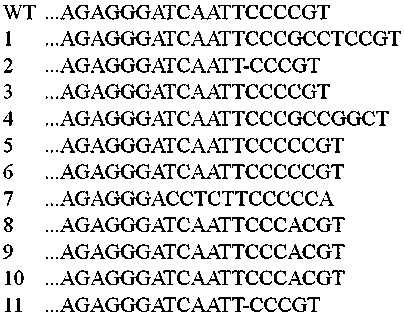Patents
Literature
5043 results about "Germplasm" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Germplasm are living genetic resources such as seeds or tissues that are maintained for the purpose of animal and plant breeding, preservation, and other research uses. These resources may take the form of seed collections stored in seed banks, trees growing in nurseries, animal breeding lines maintained in animal breeding programs or gene banks, etc. Germplasm collections can range from collections of wild species to elite, domesticated breeding lines that have undergone extensive human selection. Germplasm collection is important for the maintenance of biological diversity and food security.
Rice whole genome SNP chip and application thereof
ActiveCN102747138AImprove throughputGood repeatabilityNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementManufacturing technologyGermplasm
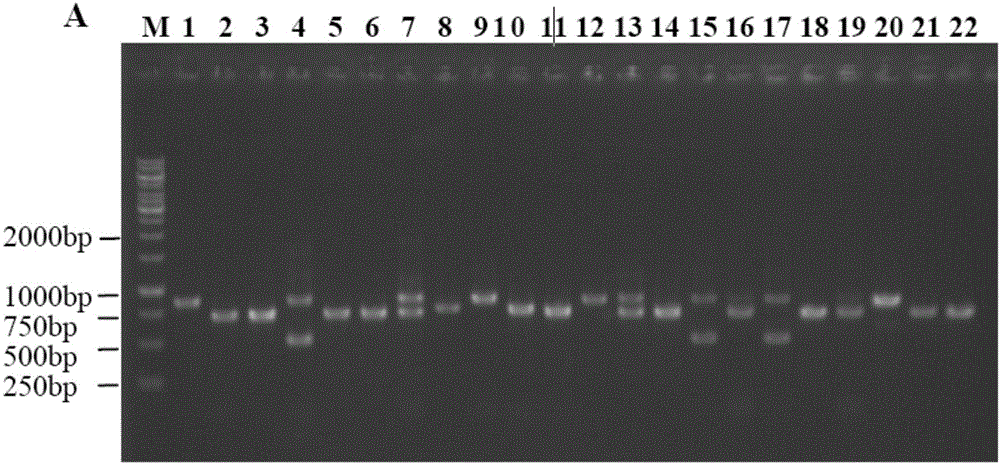
The present invention discloses a rice whole genome SNP chip and an application thereof. A method for preparing the chip comprises: (1) obtaining a first class of probes on a chip, wherein sequencing is performed to obtain a parental genome sequence, resequencing data of other rice varieties in a public database are combined, a Nipponbare genome is adopted as a reference sequence, a MAQ software is adopted to match and analyze all the sequencing data, and finally a SNP marker is screened; (2) obtaining a second class of probes on the chip, wherein a rice function gene is obtained from the public database, sequence difference reflecting gene function is searched, and a SNP / INDEL probe is designed according to the sequence difference; (3) adopting an infinium chip manufacturing technology to produce a SNP chip; and (4) testing accuracy and application efficiency of the chip. The chip of the present invention can be applicable for rice germplasm resource molecule marker fingerprint analysis, seed authenticity detection, filial generation genotyping, and other related researches.
Owner:先正达集团股份有限公司
Methods of seed breeding using high throughput nondestructive seed sampling
ActiveUS20070204366A1Improved breeding populationHigh activityMicrobiological testing/measurementOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyGermplasm
The present invention provides for novel methods to facilitate germplasm improvement activities through the use of high throughput, nondestructive sampling of seeds. In one embodiment, a high-throughput, non-destructive method for analyzing individual seeds in a population of seeds comprises removing a sample from a plurality of seeds in the population while preserving the germination viability of the seed and analyzing the sample for the presence or absence of one or more characteristics of at least one genetic or chemical trait.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Methods of seed breeding using high throughput nondestructive seed sampling
ActiveUS7703238B2High activityExpand the populationSeed and root treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementNon destructiveGermplasm
The present invention provides for novel methods to facilitate germplasm improvement activities through the use of high throughput, nondestructive sampling of seeds. In one embodiment, a high-throughput, non-destructive method for analyzing individual seeds in a population of seeds comprises removing a sample from a plurality of seeds in the population while preserving the germination viability of the seed and analyzing the sample for the presence or absence of one or more characteristics of at least one genetic or chemical trait.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Methods and compositions to enhance plant breeding
InactiveUS20060282911A1Enhanced agronomicEnhanced transgenic traitBiocideDead animal preservationGermplasmHaplotype
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Rice thousand kernel weight gene tgw6 mutant as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105063061AA New Way to SafetyEfficient new wayPlant peptidesFermentationAgricultural scienceGermplasm
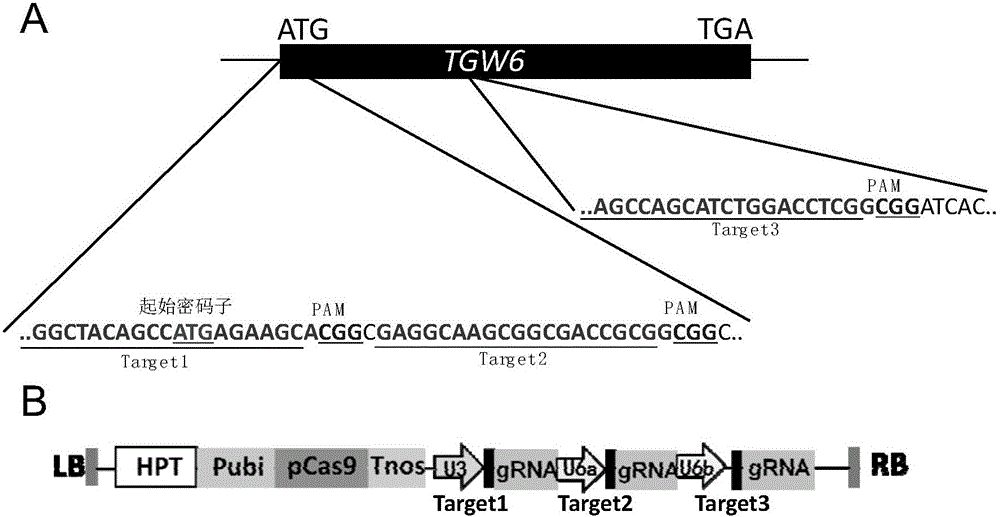
The invention belongs to the field of plant biotechnology, and in particular relates to a rice thousand kernel weight gene tgw6 mutant as well as a preparation method and application thereof. According to the invention, by designing a specific TGW6 site and by site-directed editing a TGW6 gene for regulating and controlling rice thousand kernel weight by virtue of CRISPR / Cas9 technology, a set of rice tgw6-deleted mutant new germplasm, namely Cas-tgw6-a, Cas-tgw6b or Cas-tgw6c, having an important application value can be obtained, and the mutant can cause significant influence to the thousand kernel weight of rice and can improve rice thousand kernel weight by more than 5%. The tgw6 mutant is applicable to rice high-yield and stable-yield breeding.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Salt-tolerance determining method for barley at seedling stage
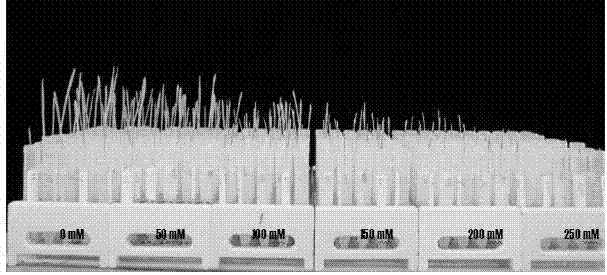
InactiveCN102860159AReduce the impactSimple methodSeed and root treatmentHorticulture methodsAgricultural scienceQuantitative trait locus
The invention relates to a determining method for indicating salt tolerance of different varieties of barleys at seedling stages and belongs to the field of agriculture. The determining method includes adopting a water culturing manner to simulate salt environment artificially, investigating salt damage degree of samples to be tested under the condition of salt stress compared with the blank control condition by measuring seedling height, root length and fresh weight of each seedling of different treatment, and finally determining salt tolerance of the variety. The determining method can be widely applied to screening and evaluation of plant stress resistance genetic resources, particularly used for screening of barley salt-tolerance variety resources, salt-tolerance QTL (quantitative trait locus) genetic analysis, salt-tolerance gene positioning and seed selection of salt-tolerance barley varieties. The determining method has the advantages of simplicity, easiness in mastering and reliable results, the whole salt-tolerance determining process is under control and is slightly affected by the environment, requirements for equipment are low so that only one common illumination culturing box is required.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Methods & Compositions for Selection of Loci for Trait Performance & Expression
InactiveUS20090031438A1Improve traitsGenetic backgrounds improvedSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsGermplasm
The present invention provides novel methods and compositions for the identification and selection of loci modulating transgene performance and expression in plant breeding. In addition, methods are provided for screening germplasm entries for the performance and expression of at least one transgene.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
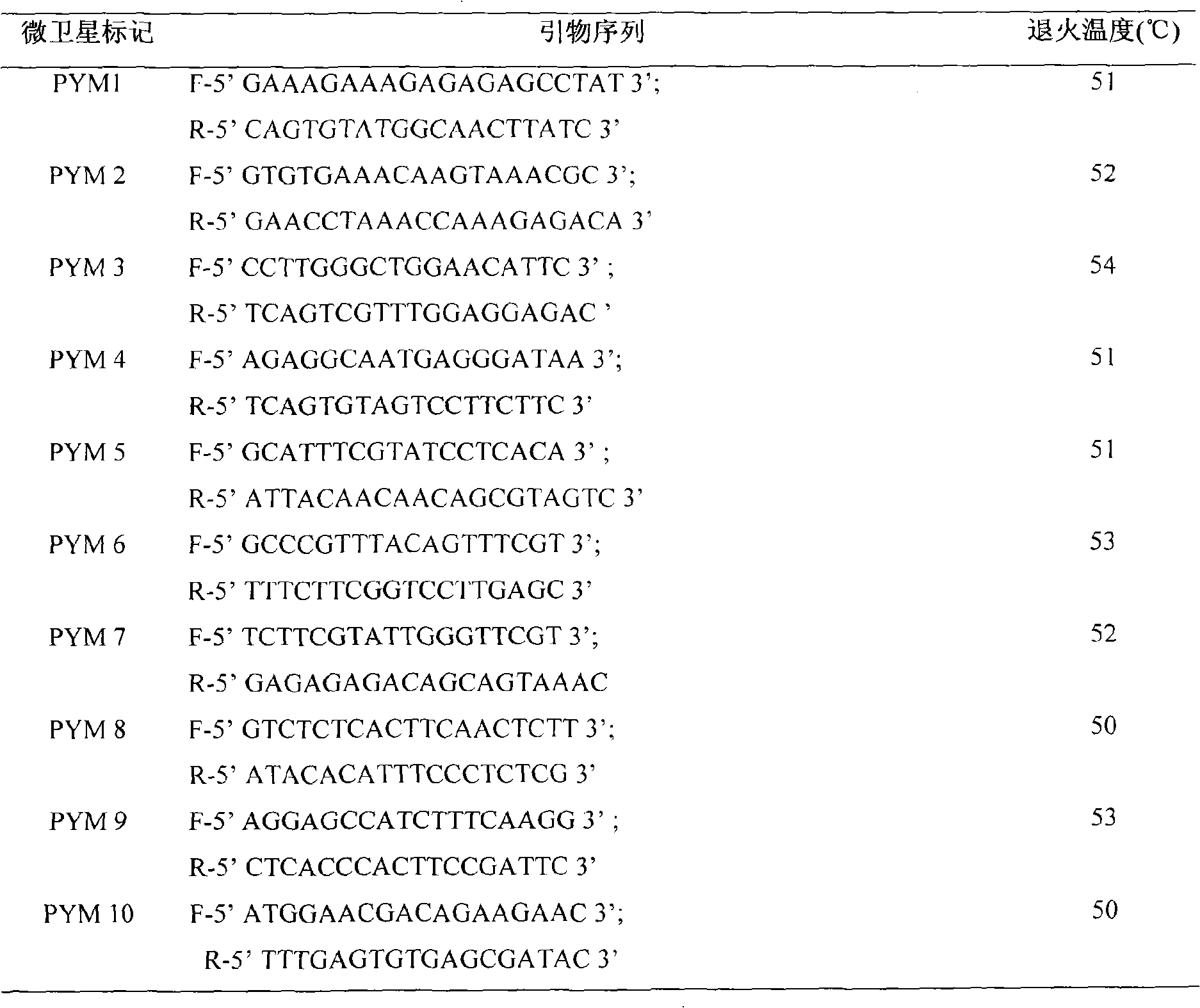
Specific primers for microsatellite markers of EST sequences of Litopenaeus vannamei and application thereof
ActiveCN101942437AScience and time savingWide range of usesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationPopulation geneticsLitopenaeus
The invention discloses specific primers for microsatellite markers of EST sequences of Litopenaeus vannamei. The specific primers are five pairs together, and the nucleotide sequences are shown as SEQIDNO:1-10. The invention also discloses application of the specific primers in screening the microsatellite markers of the EST sequences of the Litopenaeus vannamei, performing diversity analysis of germplasm resources of the Litopenaeus vannamei, performing genetic diversity analysis, identifying families, studying molecular population genetics, constructing genetic maps, positioning important economic traits, studying functional genes, and assisting the molecular genetic breeding or culture of the Litopenaeus vannamei. Compared with the prior art, the specific primers for the microsatellite markers have the characteristics of high efficiency, simpleness, convenience, and quickness in screening required microsatellite markers.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Rice salt-tolerant gene OsRR22 mutant, encoded amino acid sequence thereof, plant and making method of mutant
InactiveCN107828794AImprove salt toleranceComprehensive agronomic traits are goodPlant peptidesFermentationAgricultural scienceGermplasm
The invention relates to a rice salt-tolerant gene OsRR22 mutant, an encoded amino acid sequence thereof, a plant and a making method of the mutant, and belongs to the technical field of plant biology. A CRISPR / Cas9 technology is sued to edit self-selected rice variety WDR58 with rice salt-tolerant gene OsRR22 to obtain a rice salt-tolerant gene OsRR22 function deleted mutant new germplasm WDR58-cas-1 with important application values. The mutant can significantly increase the salt tolerance of rice, and can be applied to high-yielding salt-tolerant rice breeding.
