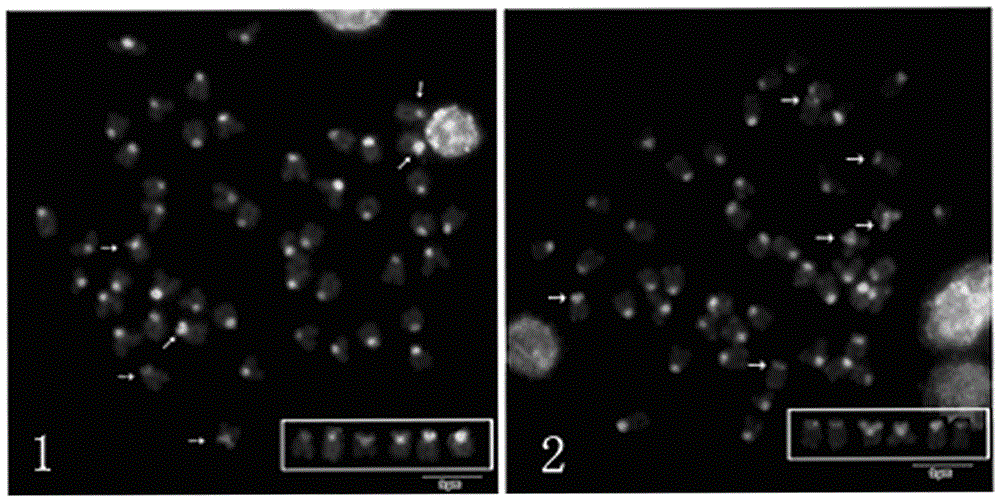
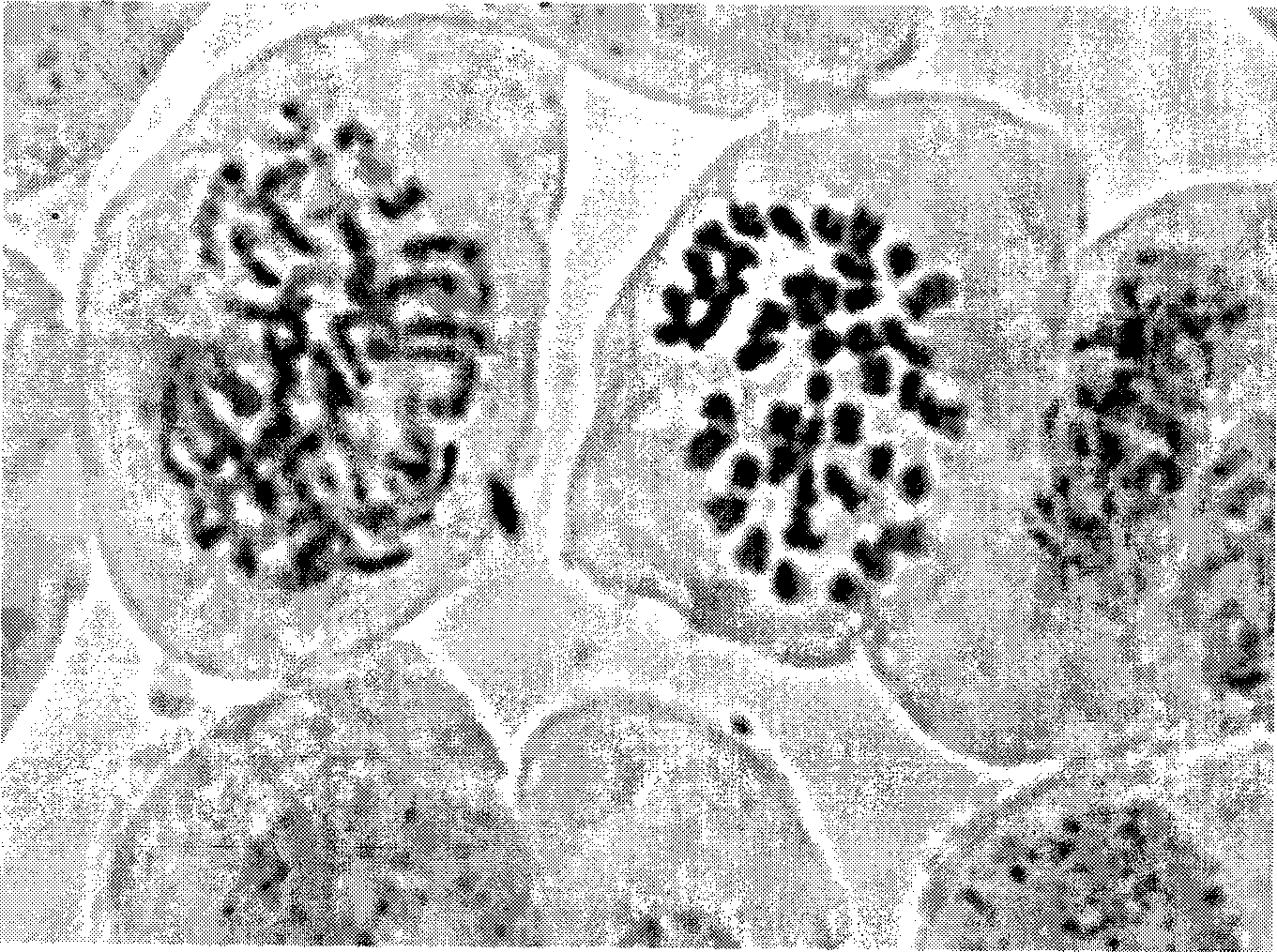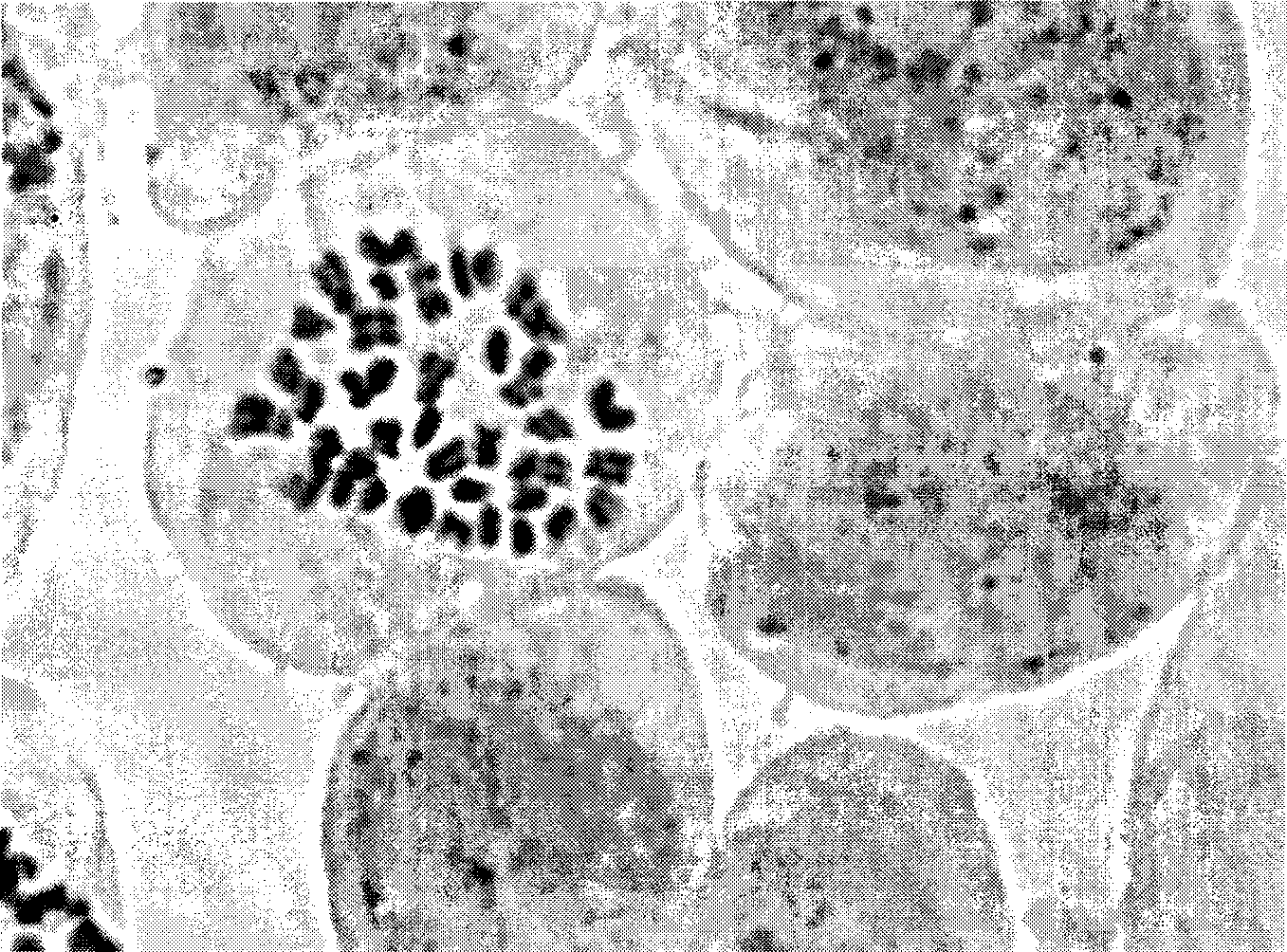Patents
Literature
47 results about "Metaphase chromosome" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
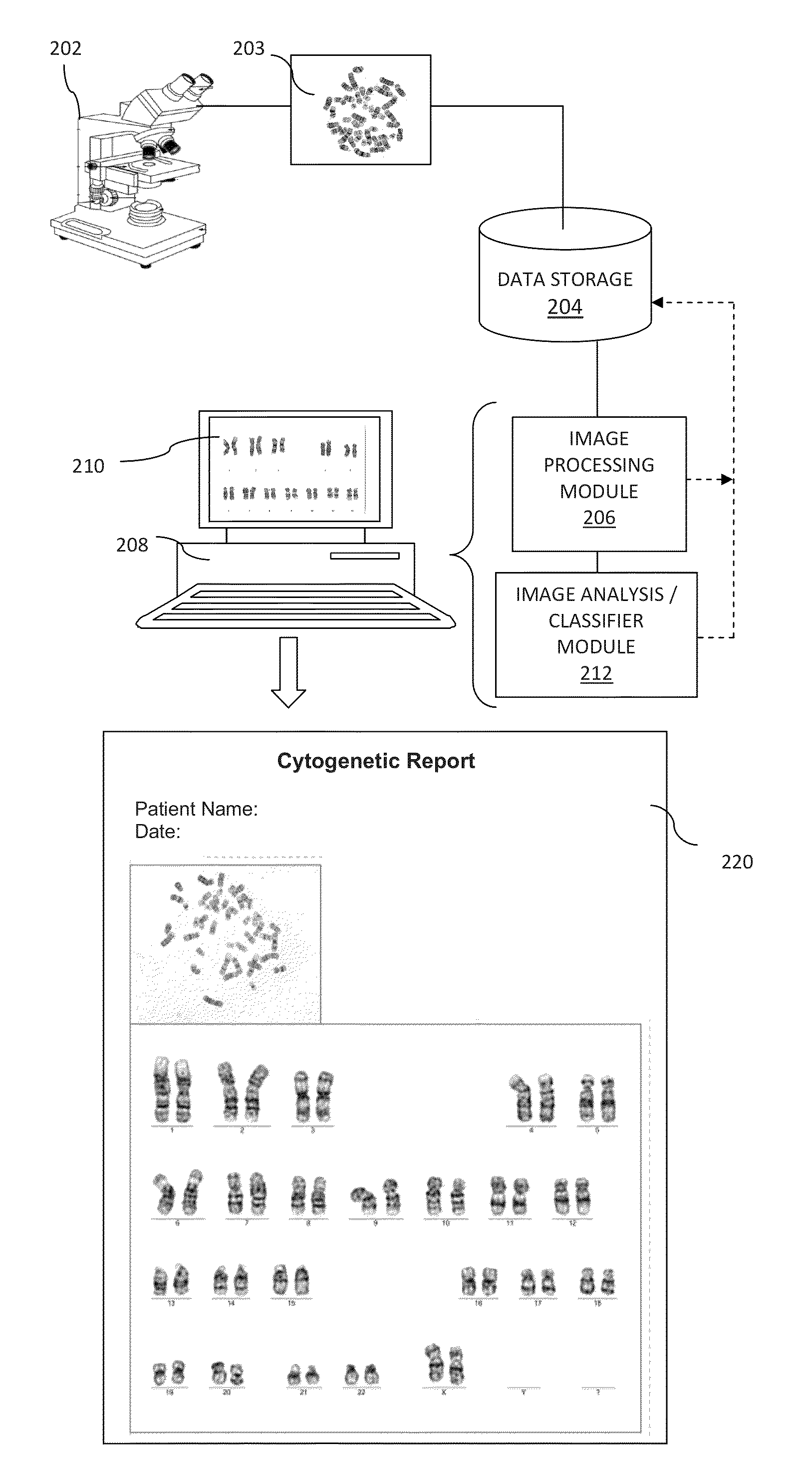
Computer-assisted karyotyping
A system and method for computer-assisted karyotyping includes a processor which receives a digitized image of metaphase chromosomes for processing in an image processing module and a classifier module. The image processing module may include a segmenting function for extracting individual chromosome images, a bend correcting function for straightening images of chromosomes that are bent or curved and a feature selection function for distinguishing between chromosome bands. The classifier module, which may be one or more trained kernel-based learning machines, receives the processed image and generates a classification of the image as normal or abnormal.
Owner:HEALTH DISCOVERY CORP
Methods of staining target chromosomal DNA employing high complexity nucleic acid probes
ActiveUS7115709B1Rapid and highly sensitive detectionEasy to analyzePeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementMetaphase chromosomeNucleic Acid Probes
Methods and compositions for staining based upon nucleic acid sequence that employ nucleic acid probes are provided. Said methods produce staining patterns that can be tailored for specific cytogenetic analyses. Said probes are appropriate for in situ hybridization and stain both interphase and metaphase chromosomal material with reliable signals. The nucleic acid probes are typically of a complexity greater than 50 kb, the complexity depending upon the cytogenetic application. Methods and reagents are provided for the detection of genetic rearrangements. Probes and test kits are provided for use in detecting genetic rearrangements, particularly for use in tumor cytogenetics, in the detection of disease related loci, specifically cancer, such as chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), retinoblastoma, ovarian and uterine cancers, and for biological dosimetry. Methods and reagents are described for cytogenetic research, for the differentiation of cytogenetically similar but genetically different diseases, and for many prognostic and diagnostic applications.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Fluorescence in situ hybridization method of prunus mume chromosome
