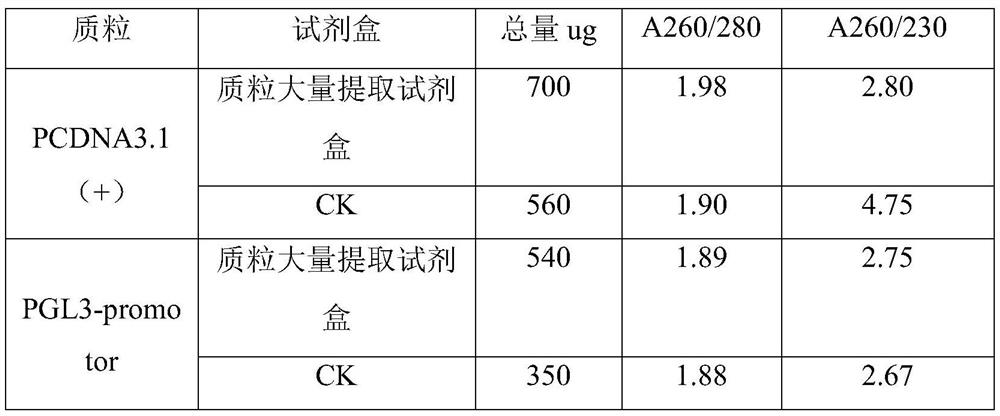
Patents
Literature
171 results about "TE buffer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
TE buffer is a commonly used buffer solution in molecular biology, especially in procedures involving DNA, cDNA or RNA. "TE" is derived from its components: Tris, a common pH buffer, and EDTA, a molecule that chelates cations like Mg²⁺. The purpose of TE buffer is to solubilize DNA or RNA, while protecting it from degradation.
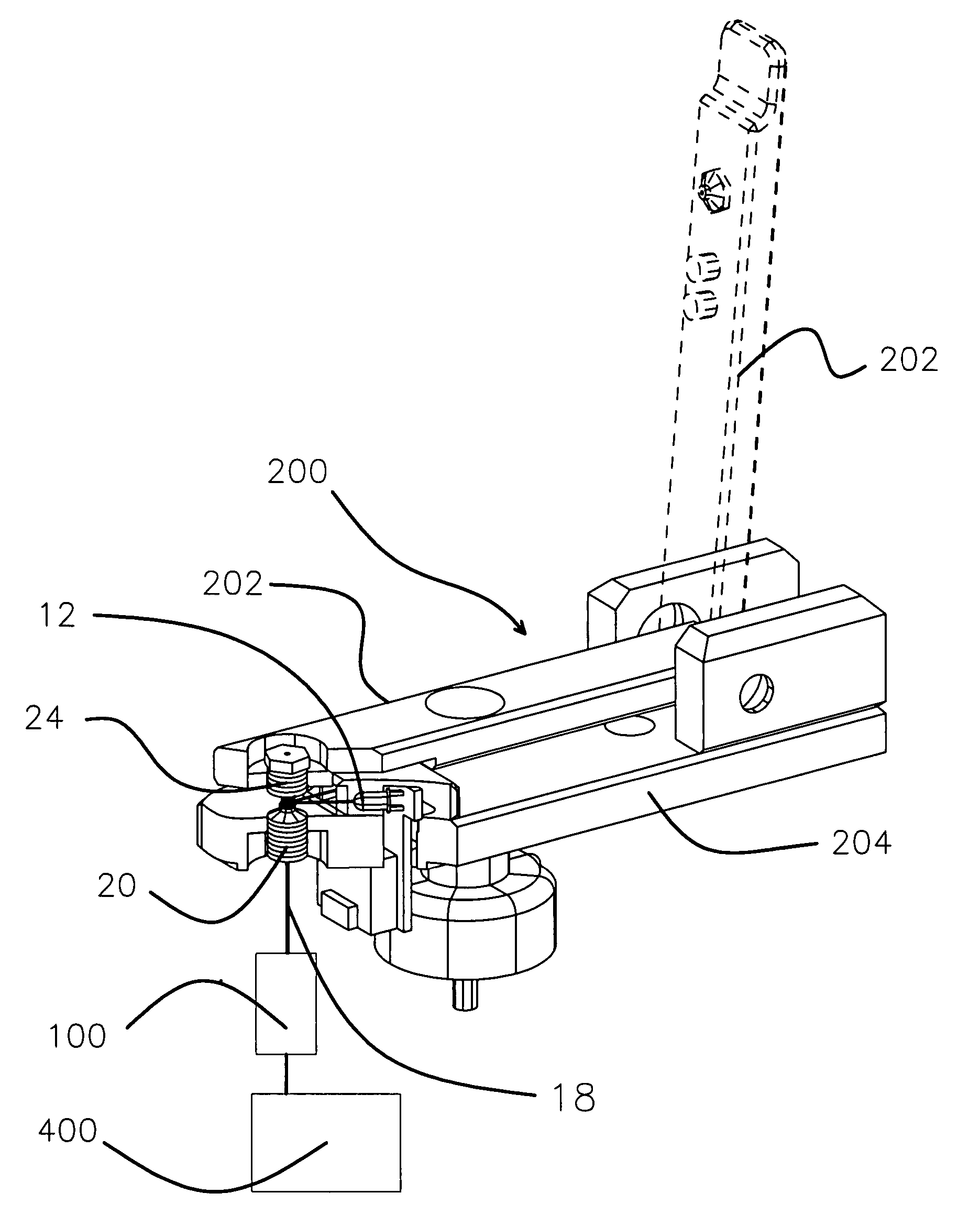
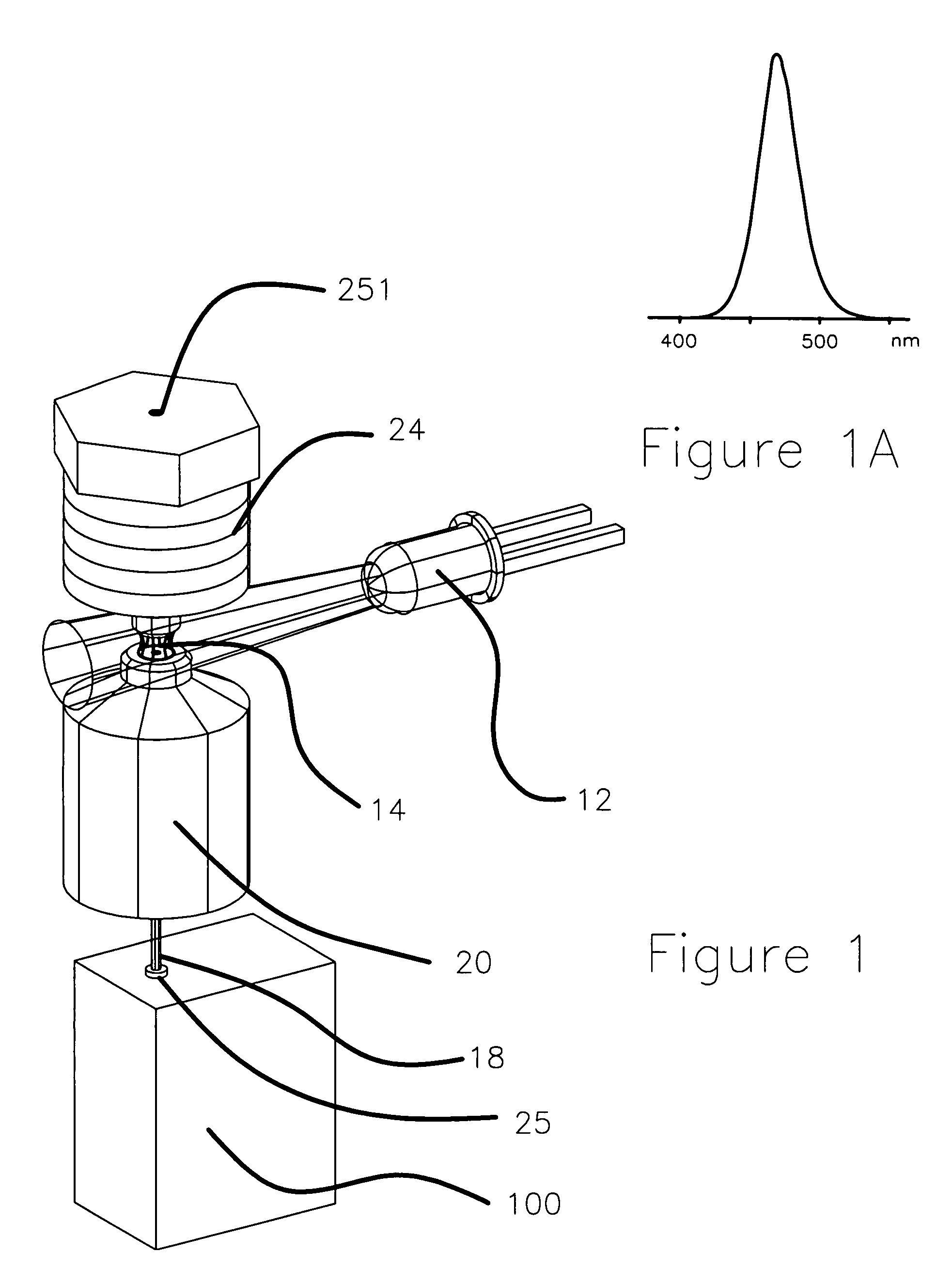
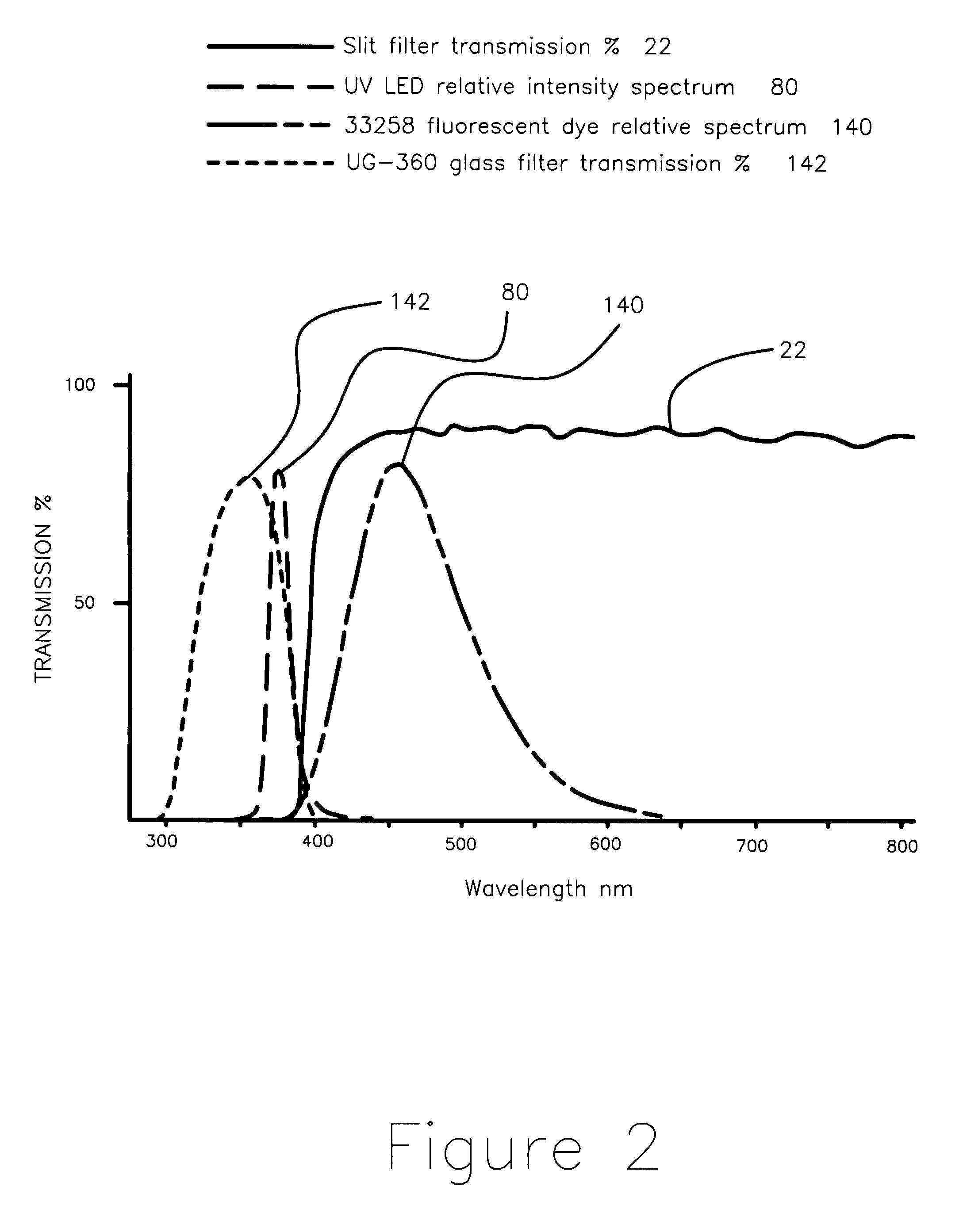
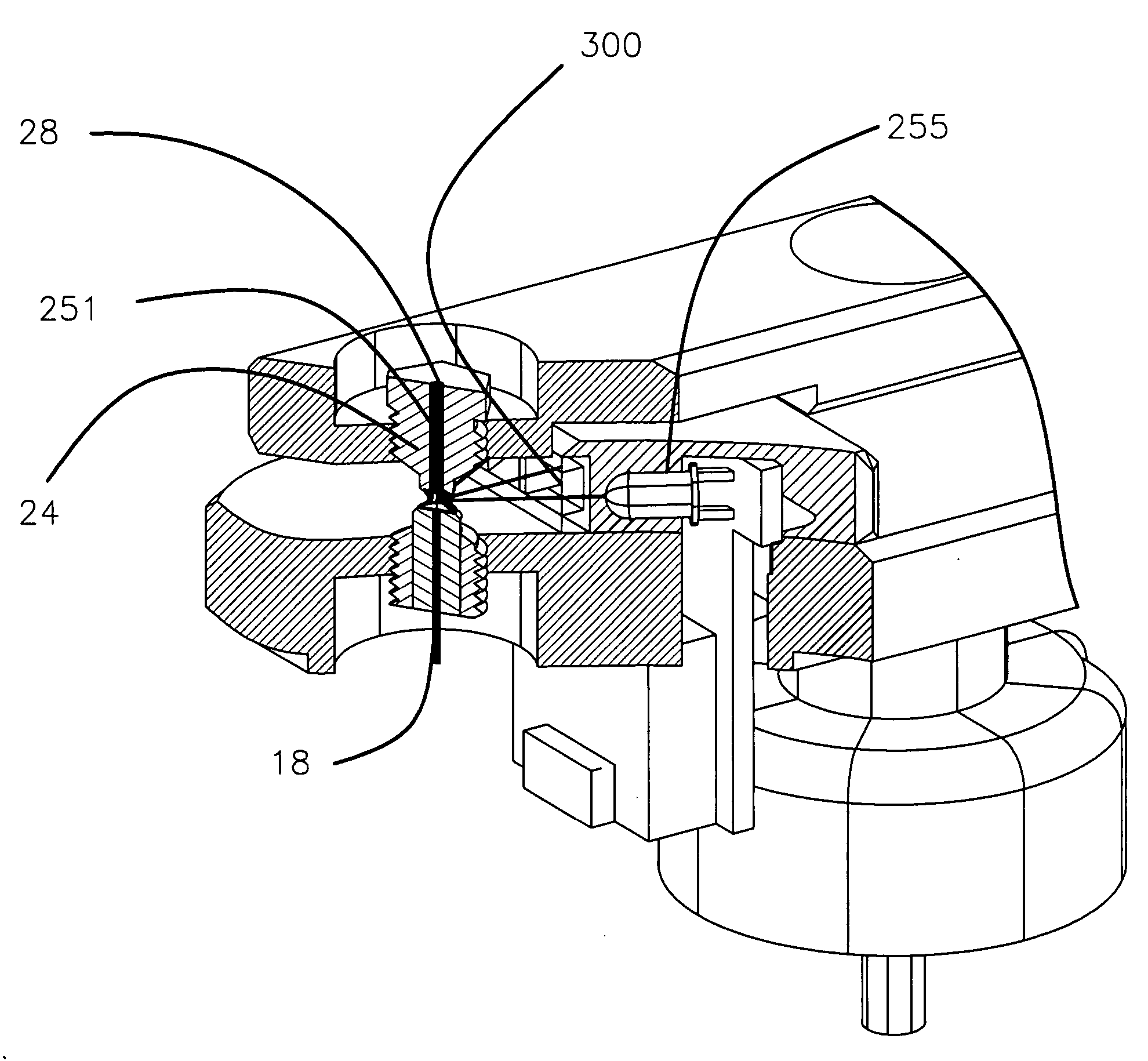
