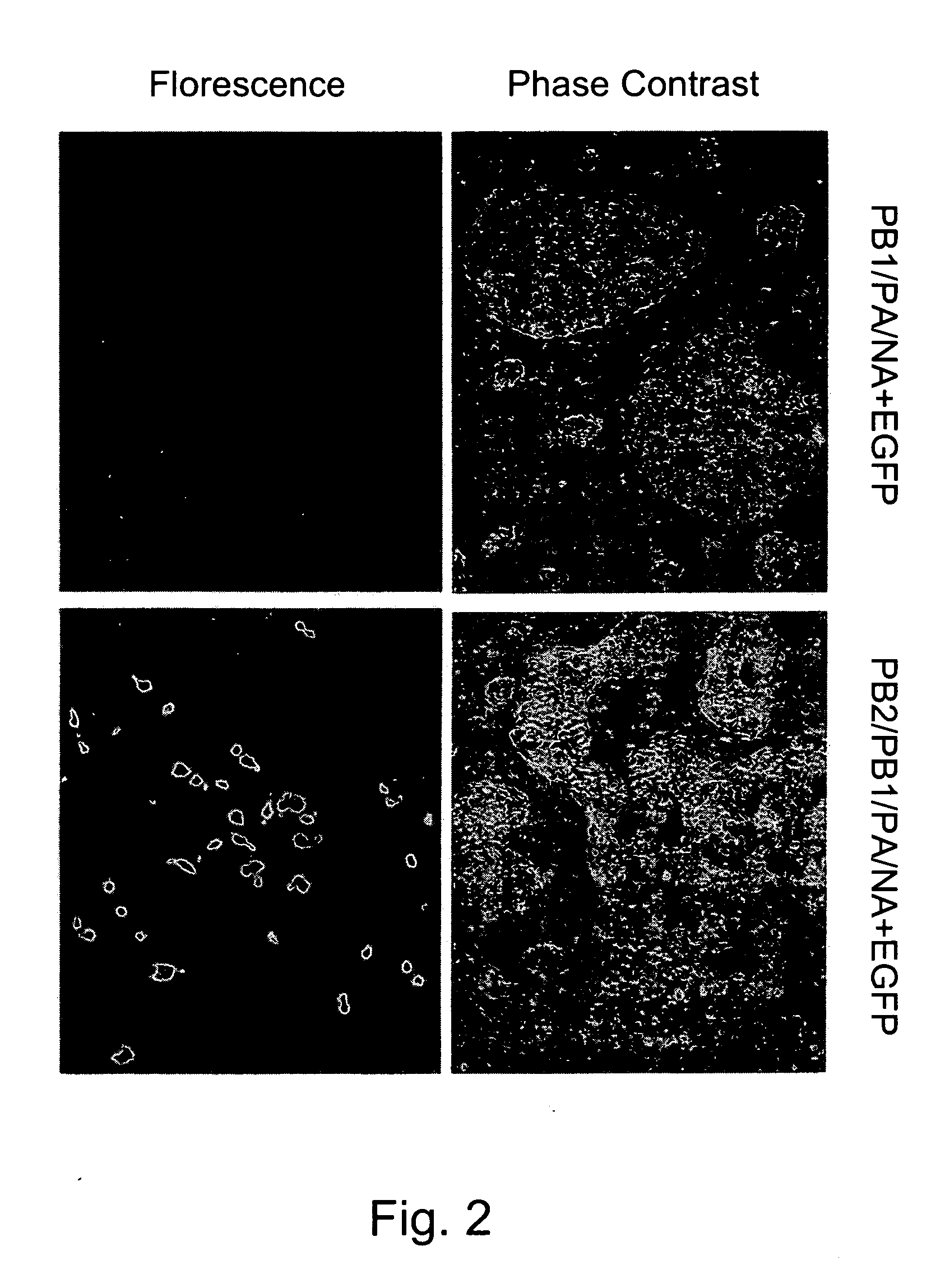
Patents
Literature
904 results about "Eukaryotic plasmids" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A plasmid is a small DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from a chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. They are most commonly found as small circular, double-stranded DNA molecules in bacteria; however, plasmids are sometimes present in archaea and eukaryotic organisms.
Truncated transcriptionally active cytomegalovirus promoters
InactiveUS6156567AProvide securityIncrease capacitySsRNA viruses negative-senseGenetic material ingredientsBiotechnologyEukaryotic plasmids
Recombinant adenoviruses, methods of making them, uses for them, including in immunological, immunogenic, vaccine or therapeutic compositions, or, as a vector for cloning, replicating or expressing DNA and methods of using the compositions and vector, expression products from them, and uses for the expression products are provided. More particularly, recombinant canine adenoviruses (CAV) and methods of making them, uses for them, expression products from them, and uses for the expression products, including recombinant CAV2 viruses are provided. Additionally, truncated promoters, expression cassettes containing the promoters, and recombinant viruses and plasmids containing the promoters or expression cassettes are provided.
Owner:VIROGENETICS
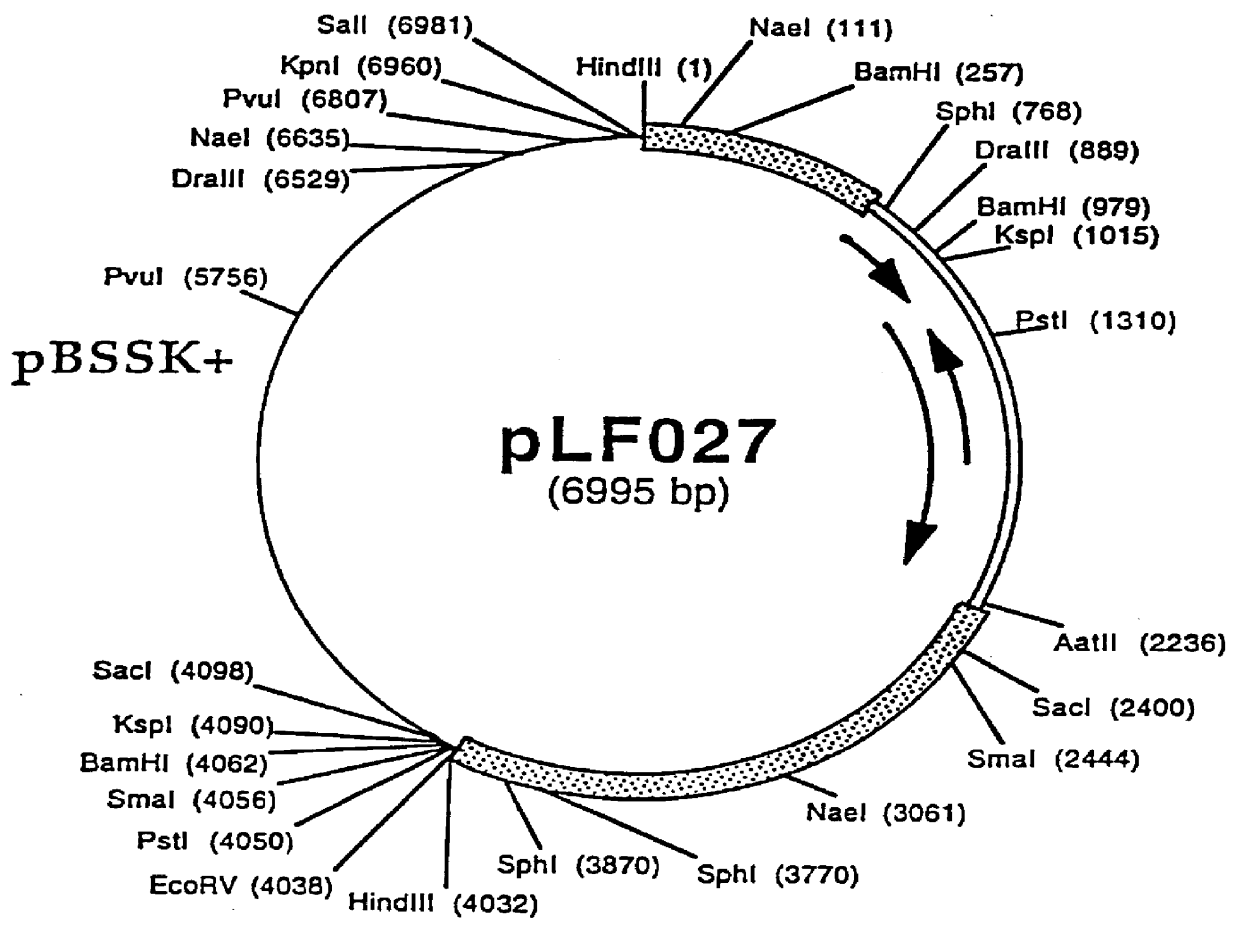
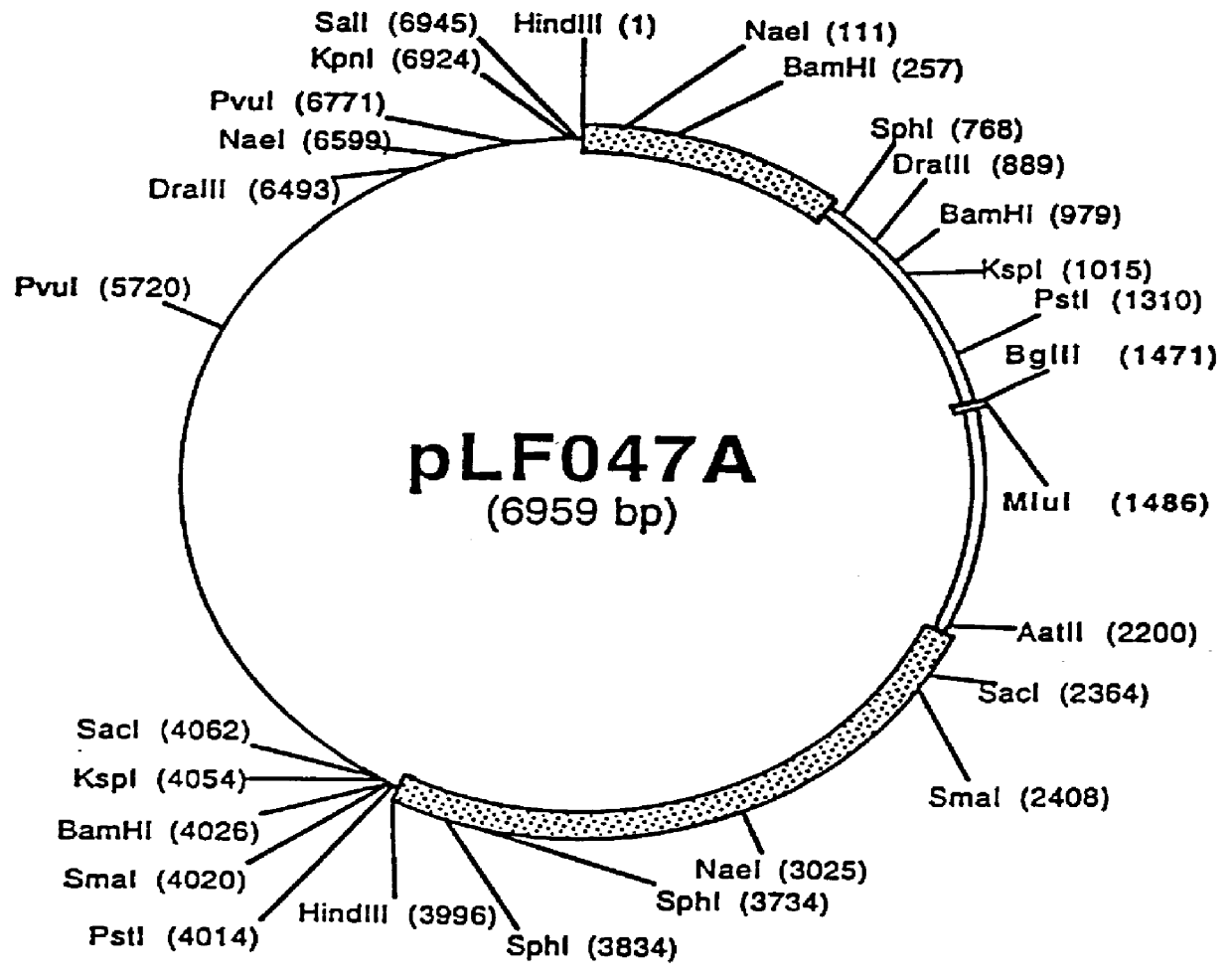
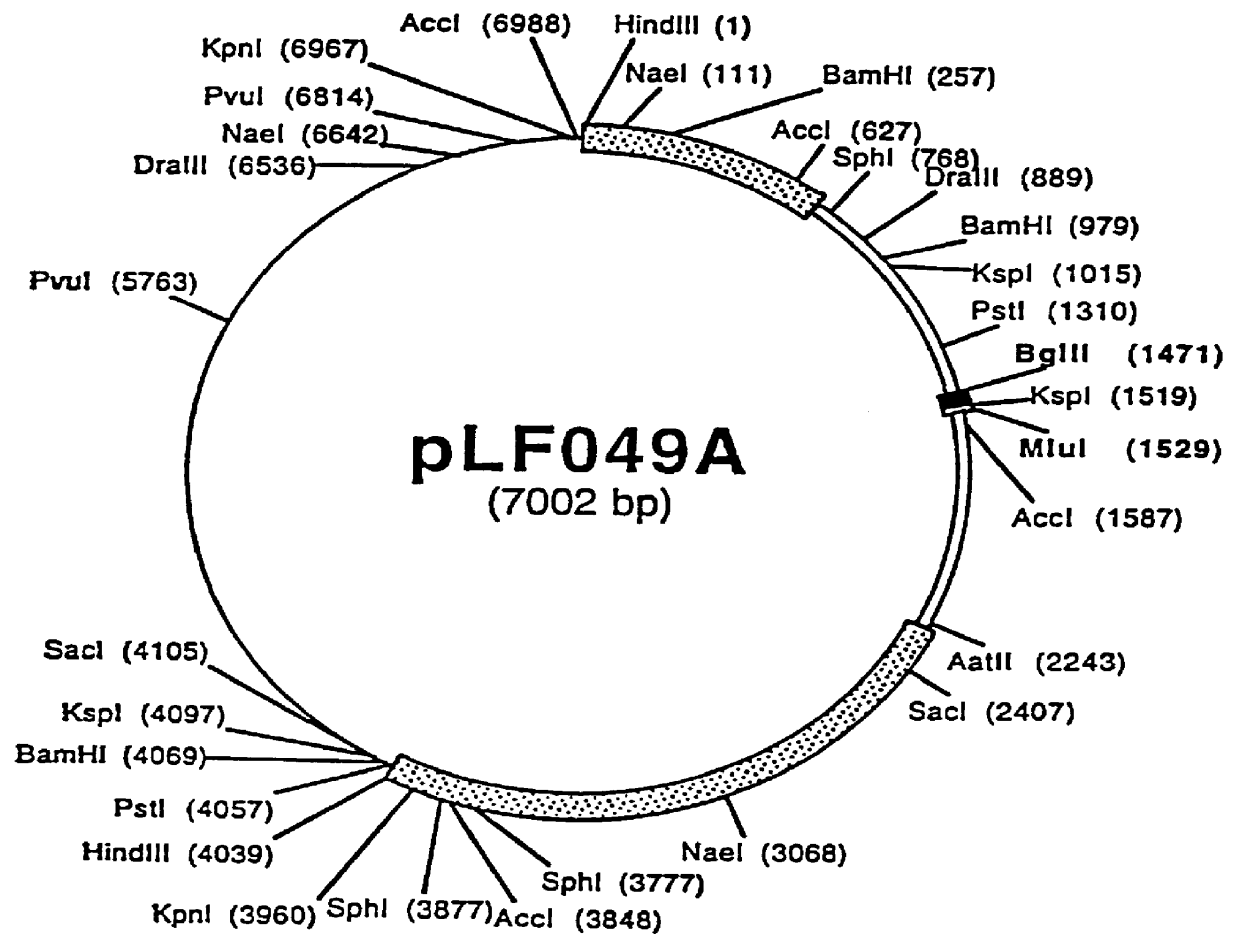
DNA vaccines encoding antigen linked to a domain that binds CD40
InactiveUS7118751B1Improve abilitiesEasy to demonstrateAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsVirus peptidesPeptide antigenEukaryotic plasmids
Vaccines that target one or more antigens to a cell surface receptor improve the antigen-specific humoral and cellular immune response. Antigen(s) linked to a domain that binds to a cell surface receptor are internalized, carrying antigen(s) into an intracellular compartment where the antigen(s) are digested into peptides and loaded onto MHC molecules. T cells specific for the peptide antigens are activated, leading to an enhanced immune response. The vaccine may comprise antigen(s) linked to a domain that binds at least one receptor or a DNA plasmid encoding antigen(s) linked to a domain that binds at least one receptor. A preferred embodiment of the invention targets HIV-1 env antigen to the CD40 receptor, resulting in delivery of antigen to CD40 positive cells, and selective activation of the CD40 receptor on cells presenting HIV-1 env antigens to T cells.
Owner:HAYDEN LEDBETTER MARTHA S +1
Multi plasmid system for the production of influenza virus
InactiveUS20050266026A1Easy to copyEnhanced ability to replicateSsRNA viruses negative-senseVectorsEmbryonated chicken eggCold adapted
Vectors and methods for the production of influenza viruses suitable as recombinant influenza vaccines in cell culture are provided. Bi-directional expression vectors for use in a multi-plasmid influenza virus expression system are provided. Additionally, the invention provides methods of producing influenza viruses with enhanced ability to replicate in embryonated chicken eggs and / or cells (e.g., Vero and / or MDCK) and further provides influenza viruses with enhanced replication characteristics. A method of producing a cold adapted (ca) influenza virus that replicates efficiently at, e.g., 25° C. (and immunogenic compositions comprising the same) is also provided.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Vaccine formulations
ActiveUS20050079185A1Improve stabilityStable and safe and easily administrableAntibacterial agentsSsRNA viruses negative-senseEukaryotic plasmidsNon ionic
The present invention provides for a novel oil-in-water (O / W) emulsion, with increased stability in the presence of bacterial or viral suspensions, especially those concentrated and non-purified or weakly purified. The emulsion of the present invention can act as vehicle for the delivery of a pharmaceutical composition comprising at least one immunogen and, in particular, an immunogen selected from the group comprising an inactivated pathogen, an attenuated pathogen, a subunit, a recombinant expression vector, and a plasmid or combinations thereof. In one embodiment, the present invention provides for an injectable oil-in-water (O / W) emulsion comprising: (1) an aqueous solution containing an immunogen, said immunogen selected from the group comprising an inactivated Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae bacterium, an inactivated porcine circovirus type 2 (PCV-2) virus or combinations thereof; (2) a mineral oil; (3) a non-ionic lipophilic surfactant; and (4) a non-ionic hydrophilic surfactant having a low HLB value which comprises ethoxylated fatty acid diesters of sorbitan (generally having HLB value between 11 and 13). In another preferred embodiment, the present invention provides for an injectable oil-in-water (O / W) emulsion comprising: (1) an aqueous solution containing an immunogen; (2) a non-ionic hydrophilic surfactant having a high hydrophilic-lipophilic balance (HLB) value greater than 13 and less than 40, in particular HLB≧13.5, and preferably HLB≧14; (3) a mineral oil; (4) a non-ionic lipophilic surfactant; and (5) a non-ionic hydrophilic surfactant having a low HLB value (HLB value of about 9 to about 13).
Owner:MERIAL INC
Multi plasmid system for the production of influenza virus
InactiveUS20050158342A1Easy to copyEnhanced ability to replicateSsRNA viruses negative-senseVectorsEmbryonated chicken eggEukaryotic plasmids
Vectors and methods for the production of influenza viruses suitable as recombinant influenza vaccines in cell culture are provided. Bi-directional expression vectors for use in a multi-plasmid influenza virus expression system are provided. Additionally, the invention provides methods of producing influenza viruses with enhanced ability to replicate in embryonated chicken eggs and / or cells (e.g., Vero and / or MDCK) and further provides influenza viruses with enhanced replication characteristics. In addition, the present invention includes an improved method of rescue, wherein animal cells (e.g., SF Vero cells) are electroporated with plasmids and vectors of the invention.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Compositions and methods for administering Borrelia DNA
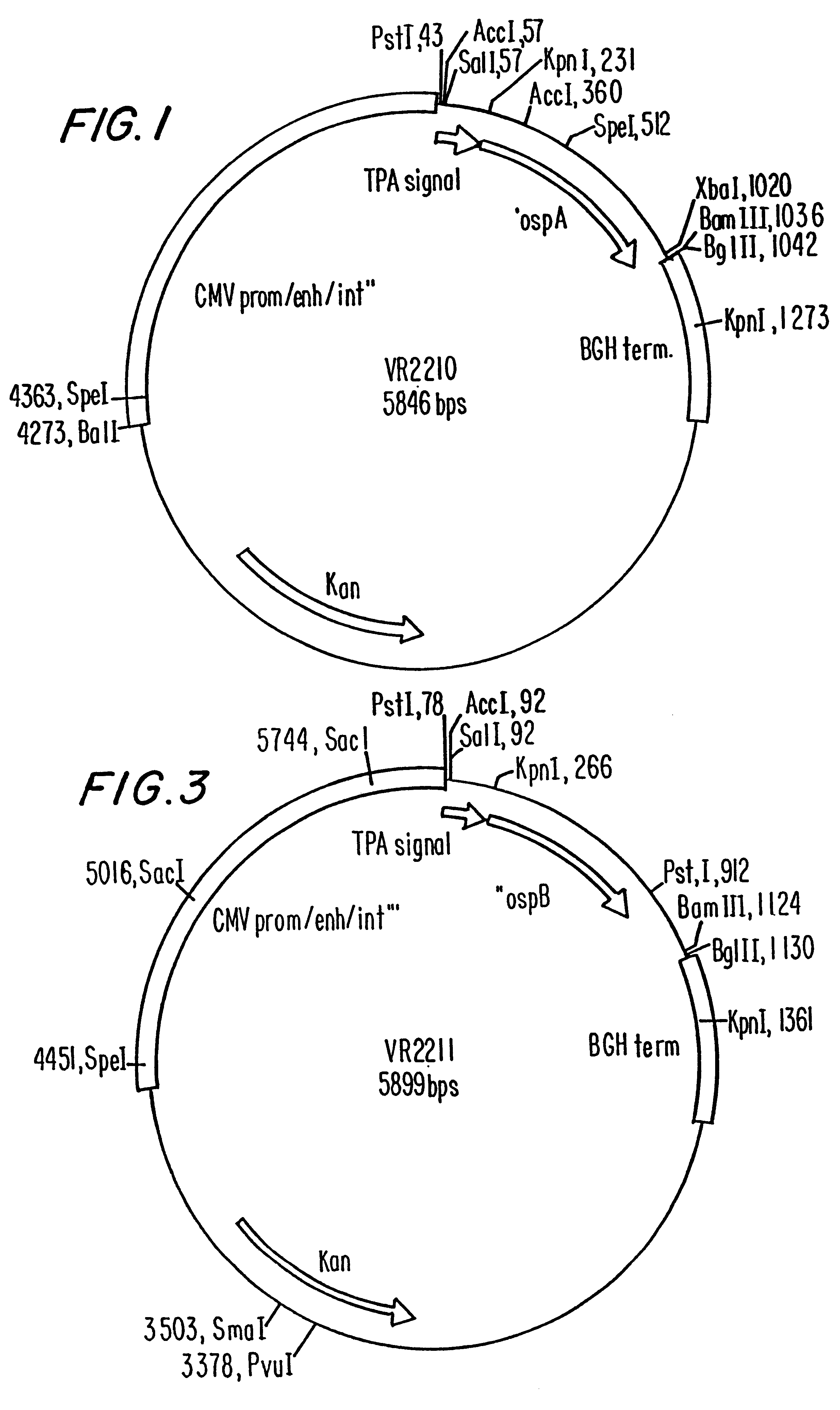
Disclosed is a vaccine against Lyme Disease or its causative agent Borrelia burgdorferi (sensu stricto or sensu lato) containing a plasmid a DNA encoding a promoter for driving expression in a mammalian cell, DNA encoding a leader peptide for facilitating secretion / release of a prokaryotic protein sequence from a mammalian cell, a DNA encoding Borrelia OspA or OspB, and a DNA encoding a terminator. Disclosed too is an immunogenic composition against Lyme Disease or its causative agent Borrelia burgdorferi (sensu stricto or sensu lato) containing a plasmid comprising a DNA encoding a promoter for driving expression in a mammalian cell, DNA encoding a leader peptide for facilitating secretion / release of a prokaryotic protein sequence from a mammalian cell, a DNA encoding a Borrelia OspC, and a DNA encoding a terminator. And, methods for making and using such vaccines and the immunogenic composition are also disclosed.