ActiveCN102787166AIncrease the success rate of hybridizationHigh hybridization specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceMetaphase chromosomeFluorescence
The invention relates to a fluorescence in situ hybridization method of a prunus mume chromosome. The method consists of: taking a prunus mume metaphase chromosome as the target DNA, adopting maize 45SrDNA as a probe, using a nick translation method to label the probe, and positioning the maize 45SrDNA probe on the prunus mume chromosome clearly. Based on the prior art, the invention improves the co-denaturation method, and employs the two steps of probe denaturation, and chromosome and probe co-denaturation to complete the denaturation process, thus greatly improving the hybridization success rate. The invention determines an appropriate denaturation temperature and denaturation time, a hybridization time and an elution method, and has high hybridization specificity, so that the FISH technology can be well applied in chromosome detection of prunus mume and other small chromosome plants, thus providing a new approach and method for in-depth study of the prunus mume chromosome.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Tabletting method for locust stem tip chromosome
InactiveCN101482515AEasy to operateGood repeatabilityPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansNitraria billardiereiMetaphase chromosome
The invention provides a robina stem-apex chromosome pressing method, comprising: taking material, preprocessing, fixing, dissociating, pressing, dyeing, striking, microscopic examining, characterized in that: taking the stem-apex of robina tissue culture seedling in vigorous growth stage at 3-5pm at the culture-room temperature 22-25 DEG C., wherein the cell of the stem-apex of robina tissue culture seedling is at vigorous division stage; preprocessing the stem-apex using 8-hydroxy quinoline 0.002-0.004m for 3-5 hours; pressing the stem-apex using a cross pressing method; dyeing the pressed stem-apex using carbol fuchsin; striking the material using a pencil head and uniformly dispersing the cells to the best. The robina stem-apex chromosome pressing method has features of simple operation, high pressing efficiency, saved medicine consumption, uniform chromosome dispersion, easy counting, very easy observation of metaphase chromosome, uniform and clear dyeing, especially suitable for chromosome pressing of tough wood material.