Owner:SHANGHAI AGROBIOLOGICAL GENE CENT
Method of increasing content of resistant starch in rice through genome editing and sgRNA special for same
ActiveCN106086028AAddressing the lack of low-glycemic foodsAvoid problemsNucleic acid vectorPlant peptidesBiotechnologyAmylase
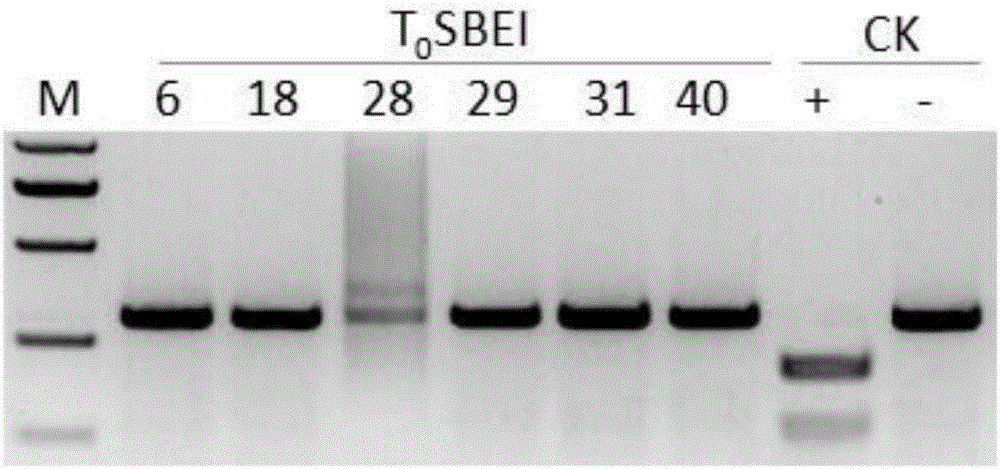
The invention discloses a method of increasing the content of resistant starch in rice through genome editing and sgRNA special for the same. The method provides a method of increasing the content of resistant starch and / or amylase in rice seeds. The method includes the following steps that expression of SBEIIb genes in the rice is inhibited; the SBEIIb genes are genes of encoding SBEIIb protein. The invention further provides a method of increasing the content of resistant starch in rice and includes the step of inhibiting the activity of the SBEIIb protein in the rice. By using the CRISPR / Cas9 technology, the rice SBEIIb genes are edited at fixed points, the rice SBEIIb genes are knocked off by causing frameshift mutation, and the new generation of new rice germplasm with the content of amylase and resistant starch obviously increased is obtained.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
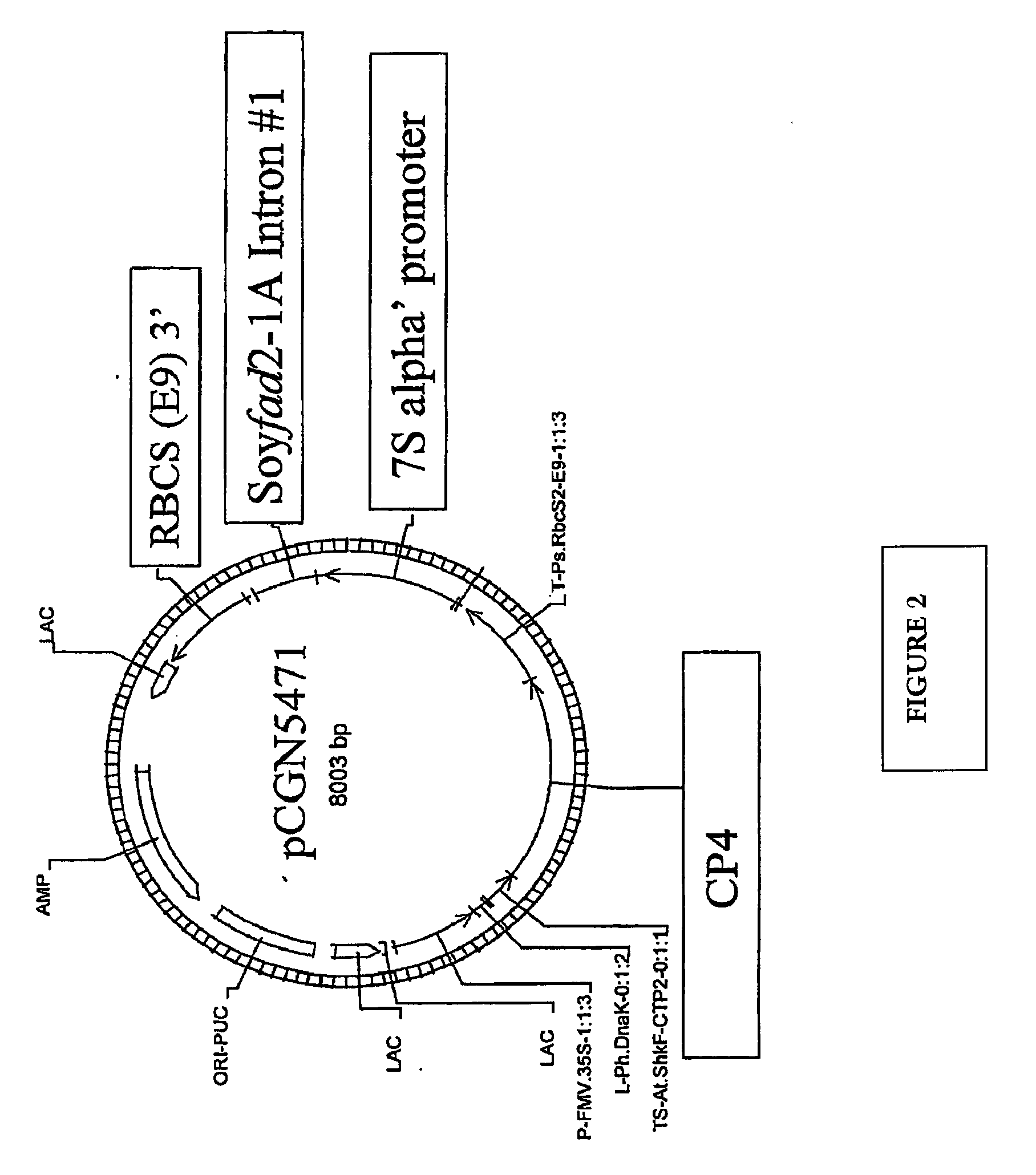
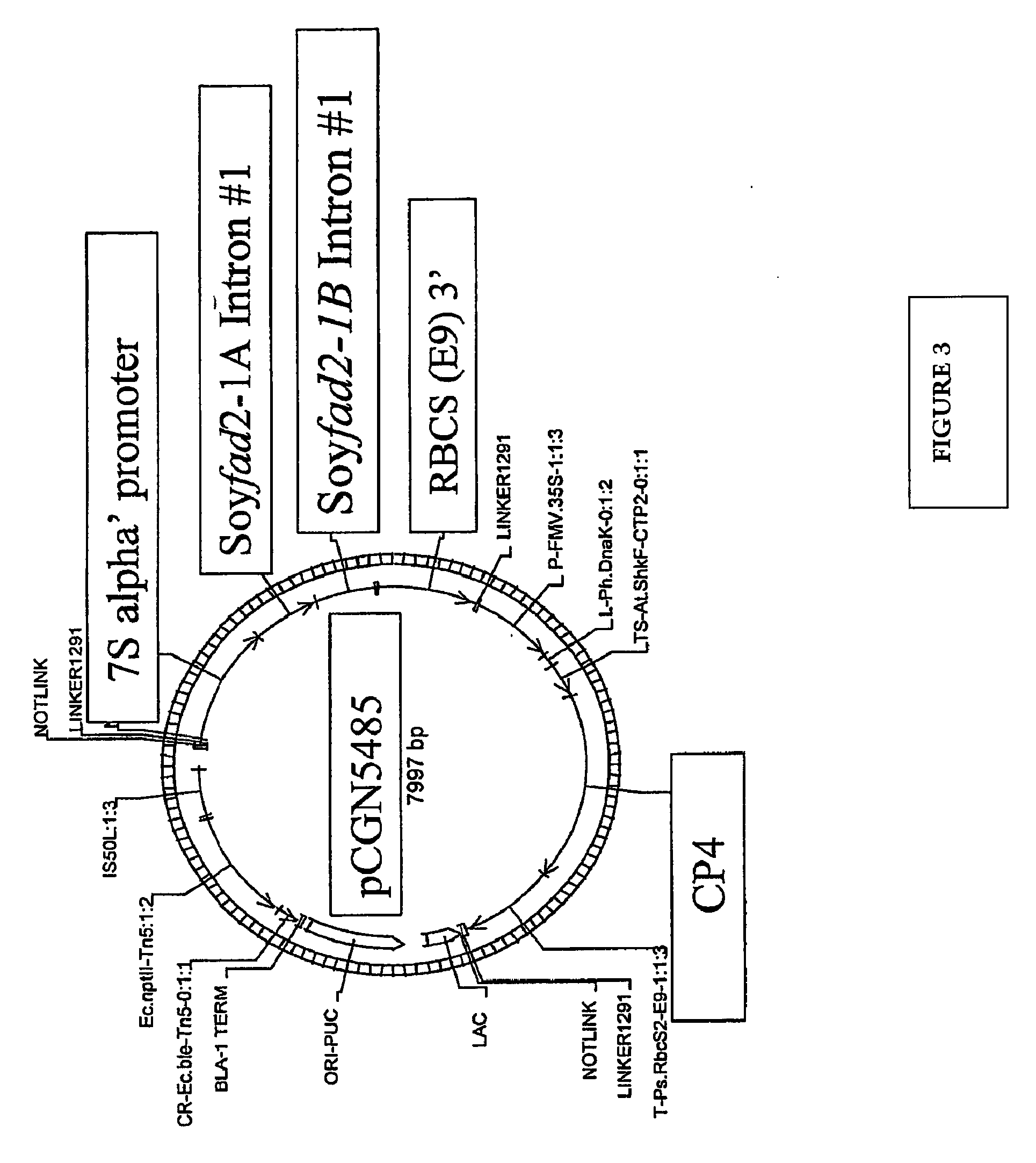
Soybean Seed And Oil Compositions And Methods of Making Same
ActiveUS20070214516A1Reduce expressionFatty acids production/refiningMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyGermplasm
Methods for obtaining soybean plants that produce seed with low linolenic acid levels and moderately increased oleic levels are disclosed. Also disclosed are methods for producing seed with low linolenic acid levels, moderately increased oleic levels and low saturated fatty acid levels. These methods entail the combination of transgenes that provide moderate oleic acid levels with soybean germplasm that contains mutations in soybean genes that confer low linolenic acid phenotypes. These methods also entail the combination of transgenes that provide both moderate oleic acid levels and low saturated fat levels with soybean germplasm that contains mutations in soybean genes that confer low linolenic acid phenotypes. Soybean plants and seeds produced by these methods are also disclosed.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Method for selectively breeding improved variety of China turtle
InactiveCN101120662AQuality improvementAnimal reproductionClimate change adaptationEcological environmentGermplasm
The present invention relates to a turtle artificial cultivating method, in particular to a method selecting and breeding the good Chinese turtle strain, which resolves the technical problems of the prior art that the turtle is not selected for breeding in different growth periods, the selection of the turtle is not enough to mix the defective turtle in different periods and the quality-degraded turtle, thereby leading to the degradation of the quality of the offspring of the cultivated parent turtle; the quality is reduced, the growth is slowed down and the disease-resistant ability is weakened. The present invention firstly selects the ecological environment and then selects the parent turtle, the fertilized egg, the juvenile turtle, the adult turtle and the reserve parent turtle in turn; wherein, the selection rate of the parent turtle is from eighty percentages to eighty five percentages; the selection rate of the juvenile turtle is from twenty five percentages to thirty five percentages; the selection rate of the adult turtle is from forty five percentages to fifty five percentages and the selection rate of the reserve parent turtle is from sixty five percentages to seventy five percentages.