Owner:PASTEUR MERIEUX SERUMS & VACCINS SA
Hydrogel bioscaffoldings and biomedical device coatings
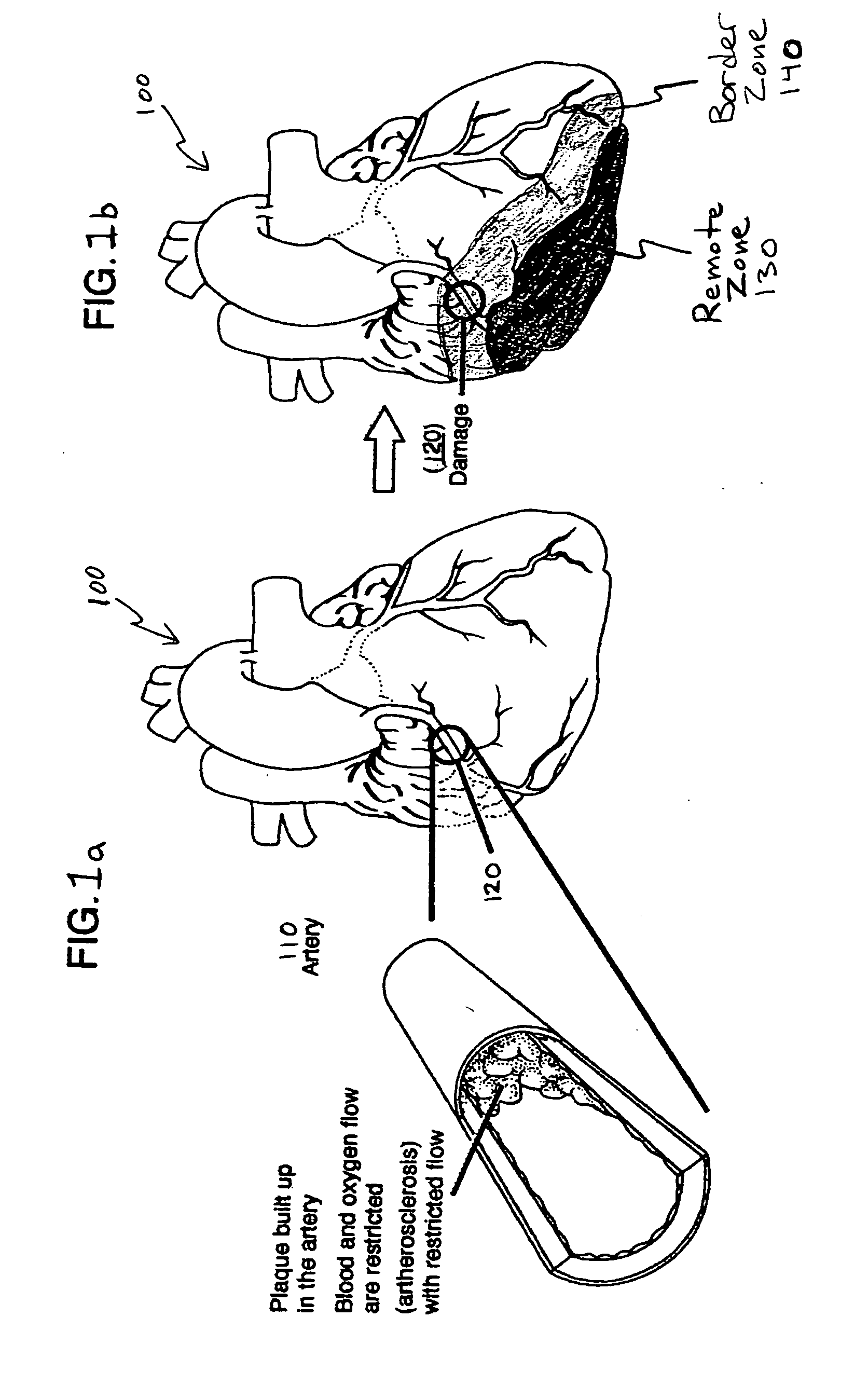
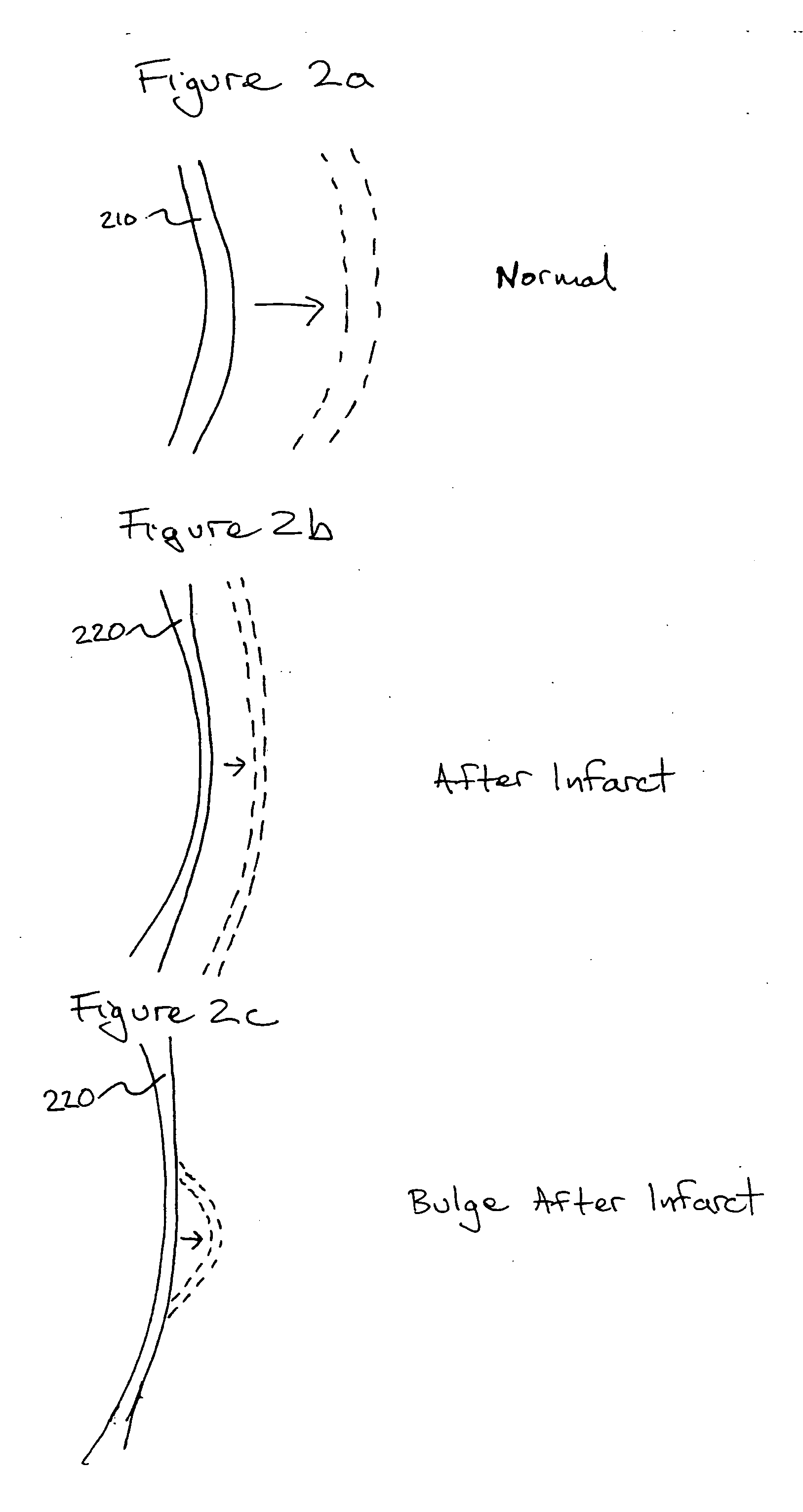
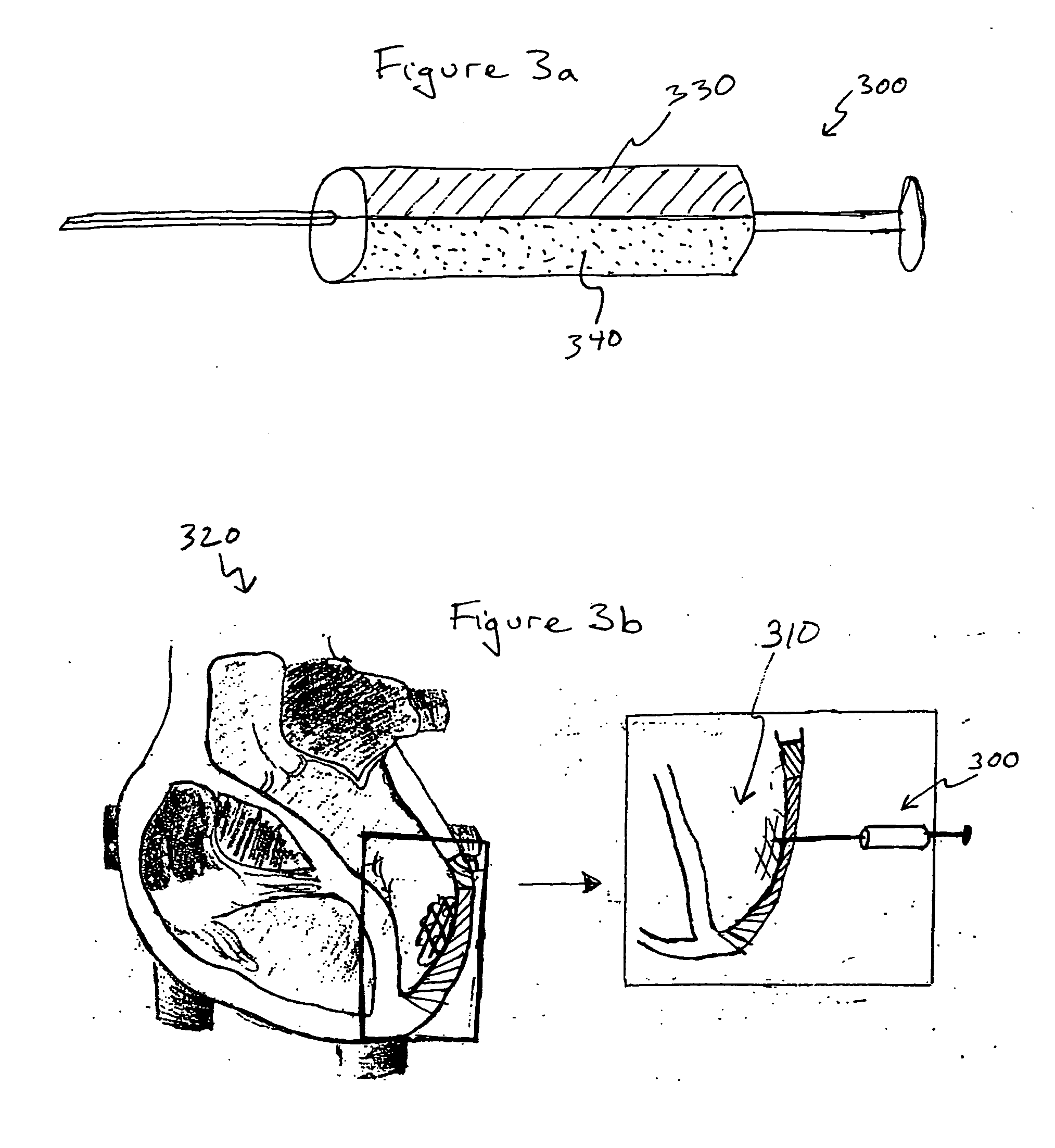
Bioscaffoldings formed of hydrogels that are crosslinked in situ in an infarcted region of the heart (myocardium) by a Michael's addition reaction or by a disulfide bond formed by an oxidative process are described. Each of the bioscaffoldings described includes hyaluronan as one of the hydrogel components and the other component is selected from collagen, collagen-laminin, poly-l-lysine, and fibrin. The bioscaffolding may further include an alginate component. The bioscaffoldings may have biofunctional groups such as angiogenic factors and stem cell homing factors bound to the collagen, collagen-laminin, poly-l-lysine, or fibrinogen hydrogel component. In particular, the biofunctional groups may be PR11, PR39, VEGF, bFGF, a polyarginine / DNA plasmid complex, or a DNA / polyethyleneimine (PEI) complex. Additionally, the hydrogel components may be injected into the infarct region along with stem cells and microspheres containing stem cell homing factors. The bioscaffolding may be formed on a stent or a cardiac medical device.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
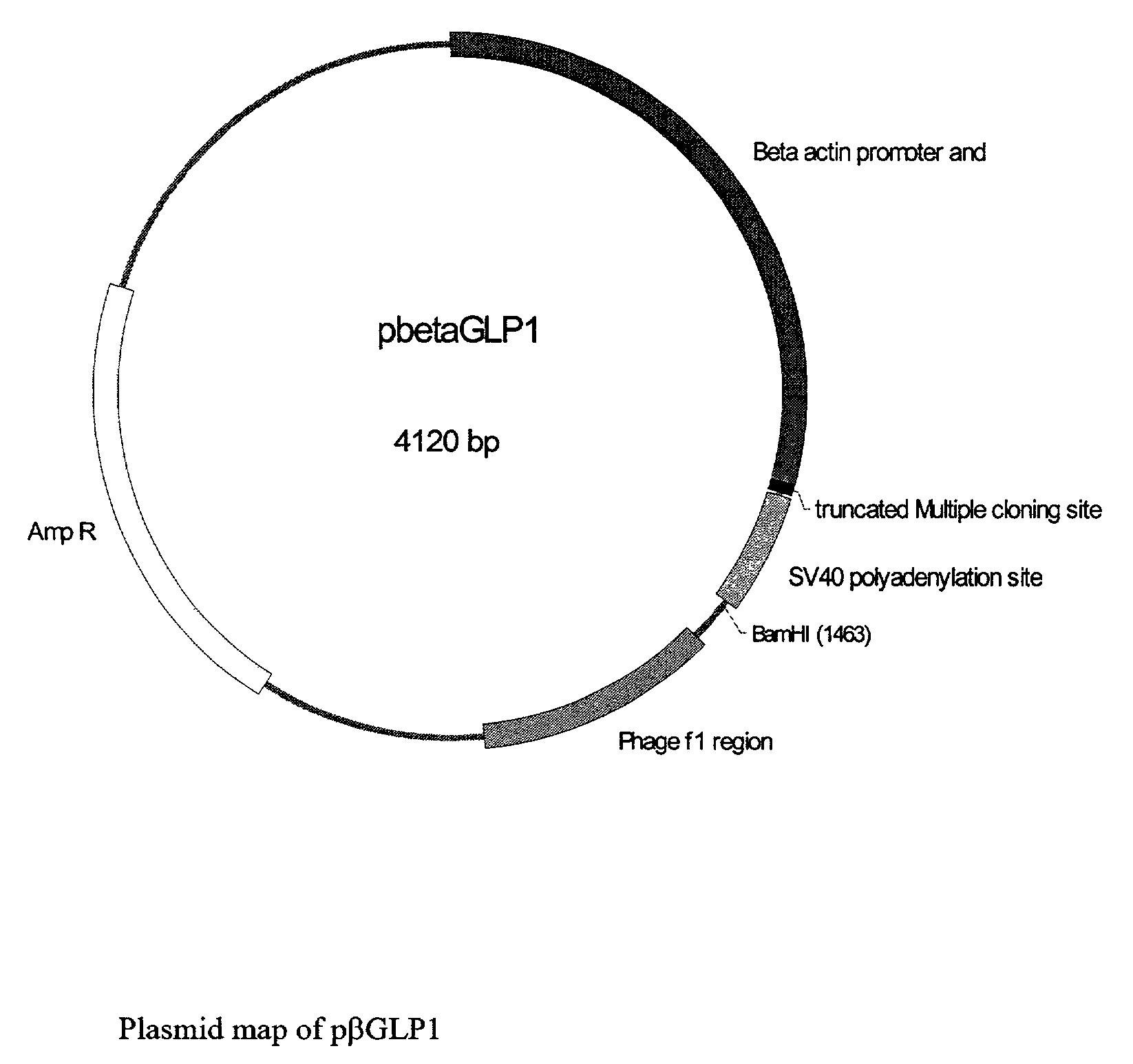
GLP-1 gene delivery for the treatment of type 2 diabetes
ActiveUS7374930B2Efficient transfectionEasy to controlSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsGene deliveryGlucose polymers
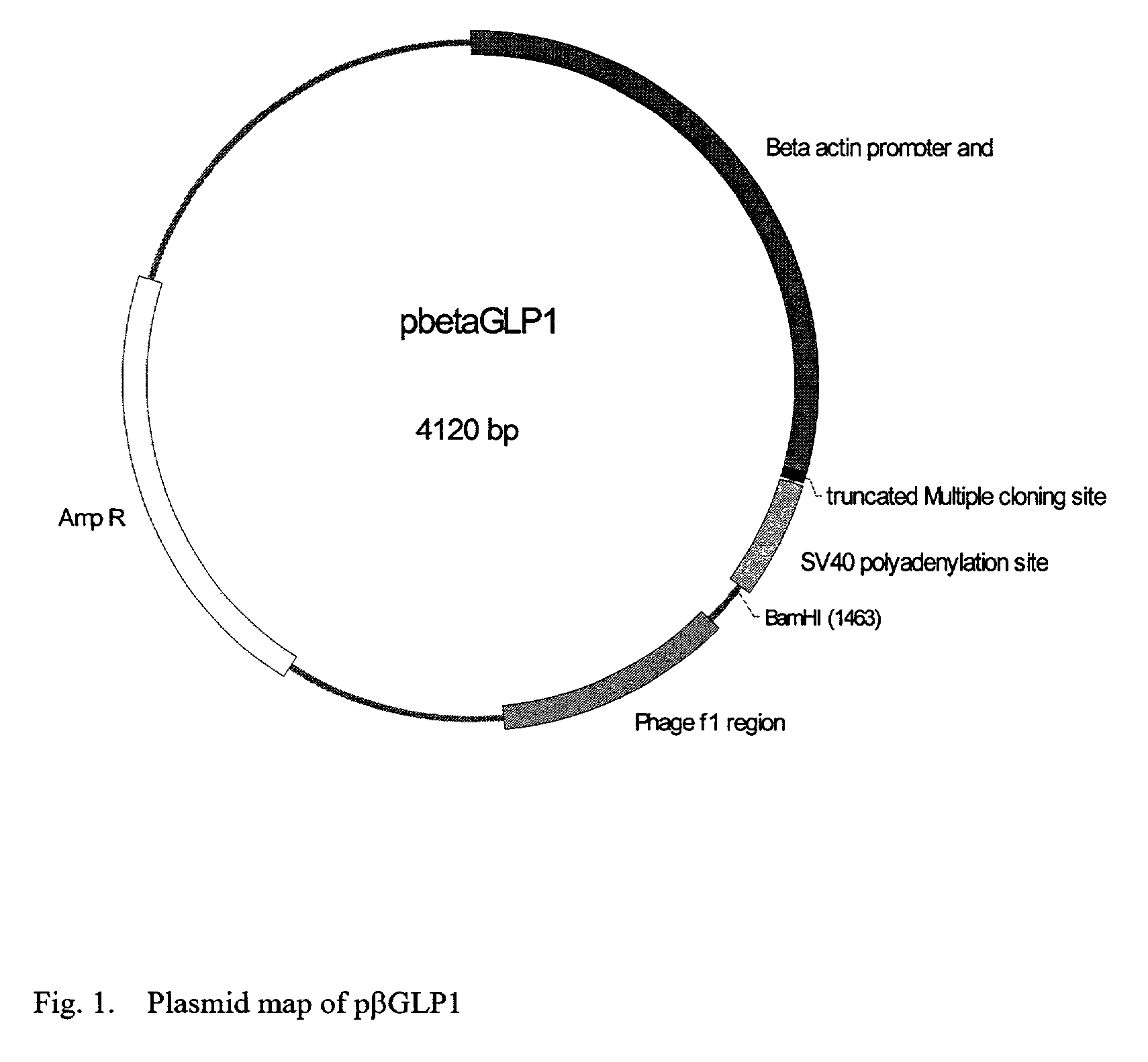
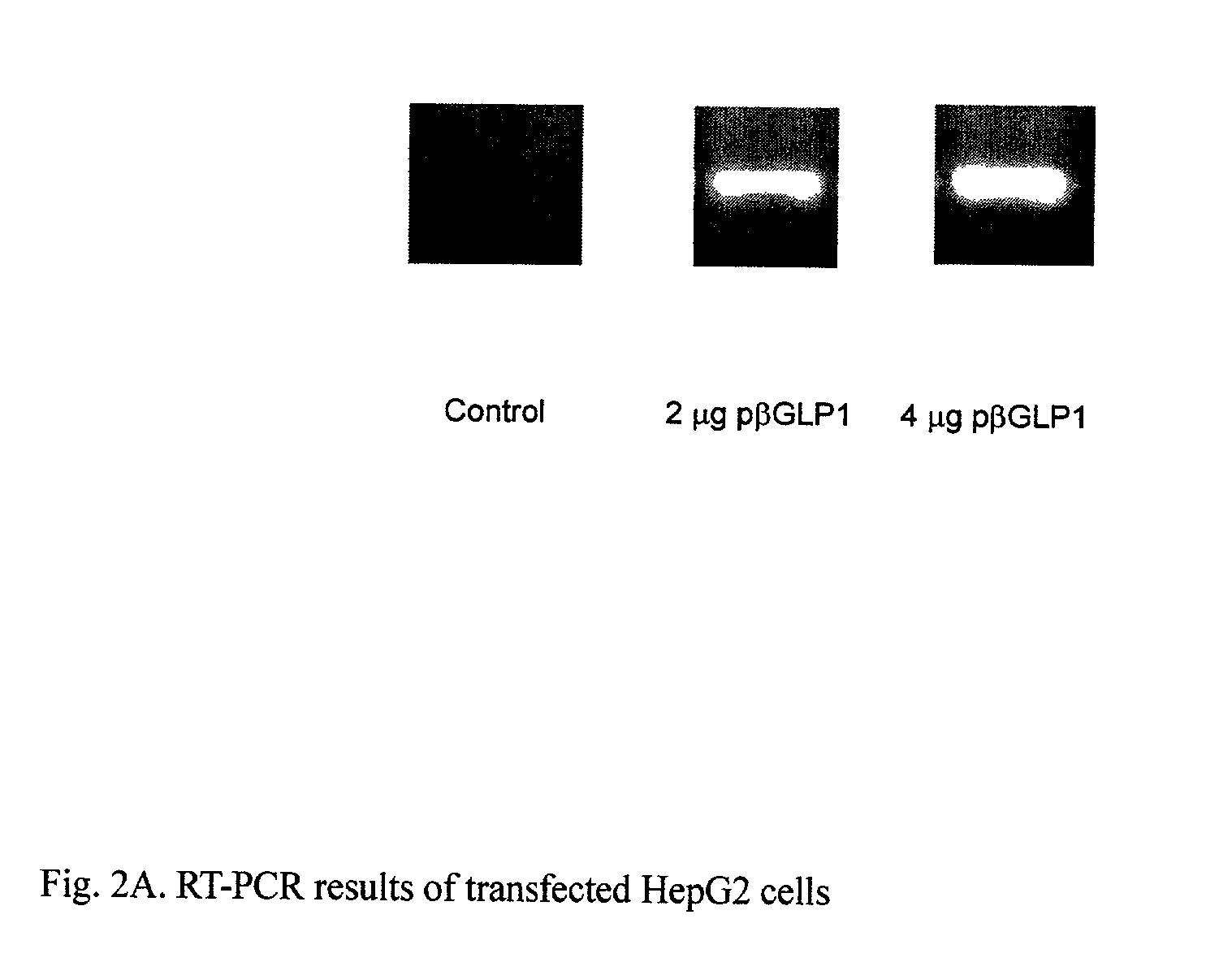
This patent discloses compositions and methods of use thereof to normalize the blood glucose levels of patients with type 2 diabetes. It relates particularly to a plasmid comprising a chicken β actin promoter and enhancer; a modified GLP-1 (7-37) cDNA (pβGLP1), carrying a furin cleavage site, which is constructed and delivered into a cell for the expression of active GLP-1.
