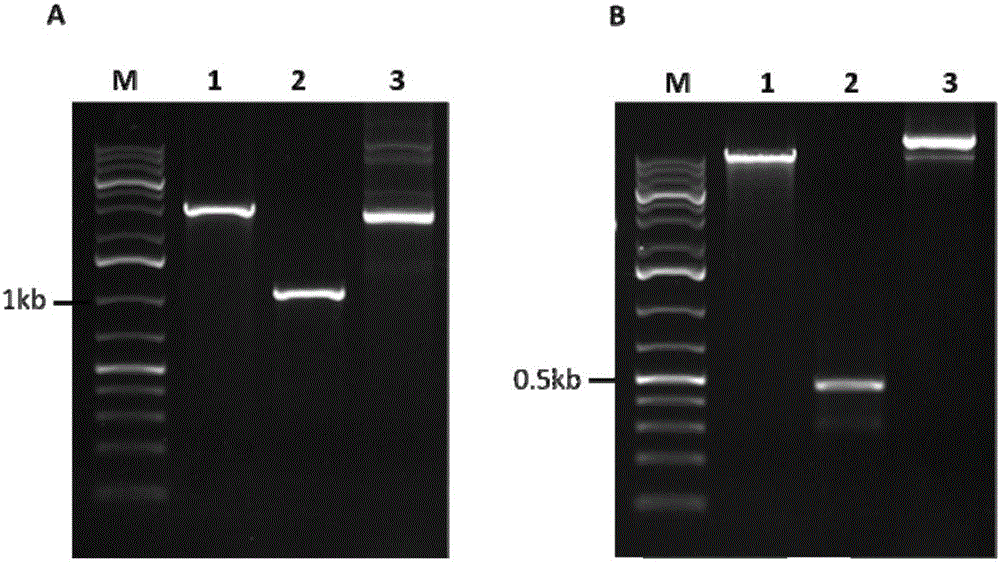
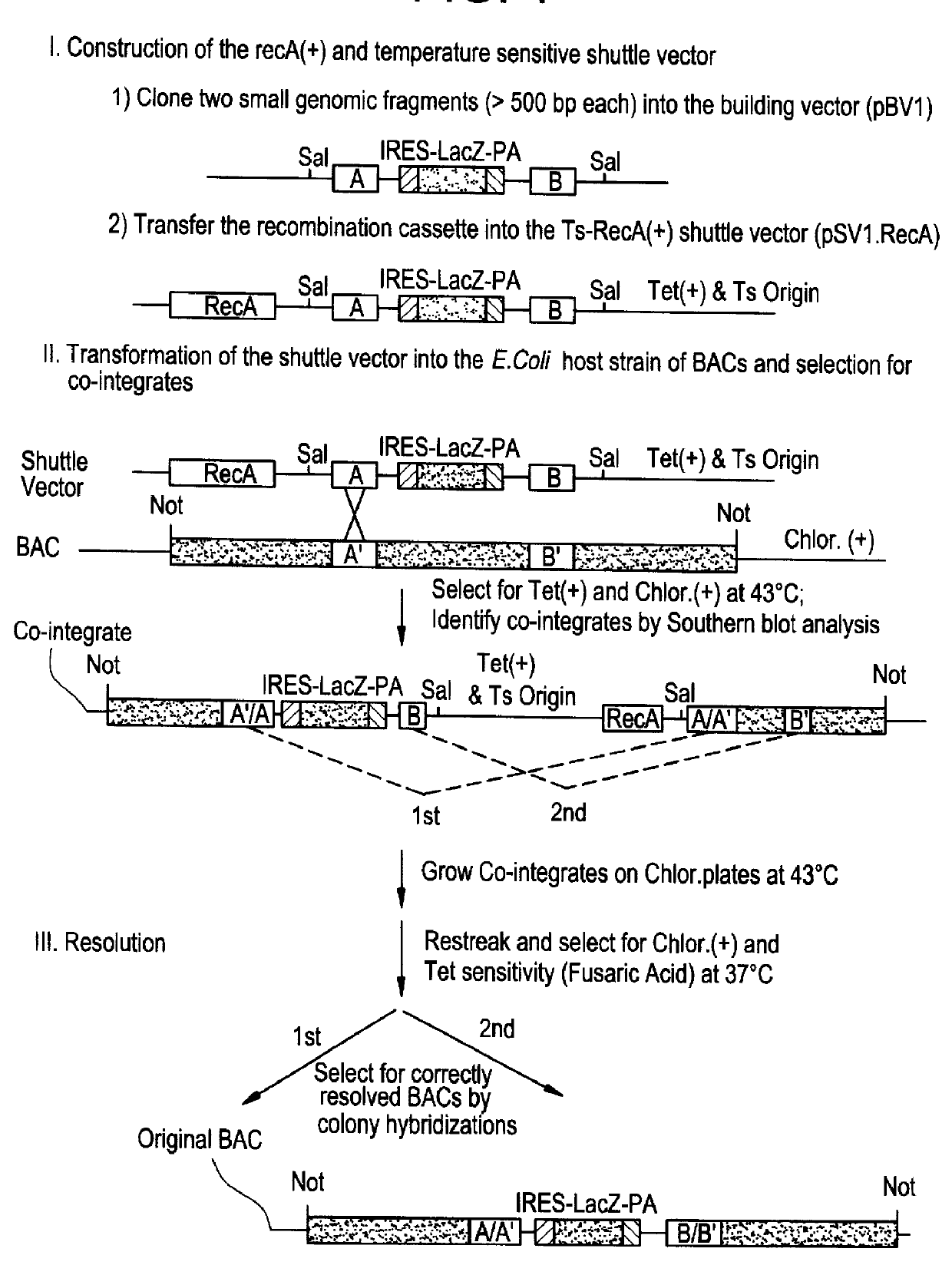
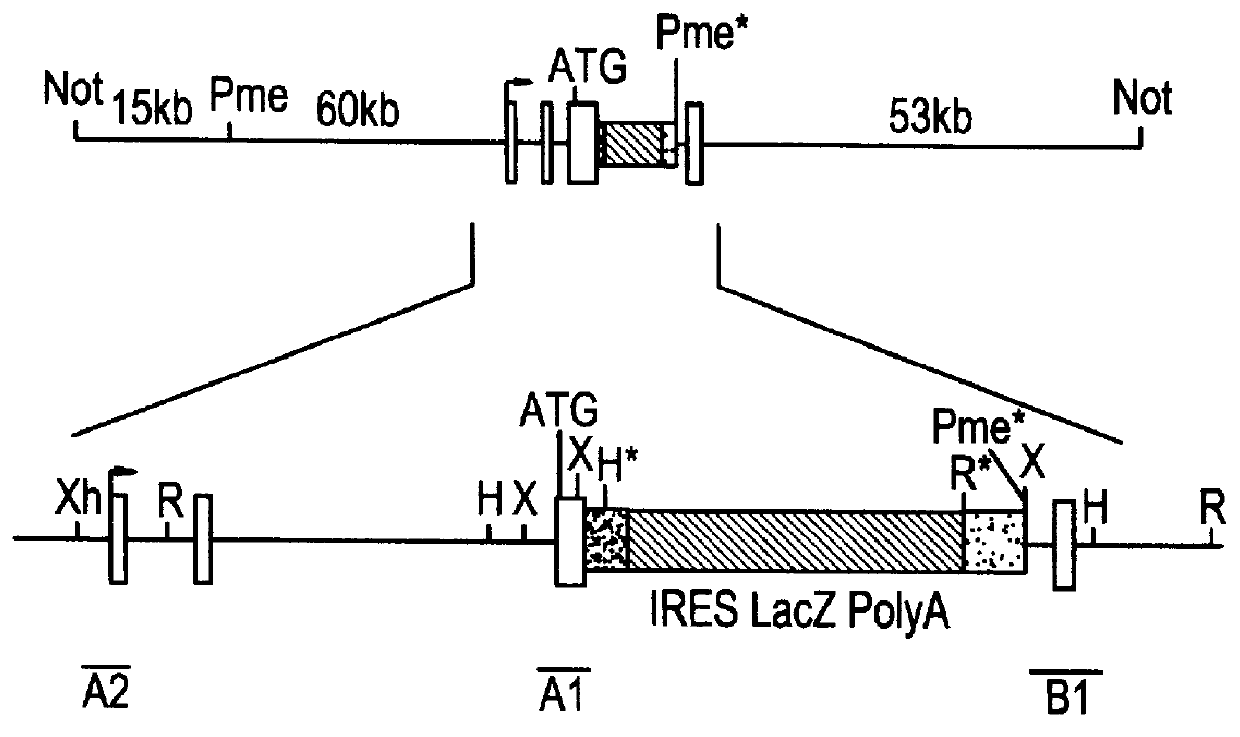
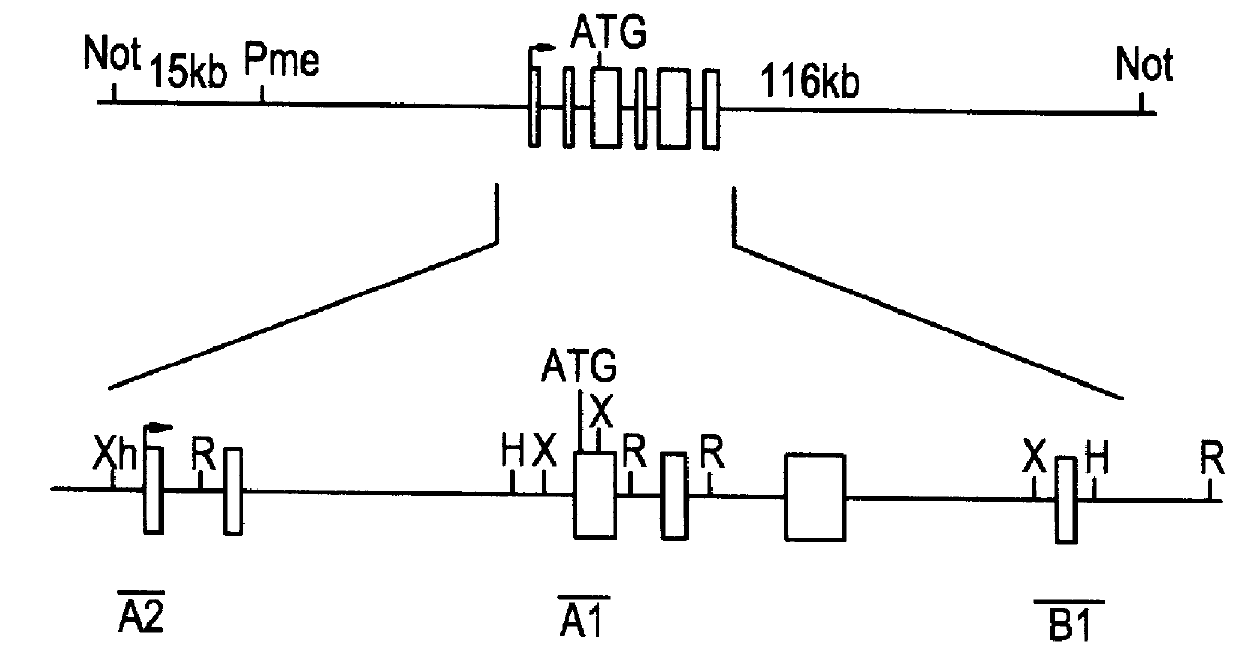
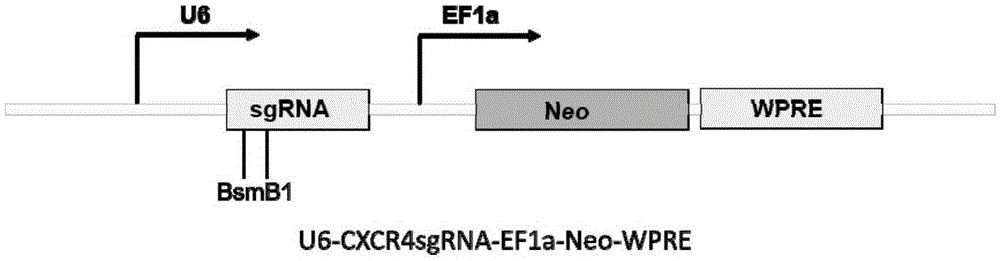
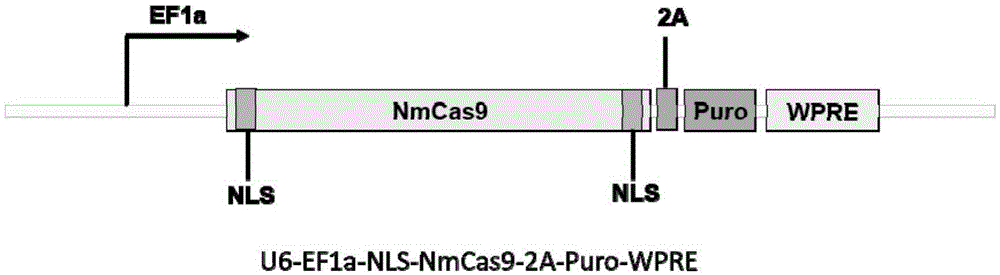
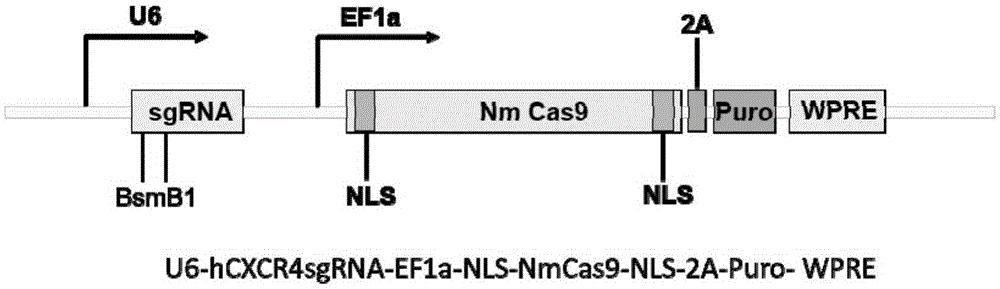
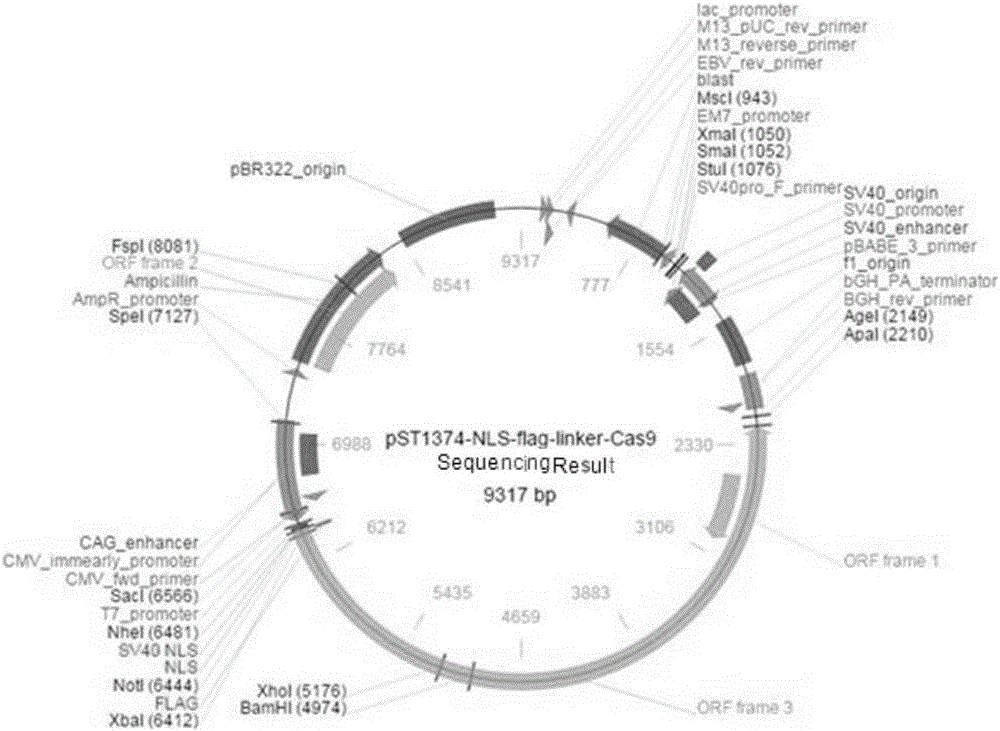
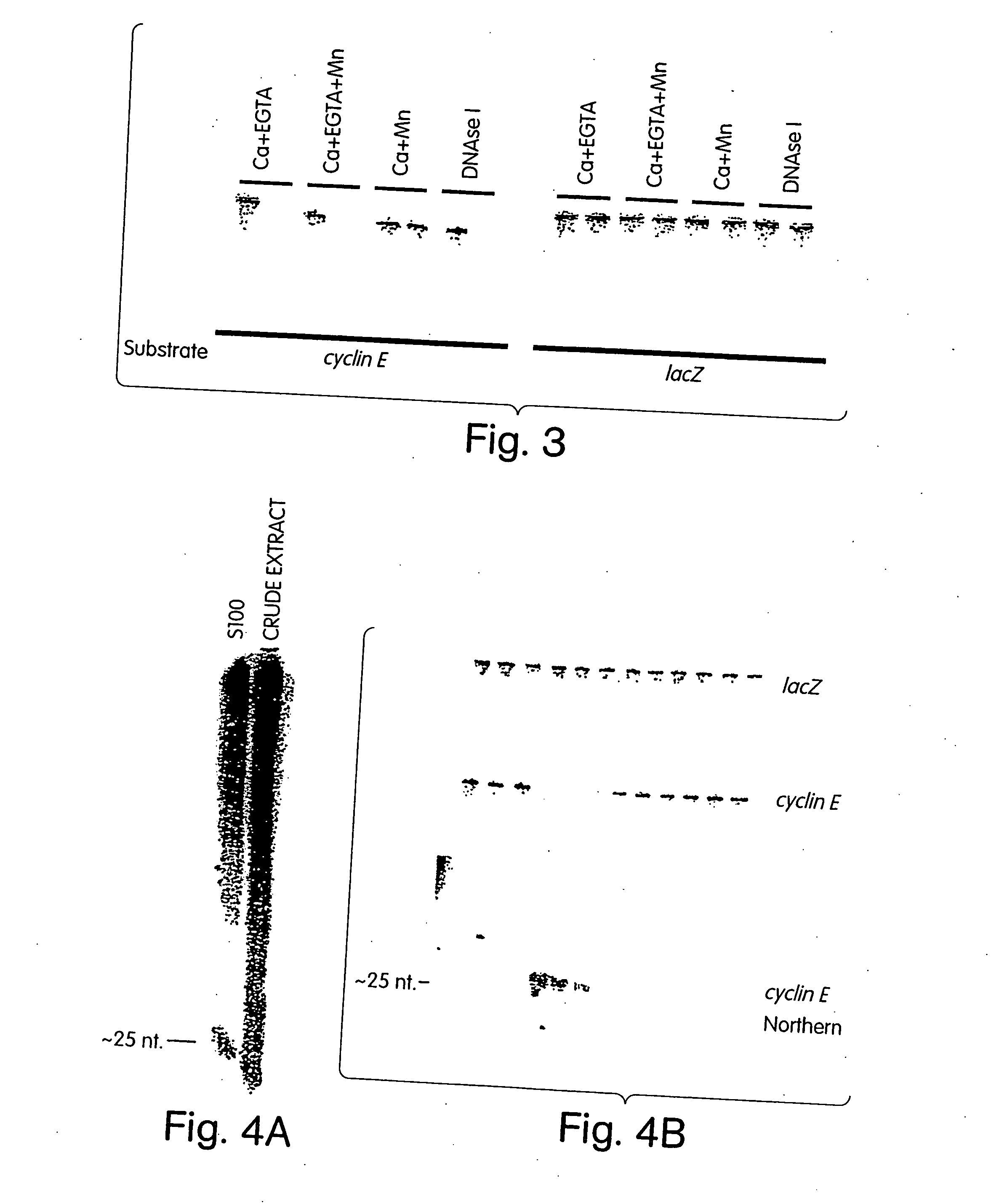
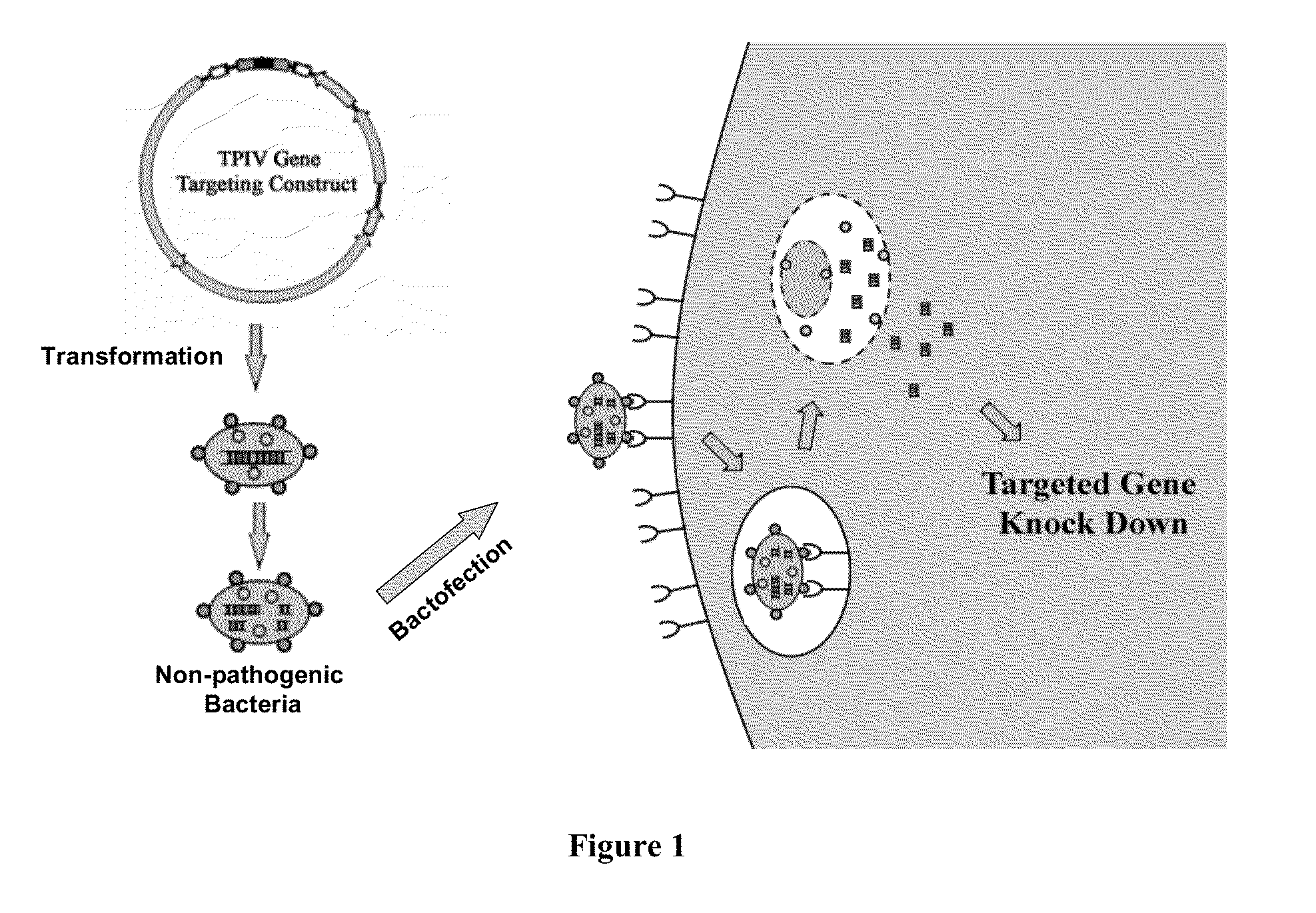
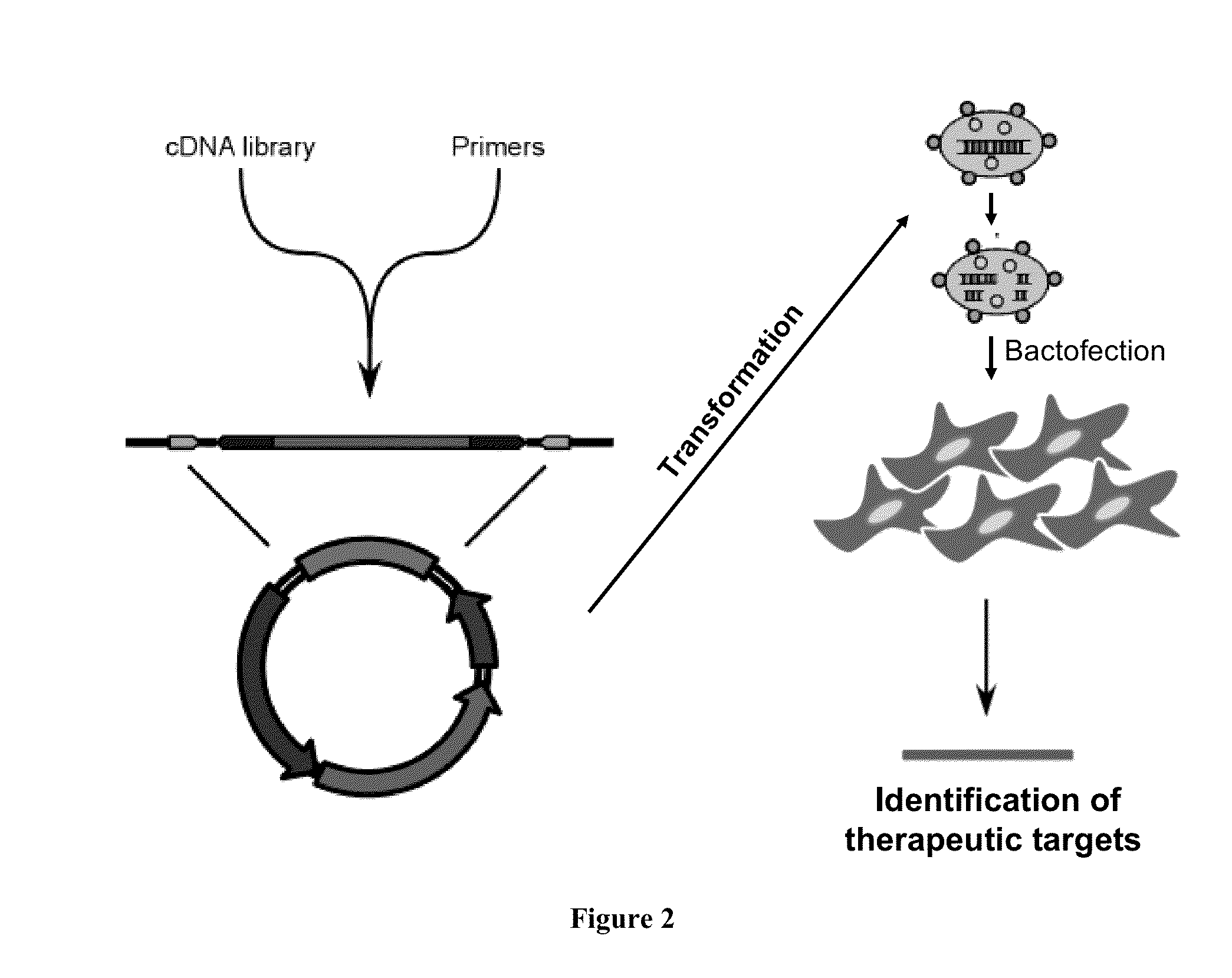
