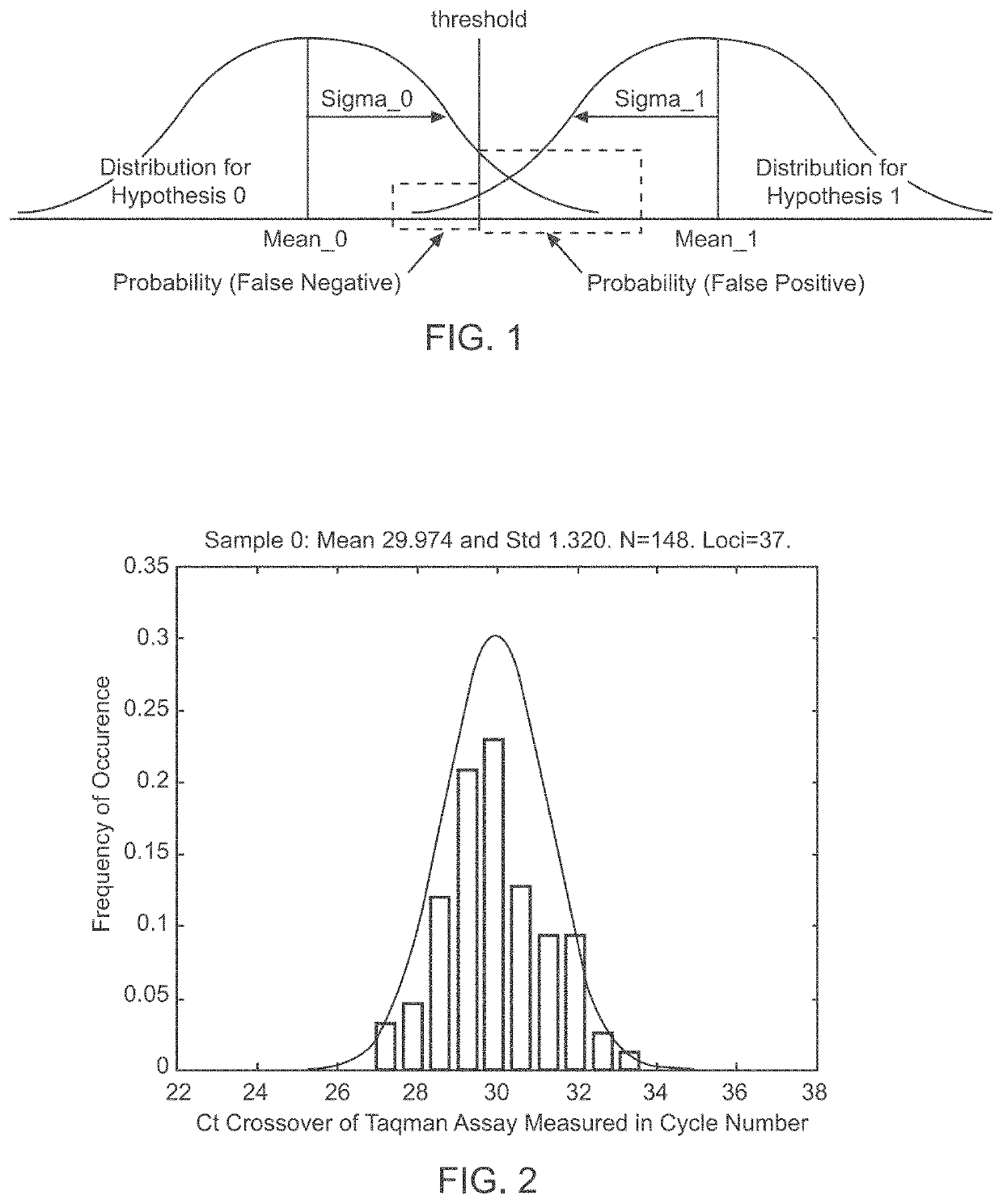
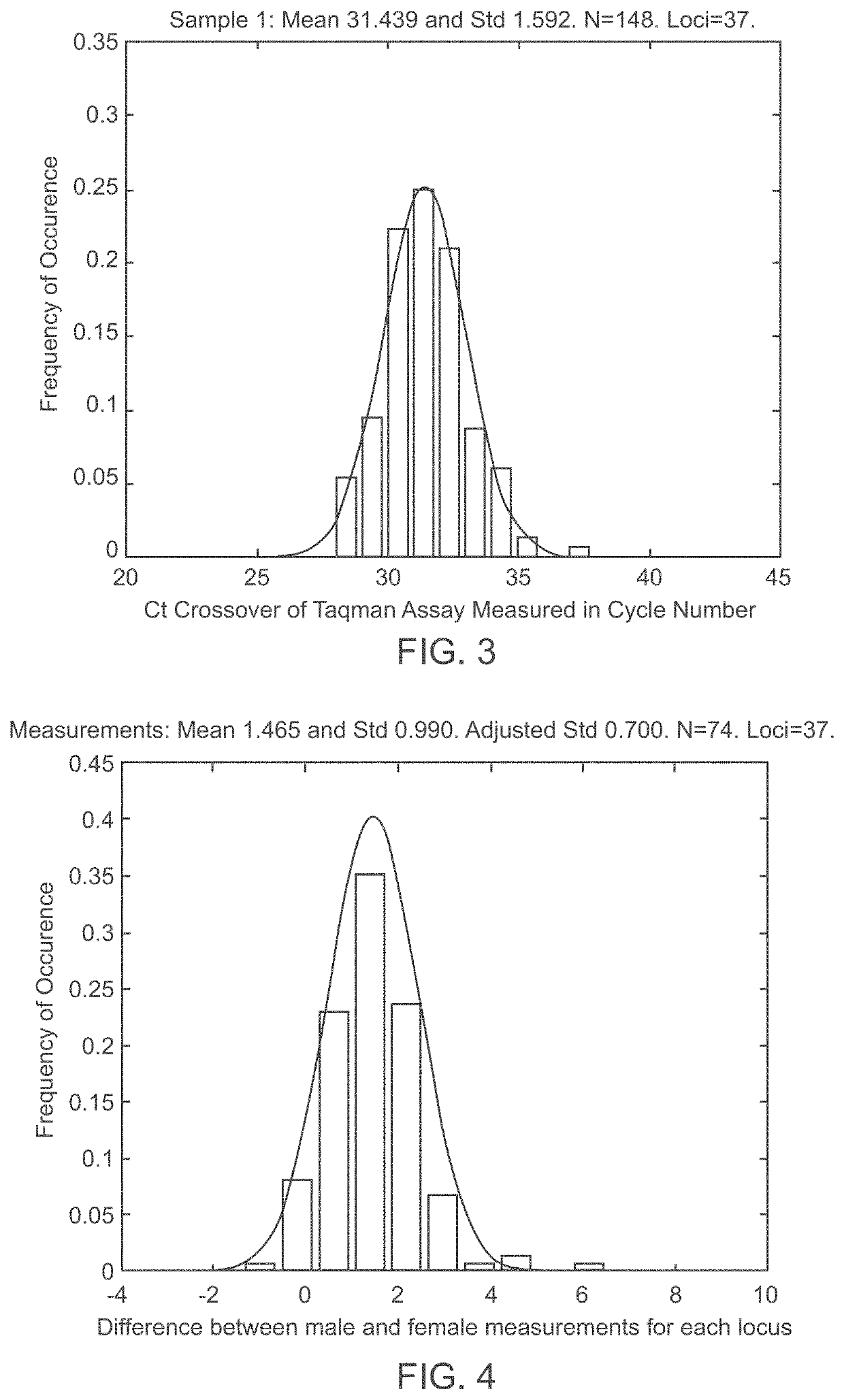
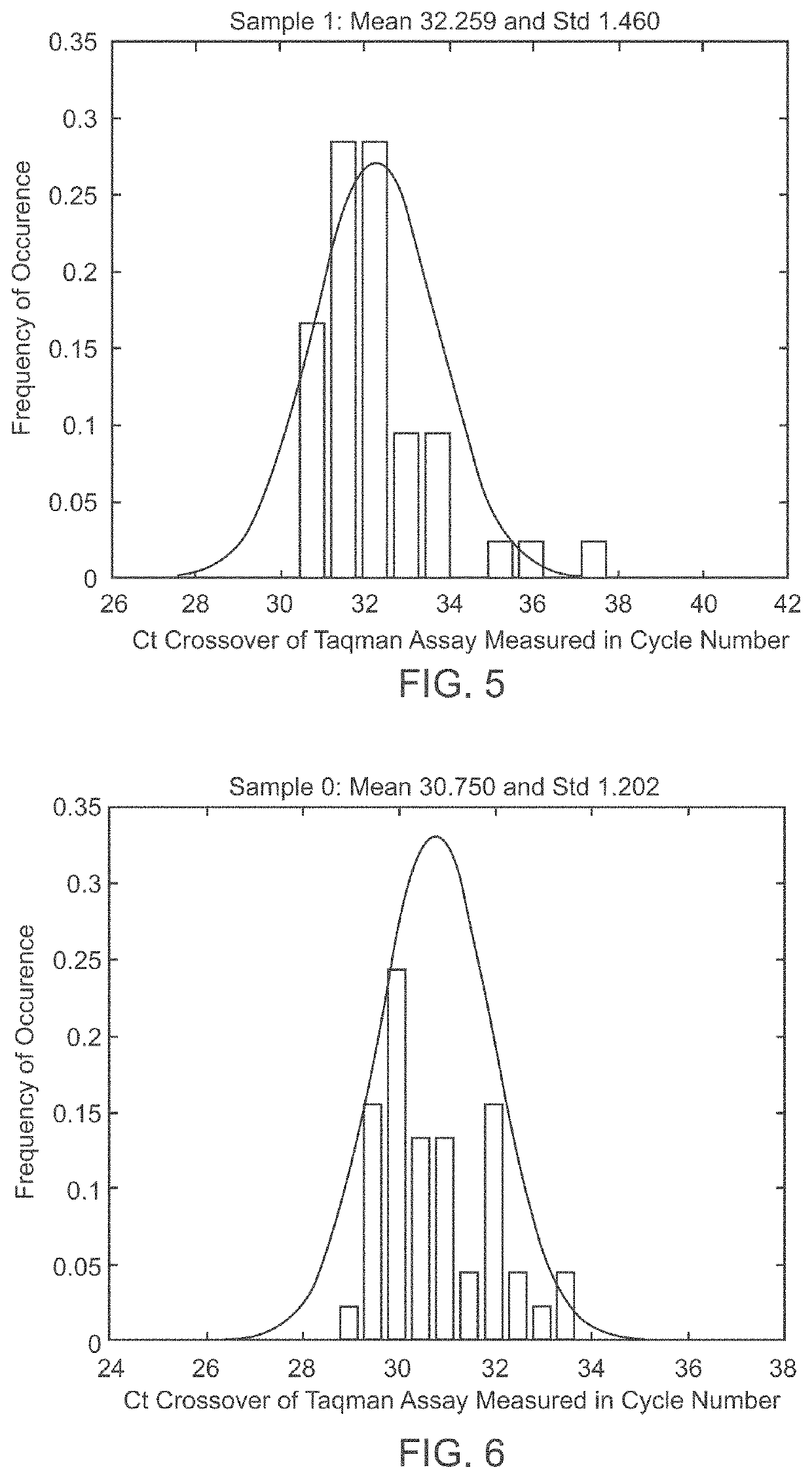
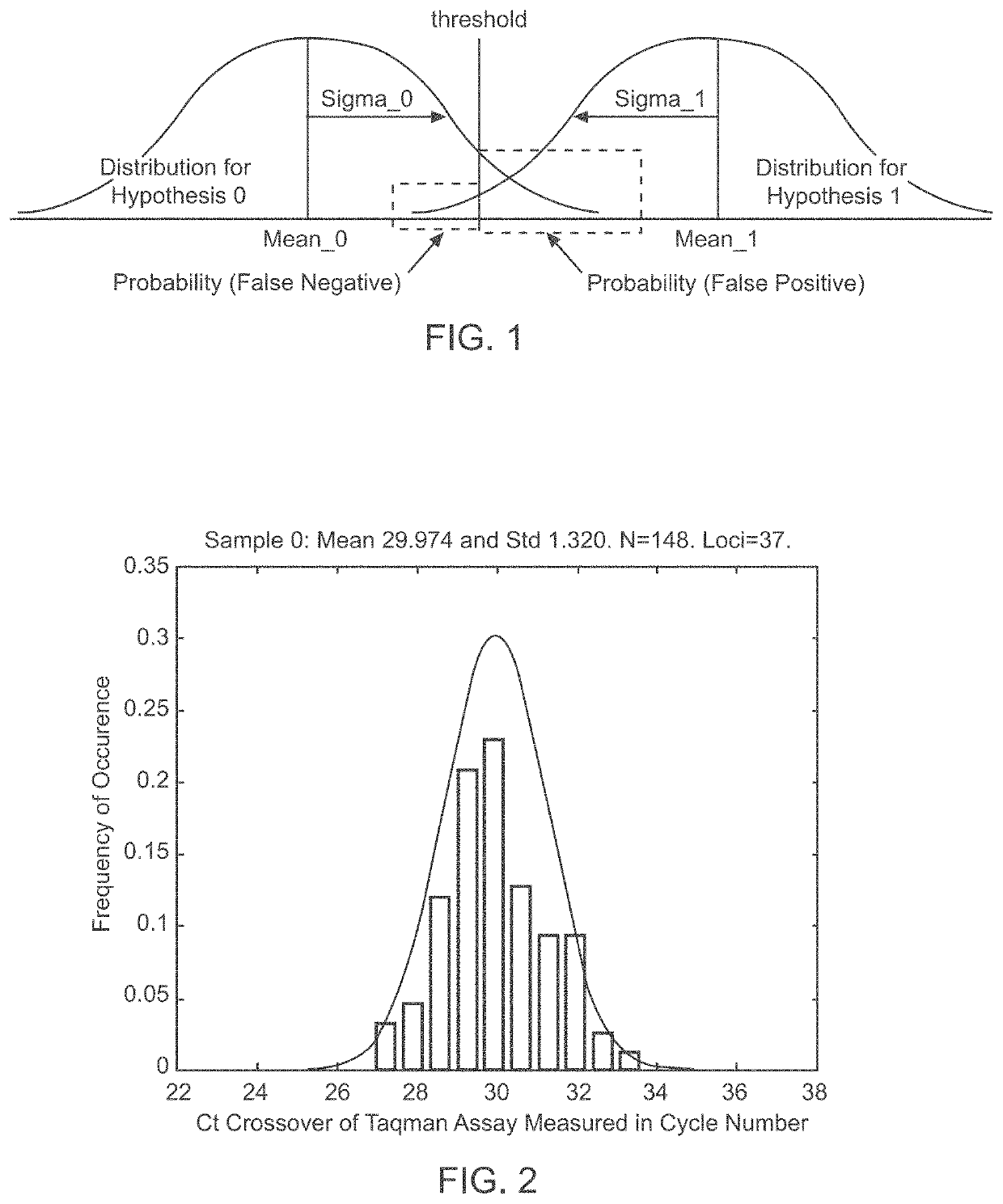
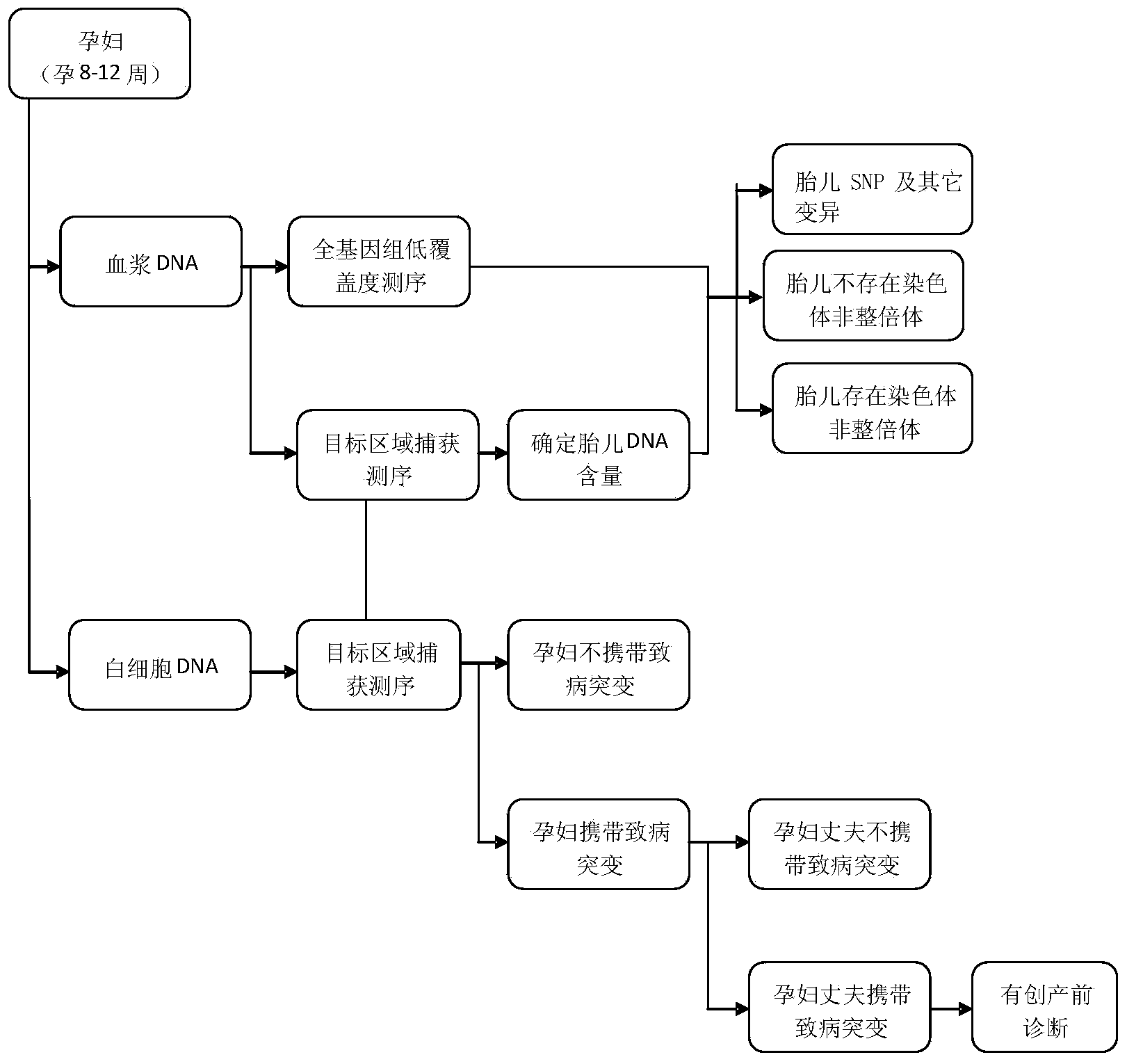
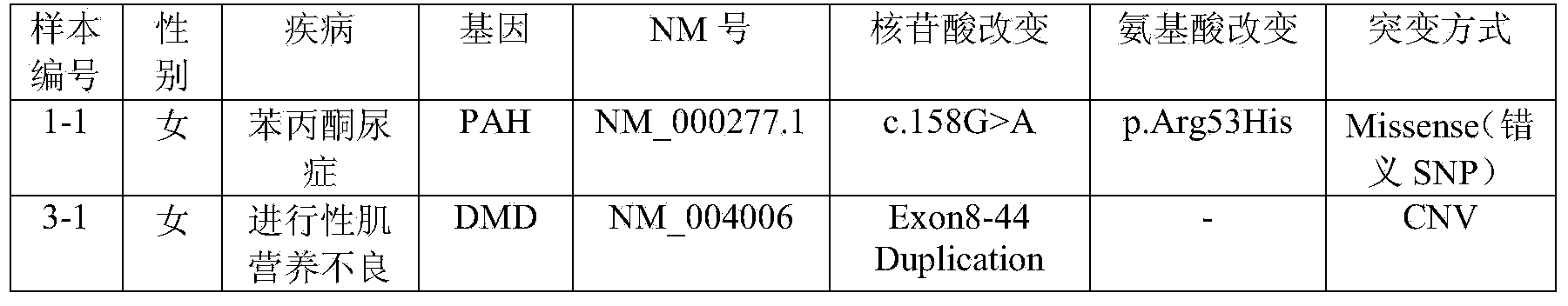
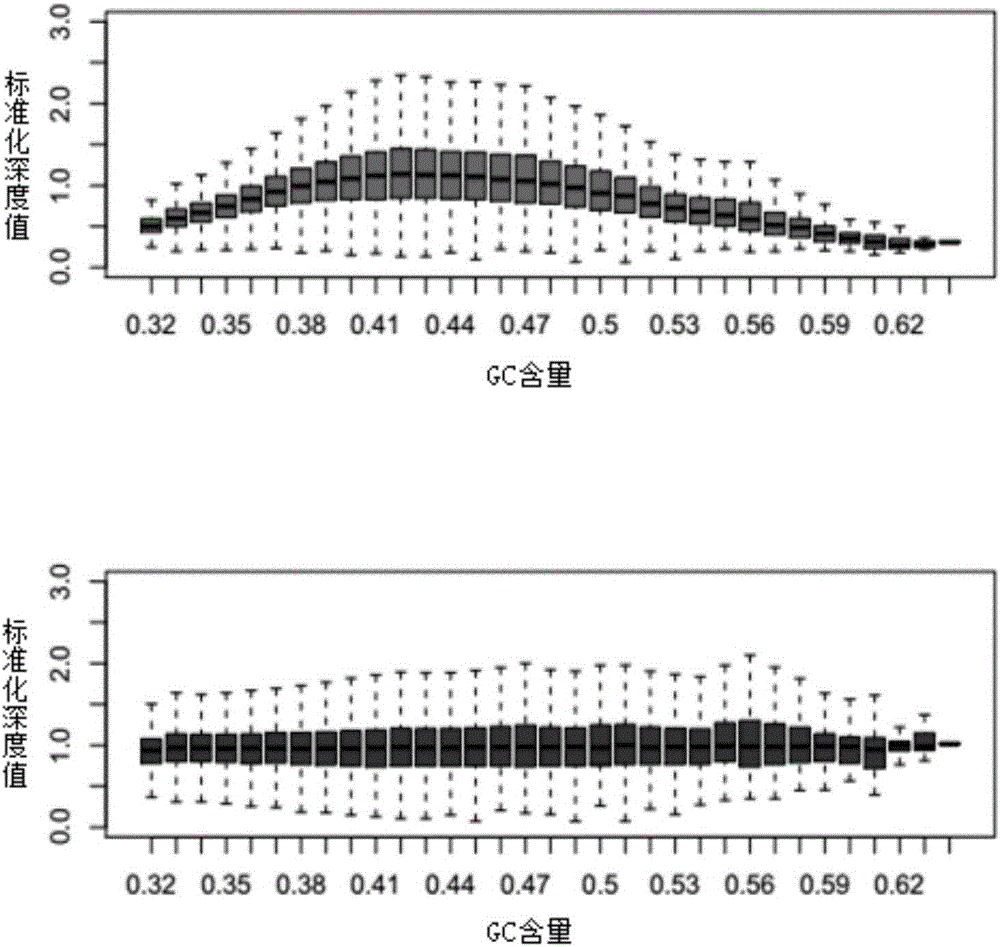
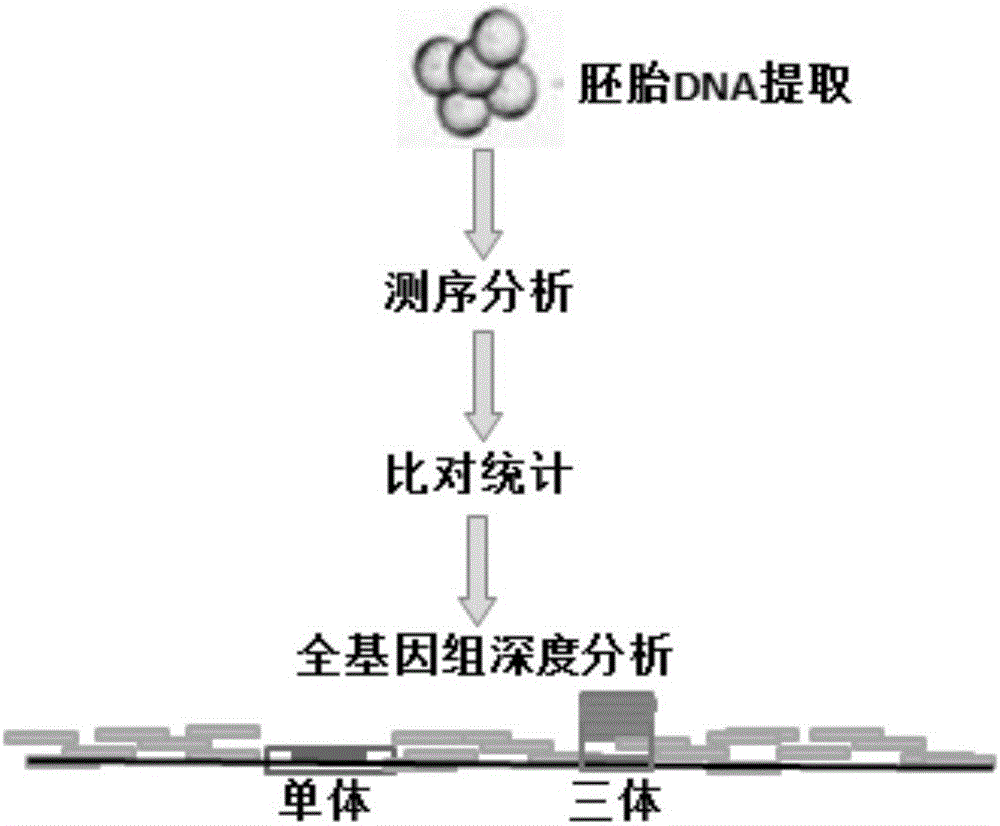
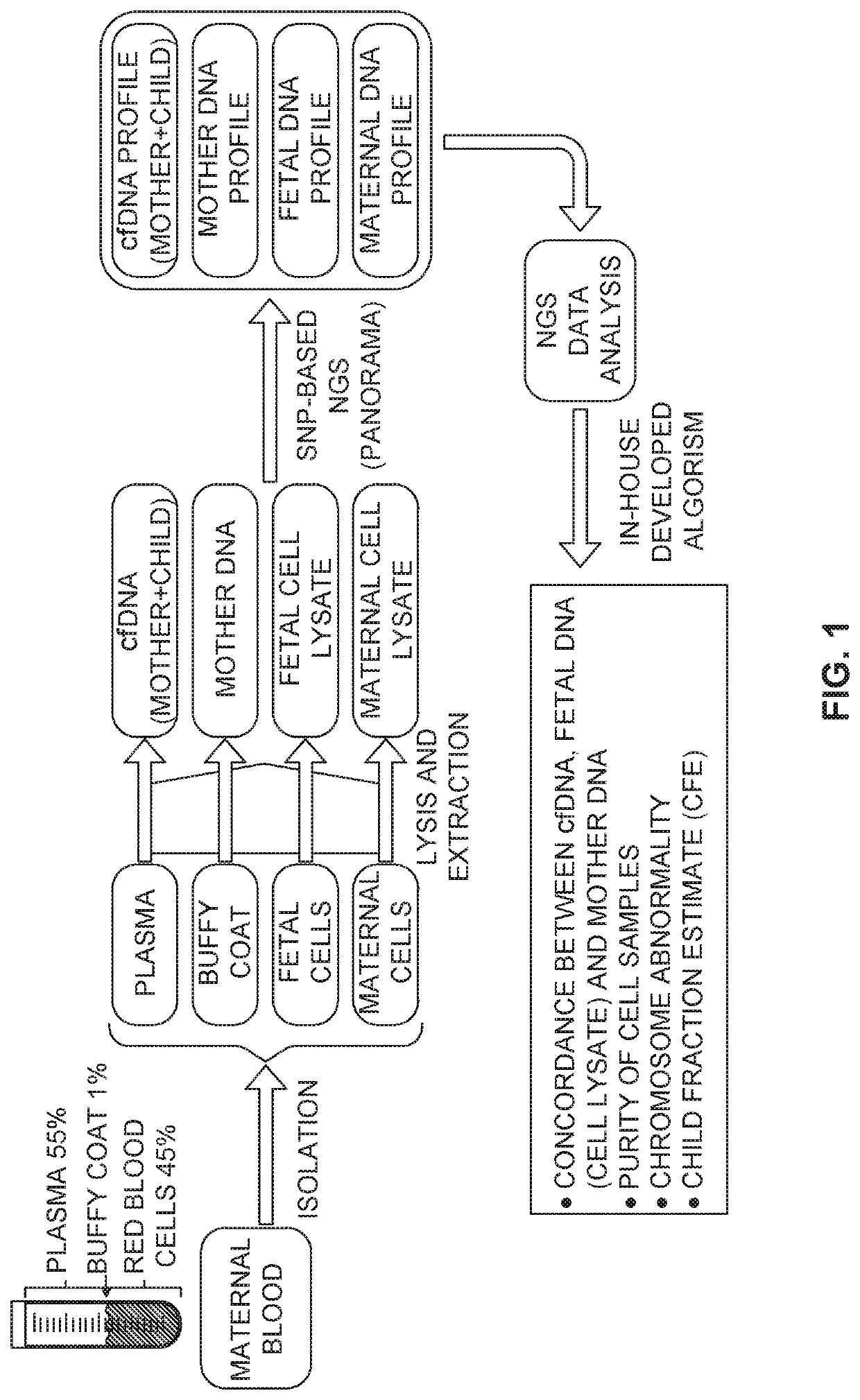
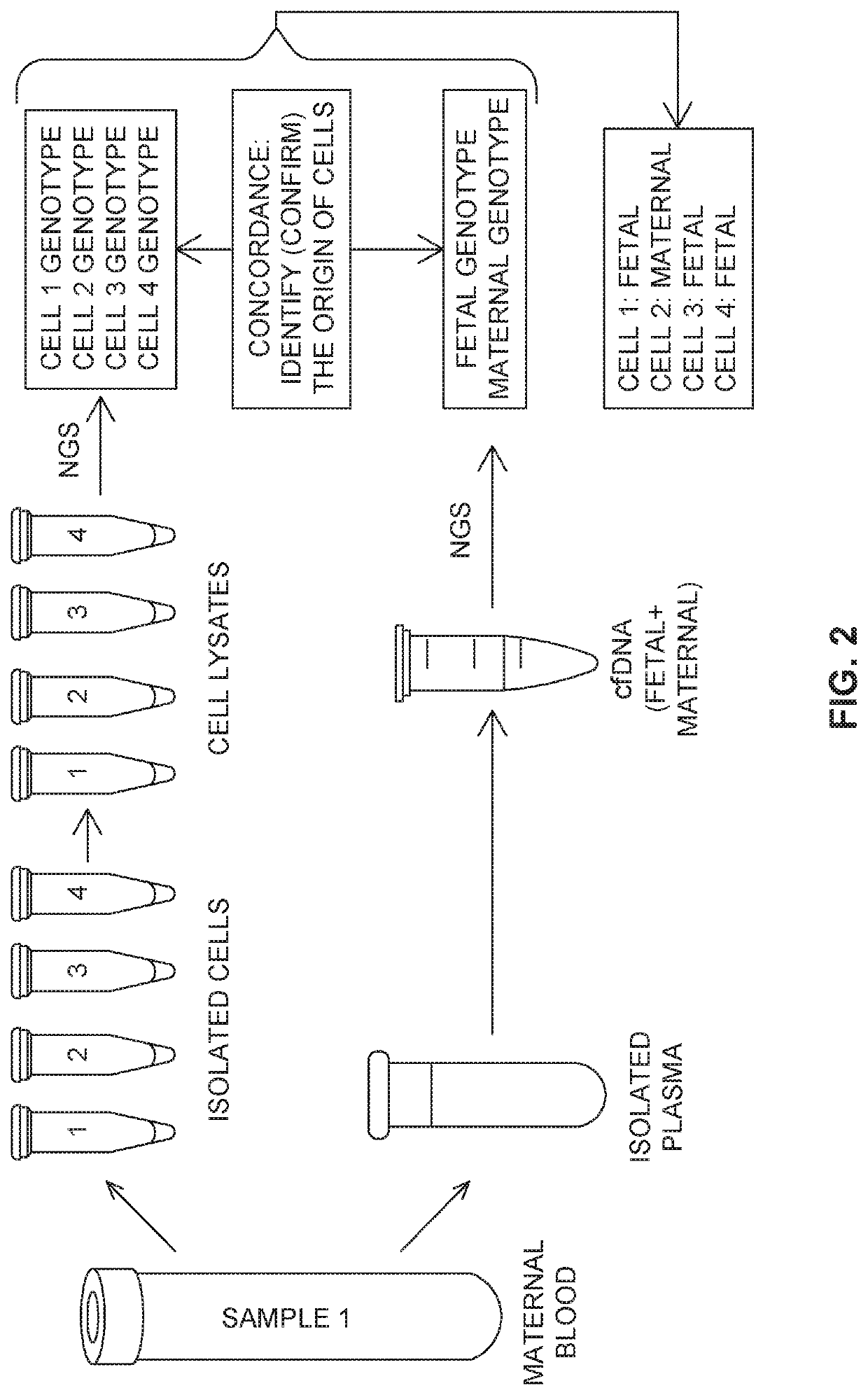
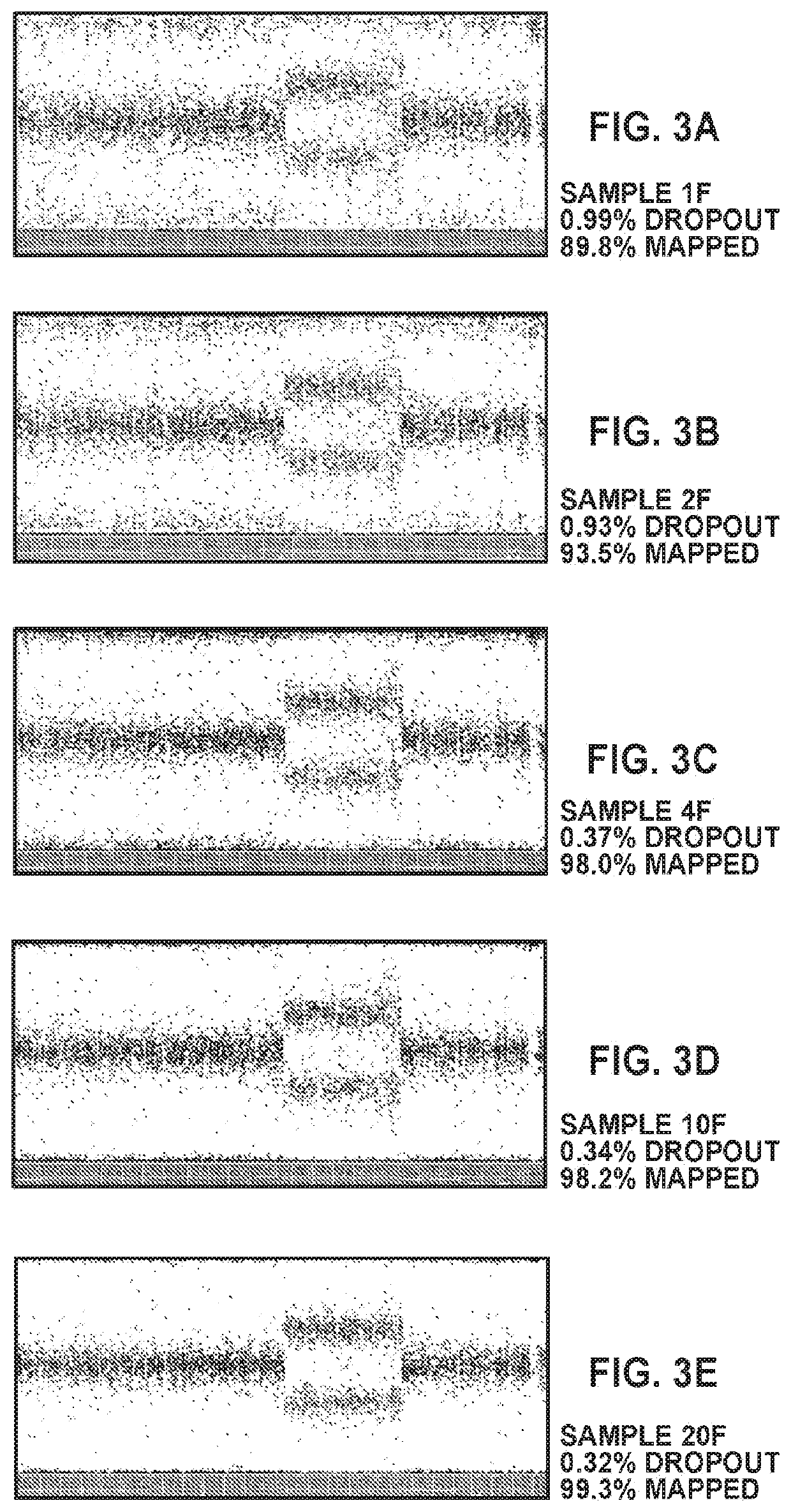
Patents
Literature
129 results about "Aneuploidy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
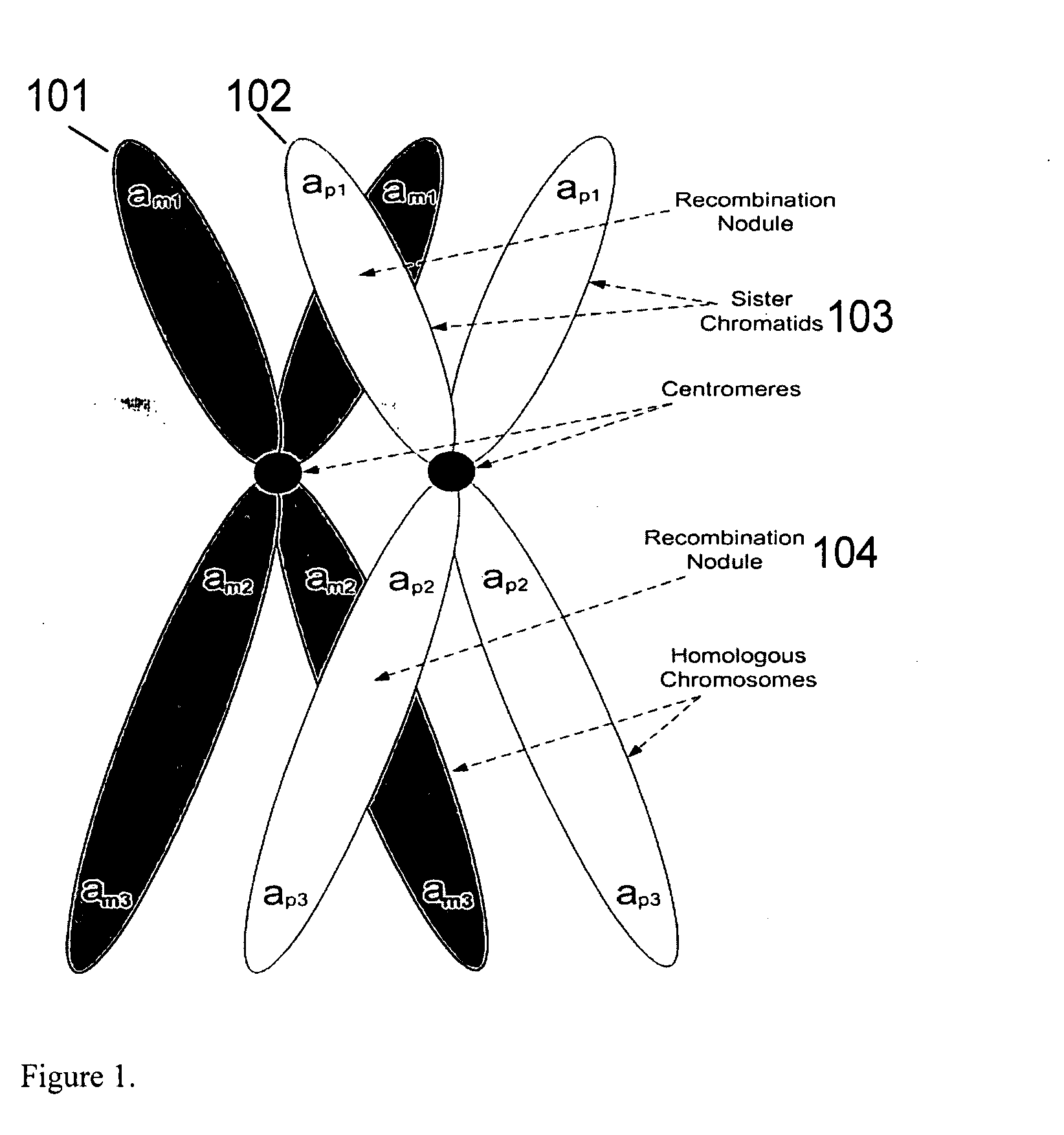
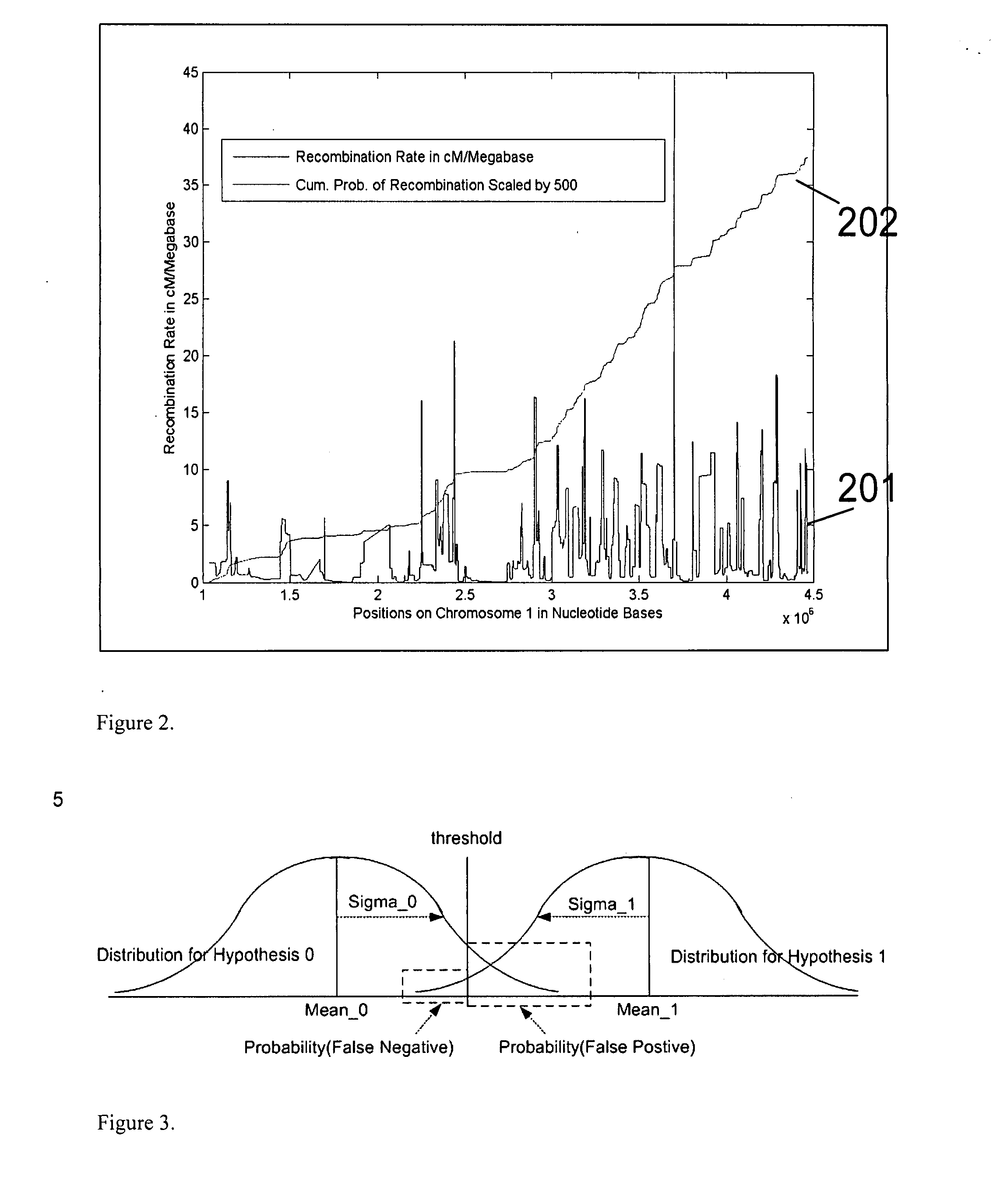
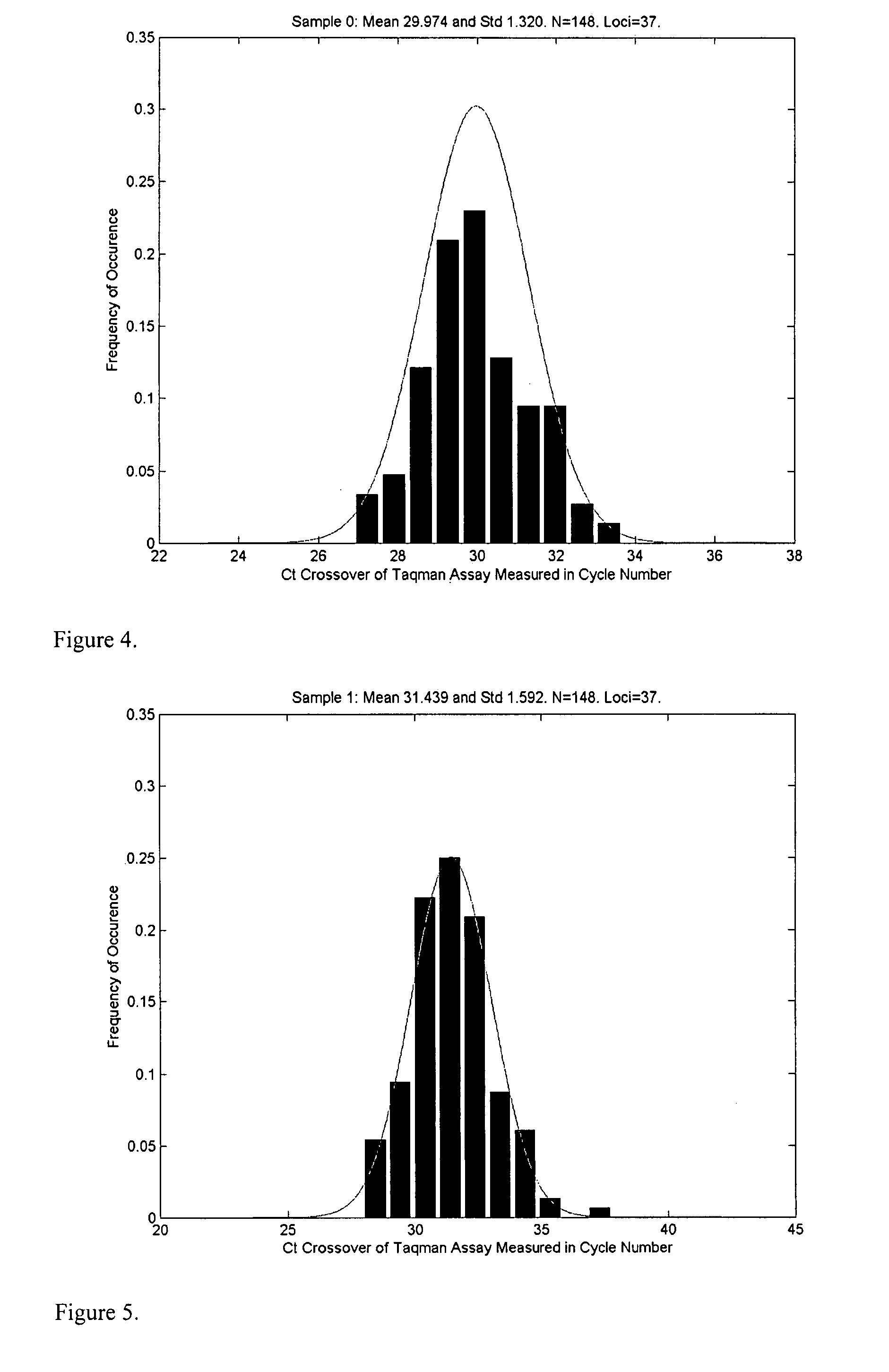