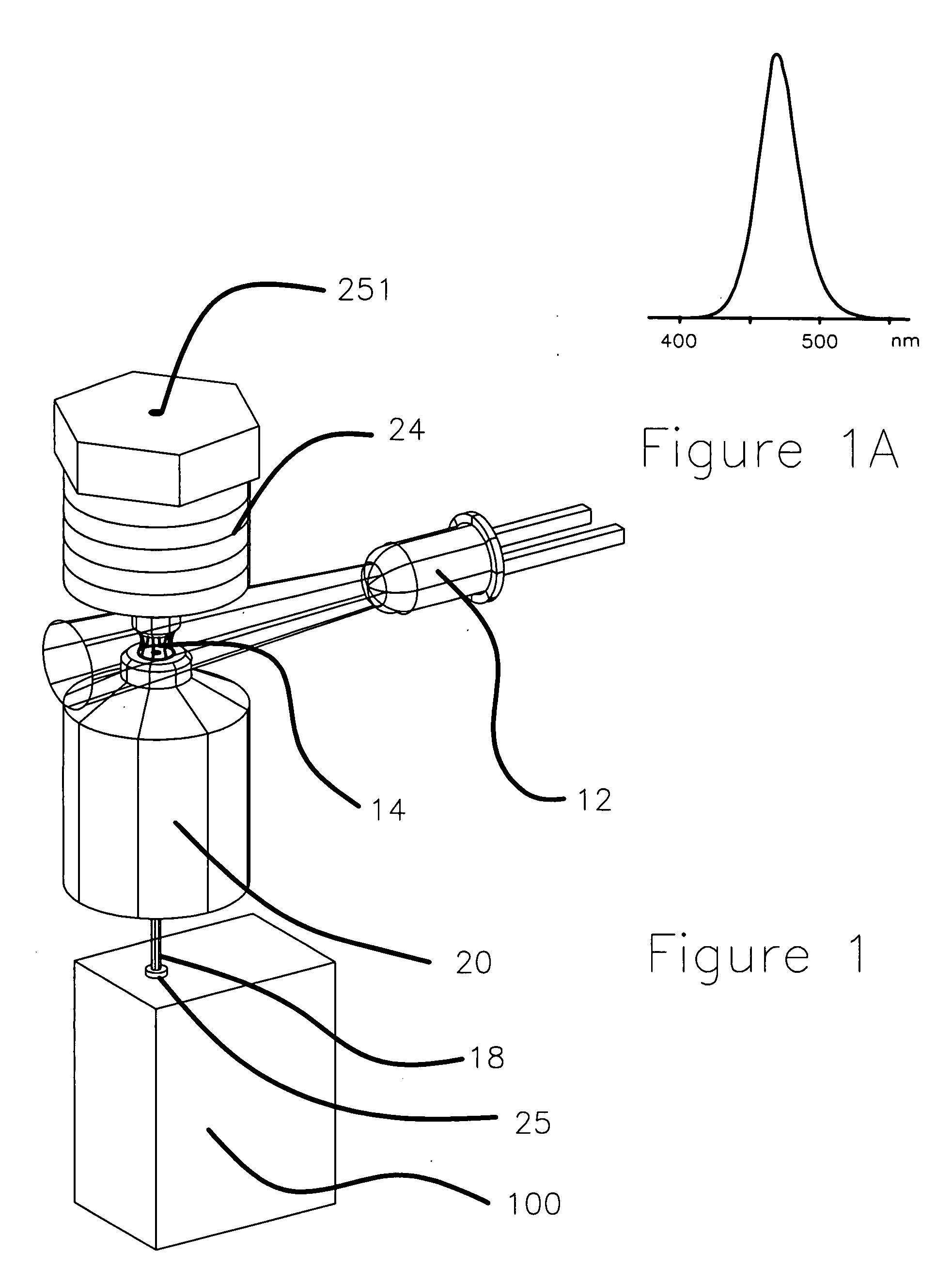
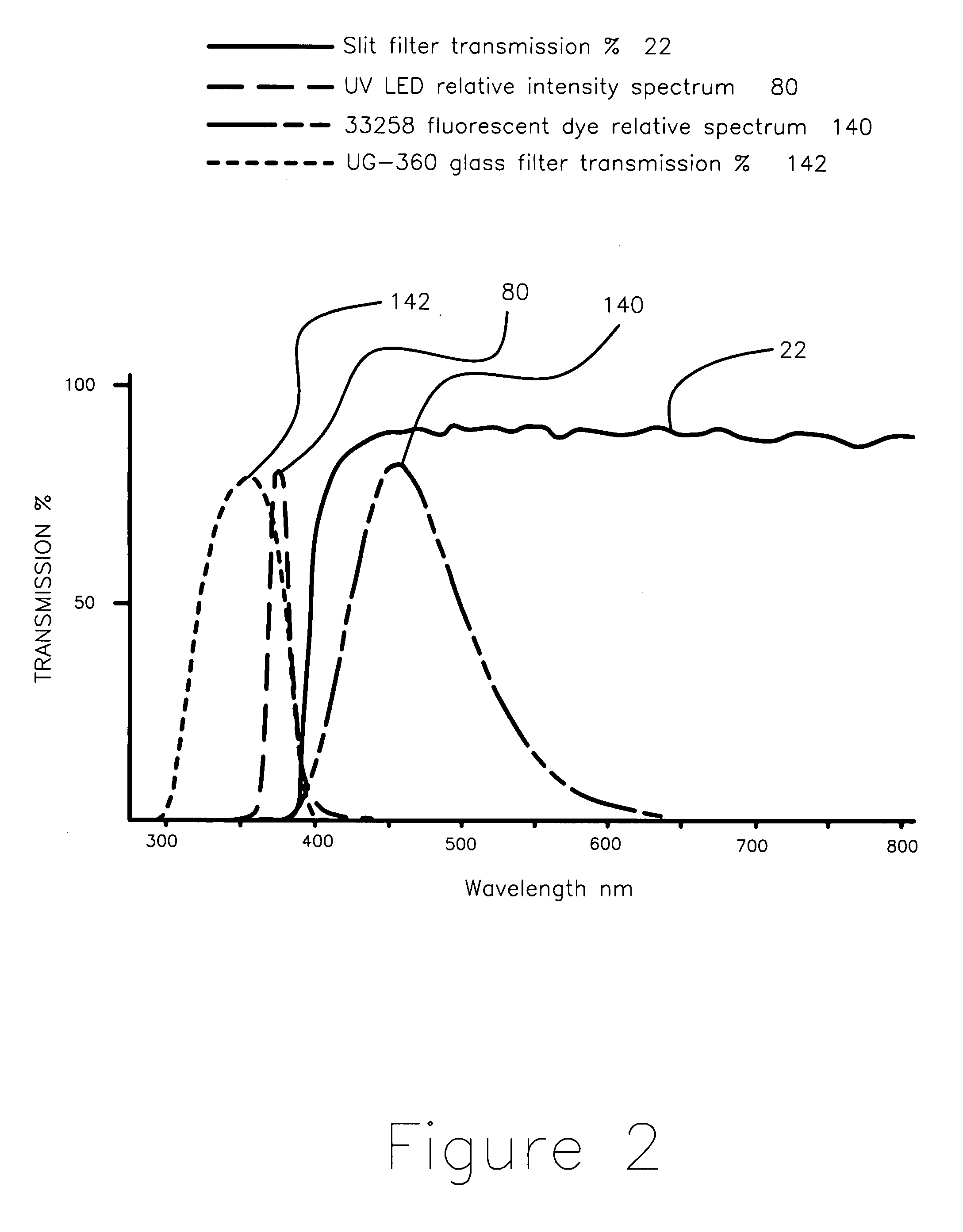
Apparatus and method for measuring the signal from a fluorescing nanodrop contained by surface tension
InactiveUS7397036B2Reduce dispersionHigh rejectionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationTE bufferFluorescence
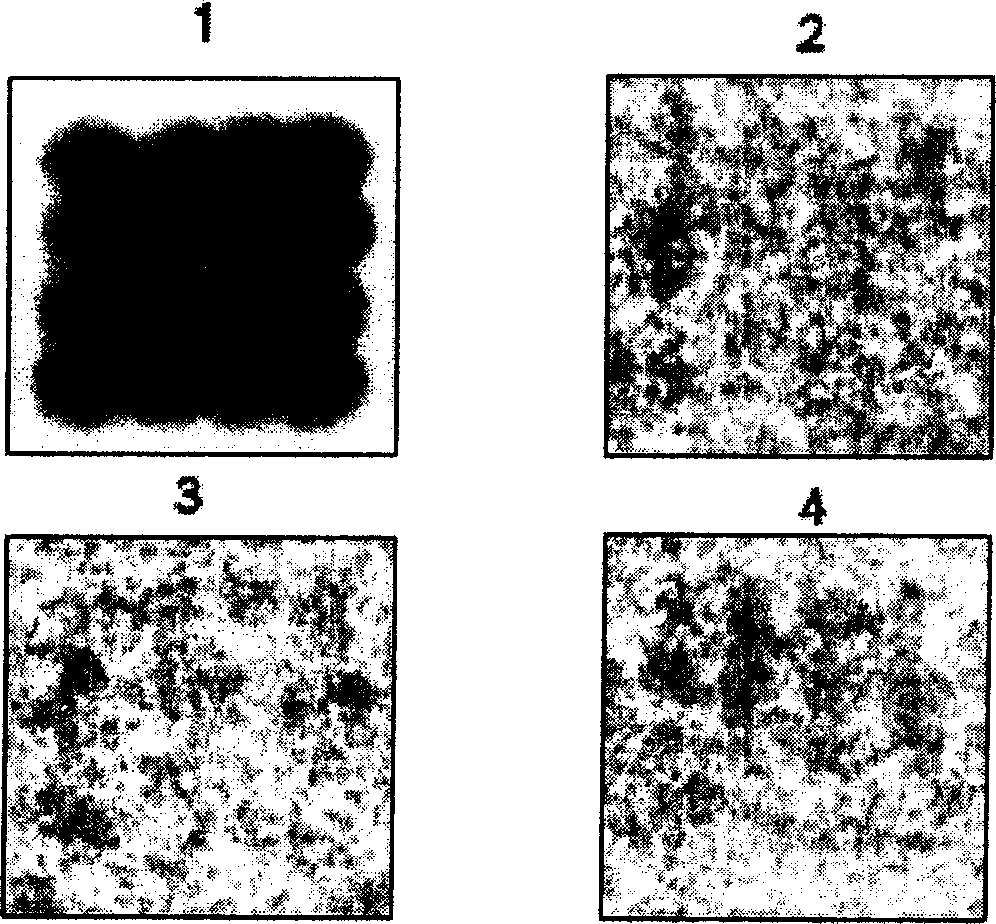
Apparatus and method for measuring the fluorescence of nanodrop liquid samples is described in which the sample is held by surface tension between two anvil surfaces. Each anvil surface has an embedded optical fiber with its end finished flush with the surface in the containment area wetted by the sample with the fiber in line. Sample excitation is provided from the side of the sample remote from the containment area. By selection of the fiber transmission numeric aperture the impact of exciting and ambient light on the measurement is minimized. A method of virtual filtering is taught in which any ambient or exciting light that does impinge on the measuring sensor is corrected by subtracting a scaled representation of the source from the measurement. The method and apparatus is capable of detecting 1 femptomole of sodium fluorescein in 1 microliter of TE buffer.
