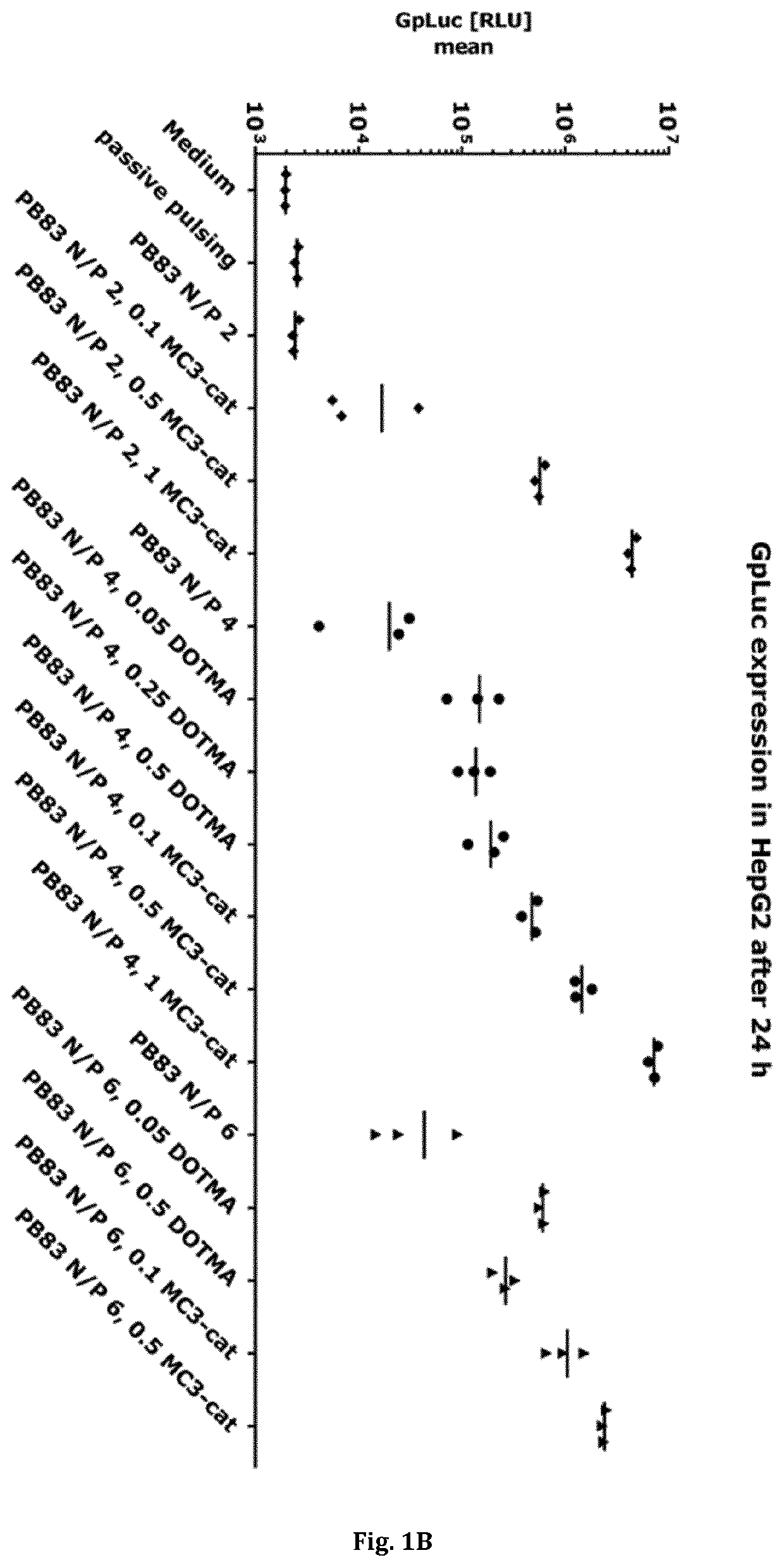
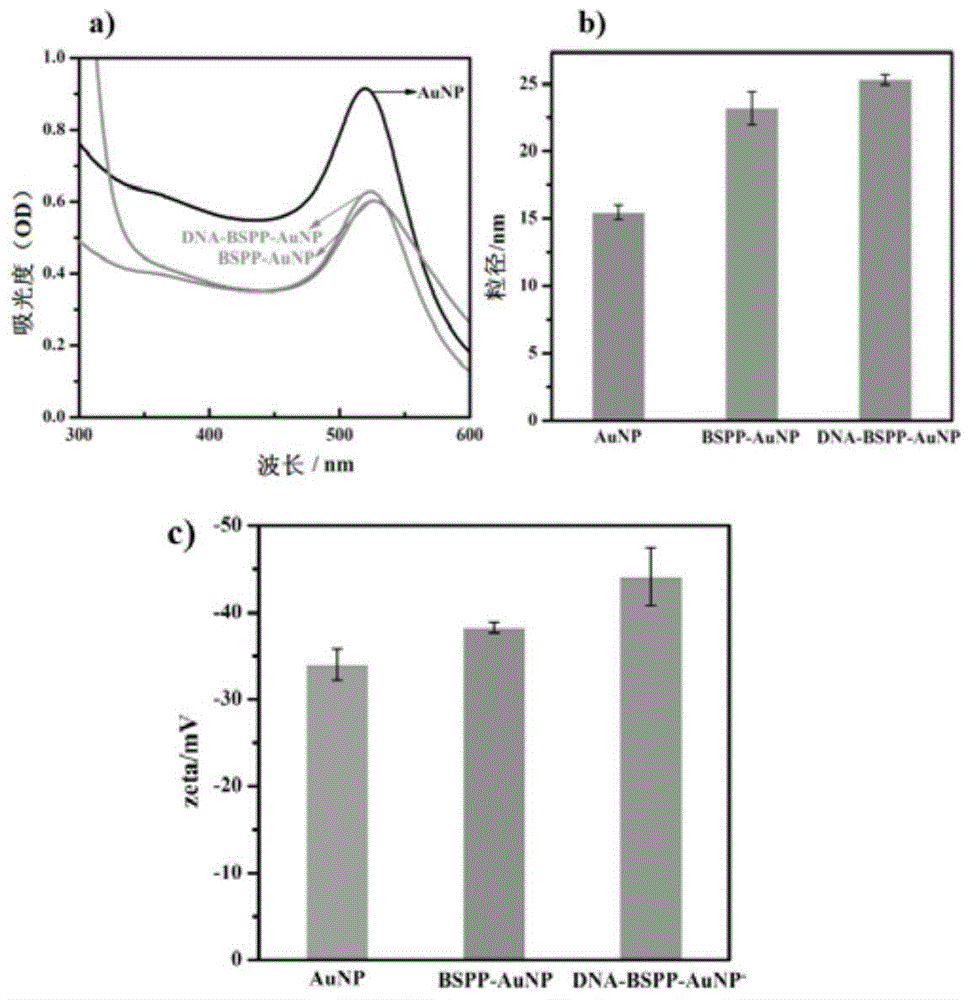
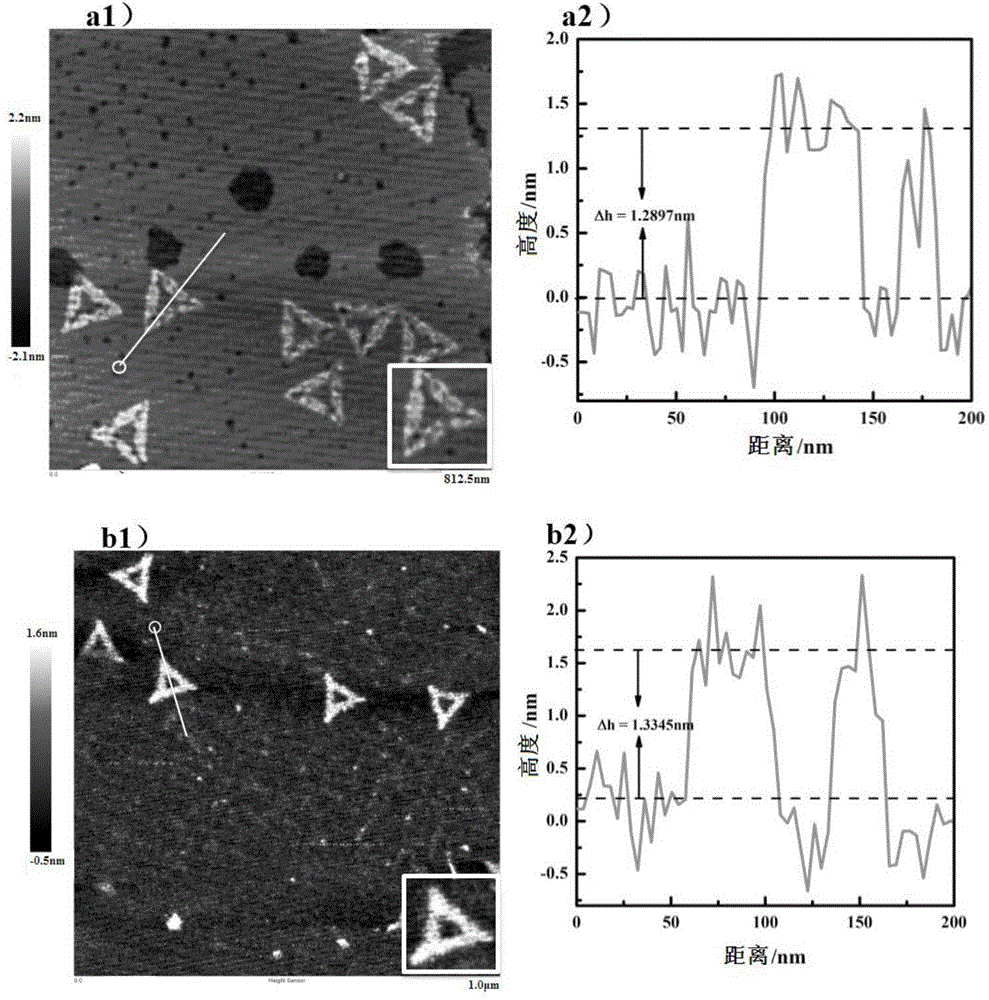
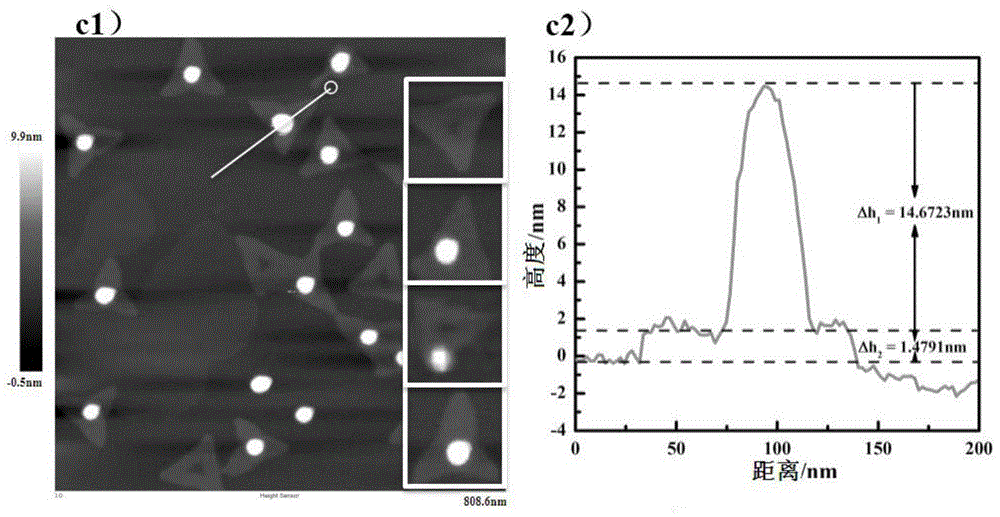
Patents
Literature
238 results about "Modified dna" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Polymerases
ActiveUS20060281109A1Improve the level ofProceed efficientlySugar derivativesHydrolasesModified dnaPolymerase L
Modified DNA polymerases have an affinity for DNA such that the polymerase has an ability to incorporate one or more nucleotides into a plurality of separate DNA templates in each reaction cycle. The polymerases are capable of forming an increased number of productive polymerase-DNA complexes in each reaction cycle. The modified polymerases may be used in a number of DNA sequencing applications, especially in the context of clustered arrays.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
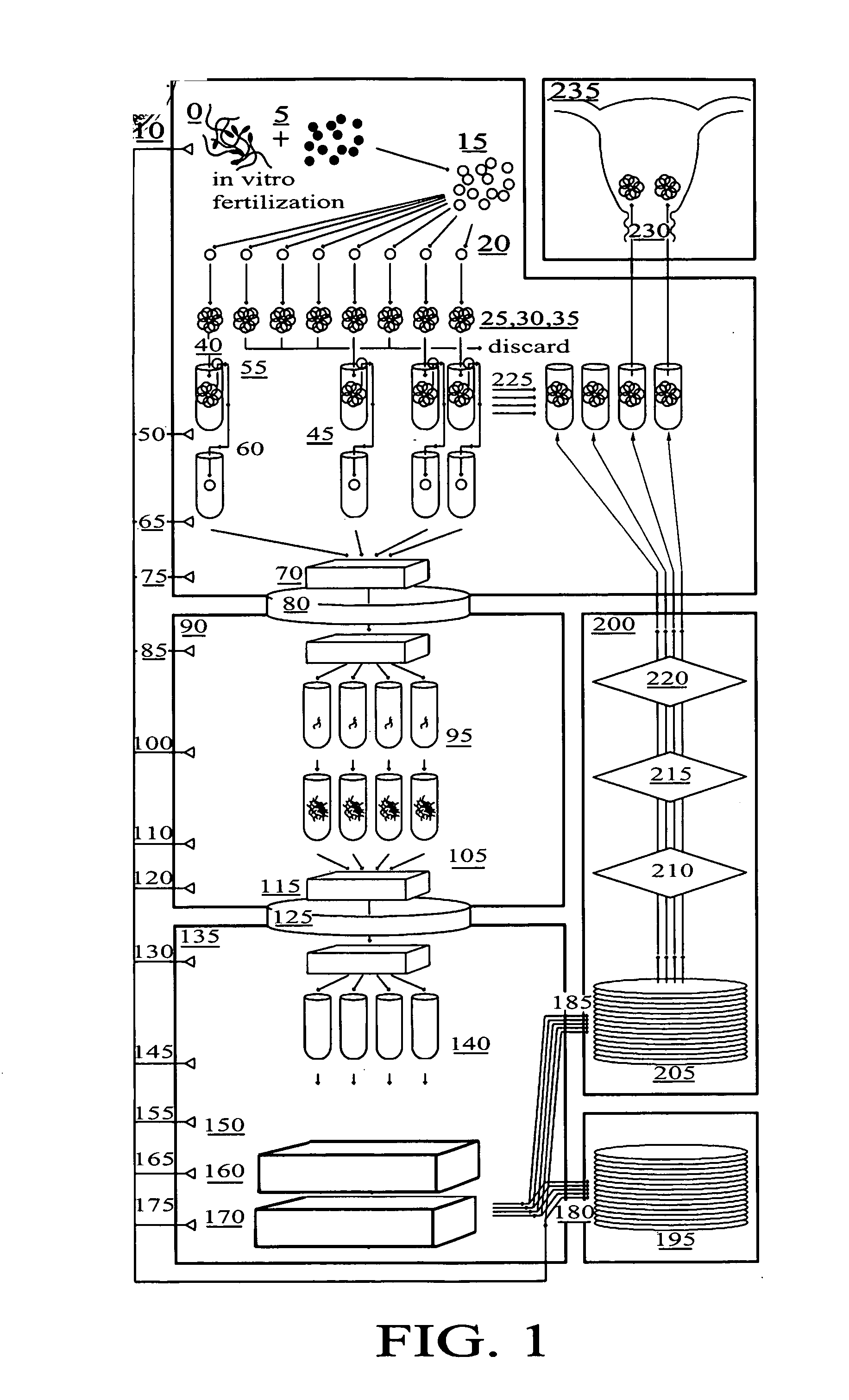
Method for genetic testing of human embryos for chromosome abnormalities, segregating genetic disorders with or without a known mutation and mitochondrial disorders following in vitro fertilization (IVF), embryo culture and embryo biopsy
InactiveUS20080085836A1Reduce significant riskImprove the level ofLibrary screeningLibrary member identificationLess invasiveContamination
We describe a method for interrogating the content and primary structure of DNA by microarray analyses and to provide comprehensive genetic screening and diagnostics prior to embryo transfer within an IVF setting. We will accomplish this by the following claims: 1) an optimized embryo grading system, 2) a less invasive embryo biopsy with reduced cellular contamination, 3) an optimized DNA amplification protocol for single cells, 4) identify aneuploidy and structural chromosome abnormalities using microarrays, 5) identifying sub-telomeric chromosome rearrangements, 6) a modified DNA fingerprinting protocol, 7) determine imprinting and epigenetic changes in developing embryos, 8) performing genome-wide scans to clarify / diagnose multi-factorial genetic disease and to determine genotype / haplotype patterns that may predict future disease, 9) determining single gene disorders with or without a known DNA mutation, 10) determining mtDNA mutations and / or the combination of mtDNA and genomic (nuclear) DNA aberrations that cause genetic disease.