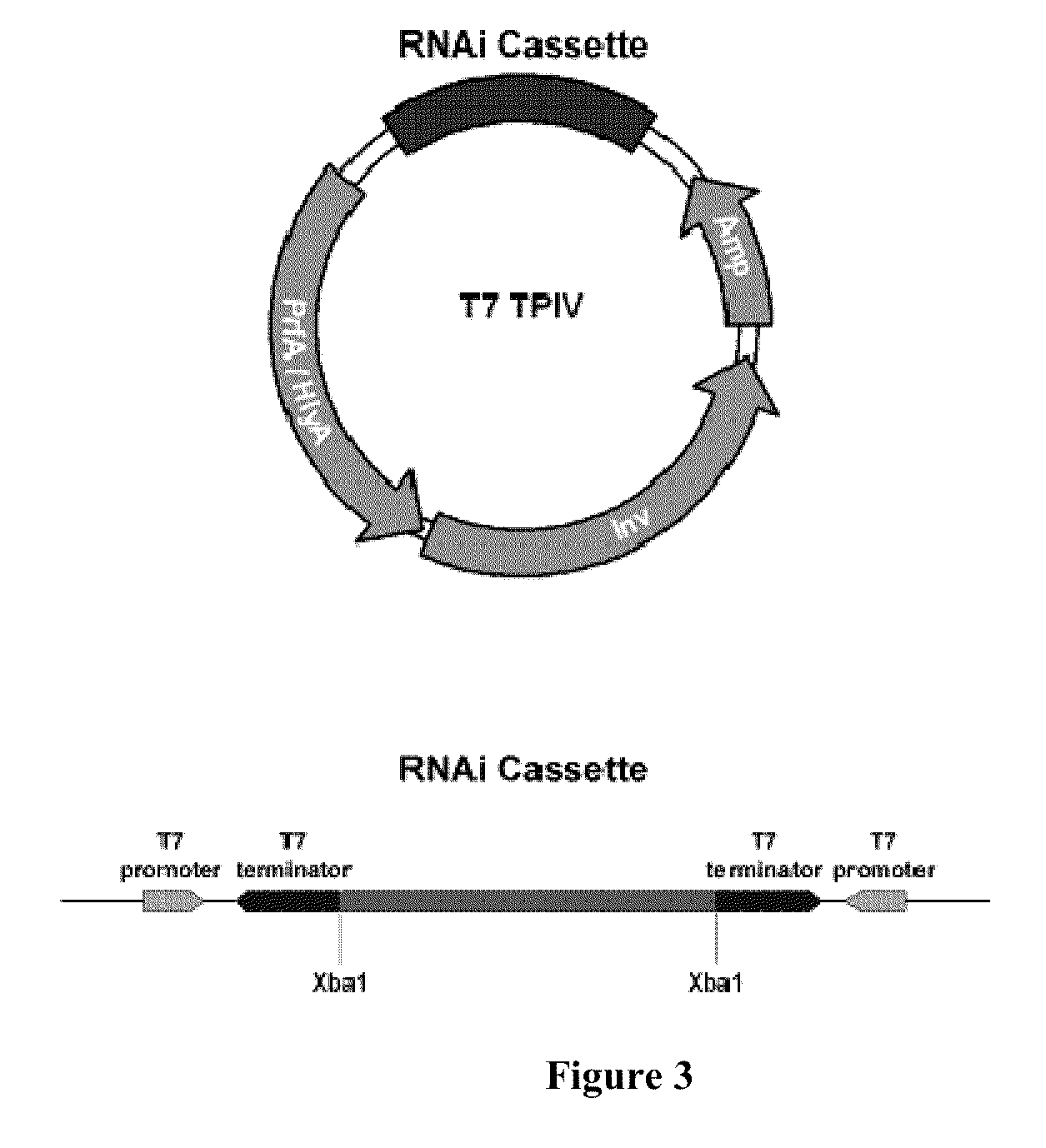
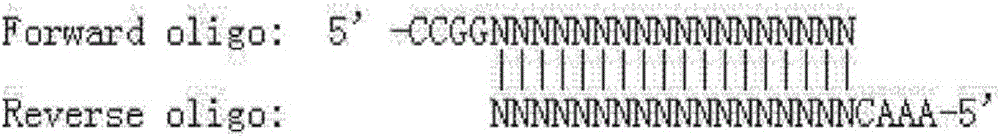Patents
Literature
602 results about "Gene targets" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Gene targeting. Gene targeting is a genetic technique that uses homologous recombination to change an endogenous gene. The method can be used to delete a gene, remove exons, add a gene, and introduce point mutations. Gene targeting can be permanent or conditional.
