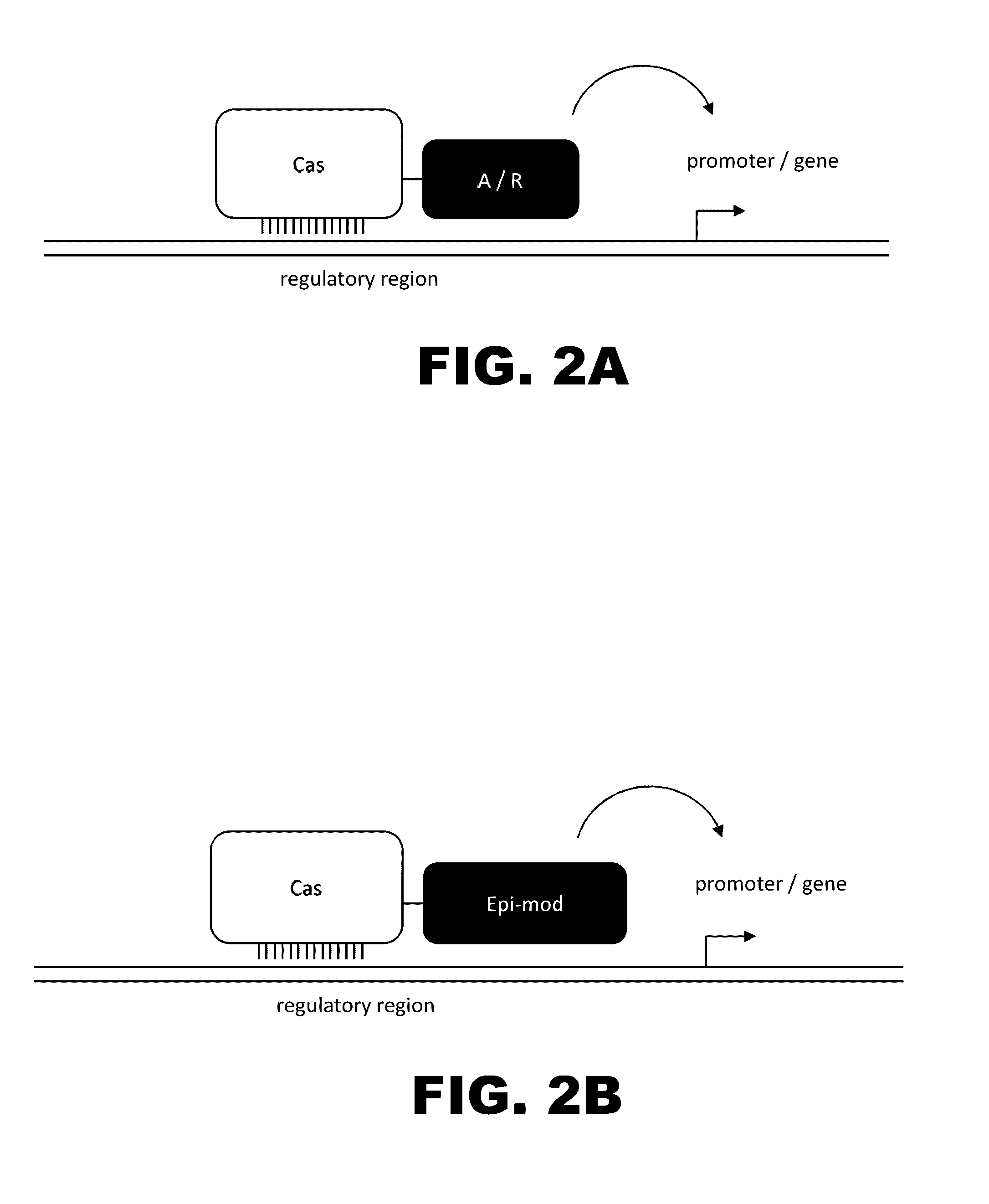
The present invention provides RNA-guided endonucleases, which are engineered for expression in eukaryotic cells or embryos, and methods of using the RNA-guided endonuclease for targeted genome modification in in eukaryotic cells or embryos. Also provided are fusion proteins, wherein each fusion protein comprises a CRISPR / Cas-like protein or fragment thereof and an effector domain. The effector domain can be a cleavage domain, an epigenetic modification domain, a transcriptional activation domain, or a transcriptional repressor domain. Also