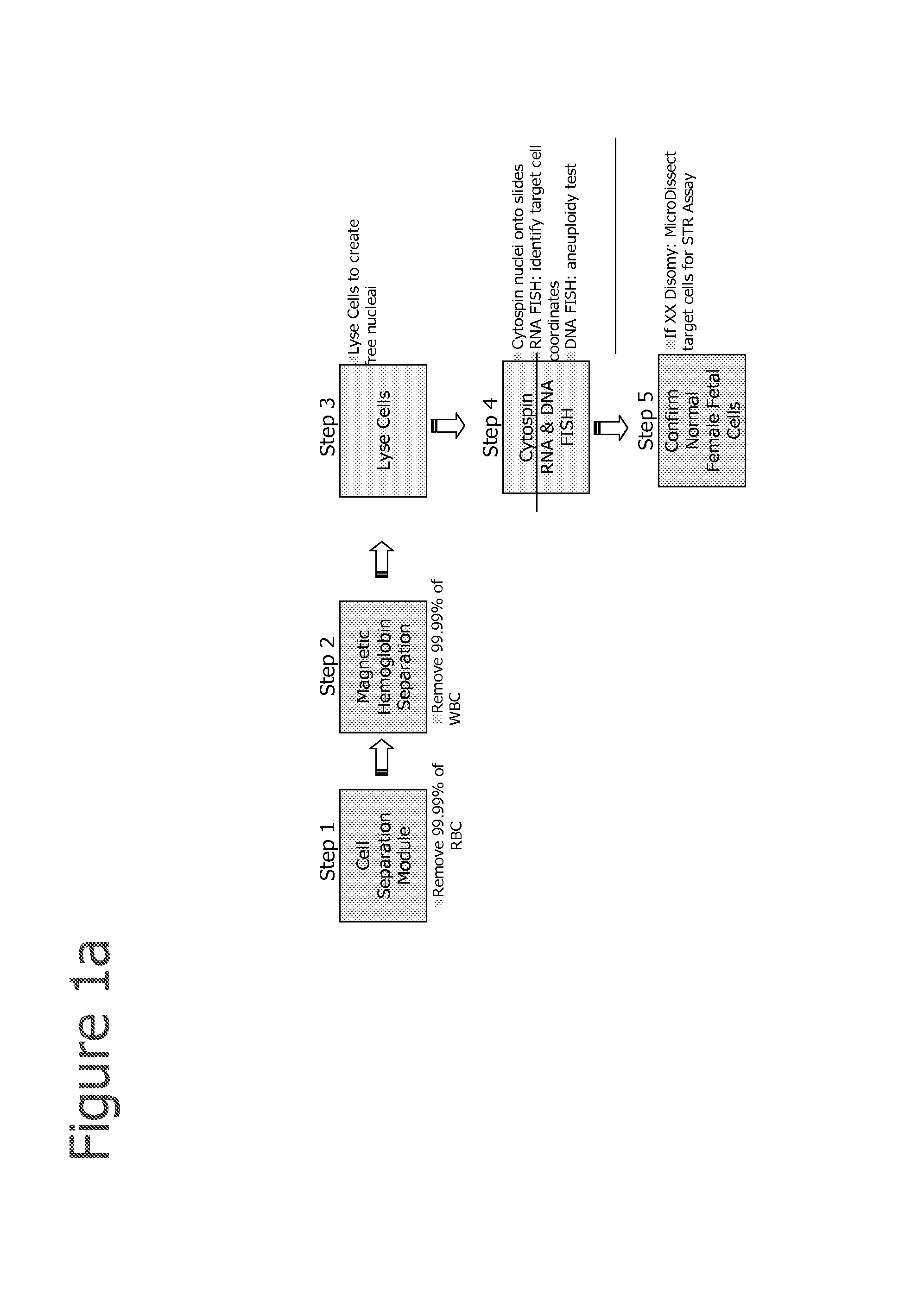
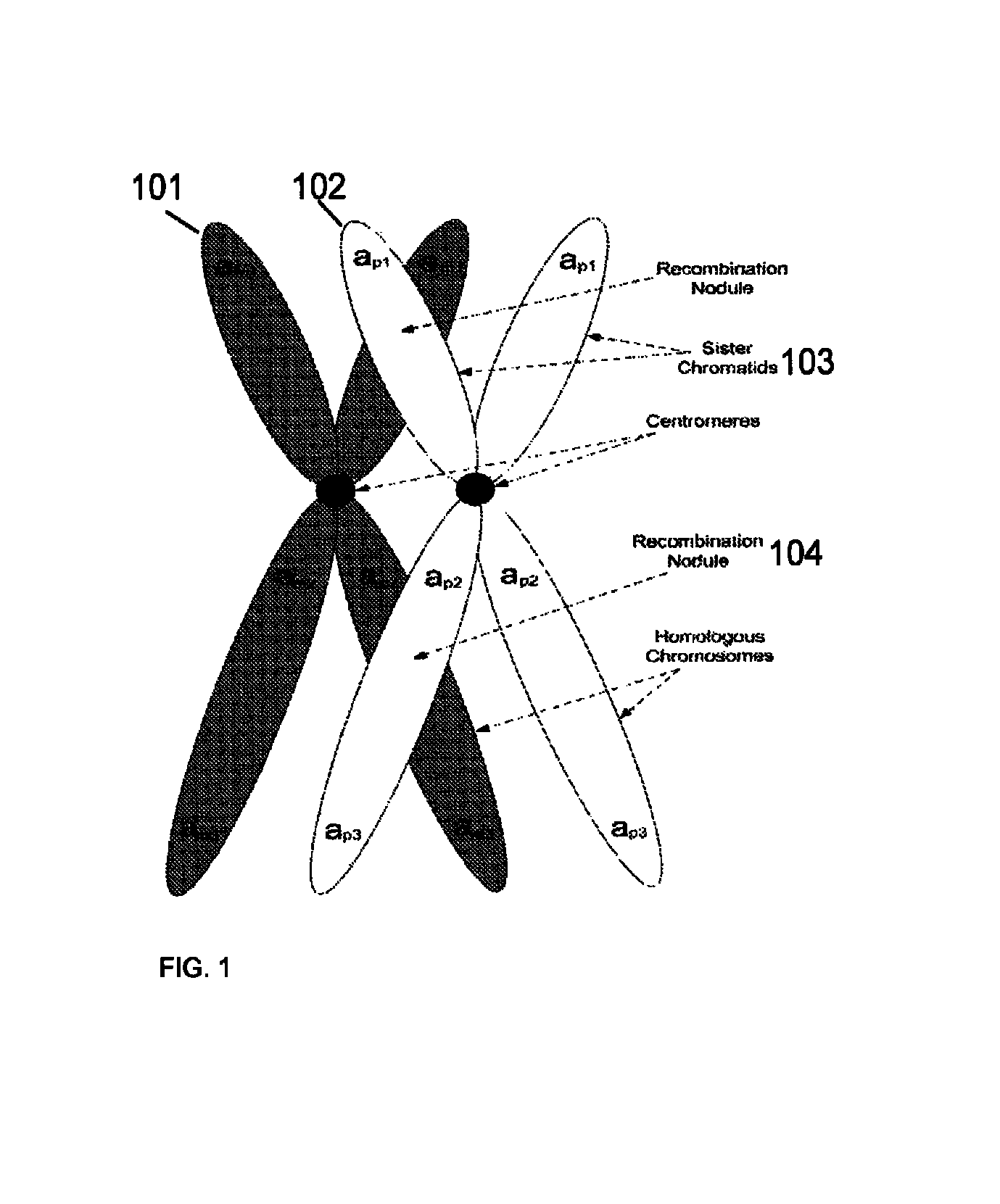
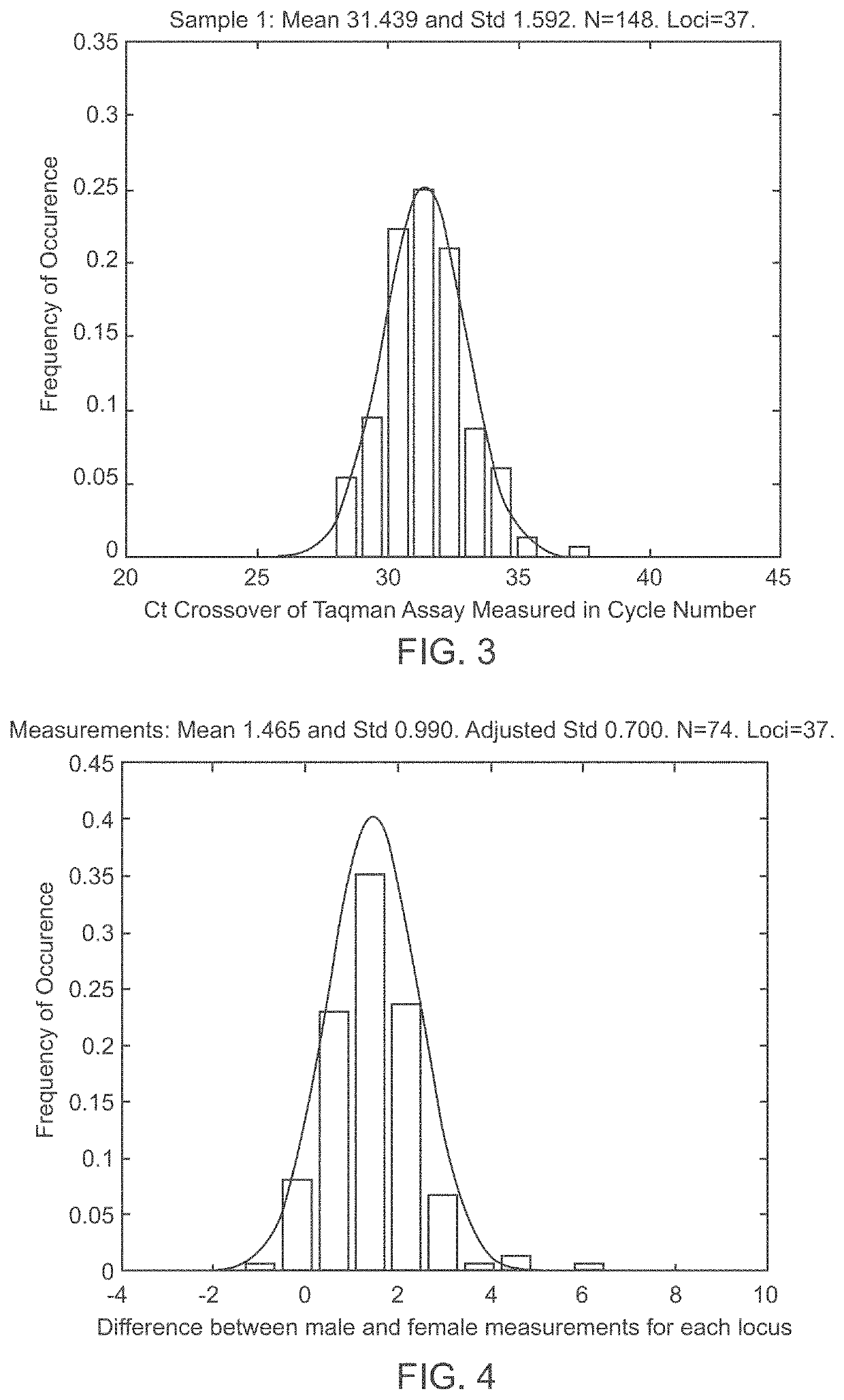
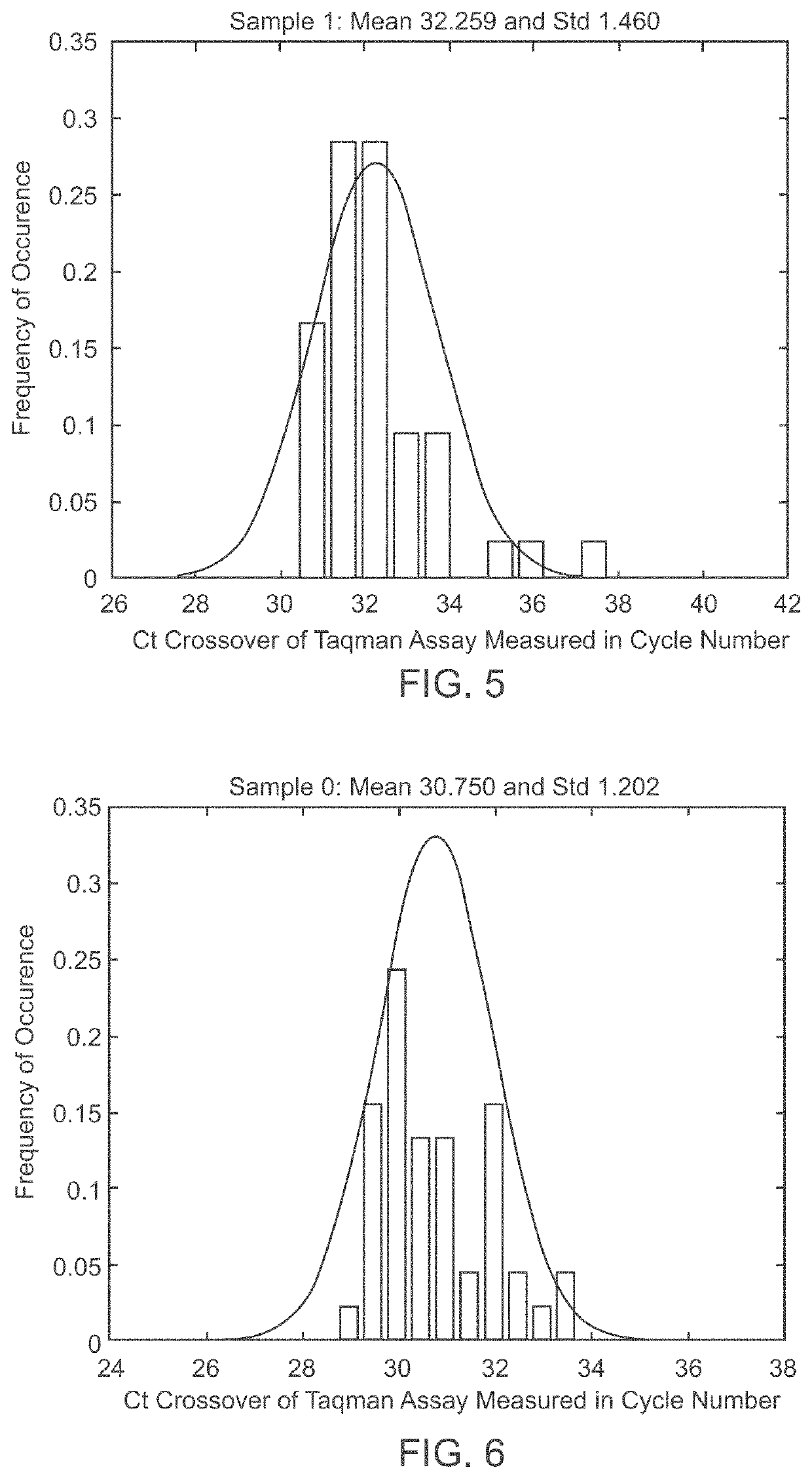
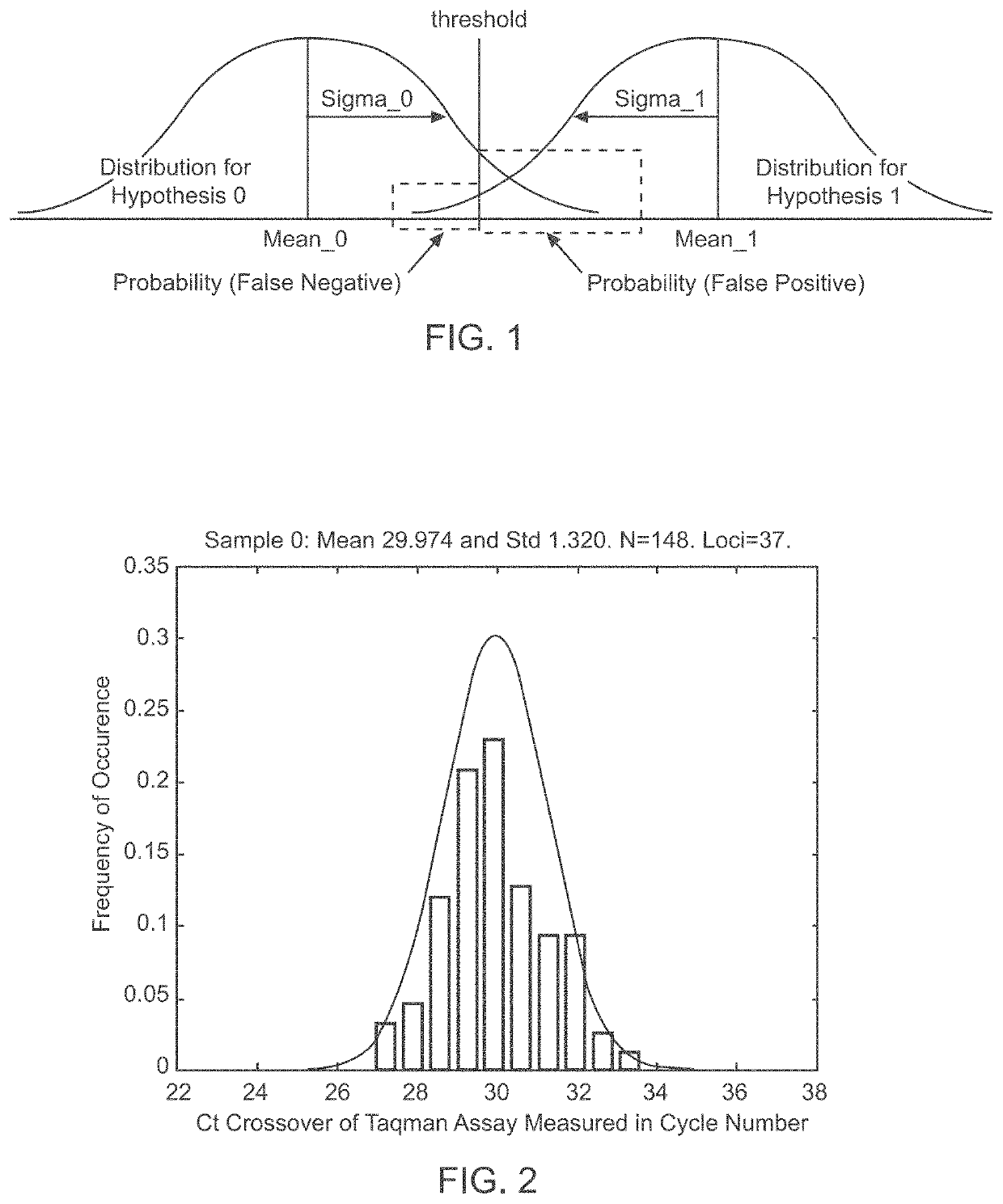
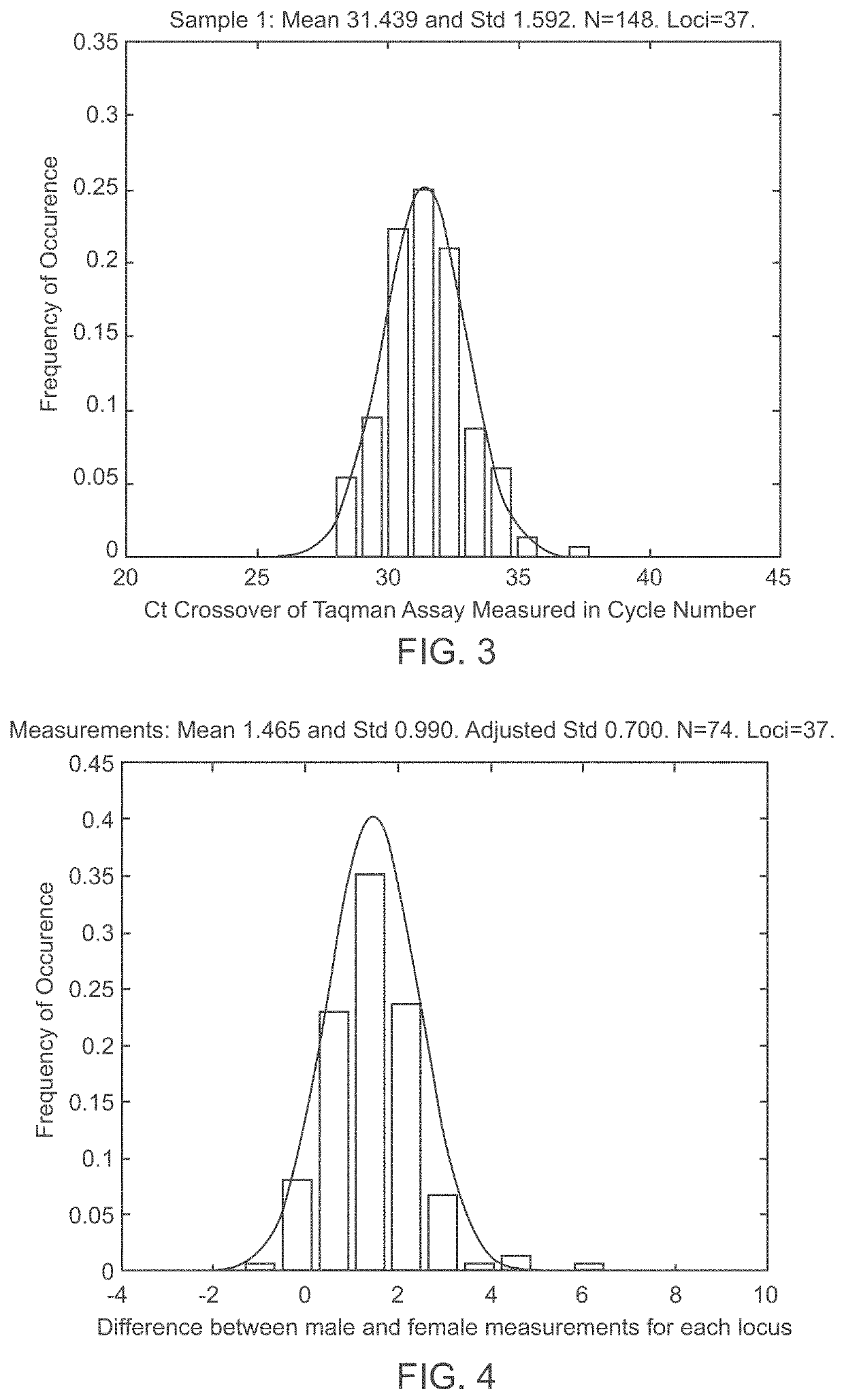
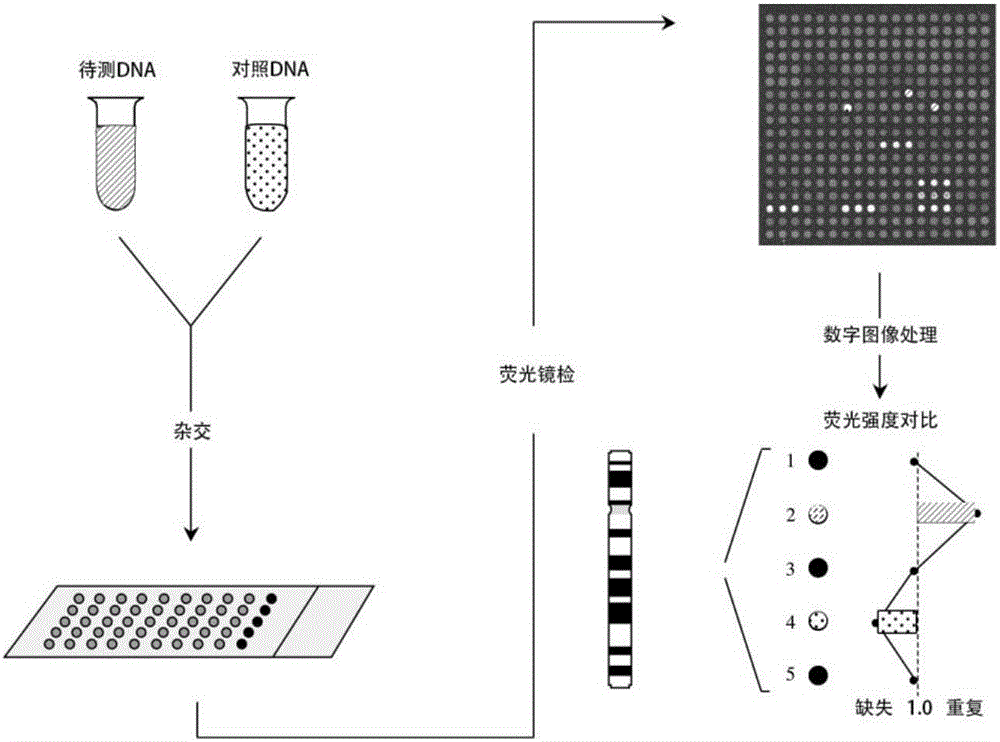
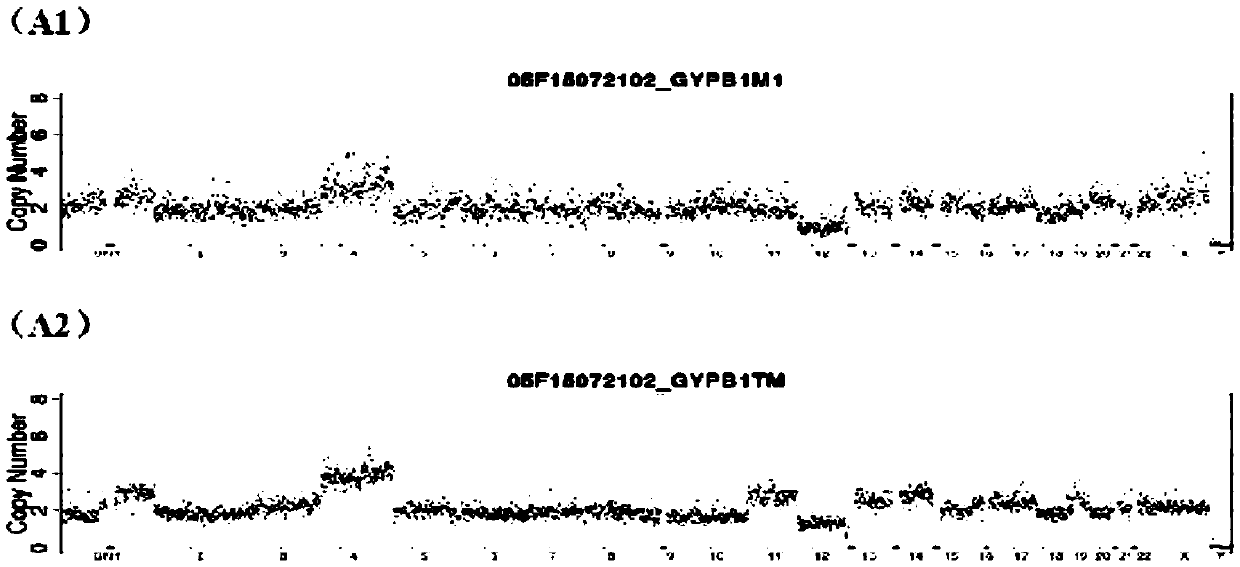
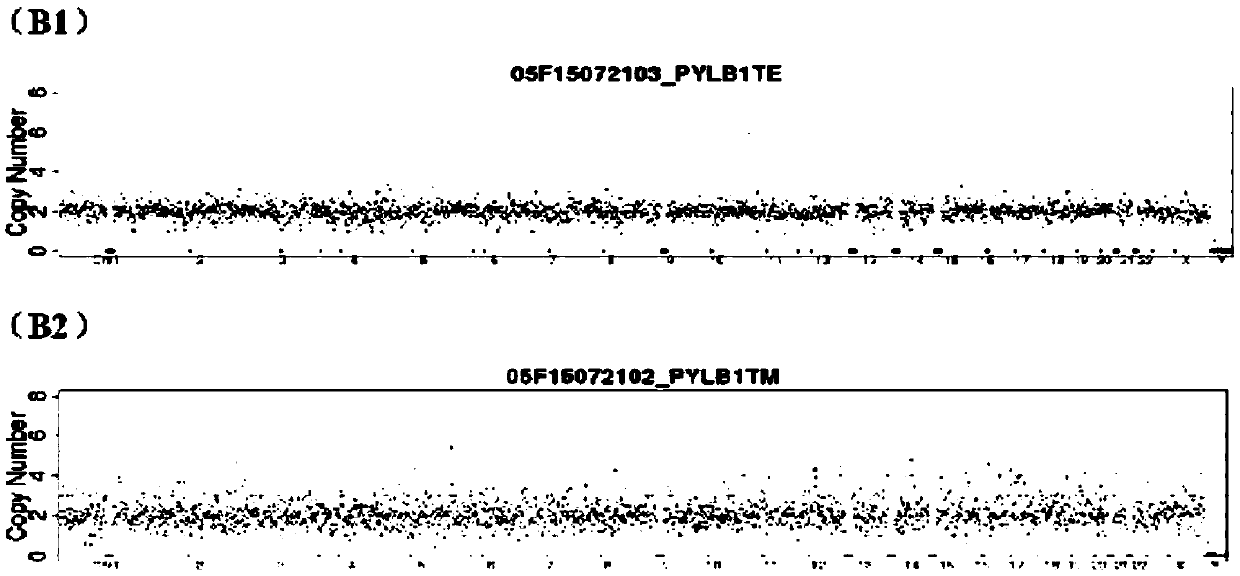
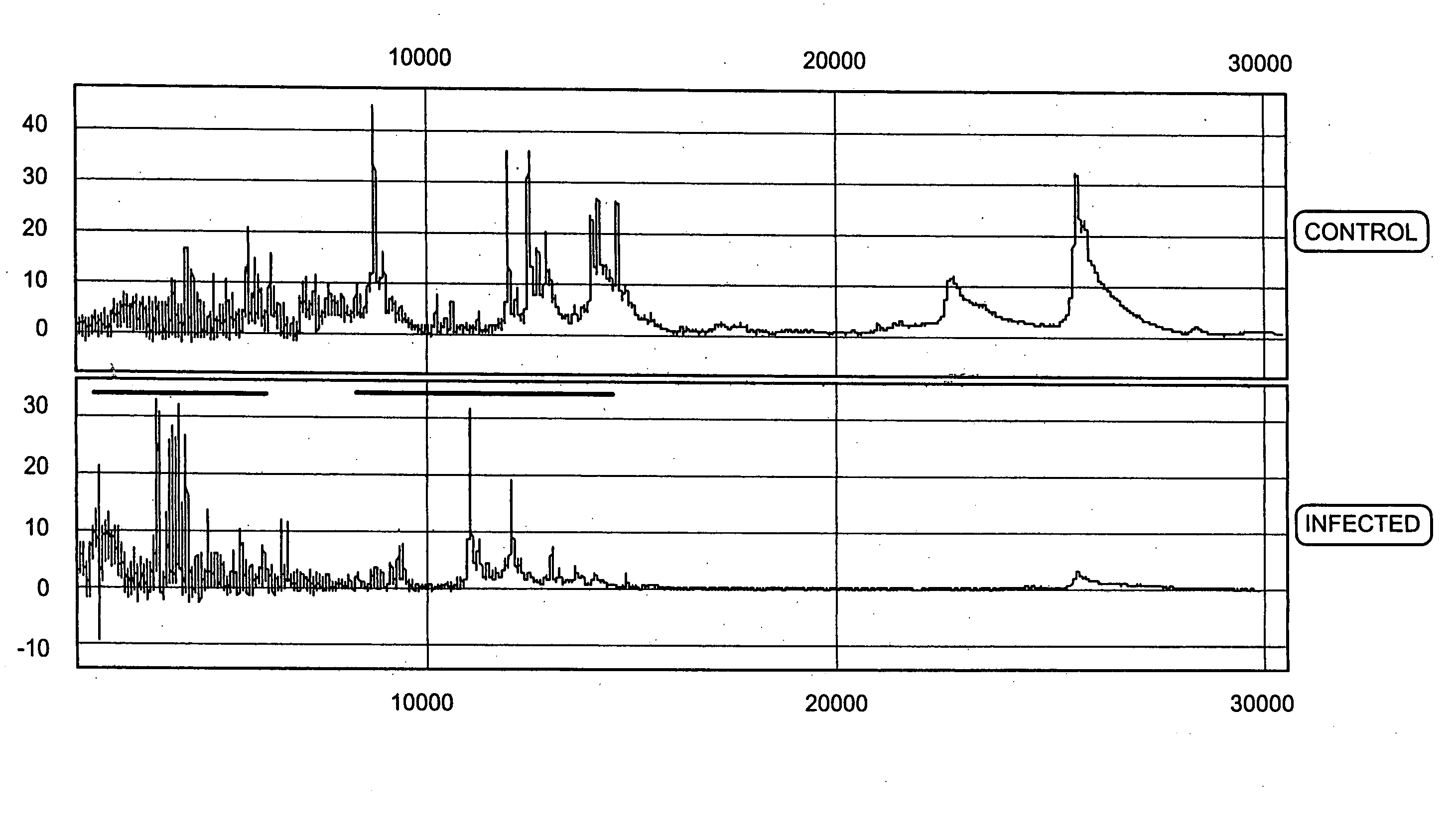
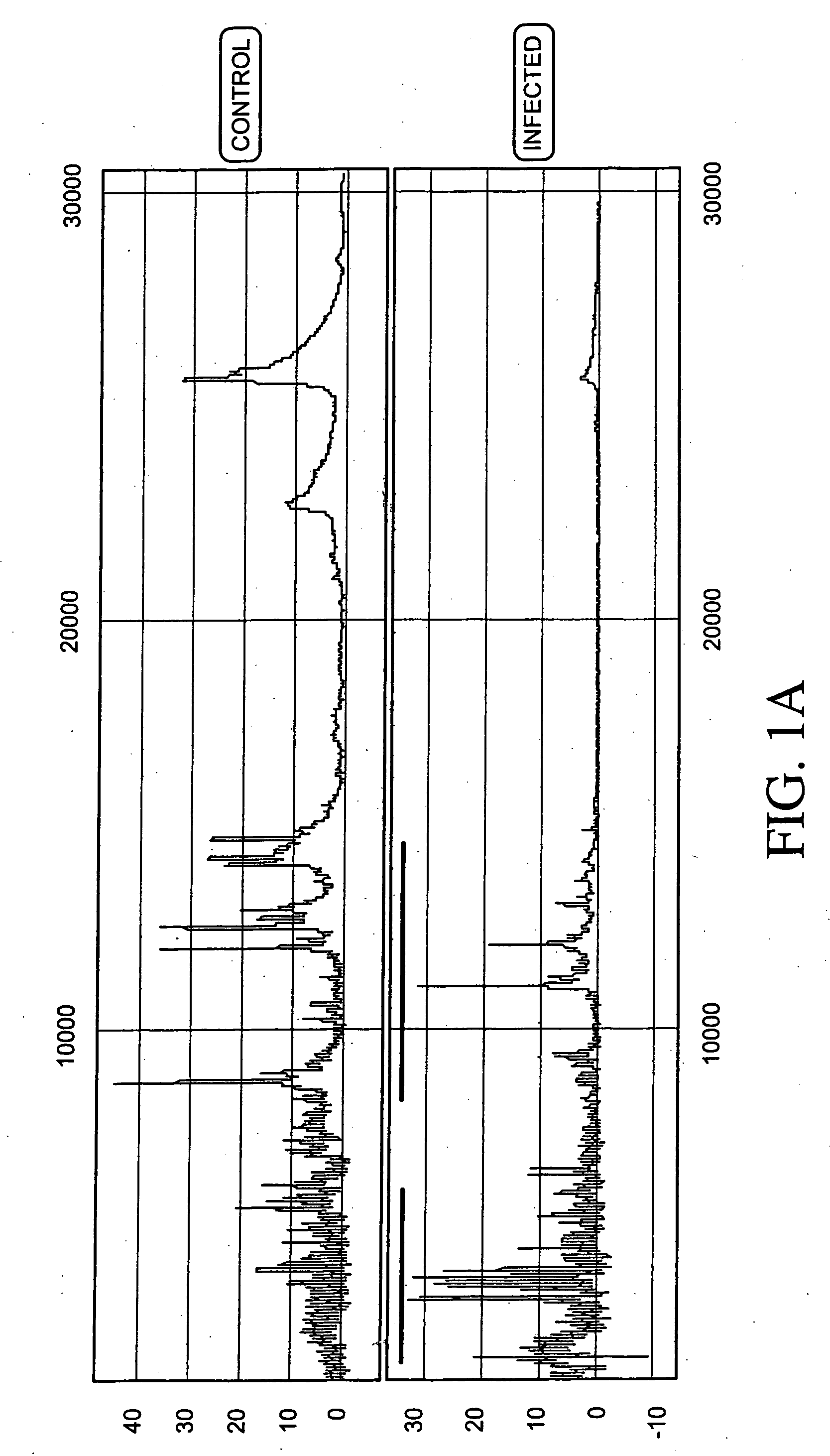
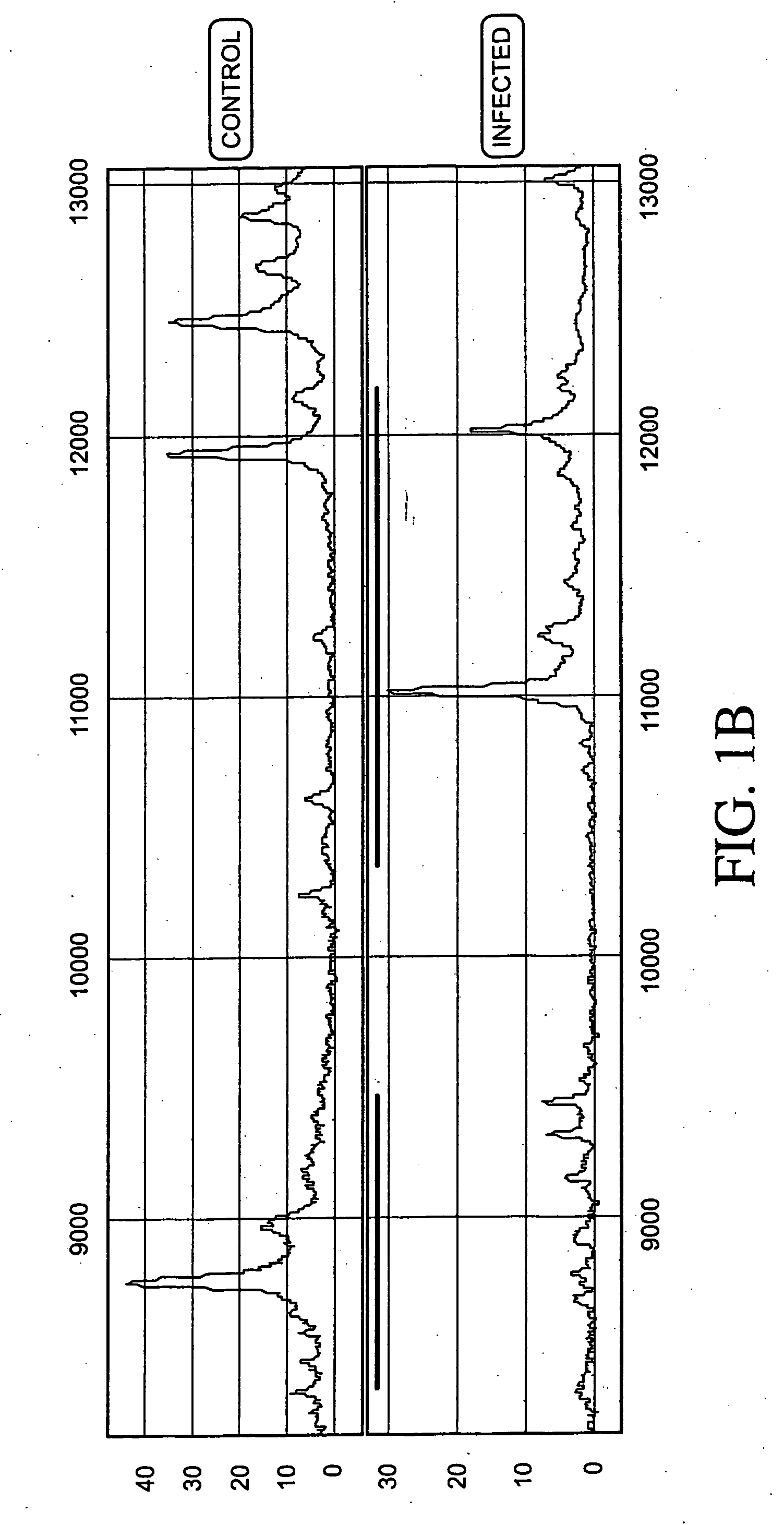
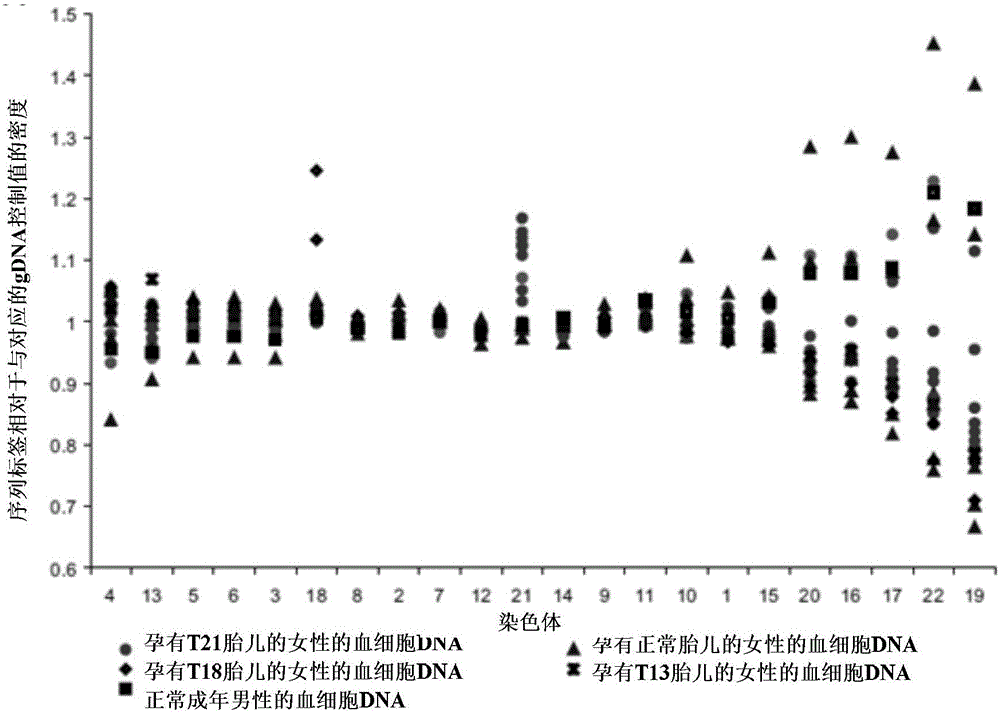
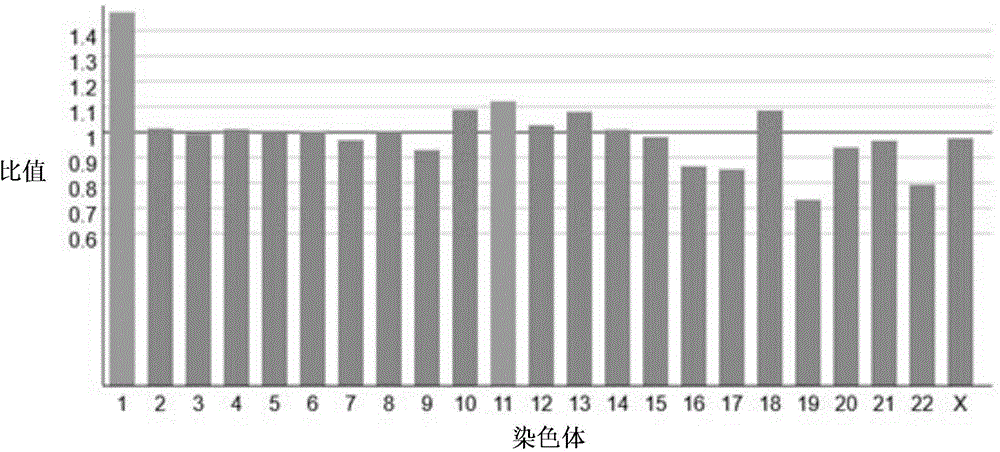
Aneuploidy is the presence of an abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell, for example a human cell having 45 or 47 chromosomes instead of the usual 46. It does not include a difference of one or more complete sets of chromosomes. A cell with any number of complete chromosome sets is called a euploid cell. An extra or missing chromosome is a common cause of genetic disorders, including some human birth defects. Some cancer cells also have abnormal numbers of chromosomes. Aneuploidy originates during cell division when the chromosomes do not separate properly between the two cells. Most cases of aneuploidy result in miscarriage and the most common extra autosomal chromosomes among live births are 21, 18, and 13.
