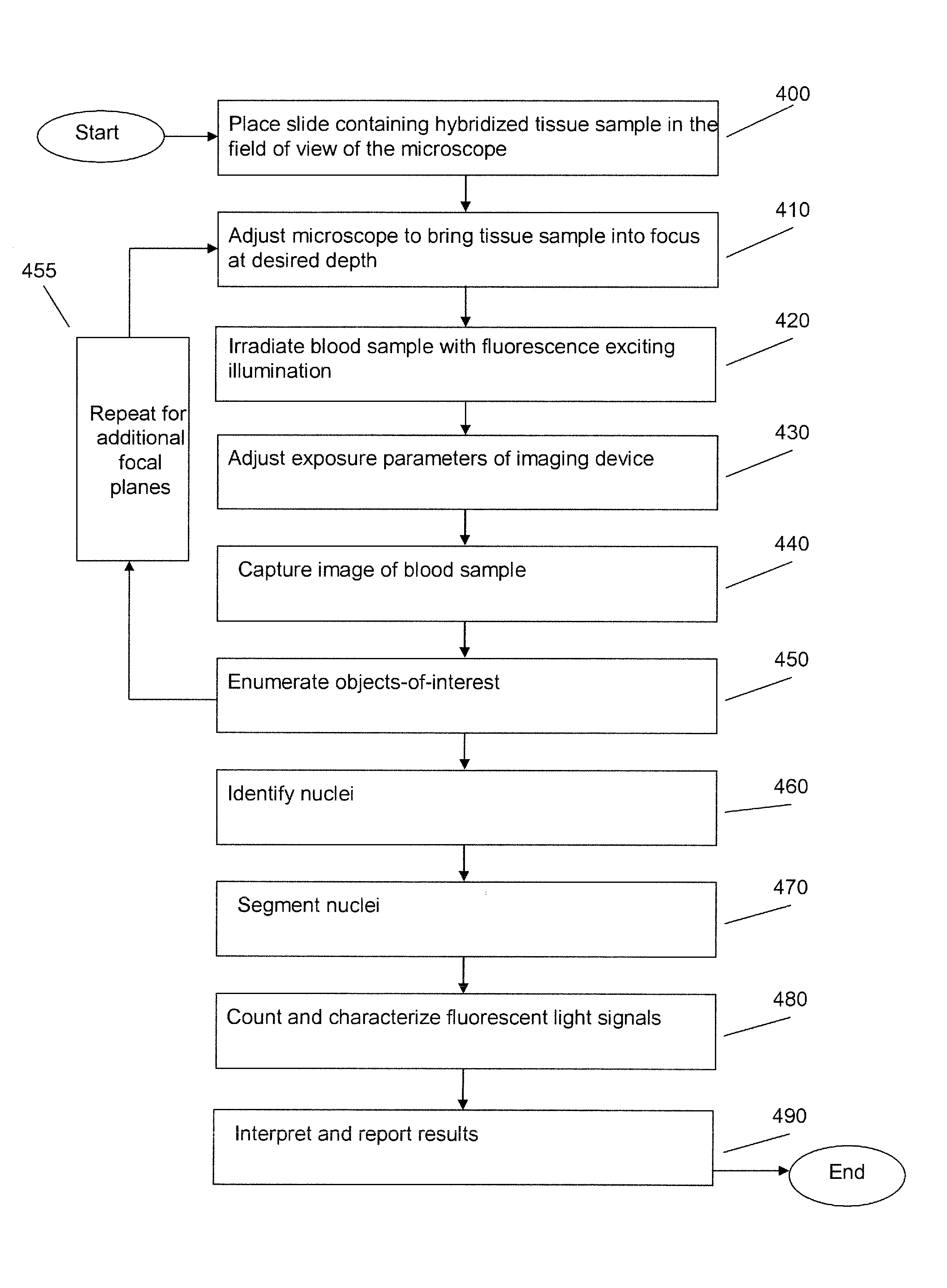
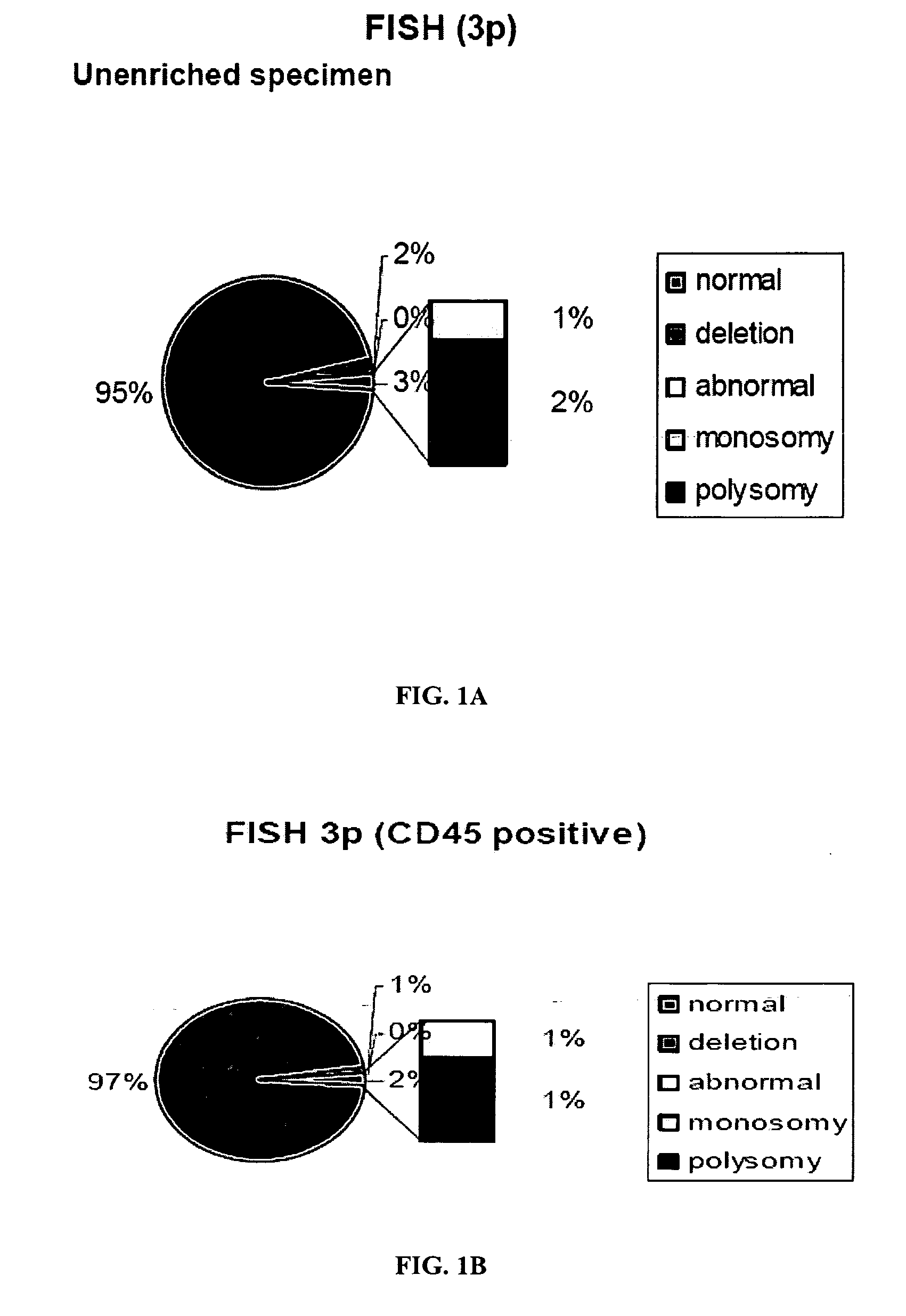
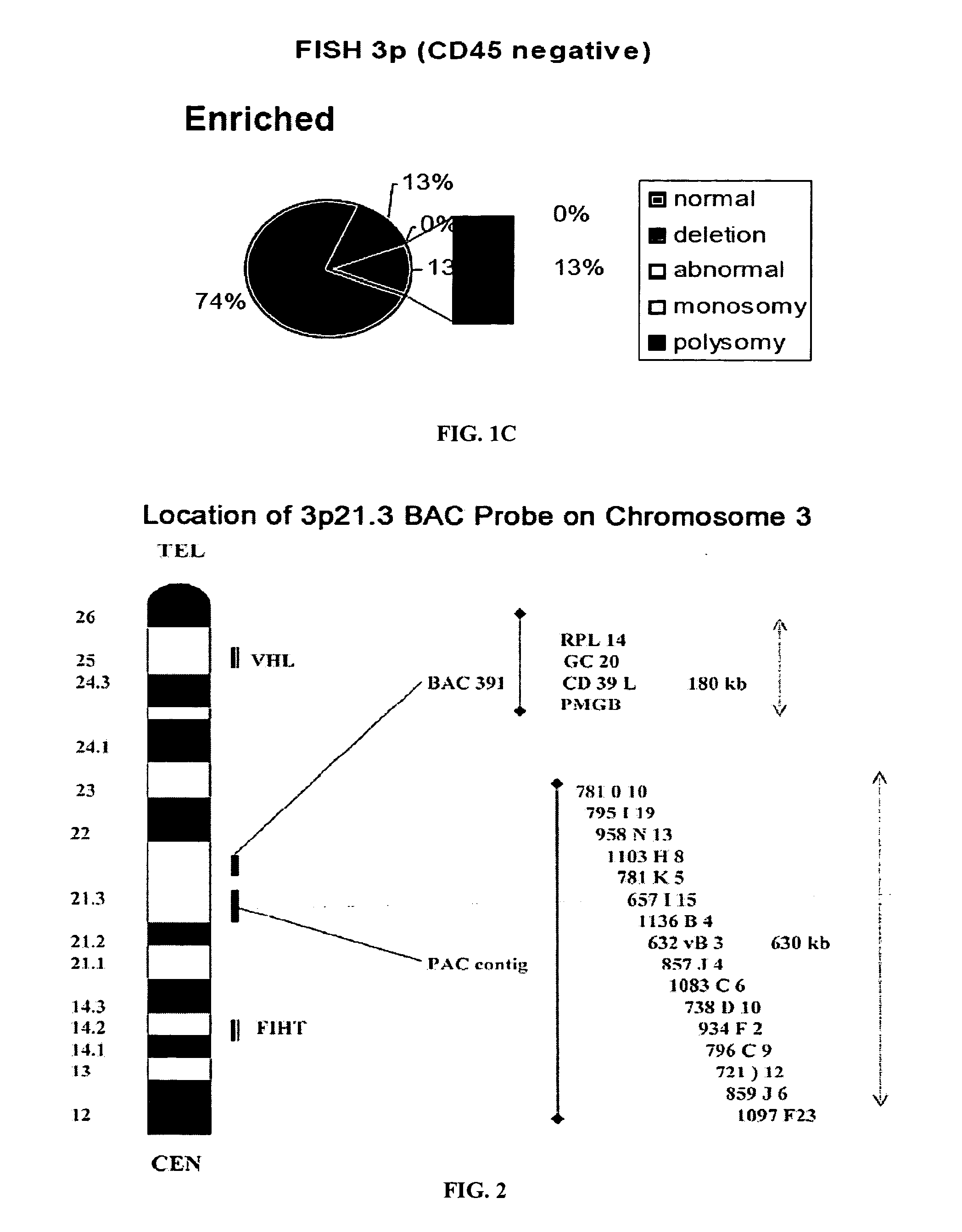
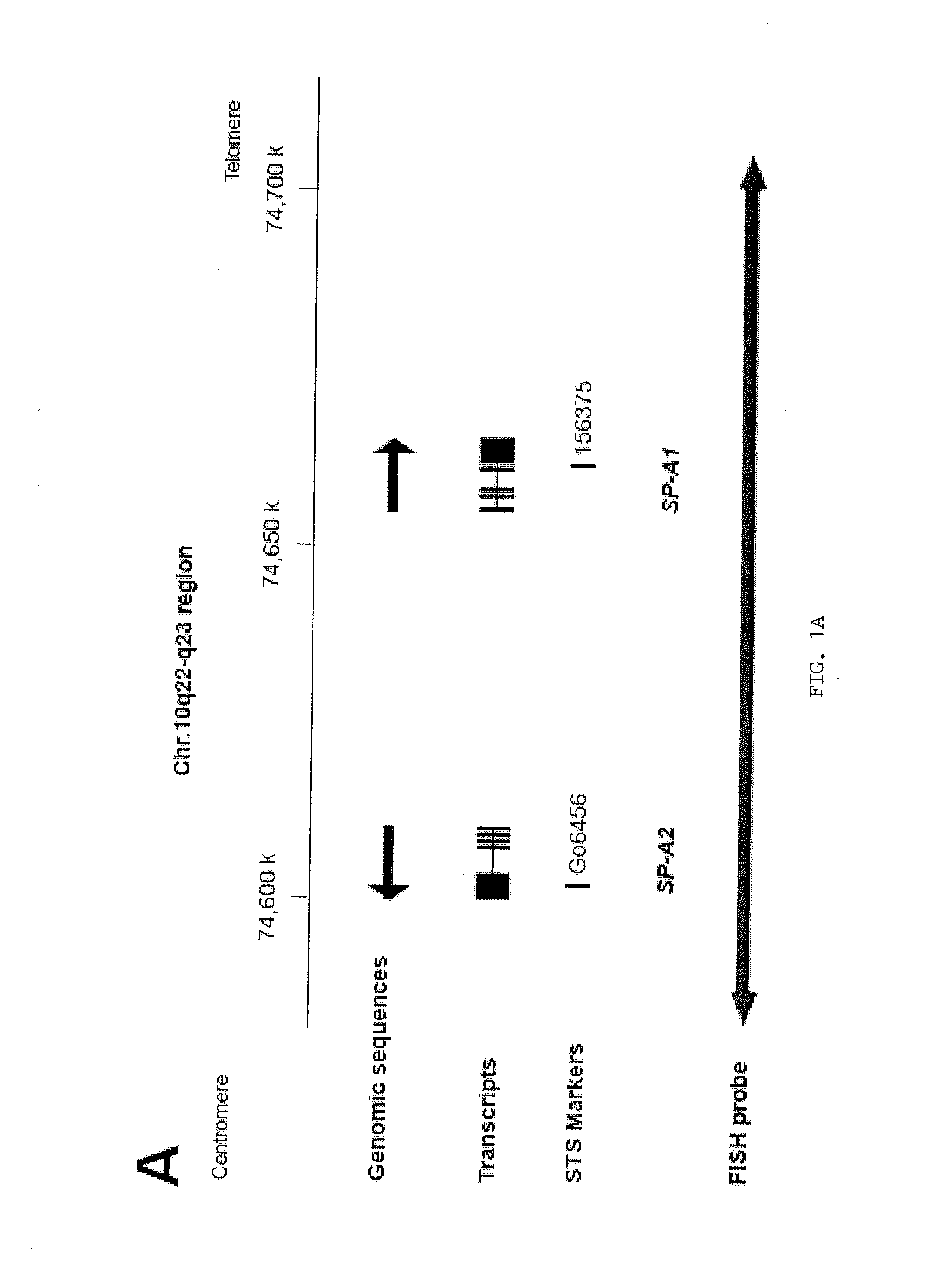
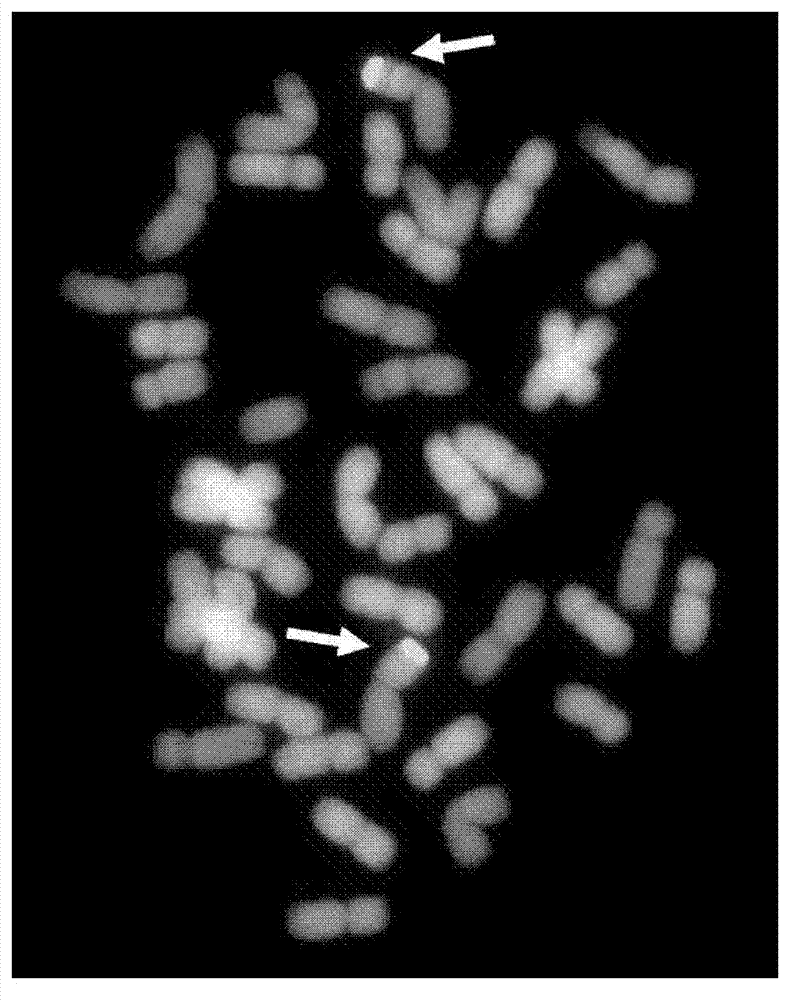
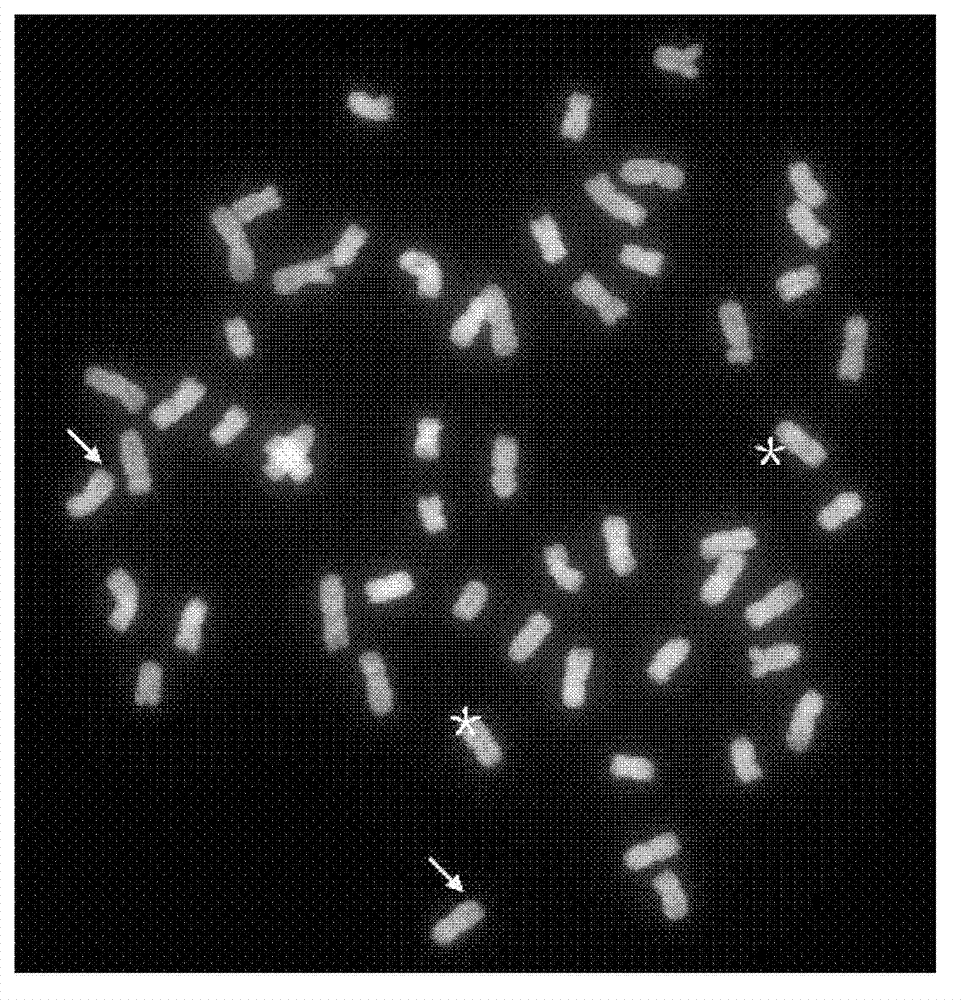
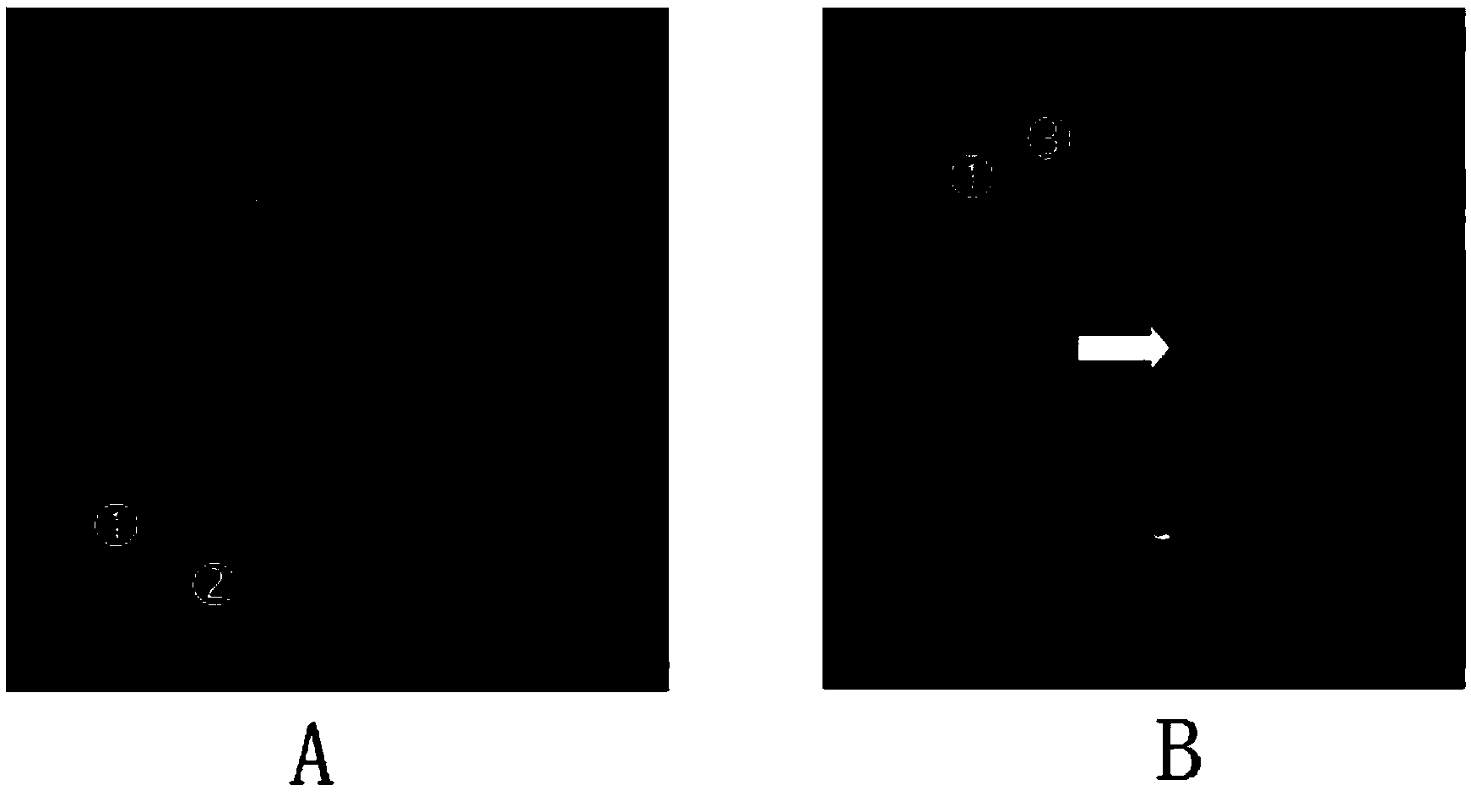Patents
Literature
350 results about "Fluorescence in situ hybridization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) is a molecular cytogenetic technique that uses fluorescent probes that bind to only those parts of a nucleic acid sequence with a high degree of sequence complementarity. It was developed by biomedical researchers in the early 1980s to detect and localize the presence or absence of specific DNA sequences on chromosomes. Fluorescence microscopy can be used to find out where the fluorescent probe is bound to the chromosomes. FISH is often used for finding specific features in DNA for use in genetic counseling, medicine, and species identification. FISH can also be used to detect and localize specific RNA targets (mRNA, lncRNA and miRNA) in cells, circulating tumor cells, and tissue samples. In this context, it can help define the spatial-temporal patterns of gene expression within cells and tissues.
Methods and compositions for identifying a fetal cell
InactiveUS20100304978A1High expressionMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningCandidate Gene Association StudyTrophoblast
The present invention provides methods and compositions for specifically identifying a fetal cell. An initial screening of approximately 400 candidate genes by digital PCR in different fetal and adult tissues identified a subset of 24 gene markers specific for fetal nucleated RBC and trophoblasts. The specific expression of those genes was further evaluated and verified in more defined tissues and isolated cells through quantitative RT-PCR using custom Taqman probes specific for each gene. A subset of fetal cell specific markers (FCM) was tested and validated by RNA fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) in blood samples