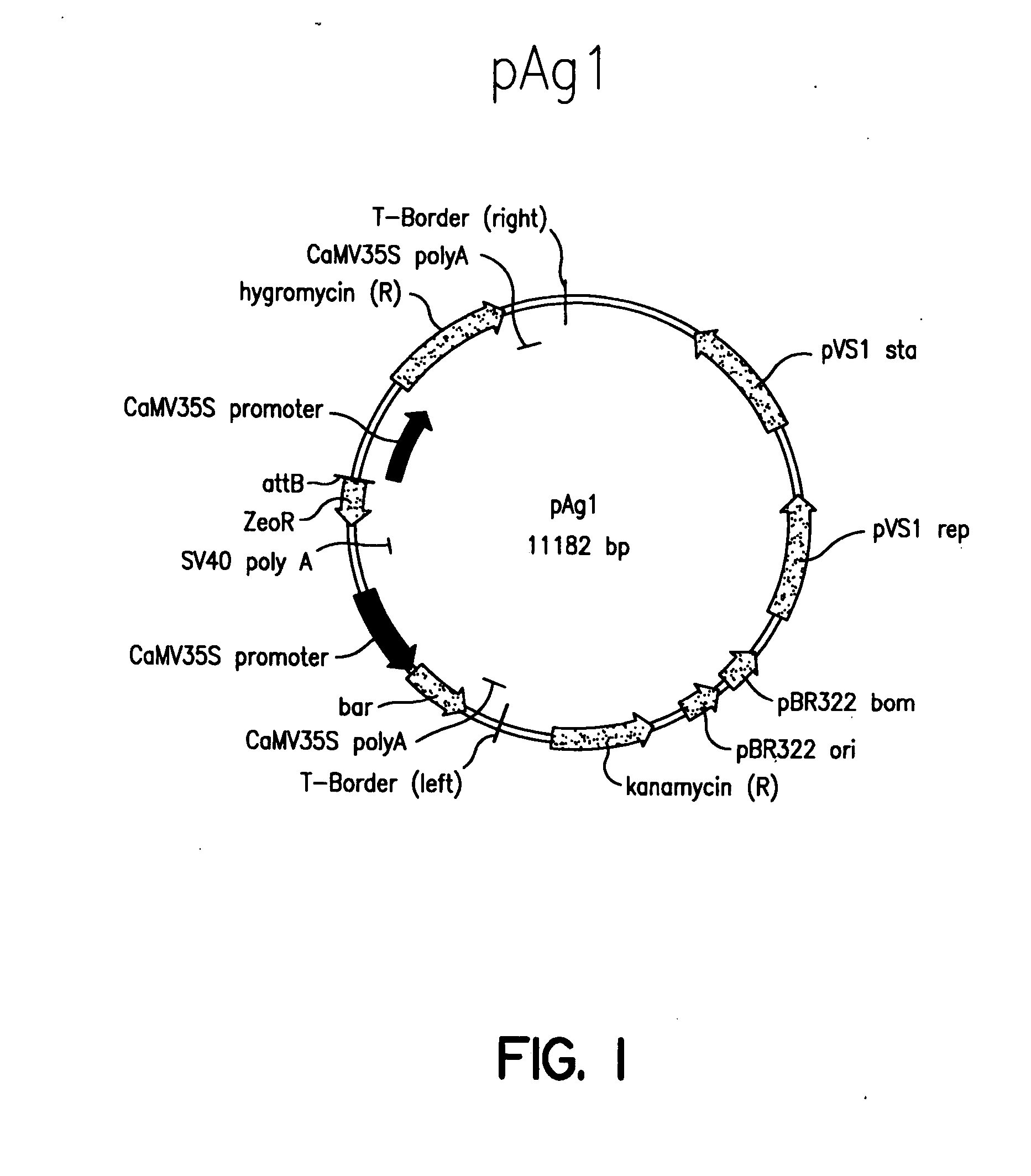
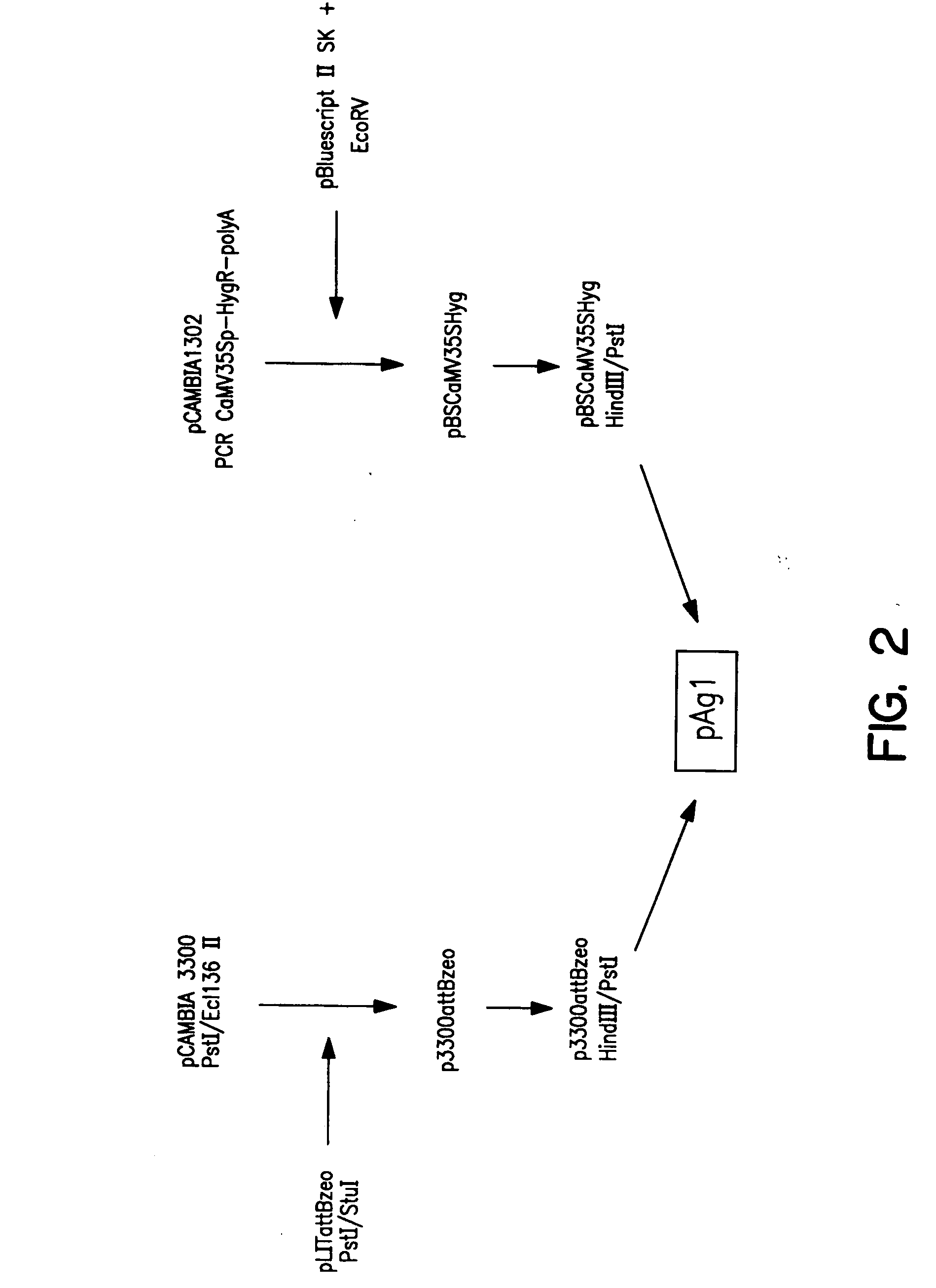
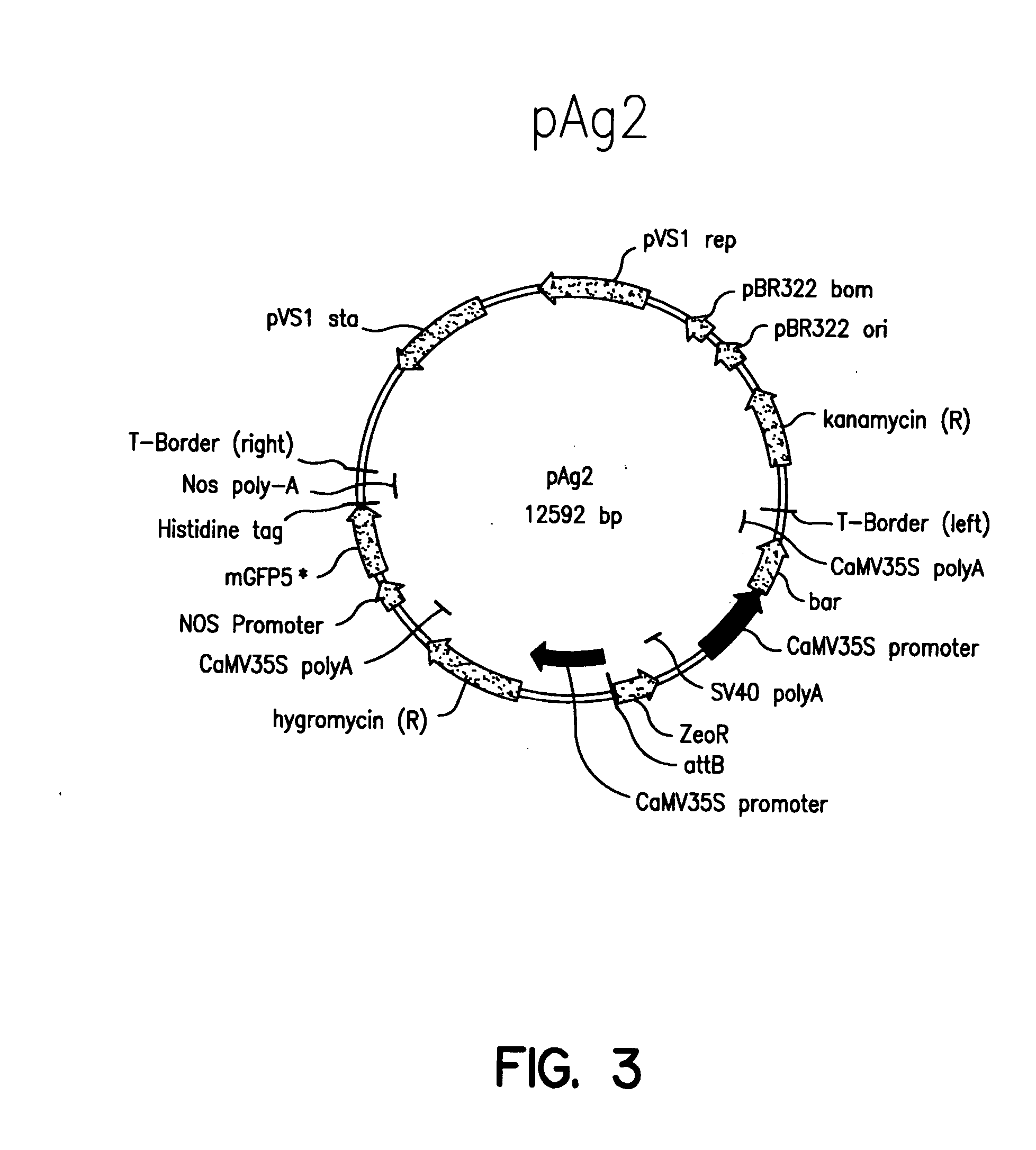
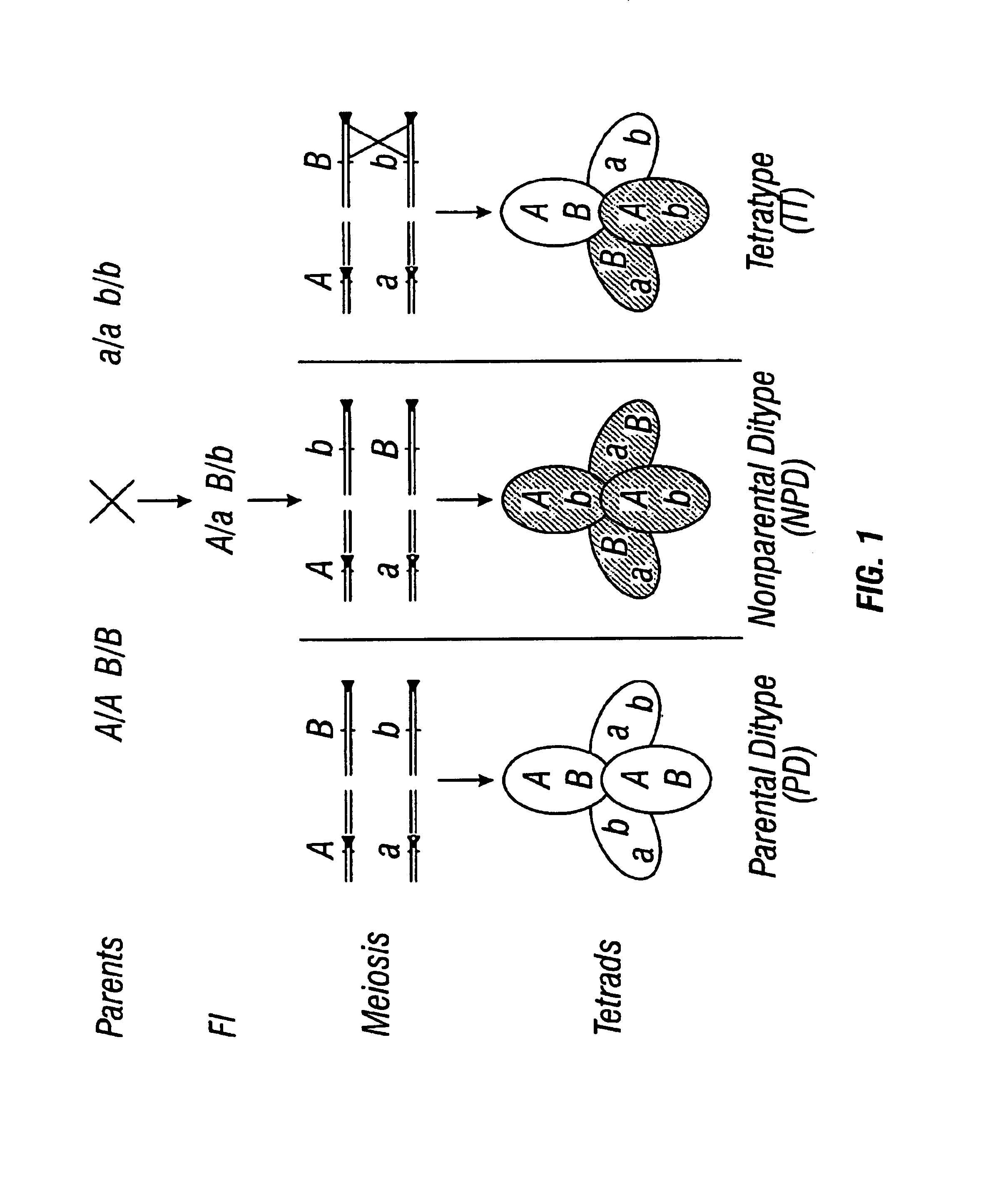
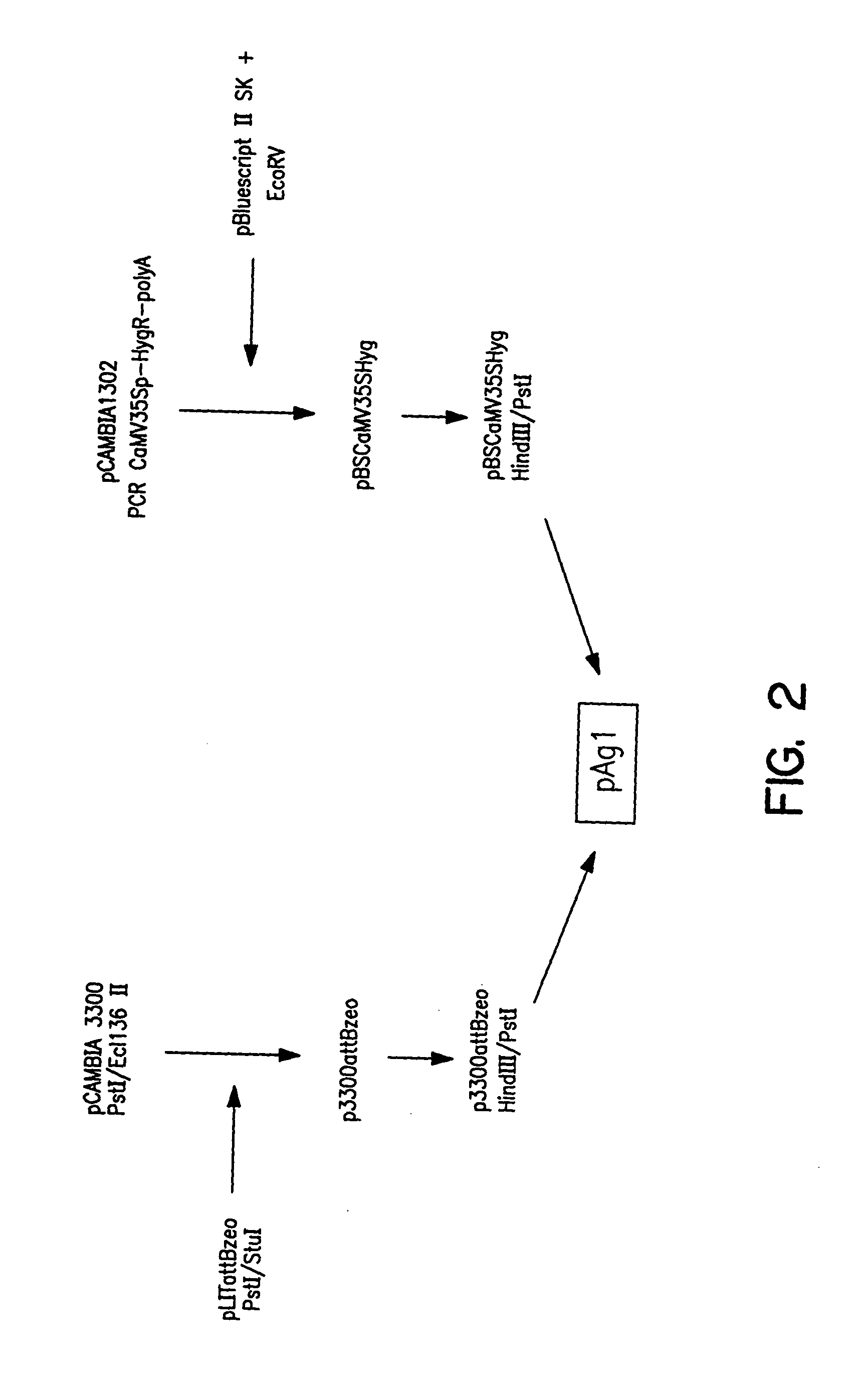
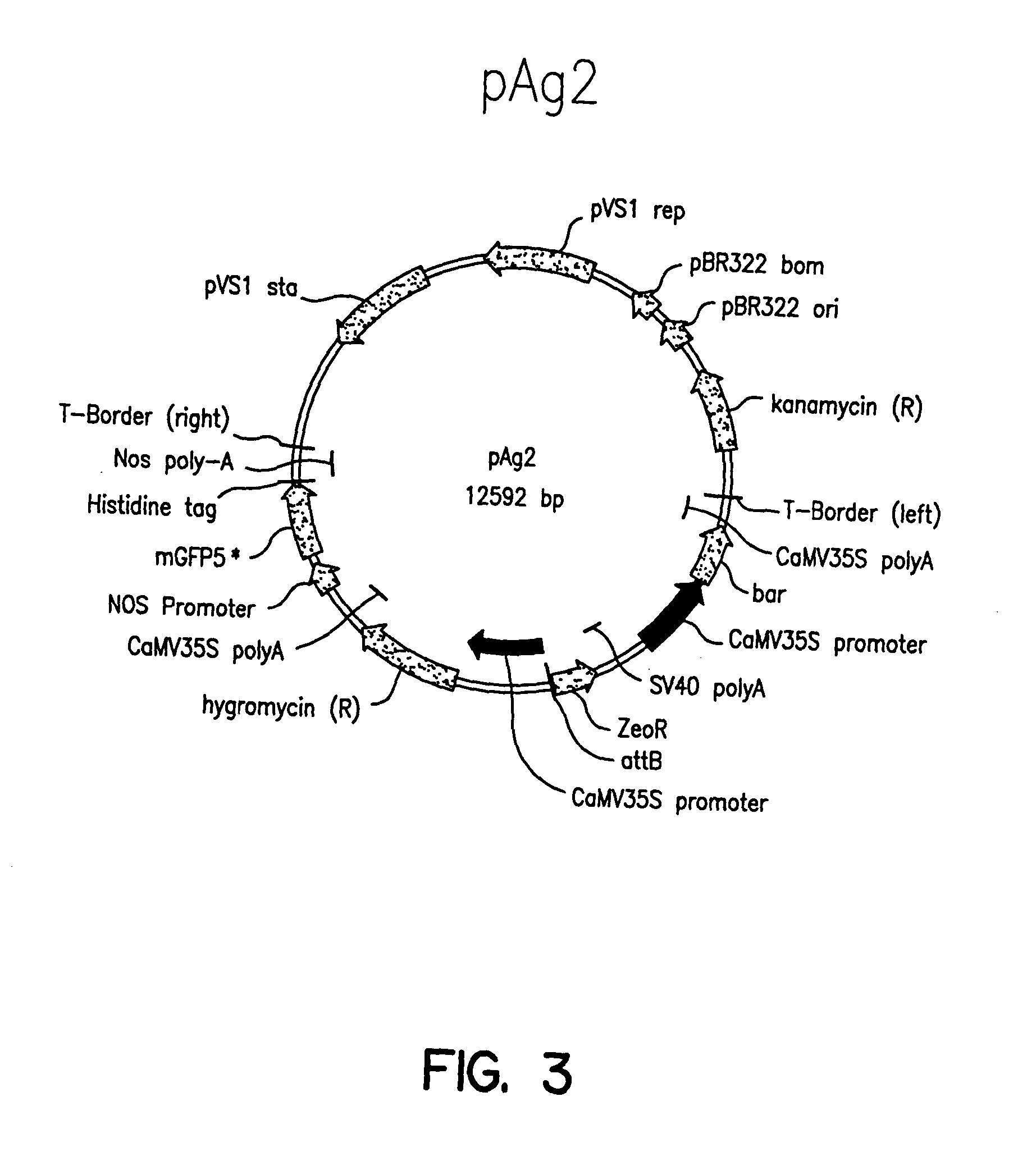
Patents
Literature
59 results about "Plant chromosomes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methods of making non-transgenic herbicide resistant plants
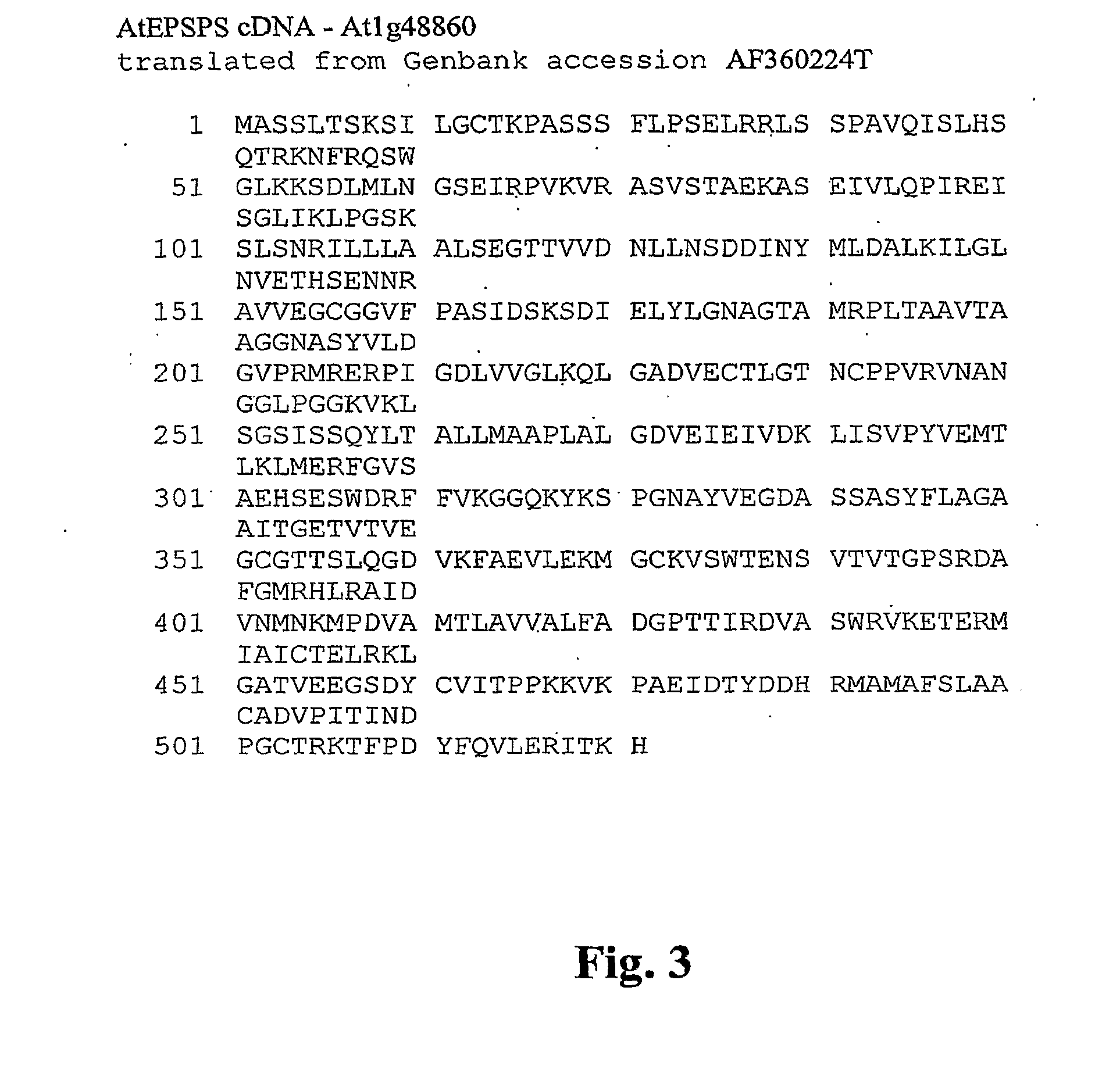
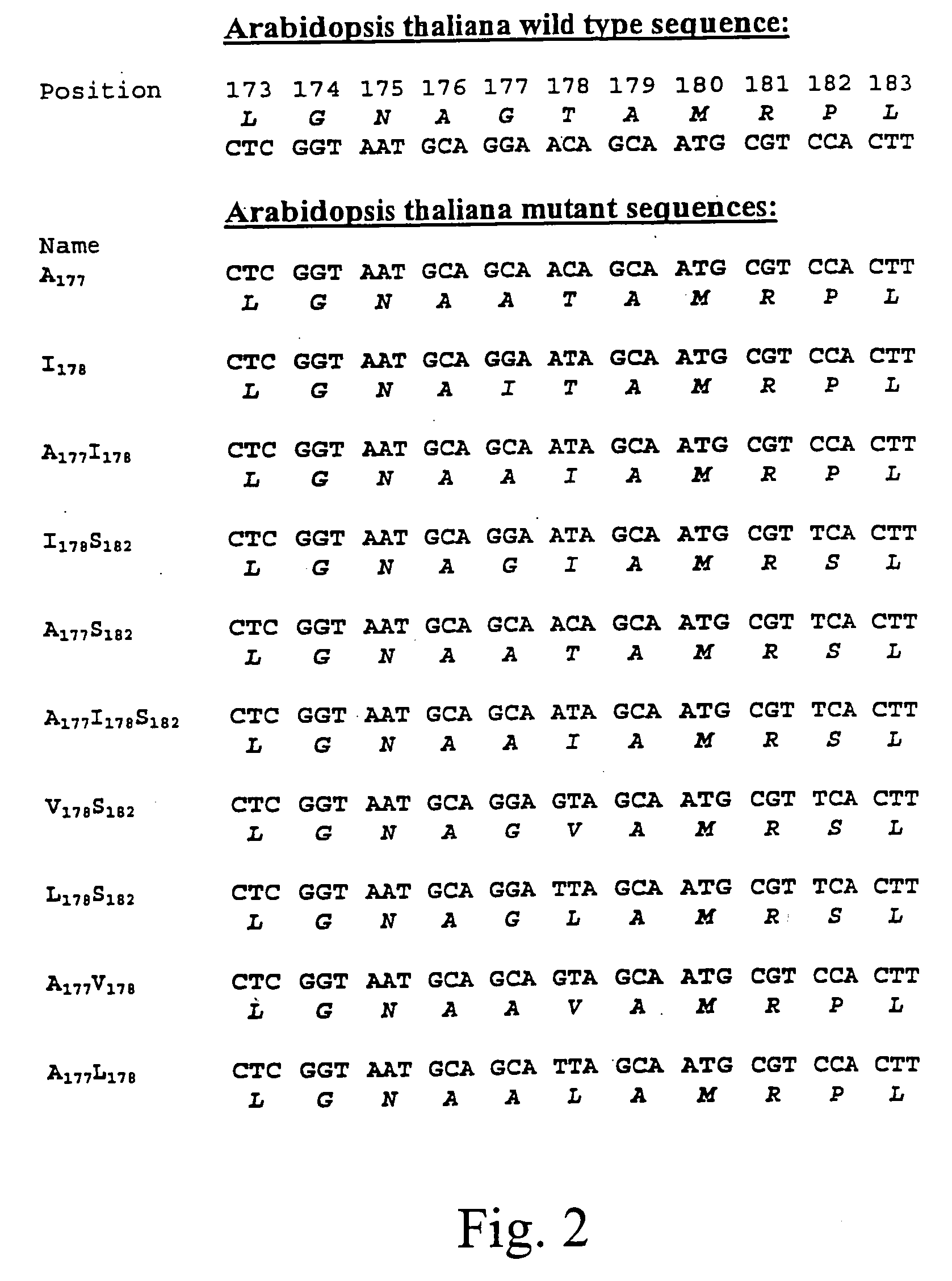
The present invention relates to the production of a non-transgenic plant resistant or tolerant to a herbicide of the phosphonomethylglycine family, e.g., glyphosate. The present invention also relates to the use of a recombinagenic oligonucleobase to make a desired mutation in the chromosomal or episomal sequences