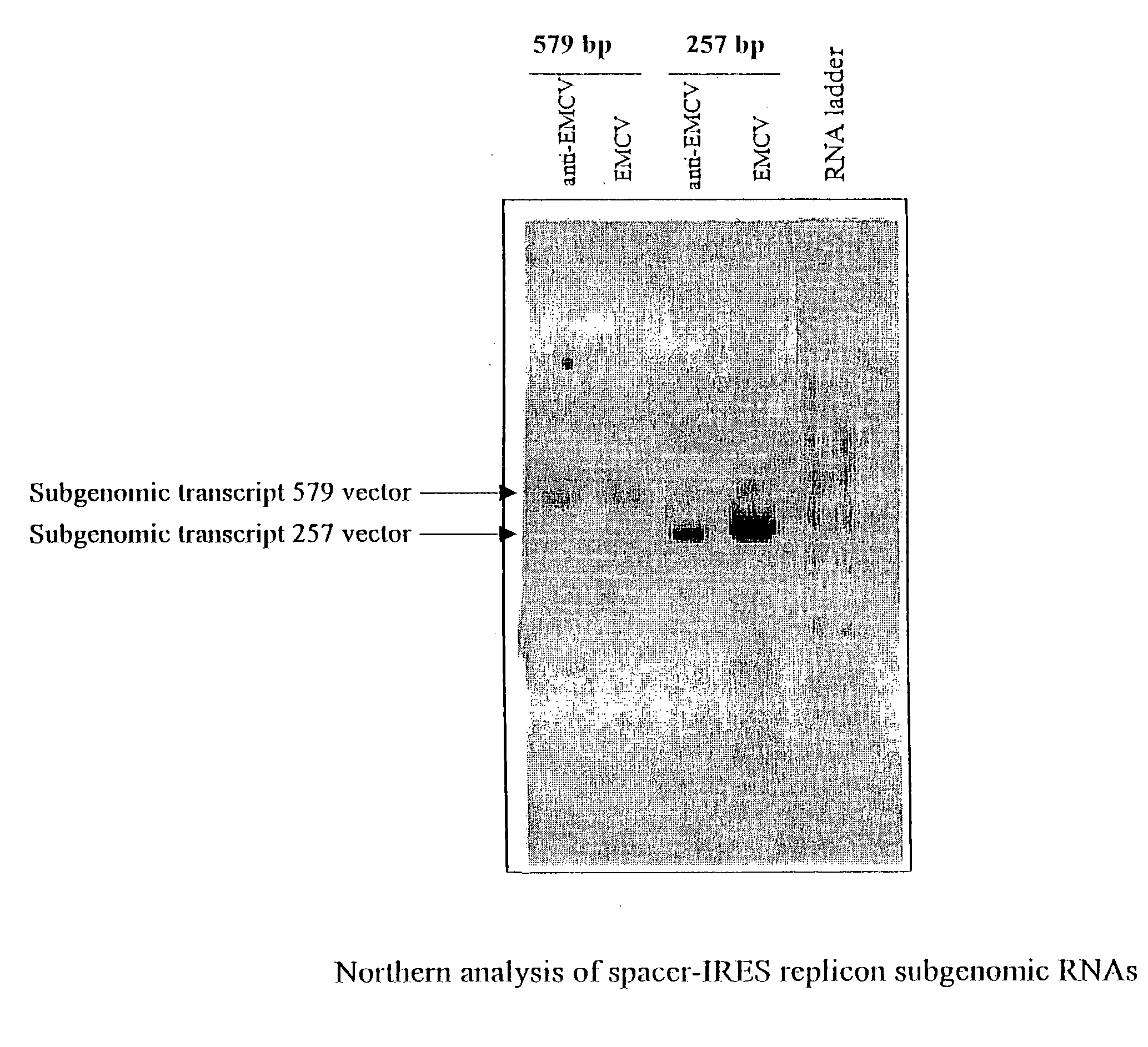
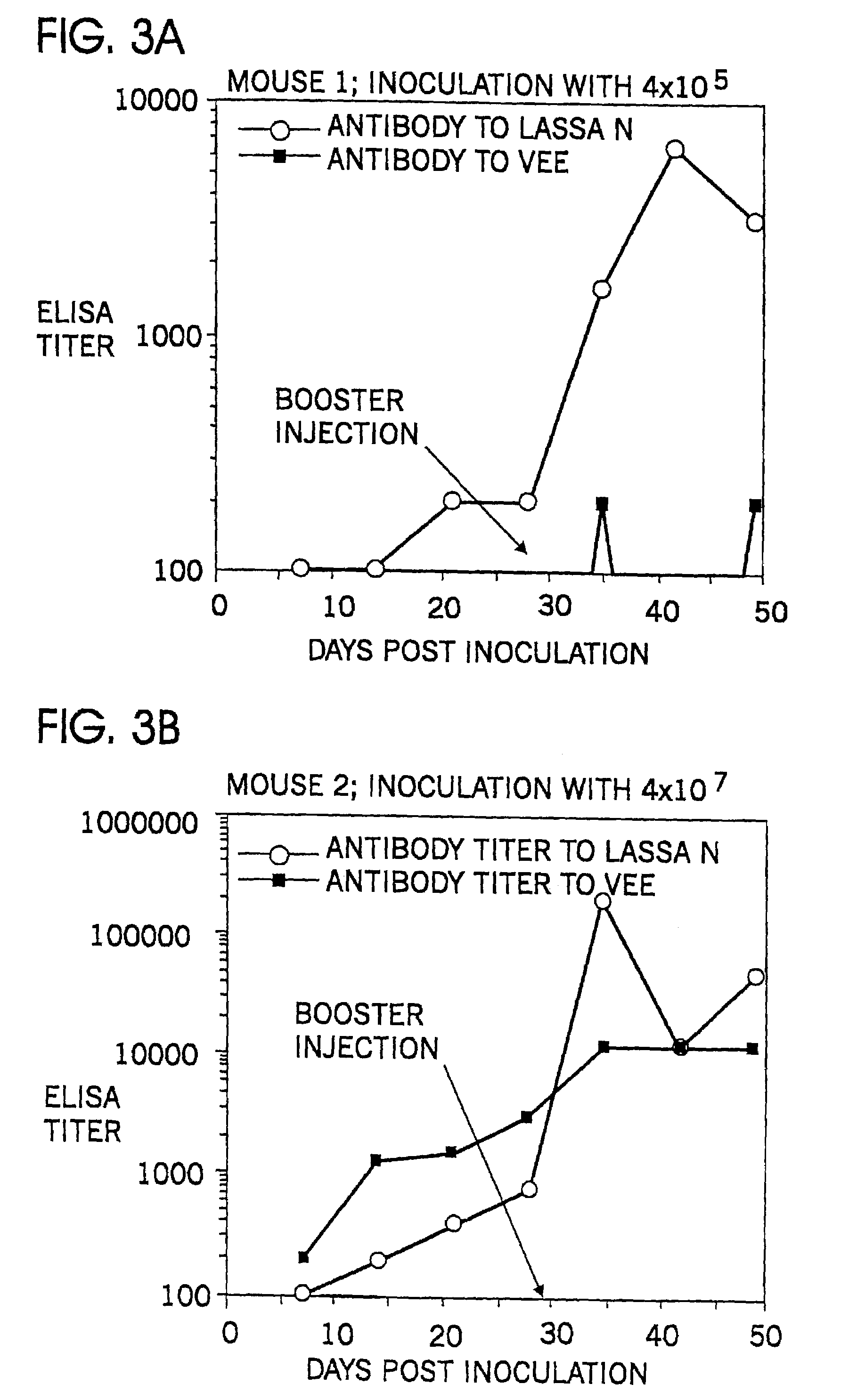
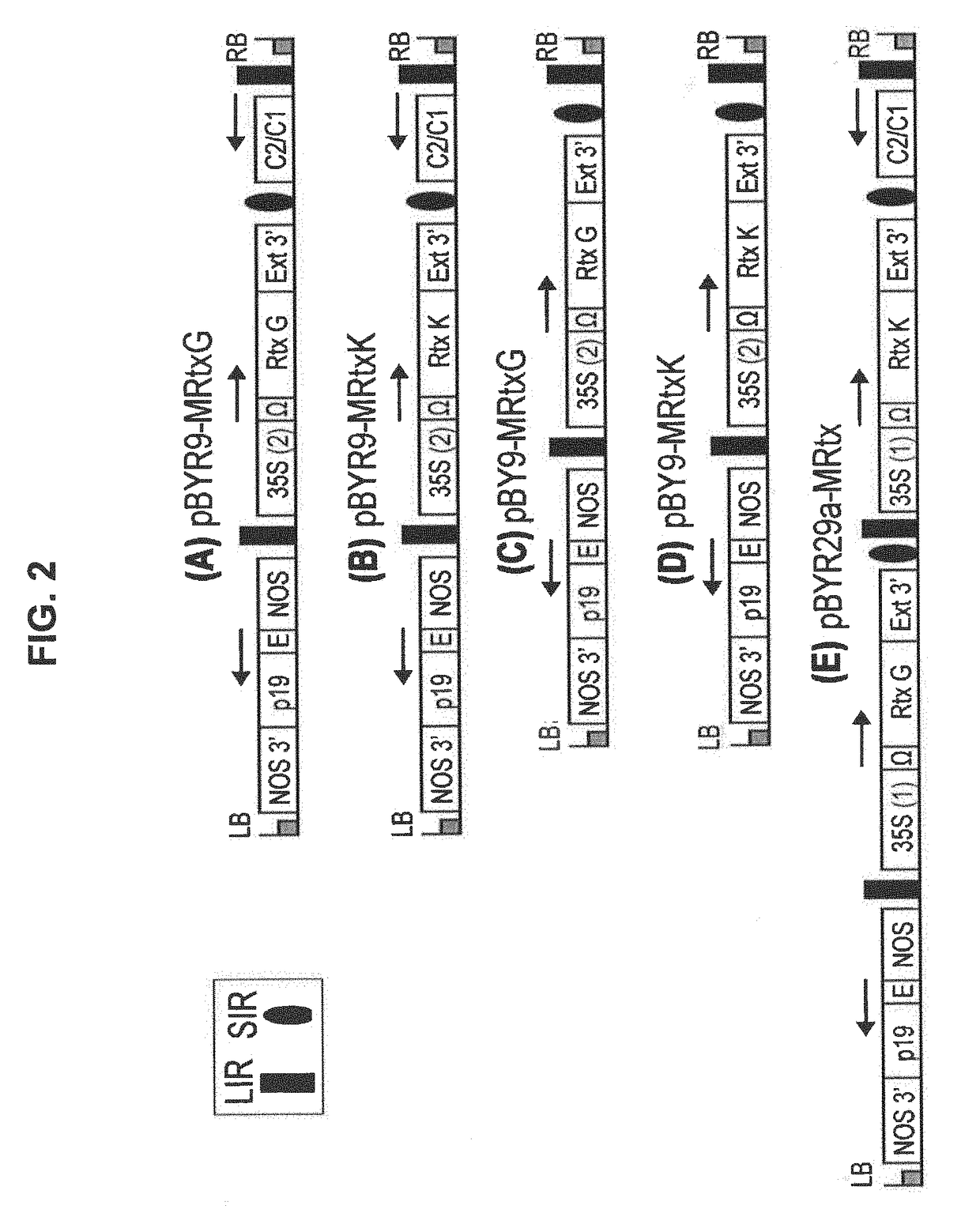
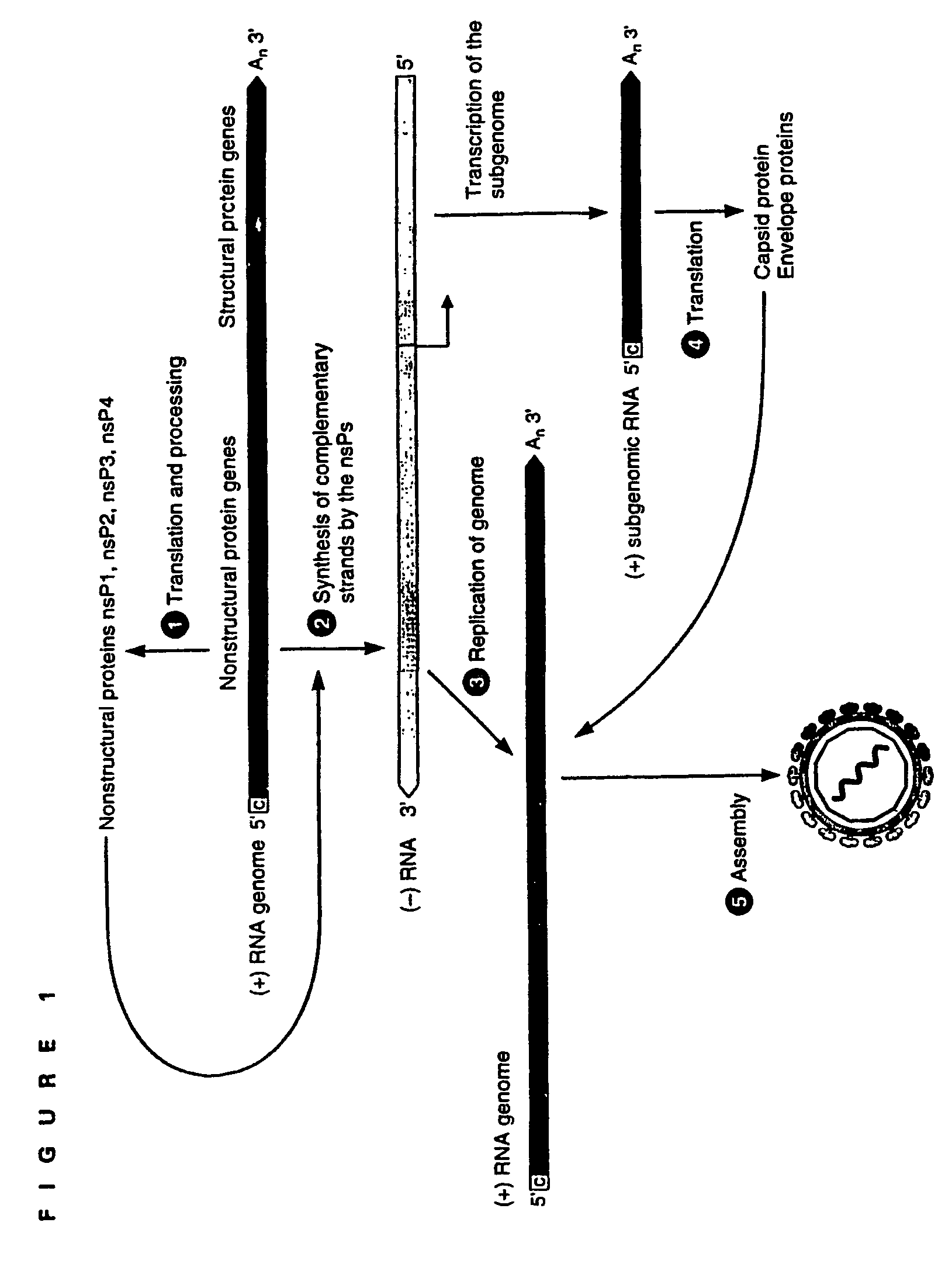
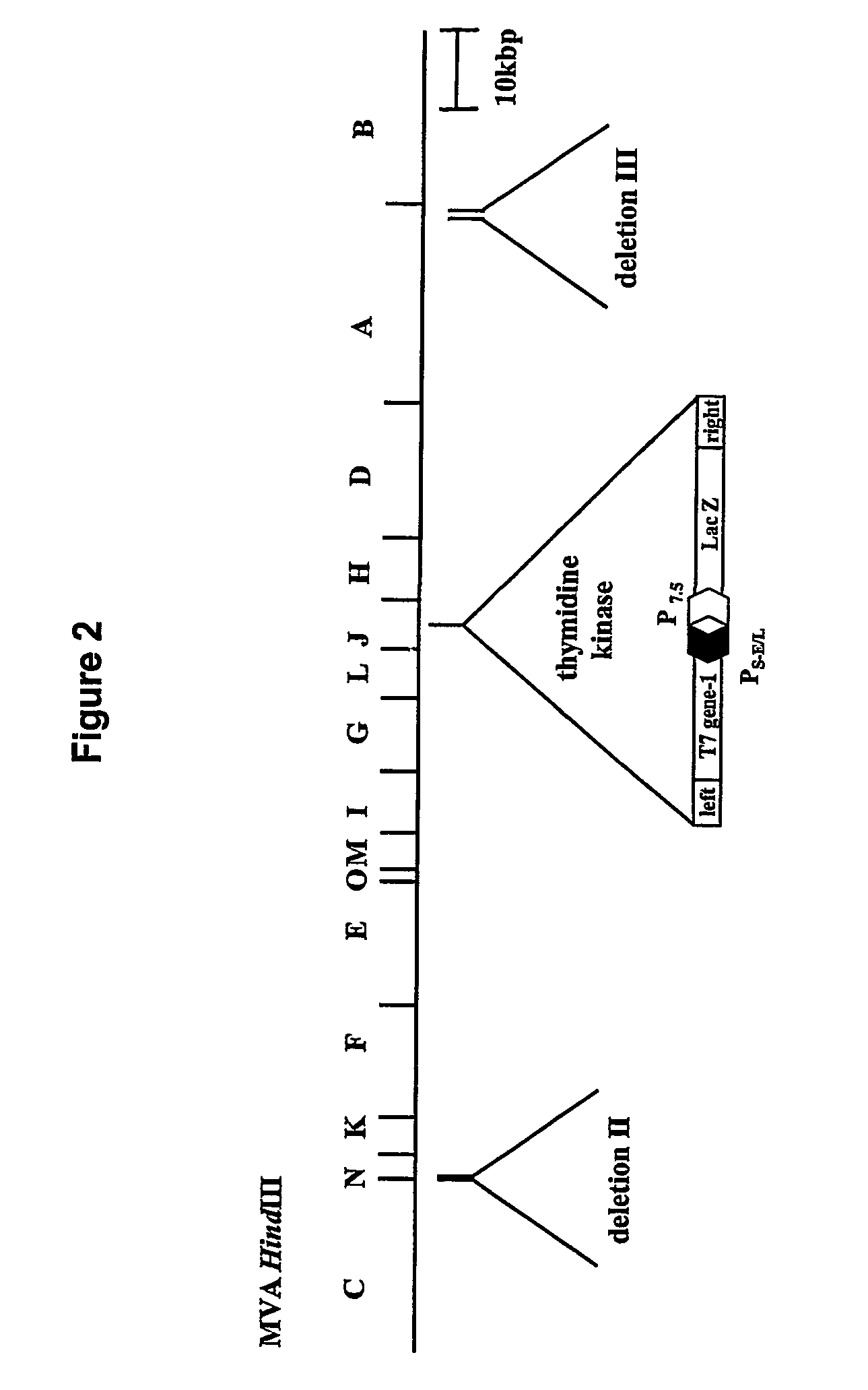
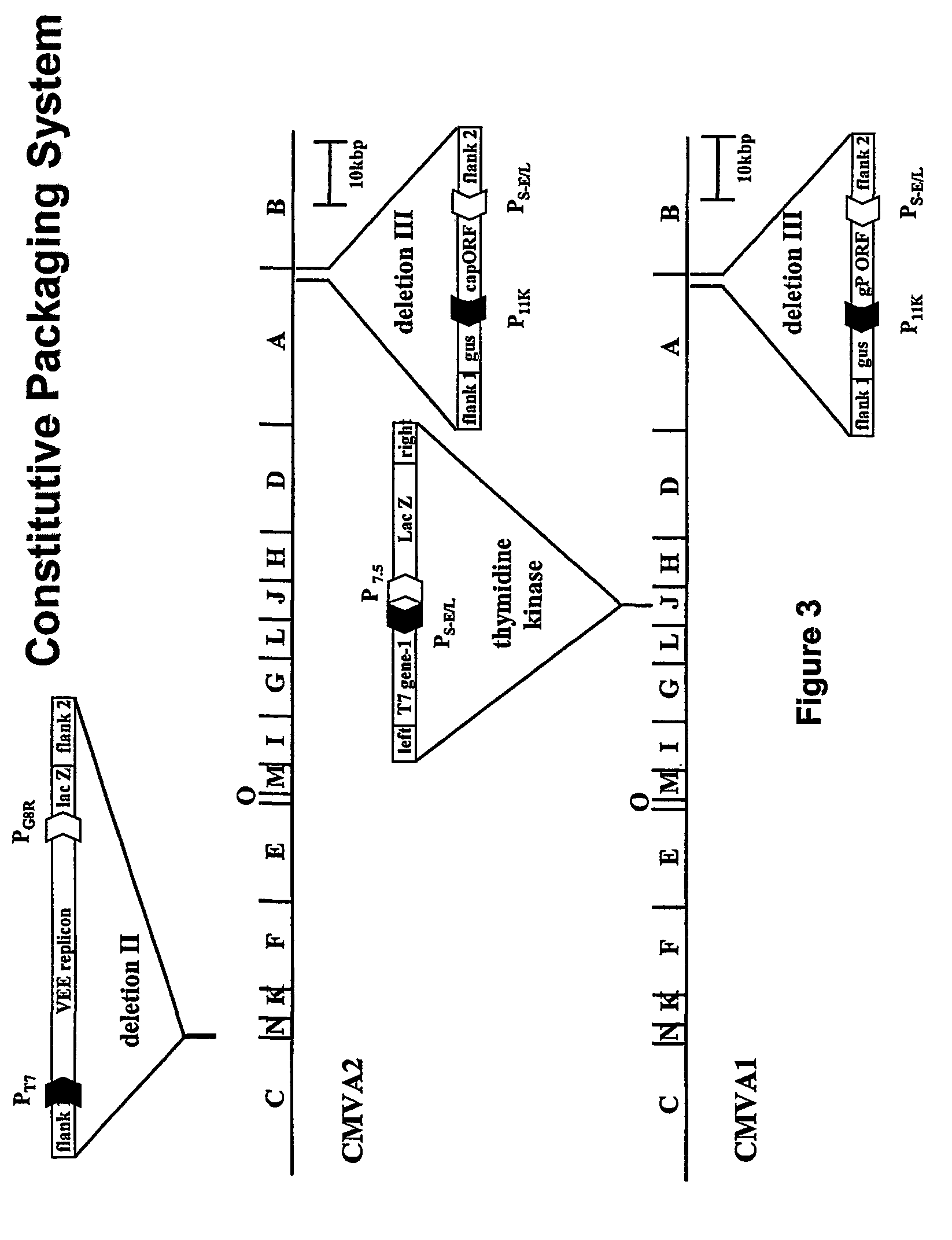
Patents
Literature
161 results about "Replicon" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
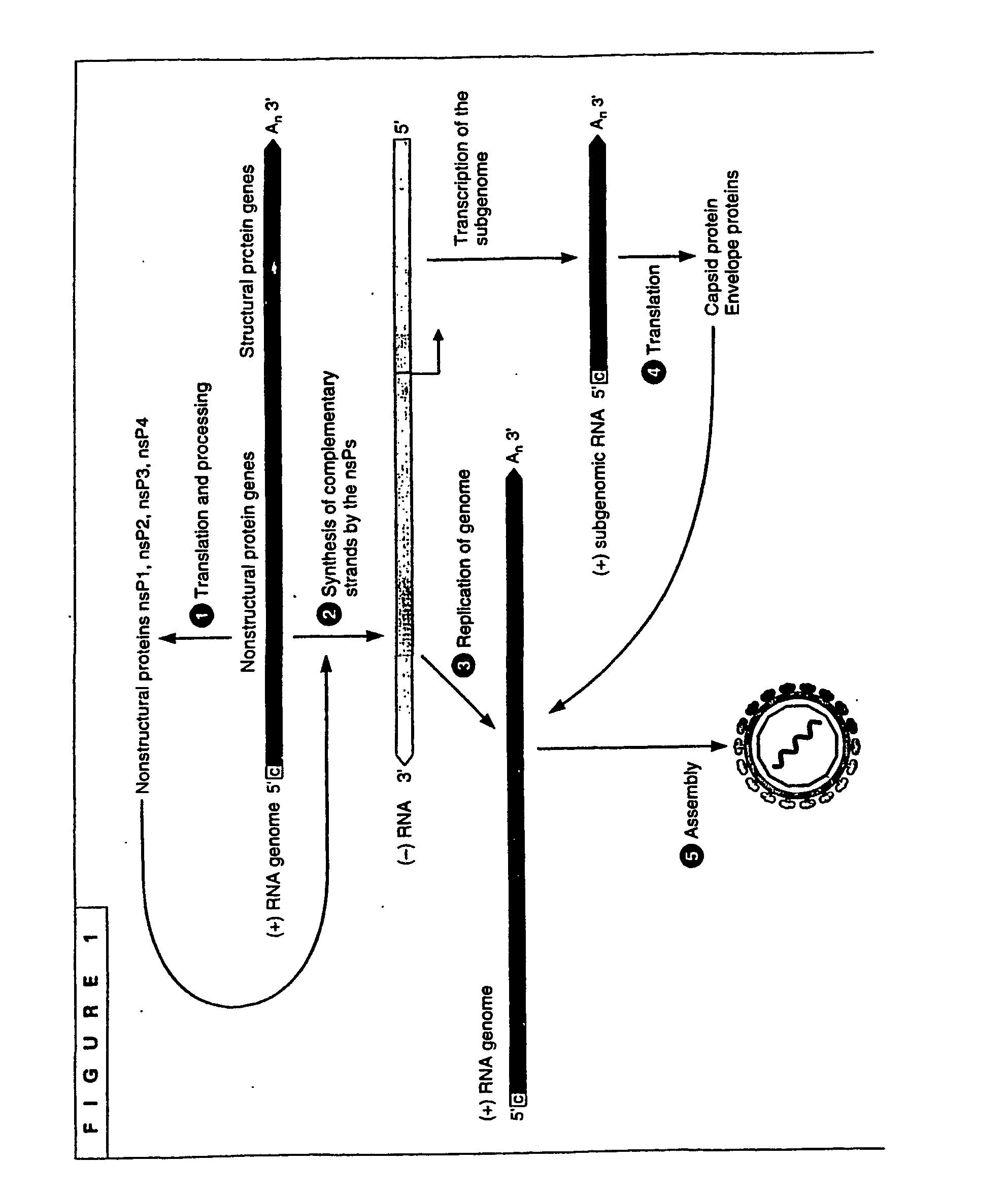
A replicon is a DNA molecule or RNA molecule, or a region of DNA or RNA, that replicates from a single origin of replication.