from non-pregnant women, and pre-termination and post-termination pregnant women. Applications of these gene markers include, but are not limited to, distinguishing a fetal cell from a maternal cell for fetal cell identification and genetic diagnosis, identifying circulating fetal cell types in maternal blood, purifying or enriching one or more fetal cells, and enumerating one or more fetal cells during fetal cell enrichment.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC
DNA amplification of a single cell
InactiveUS6673541B1Improve accuracyImprove comprehensive applicabilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle-strand conformation polymorphismComparative genomic hybridization
The present invention relates to a novel method for the amplification of DNA, this method being particularly useful for the amplification of the DNA or the whole genome of a single cell, chromosomes or fragments thereof. Described is also the use of the method in DNA analysis for medical, forensic, diagnostic or scientific purposes, like comparative genomic hybridization (CGH)-, fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH)-, polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-, single strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP)-, DNA sequence-, "loss of heterozygosity" (LOH)-, fingerprint- and / or restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP)-analysis.
Owner:AMGEN RES (MUNICH) GMBH
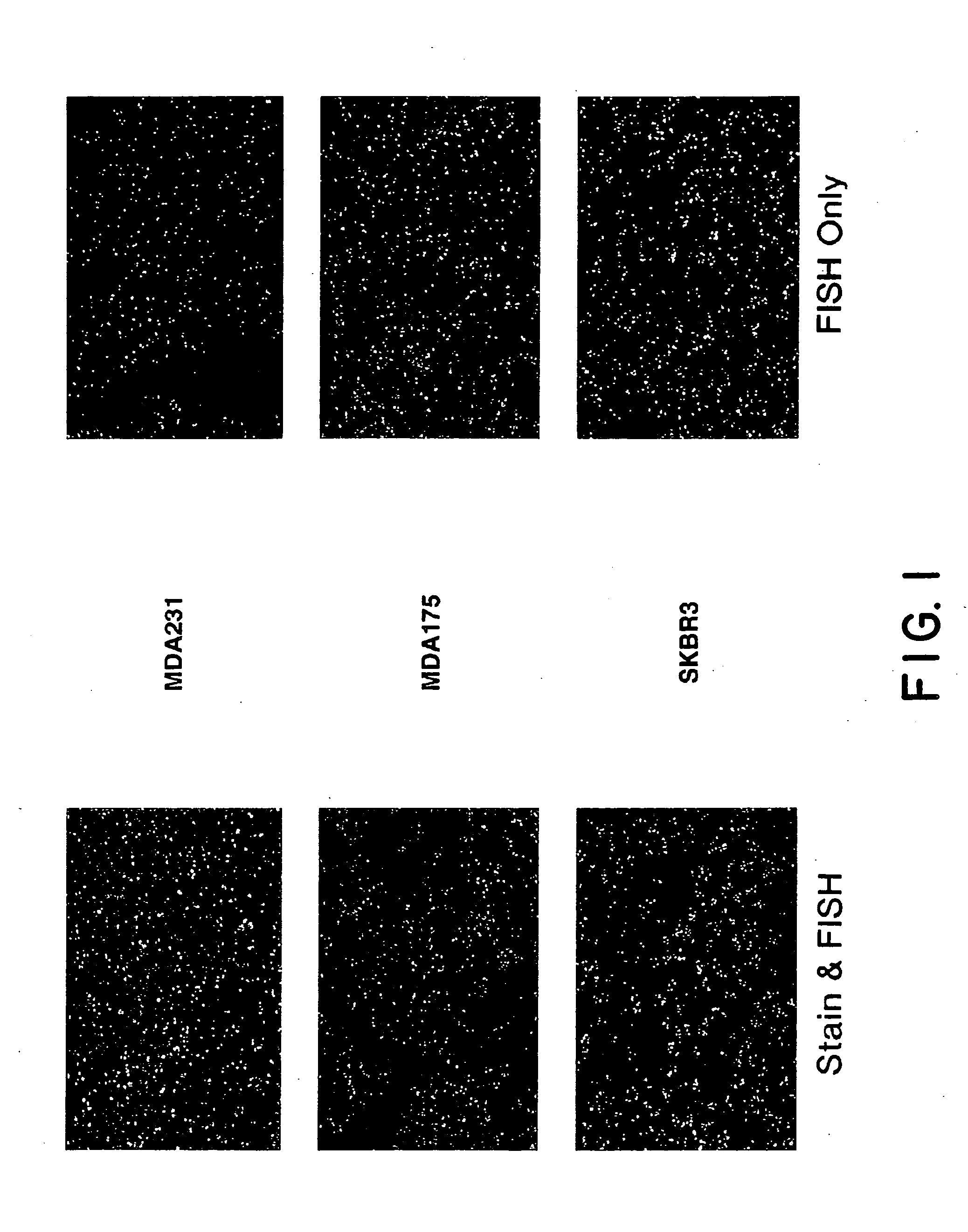
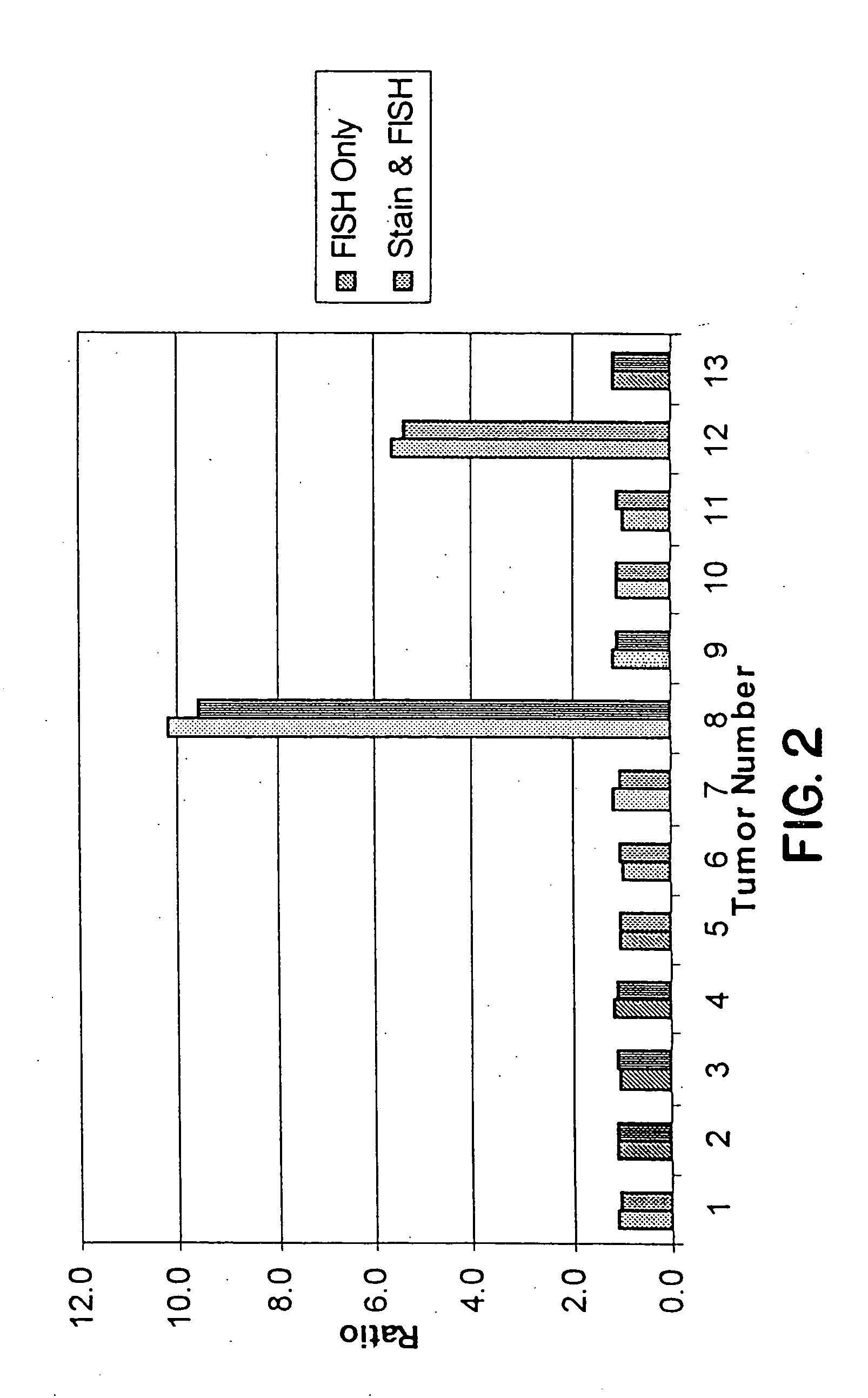
Tissue analysis and kits therefor
InactiveUS6905830B2Microbiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationIn situ hybridisationStaining
This invention relates to methods of analyzing a tissue sample from a subject. In particular, the invention combines morphological staining and / or immunohistochemistry (IHC) with fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) within the same section of a tissue sample. The analysis can be automated or manual. The invention also relates to kits for use in the above methods.