provided are methods for using the fusion proteins to modify a chromosomal sequence or regulate expression of a chromosomal sequence.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
THERAPEUTIC USES OF GENOME EDITING WITH CRISPR/Cas SYSTEMS
ActiveUS20150071889A1Effectively deletes target polynucleotide sequencesEfficiently deletingBiocideGenetic material ingredientsGenome editingBioinformatics
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
Methods, cells & organisms
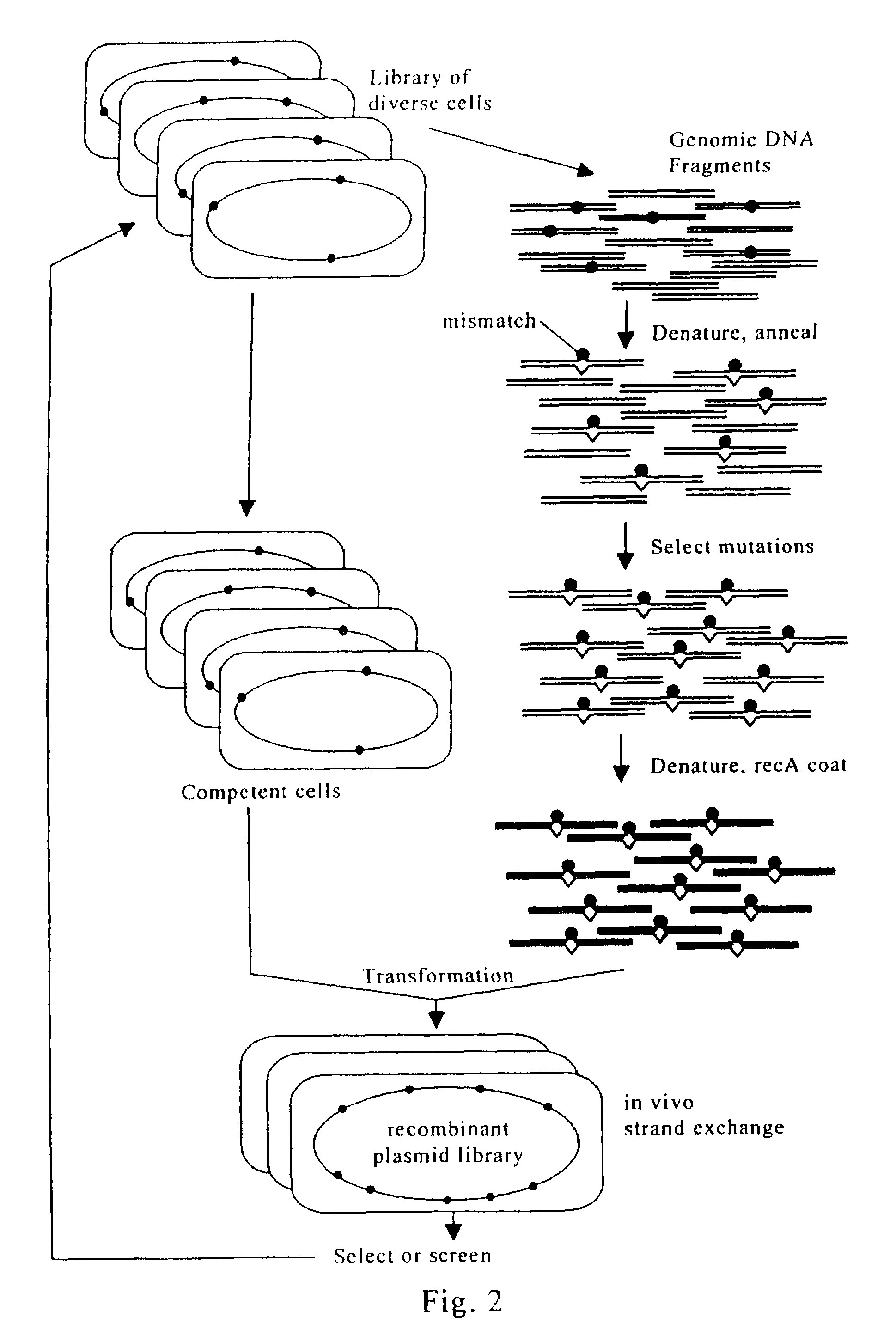
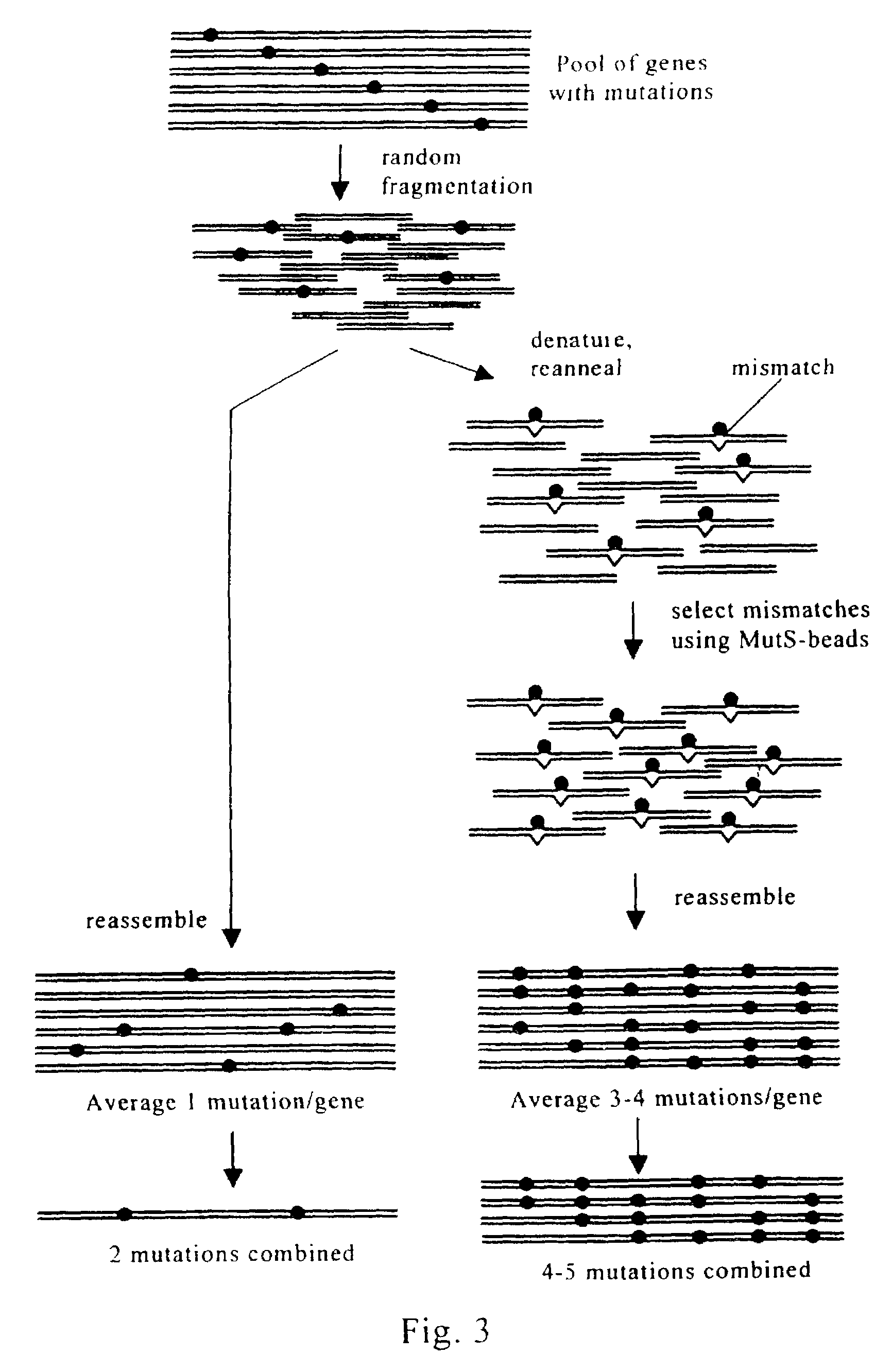
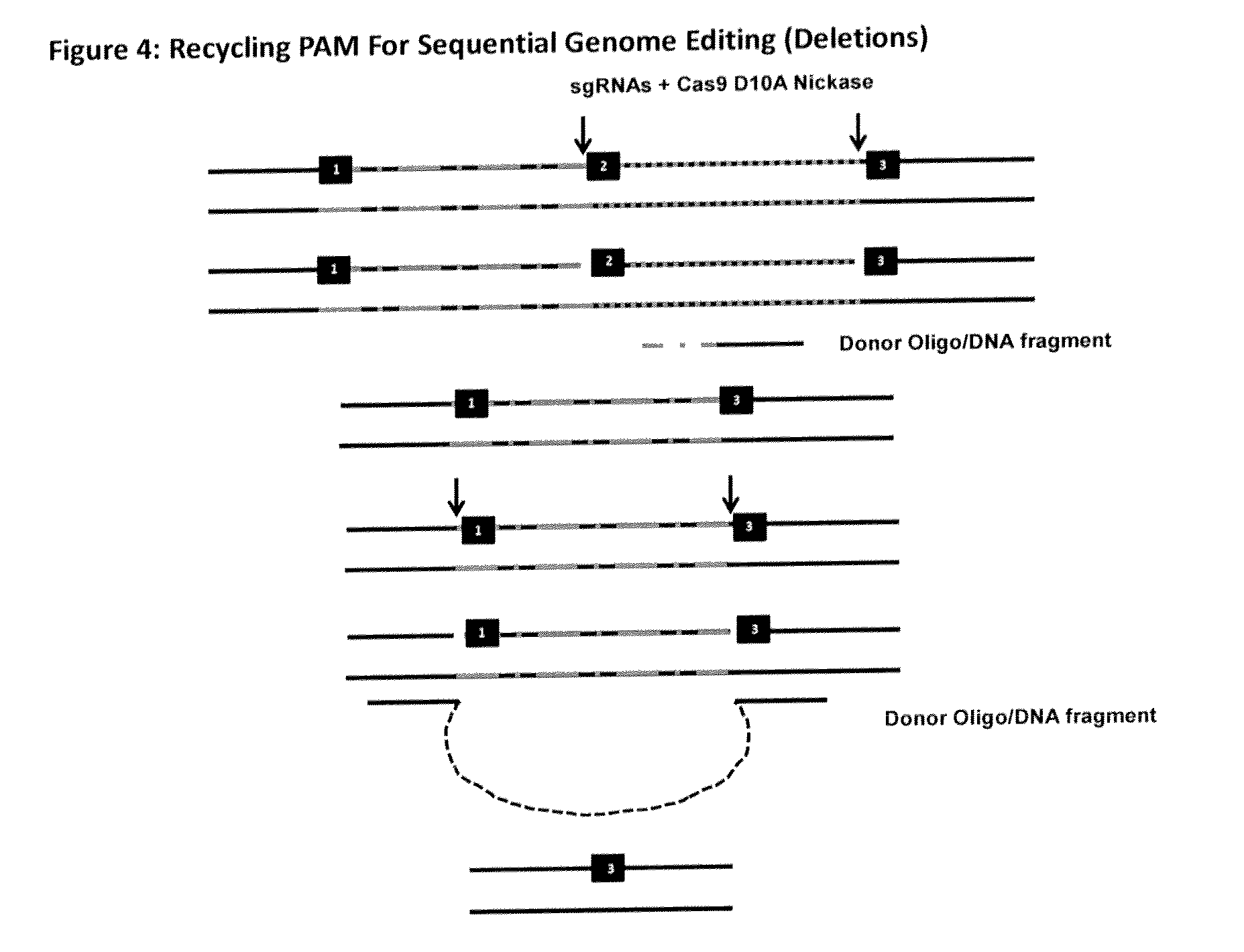