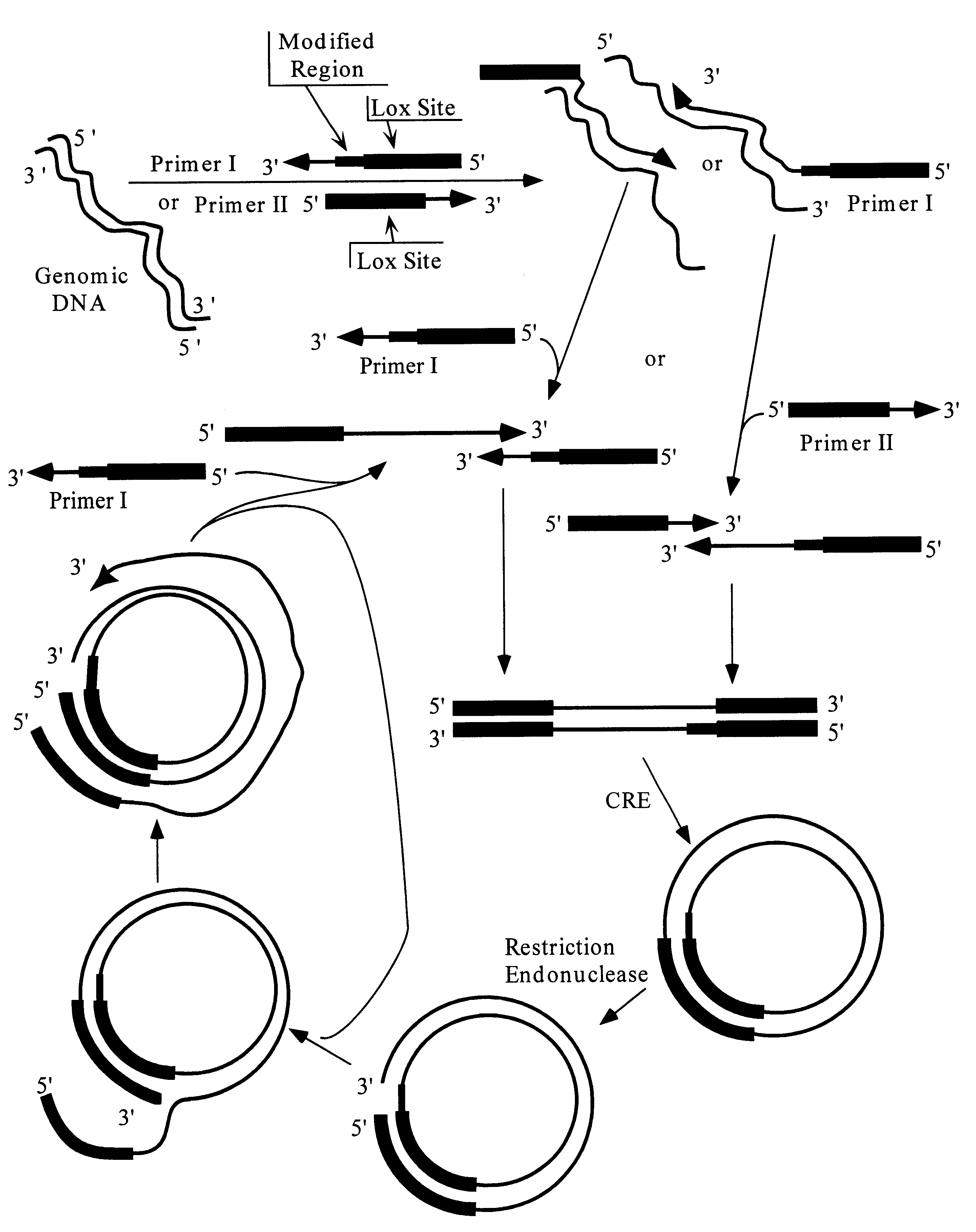
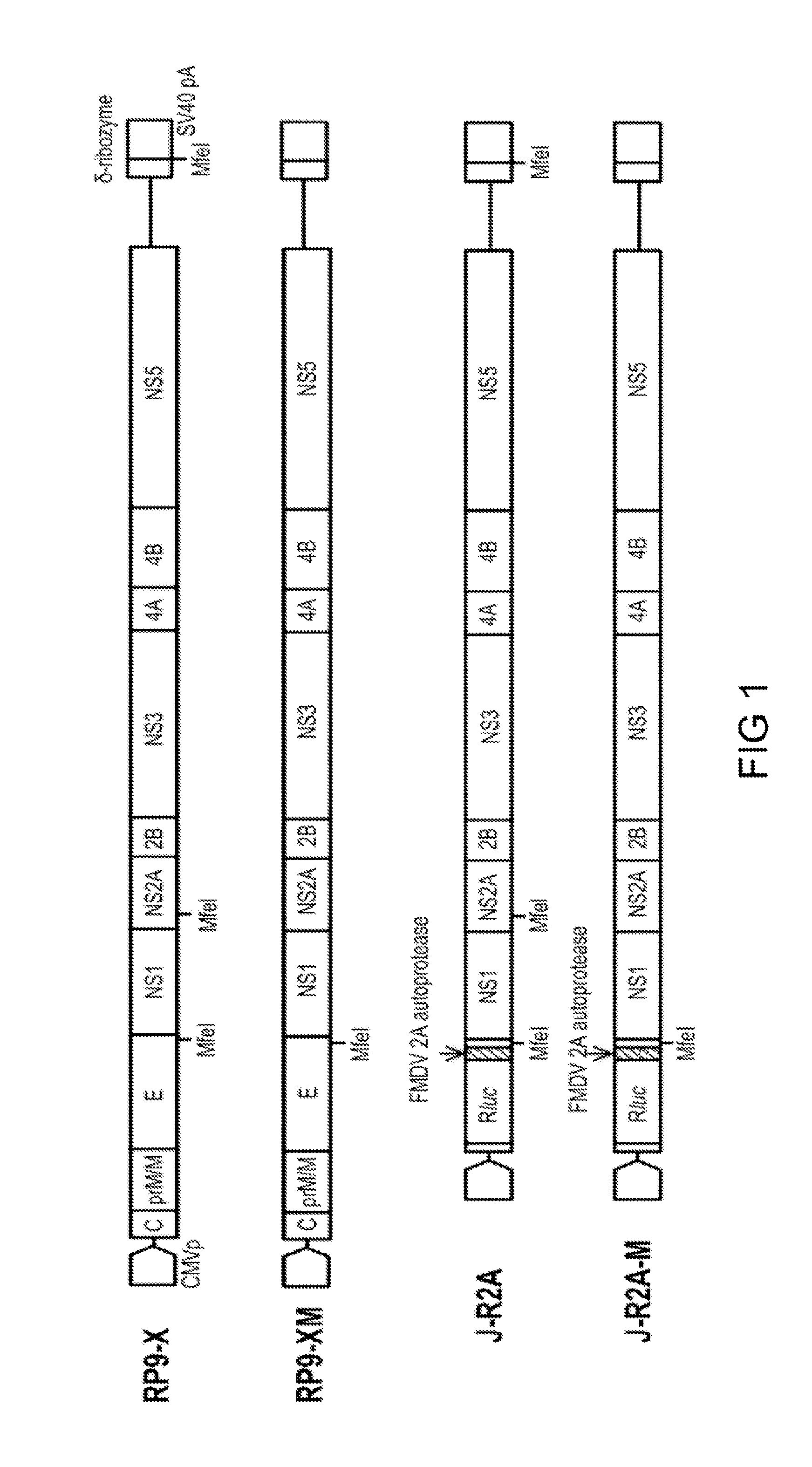
Amplification of nucleic acid molecules via circular replicons
InactiveUS6261808B1Sufficient efficiencyIncrease capacitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymeNucleic acid molecule
Methods and compositions suitable for accomplishing the in vitro amplification of nucleic acid molecules via enzymatic means are provided. The preferred means employ circular rather than linear replicons. Means for producing such circular replicons from linear reactants are also provided.
Owner:REPLICON
Screening for west nile virus antiviral therapy
InactiveUS20050058987A1Improve efficiencySsRNA viruses positive-senseVectorsHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsImmunogenicity
The instant invention provides stable and novel lineage I WNV reverse genetics systems, and methods for making the reverse genetics systems, specifically, a fully-infectious lineage I WNV cDNA or replicon system engineered with one or more nucleotide sequences each encoding a reporter gene to be used in high throughput cell-based screening assays for the identification of novel antiflaviviral chemotherapeutics and / or vaccines effective to treat and / or immunize against infections by WNV and other emerging flaviviruses, such as, for example, JEV, SLEV, AV, KV, JV, CV, YV, TBEV, DENV-1, DENV-2, DENV-3, DENV-4, YFV and MVEV. The present invention further provides methods of high throughput screening of antiflaviviral compounds or improved derivatives thereof using novel lineage I WNV reverse genetics systems and / or cell lines stably containing the reverse genetics systems. Also, the invention provides novel pharmaceutical compositions comprising an attenuated lineage I WNV that is less virulent but similarly immunogenic as the parent WNV and is capable of providing a protective immune response in a host.
Owner:HEALTH RES INC
Alphavirus replicons and helper constructs
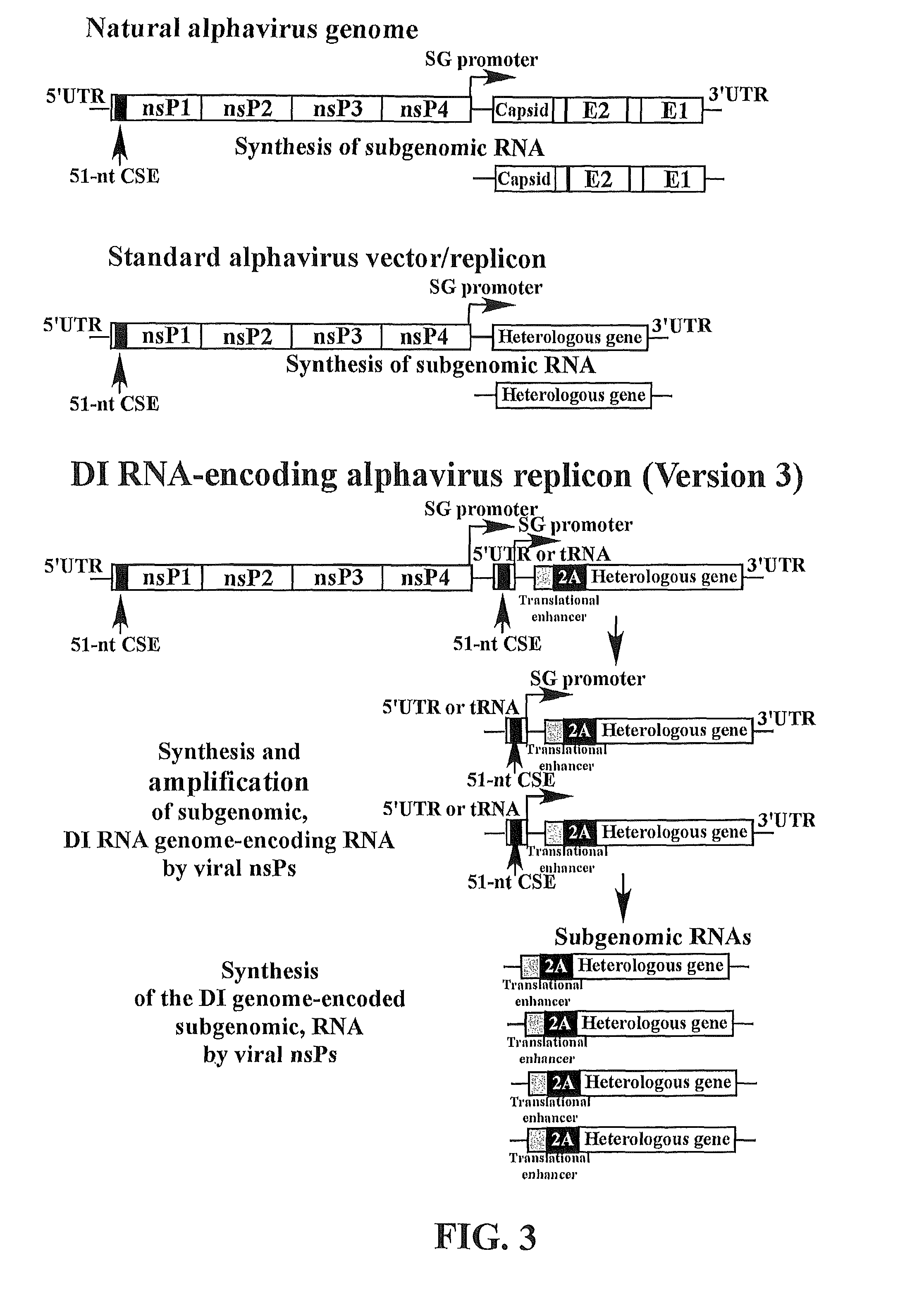
The present invention provides a recombinant nucleic acid comprising: a first nucleic acid sequence encoding a 5′ alphavirus replication recognition sequence; at least one second nucleic acid sequence encoding an alphavirus nonstructural protein; at least one alphavirus subgenomic promoter; at least one IRES element; at least one heterologous nucleic acid; and a third nucleic acid encoding a 3′ alphavirus replication recognition sequence. Further provided are methods of making alphavirus particles comprising a recombinant nucleic acid of this invention and methods of using the compositions of this invention. Also provided is a recombinant helper nucleic acid comprising: a first nucleic acid sequence encoding a 5′ alphavirus replication recognition sequence; an alphavirus subgenomic promoter; an IRES element; a second nucleic acid encoding an alphavirus structural protein; and a third nucleic acid encoding a 3′ alphavirus replication recognition sequence.