Owner:GENENTECH INC +1
Tissue analysis and kits therefor
InactiveUS20050100944A1Microbiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationStainingFluorescence
This invention relates to methods of analyzing a tissue sample from a subject. In particular, the invention combines morphological staining and / or immunohistochemistry (IHC) with fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) within the same section of a tissue sample. The analysis can be automated or manual. The invention also relates to kits for use in the above methods.
Owner:COHEN ROBERT L +3
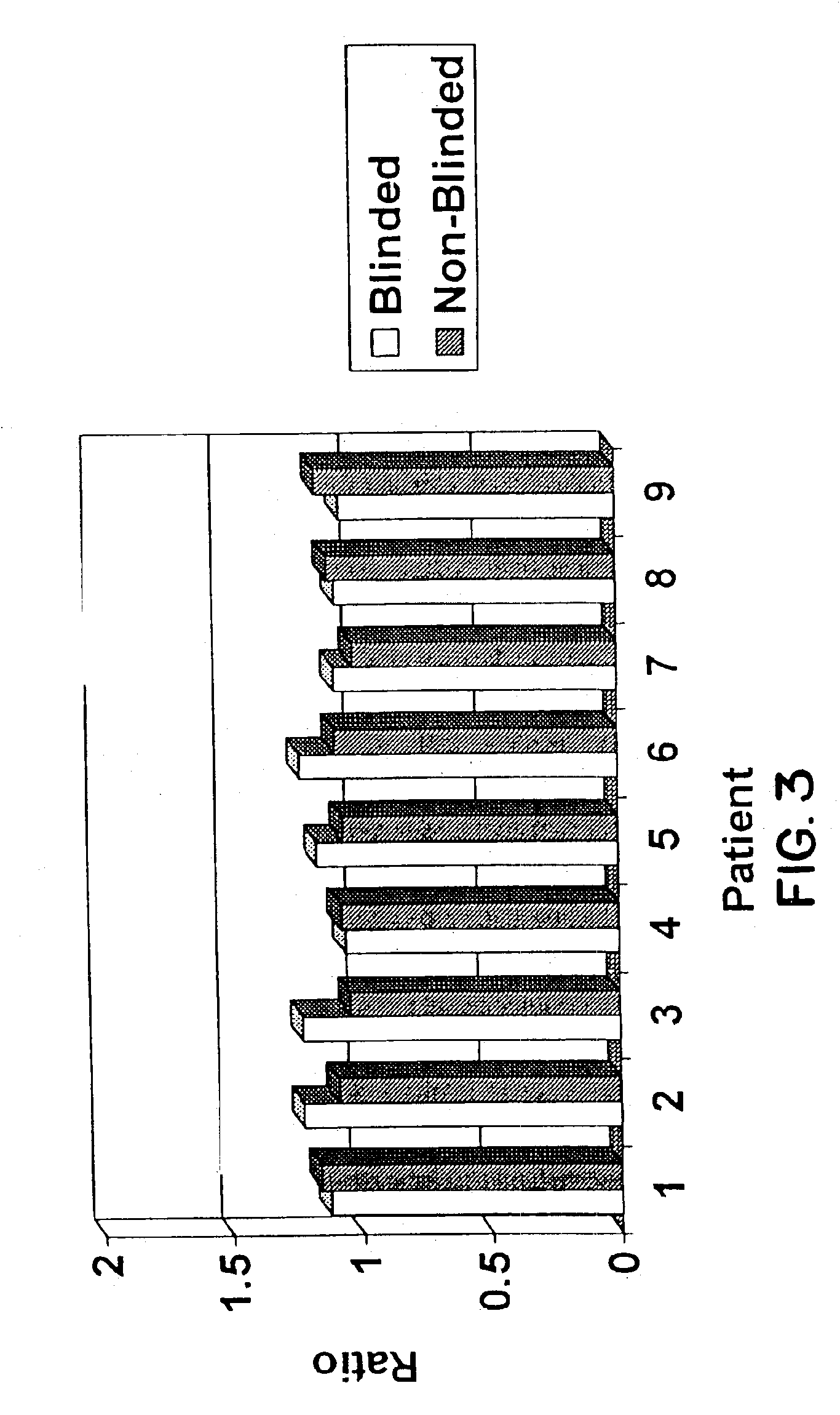
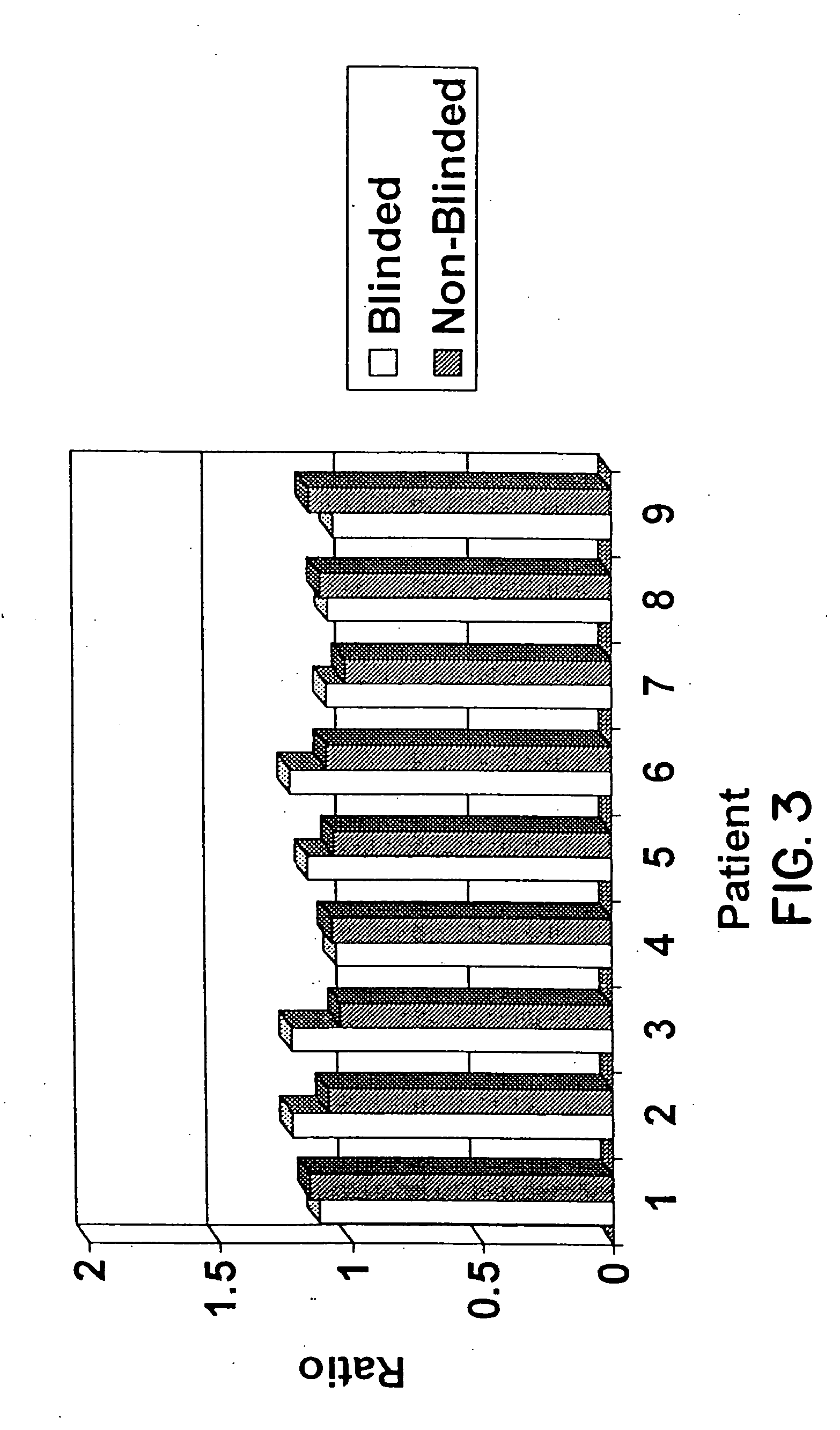
Blood test to monitor the genetic changes of progressive cancer using immunomagnetic enrichment and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH)
InactiveUS20080113350A1Accurate measurementEasy accessMicrobiological testing/measurementLymphatic SpreadGenetic Change
Amplification and overexpression of theHER-2 oncogene in breast cancer is felt to be stable over the course of disease and concordant between the primary tumor and metastases. Therefore, patients with HER-2 negative primary tumors will rarely receive anti-HER-2 antibody therapy. A very sensitive blood test is used to capture circulating tumor cells (CTC's) and evaluate their HER-2 gene status by FISH evaluation. The HER-2 status of the primary tumor and corresponding CTC's is used to assess the ratio of CTC's as a reliable surrogate marker. HER-2 expression of 10 CTC's is sufficient to make a definitive diagnosis of the HER-2 gene status for the whole population of CTC's in patients with recurrent breast cancer.
Owner:JANSSEN DIAGNOSTICS LLC
Methods and compositions for the preparation and use of fixed-treated cell-lines and tissue in fluorescence in situ hybridization
InactiveUS6995020B2Easy to detectReduced autofluorescenceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemical treatmentTreated cell
This invention relates to methods for the detection of one or more mRNA transcripts in paraffin-embedded tissue by “mRNA liberation in fixed-treated tissue or ‘MLIFTT’”. This method includes treating the tissue with ammonia-ethanol and sodium borohydride combined with pressure cooking of the tissue. The chemical treatments reduce the tissue autofluorescence and the physical treatments overcome the interference created by the fixation-induced chemical bonds. The methods of the present invention can be utilized to identify a plurality of mRNA transcripts in a microarray format.