Owner:NANODROP TECH LLC
Human feces DNA extraction method
ActiveCN102864138AQuality improvementHigh repeat stabilityDNA preparationTE bufferBovine serum albumin
The invention discloses a human feces DNA extraction method. The prior art is complicated and time-consuming; and the trace DNAs extracted by the previous sampling method is too little to perform molecular diagnosis. The extraction method uses selective sample collection PSC equipment for feces samples and adopts a low temperature preservation method. The extraction method comprises the following steps: picking a sample by using a sterilized gun head or sterilized blade and directly placing the picked sample on ice; and adding a feces lysis solution, fully cracking and evenly mixing, adding bovine serum albumin, centrifuging to remove the supernatant, adding protease K to perform a digestion reaction at 58 DEG C, then adding a protein precipitation solution to precipitate the protein, centrifuging to obtain the supernatant, adding a silica gel membrane binding solution to fully bind DNAs, centrifuging to obtain precipitates, adding a silica gel membrane washing solution to wash twice, centrifuging, and adding a TE (Tris + EDTA) buffer solution to finally obtain a preservation solution with DNAs. The human feces DNA extraction method has the advantages of high repeatability and stability, simpleness and short time.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CENTURY CONDOR MEDICAL SCI & TECHNOLOTY CORP
Preparing method and application of acellular amniotic membrane used for repairing skin wound difficult to heal
The invention relates to a preparing method and application of an amniotic membrane, in particular to a preparing method and application of an acellular amniotic membrane used for repairing skin wound difficult to heal. The preparing method specifically comprises the steps of isolating, cleaning and sterilizing an amniotic membrane tissue; arranging and drying the amniotic membrane tissue on a nitrocellulose membrane to manufacture an amniotic membrane paster; vibrating and digesting the amniotic membrane paster in mixed digestive fluid of 0.25%-0.5% of pancreatin and 0.2-0.5g / L EDTA.4Na for 10-30 minutes at a temperature of 37 DEG C; rinsing the amniotic membrane paster in TE buffer solution; vibrating overnight to fully remove amniotic membrane cells in TE-TritonX-100 solution; washing the amniotic membrane paster for three times in TE solution; vibrating and degrading the amniotic membrane paster for 2-4 hours in nucleic acid degrading solution at a temperature of 37 DEG C; washing the amniotic membrane paster for three times in the TE solution. The prepared acellular amniotic membrane paster can be stored for a long time after being refrigerated, dried, packed and sterilized by cobalt 60 irradiation and is a tissue engineering material which can be taken and used when needed. The acellular amniotic membrane paster can be easily separated from the nitrocellulose membrane to be used for repairing the skin wound after rewatered.
Owner:天晴干细胞股份有限公司
DNA extraction method suitable for structural analysis of microbial community in sediment
InactiveCN101696410AEfficient removalSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationTE bufferA-DNA
The invention discloses a DNA extraction method suitable for structural analysis of microbial community in sediment, which comprises the following steps: washing a sediment sample with TENPbuffer, and suspending the washed sediment sample in PBS buffer; repeatedly freezing and melting the pretreated sediment sample, adding muramidase, adding proteinase K and sodium dodecyl sulfate into the sediment sample, centrifuging the sample at room temperature, taking supernate, adding mixed solution of phenol, chloroform and isoamylol in equal volume into the supernate, mixing evenly by oscillation, centrifuging the obtained sample at room temperature, taking a liquid phase, adding mixed solution of chloroform and isoamylol in equal volume into the liquid phase, centrifuging the obtained sample at room temperature, taking a liquid phase, and adding precooled isopropanol into the liquid phase; centrifuging the obtained sample to remove supernate, adding precooled ethanol into the sediment, washing the sediment for three times, and centrifuging to remove the ethanol; and naturally air-drying the sample, and dissolving DNA with TE buffer solution for preservation.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Extraction method of total DNA of microorganisms from soil sample
InactiveCN104651350ALow costImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationWater bathsFreeze thawing
The invention relates to an extraction method of total DNA of microorganisms from a soil sample. The extraction method particularly includes following steps: (1) adding a DNA extraction buffer solution to the soil sample and performing repetitive freeze-thawing in liquid nitrogen and hot water bath; (2) adding a protease K, performing a water bath treatment process at 37 DEG C for 30 min; (3) adding a sodium dodecyl solution, performing a water bath treatment process at 65 DEG C for 30 min; (4) performing centrifugation to remove precipitations and collect a supernate; (5) performing extraction with a mixed solution containing phenol, chloroform and isoamylol and performing centrifugation to collect a supernate; (6) performing extraction with a mixed solution containing chloroform and isoamylol and performing centrifugation to collect a supernate; (7) adding isopropanol to the supernate in the step (6) to performing precipitation and collecting a precipitation after centrifugation; (8) adding ethanol for washing the precipitation and drying the precipitation at the room temperature; (9) adding a TE buffer solution for dissolving the precipitation to obtain a DNA crude extraction; and (10) purifying the DNA crude extraction through an adsorption column, packaging the purified DNA crude extraction and storing the purified DNA crude extraction at -20 DEG C. The extraction method is especially effective when being used in samples from deep soil and dry sand which are less in biomass and in a clayed soil sample. The DNA extraction can be directly used in subsequent molecular biological detection.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Apparatus and method for measuring the signal from a fluorescing nanodrop contained by surface tension
InactiveUS20080002181A1Increase unwanted ambientIncrease background excitation light energyRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationTE bufferFluorescence
Apparatus and method for measuring the fluorescence of nanodrop liquid samples is described in which the sample is held by surface tension between two anvil surfaces. Each anvil surface has an embedded optical fiber with its end finished flush with the surface in the containment area wetted by the sample with the fiber in line. Sample excitation is provided from the side of the sample remote from the containment area. By selection of the fiber transmission numeric aperture the impact of exciting and ambient light on the measurement is minimized. A method of virtual filtering is taught in which any ambient or exciting light that does impinge on the measuring sensor is corrected by subtracting a scaled representation of the source from the measurement. The method and apparatus is capable of detecting 1 femptomole of sodium fluorescein in 1 microliter of TE buffer.
Owner:NANODROP TECH LLC
Signal detection method for gene chip of oligonucleotide with length more than 50 basic groups
InactiveCN1661104ASave complicated proceduresAvoid harmMicrobiological testing/measurementTE bufferFluorescence
A method for detecting the signals of gene chip whose oligonucleotide has a length more than 50 bases includes such steps as PCR amplification of target gene, detecting, boiling positive product for modifying it, cooling on ice, wetting the gene chip by phosphoric acid solution, prehybridizing in prehybridizing liquid, adding said modified DNA, hybridizing, water with different lotions, dyeing, rinsing, and detecting signal under UV light or fluorescent microscope.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for extracting sedum spectabile genomic DNA
The invention discloses a method for extracting sedum spectabile genomic DNA, comprising the following steps: taking powdered sedum spectabile, and adding preheated 2% CTAB extracting solution to dissolve; carrying out warm bath at 65 DEG C for 45 minutes, adding hloroform and isoamyl alcohol mixture of same volume, mixing, and centrifuging for two times at high speed at room temperature; taking a supernatant, adding ice-cold isopropanol which is 2 / 3 the volume of the supernatant, mixing, standing at low temperature for 15-30 minutes, and settling DNA; centrifuging at high speed at low temperature, discarding the supernatant, recovering the precipitate, washing for two times by 70% ethanol, airing, adding TE buffering solution, adding RNase, digesting for 30 minutes at 37 DEG C, and preserving the obtained DNA sample at low temperature. According to the method, the added RNase which is an enzyme can remove the RNA thoroughly and effectively so that the extracted DNA has higher purity and the interference of the RNA to the subsequent experiment is avoided.
Owner:TIANJIN CITY AGRI BIO TECH RES CENT
Soil sample total DNA extraction method for improving DNA quality
InactiveCN101230342ASimple extraction methodElectrophoretic pattern is clearDNA preparationFreeze thawingSodium acetate
The invention relates to soil microbiology, in particular to a method of extracting the total DNA of the soil sample, which can improve the quality of DNA. The method includes the following steps: adding DNA extracting buffer to the soil sample, and then adding protease K; freeze thawing under -65 to 65 DEG C and centrifuging; discarding the precipitate; collecting the supernatant liquid; extracting and centrifuging by the same volume of the solution of phenol, chloroform and isoamylol, reserving the water phase; extracting one more time by the solution of chloroform and isoamylol; adding sodium acetate and cold isopropanol, and then centrifuging and collecting the DNA precipitate; washing by ethanol and drying in room temperature; adding TE buffer to dissolve, and gaining the DNA coarse extract; adding DNA extracting buffer in the coarse extract; and then adding the same volume of the solution of phenol, chloroform and isoamylol; repeating the preceding steps such as precipitating, washing and dissolving; finally, gaining the DNA of better quality. The method adopted by the invention can effectively remove the impurity in the DNA, which evidently increases the purity and quality of DNA.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPLIED ECOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Kit and method for detecting Macrobrachium rosenbergii Nodavirus
InactiveCN101875980AShorten the timeSimplify detection stepsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationTE bufferPositive control
The invention relates to a kit and a method for detecting Macrobrachium rosenbergii Nodavirus. The kit comprises a sampling tube, a rinsing tube filled with distilled water, a nucleic acid denaturation tube filled with TE buffer solution, an amplification test tube filled with amplification reaction liquid and dyes, a negative control tube, a positive control tube, an FTA membrane, quick drying liquid for shortening time of preparing a sample to be detected, namely nucleic acid, and the like. The kit combines the advantages of isothermal amplication and quick dye detection, does not need precious instruments in the detection process, and develops by adopting a dye filling method to improve the detection reliability. The kit has the advantages of low detection cost, convenient use and safety for human bodies and environment, and can replace the conventional related detection methods. The kit can be used for production field in the open field, and has important promotion and application value of enhancing the monitoring of the Macrobrachium rosenbergii Nodavirus and preventing the large-scale outbreak of the Macrobrachium rosenbergii Nodavirus.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Method for extracting high-quality cell nucleus DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) of plant rich in polysaccharide and polyphenol
The invention discloses a method for extracting a high-quality cell nucleus DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) of a plant rich in polysaccharide and polyphenol, relating to the field of plant functional genomics. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, grinding a plant material by using liquid nitrogen; secondly, resuspending by using an HB (Haemoglobin) extraction buffer solution, mixing uniformly through volution and filtering; thirdly, centrifuging, washing precipitation with an extraction buffer solution 1 three times and resuspending; fourthly, carrying out water bath by using an extraction buffer solution 2 and RnaseH at the temperature of 65DEG C for 30 minutes; fifthly, extracting once by using chloroform-isoamylol and precipitating by using isopropanol; and sixthly, washing precipitation by using 75 percent pre-cooled ethanol 1-2 times and dissolving by using a TE (Tris-Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid) buffer solution. According to the pretreatment step in the methoddisclosed by the invention, DNAs of cell organelles such as mitochondria and chloroplast can be effectively removed; the inference on the nucleic acid extraction step caused by a large mount of secondary metabolites such as polysaccharide and polyphenol existing in the plant material is avoided; and the method is suitable for healthy tissues of wide plant species or frozen tissues with more complete cell structures and is especially suitable for high throughout sequencing in the subsequent researches.