of a plant in the gene encoding for 5-enol pyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS). The mutated protein, which substantially maintains the catalytic activity of the wild-type protein, allows for increased resistance or tolerance of the plant to a herbicide of the phosphonomethylglycine family, and allows for the substantially normal growth or development of the plant, its organs, tissues or cells as compared to the wild-type plant irrespective of the presence or absence of the herbicide.
Owner:CIBUS
Chromosome doubling method
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
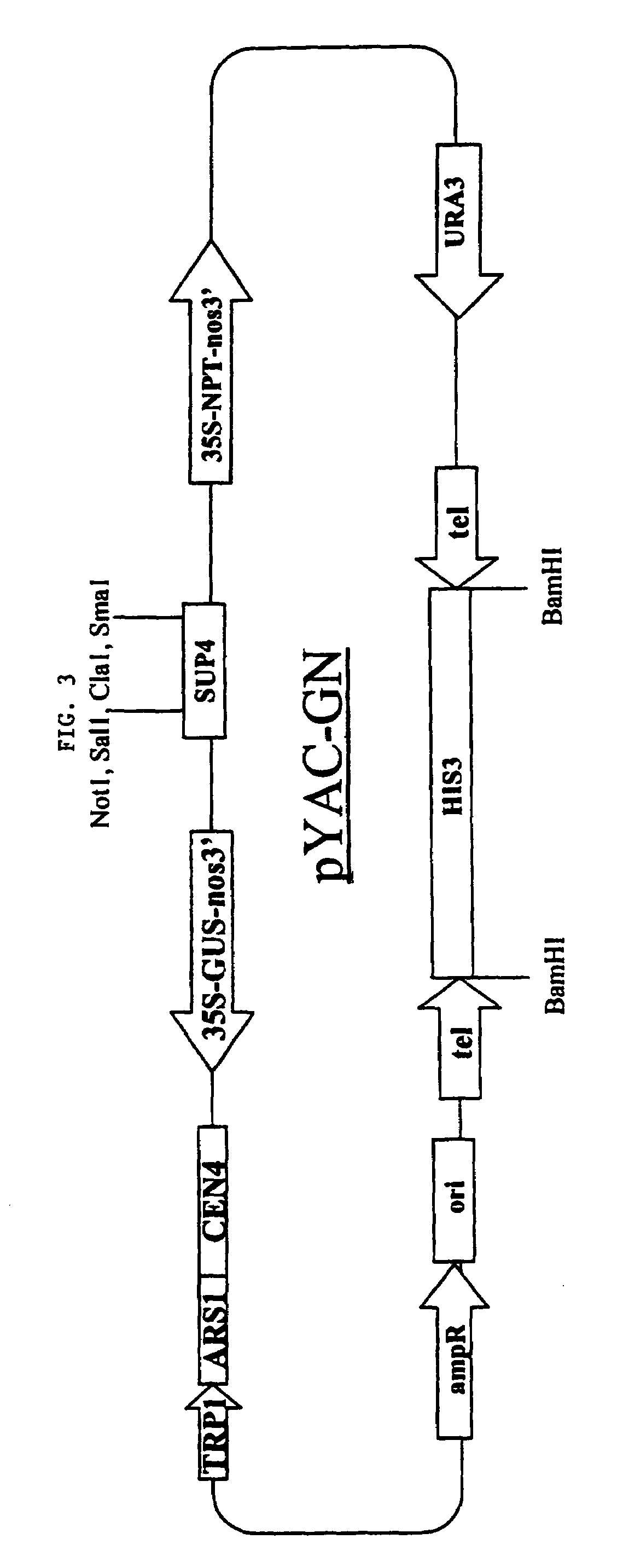
Plant artificial chromosomes, uses thereof and methods of preparing plant artificial chromosomes
InactiveUS20060143732A1Easy to zoom inSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsHeterologousEuchromatin
Methods for preparing cell lines that contain plant artificial chromosomes, methods for preparation of plant artificial chromosomes, methods for targeted insertion of heterologous DNA into plant artificial chromosomes, and methods for delivery of plant chromosomes to selected cells and tissues are provided. In particular, plant artificial chromosomes that are substantially composed of repeated nucleic acid units of varying amounts of heterochromafin and euchromatin are provided. Also provided are methods of using plant and animal artificial chromosomes in the production of valuable transgenic plants. Methods for identifying plant genes encoding particular traits using artificial chromosomes and for producing an acrocentric plant chromosome also are provided.