Owner:天津市林业果树研究所
Method for enumerating eukaryotic cell micronuclei with an emphasis on simultaneously acquiring cytotoxicity and mode of action information
InactiveUS20140017673A1Fast and reliable and accurateLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingMode of actionMetaphase chromosome
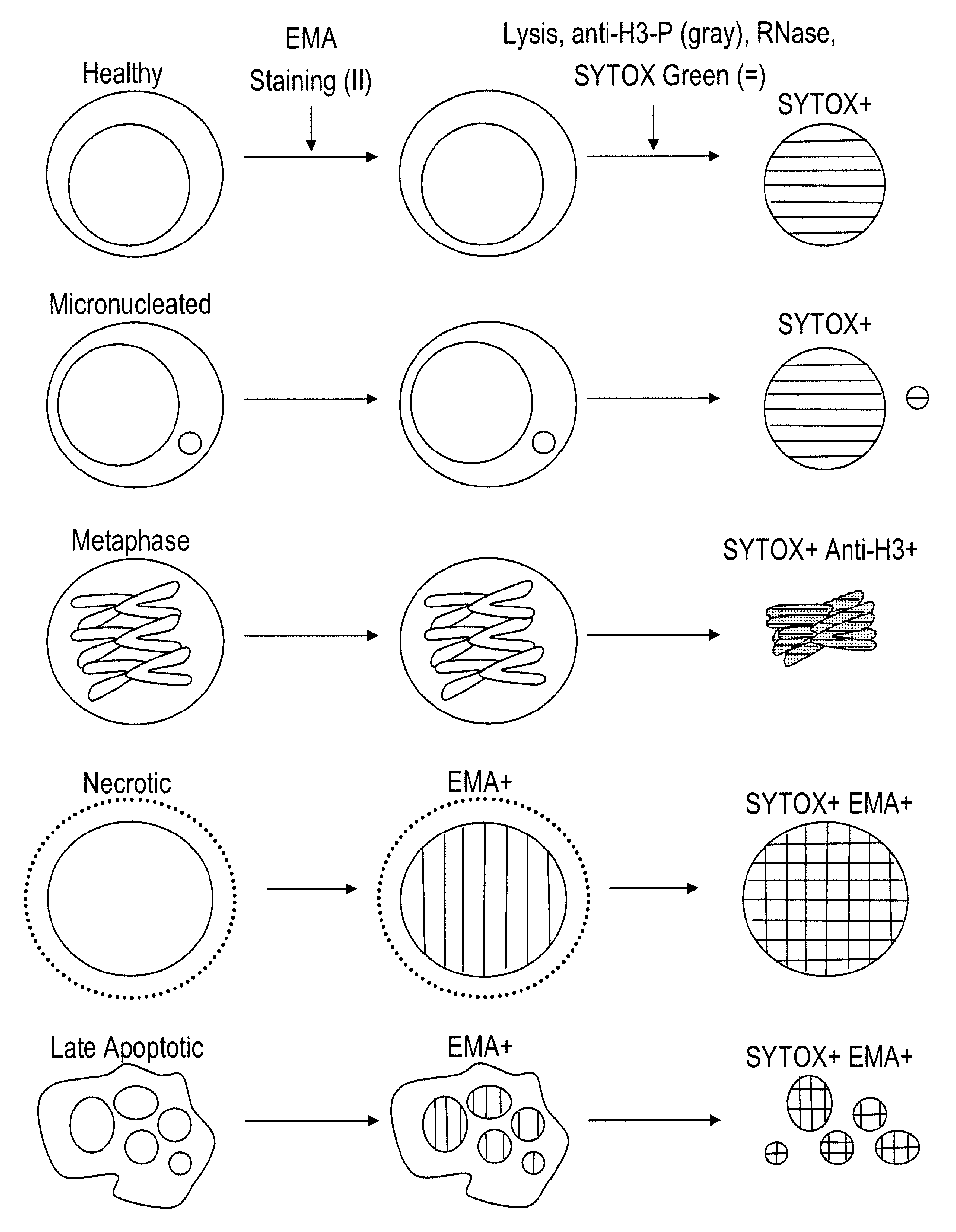
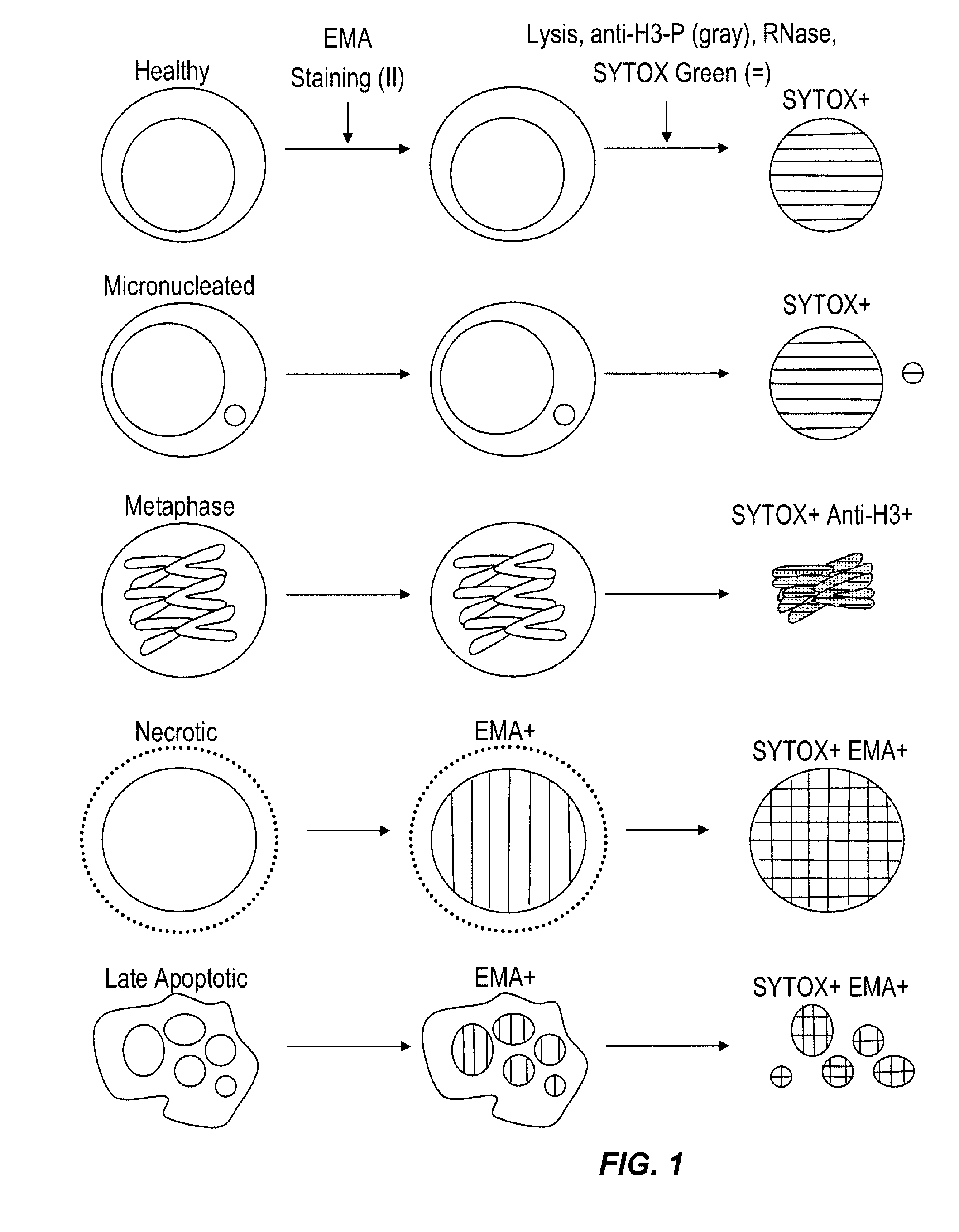
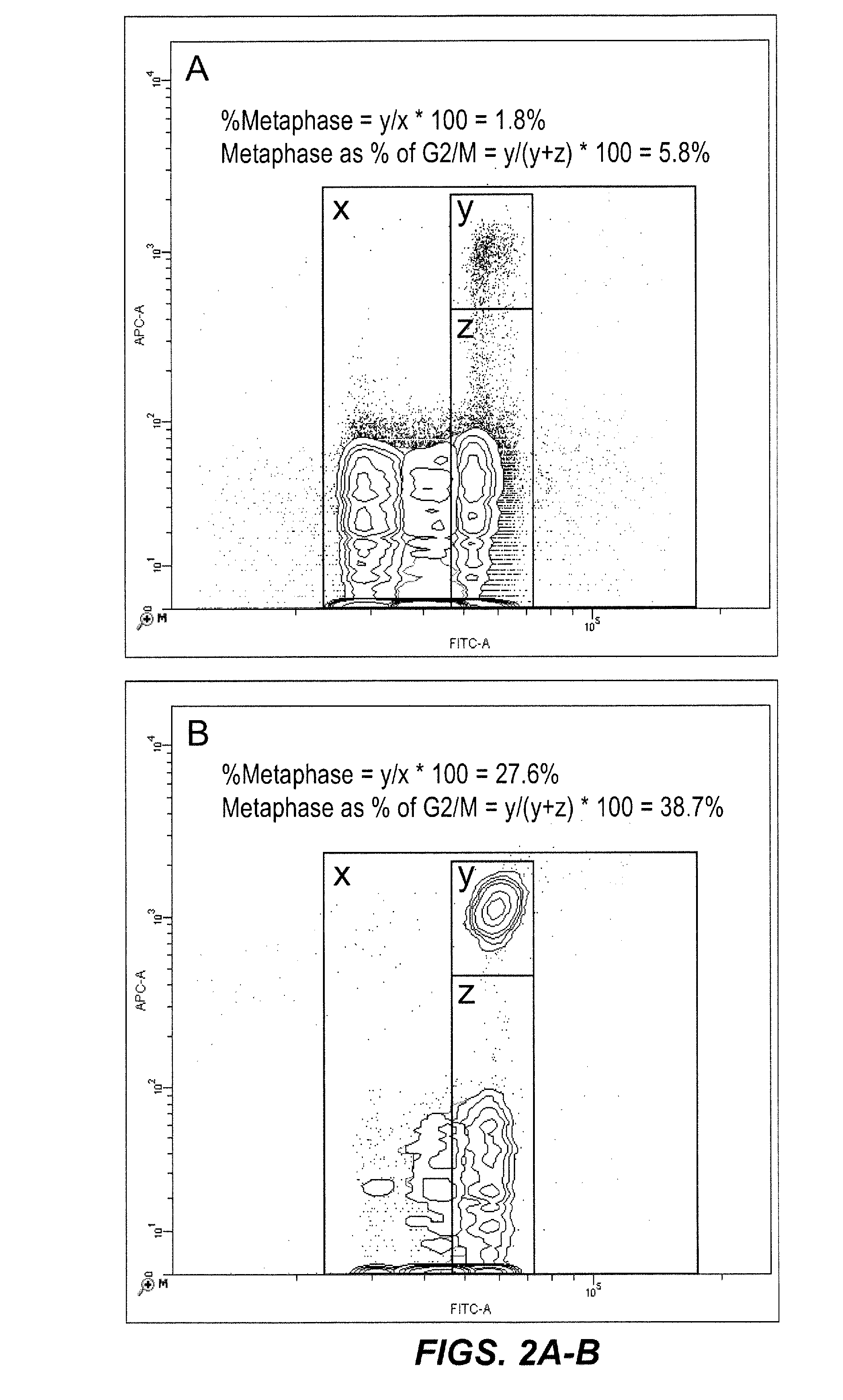
The present invention relates a method for the enumeration of eukaryotic cell micronuclei, while simultaneously acquiring cytotoxicity and mode of action information. The method utilizes differential labeling of chromatin from dead and dying cells to distinguish the chromatin from micronuclei, nuclei, and metaphase chromosomes, and differential labeling of metaphase events to provide additional information regarding cytotoxicity and genotoxic modes of action. Counting of micronuclei events relative to the number of nuclei and quantifying perturbations to the proportion of metaphase events can be used to assess the DNA-damaging potential of a chemical agent, the DNA-damaging potential of a physical agent, the effects of an agent which can modify endogenously-induced DNA damage, the effects of an agent which can modify exogenously-induced DNA damage, and genotoxic mode of action.