Owner:AUREON LAB INC +2
Methods for preparing and analyzing cells having chromosomal abnormalities
InactiveUS20060257884A1Microbiological testing/measurementFluorescenceFluorescence in situ hybridization
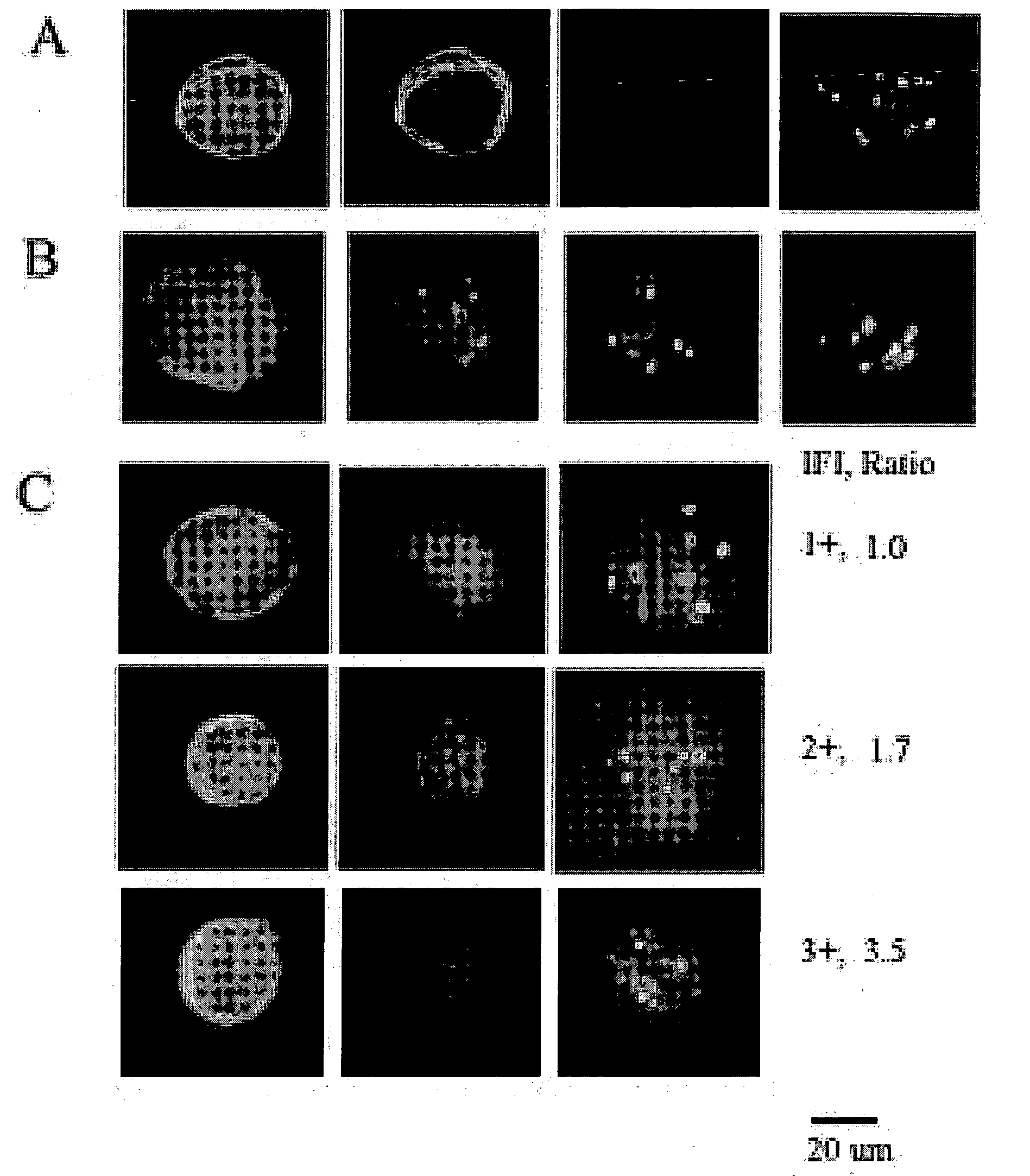
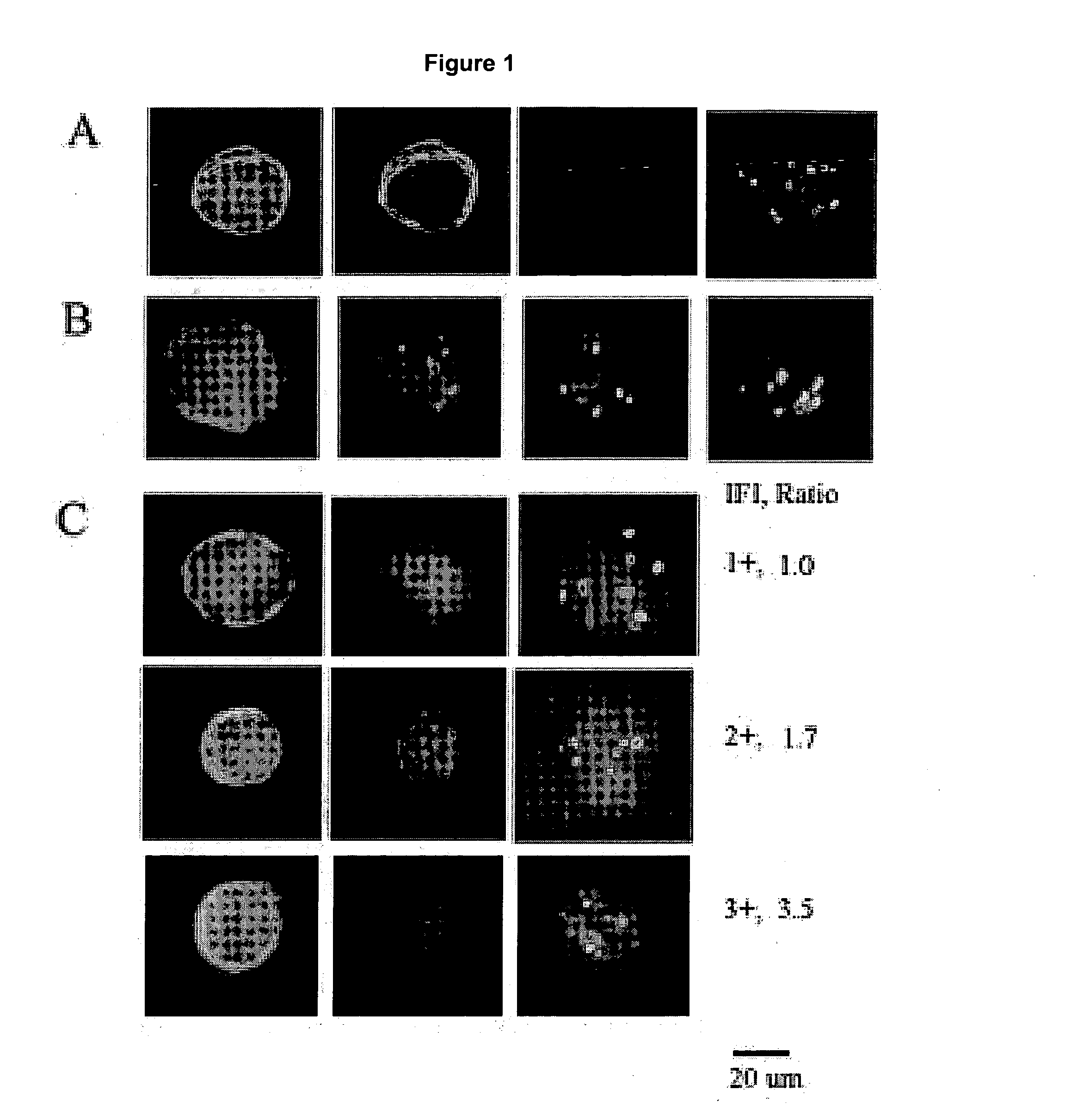
The present invention provides methods for preparing cells with highly condensed chromosomes, such as sperm, and methods for detecting and quantifying specific cellular target molecules in intact cells. Specifically, methods are provided for detecting chromosomes and chromosomal abnormalities, including aneuploidy, in intact cells using fluorescence in situ hybridization of cells in suspension, such as sperm cells.
Owner:AMNIS CORP
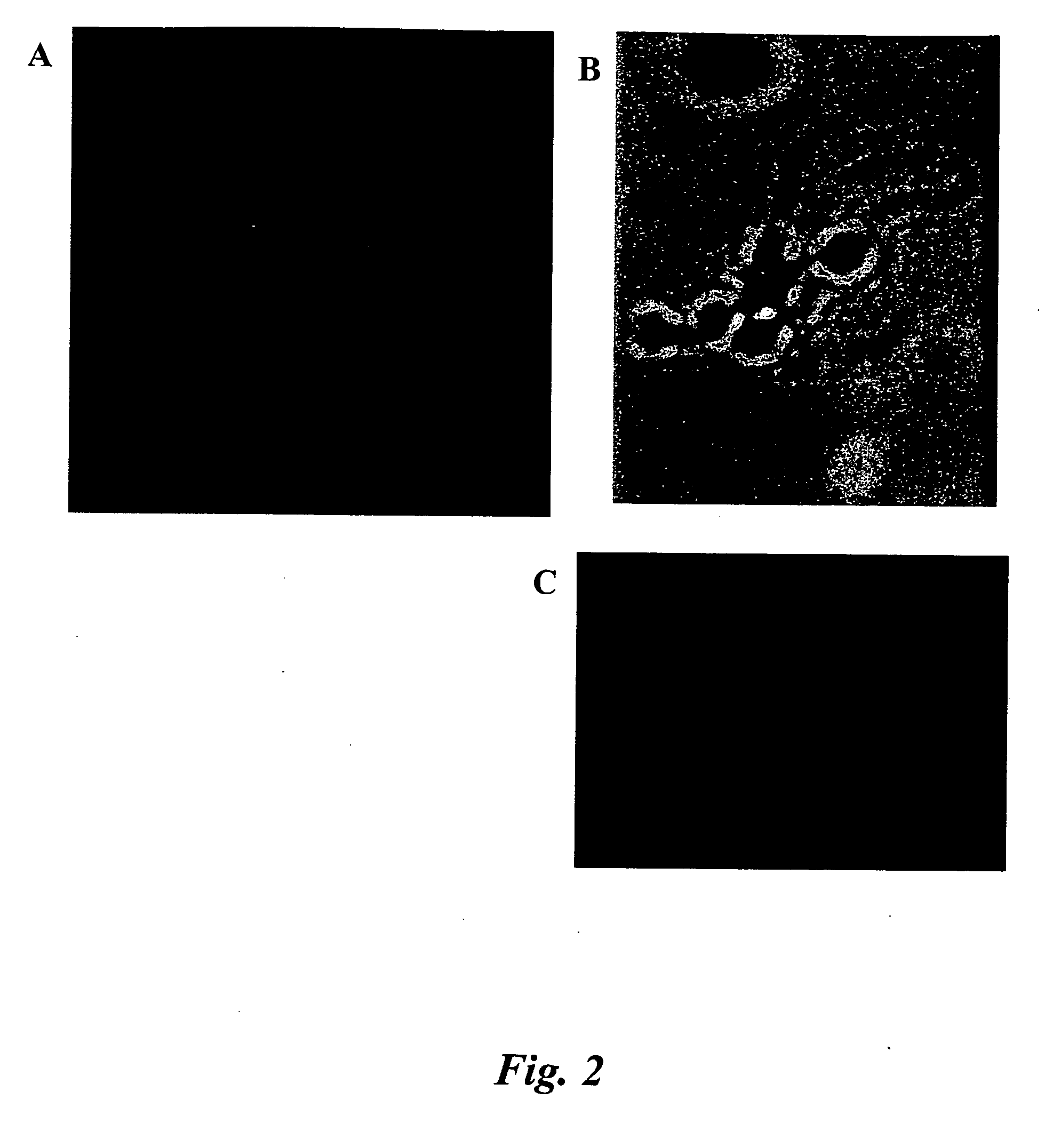
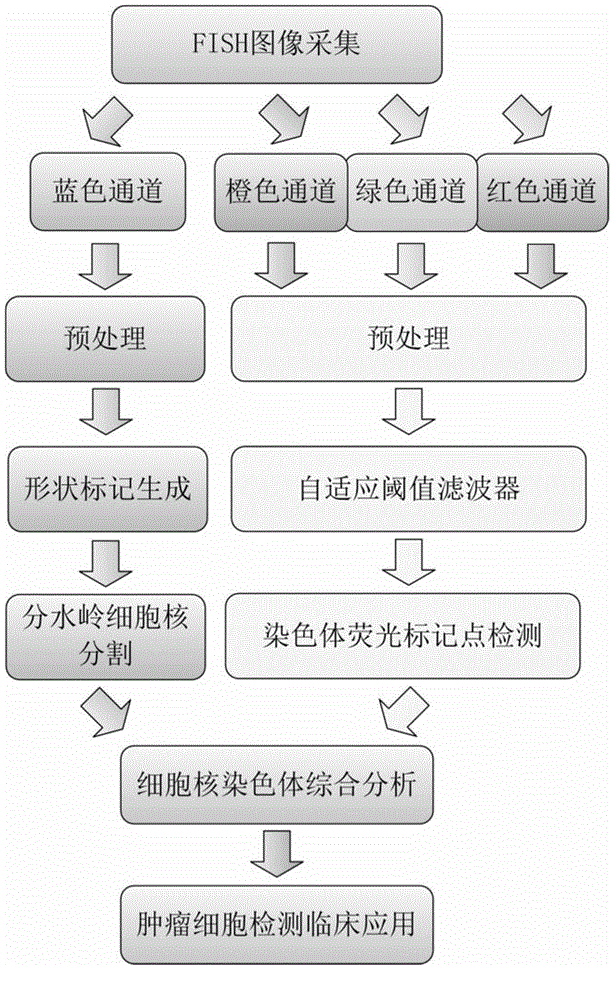
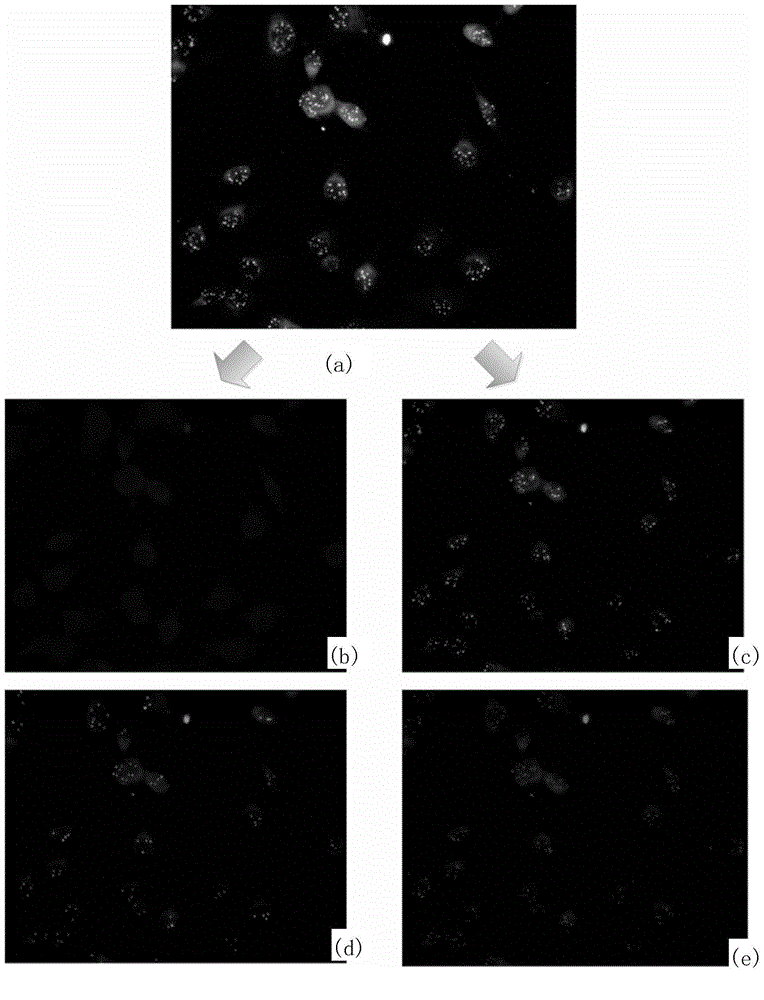
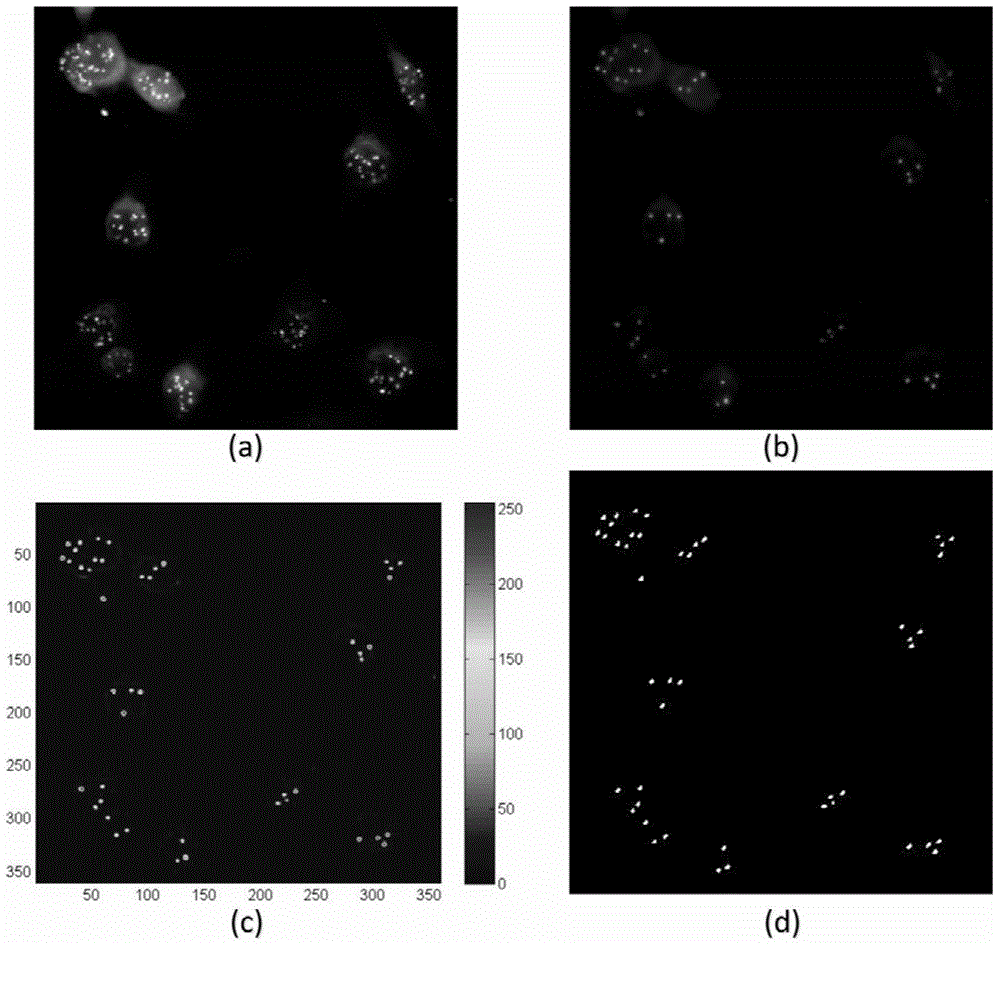
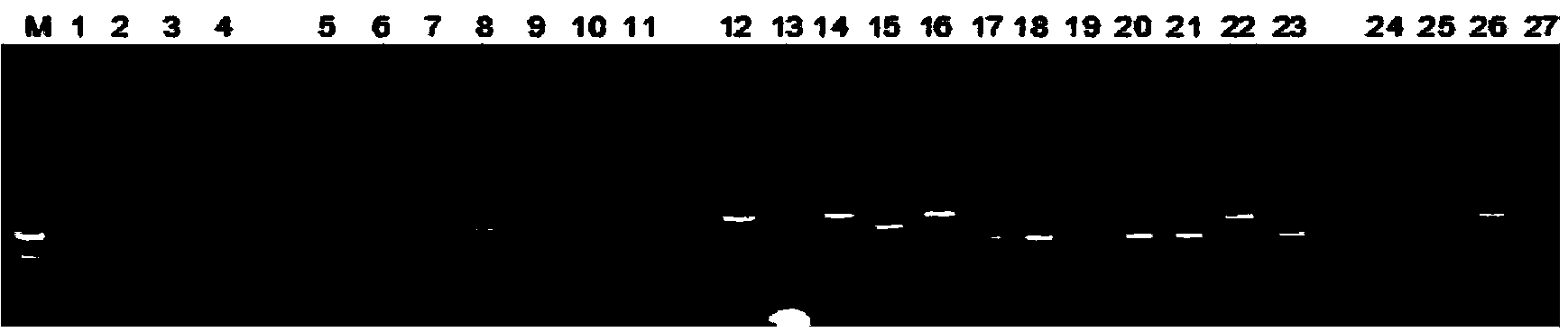
Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) image parallel processing and analysis method
ActiveCN106296635AReduce running timeImprove image processing efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisFluorescenceAlgorithm
The invention provides a fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) image parallel processing and analysis method. The method employs parallel processing, detection of chromosome fluorescent labeling points and edge detection and segmentation of nucleuses can be performed simultaneously, and the processing time is reduced; and a watershed algorithm based on adaptive shape labels is employed so that the segmentation precision of the adhered nucleuses in FISH images is substantially improved, the detection accuracy of relative positions of the nucleuses in tumor cells and the chromosome fluorescent label points is improved, and online real-time detection of the tumor cells can be realized.