Owner:CLSN LAB
Codon-optimized polynucleotide-based vaccines against human cytomegalovirus infection
InactiveUS20080085870A1Reduce in quantityDecreased immunological responseOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenAdjuvant
The invention is related to polynucleotide-based cytomegalovirus vaccines. In particular, the invention is plasmids operably encoding HCMV antigens, in which the naturally-occurring coding regions for the HCMV antigens have been modified for improved translation in human or other mammalian cells through codon optimization. HCMV antigens which are useful in the invention include, but are not limited to pp65, glycoprotein B (gB), IE1, and fragments, variants or derivatives of either of these antigens. In certain embodiments, sequences have been deleted, e.g., the Arg435-Lys438 putative kinase in pp65 and the membrane anchor and endocellular domains in gB. The invention is further directed to methods to induce an immune response to HCMV in a mammal, for example, a human, comprising delivering a plasmid encoding a codon-optimized HCMV antigen as described above. The invention is also directed to pharmaceutical compositions comprising plasmids encoding a codon-optimized HCMV antigen as described above, and further comprising adjuvants, excipients, or immune modulators.
Owner:VICAL INC
Improving sequence-specific antimicrobials by blocking DNA repair
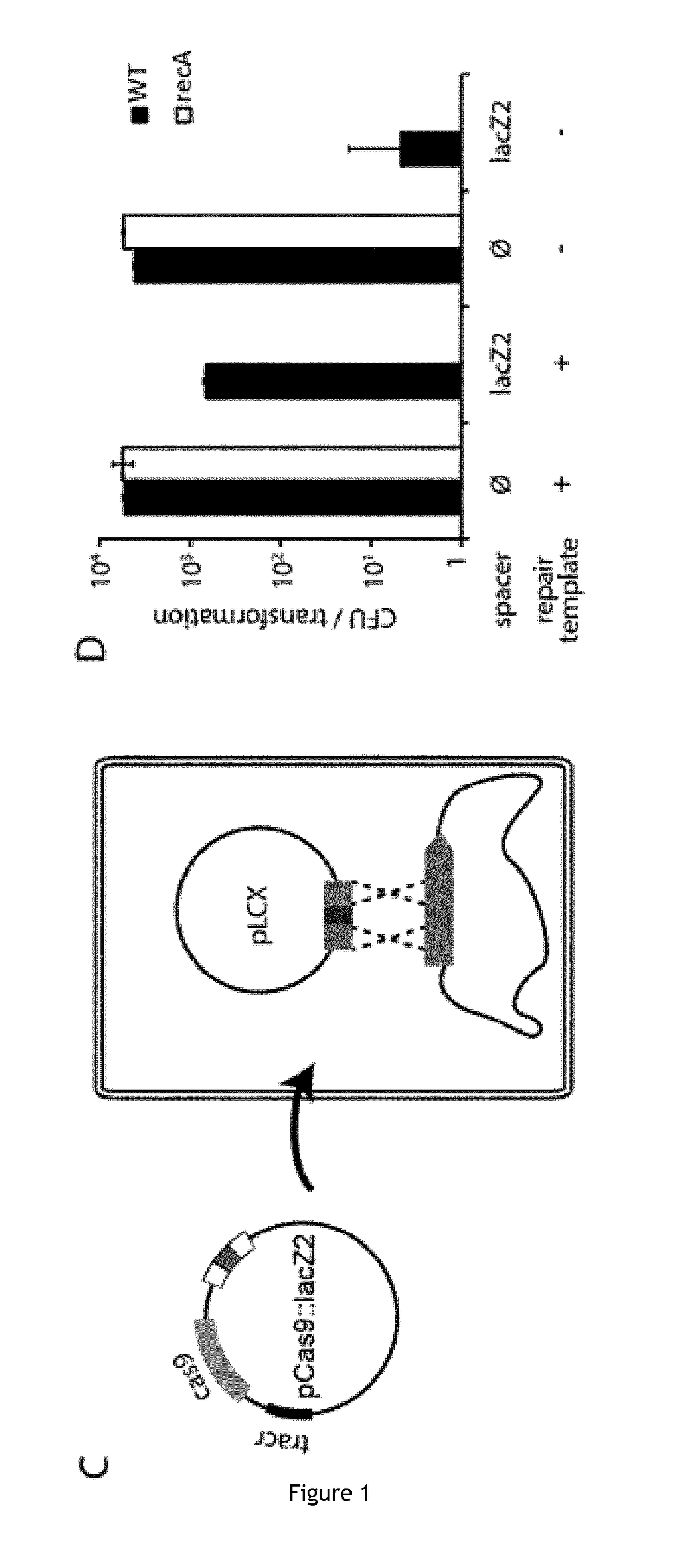
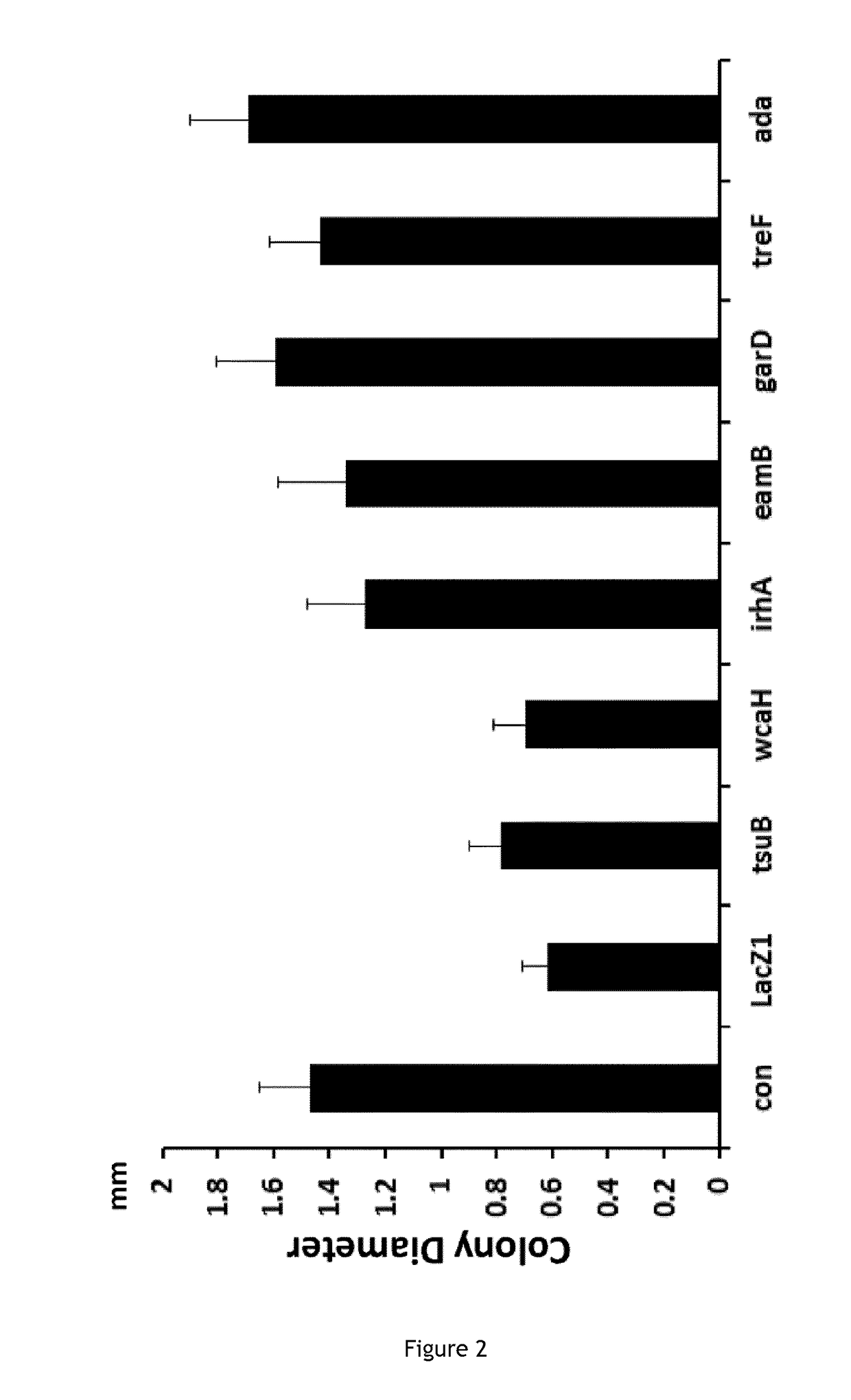
The invention relates to the improvement of endonuclease-based antimicrobials by blocking DNA repair of double-strand break(s) (DSB(s)) in prokaryotic cells. In this respect, the invention especially concerns a method involving blocking DNA repair after a nucleic acid has been submitted to DSB, in particular by a Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR) associated programmable double-strand endonuclease. The invention particularly relates to the use of an exogenous molecule that inhibits DNA repair, preferably a protein that binds to the ends of the double-stranded break to block DSB repair. The invention also relates to vectors, particularly phagemids and plasmids, comprising nucleic acids encoding nucleases and Gam proteins, and a pharmaceutical composition and a product containing these vectors and their application.
Owner:INST PASTEUR +1
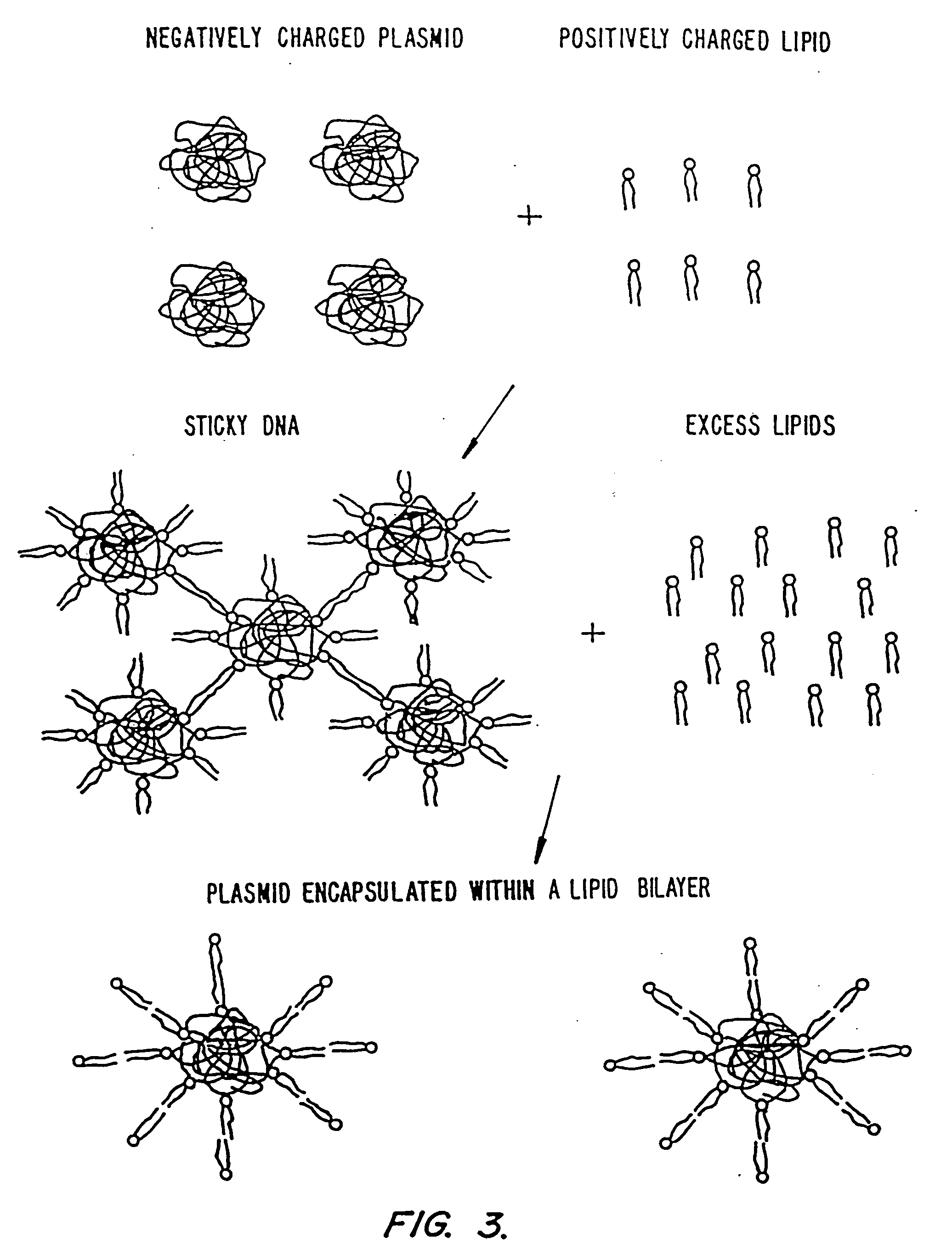
Methods for encapsulating plasmids in lipid bilayers
Plasmid-lipid particles which are useful for transfection of cells in vitro or in vivo are described. The particles can be formed using either detergent dialysis methods or methods which utilize organic solvents. The particles are typically 65-85 nm, fully encapsulate the plasmid and are serum-stable.
Owner:TEKMIRA PHARMA CORP +1
DNA transfection system for the generation of infectious influenza virus
InactiveUS20050186563A1Improve effectivenessElicit protective immunitySsRNA viruses negative-senseFungiDual promoterSingle-Stranded RNA
The present invention is based on the development of a dual promoter system (preferably a RNA pol I-pol II system) for the efficient intracellular synthesis of viral RNA. The resultant minimal plasmid-based system may be used to synthesize any RNA virus, preferably viruses with a negative single stranded RNA genome. The viral product of the system is produced when the plasmids of the system are introduced into a suitable host cell. One application of the system is production of attenuated, reassortant influenza viruses for use as antigens in vaccines. The reassortant viruses generated by cotransfection of plasmids may comprise genes encoding the surface glycoproteins hemagglutinin and neuraminidase from an influenza virus currently infecting the population and the internal genes from an attenuated influenza virus. An advantageous property of the present invention is its versatility; the system may be quickly and easily adapted to synthesize an attenuated version of any RNA virus. Attenuated or inactivated RNA viruses produced by the present invention may be administered to a patient in need of vaccination by any of several routes including intranasally or intramuscularly.