Use of chimeric nucleases to stimulate gene targeting
ActiveUS20050026157A1Ameliorate genetic disorderIncrease productionAntibacterial agentsFusion with DNA-binding domainGene targetsGenetic Change
Gene targeting is a technique to introduce genetic change into one or more specific locations in the genome of a cell. For example, gene targeting can introduce genetic change by modifying, repairing, attenuating or inactivating a target gene or other chromosomal DNA. In one aspect, this disclosure relates to methods and compositions for gene targeting with high efficiency in a cell. This disclosure also relates to methods of treating or preventing a genetic disease in an individual in need thereof. Further disclosed are chimeric nucleases and vectors encoding chimeric nucleases.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Gene targeting system
InactiveCN103224947AImprove the level ofHigh target shooting efficiencyVector-based foreign material introductionGene targetsZinc finger nuclease
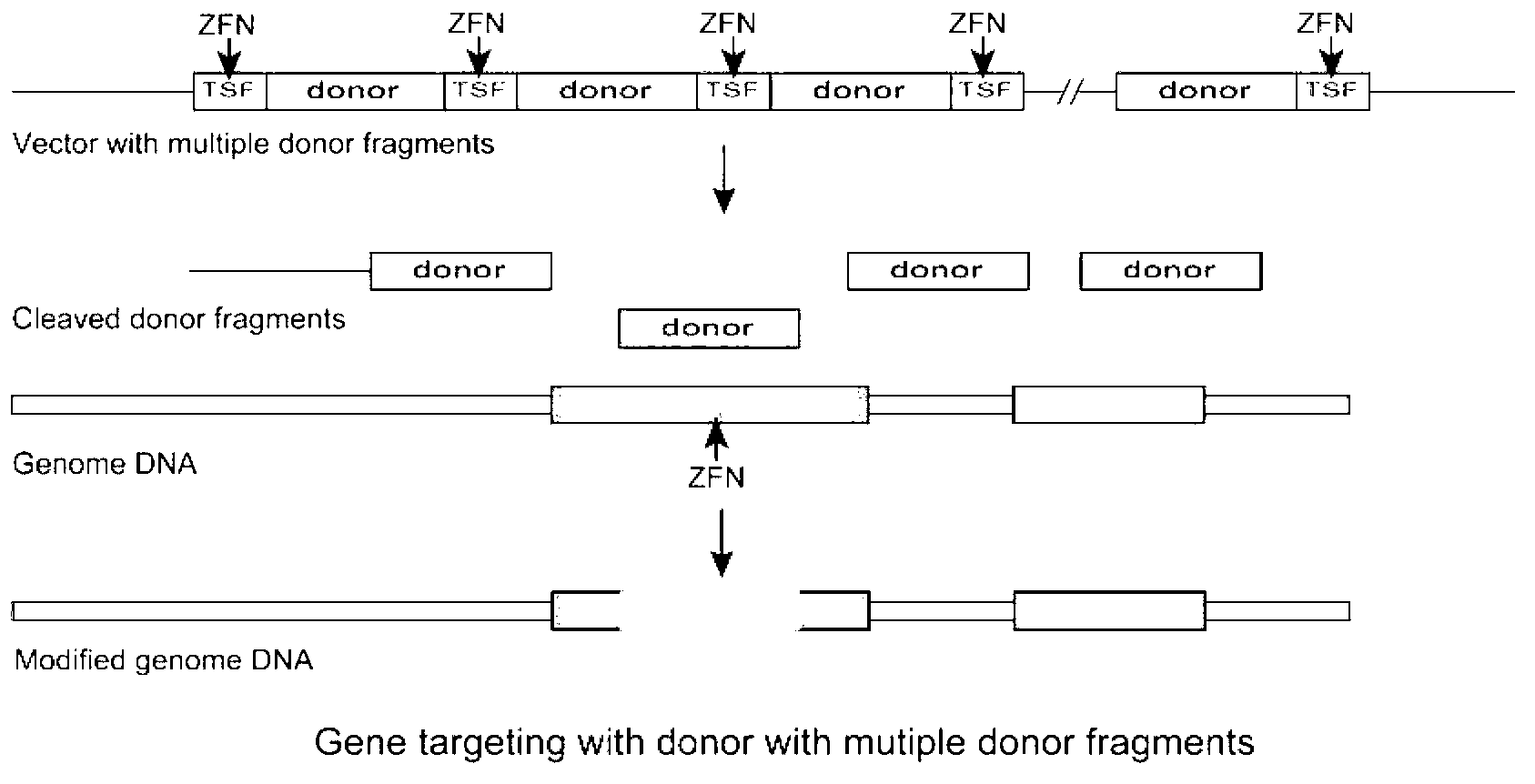
The invention relates to a gene targeting system, which comprises two parts such as a site-specific cleavage nuclease expression vector and a targeting vector, wherein the targeting vector contains 2-10 donor DNA fragments, 5' ends and 3' ends of every donor DNA fragment are respectively inserted into recognition sequences of the site-specific cleavage nuclease, the donor DNA comprises an upstream homologous arm, a downstream homologous arm and an exogenous DNA sequence positioned between the upstream homologous arm and the downstream homologous arm, and the site-specific cleavage nuclease expression vector is any one selected from an expression vector carrying zinc finger nuclease, a transcription activator-like effector nuclease expression vector, and a RNA-mediated nuclease RNA:Cas9 expression vector.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Diagnosis, prognosis and identification of potential therapeutic targets of multiple myeloma based on gene expression profiling
InactiveUS20080293578A1Microbiological testing/measurementAnalogue computers for chemical processesGene targetsGene model
Provided herein is a method for gene expression profiling multiple myeloma patients into distinct subgroups via DNA hybridization and hierarchical clustering analysis of the hybridization data where the results may further be used to identify therapeutic gene targets. Also provided is a method for controlling bone loss in an individual via pharmacological inhibitors of DKK1 protein. In addition provided herein is a method for diagnosing multiple myeloma using a 15-gene model that classifies myeloma into groups 1-7.
Owner:BIOVENTURES LLC
Multiple virus resistance in plants
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
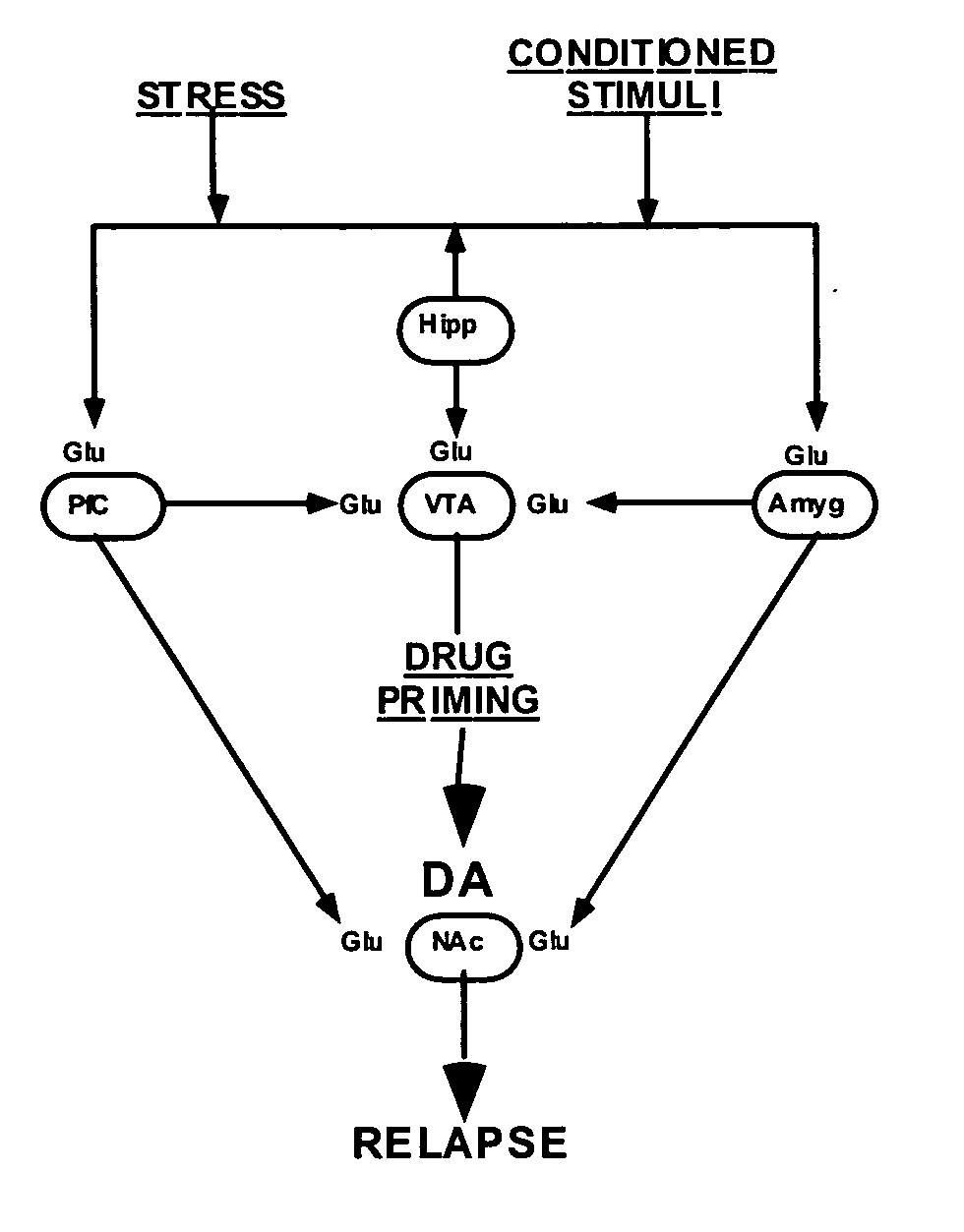
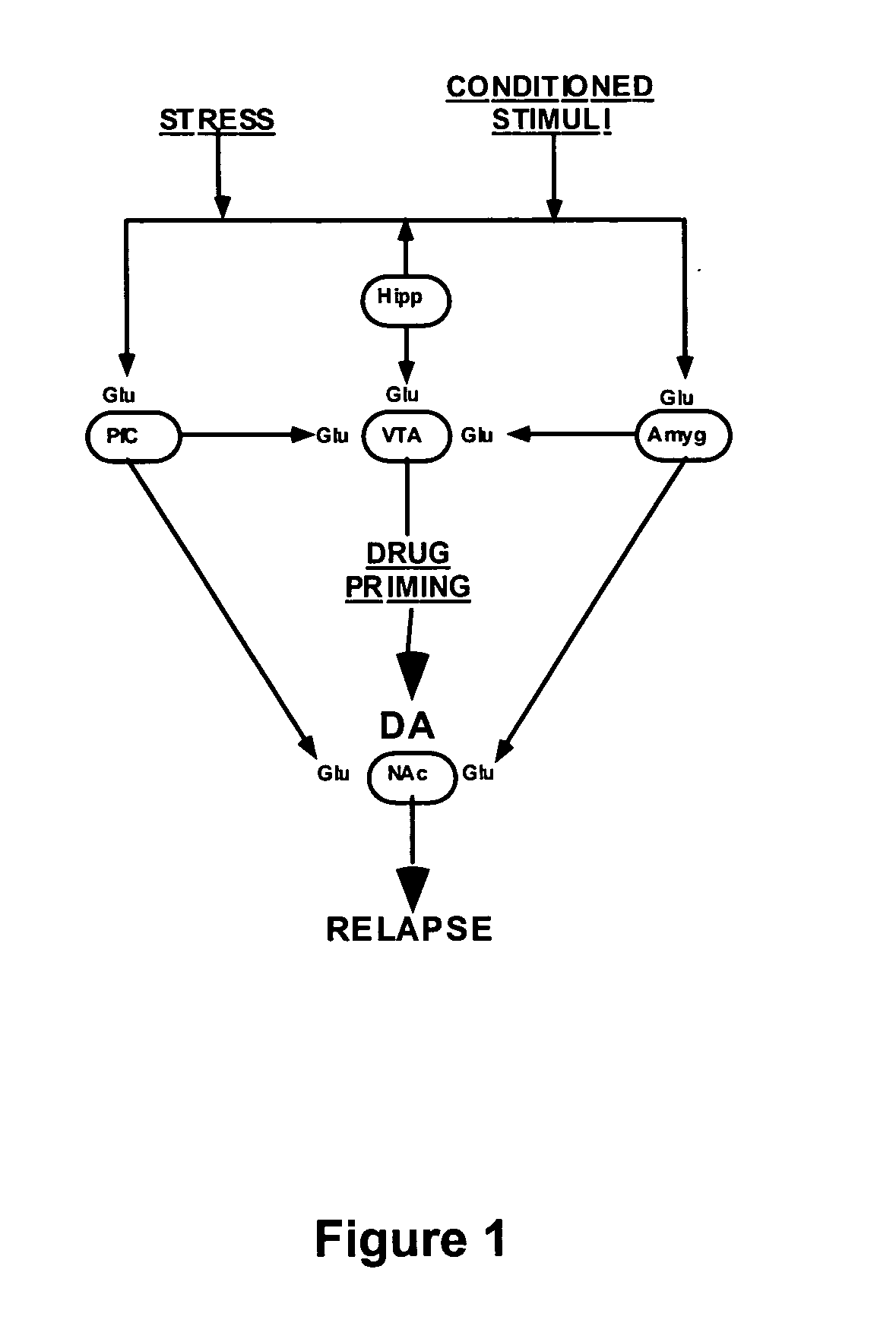
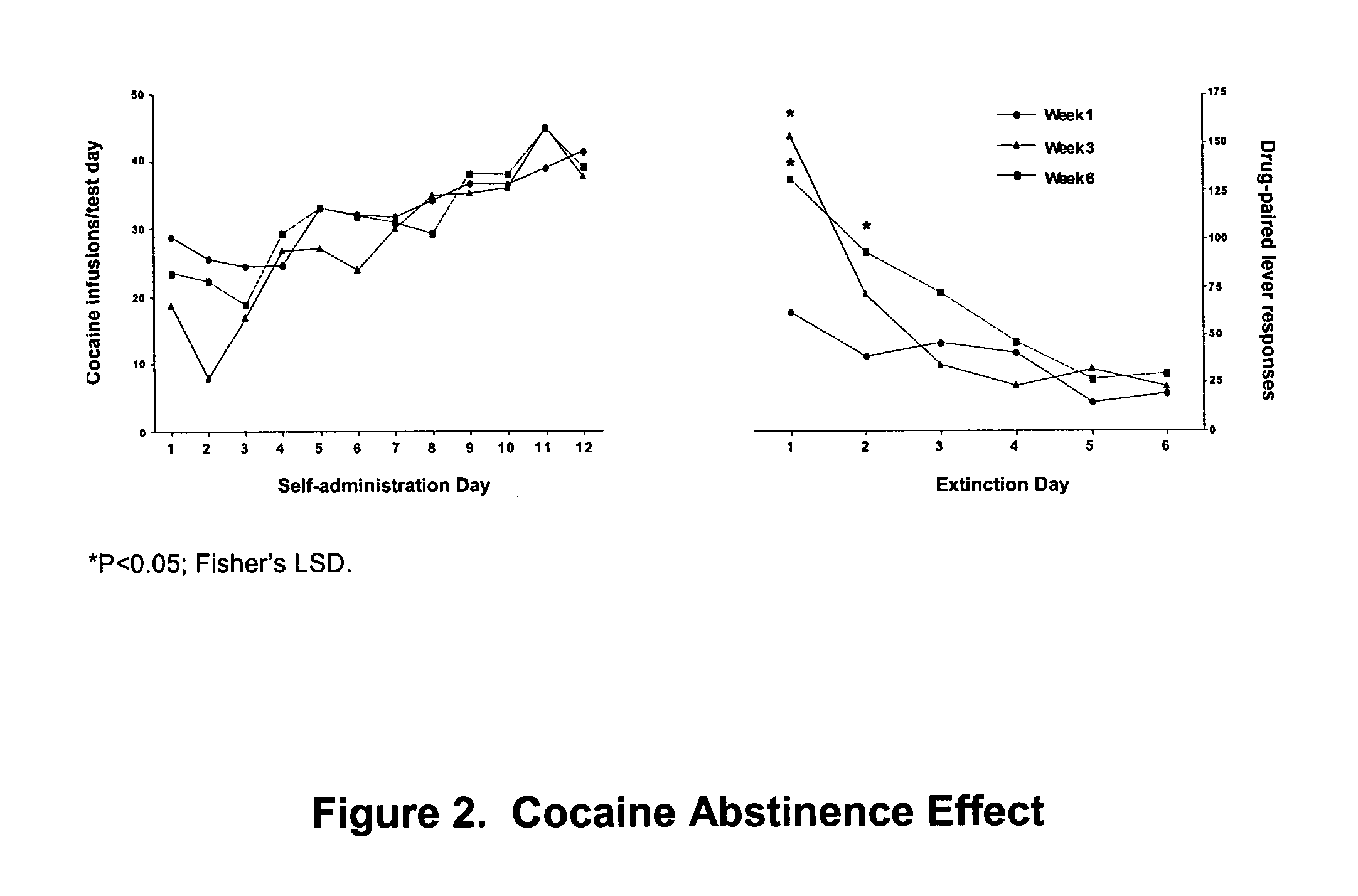
Methods for treating drug addiction
This invention describes gene targets for the development of therapeutics to treat drug addiction. Animal models of drug craving and relapse have been developed and used to find gene expression changes in key brain regions implicated in cocaine addiction. The genes whose expression levels are altered serve as pharmacological targets with the purpose of preventing or inhibiting cocaine craving and relapse in human cocaine addicts.