InactiveUS20150079680A1Reduce chanceGenetically modified cellsStable introduction of DNABiological bodyDNA fragmentation
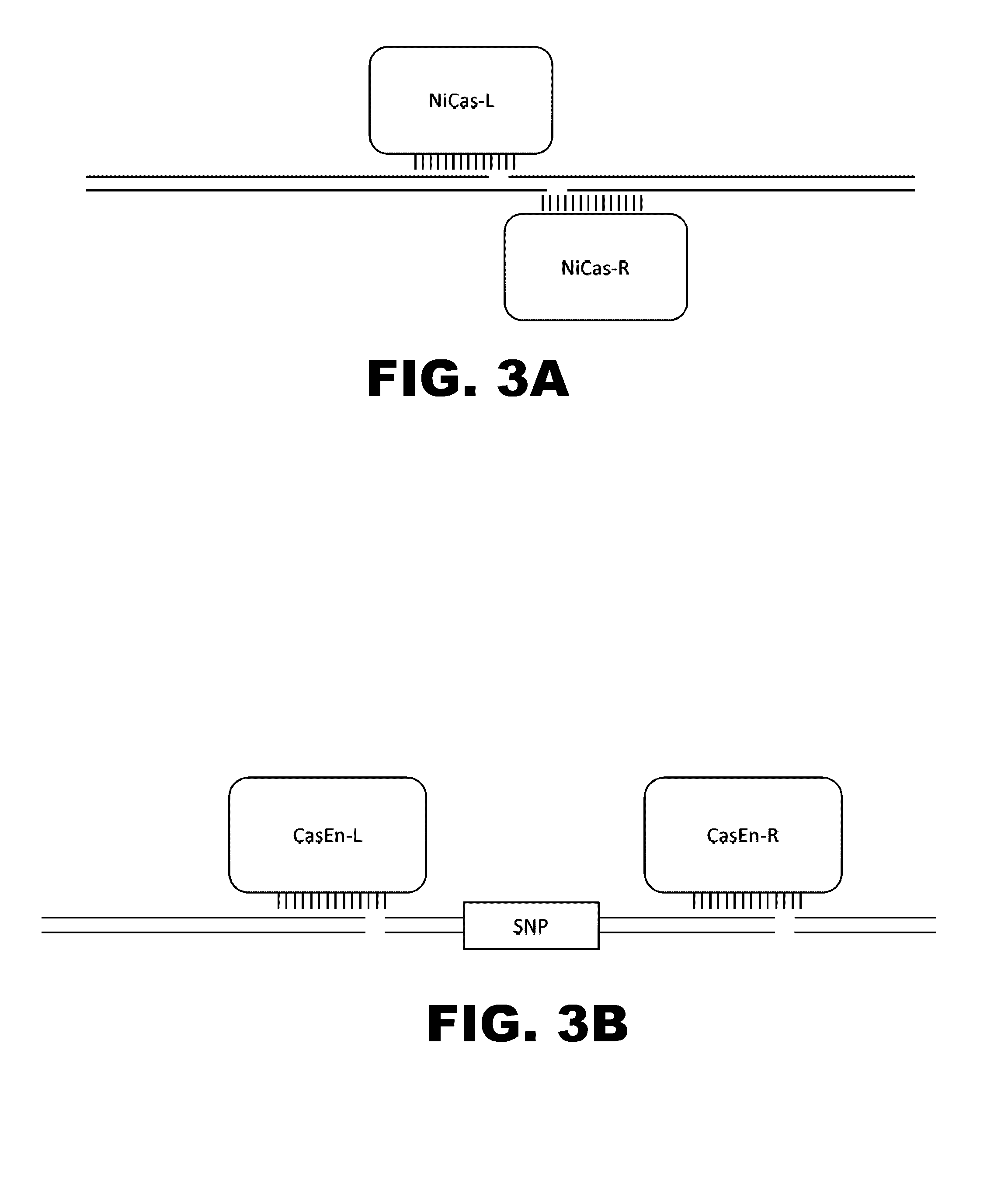
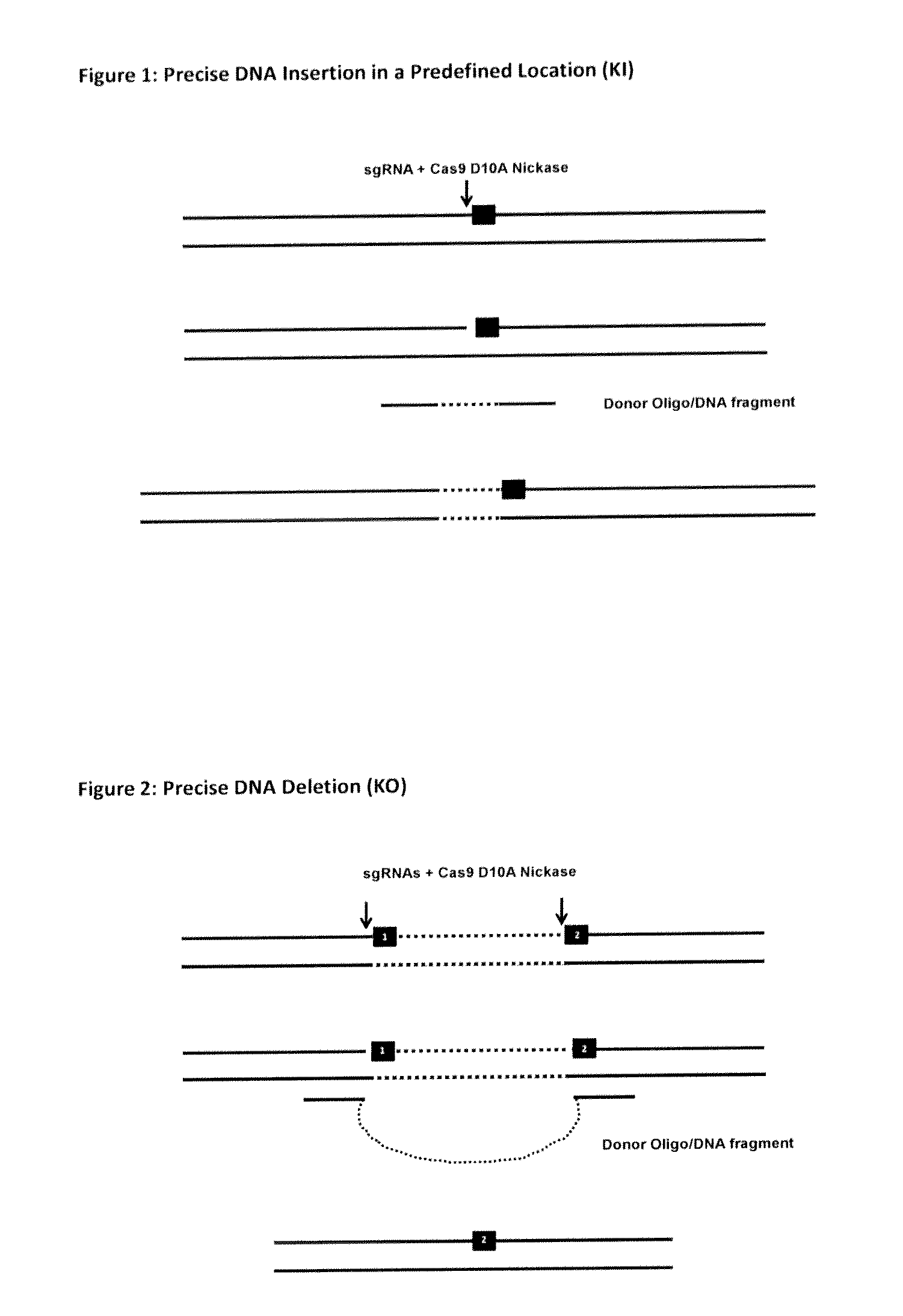
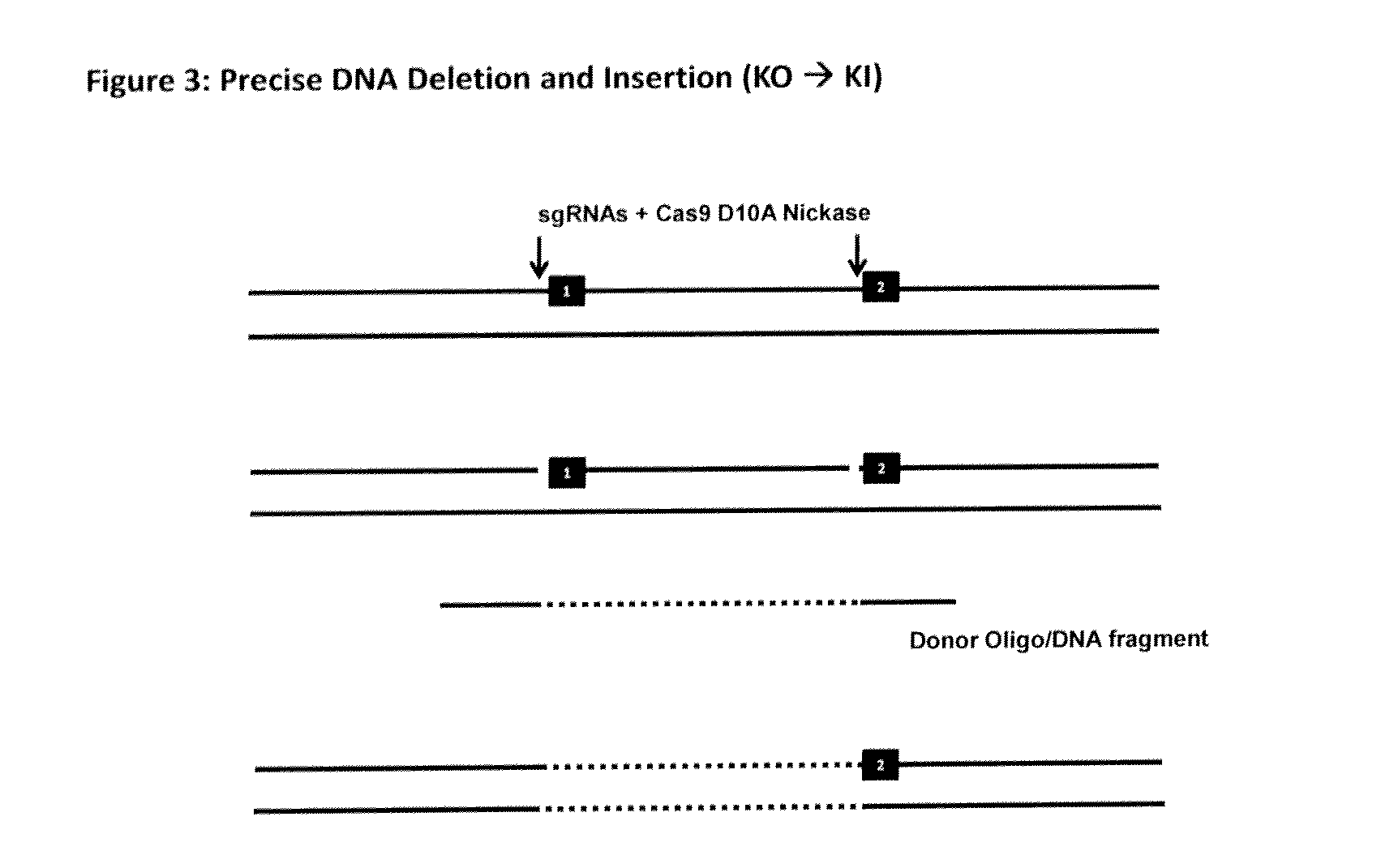
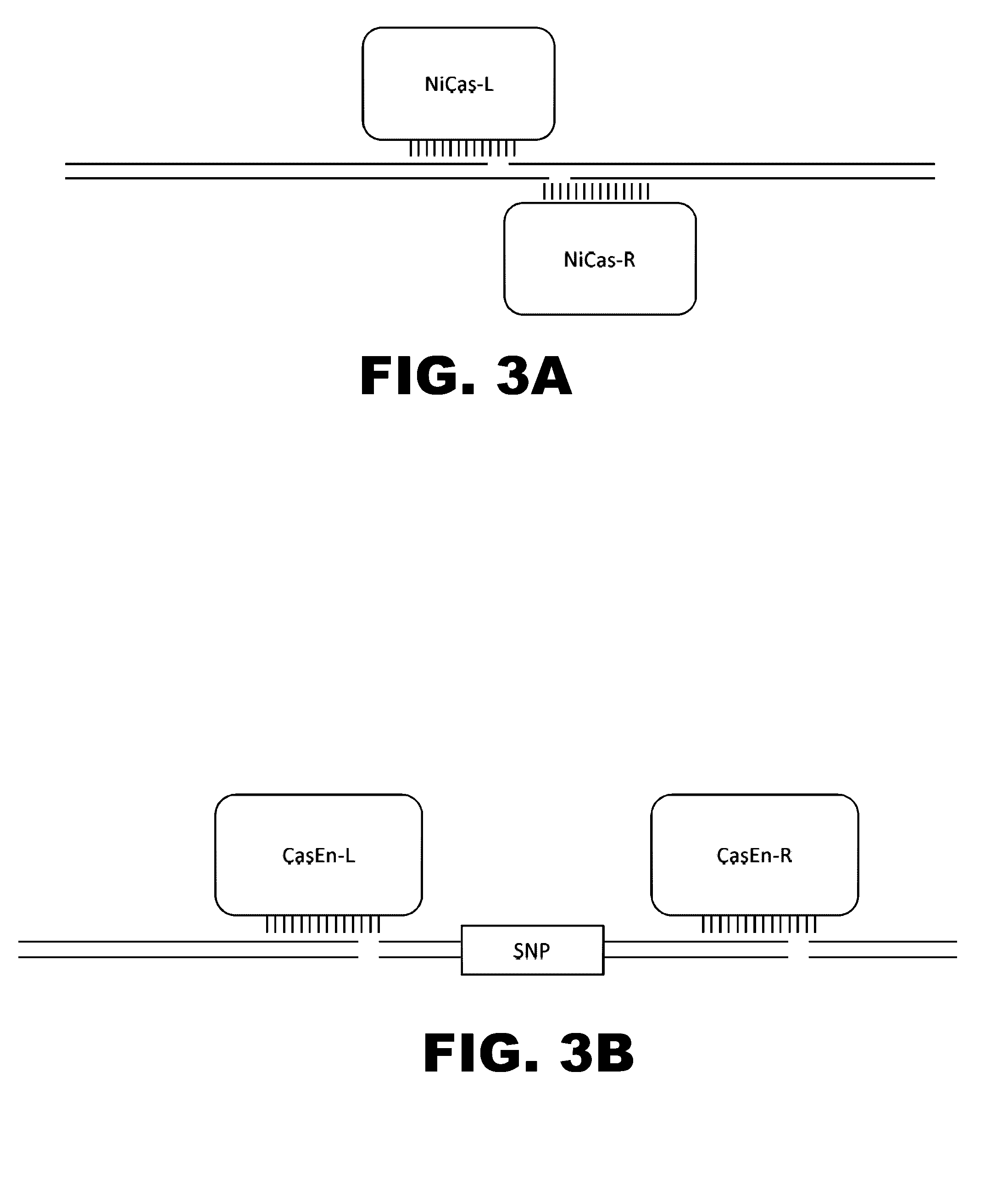
The invention relates to an approach for introducing one or more desired insertions and / or deletions of known sizes into one or more predefined locations in a nucleic acid (eg, in a cell or organism genome). They developed techniques to do this either in a sequential fashion or by inserting a