Owner:杭州萧山天福生物科技有限公司
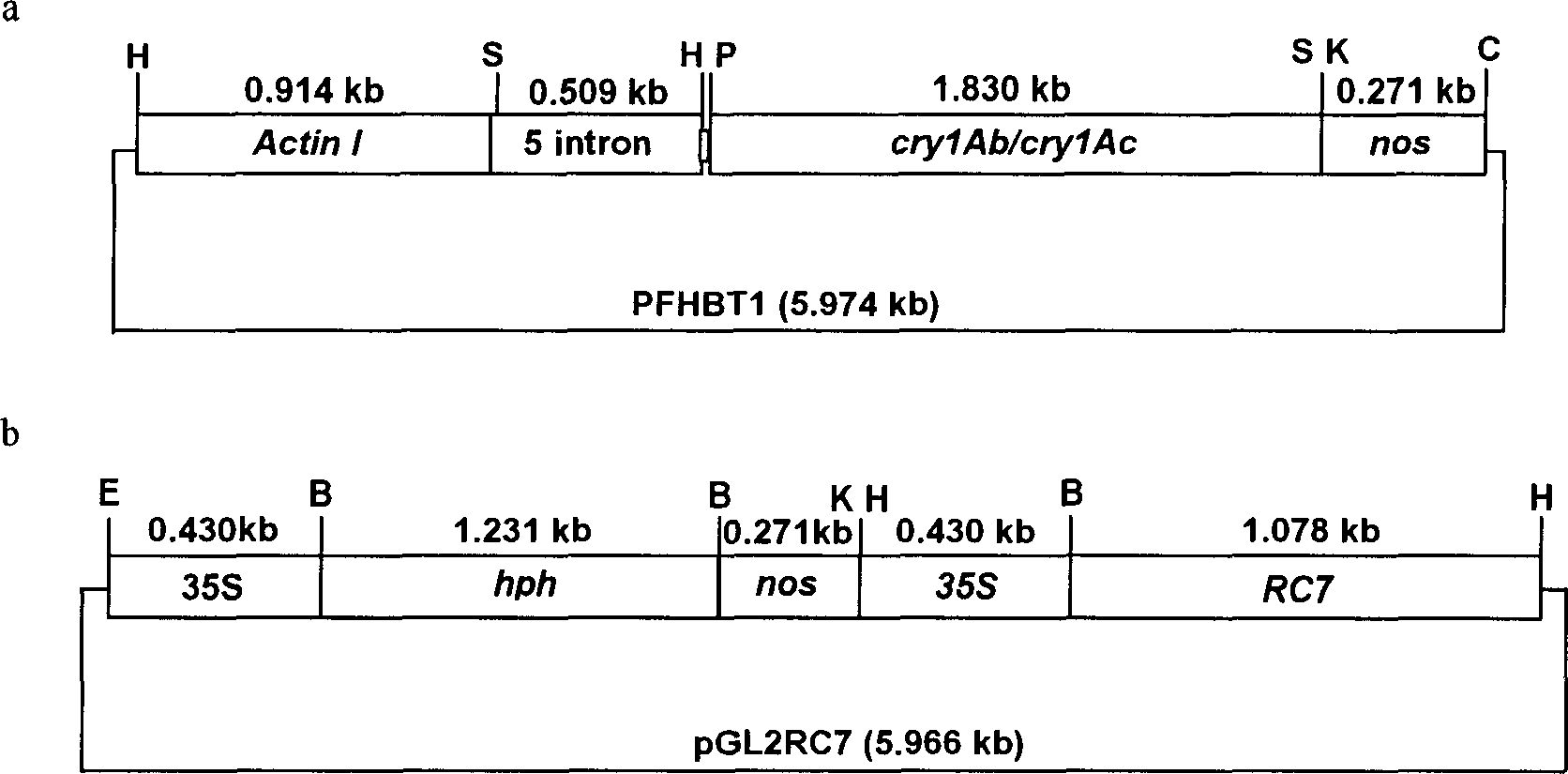
Transgenic rice culture method
InactiveCN1840655APlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsGenetically modified riceAgricultural science
The provided specific site can integrates exogenous gene to stable express and affect little to the acceptor. Besides, it also provides a composite gene structure, which can be integrated by rice gene DNA sequence near specific site and DNA sequence of exogenous gene, and be used to culture new rice series by sexual hybridization and somatic hybridization.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Upland cotton SNP marker and application thereof
InactiveCN105349537AImprove detection efficiencyImprove work efficiencyNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementAgricultural scienceHomologous sequence
The invention discloses an upland cotton SNP marker and application thereof, and belongs to the field of upland cotton SNP marker development. The upland cotton SNP marker is obtained by developing a single-copy SNP marker of an upland cotton genome via chip hybridization and homologous sequence comparison, and picking out SNP markers in a linkage disequilibrium recession distance via linkage disequilibrium analysis. The SNP marker provided by the invention can be applied to analysis of genetic diversity and group structure, or to germplasm identification of upland cotton, is single-copy, and has no remarkable linkage disequilibrium among markers, so that the efficiency of detection, adopting the SNP marker, during analysis of genetic diversity, group structure or fingerprint identification can be greatly improved, and the work efficiency is higher.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Core SNP sites combination maizeSNP384 for building of maize DNA fingerprint database and molecular identification of varieties
ActiveCN104532359AImprove stabilityGood repeatabilityNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementMolecular identificationAgricultural science
The invention discloses a core SNP sites combination maizeSNP384 for building of a maize DNA fingerprint database and molecular identification of varieties, and an application of the core SNP sites combination. The invention provides applications of 384 SNP sites in any one of the following conditions: (1) building of the maize DNA fingerprint database; (2) detecting of the authenticity of maize varieties; (3) genetic analysis of corn germplasm resources; and (4) molecular breeding of maize, wherein the physical positions of the 384 SNP sites are determined by comparison on the basis of a whole genome sequence of the maize variety B73; the version number of the whole genome sequence of the maize variety B73 is B73 RefGen V1; and the 384 SNP sites are MG001-MG384. An experiment proves that the 384 SNP sites can be applied to building of the maize variety DNA fingerprint database, identification of the variety authenticity, dividing of germplasm resource groups, and other related researches.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
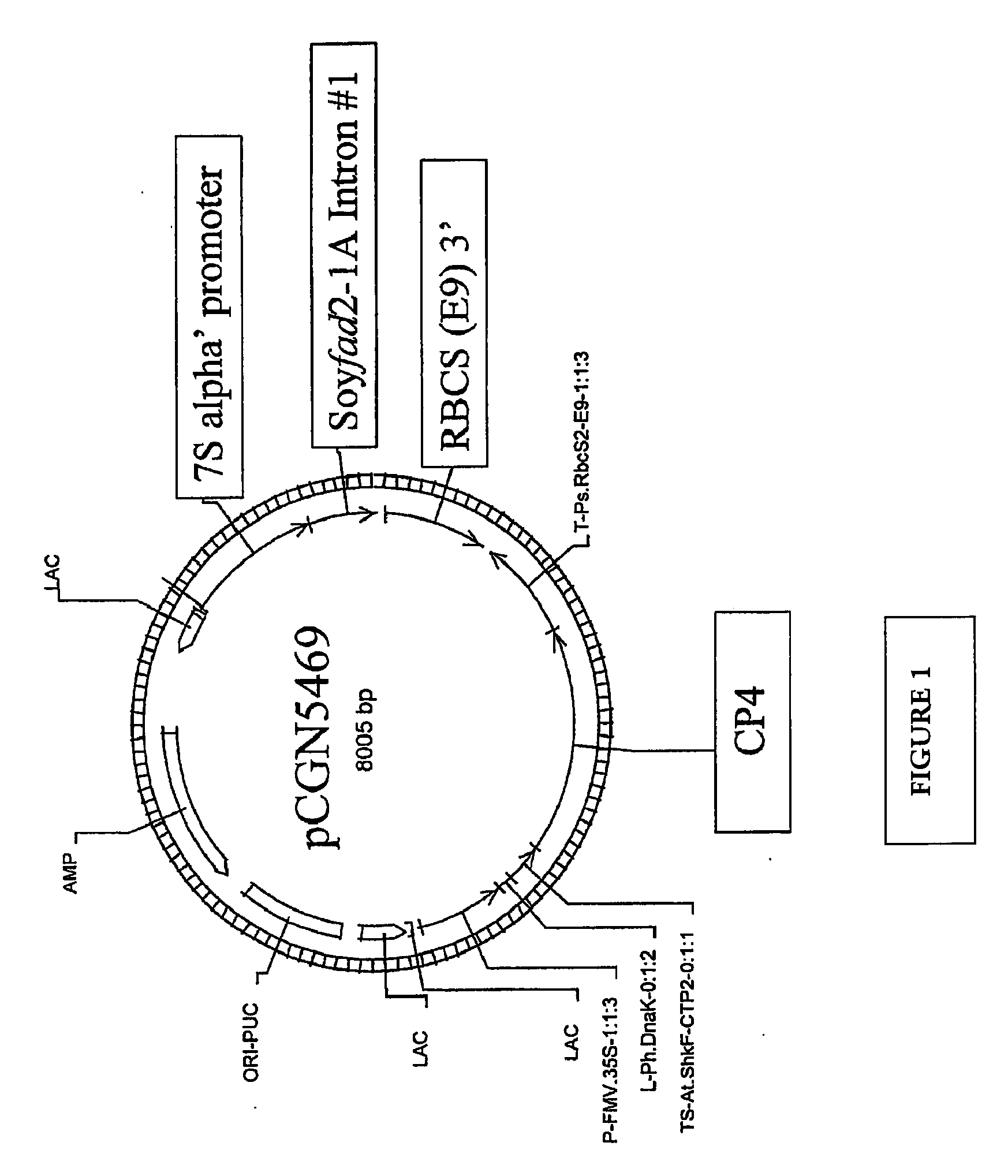
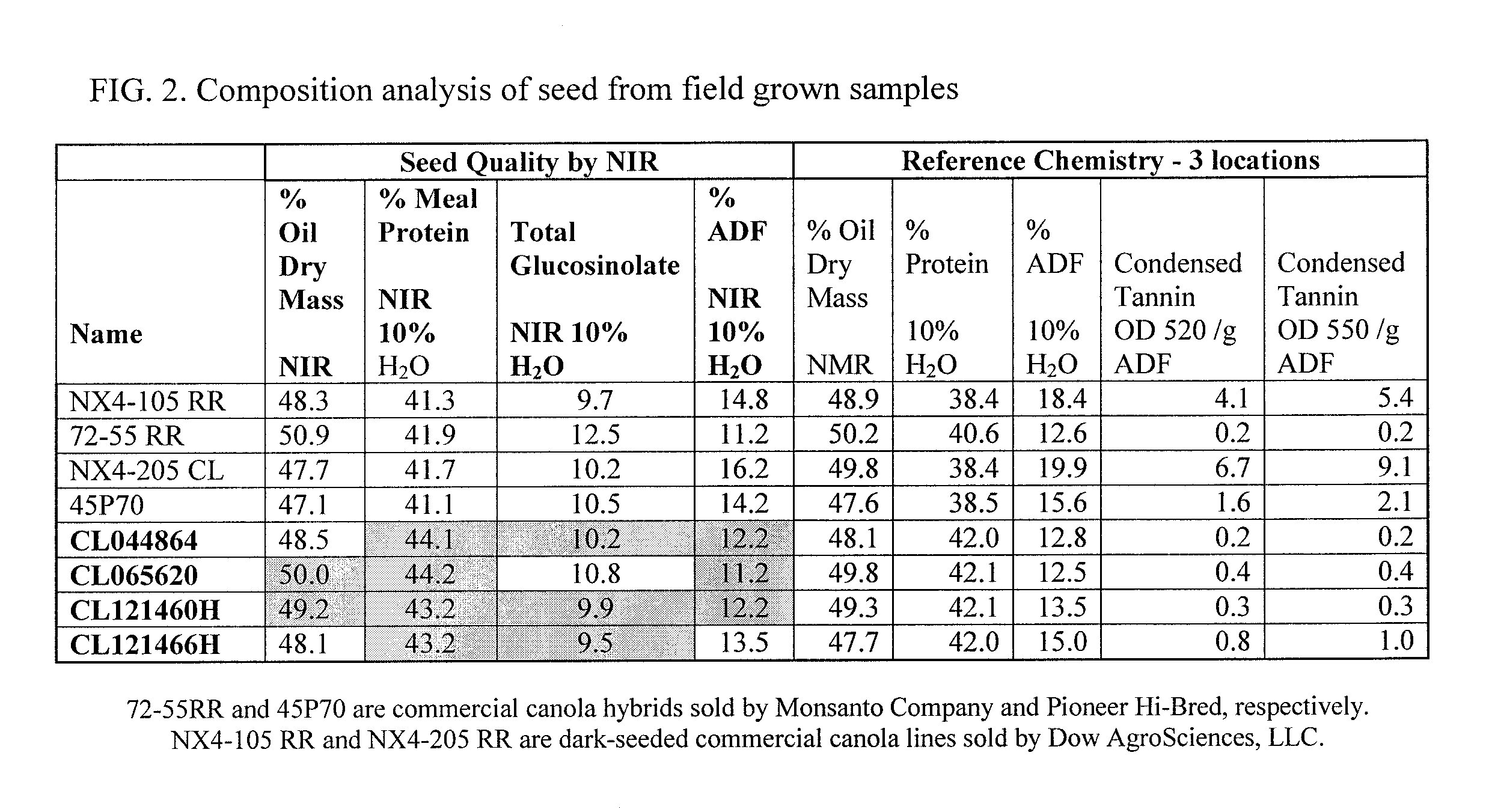
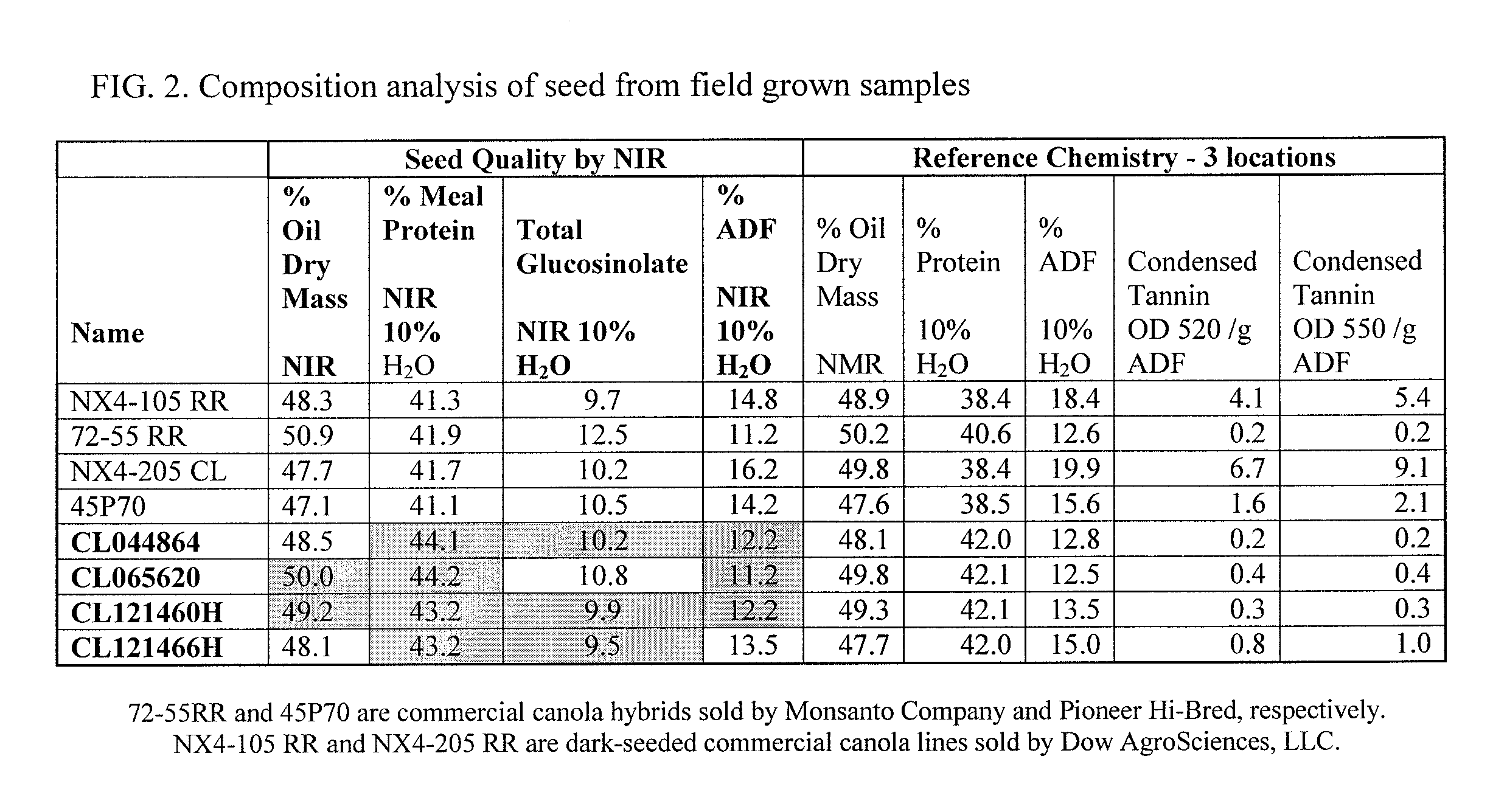
Canola Germplasm Exhibiting Seed Compositional Attributes That Deliver Enhanced Canola Meal Nutritional Value
ActiveUS20120216307A1High nutritional valueIncrease heightFood processingAnimal feeding stuffGermplasmPolyphenol