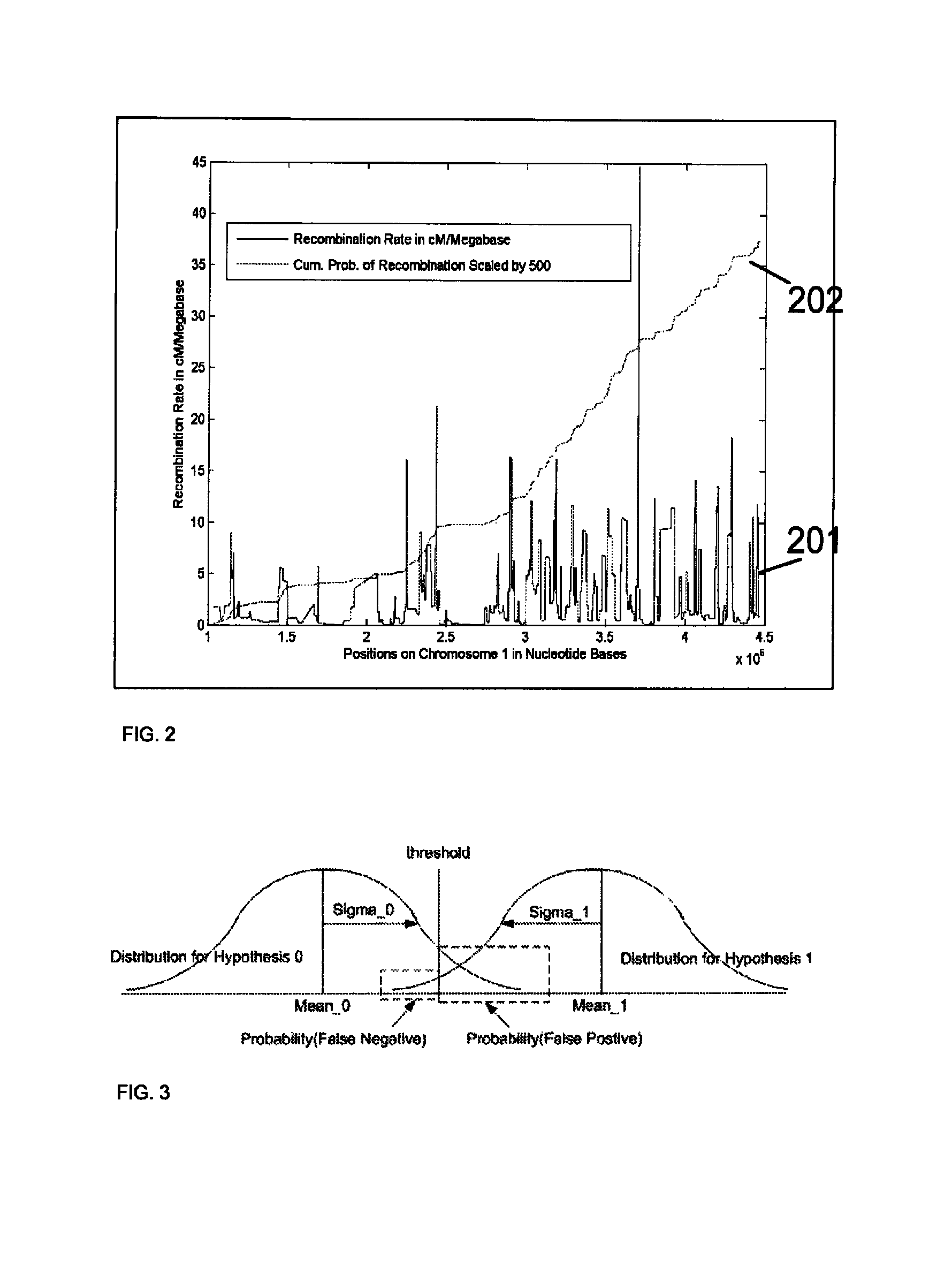
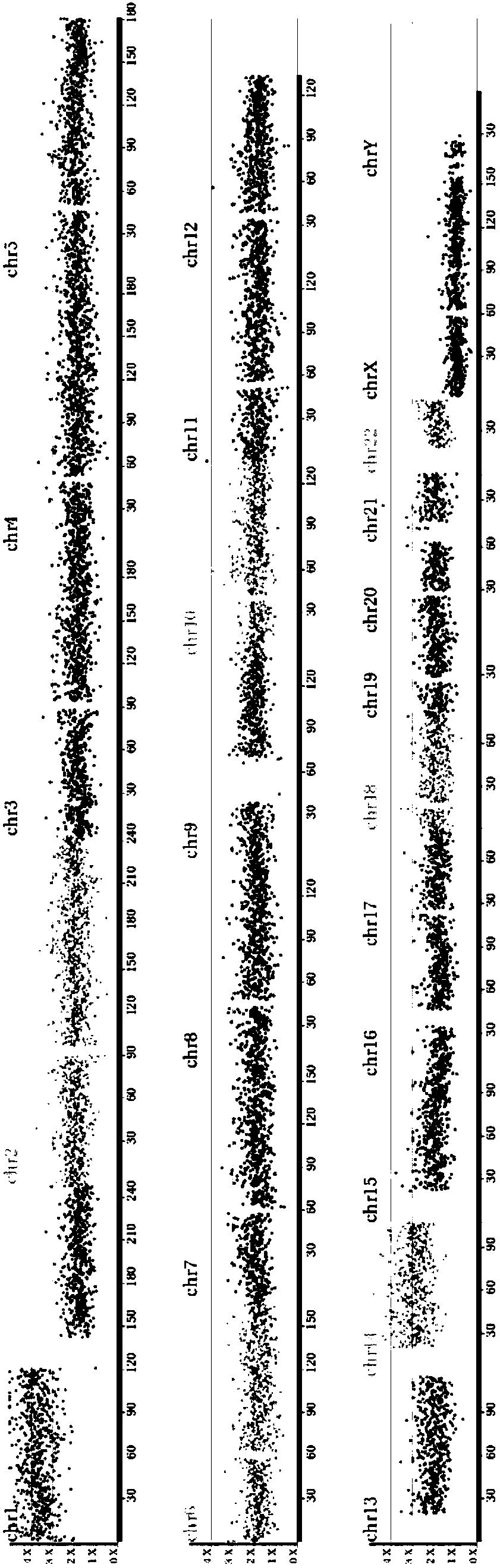
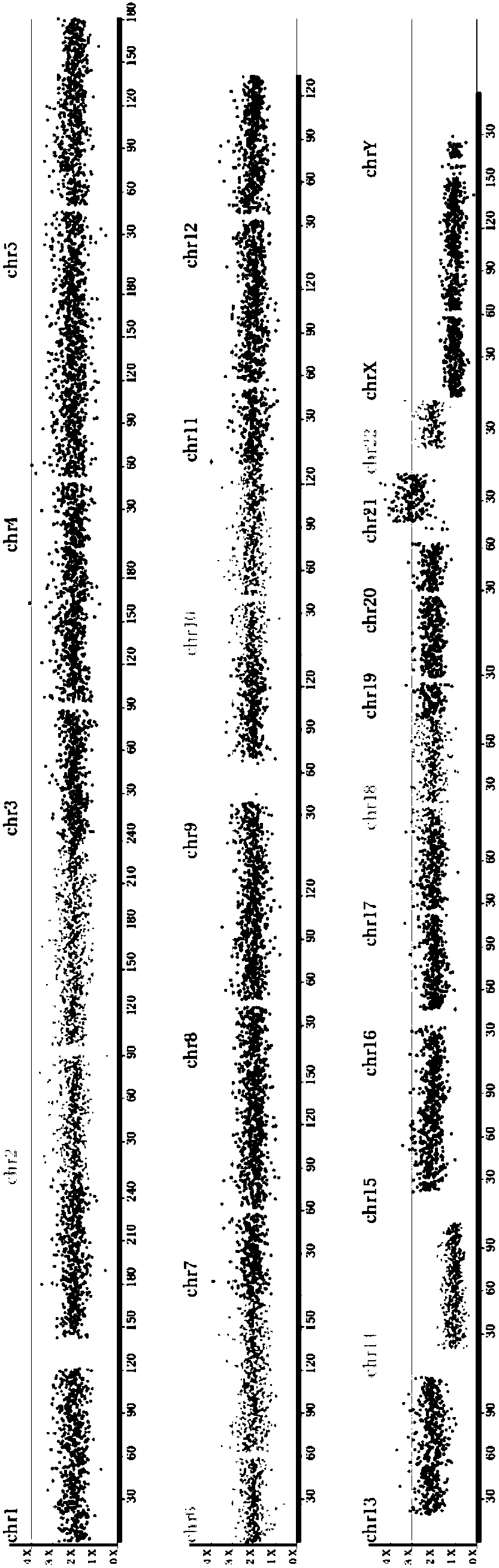
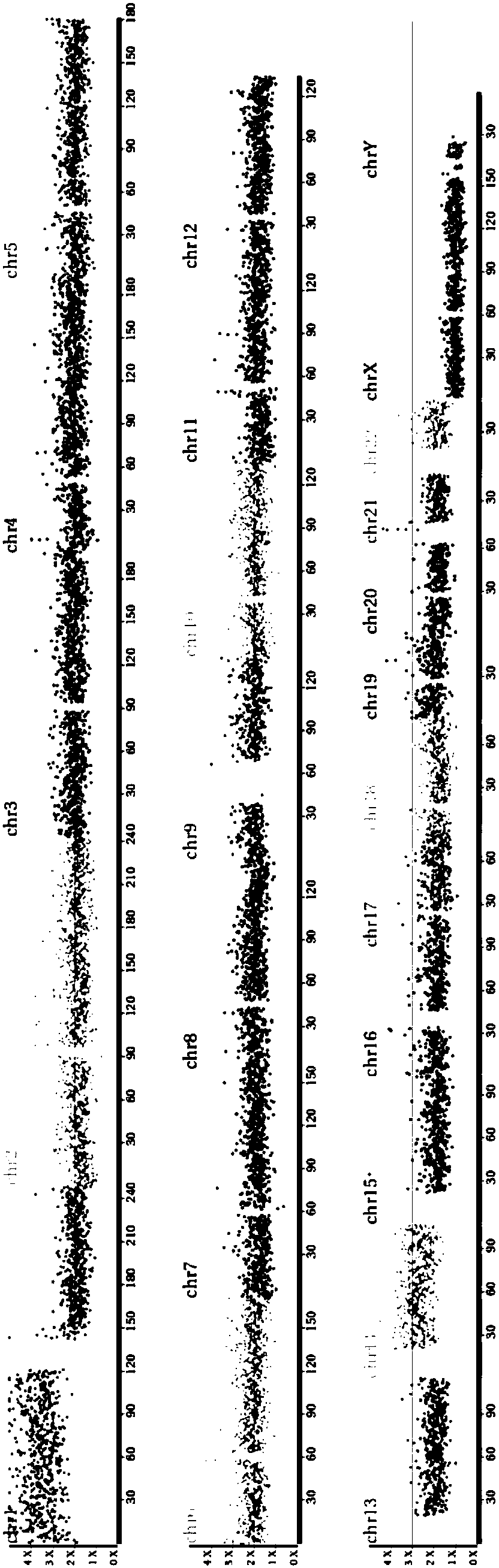
Diagnosing fetal chromosomal aneuploidy using massively parallel genomic sequencing
PendingUS20090029377A1Quantity maximizationSufficient amountMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisGenomic sequencingGenome
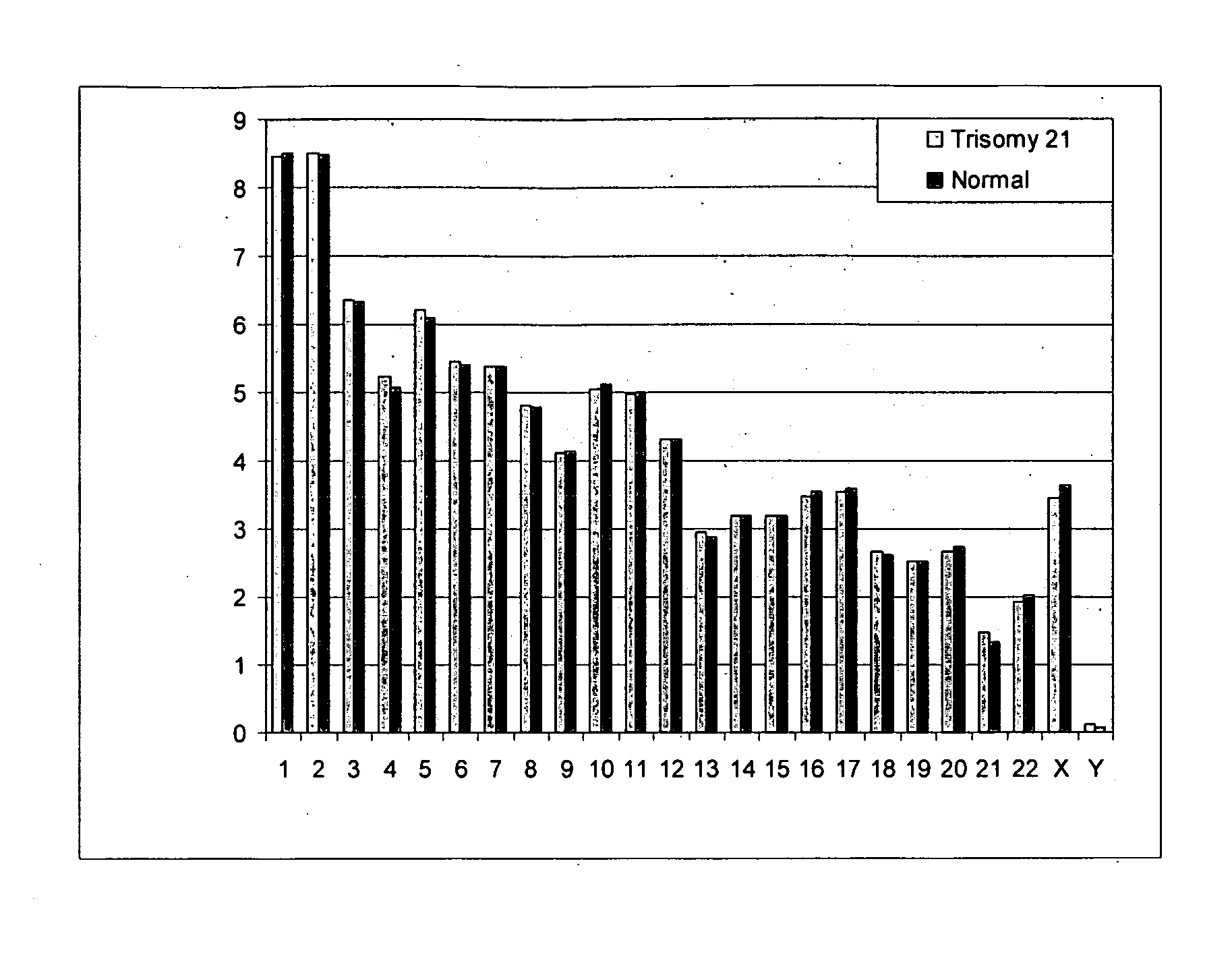
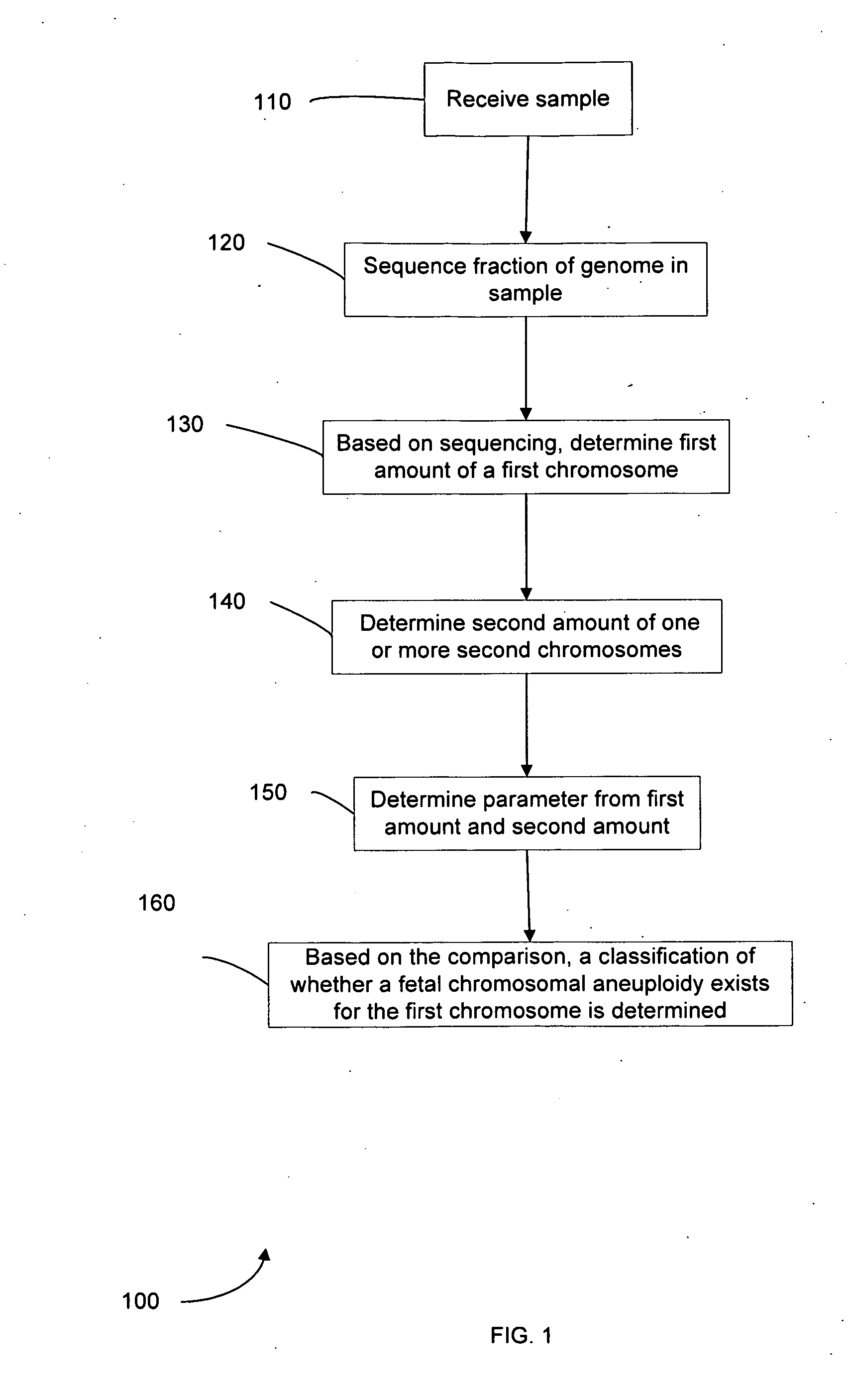
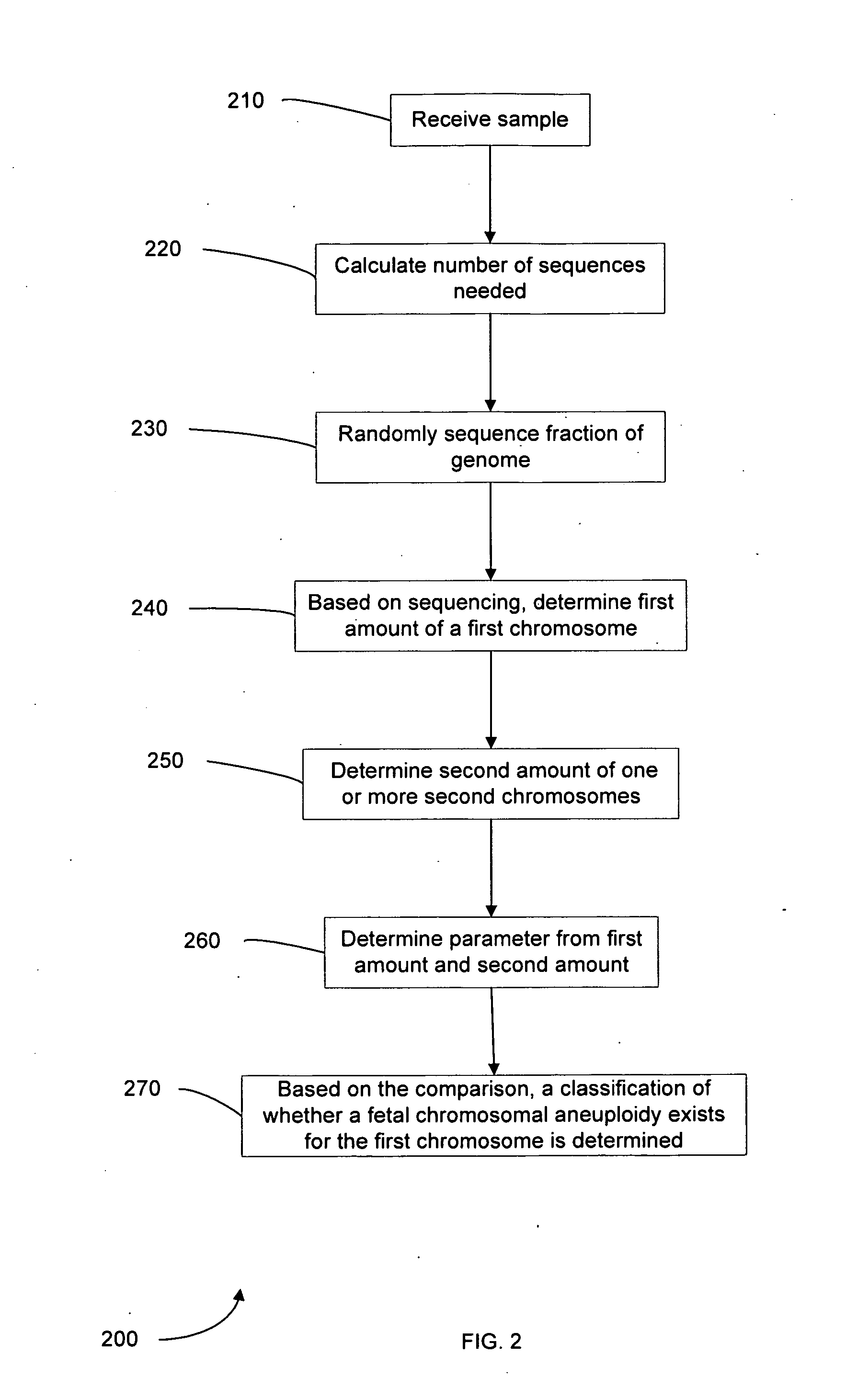
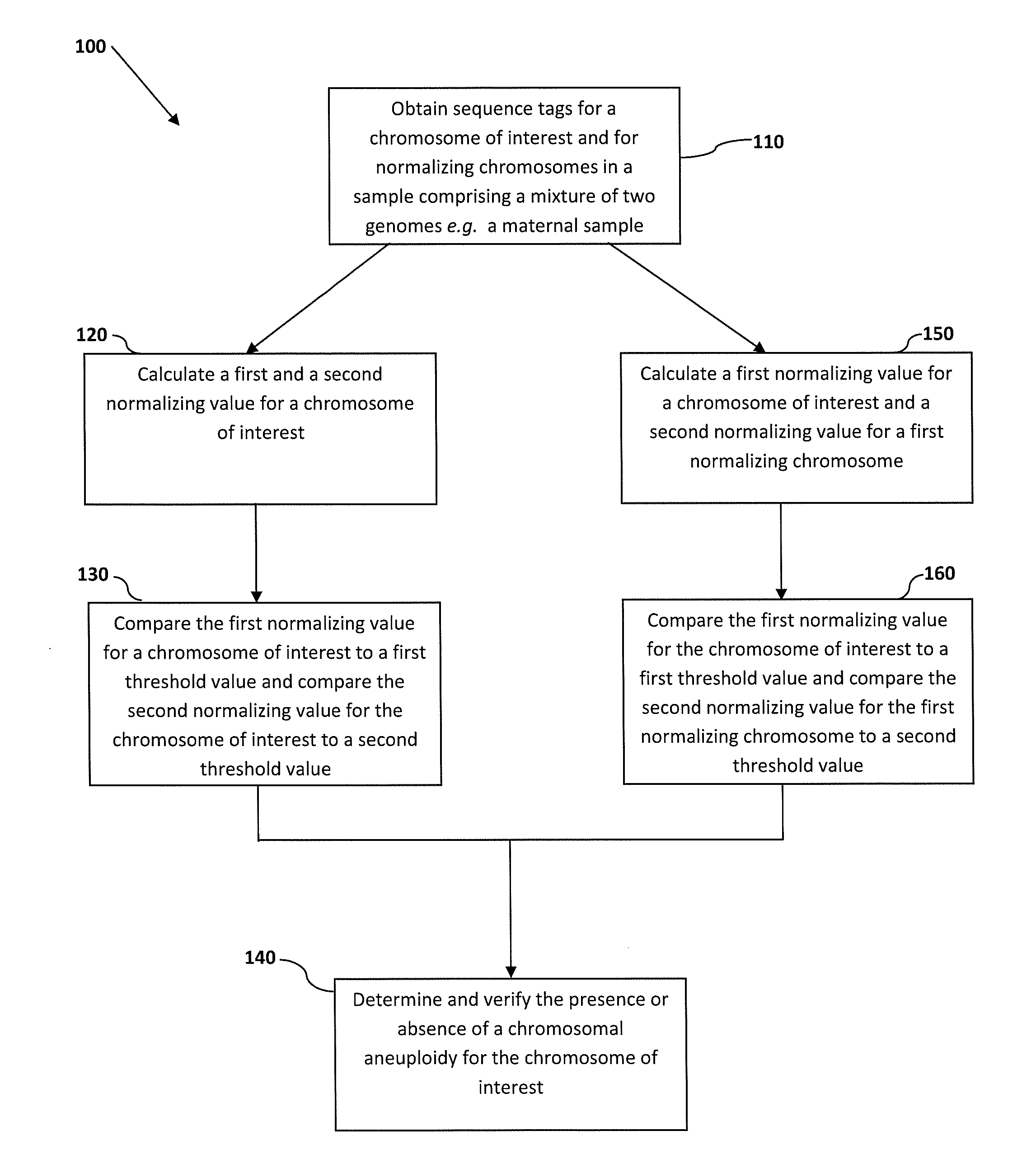
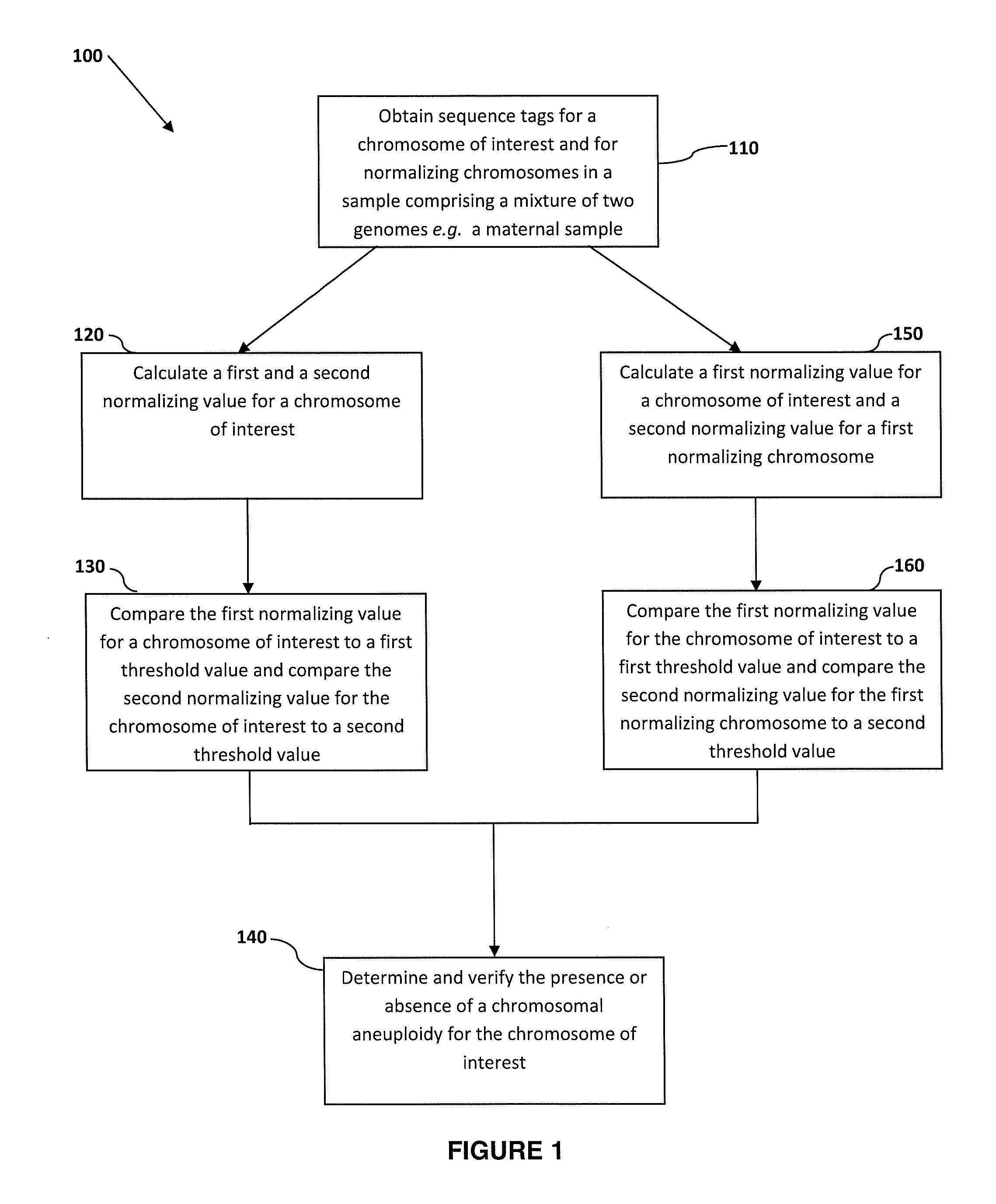
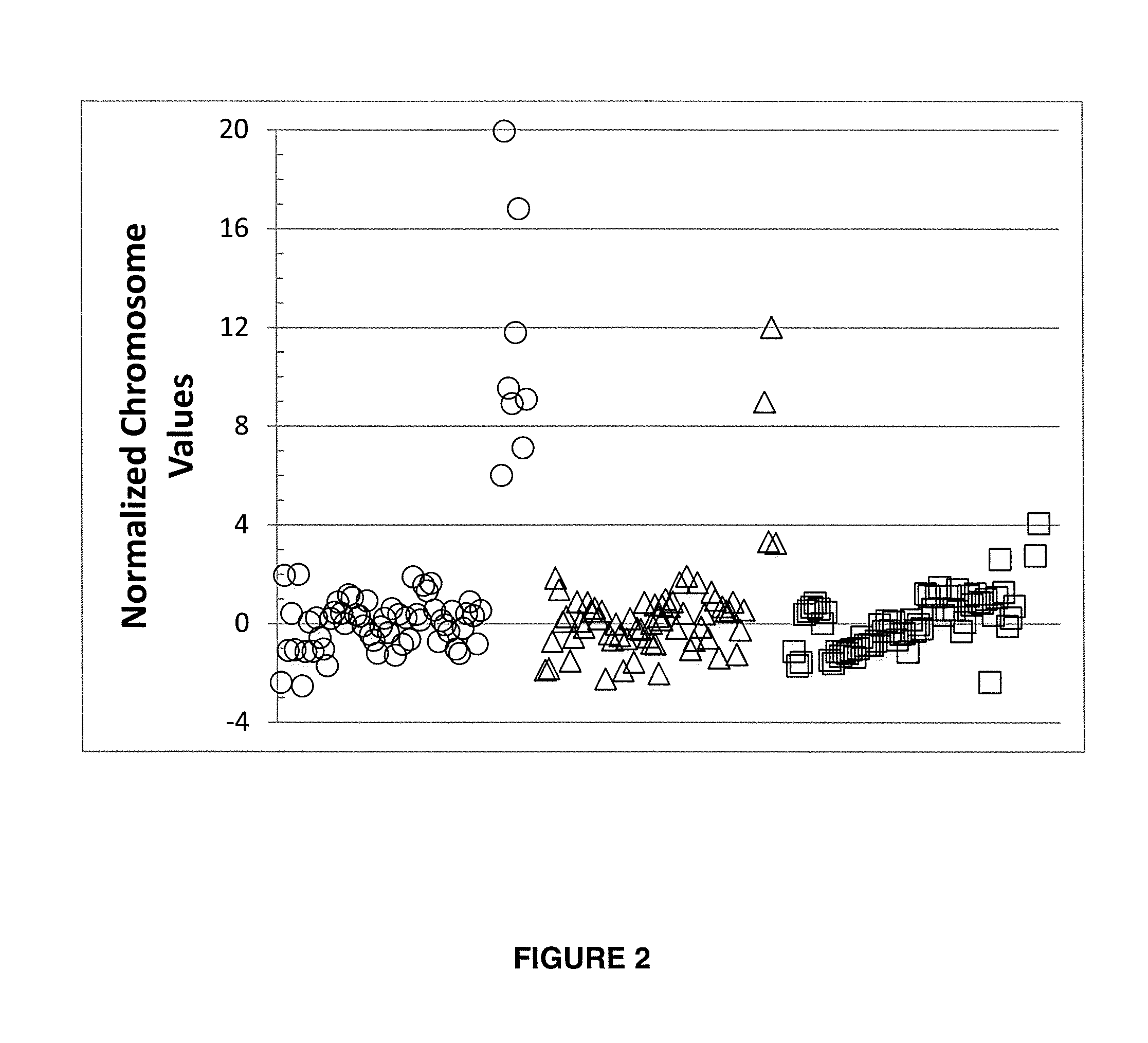
Embodiments of this invention provide methods, systems, and apparatus for determining whether a fetal chromosomal aneuploidy exists from a biological sample obtained from a pregnant female. Nucleic acid molecules of the biological sample are sequenced, such that a fraction of the genome is sequenced. Respective amounts of a clinically-relevant chromosome and of background chromosomes are determined from results of the sequencing. A parameter derived from these amounts (e.g. a ratio) is compared to one or more cutoff values, thereby determining a classification of whether a fetal chromosomal aneuploidy exists.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Sequencing methods and compositions for prenatal diagnoses
ActiveUS20110201507A1Quality improvementEasy to analyzeMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningPrenatal diagnosisGenetics
The invention provides methods for determining aneuploidy and / or fetal fraction in maternal samples comprising fetal and maternal cfDNA by massively parallel sequencing. The method comprises a novel protocol for preparing sequencing libraries that unexpectedly improves the quality of library DNA while expediting the process of analysis of samples for prenatal diagnoses.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC
System and method for cleaning noisy genetic data and determining chromosome copy number
ActiveUS20080243398A1Significant resultImprove fidelityData processing applicationsMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic MaterialsEmbryo
Disclosed herein is a system and method for increasing the fidelity of measured genetic data, for making allele calls, and for determining the state of aneuploidy, in one or a small set of cells, or from fragmentary DNA, where a limited quantity of genetic data is available. Genetic material from the target individual is acquired, amplified and the genetic data is measured using known methods. Poorly or incorrectly measured base pairs, missing alleles and missing regions are reconstructed using expected similarities between the target genome and the genome of genetically related individuals. In accordance with one embodiment of the invention, incomplete genetic data from an embryonic cell are reconstructed at a plurality of loci using the more complete genetic data from a larger sample of diploid cells from one or both parents, with or without haploid genetic data from one or both parents. In another embodiment of the invention, the chromosome copy number can be determined from the measured genetic data of a single or small number of cells, with or without genetic information from one or both parents. In another embodiment of the invention, these determinations are made for the purpose of embryo selection in the context of in-vitro fertilization. In another embodiment of the invention, the genetic data can be reconstructed for the purposes of making phenotypic predictions.
Owner:NATERA
System and method for cleaning noisy genetic data from target individuals using genetic data from genetically related individuals
ActiveUS20070184467A1Significant resultMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsUniparental disomyEmbryo