Owner:ALPHAVAX INC
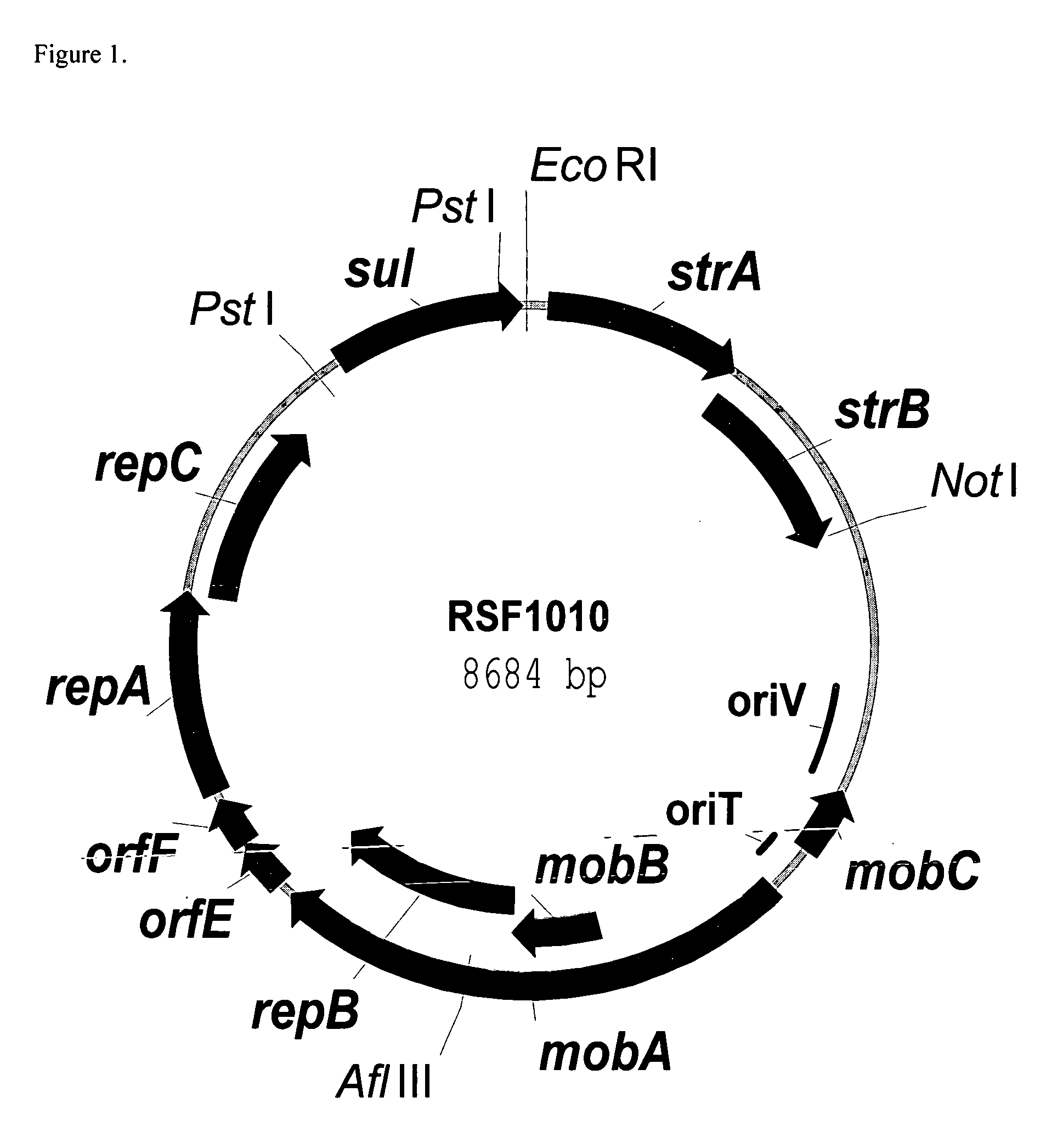
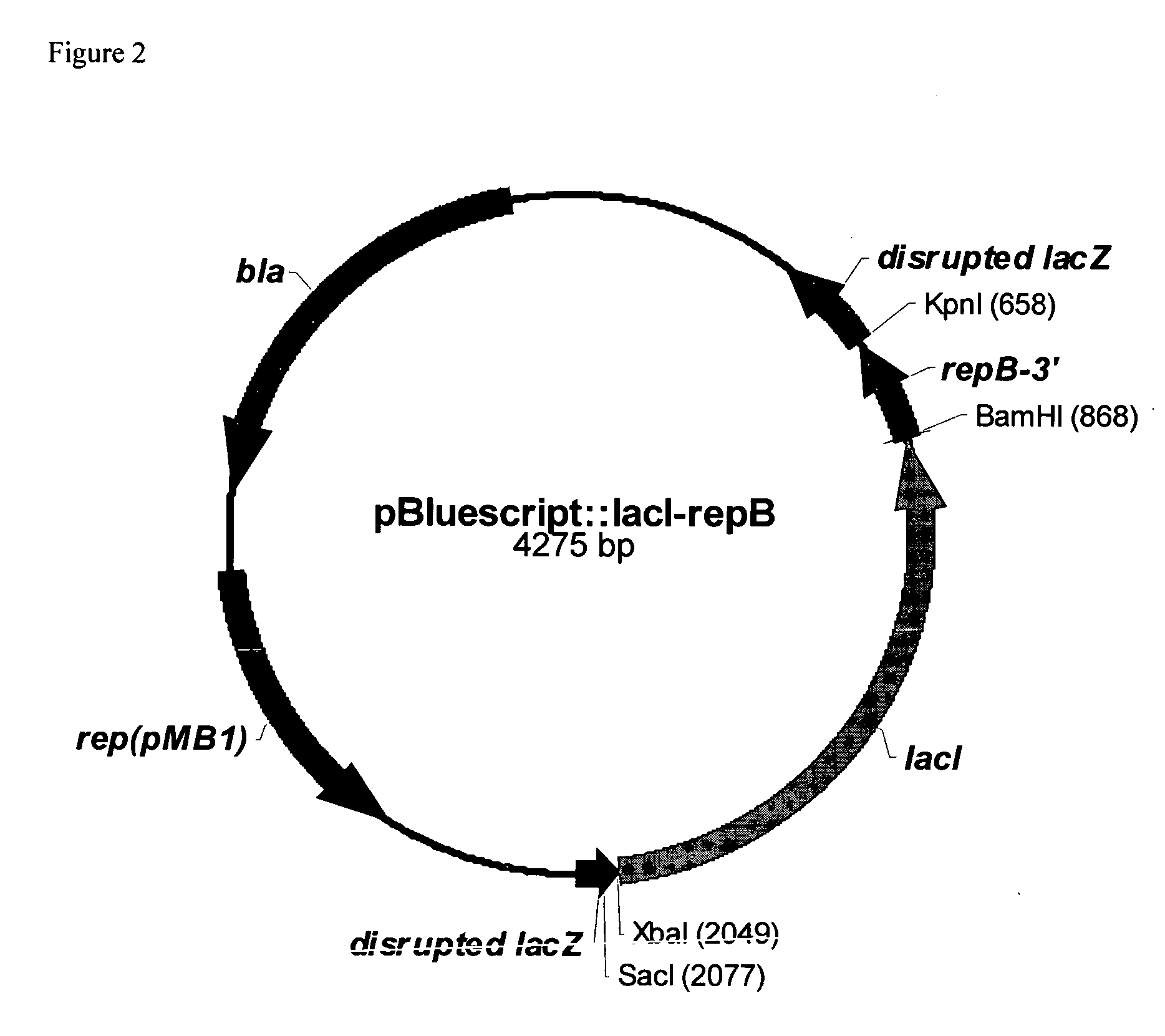
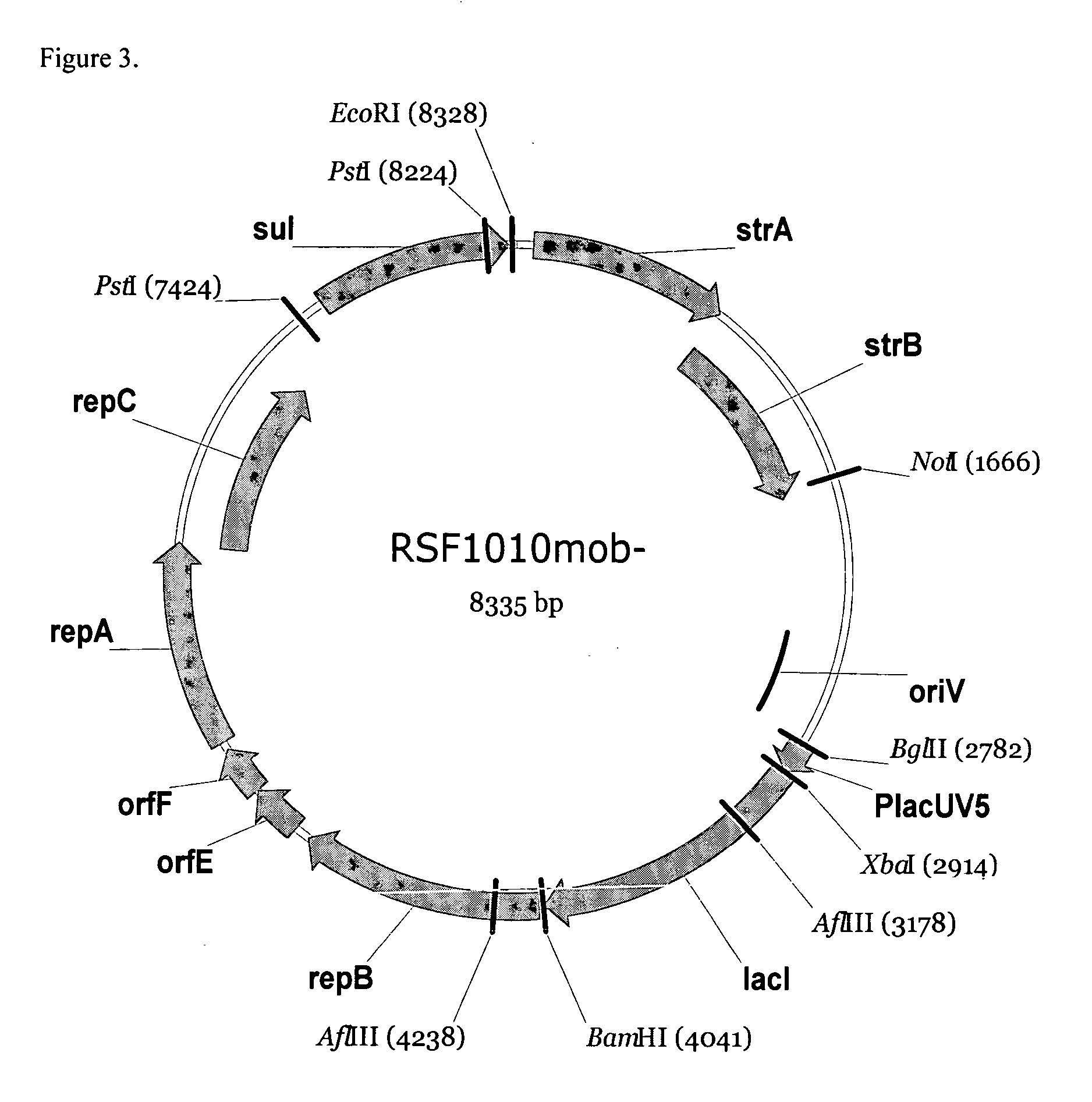
RSF1010 derivative Mob' plasmid containing no antibiotic resistance gene, bacterium comprising the plasmid and method for producing useful metabolites
A Mob− plasmid having a RSF1010 replicon, comprising a gene coding for Rep protein and said plasmid has been modified to inactivate gene related to mobilization ability. The present invention also describes a bacterium having an ability to produce useful metabolites, comprising the plasmid and said bacterium lack active thymidylate synthase coded by thyA gene and thymidine kinase coded by tdk gene, and a method for producing useful metabolites, such as native or recombinant proteins, enzymes, L-amino acids, nucleosides and nucleotides, vitamins, using the bacterium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
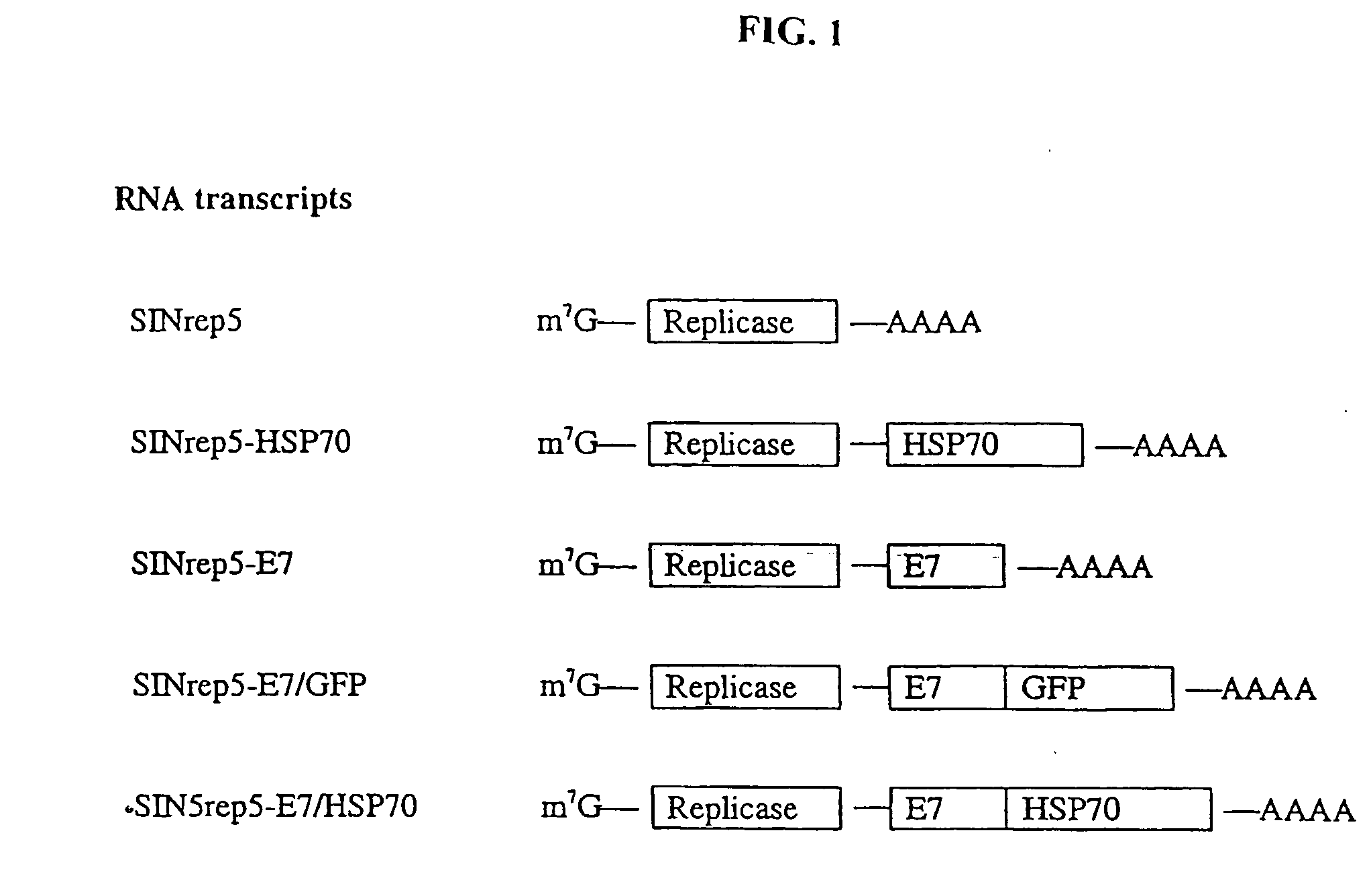
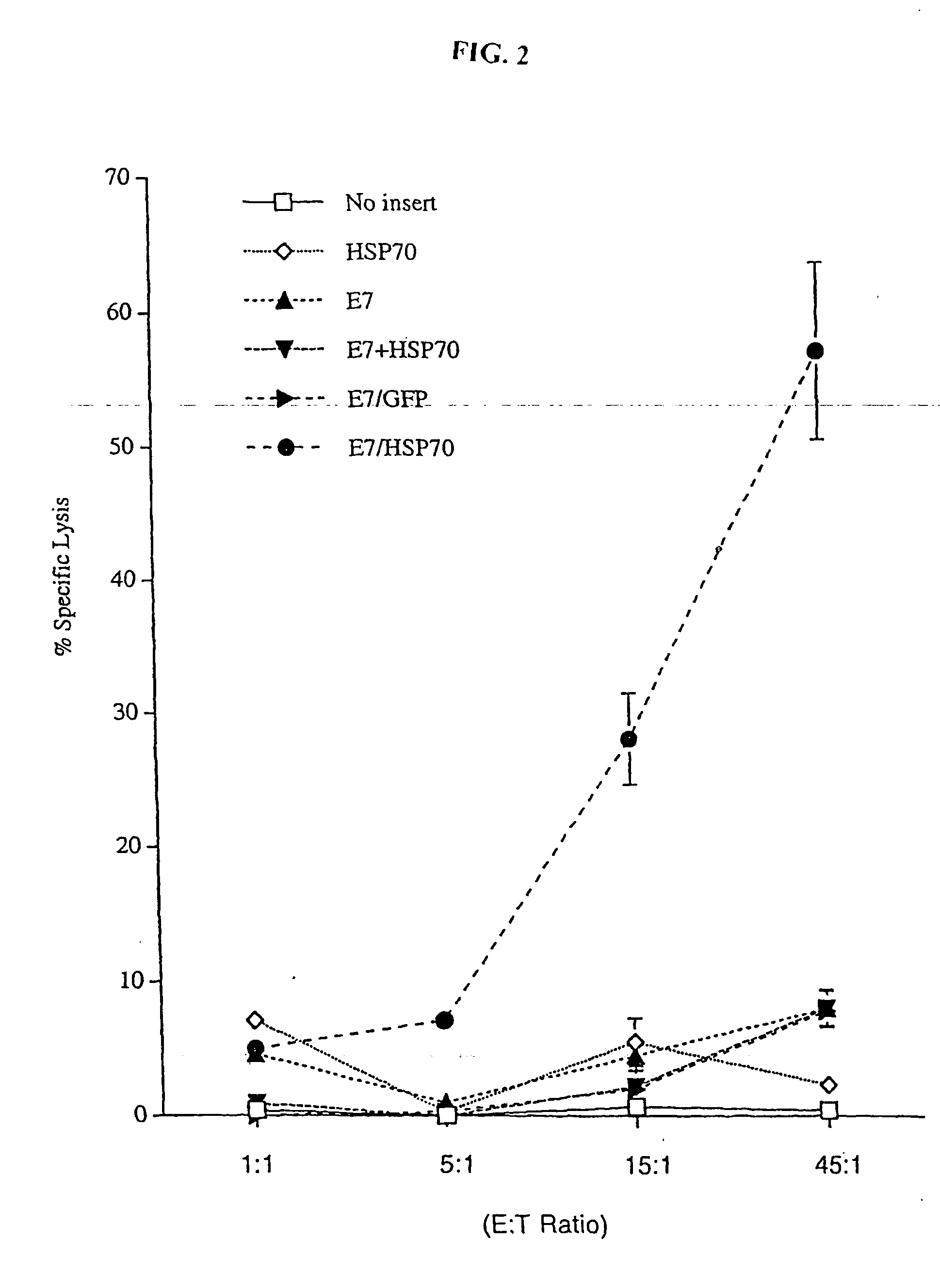
Superior molecular vaccine based on self-replicating rna, suicidal dna or naked dna vector, that links antigen with polypeptide that promotes antigen presentation
InactiveUS20050277605A1Great E7-specific T cell-mediated immunityEfficiently presentedSsRNA viruses positive-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMHC class IDisease
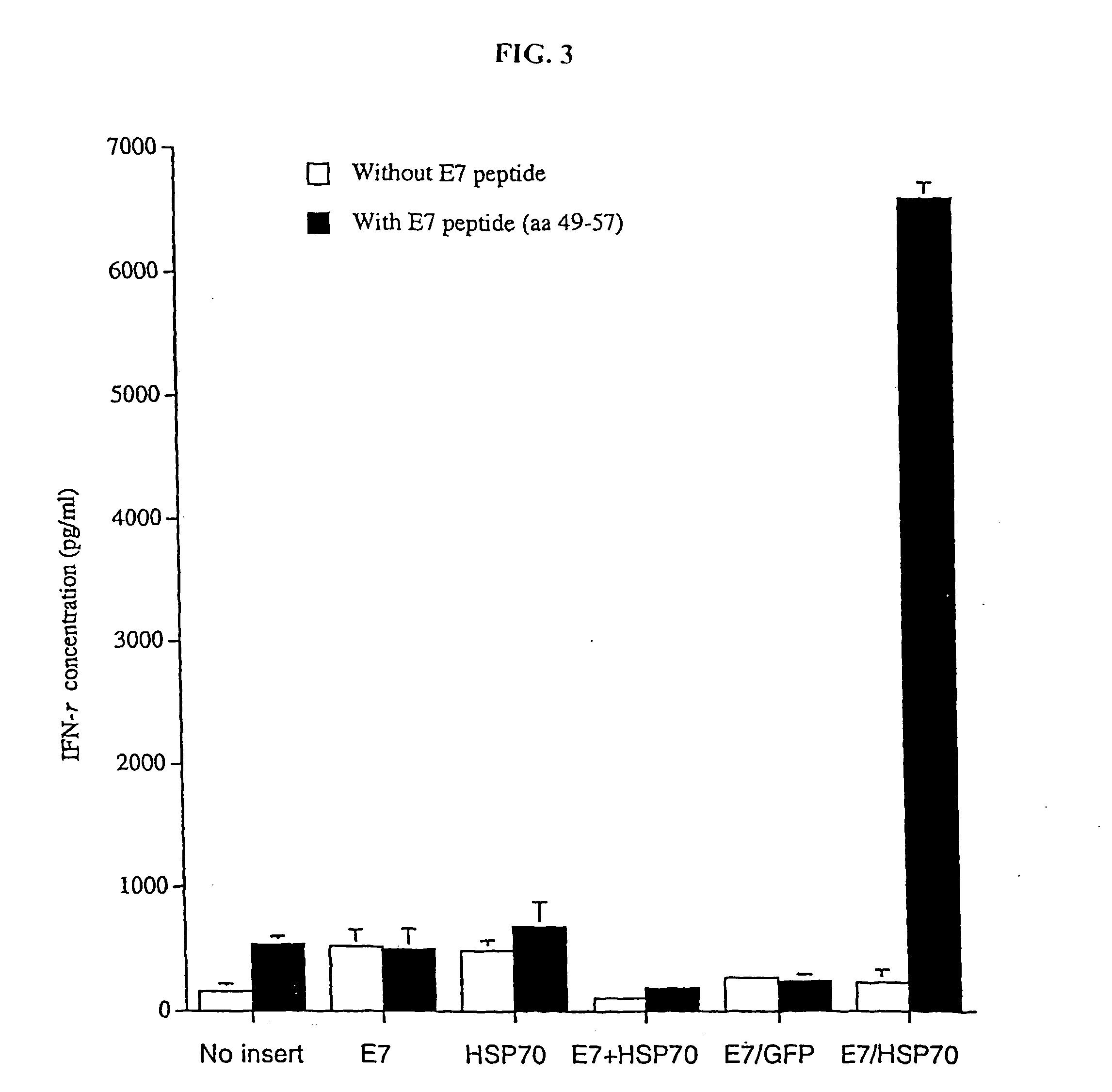
Improved molecular vaccines comprise nucleic acid vectors that encode a fusion polypeptide that includes polypeptide or peptide physically linked to an antigen. The linked polypeptide is one that (a) promotes processing of the expressed fusion polypeptide via the MHC class I pathway and / or (b) promotes development or activity of antigen presenting cells, primarily dendritic cells. These vaccines employ one of several types of nucleic acid vectors, each with its own relative advantages: naked DNA plasmids, self-replicating RNA replicons and suicidal DNA-based on viral RNA replicons. Administration of such a vaccine results in enhance immune responses, primarily those mediated by CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes, directed against the immunizing antigen part of the fusion polypeptide. Such vaccines are useful against tumor antigens, viral antigens and antigens of other pathogenic microorganisms and can be used in the prevention or treatment of diseases that include cancer and infections.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