Owner:XIAMEN LUJIA BIOTECH
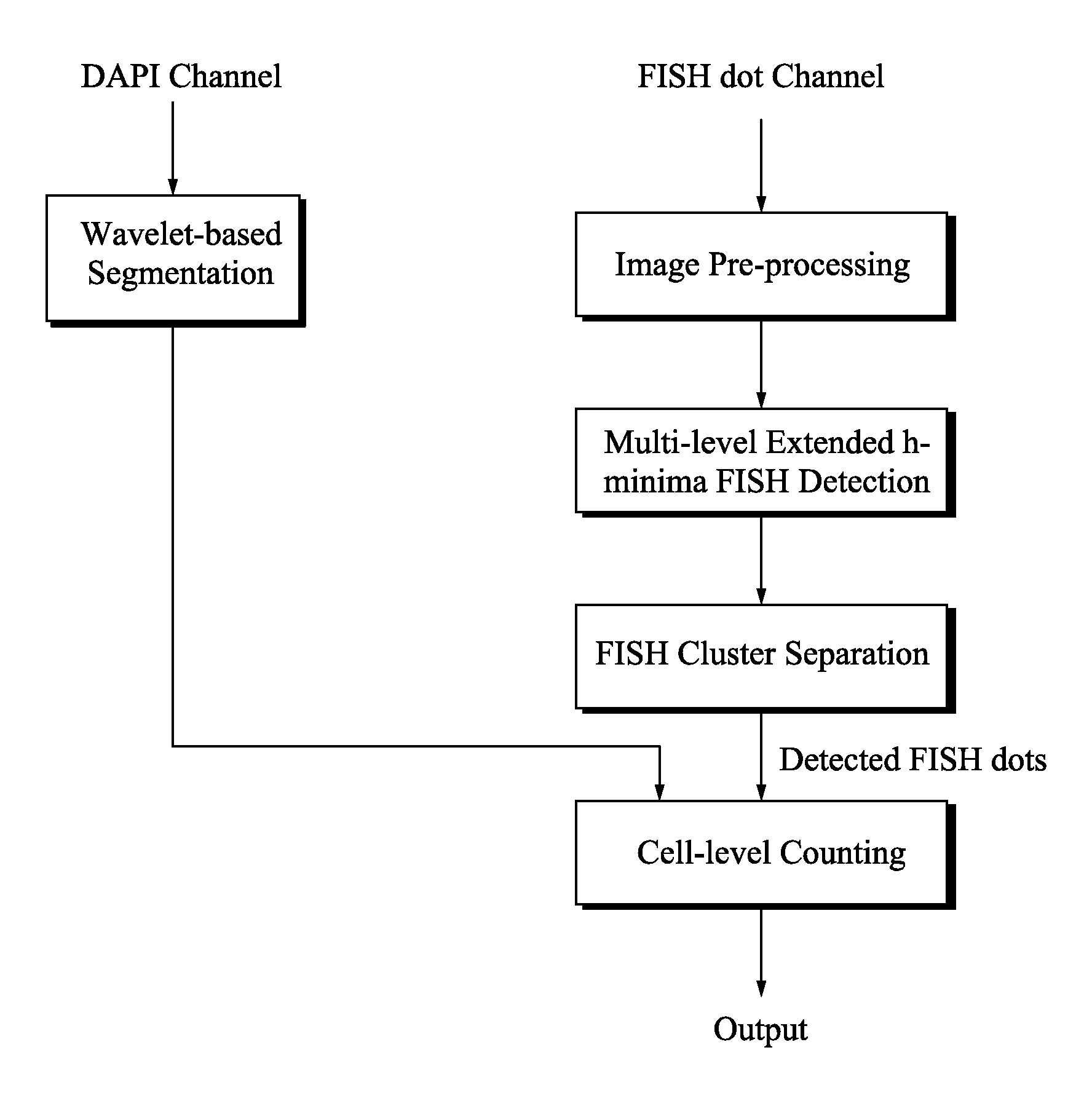
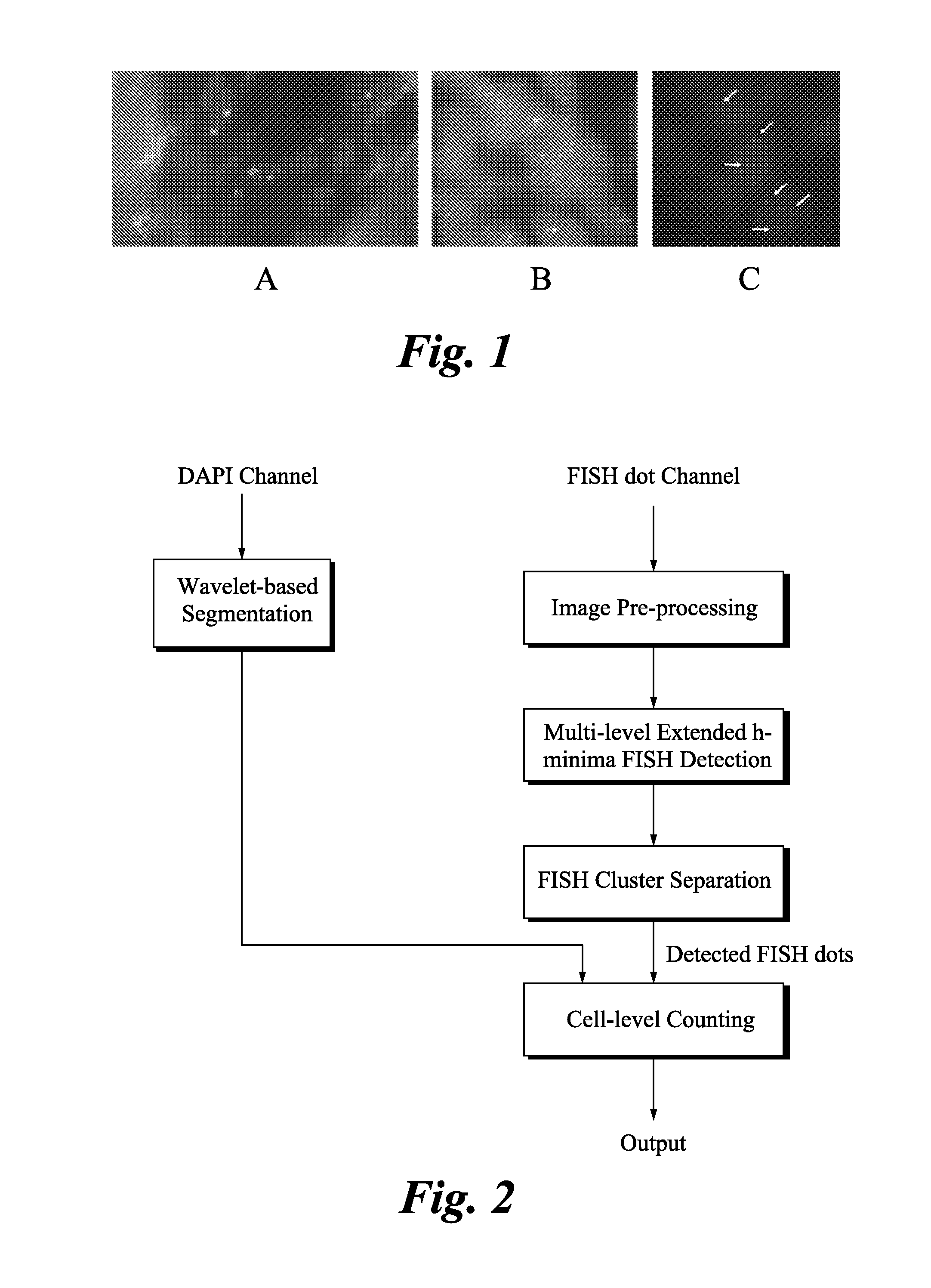
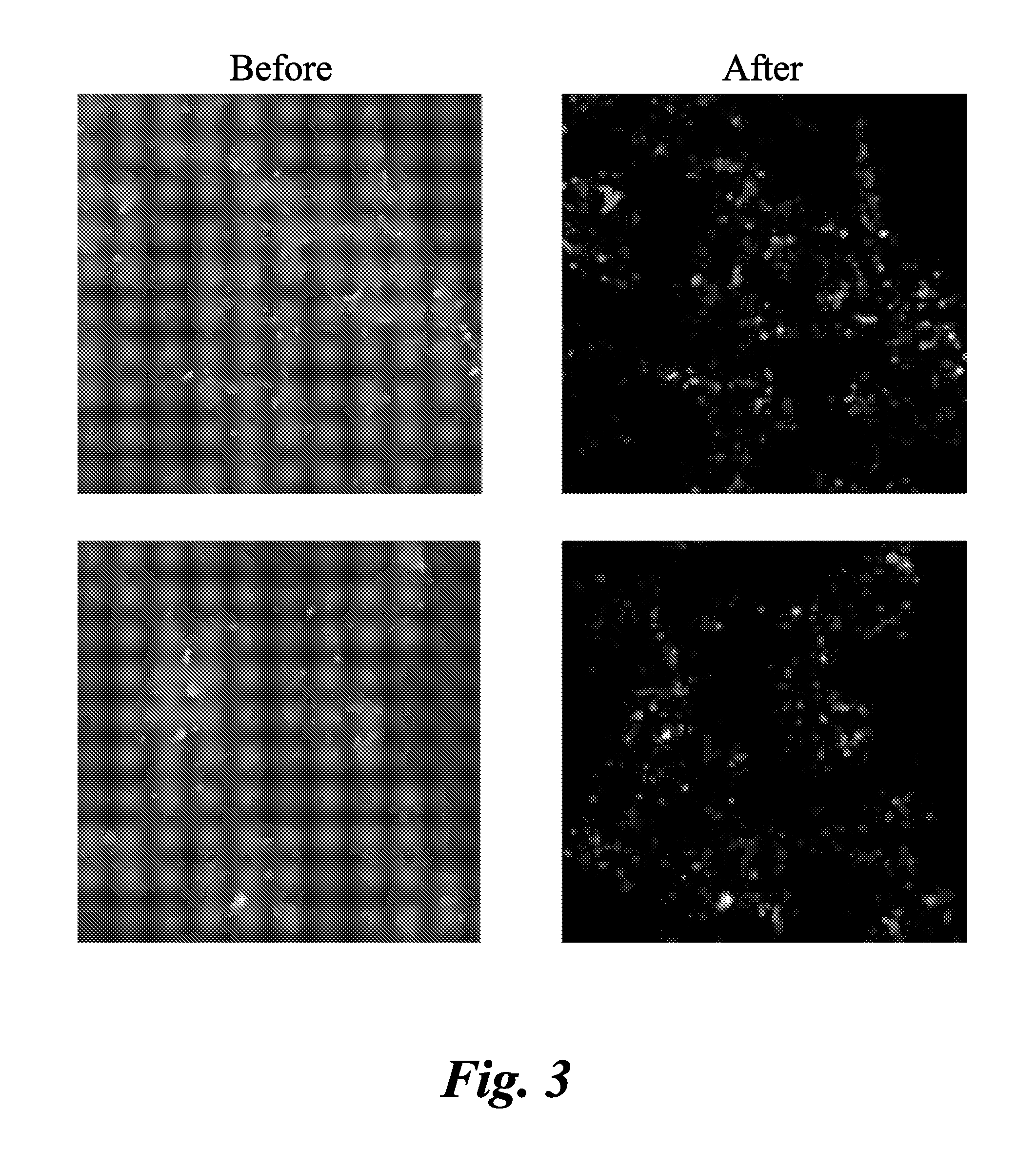
Method and systems for cell-level fish dot counting
The invention relates to a computer implemented method and systems for cell level fish dot counting. FISH (fluorescence in situ hybridization) dot counting is the process of enumerating chromosomal abnormalities in the cells which can be used in areas of diagnosis and cancer research. The method comprises in part overlaying images of a biological sample comprising a nuclear counterstain mask and a FISH binary mask. The FISH binary mask is extracted using a multi-level extended h-maxima or h-minima.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Preparation method for probes related to breast cancer molecular markers and application of same
ActiveCN102399772AImprove the detection rateAccurate typingMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceMortality rate
The invention relates to a preparation method for probes related to breast cancer molecular markers and to preparation of a breast cancer fluorescence in situ hybridization detection kit by using the probes. The breast cancer fluorescence in situ hybridization detection kit can be prepared from HER2, TOP2A and AGTR1 gene probes prepared by using the method provided in the invention, human chromosome 17 counting probe, hybridization buffer, unlabelled competitive DNA and DAPI counter strain; application of the kit enables the detection rate of breast cancers to be substantially improved and type sorting of breast cancers to be more accurate and provides guidance to formulation of an individual therapeutic schedule and selection of proper therapeutic drugs, thereby lowering down mortality, reducing recurrence risk and achieving the goal of optimizing the effect of diagnosis and treatment.