Owner:KEARNS WILLIAM G +1
Enzymes resistant to photodamage
ActiveUS20100093555A1Reduce oxidationImprove the immunitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementModified dnaPolymerase L
Provided are compositions comprising modified DNA polymerases that exhibit improved photostability compared to the parental polymerases from which they were derived. Provided are methods for generating enzymes, such as DNA polymerases, with the aforementioned phenotype. Provided are methods of using polymerases with increased resistance to photodamage to make a DNA or to sequence a DNA template.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
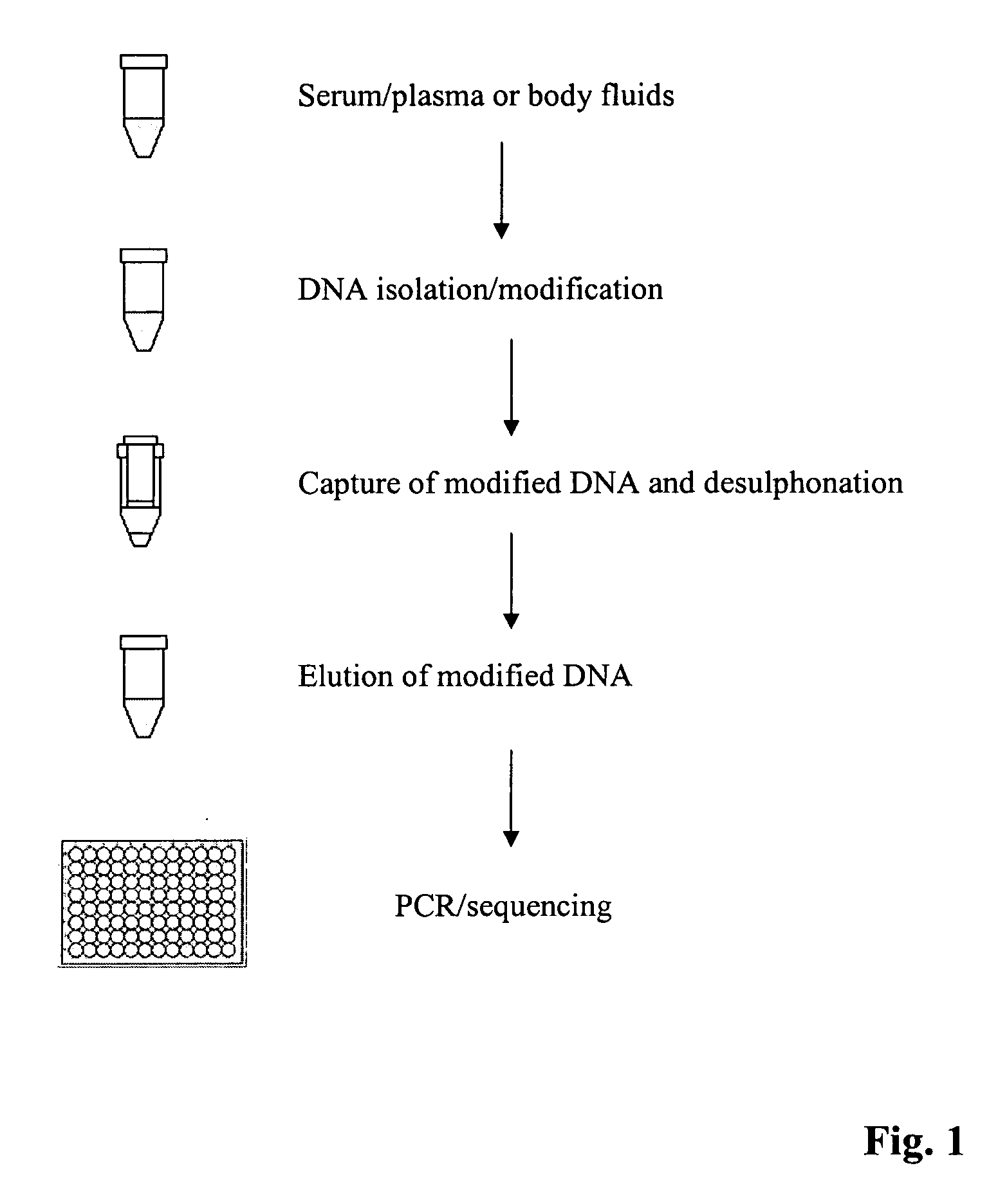
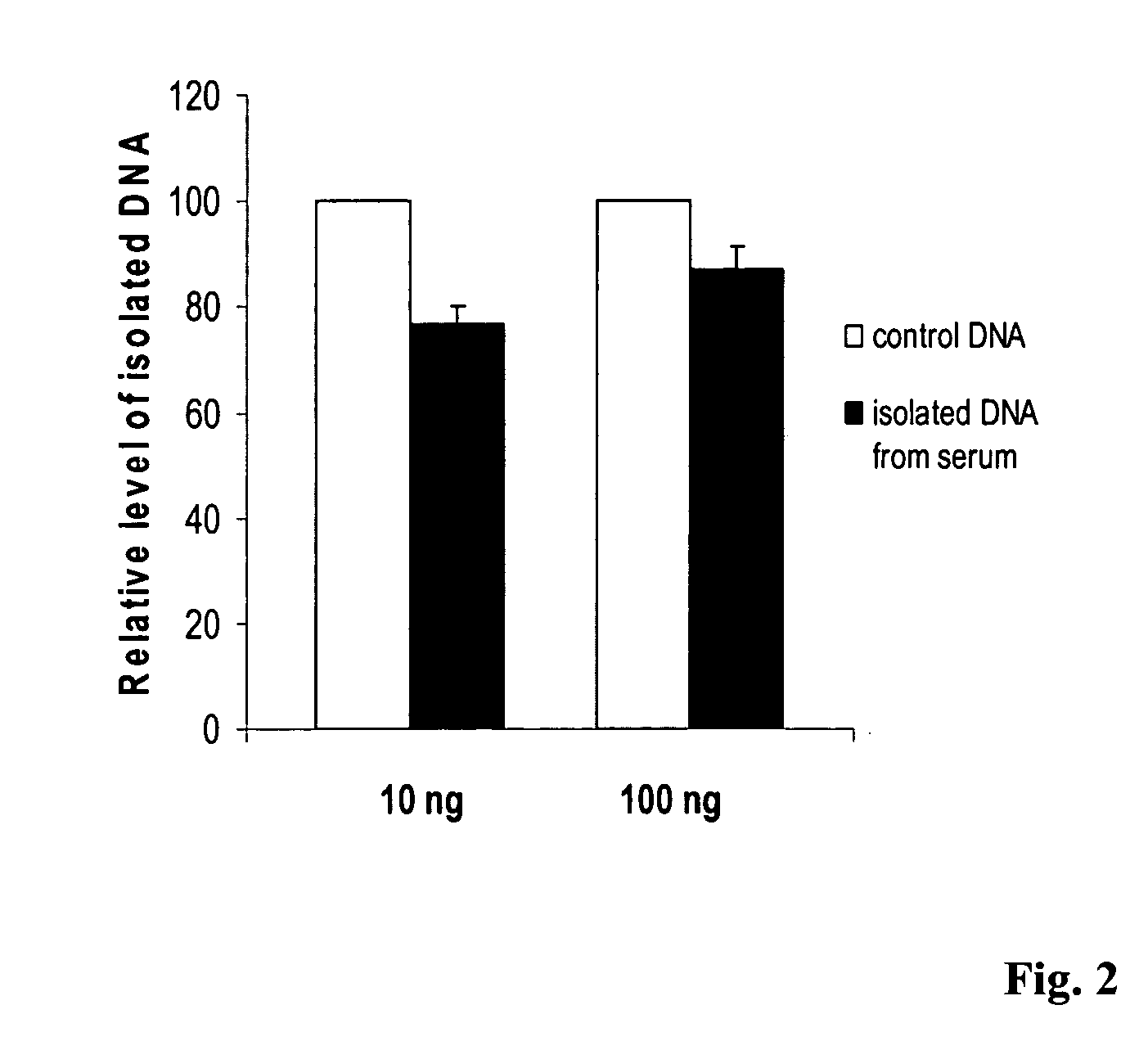
Method for isolating and modifying DNA from blood and body fluids
InactiveUS20070042384A1Highly efficient and fast isolation and modificationEasily and quickly isolatedSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementModified dnaPcr assay
This invention is related a method for rapidly isolating and modifying DNA from plasma / serum and body fluids. This invention provides a procedure and composition to obtain a high yield of modified DNA for methylation-specific PCR assay by coupling DNA isolation and modification courses.