Owner:ST JUDE CHILDRENS RES HOSPITAL INC
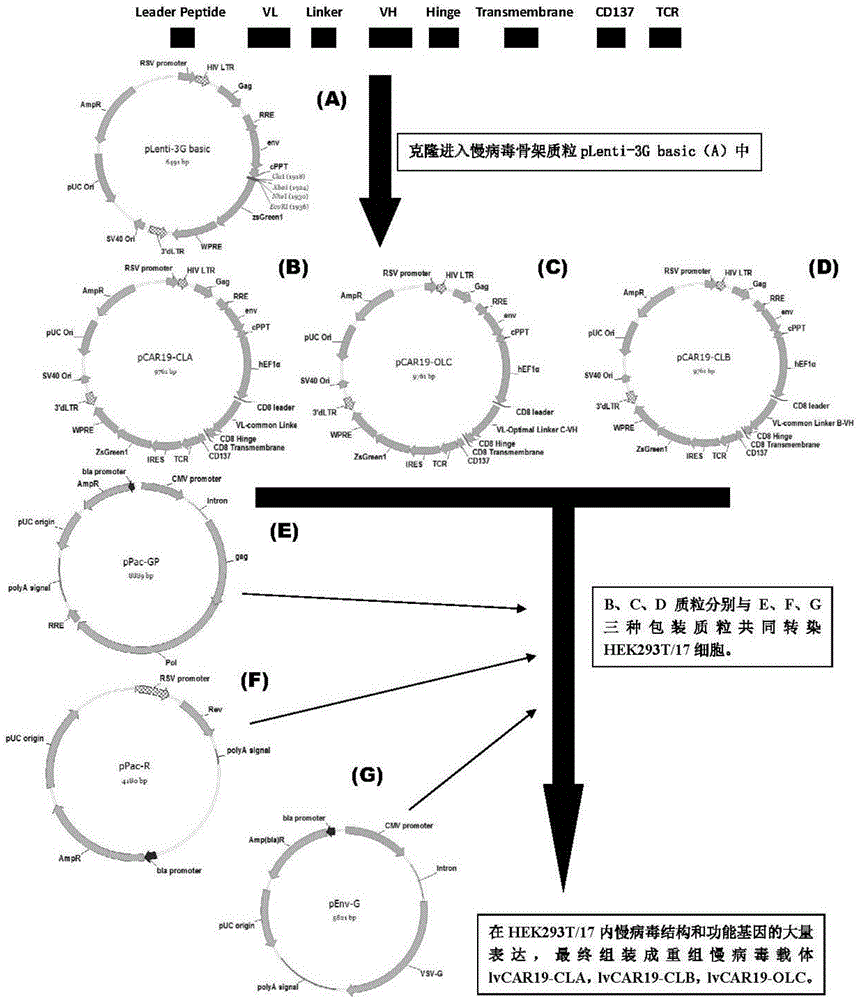
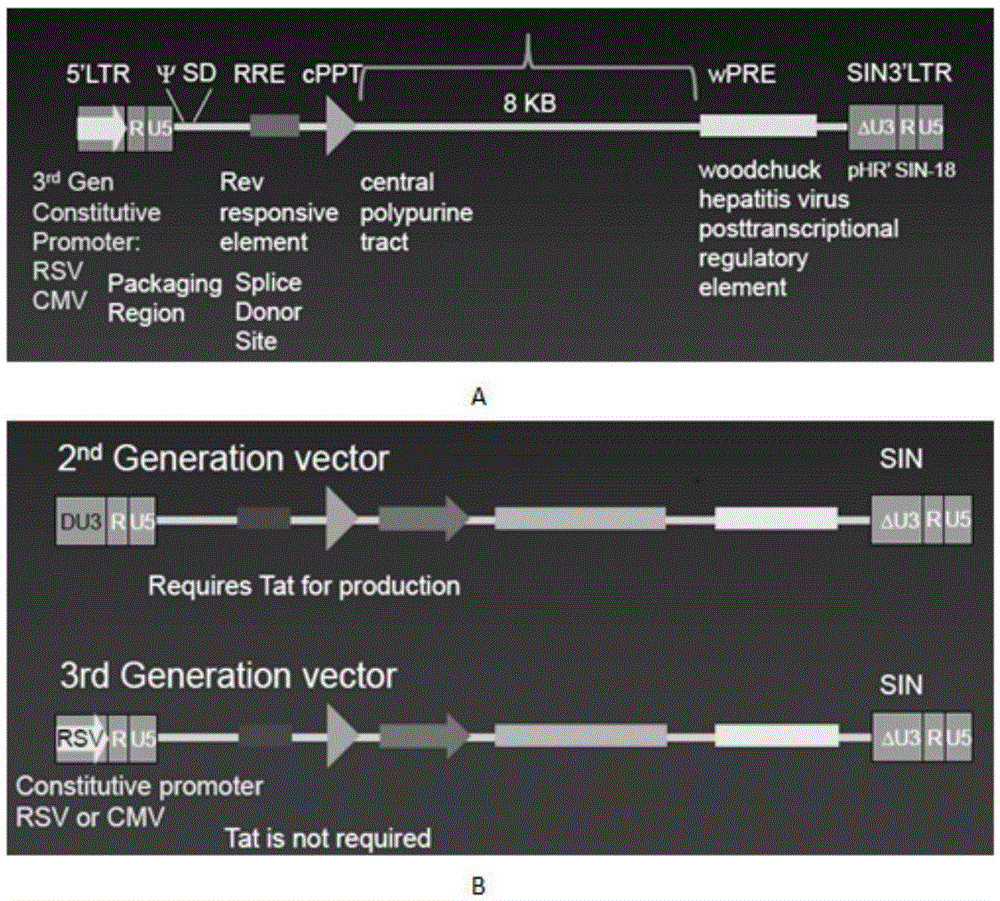
CAR-T transgene vector based on replication defective recombinant lentivirus and construction method and application of CAR-T transgene vector
ActiveCN105602992ASignificant effectPromote secretionGenetic material ingredientsFermentationEucaryotic cellAmpicillin
The invention discloses a CAR-T transgene vector based on replication defective recombinant lentivirus. The CAR-T transgene vector comprises an original nuclear replicon pUCOri sequence, a resistance gene AmpR sequence containing ampicillin, a virus replicon SV40 Ori sequence, a lentivirus packaging cis element, ZsGreen1 green fluorescent protein, an IRES ribosome binding sequence, a human EF1 alpha promoter , a chimeric antigen receptor of second-generation CAR or third-generation CAR and a regulating element, wherein the original nuclear replicon pUCOri sequence is used for plasmid replication; the resistance gene AmpR sequence is used for massively proliferating target strains; the virus replicon SV40 Ori sequence is used for enhancing replication in eukaryocyte; the lentivirus packaging cis element is used for lentivirus packaging; the ZsGreen1 green fluorescent protein is used for expressing green fluorescent for eukaryocyte; the IRES ribosome binding sequence is used for jointly transcribing and expressing protein; the human EF1 alpha promoter is used for conducting eukaryotic transcription on antigen receptor genes; the chimeric antigen receptor is used for forming the second-generation CAR or the third-generation CAR integrating recognition, transfer and start; the regulating element is used for enhancing expression efficiency of transgenes and used after eWPRE-enhanced type woodchuck hepatitis b virus is transcribed. Besides, the invention further discloses a construction method and application of the vector. By means of the CAR-T transgene vector and the construction method and application of the vector, secretion of cell factors and an in vitro killing effect of CAR-T cells can be remarkably improved, and the clinical treatment effect is remarkable.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNICAR THERAPY BIOPHARM TECH CO LTD
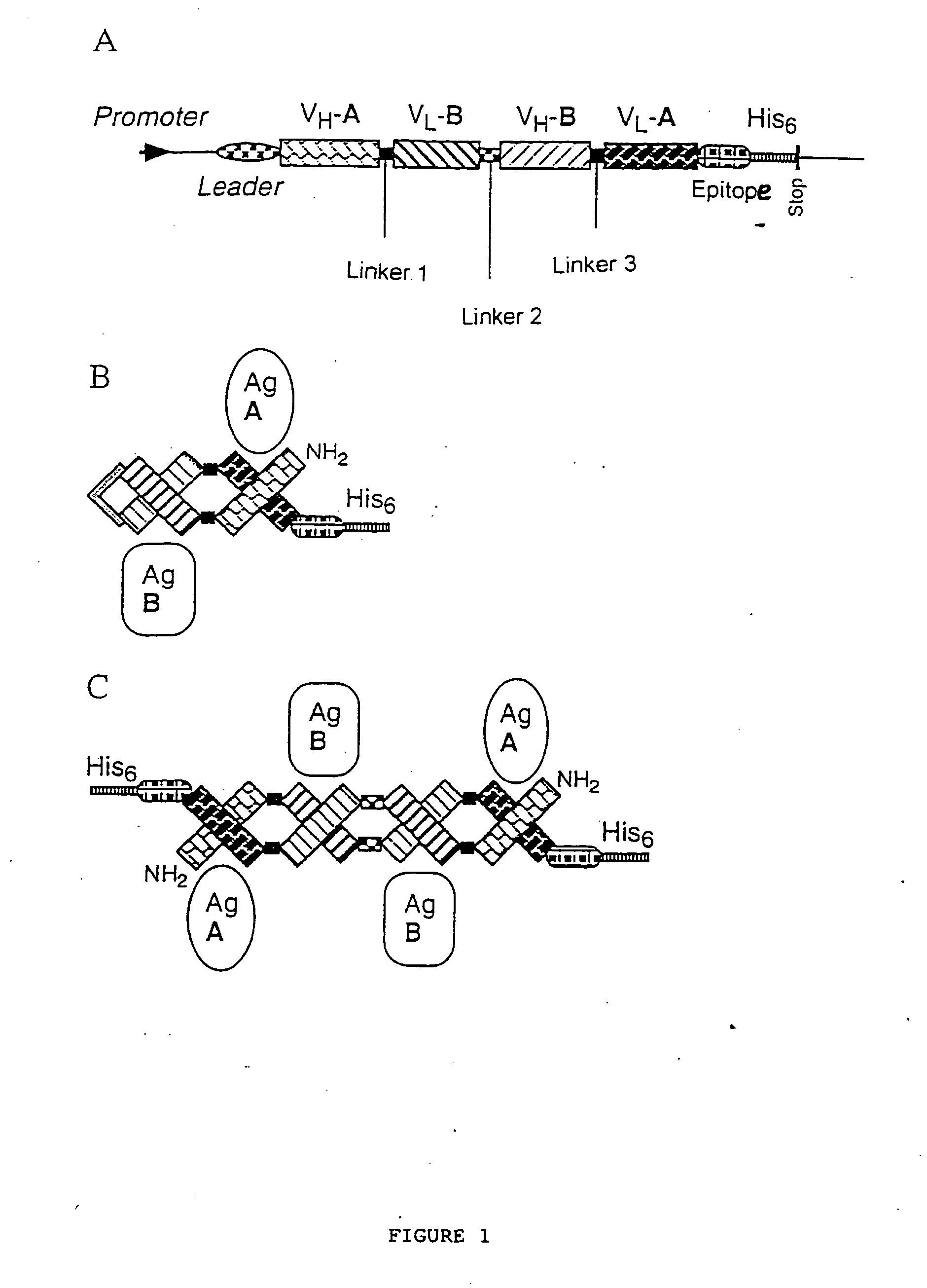
Multivalent antibody contructs
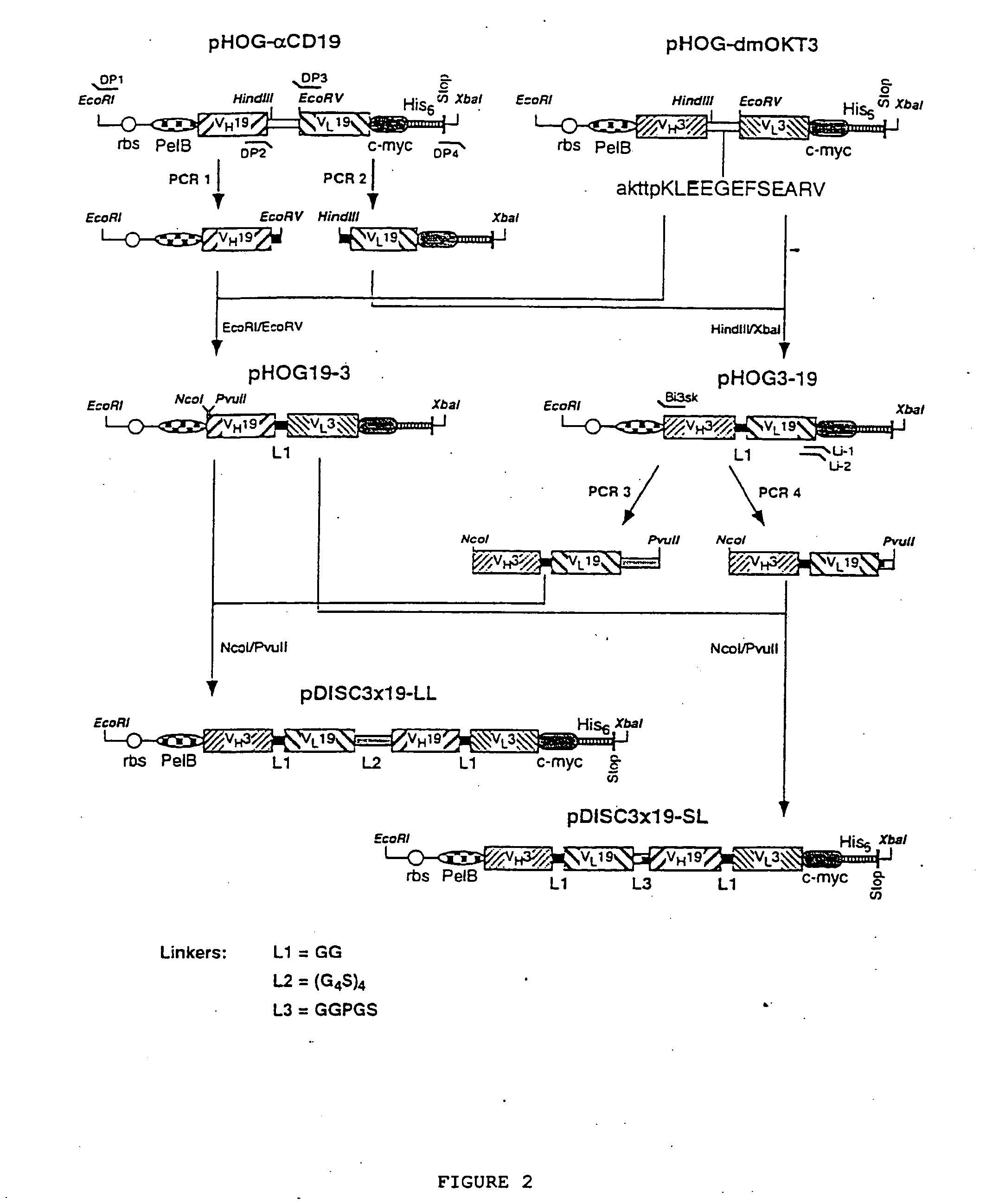
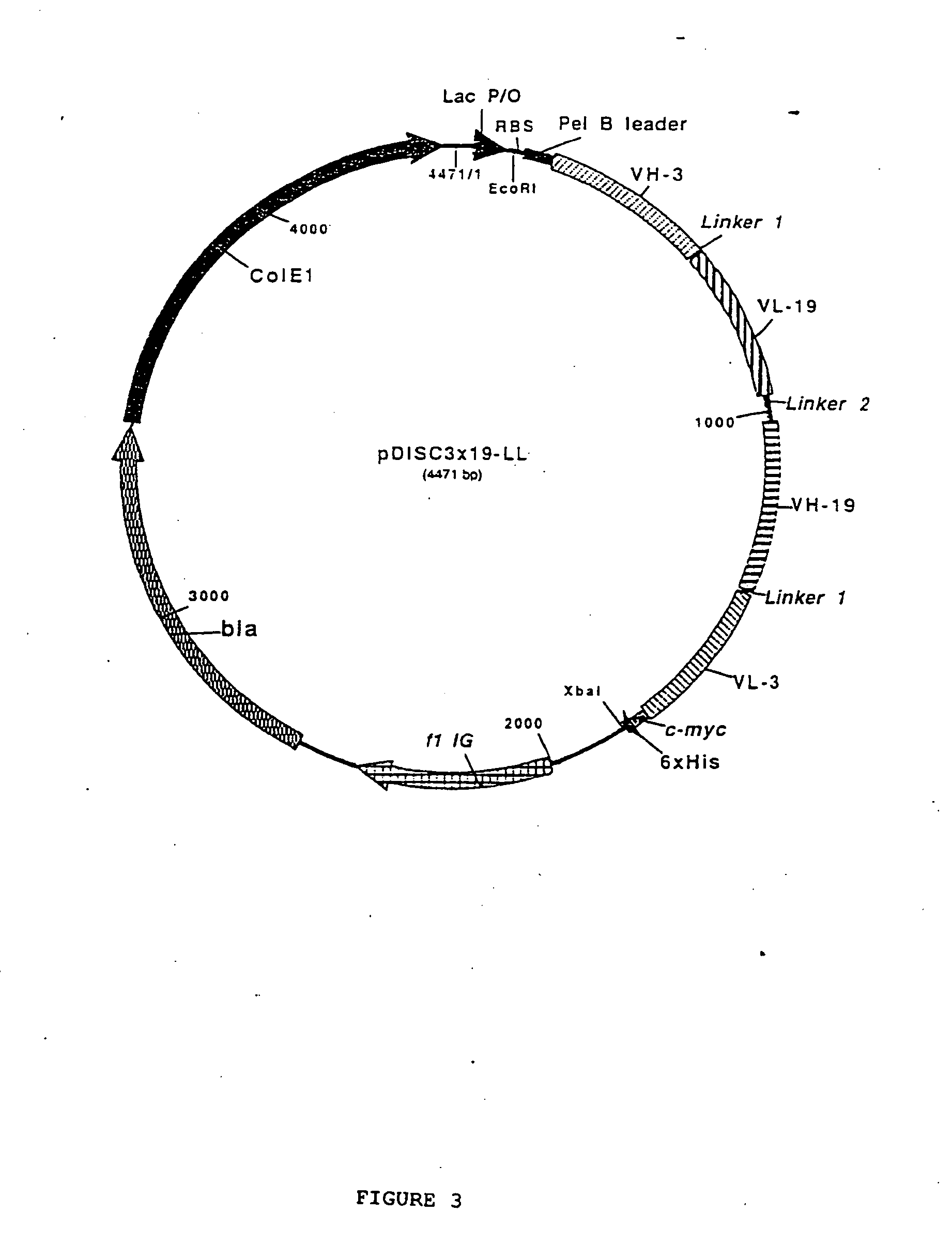
InactiveUS20070031436A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifAnimal cellsEukaryotic plasmidsVariable domain
The present invention relates to a multivalent Fv antibody construct having at least four variable domains which are linked with each over via the peptide linkers 1, 2 and 3. The invention also concerns expression plasmids which code for such an Fv antibody construct and a method of producing the Fv antibody constructs as well as their use.
Owner:DEUTES KREBSFORSCHUNGSZENT STIFTUNG DES OFFENTLICHEN RECHTS
Recombinant viruses displaying a nonviral polypeptide on their external surface
InactiveUS6297004B1Genetic material ingredientsImmunological disordersGene deliveryAntibody fragments
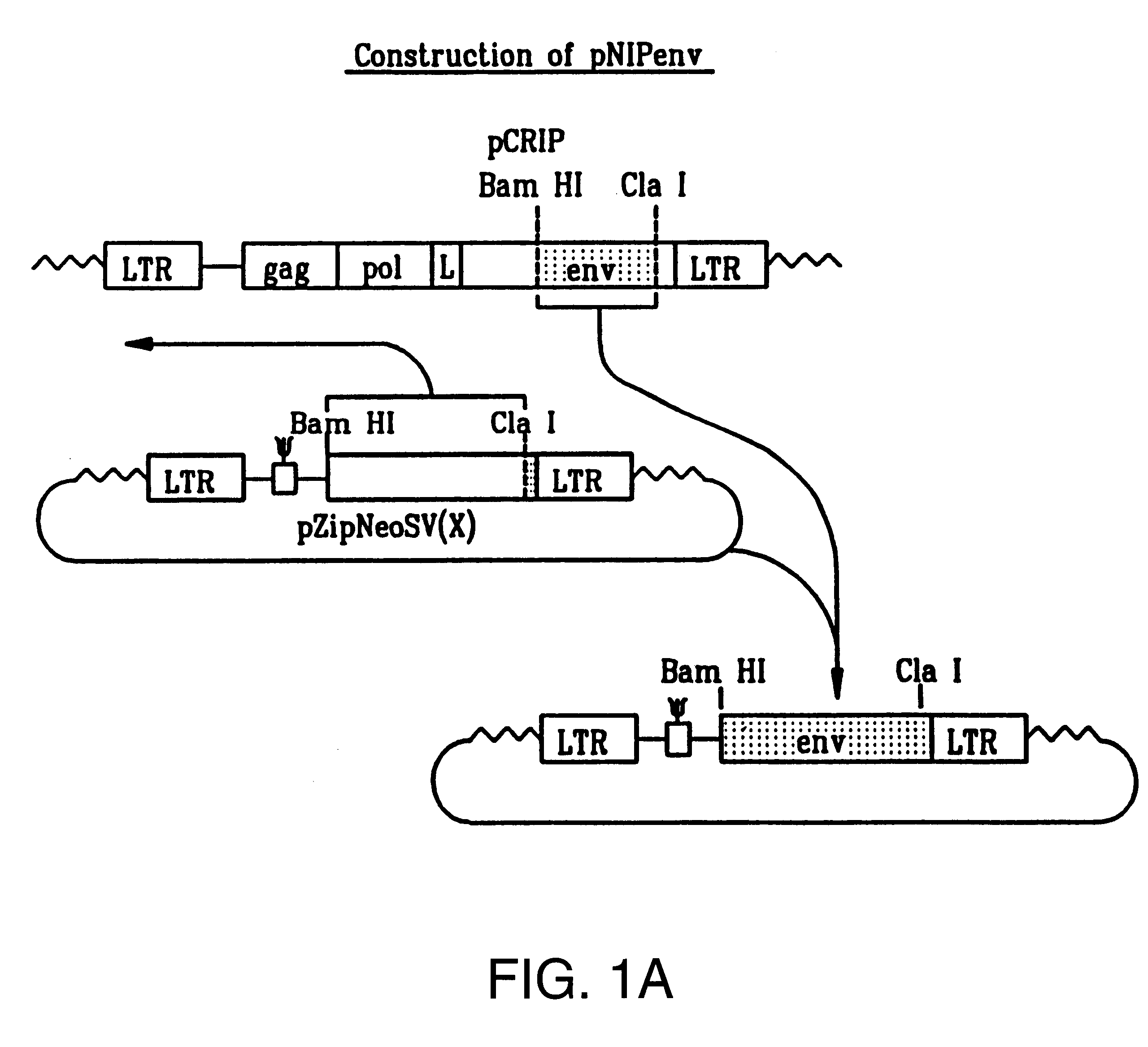
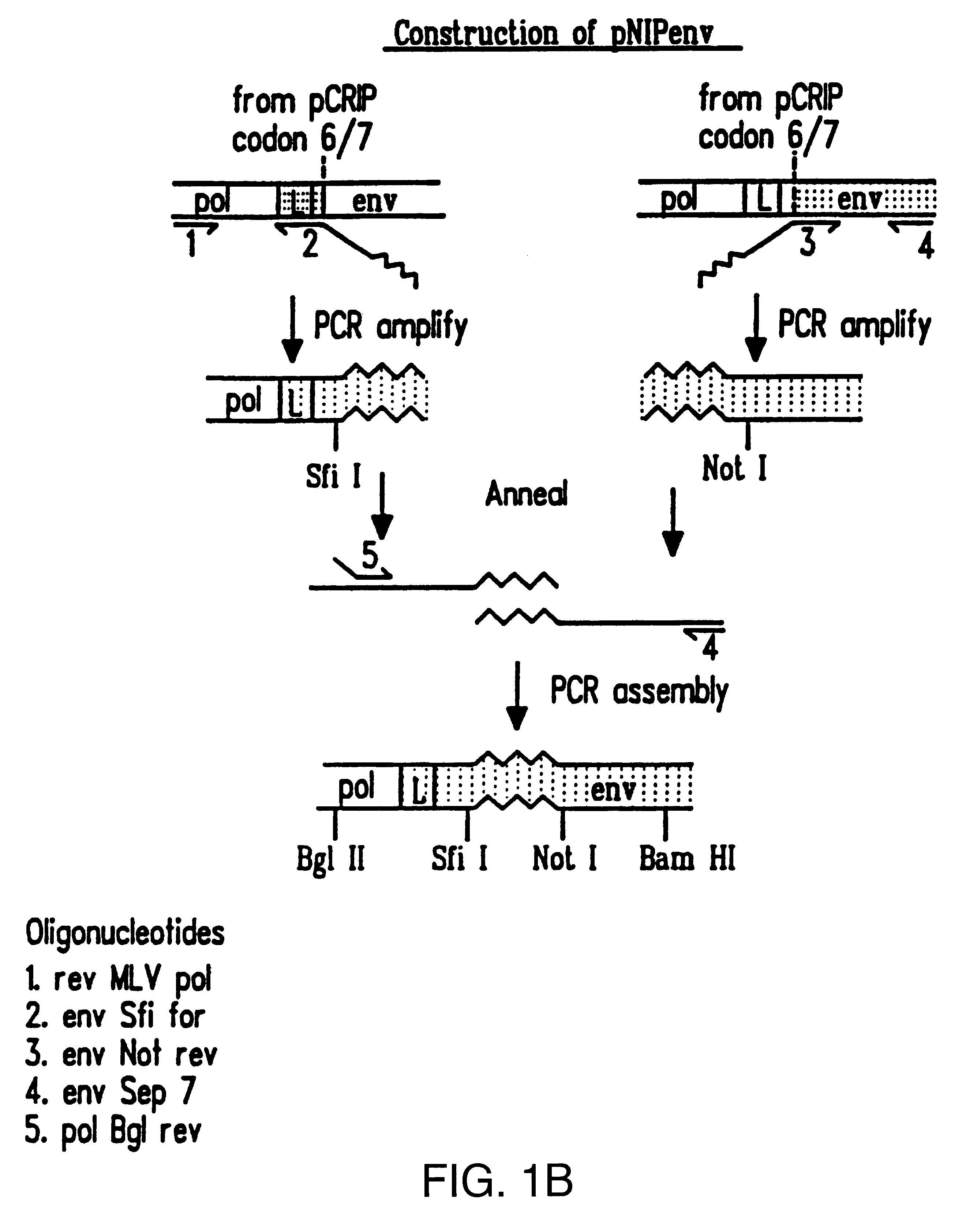
We have made retrovirus particles displaying a functional antibody fragment. We fused the gene encoding an antibody fragment directed against a hapten with that encoding the viral envelope protein (Pr80env) of the ecotropic Moloney murine leukemia virus. The fusion gene was co-expressed in ecotropic retroviral packaging cells with a retroviral plasmid carrying the neomycin phosphotransferase gene (neo), and retroviral particles with specific hapten biding activities were recovered. Furthermore the hapten-binding particles were able to transfer the neo gene and the antibody-envelope fusion gene to mouse fibroblasts. In principle, the display of antibody fragments on the surface of recombinant retroviral particles could be used to target virus to cells for gene delivery, or to retain the virus in target tissues, or for the construction of libraries of viral display packages.