Owner:DAAN GENE CO LTD
Image Processing Method for a Microscope System
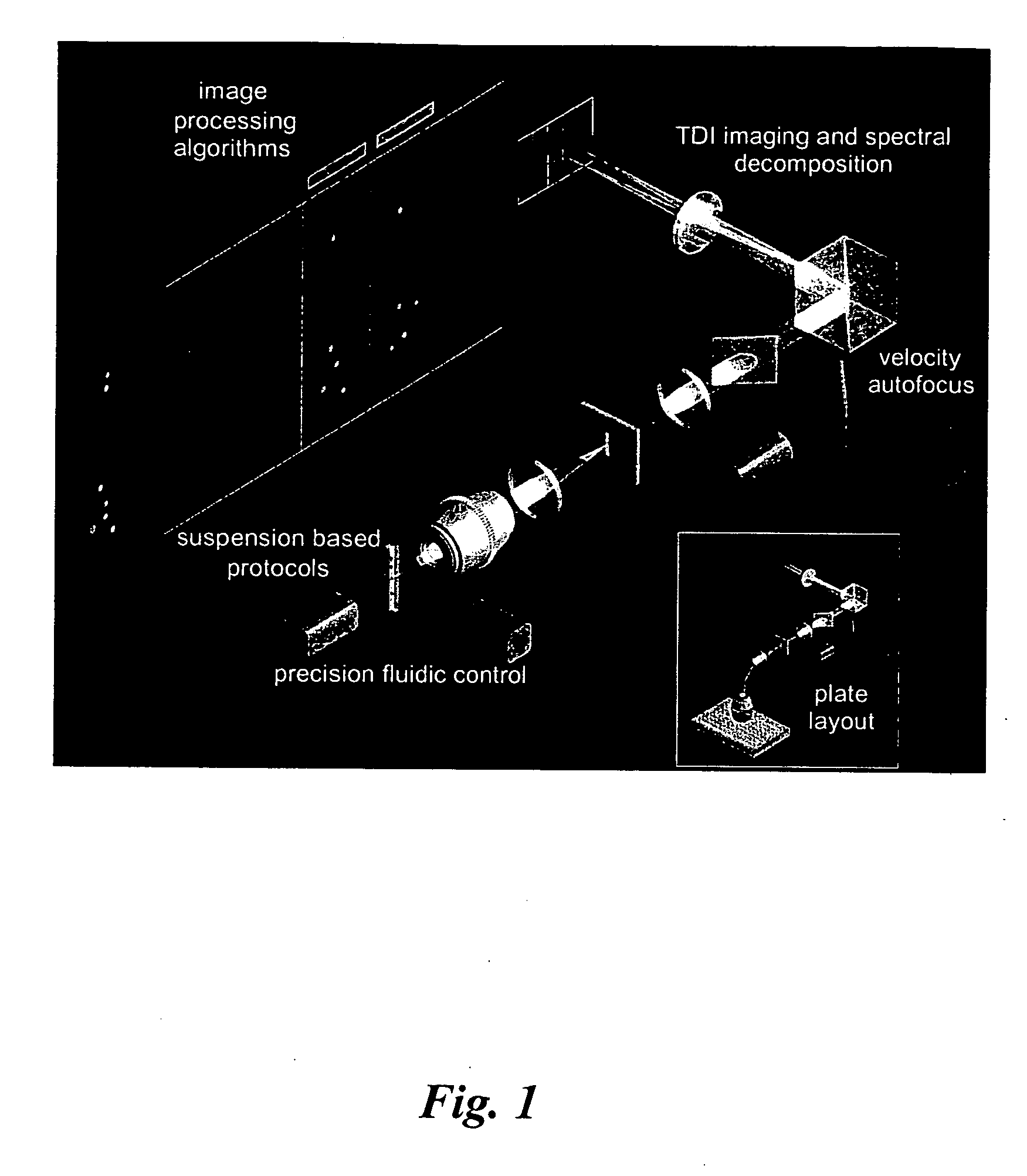
InactiveUS20080212865A1Material analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingFluorescence in situ hybridization
An embodiment is disclosed for performing the image processing for analyzing the results of a fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) microscopic automated sample analysis to determine specific chromosomal characteristics.
Owner:IKONISYS INC
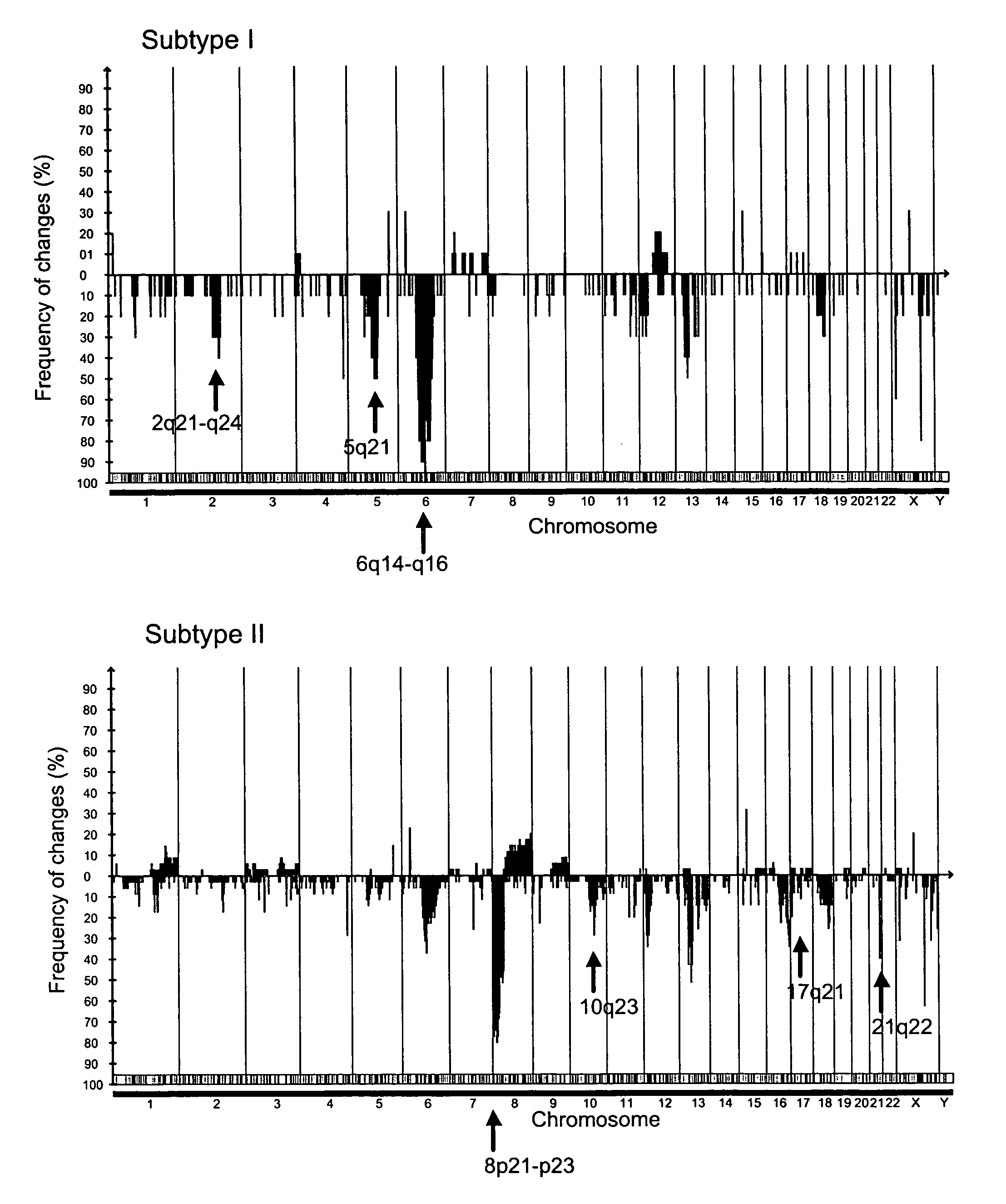
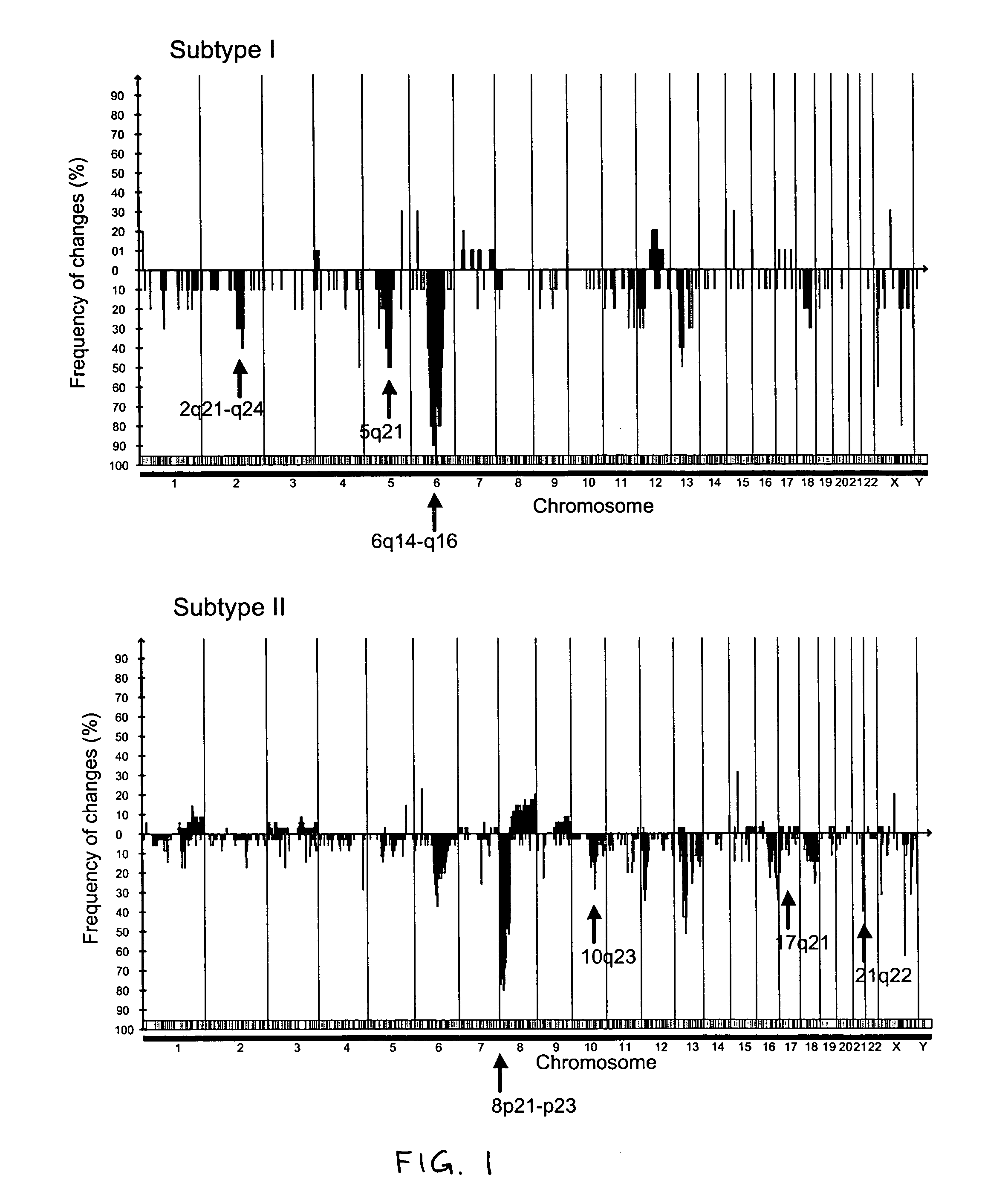
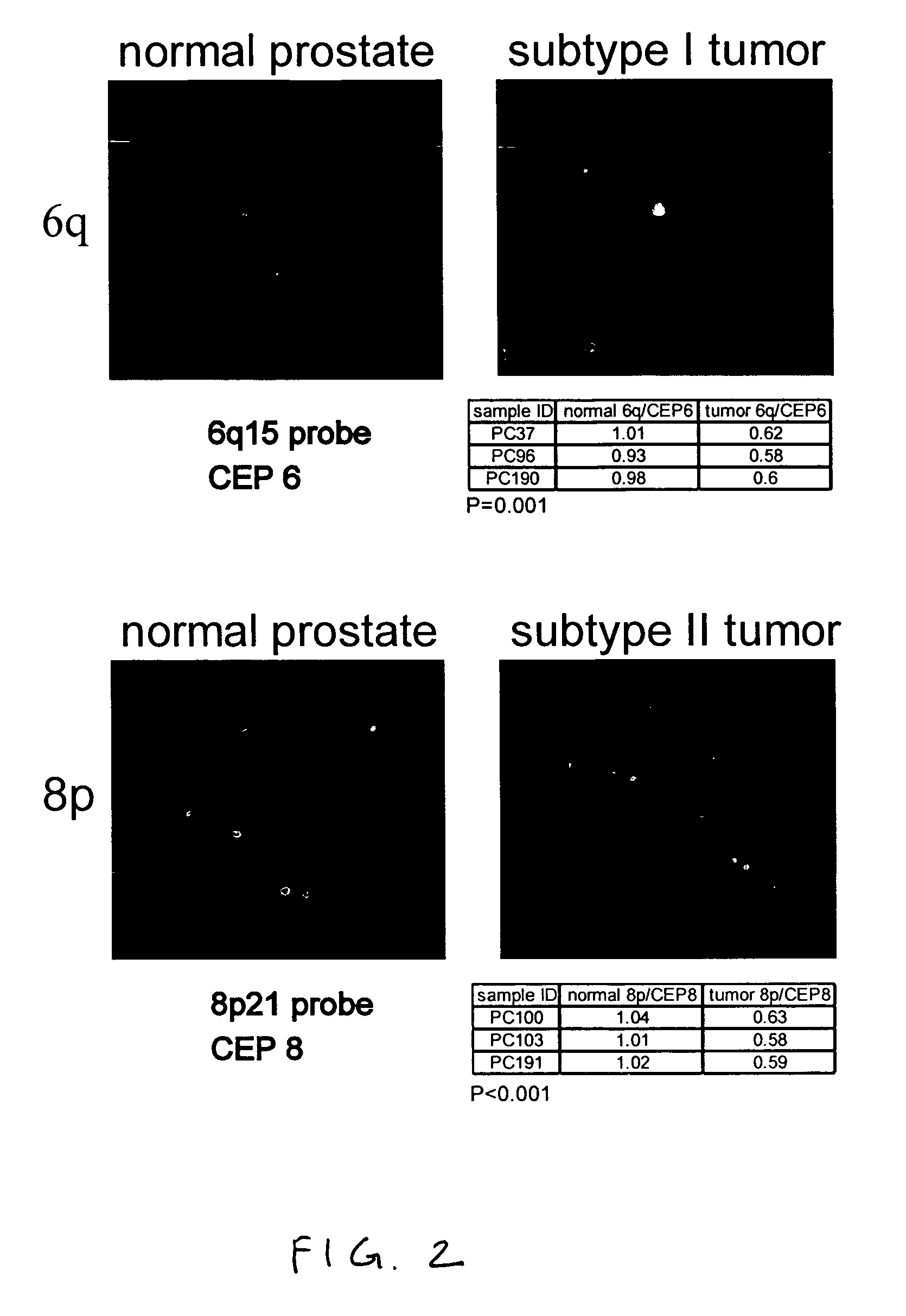
Markers of DNA copy number alteration for improved prognostication in prostate cancer
ActiveUS7638278B2Increase the number ofReduce in quantityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProstate cancerFluorescence in situ hybridization
The invention describes DNA copy number alterations (CNAs), identifiable by technologies such as array-based comparative genomic hybridization (array CGH) or fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), that define distinct genetic subtypes of prostate cancer, and are useful for improved prognostication and treatment stratification for patients with prostate cancer.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
FISH (fluorescence in situ hybridization) probe, kit and detection method for detecting Her2 (human epidermal growth factor receptor 2) gene free from repetitive sequence
ActiveCN103409504AHigh detection sensitivityImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDNA fragmentationFluorescence in situ hybridization
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and discloses a FISH (fluorescence in situ hybridization) probe, a kit and a detection method for detecting Her2 (human epidermal growth factor receptor 2) gene free from repetitive sequence. The Her2 gene is used as a template to perform polymerase chain reaction on non-repetitive sequence in the Her2 gene, the amplification product is DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) fragments with 350-800 different base pairs, the repetitive sequence in the Her2 gene is eliminated so as to form the product free from repetitive sequence; after the product is in fluorescence labeling, the Her2 gene free from repetitive FISH is obtained for the Her2 gene FISH detection. The Her2 gene FISH probe obtained by the invention can eliminate the repetitive sequence, the non-specific background signal of the Her2 gene FISH probe can be obviously reduced, and the specificity of the FISH probe is improved.