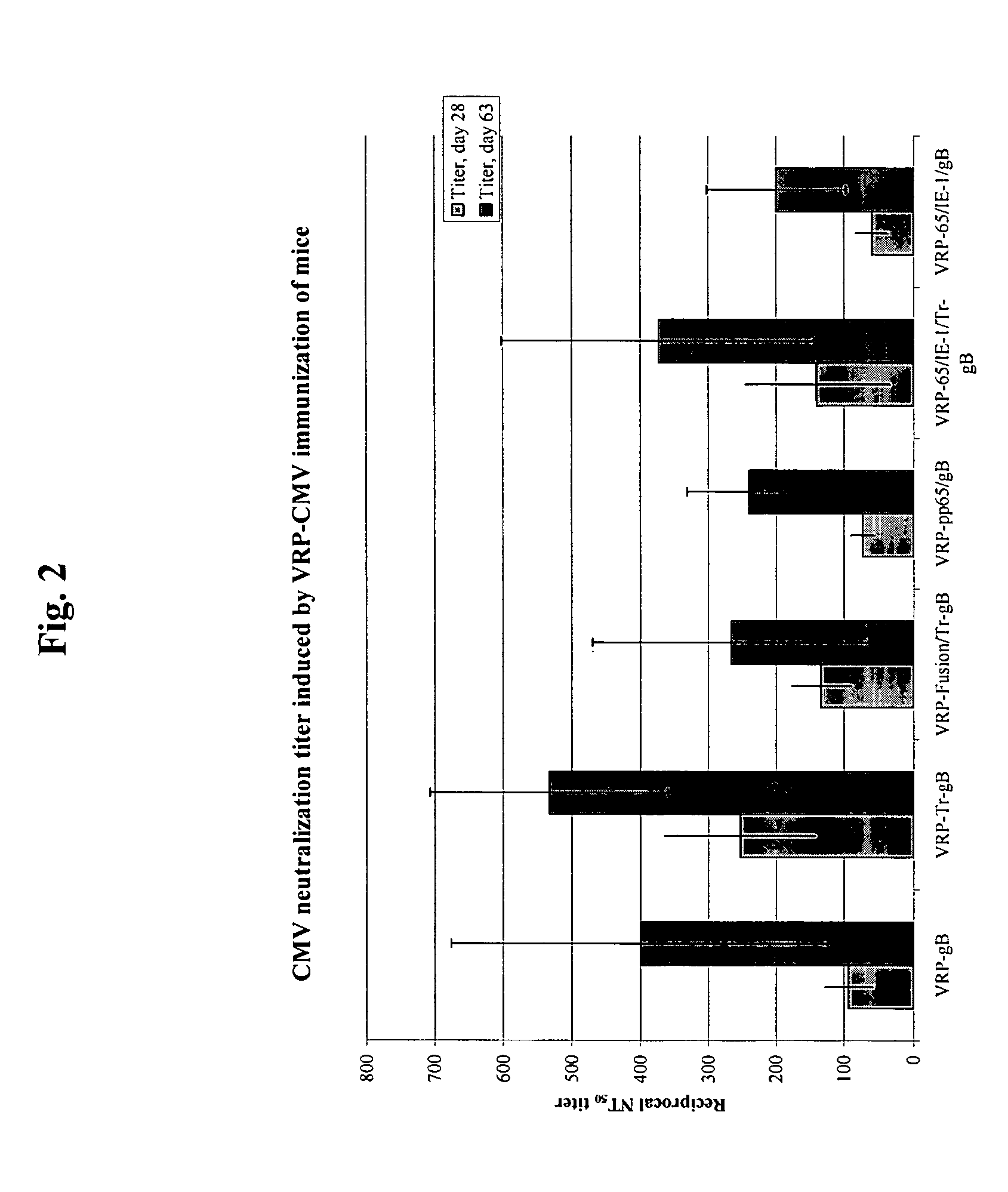
Alpha virus-based cytomegalovirus vaccines
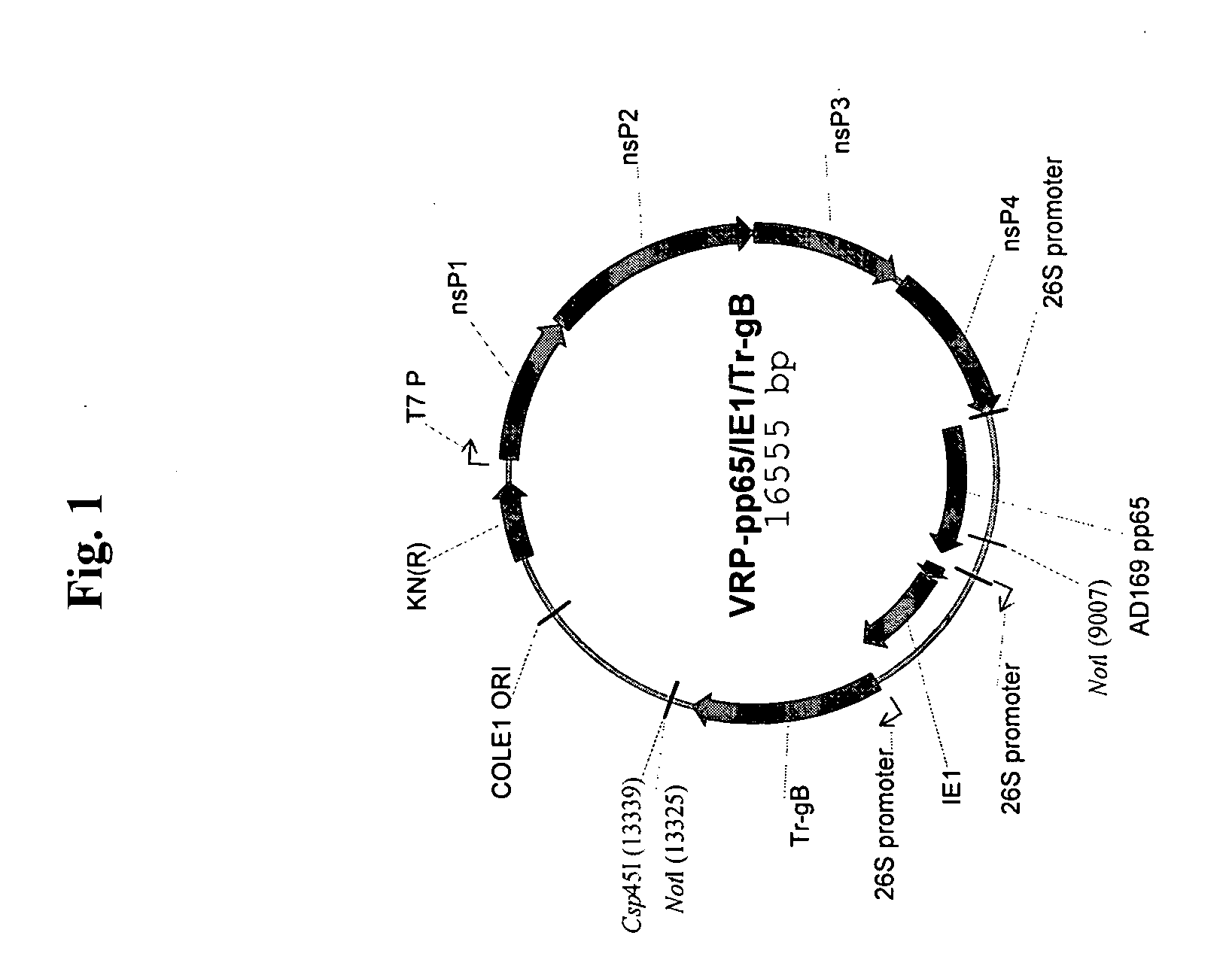
The present invention provides methods and compositions comprising a population of alphavirus replicon particles comprising alphavirus replicon RNAs, wherein a first replicon RNA comprises nucleic acid encoding cytomegalovirus pp65 and IE1 protein or immunogenic fragments thereof, and a second replicon RNA comprises nucleic acid encoding cytomegalovirus gB protein or an immunogenic fragment thereof, and wherein each of the two replicon RNAs is contained within a separate alphavirus replicon particle.
Owner:ALPHAVAX INC
Chimeric alphavirus replicon particles
Chimeric alphaviruses and alphavirus replicon particles are provided including methods of making and using same. Specifically, alphavirus particles are provided having nucleic acid molecules derived from one or more alphaviruses and structural proteins (capsid and / or envelope) from at least two or more alphaviruses. Methods of making, using, and therapeutic preparations containing the chimeric alphavirus particle, are disclosed.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Methods and compositions for alphavirus replicons
The present invention provides alphavirus replicons and methods of their use in producing heterologous protein.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND
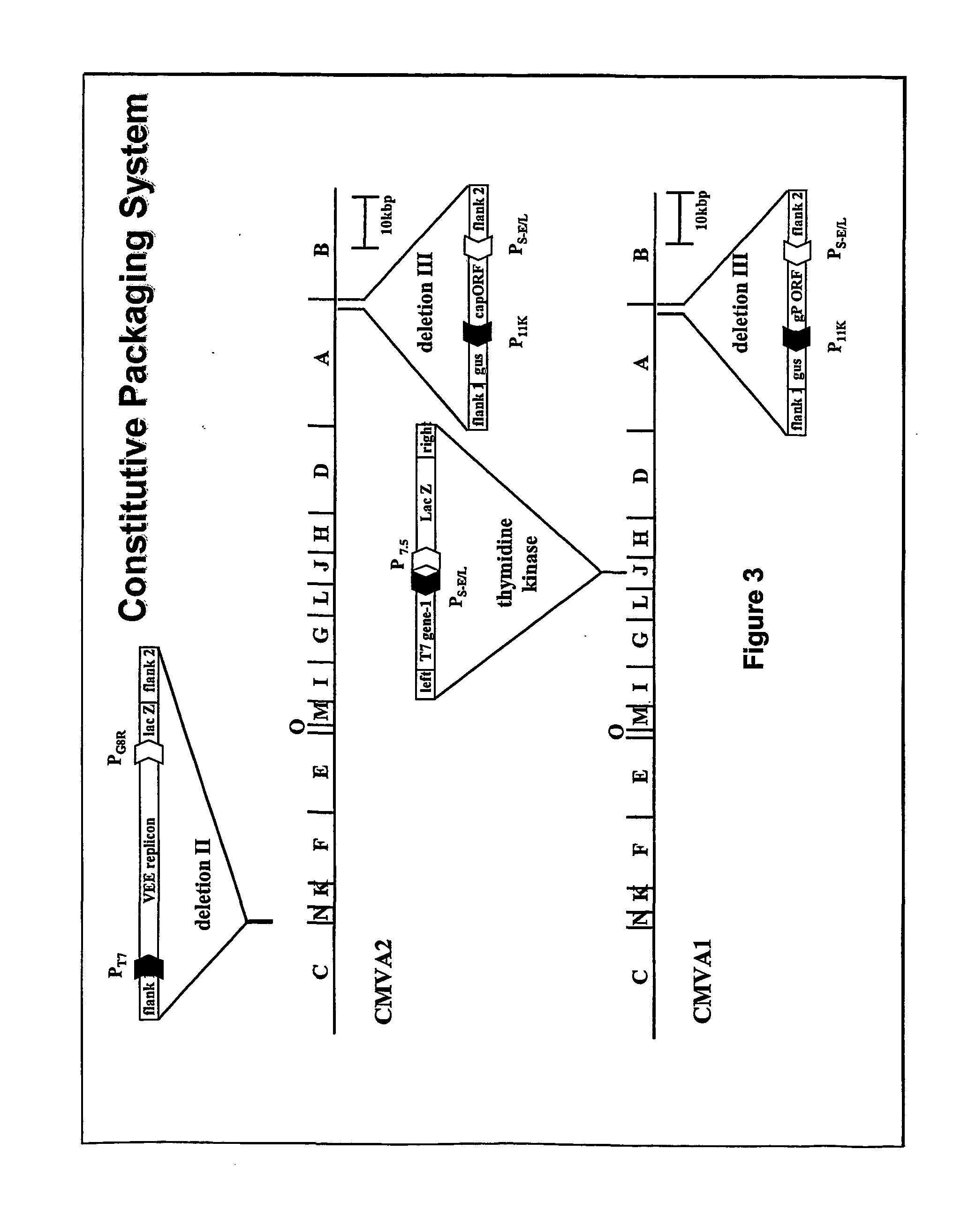
Packaging of positive-strand rna virus replicon particles
InactiveUS20040029279A1Great titerProbability of generatingFungiSsRNA viruses positive-sensePharmaceutical formulationViral vector
The invention generally relates to recombinant polynucleotides, positive-strand RNA virus (psRNAV) recombinant expression vectors, and packaging systems. The packaging systems are based on the expression of helper functions by coinfecting re-combinant poxvirus vectors comprising recombinant polynucleotides. Methods for obtaining psRNAV replicon particles using these packaging systems are disclosed. Immunogenic compositions and pharmaceutical formulations are provided that comprise replicon particles of the invention. Methods for generating an immune response or producing a pharmaceutical effect are also provided.