Owner:LITRON LAB
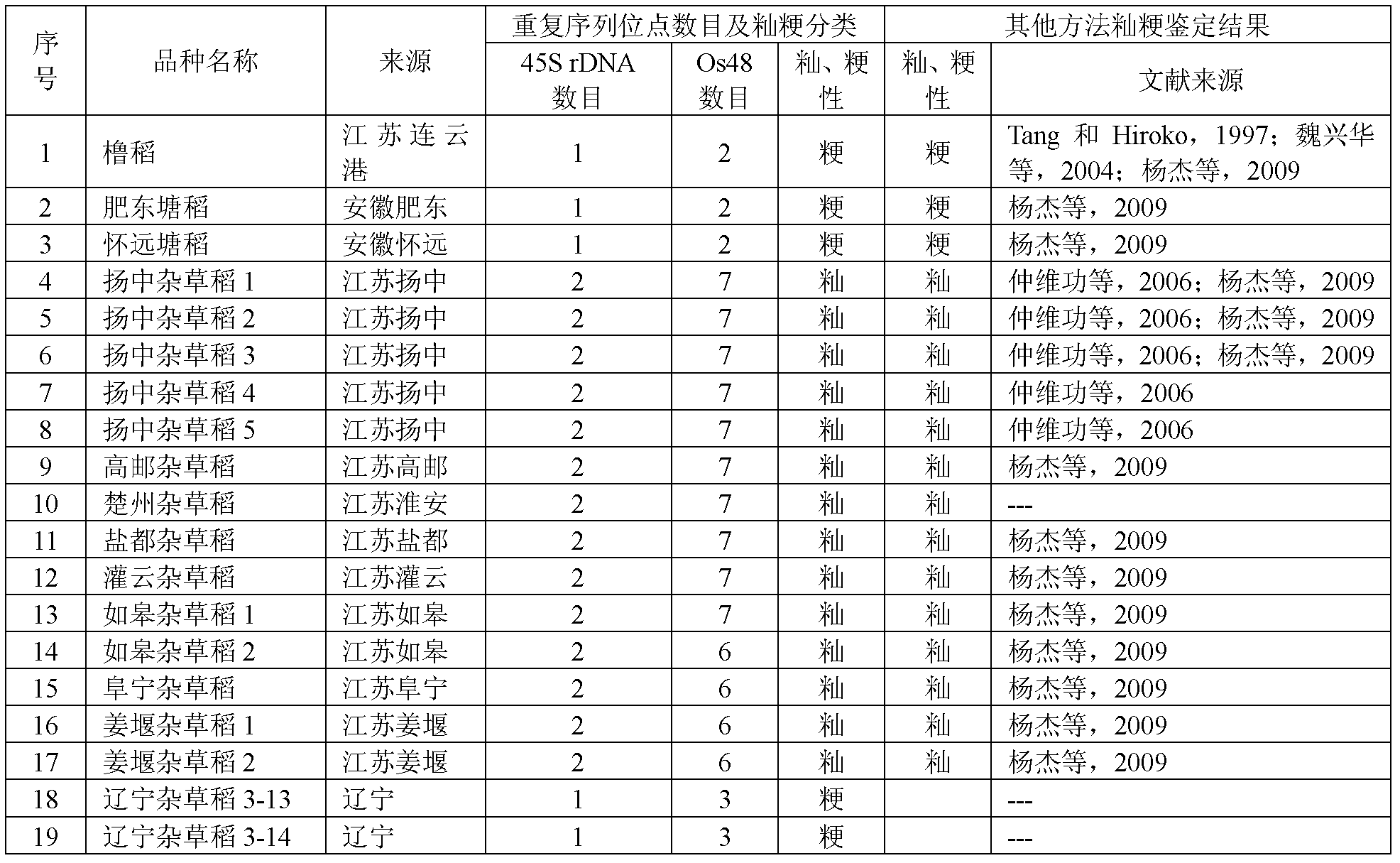
Method for differentiating indica japonica of weedy rice through two repeated DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) sequences
ActiveCN102251054AImprove reliabilityHigh degree of fitMicrobiological testing/measurementMetaphase chromosomeTriticeae
The invention relates to a method for differentiating indica japonica of weedy rice through two repeated DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) sequences. In the method, plasmid DNAs of cloning pTA71 containing wheat 45SrDNA gene sequences and cloning pOs48 containing repeated serial sequences of subtelocentric rice AA group chromosome are extracted, and 45SrDNA and Os48 probes are formed by using pOs48 labeled by using digoxin-dUTP (deoxyuridine triphosphate) and pTA71 labeled by using biotin-dUTP through a nick translation method to differentiate the indica japonica of the weedy rice. The method comprises the following steps of: flaking and denaturing a metaphase chromosome of the differentiated weedy rice before karyokinesis; carrying out two-color fluorescence in-situ hybridization between the metaphase chromosome and a denatured hybridization solution containing the probes; detecting a signal of the metaphase chromosome in the dark; and classifying the indica japonica of the weedy rice of different sources according to the locus number and distribution characteristics of the 45SrDNA and the Os48 on the metaphase chromosome of the weedy rice before the karyokinesis.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Lagerstroemia plant chromosomal in-situ hybridization method
InactiveCN103305614AGood for physical locationHigh hybridization specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementIn situ hybridisationMetaphase chromosome
The invention relates to a lagerstroemia plant chromosomal in-situ hybridization method. The method comprises seven steps such as sheet making, probe preparing, pretreating before hybridization, hybridization solution preparing, probe denaturating, chromosome denaturating, hybridizing and detecting. A lagerstroemia plant metaphase chromosome serves as a target deoxyribose nucleic acid (DNA) and maize 45SrDNA as a probe, and the maize 45SrDNA probe is clearly located on the lagerstroemia plant metaphase chromosome. By utilizing the hybridization method, background interferences can be effectively eliminated, the detection sensitivity and accuracy are improved, the hybridization method can be better applied to the chromosome detection of small chromosome plants such as lagerstroemia and the like, and a new way and a method are provided for the further research of lagerstroemia plant chromosomes.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Culture medium for amniotic fluid and chorionic villus
InactiveCN102618493AHigh rate of colony formationHigh speedEmbryonic cellsMetaphase chromosomeAntioxidant
The invention relates to a culture medium for amniotic fluid and chorionic villus, and belongs to the field of cytobiology. The culture medium for amniotic fluid and chorionic villus comprises the following components: basic culture mediums, fetal calf serums, growth factors, antioxidants, antibiotics and a buffer system. Through the invention, the cost can be lowered, the cloned number and the cell proliferation speed of amniotic fluid and chorionic villus proliferated in vitro can be effectively increased, the culture period is shortened, and the culture mediums for amniotic fluid and chorionic villus with a few of metaphase chromosomes and a formula of the culture mediums for amniotic fluid and chorionic villus are obtained.
Owner:HUIZHOU HONGYU TECH
Method for quickly establishing metaphase chromosome karyotype of cucumber through genomic in-situ hybridization
InactiveCN104004849AImprove test efficiencyProbe signal is clearMicrobiological testing/measurementDispersityMetaphase chromosome
The invention discloses a method for quickly establishing a metaphase chromosome karyotype of a cucumber through a genomic in-situ hybridization technology. The method includes the steps that genome DNA of the cucumber is extracted and marked as a probe; enzymolysis is conducted on an extracted root tip of the cucumber, a sheet is prepared through a flame drying method, and then a metaphase chromosome sheet with the good dispersity is acquired; the genome DNA serving as the probe is degenerated and then hybridized to the degenerated metaphase chromosome sheet, under the hybridization condition with the high preciseness, clear and differentiable fluorescence signals are produced through a chromosome tandem repeated sequences, and then the metaphase chromosome karyotype of the cucumber is established. The genome DNA of the cucumber serves as the probe, the metaphase chromosome karyotype of the cucumber is quickly established through one-time GISH, and then testing efficiency is improved. Through the method, based on the different signal distribution modes of the genome DNA probe of the cucumber on chromosomes, the metaphase chromosome karyotype of the cucumber can be quickly established, and a novel method and reference are provided for analytical investigation of karyotypes of species.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Cotton somatic cell chromosome Oligo-FISH (oligonucleotide-fluorescence in situ hybridization) method
The invention discloses a cotton somatic cell chromosome Oligo-FISH (oligonucleotide-fluorescence in situ hybridization) method. Compared with the prior art, the cotton somatic cell chromosome Oligo-FISH method is characterized in that according to the disclosed cotton genomic sequence information, a unpaired allosome oligonucleotide mixing pool is designed; the oligonucleotide mixing pool is subjected to emulsification PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification, in vitro transcription and inverse transcription to obtain a fluorescently-labeled ssDNA (single-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid) mixing pool, i.e., an oligonucleotide mixing probe of a target chromosome. The probe is used for performing FISH (fluorescence in situ hybridization) on the metaphase chromosome of the cotton somatic cell; the theoligo-FISH method is built; the technical support is provided for cotton chromosome DNA rearrangement, chromosome pairing, genetic relationship analysis, heterogenous chromatin identification and the like.