Owner:WUHAN HEALTHCHART BIOLOGICAL TECH
Wheat-rye T2BL.1RS translocation line germplasm breeding method
InactiveCN101263782AExcellent yield traitsPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsDiseaseHigh resistance
The invention provides a breeding method for the germ plasm of a new translocation line wheat-rye T2BL.1RS, which is characterized in that, distant hybridization is performed by taking common wheat variety Xiaoyan 6 as female parent and relative plant rye variety German White as male parent; seeds are acquired after immature embryo salvation culture, colchicine half root soaking method and chromosome doubling; backcross seeds are acquired after disease resistance identification, cytological identification and backcrossing utilizing the original parent Xiaoyan 6 as male parent; then after disease resistance identification and cytological identification, individual plants with excellent comprehensive characters are selected in direction for self crossing, and after continuous self cross selective breeding for six generations, the finally acquired individual plant is confirmed to be wheat-rye T2BL.1RS translocation line after identified by continuous total genome in situ hybridization and three-probe multicolor fluorescence in situ hybridization. The breeding method for the germ plasm of a new translocation line wheat-rye T2BL.1RS has the advantages that, the wheat-rye T2BL.1RS translocation line has high resistance to stripe rust, current prevalent fungus strain, powdery mildew and other important virus strains; the invention has excellent high yield character; the method lays an excellent germplasm base for the cultivation of breakthrough new wheat variety with disease resistance and high yield.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for identifying exogenous chromosomes and chromosome segments in plant distant hybrids
InactiveCN102876801AOvercome the problem of unsatisfactory detection effectImprovement of Chromosome Production TechnologyMicrobiological testing/measurementAgricultural scienceFluorescence
The invention provides a method for identifying exogenous chromosomes and chromosome segments in plant distant hybrids. The method includes the steps of firstly, microscopically separating monosomes or chromosome segments of chromosomes to be tested of a plant to be tested; secondly, using the separated monosomes or chromosome segments in the first step to build a fluorescence probe of the monosomes or chromosome segments; thirdly, using the fluorescence probe built in the second step to perform fluorescence in situ hybridization to chromosomes in metaphase division of the hybrids; and fourthly, analyzing the fluorescence in situ hybridization result obtained in the third step to determine distribution of fluorescence signals of the chromosomes to be tested of the plant to be tested. Exogenous chromosomes and chromosome segments in wheat distant hybrids can be identified by the method, and the method is applicable to identification of exogenous chromosomes and chromosome segments in distant hybrids of other plants.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for obtaining oligonucleotide probe
InactiveCN103710455AReduce cumbersomeEliminate failuresMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationFluorescence in situ hybridizationComputer science
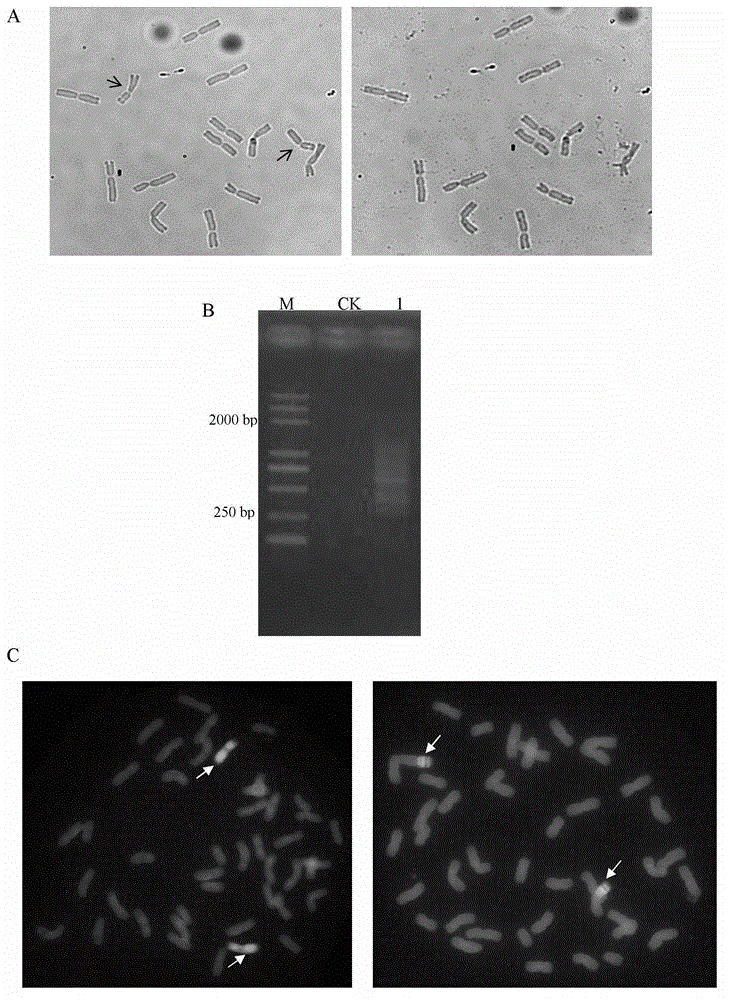
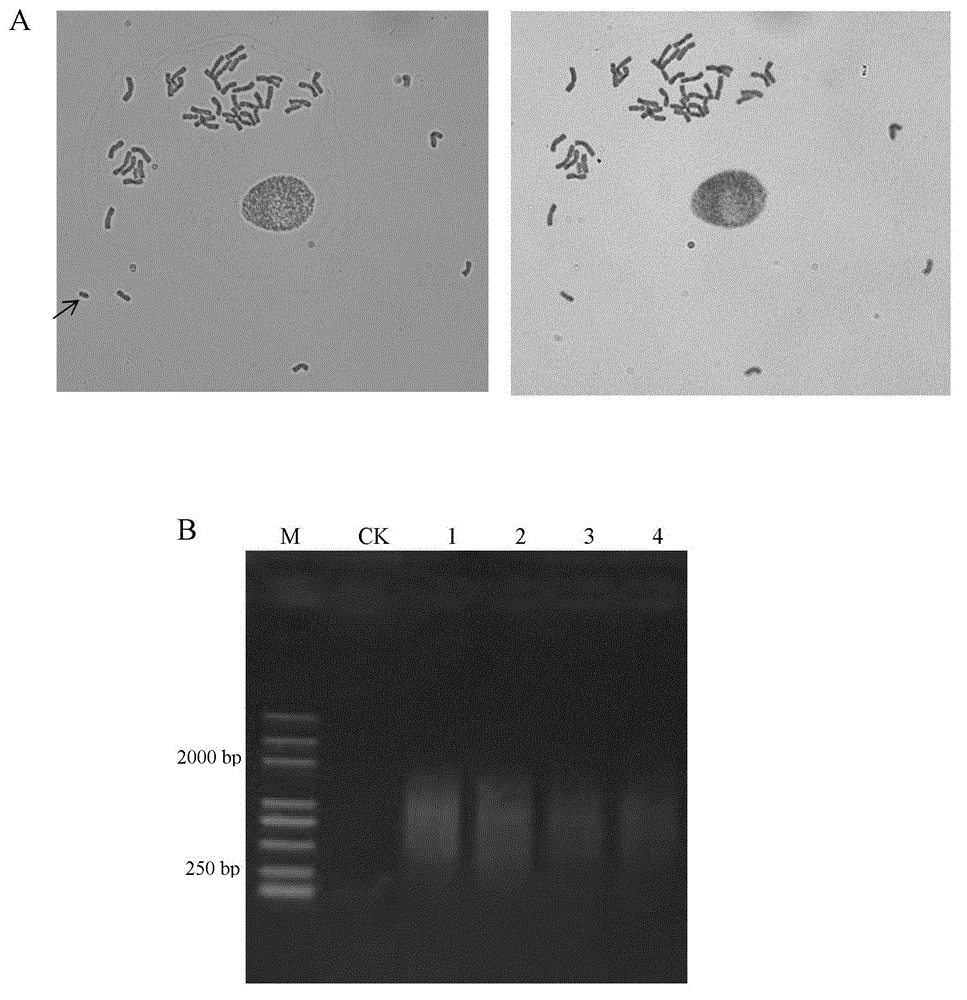
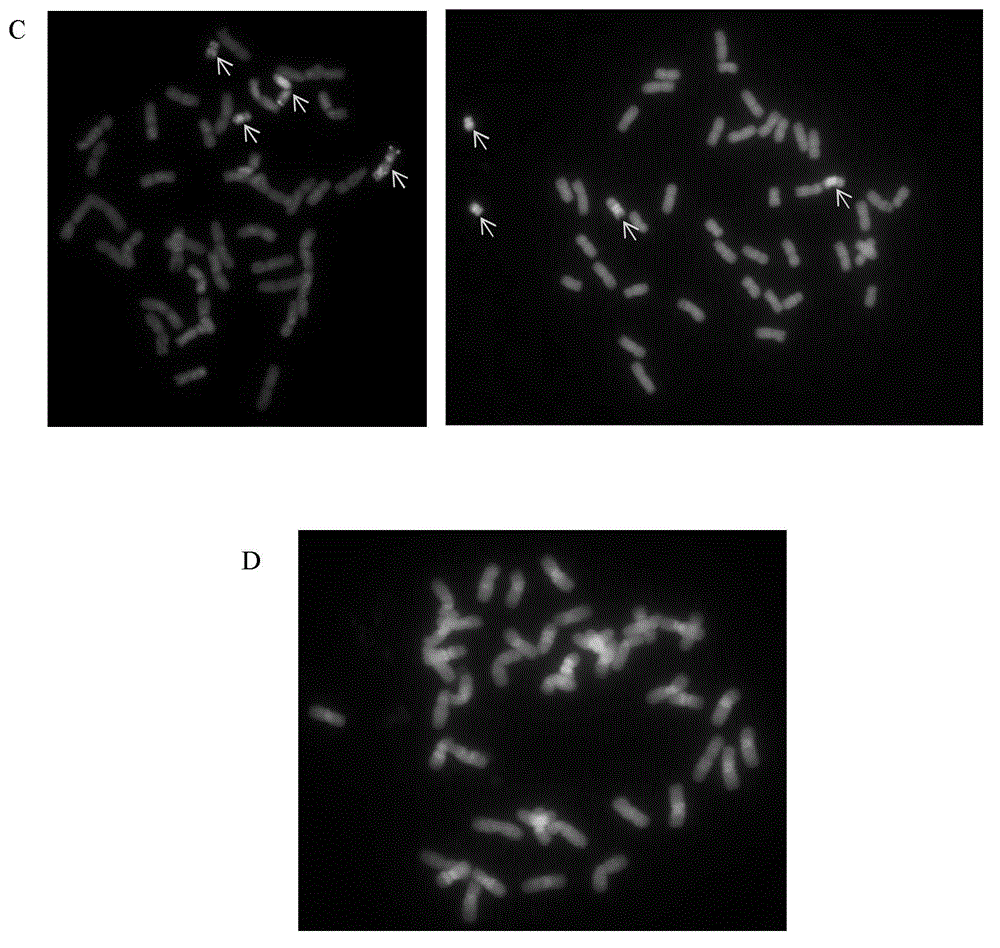
The invention discloses a method for obtaining an oligonucleotide probe. The method for obtaining the oligonucleotide probe comprises the following steps: downloading original sequences of pSc119.2, pAs1, pTa-535, pTa71, pAWRC.1 and CCS1 from a national center of biotechnology information (NCBI) website; analyzing the downloaded sequences by using bioinformatics software DNAMAN; seeking repeated core units in these sequences; returning to the NCBI website to compare by using a blastn tool for finding out a core oligonucleotide sequence of which the length is below 60bp to carry out probe synthesis; carrying out probe synthesis on a lot of oligonucleotide sequences which are primarily screened out; gradually carrying out a fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) test after probe synthesis; verifying the function of the probe, and verifying whether the synthetic oligonucleotide sequence can play the FISH effects of pSc119.2, pAs1, pTa-535, pTa71, pAWRC.1 and CCS1 or not, so as to obtain the oligonucleotide probe. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, complicated procedures of the existing probe marking technique are removed, the problem of marking failure of the probe is removed, and the cost is reduced.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Fluorescence in situ hybridization method of prunus mume chromosome
ActiveCN102787166AIncrease the success rate of hybridizationHigh hybridization specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceMetaphase chromosomeFluorescence
The invention relates to a fluorescence in situ hybridization method of a prunus mume chromosome. The method consists of: taking a prunus mume metaphase chromosome as the target DNA, adopting maize 45SrDNA as a probe, using a nick translation method to label the probe, and positioning the maize 45SrDNA probe on the prunus mume chromosome clearly. Based on the prior art, the invention improves the co-denaturation method, and employs the two steps of probe denaturation, and chromosome and probe co-denaturation to complete the denaturation process, thus greatly improving the hybridization success rate. The invention determines an appropriate denaturation temperature and denaturation time, a hybridization time and an elution method, and has high hybridization specificity, so that the FISH technology can be well applied in chromosome detection of prunus mume and other small chromosome plants, thus providing a new approach and method for in-depth study of the prunus mume chromosome.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Circulating Tumor and Tumor Stem Cell Detection Using Genomic Specific Probes
InactiveUS20110189670A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisStainingFluorescence
The present invention comprises a method of detecting circular tumor cells and methods of detecting, evaluating, or staging cancer in a patient, as well as a method of monitoring treatment of cancer in a patient using the claimed method. The method comprises contacting a sample with a CD45 binding agent; selecting the cells based on positive or negative CD45 staining; contacting the selected cells with a labeled nucleic acid probe, and detecting hybridized cells by fluorescence in situ hybridization; and analyzing a signal produced by the labels on the hybridized cells to detect the CTCs. In other embodiments, the method provides for directed to a method of determining the level of CTCs in a sample having blood cells from a patient by contacting a sample having blood cells from a patient, wherein the sample has not been pre-sorted into CD45-positive and CD45-negative cells.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
FISH (fluorescence in situ hybridization) probe, kit and detection method for detecting BCR/ABL fusion gene free from repetitive sequence
InactiveCN103409505AHigh detection sensitivityImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationRepetitive SequencesIn situ hybridisation
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and discloses a FISH (fluorescence in situ hybridization) probe, a kit and a detection method for detecting BCR / ABL fusion gene free from repetitive sequence. A BCR gene and ABL gene are used as templates to perform polymerase chain reaction on non-repetitive sequence in the BCR gene and ABL gene, the amplification product is DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) fragments with 350-800 different base-pairs, the repetitive sequences in the BCR gene and ABL gene are eliminated so as to form the product free from repetitive sequence; after the product is in fluorescence labeling, the BCR gene and ABL gene free from repetitive FISH are obtained for the BCR gene and ABL gene FISH detection. The BCR / ABL fusion gene FISH probe obtained by the invention can be used for eliminating the repetitive sequence, the non-specific background signal of the FISH probe can be obviously reduced, and the specificity of the FISH probe is improved.