Owner:CALYX BIO VENTURES +1
Plant chromosome compositions and methods
The present invention provides for the identification and cloning of functional plant centromeres in Arabidopsis. This will permit construction of stably inherited minichromosomes which can serve as vectors for the construction of transgenic plant and animal cells. In addition, information on the structure and function of these regions will prove valuable in isolating additional centromeric and centromere related genetic elements and polypeptides from other species.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
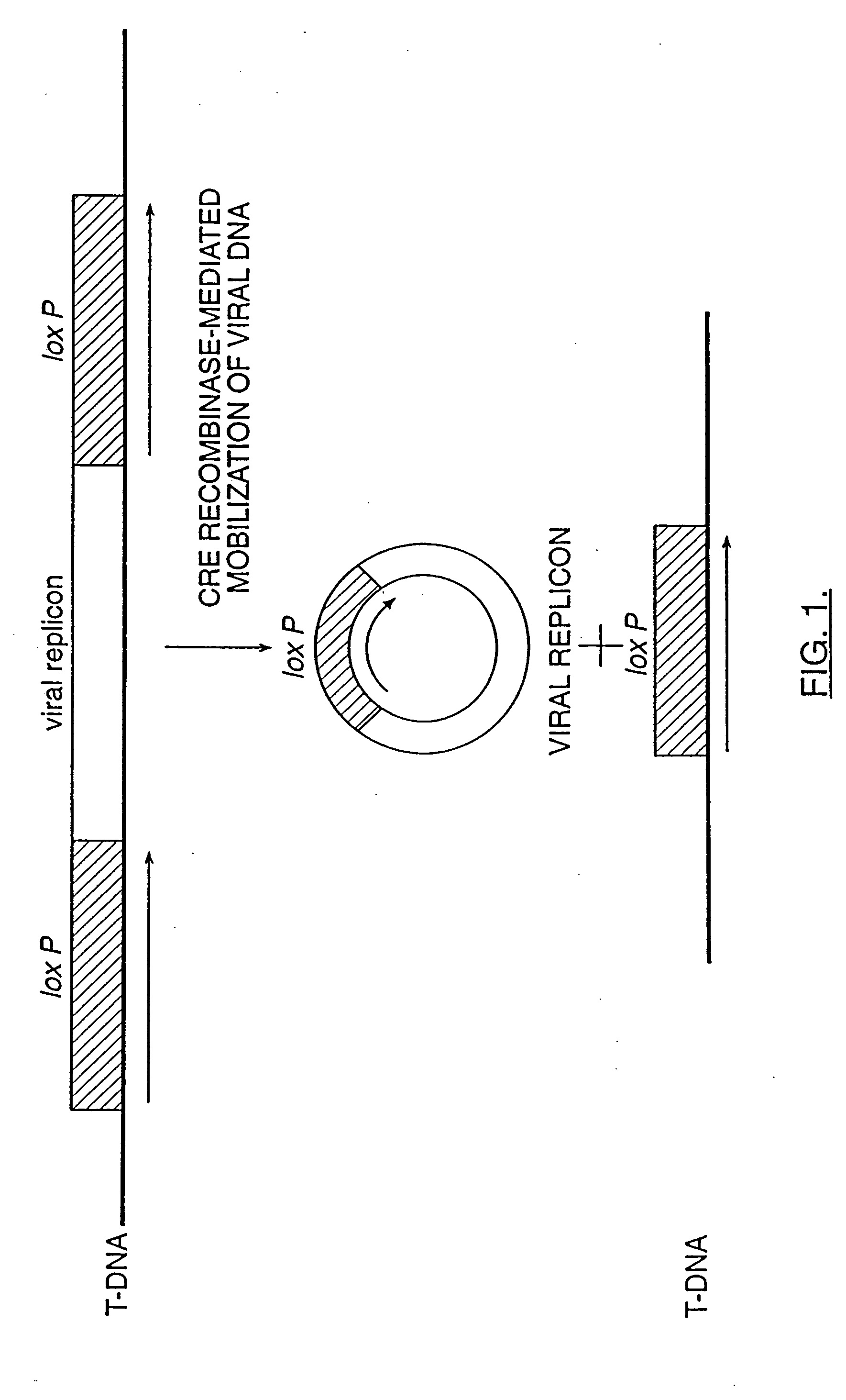
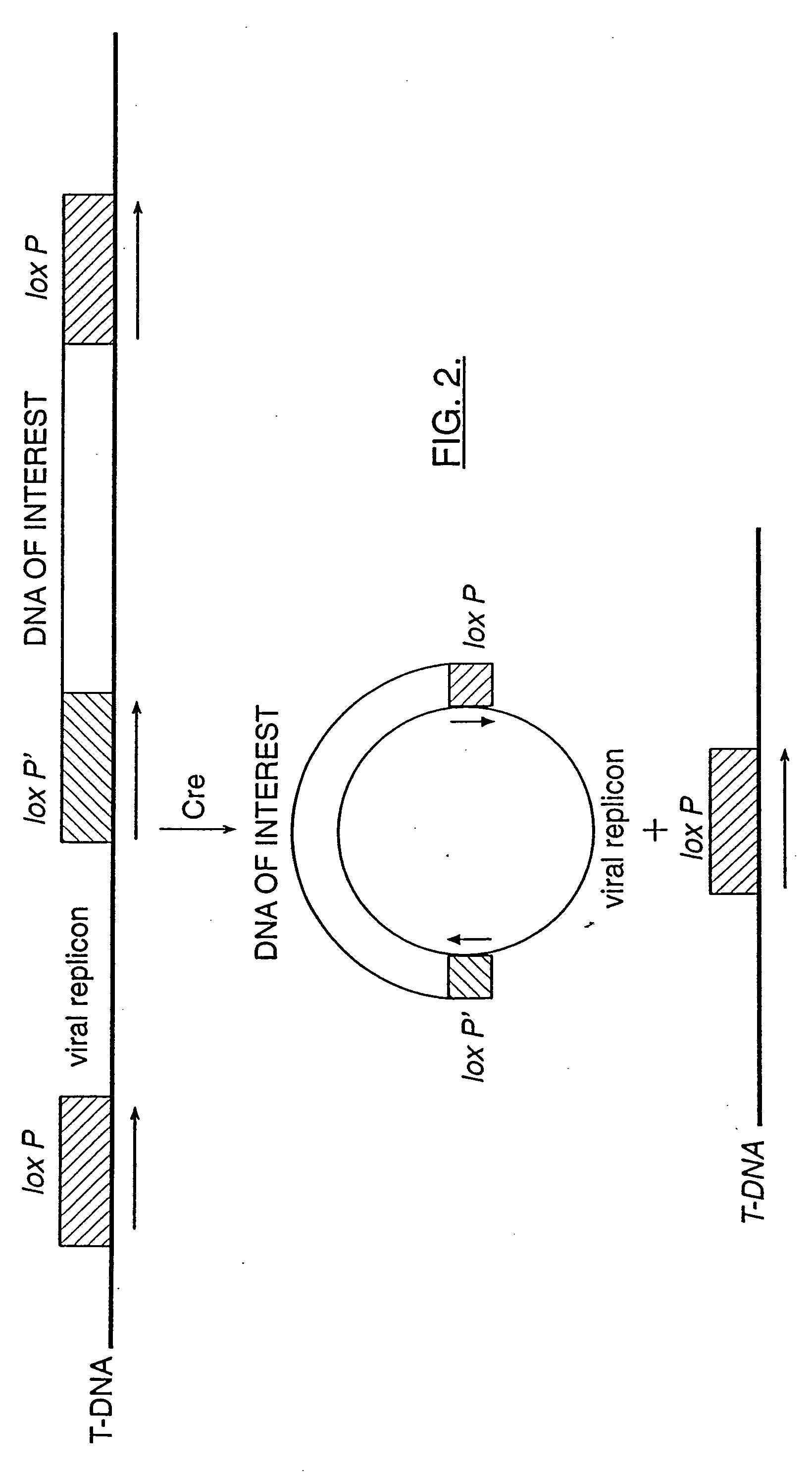
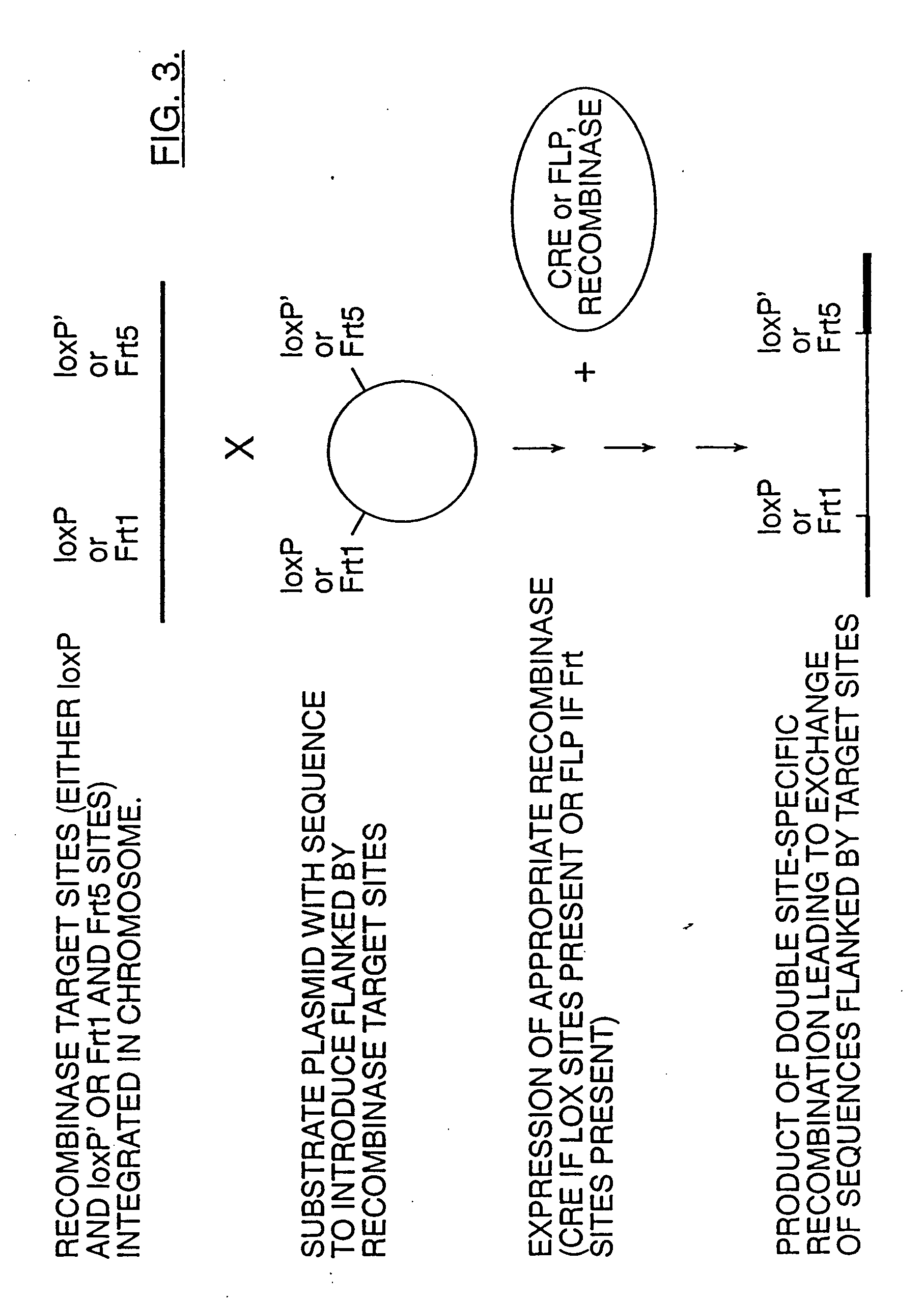
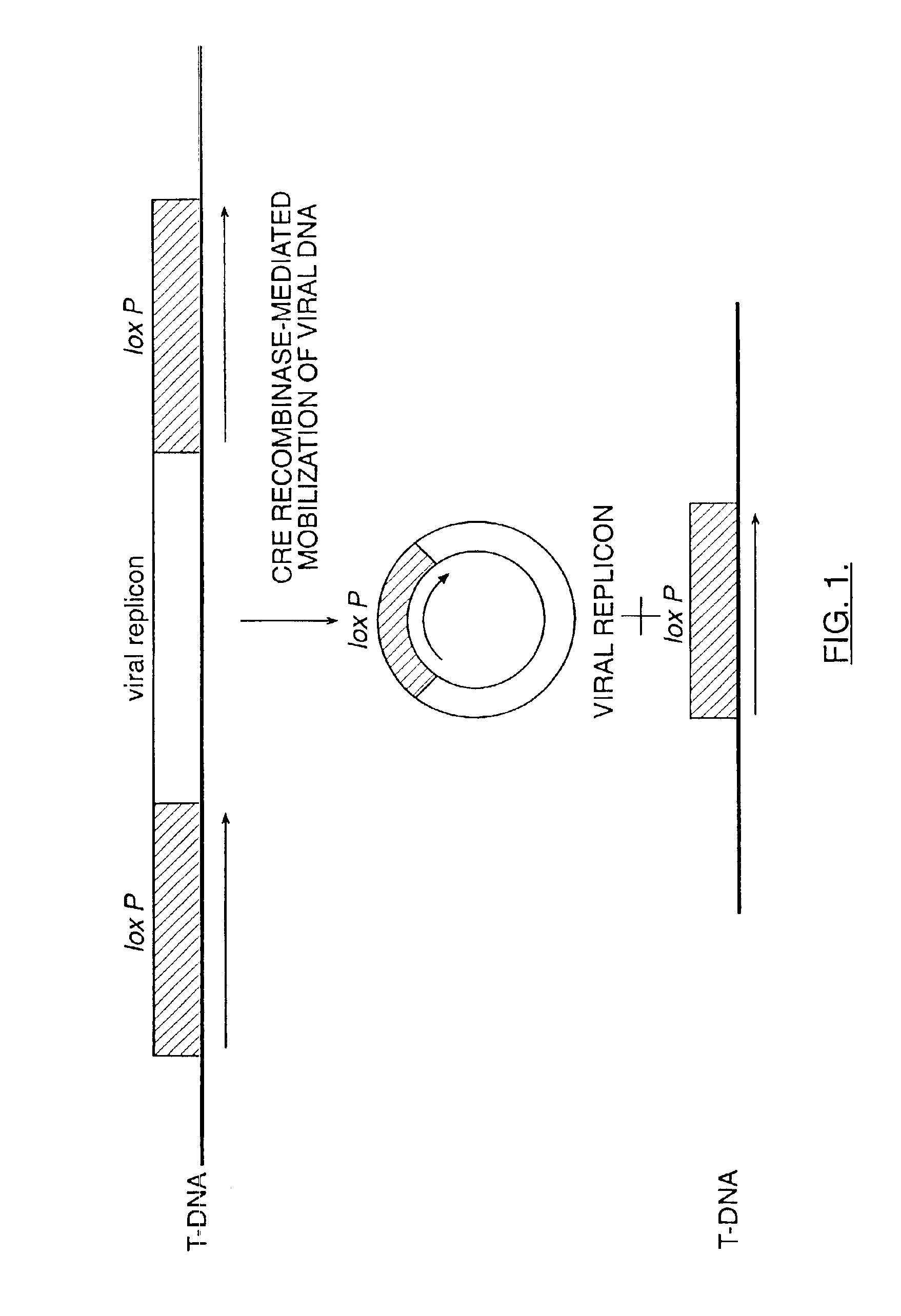
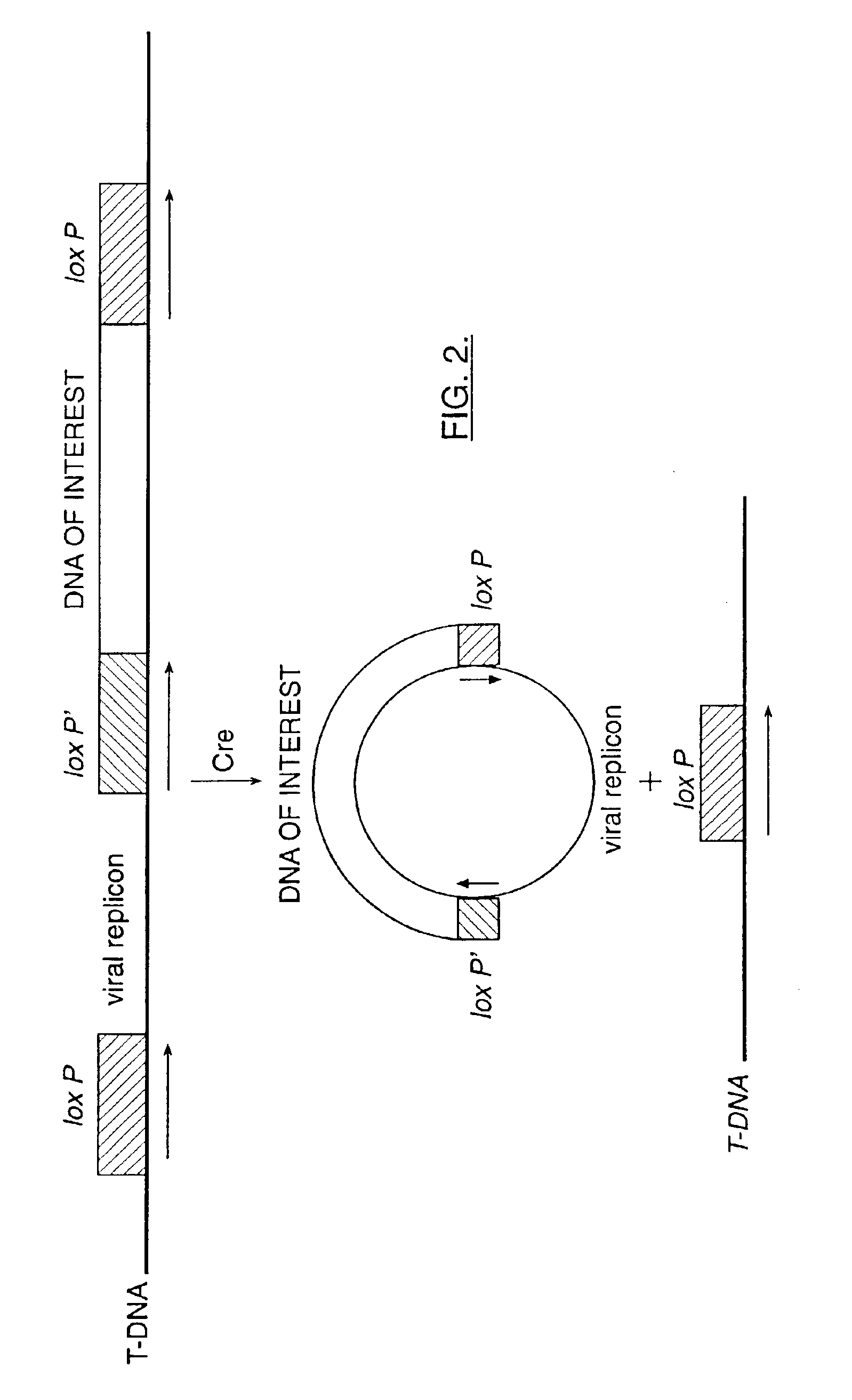
Mobilization of viral genomes from T-DNA using site-specific recombination systems
InactiveUS20060253939A1Easy constructionSimplifying stable maintenanceBacteriaSugar derivativesSite-specific recombinationPlant cell
The invention relates to methods and compositions for site-specific recombinase-mediated mobilization of viral replicons and associated DNAs of interest from T-DNA. The methods of the invention comprise Agrobacterium-mediated transfer of T-DNA to a plant cell, wherein the T-DNA contains a viral replicon flanked by directly repeated target sites for a site-specific recombinase and optionally a DNA of interest linked to the viral replicon. The DNA of interest may also contain a non-identical target site for the recombinase. An expression cassette for the site-specific recombinase is present on the T-DNA or the plant genome, or is transiently introduced into the plant cell. Expression of the site-specific recombinase in the plant cell results in excision of the viral replicon and the associated DNA of interest. The viral replicon and DNA of interest are then