Owner:ANYANG INST OF TECH +1
Perultimate chromomere marker of cotton chromosome fluorescent in situ hybridization and use thereof
InactiveCN101475992AMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationIn situ hybridisationMetaphase chromosome
The present invention provides a telomere marker suitable for cotton fluorescent in situ hybridization, which is a sequence marked by biotin shown in the SEQ ID No.1. The telomere marker is taken as probe and cotton root tip somatic cell metaphase chromosome to perform fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), and stronger hybridization signals occur at the end of the chromosome. Further experiments confirm that the in situ hybridization signal is located at the extreme end of chromosome, that is, the hybridization signal is the telomere signal. Therefore, the length of the cotton somatic cell metaphase chromosome can be estimated by the telomere marker located at the end of chromosome, so as to lay the foundation for further karyotype analysis.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
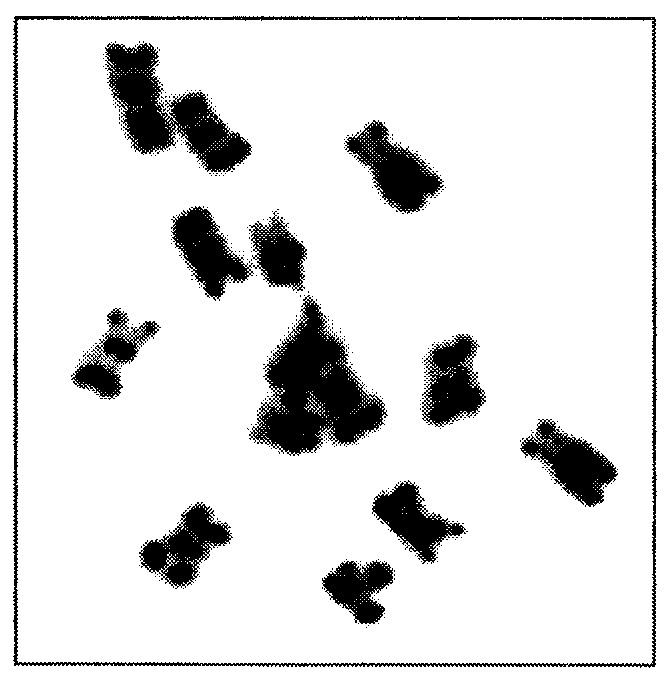
Method for preparing metaphase specimen of mammalian cell chromosome
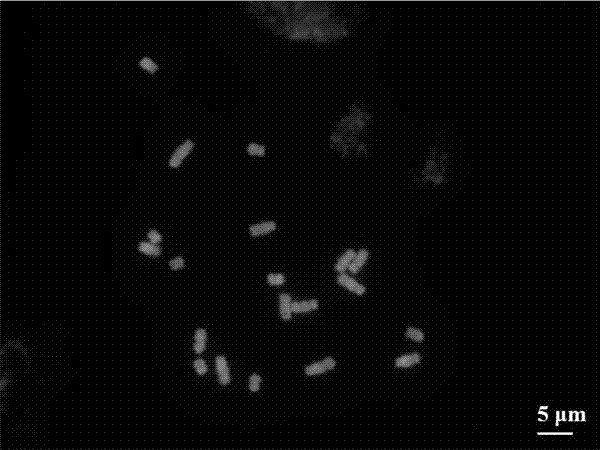
The invention provides a method for preparing a metaphase specimen of mammalian cell chromosome. The method comprises the following step of: dripping mammalian cell suspension onto a glass slide at the temperature of 20-30 DEG C and under the relative humidity of 45-50%. The metaphase chromosome obtained with the method is good in quality, shape and dispersion degree, and is a metaphase chromosome specimen easy for chromosome evaluation.
Owner:天津天诚新药评价有限公司 +1
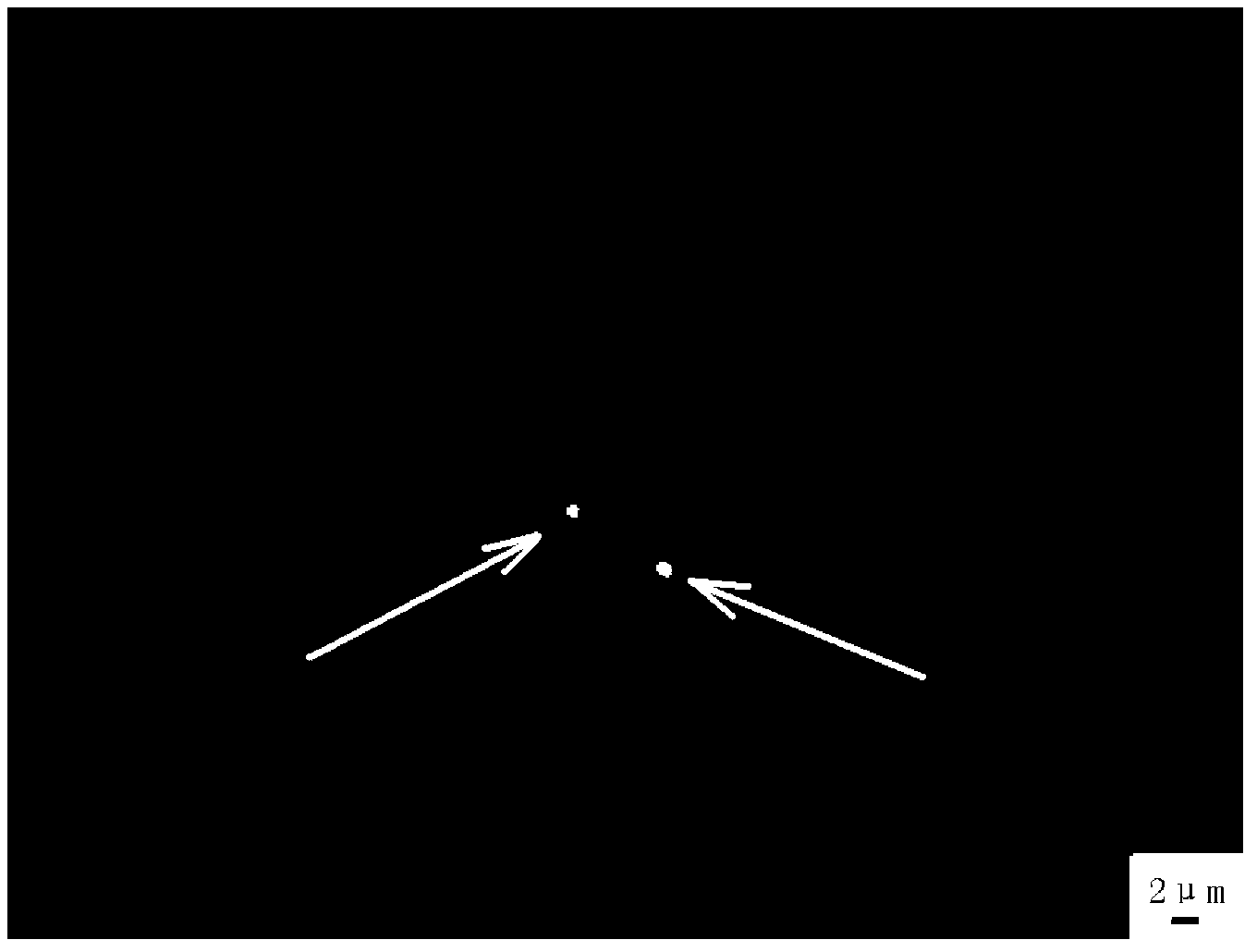
Method for displaying centromeres and short arms of Larimichthys crocea
The invention discloses a method for displaying centromeres and short arms of large yellow croaker, and belongs to the field of molecular cytogenetics. A molecular marker is a segment of a 28S rDNA sequence cloned from human saliva, and is processed to prepare a probe (named as H-P3K), and the probe is crossed with metaphase chromosomes of Larimichthys crocea to obtain a positive signal. The positive signal in the centromeres and the short arms of every metaphase chromosome can be detected when FISH of the Larimichthys crocea chromosomes is carried out by the probe, the short arm signal intensity of one chromosome is weaker than the centromere signal intensity of the same chromosome, and the centromere signal intensities of different chromosomes are different. The method is used for determining the position of the centromere, analyzing the chromosome karyotype and researching the chromosome structure; and the positive signal can be used as a chromosome identifying and pairing marker.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Method for preparing conventional slide of chromosomes from grapevine root tips
InactiveCN107389411APromote rootingEasy to manufacturePreparing sample for investigationMetaphase chromosomeDecomposition
The invention discloses a method for preparing a conventional slide of chromosomes from grapevine root tips. The method comprises the following steps: material culture, pretreatment, immobilization, preservation, dissociation, dyeing, slide preparation and microscopic examination. According to the invention, rooting of grapevine twigs is easy, and root tips are moderately thick and facilitate preparation of a chromosome slide; the prepared slide is flat in specimen cells and dispersed in chromosomes; pretreatment with a saturated p-dichlorobenzene solution can improve the success rate of slide preparation, enables chromosomes to be shortened and thickened, reduces the viscosity of cytoplasm and allows more metaphase chromosomes to be obtained; and a mixed enzyme solution with a concentration of 3.5% is used for enzymatic hydrolysis, so cell walls are decomposition, pectic substances among meristematic cells are decomposed, cells are well dispersed, and chromosomes are large in dispersion space and uniform in dispersion and are thus easy to count. The preparation method of the invention has the advantages of easiness, quick preparation, low preparation cost and easy operation, and obtained cells are good in division phase and high in accuracy, which are of great significance to understanding of the genetic background of grapes, the selection of parents in breeding and post-identification.