Owner:IRM
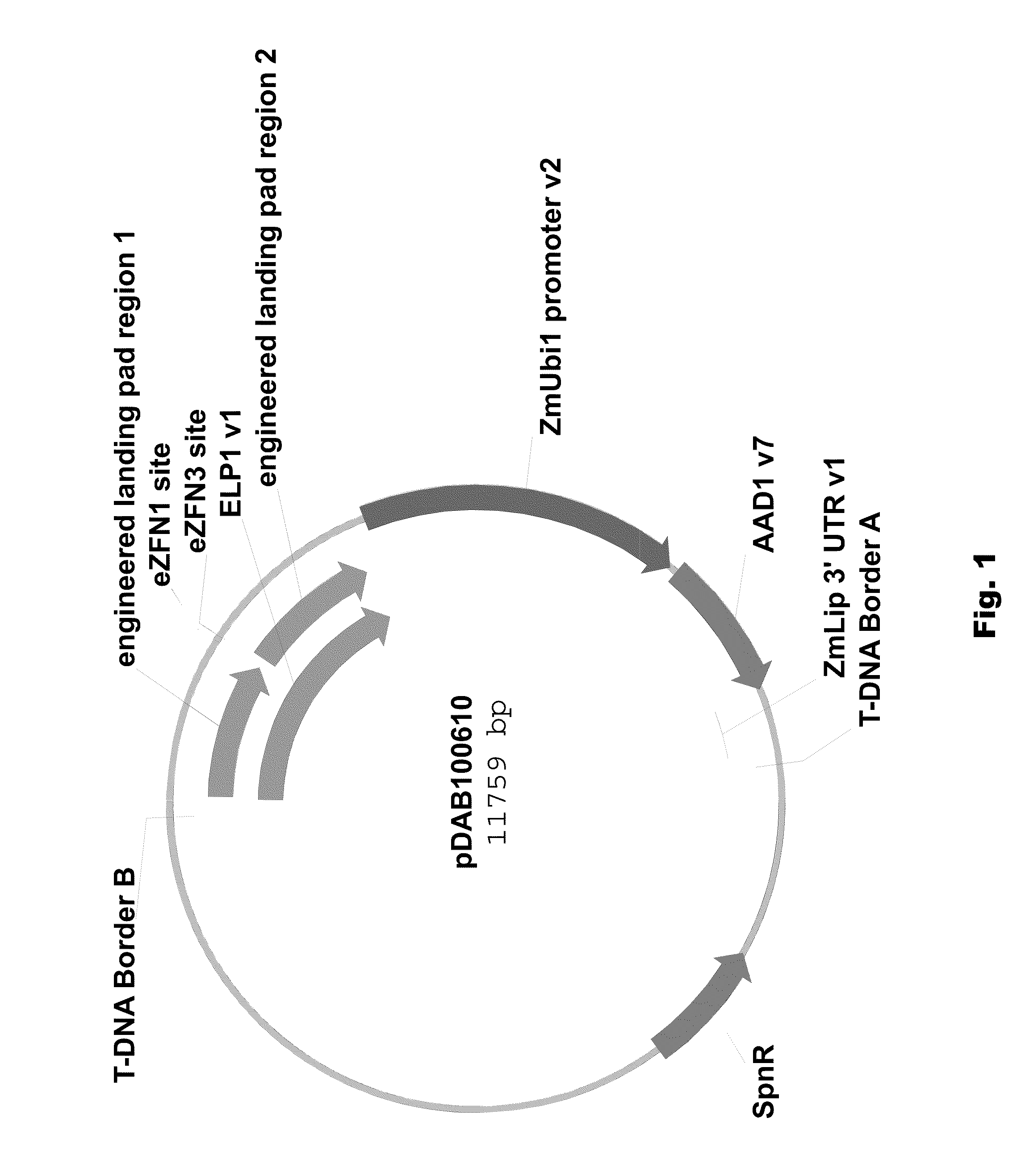
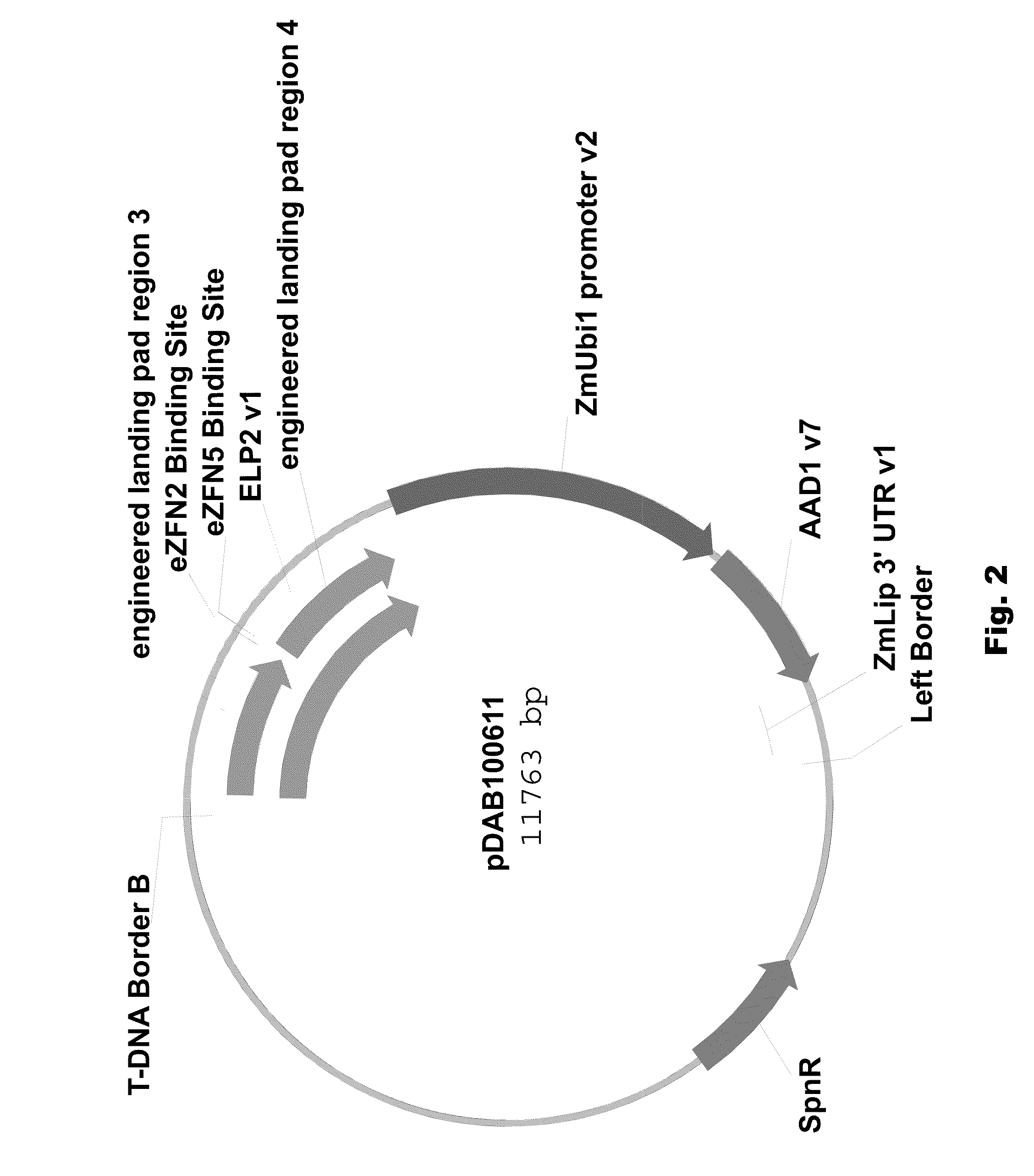
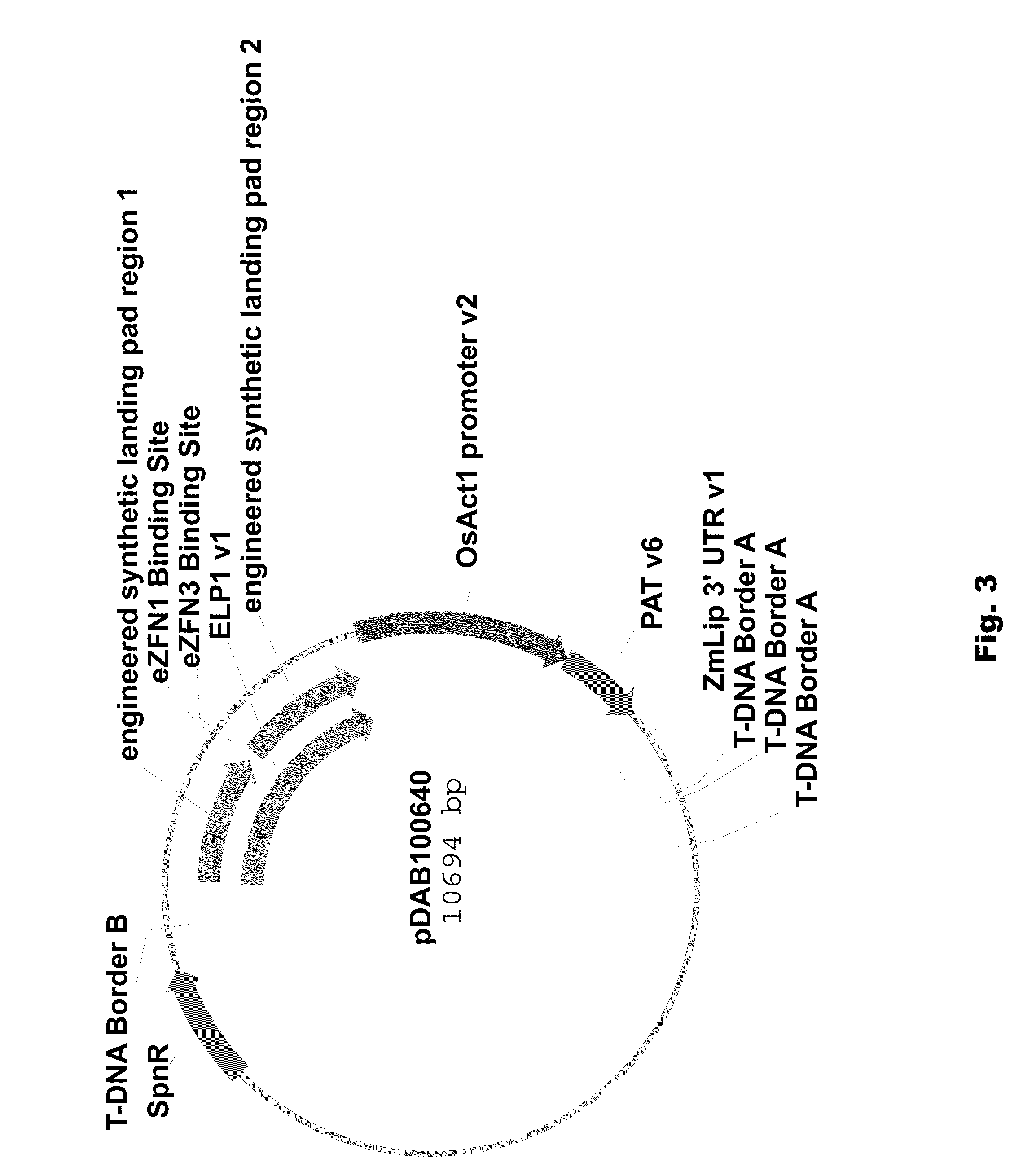
Engineered landing pads for gene targeting in plants
InactiveUS20110191899A1Reduce and eliminate needEasy to reorganizeOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationZinc finger nucleaseGene targets
A method for producing a transgenic plant includes providing a nucleic acid molecule comprising at least two regions of nucleic acid sequence that lack sequence homology with genomic DNA of the plant cell, and at least two zinc finger nuclease recognition sites, wherein the at least two regions of nucleic acid sequence that lack sequence homology with genomic DNA of the plant cell flank the at least two zinc finger nuclease recognition sites. A plant cell or tissue having the nucleic acid molecule stably integrated into the genome of the plant cell is transformed. A plant is regenerated from the plant cell. Transgenic plants are produced by the method. Seeds are produced by the transgenic plants.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
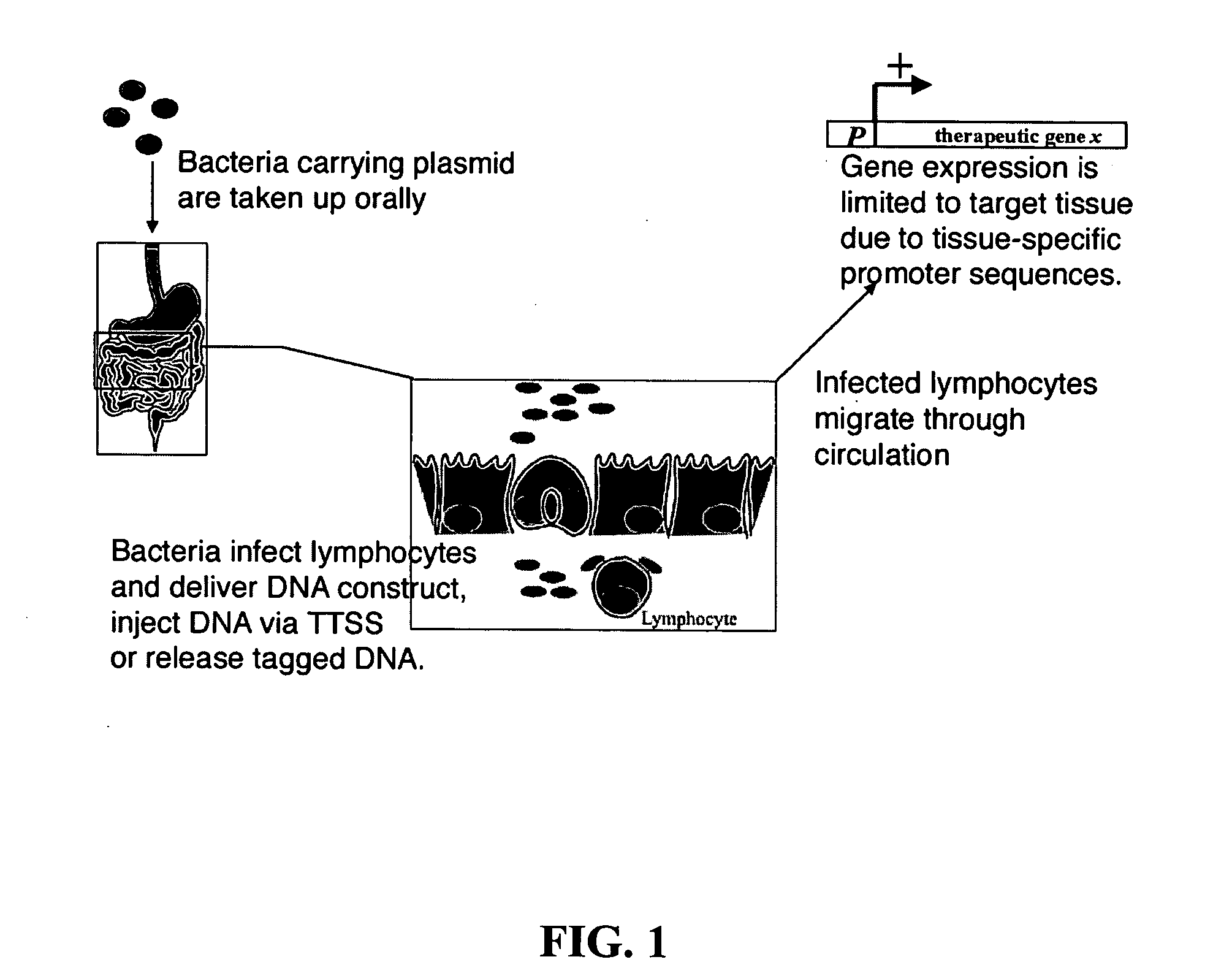
Bacterial vector systems
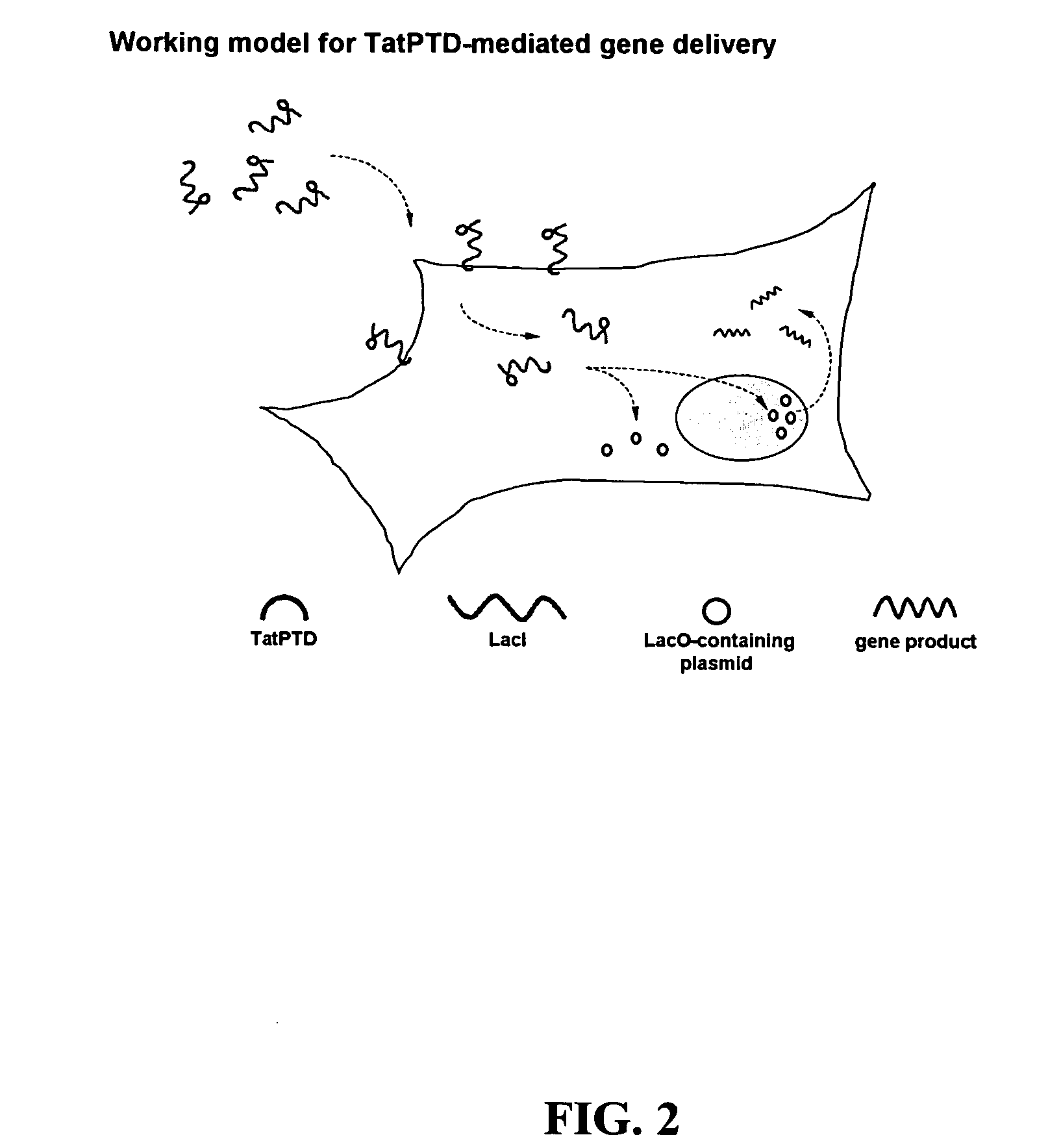
InactiveUS20060068469A1Efficient rapid deliveryFusion with DNA-binding domainBacteriaGene deliveryGene targets
The present invention provides bacterial vectors and fusion proteins containing a TTSS polypeptide, compositions of such fusion proteins including polynucleotides, and methods of delivering one or more genes into a target cell that involve contacting the cell with a composition that includes such a fusion protein. Compositions and methods of gene delivery that involve a bacterium and a TAT, Antp, or HSV VP22 polypeptide are also disclosed. The invention also concerns methods of delivering one or more genes into a target cell utilizing a bacterium capable of becoming internalized within the cell, wherein the bacterium includes one or more genes targeted for delivery to the cell, a gene encoding an RNA polymerase, and a gene that causes lysis of the bacterium.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
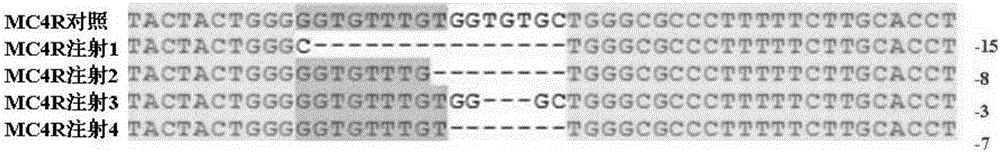
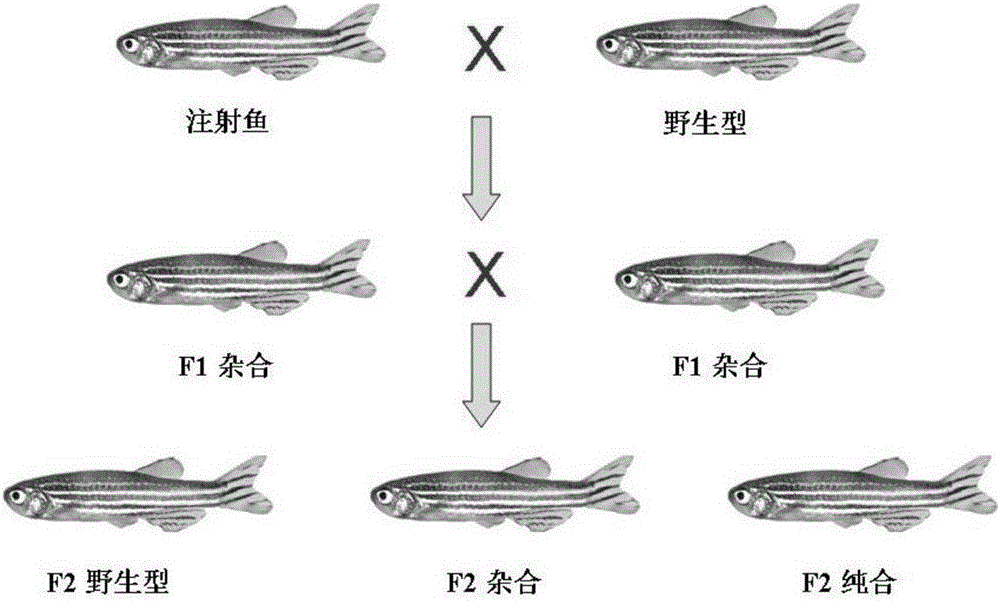
Breeding method for knocking out fish MC4R gene by using CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats)-Cas9 system
ActiveCN106191114AImprove accuracyLow costNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionGene targetsAcquisition time
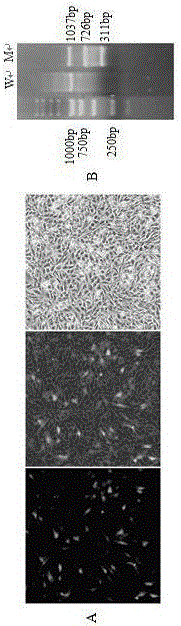
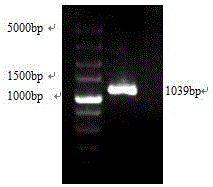
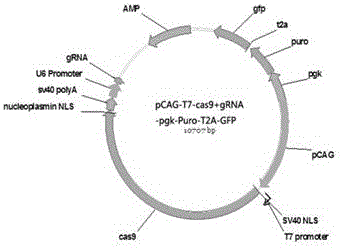
The invention provides a breeding method for knocking out fish MC4R gene by using a CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats)-Cas9 system. The method comprises the following steps: determination of MC4R gene targeted site, preparation of gRNA, in-vitro microinjection and knock-out verification, screening of MC4R-gene-knock-out fish, culture of hybrid fish, and the like. The breeding method is suitable for all commercial fishes, and can implement quick growth and breeding of fishes by knocking out the fish MC4R gene. Compared with the traditional breeding process, the method provided by the invention has the characteristics of high accuracy, low cost and short pure line acquisition time. Compared with the transgenic breeding, the gene knock-out can cause gene malfunction of the fish, and can not bring in any external gene, thereby avoiding the problem of transgenic safety.
