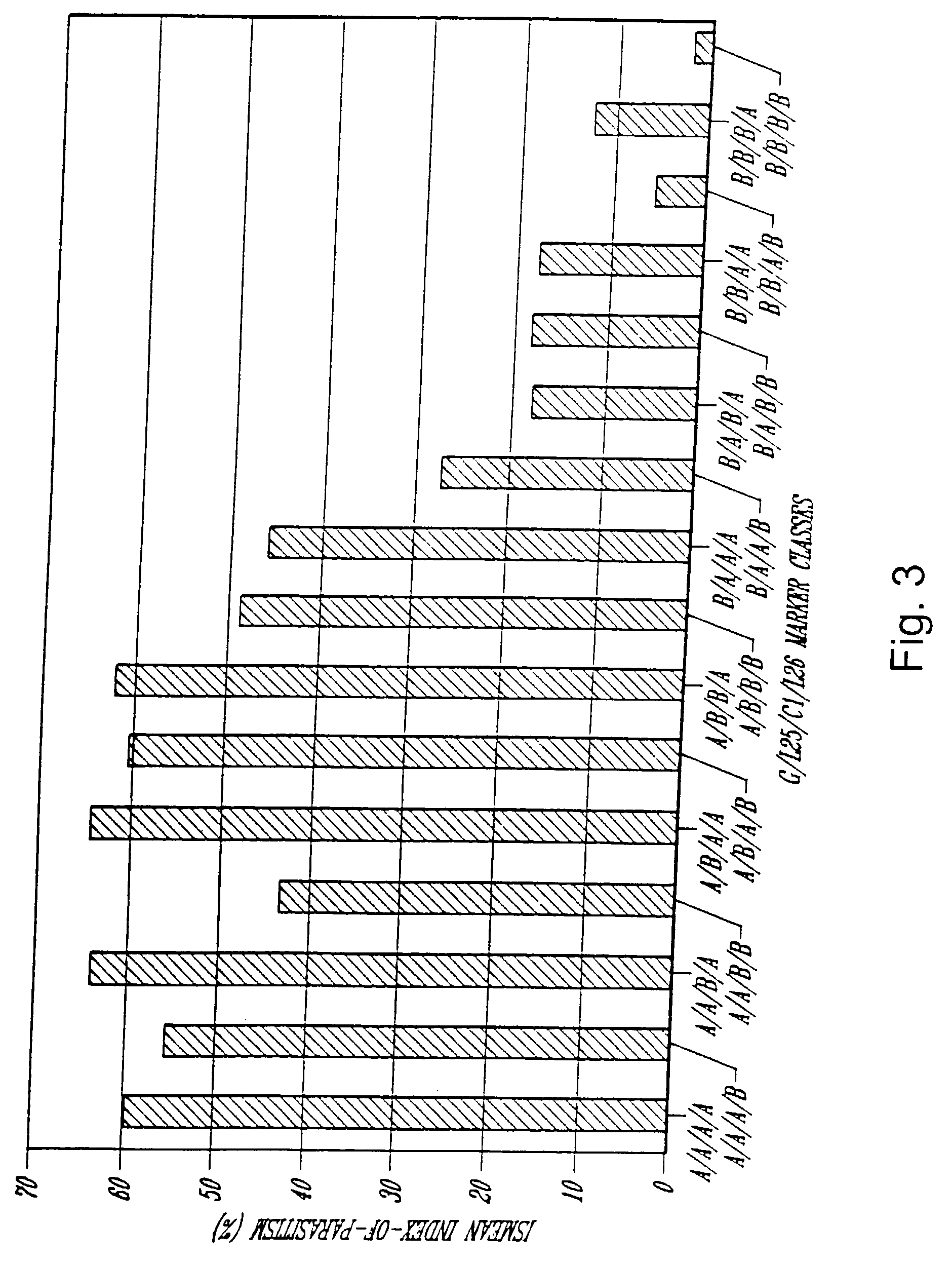
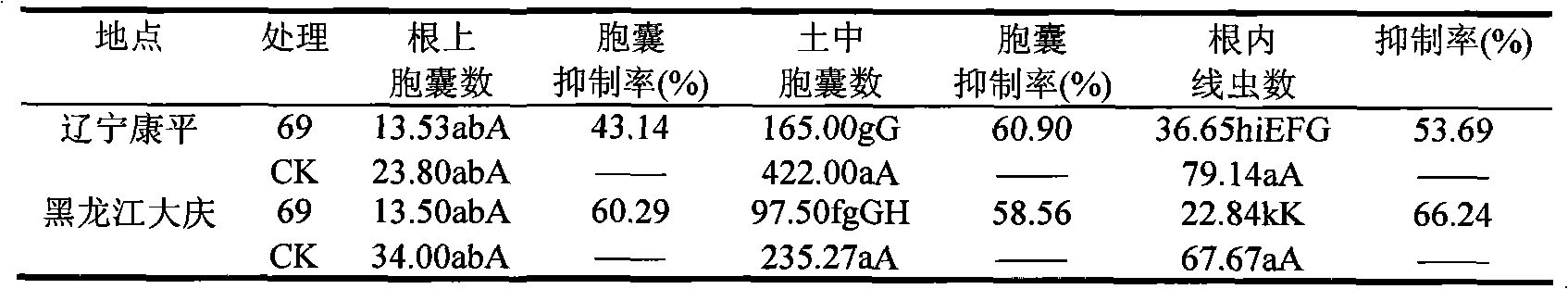
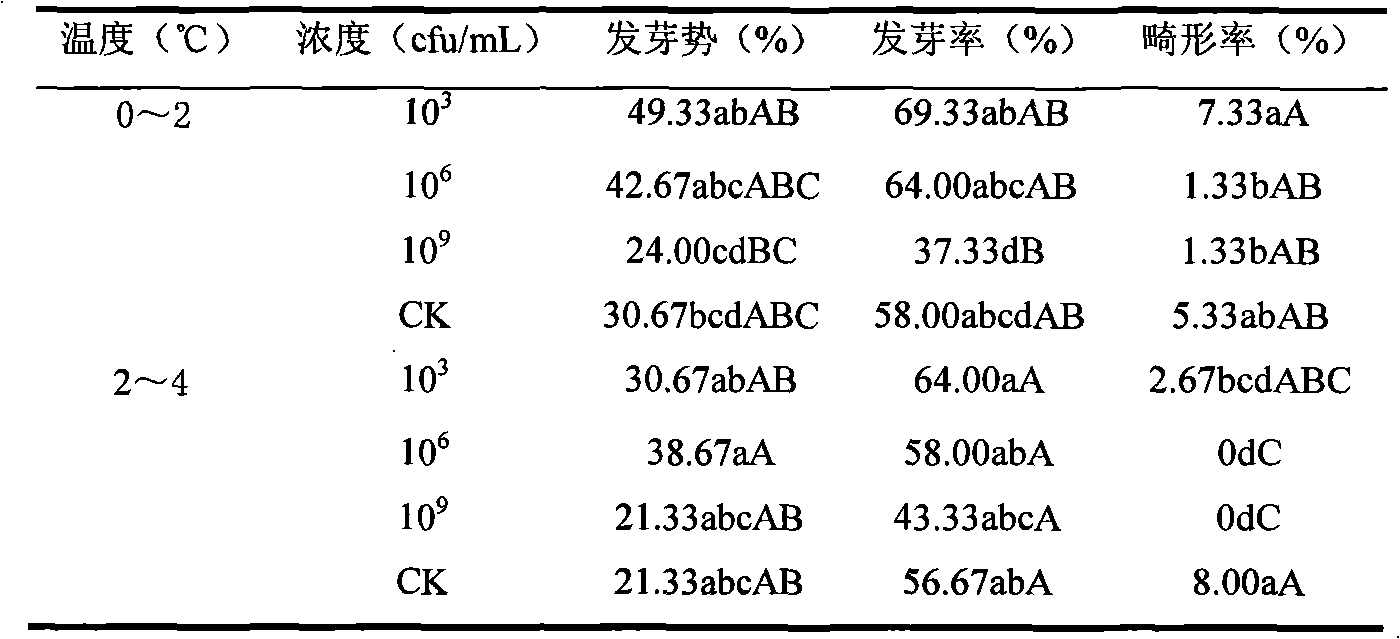
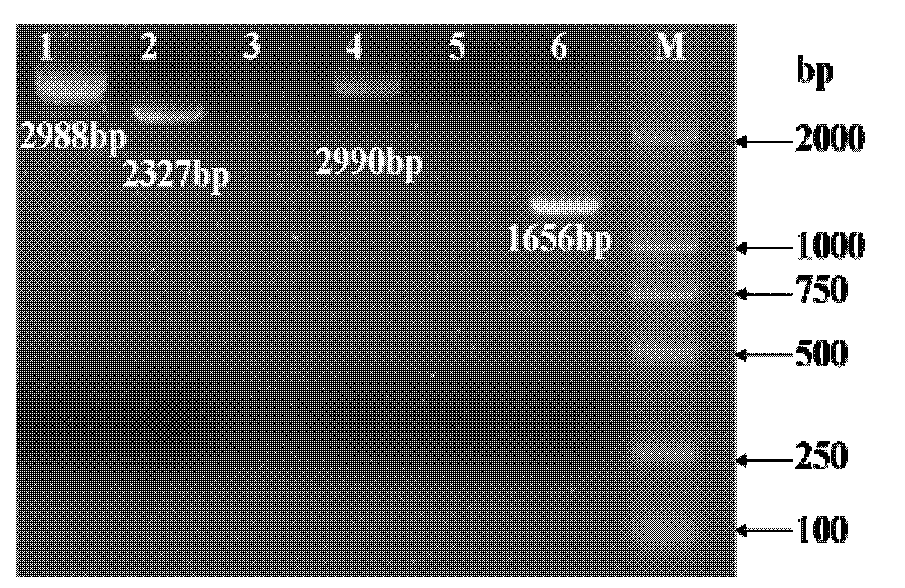
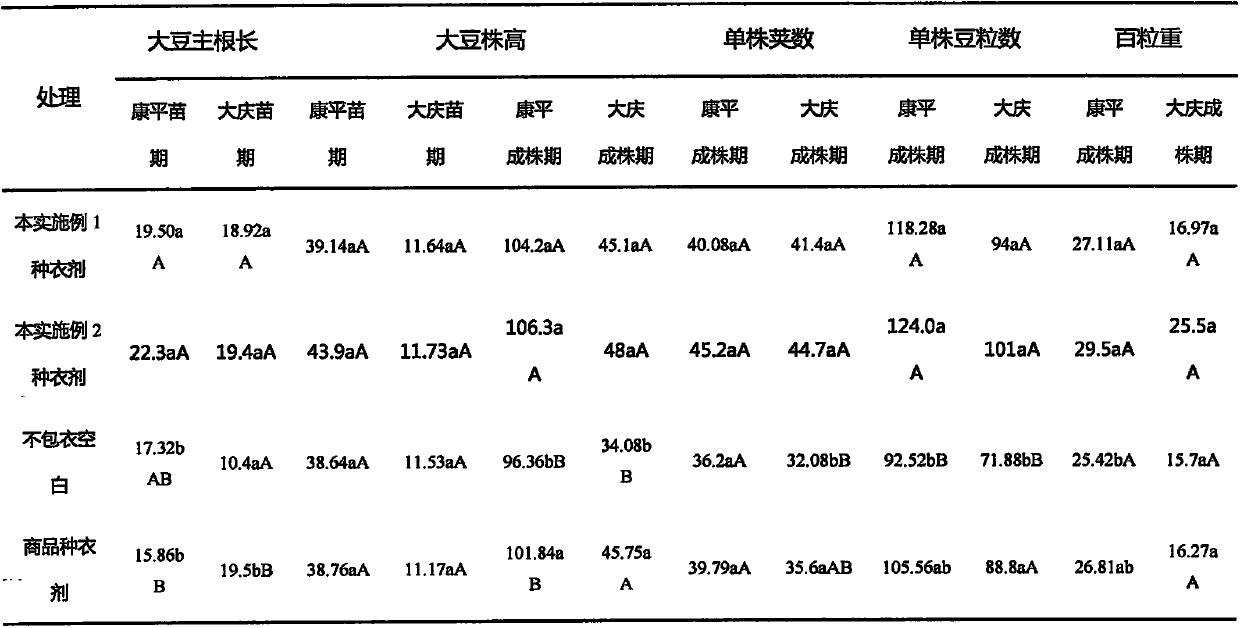
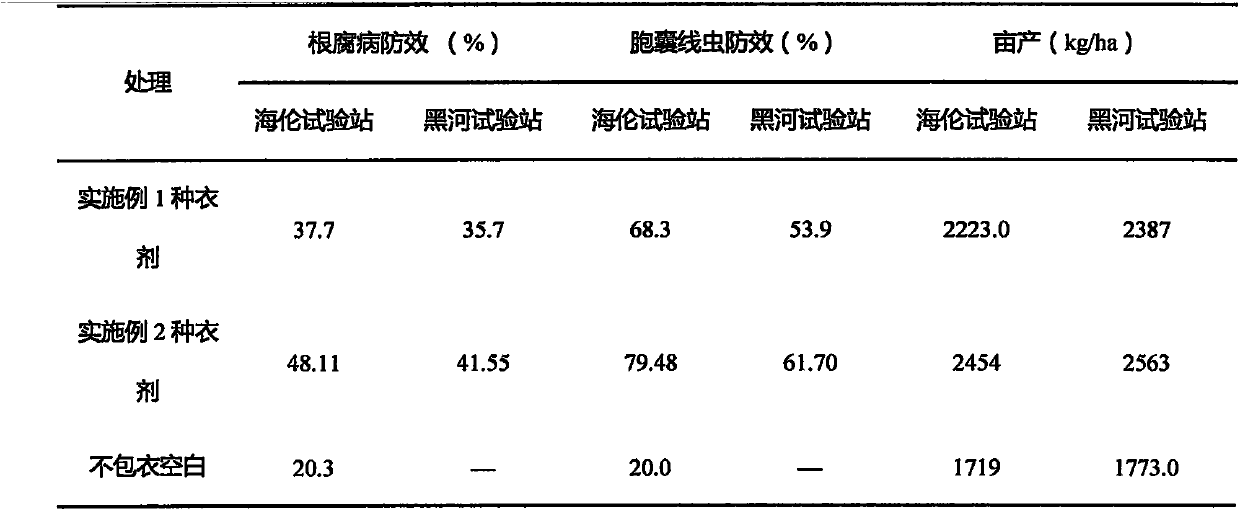
Patents
Literature
157 results about "Soybean cyst nematode" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The soybean cyst nematode (SCN), Heterodera glycines, is a plant-parasitic nematode and a devastating pest of the soybean (Glycine max) worldwide. The nematode infects the roots of soybean, and the female nematode eventually becomes a cyst. Infection causes various symptoms that may include chlorosis of the leaves and stems, root necrosis, loss in seed yield and suppression of root and shoot growth. SCN has threatened the U.S. crop since the 1950s, reducing returns to soybean producers by $500 million each year and reducing yields by as much as 75 percent. It is also a significant problem in the soybean growing areas of South America and Asia.
Automated plant analysis method, apparatus, and system using imaging technologies
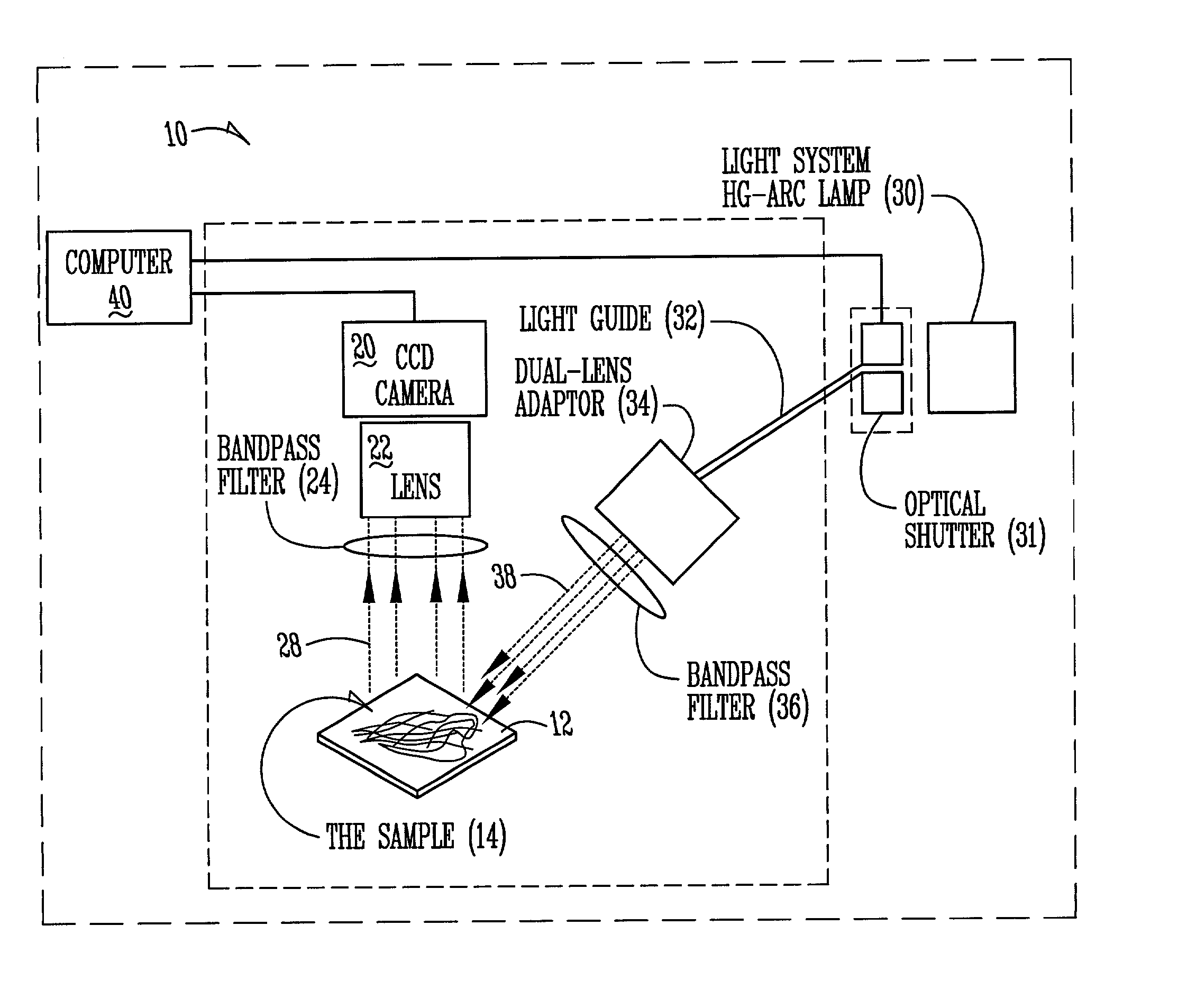
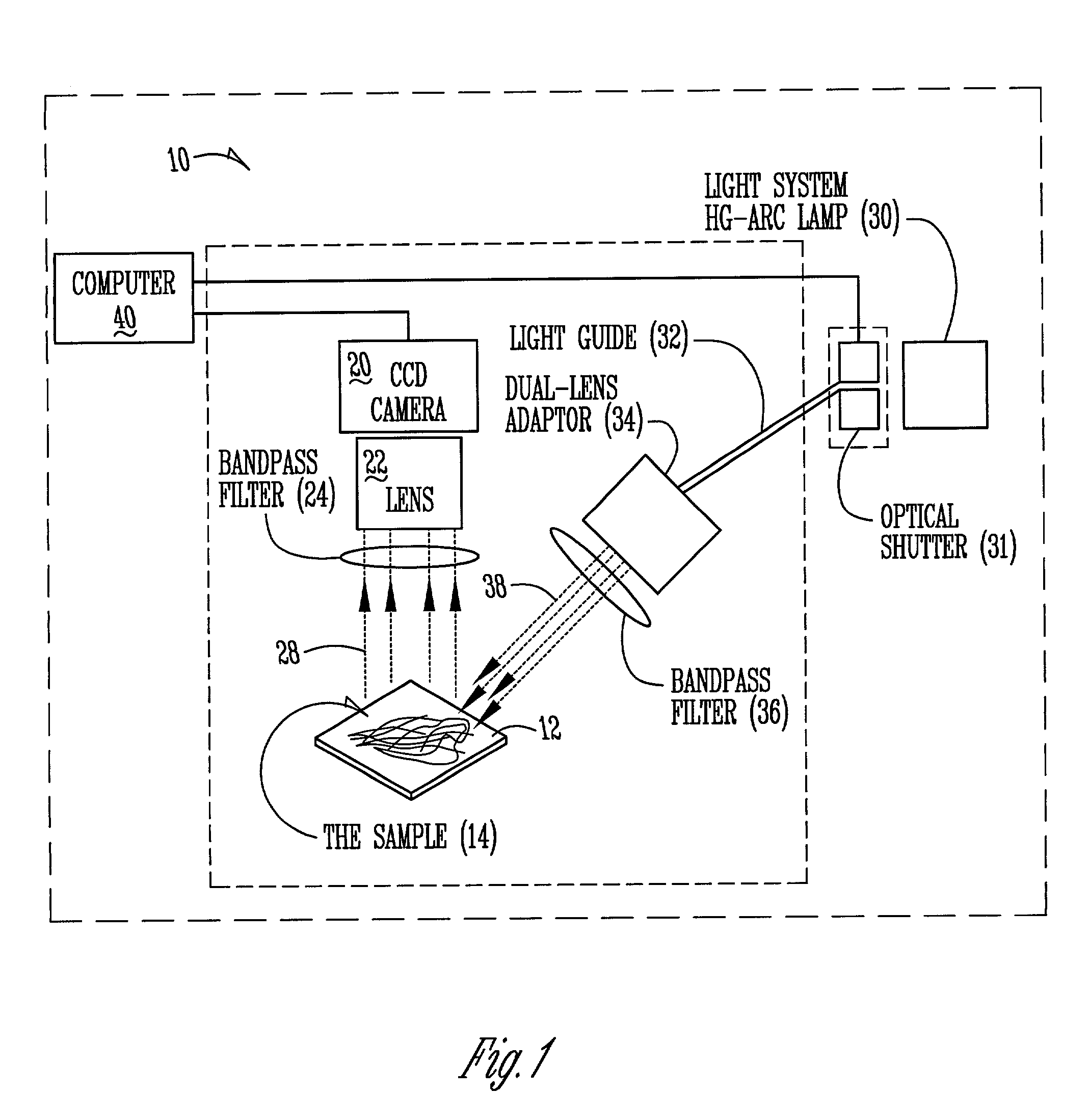
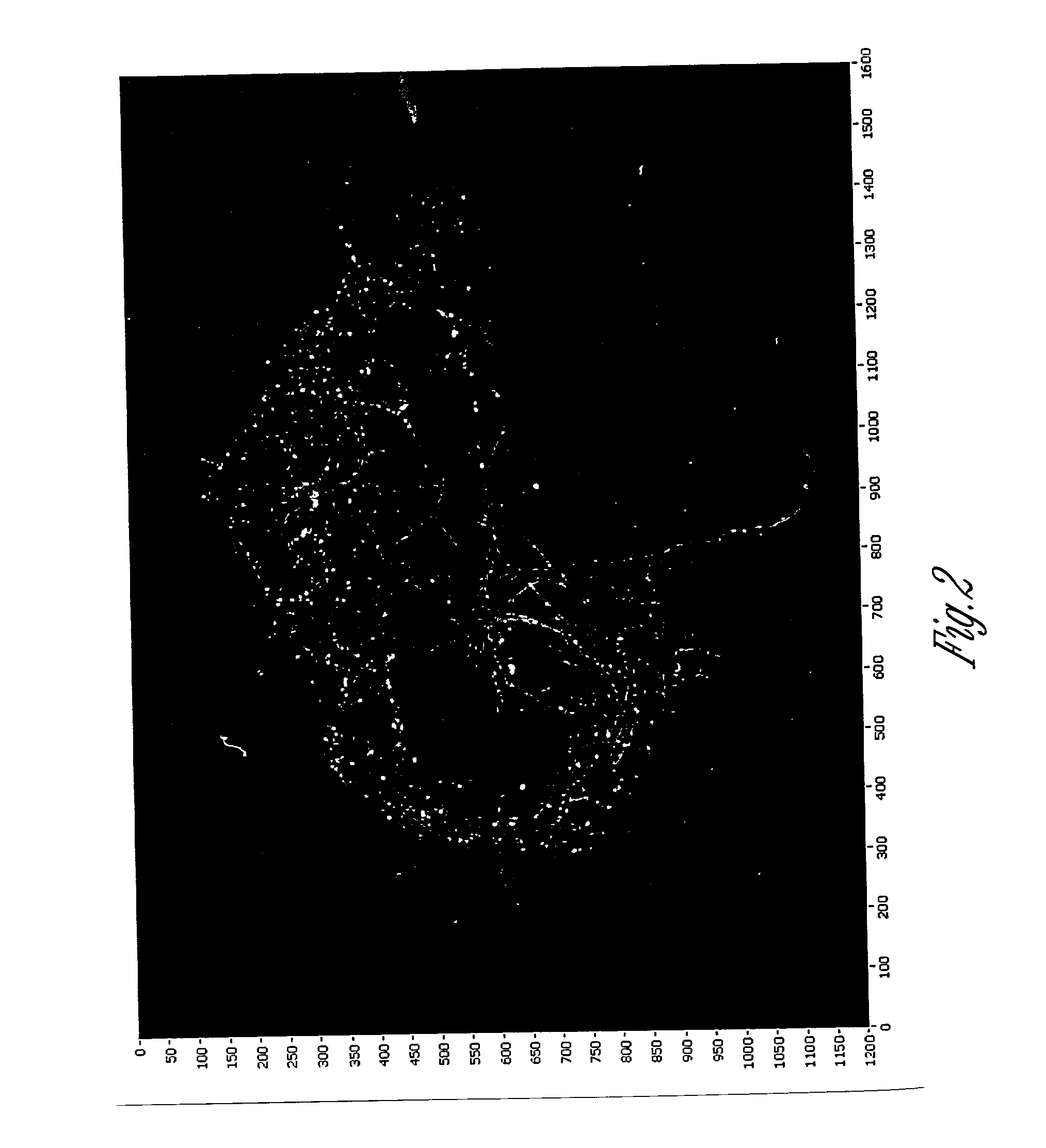
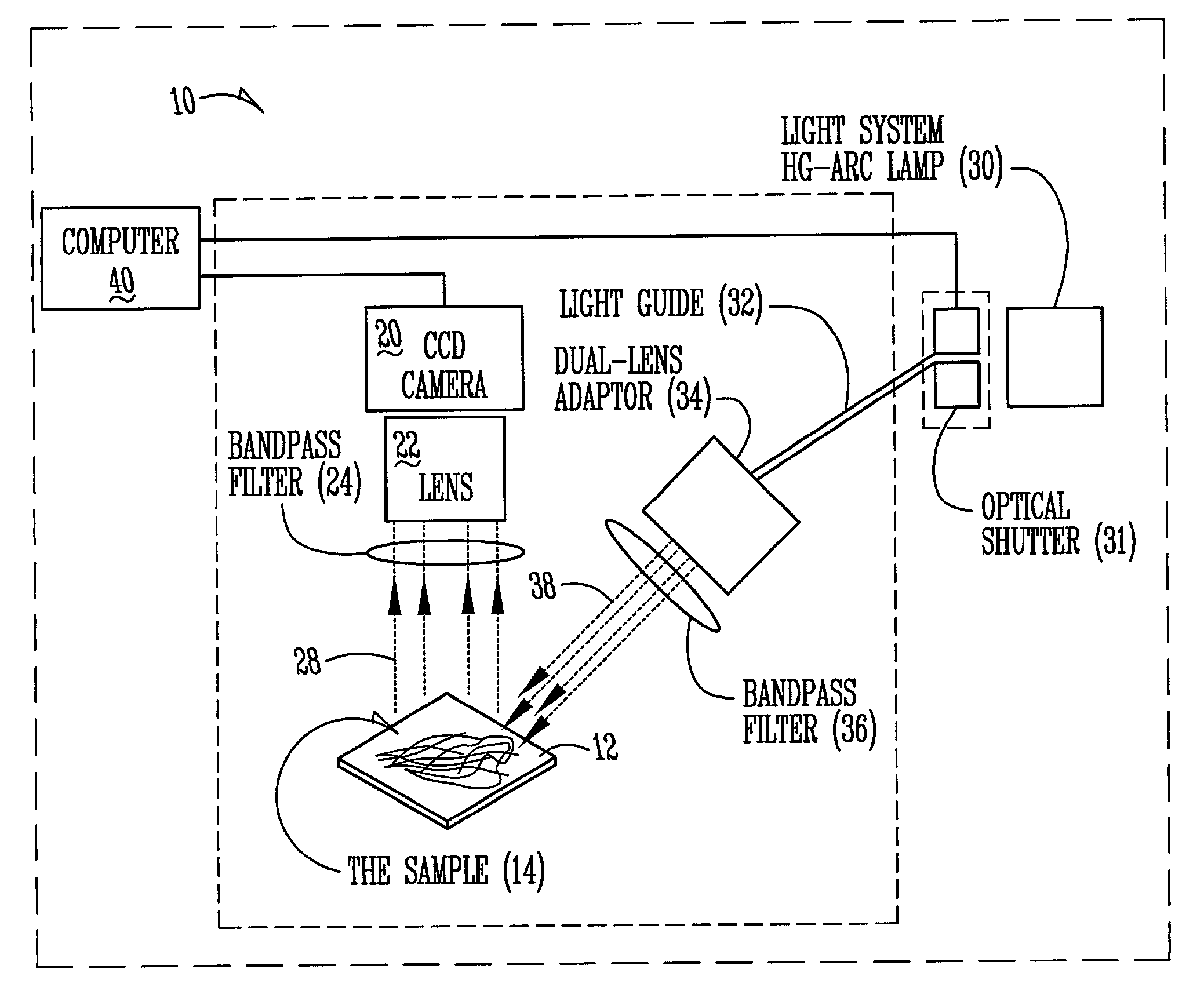
ActiveUS20030142852A1Promotes good identificationPromotes discriminationRadiation pyrometryColor measuring devicesPlant rootsCyst