Owner:SHANXI AGRI UNIV
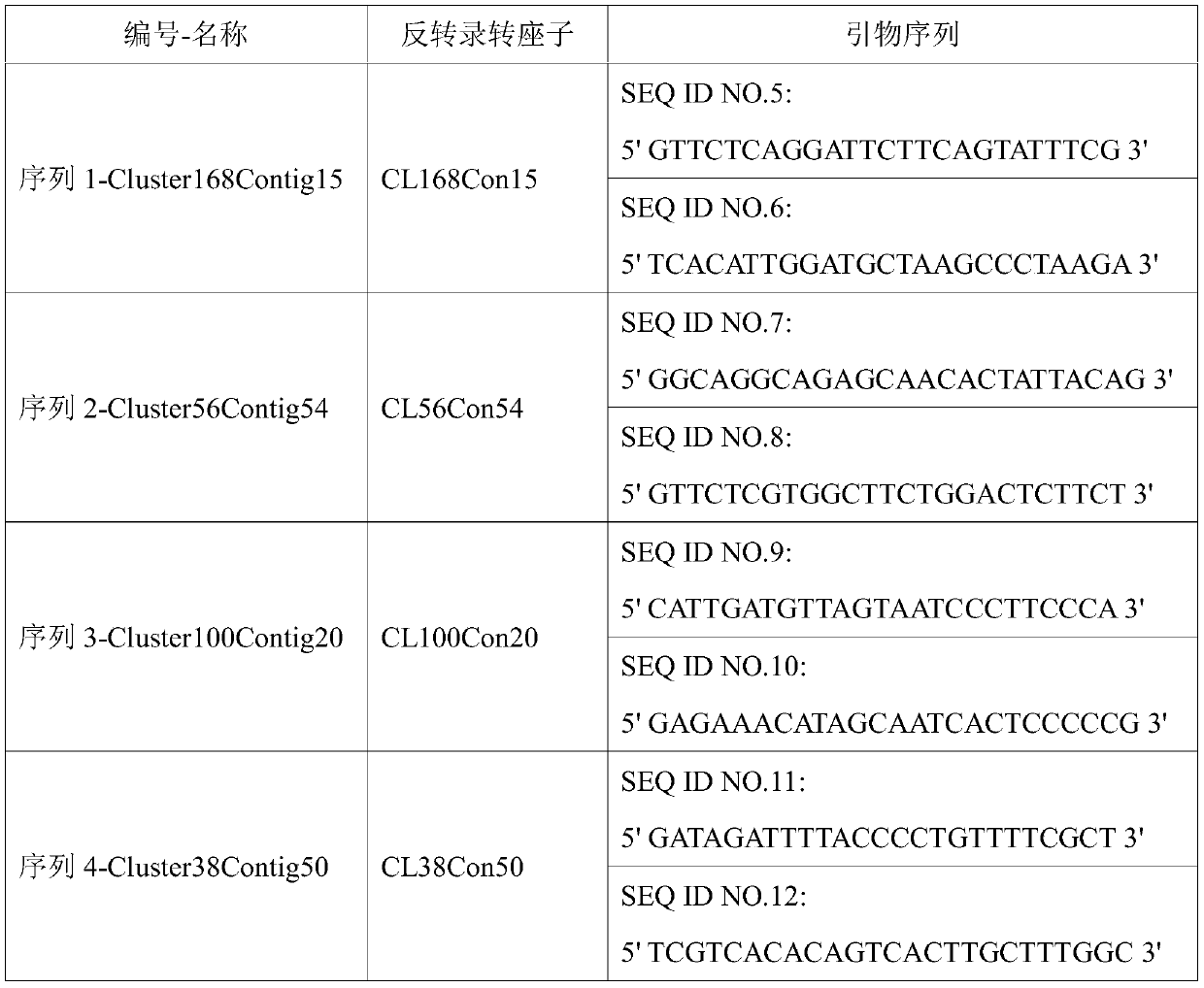
Saccharum spontaneum retrotransposon sequence and identification method thereof
ActiveCN110184267AStrong specificityFacilitate identification researchMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceMetaphase chromosome
The invention discloses a saccharum spontaneum retrotransposon sequence and an identification method of the saccharum spontaneum retrotransposon sequence. Four saccharum spontaneum retrotransposon sequences are screened out using cluster analysis of genome data of saccharum spontaneum and a tropical species; primers are designed separately according to the sequences for amplification to form a full-length sequence; then, a probe is prepared; fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) identification is performed on metaphase chromosomes of the saccharum spontaneum and the tropical species; and aresult shows that the four retrotransposon sequences generate clear and bright signals on the saccharum spontaneum chromosomes. The retrotransposon sequence can be directly used for specific identification of the saccharum spontaneum chromosomes, provides more accurate information for blood relationship identification of the saccharum spontaneum in cultivated sugarcane varieties, and lays a foundation for chromosome engineering breeding of sugarcane.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
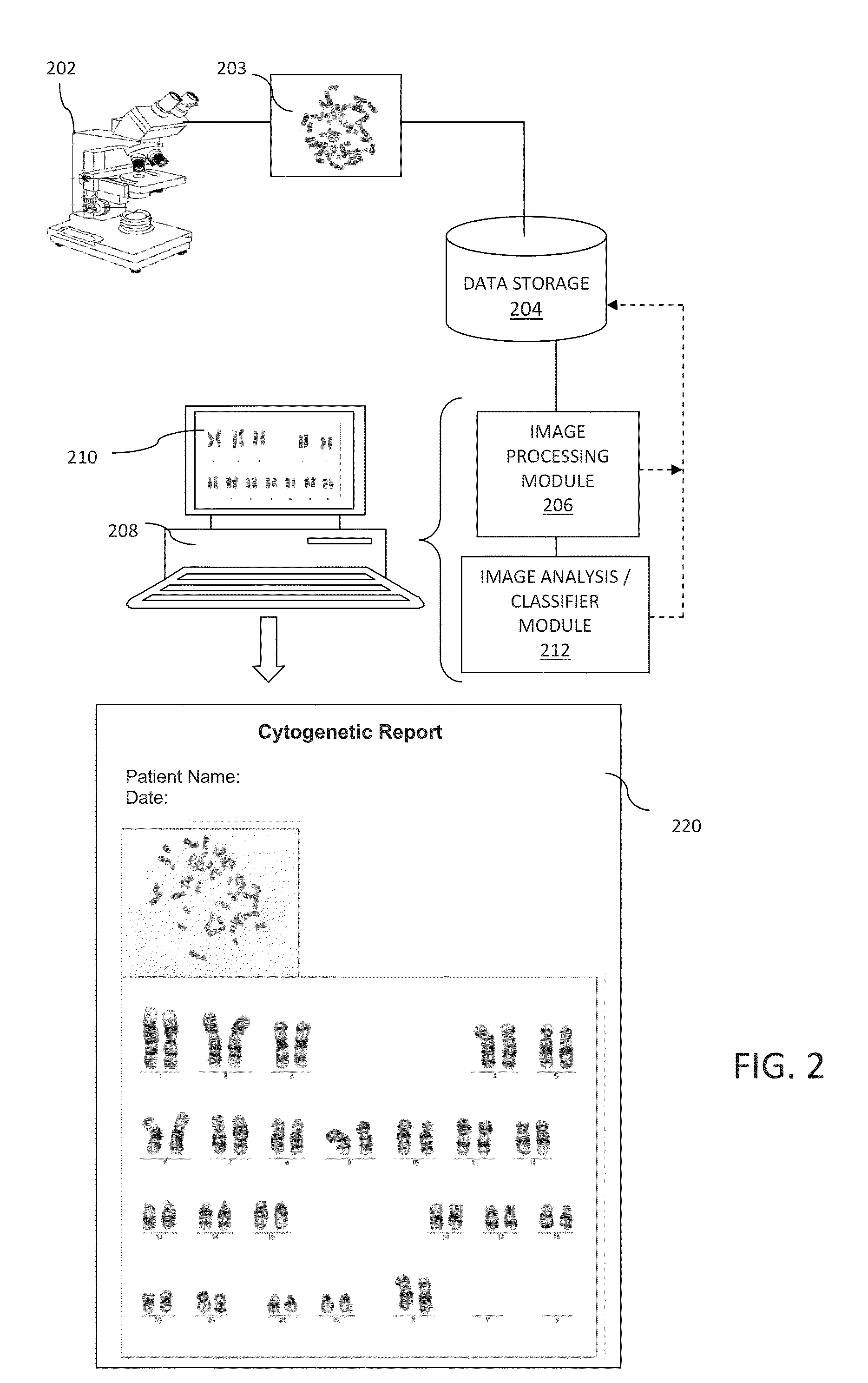
Computer-assisted karyotyping
A system and method for computer-assisted karyotyping includes a processor which receives a digitized image of metaphase chromosomes for processing in an image processing module and a classifier module. The image processing module may include a segmenting function for extracting individual chromosome images, a bend correcting function for straightening images of chromosomes that are bent or curved and a feature selection function for distinguishing between chromosome bands. The classifier module, which may be one or more trained kernel-based learning machines, receives the processed image and generates a classification of the image as normal or abnormal.