Owner:LI WEIWEI +1
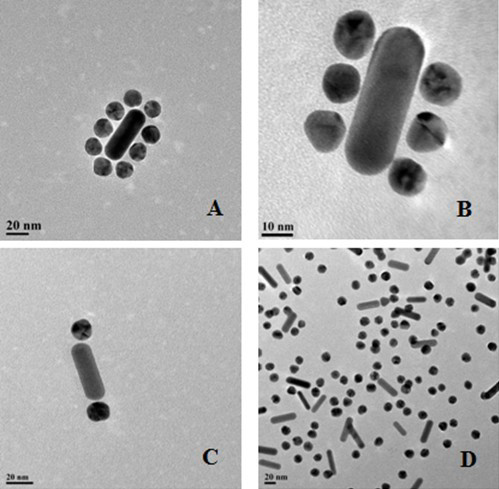
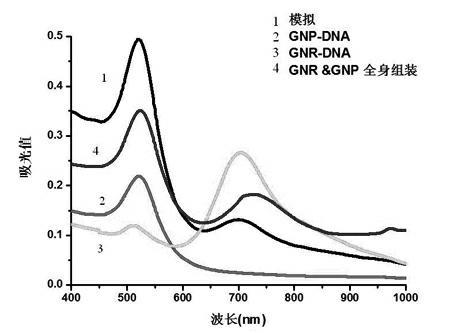
Preparation method of self-assembly material having surface-enhanced Raman activity
InactiveCN102127542AUniform assembly structureRaman activeDNA/RNA fragmentationModified dnaSelf-assembly
The invention relates to a preparation method of a self-assembly material having surface-enhanced Raman activity, belonging to the technical field of material chemistry. The preparation method comprises the following steps: synthesizing gold nano particles; synthesizing gold nano rods; modifying DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) 1 with the gold nano particles; modifying DNA 2 with the gold nano rods; coupling the gold nano rods with Raman beacon molecules; and assembling and characterizing the gold nano rods and the gold nano particles. The nano material assembly body prepared by the invention has a uniform and controllable assembly structure and has Raman activity, thereby making monomolecular detection possible.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Polymerases
Modified DNA polymerases have an affinity for DNA such that the polymerase has an ability to incorporate one or more nucleotides into a plurality of separate DNA templates in each reaction cycle. The polymerases are capable of forming an increased number of productive polymerase-DNA complexes in each reaction cycle. The modified polymerases may be used in a number of DNA sequencing applications, especially in the context of clustered arrays.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
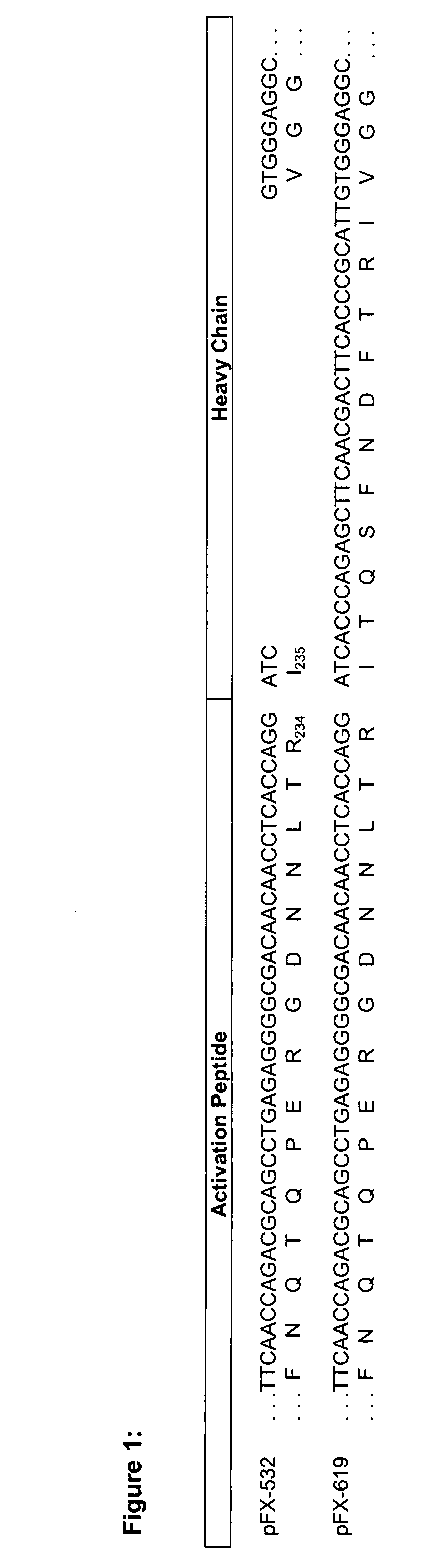
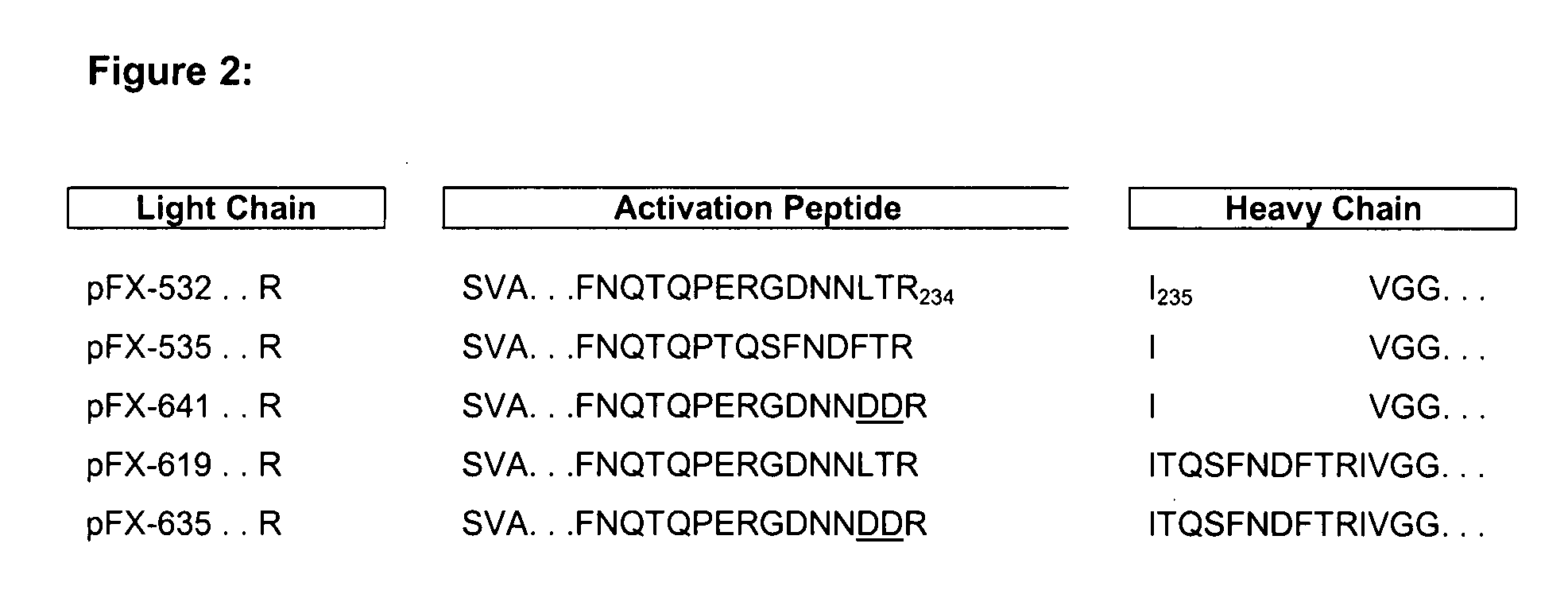
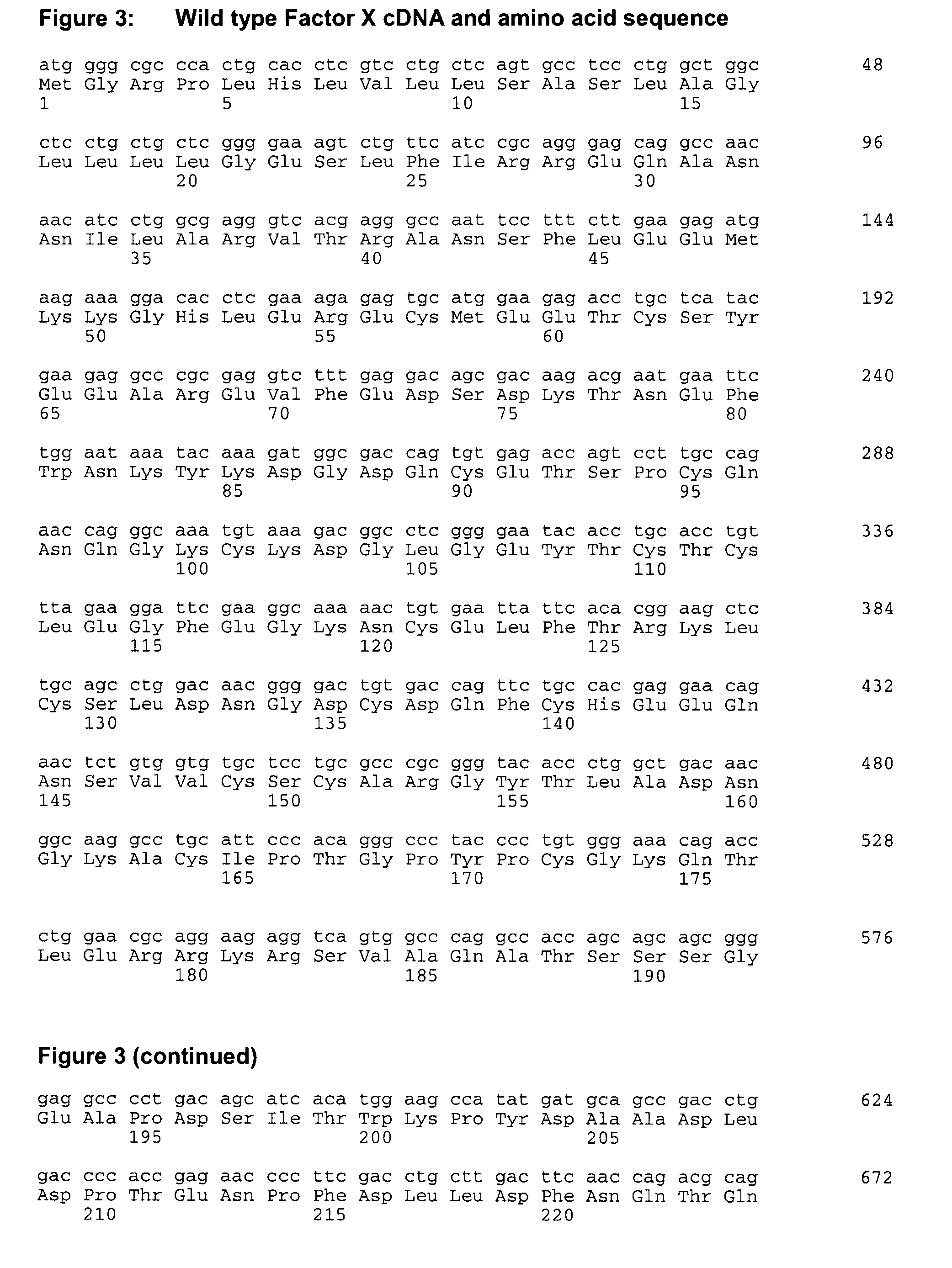
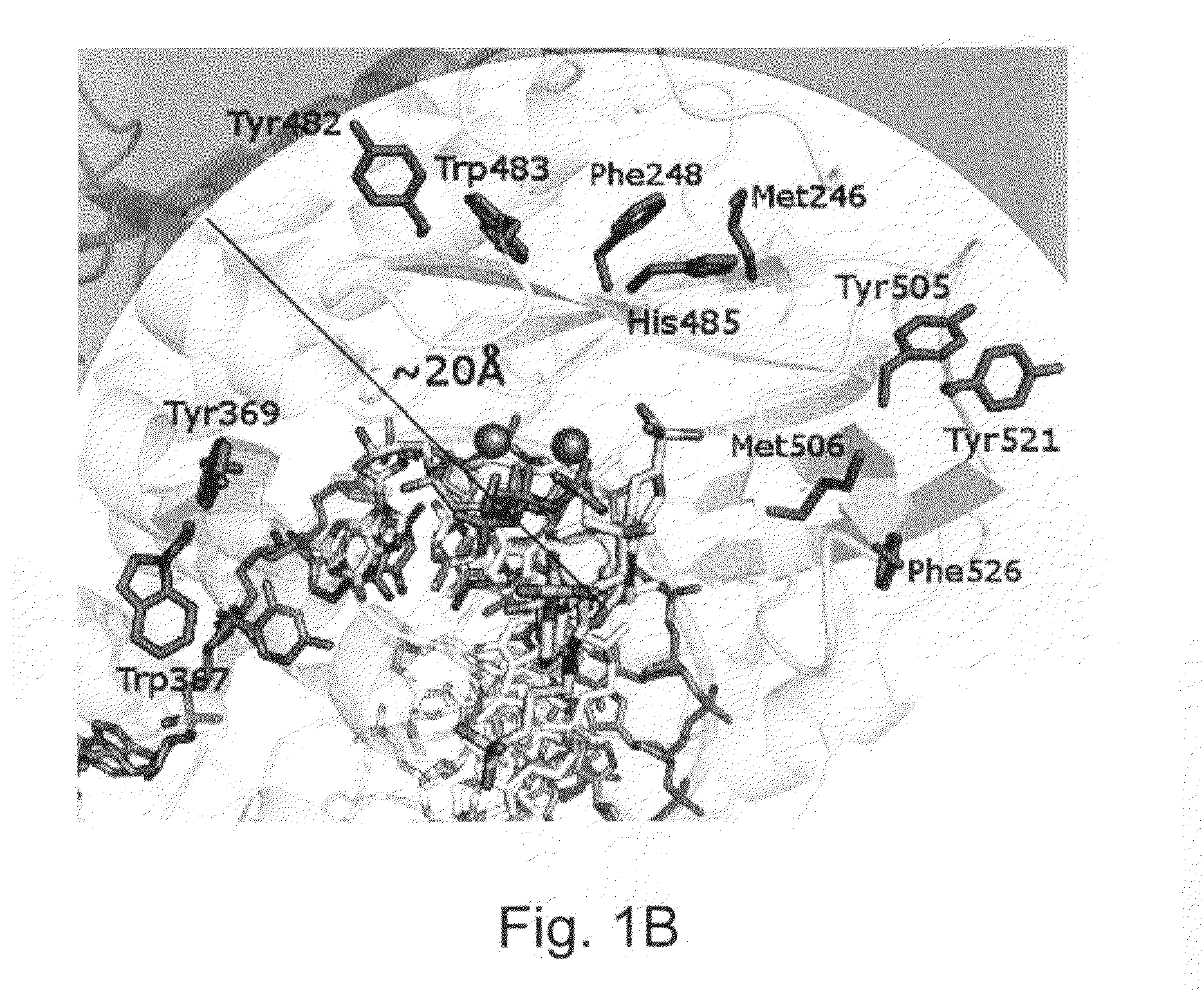
Coagulation factor x polypeptides with modified activation properties
The present invention relates to modified cDNA sequences coding for human Factor X and their derivatives with improved stability and modified activation sequences, recombinant expression vectors containing such cDNA sequences, and host cells transformed with such recombinant expression vectors. The invention also relates to recombinant factor X polypeptides and derivatives which have biological activities of the unmodified wild type protein but with improved stability and processes for the manufacture of such recombinant proteins and their derivatives. The invention also covers a transfer vector for use in human gene therapy, which comprises such modified DNA.