Owner:WYETH HOLDINGS CORP
Corynebacterium gene continuous knockout system, as well as construction method and application thereof
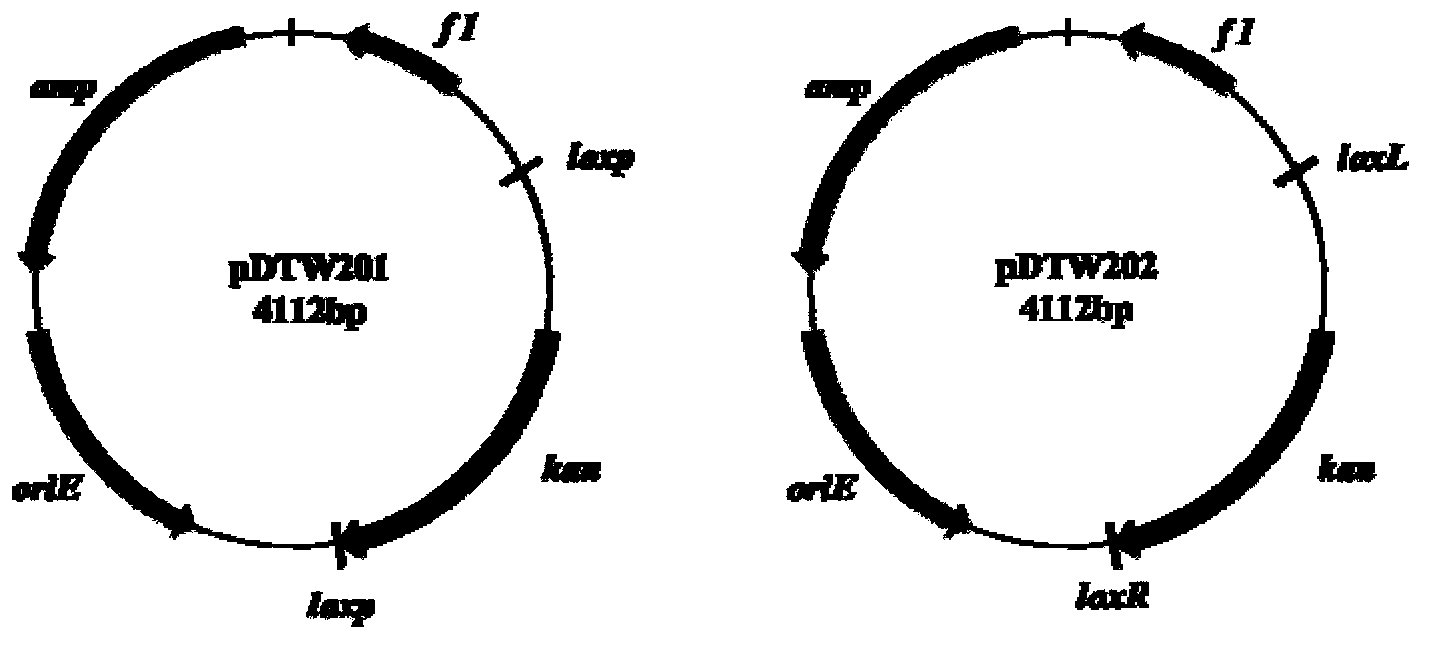
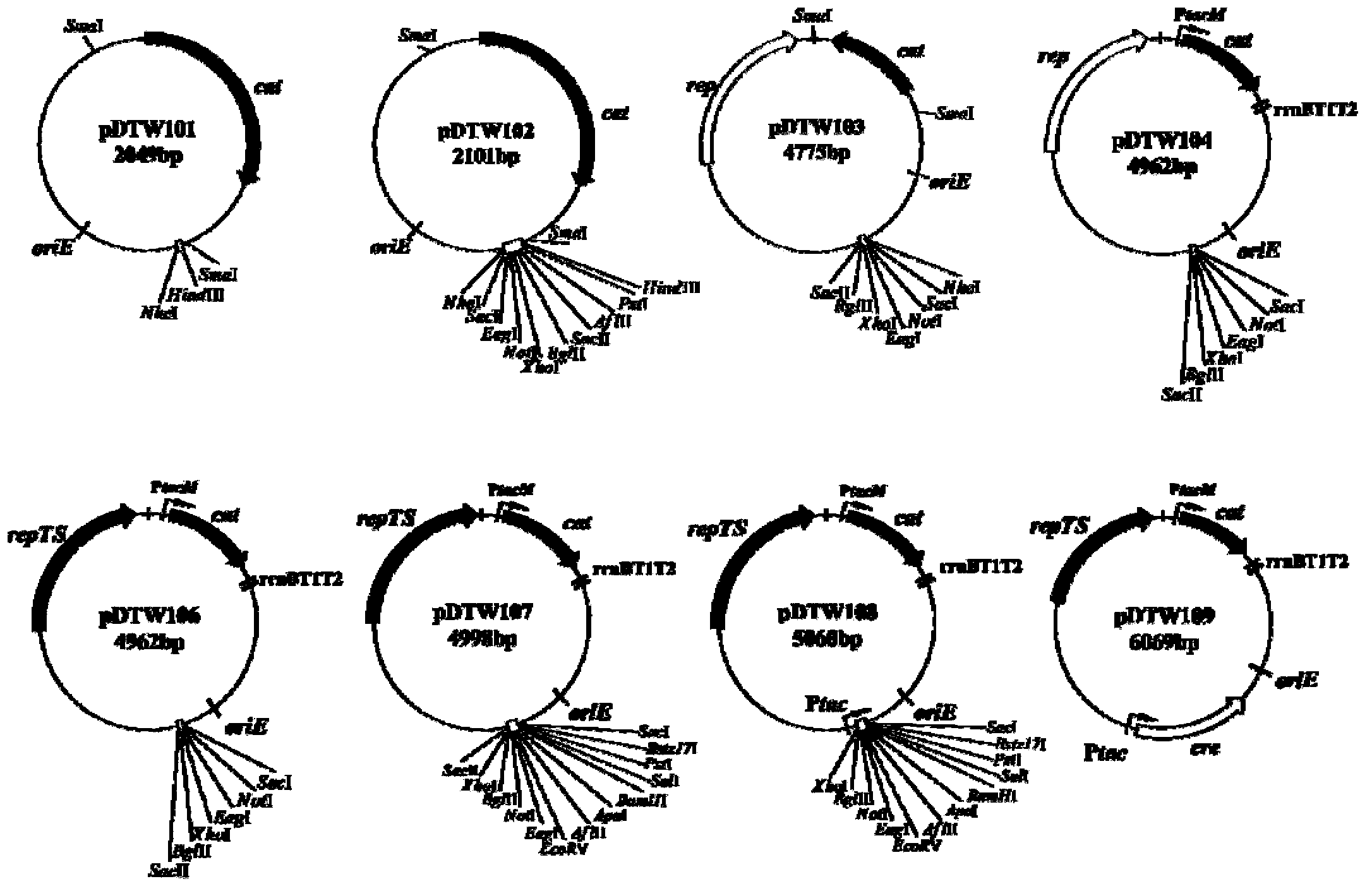
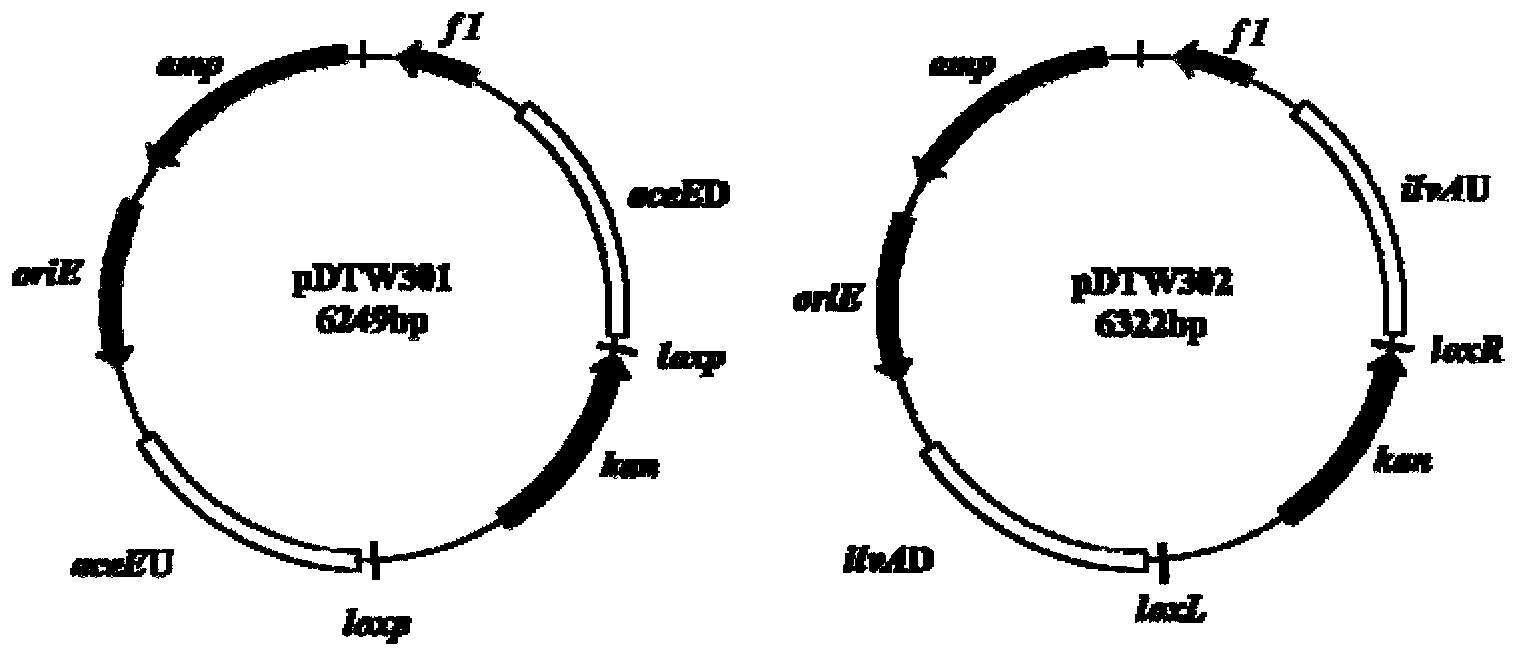
The invention discloses a construction method and an application of a corynebacterium gene continuous knockout system, belonging to the technical field of genetic engineering. The corynebacterium gene continuous knockout system comprises a template plasmid and a temperature-sensitive expression plasmid, wherein the template plasmid provides a kan fragment (also known as a kan box) with loxp or variant loxL / R sites at two ends; and the temperature-sensitive expression plasmid carries a Cm resistance gene cat and a temperature-sensitive C. glutamicum replicon, expresses a Cre recombinant enzyme and is used for removing a Km resistance gene kan. The corynebacterium continuous knockout system disclosed by the invention can be generally used for continuous gene transformation of corynebacterium and has the advantages of simplicity and convenience in operation and high efficiency. By utilizing the knockout system, gene (continuous) knockout of three major typical subspecies genomes of the corynebacterium can be successfully completed, and the system is proved to be applicable to research and production of corynebacterium metabolites.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Chimeric vectors
ActiveUS20060073594A1Less cytopathicSsRNA viruses positive-senseNucleic acid vectorHeterologousViral vector
The present invention relates to chimeric vectors. More specifically, the invention relates to recombinant poxvirus vectors and viruses that are capable of expressing an alphaviral RNA replicon expressing a heterologous sequence of interest.
Owner:MERIAL INC
Methods of genetic analysis involving the amplification of complementary duplicons
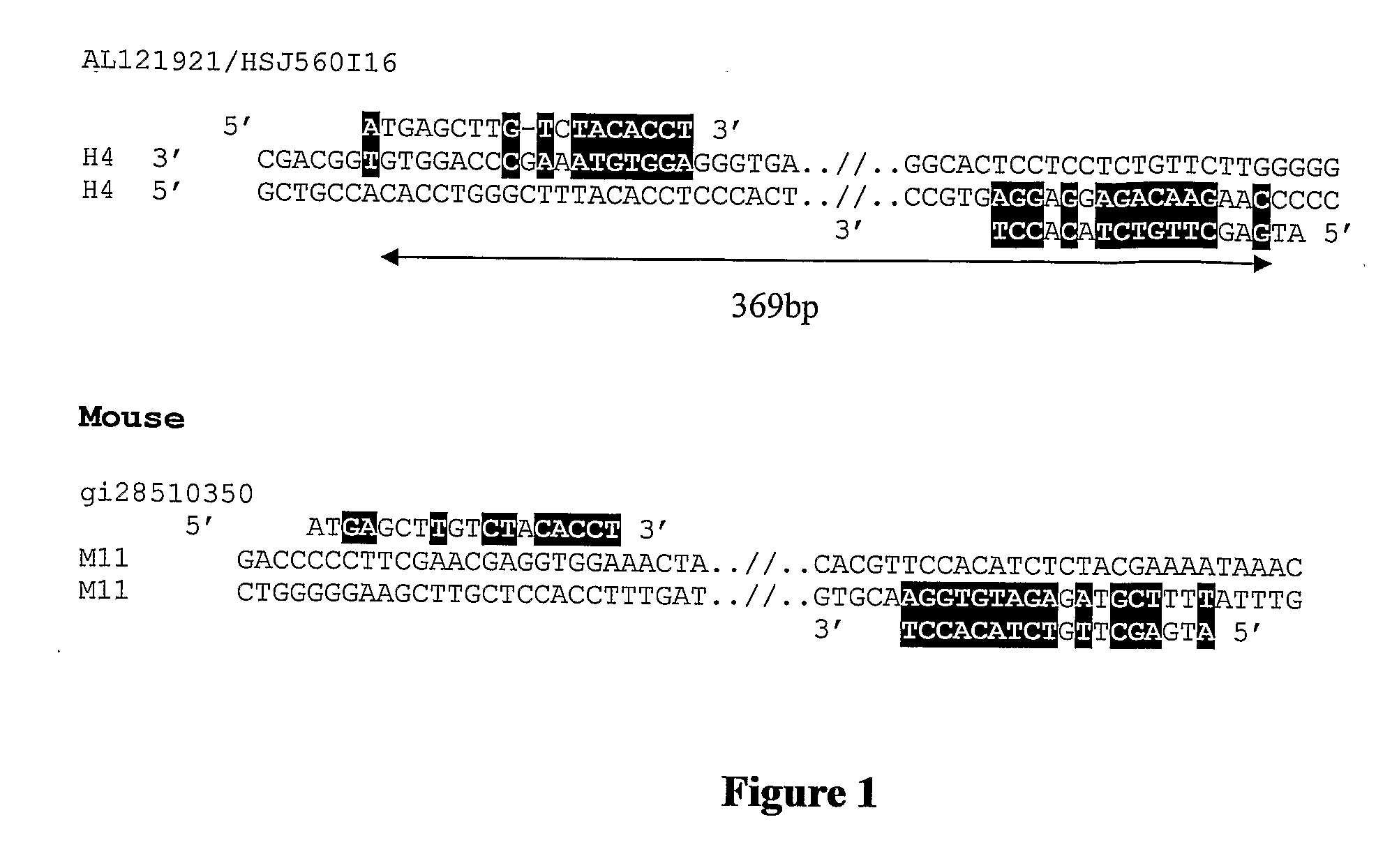
The invention relates to methods for genetic analysis of DNA sequences containing complementary duplicons which are duplicated and linked DNA sequences separated by an intermediate sequence. Furthermore, the invention relates to the Bidirectional Amplification of Complementary Duplicons (BACD) using a single primer. The amplification of complementary duplicons can be used for a variety of purposes such as, but not limited to, determining the species from which a sample comprising genomic DNA is derived, or used as a marker for a trait of interest. Also provided are means for analysing large datasets which can be used to identify primers useful for the genetic analysis methods of the invention.
Owner:CY OCONNOR ERADE VILLAGE FOUND
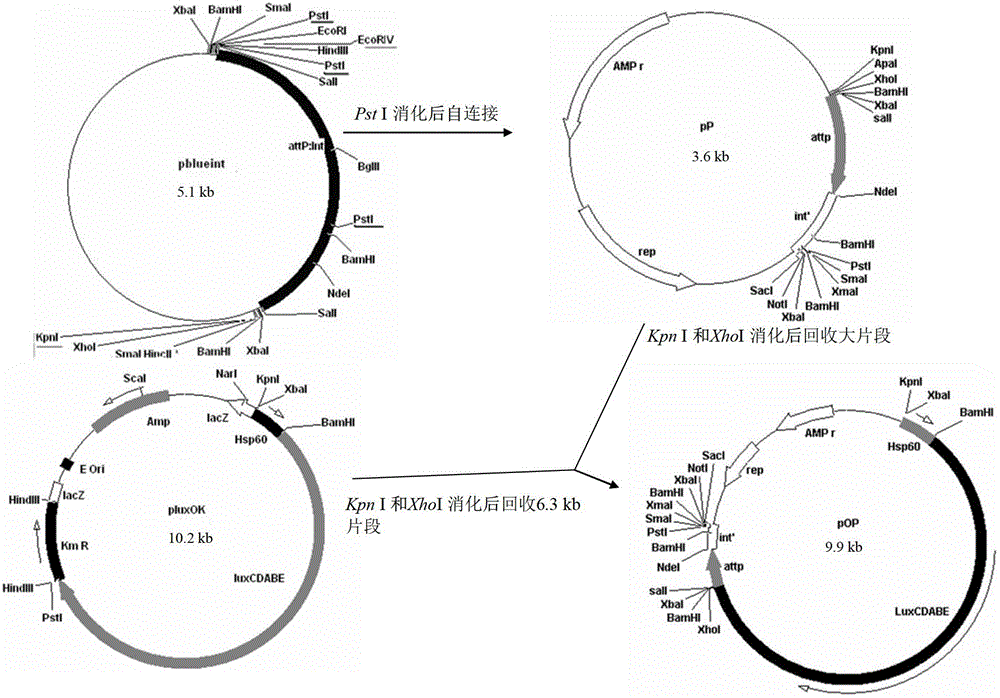
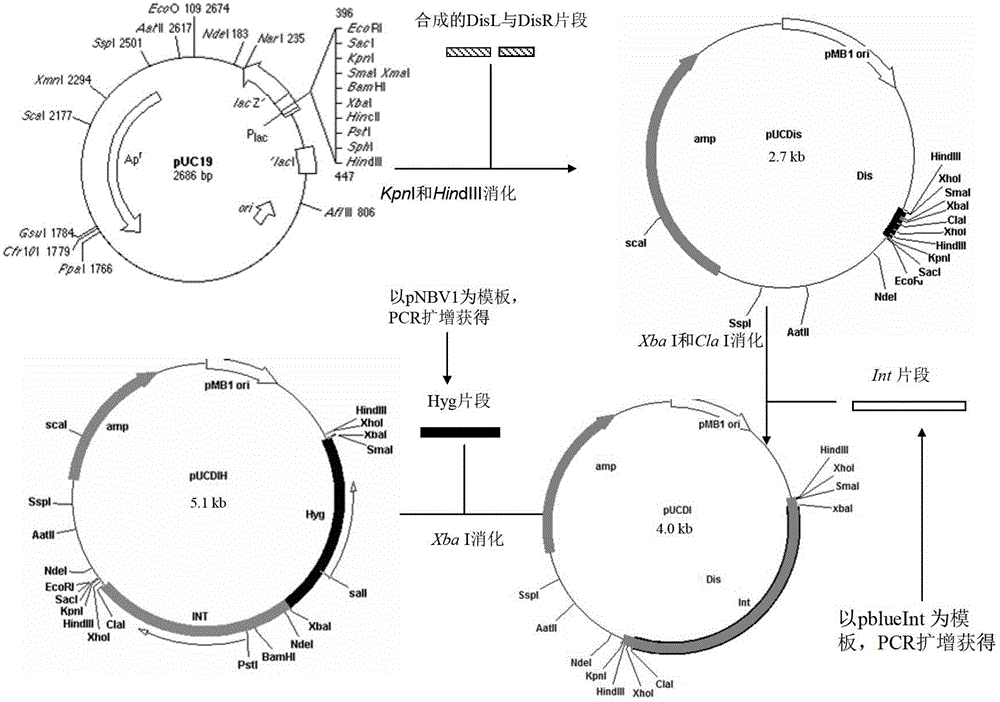
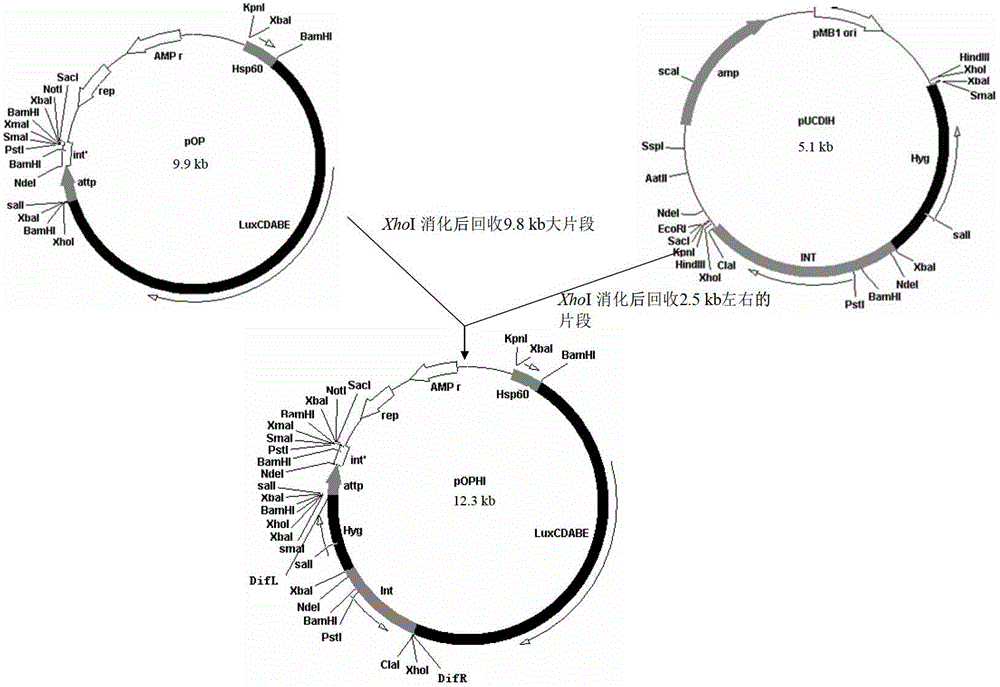
Integrative plasmid pOPHI and resistance screening marker-free self-luminescent mycobacterium
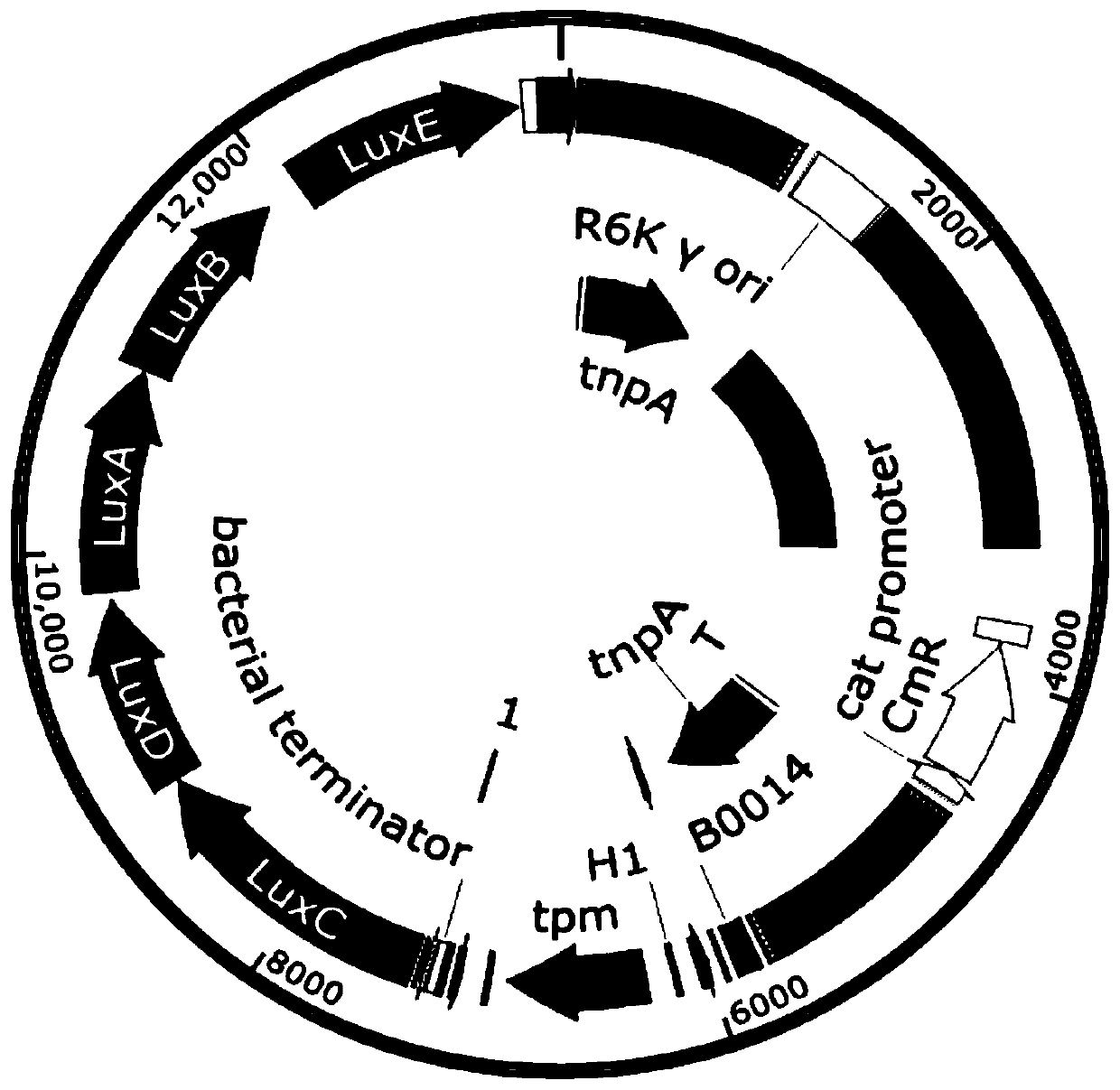
ActiveCN102719471AExperimental data is credibleHigh sensitivityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEnzyme GeneDirect repeat
The invention discloses an integrative plasmid pOPHI and a resistance screening marker-free self-luminescent mycobacterium. The integrative plasmid pOPHI comprises a promoter, an enzyme gene (LuxCDABE) needed for luminescence, a fusion gene of an integrase gene (Int) and a resistance screening gene, direct repeat sequences DifR and DifL positioned on two ends of the fusion gene, a phage integration site (attP) and a replicon. After the integrative plasmid pOPHI is transferred into the mycobacteria, a photobacterium of which the resistance gene and the integrase gene are lost is screened out by subculturing, and the photobacterium is the resistance screening marker-free self-luminescent mycobacterium. Whether the resistance screening marker-free self-luminescent mycobacterium obtained by construction is dead or not is judged according to whether the bacterium is luminescent or not, the mycobacterium can be used for a plurality of detections of experiments, and credible experimental data can be quickly obtained.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Two-Component Rna Virus-Derived Plant Expression System
ActiveUS20070300330A1Improve efficiencyProvide efficiencySugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesSingle-Stranded RNAWhole body
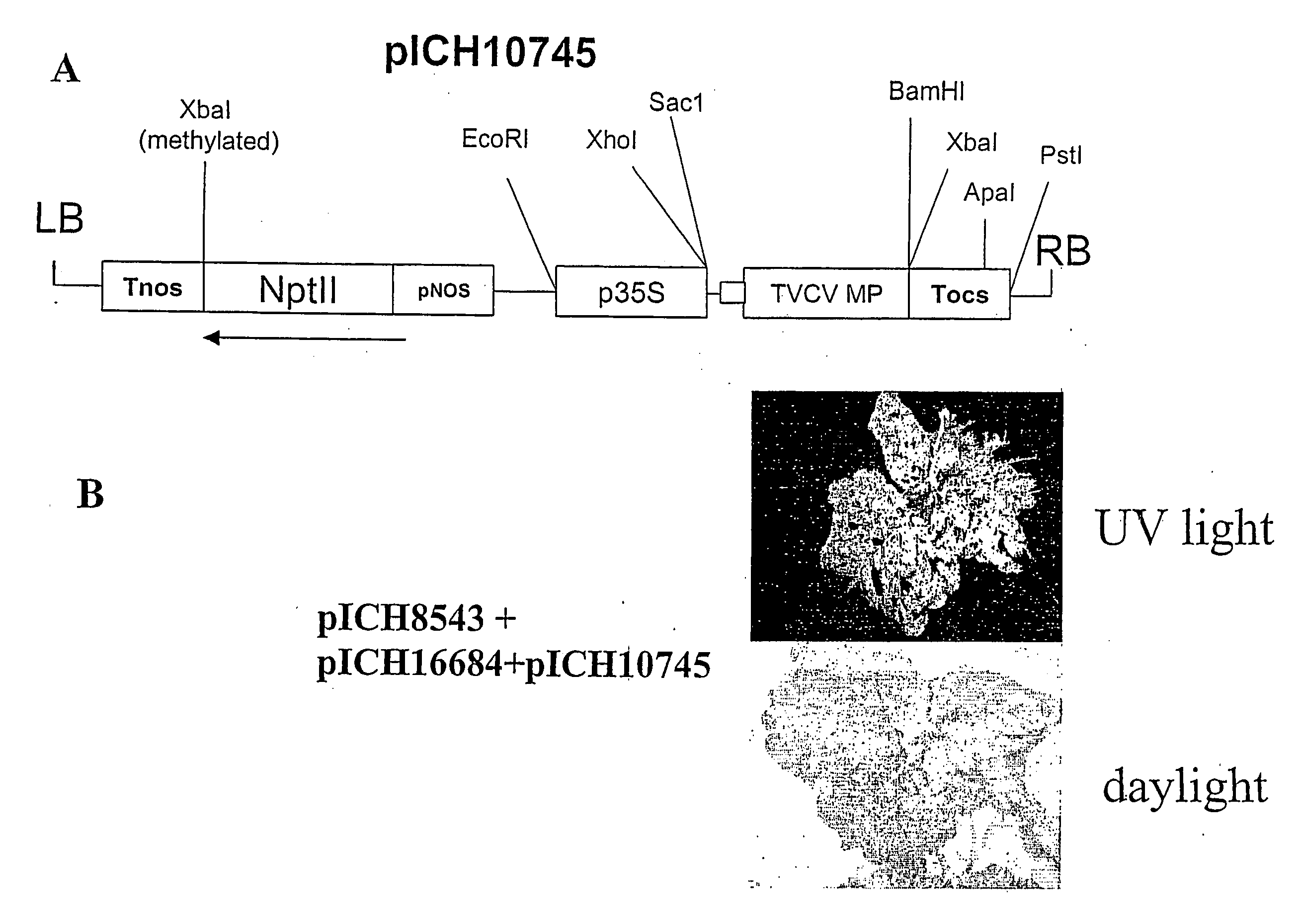
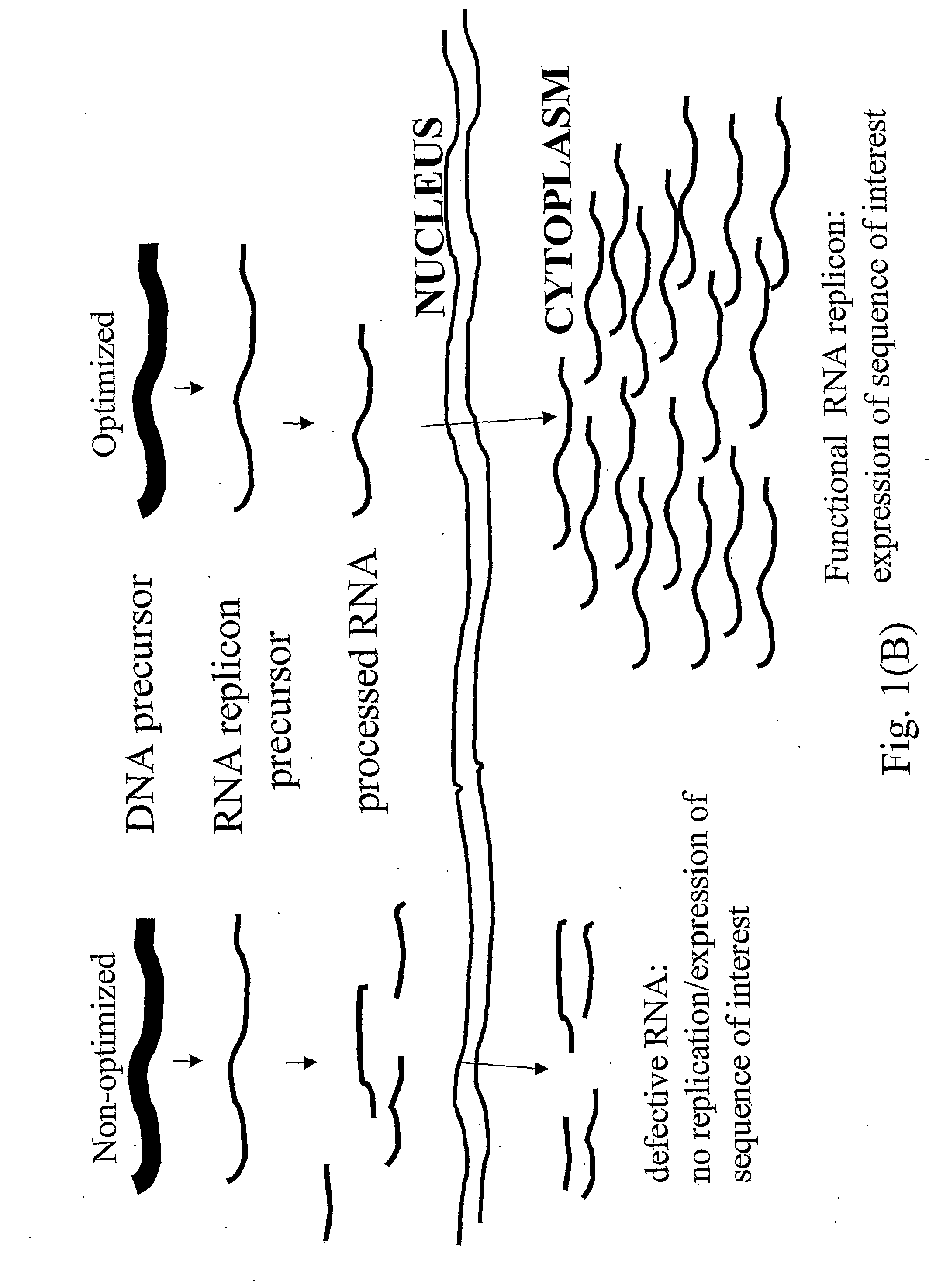
A process for replicating or for replicating and expressing a sequence of interest in a plant, comprising: (i) an RNA replicon or a precursor thereof, said RNA replicon being derived from a plus-sense single stranded RNA virus and comprising at least one sequence of interest; and (ii) a helper replicon, or a precursor thereof, wherein said helper replicon is (a) incapable of systemic movement in said plant both in the presence and in the absence of said RNA replicon (i) and (b) capable of expressing in a plant one or more proteins necessary for systemic movement of said RNA replicon (i), whereby said RNA replicon (i) is capable of replicating or replicating and expressing said sequence of interest in said plant, but unable to move systemically in said plant in the absence of said one or more proteins expressed by said helper replicon (ii).
Owner:ICON GENETICS
Chimeric alphavirus replicon particles