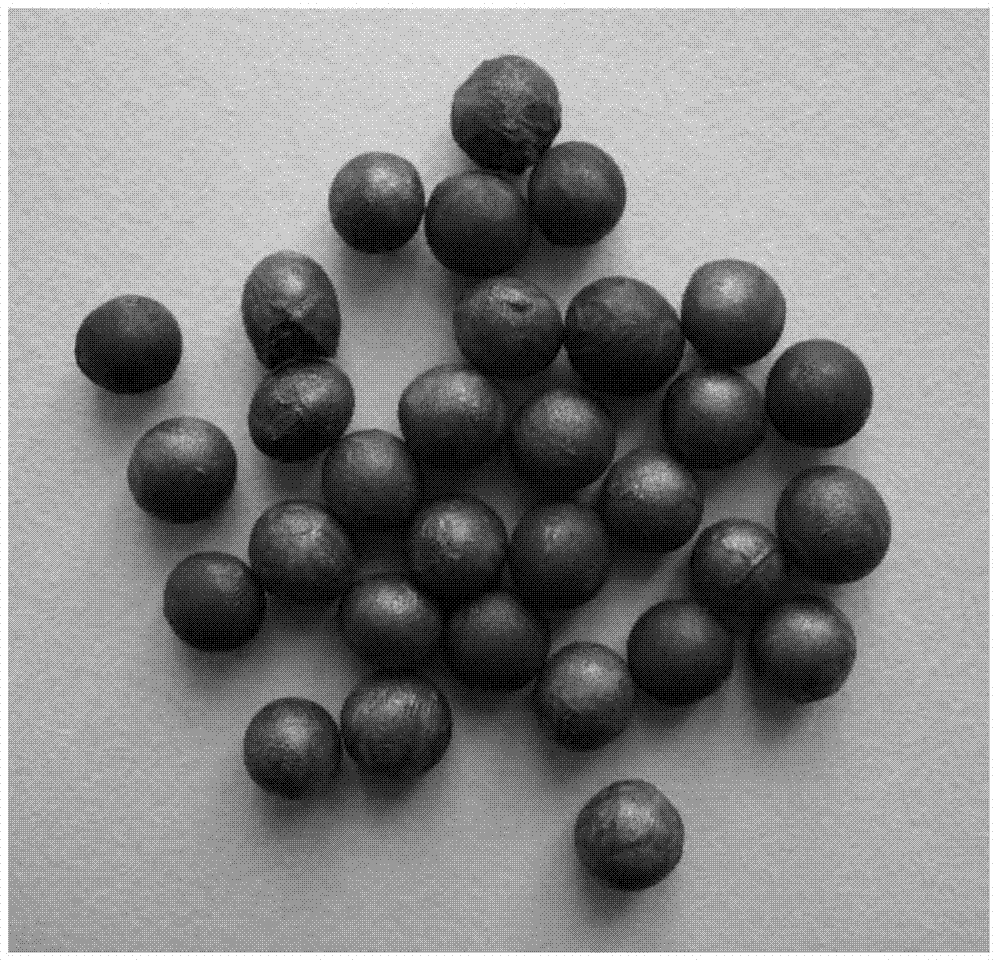
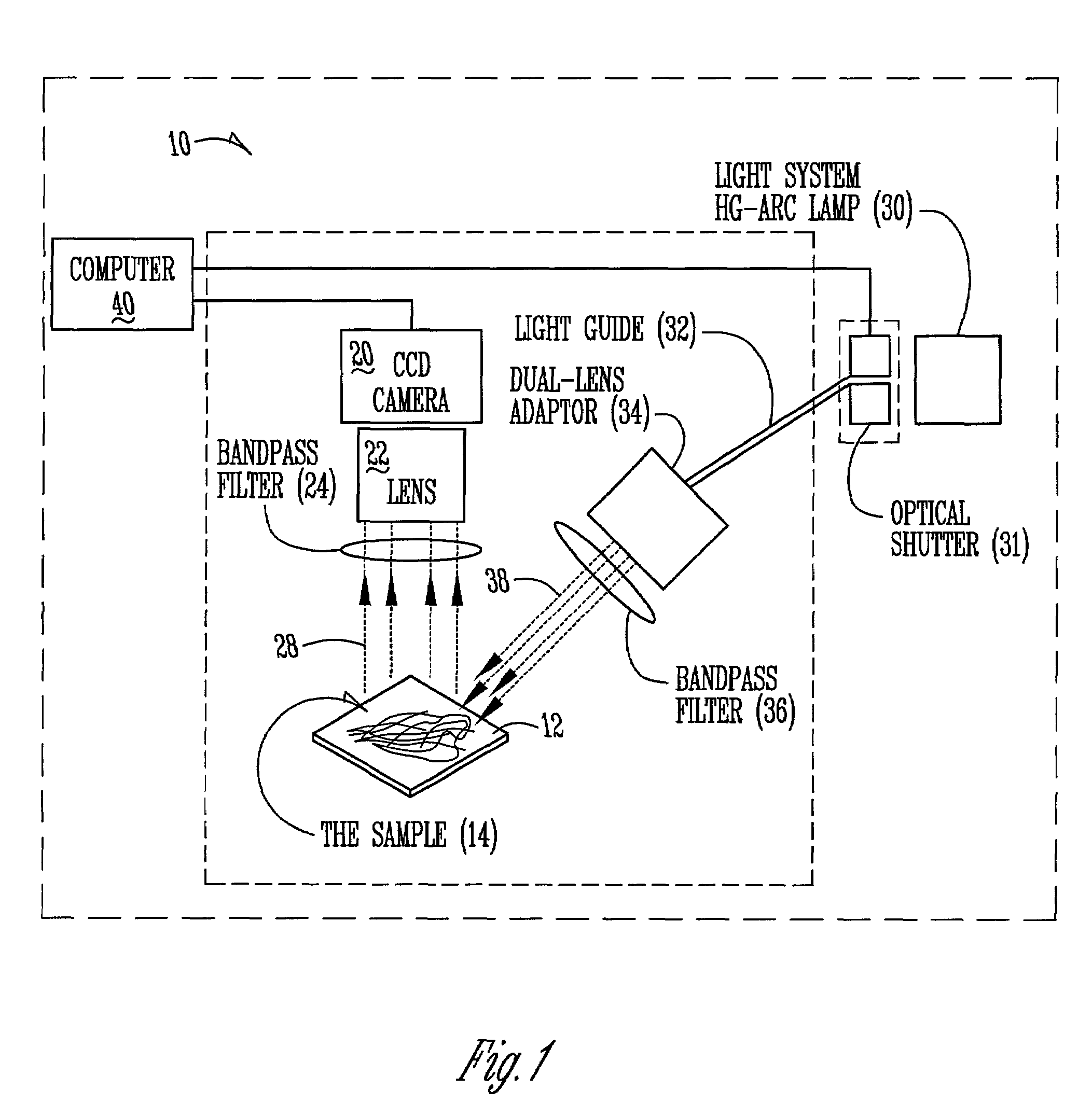
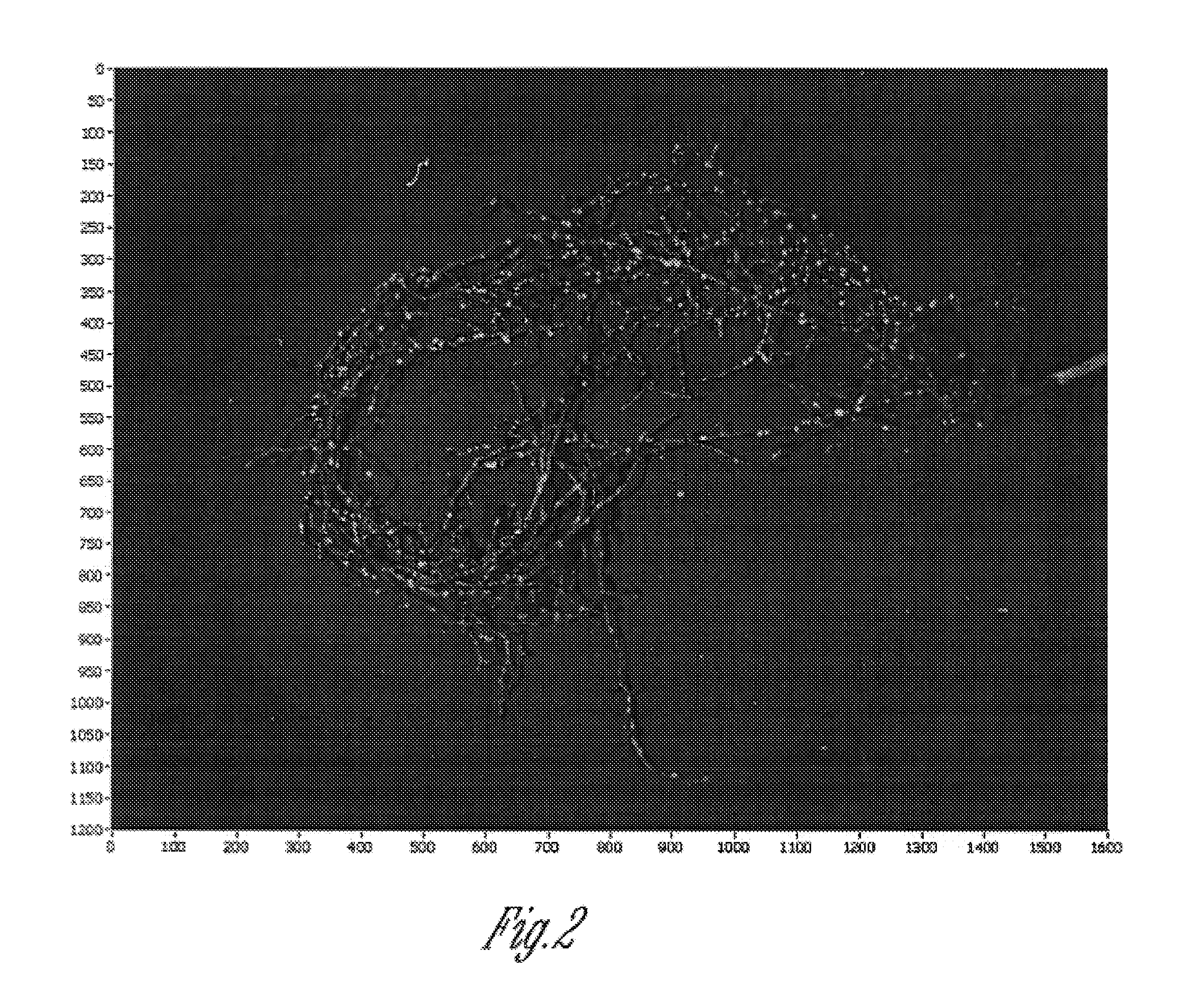
The present invention relates to an apparatus, method, software algorithm and system for evaluating plants for conditions or characteristics. In one aspect, the method can include imaging at least a portion of the plant and evaluating the image for discriminating condition(s) or characteristic(s) of interest. In one example, soybean roots are imaged and the image is evaluated to discriminate between soybean cyst nematode (SCN) cysts and the plant roots to count the number of SCN cysts for the plant. In another embodiment, a plant is illuminated by a ultra-violet radiation selected to cause photo-induced fluorescence of a target, e.g. SCN cysts. The fluorescence emitted is collected and analyzed to discriminate between the target and the remainder of the plant.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Automated plant analysis method, apparatus, and system using imaging technologies
The present invention relates to an apparatus, method, software algorithm and system for evaluating plants for conditions or characteristics. In one aspect, the method can include imaging at least a portion of the plant and evaluating the image for discriminating