Owner:BIOFOCUS DICOVERY
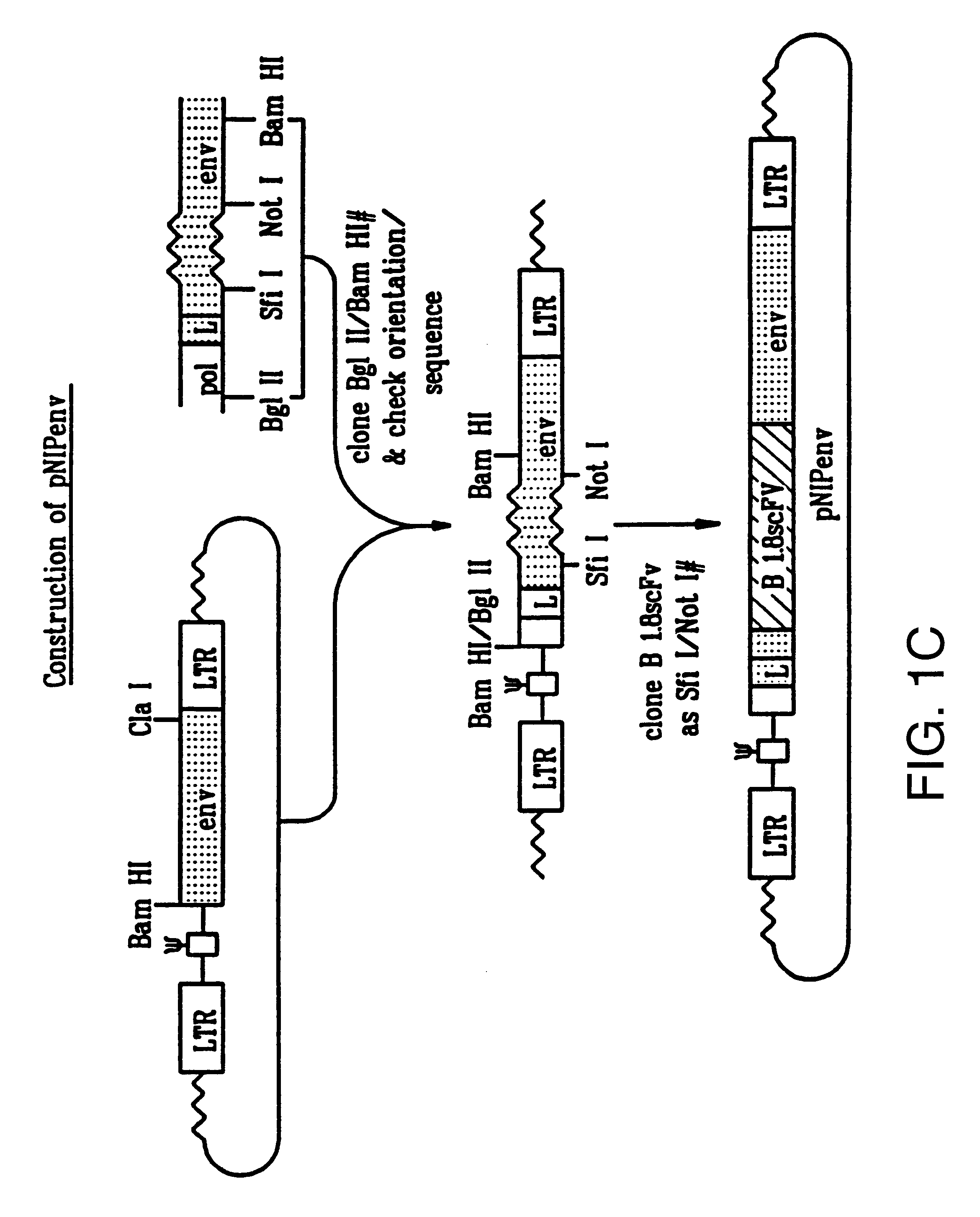
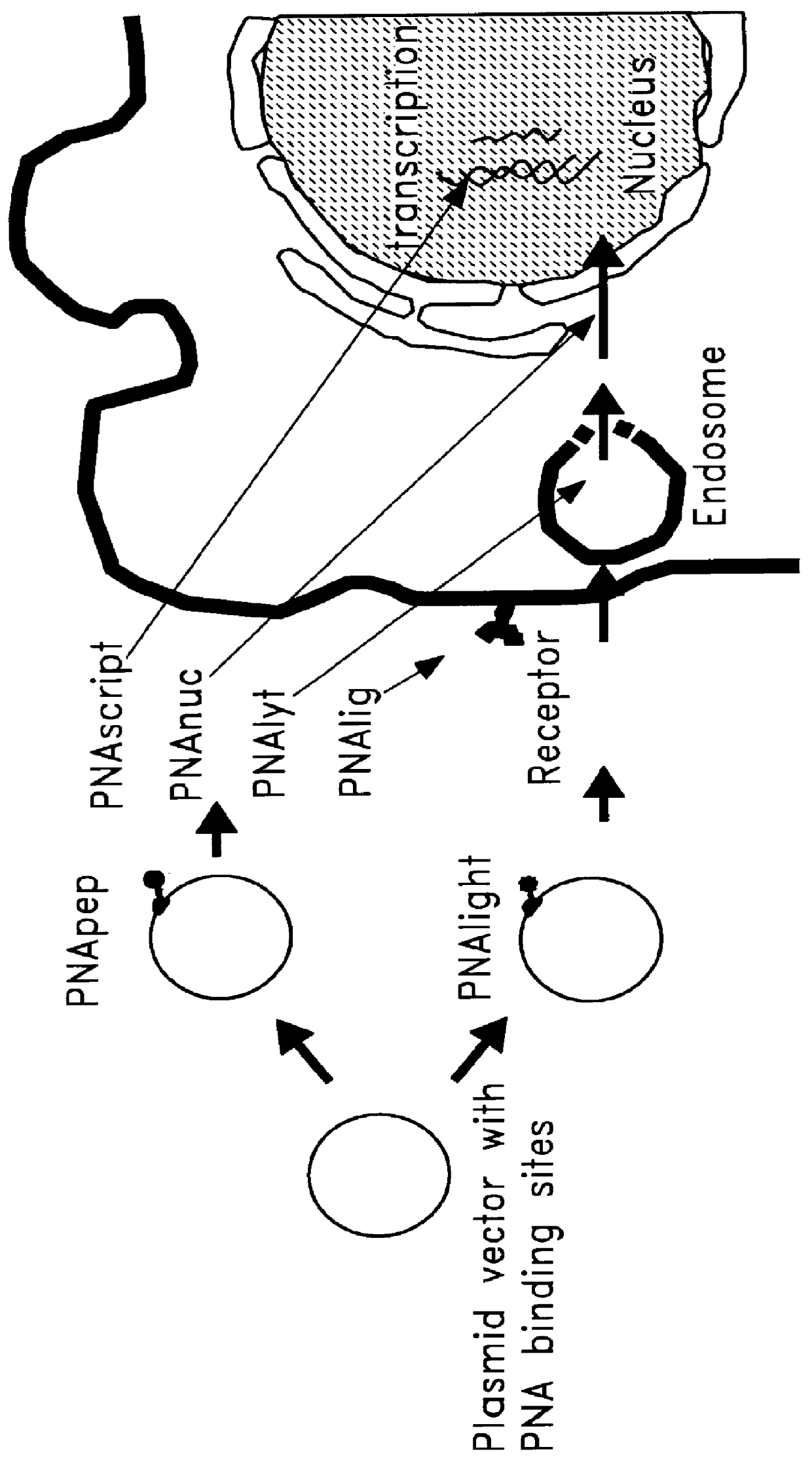
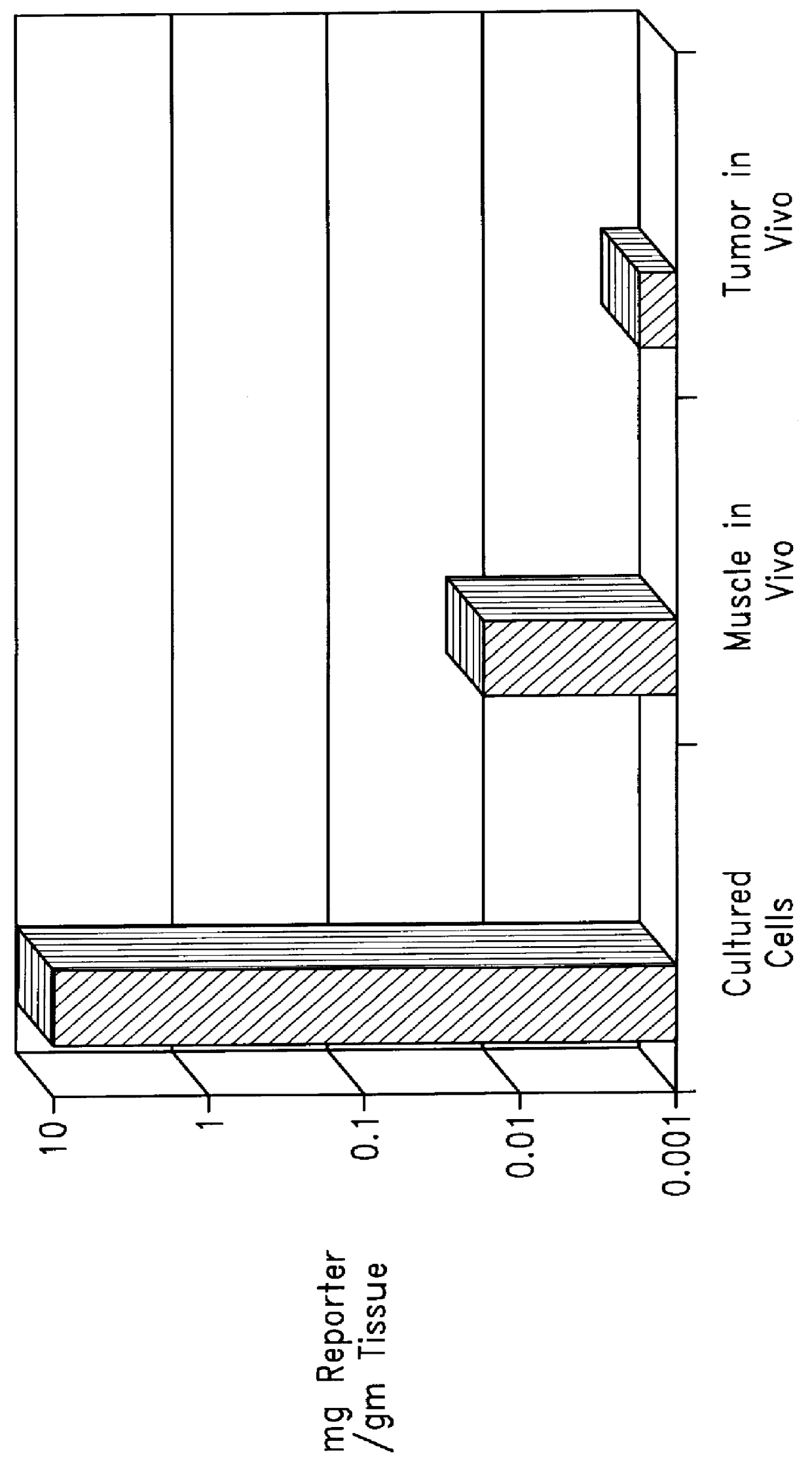
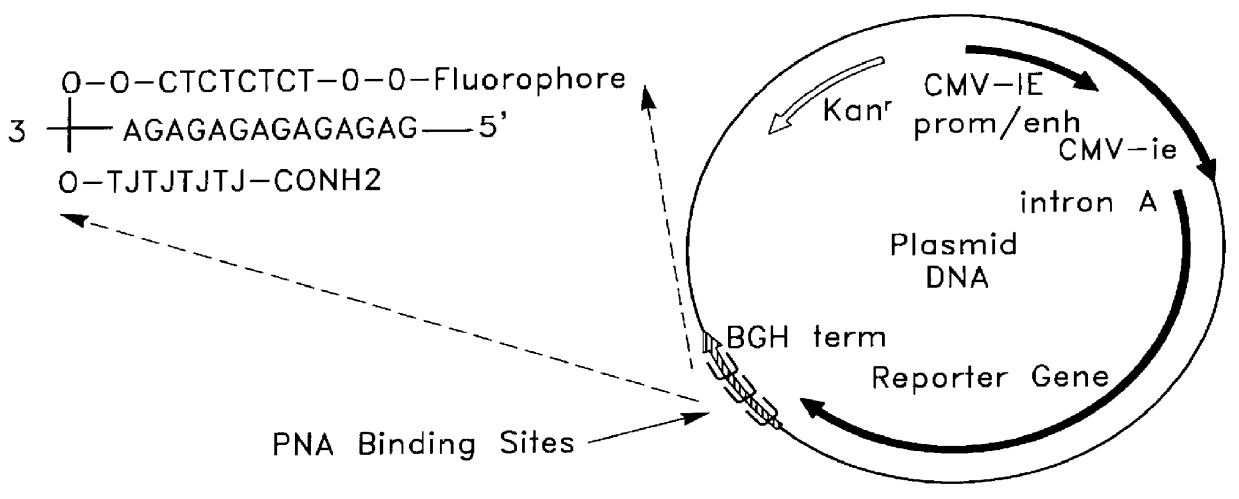
Chemical modification of DNA using peptide nucleic acid conjugates
InactiveUS6165720AReduce deliveryHigh transfection efficiencyFungiBacteriaEukaryotic plasmidsBiological activation
Complexes comprising a nucleic acid molecule and a conjugated peptide nucleic acid (PNA). The PNA may be labeled or conjugated to a protein, peptide, carbohydrate moiety or receptor ligand. These complexes are used to transfect cells to monitoring plasmid biodistribution, promote nuclear localization, induce transcriptional activation, lyse the endosomal compartment and facilitate transfection. These complexes increase the efficiency of expression of a particular gene.
Owner:GENE THERAPY SYST +1
Plants with improved water deficit and cold tolerance
The present invention provides nucleic acid constructs, including plasmids, expression vectors or expression cassettes comprising polynucleotides encoding CCAAT-binding transcription factor polypeptides that have the ability to increase a plant's tolerance to abiotic stress. Polynucleotides encoding functional CCAAT-binding transcription factors were incorporated into expression vectors, introduced into plants, and ectopically expressed. The encoded polypeptides of the invention significantly increased the cold and water deficit tolerance of the transgenic plants, as compared to tolerance to these stresses of control plants.
Owner:MENDEL BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
Delivering functional nucleic acids to mammalian cells via bacterially-derived, intact minicells
ActiveUS20070298056A1Eliminate side effectsPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsEukaryotic plasmidsDrug resistance
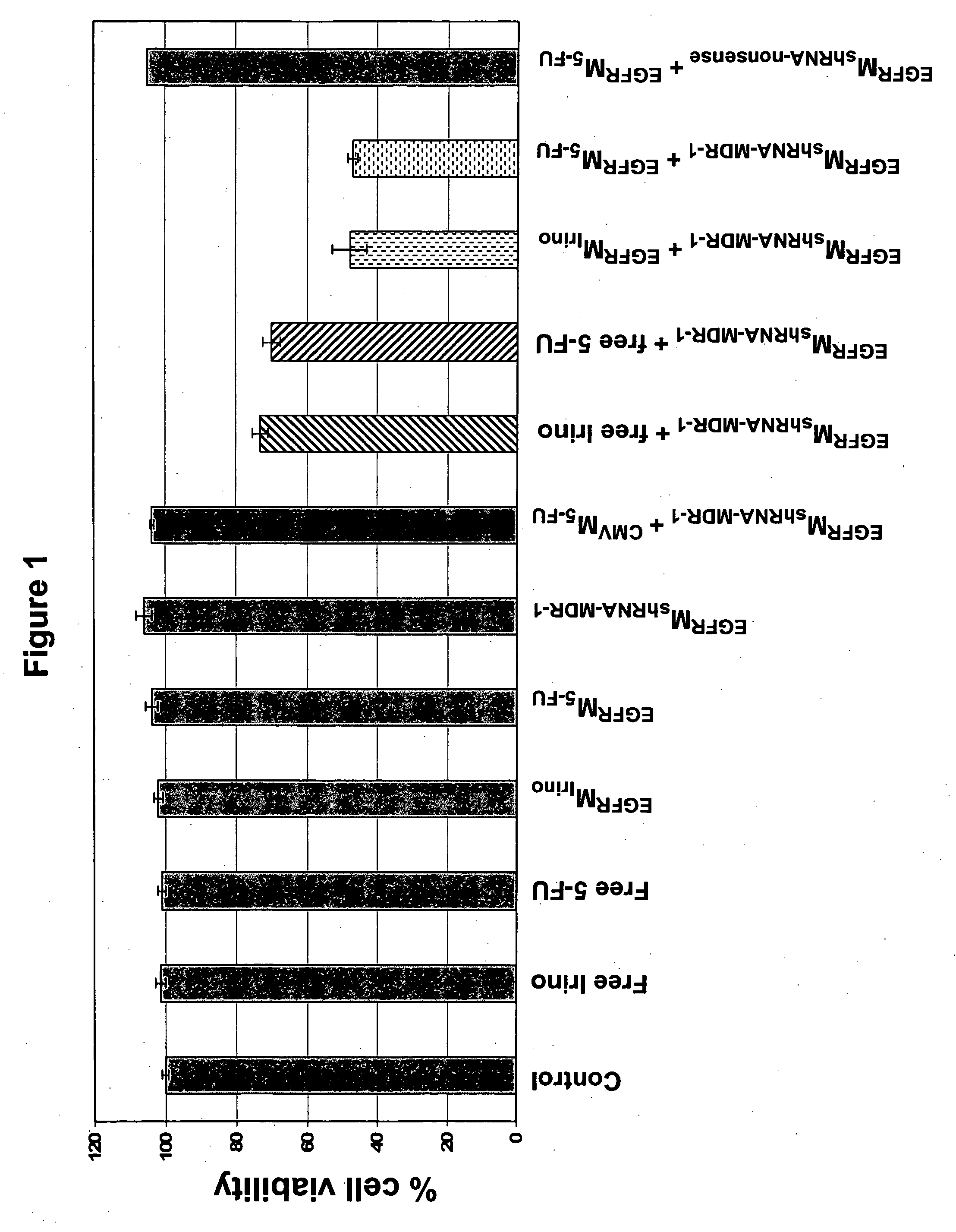
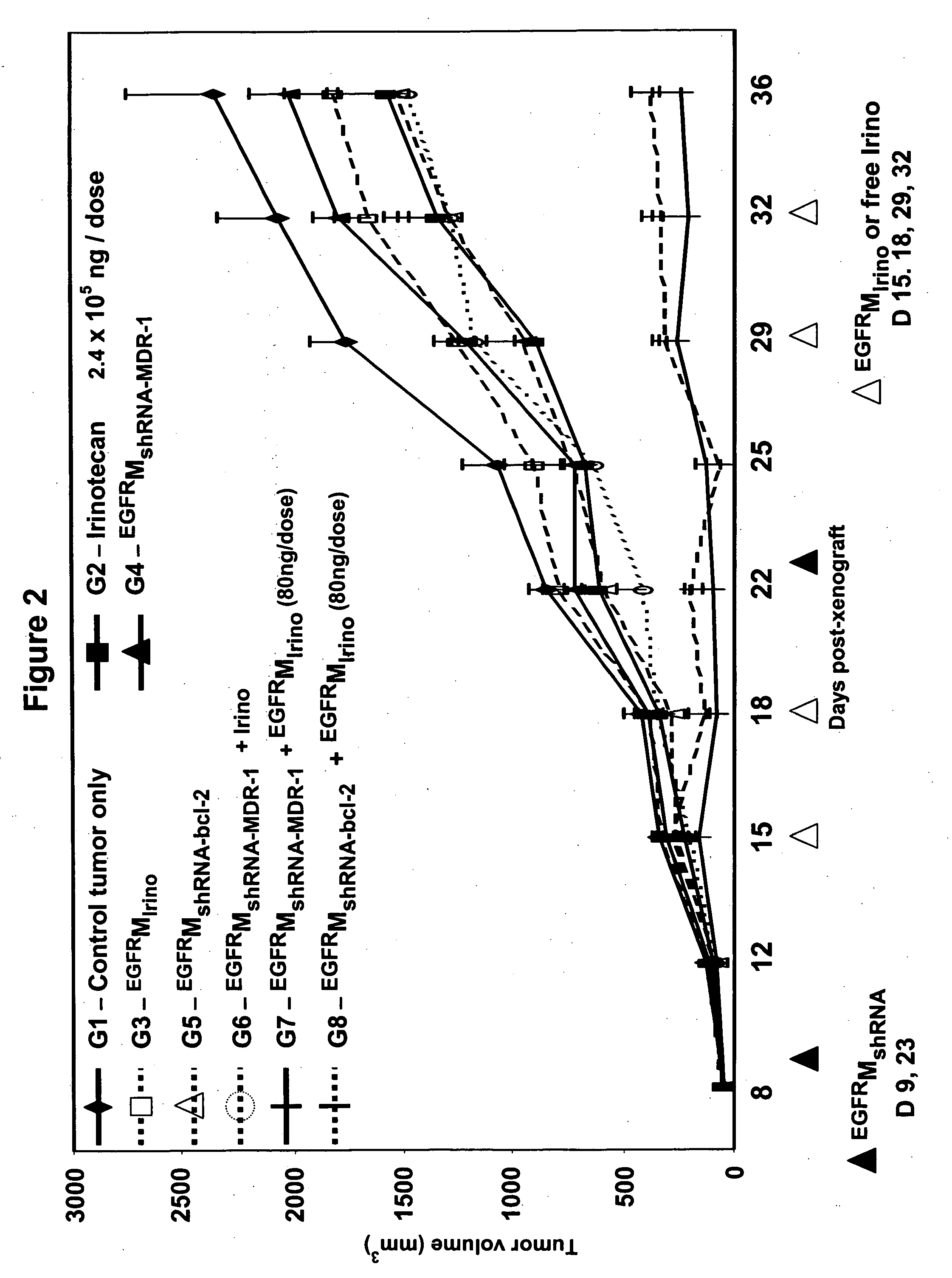
Intact bacterially derived minicells containing functional nucleic acids or plasmids encoding functional nucleic acids can reduce, in targeted mammalian cells, drug resistance, apoptosis resistance, and neoplasticity, respectively. Methodology that employs minicells to deliver functional nucleic acids, targeting the transcripts of proteins that contribute to drug resistance or apoptosis resistance, inter alia, can be combined with chemotherapy to increase the effectiveness of the chemotherapy.