discrete DNA fragment of defined size into the genome precisely in a predefined location or carrying out a discrete deletion of a defined size at a precise location. The technique is based on the observation that DNA single-stranded breaks are preferentially repaired through the HDR pathway, and this reduces the chances of indels (eg, produced by NHEJ) in the present invention and thus is more efficient than prior art techniques. The invention also provides sequential insertion and / or deletions using single- or double-stranded DNA cutting.
Owner:KIMAB LTD
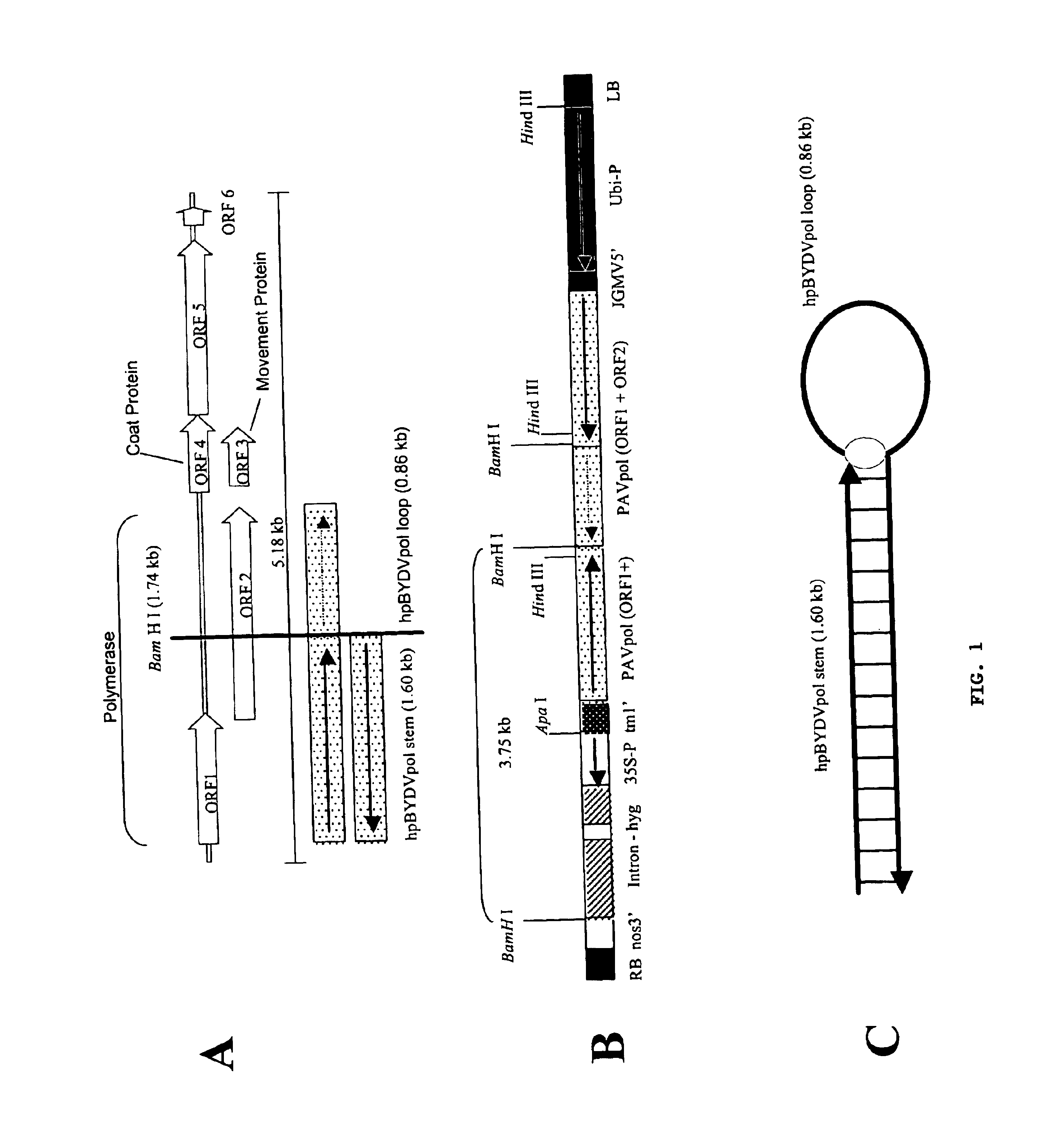