Owner:WUHAN BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Plasmid extraction kit and extraction method
The invention discloses a high-purity plasmid extraction kit. The high-purity plasmid extraction kit comprises an S I buffer solution, an S II buffer solution, an S III buffer solution, a PS cleaningsolution, an elution buffer solution, a TE buffer solution and a novel centrifugal column, wherein the S I buffer solution comprises Tris-HCl of 1 M, EDTA of 0.5 M and glucose of 1 M, and the pH valueis 8.0; the S II buffer solution comprises NaOH of 2 M and 10% SDS; the buffer solution S III comprises potassium acetate of 3 M, guanidine hydrochloride of 2 M and acetic acid of 2 M, and the pH value is 3.6-4.2; the PS cleaning solution is an isopropyl alcohol solution containing 5-10% of TritonX-114; and the elution buffer solution is 75% ethanol. The invention further provides a method for extracting a large number of plasmids by using the kit. According to the method, the novel centrifugal column is combined with a classic strong base-SDS bacterial cell cracking method, so that a plasmidDNA sample is centrifugally combined to a purification column, plasmid DNA can be fully eluted under a certain condition, rapid purification of plasmids is realized, phenol chloroform extraction is not needed in the whole process, high-purity plasmid DNA can be obtained, and the use of eukaryotic cell transfection can be met.
Owner:JIANGSU KEYGEN BIOTECH CORP LTD
PCR diagnostic kit for porcine infectious pleuropneumonia
InactiveCN101724709AThe test result is accurateThe detection method is simpleMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesPositive controlTE buffer
The invention discloses a PCR diagnostic kit for porcine infectious pleuropneumonia, which comprises 400mu L of proteinase K with the concentration of 20mg / mL, 1000mu L of cracking solution, 1500mu L of TE buffer solution, 250mu L of PCR enzyme, 170mu L of ultra-pure water, 50mu L of MarkerDL2000, 40mu L of primer P1 and primer P2 which are mixed in the same volume and have the same concentration of 20mu M, 20mu L of negative control and 20mu L of positive control. By optimizing the PCR reaction conditions, the invention develops a PCR kit for detecting the actinobacillus of the porcine infectious pleuropneumonia; and by comparing the PCR detection result with the negative control and the positive control, detection conclusions can be obtained, thereby achieving the aim of quickly detecting whether a sample has porcine infectious pleuropneumonia or not. The invention has accurate detection result, quick and sensitive detection process, simple detection mode and good using effect.
Owner:GUIZHOU INST OF ANIMAL HUSBANDRY & VETERINARY
Extraction method of microorganism genome DNA
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology, and discloses an extraction method of microorganism genome DNA. The extraction method comprises the following steps: (1) collecting sample thallus, adding a STES buffer solution, re-suspending, adding glass beads, and dissolving by virtue of a TE buffer solution; (2) adding an equal volume of phenol / chloroform solution, oscillating, mixing, and primarily centrifuging; (3) adding an equal volume of chloroform / isoamylol solution into an upper layer of water after the primary centrifuging, mixing, and secondarily centrifuging; (4) adding an equal volume of isopropanol or twice volume of anhydrous ethanol into an upper layer of water after the secondary centrifuging, precipitating under the room temperature, tertiarily centrifuging, and collecting precipitates; (5) washing the precipitates by utilizing ethanol, re-centrifuging to obtain DNA precipitates, dissolving the DNA precipitates by utilizing sterile water, carrying out the magnetic-ball passivation, to obtain extracted microorganism genome DNA. The genome DNA obtained by virtue of the method has advantages of high concentration, single banding and no pollution, and satisfies the three-generation sequencing requirement.
Owner:SHANGHAI PASSION BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Medium for adsorbing stored DNA and preparation method
ActiveCN101912768AReduce lossesWith preservationOther chemical processesDNA preparationTE bufferDistilled water
The invention discloses a medium for adsorbing stored DNA and a preparation method. The preparation method of the medium for adsorbing the stored DNA is as follows: (1) dissolving a cationic polymer in a water solution of acid the mass concentration of which is 0.1%-10% or in water to prepare a cationic polymer solution; mixing a TE buffer solution and cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) to prepare a solution A; and (2) immersing a filter paper in the cationic polymer solution, soaking and taking out, washing by distilled water, putting into the solution A for soaking, and then taking out and drying to obtain the medium for adsorbing the stored DNA. In the invention, a protein denaturing agent is used to ensure the medium to have antibacterial activity, so that the medium can directly extract DNA from the solid medium adsorbing a biological sample or apply a PCR method for amplification, and can be used for medical diagnosis, criminal site sampling, physical evidence preservation, biological sample mailing, epidemiology detection, etc.
Owner:天津金歌联合生物科技有限公司
Saliva preservation solution, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106561631AProtection from pollutionNot pollutedDead animal preservationEthylenediamineTE buffer
The invention provides a saliva preservation solution, and a preparation method and application thereof. The saliva preservation solution comprises a DNA stabilizer including disodium edentate, tartaric acid and at least one selected from a group consisting of nitrilotriacetic acid and dihydroxyethylglycine; a microbial inhibitor including penicillin, streptomycin, geneticin and at least one selected from a group consisting of potassium sorbate, sodium benzoate, ethylparaben sodium, ketoconazole and puromycin; and a buffer solution including a TE buffer solution and at least one selected from a group consisting of a PBS buffer solution and a sodium chloride glucose buffer solution. According to the invention, through preparation of the saliva preservation solution, the morphology of cells in a saliva swab is maintained and prevented from disruption, and the growth of microorganisms in the saliva swab and the saliva preservation solution is inhibited.
Owner:刘鹏飞
Detection method of prawn IHHNV (infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus) and used nucleic acid isothermal amplification detection kit
InactiveCN101792817AEfficient detectionEasy to handleMicrobiological testing/measurementSodium acetatePositive control
The invention discloses a prawn IHHNV (infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus) nucleic acid isothermal amplification detection kit which comprises a grinding fluid tube containing a grinding fluid, a nucleic acid extracting solution tube A containing a sodium acetate solution, a nucleic acid extracting solution tube B containing absolute ethyl alcohol, a nucleic acid extracting solution tube C containing an alcohol solution with a mass concentration of 70 percent, a TE (tellurium) buffer solution tube containing a TE buffer solution, a UNG (uracil-DNA glycosidase) enzyme tube containing uracil DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) glycosylase, an LAMP (Loop-mediated isothermal amplification) reaction liquid tube containing an LAMP reaction liquid, a BstDNA polymerase tube containing Bst DNA polymerase, a color-developing agent tube containing nucleic acid dye SYBR Green I, a positive control nucleic acid tube containing prawn IHHNV positive DNA and a negative control tube containing sterilizing double distilled water. The invention also provides a method for detecting the prawn IHHNV by utilizing the detection kit. The method has the characteristics of low cost, high detection sensitivity and easy site operation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) preserving solvent and DNA preserving method
The invention discloses a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) preserving solvent and a DNA preserving method. The DNA preserving solvent comprises glycerol, TE buffer solution and 1-carboxyl-N, N, N-trimethyl-B lactone, wherein the final volume of the glycerol is 25-80%, the final concentration of the TE buffer solution is 1*TE-5*TE, and the final concentration of the 1-carboxyl-N, N, N-trimethyl-B lactone is 1-6mol / L. The DNA preserving method comprises the following steps of: (1) extracting DNA; and (2) dissolving the DNA in the DNA preserving solvent to be preserved. The DNA preserving solvent disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple preparation, low cost, good preserving effect and long shelf life and is prevented from freezing and thawing repeatedly. The invention provides initial DNA records for genomics research, identity authentication, gene diagnosis, gene therapy, organ transplantation and the like in the future.