Owner:CSL BEHRING GMBH
Enzymes resistant to photodamage
ActiveUS9127259B2Improve the immunityReduce oxidationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementModified dnaPolymerase L
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Method for preparing meso-porous silicon nano medicine carrier with cell specificity target, reduction responsiveness and triple anticancer treatment effects
InactiveCN104013965AOvercome toleranceEasy to operatePowder deliveryMacromolecular non-active ingredientsCell membraneCarrier system
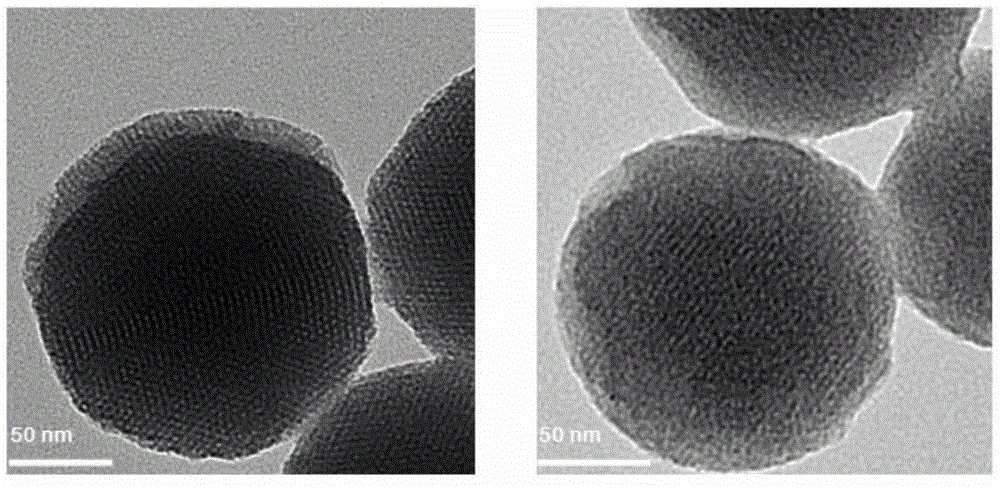
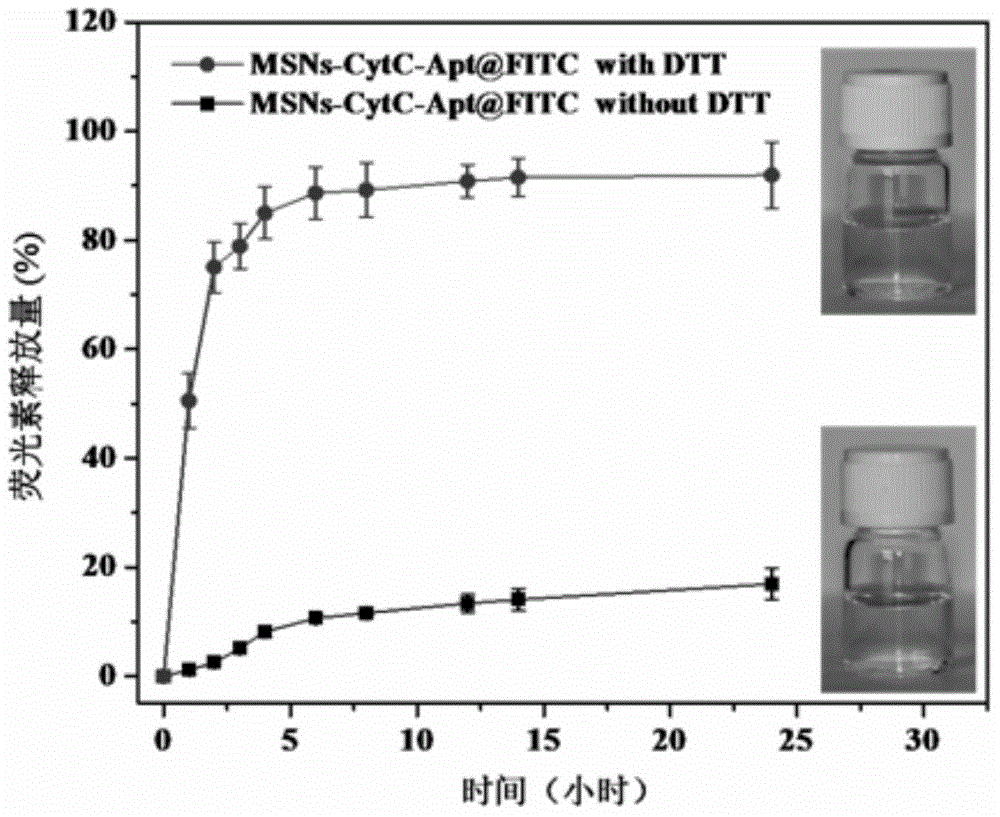
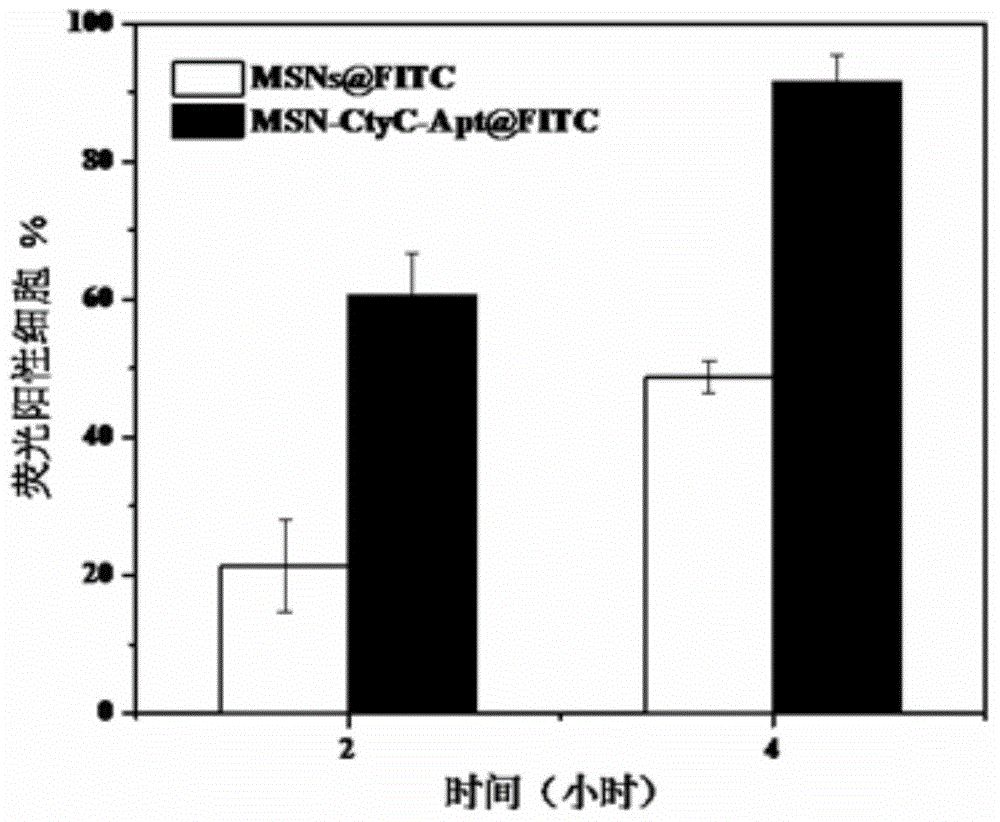
The invention discloses a method for preparing a meso-porous silicon nano medicine carrier with cell specificity target, reduction responsiveness and triple anticancer treatment effects. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, synthesizing meso-porous silicon nano particles by using a gel dissolution method, subsequently, introducing a disulfide bond onto the surface of a meso-porous silicon nano reservoir by using a chemical modification method, innovatively fixing cytochrome C with an apoptosis-inducing function onto the surface of the meso-porous silicon nano reservoir, blocking meso-porous channels with medicines, finally modifying DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) aptamer single chain molecules (AS1411, with a cancer cell apoptosis-inducing function) onto the surface of a meso-porous silicon / cytochrome C nano composite system, and taking the system as specificity ligand of a receptor (nucleolin protein) which is overexpressed on the surface of liver cancer cytomembrane, thereby establishing a multifunctional composite type nano medicine carrier system for achieving triple anticancer treatment under combined action of medicines, blocking substances and target molecules inside meso-pores.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Method for portably and rapidly detecting ochratoxin A
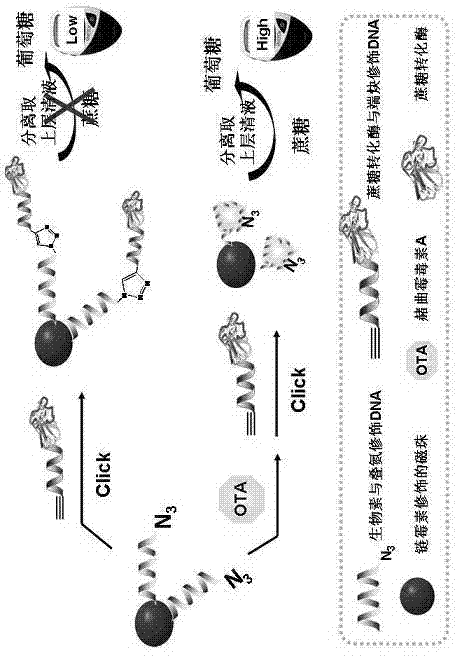
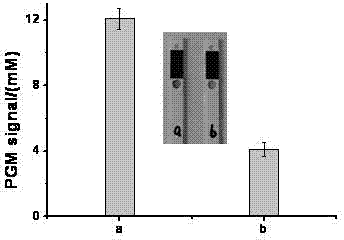
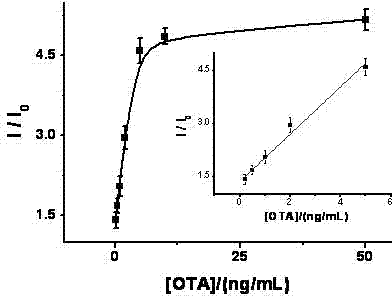
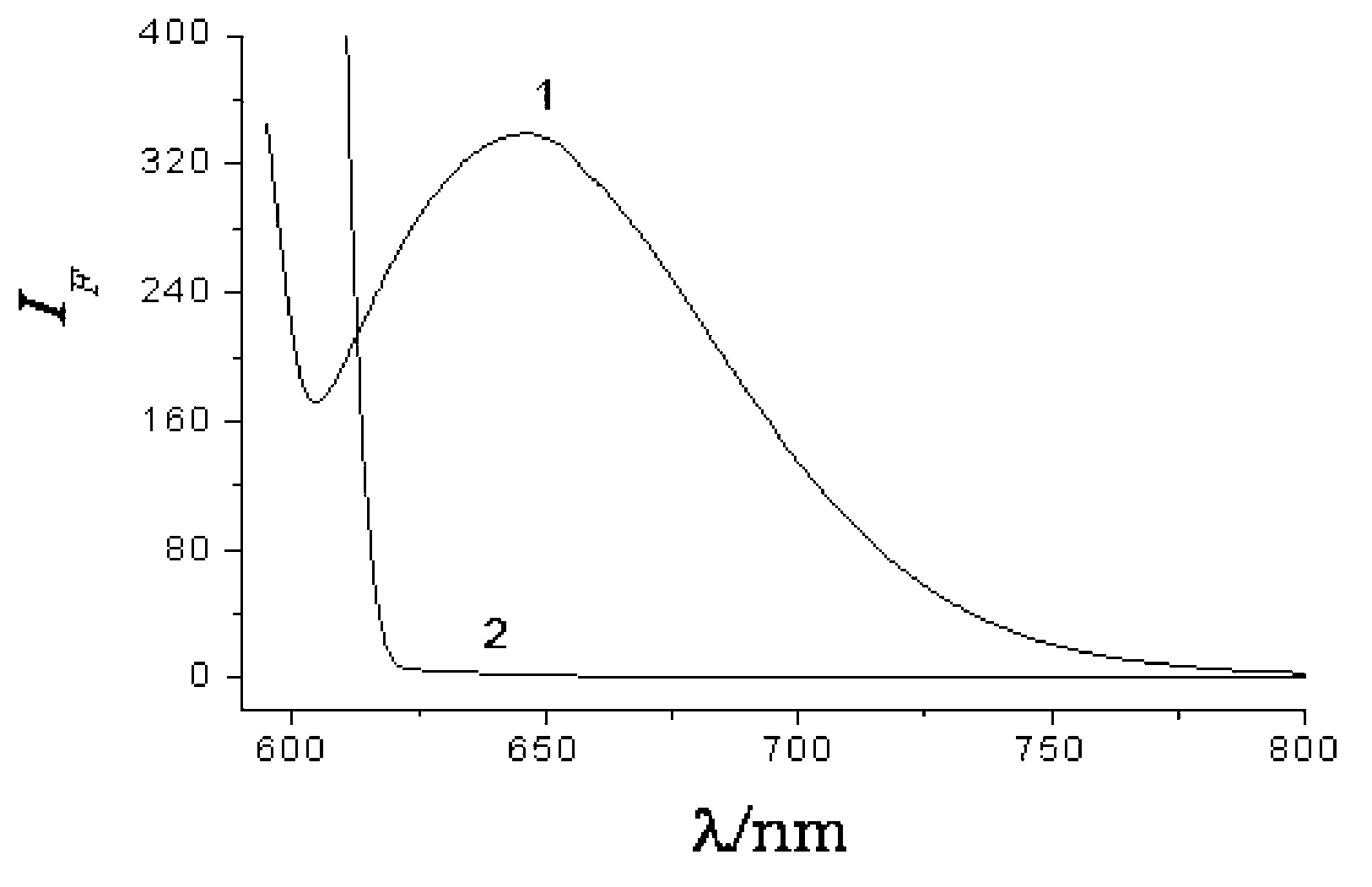
ActiveCN103808716AStrong specificityReduce complexityMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorModified dnaMagnetic bead
The invention discloses a method for portably and rapidly detecting ochratoxin A. The method comprises the following steps: first, preparing sucrose invertase-terminal alkyne modified DNA; subsequently, combining biotin-nitrine modified DNA with the surface of a magnetic bead, adding the ochratoxin A with different concentration, and mixing; adding the previously-prepared sucrose invertase-terminal alkyne modified DNA, a CuSO4 solution and an ascorbic acid solution, wherein the ascorbic acid solution can be used for reducing Cu(II) to obtain a Cu(I) compound so as to catalyze the biotin-nitrine modified DNA and the sucrose invertase-terminal alkyne modified DNA to have a click chemistry reaction; taking a supernatant liquor after the reaction is ended, then adding the supernatant liquor into a sucrose solution, wherein the sucrose invertase can effectively catalyze the sucrose in the solution to be transformed into glucose; and finally, measuring by adopting a glucometer. The method is used for organically combining the rapid reaction advantage of the click chemistry reaction with the high specificity characteristic of an aptamer, and adopting the simple and portable glucometer to acquire data, thus the operation complexity and detection cost are greatly reduced, and the sensitivity and selectivity are improved.