A system and method for determining the genetic data for one or a small set of cells, or from fragmentary DNA, where a limited quantity of genetic data is available. Genetic data for the target individual is acquired and amplified using known methods, and poorly measured base pairs, missing alleles and missing regions are reconstructed using expected similarities between the target genome and the genome of genetically related subjects. In accordance with one embodiment of the invention, incomplete genetic data from an embryonic cell is reconstructed using the more complete genetic data from a larger sample of diploid cells from one or both parents, with or without genetic data from haploid cells from one or both parents, and / or genetic data taken from other related individuals. In accordance with another embodiment of the invention, incomplete genetic data from a fetus is acquired from fetal cells, or cell-free fetal DNA isolated from the mother's blood, and the incomplete genetic data is reconstructed using the more complete genetic data from a larger sample diploid cells from one or both parents, with or without genetic data from haploid cells from one or both parents, and / or genetic data taken from other related individuals. In one embodiment, the genetic data can be reconstructed for the purposes of making phenotypic predictions. In another embodiment, the genetic data can be used to detect for aneuploides and uniparental disomy.
Owner:NATERA
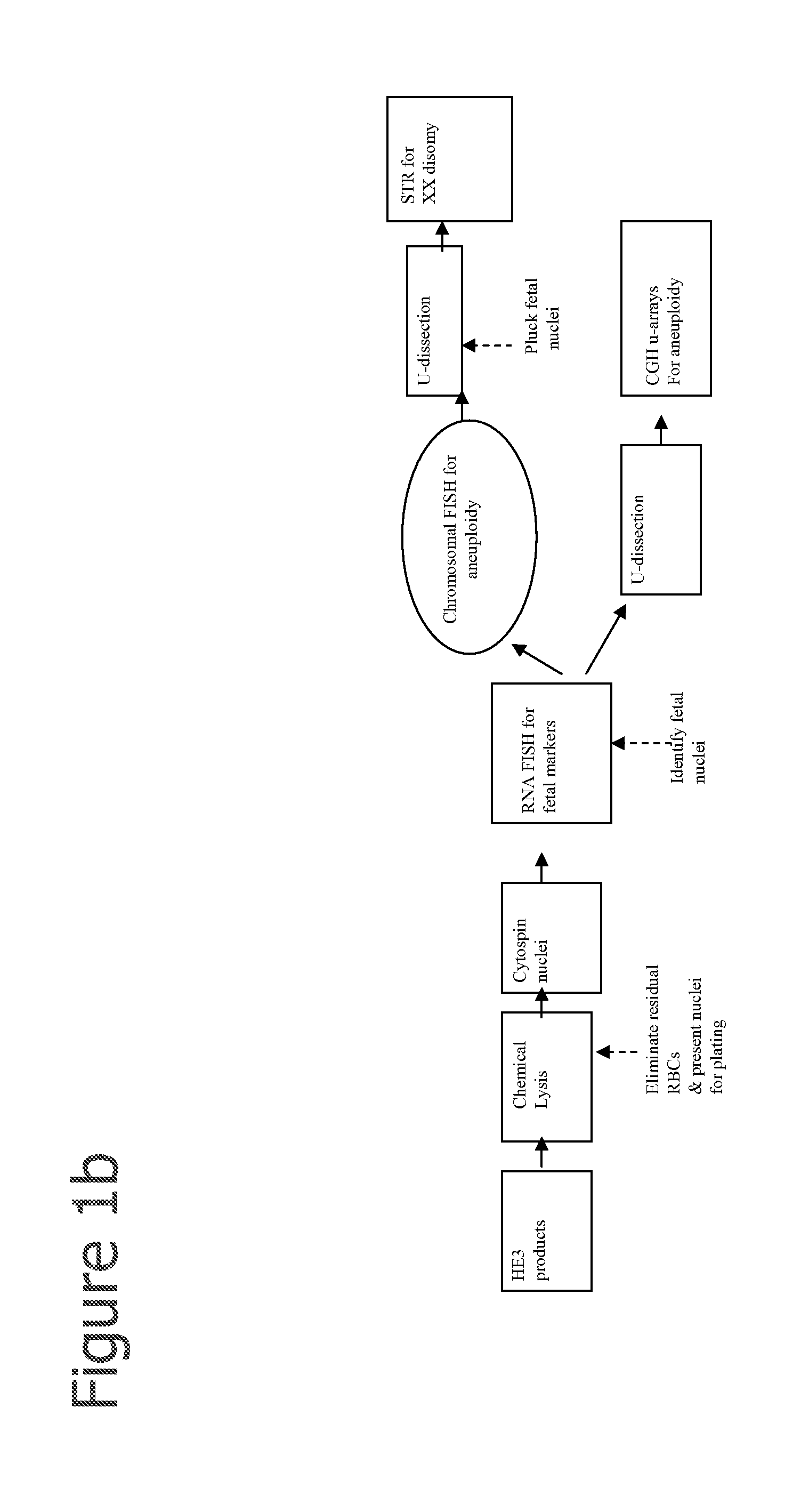
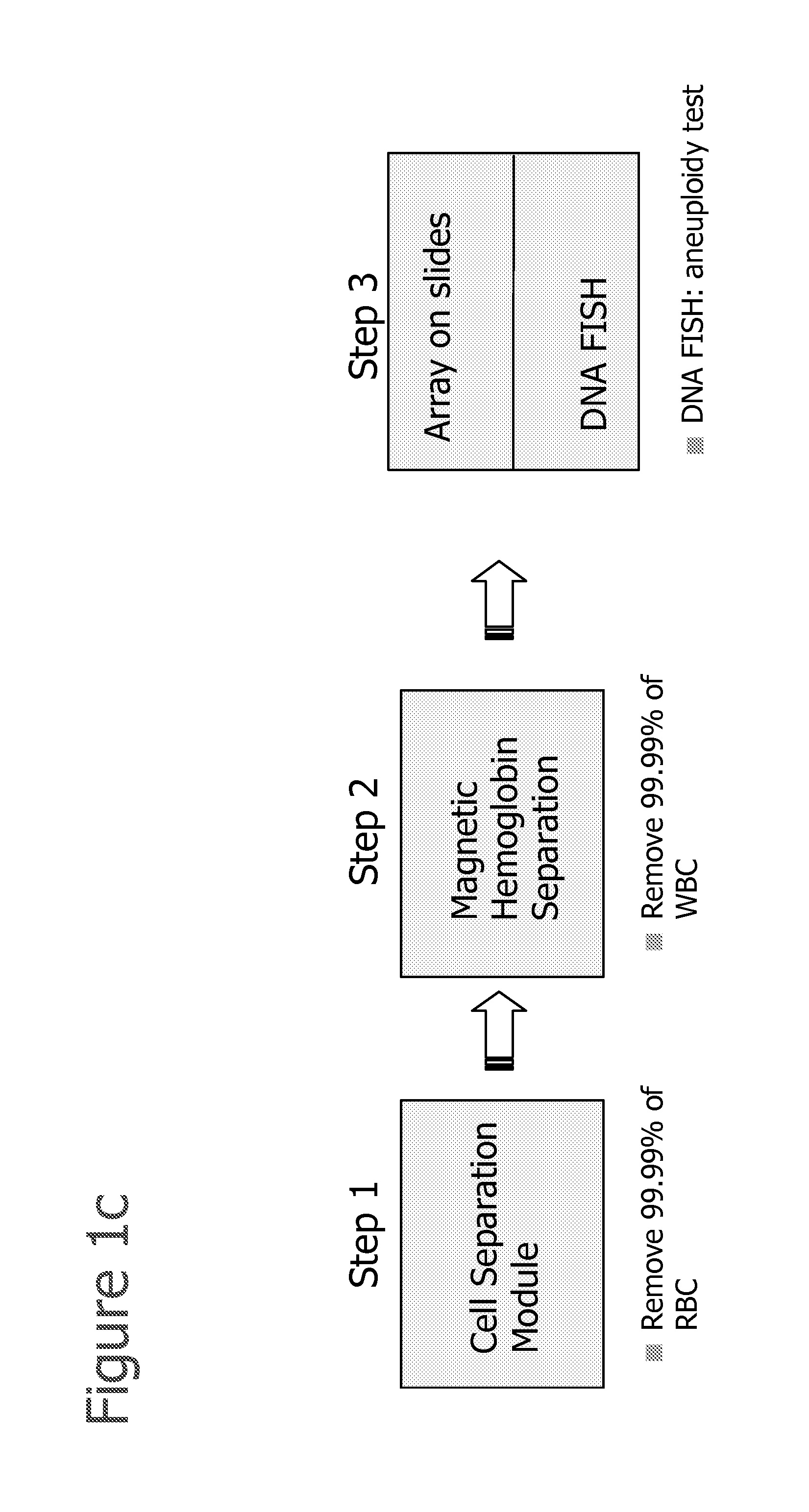
Selection of cells using biomarkers
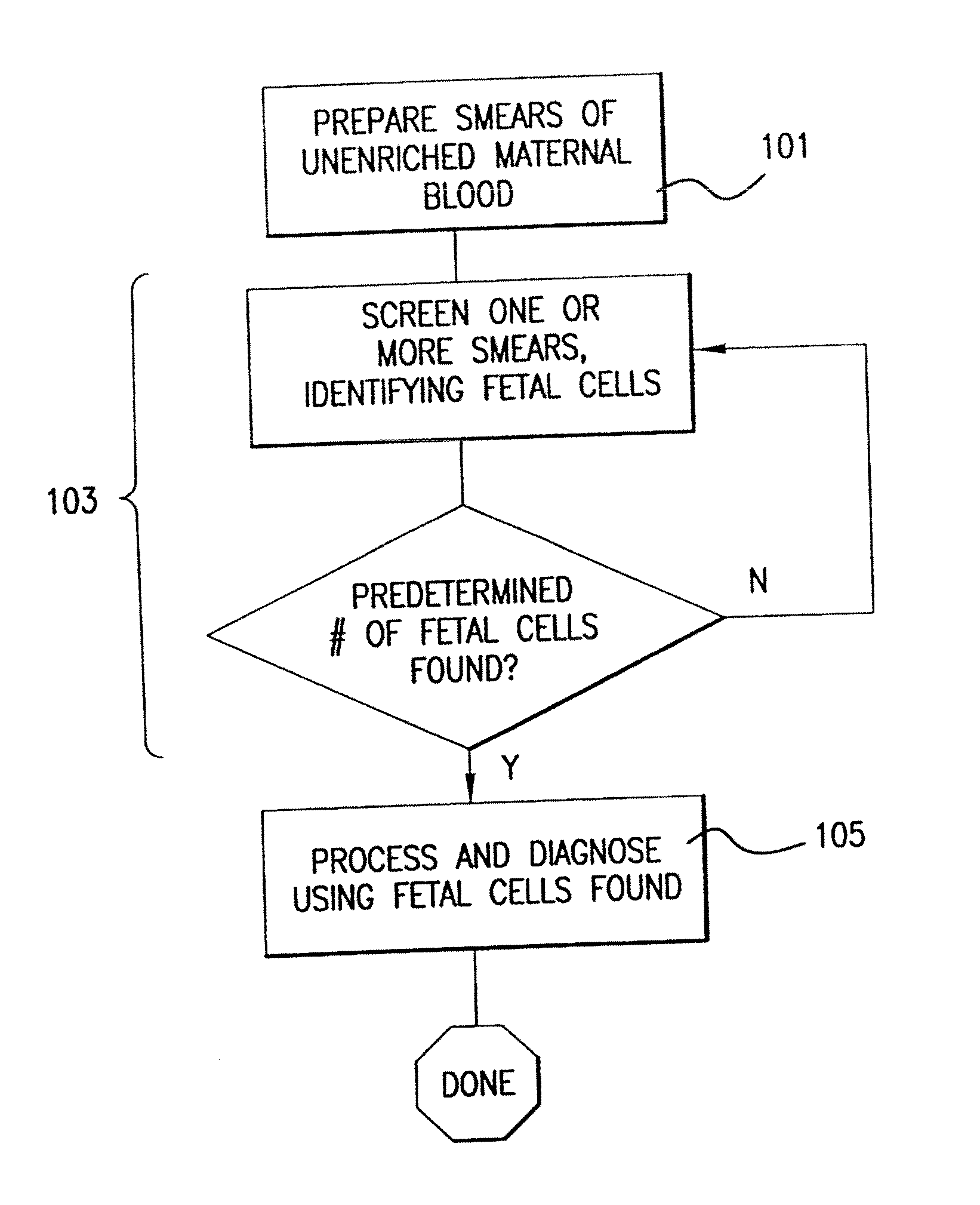
InactiveUS20080113358A1Easy to separateIncrease the number ofMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisFetal abnormalityFetal cell
The present invention provides systems, apparatuses, and methods to isolate, select or detect the presence of a target cell (e.g., fetal cells) in a sample comprising mixed populations of cells that vastly outnumber the target cells. Target cells include fetal cells, such as nucleated red blood cells, and methods of selecting such cells include diagnosis of fetal abnormalities, i.e., aneuploidy. Furthermore, methods comprise utilizing fetal biomarkers to select fetal cells in a sample comprising fetal and adult cells.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +2
Method for determining the number of copies of a chromosome in the genome of a target individual using genetic data from genetically related individuals
A system and method for determining the genetic data for one or a small set of cells, or from fragmentary DNA, where a limited quantity of genetic data is available. Genetic data for the target individual is acquired and amplified using known methods, and poorly measured base pairs, missing alleles and missing regions are reconstructed using expected similarities between the target genome and the genome of genetically related subjects. In accordance with one embodiment of the invention, incomplete genetic data from an embryonic cell is reconstructed using the more complete genetic data from a larger sample of diploid cells from one or both parents, with or without genetic data from haploid cells from one or both parents, and / or genetic data taken from other related individuals. In accordance with another embodiment of the invention, incomplete genetic data from a fetus is acquired from fetal cells, or cell-free fetal DNA isolated from the mother's blood, and the incomplete genetic data is reconstructed using the more complete genetic data from a larger sample diploid cells from one or both parents, with or without genetic data from haploid cells from one or both parents, and / or genetic data taken from other related individuals. In one embodiment, the genetic data can be reconstructed for the purposes of making phenotypic predictions. In another embodiment, the genetic data can be used to detect for aneuploides and uniparental disomy.