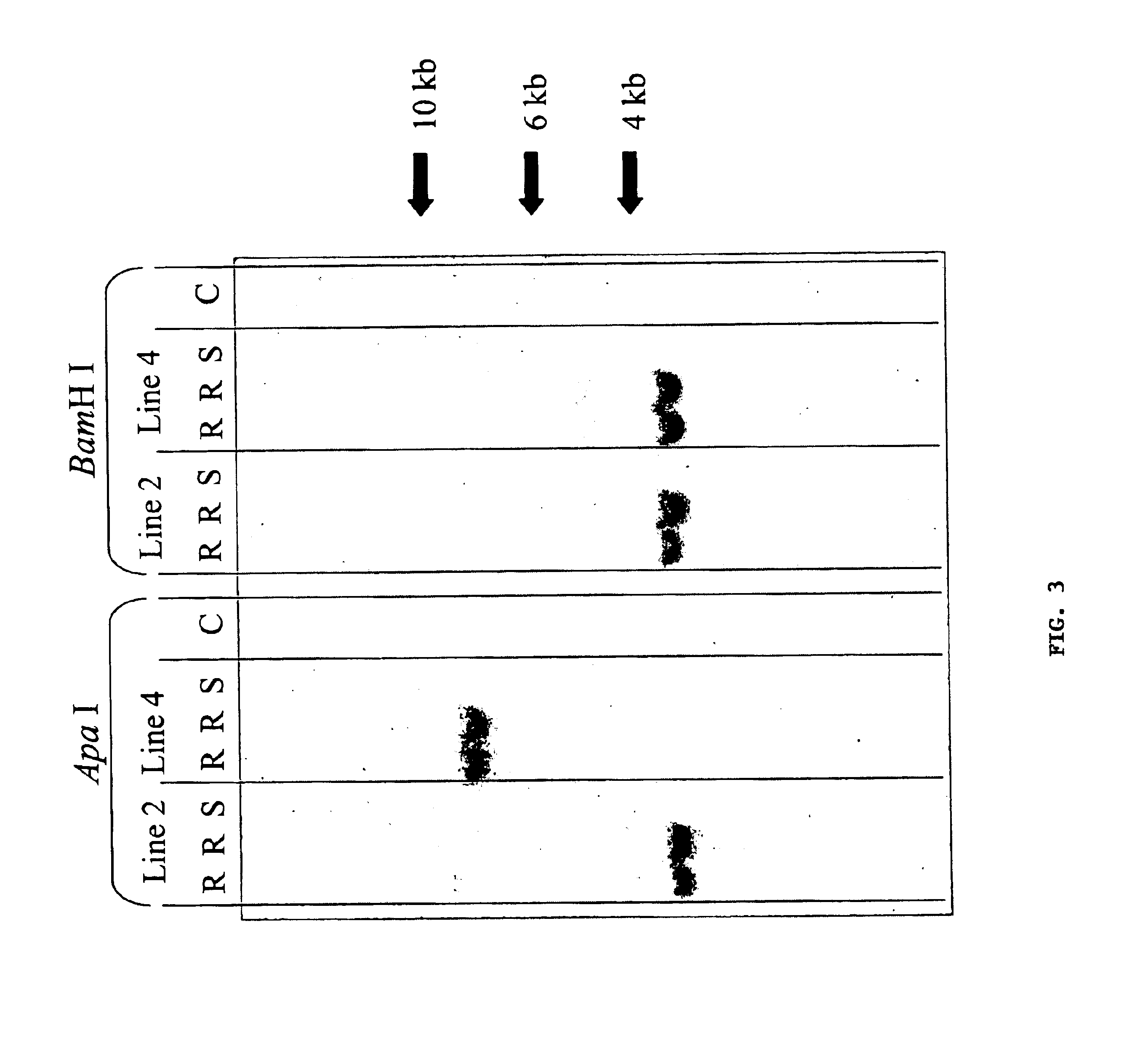
Methods and means for producing barley yellow dwarf virus resistant cereal plants
The invention relates to methods for producing transgenic cereal plants resistant to Barley Yellow Dwarf Virus, particularly in the presence of co-infecting Cereal Yellow Dwarf Virus, by stably integrating into the cells of the transgenic plant a chimeric gene comprising a DNA region operably linked to plant expressible promoter in such a way that the RNA molecule may be transcribed from the DNA region, the RNA molecule comprising both sense and antisense RNA capable of pairing and forming a double stranded RNA molecule or hairpin RNA.