Owner:SHANGHAI YUAJIRO BIOTECH
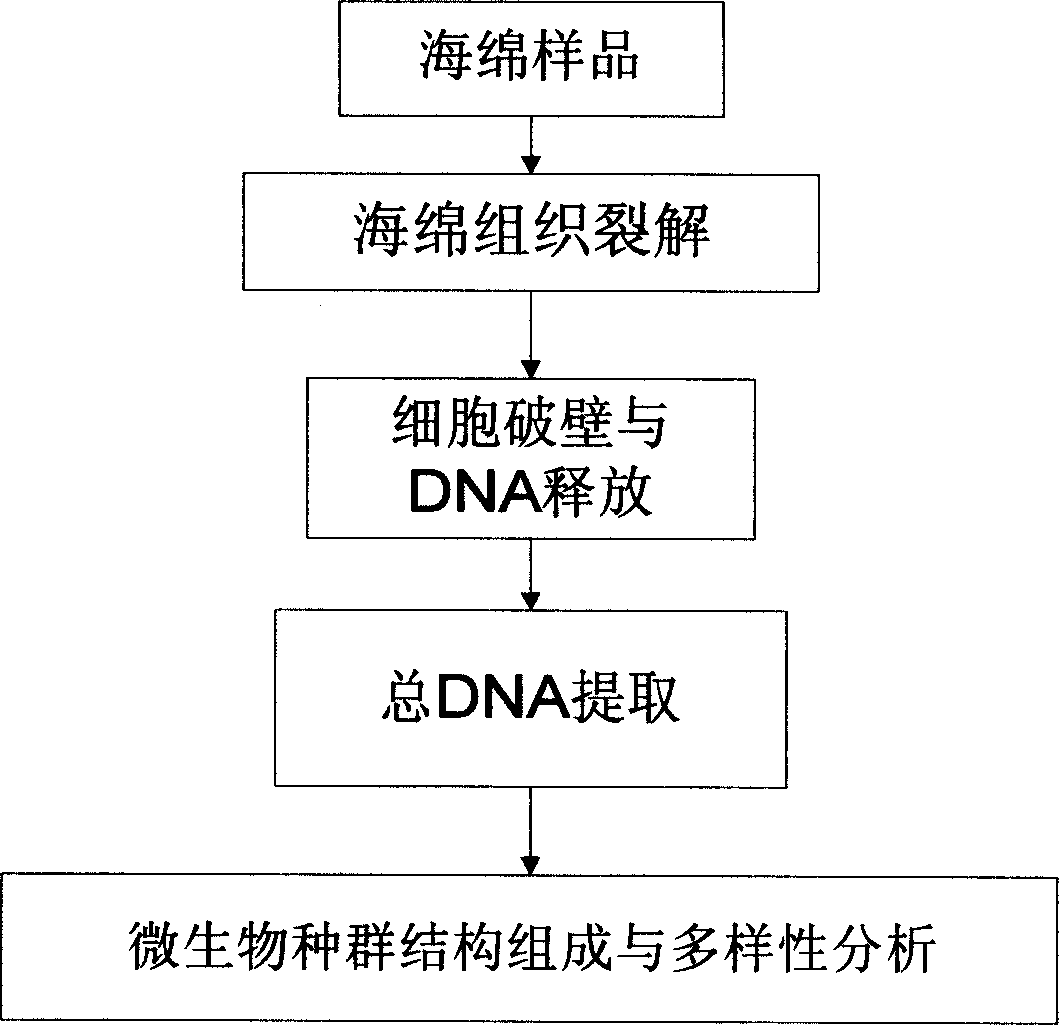
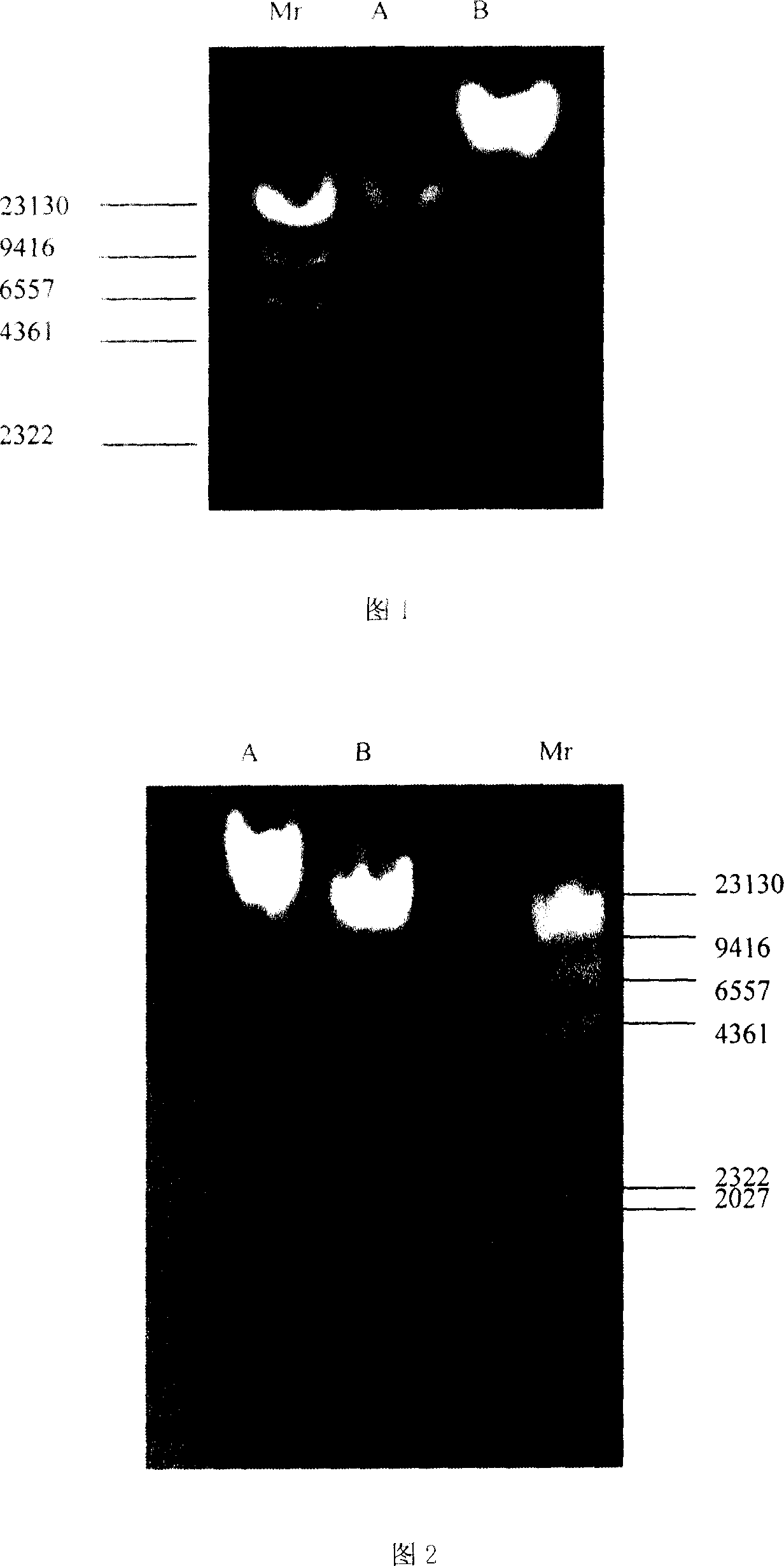
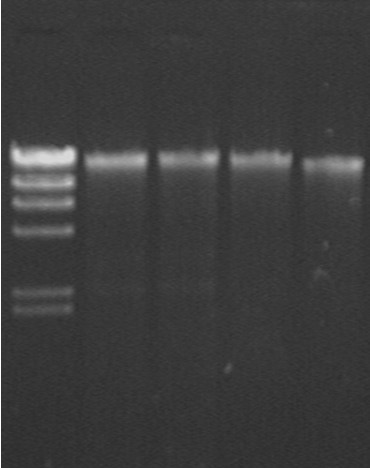
Fast extraction method of adnascent microbe community total DNA of sponge
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
General detection method for pathogenic vibrios and nucleic acid isothermal amplification detection kit used in same
InactiveCN102154469AEfficient detectionEasy to handleMicrobiological testing/measurementSodium acetatePositive control
The invention discloses a general nucleic acid isothermal amplification detection kit for pathogenic vibrios of mariculture animals. The detection kit comprises a grinding liquid tube into which grinding liquid is filled, a nucleic acid extracting solution tube A into which solution of sodium acetate is filled, a nucleic acid extracting solution tube B into which absolute ethanol is filled, a nucleic acid extracting solution tube C into which 70 mass percent ethanol solution is filled, a tris-hydrogen chloride ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid (TE) buffer solution tube into which TE buffer solution is filled, a uracil-DNA-glycosylase (UNG) tube into which uracil-DNA-glycosylase is filled, a loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) reaction liquid tube into which LAMP reaction liquid is filled, a bacillus stearothermophilus deoxyribonucleic acid (Bst DNA) polymerase tube into which Bst DNA polymerase is filled, a color-developing agent tube into which a nucleic acid dye SYBR Green I is filled, a positive control nucleic acid tube into which positive DNA of the vibrios is filled and a negative control tube into which sterilized double distilled water is filled. The invention also discloses a method for detecting the pathogenic vibrios of the mariculture animals by utilizing the detection kit.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Concentration-gradient fluorescent calibration piece for laser microarray chip scanner
InactiveCN108444966AThe preparation method is simple and quickShorten the production cycleFluorescence/phosphorescenceTE bufferAlexa Fluor
The invention provides a concentration-gradient fluorescent calibration piece for a laser microarray chip scanner. The concentration-gradient fluorescent calibration piece comprises a glass substrateand an organic fluorescence mixed liquor, wherein the organic fluorescence mixed liquor is uniformly distributed on the glass substrate in a lattice manner and comprises an Alexa Fluor 488 fluorescentdye, a Cy3-dCTP fluorescent dye and a diluent, the diluent is a phosphate buffer liquor, a TE buffer liquor or an aqueous liquor, and the surface of the glass substrate is chemically modified or coated with a polymer piece. The lattice of the organic fluorescence mixed liquor on the glass substrate comprises 1-8 branch lattices, each branch lattice is arranged on the glass substrate in a uniformdistribution manner, organic fluorescence mixed liquor droplets of each branch lattice are arranged in A rows* B lines, A ranges from 20 to 40, and B ranges from 5 to 20. The concentration-gradient fluorescent calibration piece has the beneficial effects that the concentration-gradient fluorescent calibration piece is simple to produce, short in production period and low in cost and has outstanding detection effect.