Owner:NATERA
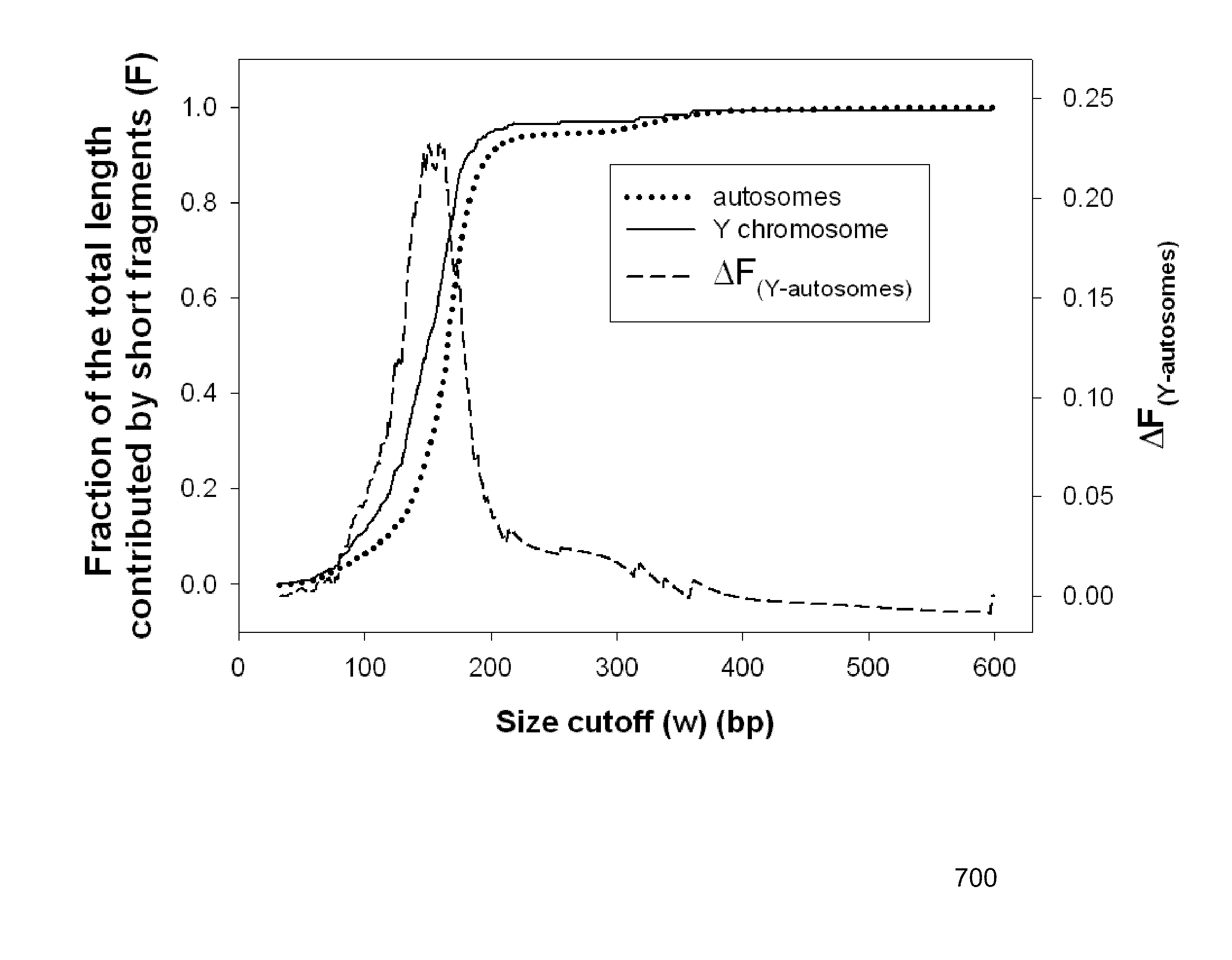
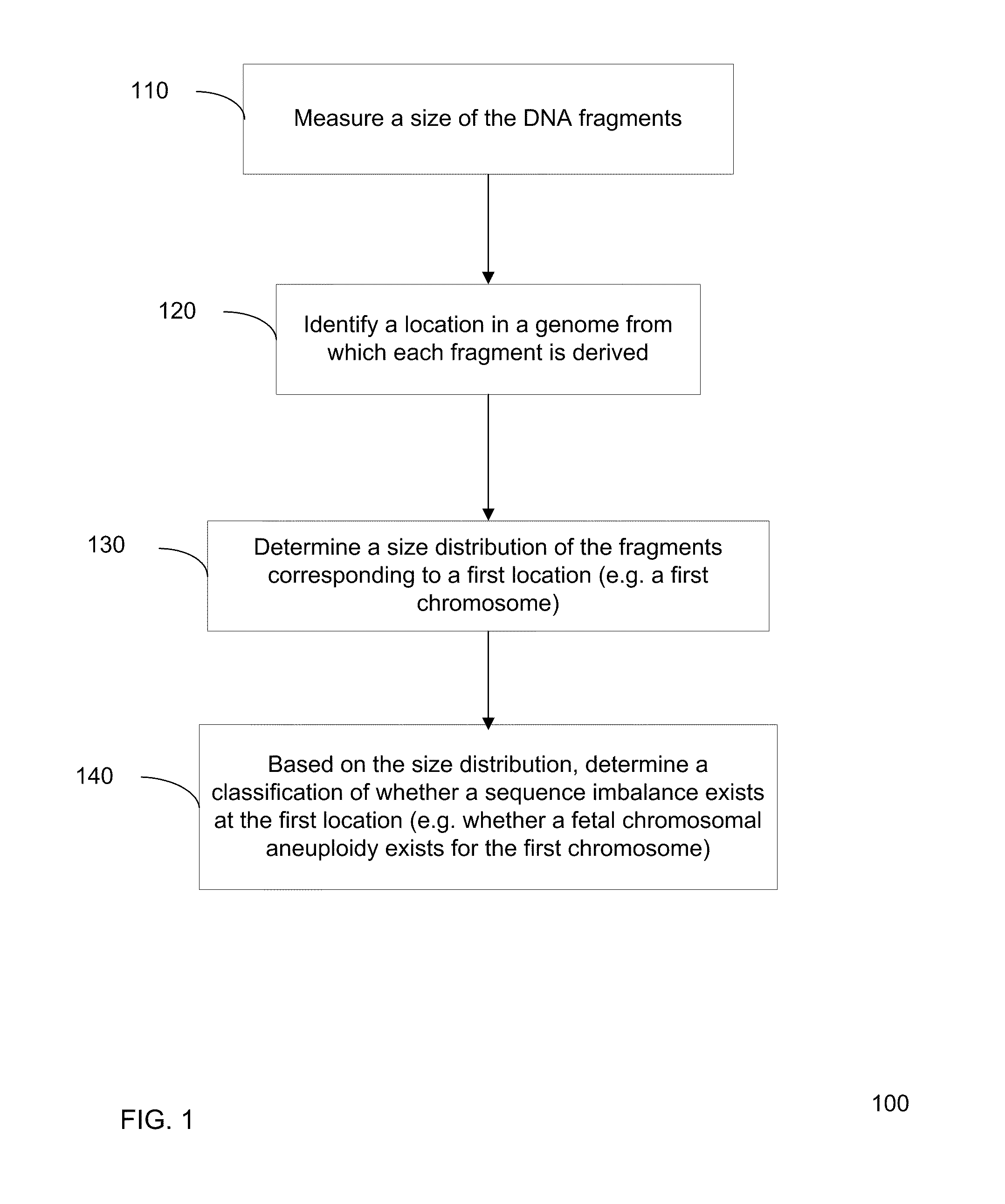
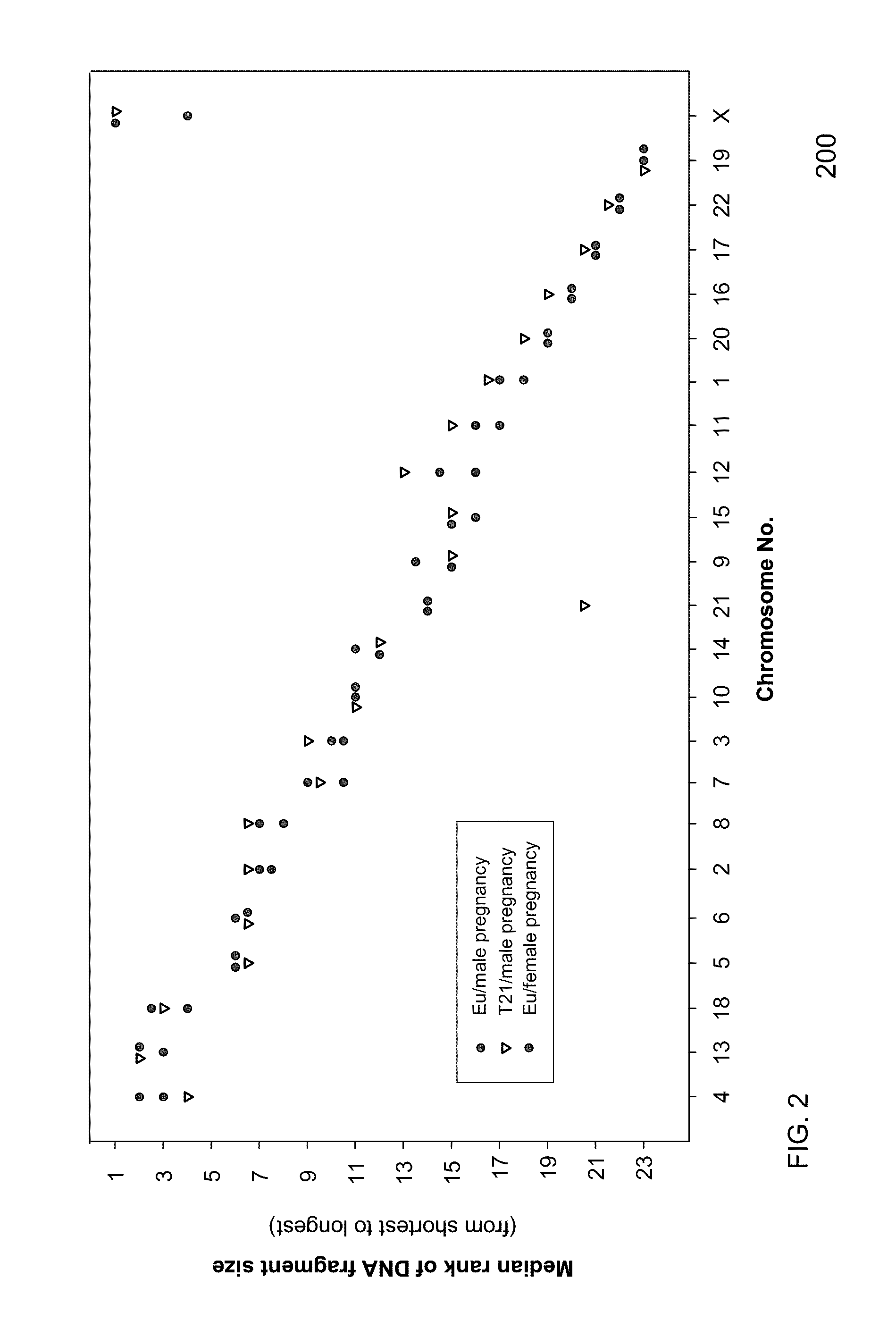
Size-based genomic analysis
Systems, methods, and apparatuses for performing a prenatal diagnosis of a sequence imbalance are provided. A shift (e.g. to a smaller size distribution) can signify an imbalance in certain circumstances. For example, a size distribution of fragments of nucleic acids from an at-risk chromosome can be used to determine a fetal chromosomal aneuploidy. A size ranking of different chromosomes can be used to determine changes of a rank of an at-risk chromosome from an expected ranking. Also, a difference between a statistical size value for one chromosome can be compared to a statistical size value of another chromosome to identify a significant shift in size. A genotype and haplotype of the fetus may also be determined using a size distribution to determine whether a sequence imbalance occurs in a maternal sample relative to a genotypes or haplotype of the mother, thereby providing a genotype or haplotype of the fetus.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
System and method for cleaning noisy genetic data and determining chromosome copy number
ActiveUS20140032128A1Significant resultImprove fidelityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsDiploid cellsEmbryo
Disclosed herein is a system and method for increasing the fidelity of measured genetic data, for making allele calls, and for determining the state of aneuploidy, in one or a small set of cells, or from fragmentary DNA, where a limited quantity of genetic data is available. Poorly or incorrectly measured base pairs, missing alleles and missing regions are reconstructed using expected similarities between the target genome and the genome of genetically related individuals. In accordance with one embodiment, incomplete genetic data from an embryonic cell are reconstructed at a plurality of loci using the more complete genetic data from a larger sample of diploid cells from one or both parents, with or without haploid genetic data from one or both parents. In another embodiment, the chromosome copy number can be determined from the measured genetic data, with or without genetic information from one or both parents.
Owner:NATERA
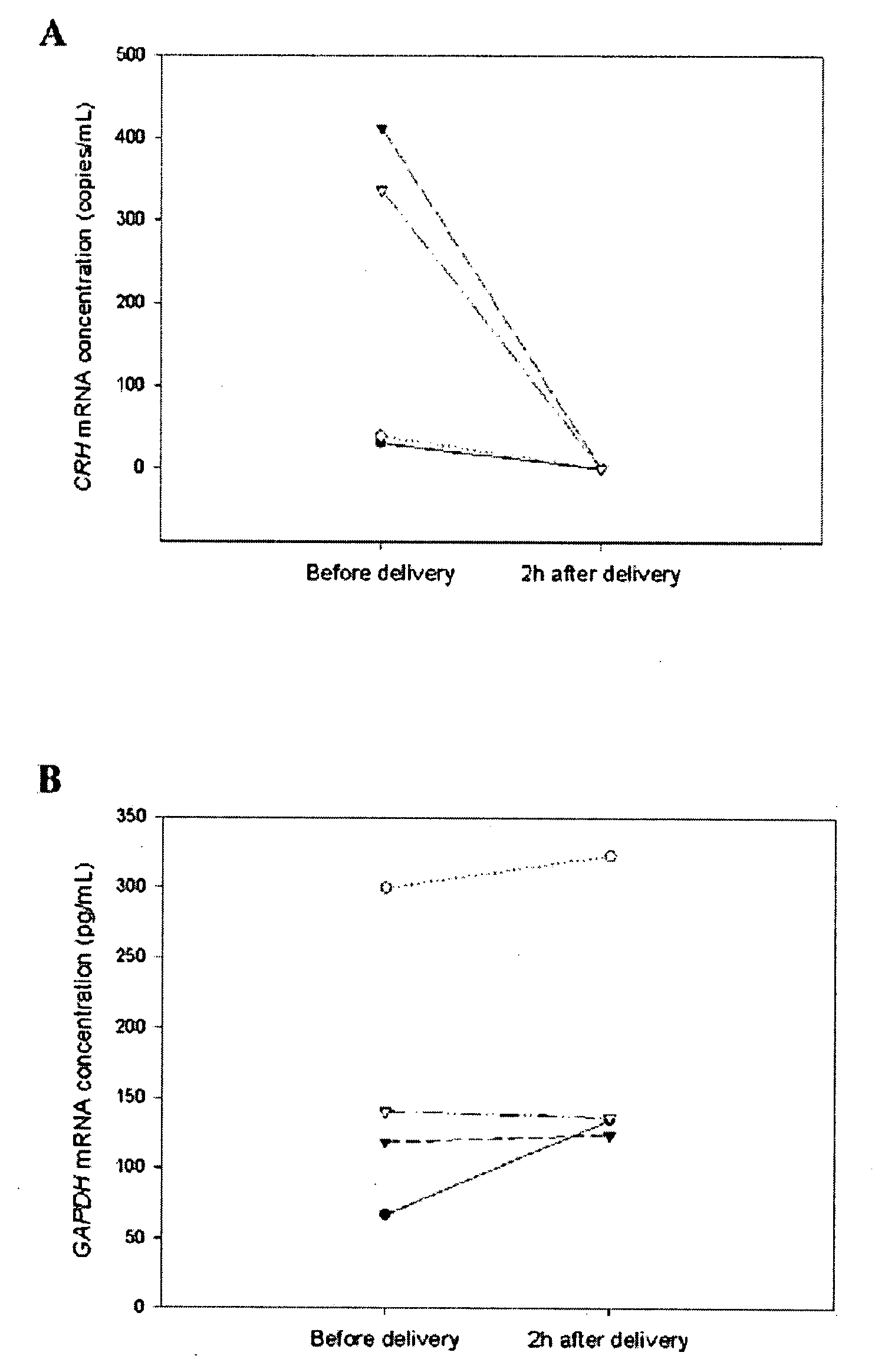
Circulating mRNA as diagnostic markers
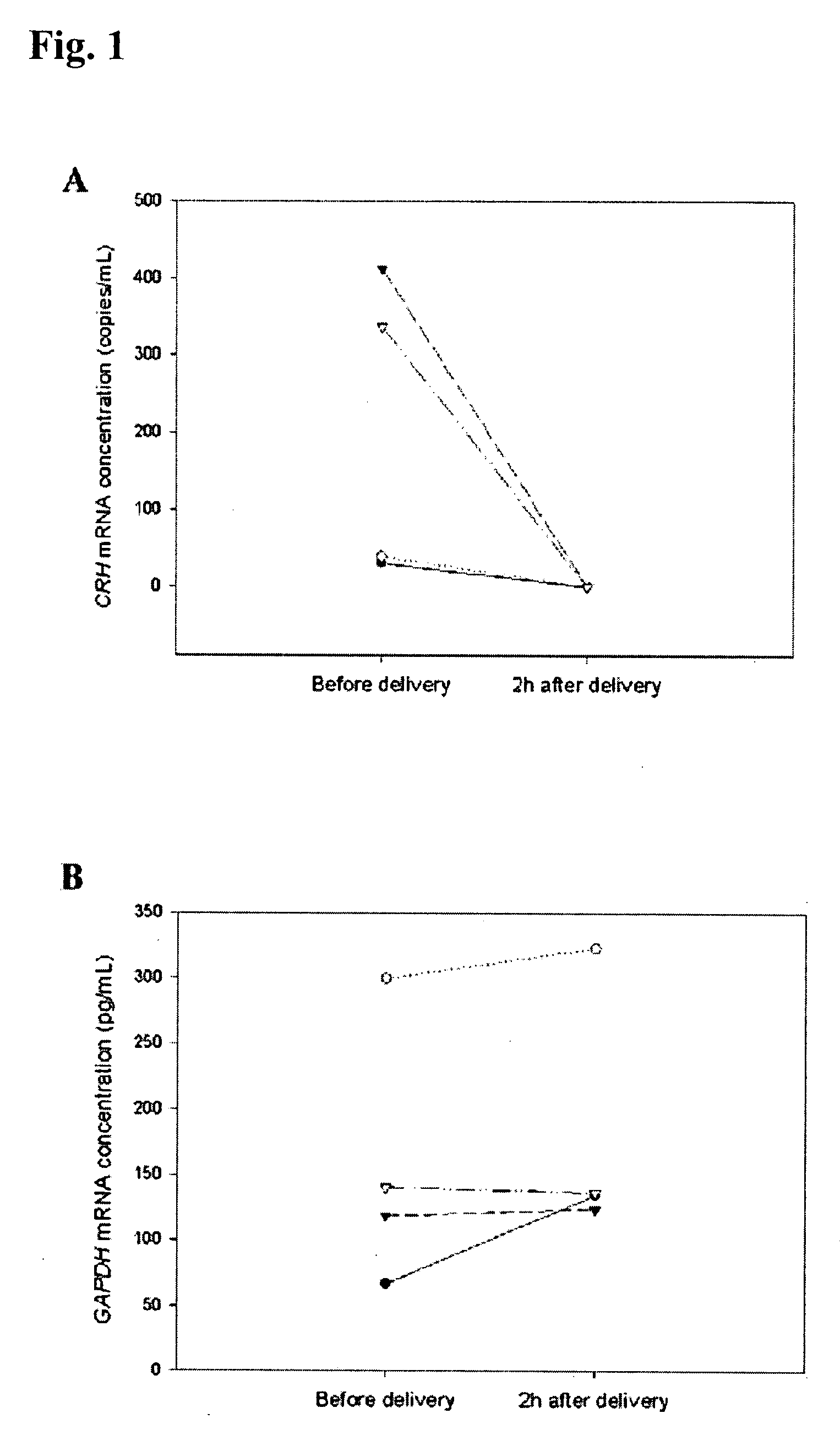
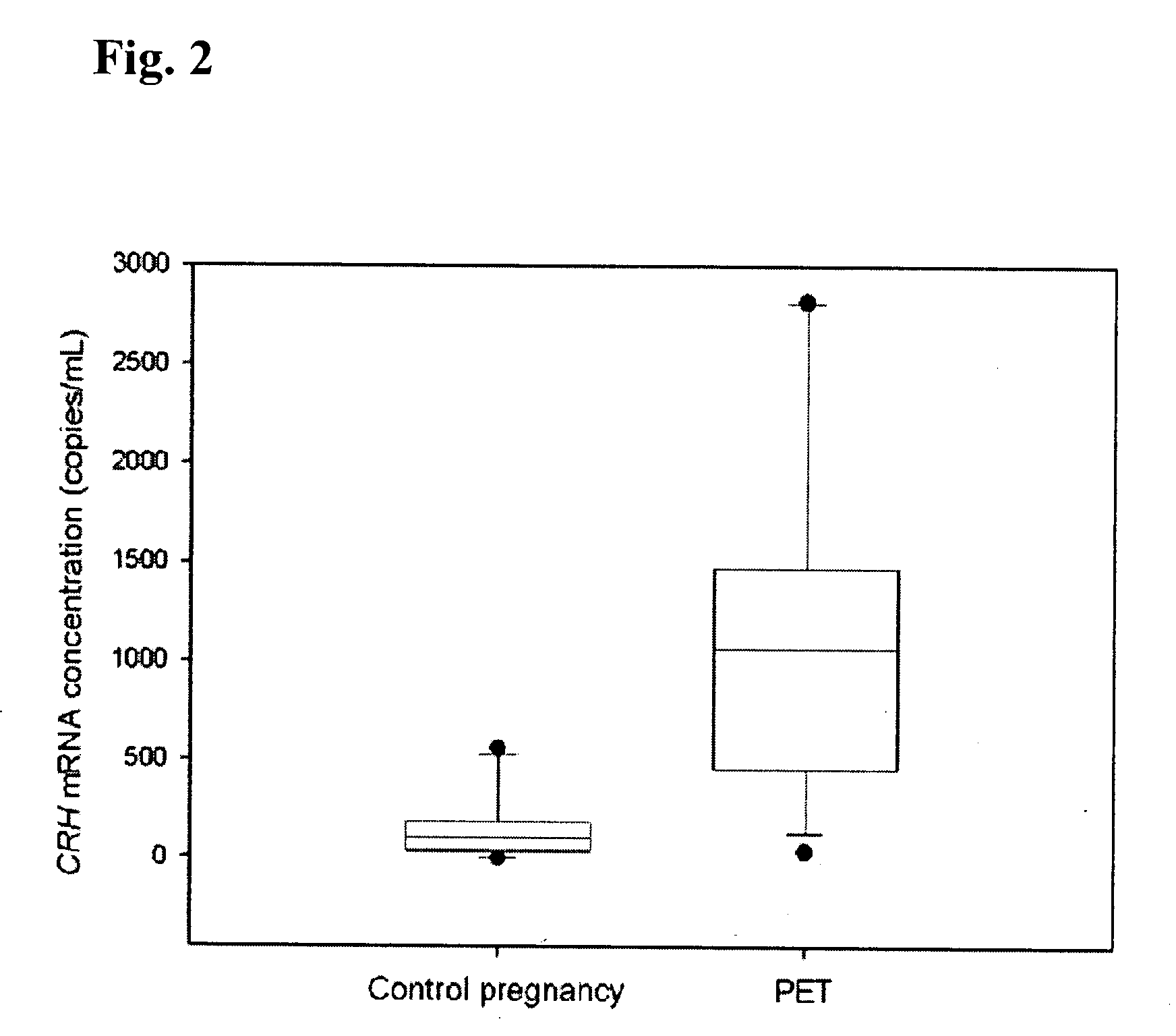
Methods and kits are provided for diagnosing, monitoring, or predicting the conditions of pre-eclaimpsia, fetal chromosomal aneuploidy, and pre-term labor in a pregnant woman, as well as for detecting pregnancy in a woman, by quantitatively measuring in the maternal blood the amount of one or more mRNA species encoding human chorionic gonadotropin β subunit (hCG-β), human placental lactogen (hPL), human corticotropin releasing hormone (hCRH), KiSS-1 metastasis-suppressor (KISS1), tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 (TPFI2), placenta-specific 1 (PLAC1), or glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), and comparing the amount of the mRNA species with a standard control.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Proteomic analysis of biological fluids
ActiveUS20070161125A1Eliminate needMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalogue computers for chemical processesDiseaseGynecology
The invention concerns the identification of proteomes of biological fluids and their use in determining the state of maternal / fetal conditions, including maternal conditions of fetal origin, chromosomal aneuploidies, and fetal diseases associated with fetal growth and maturation. In particular, the invention concerns a comprehensive proteomic analysis of human amniotic fluid (AF) and cervical vaginal fluid (CVF), and the correlation of characteristic changes in the normal proteome with various pathologic maternal / fetal conditions, such as intra-amniotic infection, pre-term labor, and / or chromosomal defects. The invention further concerns the identification of biomarkers and groups of biomarkers that can be used for non-invasive diagnosis of various pregnancy-related disorders, and diagnostic assays using such biomarkers.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
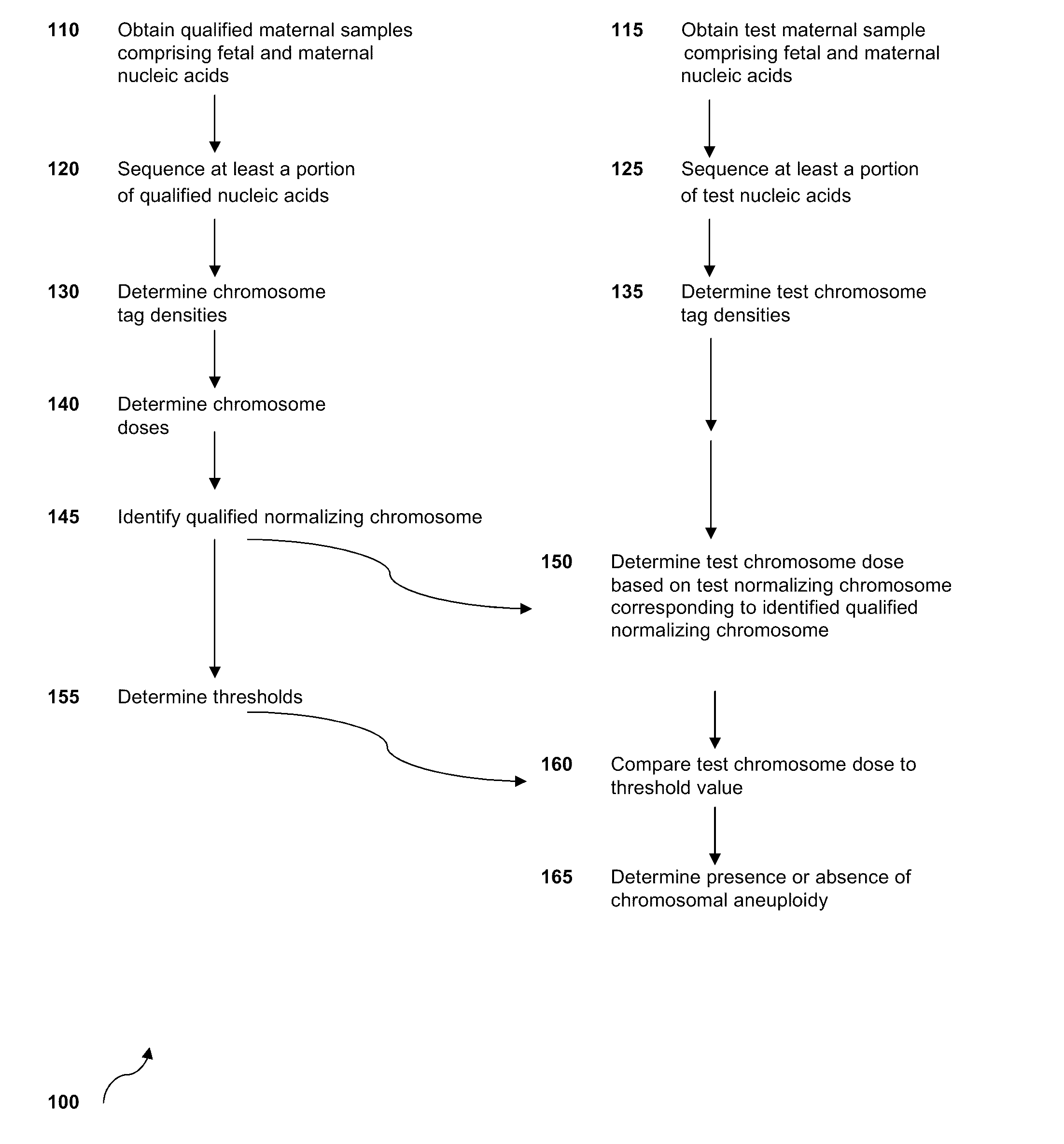
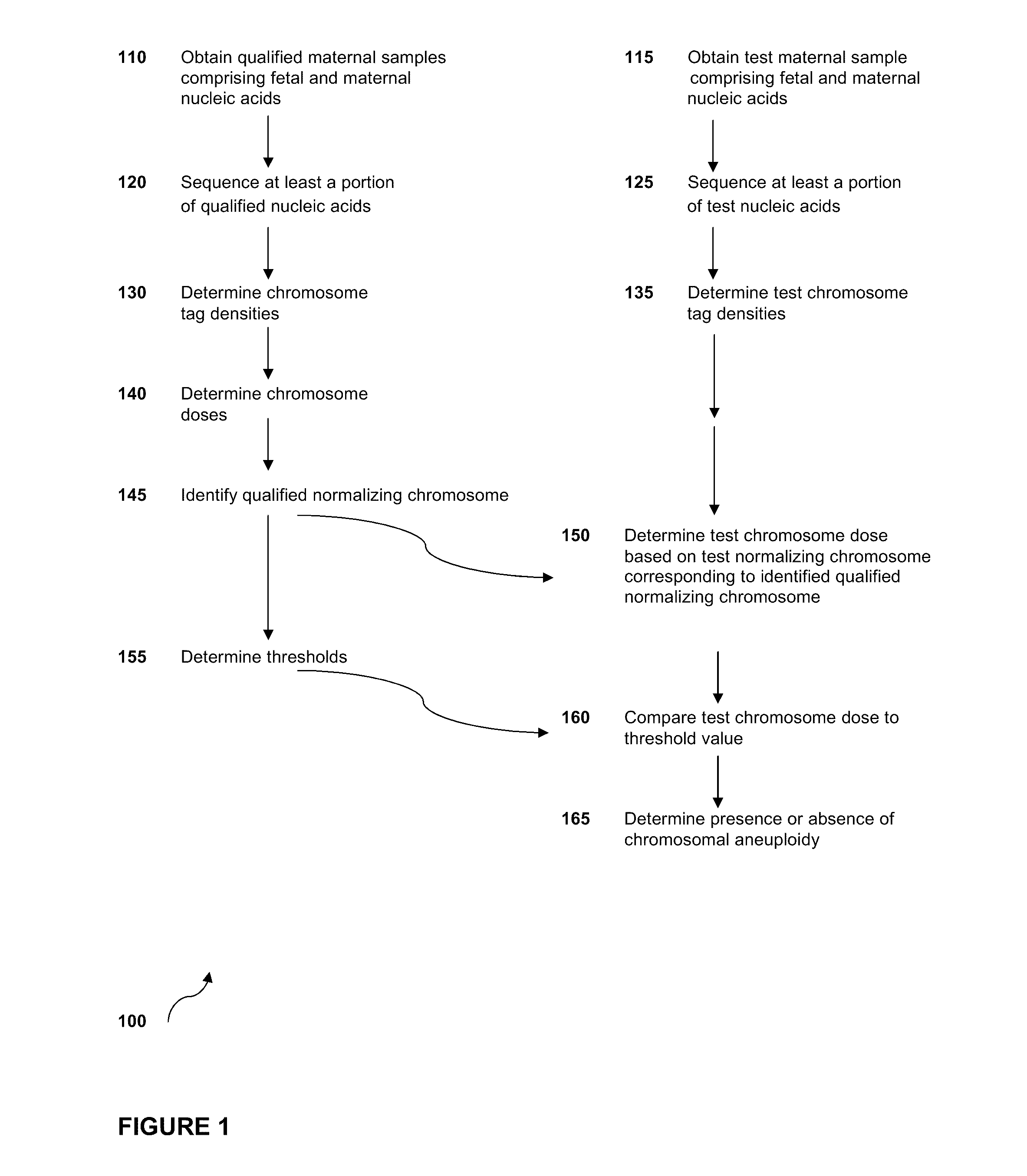
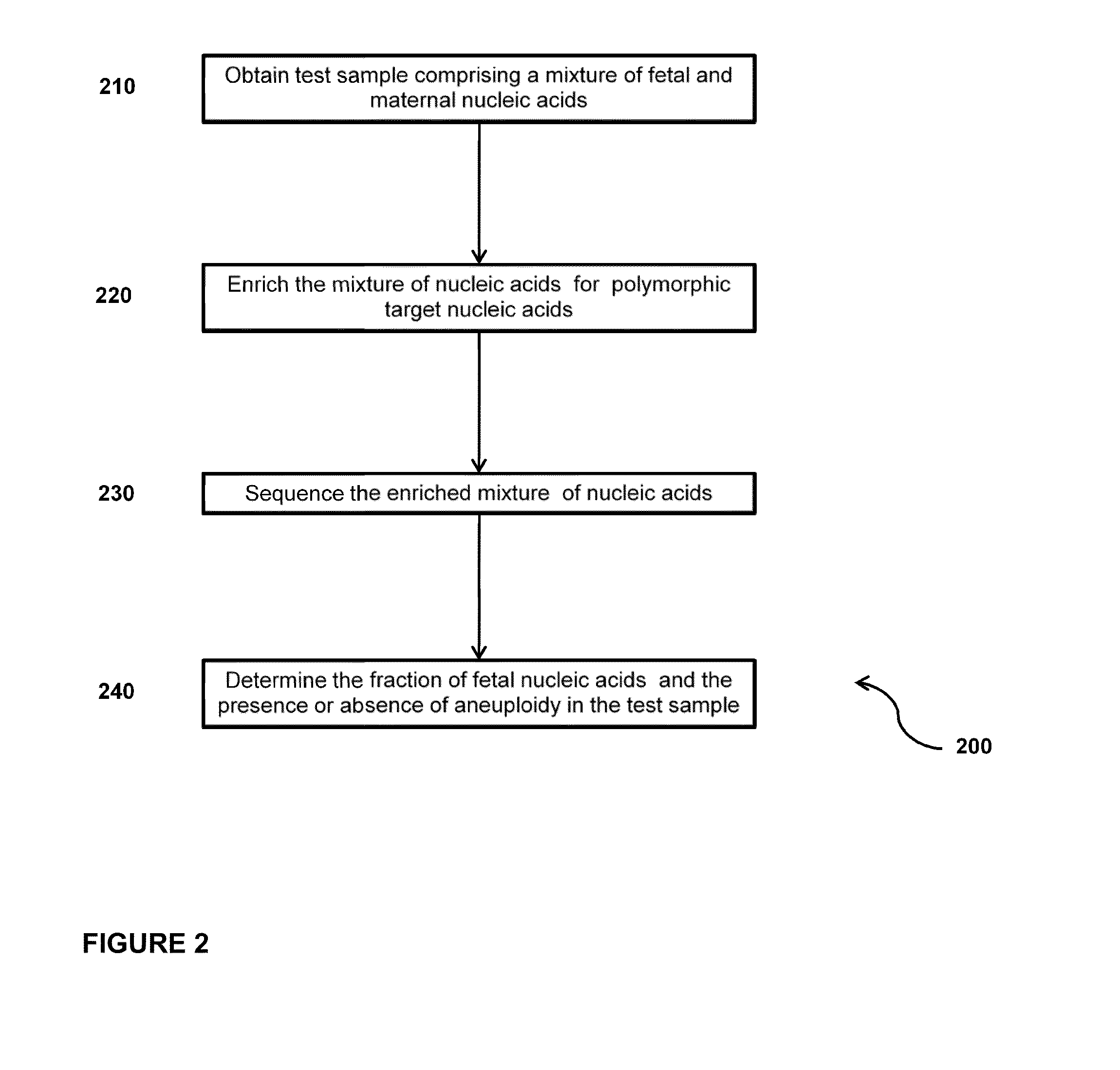
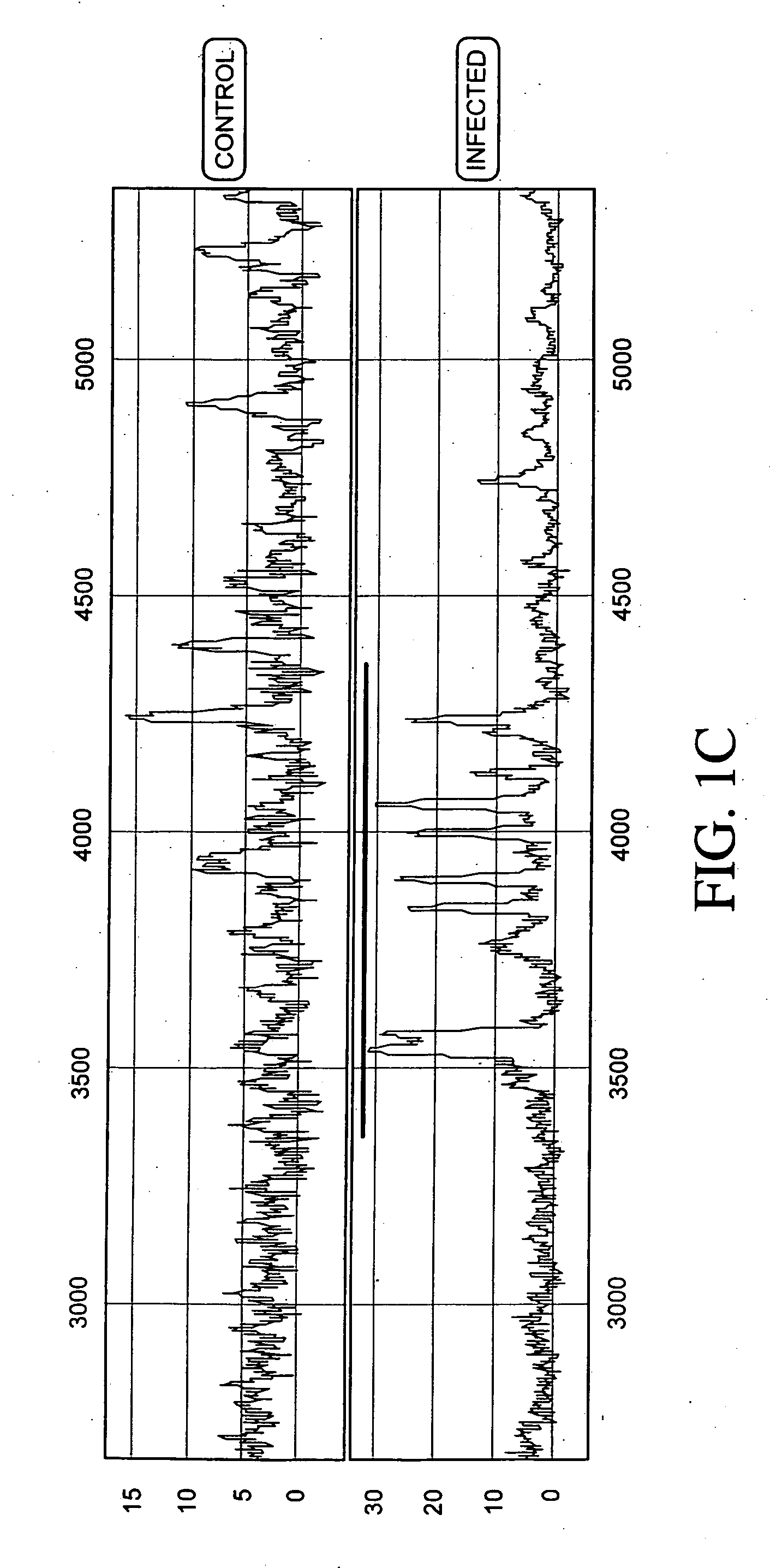
Normalizing chromosomes for the determination and verification of common and rare chromosomal aneuploidies
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC
System and method for cleaning noisy genetic data and determining chromosome copy number
InactiveUS20200224273A1Improve fidelityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsGenetic correlationDiploid cells
Disclosed herein is a system and method for increasing the fidelity of measured genetic data, for making allele calls, and for determining the state of aneuploidy, in one or a small set of cells, or from fragmentary DNA, where a limited quantity of genetic data is available. Poorly or incorrectly measured base pairs, missing alleles and missing regions are reconstructed using expected similarities between the target genome and the genome of genetically related individuals. In accordance with one embodiment, incomplete genetic data from an embryonic cell are reconstructed at a plurality of loci using the more complete genetic data from a larger sample of diploid cells from one or both parents, with or without haploid genetic data from one or both parents. In another embodiment, the chromosome copy number can be determined from the measured genetic data, with or without genetic information from one or both parents.