The present invention concerns a canola germplasm comprising at least 45% crude protein and not more than 18% acid detergent fiber content on an oil-free, dry matter basis. Certain embodiments further comprise one or more traits selected from the group consisting of reduced polyphenolic content and increased phosphorous content. In particular embodiments, the invention concerns canola plants comprising such germplasm and plant commodity products (e.g., seeds) produced therefrom. Canola plants comprising a germplasm of the invention may exhibit favorable seed composition characteristics that make them particularly valuable as a source for canola meal, and for methods of introducing at least one trait selected from the group consisting of high protein content, low fiber content, reduced polyphenolic content and increased phosphorous contentinto a canola variety in a seed coat color-independent manner.
Owner:AGRI GENETICS
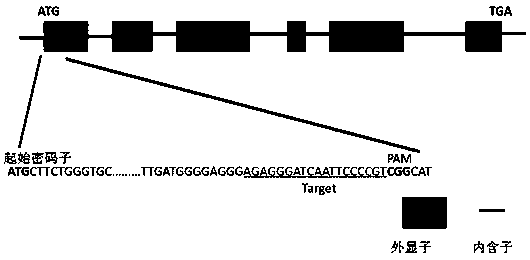
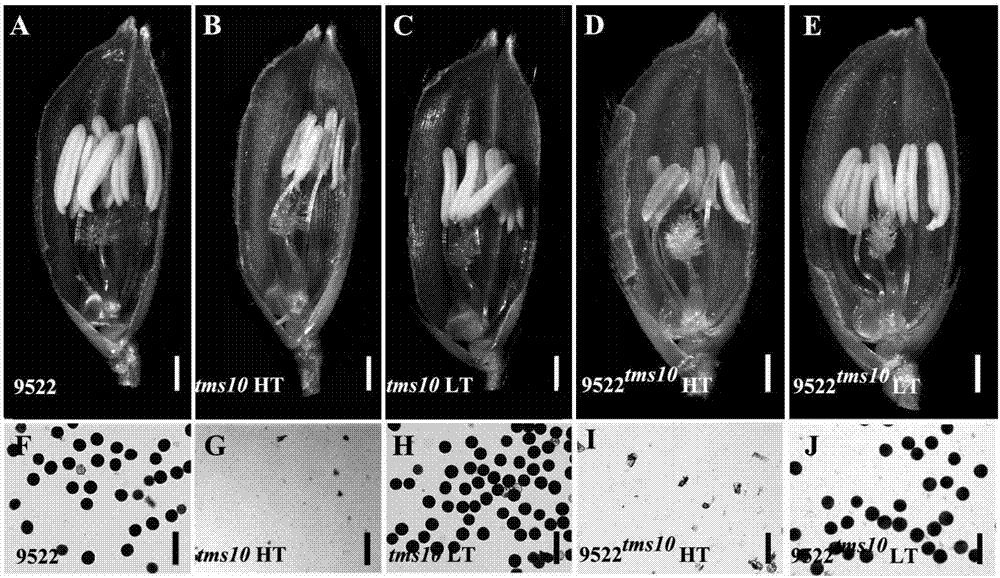
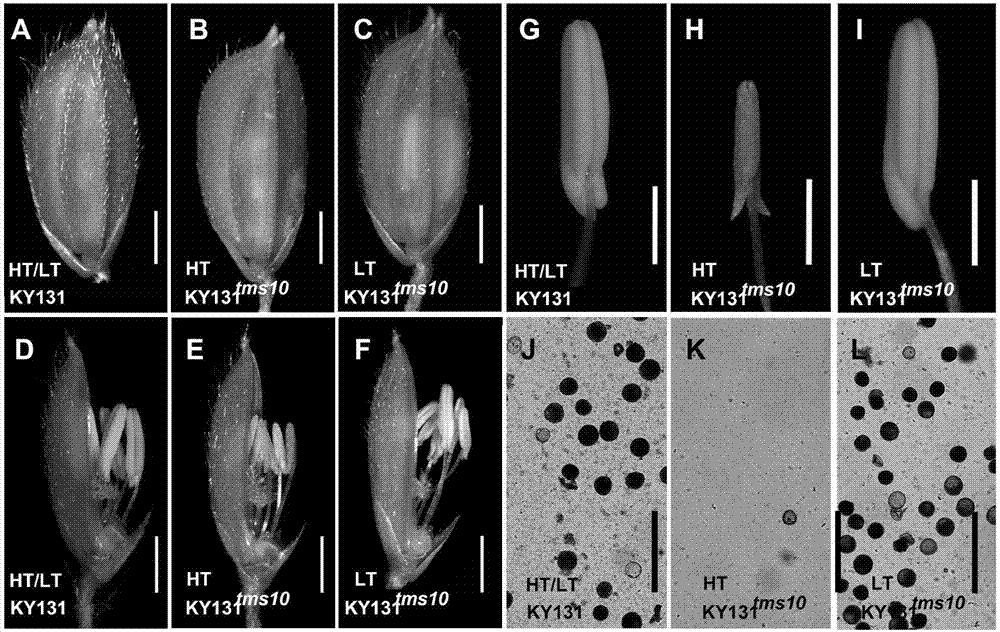
Site-directed knockout system for rice TMS10 gene, and applications thereof
InactiveCN107326042AExhibit male sterilityEfficient breedingTransferasesNucleic acid vectorBiotechnologyGermplasm
The present invention relates to a site-directed knockout system for a rice TMS10 gene, and applications thereof. The site-directed knockdown system comprises a CRISPR / Cas9 system and a sgRNA target, wherein the sgRNA target is the sequence containing PAM or NGG in a rice male sterile gene TMS10, the CRISPR / Cas9 system is CC-TMS10-1, and the CC-TMS10-1 target sequence is a SEQ ID NO.1 sequence from site 2281 to site 2299. The applications comprise carrying out targeted knockout on the TMS10 genes of different japonica rice varieties and different Indica rice varieties by separately using CC-TMS10-1, wherein the experiment results prove that the heterozygous mutation transformation plant produced through the site-directed knockout induction in different rice varieties shows the temperature sensitive male sterility characteristic. According to the present invention, the site-directed knockout system provides the efficient breeding method for the creation of the temperature sensitive male sterile line germplasm resources based on the rice temperature-sensitive male sterile gene TMS10 and the rice hybridization breeding.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Canola Germplasm Exhibiting Seed Compositional Attributes That Deliver Enhanced Canola Meal Nutritional Value Having Omega-9 Traits
ActiveUS20120213909A1High nutritional valueIncrease heightFruit and vegetables preservationFood processingFiberGermplasm
A canola germplasm confers on a canola seed the traits of high protein content and low fiber content, wherein the canola plant produces a seed having, on average, at least 68% oleic acid (C18:1) and less than 3% linolenic acid (C18:3). The canola seed traits may also include at least 45% crude protein and not more than 18% acid detergent fiber content on an oil-free, dry matter basis. Certain embodiments further comprise one or more traits selected from the group consisting of reduced polyphenolic content and increased phosphorous content. In particular embodiments, the invention concerns canola plants comprising such germplasm and plant commodity products (e.g., seeds) produced therefrom. Canola plants comprising a germplasm of the invention may exhibit favorable seed composition characteristics that make them particularly valuable as a source for canola meal.