Owner:成都博奥晶芯生物科技有限公司
Method for extracting high molecular genome from bacterium
InactiveCN1952150AGood repeatabilityEasy to operateGenetic engineeringFermentationTE bufferGenomic DNA
The invention discloses a method of extracting high molecular genome from the bacteria. The method contains the steps of: breaking cell wall using lysozyme +protease +SDS or protease +SDS, extracting in TE buffer (removing proteins and polysaccharides), and preciping, washing, drying and dissolving. The invention begins with the factors influencing extracted DNA fragment length and obtains high molecular DNA fragment longer than fragments extracted by conventional method. The genomic DNA extracted in the method has more than 40 kb with OD260 / OD280 between 1.8 and 2.0 detecting by absorbance. The method has the advantages of good repeatability and simple operation and can meet the need of the above molecular operation.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for extracting bacterium genomic DNA by using magnetic nanoparticles
InactiveCN102121002AThe experiment takes a short timeEasy to operateFermentationPlant genotype modificationTE bufferMagnetite Nanoparticles
The invention discloses a method for extracting bacterium genomic DNA by using magnetic nanoparticles, belonging to the technical field of nanomaterials and molecular biology. The method comprises the steps of: preparing a magnetic nanoparticle aggregate, preparing a bacterium lysing solution, preparing and adding an absorption buffer solution, absorbing with a magnet, rinsing with 70 percent alcohol, and eluting with a TE buffer solution to obtain a bacterium genomic DNA solution. Compared with the traditional phenol / chloroform DNA extracting method, the method for extracting the bacterium genomic DNA by using magnetic nanoparticles has the advantages of short experiment time, simpleness in operation, high extraction efficiency, rapidness, convenience, sensitivity, high yield and the like; and the extracted bacterium genomic DNA can be completely used for subsequent experiments, such as DNA hybridization, PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction), and the like, and provides the basis for the subsequent research and analysis.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
On-site rapid high-sensitivity detection kit of prawn infectivity muscle necrosis virus and detection method thereof
InactiveCN101921873AShorten the timeShorten detection timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseTE buffer
The invention relates to an on-site rapid high-sensitivity detection kit of prawn infectivity muscle necrosis virus and a detection method thereof. The detection kit comprises a sampling tube, a rinsing tube filled with distilled water, a nucleate degeneration tube filled with a TE buffer solution, an amplification detection tube filled with amplification reaction liquid and nucleic acid dye, a negative control tube, a positive control tube, an FTA membrane, rapid drying liquid, and the like. Compared with the RT-PCR detection method, the detection method in the invention has the advantages of higher specificity, sensitivity and convenience, low cost, convenient use, more accurate and rapid detection and extremely sensitivity, is safe to both human and the environment and can substitute the traditional relevant detection method. The invention can be used in both the indoor laboratory and outdoor production field, has great significance for strengthening the epidemiological monitoring of prawn infectivity muscle necrosis virus, prawn cultivation waterbody monitoring and disease prevention and control and has great promotion and application value.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Simple preparation method of fungi molecular biological identification DNA template, and PCR amplification method
InactiveCN102559848AReduce usageSimple stepsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyTE buffer
The invention belongs to the technical field of environmental biology, and specifically relates to a PCR template simple preparation method and a PCR amplification method that can be used in large-scale fungi strain identification. With the methods, fungi DNA extraction is not required. According to the fungi DNA simple preparation method, a PCR tube containing a small amount of mycelium and a small amount of a TE buffering solution is heated and broken by using a PCR amplification apparatus, such that a small amount of fungi DNA is obtained; combined with a modified PCR amplification system, a fungi DNA fragment required by the fungi identification is obtained. The method is advantaged in less steps, low cost, simple operation, good amplification effect, and environment-friendliness. The method is suitable for large-scale fungi molecular biological identifications.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Extraction method of strawberry genome DNA
InactiveCN104805071AQuality improvementGood amplification resultDNA preparationSodium acetateWater baths
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology, and discloses an extraction method of strawberry genome DNA. The extraction method comprises following steps: liquid nitrogen is used for smashing samples into powder; CTAB extracting solution is added; an obtained mixture is subjected to water bath at 55 to 65 DEG C and then is cooled to room temperature; potassium acetate is added, and ice bath is carried out; a chloroform / isoamyl alcohol mixed liquid of a same volume is added; an obtained mixed material is mixed uniformly, and is subjected to centrifugation; the chloroform / isoamyl alcohol mixed liquid of a same volume is added into an obtained supernate A; an obtained product is mixed uniformly, is allowed to stand, and is subjected to centrifugation so as to obtain a supernate B; isopropyl alcohol is added into the supernate B, an obtained mixed solution is subjected to centrifugation so as to obtain a precipitate; a supernate C obtained via centrifugation is removed; TE buffer containing RNase is subjected to water bath at 37 DEG C; the chloroform / isoamyl alcohol mixed liquid of a same volume is added, an obtained mixed liquid is subjected to uniform mixing, is allowed to stand, and is subjected to centrifugation so as to obtain a supernate D; sodium acetate and absolute ethyl alcohol are added into the supernate D; an obtained mixed product is subjected to centrifugation so as to remove an obtained supernate E; TE buffer is added into an obtain precipitate product so as to dissolve the precipitate product, and a strawberry genome DNA solution is obtained. According to the extraction method, characteristics of CTAB and SDS extraction methods are combined, and high quality genome DNA of strawberry which is abundant in glucose and polyphenols is obtained.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Extraction method of genome DNA of isolated soy proteins