Owner:INST OF AGRI PROD QUALITY SAFETY & STANDARD JIANGXI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for synthesizing fluorescent silver nano clusters by taking general DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) as stabilizer
The invention belongs to the field of chemical engineering, and particularly relates to a method for large-scale synthesization of fluorescent silver nano clusters by taking general modified DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) as a stabilizer. The method mainly comprises the following steps: (1) mixing the general modified DNA with a silver ion solution and reacting in a refrigerator of 4 DEG C for 24 h; and (2) adding a NaBH4 solution into a mixed solution in the step (1) and reacting for 3 h at the room temperature of 10-25 DEG C to obtain a silver nano cluster solution. According to the method, the general modified DNA is taken as the stabilizer for the convenience of large-scale synthesization of the fluorescent silver nano clusters; and the synthetic method is economic, the particle size is smaller, the particle distribution is uniform, and strong fluorescent light can be generated.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Improved polymerases
Modified DNA polymerases have an affinity for DNA such that the polymerase has an ability to incorporate one or more nucleotides into a plurality of separate DNA templates in each reaction cycle. The polymerases are capable of forming an increased number of productive polymerase-DNA complexes in each reaction cycle. The modified polymerases may be used in a number of DNA sequencing applications, especially in the context of clustered arrays.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
Methods for genome amplification
A method for whole genome amplification comprising (a) treating genomic DNA with a modifying agent which modifies cytosine bases but does not modify 5′-methyl-cytosine bases under conditions to form single stranded modified DNA; (b) providing a population of random X-mers of exonuclease-resistant primers capable of binding to at least one strand of the modified DNA, wherein X is an integer 3 or greater; (c) providing polymerase capable of amplifying double stranded DNA, together with nucleotides and optionally any suitable buffers or diluents to the modified DNA; and (d) allowing the polymerase to amplify the modified DNA.
Owner:HUMAN GENETIC SIGNATURES PTY LTD
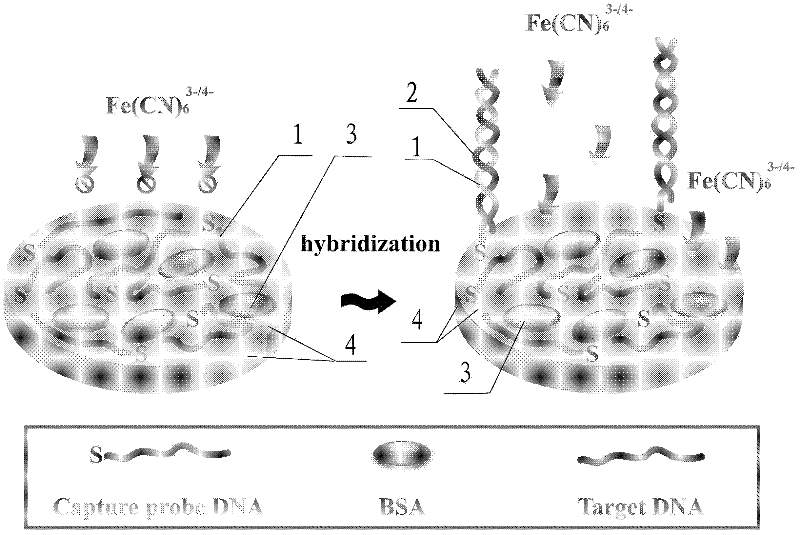
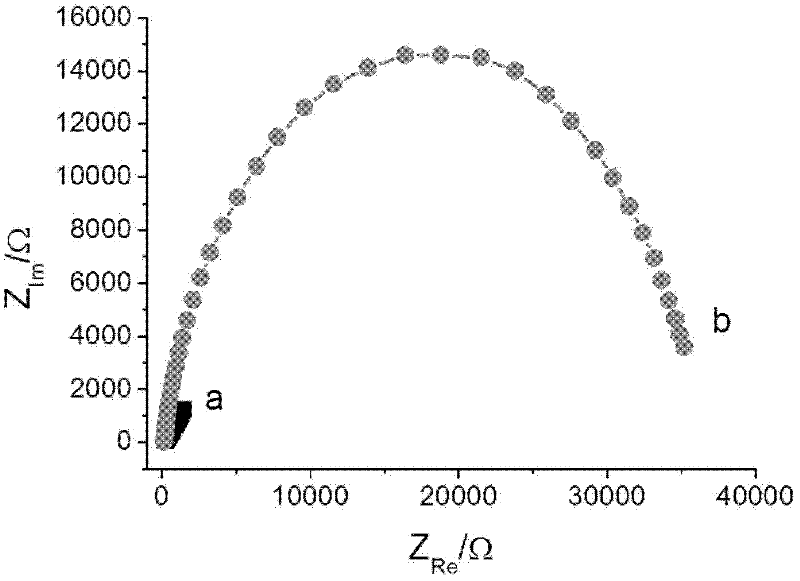
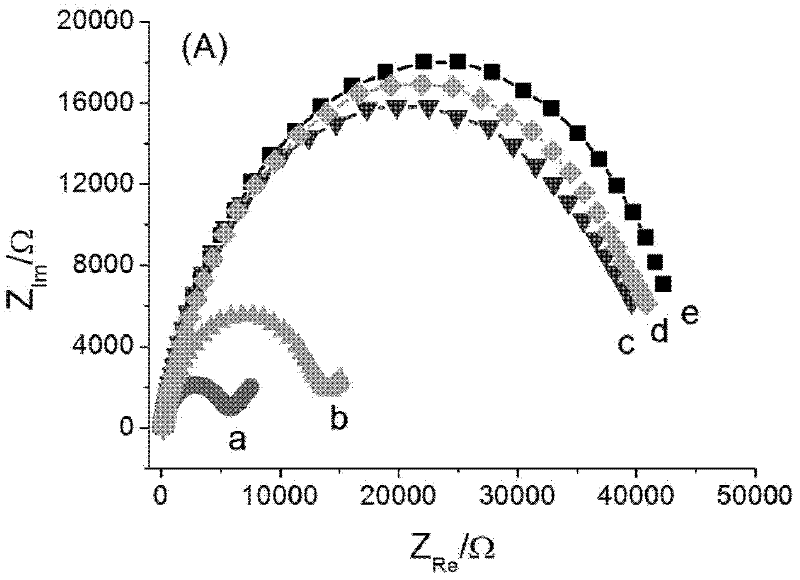
Composite film modified DNA sensor and its preparation method and application in detection of lignin peroxidase (Lip) specific coding gene segment
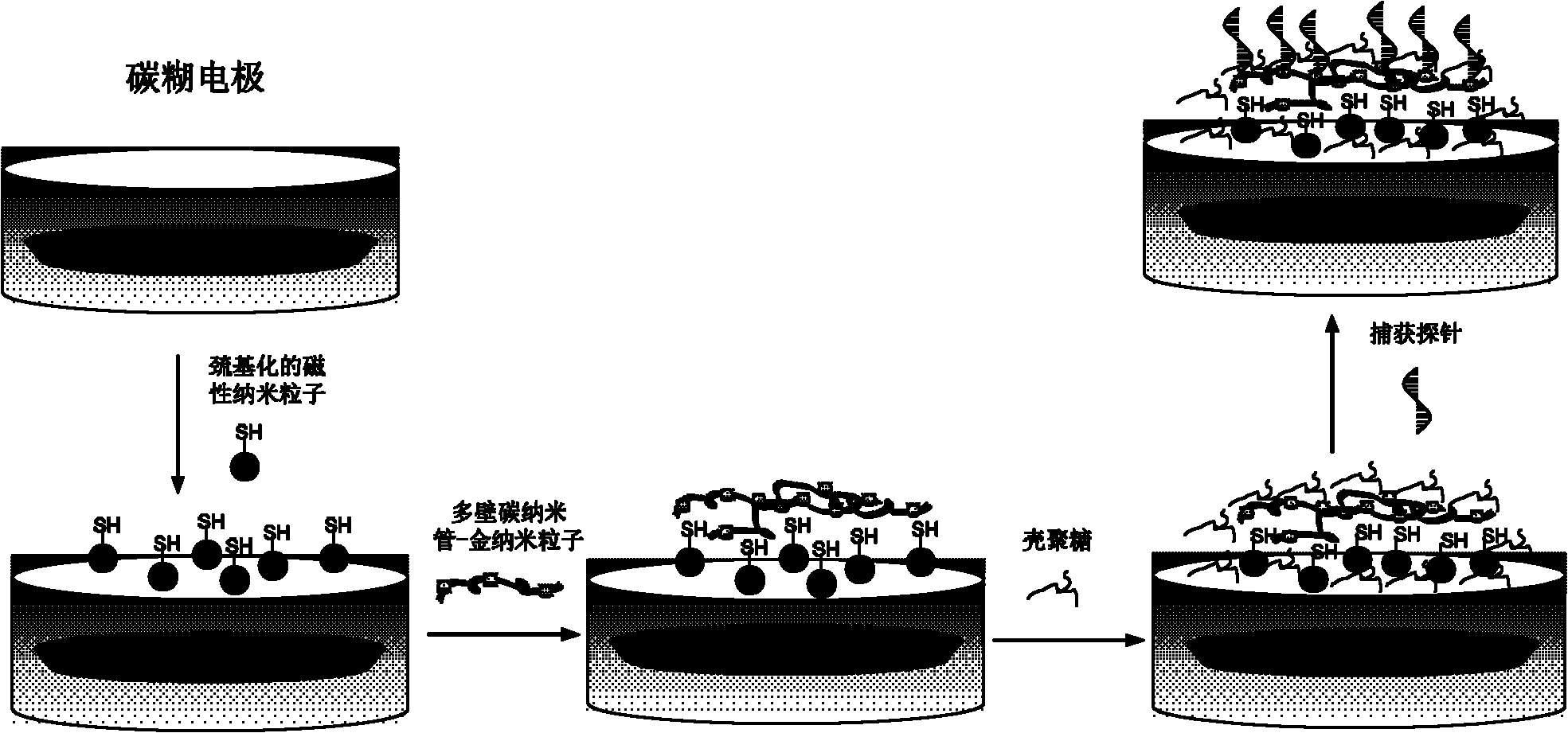
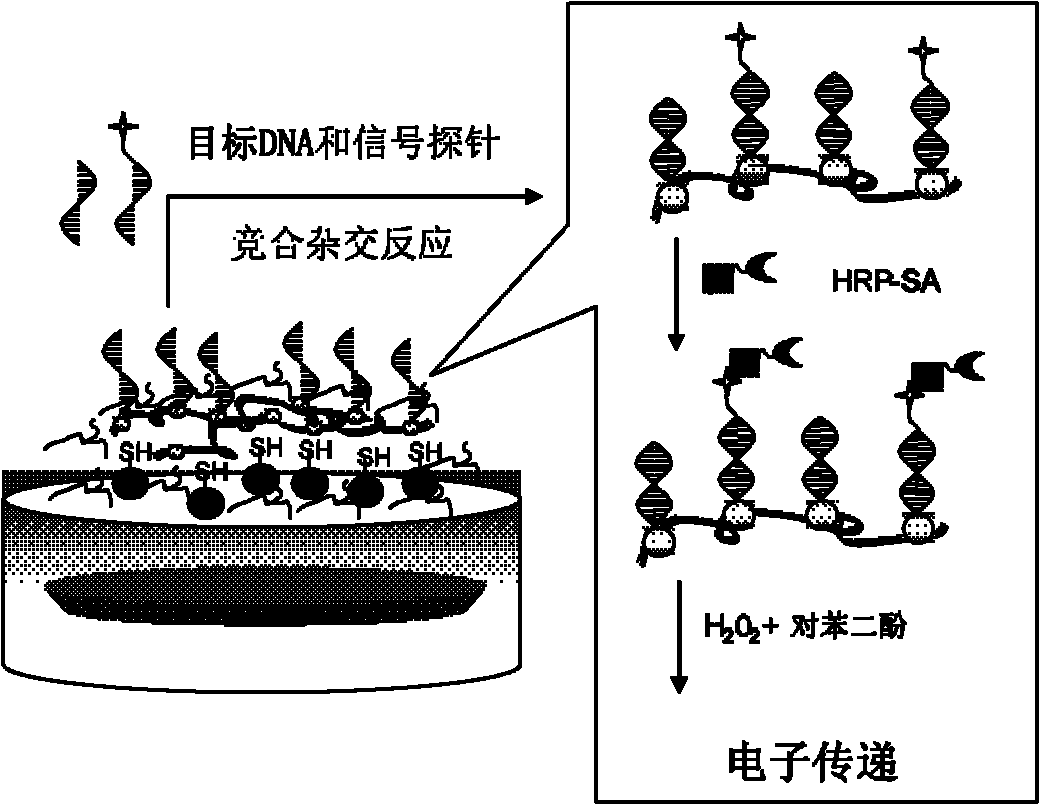
InactiveCN102253092AImprove electronic conductivityLow Dynamic SituationMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial electrochemical variablesComposite filmMagnetite Nanoparticles
The invention discloses a composite film modified DNA sensor. The DNA sensor is characterized in that the sensor comprises a carbon paste electrode; the carbon paste electrode comprises a carbon rod, a Teflon tube, a magnet, and carbon paste; an induction end of the carbon paste electrode is coated with a sensitive substance; the sensitive substance comprises a composite film and a DNA capture probe; magnetic nanoparticles, multi-walled carbon nanoscale tube-gold nanoparticles and chitosan are utilized for modifying orderly the surface of the carbon paste electrode and compose the composite film; and the DNA capture probe is utilized for modifying the surface of the multi-walled carbon nanoscale tube-gold nanoparticles. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the DNA sensor. The preparation method comprises the processing steps of manufacturing a carbon paste electrode, modifying the surface of an induction end of the manufactured carbon paste electrode by a sensitive substance, and the like. The invention further discloses an application of the DNA sensor in detecting a lignin peroxidase (Lip) specific coding gene segment. Because a sensitive substance is utilized for modifying the surface of a carbon paste electrode of the DNA sensor, the DNA sensor has a strong capacity of electron conduction and a high accuracy of detection. The preparation method has the advantages of low cost and simple process.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
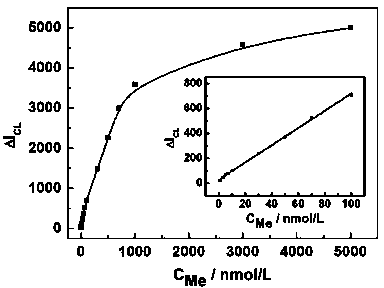
Method for determining melamine (Me) by chemiluminescence
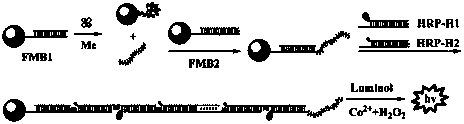
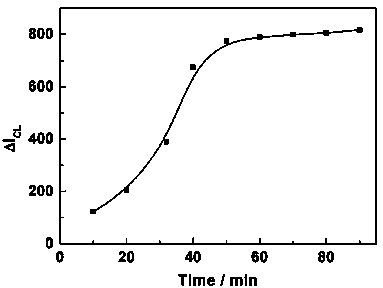
The invention belongs to the field of chemiluminescence sensors, and relates to a method for determining melamine (Me), which is implemented by using a target induced chain releasing technique and combining with a hybrid chain reaction and a chemiluminescence technique. When a target Me exists, the Me acts with aptamer DNA1 (deoxyribonucleic acid 1) in double-stranded DNA on the surface of a functionalized magnetic bead (FMB1) so as to release a complementary sequence DNA2 of the aptamer; and the released complementary sequence DNA2 acts with another functionalized magnetic bead (FMB2), and a chain hybridization reaction is performed in the presence of hairpin DNA (HRP-H1 and HRP-H2) for modifying HRP, so that the two kinds of modified DNA grow into long double-stranded DNA. Through magnetic separation, and by using the catalytic action of HRP on a luminol-H2O2 chemiluminescence system, chemiluminescence is produced, and then the determination of the Me is realized through determining the chemiluminescence intensity. The method is high in selectivity and detection sensitivity.
Owner:广州倍腾新材料有限公司
Construction method of plasma free DNA library
The invention discloses a 'construction method for a small amount of DNA library'. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out end repairing on plasma free DNA or fragmented DNA and simultaneously carrying out phosphorylation modifying on 5' terminal to obtain modified DNA; later, implementing blunt end linking directly to an artificial linker and purifying to obtain relatively pure linker-containing DNA having a gap on joint; then repairing the gap by virtue of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) polymerase before PCR amplification to obtain repaired complete linker-containing DNA; and carrying out PCR amplification reaction and purifying a finished product to obtain a final high-throughput sequencing library. The method is not only simple, convenient and efficient, and is capable of avoiding a purification step and reducing DNA loss in a library construction process, but also can effectively solve a problem of linker self-linking which is easy to occur in a micro-DNA library construction process by virtue of a special linker and blunt end linking way; and meanwhile, by repairing the gap before amplification, sufficient complete templates are provided before amplification for the amplification reaction.