Owner:CHONGQING INST OF GREEN & INTELLIGENT TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Directional knockout on sheep MSTN gene and detection method for influence thereof on myogenic differentiation
InactiveCN105821116ALow toxicityHigh targeted knockout efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisSide effectGene targeting
The invention discloses directional knockout on sheep MSTN gene by applying the CRISPR / Cas9 technology, and a method for verifying the impact effect of directional knockout on skeletal muscle satellite cell differentiation. The concrete contents are as follows: firstly, target gene cloning; secondly, gRBA design and synthesis; thirdly, CRISPR / Cas9 gene knockout vector construction; fourthly, CRISPR / Cas9 gene knockout vector exogenous activity detection; fifthly, CRISPR / Cas9 gene knockout vector endogenous activity detection; sixthly, CRISPR / Cas9 gene knockout vector knockout effect detection. The method has the following advantages: firstly, the experimental period is shorter; secondly, the method is simple and practicable, has high repeatability, and can be performed in common laboratories; thirdly, active vector constructed through the method is small in toxic and side effects, and can be applied to the preparation and production of transgenic animals; fourthly, the method is small in non-specific shear, and obviously improves the gene targeting knockout efficiency; fifthly, the method is high in applicability.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
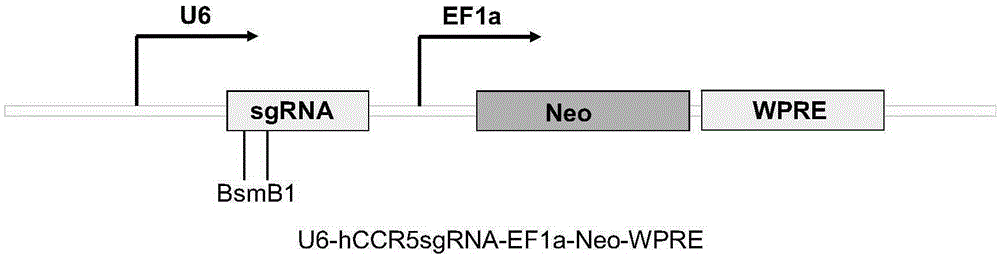
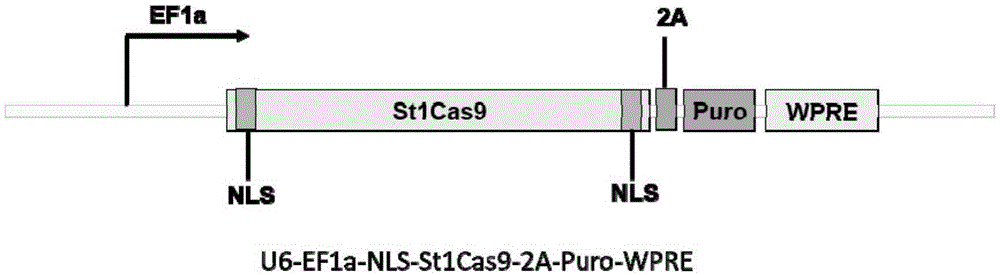
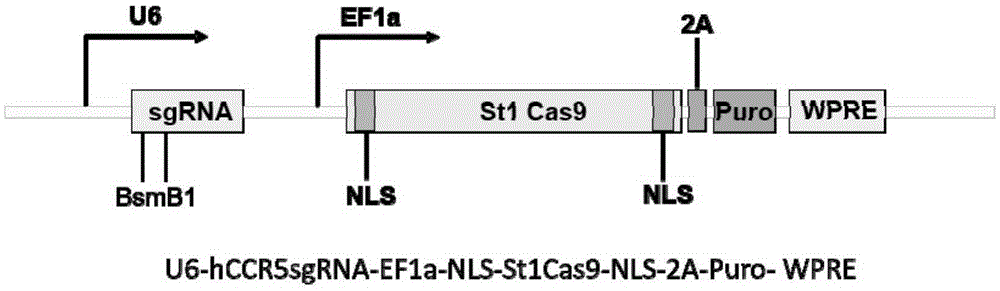
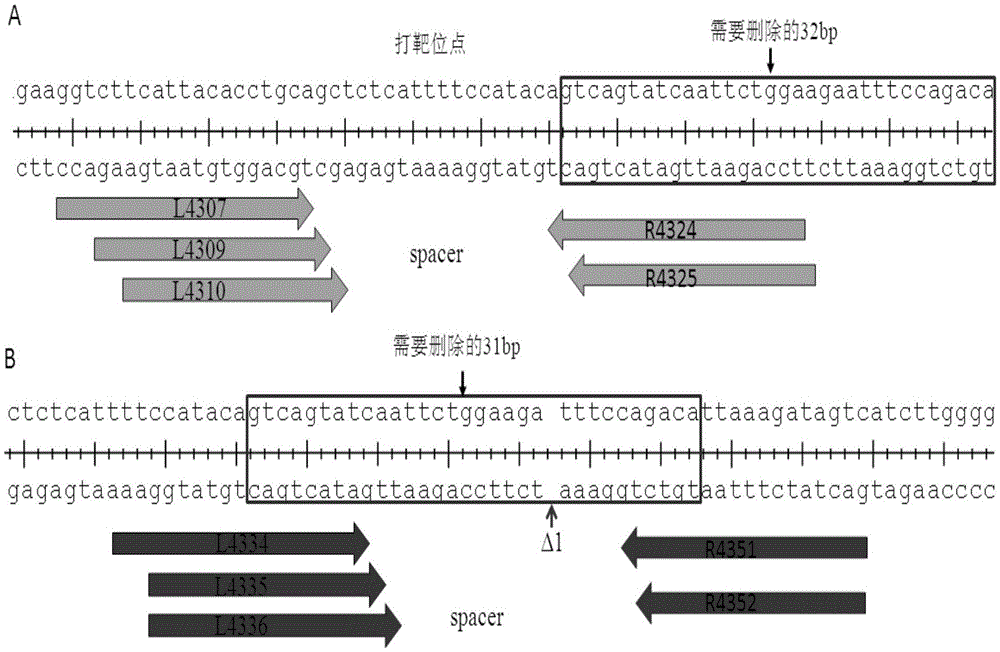
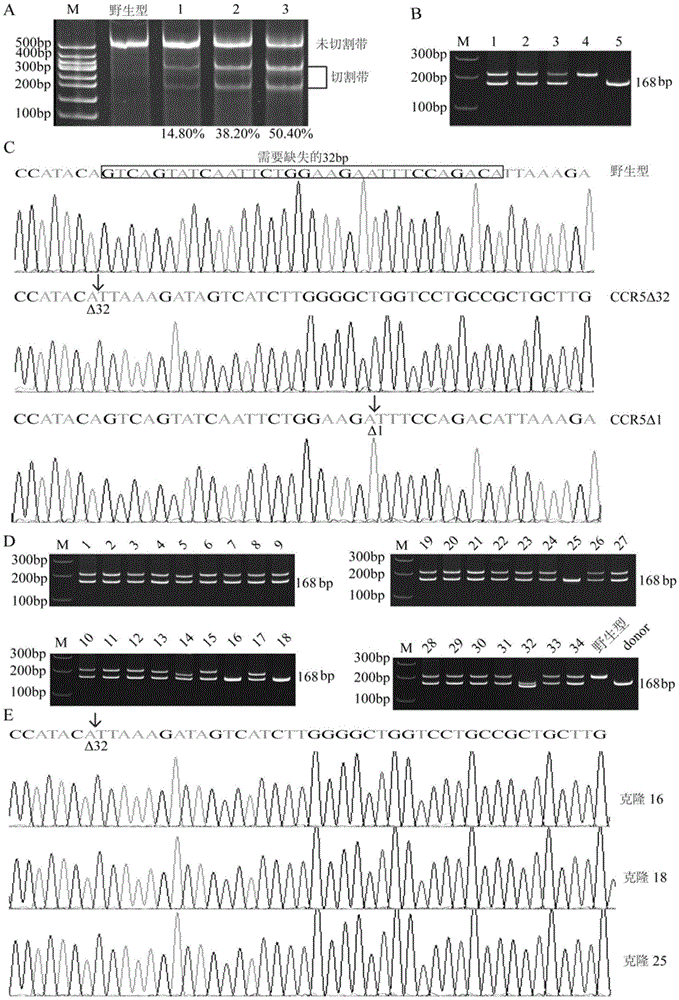
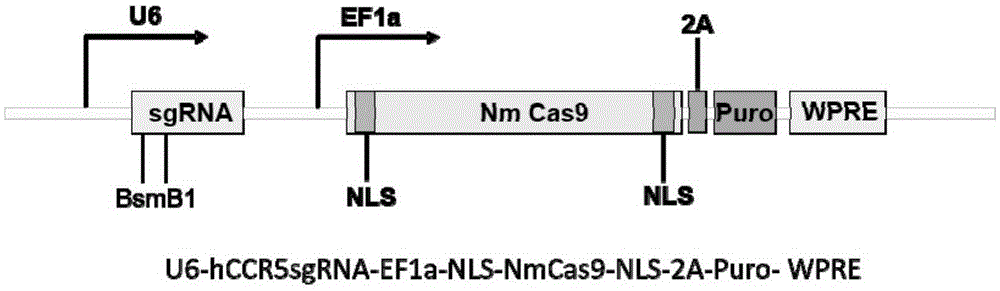
Human CCR5 gene target sequence recognized by streptococcus thermophilus CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat)-Cas9 (CRISPR-associated protein 9) system, sgRNA (single guide ribonucleic acid) and application
InactiveCN105331607AAchieve preventionAchieve therapeutic effectGenetic material ingredientsAntiviralsGene targetsA-DNA
Owner:张竞方
Method for precisely editing genome DNA sequence
InactiveCN105567734ASolve the problem that the fixed-point insertion of genes cannot be realizedSolve the characteristicsNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionGene targetsGene targeting
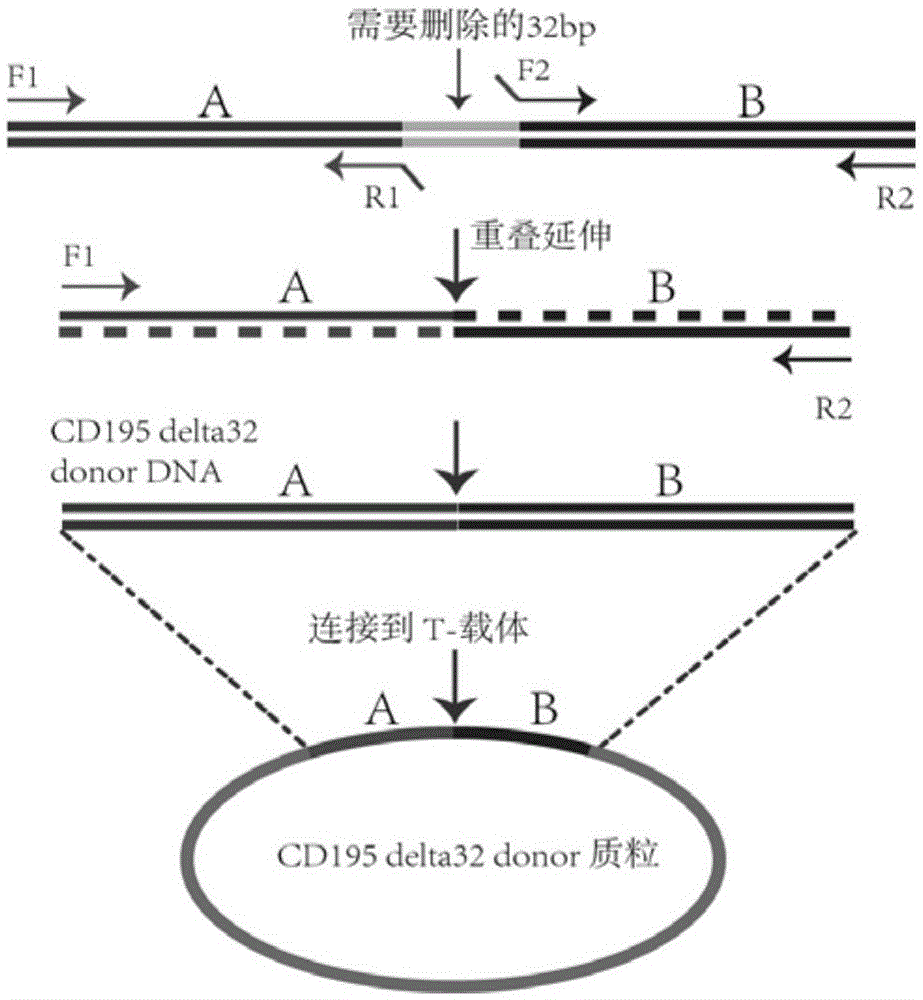
The invention provides a method for precisely editing a genome DNA sequence. A TALEN, CRISPR / Cas9 and other gene targeting technologies and homologous recombination technologies are utilized in a combined mode for precisely editing the genome DNA sequence. According to the method, the technical problem that in the prior art, a specific sequence cannot be deleted is solved, the specific base sequence can be seamlessly inserted or deleted in a fixed point mode, and seamless free modification of the genome DNA sequence of eukaryocyte is achieved for the first time.