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
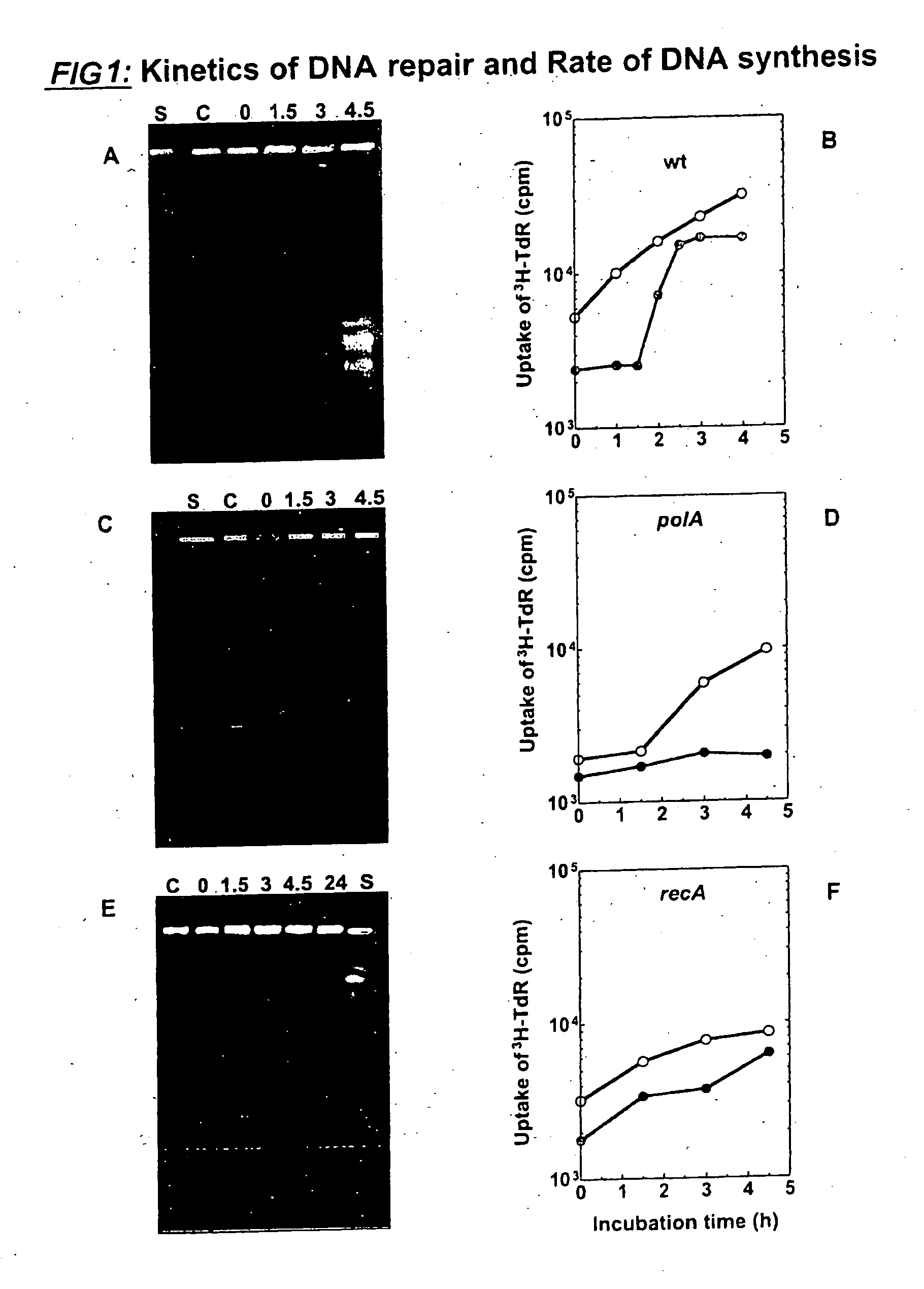
Process for Chromosomal Engineering Using a Novel Dna Repair System
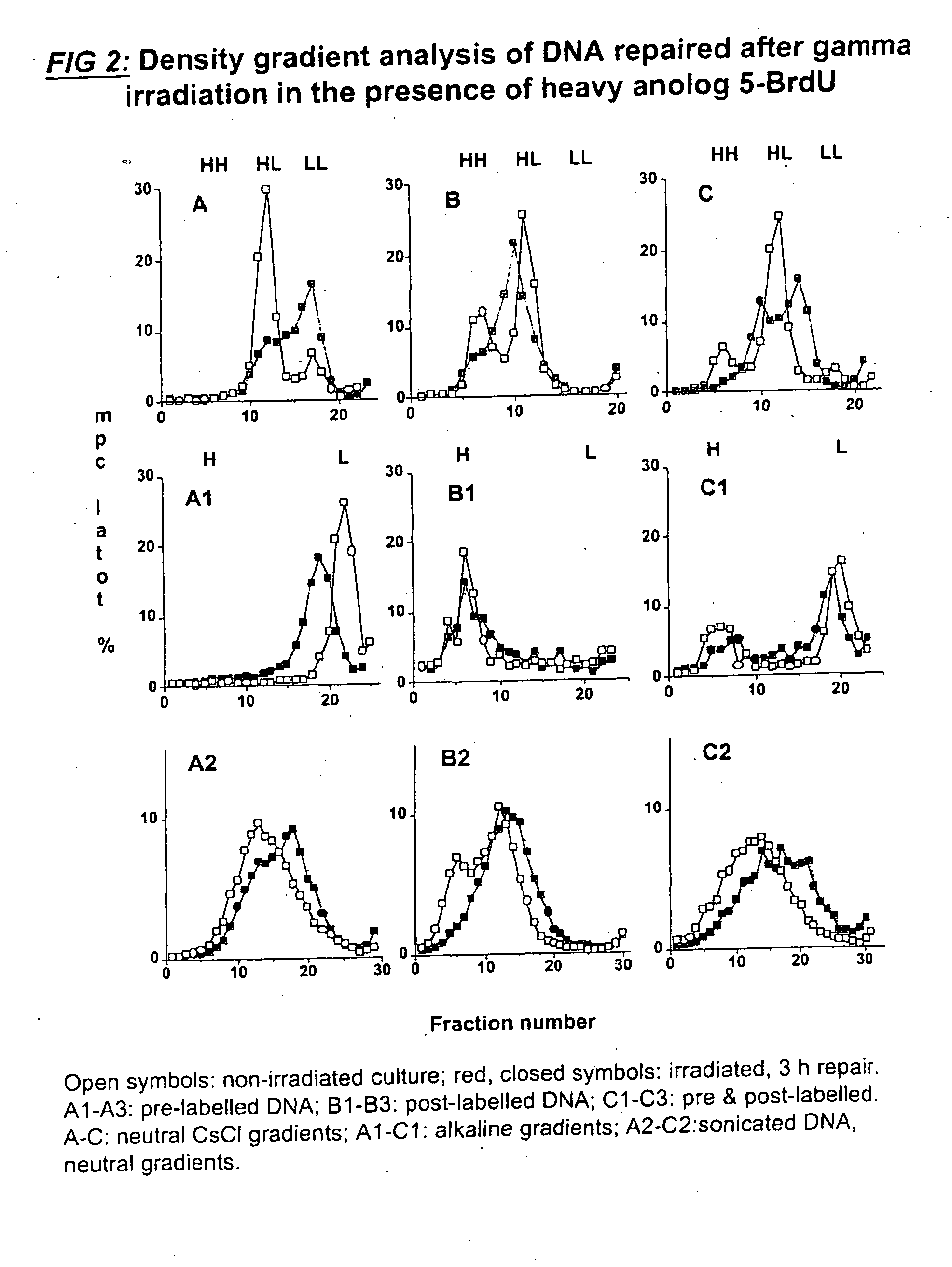
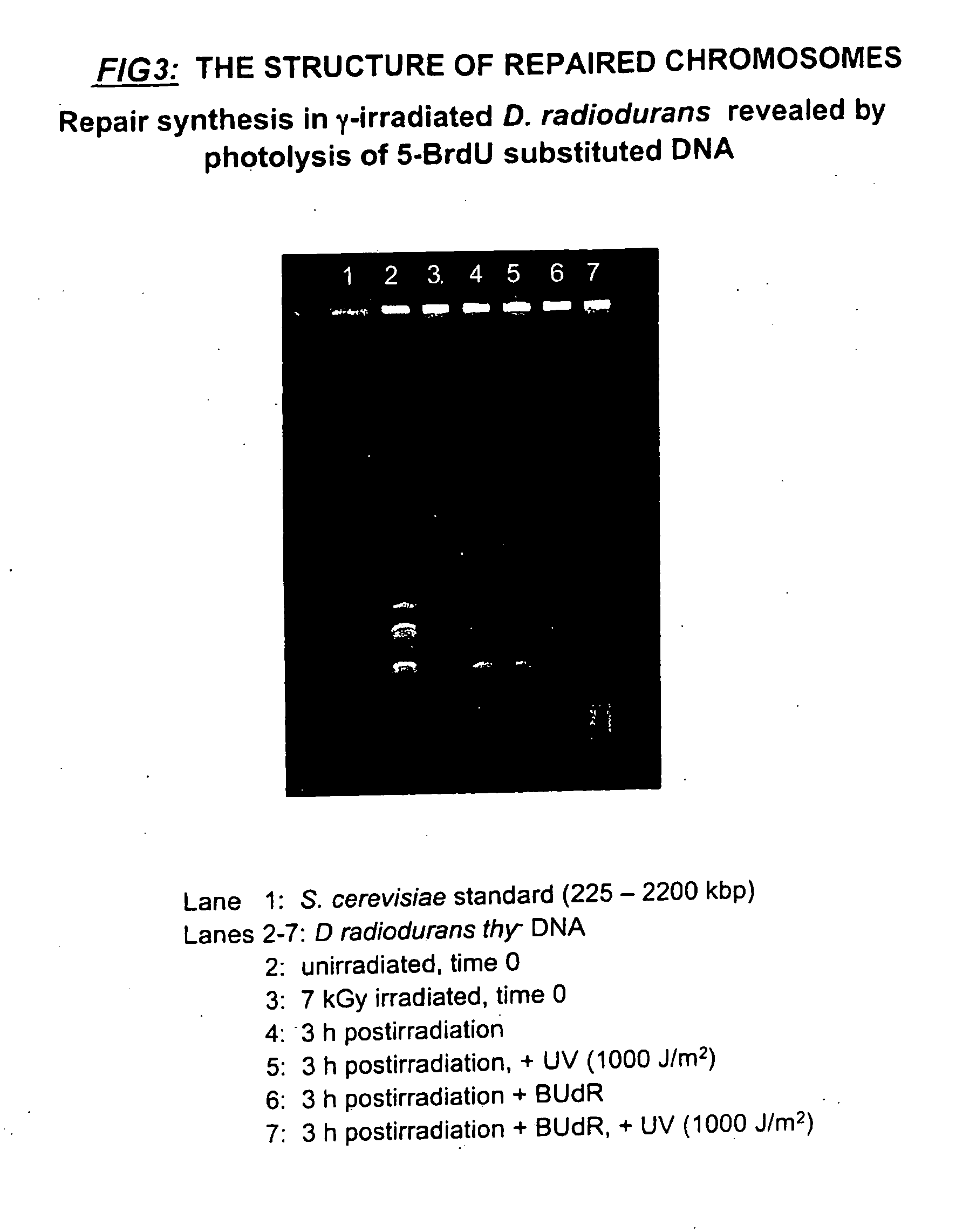
This invention relates to chromosomal engineering via DNA repair process. The process of the invention comprises the steps of: 1) submitting at least one source of biological activity, e.g. Deinococcus radiodurans, to radiation, desiccation and / or chemical treatment liable to damage the DNA, so as to substantially shatter its chromosomes into short fragments; 2) annealing complementary single strand tails extended by the synthesis templated on partially overlapping DNA fragments of said shattered chromosomes; 4) converting the resulting long linear DNA intermediates into intact circular chromosomes, by means of a RecA dependent homologous recombination; whereas at least one foreign source of genetic material, e.g. DNA, can be introduced during steps 2 and / or 3; and 4) optionally separating and collecting the recombined chromosomes thus obtained.