condition(s) or characteristic(s) of interest. In one example, soybean roots are imaged and the image is evaluated to discriminate between soybean cyst nematode (SCN) cysts and the plant roots to count the number of SCN cysts for the plant. In another embodiment, a plant is illuminated by a ultra-violet radiation selected to cause photo-induced fluorescence of a target, e.g. SCN cysts. The fluorescence emitted is collected and analyzed to discriminate between the target and the remainder of the plant.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Soybean sudden death syndrome resistant soybeans, soybean cyst nematode resistant soybeans and methods of breeding and identifying resistant plants
InactiveUS20020129402A1Solves the problem quickly and cheaply selecting resistant cultivarsImprove selection for SDS and SCN resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyMarker-assisted selection
The invention provides a method of introgressing soybean sudden death syndrome (SDS) or soybean cyst nematode (SCN) resistance into non-resistant soybean germplasm. Loci associated with SDS resistance or with SCN resistance in soybean lines known to be resistant to SDS or to SCN are used in marker assisted selection during introgression of SDS or SCN resistance into elite germplasm. In addition, the method may be used to confirm selection of resistance in new soybean cultivars.
Owner:SOUTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY
Soybean cultivar BA922834
ActiveUS7304217B1Modifying grain digestibilityModifying nutrient availabilityHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureSoybean cyst nematodeHeterodera
A soybean cultivar designated BA922834 with high yield potential, tolerance to Roundup™ herbicide, MG VI maturity, resistance to race 3 of soybean cyst nematode (Heterodera glycines), and resistance to frogeye leaf spot, further including the plants and seeds of the cultivar BA922834, methods for producing a soybean plant by crossing the cultivar BA922834 with itself or another soybean plant. The invention also relates to soybean cultivar BA922834 further comprising one or more single gene traits, and to methods of producing a soybean having such traits by introgression, transformation or mutagenesis. The invention also includes using the soybean cultivar BA922834 to produce other soybean cultivars, breeding lines, and progeny.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
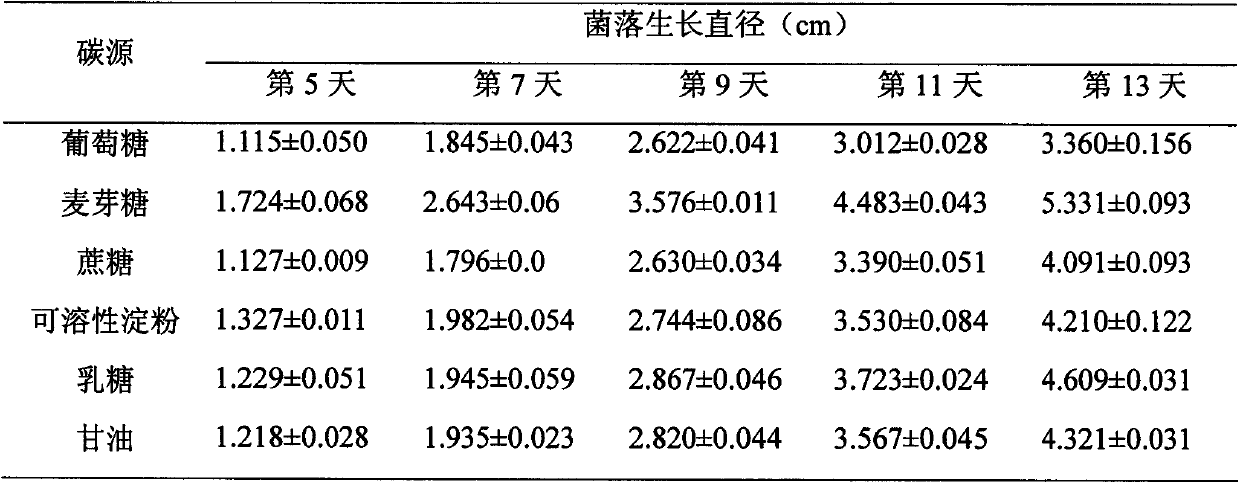
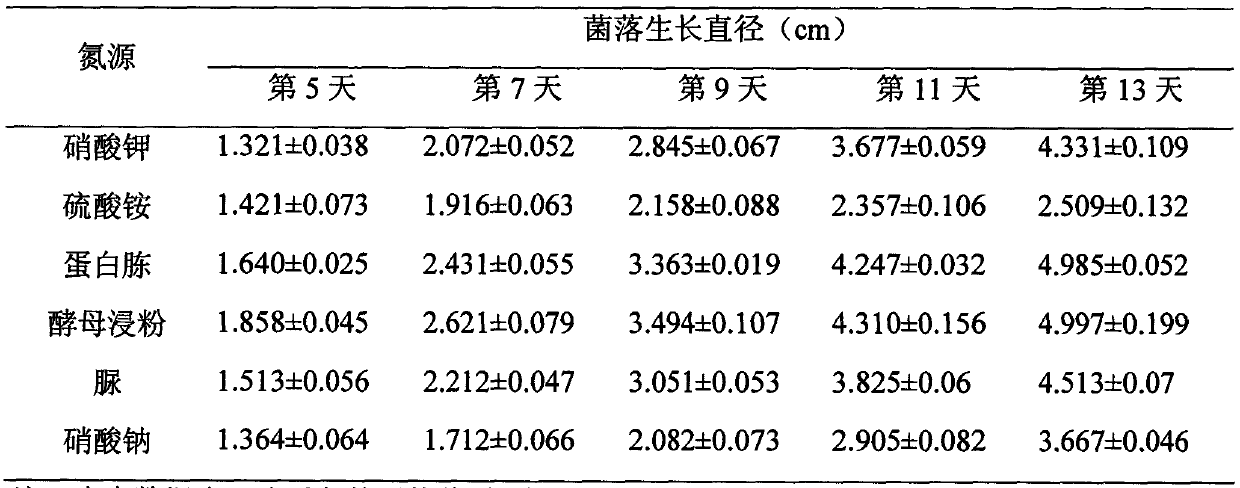
Paecilomyces lilacinus, culture method of paecilomyces lilacinus and use of paecilomyces lilacinus in prevention and control of diseases and pests of crops
The invention discloses a paecilomyces lilacinus strain and its culture method and use. The paecilomyces lilacinus strain is paecilomyces lilacinus CPLI0708, is preserved in the China general microbiological culture collection center (CGMCC) and has an accession number of CGMCC No.8450. The culture method of the paecilomyces lilacinus strain comprises the following steps of A, bacterial strain activation: carrying out bacterial strain streak cultivation activation on a PDA inclined plane, B, bacterial strain liquid fermentation culture: transferring the activated bacterial strain into a triangular flask with a liquid medium and carrying out shaking culture, and C, bacterial strain solid fermentation culture: mixing a carrier, a nutrition matrix and water according to a volume ratio to form a uniform mixture which is a solid fermentation medium, putting the solid fermentation medium into a fresh-keeping bag, inoculating the solid fermentation medium with a liquid fermentation seed, carrying out stirring to obtain a uniform mixture and carrying out culture. The bacterial strain conidiospore has strong effects of killing sucking-type insects such as greenhouse aphids and whitefly and the fermentation broth has strong effects of killing larvas of soybean cyst nematode and can be used for pollution-free vegetable production.