Owner:WUHAN DANMIYOU BIOLOGICAL MEDICAL
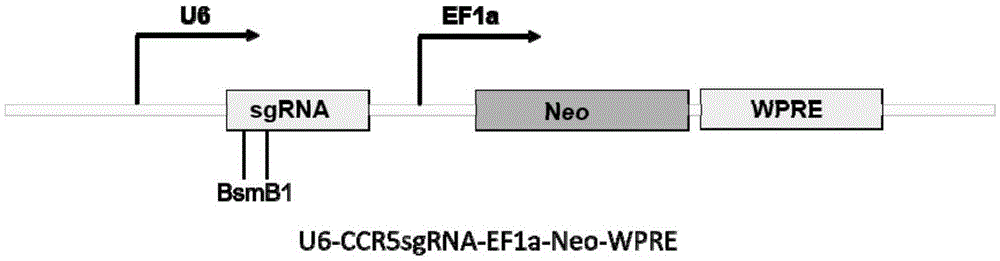
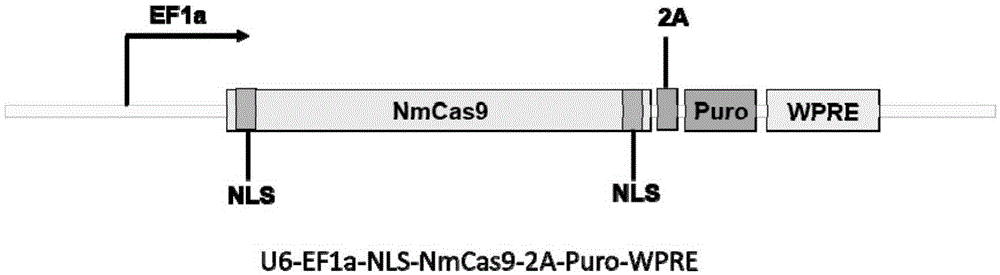
Human CCR5 gene target sequence identified by neisseria meningitidis CRISPR-Cas9 system, sgRNA and application of target sequence and sgRNA
InactiveCN105331609AAchieve preventionAchieve therapeutic effectOrganic active ingredientsHydrolasesGene targetsHIV receptor
The invention belongs to the field of gene engineering and discloses a target sequence identified by a CRISPR-Cas9 system from neisseria meningitidis. The target sequence is as shown in the nth-24th sites of optional one of SEQ ID No. 1-20, and n=1-9. The invention further discloses sgRNA and coding DNA molecules thereof, the sequence of the sgRNA is 5'-identificiation sequence-sequence recruiting Cas9 protein-3', and the DNA sequence corresponding to the identification sequence is identical with the target sequence. The invention also discloses the CRISPR-Cas9 system which comprises the Cas9 protein, the sgRNA and / or a coding sequence carrying the Cas9 protein and a vector of the coding sequence of the sgRNA. The invention also discloses application of the CRISPR-Cas9 system to editing of CCR5 genes and preparation of medicine for HIV infection. By the CRISPR-Cas9 system, the CCR5 genes can be edited, and cells cannot be infected by HIV.
Owner:张竞方
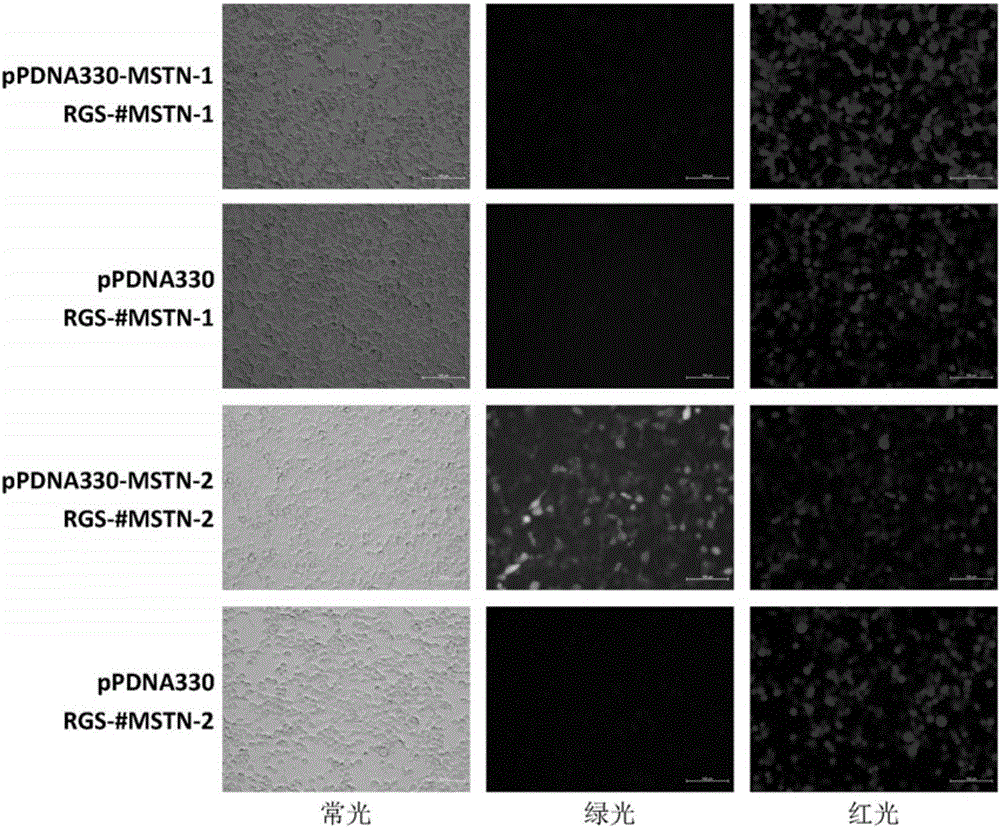
Method for knocking out MSTN (myostatin) genes in targeted manner by utilizing CRISPR-Cas9
InactiveCN106119283AImprove universalityReduced editing efficiencyNucleic acid vectorReceptors for growth factors/regulatorsMyostatinDouble strand
The invention discloses a method for knocking out MSTN (myostatin) genes in a targeted manner by utilizing CRISPR-Cas9. According to the method, multiple species are subjected to homology comparison, two pairs of MSTN gene target sequences are selected, two pairs of DNA double strands which have the sequences different from the target sequences, the same expression protein and the same BsmBi sticky ends are synthesized according to the design principle of PAM of gRNA, the double strands are connected with pPDNA330 plasmids, a recombinant vector carrying MSTN homologous genes of multiple species is obtained and is used for detecting the gene knockout efficiency with a fluorescent protein expression method, carrier-transfected receptor cells, having higher knockout efficiency, of multiple species are selected, gene knockout and verification are performed, and simple, efficient and accurate gene knockout on the MSTN genes of the multiple species is completed.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHUANG AUTONOMOUS REGION BUFFALO INST
Site-specific insertional inactivation method and application mediated by agrobacterium tumefaciens and CRISPR/Cas9
ActiveCN106434651ASpecify the direction of insertionRealize fixed-point insertionPeptidesNucleic acid vectorGenomicsMobile DNA
The invention discloses a site-specific insertional inactivation method mediated by agrobacterium tumefaciens and CRISPR / Cas9. Endogenous snRNA promoter of Ustilago scitaminea (u6 promoter of Ustilago scitaminea) is used to drive sgRNA expression cassette. CRISPR / Cas9 system integrates with Ti plasmid of agrobacterium tumefaciens to construct the Ustilago scitaminea site-specific insertional inactivation system mediated by agrobacterium tumefaciens with hygromycin as a selection marker. Specific sequence of the objective gene is cloned into sgRNA expression cassette for transformation of Ustilago scitaminea basidiospores, thus the mobile DNA fragment is exactly inserted into the objective gene sequence of Ustilago scitaminea, achieving the goal of damage to gene function. The invention provides an important tool for study of Ustilago scitaminea functional genomics. The system has the advantages of high efficiency and accuracy, and is convenient to use to conduct gene function researches in Ustilago scitaminea.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Method for improving gene targeting efficiency and method for carrying out in-situ repair on base on beta-globulin gene locus
InactiveCN106244555AShorten the construction experiment cycleHigh miss rateNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionGene targetsGene Modification
The invention provides a method for improving the gene targeting efficiency and a method for carrying out in-situ repair on the base on a beta-globulin gene locus. The method for improving the gene targeting efficiency comprises the following steps of: S10, determining a gene locus to undergo in-situ repair; and S20, introducing a CRISPR / Ca system to cleave editing lotus DNA to cause DNA damage and simultaneously providing a repair template segment. Based on the deficiency of existing gene modification, the gene modification efficiency, the timeliness and the modification quality are improved after single-stranded oligonucleotides (ss ODNs) and a small molecule compound participate in a CRISPR / Cas9 gene modification system.
Owner:THE THIRD AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Methods of performing homologous recombination based modification of nucleic acids in recombination deficient cells and use of the modified nucleic acid products thereof
A simple method for modifying genes in a recombination deficient host cell is disclosed. Such modifications include generating insertion, deletions, substitutions, and / or point mutations at any chosen site in the independent origin based cloning vector. The modified gene can be contained in an independent origin based cloning vector that is used to introduce a modified heterologous gene into a cell. Such a modified vector may be used in the production of a germline transmitted transgenic animal, or in gene targeting protocols in eukaryotic cells.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Human CXCR4 gene target sequence identified by neisseria meningitidis CRISPR-Cas9 system, sgRNA and application of target sequence and sgRNA
InactiveCN105331608AAchieve preventionAchieve therapeutic effectOrganic active ingredientsHydrolasesGene targetsRecognition sequence
The invention belongs to the field of gene engineering and discloses a target sequence identified by a CRISPR-Cas9 system from neisseria meningitidis. The target sequence is as shown in the nth-24th sites of optional one of SEQ ID No. 1-15, and n=1-9. The invention further discloses sgRNA and coding DNA molecules thereof, the sequence of the sgRNA is 5'-identificiation sequence-sequence recruiting Cas9 protein-3', and the DNA sequence corresponding to the identification sequence is identical with the target sequence. The invention also discloses the CRISPR-Cas9 system which comprises the Cas9 protein, the sgRNA and / or a coding sequence carrying the Cas9 protein and a vector of the coding sequence of the sgRNA. The invention also discloses application of the CRISPR-Cas9 system to editing of CXCR4 genes and preparation of medicine for HIV infection. By the CRISPR-Cas9 system, the CXCR4 genes can be edited, and cells cannot be infected by HIV.
Owner:张竞方
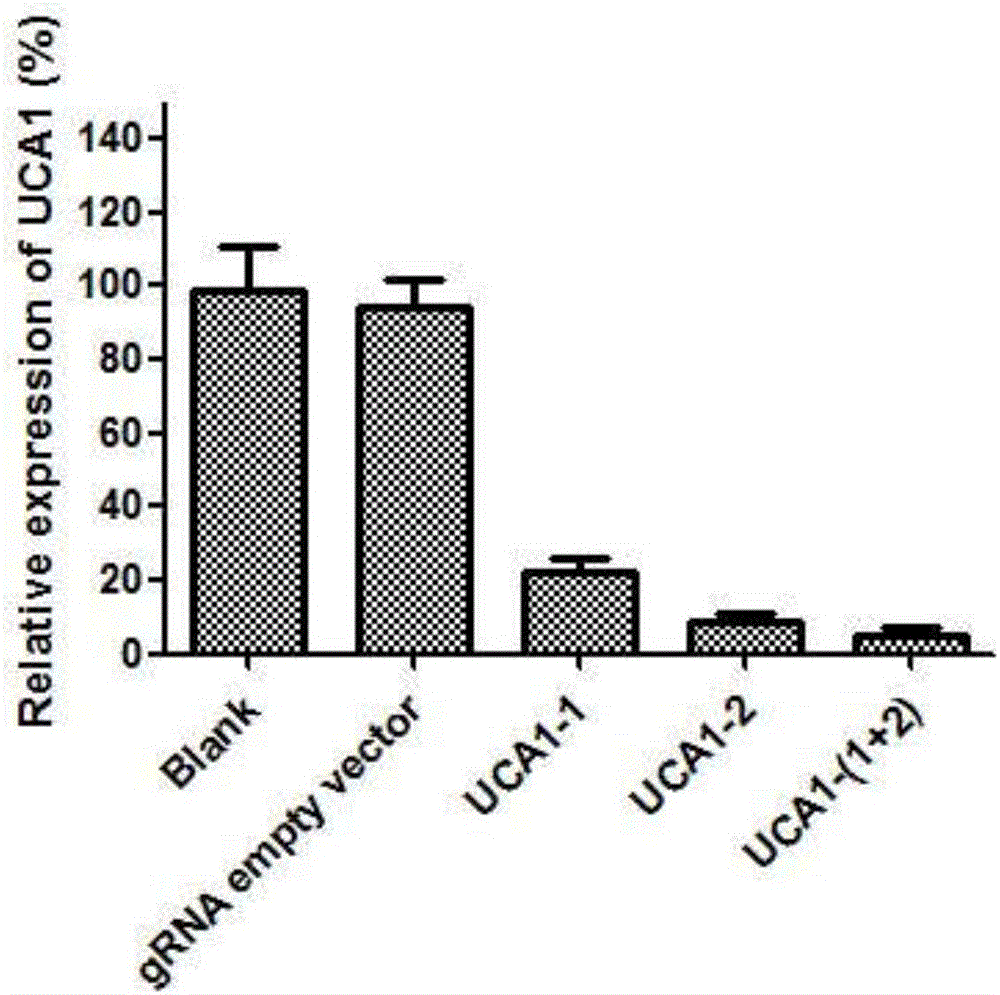
sgRNA and gene vector for inhibiting bladder cancer by targeting human lncRNA-UCA1 and application of sgRNA
ActiveCN106399306AImprove targetingGrowth inhibitionOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsCancer cellEukaryotic plasmids
The invention provides sgRNA and a gene vector for inhibiting bladder cancer by targeting human lncRNA-UCA1 and an application of the sgRNA; specifically, sgRNA sequences of an lncRNA-UCA1 gene and a PD-1 gene suitable for CRISPR-Cas9 targeted splicing are designed; by transforming plasmids of specific splicing lncRNA-UCA1 gene and CRISPR-Cas9 nuclease gene into human bladder cancer cells, the expression of the lncRNA-UCA1 gene drops so as to inhibit the growth of tumor cells; and the plasmid, together with a human PD-1 gene targeted knockout vector, is transformed into a humanized mouse model of bladder cancer transplanted tumor, so as to obviously inhibit the growth of tumors. According to the invention, the vector is simple in preparing steps, the sgRNA is good in targeting property and the CRISPR-Cas9 is high in knockout efficiency.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF XIAN JIAOTONG UNIV
Methods and compositions for RNA interference
InactiveUS20060135456A1Avoid complicationsDecrease and eliminates MHC expressionOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsGene targetsNucleotide
The present invention provides methods for attenuating gene expression in a cell, especially in a mammalian cell, using gene-targeted double stranded RNA (dsRNA), such as a hairpin RNA. The dsRNA contains a nucleotide sequence that hybridizes under physiologic conditions of the cell to the nucleotide sequence of at least a portion of the gene to be inhibited (the “target” gene).
