Carrier capable of showing and expressing heterologous gene on surface of lactococcus lactis, and preparation method and application of carrier
A Lactococcus lactis, expression vector technology, applied in microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, using vectors to introduce foreign genetic material, etc., can solve problems such as unfavorable research and development of oral vaccines, affecting the application scope of lactic acid bacteria expression system, etc., Achieve far-reaching application prospects, great application value, and good immune effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
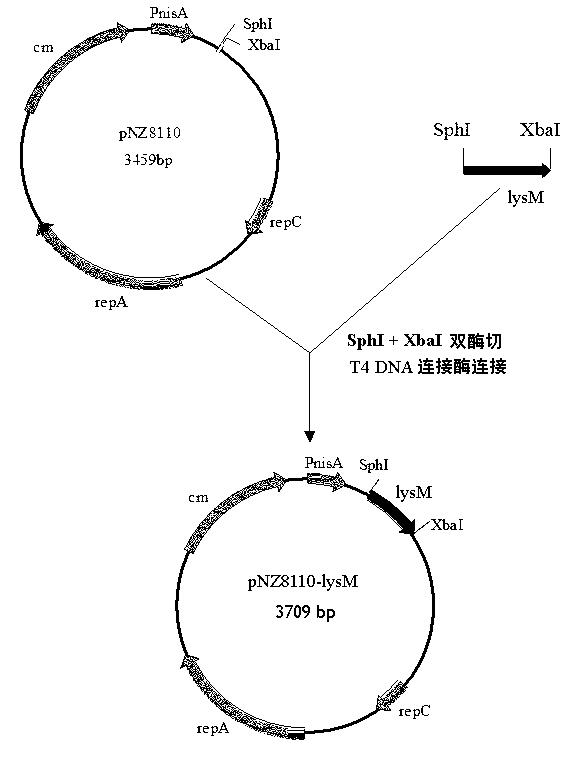
[0052] Example 1 Construction of L.lactis expression vector pNZ8110-lysM
[0053] Construction of L. lactis expression vector pNZ8110-lysM see figure 1 .
[0054] 1. Preparation of L. lactis lysM gene
[0055] 1.1 Extraction of Genomic DNA of L.lactis NZ3900 Strain
[0056] ⑴ Take out the L.lactis NZ3900 strain preservation tube from the -80°C refrigerator, and inoculate 5ml GM with 100μl of the bacteria solution 17 culture medium at 30°C, 5% CO 2 Place the culture in the incubator for 12h to 14h, take 1.5ml to 3ml of bacterial liquid, centrifuge at 5000r / min for 5min, and collect the bacterial cells.
[0057] (2) Wash the bacteria once with 500μl TE buffer (10mM Tris-Cl, 1mM EDTA, pH8.0).
[0058] (3) Resuspend the cells in 50 μl TE buffer, add lysozyme to a final concentration of 10 mg / ml, and bathe in water at 37°C for 60 minutes.
[0059] (4) Add proteinase K to a final concentration of 50 μg / ml, mix well, add SDS solution to a final concentration of 10 g / L, and bat...
Embodiment 2
[0113] Example 2 Construction of recombinant strain L.lactis NZ3900 / pNZ8110
[0114] The recombinant strain L.lactis NZ3900 / pNZ8110 can be prepared according to the technical method provided by the seller of the strain L.lactis NZ3900, NIZO Food Research in the Netherlands or Mobitec in Germany, or by the following method:
[0115] 1. Preparation of L.lactis NZ3900 Competent Cells
[0116] 1.1 Inoculate 5ml liquid GSGM with 200μl bacterial solution from the L.lactis NZ3900 strain preservation tube stored at -80℃ 17 culture medium, put CO 2 Incubator, 30°C, 5% CO 2 Static culture overnight (in this specification, overnight refers to the duration of 12h ~ 14h).
[0117] 1.2 Take 5ml bacterial liquid and add 50ml GSGM 17 medium, 30°C, 5% CO 2 Static culture for 12h.
[0118] 1.3 Take 50ml of bacterial liquid and transfer it to 400ml GSGM 17 Medium, 30°C, 5% CO 2 static culture to OD 600 About 0.3.
[0119] 1.4 Centrifuge the bacterial liquid at 4000r / min, 4°C for 20min,...
Embodiment 3
[0143] Example 3 Construction of the L.lactis expression vector for surface display and expression of EGFP
[0144] For the construction of the L.lactis expression vector expressing EGFP on the surface, see Figure 4
[0145] 1. PCR amplification of EGFP gene
[0146] According to the EGFP gene sequence (GenBank: JN255744.1) in the Genbank nucleic acid database, PCR primers were designed using the biological software Primer5.0, and the upstream primer P3 sequence was 5-ATA GCCGGC ATG GTGAGCAAGGGCGAGG-3'(SEQ ID NO.6), a NaeI restriction enzyme site was introduced at its 5' end; the downstream primer P4 sequence is 5-ACAT GCATGC CTTGTACAGCTCGTCCATGCCG-3' (SEQ ID NO.7), a SphI restriction enzyme site was introduced at the 5' end of the downstream primer.
[0147] PCR reaction system: Using the plasmid pIRES2-EGFP (BD Biosciences Corporation, USA) as a template, prepare a reaction system: 1 μl of 20 μM upstream primer, 1 μl of 20 μM downstream primer, 25 μl of 2×Taq PCR Master...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com