Owner:谢明
Soy bean cyst roundworm specific SCAR label, specific primer and quick PCR detecting method
InactiveCN1900282AAccurate detectionQuick checkSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCystNucleotide
The present invention is specific SCAR label and specific primer of soybean cyst roundworm and their quick PCR detection method, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. The specific SCAR label of soybean cyst roundworm features its nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ No. 1. The specific primers SCNF1 and SCNR1 designed based on the specific SCAR label of soybean cyst roundworm may be used in the quick PCR detection of soybean cyst roundworm and can amplify a 500 bp segment. It is also possible to add primers D2A and D3B as internal standards to amplify a 800 bp segment simultaneously. The present invention has raised molecular detection sensitivity, fast detection speed, accurate detection result and very high application value in the early detection of soybean cyst roundworm and the early diagnosis of soybean cyst roundworm disease.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Preparation and application of soil ecosystem nursing microorganism bacterial fertilizer
InactiveCN104761308AAvoid harmIncrease profitBio-organic fraction processingOrganic fertiliser preparationBiotechnologyContinuous cropping
The invention discloses preparation and application of a soil ecosystem nursing microorganism bacterial fertilizer. The soil ecosystem nursing microorganism bacterial fertilizer contains abundant organic matters and beneficial bacteria, especially paecilomyces lilacinus. The preparation method for the fertilizer mainly comprises the following steps: preparation of a paecilomyces lilacinus strain; enlarged cultivation of a liquid strain used for production; preparation of a medium; addition of the paecilomyces lilacinus strain for enlarged cultivation; secondary fermentation; etc. The microorganism bacterial fertilizer is applied as a base fertilizer to soil according to an amount of 100 to 200 kg / mu, can improve soil, especially soil in a greenhouse, is capable of obviously mitigating harm of a plurality of plant nematode diseases caused by root-knot nematode, soybean cyst nematode, stem eelworm and the like, and alleviates continuous cropping obstacles.
Owner:宁土建工(苏州)环境修复科技有限公司
Envirconmental protection typed dedicated fertilizer for soybean in coming crop
InactiveCN1498879AReduce morbidityThe effect of increasing production is obviousBiocideAnimal repellantsTrace elementPlant nutrition
An environment protection type fertilizer dedicated for the regrowth of soybean plant by eliminating the cystnematode and fungus contains N, P2O5 K2O and trace elements in weight ratio of 1:2:(0-5):(0-0.429). It can increase yield of soybean and improve the quality of soybean.
Owner:天津市福升肥料有限公司 +1
Genes Implicated In Resistance To Soybean Cyst Nematode Infection And Methods Of Their Use
ActiveUS20120260368A1Increased nematode resistanceInhibit expressionClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyPlant roots
Genes whose expressions are up-regulated or down-regulated in plant roots in response to nematode infection are disclosed. These genes may play an important role in plant defense against SCN infection. Several nematode-inducible promoters have also been identified in plants which ma be used in nematode inducible gene expression construct. Expression of these SCN responsive genes may be manipulated to obtain SCN resistant lines.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Trichoderma epiphyte having nematicidal activity as well as preparation method and uses thereof
The invention relates to a method for cultivating a fungus capable of poisoning and killing plant parasitic nematodes and a method for preparing and using metabolites thereof, belonging to the technical field of microbial pesticides. The Trichoderma strain Snef85 involved in the present invention is Trichoderma harzianum, which has been preserved on October 30, 2007 in the General Microorganism Center of China Committee for the Collection of Microorganisms (address: Datun Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, postal code 100101), The deposit number is CGMCC No.2235. The taxonomic status of the Trichoderma strain Snef85 is Deuteromycotina, Hyphomycetes, Trichosporales, Trichosporaceae, Trichoderma, and Trichoderma harzianum. It is prepared by liquid fermentation culture, and its metabolites have high toxicity to plant parasitic nematodes, especially root-knot nematodes incognita, rice stem-point nematodes and soybean cyst nematodes, and outstanding nematicidal effect. The fermentation broth of the strain has obvious control effects on root-knot nematode (Meloidogynes pp.), rice stem-point nematode (Aphelenchoides besseyi) and soybean cyst nematode (Heterodera glycines). There are significant differences between the treatment of fermented liquid with different dilution concentrations and the treatment of aseptic water, and the nematode killing effect of fermented liquid can reach more than 95%, which has good application and development prospects.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
Soybean cultivar MT017827
InactiveUS7208657B1Modifying grain digestibilityModifying nutrient availabilityOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationSoybean cyst nematodeSingle gene