Owner:BEIJING MICROREAD GENE TECH
Adriamycin-loaded aptamer-modified DNA nanocage and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107050464APromote accumulationSmall toxicityOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAptamerTumor target
The invention discloses an adriamycin-loaded aptamer-modified DNA nanocage and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of medicine science and technology. Oligonucleotide sequences of MUC1 mucoprotein aptamers are modified onto four oligonucleotide sequences of a DNA regular tetrahedron structure through nucleotide sequence synthesis; and on the basis of a base complementation pairing rule, the stable DNA regular tetrahedron structure is formed through self-assembling under certain conditions, so that the DNA nanocage which is modified with different numbers of the MUC1 mucoprotein aptamers at various vertexes, and adriamycin is loaded through physical trapping so as to achieve a purpose of conducting targeting therapy of tumors. Experiments prove that the drug-loaded DNA nanocage can be formed through self-assembling of a nanocage nucleic acid skeleton, without the participation of complex preparation steps; efficient targeted intake of human breast cancer MCF-7 cells is achieved on the basis of a targeting effect of the MUC1 mucoprotein aptamers and a transmembrane transport property of the DNA nanocage; and meanwhile, the aptamers are protected from being degraded by nuclease in vivo; therefore, a novel drug-delivery system is provided for tumor-targeted delivery of chemotherapeutics.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Cationic carriers for nucleic acid delivery
InactiveUS20190336608A1Efficient deliveryGood effectOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryModified dnaIonophore
Compositions for nucleic acid delivery are provided which comprise a relatively low amount a permanently cationic lipid or lipidoid, such as a lipid comprising a quaternary ammonium group. The compositions are suitable for the delivery of chemically modified or unmodified DNA or RNA. Moreover, the compositions are suitable for local administration, such as by extravascular injection.
Owner:CUREVAC AG
DNA flexagon nano structure-nanogold biosensor based on adapter modification and preparing method and application of DNA flexagon nano structure-nanogold biosensor
ActiveCN104962615AExact Space AddressabilityOvercoming the disadvantages of poor autoimmunityMicrobiological testing/measurementNano structuringAutoimmunity
The invention discloses a DNA flexagon nano structure-nanogold biosensor based on adapter modification and a preparing method and application of the DNA flexagon nano structure-nanogold biosensor. The biosensor comprises DNA flexagon and nanogold, the DNA flexagon comprises an adapter nucleotide sequence of a detected object, and the nanogold is nanogold modified by a DNA fragment complementary with the adapter nucleotide sequence. The method includes the following beneficial effects that the DNA flexagon has the accurate space addressability, and the complicated marking step is avoided after the nanogold is added; an adapter can be synthesized in batch with a chemical method, so that the cost is greatly reduced; the shortcoming that the autoimmunity of micromolecule matter is poor is overcome; the DNA flexagon nano structure-nanogold biosensor has the lower detection limit, and LOD reaches the nanogram stage; an atomic force microscope and electrophoresis are adopted for conducting representation, qualitative and quantitative analysis is carried out by using the characteristic that the nanogold is high in light in an atomic force microscope height map; and compared with a traditional survey method, the advantages of being easy and convenient, reliable, lower in requirement for experiment conditions and the like are achieved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Method for orderly assembling DNA and graphene on gold electrode surface
InactiveCN104698055AImprove conductivityImprove electrochemical performanceMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansModified dnaElectrochemical biosensor
The invention relates to a new biosensing method for orderly assembling DNA and graphene quantum dots on a gold electrode surface through chemical bond combination, belonging to the field of a chemicobiological sensor. The method is characterized in that DNA-terminal modified amino groups and GQDs edge carboxy groups are subjected to addition reaction through EDC and NHS by adopting the property of carboxyl functional groups on the GQDs surface in the electrode modification process, thereby forming the stacked structure of DNA-GQDs-DNA. In comparison with original DNA / Au electrodes, modified DNA / GQDs / DNA / Au electrodes are excellent in conductivity and electrochemical performances, and can be used for measuring gene segments of Micro RNA and other specific sequences. The electrode modification method has the advantages that the manufacturing process is simple, the manufacturing cost is low, and besides, the electrodes can be conserved for a longer time in air, and thus the method is conveniently applied to research and actual detection.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Gene methylation detection method
InactiveCN104131070AImprove accuracyGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementReference genesDuplex pcr
The invention discloses a gene methylation detection method. The method comprises the steps of: subjecting a to-be-detected DNA sample, a negative control, a positive control and a no template control to PCR amplification reaction, with the DNA sample in the PCR amplification reaction being bisulfite modified DNA, carrying out duplex PCR amplification reaction on a detection gene and a reference gene, and interpreting a parameter range to judge the methylation condition of the detection gene of the to-be-detected DNA sample. By the mode, the gene methylation detection method provided by the invention has the advantages of strong specificity, duplex reaction, high sensitivity, small pollution, simple and quick operation, and safety, etc., and the detection result has good accuracy and repeatability. Thus, the method has certain auxiliary diagnosis effect on early detection of colorectal cancer and other cancers.