Owner:NATERA
System and method for cleaning noisy genetic data and determining chromosome copy number
PendingUS20200248264A1Improve fidelityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsGenetic correlationDiploid cells
Disclosed herein is a system and method for increasing the fidelity of measured genetic data, for making allele calls, and for determining the state of aneuploidy, in one or a small set of cells, or from fragmentary DNA, where a limited quantity of genetic data is available. Poorly or incorrectly measured base pairs, missing alleles and missing regions are reconstructed using expected similarities between the target genome and the genome of genetically related individuals. In accordance with one embodiment, incomplete genetic data from an embryonic cell are reconstructed at a plurality of loci using the more complete genetic data from a larger sample of diploid cells from one or both parents, with or without haploid genetic data from one or both parents. In another embodiment, the chromosome copy number can be determined from the measured genetic data, with or without genetic information from one or both parents.
Owner:NATERA
System and method for cleaning noisy genetic data and determining chromosome copy number
ActiveUS20200232036A1Significant resultImprove fidelityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsGenetic correlationDiploid cells
Disclosed herein is a system and method for increasing the fidelity of measured genetic data, for making allele calls, and for determining the state of aneuploidy, in one or a small set of cells, or from fragmentary DNA, where a limited quantity of genetic data is available. Poorly or incorrectly measured base pairs, missing alleles and missing regions are reconstructed using expected similarities between the target genome and the genome of genetically related individuals. In accordance with one embodiment, incomplete genetic data from an embryonic cell are reconstructed at a plurality of loci using the more complete genetic data from a larger sample of diploid cells from one or both parents, with or without haploid genetic data from one or both parents. In another embodiment, the chromosome copy number can be determined from the measured genetic data, with or without genetic information from one or both parents.
Owner:NATERA
Proteomic analysis of biological fluids
ActiveUS7191068B2Eliminate needMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingDiseaseFetal growth
The invention concerns the identification of proteomes of biological fluids and their use in determining the state of maternal / fetal conditions, including maternal conditions of fetal origin, chromosomal aneuploidies, and fetal diseases associated with fetal growth and maturation. In particular, the invention concerns the identification of the proteome of amniotic fluid (multiple proteins representing the composition of amniotic fluid) and the correlation of characteristic changes in the normal proteome with various pathologic maternal / fetal conditions, such as intra-amniotic infection, or chromosomal defects.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC +1
Method and system for noninvasive detection of fetus chromosome aneuploid
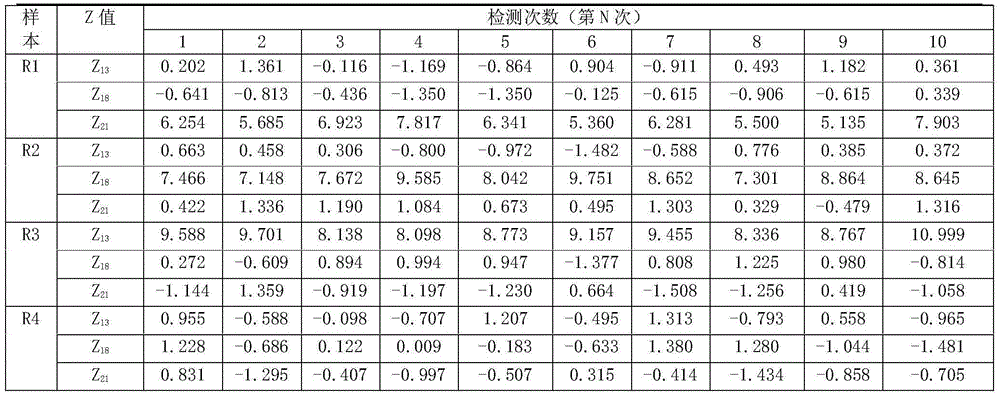
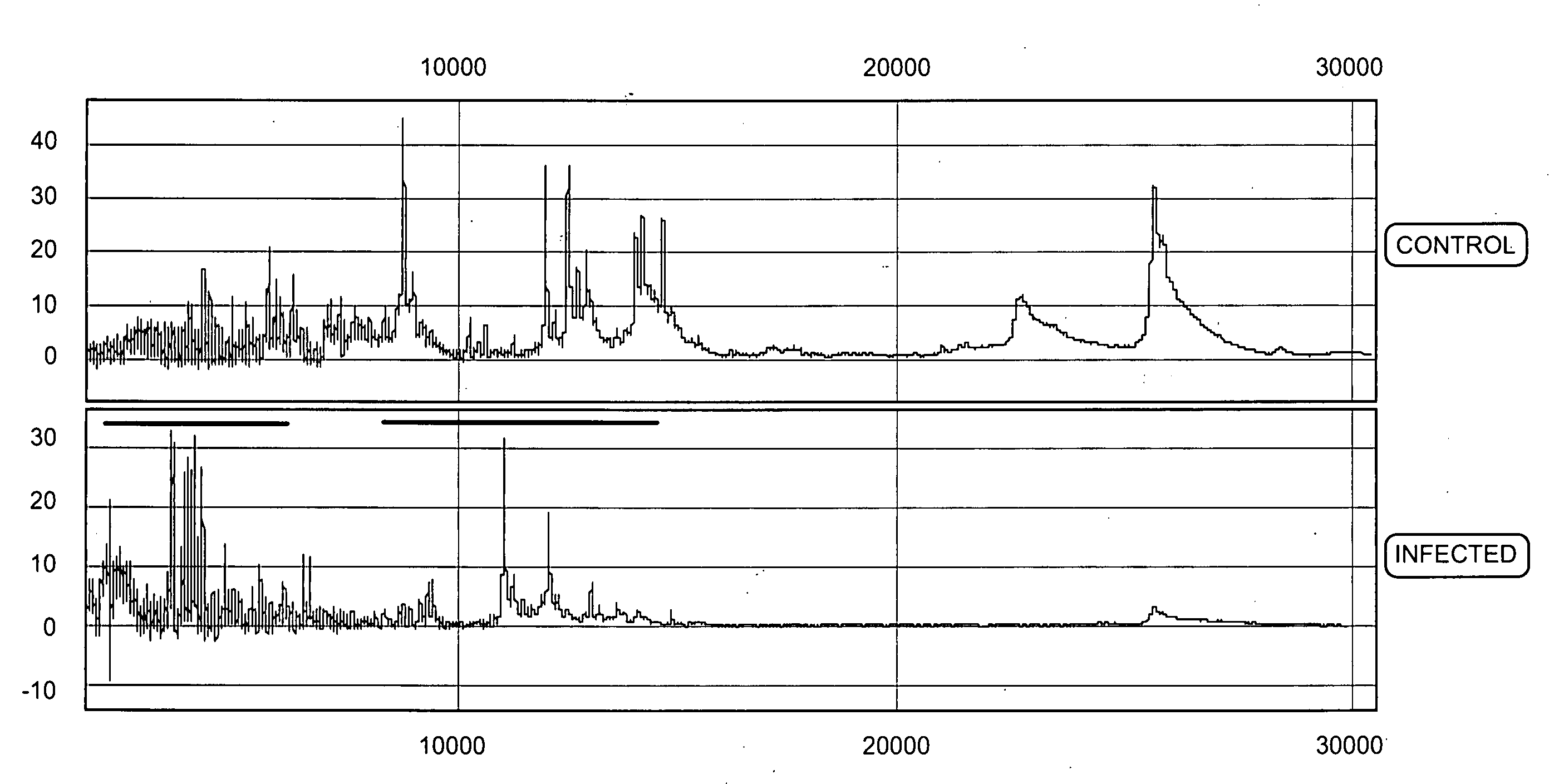
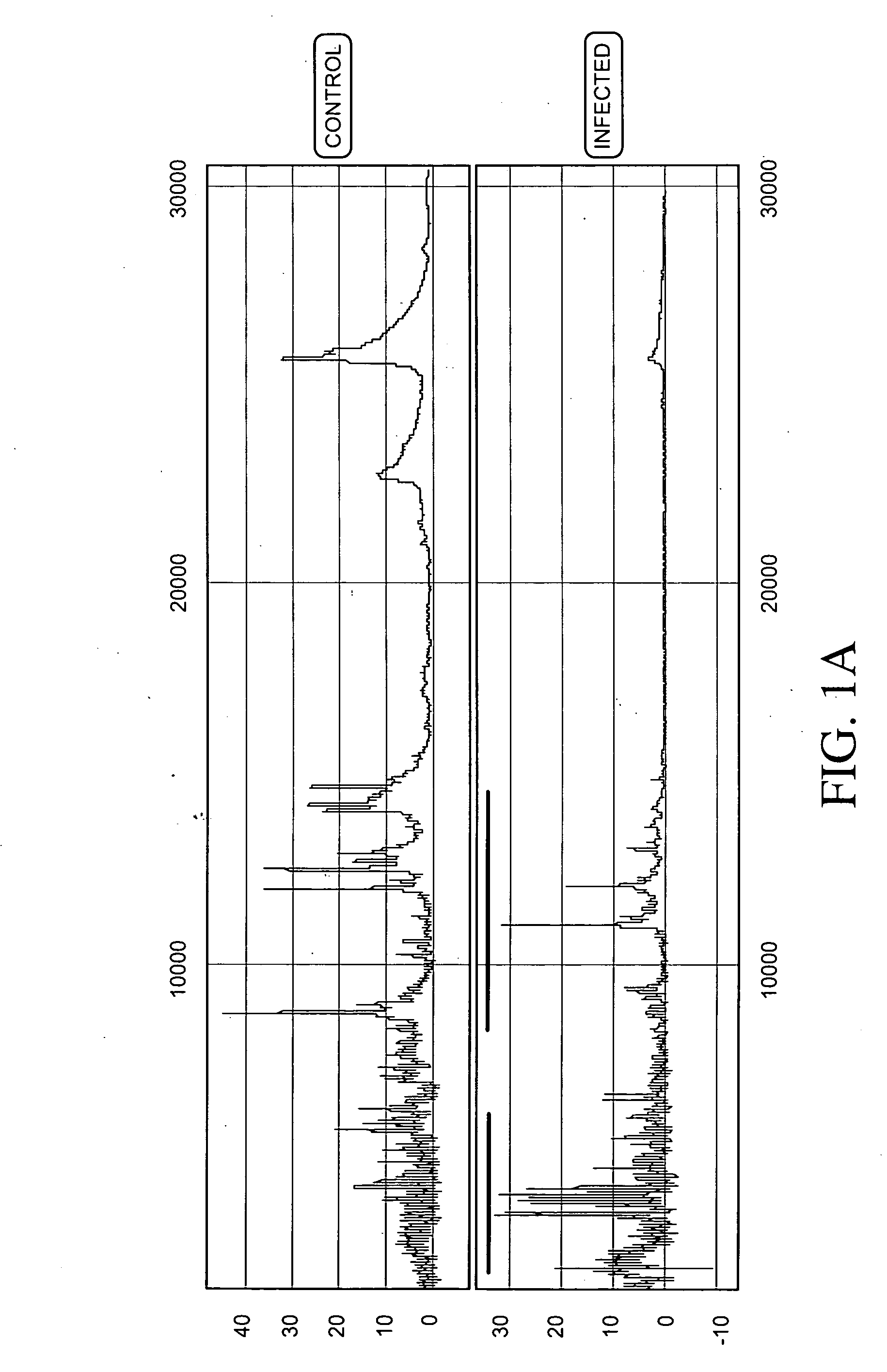
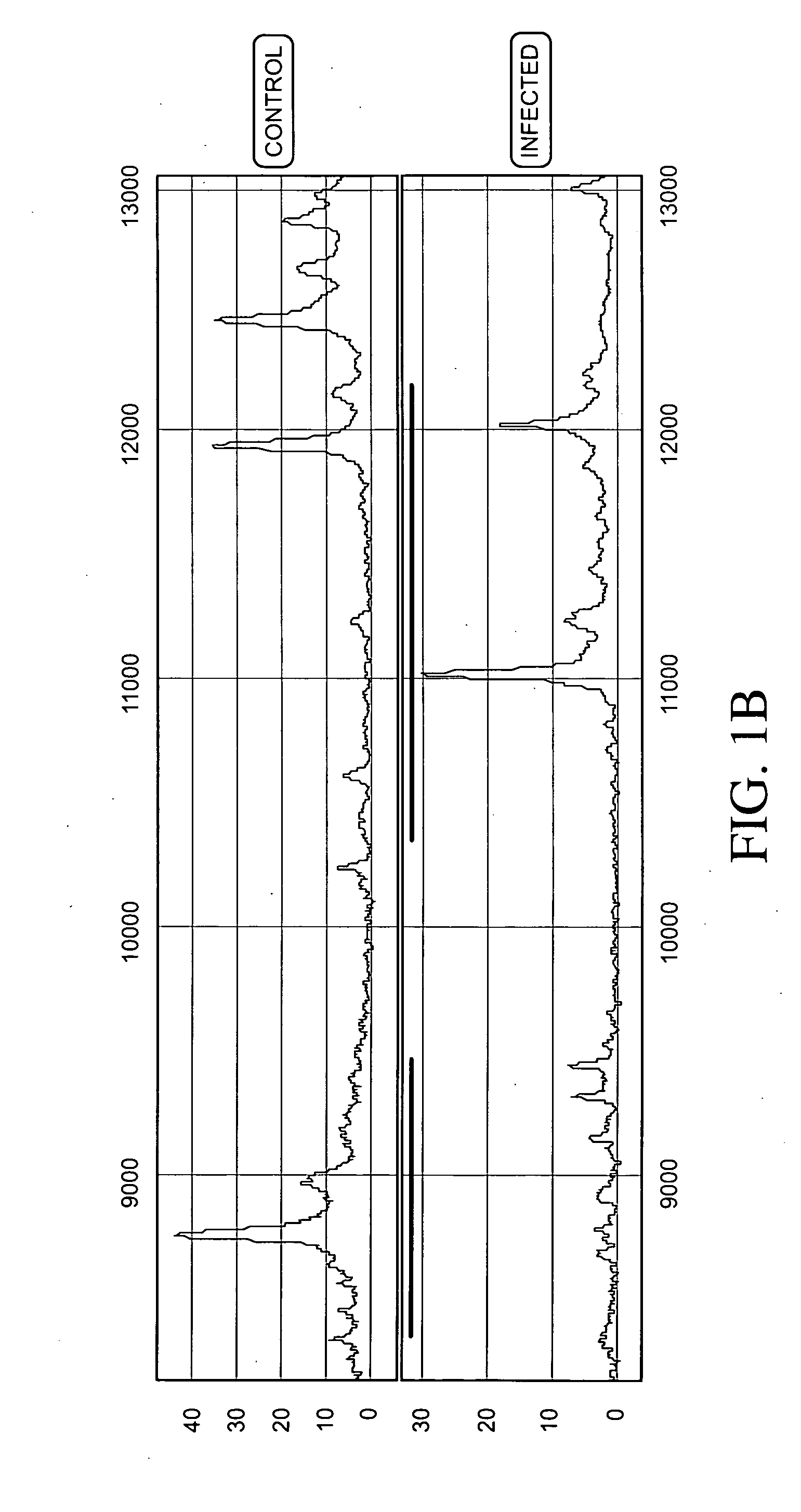
ActiveCN103525939AImprove scalabilityBirth rate controlMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsX chromosomeRelational model
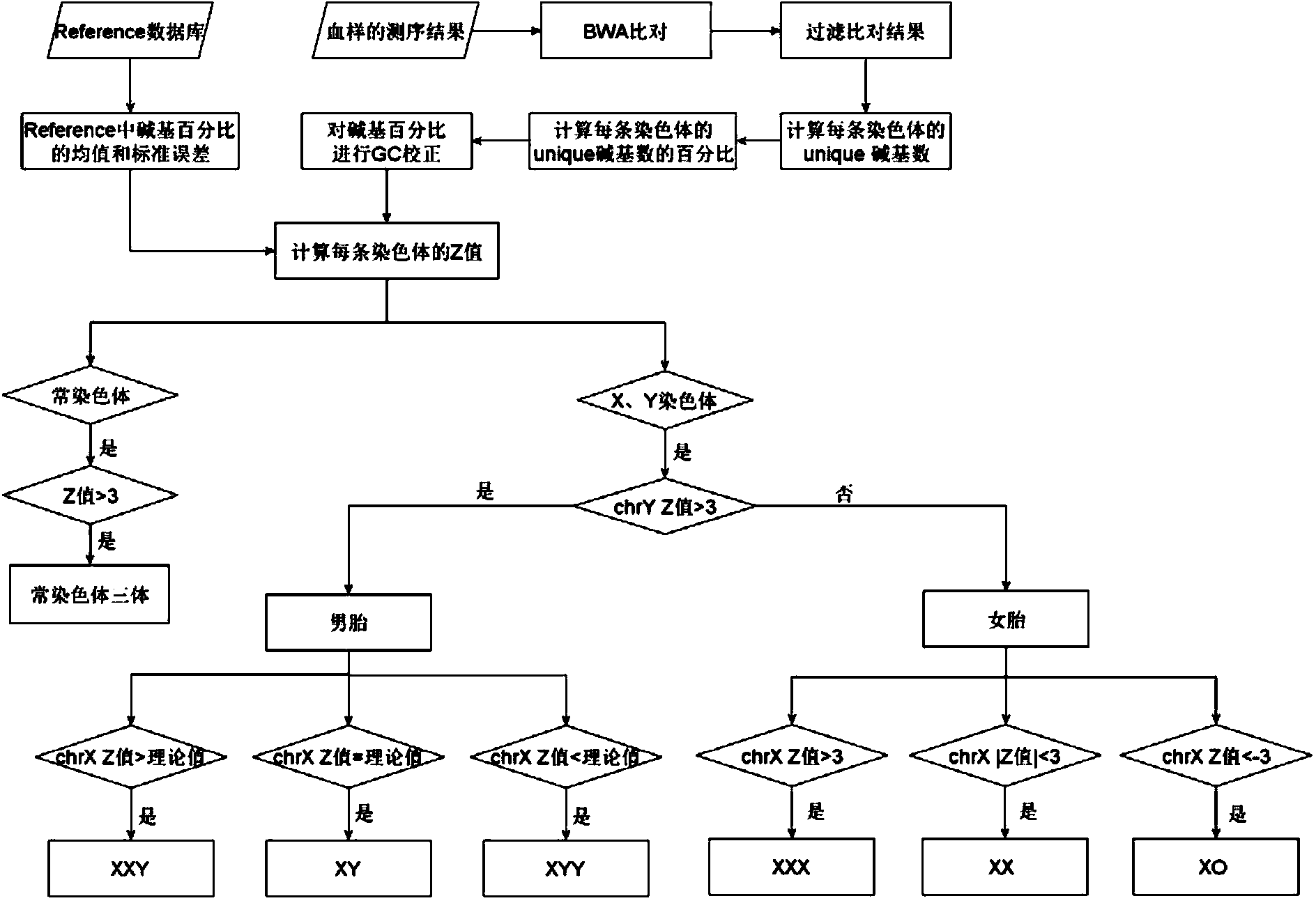
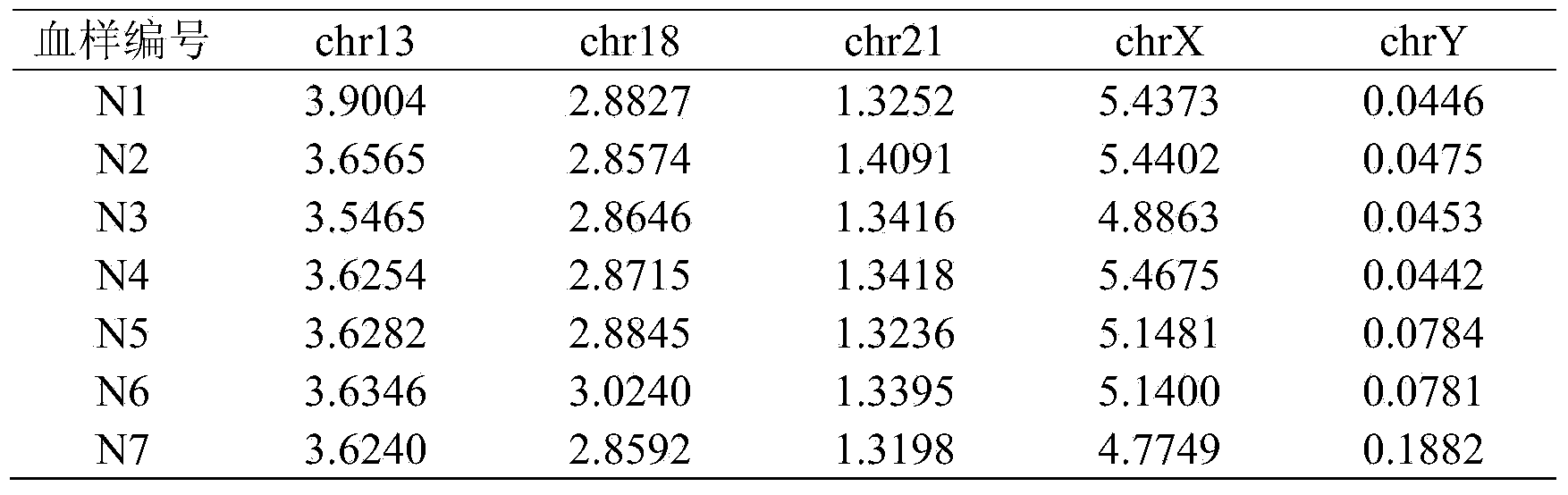
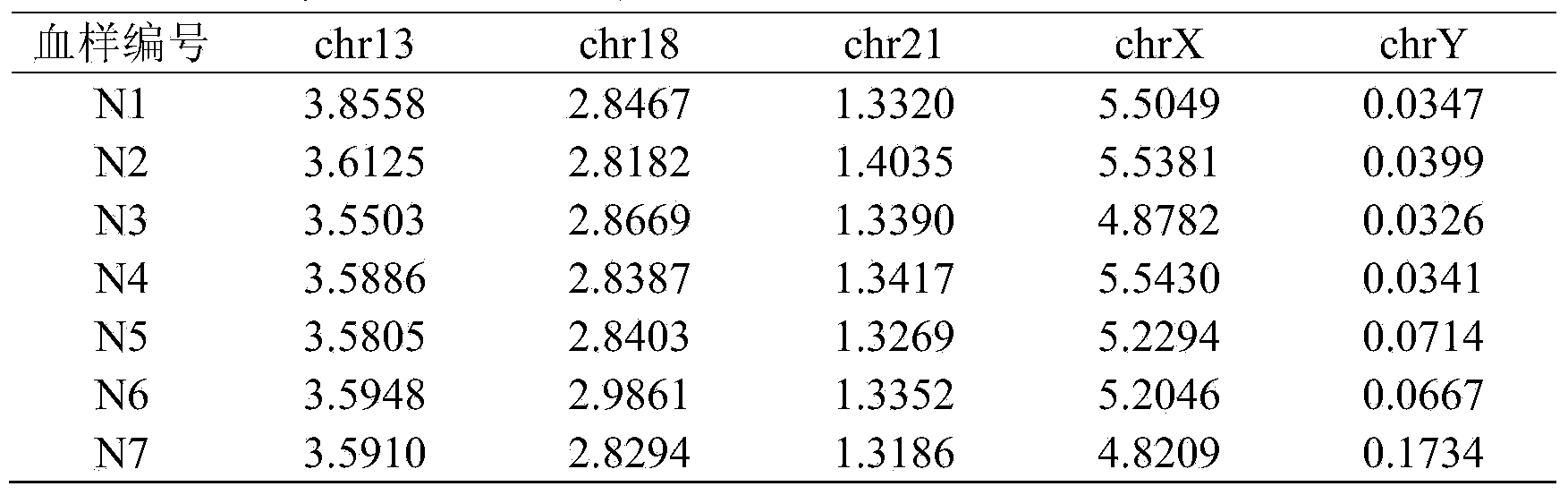
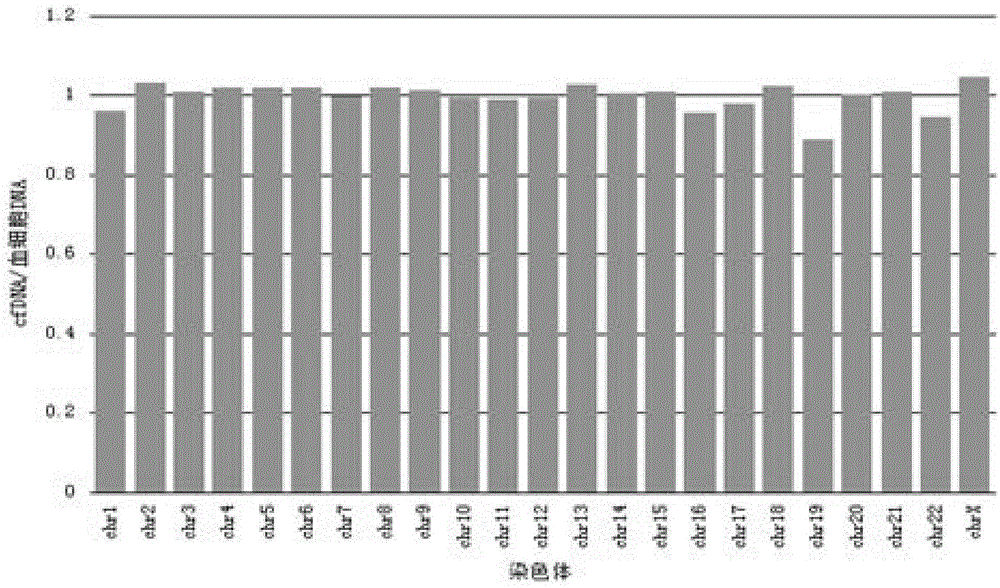
The invention belongs to the medical detection field, and discloses a method and a system for noninvasive detection of fetus chromosome aneuploid. The disclosed detection method and system also relate to a method and a system for elimination of sequencing GC preference in chromosomes and among chromosomes and a method and a system used for the relation model of the Z values of X and Y chromosomes in a normal male fetus. Through elimination of influences of sequencing GC preference in chromosomes and among chromosomes, the relation model of the Z values of X and Y chromosomes in a normal male fetus is built, and the determination threshold of difference between the theoretical value and the actual value of the Z value of the X chromosome is built. The accurate detection of fetus chromosome aneuploid, especially sex chromosome aneuploid is achieved.