A soybean cultivar designated MT017827 with high yield potential, tolerance to Roundup™ herbicide, early Group 1 maturity, and is resistant to race 3 and moderately resistant to race 14 of Soybean Cyst Nematode, further including the plants and seeds of the cultivar MT017827, methods for producing a soybean plant by crossing the cultivar MT017827 with itself or another soybean plant. The invention also relates to soybean cultivar MT017827 further comprising one or more single gene traits, and to methods of producing a soybean having such traits by introgression, transformation or mutagenesis. The invention also includes using the soybean cultivar MT017827 to produce other soybean cultivars, breeding lines, and progeny.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
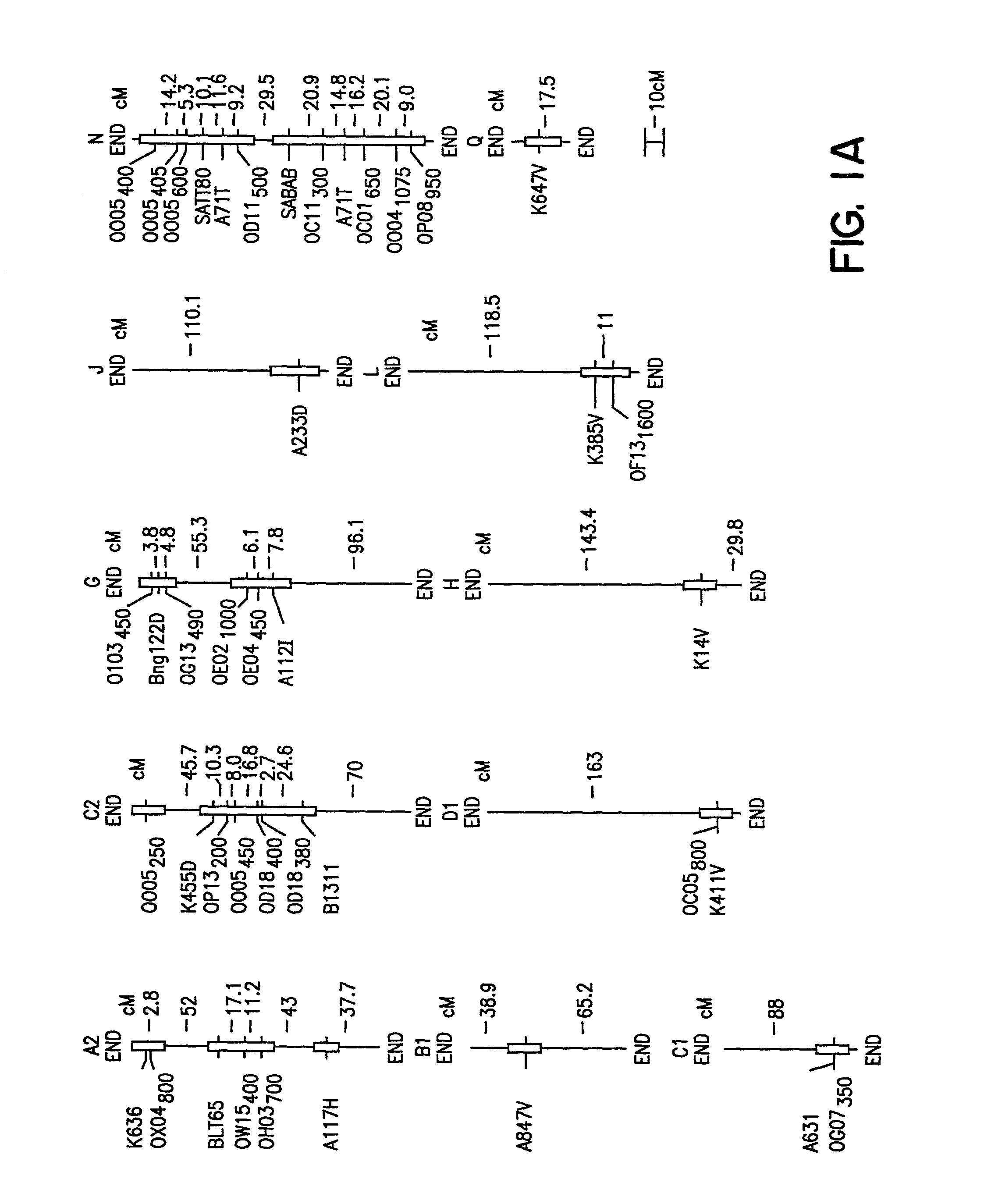
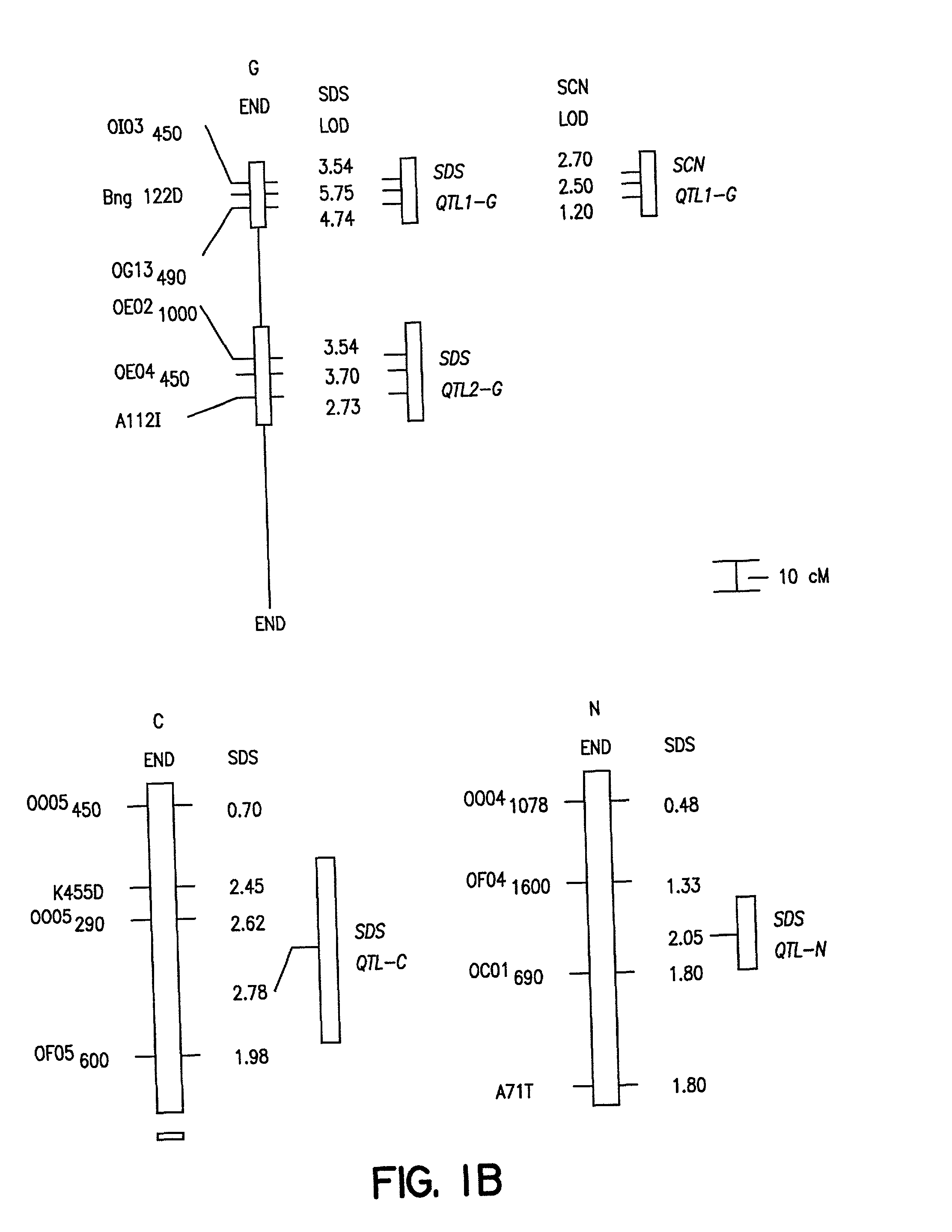
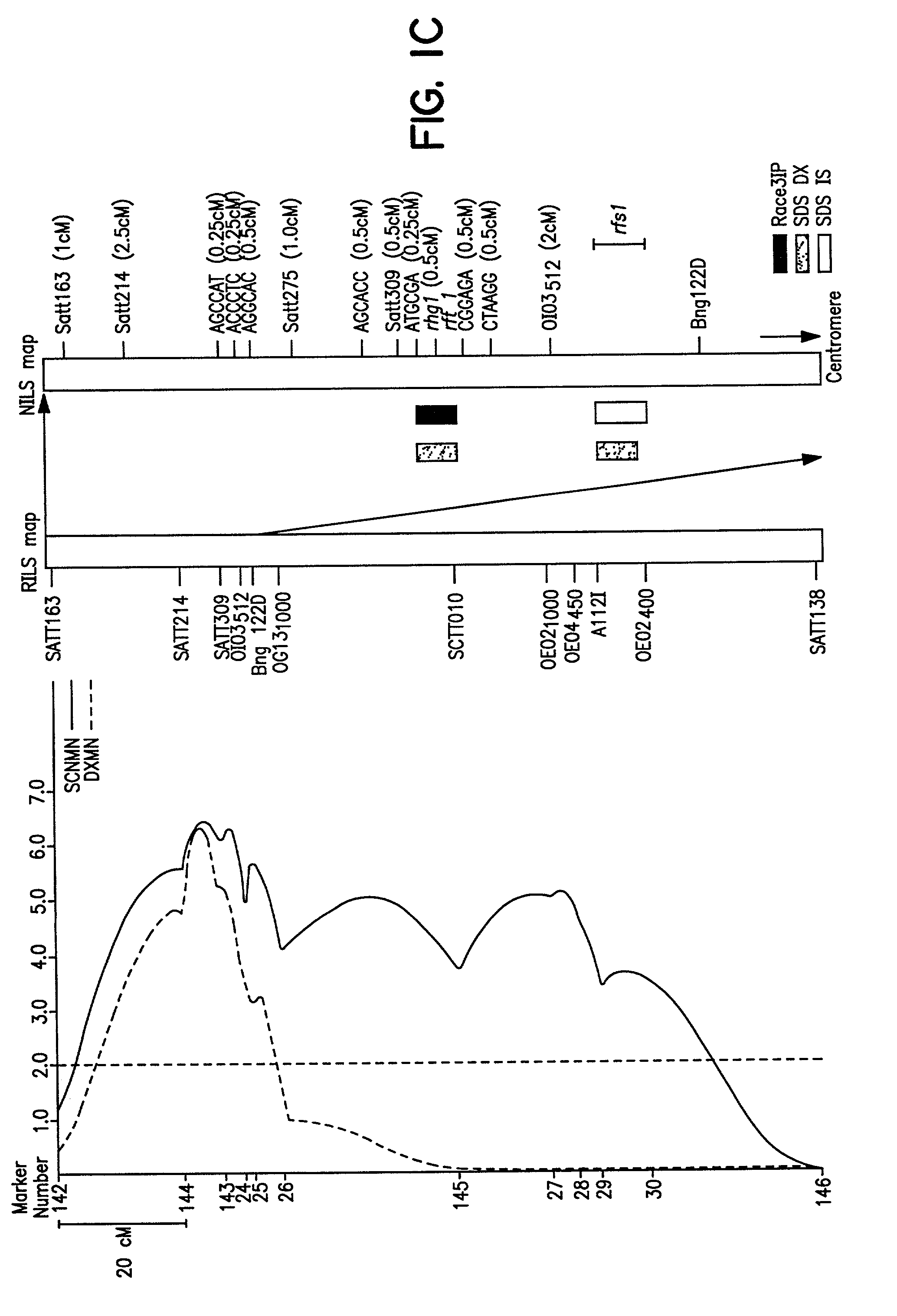
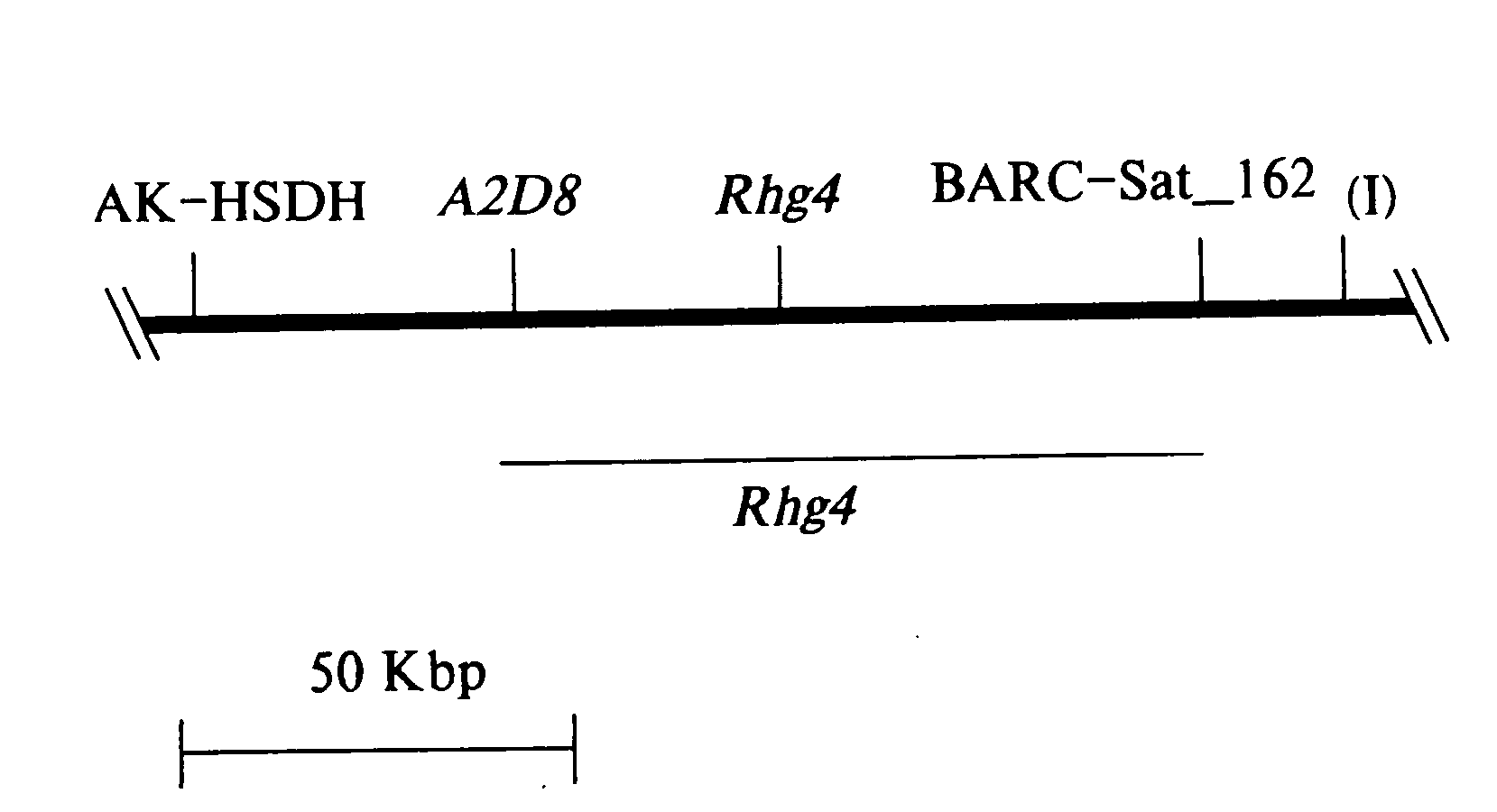
Quantitative trait loci associated with soybean cyst nematode resistance and uses thereof
InactiveUS7872171B2Microbiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationMarker-assisted selectionSoybean cyst nematode
A method for selecting a soybean cyst nematode resistant plant by marker assisted selection of quantitative trait loci associated with soybean cyst nematode resistance. The method employs nucleic acid markers genetically linked to quantitative trait loci to select the soybean cyst nematode resistant plant. Methods for identifying quantitative trait loci associated with soybean cyst nematode resistance in a plant.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Bacillus megaterium with capability of inducing stress resistance of soybeans and application thereof
The invention relates to a culture method of bacillus megaterium Sneb69 which can induce soybeans to withstand low temperature in early spring and soybean cyst nematode after processing soybean seeds and an application thereof, and belong to the technical field of microbial pesticides. A bacterial strain Sneb69 in the invention was collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on November 2, 2010 with the collection number of CGMCC No.4296. Through liquid fermentation, culture and preparation, the soybeans can withstand the low temperature in the early spring and the soybean cyst nematode after the soybean seeds are processed by metabolites. The soybeans after being processed by the metabolites of the bacteria can be sown in the early spring, and be grown in soil with serious soybean cyst nematode. By adopting the invention, difficult problems that the effective accumulated temperature for growth of the soybeans in high-altitude regions all the year around is less, and seasons which are suitable for the growth of the soybeans are short are solved, so that the culture method has a good application and development prospects.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
Soybean cyst nematode resistance gene and application thereof
InactiveCN102206651AEffective guidanceEffectively guide conventional breedingFungiBacteriaGlycineAgricultural science
The invention relates to a soybean cyst nematode resistance gene and application thereof. The cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) fragment (SRC-J-6) provided by the invention is derived from soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merrill.) variety L-10, and has a nucleotide sequence shown in 1) a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO. 1; 2) a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) molecule capable of hybridizingwith the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO. 1 and being expressed under strict conditions; 3) an mRNA (messenger ribonucleic acid) molecule, which has homology of more than 90% with the nucleotide sequence shown in 1) and can be expressed; or 4) a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) molecule, which has homology of more than 90% with the nucleotide sequence shown in 1) and can be expressed. After theplant tissues are transformed by the gene disclosed by the invention, the resistance to cyst nematode of the transgenic soybean is significantly improved. The soybean cyst nematode resistance gene provided by the invention has important significance, not only can effectively guide conventional breeding, can also provide excellent genetic resources for the transgenic breeding of soybean and has broad application prospects in the soybean production.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Soybean cultivar M08851
ActiveUS7126047B1Modifying grain digestibilityModifying nutrient availabilityOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationSoybean cyst nematodeSingle gene
A soybean cultivar designated M08851 with high yield potential, tolerance to Roundup™ herbicide, mid-to-late Group 1 maturity and resistant to race 3 and moderately resistant to race 14 of Soybean Cyst Nematode, further including the plants and seeds of the cultivar M08851, methods for producing a soybean plant by crossing the cultivar M08851 with itself or another soybean plant. The invention also relates to soybean cultivar M08851 further comprising one or more single gene traits, and to methods of producing a soybean having such traits by introgression, transformation or mutagenesis. The invention also includes using the soybean cultivar M08851 to produce other soybean cultivars, breeding lines, and progeny.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Soybean cultivar BA947474
InactiveUS7220898B1High yield potentialModerate resistanceOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationRoot-knot nematodeSoybean cyst nematode