Owner:HEALTH DISCOVERY CORP
Centromere mark realizing fluorescence in situ hybridization with asparagus chromosome and applications of centromere mark
InactiveCN105950725AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationIn situ hybridisationMetaphase chromosome
The invention relates to a centromere mark realizing fluorescence in situ hybridization with the asparagus chromosome and applications of the centromere mark, wherein the centromere mark is a Texas red mark, and the nucleotide sequence of the centromere mark is shown as SEQ ID No.1. The marked sequence is taken as a probe to be subjected to fluorescence in situ hybridization with the metaphase chromosome of the root tip of the asparagus, and a concentrated, clear and bright hybridization signal is generated at the centromere position of the chromosome. The developed centromere mark can be applied to the genetic mapping of the centromere position of the asparagus genetic map, and a foundation is laid for the cellular experiments including the karyotype analysis, pachytene stage FISH and fiber-FISH of asparagus.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
Process for preparing triticeae chromosome specimen
InactiveCN1279343CEasy to operateSufficient metaphaseImmobilised enzymesDead plant preservationMetaphase chromosomeTriticeae
The invention belongs to the field of cytogenetics and cell biology, and relates to a method for preparing a chromosome sample. Aiming at the problem that it is often difficult for operators to obtain enough metaphase chromosome specimens in the production of chromosome specimens, the present invention discloses a method for preparing wheat chromosome specimens, which includes seed soaking, germination, low temperature treatment, rewarming growth, pre- Processing, fixation and other steps. The method of the invention is simple to operate, and even a beginner can obtain enough metaphase cleavage phase by using the method.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
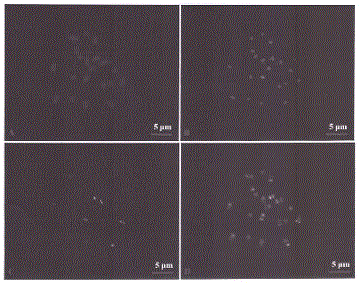
Chromosome-specific staining to detect genetic rearrangements
InactiveUSRE40494E1Efficient and rapid detectionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMetaphase chromosomeNucleic Acid Probes
Methods and compositions for staining based upon nucleic acid sequence that employ nucleic acid probes are provided. Said methods produce staining patterns that can be tailored for specific cytogenetic analyses. Said probes are appropriate for in situ hybridization and stain both interphase and metaphase chromosomal material with reliable signals. The nucleic acid probes are typically of a complexity greater than 50 kb, the complexity depending upon the cytogenetic application. Methods and reagents are provided for the detection of genetic rearrangements. Probes and test kits are provided for use in detecting genetic rearrangements, particularly for use in tumor cytogenetics, in the detection of disease related loci, specifically cancer, such as chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), retinoblastoma, ovarian and uterine cancers, and for biological dosimetry. Methods and reagents are described for cytogenetic research, for the differentiation of cytogenetically similar but genetically different diseases, and for many prognostic and diagnostic applications.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Identification method for cucumber-sour cucumber alien addition line material
InactiveCN107326068APromoting Breeding ResearchIntuitiveMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationRepetitive SequencesHeterologous
The invention discloses an identification method for a cucumber-sour cucumber alien addition line material. The identification method comprises: carrying out backcross on a Cucumis allotriploid and diploid cultivation cucumber to obtain a cucumber-sour cucumber alien addition line candidate material, wherein a Cucumis amphidiploid new variety and diploid cucumber are subjected to reciprocal hybridization to obtain the Cucumis allotriploid; labeling a cucumber centromere specific repetitive sequence Type III by using a probe; taking the root tip of the cucumber-sour cucumber alien addition line candidate material, carrying out enzymolysis, and preparing a slice by using a flame drying method to obtain a metaphase chromosome slice having good dispersion; and denaturing the cucumber centromere specific repetitive sequence Type III probe, hybridizing the denatured probe onto the denatured metaphase chromosome slice, and making the Type III produce the clear and distinguishable fluorescent signal by using highly stringency hybridization conditions, such that the cucumber-sour cucumber alien addition line material and the number of the added sour cucumber chromosomes are identified. According to the present invention, the identification method creates the conditions for the transfer of the wild sour cucumber excellent gene in the alien addition line material and the cultivation of the new cucumber variety.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for rapidly preparing metaphase chromosomes of marine valuable and rare fishes or shellfishes
ActiveCN106244693AThe method is simple and fastEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementCell divisionMetaphase chromosome
The invention provides a method for rapidly preparing metaphase chromosomes of marine valuable and rare fishes or shellfishes, and belongs to the technical field of marine organisms. The method comprises the steps that 1, test fishes or shellfishes are temporarily cultured, and glass slides are cleaned; 2, after it is guaranteed that the survival state of the test animals is good, the fishes or shellfishes of which fin rays or grills have wounds are selected to be independently cultured; 3, healing and proliferating tissue at the wounds of the test animals is taken to be subjected to chromosome preparation. The method for preparing the metaphase chromosomes is simple and rapid and convenient to operate, the vigorous division and proliferation capacity of the healing and proliferating tissue is fully utilized, it is basically guaranteed that the test animals still can be healthy and be survived after chromosome preparation, multiple times of preparation can be repeated, the needed test animal can be least to one individual, and the method is suitable for various marine valuable and rare fishes and shellfishes. According to the method, freshness of the experiment samples can be guaranteed, the cell activity is good, the defects that most of the valuable and rare fishes or shellfishes are in a mature or aged state, and cell division is not vigorous are overcome, the prepared metaphase chromosomes are good in morphology and dispersion degree, and therefore observation and counting are convenient.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Method for preparing asparagus root tip cell chromosome metaphase split-phase specimen
InactiveCN106932256ARaise the ratioHelp removePreparing sample for investigationMetaphase chromosomeCytology
The invention discloses a method for preparing an asparagus root tip cell chromosome metaphase split-phase specimen, and belongs to the technical field of plant cell genetics. The method adopts the technical scheme that hydroxyurea and a N2O dual-block method are used for inducing asparagus cells to be subjected to synchronous mitosis so as to obtain massive metaphase split-phase cells, and through the steps of low-seeping, fixation and making, massive chromosome glass specimens being clear in shape, favorable in dispersibility and suitable for subsequent cytology research are obtained. According to the method disclosed by the invention, HU is used as a blocker, and in combination with renewal cultivation and N2O treatment, the asparagus metaphase split-phase cells are greatly increased; a conventional tabletting method is used, so that the metaphase cells are 50% or above of the total number of cells, and besides, metaphase chromosome after the N2O treatment is favorable in shape; and therefore, the asparagus chromosome tableting success rate and the stability are greatly increased, and the method provides great convenience for the application of techniques of asparagus karyotype analysis, fluorescence in situ hybridization and the like.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
Method for detecting chromosomal abnormalities
The invention relates to an in vitro method for detecting chromosomal abnormalities in a mammal, comprising the in situ hybridization of n chromosomes from a metaphase chromosome preparation with sets of a plurality of nucleic acids, each set hybridizing, over a length of 700 000 to 3 000 000 contiguous bp, specifically to the subtelomeric ends specific to said chromosomes, each set being detectably labeled with a fluorochrome, such that each chromosome is distinguishable by a particular fluorochrome or a particular fluorochrome combination.
Owner:ASSISTANCE PUBLIQUE HOPITAUX DE PARIS +1
A method for creating high-quality powdery mildew resistant breeding elements based on tufted wheat
ActiveCN105145339BHigh resistance to powdery mildewIncrease crude protein contentMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationVillosaAgricultural science
The invention discloses a creation method for a dasypyrum villosum-based high-quality powdery mildew-resistant breeding element. By backcrossing a top small fragment translocation line Nj1 or a small fragment intercalary translocation line Nj2 carrying the powdery mildew-resistant pm21 gene of dasypyrum villosum with a powdery mildew-infected wheat variety, Zhenmai No. 168 or Zhenmai No. 8, for multiple times and simultaneously screening a homozygous alien chromosome family from backcross descendants in combination with the genomic in-situ hybridization (GISH) of metaphase chromosomes of root-tip cell mitosis, a small fragment translocation homozygous plant which is uniform in agronomic traits and cytogenetically stable and keeps excellent powdery mildew resistance is obtained in order for breeders to improve wheat varieties.