Owner:ENGENEIC MOLECULAR DELIVERY PTY LTD
Genetically modified Cyanobacteria for the production of ethanol, the constructs and method thereof
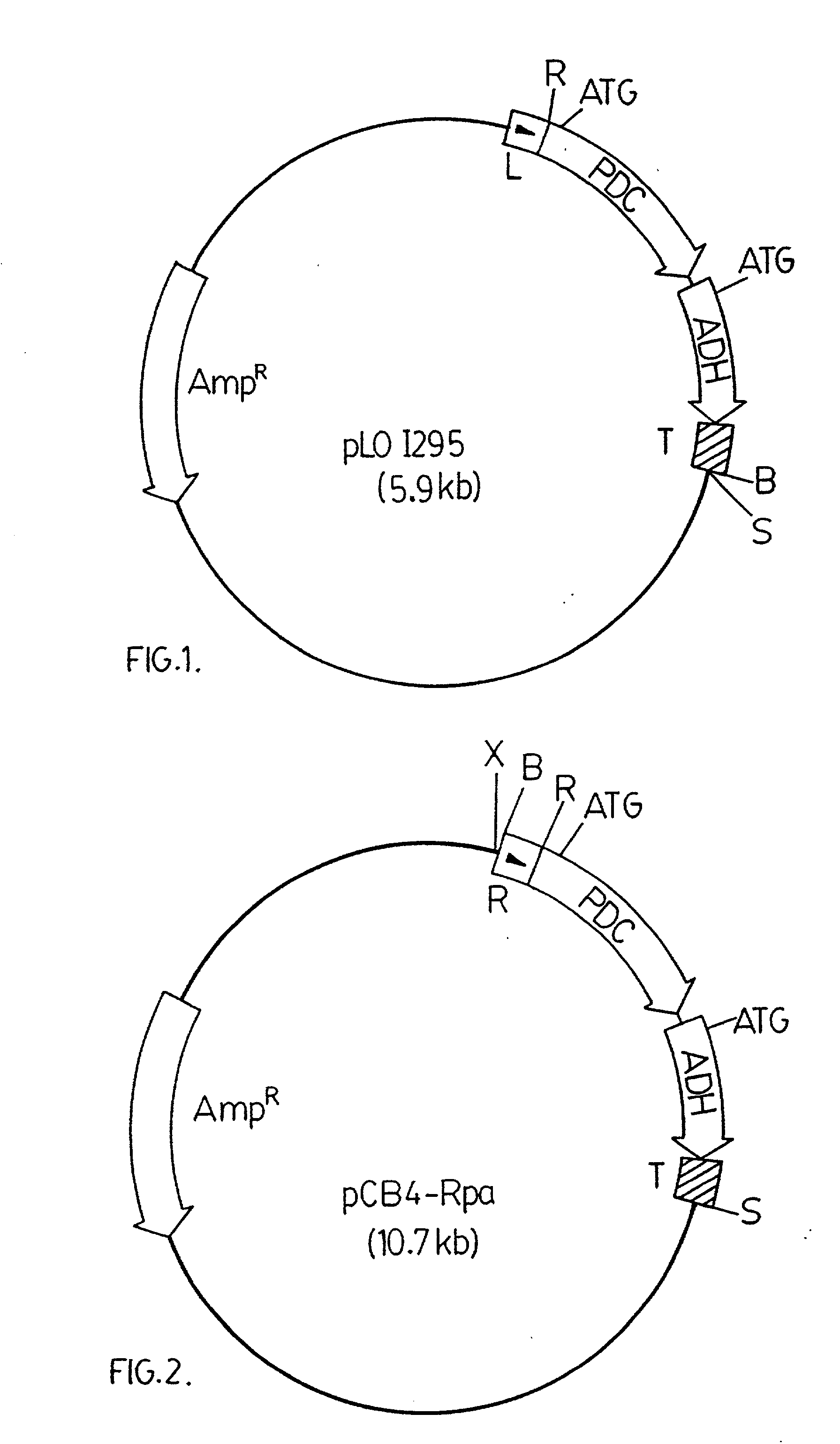
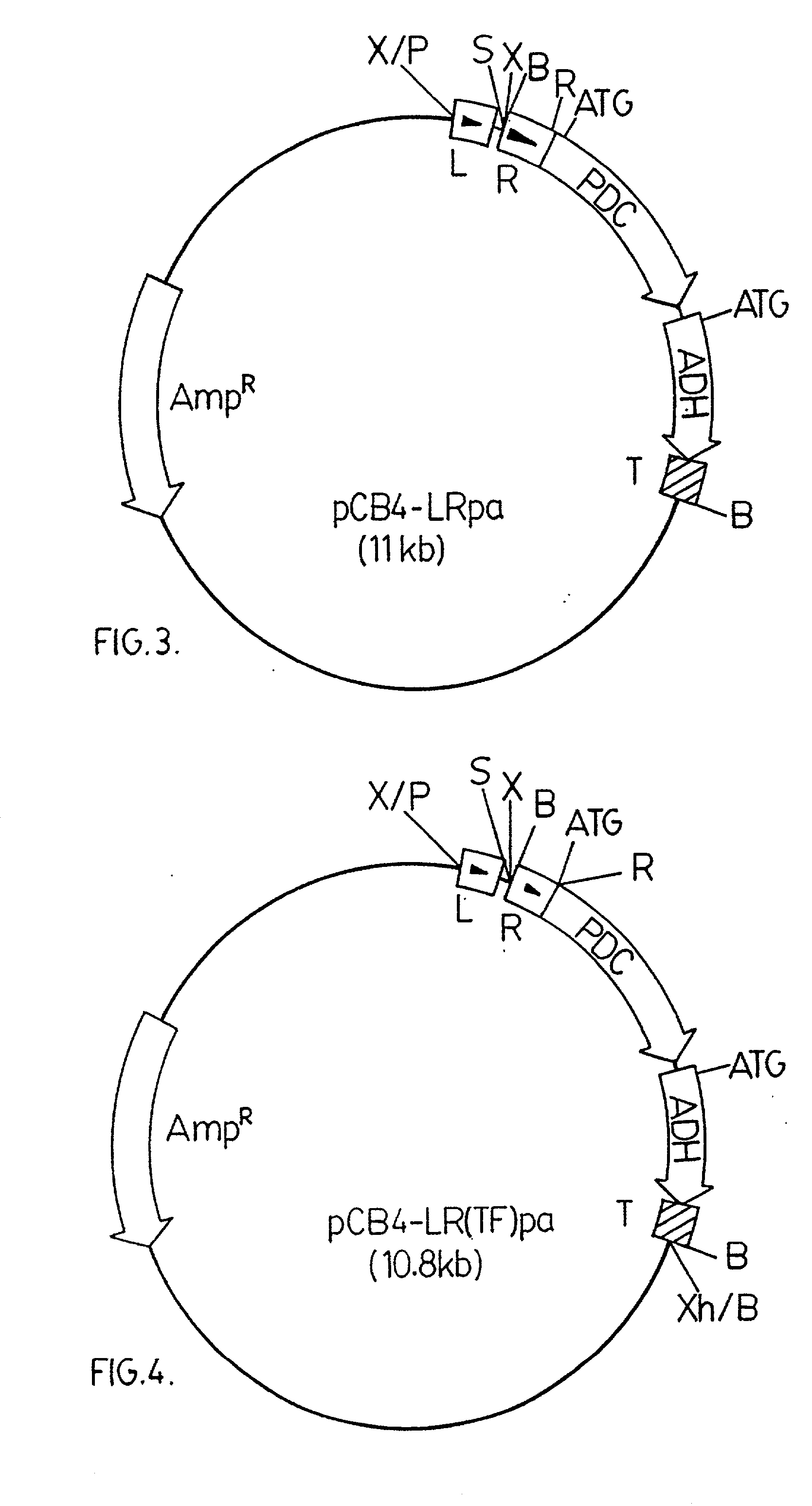
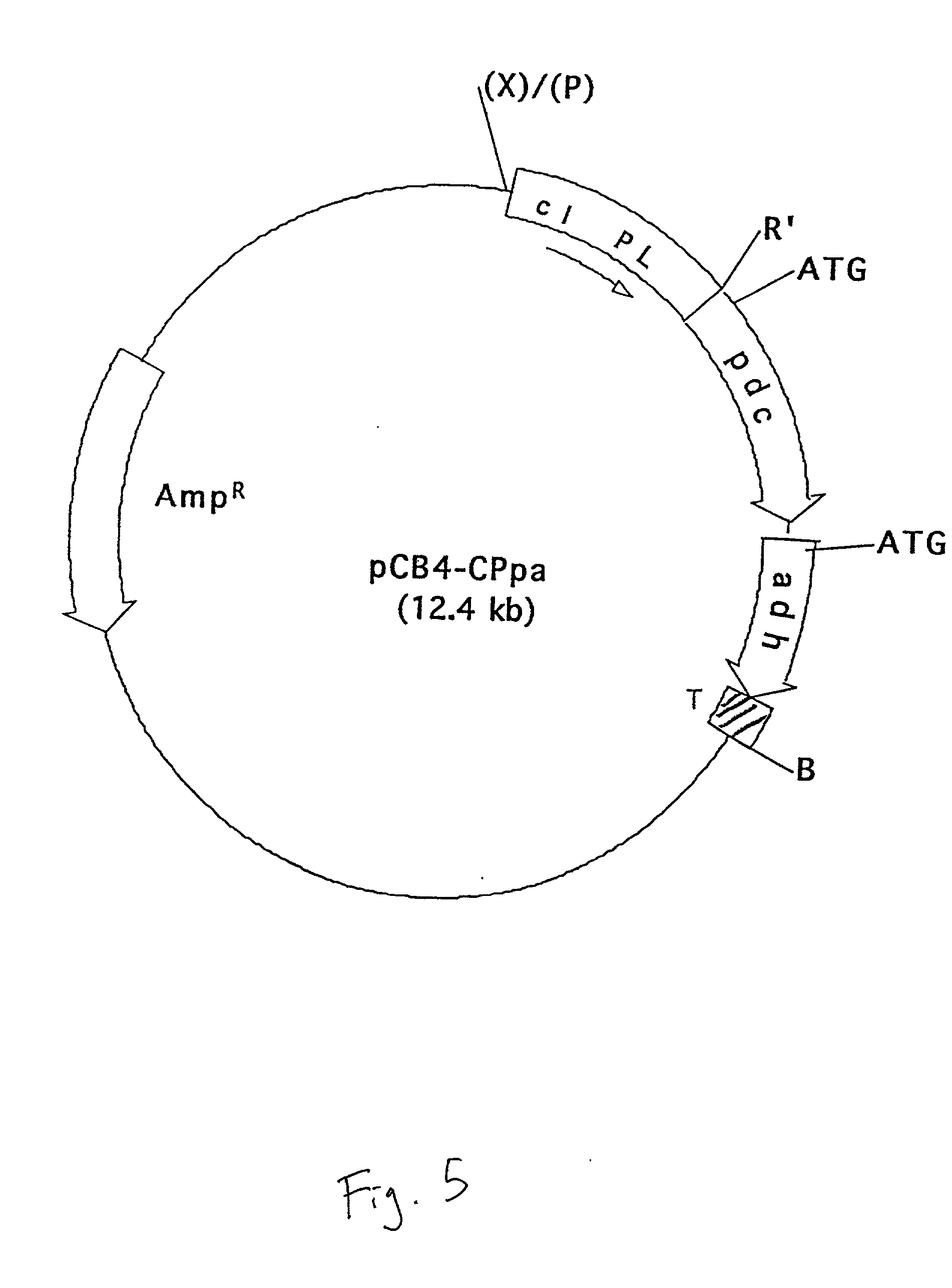
The invention provides a genetically modified Cyanobacteria having a construct comprising DNA fragments encoding pyruvate decarboxylase (pdc) and alcohol dehydrogenase (adh) enzymes obtained from the Zymomonas mobilis plasmid pLOI295. The Cyanobacteria are capable of producing ethanol in recoverable quantities of at least 1.7 mumol ethanol per mg of chlorophyll per hour.
Owner:ENOL ENERGY
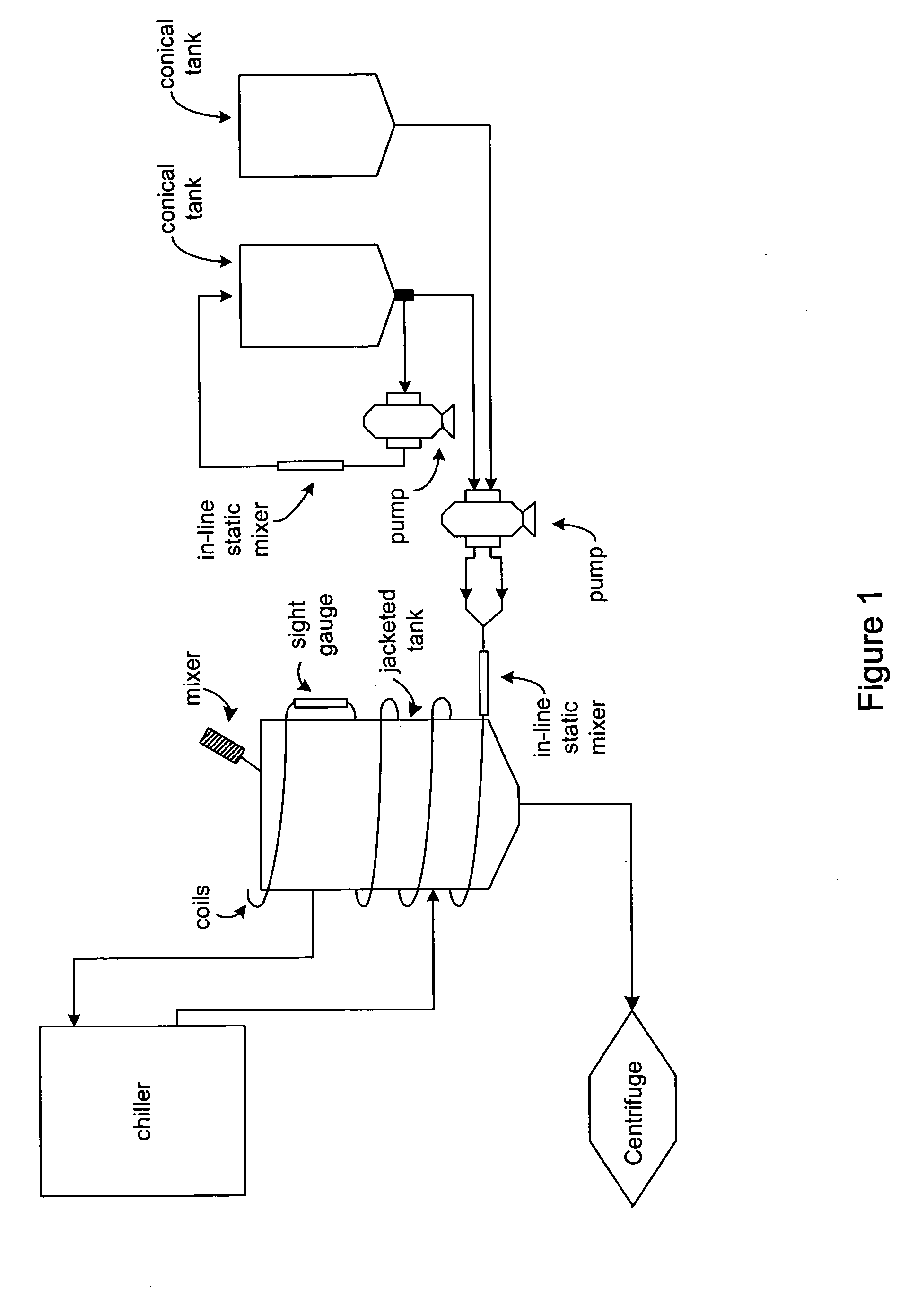
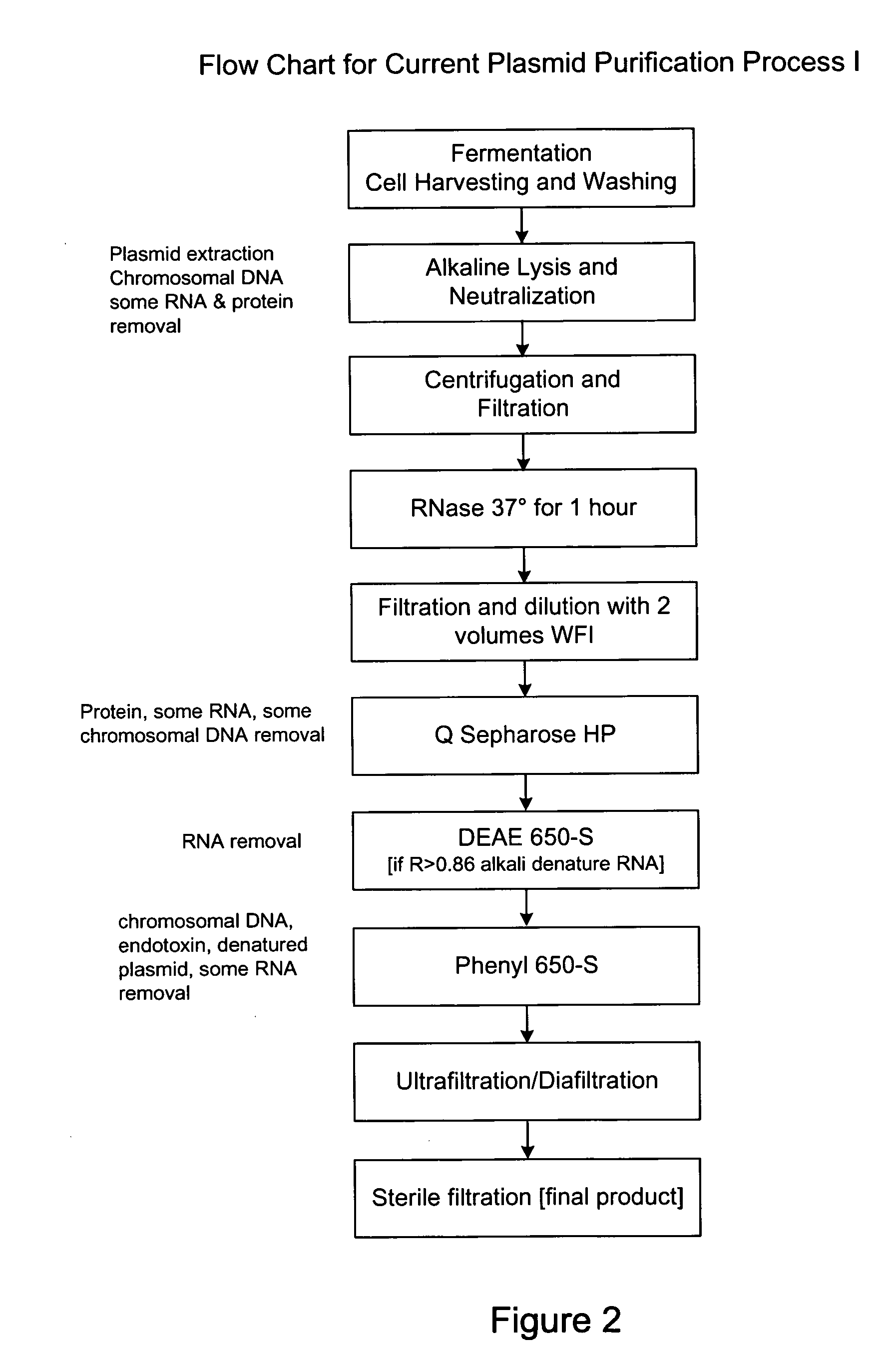
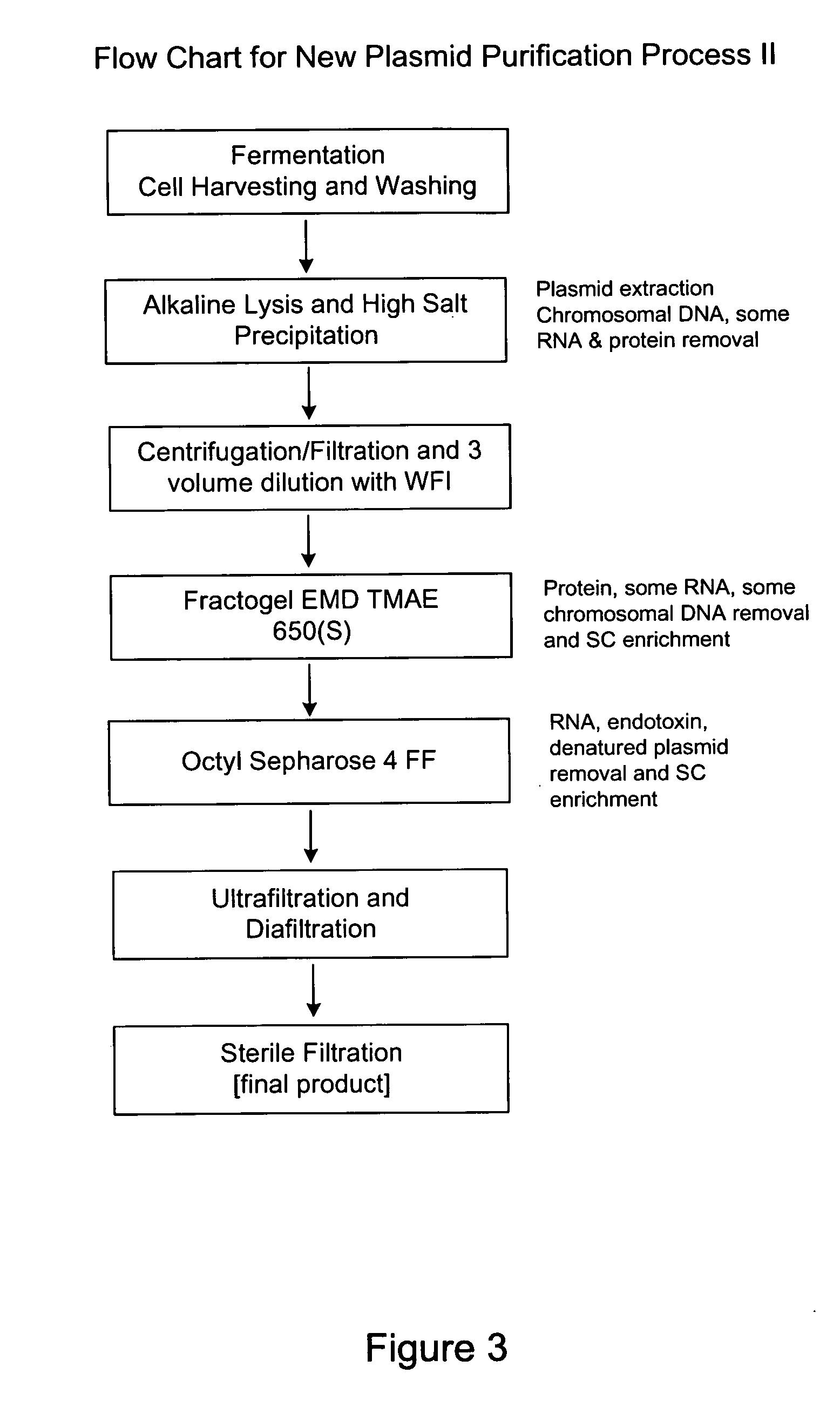
Process and equipment for plasmid purfication
InactiveUS20060106208A1Easy to operateConsistent levelCation exchanger materialsIon-exchanger regenerationLysisGram
A scalable alkaline lysis process, including procedures and devices for the isolation of large quantities (grams and kilograms) of plasmid DNA from recombinant E. coli cells. Effective, controllable, and economical operation, and consistent low level of host chromosomal DNA in the final plasmid product. Involves a series of new unit operations and devices for cell resuspension, cell lysis, and neutralization.