Owner:AGRI GENETICS
Kiwi seedling cultivation method
InactiveCN103270920AMeet the needs of cultivating high-quality seedlings of kiwifruitSeed and root treatmentCultivating equipmentsStratification (seeds)Seeds source
The invention relates to a kiwi seedling cultivation method, belongs to the technical field of kiwi cultivation, and solves the problems that the existing kiwi seedling cultivation technique fails to meet the needs of standard production, large-scale gardening, germplasm resources transferring and conservation, and planting in protected areas due to the factors such as long seedling cultivation period, low seedling emergence rate, few seed sources and slow cultivation. The method includes using of greenhouses, trays, plastic-covered tunnels and plastic film mulching; cold storage, stratification, sowing, stock cultivation, branch grafting, field management and outplanting of stock seeds. The whole cultivation process starts from January and ends before soil freezing in November and is under quality control. According to the method, seeding, grafting and outplanting all occur in one year. The time from storing seeds in sand to emergence of seedlings lasts for 11 months, namely the seedling cultivation time is 11 months, the rate of first-grade seedlings is up to 90%, and the need of standard, large-scale planting and demonstrative popularization of kiwi and the need of germplasm resources expansion and protection are met.
Owner:贾兰虹
Natural sea area large-scale ecological breeding method of stichopus japonicus
InactiveCN101692796AOvercoming technological biases that cannot be cultivated in natural seasChange the way of productionClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaDiseaseStichopus
The invention relates to a natural sea area large-scale ecological breeding method of stichopus japonicus, belonging to the field of aquiculture. The method can realize large-scale stichopus japonicus seedling breeding at the natural sea area by the steps of selecting and culturing parent stichopus japonicus, daily management of the parent stichopus japonicus, egg taking and incubating, culturing the young, culturing young stichopus japonicus, classifying offspring seeds and temporary culturing. The method solves the problems of degraded seedling quality, reduced production quality of the seedlings, gradual increment of stichopus japonicus diseases, high energy consumption of a seedling breeding room and the like in the process of seedling cultivation in the existing artificial seedling breeding room, overcomes the technical prejudice that sea cucumber seedlings can not be cultured at the natural sea area in the traditional view, breaks through the inherent thinking set, changes the traditional production way of the artificial seedling breeding room, and can realize ecological breeding in the natural sea area. Furthermore, the method has the remarkable advantages of high survival rate, no pollution and chemical dosing as well as being nuisanceless.
Owner:大连北方海洋生态苗业有限公司
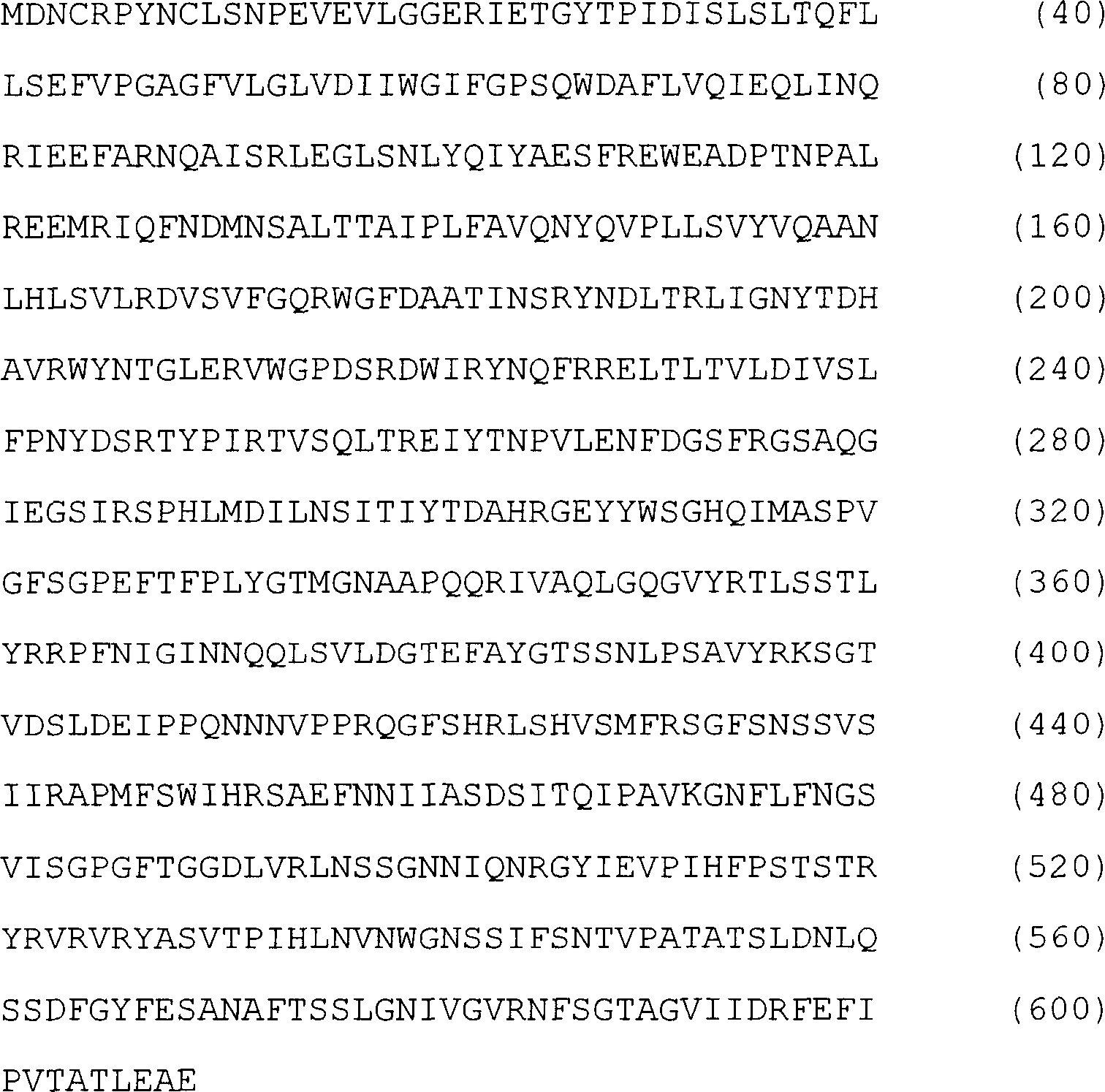
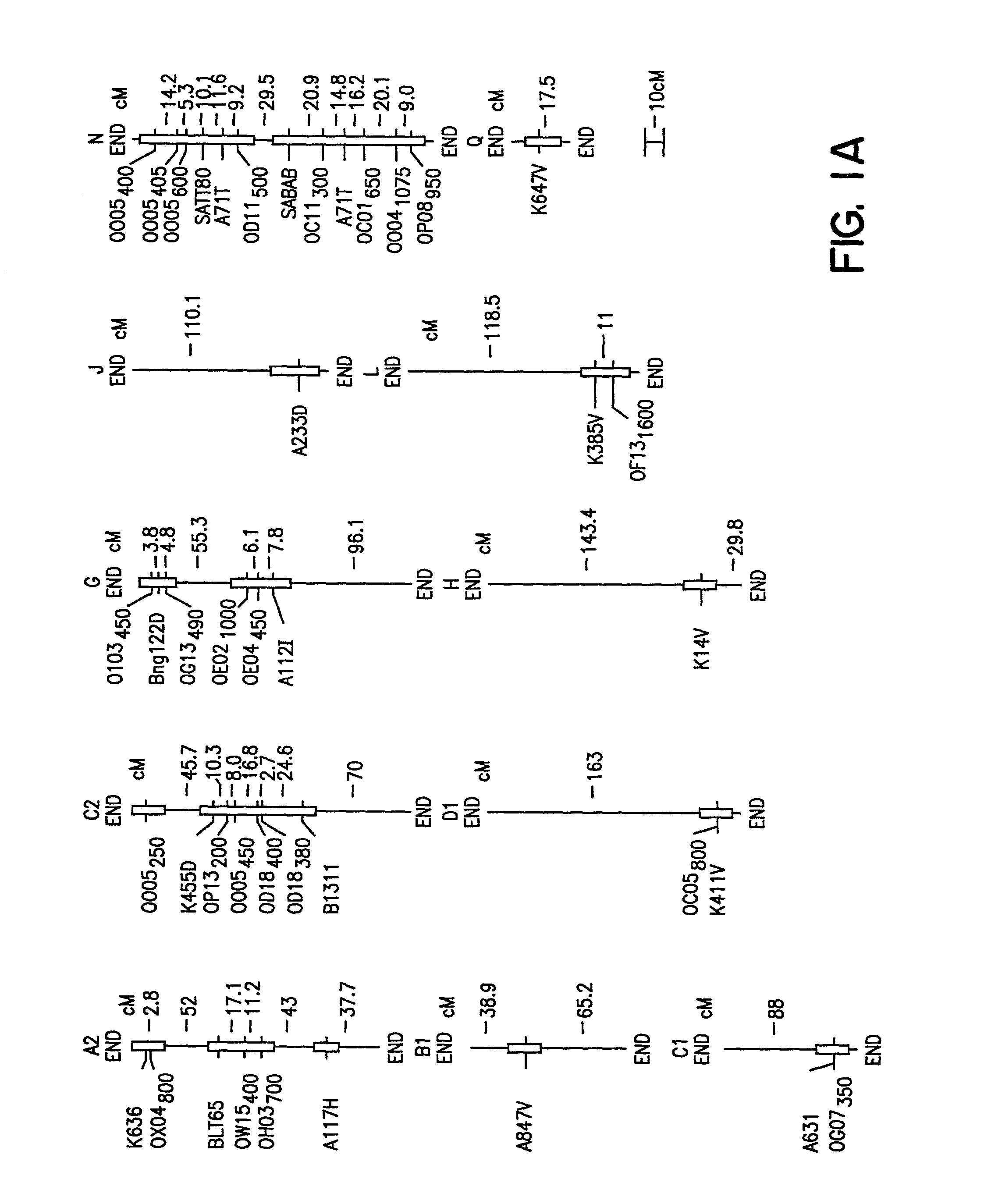
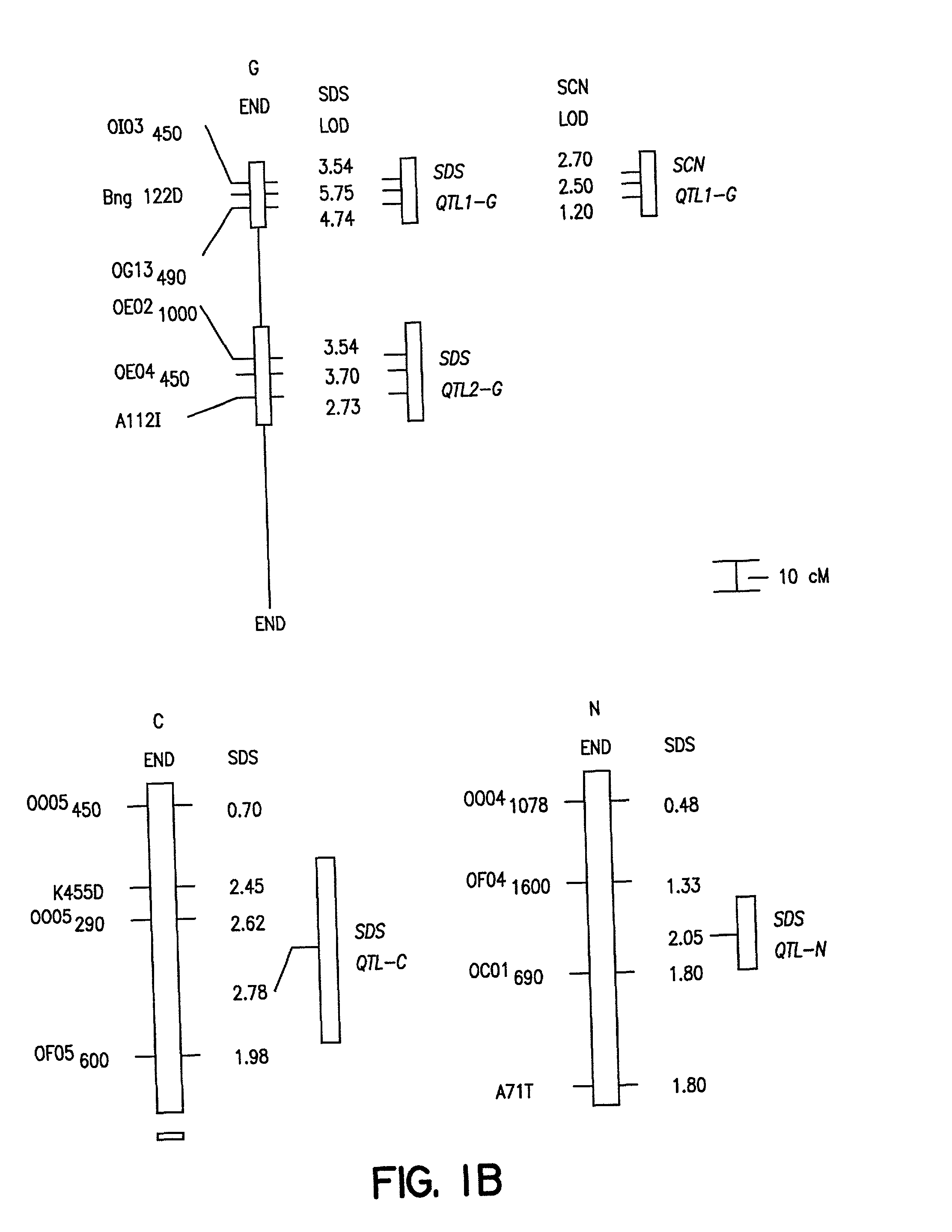
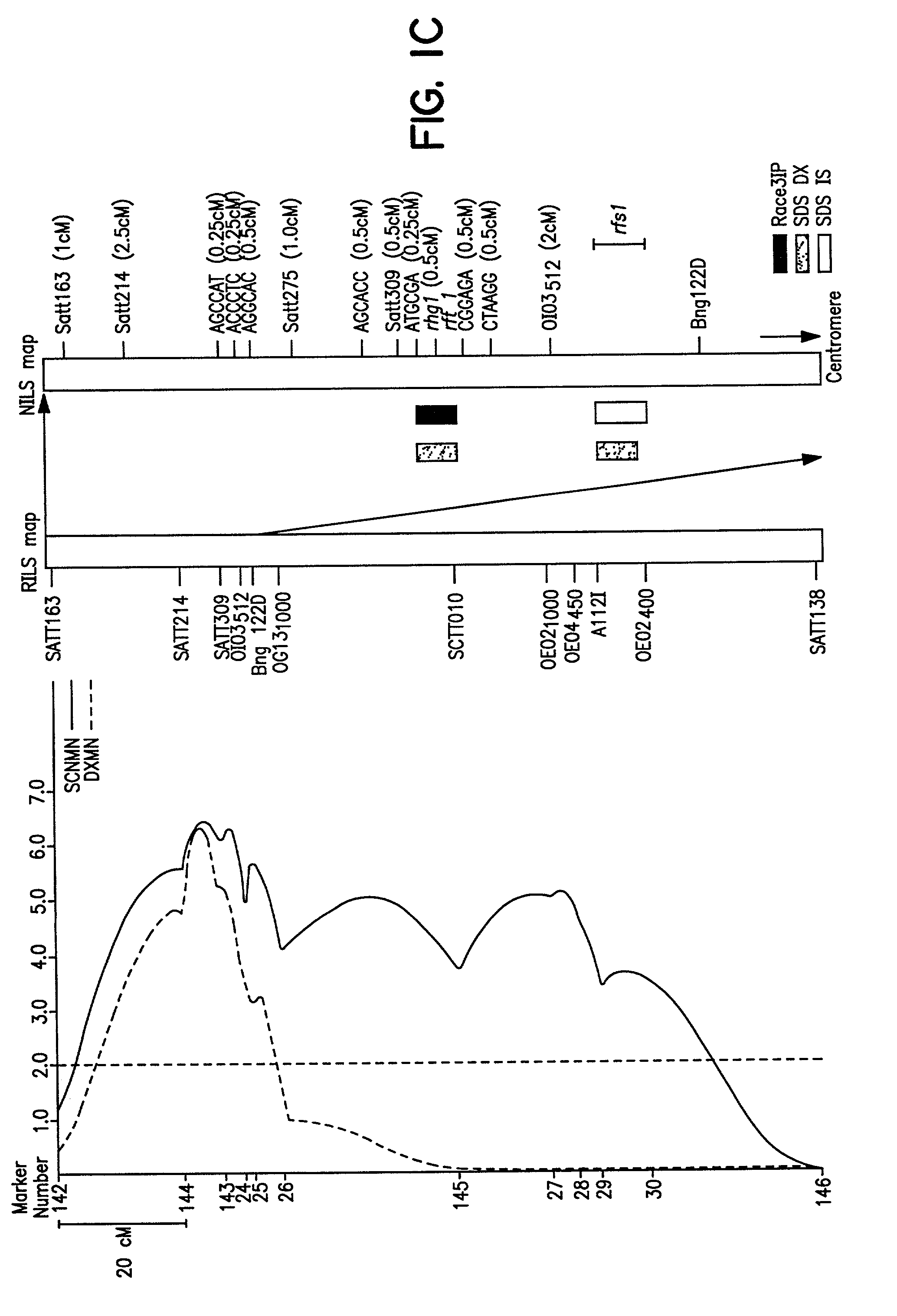
Soybean sudden death syndrome resistant soybeans, soybean cyst nematode resistant soybeans and methods of breeding and identifying resistant plants
InactiveUS20020129402A1Solves the problem quickly and cheaply selecting resistant cultivarsImprove selection for SDS and SCN resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyMarker-assisted selection