Chimeric alphaviruses and alphavirus replicon particles are provided including methods of making and using same. Specifically, alphavirus particles are provided having nucleic acid molecules derived from one or more alphaviruses and structural proteins (capsid and / or envelope) from at least two or more alphaviruses. Methods of making, using, and therapeutic preparations containing the chimeric alphavirus particle, are disclosed.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Alphavirus RNA replicon systems
InactiveUS7235235B2Reduced virulenceLow toxicityBiocideSsRNA viruses positive-senseStructural proteinVirology
The present invention provides a helper cell for expressing an infectious, replication defective, alphavirus particle in an alphavirus-permissive cell. The helper cell includes (a) a first helper RNA encoding (i) at least one alphavirus structural protein, and (ii) not encoding at least one alphavirus structural protein; and (b) a second helper RNA separate from the first helper RNA, the second helper RNA (i) not encoding the alphavirus structural protein encoded by the first helper RNA, and (ii) encoding the at least alphavirus one structural protein not encoded by the first helper RNA, such that all of the alphavirus structural proteins assemble together into alphavirus particles in the cell. Preferably, the helper cell also includes a replicon RNA encoding an alphavirus packaging sequence and an inserted heterogeneous RNA.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Geminiviral vector for expression of rituximab
ActiveUS10125373B2VaccinesImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsNicotiana tabacumHeavy chain
A single vector or multiple separate vectors that contain two or more non-competing replicons for transient expression of the heavy and light chains of Rituximab in Nicotiana benthamiana leaves is described. The correct assembly of these subunit proteins into functional oligomeric structures to optimize the expression is also described. This system advances plant transient expression technology by eliminating the need for non-competing viruses, and thus, enhances the realistic commercial application of the multi-replicon single vector system for producing Rituximab in plant cells.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
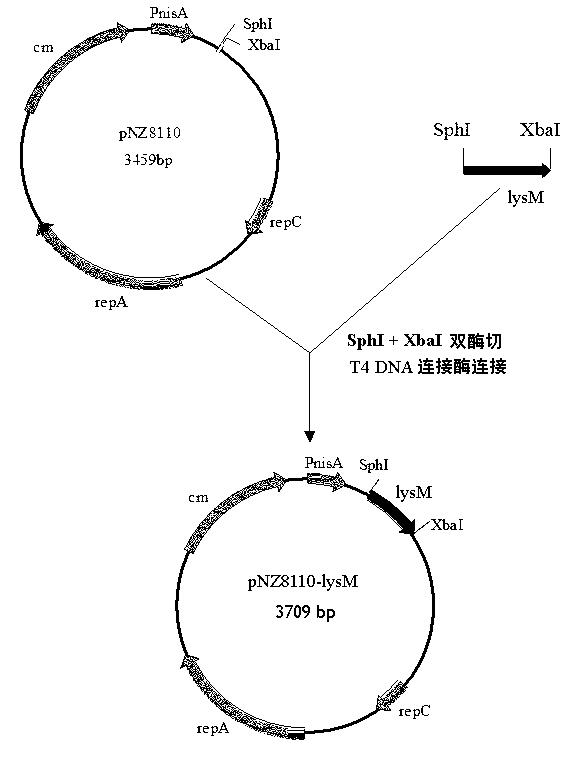
Carrier capable of showing and expressing heterologous gene on surface of lactococcus lactis, and preparation method and application of carrier
InactiveCN102796756AExcellent oral immunityGood immune effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHeterologousEnzyme digestion
The invention relates to a carrier capable of showing and expressing a heterologous gene on the surface of lactococcus lactis, and a preparation method and application of the carrier. The carrier has the nucleotide sequence which is shown as SEQ ID NO.1 in a sequence table, and contains promoter Pnis and lysM genes, a signal peptide secretion sequence ssusp45, a multiple cloning endonuclease site, and replicon repA and repC components. A method for constructing the carrier has the following steps of: amplifying a lactococcus lactis NZ3900 strain autolysin (AcmA) anchoring area gene lysM by applying a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technology, performing enzyme digestion on the lysM and a carrier pNZ8110 and connecting, wherein a connection product is used for transforming a E.coli MC1061 strain, and extracting recombinant plasmid from positive transformed bacteria which are subjected to enzyme digestion and sequencing identification to obtain the expression carrier. The exogenous gene and the carrier are connected and then transferred into lactococcus lactis NZ3900, and the expression of the exogenous gene and the combination of expression protein and host cell walls can be realized by induction of nisin. The carrier can be used for expressing foreign proteins including vaccine antigens and has a wide application range.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Packaging of positive-strand RNA virus replicon particles
InactiveUS7034141B2Great titerProbability of generatingFungiSsRNA viruses positive-senseRepliconNucleotide
The invention generally relates to recombinant polynucleotides, positive-strand RNA virus (psRNAV) recombinant expression vectors, and packaging systems. The packaging systems are based on the expression of helper functions by coinfecting recombinant poxvirus vectors comprising recombinant polynucleotides. Methods for obtaining psRNAV replicon particles using these packaging systems are disclosed. Immunogenic compositions and pharmaceutical formulations are provided that comprise replicon particles of the invention. Methods for generating an immune response or producing a pharmaceutical effect are also provided.
Owner:WYETH HOLDINGS CORP
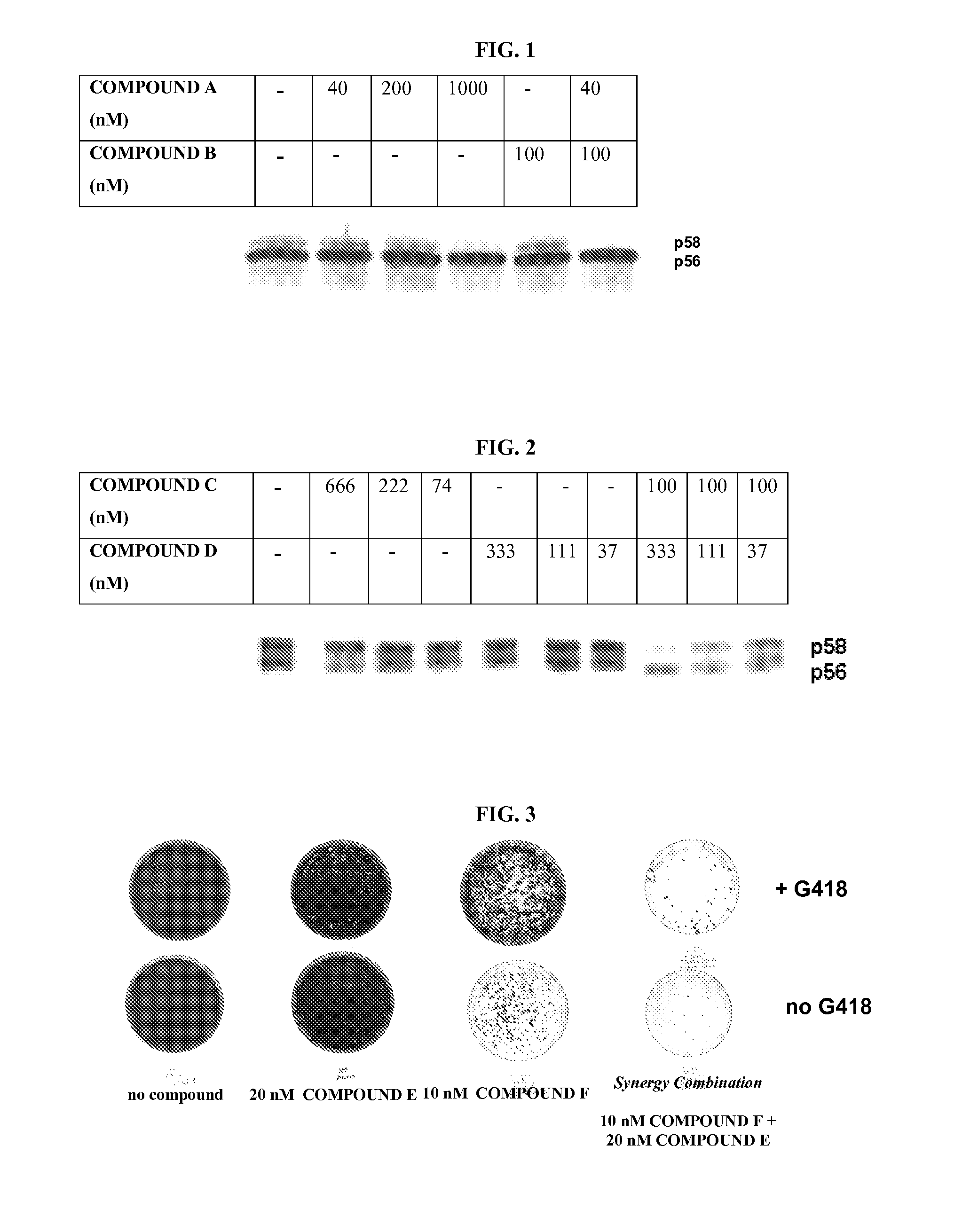
Methods to identify combinations of ns5a targeting compound that act synergistically to inhibit hepatitis c virus replication
InactiveUS20130157894A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningWild typeCombination therapy
The present invention is based on the surprising finding that pairs of HCV NS5A-targeting inhibitors can be identified which display similar resistance profiles yet, when combined, exhibit synergistic inhibition of wild type replicons and / or replicons carrying mutations conferring resistance to the HCV NS5A-targeting inhibitor. In addition, combinations of these molecules result in a higher genetic barrier to resistance, demonstrating their potential utility as novel combination therapies for treatment of HCV.