Owner:赫聪
Method for detecting forest chromosome end by using oligo sequence
ActiveCN108441539AEasy to prepareFast preparationMicrobiological testing/measurementSSC bufferMetaphase chromosome
The invention provides a method for detecting the forest chromosome end by using an oligo sequence. The method is implemented by an (AGGGTTT)3 oligo sequence probe and a kit comprising the probe, thebase sequence of the (AGGGTTT)3 oligo sequence probe is: 5'-AGGGTTTAGGGTTTAGGGTTT-3',and the probe is used for identifying and labeling the forest chromosome end; the kit comprises the probe, an enzymatic hydrolysate, a 20*SSC buffer liquor, a 2*SSC buffer liquor, a 70% FA liquor, a 50% DS liquor and salmon sperm DNA. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining of a forest chromosome slidespecimen; denaturing; FISH (fluorescence in-situ hybridization); signal detection; slide recovery. According to the method, a slide can be used repeatedly, the probe is easy and quick to prepare andhigh in sensitivity. The probe is only directed at the oligo sequence at the chromosome end, the root slide is easy to make, the metaphase chromosome is convenient to obtain, and the whole experimental process requires short time and is easy to operate.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Fluorescence in situ hybridization method for metaphase chromosomes of Zanthoxylum bungeanum
InactiveCN107557491BEasy accessImprove detection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementIn situ hybridisationZanthoxylum bungeanum
The invention provides a fluorescence in situ hybridization method for zanthoxylum armatum metaphase chromosome. The fluorescence in situ hybridization method comprises the steps of zanthoxylum armatum metaphase chromosome glass slide specimen preparation, fluorescence in situ hybridization, signal detection and glass slide recovery. The fluorescence in situ hybridization method disclosed by the invention is beneficial to establishing a stable and convenient metaphase chromosome fluorescence in situ hybridization reaction system, greatly improves the detection efficiency of the zanthoxylum armatum metaphase chromosome and provides a novel method for detecting the anthoxylum armatum chromosome and even zanthoxylum species chromosome.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Flaking method for distantly-hybridized sugarbeet chromosome
InactiveCN109490036AImprove experimental efficiencyImprove work efficiencyPreparing sample for investigationMetaphase chromosomeMicroscopic exam
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant flaking and discloses a flaking method for a distantly-hybridized sugarbeet chromosome. The flaking method comprises the steps: sampling, namely selecting young leaves of distantly-hybridized sugarbeet; pretreatment, namely pretreating interior leaves or root tips of sugarbeet by using 8-hydroxyquinoline for 2-4 h; washing; dissociation; dyeingand tabletting; and microscopic examination observation, namely finding a split phase of a metaphase chromosome, and carrying out observation and counting. The flaking method is beneficial to the recognition and observation of the distantly-hybridized sugarbeet chromosome; the pretreatment time is prolonged; and the condition of the additional chromosome of the distantly-hybridized sugarbeet canbe clearly observed, and the experiment efficiency can be remarkably increased. The flaking method is simple, convenient and feasible, low in cost, good in effect, easy to operate and master and capable of increasing the work efficiency, saving time and labor and realizing observation by using a common optical microscope. A monomer addition line sugarbeet M14, allotriploid sugarbeet, beta corolliflora and common cultivated sugarbeet are respectively flaked and observed by using an improved flaking method, and the flaking method is very good in effect and repeatable. The method is also suitablefor a dropping method and a smearing method.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV
Chromosome-specific staining to detect genetic rearrangements
InactiveUS8415464B2Rapid and highly sensitive detectionEasy to analyzeSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseMetaphase chromosome
Methods and compositions for staining based upon nucleic acid sequence that employ nucleic acid probes are provided. Said methods produce staining patterns that can be tailored for specific cytogenetic analyzes. Said probes are appropriate for in situ hybridization and stain both interphase and metaphase chromosomal material with reliable signals. The nucleic acid probes are typically of a complexity greater than 50 kb, the complexity depending upon the cytogenetic application. Methods and reagents are provided for the detection of genetic rearrangements. Probes and test kits are provided for use in detecting genetic rearrangements, particularly for use in tumor cytogenetics, in the detection of disease related loci, specifically cancer, such as chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) and for biological dosimetry. Methods and reagents are described for cytogenetic research, for the differentiation of cytogenetically similar but genetically different diseases, and for many prognostic and diagnostic applications.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Method for Rapidly Preparing Metaphase Chromosomes of Rare Marine Fish or Shellfish
ActiveCN106244693BThe method is simple and fastEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementCell divisionMetaphase chromosome
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
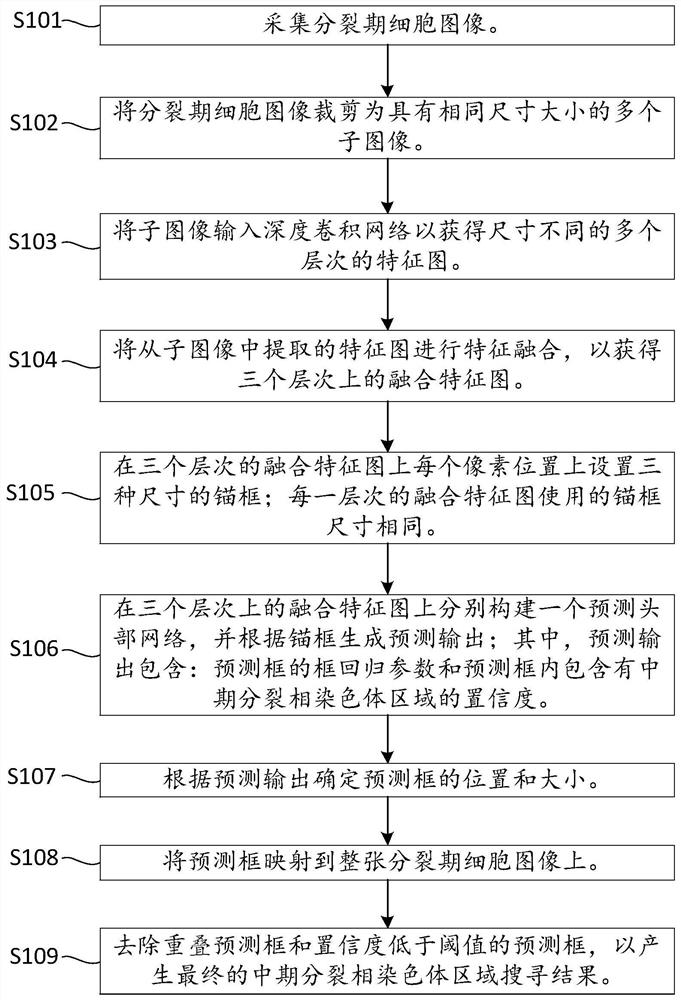
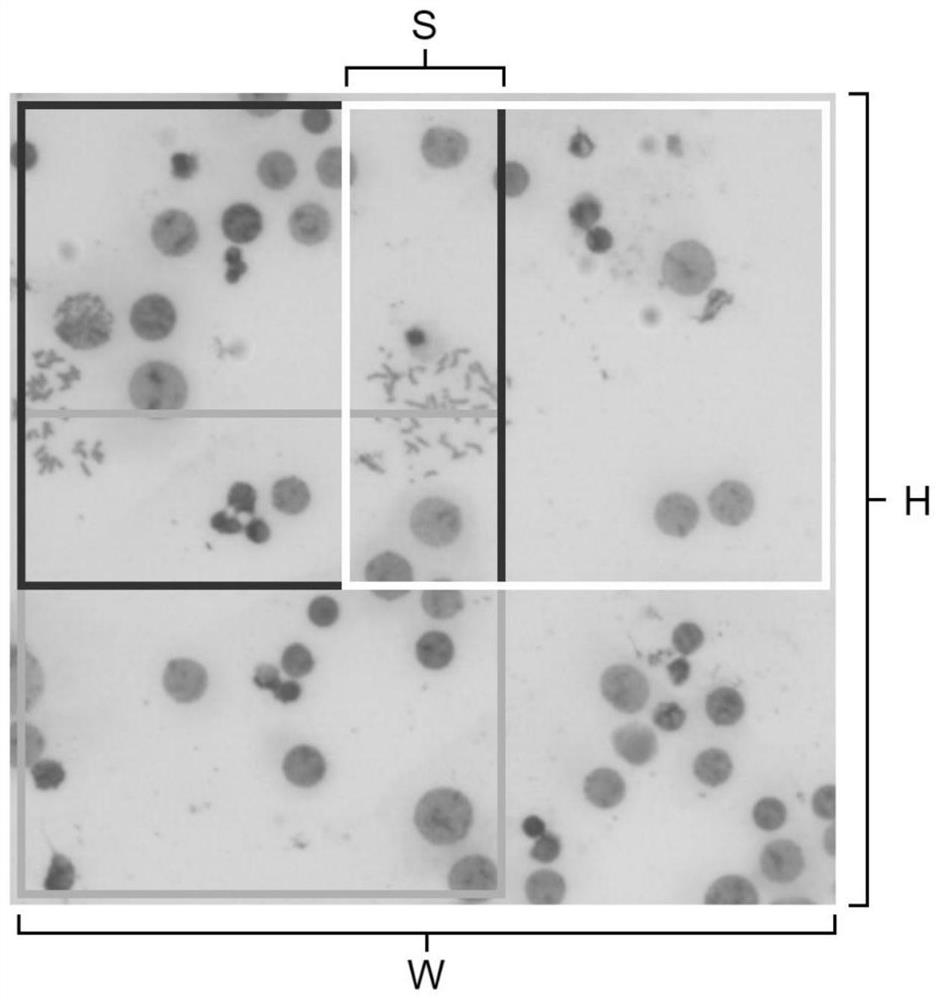
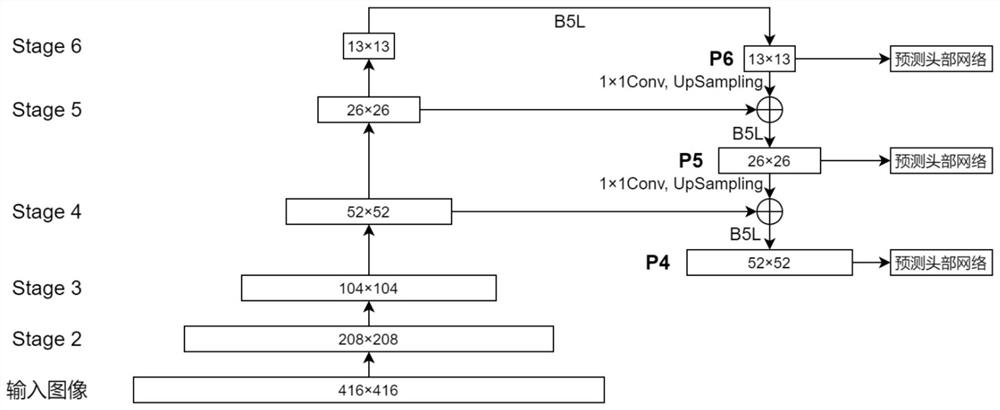
Metaphase split-phase chromosome region searching method and device
InactiveCN111833992AAvoid interferenceImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisMetaphase chromosomeFeature extraction
The invention provides a metaphase split-phase chromosome region searching method and device, and relates to the technical field of medical images. The metaphase split-phase chromosome region searching method comprises the following steps: acquiring a split-phase cell image; inputting the clipped division-stage cell image into a deep convolutional network; automatically completing a feature extraction process by the network, and further fusing the features of different levels; generating mid-metaphase chromosome region prediction results at multiple levels. According to the technical scheme provided by the invention, the efficiency and accuracy of searching for a metaphase chromosome region can be improved, and the method can be suitable for images in different shooting environments.
Owner:湖南品信生物工程有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com