Owner:WUHAN HEALTHCHART BIOLOGICAL TECH
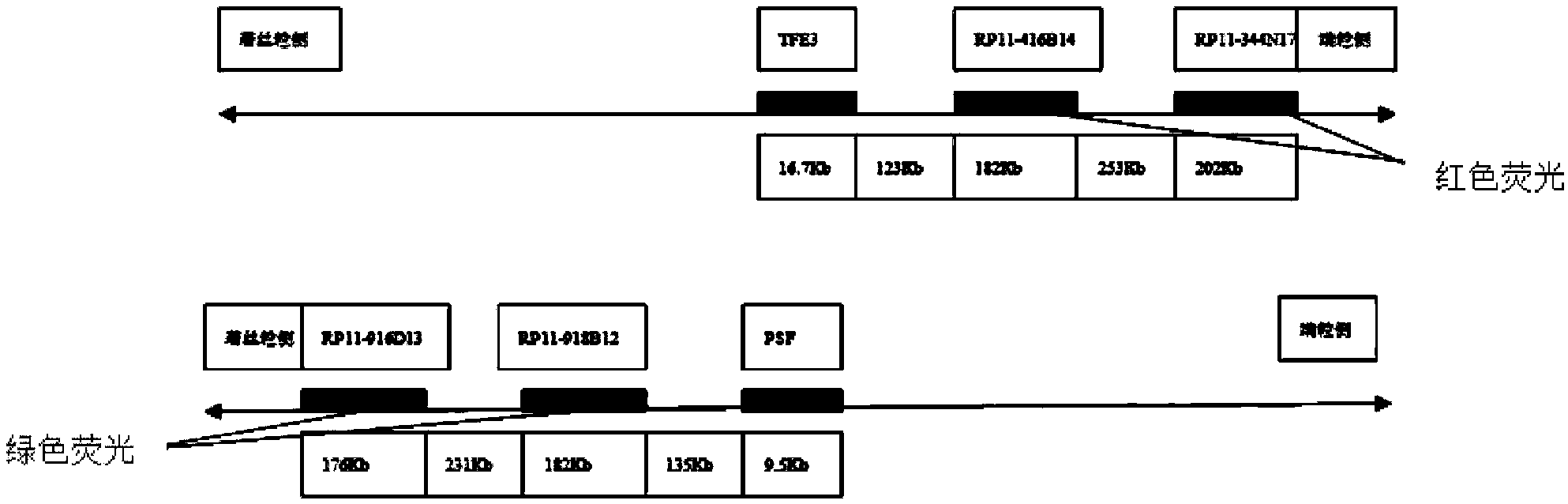
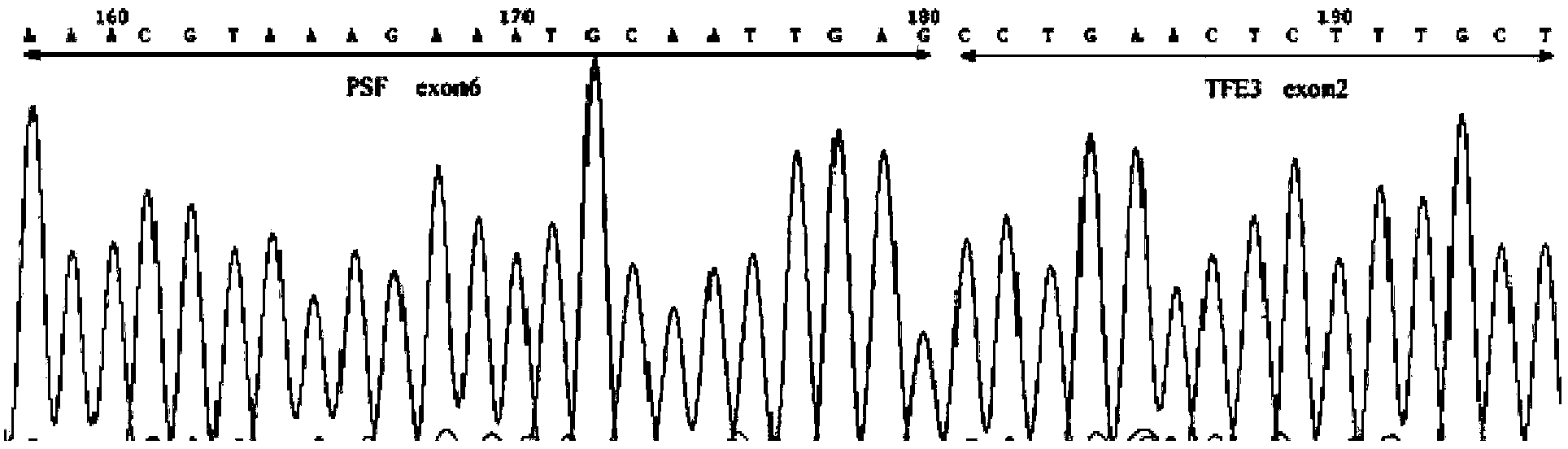
Probe set for diagnosing Xp11.2 ectopic perivascular epithelioid cell neoplasm and application of probe set
ActiveCN104212889AImprove accuracyIncrease success rateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBac cloneFluorescence
The invention belongs to the application field of fluorescence in situ hybridization probes and discloses a probe set for diagnosing Xp11.2 ectopic perivascular epithelioid cell neoplasm and application of the probe set. The probe set includes BAC clonal fragments RP11-918B12, RP11-916D13, RP11-416B14 and RP11-344N17. The probe set is capable of diagnosing the specificity and the sensibility of Xp11.2 ectopic PEComa 100%, is convenient, quick and reliable, and can ensure a high success rate. And moreover, the probe set can be used for preparing an Xp11.2 ectopic PEComa diagnostic kit.
Owner:NANJING GENERAL HOSPITAL NANJING MILLITARY COMMAND P L A
Method for detecting polymorphism of flora of prawn culture water body
InactiveCN101724690AEffective qualitativeEffective quantitative analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescencePrawnFluorescence
The invention discloses a method for detecting polymorphism of a flora of a prawn culture water body. The method comprises the following steps: (1) extracting total genomic DNA of mixed microbes in a prawn culture water body sample; (2) designing a specificity T-RFLP-PCR universal primer and performing PCR circulating reaction; (3) purifying a product and performing enzyme cutting on DNA by a specific restriction enzyme Hae III; (4) performing ionophortic separation on DNA segments by 1 percent agarose gel, performing fluorescent scanning on the DNA segments; (5) analyzing a polymorphism structure of a microbe flora; and (6) performing quantitative detection on predominant bacteria of the flora through fluorescence in situ hybridization technology. The method improves detection technology combining T-RFLP-PCR with FISH, uses fluorescence to mark a specific primer; and compared with the modern technology, the method has the characteristics of high repeatability, sensitivity, rapidness, accuracy, stability and the like, and can qualitatively and quantitatively analyze the ecological diversity of the microbes in the prawn culture water body along with time change and the dynamic change of a composite structure of the predominant flora.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method of prognosis of metastasis by detection of FRA12E fragile site within the SMRT gene/locus at chromosome 12q24
Provided are methods for prognostic prediction of metastasis. The method comprises identifying the presence or absence of a fragile site FRA12E on chromosome 12q24 at the SMRT gene locus. The presence of FRA12E in an individual can be determined in cell samples obtained from the individual by hybridization techniques such as fluorescence in situ hybridization techniques. The presence of this fragile site at this locus is indicative of higher likelihood of metastasis than if the fragile site is absent. Also provided are kits for the determination of likelihood of metastasis.
Owner:HEALTH RES INC
Method for discriminating non-blood-borne nucleated cells enriched from human or animal biological fluid
ActiveCN103091491AHigh recovery rateAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationHuman bodyStaining
Owner:有限会社林平
Detection and diagnosis of smoking related cancers
Gene probes for specific regions of chromosomes 1, 3, 9, 10 and 17 are now shown to be useful in the diagnosis and prognosis of smoking related cancers such as non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). For example, these probes can be used with fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), and used to stratify smokers into high and low risk groups, to determine susceptibility to the development of smoking related cancers, to predict cancer progression and treatment efficacy, and to rule out other diseases.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Method for highly fine three-dimensional modeling of complex earth surface
InactiveCN103150758ASimplify the modeling processImprove modeling efficiencySpecial data processing applications3D modellingAnalogue computationDesign software
Owner:HEBEI IRON & STEEL GRP MINING +2
Multicolor fluorescence in situ hybridization (MFISH) method for quickly analyzing and identifying alien chromosome of wheat
ActiveCN103205500AAvoid deformationAvoid problems such as loss of deformationMicrobiological testing/measurementAlien chromosomeTriticeae
The invention provides a multicolor fluorescence in situ hybridization (MFISH) method for quickly analyzing and identifying alien chromosome of wheat. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preprocessing actively dividing tissues in meristematic zone of wheat root tip by N2O and conducting enzymolysis on the actively dividing tissues to obtain a metaphase specimen with clear images and uniform distribution of chromosomes; (2) marking a fluorescent probe of fundamental genome of wheat by nick translation method; (3) conducting fluorescence in situ hybridization on chromosomes at mitosis metaphase obtained in step (1) by using the constructed fluorescent probe in step (2); and (4) analyzing the fluorescence in situ hybridization results obtained in step (3). According to the method provided by the invention, not only can alien chromosomes and chromosome segments in distant hybrid wheat be identified, but also alien chromosomes and chromosome segments of distant hybrids of other crops can be identified.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Probe and kit for detecting HER-2 (human epidermal growth factor receptor-2) gene amplification
ActiveCN105087769AProlong lifeImprove the quality of lifeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationHybridization probeFluorescence
The invention discloses a fluorescence in situ hybridization probe and kit for detecting HER-2 (human epidermal growth factor receptor-2) gene amplification and relates to an FISH (fluorescence in situ hybridization) kit. The fluorescence in situ hybridization kit for detecting HER-2 gene amplification comprises an LSP HER-2 / CSP 17 probe and DAPI redyeing liquid; and the probe is marked by adopting a random primer method and is a fluorescence in situ hybridization double-color probe, an HER-2 gene is indicated by a red signal, and the internal control CSP17 is indicated by a green signal. An FFPE tissue slice is used as a detection sample, the FISH method is adopted for detecting the HER-2 gene amplification state, and the probe and the kit can be used for diagnosis of molecular markers for invasive breast cancer and stomach cancer and assisting in clinical medication selection.
Owner:AMOY DIAGNOSTICS CO LTD
Gene probe composition and kit for acute lymphocytic leukemia detection
ActiveCN102978279AEasy to detectImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceIn situ hybridisationFluorescence
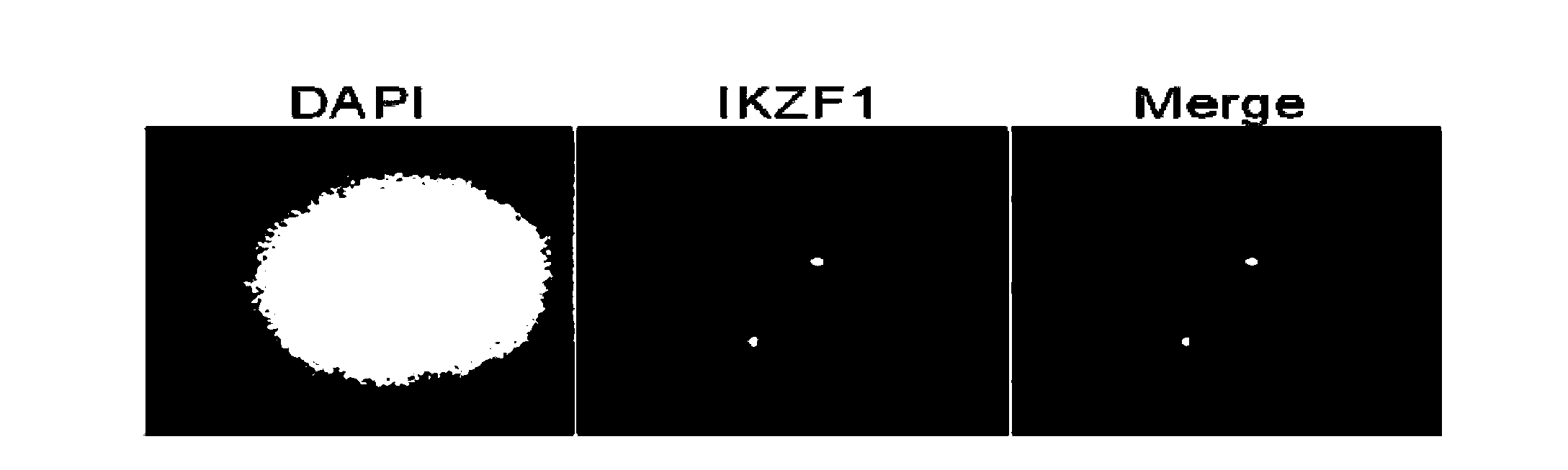
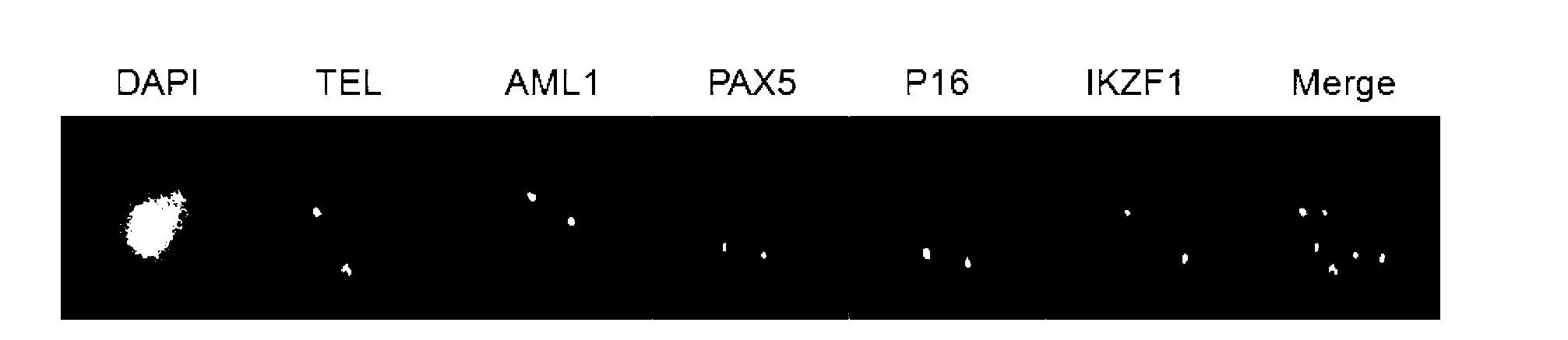
The present invention relates to a gene probe composition and a kit for acute lymphocytic leukemia detection. The gene probe composition comprises a TEL gene probe, an AML1 gene probe, a PAX5 gene probe, a P16 gene probe and an IKZF1 gene probe. The present invention further provides an acute lymphocytic leukemia fluorescence in situ hybridization detection kit, wherein the kit comprises the gene probe composition. With the kit, concurrent five gene detection can be performed on the same sample even the single leukemia cell, and detection capability and efficiency are significantly improved.
Owner:INST OF HEMATOLOGY & BLOOD DISEASES HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI & PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE
Oligonucleotide probe and acquisition method thereof
ActiveCN106566876ASimple designLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridisationRepetitive SequencesIn situ hybridisation
The invention relates to a method for acquisition of an oligonucleotide probe. The method comprises the following steps: downloading genomic sequence of crop species from a public database, filtering and finding out tandem repeat sequences, screening preliminarily found repetitive sequences, comparing residual tandem repeat sequence and known probe sequence, removing already used probe sequence, comparing residual screened tandem repeat sequences, carrying out probe design and synthesizing and verifying the designed probe sequence so as to obtain effective oligonucleotide sequence. According to the invention, cost is low and efficiency is high. The probe can be used for non-degenerated fluorescence in situ hybridization (ND-FISH) analysis of crop chromosome, determination of distribution of tandem repeat sequences represented by the probe on chromosome, understanding of the structure characteristics of chromosome and establishment of specific landmark of chromosome. Thus, specific chromosome or chromosome region of crops is identified, and the developed new oligonucleotide probe has specificity of chromosome or chromosome region.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Fluorescence in situ hybridization method for positioning 45S rDNA on plant chromosome
ActiveCN103409524ASimple methodLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementIn situ hybridisationFluorescence in situ hybridization
The invention discloses a fluorescence in situ hybridization method for positioning the 45S rDNA on a plant chromosome. The fluorescence in situ hybridization method mainly comprises the following steps of preparation of a chromosome specimen, preparation of 45S rDNA probes, fluorescence in situ hybridization of the chromosome and hybridization signal detection. The provided method for probe marking and hybridization is simple, convenient, quick and accurate, and mainly solves the problem about complex and cumbersome marking of the existing probes for fluorescence in situ hybridization. The probes provided by the invention are oligonucleotide probes which are not marked any more, and a fluorophore for modification can be added during synthesis of the probes, and compared with the prior art, the method is simple and the cost is low. By utilizing the technology, FISH positioning of the 45S rDNA on the chromosome can be completed within 3 hours.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com