Owner:COLD SPRING HARBOR LAB INC
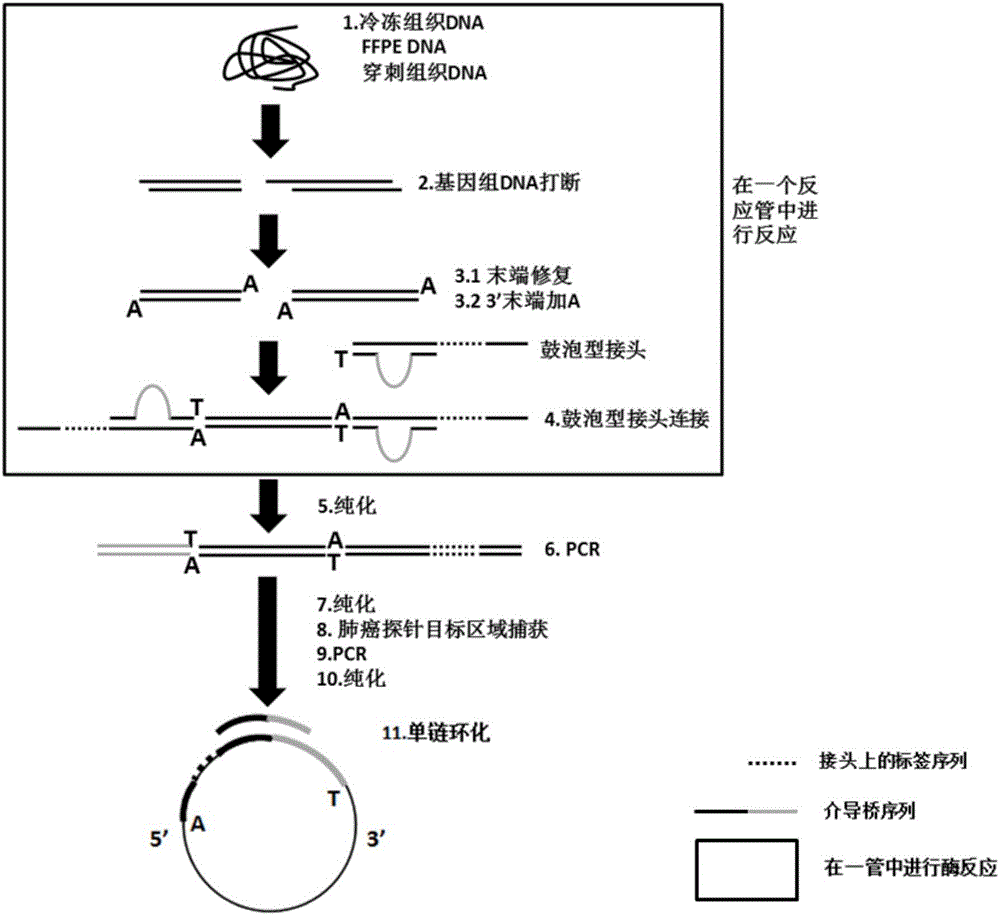
Building method of library for detecting non-small cell lung cancer gene mutation and kit
PendingCN106497920AImprove recycling efficiencyImprove utilization efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationGene targetingGene mutation
The invention discloses a building method of a library for detecting non-small cell lung cancer gene mutation and a kit. The method includes: using tubular reaction to complete genome DNA breaking and connector connection, performing hybrid capture on connection products after amplification and non-small cell lung cancer related gene target area probes, and performing BGISEQ-500 / 1000 platform sequencing and data analysis to obtain mutation conditions. The method has the advantages that the experiment flow is optimized greatly by the tubular reaction, operation complexity and time are reduced, and the requirements on clinical sample initial amount are lowered; multiple genes and multiple sites can be detected in one step, point mutation, insertion and deletion, structural variation and copy number variation are covered, the detecting result is accurate and overcomes the defect that a PCR capture method cannot detect the structural variation in one step, and the effectiveness of the high-throughput sequencing applied to the detection of the non-small cell lung cancer gene mutation; the method is wide in coverage, high in cost performance, capable of providing a reference basis for the diagnosing, treatment and drug use performed by doctors, and the method is suitable for being popularized and used in a large-scale manner.
Owner:BGI BIOTECH WUHAN CO LTD
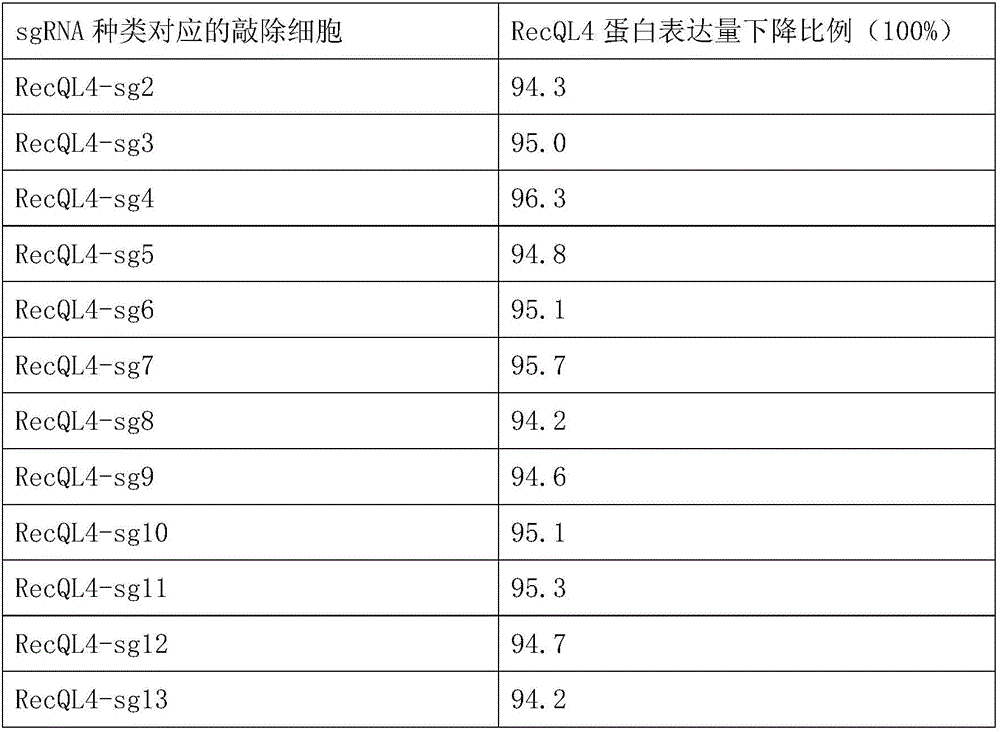
CRISPR-Cas9 system and application therefore in treating breast cancer diseases
ActiveCN106191071AThe identification rules are simpleEasy to analyzeOrganic active ingredientsNucleic acid vectorDiseaseGene targets
The invention provides a CRISPR-Cas9 system and an application thereof in treating breast cancer diseases, wherein by providing a plurality of sgRNAs (single guide RNAs), the efficient knockout of an RecQL4 gene can be achieved. In comparison with ZFNs and TALENs complex expression structures, siRNA is low in using complexity and efficiency; a Cas9 expression structure in the CRISPR-Cas9 system is fixed; for different genes, system building can be completed by interpolating recognition sequences into the sgRNA expression structure, so that operations are simplified and cost is reduced; and the system is applicable to mammal gene targeting in a large scale.
Owner:广东龄值生物科技有限公司
Artificial fixed-point rice dense and erect panicle (DEP1) gene mutant body and application thereof
The invention discloses an artificial fixed-point rice dense and erect panicle (DEP1) gene mutant body and application thereof. The rice DEP1 gene mutant body as well as a corresponding allele is obtained by modifying a 5th exon of a DEP1 gene by adopting a CRISPR / Cas9 gene targeting modification technology, so that a base of the 5th exon is replaced, lost and inserted. The artificial fixed-point rice DEP1 gene mutant body and the application thereof disclosed by the invention have the benefits that the artificial mutation is performed on the 5th exon of the rice DEP1 gene by adopting the CRISPR / Cas9, and the mutant body capable of obviously improving the rice yield and the allele are screened; the DEP1 gene mutant body disclosed by the invention as well as the corresponding allele can improve the yield of rice plants by 13-51 percent and is even superior to a natural mutation type.
Owner:云南纳博生物科技有限公司
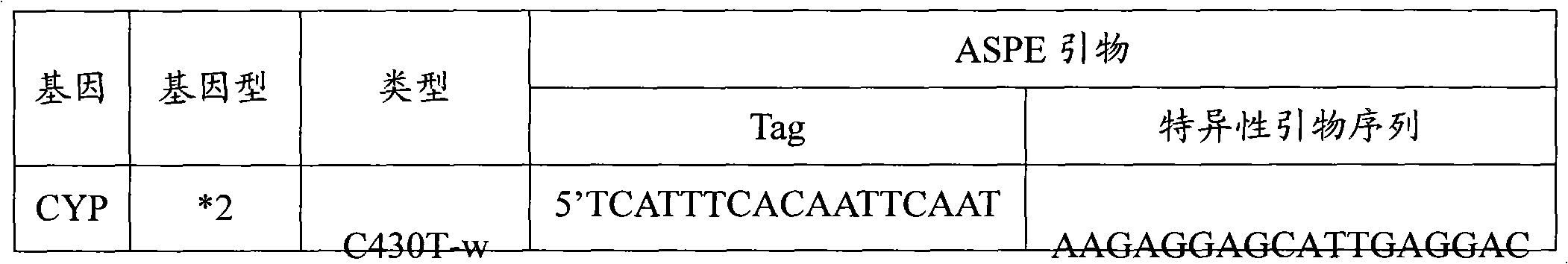
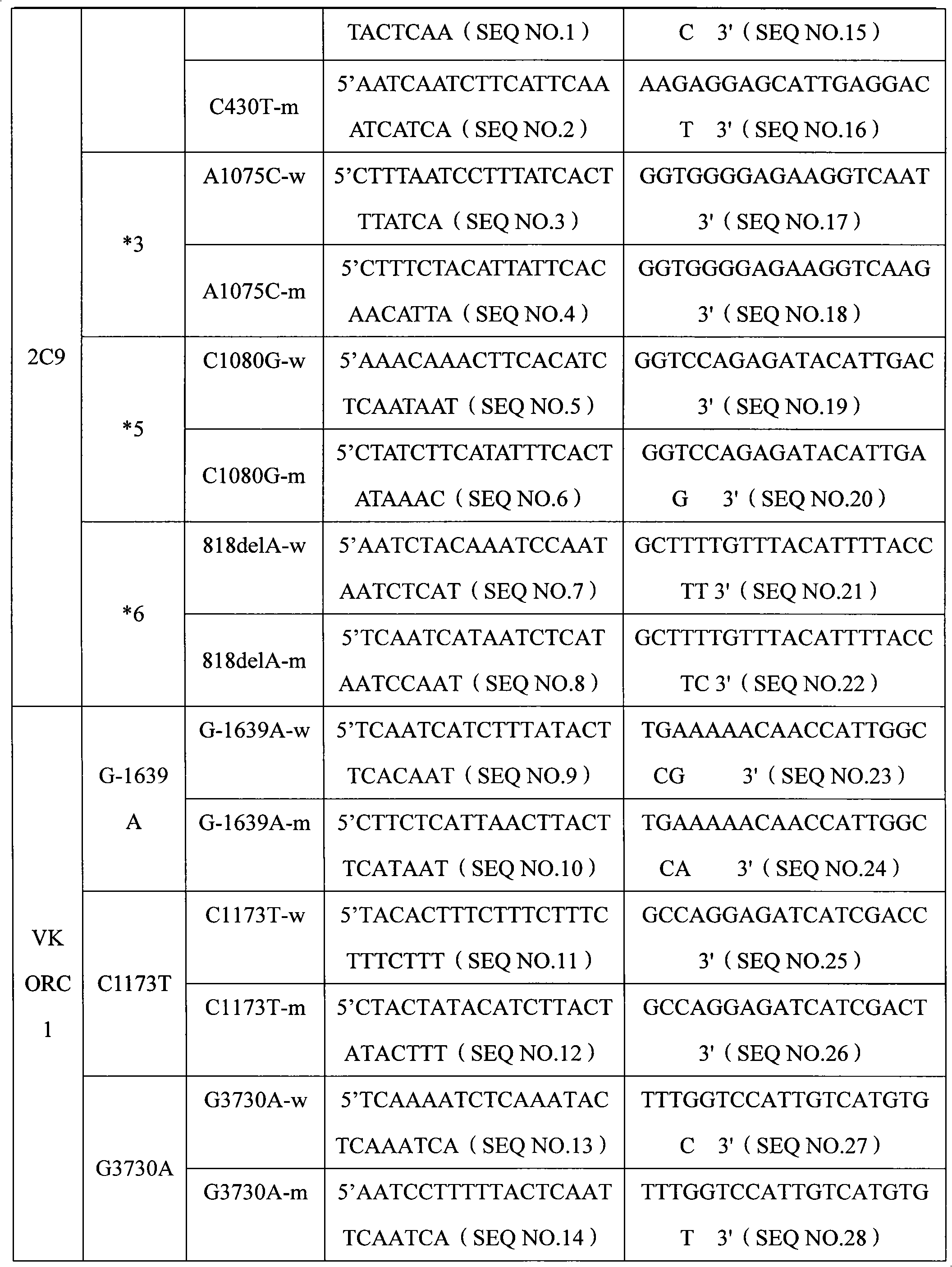
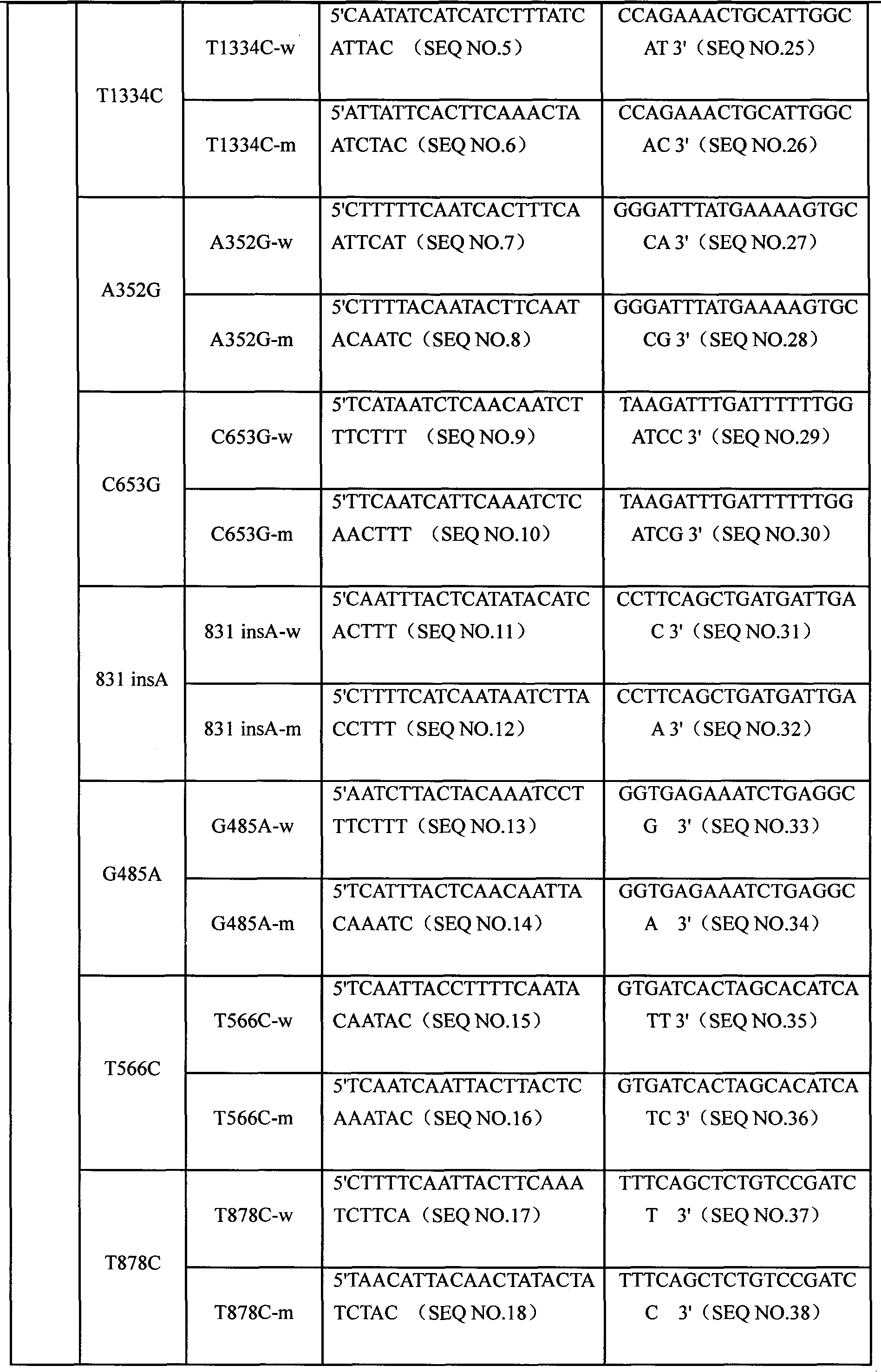
Specific primer, liquid-phase chip and method for SNP detection of CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genes
ActiveCN101824466AImprove signal-to-noise ratioImplement parallel detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationVKORC1Microsphere
The invention discloses a specific primer, a liquid-phase chip and a method for SNP detection of CYP2C9 and VKORC1 genes. The liquid-phase chip comprises wild-type and mutable-type ASPE primer pairs and microspheres coated by a specific anti-tag sequence respectively, which are designed respectively aiming at each type of mutable loci, primers used for amplifying a CYP2C9 gene target sequence having CYP2C9*2, CYP2C9*3, CYP2C9*5 and CYP2C9*6SNP loci, and / or primers used for amplifying a VKORC1 gene target sequence having G1639A, G1173T and G3730A SNP loci. The liquid phase chip of the invention has a quite good signal-noise ratio, and the cross reaction does not happen between a designed probe and the anti-tag sequence basically; the ASPE primer designed by the invention has quite good specificity, and can accurately differentiate various types of mutable loci; and the detection method has the advantages that: a few steps are adopted, 7 types of SNP loci can be detected in one step, the operation is convenient, a lot of uncertain factors existing in a process of repeated operations can be avoided, and the detection accuracy is greatly improved.