The invention provides a method of introgressing soybean sudden death syndrome (SDS) or soybean cyst nematode (SCN) resistance into non-resistant soybean germplasm. Loci associated with SDS resistance or with SCN resistance in soybean lines known to be resistant to SDS or to SCN are used in marker assisted selection during introgression of SDS or SCN resistance into elite germplasm. In addition, the method may be used to confirm selection of resistance in new soybean cultivars.
Owner:SOUTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY
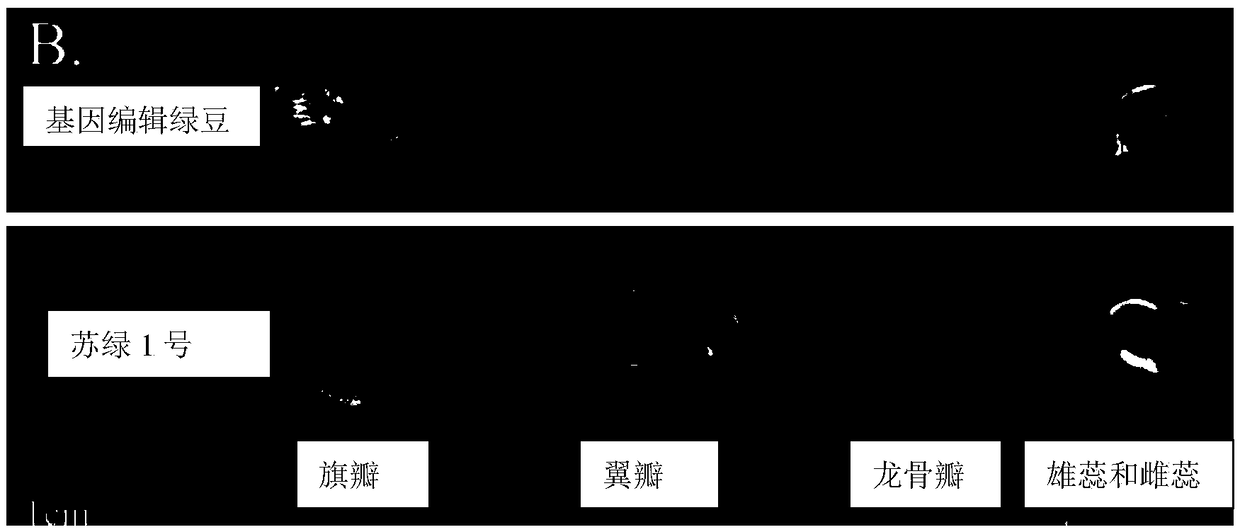
Method for breeding mung bean flowering pollination mutant based on CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing technology and special gRNA
InactiveCN108642078ASimple methodMethod orientationVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsGermplasmPetal
The invention discloses a method for breeding a mung bean flowering pollination mutant based on CRI SPR / Cas9 gene editing technology and a special gRNA. The method comprises the following steps of: transferring the CRISPR / Cas9 plasmid of a plant containing a gRNA sequence into a mung bean, and thereby, editing the ORF region of the Cha gene of the mung bean shown in SEQ ID NO. 1, wherein the DNA sequence corresponding to the gRNA is shown in any one of SEQ ID NO. 2 to SEQ NO. 21. According to the invention, a gene for coding the YUCCA protein of the mung bean is edited by using the CRISPR / Cas9gene editing technology, and a new mung bean germplasm with missing keel petals and exposed stigmas and anther is obtained, thus providing a basis for cross breeding of mung beans.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
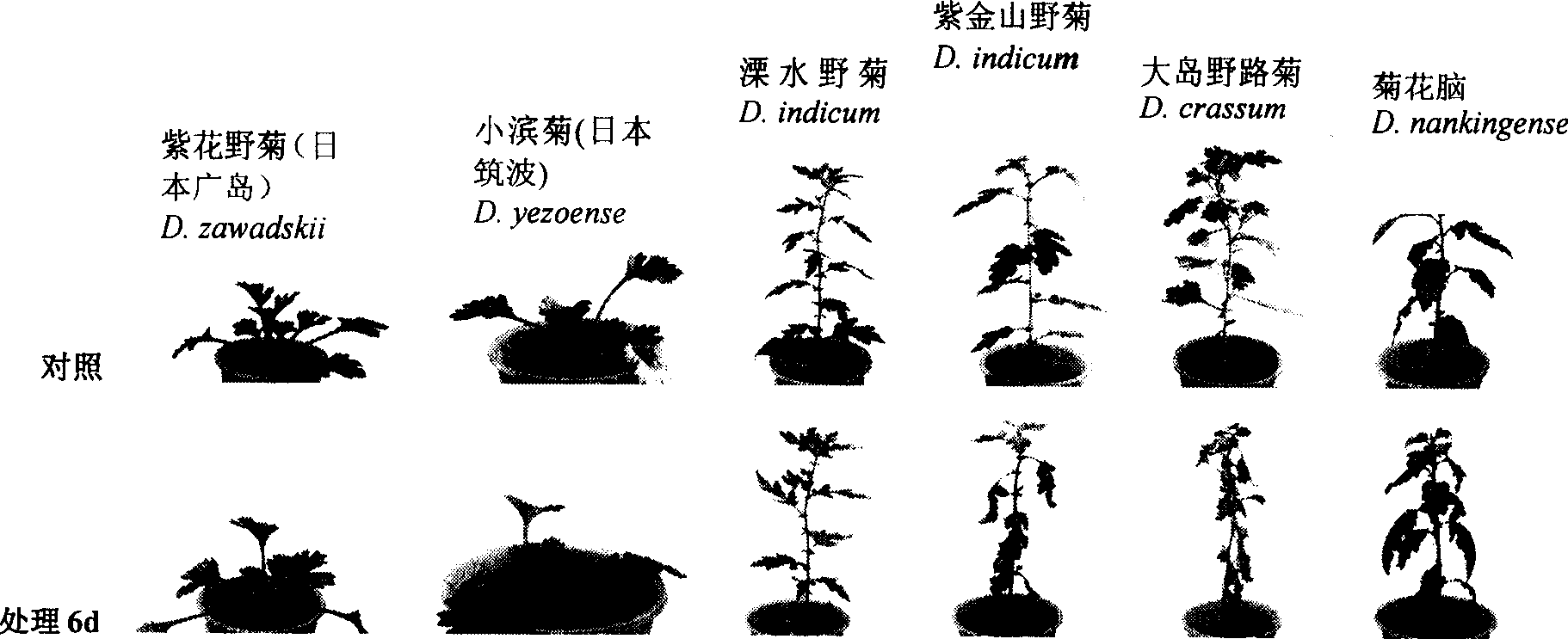
Evaluating and identifying method for waterlogging tolerance of chrysanthemum
The invention relates to an evaluation identification method for chrysanthemum flooding tolerance, belonging to the plant cultivation and breeding technical field, which comprises: according to the figure change of a chrysanthemum in blood, dividing the figure flood injury index into 7 levels, using four appearance figure indexes as leaf color, leaf figure, stem color and stem figure to quantitatively and classify the figure flood injury indexes, establishing a level score standard and an evaluation scheme, using the sum of the index scores to comprehensively evaluate the flooding tolerance, establishing an evaluation system; using a potted plant flooding identification method to process seedling stage flooding tolerance identification on 45 chrysanthemum closely related varieties, selecting 6 excellent varieties of strong flooding tolerance, and considering that the system can obtain reliable result. The invention establishes a fast and simple flooding tolerance evaluation system in first time and can evaluate and identify the flooding tolerance resources, to find the flooding tolerance level of chrysanthemum closely related varieties and establish a base for chrysanthemum flooding tolerance breeding and large-scale chrysanthemum varieties.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method to identify disease resistant quantitative trait loci in soybean and compositions thereof
ActiveUS20080166699A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGlycineQuantitative trait locus
The present invention is in the field of plant breeding and genetics, particularly as it pertains to the genus, Glycine. More specifically, the invention relates to a method for screening soybean plants containing one or more quantitative trait loci for disease resistance, species of Glycine having such loci and methods for breeding for and screening of Glycine with such loci. The invention further relates to the use of exotic germplasm in a breeding program.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
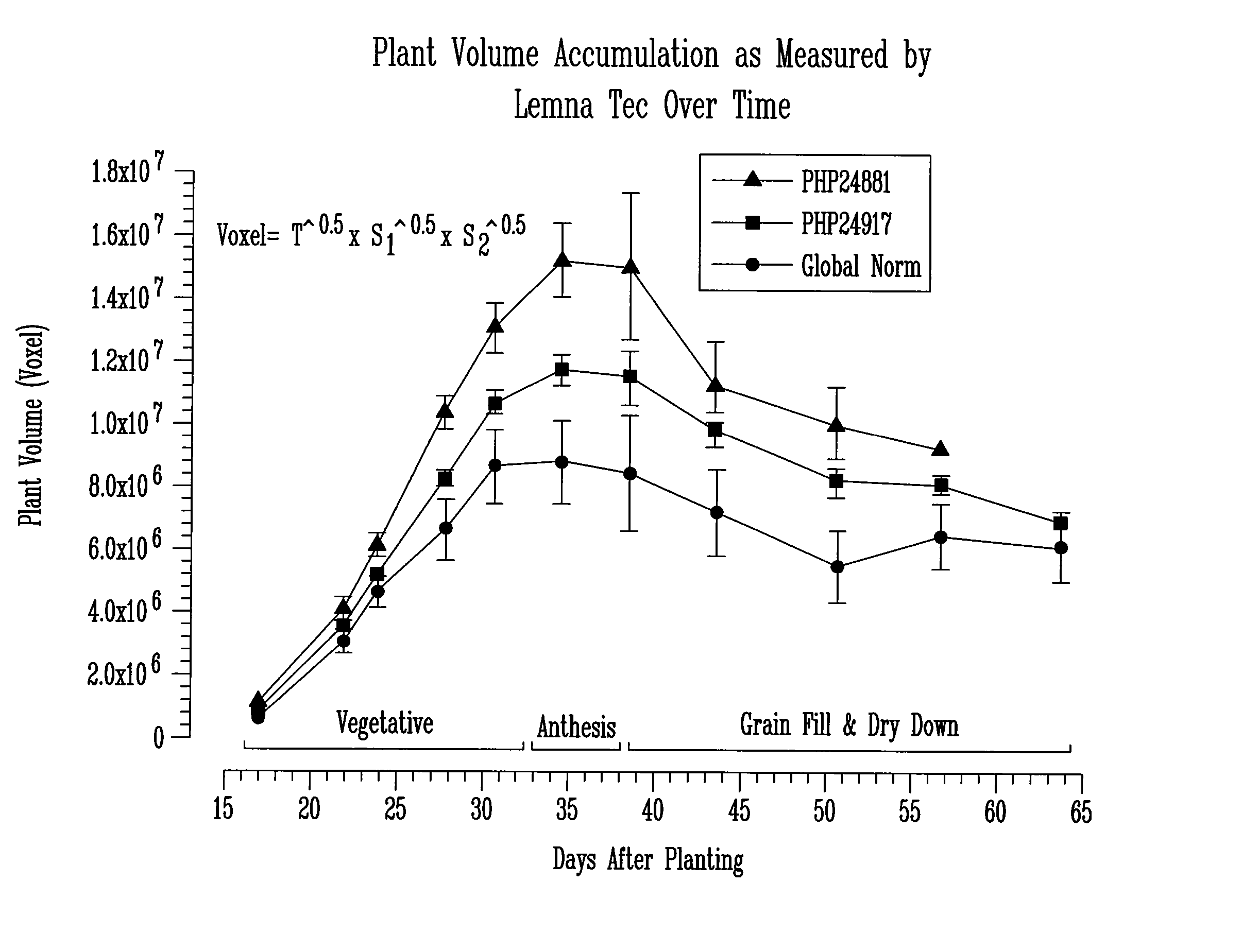
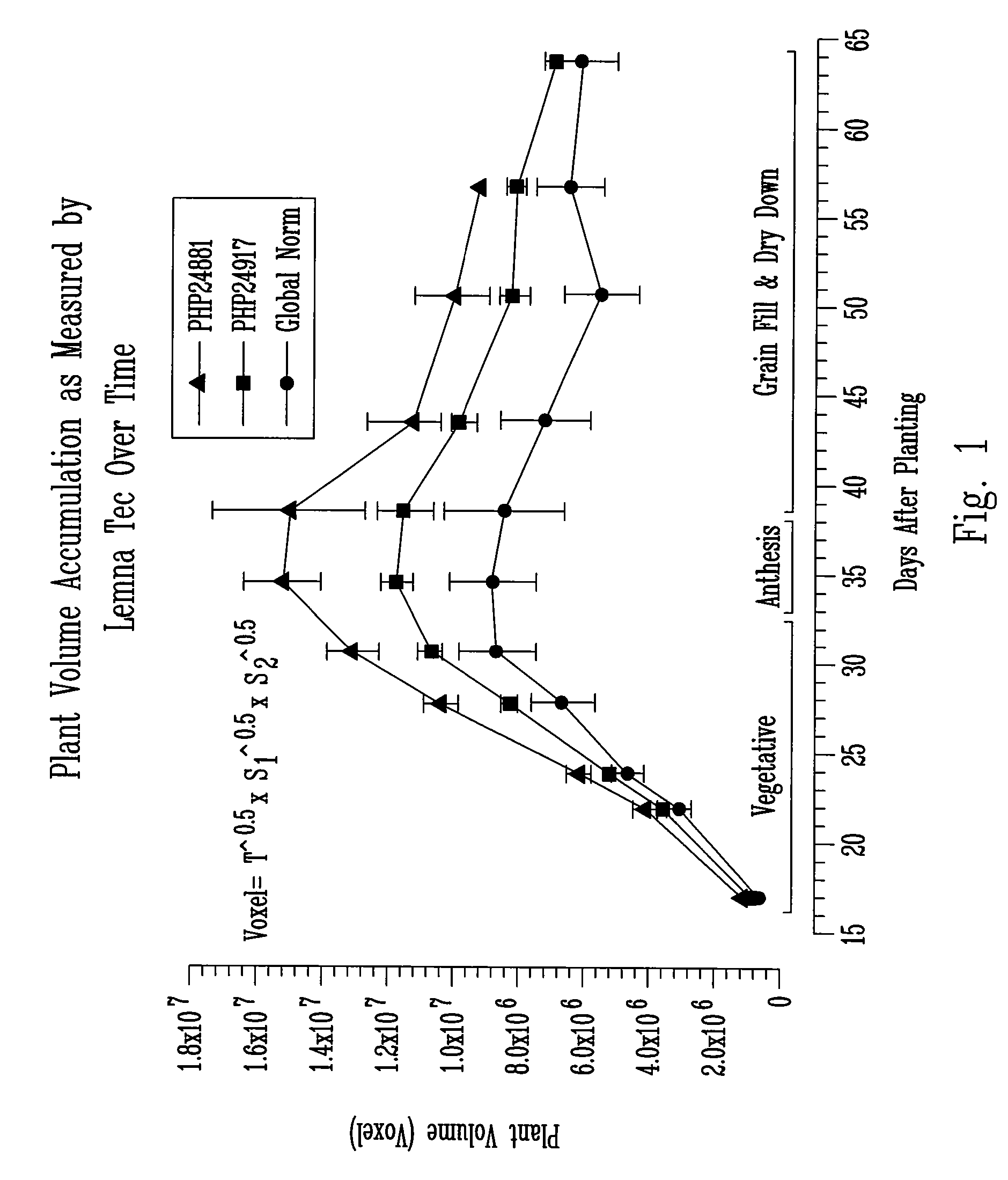