Owner:BOAO BIOLOGICAL CO LTD
Method and device for simultaneously determining fetal nucleic acid content and aneuploidy of chromosome
ActiveCN104232777AAccurate detectionApplicable detectabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGenotypeBiology
Owner:TIANJIN MEDICAL LAB BGI +2
Chromosomal aneuploid and copy number variation detecting method and application thereof
PendingCN106520940AShorten detection timeGuaranteed accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementInformation analysisEmbryo
The invention provides a chromosomal aneuploid and copy number variation detecting method and application thereof. Particularly, sequencing is performed on whole genomes of to-be-detected samples, and sequencing data of the samples are obtained. When a certain chromosome in an embryonic cell is a trisomy chromosome or haplochromosome, the copy rate of the chromosome is increased or decreased compared with that of a normal diploid chromosome, information analysis is performed through biostatistics, and aneuploids can be accurately detected. An experimental result shows that the chromosomal aneuploid and copy number variation can be simply, rapidly and accurately detected through the method.
Owner:BGI BIOTECH WUHAN CO LTD
Method for detecting embryo chromosome abnormality by utilizing blastula culture solution
ActiveCN105368936AAvoid lostAvoid damageMicrobiological testing/measurementMedical automated diagnosisEmbryoNon invasive
Owner:XUKANG MEDICAL SCI & TECH (SUZHOU) CO LTD
Methods for preparing and analyzing cells having chromosomal abnormalities
InactiveUS20060257884A1Microbiological testing/measurementFluorescenceFluorescence in situ hybridization
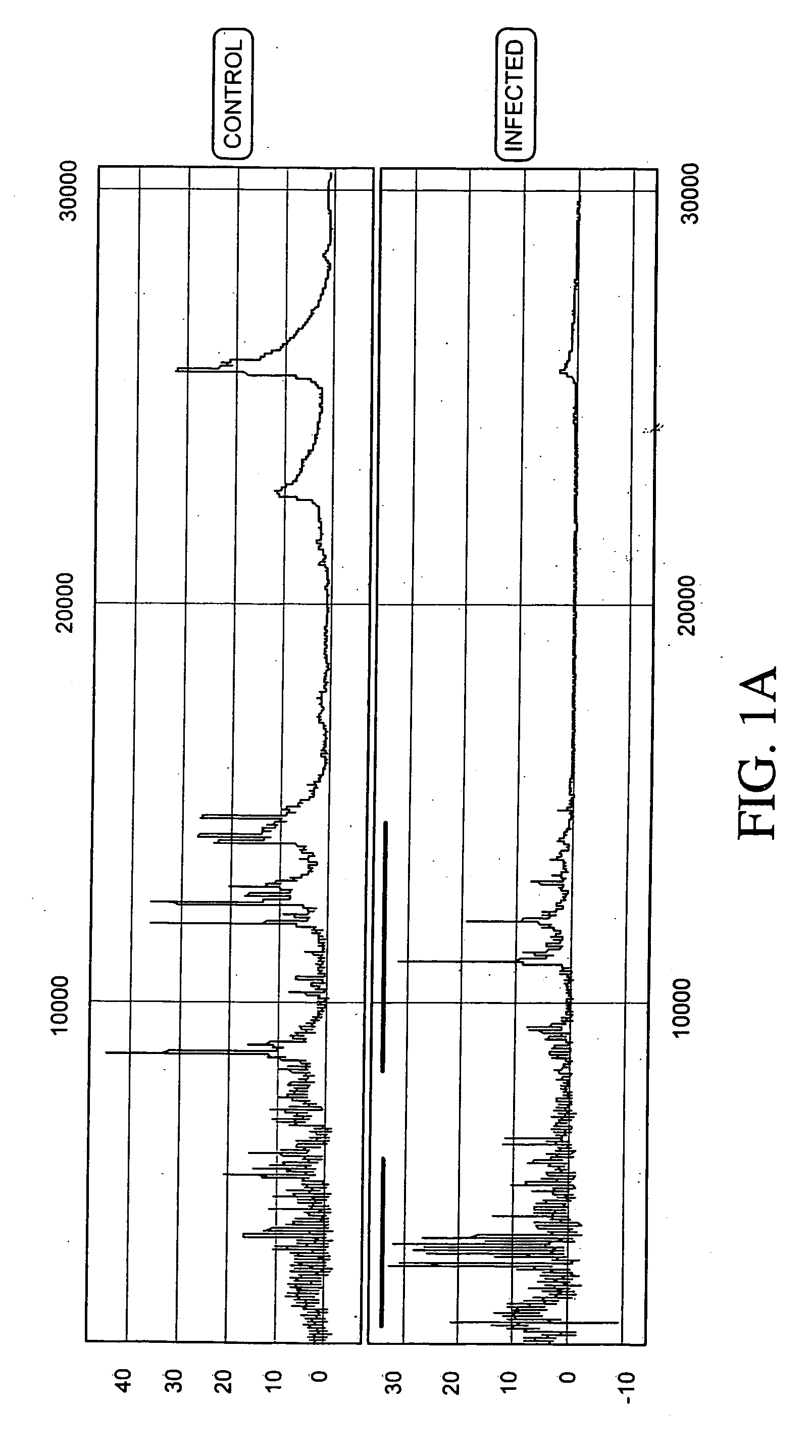
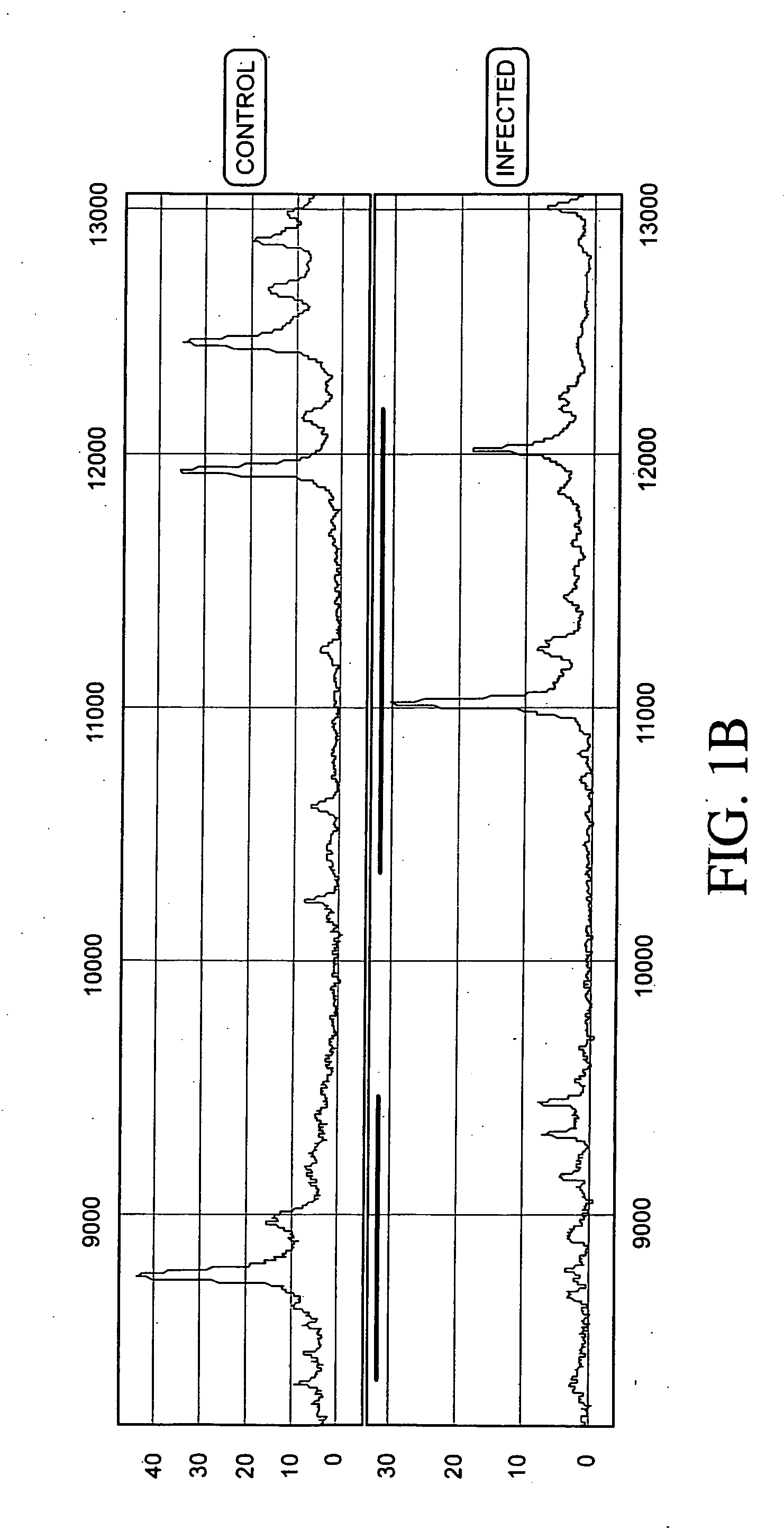
The present invention provides methods for preparing cells with highly condensed chromosomes, such as sperm, and methods for detecting and quantifying specific cellular target molecules in intact cells. Specifically, methods are provided for detecting chromosomes and chromosomal abnormalities, including aneuploidy, in intact cells using fluorescence in situ hybridization of cells in suspension, such as sperm cells.
Owner:AMNIS CORP
Methods for analysis of circulating cells
PendingUS20220056534A1Accurate informationAccurate analysis and characterizationMicrobiological testing/measurementFetal cellOncology
The invention provides methods for characterizing and analyzing circulating cells. In particular, the invention provides methods for confirming the identity of an individual cell and that the obtained sample was derived from a single cell of a defined identity. Additional methods are provided for analyzing single cell samples to determine copy number variation and aneuploidy in the context of circulating fetal cells, microdeletions, single nucleic acid variations associated with cancer, or early relapse of cancer and metastasis.
Owner:NATERA
Proteomic analysis of biological fluids
InactiveUS20090055099A1Eliminate needBiological testingSpecial data processing applicationsDiseaseObstetrics
The invention concerns the identification of proteomes of biological fluids and their use in determining the state of maternal / fetal conditions, including maternal conditions of fetal origin, chromosomal aneuploidies, and fetal diseases associated with fetal growth and maturation. In particular, the invention concerns the identification of the proteome of amniotic fluid (multiple proteins representing the composition of amniotic fluid) and the correlation of characteristic changes in the normal proteome with various pathologic maternal / fetal conditions, such as intra-amniotic infection, or chromosomal defects.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
Method, apparatus, and system for detecting fetus gene information
ActiveCN104830986AEliminate systematic errorsImprove robustnessMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisMutation detectionGene Abnormality
The invention discloses a method for extracting fetus gene information. In the provided method, maternal cell DNA and acellular DNA are separated from a maternal sample, wherein the acellular DNA is from the fetus. Two DNA samples are strictly processed by same reagents and methods and subjected to parallel sequencing in a same sequencing reaction; and the fetus gene information and fetus gene abnormity can be obtained by comparing the sequencing results of two DNA samples. The provided autologous comparing method can be applied to detection of chromosome aneuploidy, and can also be applied to gene detections such as chimera detection, copy number variation detection, single point mutation detection, and the like.
Owner:CHI BIOTECH CO LTD
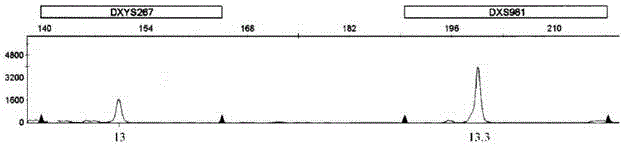
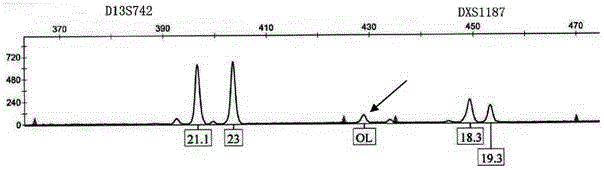
Kit for detecting aneuploidy of five human chromosomes through monotube multiple amplification
ActiveCN103555849AHigh detection sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementTrisomy 13 SyndromeReference product
The invention relates to a kit for detecting the STR (Short Tandem Repeat) genetype of human chromosomes 21, 18 and 13 and sex chromosomes, and particularly relates to a QF-PCR (Quantitative Fluorescence-Polymerase Chain Reaction) kit for detecting the number of the chromosomes 21, 18 and 13 and the sex chromosomes by adopting five-color fluorescence labeling monotube fast multiple amplification and mainly for diagnosing 21 trisomy syndrome, 18 trisomy syndrome, 13 trisomy syndrome and the aneuploid abnormality of the sex chromosomes. The kit comprises a primer mixture, a hot start C-Taq enzyme, an amplification reaction solution, a positive quality control product, a negative reference product, a fluorescence interior label Siz-500 and an allelic gene typing standard substance. Compared with the traditional antenatal diagnosis method, the kit disclosed by the invention can realize high-flux, fast, reliable and standardized detection.
Owner:AGCU SCIENTECH +1
Methods and systems for determining fetal chromosomal abnormalities
InactiveUS20130261984A1Minimize or eliminate false negativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMedical automated diagnosisTrisomyGenotype
The present disclosure provides methods and systems for determining the presence or absence of aneuploidy in a fetus. In particular, the present disclosure provides noninvasive methods and systems for detecting the presence of fetal trisomy and other fetal chromosomal anomalies, paternity of a fetus and fetal genotype.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Method of performing scRRBS analysis on embryo culture solution
PendingCN107760773AAssess developmental potentialEasy accessMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA methylationEmbryo
The invention provides a method of performing scRRBS (single-cell reduced-representation bisulfite sequencing) on an embryo culture solution. According to the method provided by the invention, medicalwaste (blastula culture solution) generated by 'test-tube baby' operation is adopted as a raw material, double analysis can be performed on the chromosome aneuploidy status and DNA methylation statusof the embryo, development potential of the embryo is evaluated from a brand new angle of epigenetics and reaction between the embryo and the culture environment, new reference is provided for selecting a 'correct' embryo in assisted reproduction, and powerful support is provided for increasing the success rate of the period of the test-tube baby.
Owner:BEIJING ZHONGYI KANGWEI MEDICAL INSTR
Methods for prenatal diagnosis of aneuploidy
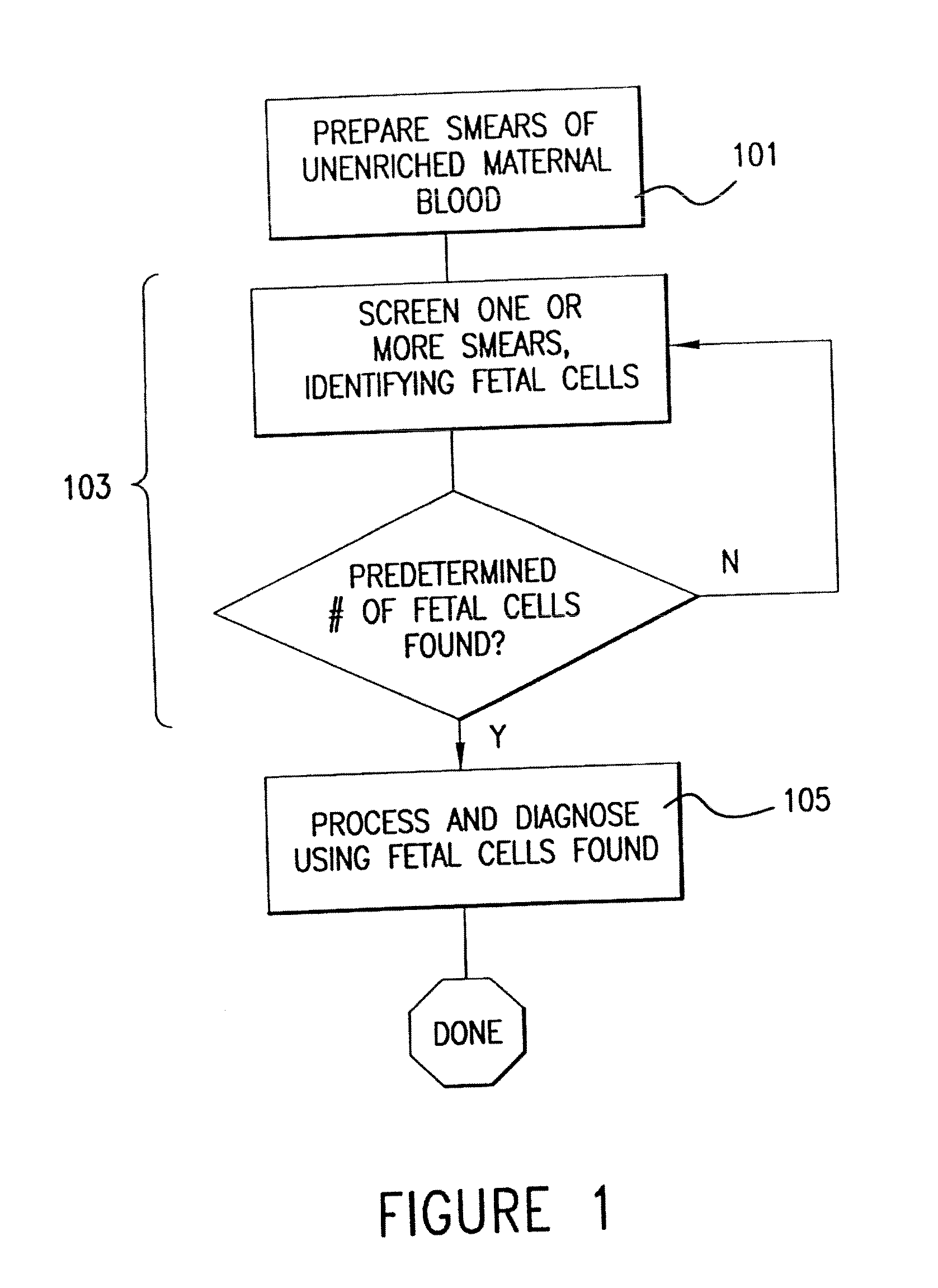
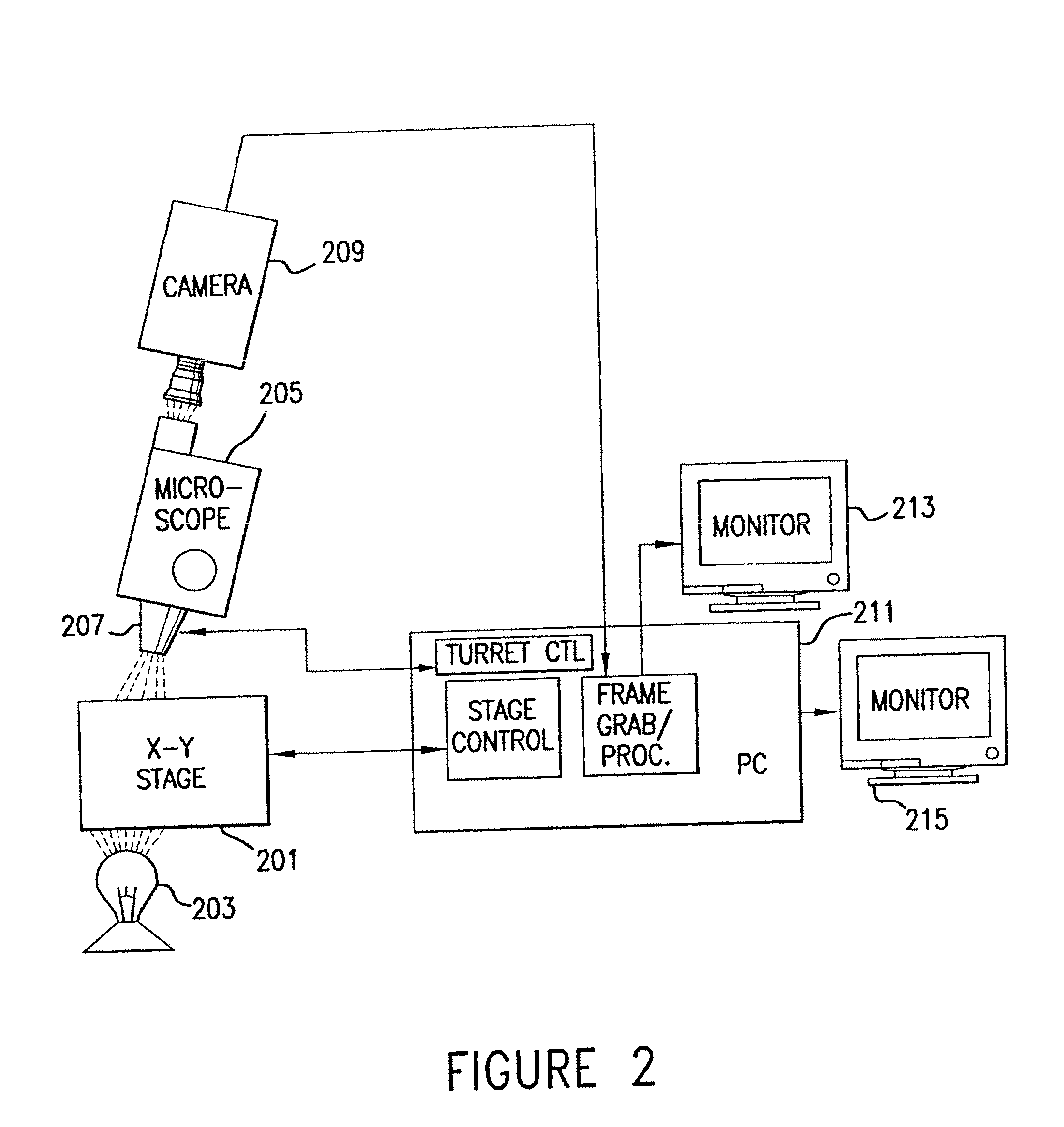
InactiveUS20080241848A1Suitable controlSuitable for processingImage enhancementImage analysisPrenatal diagnosisFluorescence microscope
Methods are disclosed for the automated prenatal genetic diagnosis of aneuploidy using an automated fluorescence microscope, conducted on samples of maternal blood that have been hybridized with FISH probes.
Owner:IKONISYS INC
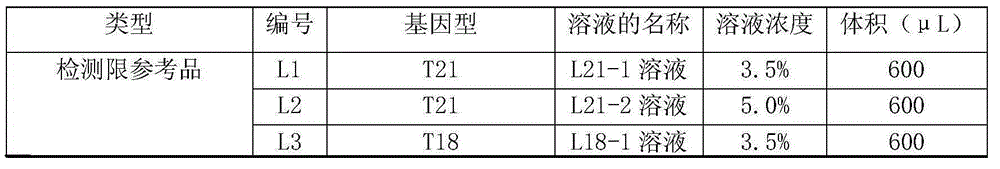
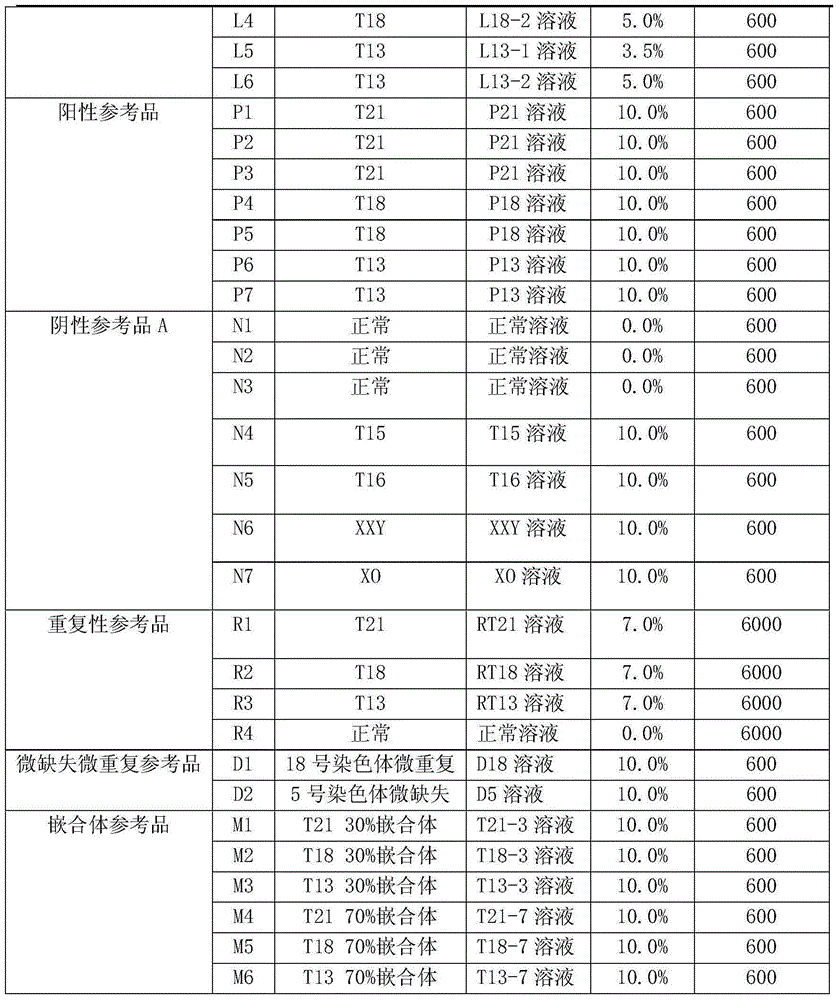
Quality control material of chromosome aneuploid (T21, T18 and T13) detection kit and application of quality control material
ActiveCN105039571AMeet testing needsHigh precisionMicrobiological testing/measurementKaryotypeQuality control
The invention discloses a quality control material of a chromosome aneuploid (T21, T18 and T13) detection kit. The quality control material comprises a positive reference material and a negative reference material. The positive reference material is a reference material set composed of a solution P21, a solution P18 and a solution P13, wherein the solution P21 is composed of solute and solvent, the solution P18 is composed of solute and solvent, the solution P13 is composed of solute and solvent, and the solvent of the solution P21, the solvent of the solution P18 and the solvent of the solution P13 are normal solutions. The normal solutions are in-vitro plasma of normal non-pregnant women of which the chromosome karyotype is 46, XX according to the analysis result. The solute of the solution P21 is PL21, the solute of the solution P18 is PL18, and the solute of the solution P13 is PL13. The quality control material is economical, simple and convenient to use and effectively achieves quality verification and performance evaluation of the chromosome aneuploid (T21, T18 and T13) detection kit.
Owner:CAPITALBIO CORP +1
Proteomic analysis of biological fluids
InactiveUS20080299594A1Eliminate needMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingDiseaseFetal growth
The invention concerns the identification of proteomes of biological fluids and their use in determining the state of maternal / fetal conditions, including maternal conditions of fetal origin, chromosomal aneuploidies, and fetal diseases associated with fetal growth and maturation. In particular, the invention concerns the identification of the proteome of amniotic fluid (multiple proteins representing the composition of amniotic fluid) and the correlation of characteristic changes in the normal proteome with various pathologic maternal / fetal conditions, such as intra-amniotic infection, or chromosomal defects.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
Nucleic acids and methods for detecting chromosomal abnormalities
ActiveUS20170183731A1Microbiological testing/measurementMedical automated diagnosisChromatosomeChromosomal Abnormality
Methods and nucleic acid molecules for detecting chromosomal abnormalities such as aneuploidy. Methods for selecting nucleic acid molecules for use in the methods of the disclosure.
Owner:BIORA THERAPEUTICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com