Owner:DEINOVE SA
Crispr-based genome modification and regulation
The present invention provides RNA-guided endonucleases, which are engineered for expression in eukaryotic cells or embryos, and methods of using the RNA-guided endonuclease for targeted genome modification in in eukaryotic cells or embryos. Also provided are fusion proteins, wherein each fusion protein comprises a CRISPR / Cas-like protein or fragment thereof and an effector domain. The effector domain can be a cleavage domain, an epigenetic modification domain, a transcriptional activation domain, or a transcriptional repressor domain. Also provided are methods for using the fusion proteins to modify a chromosomal sequence or regulate expression of a chromosomal sequence.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
Methods and compositions for genomic modification
InactiveUS20040203152A1Genetic material ingredientsStable introduction of DNAEucaryotic cellSite-specific recombination
The present invention provides methods of site-specifically integrating a polynucleotide sequence of interest in a genome of a eucaryotic cell, as well as, enzymes, polypeptides, and a variety of vector constructs useful therefore. In the method, a targeting construct comprises, for example, (i) a first recombination site and a polynucleotide sequence of interest, and (ii) a site-specific recombinase, which are introduced into the cell. The genome of the cell comprises a second recombination site. Recombination between the first and second recombination sites is facilitated by the site-specific recombinase. The invention describes compositions, vectors, and methods of use thereof, for the generation of transgenic cells, tissues, plants, and animals. The compositions, vectors, and methods of the present invention are also useful in gene therapy techniques.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Crispr-based genome modification and regulation
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
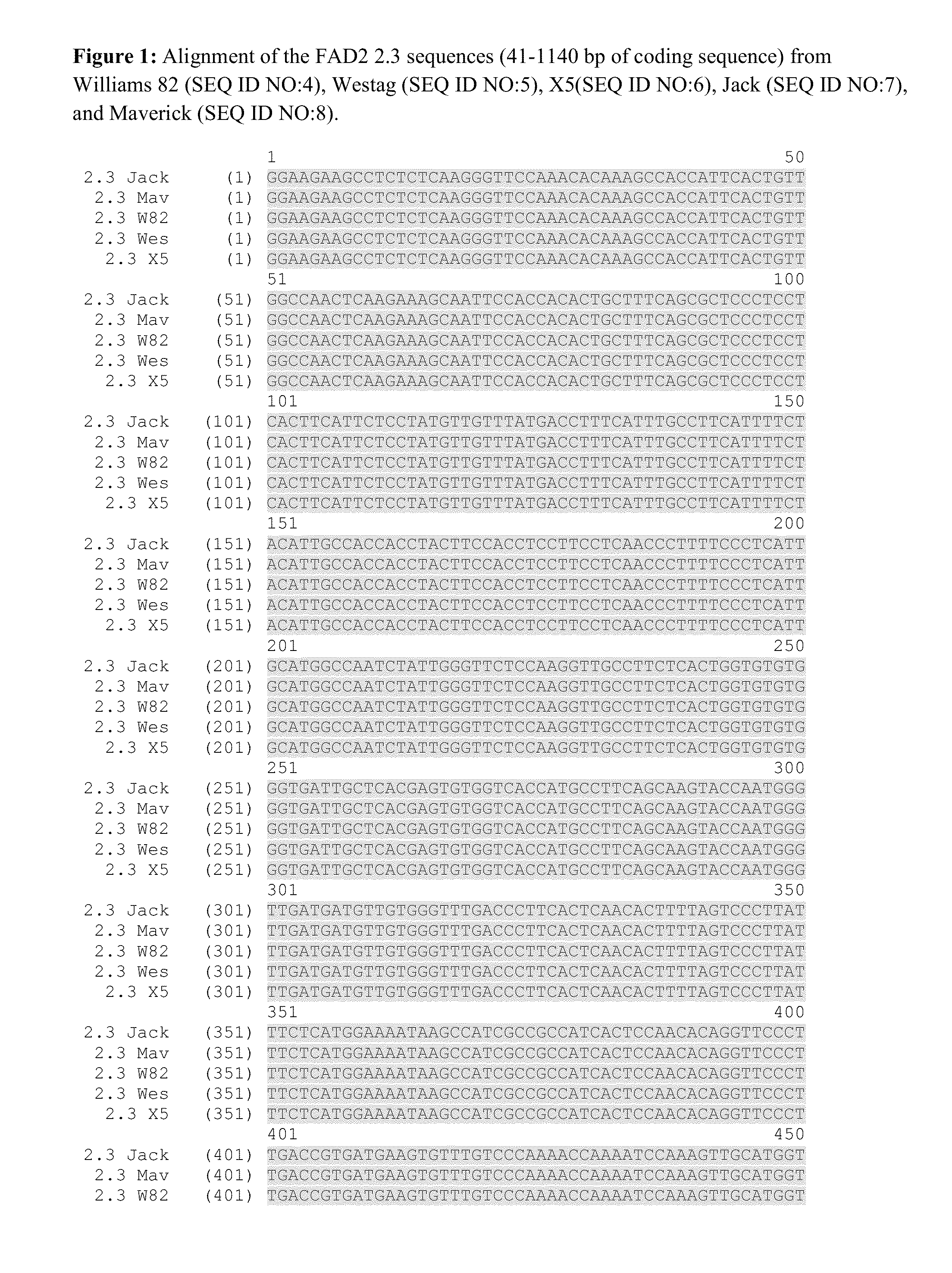
Fad2 performance loci and corresponding target site specific binding proteins capable of inducing targeted breaks
ActiveUS20140090116A1Minimal adverse impactFusion with DNA-binding domainHydrolasesA-siteBioinformatics
Methods and compositions for gene disruption, gene editing or gene stacking within a FAD2 loci by cleaving, in a site directed manner, a location in a FAD2 gene in a soybean cell, to generate a break in the FAD2 gene and then optionally integrating into the break a nucleic acid molecule of interest is disclosed.
Owner:SANGAMO BIOSCIENCES INC +1
Enhanced sleeping beauty transposon system and methods for using the same
Methods and compositions for introducing a nucleic acid into the genome of a cell are provided. In the subject methods, a Sleeping Beauty transposon that includes the nucleic acid is introduced into the cell along with a source of a mutant Sleeping Beauty transposase that provides for enhanced integration as compared to the wild-type Sleeping Beauty transposase having an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:01. Introduction of the mutant Sleeping Beauty Transposase and transposon results in integration of the nucleic acid into the cell genome. Also provided are mutant transposases and transposons, as well as systems and kits thereof, that find use in practicing the subject methods. The subject methods and compositions find use in a variety of different applications.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com