Method for high throughput transgene function analysis for agronomic traits in maize
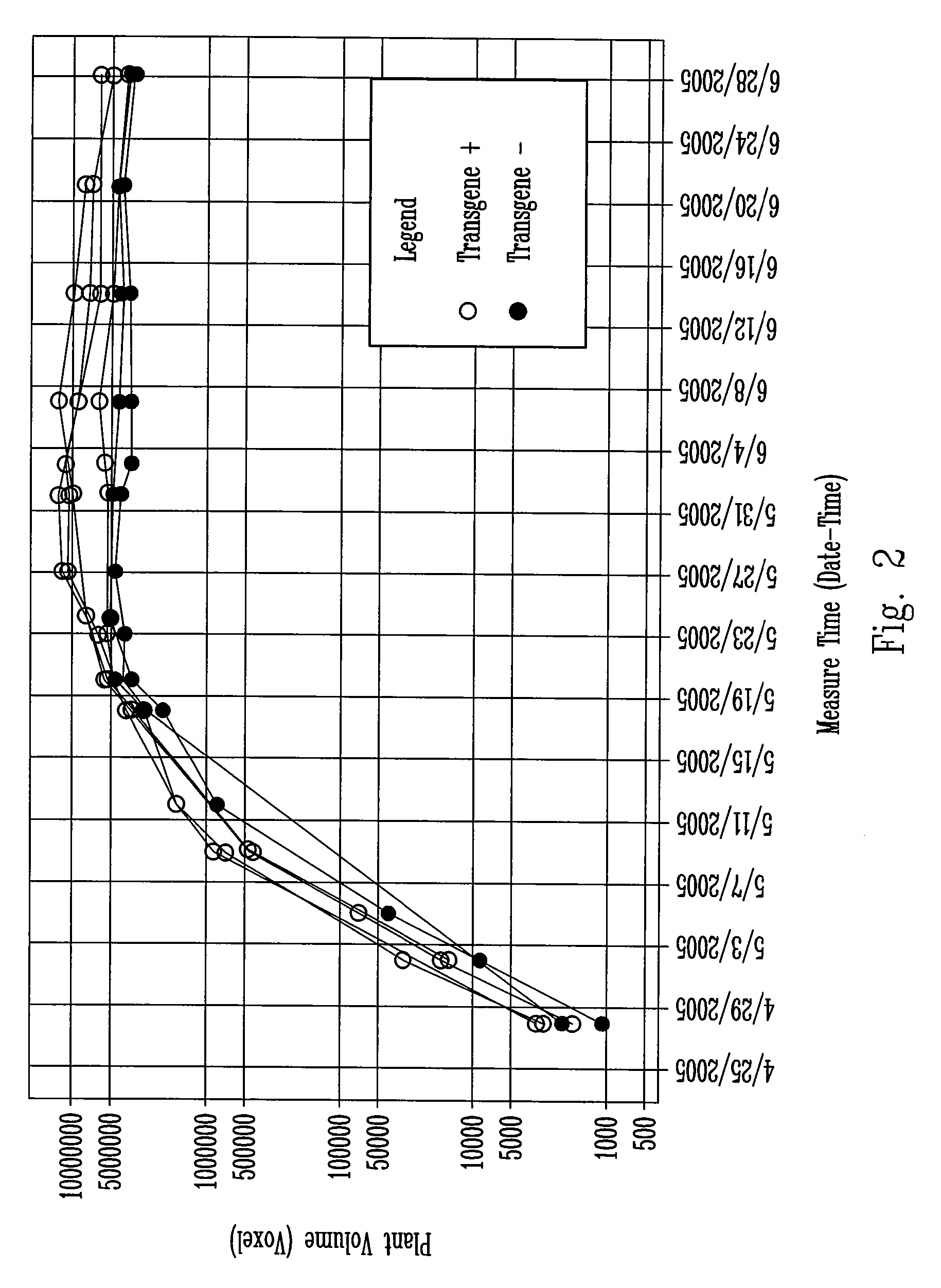
InactiveUS20070186313A1Determine effectRapid assessmentImage enhancementImage analysisGermplasmField trial
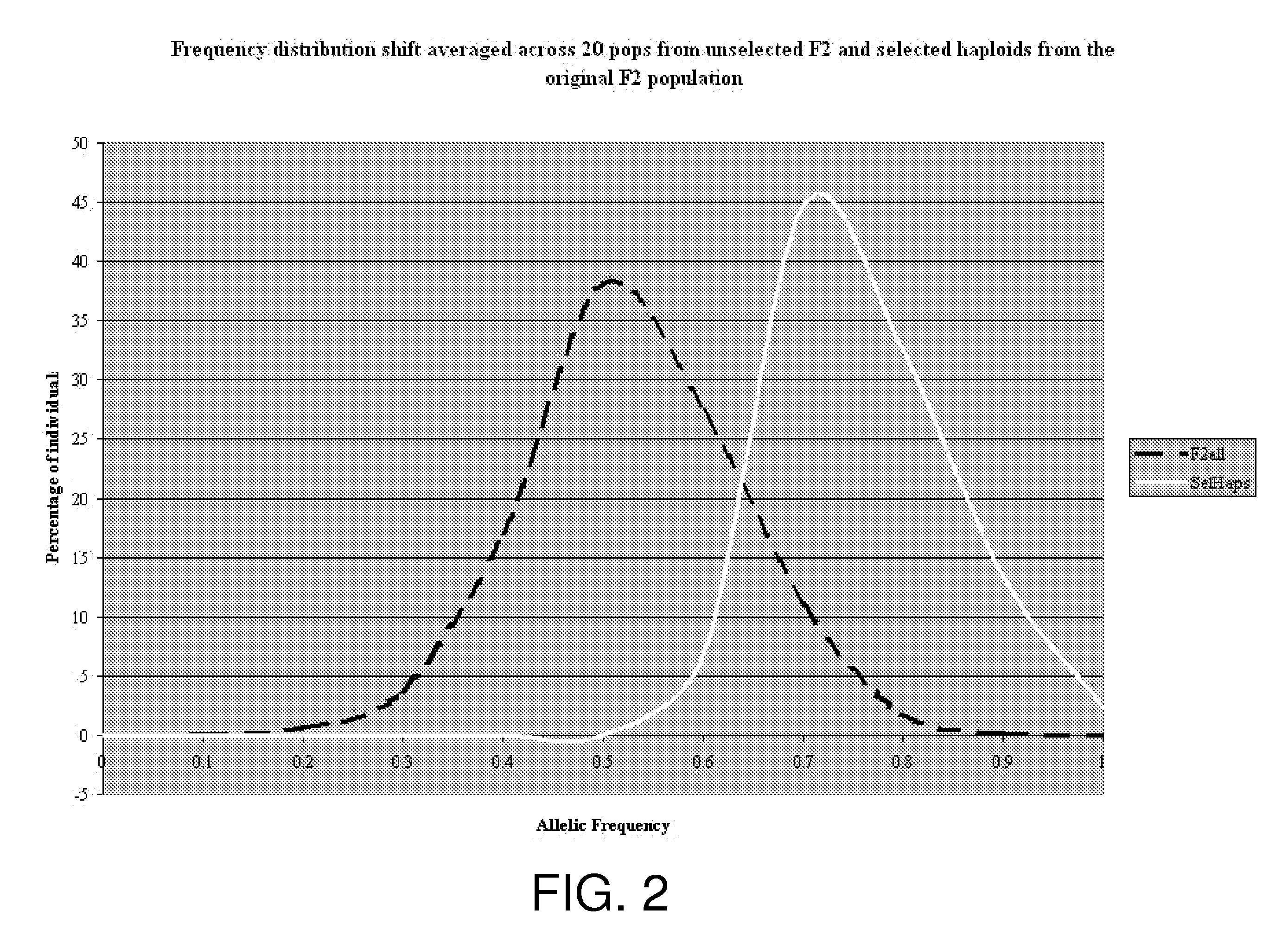
A method for the rapid evaluation of transgene function in maize plants. The method combines high throughput gene construction methods and high efficiency plant transformation techniques in a specifically developed germplasm. In one as aspect, the method uses quantitative, non-destructive imaging technology applied in a portion or throughout the entire life cycle of a test plant to evaluate agronomic traits of interest in a controlled, statistically relevant greenhouse environment. The method reports transgene function early in the transgenic variety development process, eliminating the need to generate seed necessary for multi-location replicated field trials.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Virus removal and rapid propagation technology of sweet potato variety 'Shangshu 19' and culture material
InactiveCN101611697AImprove immunitySolve the serious sweet potato virus diseaseCultivating equipmentsPlant tissue cultureDiseaseGermplasm
The invention is a virus removal and rapid propagation technology of sweet potato variety 'Shangshu 19', comprising the following steps: selecting plants which are robust without diseases and insect pests and have characteristics of the variety from growing plants; clipping stem with stem tip; removing visible leaves; sterilizing; peeling the stem tip with 1-2 leaf primodia via a dissecting needle; quickly inoculating into a differentiation and induction culture medium; trimming the sterilized seedling into stem segments with 1-2 internode(s) and switching into an enrichment medium after virus detection; selecting sterilized seedling in vigorous growth to cut into small segments with 1-2 internode(s) and switch into a rooting medium; carrying out domestication on seedling after rooting. The invention has stem tip in virus removal and stem segment in rapid propagation, solves the problems of severe virus disease for sweet potato, poor quality of new cultured breed, germplasm degradation, low yield and the like propagated by using sweet potato block and stem. The invention can artificially control the growing conditions, can not be influenced by nature, and has the advantages of small amount of material use, economical culturing materials, short growth cycle, large propagation coefficient and convenient management and is favor of industrial production.
Owner:周玉玲
Porphyra yezoensis microsatellite marker screening method and use thereof
InactiveCN101550434AImprove reliabilityHigh yieldMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationResource protectionGermplasm
The invention belongs to molecular biology DNA labeling technique and application field, concretely relates to a porphyra yezoensis microsatellite marker screening method, and a method for analyzing germplasm genetic diversity by the makers, thereby lay foundations for genetic structure analysis of porphyra yezoensis, germplasm resource protection and molecular marker auxiliary breeding.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Cultivation method of white peony root
InactiveCN101889520APromote sustainable developmentQuality improvementHarvestersPlant protectionDiseaseGermplasm