replicated to high copy number in the host plant cell. The compositions of the invention comprise nucleic acids, such as T-DNAs containing a viral DNA flanked by directly repeated target sites for a site-specific recombinase. The nucleic acids of the invention may additionally contain expression cassettes encoding the cognate site-specific recombinase for the target sites flanking the viral genome. The compositions of the invention further comprise Agrobacterium containing the nucleic acids of the invention. The compositions and methods of the invention have use in increasing the efficiency of agroinfection, providing high copy numbers of a DNA of interest for transient expression or for integration into a plant chromosome, and in simplifying the construction and stable maintenance of vectors for agroinfection and transformation.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
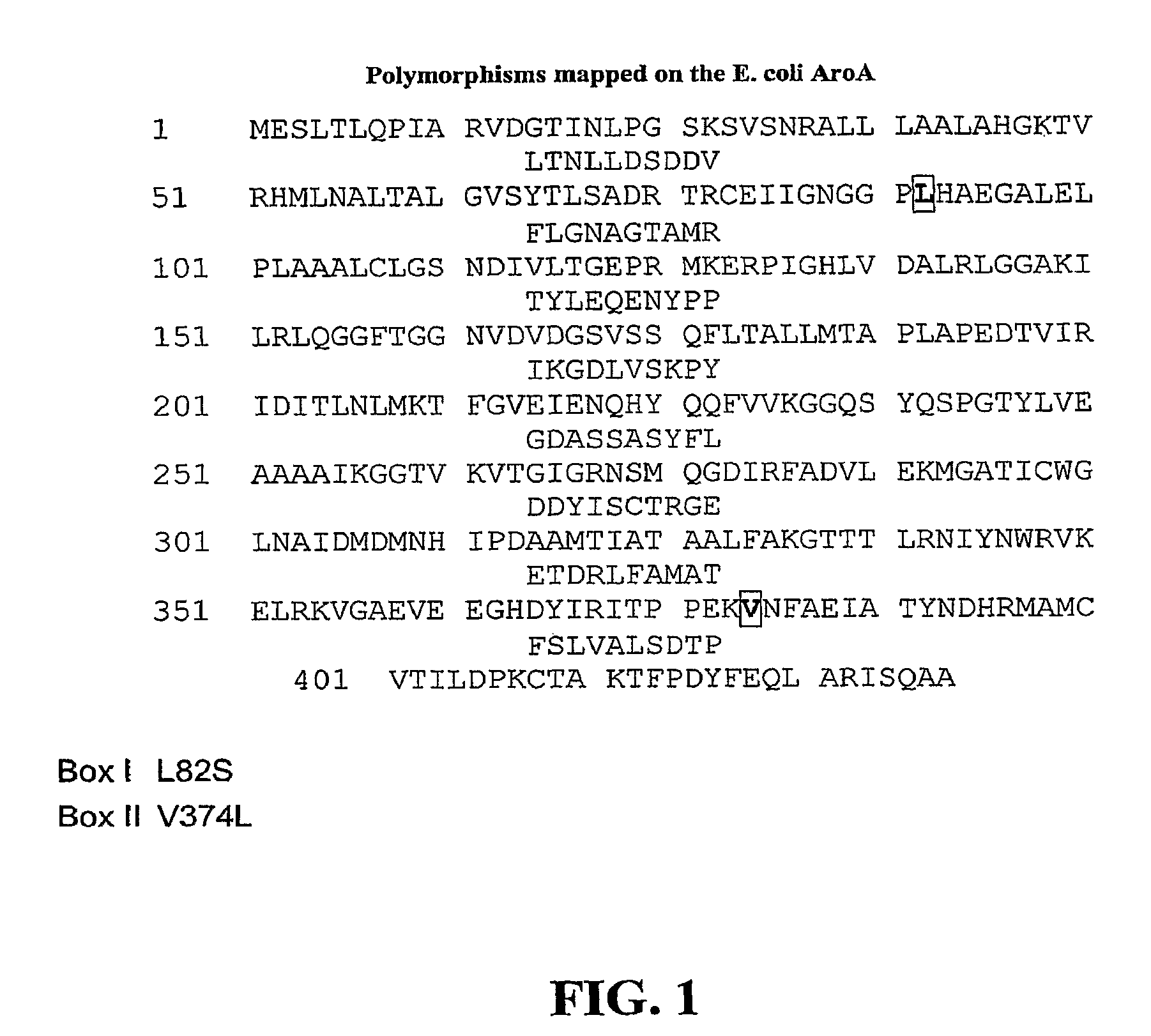
EPSPS mutants
The present invention relates to the production of a non-transgenic plant resistant or tolerant to a herbicide of the phosphonomethylglycine family, e.g., glyphosate. The present invention also relates to the use of a recombinagenic oligonucleobase to make a desired mutation in the chromosomal or episomal sequences of a plant in the gene encoding for 5-enol pyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS). The mutated protein, which substantially maintains the catalytic activity of the wild-type protein, allows for increased resistance or tolerance of the plant to a herbicide of the phosphonomethylglycine family, and allows for the substantially normal growth or development of the plant, its organs, tissues or cells as compared to the wild-type plant irrespective of the presence or absence of the herbicide. Additionally the present invention relates to mutant E. coli cells that contain mutated EPSPS genes.