Owner:JIANGSU MICRODIAG BIOMEDICINE TECH CO LTD
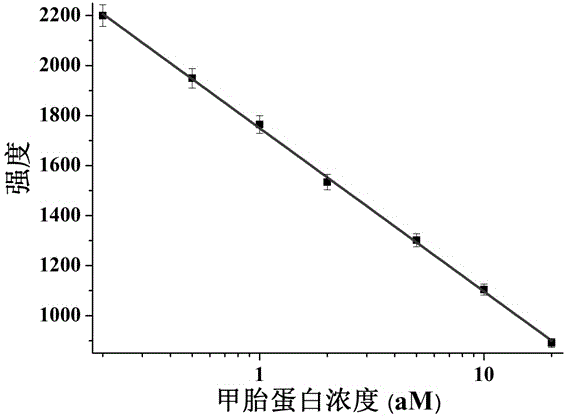
Method for super-sensitively detecting alpha fetalprotein based on surface enhanced raman scattering effect of silver nanoparticle tripolymer
ActiveCN104931478AStrong plasmon resonanceLow detection limitRaman scatteringModified dnaAlpha-fetoprotein
The invention provides a method for super-sensitively detecting alpha fetalprotein based on the surface enhanced raman scattering effect of a silver nanoparticle tripolymer and belongs to the technical field of analytical chemistry. The method comprises the following steps: synthetizing silver nanoparticles with the grain sizes of 15 nm, modifying DNA by the silver nanoparticles, assembling the silver nanoparticle tripolymer, and conducting TEM characterizing and raman signal testing on the silver nanoparticle tripolymer. The silver nanoparticle tripolymer is assembled for the first time, and has a strong raman signal, the raman signal changes after the alpha fetoprotein is added, and the quick super-sensitive detection of the alpha fetalprotein is achieved by the change of the raman signal.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
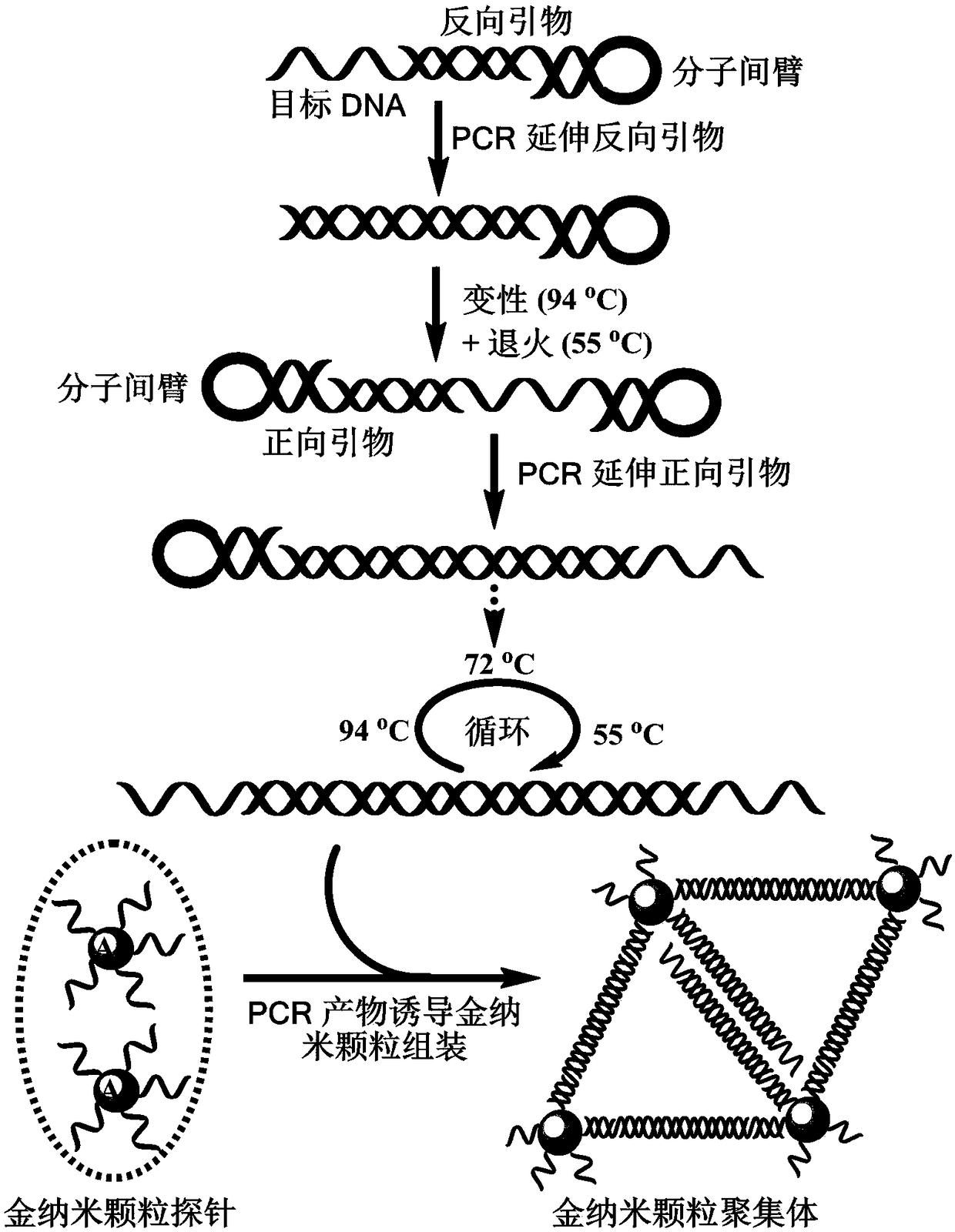
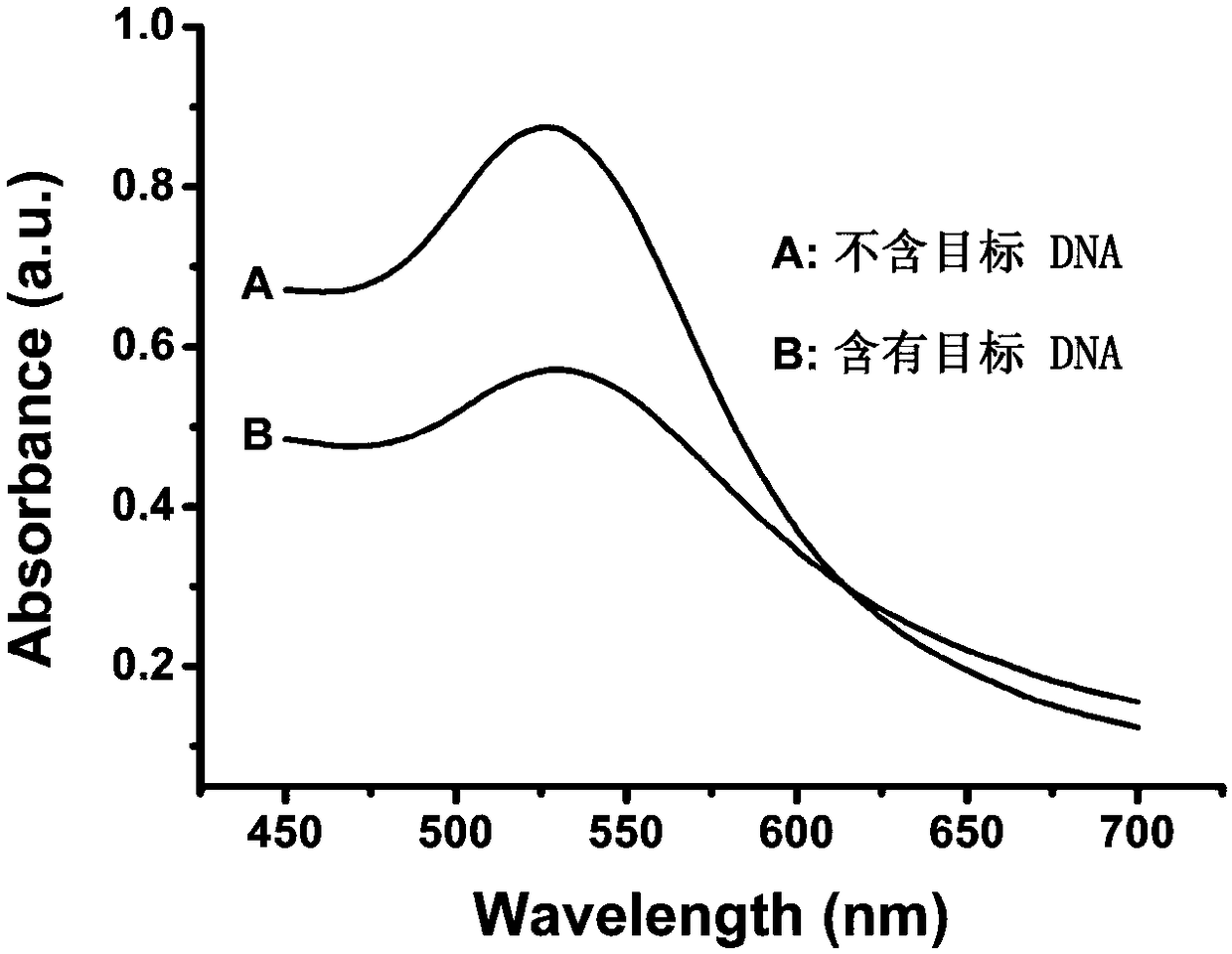
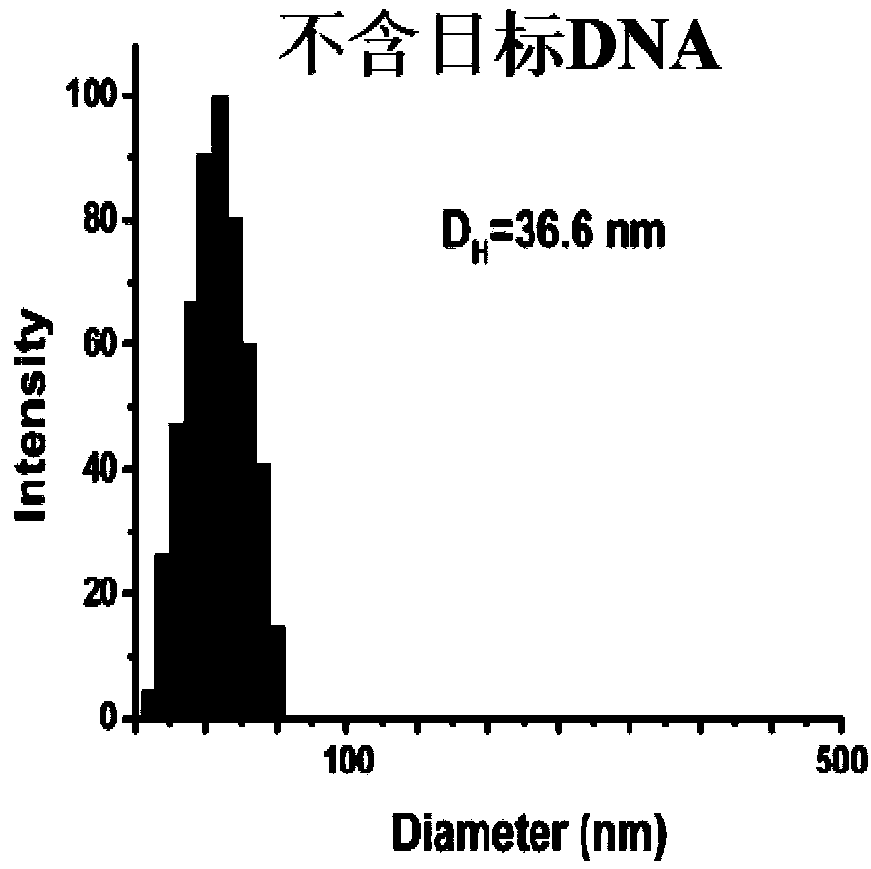
Quantitative PCR detection method based on gold nanoparticles
ActiveCN108342459ARealize highly sensitive quantitative analysisEfficient detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationModified dnaDynamic light scattering
The invention provides a design method of amplification primers. The design method is characterized in that the amplification primers adopting hairpin structures are designed and single-stranded DNA fragments are formed at the two ends of an amplification product. The invention provides two gold nanoparticle probes; DNA sequences modified by the probes are complementary to the single-stranded DNAfragments at the two ends of a PCR product of DNA to be detected. The invention provides a quantitative PCR detection method based on gold nanoparticles. The quantitative PCR detection method comprises the following steps: (1), selecting a DNA sequence to be detected, and designing a pair of specially-structured amplification primers, wherein the pair of specially-structured amplification primersare designed to be the hairpin structures; (2), performing a PCR reaction in a system containing a DNA template to be detected, the pair of specially-structured amplification primers, Taq DNA polymerase and dNTP to obtain the PCR product; (3), preparing DNA-modified gold nanoparticle probes; (4), adding the probes into the PCR product, and hybridizing with the PCR product; (5), measuring the change of the absorbance or a dynamic light scattering signal of the gold nanoparticles. With the quantitative PCR detection method, the operation is simple, the PCR product can be rapidly detected, and the sensitivity is high.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
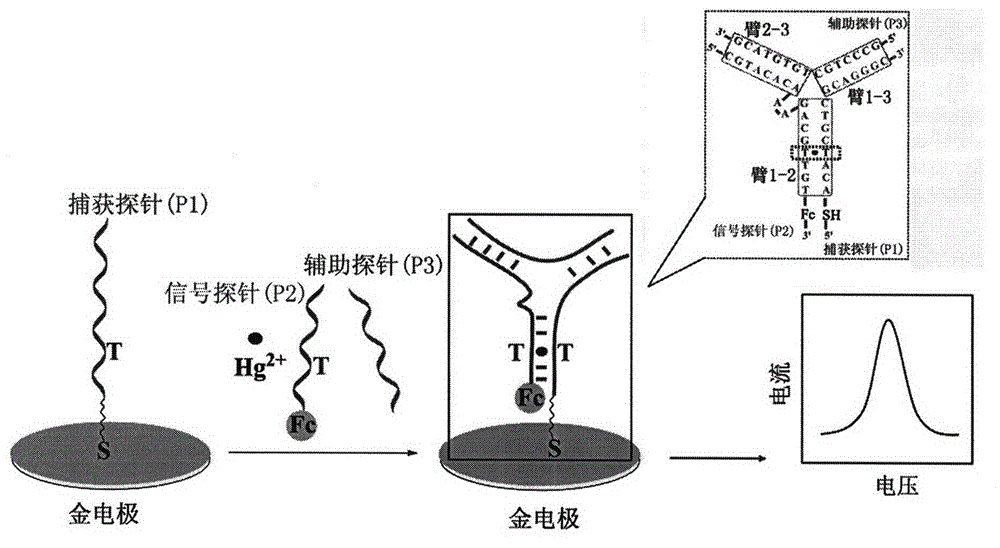
High-sensitivity and high-selectivity metal mercury ion electrochemical sensor
ActiveCN104569085AHighly Selective Electrochemical DetectionFast deliveryMaterial electrochemical variablesModified dnaFerrocene
The invention relates to a high-sensitivity and high-selectivity metal mercury ion (Hg<2+>) electrochemical sensor. Based on an Au-S bonding effect, an Hg<2+>electrochemical sensor interface is constructed by self-assembling a sulfydryl-modified DNA capturing probe on the surface of a gold electrode. A synergetic hybrid effect can be generated by the strong affinity effect between thymine (T) of DNA and the Hg<2+> when the Hg<2+>, a DNA auxiliary probe and an electrochemical active molecule ferrocene (Fc) modifying DNA signal probe coexist; and a three-arm DNA Y-shaped structure is formed on the surface of the gold electrode so that an Fc molecule is close to the surface of the electrode. The size of oxidization current of the Fc is directly detected so that the concentration of the Hg<2+> in a solution is determined. The single Hg<2+> can be induced on the surface of the electrode to form one DNA Y-shaped structure so that the sensitivity and selectivity for detecting the Hg<2+> are very high. The sensor can be simply prepared, has short analysis time and good repeatability, is easy to update, and can be applied to the fields of environment monitoring, food safety and the like very well.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Modificatory DNA incision enzyme and its application method
Compositions and methods are provided that relate to a modified DNA cleaving enzyme having at least 35% amino acid sequence identity with T7 Endo I. The modifed enzyme includes two catalytic centers separated by a beta-bridge where the beta-bridge contains at least one mutation having an effect of altering enzyme cleavage activity compared to the unmodified enzyme. Activities associated with the modified DNA cleaving enzyme that can be modulated in different reaction conditions include at least one of: (a) non-sequence specific nicking activity; (b) cleaving the second strand of a duplex DNA at a preexisting nick site to produce a linear duplex with a single strand overhang; (c) non-sequence specific DNA cleavage; (d) cleaving DNA flanking a mismatch; and (e) cleavage at a cruciform structure in a DNA duplex.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
AC Impedance-Type DNA Electrochemical Sensor Based on Probe DNA Controlled Assembly Interface
InactiveCN102286371ALower impedanceSlow transfer rateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBovine serum albuminDna assembly
The invention discloses an alternating current impedance type deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) electrochemical sensor based on a probe DNA control assembly interface, which comprises an electrode and capture probe DNA, wherein the electrode adopts a gold electrode, and the capture probe DNA adopts sulfydryl modified DNA. The alternating current impedance type DNA electrochemical sensor is characterized in that the sulfydryl modified DNA is modified onto the surface of the gold electrode through the chemical bonding effect of Au-S bonds with the gold electrode at the room temperature and the absorption effect of the probe basic group parts and the gold so that the capture probe DNA flatly lies on the surface of the gold electrode for forming a capture probe DNA assembly layer, and bovine serum albumin exists on the surface of the capture probe DNA assembly layer and is used as sealing agents and protection agents. The impedance change before and after the hybridization is used as indicationsignals, the method adopts the surface assembly chemical technology for building the flat lying type DNA probe identification interface, simultaneously, the form of the probe maintains the flat lyingstate on the surface of the electrode without being influenced by the blank hybrid condition, and the method has the characteristics of high sensitivity, good specificity and the like.