Owner:SUREXAM BIO TECH
Non-invasive gene targeting to ocular cells
Liposomes containing therapeutic genes are conjugated to multiple targeting agents to provide transport of the encapsulated gene across the blood-retinal barrier and the plasma membrane of ocular cells. Once across the blood-retinal barrier and ocular cell membrane, the encapsulated gene expresses the encoded therapeutic agent within the ocular cells to provide diagnosis and / or treatment of disease.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Gene set for liver cancer detection and detection and design method of panel of gene set
ActiveCN108753967AWide variety of sourcesEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementGene targetsTyping
The invention discloses a preparation method of a liver cancer detection panel. The preparation method comprises the following steps: screening liver cancer information and related genes thereof, thusobtaining a gene set; selecting a gene target zone; designing a panel probe; synthesizing an RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) single-stranded probe, thus obtaining the gene detection panel. The gene detectionpanel designed by the invention can be used for diagnosis, typing and prognosis of liver cancer, has wide gene coverage degree and strong transferability and is suitable for newly-developed detectionplatforms.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV +1
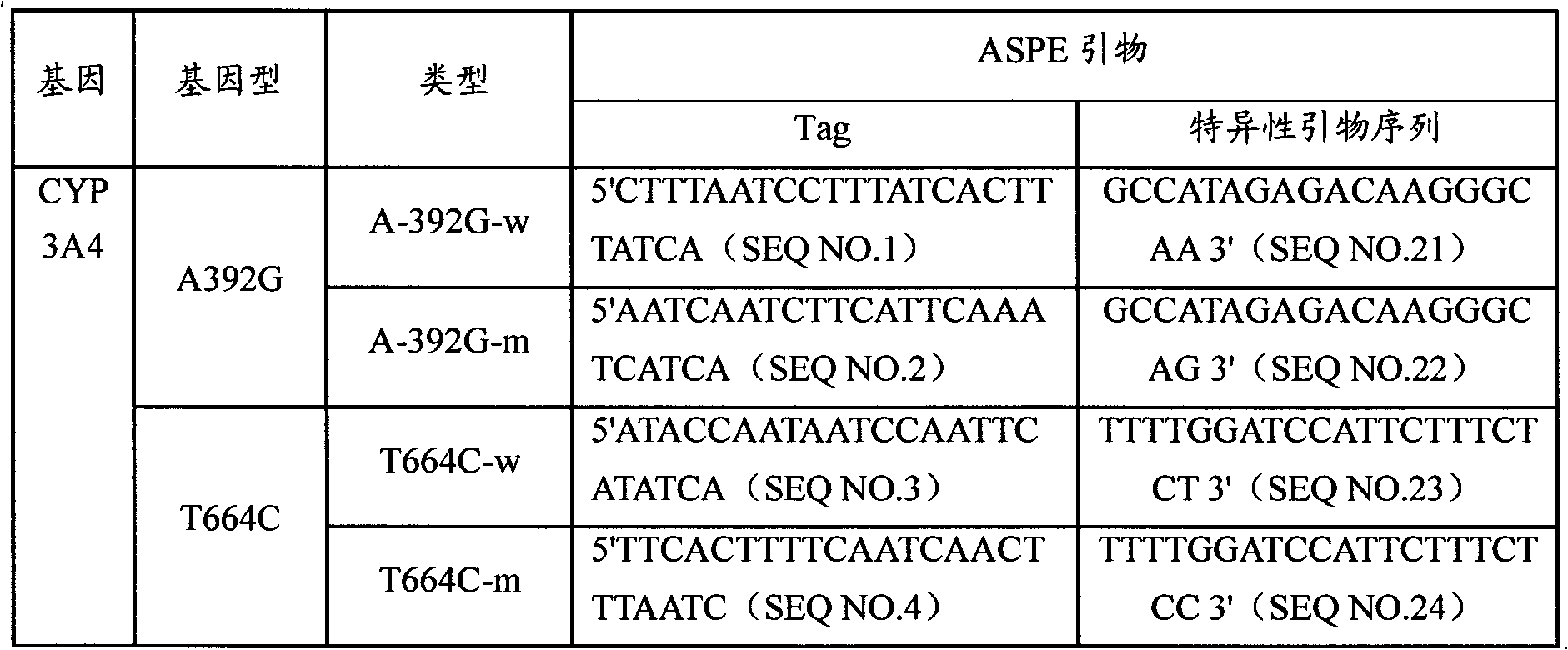
CYP3A4 gene SNP detection specific primer, liquid-phase chip and method
InactiveCN101812511AImplement parallel detectionImprove signal-to-noise ratioMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGene targetsMicrosphere
The invention discloses a CYP3A4 gene SNP detection specific primer, a liquid-phase chip and a method; and the liquid-phase chip comprises wild-type and mutant ASPE primers which are respectively designed for each type of mutation points, microspheres which are respectively coated with specific anti-tag sequences, and the primer which is used for amplifying a CYP3A4 gene target sequence with CYP3A4*1B, CYP3A4*2, CYP3A4*3, CYP3A4*4, CYP3A4*5, CYP3A4*6, CYP3A4*15, CYP3A4*17, CYP3A4*18 and / or CYP3A4*19SNP sites. The CYP3A4 gene SNP detection liquid-phase chip has very good signal-noise ratio, and a designed probe and the anti-tag sequences essentially have no cross reaction. The designed ASPE primers have very good specificity and can accurately distinguish all types of mutation points. The detection method has simple steps and ten types of SNP sites can be detected at one step, so that the operation is convenient, thereby preventing a plurality of uncertain factors in a plurality of operation processes, and greatly improving the detection accuracy rate.
Owner:SUREXAM BIO TECH
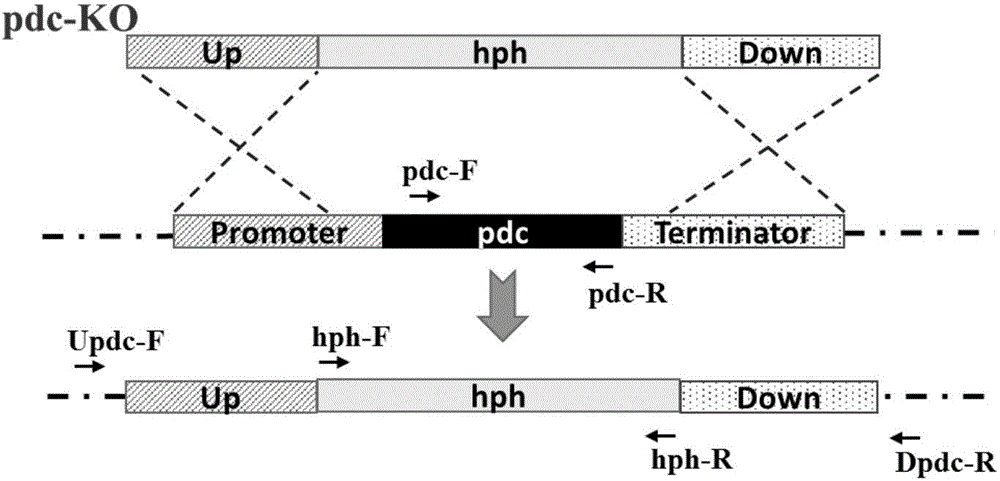
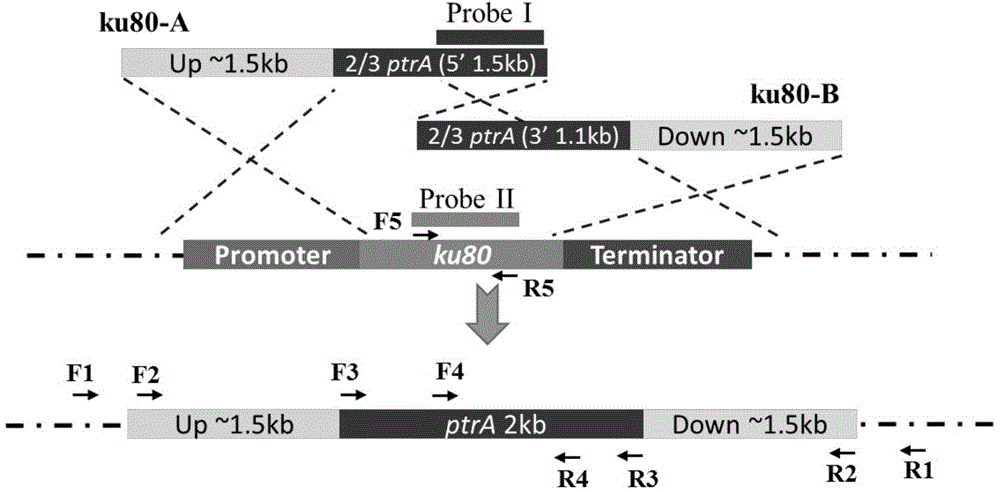
Method and application for improving application efficiency of gene targeting technique in aspergillus terreus
ActiveCN104894165AHigh gene targeting efficiencyHigh homologous recombination efficiencyFungiMicroorganism based processesBinding siteLIG4
The invention discloses a method and application for improving application efficiency of a gene targeting technique in aspergillus terreus, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, by taking Aspergillus terreus as an initial bacterium, knocking off a ku80 gene or an lig4 gene so as to increase the exogenous DNA homologous recombination probability of a strain; secondly, establishing a pyrG gene deletion uracil auxotroph stain, establishing a inheritance conversion system based on a pyrG gene as a screening tag; and finally, cutting off the screening tag by using a Cre / LoxP specific binding site recombinant system, thereby obtaining a uracil auxotroph stain which can be applied to genetic modification again. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, an efficient aspergillus terreus gene targeting platform can be established, the method has the advantages that high homologous recombination efficiency can be achieved, the bidirectional screening of the conversion system can be achieved, a screening tag cutting method is simple and feasible, the screening tag can be recycled, and the like, and basic support can be provided for efficient genetic modification of aspergillus terreus by using the gene targeting technique.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Screening systems utilizing RTP801
InactiveUS20070281326A1Useful in treatmentCompound screeningApoptosis detectionGene targetsUnique gene
RTP801 represents a unique gene target for hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1). Down-regulation of the mTOR pathway activity by hypoxia requires de novo mRNA synthesis and correlates with increased expression of RTP801. The present invention relates to screening systems utilizing RTP801 and / or RTP801 interactors and / or RTP801 biological activity, to drug candidates identified by such screening systems, and to the use of such drug candidates in the treatment of various disorders.
Owner:QUARK FARMACUITIKALS INC
ENABLING THE USE OF LONG dsRNA FOR GENE TARGETING IN MAMMALIAN AND OTHER SELECTED ANIMAL CELLS
ActiveUS20130330824A1Simplified and advanced gene targetingRegulate expressionSpecial deliveryAntiviralsMammalGene silencing
Owner:1GLOBE BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
Primers and probes for detecting human EGFR gene mutations as well as use method thereof
ActiveCN101608240AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceBioinformaticsGene targets
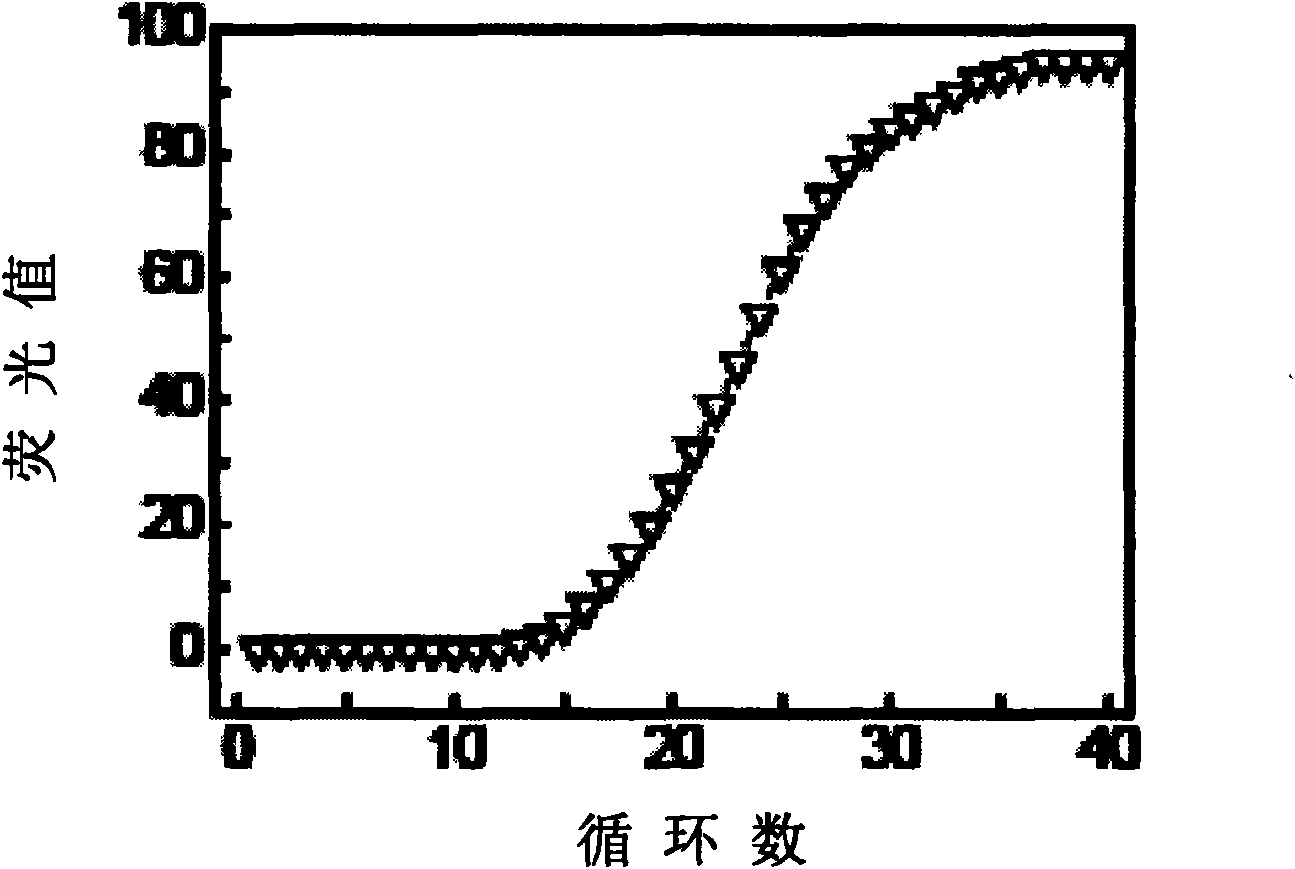
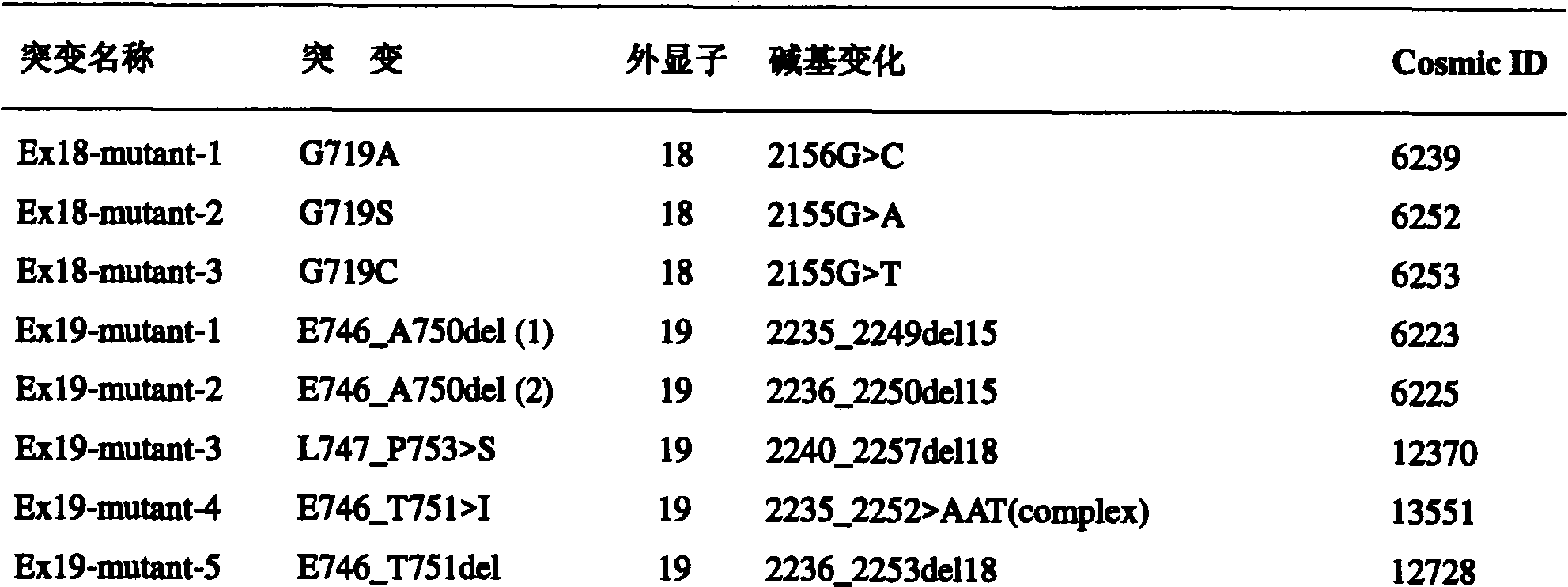
The invention discloses primers and probes for detecting human EGFR gene mutations as well as a use method, relating to the detection of gene mutation. The method of the invention comprises the following steps: (1) providing the primers and the probes; (2) processing the sample to be detected and extracting a template; (3) preparing a reaction system of fluorescent PCR amplification mutation gene sequence; (4) amplifying the mutable gene target sequence by the primers and the probes in the step (1); (5) detecting the fluorescence intensity of FAM and HEX or ROX of the reaction system as the judgment standard of results by adopting hybridization of a dual ring probes and an amplification product. The primers, the probes and the method of the invention can simultaneously detect 29 deletion mutations of EGFR gene, and features high sensitivity, strong specificity, strong selective capacity and fast detection speed demonstrated by completing the whole detection process in only 90 minutes.
Owner:AMOY DIAGNOSTICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com