Owner:CIBUS
Mobilization of viral genomes from T-DNA using site-specific recombination systems
InactiveUS7179599B2Simplifying construction and stable maintenanceImprove efficiencyBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSite-specific recombinationPlant cell
The invention relates to methods and compositions for site-specific recombinase-mediated mobilization of viral replicons and associated DNAs of interest from T-DNA. The methods of the invention comprise Agrobacterium-mediated transfer of T-DNA to a plant cell, wherein the T-DNA contains a viral replicon flanked by directly repeated target sites for a site-specific recombinase and optionally a DNA of interest linked to the viral replicon. The DNA of interest may also contain a non-identical target site for the recombinase. An expression cassette for the site-specific recombinase is present on the T-DNA or the plant genome, or is transiently introduced into the plant cell. Expression of the site-specific recombinase in the plant cell results in excision of the viral replicon and the associated DNA of interest. The viral replicon and DNA of interest are then replicated to high copy number in the host plant cell. The compositions of the invention comprise nucleic acids, such as T-DNAs containing a viral DNA flanked by directly repeated target sites for a site-specific recombinase. The nucleic acids of the invention may additionally contain expression cassettes encoding the cognate site-specific recombinase for the target sites flanking the viral genome. The compositions of the invention further comprise Agrobacterium containing the nucleic acids of the invention. The compositions and methods of the invention have use in increasing the efficiency of agroinfection, providing high copy numbers of a DNA of interest for transient expression or for integration into a plant chromosome, and in simplifying the construction and stable maintenance of vectors for agroinfection and transformation.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Plant chromosome compositions and methods
The present invention provides for the identification and cloning of functional plant centromeres in Arabidopsis. This will permit construction of stably inherited minichromosomes which can serve as vectors for the construction of transgenic plant and animal cells. In addition, information on the structure and function of these regions will prove valuable in isolating additional centromeric and centromere related genetic elements and polypeptides from other species.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Composite multiplying agent for plant chromosome and multiplying method
The invention discloses a reagent formula for multiplying a plant chromosome by using a composite reagent without colchicines and a multiplying method. The plant chromosome is multiplied by using a composite formula prepared from multiple mitosis inhibitors and tubulin inhibitors; compared with a conventional chromosome multiplying method, the method has the characteristics of low toxicity, high efficiency and wide application range; cooperative use of three compounds such as a multiplying agent, an aid and a detoxicant with different functions is the key point of the reagent formula, and functions of improving multiplying effects and reducing medicine damage are achieved; by adopting the reagent formula, the problems that growth abnormity, malformation or even death of a treated plant material are generally caused, and the multiplication success rate is relatively low since the treated plant material is seriously damaged in conventional process that a plant chromosome is multiplied byusing colchicines, are solved; and more importantly, the problems that the colchicines are highly toxic, have potential carcinogeneses for mammals including human beings, and can cause serious harm to health of operators and environment security, can be solved.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
Fluorescence in situ hybridization method for positioning 45S rDNA on plant chromosome
ActiveCN103409524ASimple methodLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementIn situ hybridisationFluorescence in situ hybridization
The invention discloses a fluorescence in situ hybridization method for positioning the 45S rDNA on a plant chromosome. The fluorescence in situ hybridization method mainly comprises the following steps of preparation of a chromosome specimen, preparation of 45S rDNA probes, fluorescence in situ hybridization of the chromosome and hybridization signal detection. The provided method for probe marking and hybridization is simple, convenient, quick and accurate, and mainly solves the problem about complex and cumbersome marking of the existing probes for fluorescence in situ hybridization. The probes provided by the invention are oligonucleotide probes which are not marked any more, and a fluorophore for modification can be added during synthesis of the probes, and compared with the prior art, the method is simple and the cost is low. By utilizing the technology, FISH positioning of the 45S rDNA on the chromosome can be completed within 3 hours.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Chinese cabbage fertility relevant gene and method of using the gene in constituting artificial male sterility line of Chinese cabbage and similar crops
InactiveCN1453359AAvoid restrictionsMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationPlant genetic engineeringFertility
By means of plant gene engineering, primer is designed from No. 901 base to No. 1338 base inside the fertility relevant gene, 438 bp sequence is amplified as anti-sense gene segment and introduced into plant chromosome to obtain regenerative plant and artificial male sterile common Chinese cabbage and core. The said method is suitable for rape genus plants and may be used in fast constituting the male sterility line of different Chinese cabbage and similar vegetable crops without the limitation similar to that of seeking natural sterile source. The present invention opens one new way the wide application of plant gene engineering technology in agricultural production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
EPSPS Mutants
ActiveUS20090307802A1Increase resistanceImprove toleranceBacteriaImmunoglobulinsMutated proteinPhosphate
The present invention relates to the production of a non-transgenic plant resistant or tolerant to a herbicide of the phosphonomethylglycine family, e.g., glyphosate. The present invention also relates to the use of a recombinagenic oligonucleobase to make a desired mutation in the chromosomal or episomal sequences of a plant in the gene encoding for 5-enol pyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS). The mutated protein, which substantially maintains the catalytic activity of the wild-type protein, allows for increased resistance or tolerance of the plant to a herbicide of the phosphonomethylglycine family, and allows for the substantially normal growth or development of the plant, its organs, tissues or cells as compared to the wild-type plant irrespective of the presence or absence of the herbicide. Additionally the present invention relates to mutant E. coli cells that contain mutated EPSPS genes.
Owner:CIBUS
Lagerstroemia plant stem tip chromosome tablet preparation method
ActiveCN102645360AAvoid toxic effectsAvoid destructionPreparing sample for investigationBiologyPlant chromosomes
The invention discloses a lagerstroemia plant stem tip chromosome tablet preparation method which comprises the following steps of: selecting a part with a length of 0.5-1.0 cm at the innermost side of a lagerstroemia plant annual branch stem tip growing point or a newly-grown stem tip growing point after a branch which is pruned or refrigerated in early winter is subjected to water culture, fixing with stationary liquid (Ethanol: glacial acetic acid: chloroform is equal to 5:3:2 according to the to volume ratio), carrying out hypotonic treatment, carrying out hypotonic treatment again after mixed enzyme liquid is subjected to enzymatic hydrolysis and preparing a tablet by adopting a flame drying method. The chromosome tablet preparation method has the beneficial effects that the processes of pretreatment, dissociation and chromosome tabletting are omitted, the tablet preparation efficiency is improved through directly fixing, the toxic effect of pretreatment liquid and dissociation liquid on a chromosome is avoided, the original form of the chromosome is maintained, the better chromosome dispersion effect is obtained, and meanwhile, the sampling range and the time of lagerstroemia plant stem tip chromosome preparation are enlarged. The tablet prepared by the method can be used for a fluorescence in-situ hybridization experiment to lay a good foundation for the further research of a lagerstroemia genome.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Non-transgenic herbicide resistant plants
The present invention relates to the production of a non-transgenic plant resistant or tolerant to a herbicide of the phosphonomethylglycine family, e.g., glyphosate. The present invention also relates to the use of a recombinagenic oligonucleobase to make a desired mutation in the chromosomal or episomal sequences of a plant in the gene encoding for 5-enol pyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS). The mutated protein, which substantially maintains the catalytic activity of the wild-type protein, allows for increased resistance or tolerance of the plant to a herbicide of the phosphonomethylglycine family, and allows for the substantially normal growth or development of the plant, its organs, tissues or cells as compared to the wild-type plant irrespective of the presence or absence of the herbicide. The present invention also relates to a non-transgenic plant cell in which the EPSPS gene has been mutated, a non-transgenic plant regenerated therefrom, as well as a plant resulting from a cross using a regenerated non-transgenic plant having a mutated EPSPS gene.
Owner:BEETHAM PETER +3
Fluorescence in situ hybridization method of 5S rDNA on plant chromosome
ActiveCN103409523ASimple methodLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementIn situ hybridisationFluorescence
The invention discloses a fluorescence in situ hybridization method of 5S rDNA on a plant chromosome. The fluorescence in situ hybridization method mainly comprises the steps of chromosome specimen preparation, 5S rDNA probe preparation, chromosome fluorescence in situ hybridization, hybridization signal detection and the like. The invention mainly solves the problem that the labeling of the conventional fluorescence in situ hybridization probe is complicated and cumbersome and provides the simple, convenient, fast and accurate probe labeling and hybridization method. According to the fluorescence in situ hybridization method, the FISH positioning of the 5S rDNA on the plant chromosome can be completed within three hours. The 5S rDNA probe is an oligonucleotide probe. When the 5S rDNA probe is synthesized, fluorophore can be added into the 5S rDNA probe to modify the 5S rDNA probe, so that labeling is not needed. Compared with the prior art, the fluorescence in situ hybridization method is simple and low in cost.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
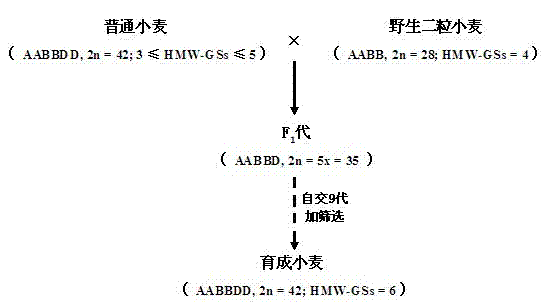
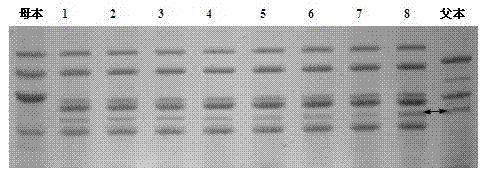
Cultivation method of common wheat capable of stably expressing six HMW-GS (High Molecular Weight-Glutenin Subunits)
InactiveCN103039357AExcellent grain volume traitsExcellent yield traitsPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyHybrid seed
The invention relates to a cultivation method of common wheat capable of stably expressing six HMW-GS (High Molecular Weight-Glutenin Subunits) and belongs to the field of plant chromosome engineering technologies. The method comprises the following steps of: taking common wheat as a female parent and wild emmer wheat as a male parent; pollinating pollen of the wild emmer wheat with four HMW-GS to sextuploid common wheat; and carrying out inter-specific crossing distant hybridization, multi-generation selfing and identification to breed the common wheat capable of stably expressing the six HMW-GS. The novel common wheat with the six HMW-GS, which is cultivated by the method, not only has a strain leave type which is similar with the male parent, but also has a purple stalk property which does not exist in the female parent, and has better grain setting property, output property and excellent quality property when being compared with the female parent; and HMW-GS detection is continuously carried out on grains of F10, F11 and F12 generations of hybrid seeds so as to testify that 1Ay genes can be stably transmitted and expressed generation by generation.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Plant artificial chromosomes, uses thereof and methods of preparing plant artificial chromosomes
InactiveUS20050287647A9Easy to zoom inGood effectSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsHeterologousEuchromatin
Methods for preparing cell lines that contain plant artificial chromosomes, methods for preparation of plant artificial chromosomes, methods for targeted insertion of heterologous DNA into plant artificial chromosomes, and methods for delivery of plant chromosomes to selected cells and tissues are provided. In particular, plant artificial chromosomes that are substantially composed of repeated nucleic acid units of varying amounts of heterochromatin and euchromatin are provided. Also provided are methods of using plant and animal artificial chromosomes in the production of valuable transgenic plants. Methods for identifying plant genes encoding particular traits using artificial chromosomes and for producing an acrocentric plant chromosome are also provided.