Owner:URIGEN PHARMA INC
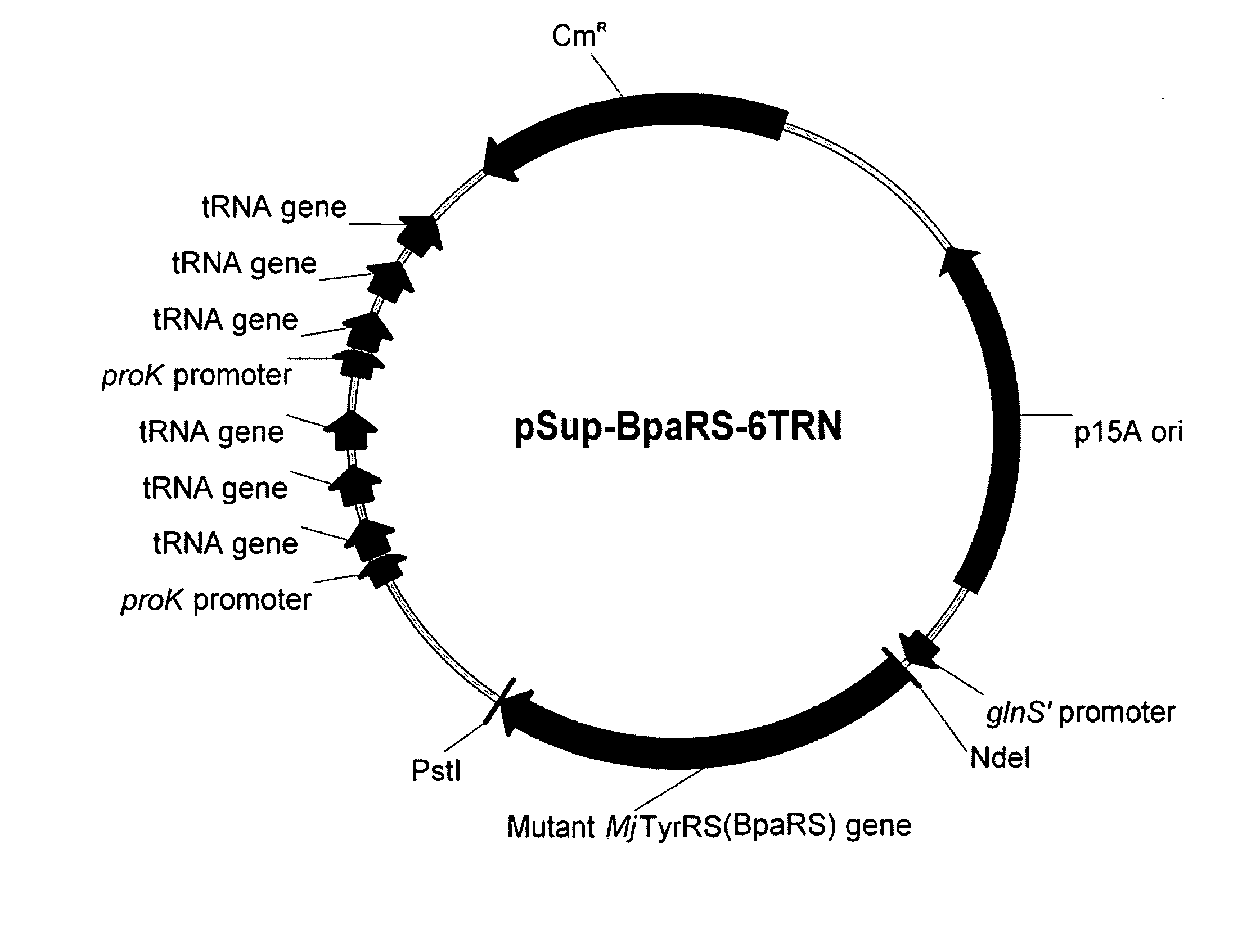
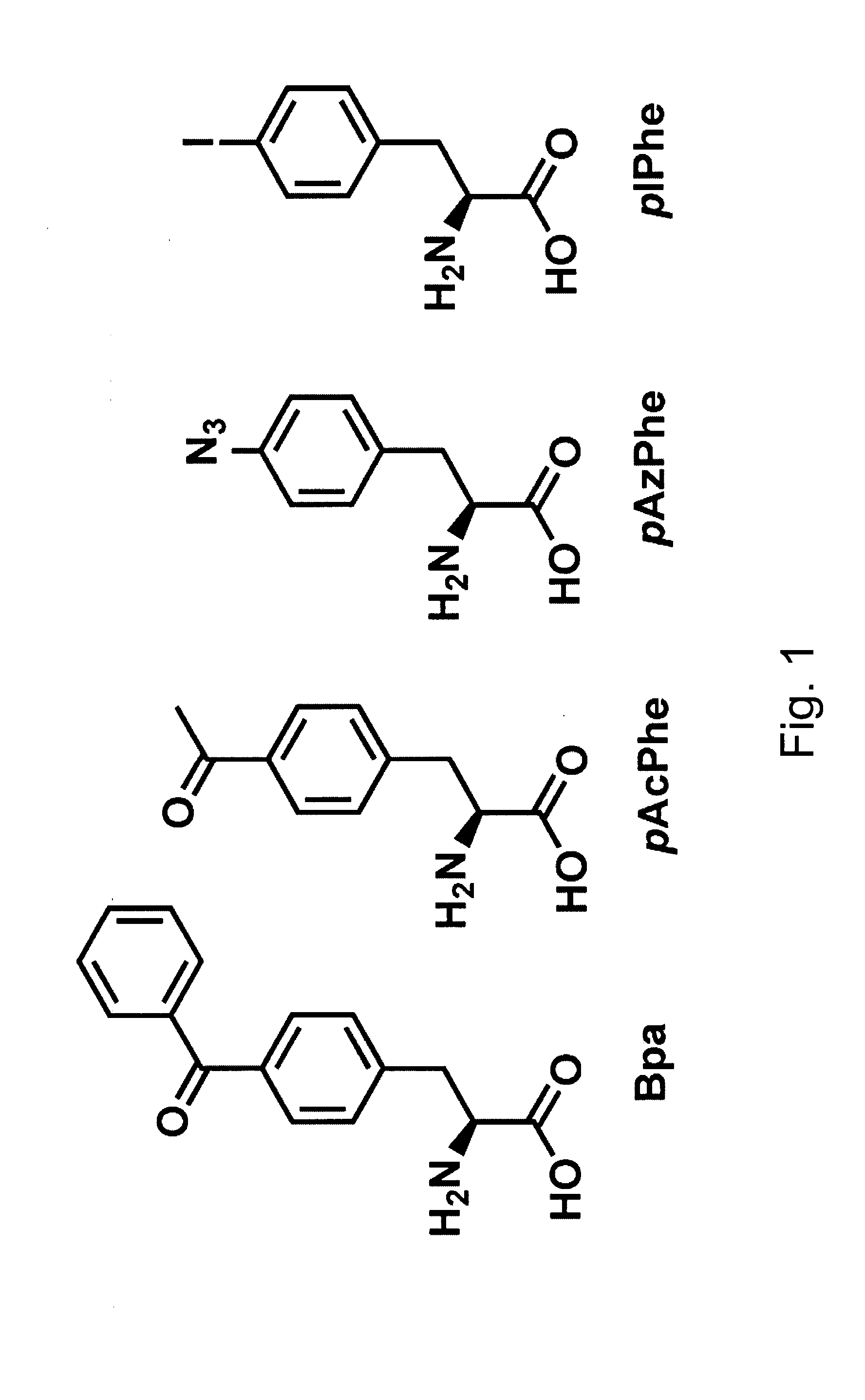
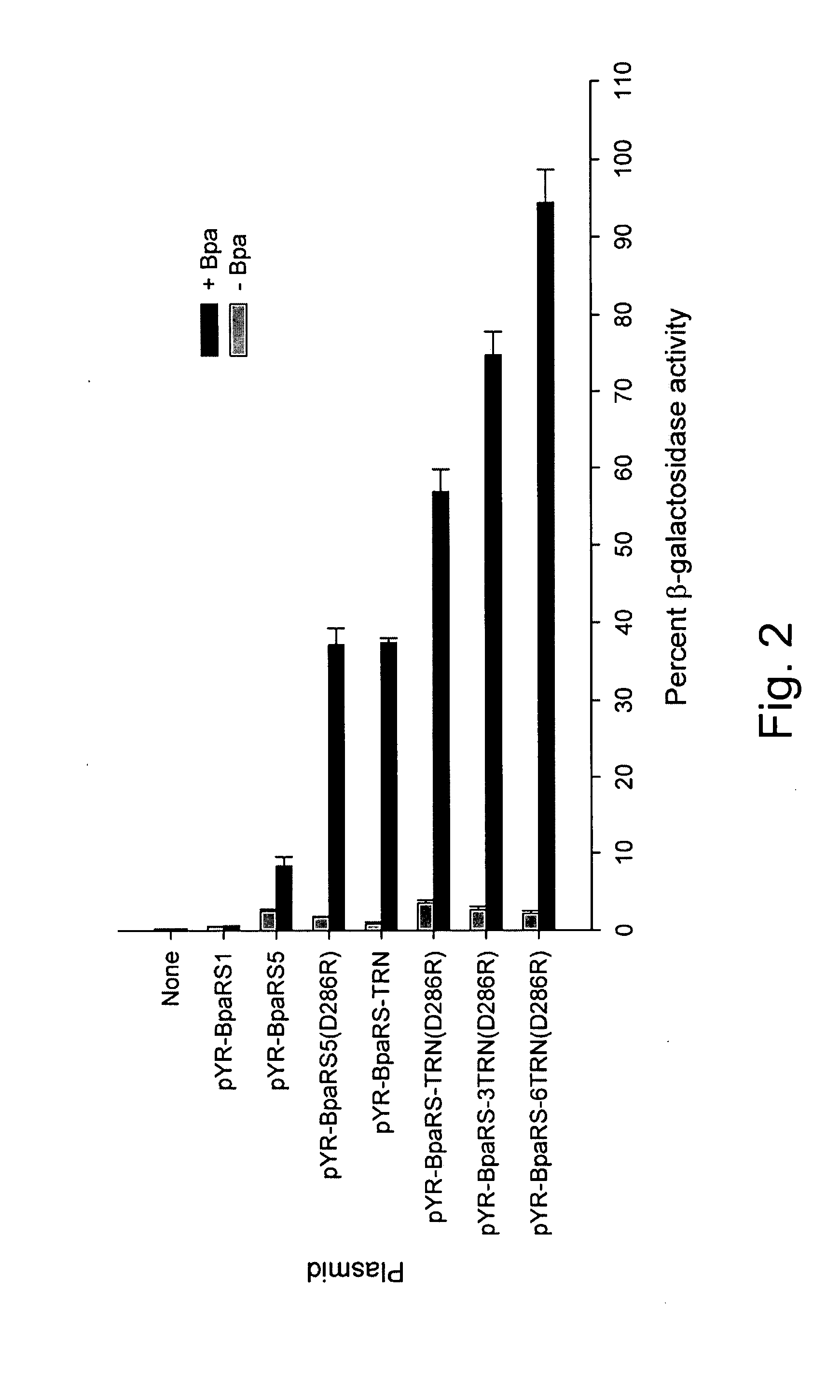
Systems for the expression of orthogonal translation components in eubacterial host cells
ActiveUS20070281335A1Improve efficiencyEfficient expressionSugar derivativesBacteriaEukaryotic plasmidsIn vivo
The invention relates to compositions and methods for the in vivo production of polypeptides comprising one or more unnatural amino acids. Specifically, the invention provides plasmid systems for the efficient eubacterial expression of polypeptides comprising one or more unnatural amino acids at genetically-programmed positions.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
DNA vaccines encoding antigen linked to a domain that binds CD40
InactiveUS20070025982A1Improve abilitiesEasy to demonstrateAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsVirus peptidesPeptide antigenEukaryotic plasmids
Vaccines that target one or more antigens to a cell surface receptor improve the antigen-specific humoral and cellular immune response. Antigen(s) linked to a domain that binds to a cell surface receptor are internalized, carrying antigen(s) into an intracellular compartment where the antigen(s) are digested into peptides and loaded onto MHC molecules. T cells specific for the peptide antigens are activated, leading to an enhanced immune response. The vaccine may comprise antigen(s) linked to a domain that binds at least one receptor or a DNA plasmid encoding antigen(s) linked to a domain that binds at least one receptor. A preferred embodiment of the invention targets HIV-1 env antigen to the CD40 receptor, resulting in delivery of antigen to CD40 positive cells, and selective activation of the CD40 receptor on cells presenting HIV-1 env antigens to T cells.
Owner:LEDBETTER JEFFREY A +1
Methods and compositions for diagnosis and treatment of pathological conditions related to abnormal dopamine receptor expression
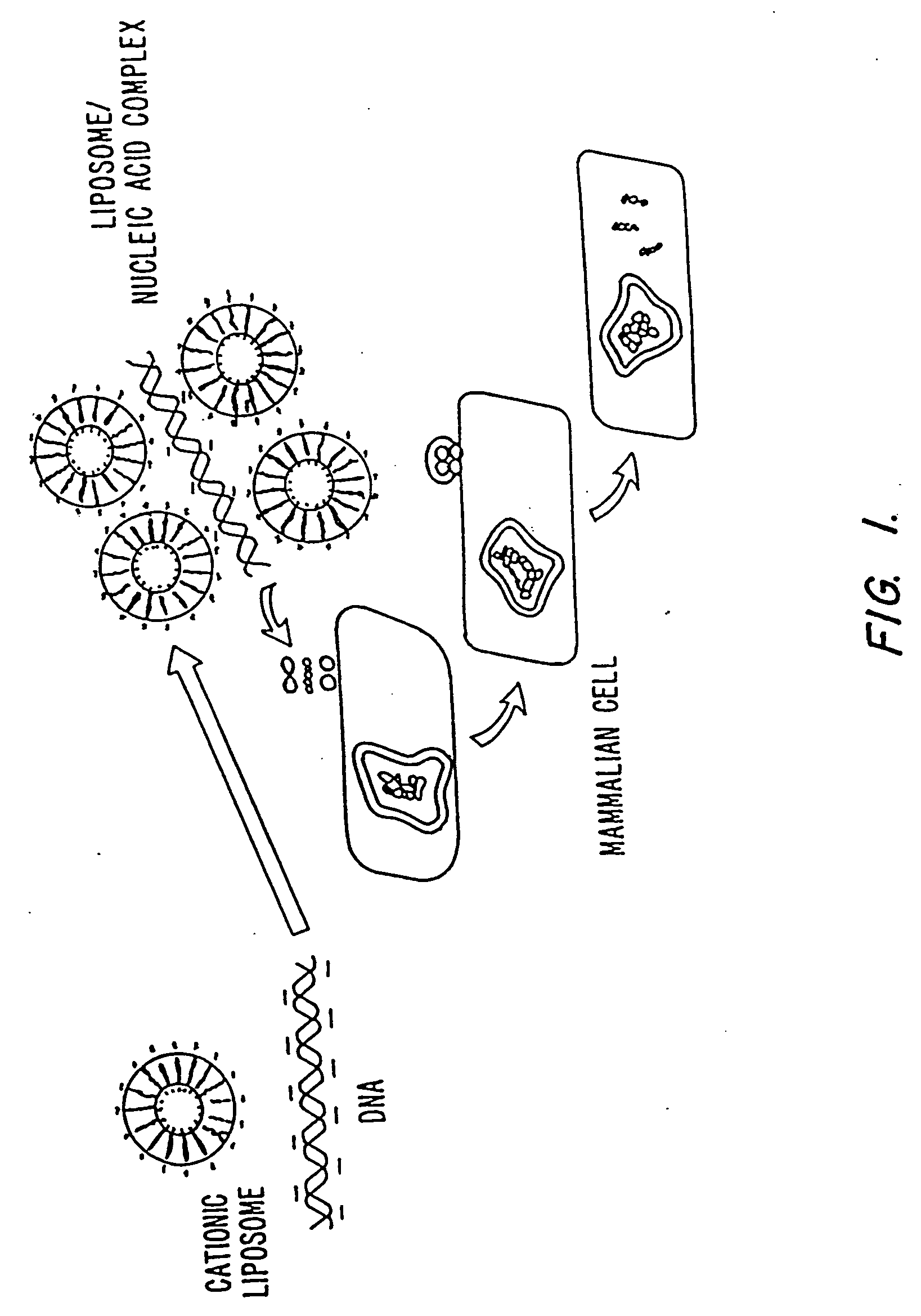
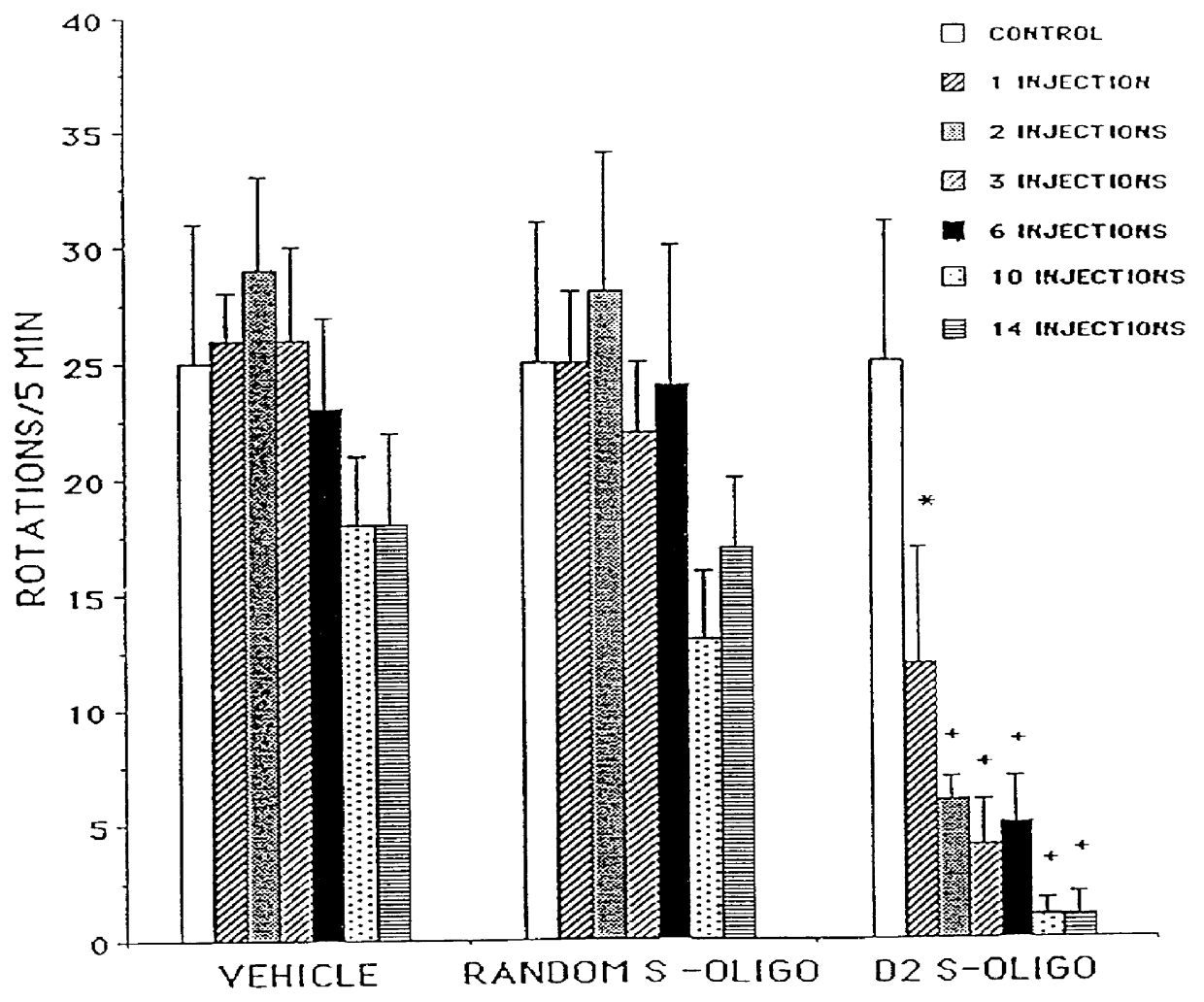
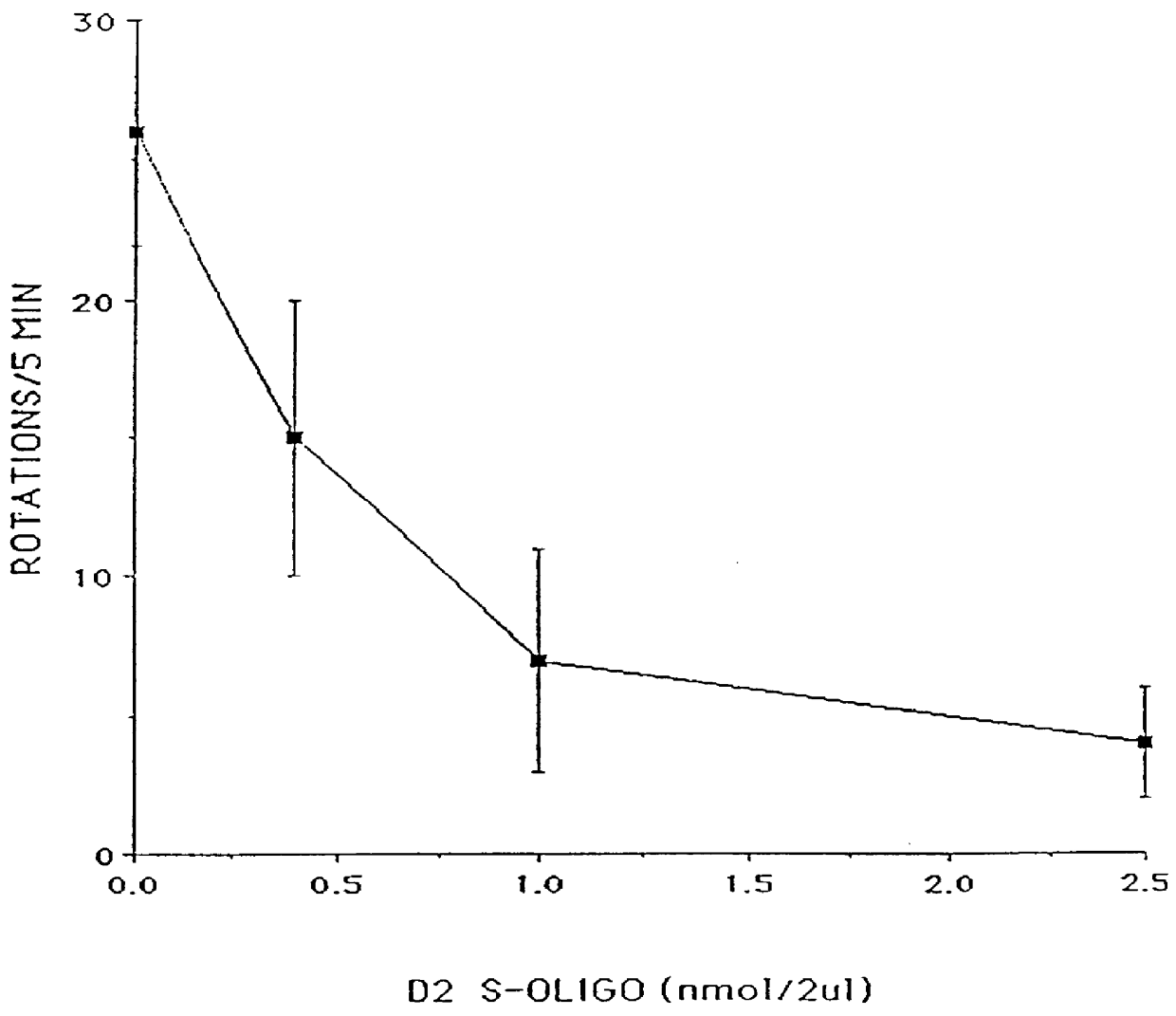
InactiveUS6025193ANot limitedProducing selective changeNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsEukaryotic plasmidsLiposome
Methods and compositions are provided for diagnosing and treating pathological conditions related to a dopamine receptor abnormality. The methods comprise administering to a patient having such a pathological condition a plasmid encoding an oligonucleotide, antisense to one or more RNA molecules encoding one of the several dopamine receptors, thereby selectively controlling expression of one or more dopamine receptor subtypes, and alleviating the pathological conditions related to their expression. The vectors are targeted to specific regions of the brain via complexation with antibody studded liposomes.
Owner:ALLEGHENY UNIV OF THE HEALTH SCI
Genetically stable recombinant modified vaccinia ankara (RMVA) vaccines and methods of preparation thereof
ActiveUS20100316667A1Elicit immune responseVectorsSugar derivativesHeterologousModified vaccinia Ankara
A vaccine comprising an immunologically effective amount of recombinant modified vaccinia Ankara (rMVA) virus which is genetically stable after serial passage and produced by a) constructing a transfer plasmid vector comprising a modified H5 (mH5) promoter operably linked to a DNA sequence encoding a heterologous foreign protein antigen, wherein the expression of said DNA sequence is under the control of the mH5 promoter; b) generating rMVA virus by transfecting one or more plasmid vectors obtained from step a) into wild type MVA virus; c) identifying rMVA virus expressing one or more heterologous foreign protein antigens using one or more selection methods for serial passage; d) conducting serial passage; e) expanding an rMVA virus strain identified by step d); and f) purifying the rMVA viruses from step e) to form the vaccine. One embodiment is directed to a fusion cytomegalovirus (CMV) protein antigen comprising a nucleotide sequence encoding two or more antigenic portions of Immediate-Early Gene-1 or Immediate-Early Gene-2 (IEfusion), wherein the antigenic portions elicit an immune response when expressed by a vaccine.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
Codon-optimized polynucleotide-based vaccines against human cytomegalovirus infection
InactiveUS7410795B2Enhance transfectionHigh expressionPeptide/protein ingredientsVirus peptidesAntigenAdjuvant
The invention is related to polynucleotide-based cytomegalovirus vaccines. In particular, the invention is plasmids operably encoding HCMV antigens, in which the naturally-occurring coding regions for the HCMV antigens have been modified for improved translation in human or other mammalian cells through codon optimization. HCMV antigens which are useful in the invention include, but are not limited to pp65, glycoprotein B (gB), IE1, and fragments, variants or derivatives of either of these antigens. In certain embodiments, sequences have been deleted, e.g., the Arg435-Lys438 putative kinase in pp65 and the membrane anchor and endocellular domains in gB. The invention is further directed to methods to induce an immune response to HCMV in a mammal, for example, a human, comprising delivering a plasmid encoding a codon-optimized HCMV antigen as described above. The invention is also directed to pharmaceutical compositions comprising plasmids encoding a codon-optimized HCMV antigen as described above, and further comprising adjuvants, excipients, or immune modulators.