Owner:SUN JIN HUA +6
Recombinant flaviviral constructs and uses thereof
InactiveUS20130243809A1Successfully expressingHigh insertion capacitySsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsStructural proteinViral replication
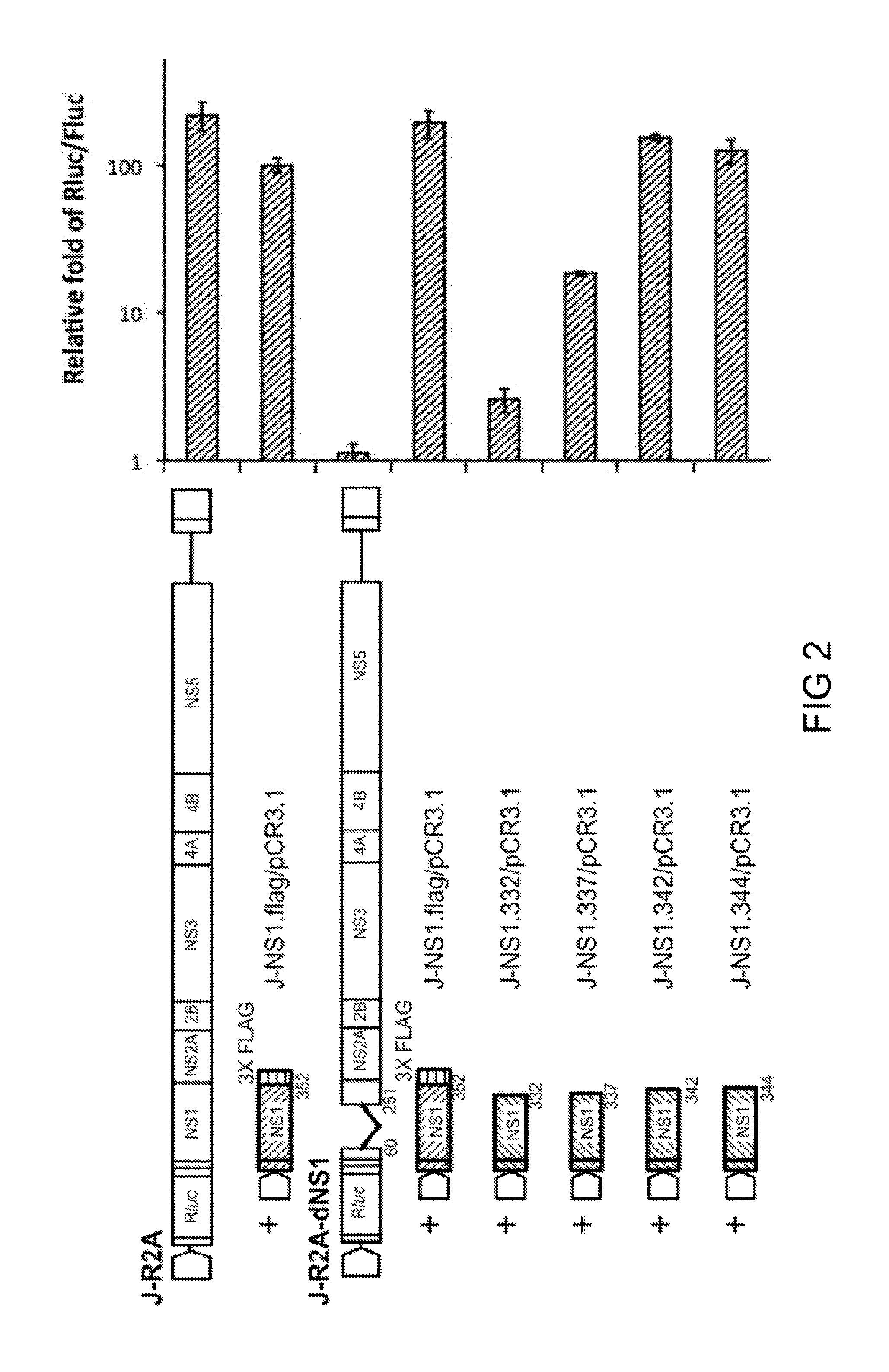
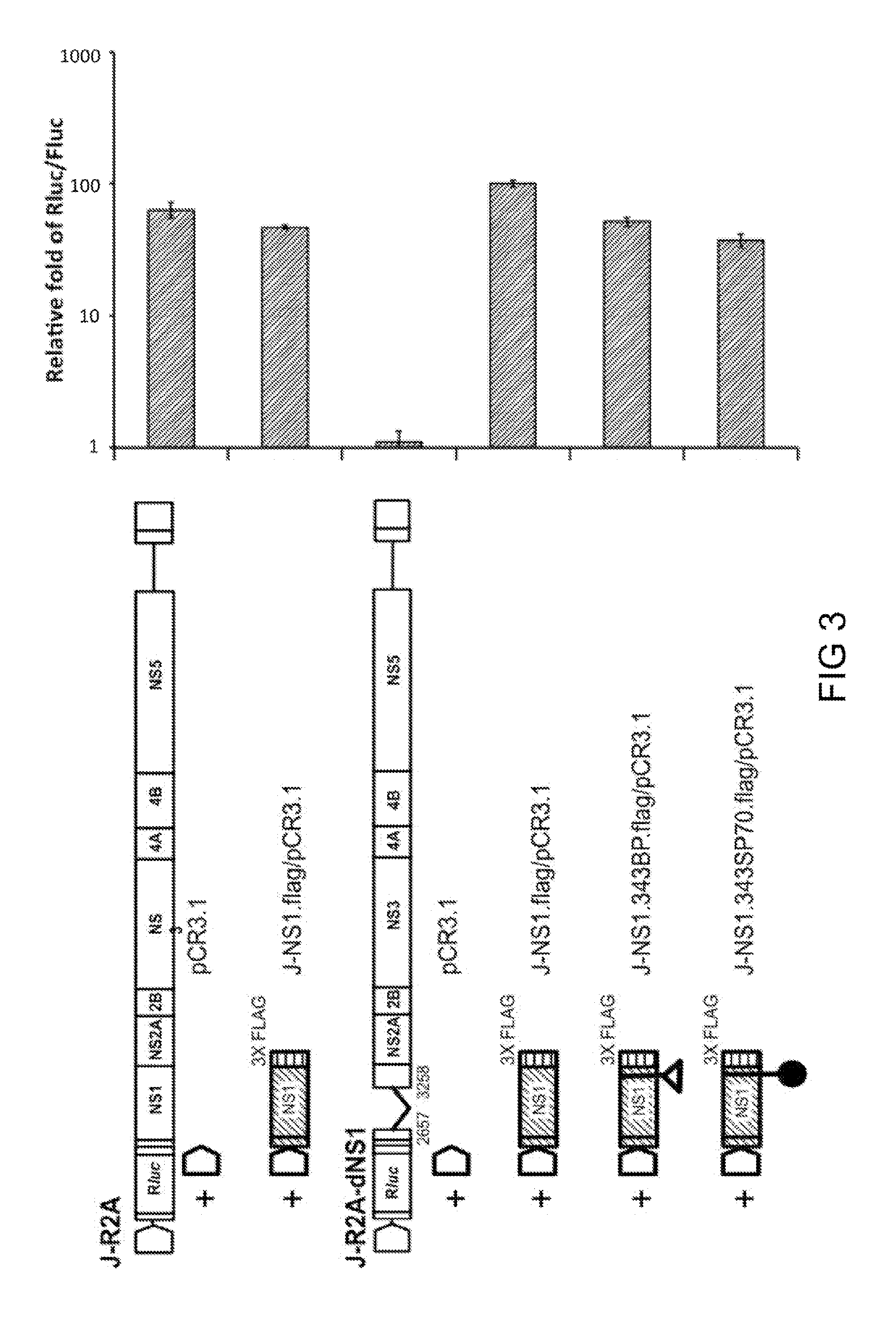
A recombinant viral construct for expressing an exogenous polypeptide in a cell and uses thereof are provided. The recombinant viral constructs are derived from Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV). The recombinant viral constructs encodes a fusion protein, which includes an exogenous (i.e., non-JEV) polypeptide and a JEV non-structural protein 1 (JEV NS1) or a segment thereof. Particularly, the exogenous polypeptide is inserted into the carboxyl-terminus of the JEV NS1, and the production of the recombinant fusion protein does not affect viral replication. Upon infection a cell with such recombinant viral constructs, JEV particles comprising limited multiplicative virions (LMV) may be produced. Each LMV comprises the as-described JEV replicon. The JEV particles are useful in eliciting an immune response to the exogenous polypeptide in a host and thereby confer the host with protective immunization against the exogenous polypeptide.
Owner:NAT DEFENSE MEDICAL CENT
Fluorescent strain E. coli C600 and construction method and application thereof
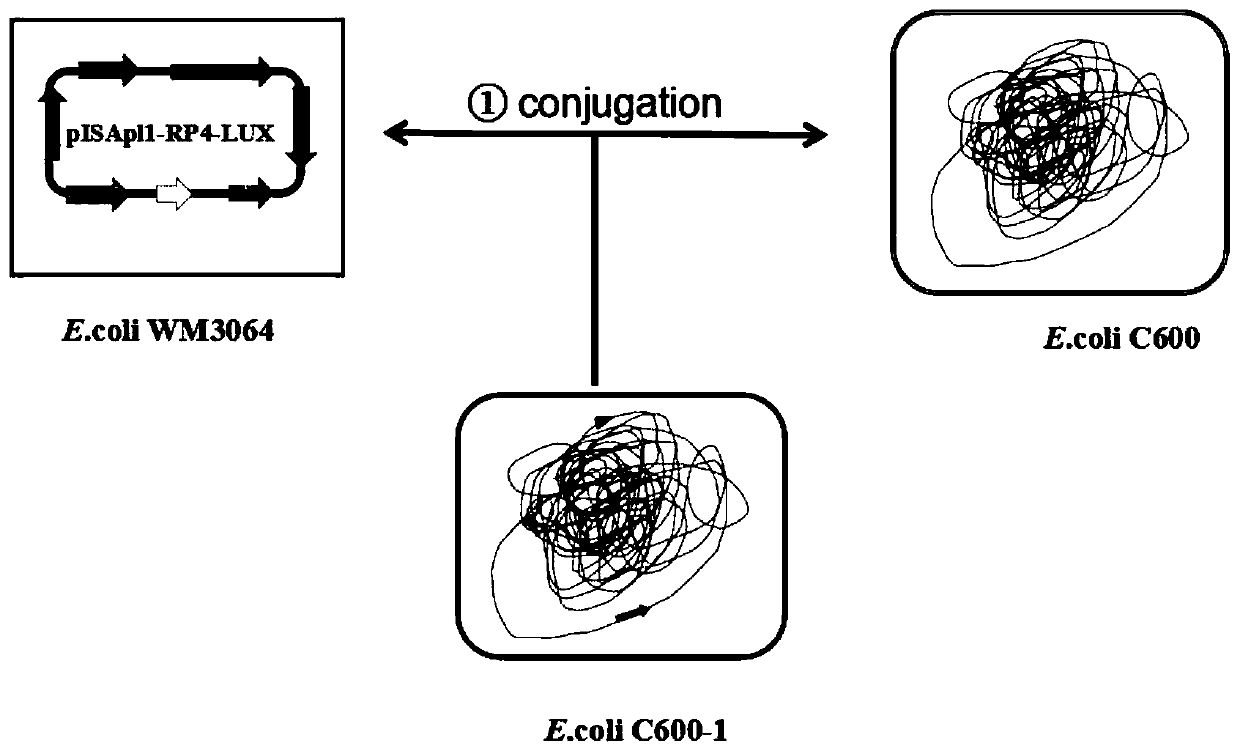
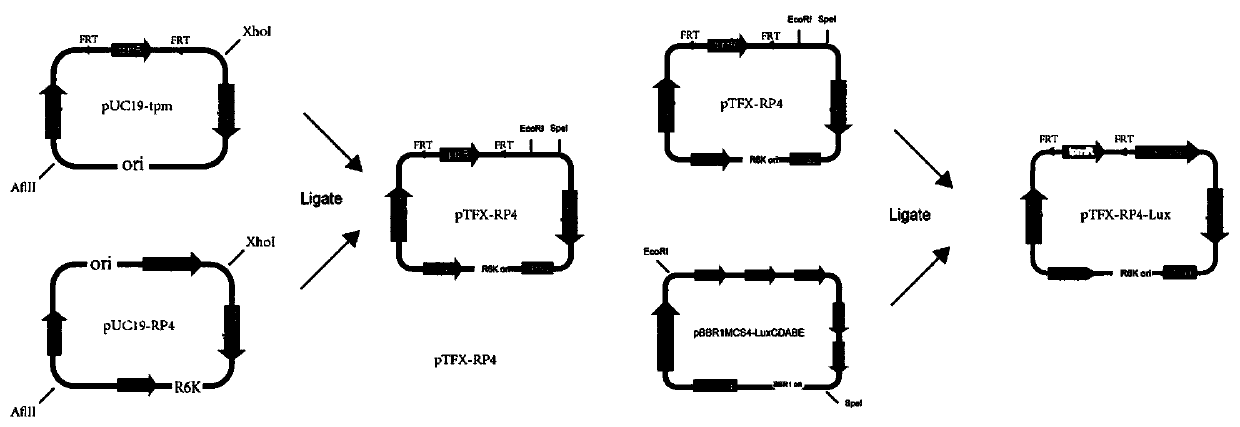
ActiveCN110066820AImprove stabilityGenetic stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesTransfer geneMixed culture
The invention provides a fluorescent strain E. coli C600 and a construction method and application thereof. By constructing a recombinant plasmid containing an R6k replicon, a transposition unit and an RP4 conjugative transfer gene, the recombinant plasmid is transferred to a host bacterium in which the recombinant plasmid can replicate to obtain a recombinant strain, the recombinant strain and E.coli C600 are subjected to mixed culture, and then the fluorescent strain E. coli C600 can be obtained through screening, wherein the transposition unit is formed by using two ISApl1 for sandwichinga Lux gene cluster and a tellurite drug-resistance gene in the middle. The exogenous gene acquiring capability of the fluorescent strain E. coli C600 is not influenced, the stability is high, stable inheritance can be ensured, the fluorescent property cannot lose along with bacterium passage, and thus the fluorescent strain E. coli C600 can serve as a recipient bacterium for conjugation experiments. By adopting the fluorescent strain E. coli C600, recipient bacteria and zygotes can be identified more efficiently and more intuitively in the fields related to plasmid conjugational transfer, andtherefore the fluorescent strain E. coli C600 has good application prospects.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
PTerm-SC plasmid as well as construction method and application thereof
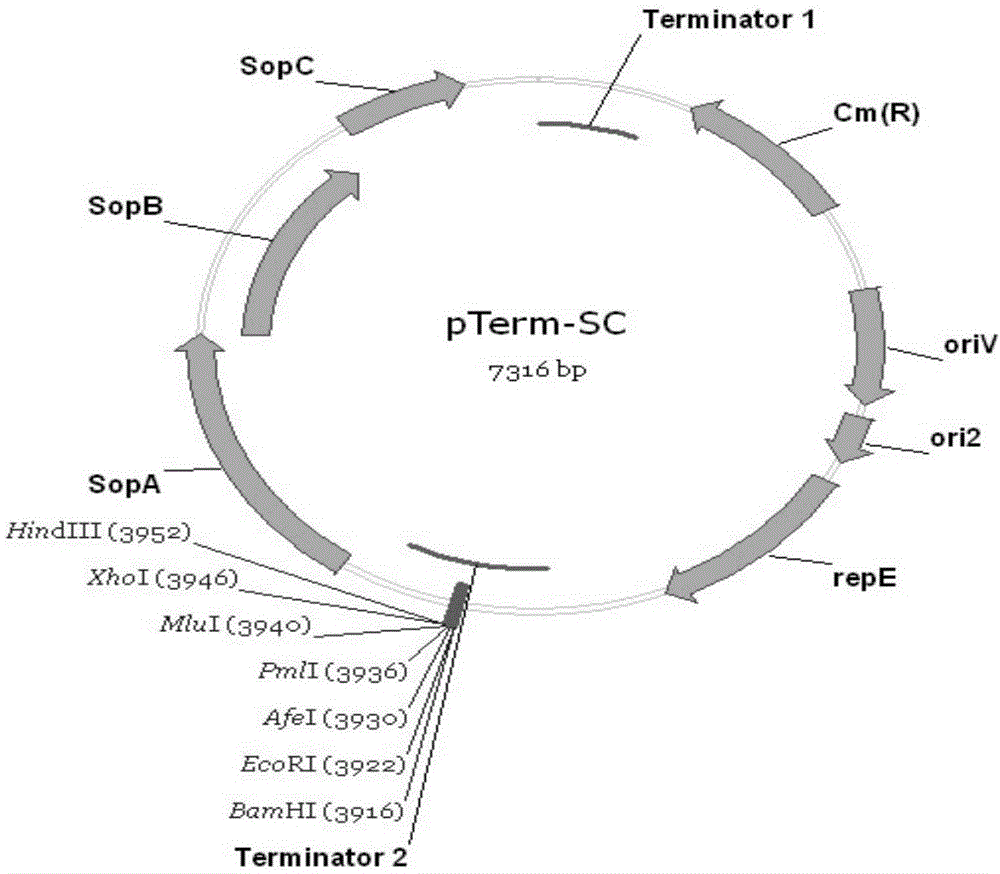
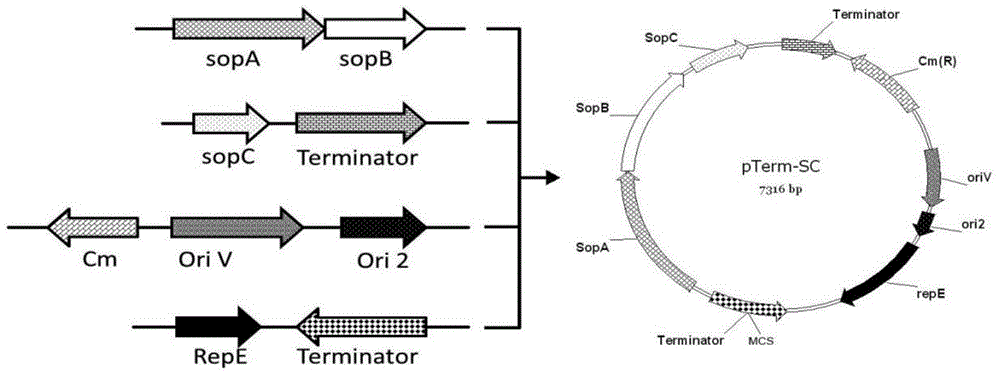
ActiveCN104480130AEasy extractionTranscriptional repressionMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionAntibiotic YGene engineering
The invention relates to a pTerm-SC plasmid as well as a construction method and application thereof. The pTerm-SC plasmid comprises a repE gene, a sopA gene, a sopB gene, a sopC gene, an ori2 replicon, an oriV replicon, prokaryote transcription terminators and antibiotics resistance genes. The pTerm-SC plasmid has the characteristics of very low copy number, high volume and stability and the like, can be applied to gene engineering fields such as the cloning, the screening, sequencing and the genome construction of complex-structure genes including repetitive-sequence genes, instable genes and long-fragment genes and has important role in the high-efficiency and high-quality synthesis of genes.