Owner:FUJIAN MEDICAL UNIV
Targeting nano carrier bearing nucleoside anti-tumor drugs and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN109224080AGood biocompatibilityPromote degradationPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsHigh cellTumor target
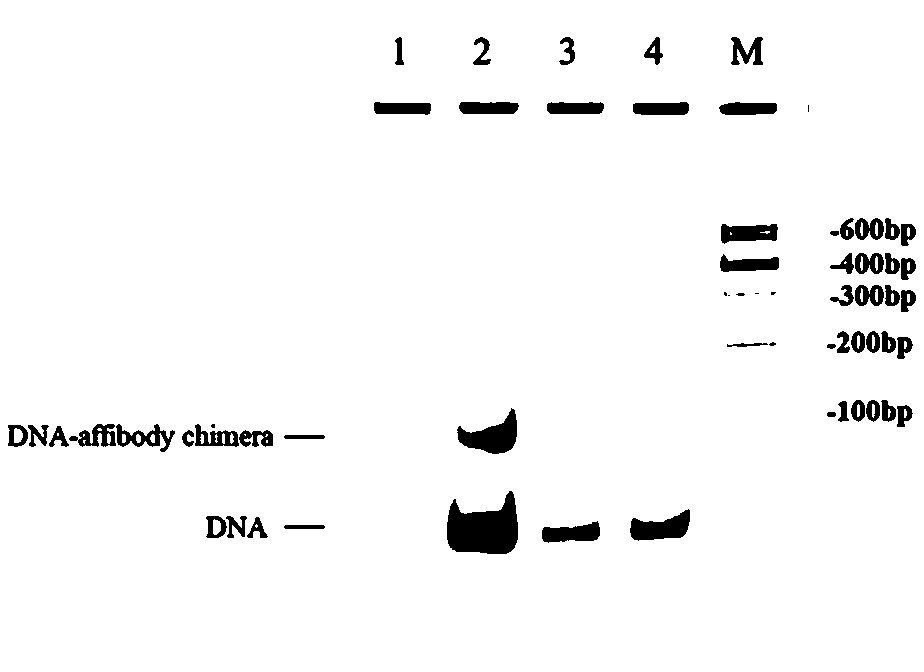
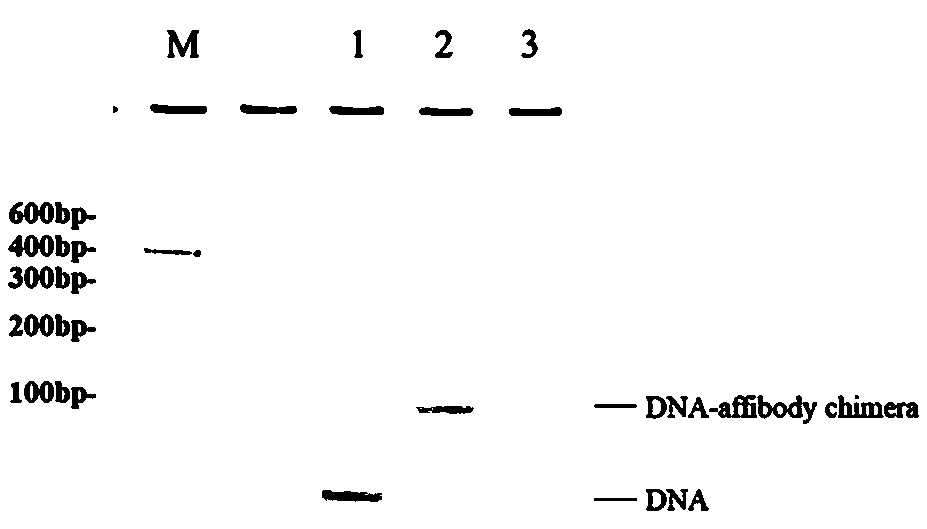
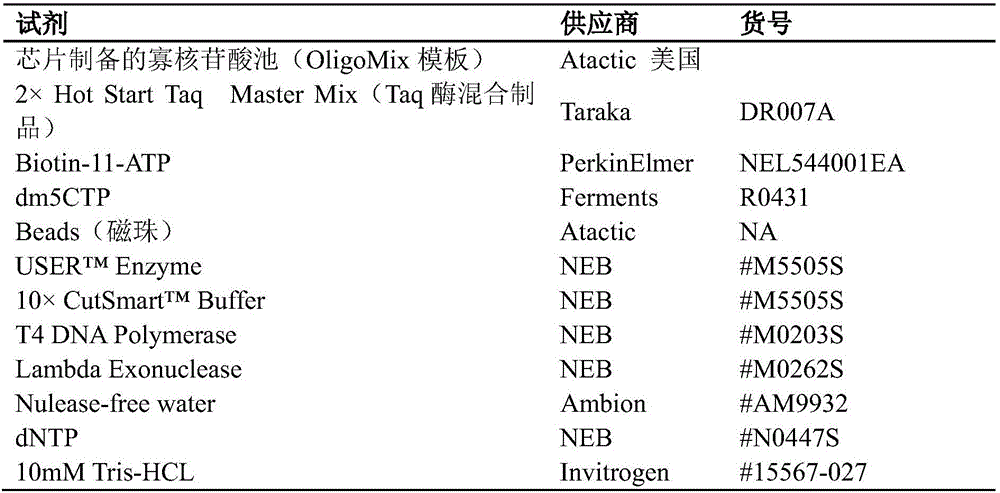
The invention provides a targeting nano carrier bearing nucleoside anti-tumor drugs and preparation method and application thereof. The targeting nano carrier comprises DNA tetrahedron, Affibody molecule and nucleoside anti-tumor drugs. The preparation method comprises the following steps: a, the nucleoside anti-tumor drugs are modified with phosphoramidite; B, synthesizing four DNA single strandsby DNA solid phase synthesis technology, integrating the nucleoside anti-tumor drugs into the 5 'ends of the four DNA single strands, and modifying NH2 at the 3' ends of one of the DNA single strands; C, linking the affibody molecule to the 3 'end of the NH2-modified DNA single strand through a linker; (d) mix and assembling that four DNA single strand in a molar ratio of 1: 1: 1: 1 to obtain DNAtetrahedron; and (d) assembling the four DNA single strands in a molar ratio of 1: 1: 1 to obtain DNA tetrahedron; Affibody targeting nanoparticles. The targeting nano carrier of the invention can precisely control the combined quantity of drugs, has faster tumor targeting ability and higher cell, tissue penetration ability, good pharmaceutical effect, and is suitable for popularization and application.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of modified DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) hybridization probe for targeted hybrid capture
ActiveCN105647907AImprove bindingLow environmental requirementsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationHybridization probeEnzyme digestion
Owner:HANGZHOU LC BIOTECH
Method for Achieving High-Level Expression of Recombinant Human Interleukin-2 Upon Destabilization of the Rna Secondary Structure
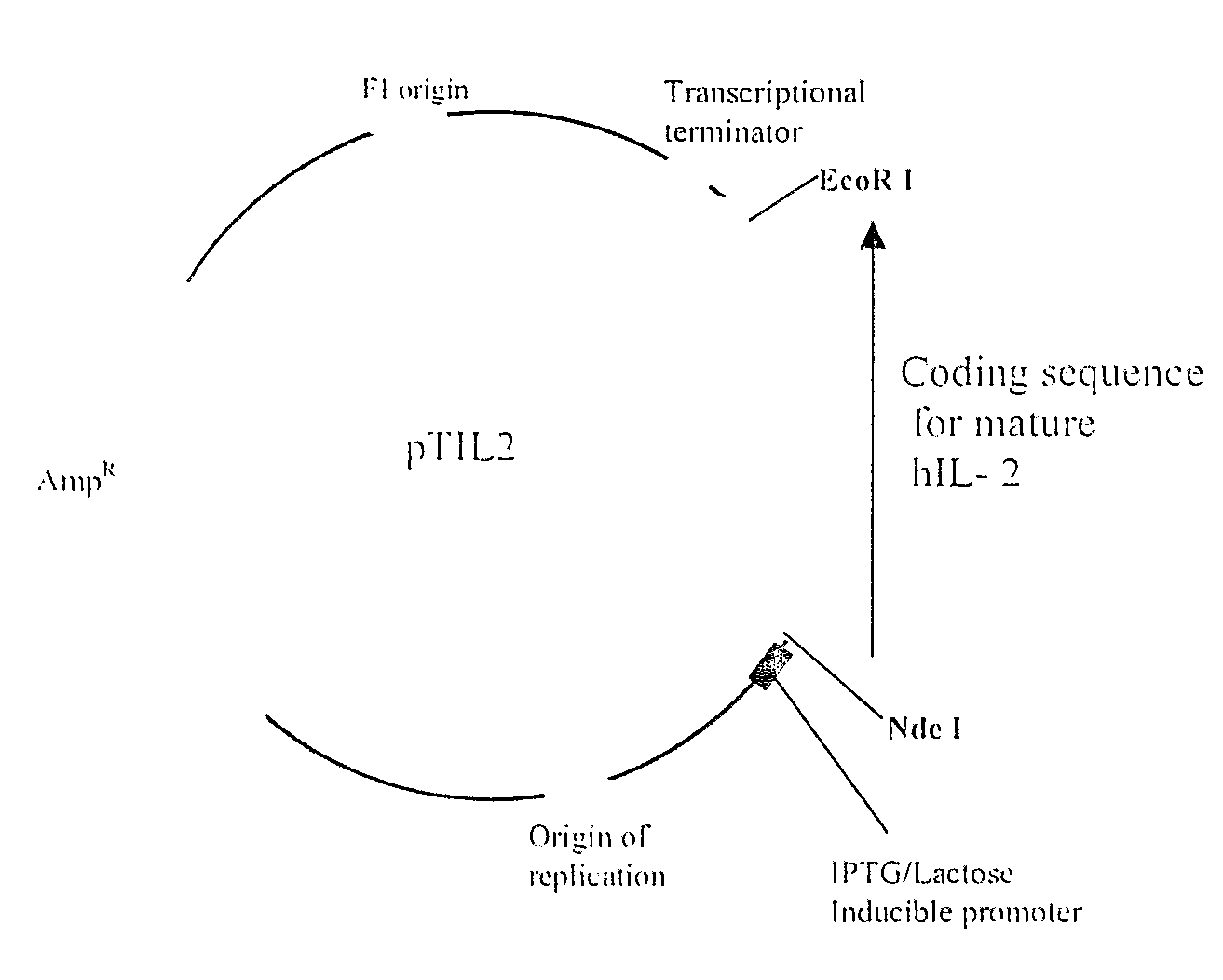
InactiveUS20080268503A1Increase free energyMass productionFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionHigh level expressionFactor ii
The present invention provides a method for achieving high-level expression of the therapeutically important lymphokine (human IL-2). The method comprises of identifying the secondary structure in the 5′ region of human IL-2 mRNA, modifying the 5′ region of the human IL-2 DNA sequence to produce a new DNA sequence wherein the mRNA transcribed from the modified human IL-2 DNA sequence has the predicted 5′ secondary structure destabilized with increased free energy compared to that of the secondary structure of the mRNA transcribed from the native DNA sequence without altering the sequence of the encoded amino acids; and using this modified DNA sequence of human IL-2 for high level recombinant expression in a microbial host for large scale production. This method is also applicable to other expression host like yeasts and mammalian cells.
Owner:ZENOTECH LAB LTD
TNF binding proteins
InactiveUS7238776B2Improve adverse effectsBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsModified dnaHost organism
The present invention provides DNA sequences coding for a TNF-binding protein and for the TNF receptor of which this protein constitutes the soluble domain. The DNA sequences can be used for preparing recombinant DNA molecules in order to produce TNF-binding protein and TNF receptor. Recombinant TNF-binding protein is used in pharmaceutical preparations for treating indications in which TNF has a harmful effect. With the aid of the TNF receptor or fragments thereof or with the aid of suitable host organisms transformed with recombinant DNA molecules containing the DNA which codes for the TNF receptor or fragments or modifications thereof, it is possible to investigate substances for their interaction with the TNF receptor and / or for their effect on the biological activity of TNF.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com