The invention discloses an extraction method of the genome DNA of isolated soy proteins, comprising the following steps of: firstly sufficiently mixing isolated soy proteins and a TE buffer solution to prepare a TE mixed solution; then adding a guanidinium isothiocyanate lysis solution with volume twice larger than that of the TE mixed solution, sufficiently uniformly mixing, and lysing at room temperature; adding isometric phenol and chloroform / isoamylol to extract proteins; centrifugalizing, and then adding isometric chloroform / isoamylol to a supernate to extract the proteins; centrifugalizing, and then adding isometric chloroform to the supernate to extract the proteins; centrifugalizing, and precipitating the supernate by using isopropanol; centrifugalizing, and washing by using ethanol for precipitation; airing at the room temperature; and dissolving in the TE buffer solution so as to obtain the TE solution of the genome DNA. According to the extraction method, the genome DNA which has high quality and is suitable for PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection is extracted from the isolated soy proteins, the concentration of the genome DNA is 1558 micrograms / ml, and the value of OD260 / OD280 is 1.666; and in addition, the invention has the advantages of easy operation and short consuming time and is beneficial to fast detection.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for separating isomerism protein from recombinant human ciliary neurotrophy factor and its mutant
InactiveCN101113174AEfficient separationGood treatment effectPeptide preparation methodsGrowth factors/regulatorsTE bufferInclusion bodies
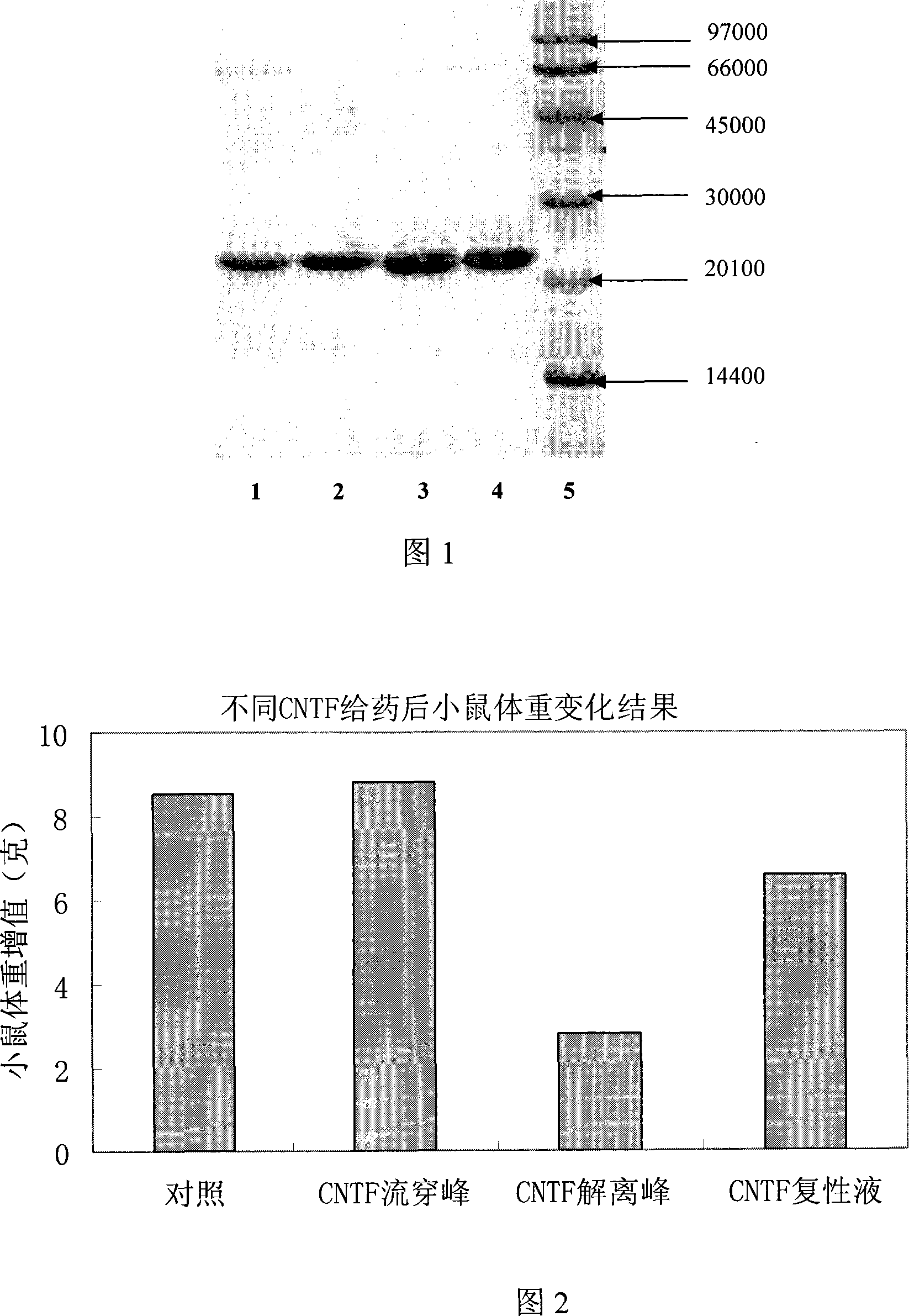
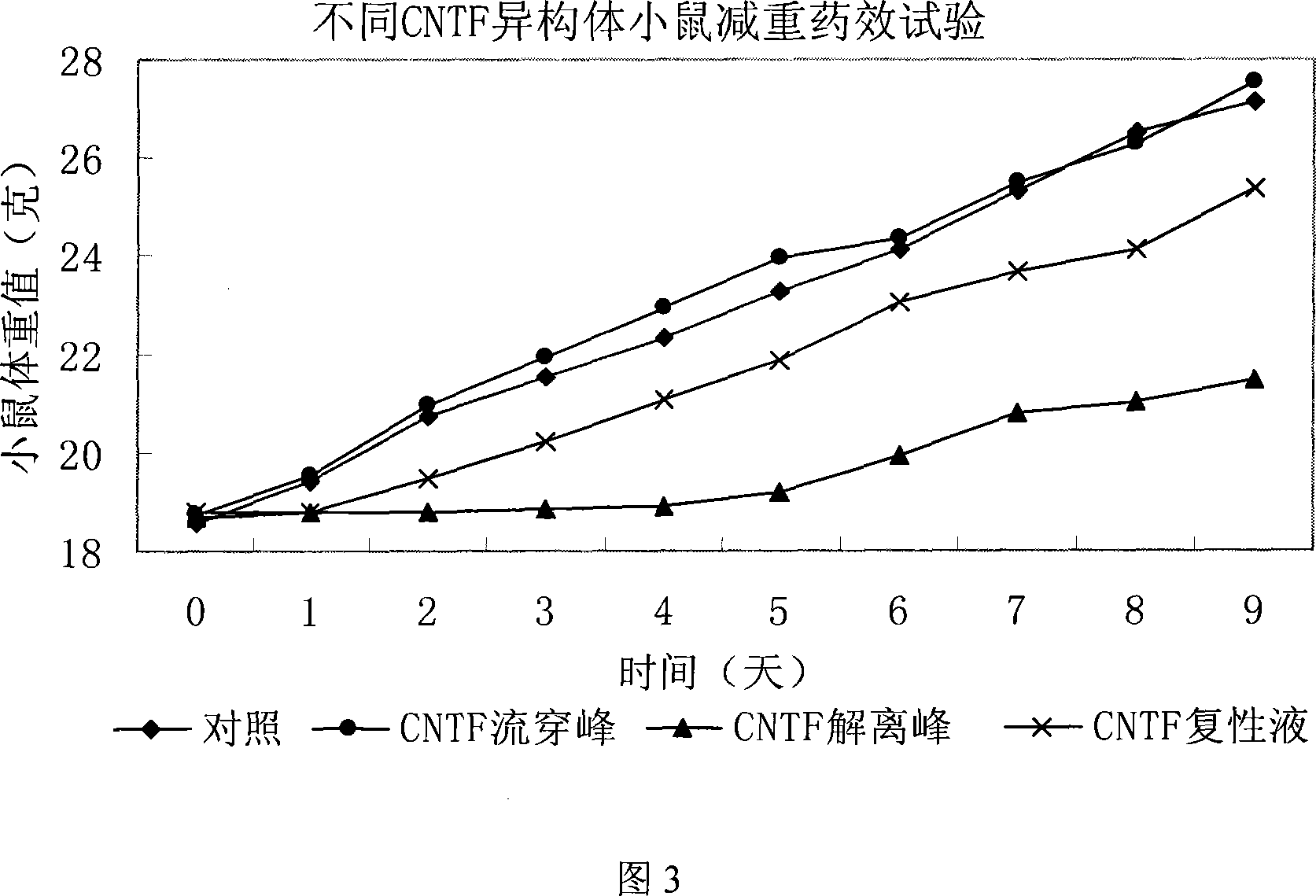
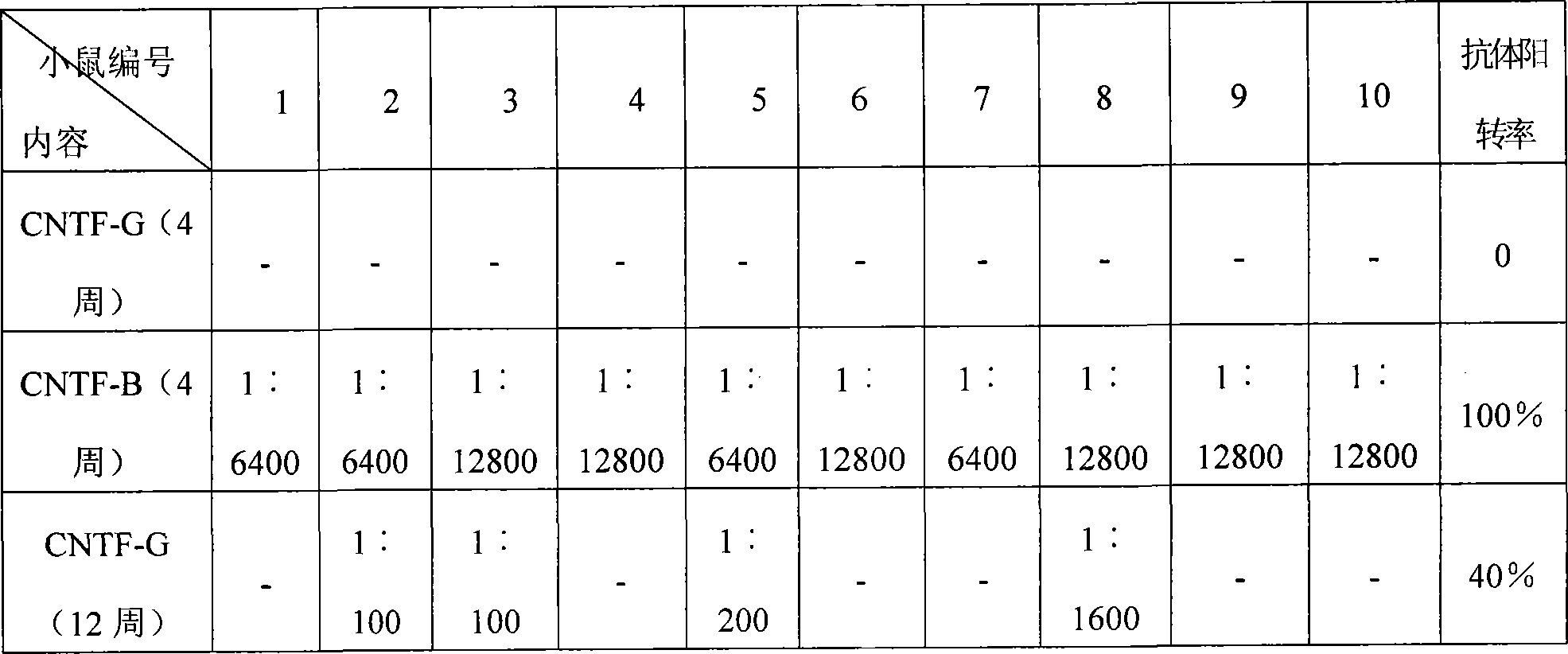
The invention relates to a method to separate isomeric protein form gene recombinant expression protein. The method of the invention is that: the collected wet bacterium is made into bacterium soliquoid in a cleaning buffer liquid, and shattered and decentered by ultrasonic, and the clear liquid is abandoned, the precipitation is cleaned by TE buffer liquid containing urea and TritonX-100, then protein endosome is acquired, and the endosomes is fully dissolved by a buffer liquid containing guanidine hydrochloride or urea; the dissolving liquid is diluted and renatured by the buffer liquid containing Tris-HCl, arginine and EDTA, then stand for 24-48h, and becomes a CNTF renatured protein liquid; after being ultrafiltered and concentrated, the renatured protein is transferred into the Tris buffer liquid through gel filtration chromatography to collect protein peak; finally the CNTF renatured protein liquid with transferred liquid is sent to Q sephrose-Fast Flow anion exchange column, to remove unrenatured CNTF proteins and other proteins.
Owner:兰州生物制品研究所
Field fast high-sensitive detecting kit of monodon baculovirus and detecting method
InactiveCN101624634AQuick checkShort manufacturing timeMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesDiseaseTE buffer
The invention relates to a field fast high-sensitive detecting kit of monodon baculovirus and a detecting method. The detecting kit comprises a sampling pipe, a rinsing pipe internally filled with distilled water, a nucleic acid denaturation pipe internally filled with TE cushion fluid, an amplified detecting pipe internally filled with amplified reaction liquid and nucleic acid dye, a negative tube, a positive tube, an FTA membrane, a fast drying liquid thereof, etc. Compared with the common PCR detecting method, the detecting method has higher specificity, sensitivity and convenience, has extreme low cost, nontoxicity, safety, convenient use, more exact detecting, fastness and extreme high sensitivity, and can replace the relevant existing detecting method such as a pathological section method, an electronic speculum observation method, an antibody detecting method and a PCR detecting method. The detecting kit and the detecting method not only can be used for an indoor laboratory, but also can be used for a wild production field, have significant meaning for enhancing epidemiological surveillance and disease control as well as prevention to the monodon baculovirus, and have extreme high population application value.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Kit for quickly detecting cryptosporidium
InactiveCN101289689AQuick checkSensitive detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesTE bufferMicrobiology
The invention relates to a kit capable of rapidly detecting the cryptosporidium in food. The kit mainly solves the technical problems of the absence of a detecting method at both home and abroad and too long detection time. The kit capable of rapidly detecting the cryptosporidium in food consists of the following agents: an agent A: a fixed-DNA FTA card consisting of an FTA card, an FTA purifying reagent and an FTA cleaning reagent (TE buffer:0.01mol / L Tris, pH 8.0; 0.1 mmol / L EDTA); an agent B: PCR reaction liquor containing two specific primer pairs of CryoutL and CryoutR which respectively have the sequences of 5'-TTCTAGAGCTAATACATGCG-3' and 5'-CCCACTT CTTCGAAGCAGGA-3'; an agent C: PCR reaction liquor containing two specific primer pairs of CryinL and CryinR which respectively have the sequences of 5'-GGAAGGGTTGTATTTATTAGATAAAG-3' and 5'- CTCATAAGGTGCTGAAGGAGTA-3'. The method is used to detect the cryptosporidium in a sample.
Owner:SHANGHAI ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU OF P R C
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com