Owner:GENEWIZ INC SZ
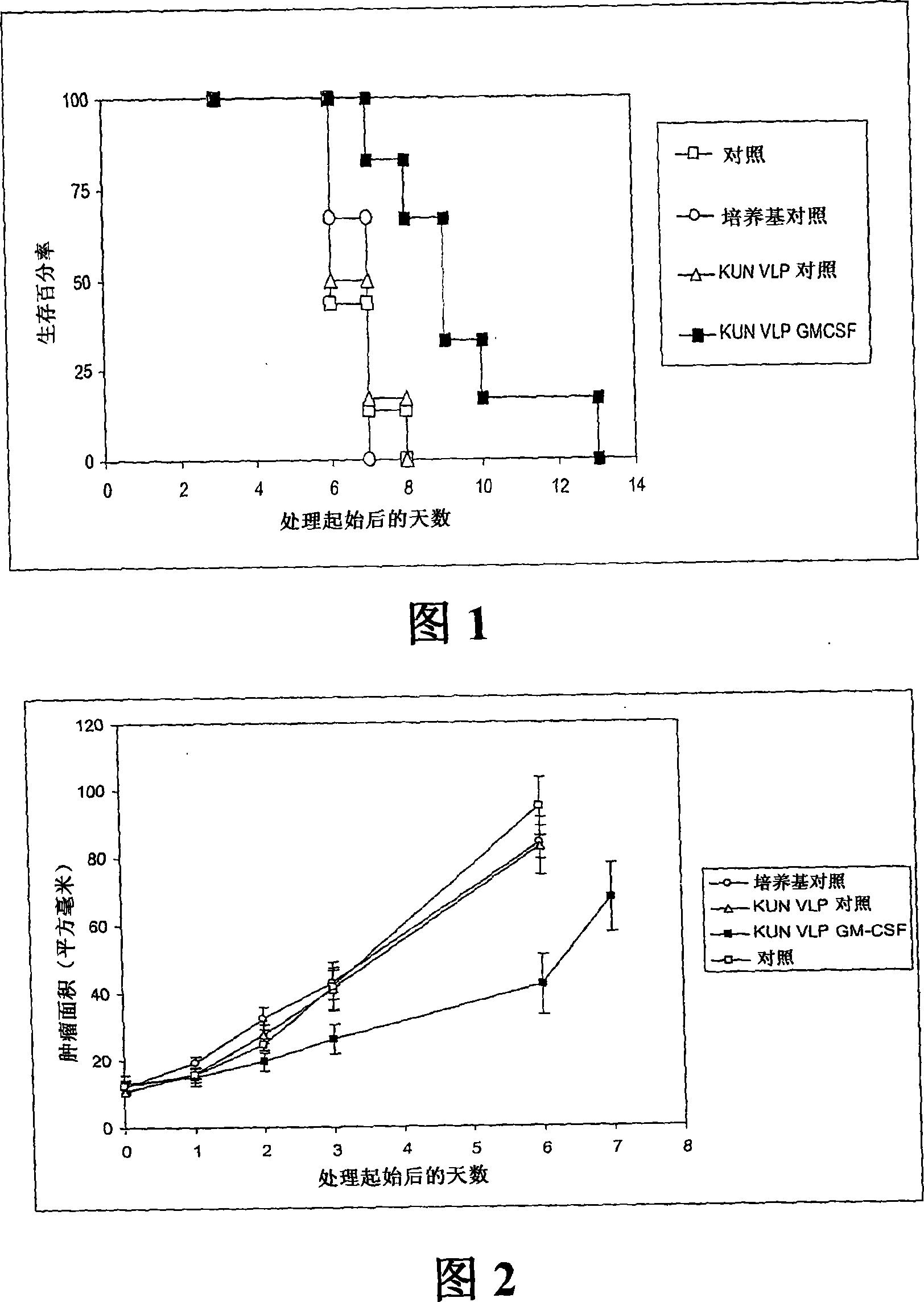
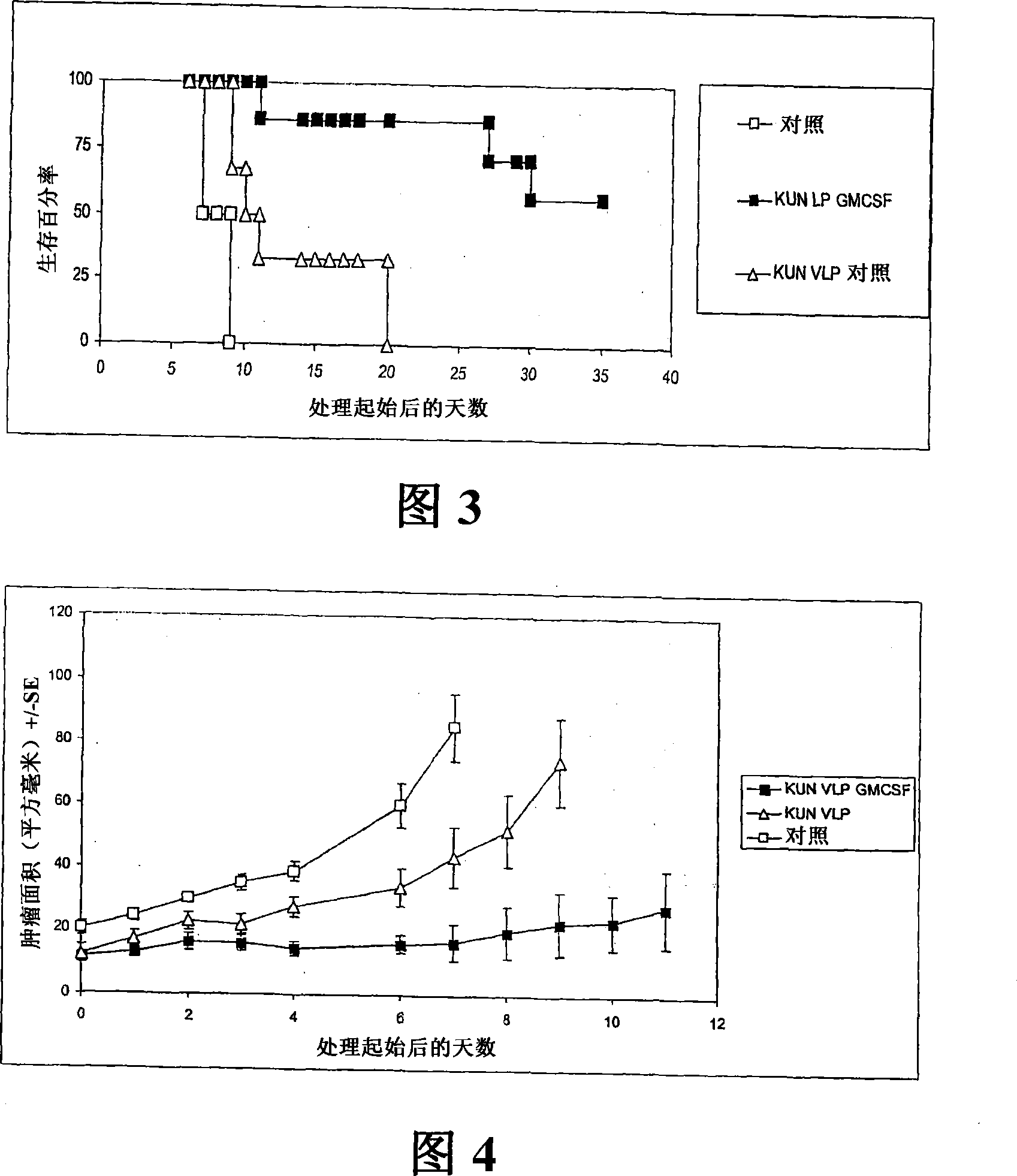
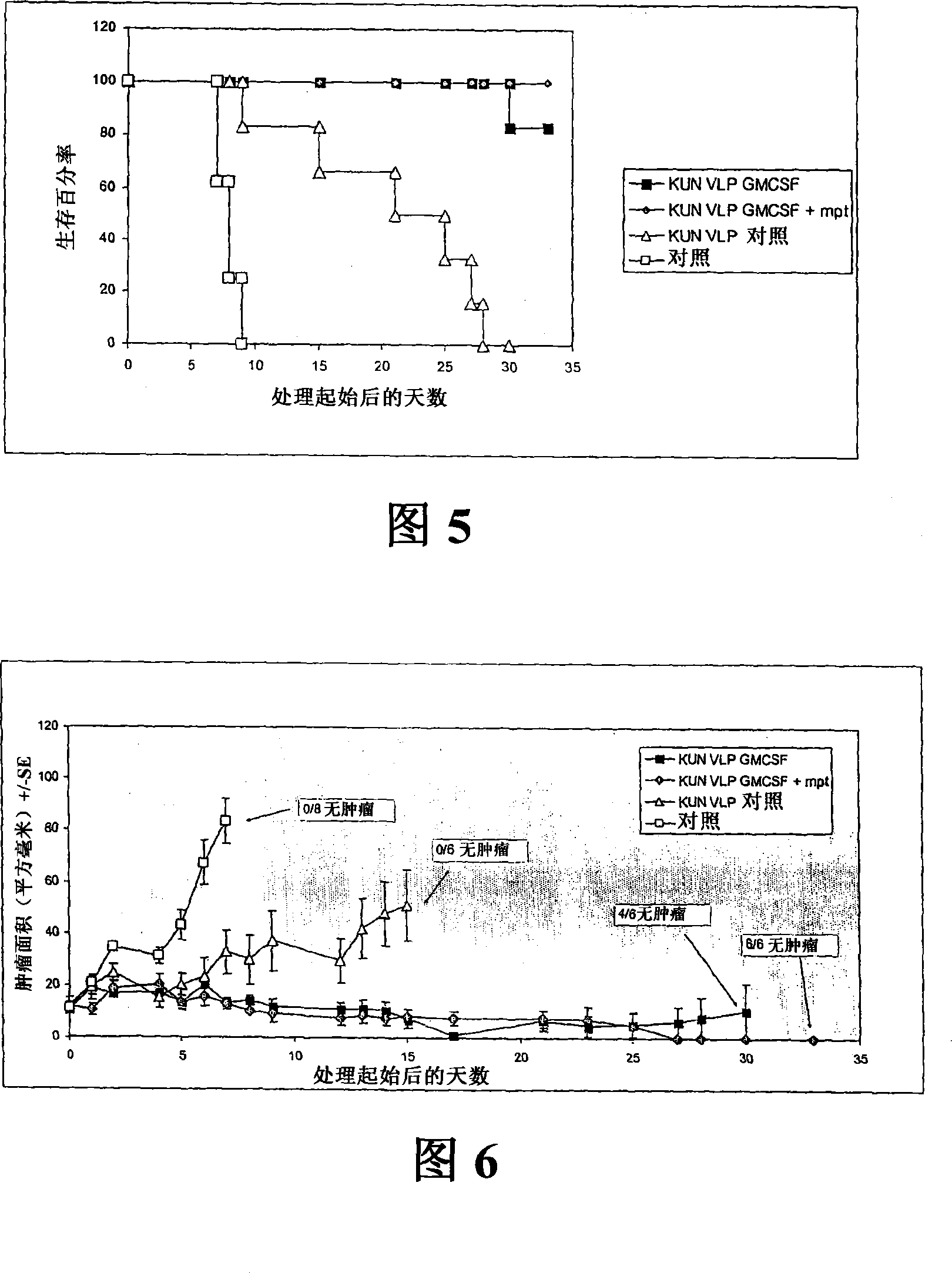
Flavivirus replicon constructs for tumour therapy
InactiveCN101120086AOrganic active ingredientsSsRNA viruses positive-senseParanasal Sinus CarcinomaMelanoma
Owner:レプリカン バイオテク プロプライエタリー リミテッド
Recombinant expression plasmids used for packaging coxsackievirus B5 (CV-B5) pseudovirus, pseudovirus, kit and method
PendingCN106884017ADetection securityQuick checkViruses/bacteriophagesFermentationCoxsackievirusStructural protein
The invention relates to recombinant expression plasmids used for packaging a coxsackievirus B5 (CV-B5) pseudovirus, the pseudovirus, a kit and a method. The recombinant expression plasmids used for packaging the coxsackievirus B5 pseudovirus are respectively named as the pEGFP-CV-B5 (417) plasmid and the pCVB3-replicon, the CV-B5 structural protein expressed by the pEGFP-CV-B5 (417) plasmid can be used for packaging CV-B3 subgenome RNA transcribed by the pCVB3-replicon in the cell, thus the CV-B5 pseudovirus is generated, the pseudovirus can be used for detecting the neutralizing antibody, and since the pseudovirus with single-cycle infection is adopted, the safety problem caused when the live virus is used is avoided. After a plurality of experiments, the result shows that the invention provides the method for detecting the CV-B5 neutralizing antibody which is safe, sensitive, rapid, specific, simple and convenient, and is low in cost. Based on the abovementioned features, the method is particularly suitable for the experiment for rapidly detecting the neutralizing antibody in large scale, and thus the method has the significant application value in developing viral vaccines and detecting the level of the CV-B5 specific neutralizing antibody of individual and group patients.
Owner:NAT INST FOR FOOD & DRUG CONTROL
Chimeric alphavirus replicon particles
Chimeric alphaviruses and alphavirus replicon particles are provided including methods of making and using same. Specifically, alphavirus particles are provided having nucleic acid molecules derived from one or more alphaviruses and structural proteins (capsid and / or envelope) from at least two or more alphaviruses. Methods of making, using, and therapeutic preparations containing the chimeric alphavirus particle, are disclosed.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Japanese encephalitis virus like particles as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102329784AReserve spaceReserved epitopeViral antigen ingredientsInactivation/attenuationJapanese B Encephalitis VirusReverse transcriptase
The invention discloses Japanese encephalitis virus like particles as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The Japanese encephalitis virus like particles are prepared by assembling a PrM / E gene of a Japanese Encephalitis virus (JEV) and a JEVRNA replicor with a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. The preparation method of the Japanese encephalitis virus like particles comprises the steps of: connecting the JEV PrM / E gene amplified by an RT-PCR (Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction) to a plasmid pTRE-Tight of a Tet-on advance expression system to form a recombination vector, transfecting a Hela Tet-on advanced cell by using an Xfect method, after screening and identifying through HygB, obtaining a Hela cell line for controllably and stably expressing the PrM / E gene through a limiting dilution process, inducing for expressing a PrM / E protein, and packaging to obtain the conventional virus like particles; and transfecting the Hela cell line by using a JEV replicor RNA vector and packaging to obtain the virus like particles with a capacity of transient infection. The Japanese encephalitis virus like particles can be used for preparing a vaccine or used as a detection agent, has better immunogenicity and reactivity, and is safe and reliable.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Biologically Safe Transient Protein Expression in Plants
ActiveUS20080057563A1Efficient systemImprove efficiencySugar derivativesBacteriaBiotechnologyHeterologous
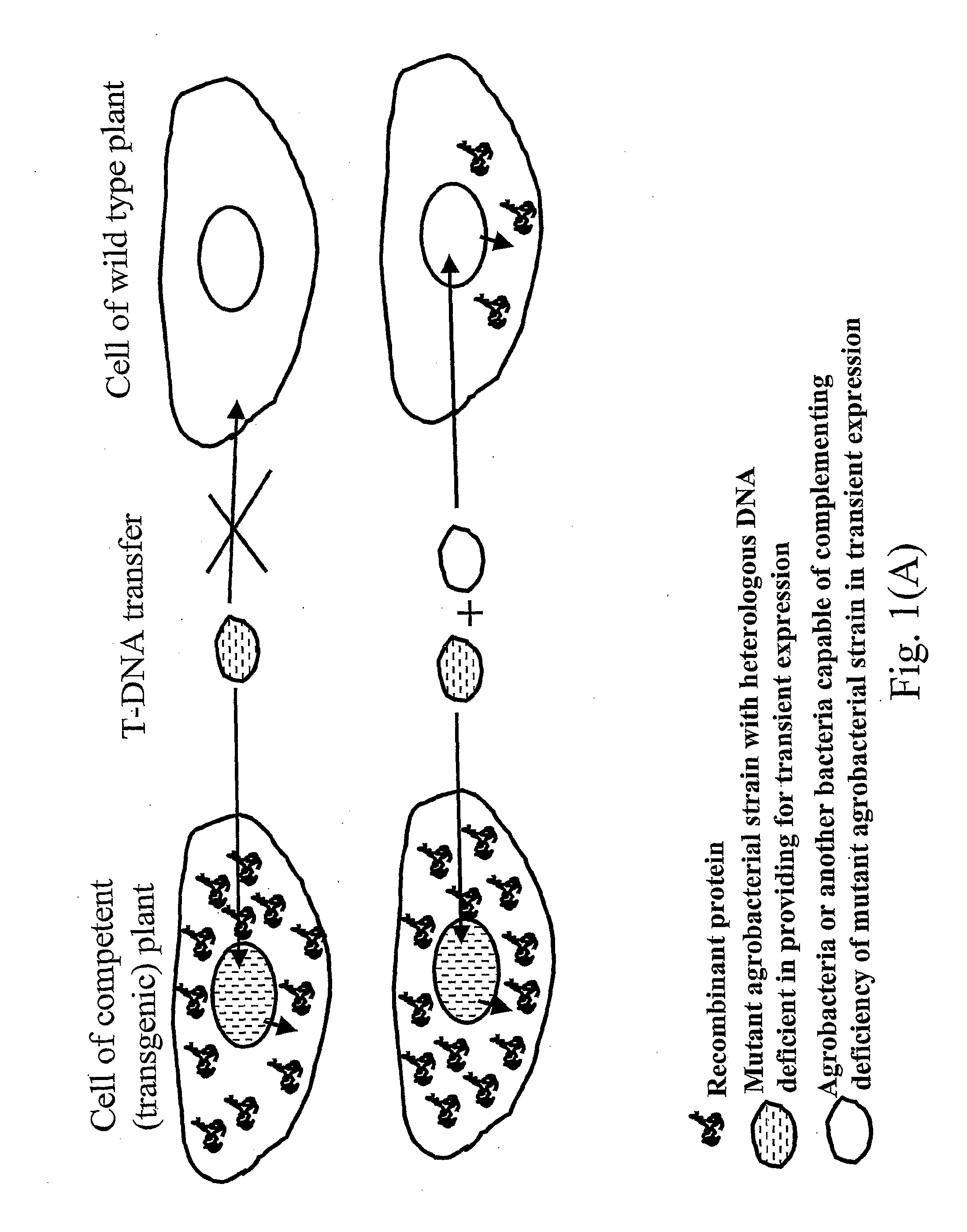
A process of producing a protein of interest by expression of said protein of interest from a sequence of interest in a plant or in plant leaves, comprising: (a) transfecting said plant or said plant leaves by infiltrating said plant or said plant leaves with an Agrobacterium strain in the presence of a complementing factor, said Agrobacterium strain containing in T-DNA a heterologous DNA sequence having a sequence portion encoding a replicon, wherein said sequence encoding a replicon contains sequences necessary for replicon function of said replicon, said sequences being derived from a plant virus, and said sequence of interest to be expressed from said replicon, (b) isolating said protein of interest from said plant or said plant leaves infiltrated in step (a), wherein said Agrobacterium strain is provided with a first genetic modification rendering said Agrobacterium strain defective for transfecting organisms with said T-DNA in the absence of said complementing factor.
Owner:ICON GENETICS
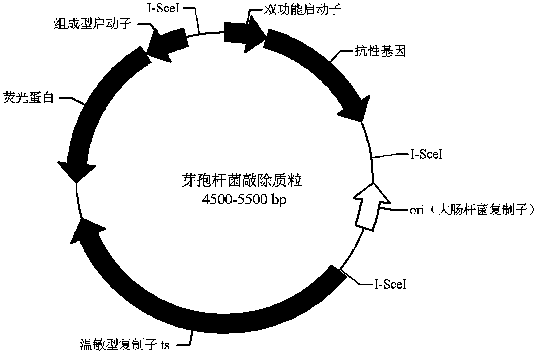
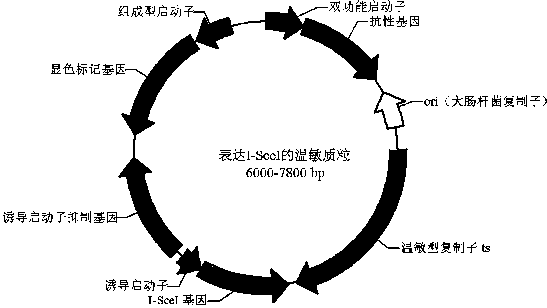
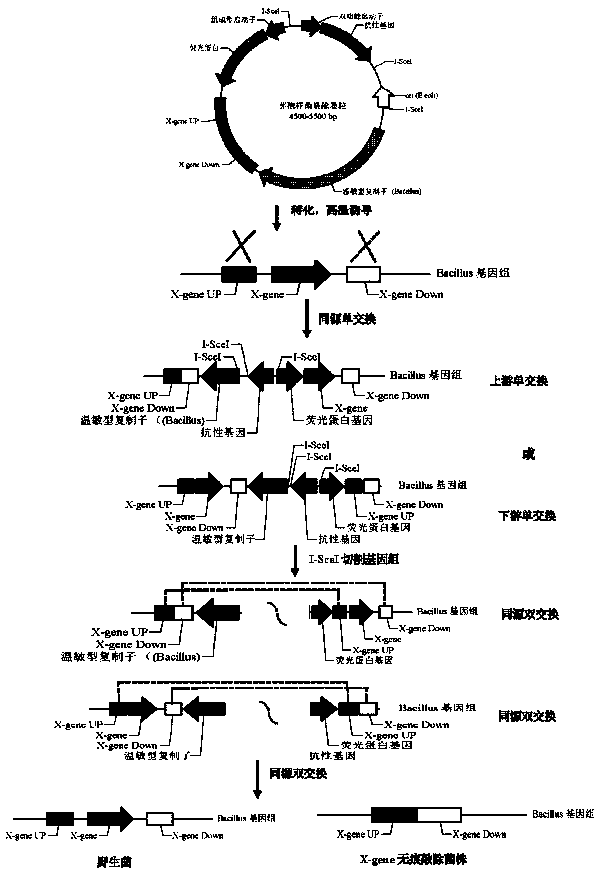
Bacillus gene traceless knockout/knockin plasmid and method, and kit
ActiveCN105505975AEasy to filterImprove efficiencyNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliPromoter
The invention discloses a bacillus gene traceless knockout / knockin plasmid and method, and a kit. The genome of the bacillus gene traceless knockout / knockin plasmid contains only one kind of resistance gene marked with a positive selection marker, a replicon capable of being duplicated in escherichia coli, a thermo-sensitive type replicon capable of being duplicated in bacillus, at least one I-Scel enzyme cutting site and only one kind of chromogenic protein gene, wherein promoters in front of the resistance gene and the chromogenic protein gene are both constitutive promoters in bacillus. The invention further provides a helper plasmid used for improving the knockout / knockin efficiency of the bacillus gene traceless knockout / knockin plasmid, and resistance gene and chromogenic protein gene in the genome of the helper plasmid are different from those of the knockout / knockin plasmid. By the adoption of the two plasmids, one or more target DNA sequences in the genome of bacillus can be modified continuously or iteratively, and the plasmids can be applied to multiple fields including bacillus genetic modification, metabolic process researching, functional genome researching and industrial application researching.
Owner:WUHAN KANGFUDE BIOTECH CO LTD
Japanese encephalitis virus JEV replicon vector and application thereof
InactiveCN101712965AFree from virus attacksViral antigen ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsForeign proteinTerra firma
The invention provides a replicon vector taking Japanese encephalitis virus genome as a framework, as well as a cell line for packaging the same and a packaging system. The JEV replicon vector has the capability of efficiently expressing foreign protein. Mice are immunized with the replicon vector, and the titer of an anti-JEV antibody reaches 1:1280 after three immunizations so as to protect 75 percent of suckling mice from virus attack. The cell line provided can produce 1.6*105 U / ml of pseudovirus particles after packaging JEV replicon, and the titer of the anti-JEV antibody reaches 1:2560 after two immunizations so as to protect 73 percent of suckling mice from virus attack. The invention establishes a technical platform for a JEV replicon vector system for the first time, and explores the feasibility of researching replicon vaccines and pseudovirus vaccines through the JEV replicon vector system, thereby laying a solid foundation for developing and researching a plurality of novel vaccines used to prevent and treat tumors and viral diseases in future.
Owner:INST OF BIOENG ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE CHINESE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com