The invention discloses a cultivation method of white peony root, comprising the following steps of: site selection and soil preparation, propagation and cultivation, field management, disease and pest control, harvesting and processing as well as packaging, storage and transportation. The invention has remarkable social, economic and ecological benefits as follows: (1) germplasm for producing white peony can be unified and optimized, and the quality of the white peony can be greatly improved and stabilized by large-area popularization, thereby playing a role of realizing the standardized cultivation of the white peony root, prompting the modernization progress of the white peony root industry in China and satisfying the social medicinal requirements; (2) a germplasm support is provided for the standardized cultivation of the white peony root, which is beneficial to improving the yield of the white peony root medicine, laying a favorable foundation for realizing the production scale and industrialization and promoting the sustainable development of the white peony root industry; and (3) by storing and optimizing the germplasm resources, the cultivation method is beneficial to maintaining the biological diversity and lays the foundation for the sustainable development and utilization of the white peony root resources.
Owner:安徽沪谯中药科技有限公司
Breeding method of high-quality disease-resistant high-temperature-resistant rice two-line sterile line
ActiveCN104839010AImprove the rice polishing rateGood outbreeding characteristicsPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyGermplasm
The invention relates to a breeding method of a high-quality disease-resistant high-temperature-resistant rice two-line sterile line, and belongs to the technical field of crop genetic breeding. The method is involved in rice germplasm breeding with long grain polymerization, high head rice rate and excellent economical characters such as high seed production temperature resistance and disease resistance, and the rice two-line sterile line with long grains, high head rice rate, high seed production temperature resistance, good out-crossing feature, stable fertility, good disease resistance and excellent comprehensive characters are bred. Great assembling is carried out by utilizing the sterile line, and a novel two-line hybrid rice assembly which is high in quality, disease-resistant and beneficial for seed production is screened out hopefully.
Owner:FUJIAN KINGSANTO DEV CO LTD
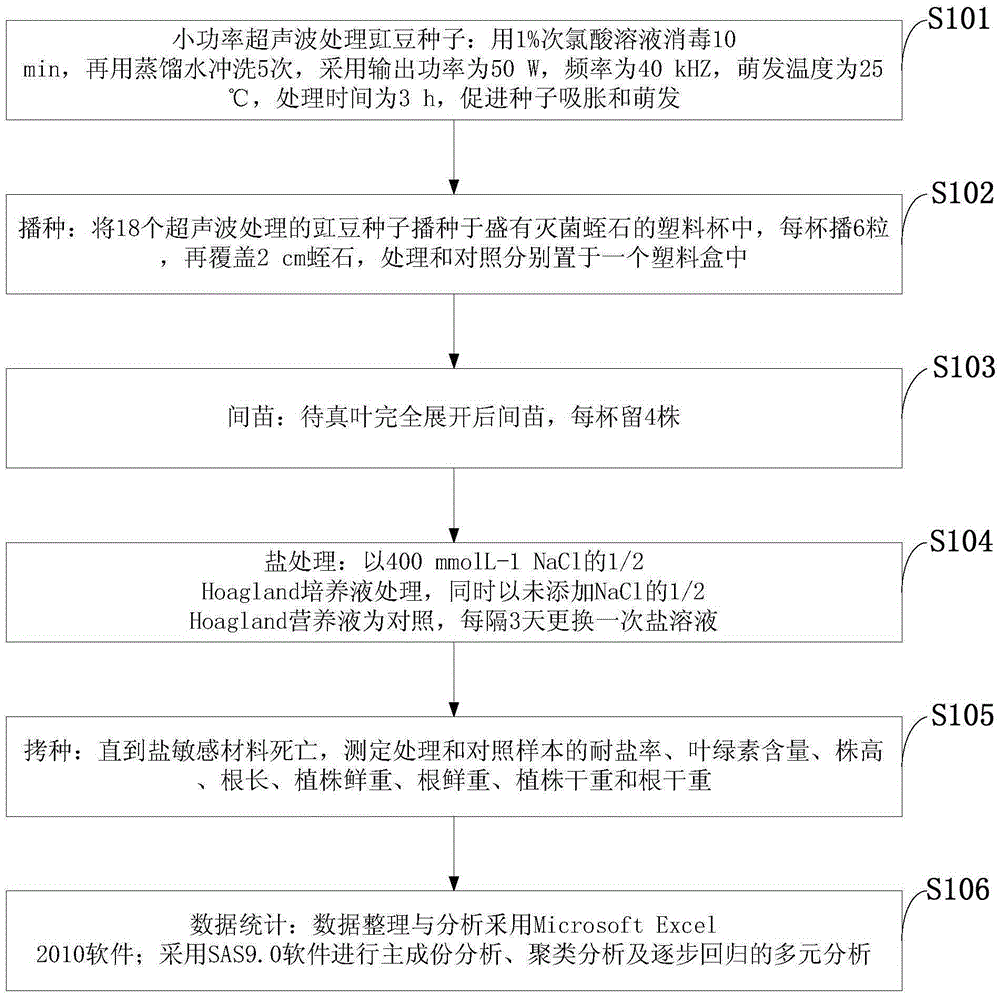
Identification method of salt-tolerant resource in seedling period of cowpea
InactiveCN105325192ASeed and root treatmentHorticulture methodsDry weightPrincipal component analysis
The invention discloses an identification method of a salt-tolerant resource in the seedling period of cowpea, which is easy to operate and reliable in identification result. The identification method comprises the steps of carrying out germination experiment by adopting one cowpea variety to screen the optimal ultrasonic treatment method and determine the germination conditions; carrying out salt treatment experiment on three varieties by adopting salt solutions of multiple gradients to determine the optimal treatment condition; carrying out salt-tolerant experiment on 18 cowpea varieties of different genes, and carrying out principal component analysis to determine the optimal regression model. The identification method is used for identifying the salt-tolerant capability of the cowpea with 15d, and is short in identification time; the optimal salt-tolerant indexes of the cowpea are plant height, root length, plant dry weight and root dry weight, the identification method with simple operation and definite index is established, the shape indexes are visualized and convenient to count, and the standard identification method is provided for large-scale rapid identification of salt tolerance in the seedling period of the germplasm resource of the cowpea as well as the salt-tolerant variety selection and salt-tolerant mechanism.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com