Owner:CHROMOS MOLECULAR SYST +1
Lagerstroemia plant chromosomal in-situ hybridization method
InactiveCN103305614AGood for physical locationHigh hybridization specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementIn situ hybridisationMetaphase chromosome
The invention relates to a lagerstroemia plant chromosomal in-situ hybridization method. The method comprises seven steps such as sheet making, probe preparing, pretreating before hybridization, hybridization solution preparing, probe denaturating, chromosome denaturating, hybridizing and detecting. A lagerstroemia plant metaphase chromosome serves as a target deoxyribose nucleic acid (DNA) and maize 45SrDNA as a probe, and the maize 45SrDNA probe is clearly located on the lagerstroemia plant metaphase chromosome. By utilizing the hybridization method, background interferences can be effectively eliminated, the detection sensitivity and accuracy are improved, the hybridization method can be better applied to the chromosome detection of small chromosome plants such as lagerstroemia and the like, and a new way and a method are provided for the further research of lagerstroemia plant chromosomes.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Single chromosome producing method through micro cutting plant chromosomes
InactiveCN102352352AOvercome the difficulty of complete recovery, complex operating equipment and other problemsEasy to cutMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationLaser cuttingPlant chromosomes
The invention discloses a single chromosome producing method through micro cutting plant chromosomes, which comprises the steps that: under a microscope, the cool laser is adopted to cut and separate the seed plant chromosomes or chromatid segments of a specific section which is required to be researched according to the user requirement, and accordingly, any one chromatid or chromatid segment can be quickly and accurately obtained. The method adopts cool laser cutting, the laser is not directly contacted with the separated sample, the chromosome sample cannot be damaged due to the heat effect, and the problems that serious pollution is caused, the separated target chromosome is difficult to completely recovery, the operation equipment is complicated and the like in the former chromosome cutting technology are solved.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Improved and simplified plant chromosome fluorescence in-situ hybridization method
ActiveCN105296649AFew reaction stepsShorten experiment timeMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant rootsQuinoline
Owner:INST OF BOTANY JIANGSU PROVINCE & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method of making plant artificial chromosomes
InactiveUS7247768B1Repair damageOther foreign material introduction processesFused cellsProtoplastPlant chromosomes
Disclosed are methods of making plant artificial chromosomes. In one embodiment, the method entails: (a) preparing recombinant protoplasts of a first plant species containing an exogenous nucleic acid (e.g., DNA) of interest; (b) producing chromosome fragments of chromosomes contained in the recombinant protoplasts; (c) fusing the recombinant protoplasts of (b) with protoplasts of a second plant species to produce fused protoplasts, wherein the first and second plant species may be the same or different; and (d) identifying fused protoplasts of (c) or cells derived from the fused protoplasts of (c) that contain chromosome fragments that exhibit normal plant chromosomal properties. The chromosome fragments may be moved from one plant species to another. Whole plants, plant cell cultures and intermediates of same are also provided.
Owner:ICON GENETICS
New wheat stripe rust resisting polygene-polymerized flower-nurture breeding method
InactiveCN101558735AWide resistanceResistance spectrum widthHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureHigh resistanceLesser florican
The invention discloses a new wheat stripe rust resisting polygene-polymerized flower-nurture breeding method. Wheat-breeding parent materials with excellent agronomic characters are selected; 3 major micro-species of puccinia striiformis, which are recently popular, are used to evaluate stripe rust resistance of the wheat-breeding parent materials at seedling stage and adult stage; 3 wheat-breeding parent materials, which have high-resistance immunity to major popular individual micro-species of various puccinia striiformis, are sieved; the 3 wheat-breeding parent materials are hybridized and duplex hybridized to obtain duplex hybridized polygene-polymerized subsequent generation; the duplex hybridized subsequent generation is then cultured and wheat anther tissue is inoculated to one-step seeding culture medium of wheat anther, thereby obtaining complete pollen plant; chromosome doubling liquid with colchicines and dimethyl sulfoxide is injected to tillering node, thereby carrying out pollen plant chromosome doubling to obtain doubly purified individuals of doubled haploid which can be self-hybridized to form a stable doubled haploid system; and stripe rust resisting individual micro-species validation is carried out on the doubled haploid system, so as to obtain a new stripe rust resisting type or species system which is polymerized with 3 stripe rust resisting genes.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Dripping piece preparation method of plant chromosome
InactiveCN106350593AIncrease the number ofEasy to observeMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism lysisDispersityCell wall
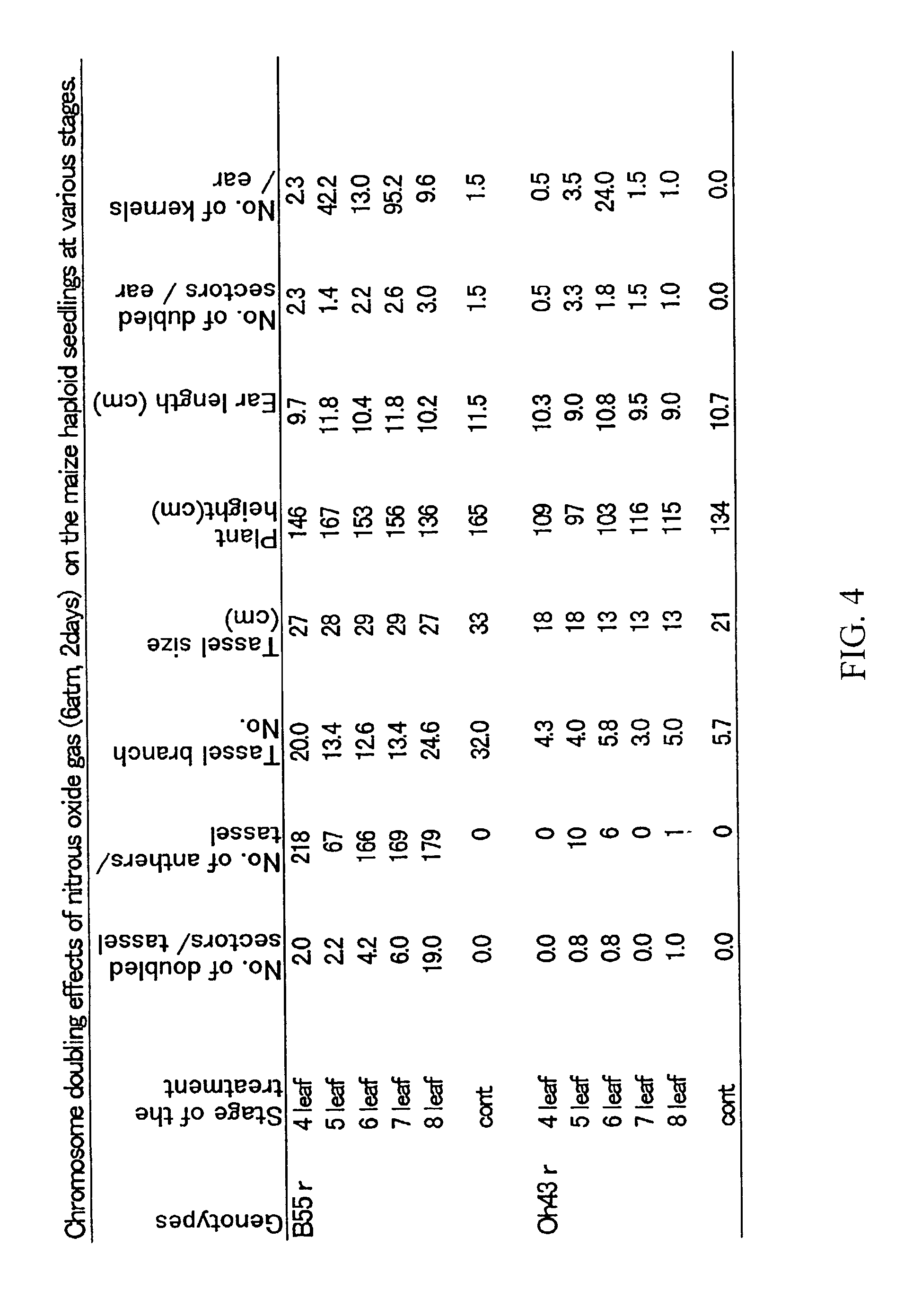
The invention provides a dripping piece preparation method of plant chromosome. The dripping piece preparation method includes steps of placing a plant organ in nitrous oxide gas for pretreatment, and then fixing the plant organ after pretreatment by stationary liquid, and performing enzymolysis on a cell wall of the plant organ by enzyme, and breaking the plant organ after enzymolysis, and preparing the cell suspension liquid; dripping the cell suspension liquid on a glass slide or a cover glass; forming a plant chromosome specimen. The reagent applied to the method is low in toxicity; the crack obtained through treatment is dispersed in a circular or ellipse form by comparing with regular piece making method, the distribution is uniform, and chromosome intersection is few, and dispersing degree is good; a complete chromosome can be obtained; the preparation method can prepare the chromosome slice with stable quality, clear chromosome and good dispersity; the prepared chromosome slice can be applied to cytological identification, manufacturing of permanent slice, hybridization in-situ, microdissection, and microscope separation, and so on.