Owner:VICAL INC
Gene knockout vector and zebra fish glioma model thereof
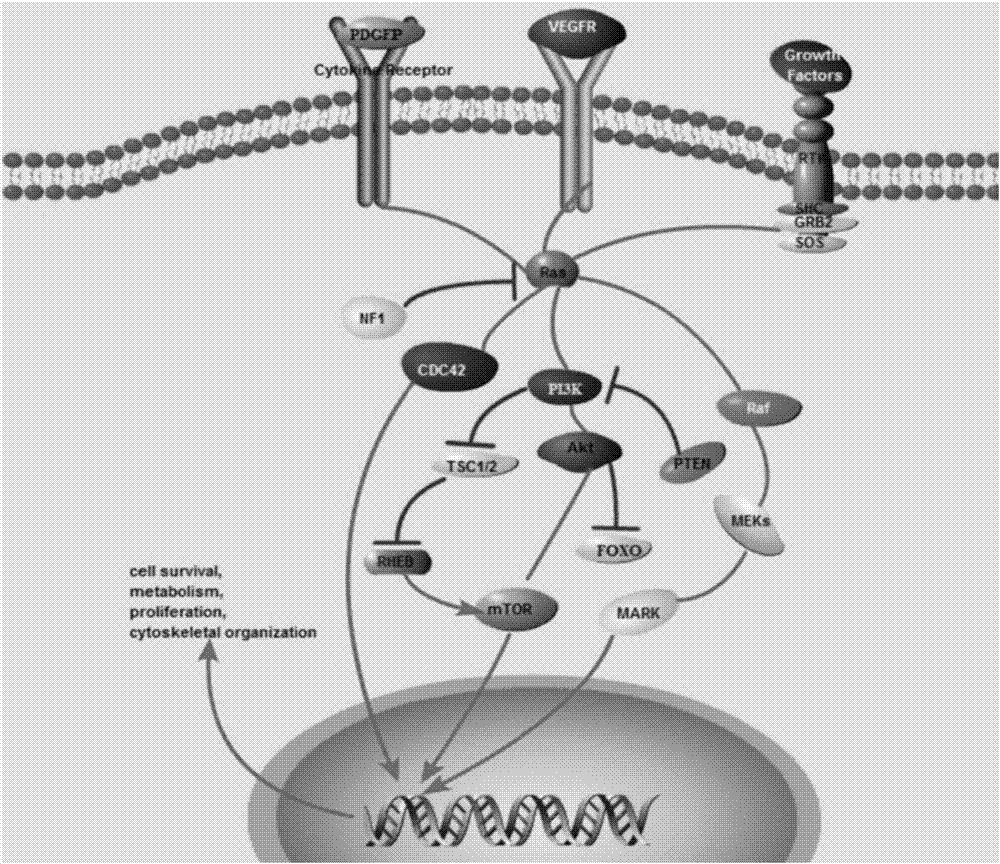
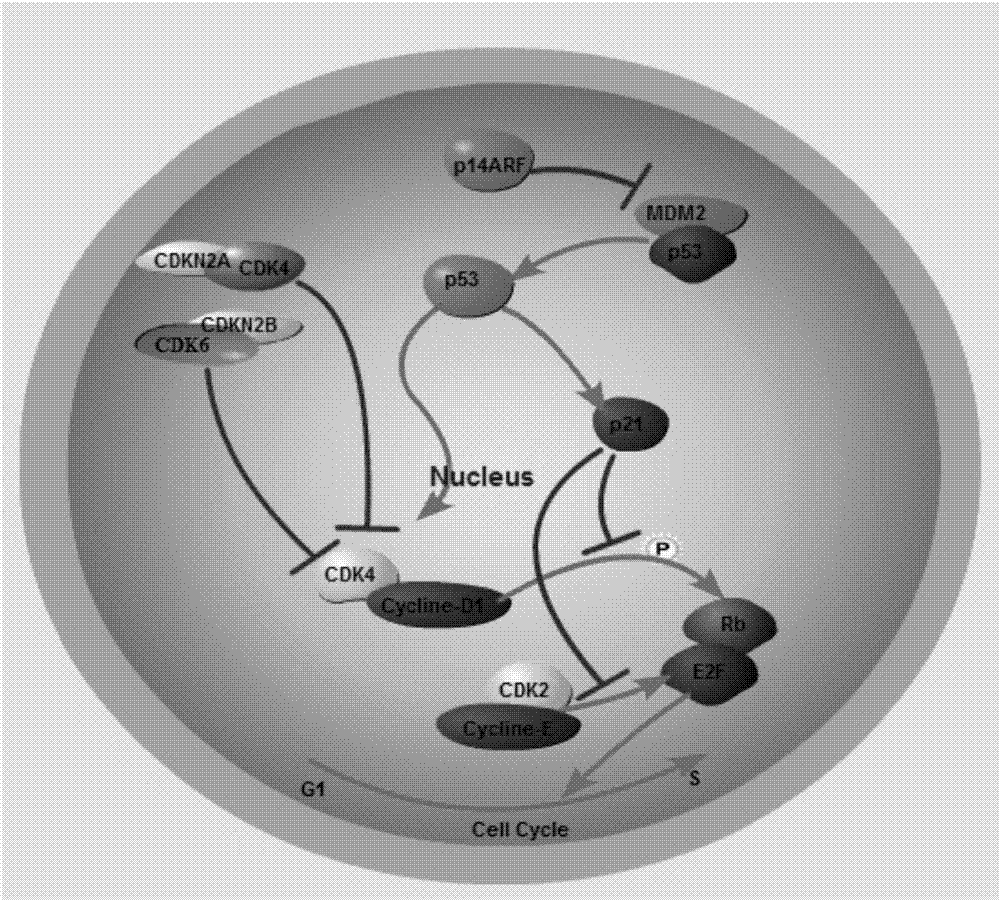
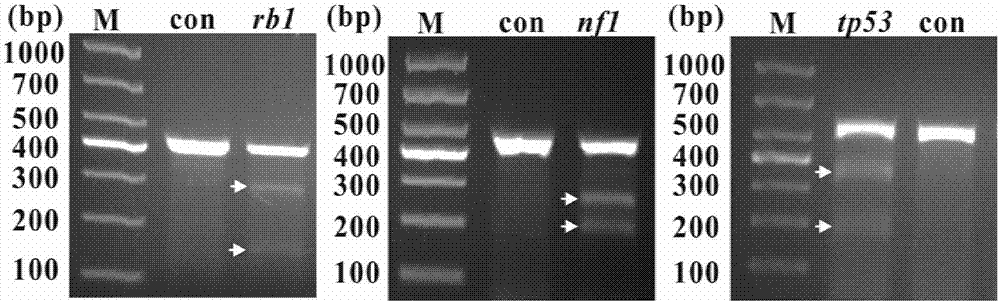
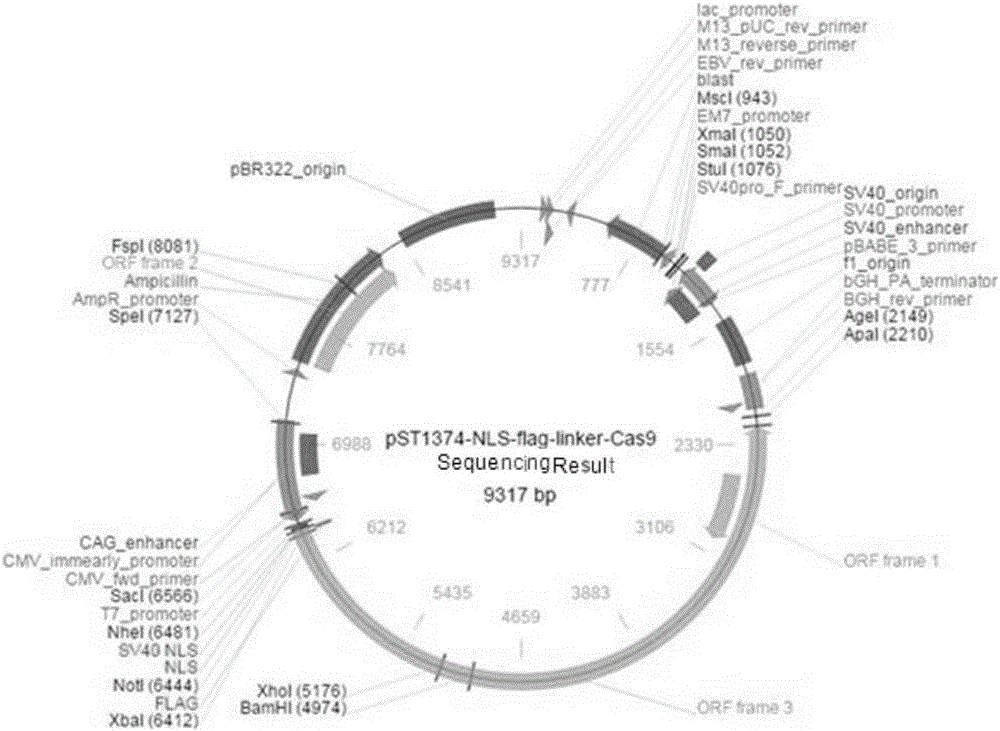
The invention provides a gene knockout vector and a zebra fish glioma model thereof. The gene knockout vector is obtained by connecting a target sequence to plasmids capable of expressing CRISPR-Cas9gene editing system related enzymes, and the target gene is a p53, Rb1 or Nf1 gene. The CRISPR / CAS9 technology is utilized for performing targeted knockout of rb1, nf1 and tp53 genes, an established transgene-induced malignant glioma zebra fish model can observe occurrence of malignant gliomas, tumor-induced angiogenesis and glioma stem cell generating processes through real-time fluorescence, andthe difference of pathogenesis of gliomas under different genetic background conditions is studied through the molecular biotechnology.
Owner:SHANTOU UNIV MEDICAL COLLEGE
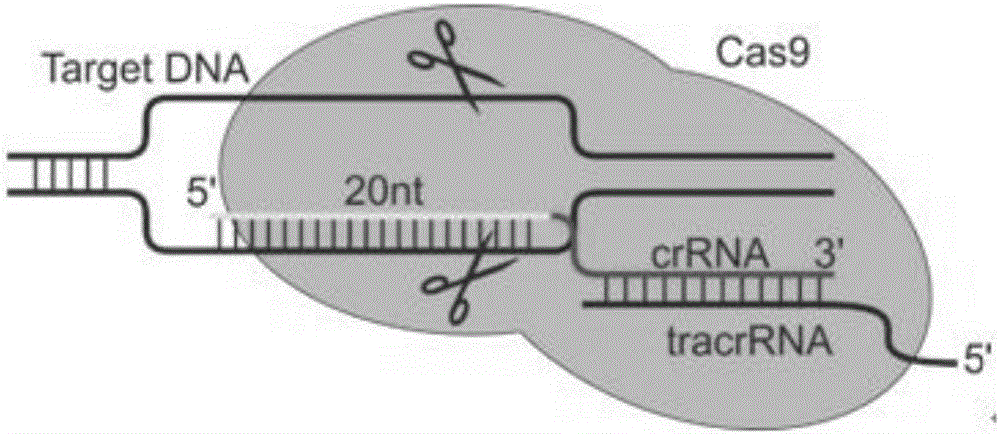
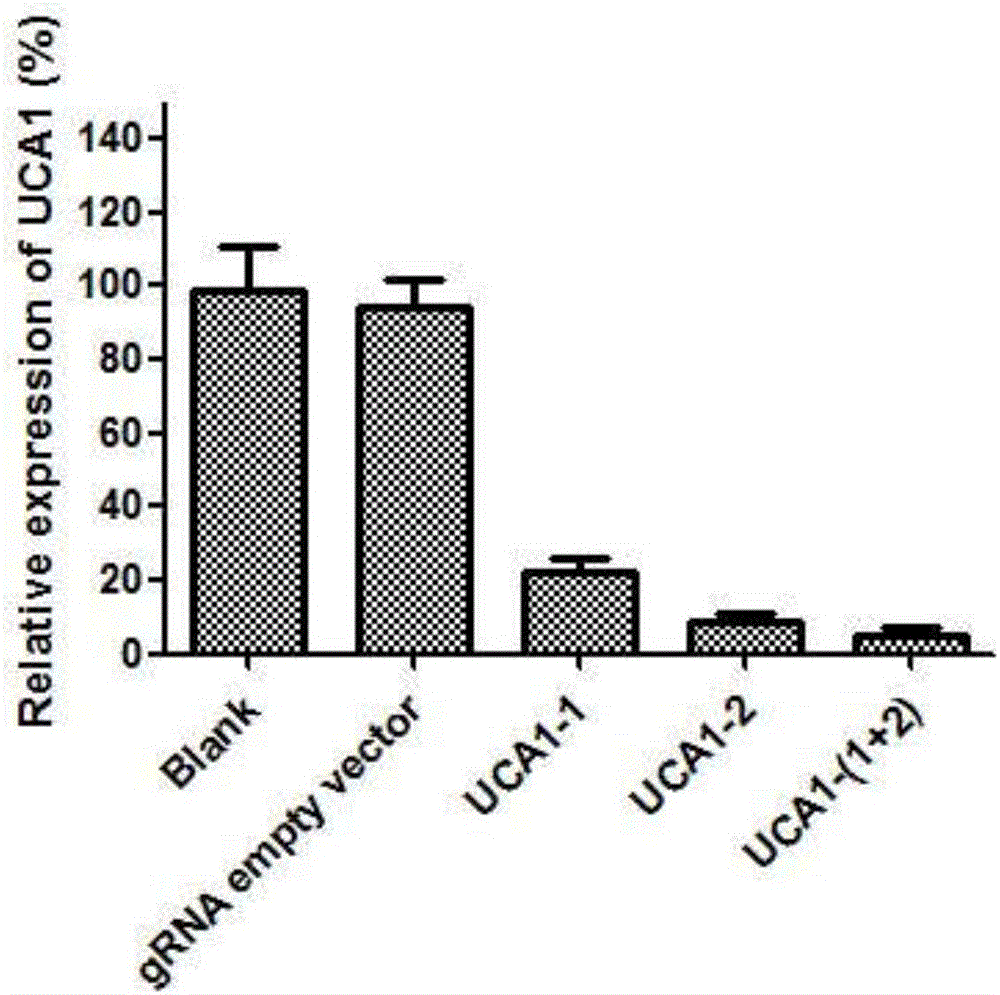
sgRNA and gene vector for inhibiting bladder cancer by targeting human lncRNA-UCA1 and application of sgRNA
ActiveCN106399306AImprove targetingGrowth inhibitionOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsCancer cellEukaryotic plasmids
The invention provides sgRNA and a gene vector for inhibiting bladder cancer by targeting human lncRNA-UCA1 and an application of the sgRNA; specifically, sgRNA sequences of an lncRNA-UCA1 gene and a PD-1 gene suitable for CRISPR-Cas9 targeted splicing are designed; by transforming plasmids of specific splicing lncRNA-UCA1 gene and CRISPR-Cas9 nuclease gene into human bladder cancer cells, the expression of the lncRNA-UCA1 gene drops so as to inhibit the growth of tumor cells; and the plasmid, together with a human PD-1 gene targeted knockout vector, is transformed into a humanized mouse model of bladder cancer transplanted tumor, so as to obviously inhibit the growth of tumors. According to the invention, the vector is simple in preparing steps, the sgRNA is good in targeting property and the CRISPR-Cas9 is high in knockout efficiency.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF XIAN JIAOTONG UNIV
Helicobacter System And Uses Thereof
Helicobacter based preparations comprising a pharmacologically active molecule of interest are disclosed, as well as methods of preparing and using said preparations. In particular, Helicobacter pylori vectors, vector plasmids and recombinant cells that include a sequence encoding a pharmacologically active molecule of interest useful in therapeutic treatments and / or vaccination against disease are provided. Delivery of the pharamacologically active molecules is provided at the mucosal surface, such as the gastric mucosa or nasal membranes, to provide effective and continuous delivery of a pharmacologically active agent. In some embodiments, the Helicobacter provides exposure of a desired molecule of interest though the surface of the Helicobacter, providing exposure of the antigen to the host at the gastric mucosa. Live Helicobacter pylori vaccines are also provided. Vectors and shuttle vector constructs of the Helicobacter are also disclosed.
Owner:ONDEK
Biological gene transfer system for eukaryotic cells
InactiveUS20050289672A1Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationEucaryotic cellPlant cell
This invention relates generally to technologies for the transfer of nucleic acids molecules to eukaryotic cells. In particular non-pathogenic species of bacteria that interact with plant cells are used to transfer nucleic acid sequences. The bacteria for transforming plants usually contain binary vectors, such as a plasmid with a vir region of a Ti plasmid and a plasmid with a T region containing a DNA sequence of interest.
Owner:CENT FOR THE APPL OF MOLECULAR BIOLOGY TO INT AGRI
Hepatitis b virus (HBV) vaccines and uses thereof
ActiveUS20190185828A1High cure rateProvide immunityViral antigen ingredientsVirus peptidesPolymerase LEukaryotic plasmids
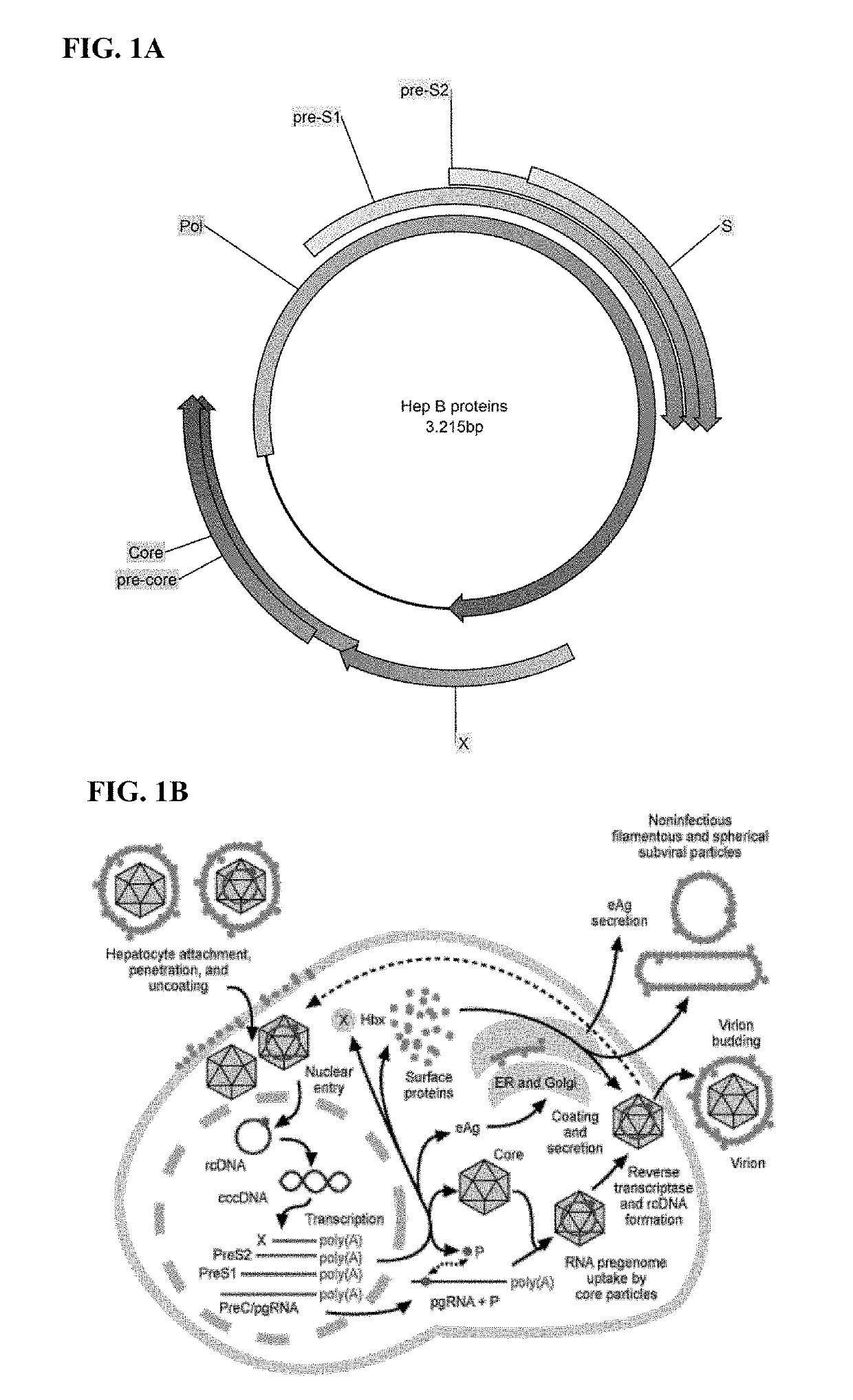
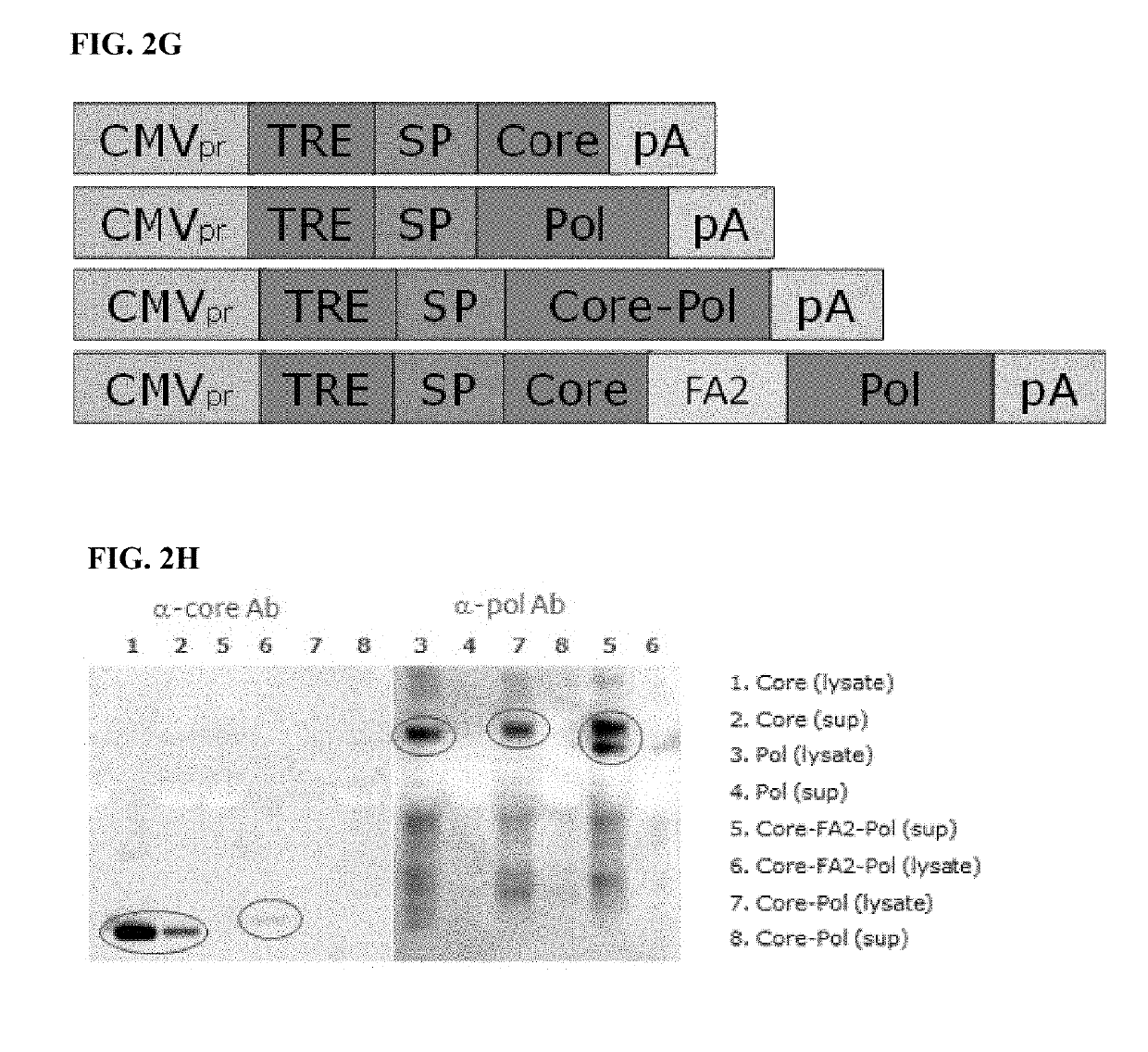
Polynucleotides encoding hepatitis B virus (HBV) core antigen and polymerase antigen, and related combinations are described. Also described are vectors, such as DNA plasmids or viral vectors, expressing the HBV core and polymerase antigens, and immunogenic compositions containing the expression vectors. Methods of inducing an immune response against HBV or treating a HBV-induced disease, particularly in individuals having chronic HBV infection, using the immunogenic compositions are also described.
Owner:JANSSEN SCI IRELAND UC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com