Owner:YANGTZE NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Multi-color in-situ hybridization method for rapidly analyzing and detecting triticeae plant chromosome configuration
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, and especially relates to a multicolor in-situ hybridization method for rapidly analyzing and detecting triticeae plant chromosome configuration. The method is characterized in that mc-GISH is used for analysis of a chromosome pairing behavior during a pollen blast cell meiosis process, one-time hybridization can effectively identify the chromosome pairing condition during a meiosis process of triticeae at different genomes, and the method provides a powerful tool for analyzing a genetic relationship between the different genomes of triticeae, and especially for identifying the synapsis and pairing behaviors between different genomes of artificial created polyploid species.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
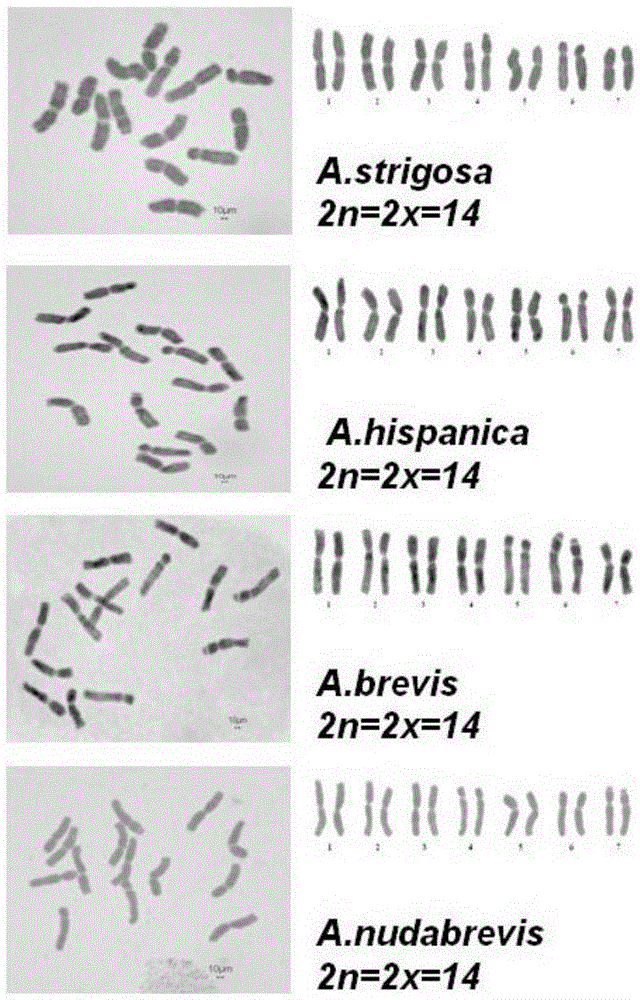
Method for quickly identifying chromosome number of rosa plant
InactiveCN103710439AAccurate material sizeAccurate locationMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationMicroscopic examElectron microscope
The invention provides a method for quickly identifying chromosome number of a rosa plant. The method comprises the steps of drawing materials, pretreatment, fixing, disaggregating, dyeing, tabletting, microscopic examination and the like. The tabletting process is digitalized in the tabletting step, and cover glass on the material is vertically knocked on by 28-34N of force for 160-200 times for the best. In preferable embodiments, the stem tip and / or blossom bud are adopted as materials for counting and analyzing the chromosomes. In preferable embodiments, the materials are obtained between nine and eleven in the morning or between three and four in the afternoon. In embodiments, growth points and positions of the materials are confirmed by an electron microscope in a scanning manner. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of diversified materials, accurate tabletting and the like, and is quick, accurate and efficient, and is especially applicable to quick and accurate identification of the chromosome number of the rosa plants on a large scale. Thus, the method is applied to quick and accurate identification of the chromosome number of the rosa plants on a large scale.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for rapidly obtaining herba erigernotis triploid
The invention discloses a method for rapidly obtaining herba erigernotis triploid. The method comprises the following steps: processing plump herba erigernotis seeds picked in the same year with a water solution of a cell microtubule inhibitor Oryzalin to induce the chromosome doubling of the germ growing point cells; continuously carrying out two times of leaf air hole identification in the seedling stage and the squaring stage, carrying out rapid screening so as to obtain tetraploid variant plants; and hybridizing the tetraploid variant plants with diploid plants (namely fusing egg cells having doubled chromosome with normal sperm cells) so as to obtain ploidy-homozygous triploid. The method utilizes the fusion of single cells (egg cells) with single cells (sperm cells) during the fertilization process of sexual reproduction of angiosperm, simultaneously achieves the ploidy purification of plant chromosome and obtaining of triploid, avoids a large amount of tedious work on purifying the ploidy of the tetraploid variant plants, and provides technical support for cultivating abundant herba erigernotis triploid novel germplasm and breeding triploid novel species.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANTS YUNNAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Plant chromosome tablet observation method
InactiveCN104374618AImprove dyeing effectConvenient for microscopic examinationPreparing sample for investigationBiotechnologyHigh concentration
The invention discloses a technology for observing a plant chromosome in a tabletting method. The method comprises the steps of preprocessing a testing material subjected to active cell division, fixing the chromosome, carrying out acid digestion on cells, neutralizing with alkali, dyeing, and observing tablets. 1cm to 2cm of a part, subjected to the active cell division, of the test material is preprocessed in a processing solution under a dark condition, after a preprocessed sample is well fixed by a fixed solution, the walls of the cells are subjected to acid digestion by high-concentration hydrochloric acid, the surplus hydrochloric acid is neutralized by weak protoplast base, then the dyeing and tabletting are carried out, and finally the division situation of the chromosome is observed under a microscope.
Owner:SHANDONG INST OF POMOLOGY
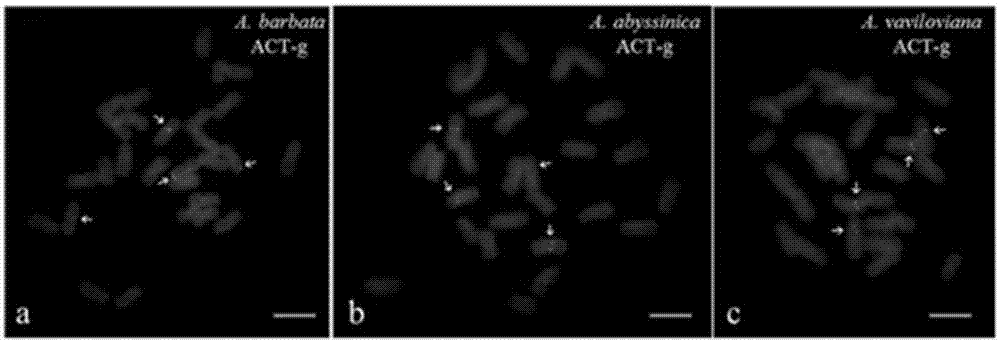
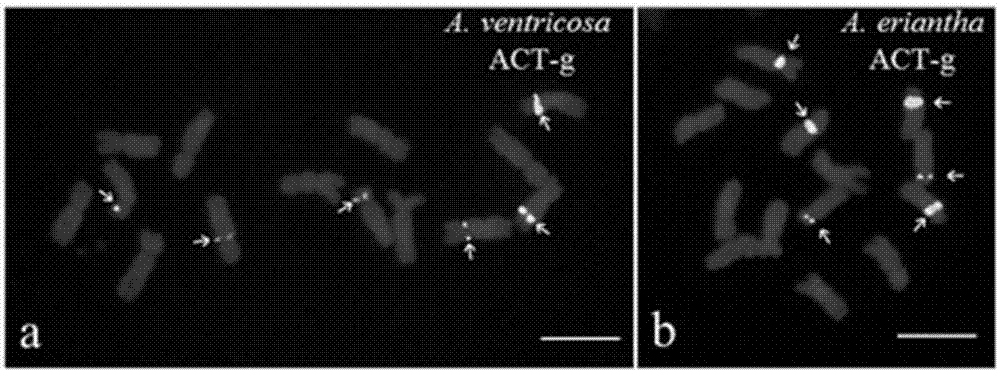
Probe group for detecting avena plant chromosome, and kit and application
InactiveCN107574229ASimple compositionEasy accessMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationReaction systemBiology
The invention provides a probe group for detecting an avena plant chromosome and a kit and an application. The probe group comprises four probes of Aml, (ACT)6, (GAA)6 and (TTG)6, wherein the base sequence of Aml is 5'-GATCCATGTGTGGTTTGTGGAAAGAACAC ACATGCAATGACT CTAGTGGTT-3'; the base sequence of (ACT)6 is 5'-ACTACTACTACTACTACT-3'; the base sequence of (GAA)6 is 5'-GAAGAAGAAGAAGAAGAA-3'; and the base sequence of (TTG)6 is 5'-TTGTTGTTGTTGTTGTTG-3'. The probe group consists of 18-51bp oligo-sequence probes for recognizing avena plant chromosomes, and is beneficial to establishment of stable andconvenient fluorescent in-situ hybridization reaction systems.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
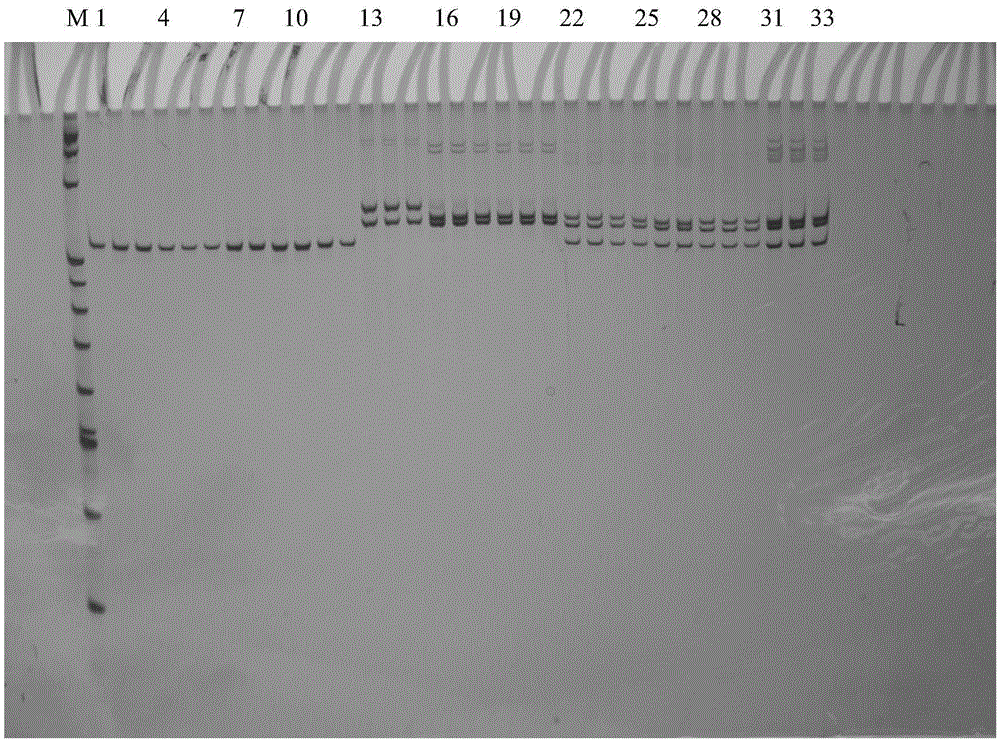
A method for rapid identification of chromosomal ploidy in Avena plants and its application
InactiveCN104357577BRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationRapid identificationPloidy
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant biotechnology, and specifically discloses a method for rapidly identifying chromosome ploidy of an avena plant. An SSR (Simple Sequence Repeats) molecule is utilized to mark characteristics that avena plants with different ploidy have different sizes and copy numbers, and the chromosome ploidy of the avena plants can be identified rapidly by combining a PCR amplification technology and a gel electrophoresis technology by virtue of different numbers of amplified product segments. The method for rapidly identifying chromosome ploidy of the avena plant has the advantage that ploidy of the plant can be identified rapidly under the condition that the ploidy of the avena plan is not known in advance, and the method is applicable to avena plants.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Novel method for inducing plant chromosome variation by injecting zebularine in booting stage
The invention belongs to the technical field of agricultural biology, and provides a novel method for inducing plant chromosome number and structure variation through a DNA transmethylase inhibitor zebularine.According to the method, octaploid jinghui-No.1 triticale is taken as a test material, zebularine is directly injected into plants in a booting stage, selfed seeds are harvested and subjected to chromosome identification, the chromosome number and structure variation which can be stably transferred is found from chromosome identification, and a novel method is supplied to plant chromosome engineering breeding and relevant theoretical research thereof.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com