A soybean cultivar designated BA947474 with high yield potential, tolerance to Roundup™ herbicide, MG VIII maturity, resistance to race 3 of soybean cyst nematode (Heterodera glycines), and moderate resistance to southern root knot nematode and southern stem canker, further including the plants and seeds of the cultivar BA947474, methods for producing a soybean plant by crossing the cultivar BA947474 with itself or another soybean plant. The invention also relates to soybean cultivar BA947474 further comprising one or more single gene traits, and to methods of producing a soybean having such traits by introgression, transformation or mutagenesis. The invention also includes using the soybean cultivar BA947474 to produce other soybean cultivars, breeding lines, and progeny.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Soybean cultivar SJ919784
A soybean cultivar designated SJ919784 with high yield potential, tolerance to Roundup™ herbicide, early Group 3 maturity, and resistance to races 3 and 14 of Soybean Cyst Nematode, further including the plants and seeds of the cultivar SJ919784, methods for producing a soybean plant by crossing the cultivar SJ919784 with itself or another soybean plant. The invention also relates to soybean cultivar SJ919784 further comprising one or more single gene traits, and to methods of producing a soybean having such traits by introgression, transformation or mutagenesis. The invention also includes using the soybean cultivar SJ919784 to produce other soybean cultivars, breeding lines, and progeny
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Bacillus simplex for inducing soybean to generate soybean cyst nematode resistance and application
The invention relates to a method for culturing a Bacillus simplex Sneb545 for inducing soybean to generate soybean cyst nematode resistance after soybean seed treatment and an application of the Bacillus simplex Sneb545, and belong to the technical field of microbial pesticides. The bacterial strain Sneb545 related in the invention is preserved in the China general microbiological culture collection center in October 11th, 2012, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.6650. After the strain is subjected to fermentation cultivation through conventional liquid, the metabolic products of the strain can be used to develop a seed treating agent for treating soybean seeds, and the treated soybean seeds can induce the soybeans to generate the soybean cyst nematode resistance. The soybean seeds which is treated through the metabolic products of the Bacillus simplex Sneb545 can induce the soybeans to generate obvious resistance to the first generation of soybean cyst nematode during the seedling stage, the Bacillus simplex Sneb545 has an obvious function of inhibiting the cytocyst of the soybean cyst nematode from forming and is a potential biocontrol bacterium, and a new method is provided for preventing the soybean cyst nematode.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
Nematicidal compound derived from trichoderma virens as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102532247ASignificant broad-spectrum nematicidal activityGood prospects for industrial promotion and applicationBiocideMicroorganism based processesSoybean cyst nematodeMeloidogyne incognita
The invention discloses a compound which is derived from trichoderma virens and has nematicidal activity as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The compound viridiol has a structure as shown in a formula (I). The compound disclosed by the invention has strong killing effects on various nematodes such as soybean cyst nematode, pine wood nematode, meloidogyne javanica and meloidogyne incognita, can be applied to making preparations for preventing and controlling nematodes, and has the advantages of high efficiency, low toxicity, broad spectrum, good industrial prospect and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Pesticide composition for preventing and treating soybean cyst nematode
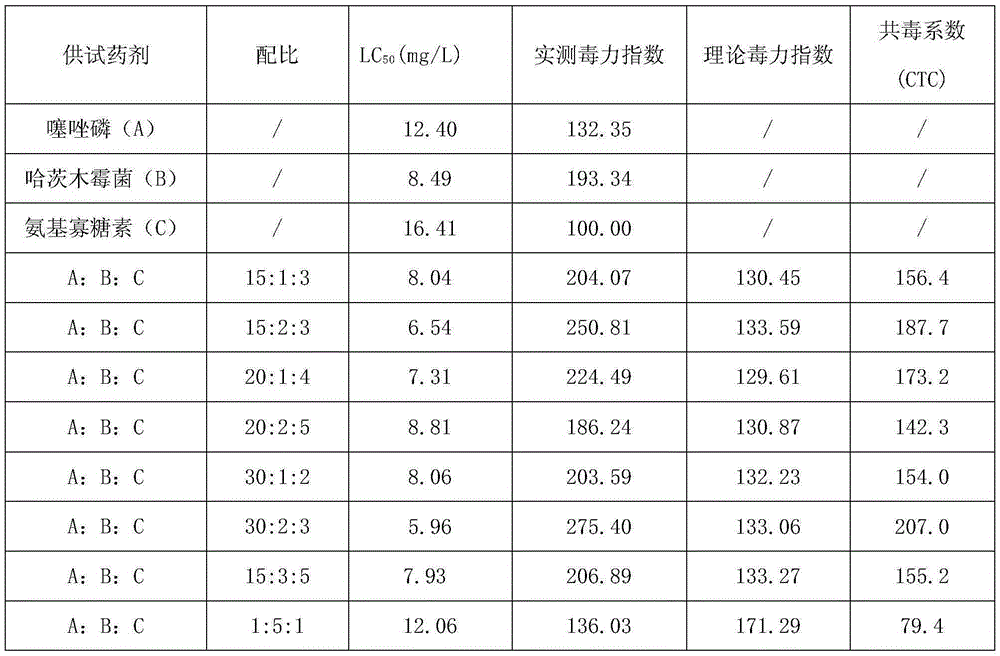
InactiveCN105284906AAdvantages and significant technical effectsGood technical effectBiocideFungicidesDiseaseTreatment effect
The invention relates to a pesticide composition for preventing and treating soybean cyst nematode. The pesticide composition comprises active components of lythidathion, trichoderma harzianum and amino-oligosaccharin. Trichoderma harzianum utilizes a mother drug with content of 30 billion CFU / g as 100% mother drug. A weight ratio of lythidathion, trichoderma harzianum to amino-oligosaccharin is 15-30: 1-3: 1-5. The active components are mixed, produce synergism, have good prevention and treatment effects on root-knot nematode and cyst nematode, can effectively prevent and treat root fungous diseases such as root rot, damping off and sheath blight, effectively prevent complex infection of root fungous diseases and nematode diseases, is safe for crops, can be used in broadcast and basal application ways, can be prepared to form granules and is convenient for use.
Owner:南京溧水石湫机场科技工业园开发有限公司
Agritol suspension seedling-coating agent
InactiveCN1849890AHigh retention rateNo pollution in the processBiocideAnimal repellantsBacillus thuringiensisPhosphate
The present invention relates to a bacillus thuringiensis suspension seed dressing agent for controlling soybean sporangium nematode. Its composition includes (by wt%) 20-90% of bacillus thuringiensis slurry, 2.5-5.0% of nutrient agent, 0.1-0.8% of film-forming agent, 6-9% of ethyl alcohol, 0.6-0.75% of acid red B, 0.2-0.45% of sodium benzoate and the rest is water. The described nutrient agent is one of phosphate and sulfate or their mixture, and the described film-forming agent is one of xanthan, methyl cellulose and polyethylene glycol or their mixture.
Owner:HUBEI BIOPESTICIDE ENG RES CENT
Microbial insecticide for controlling wireworm and application thereof
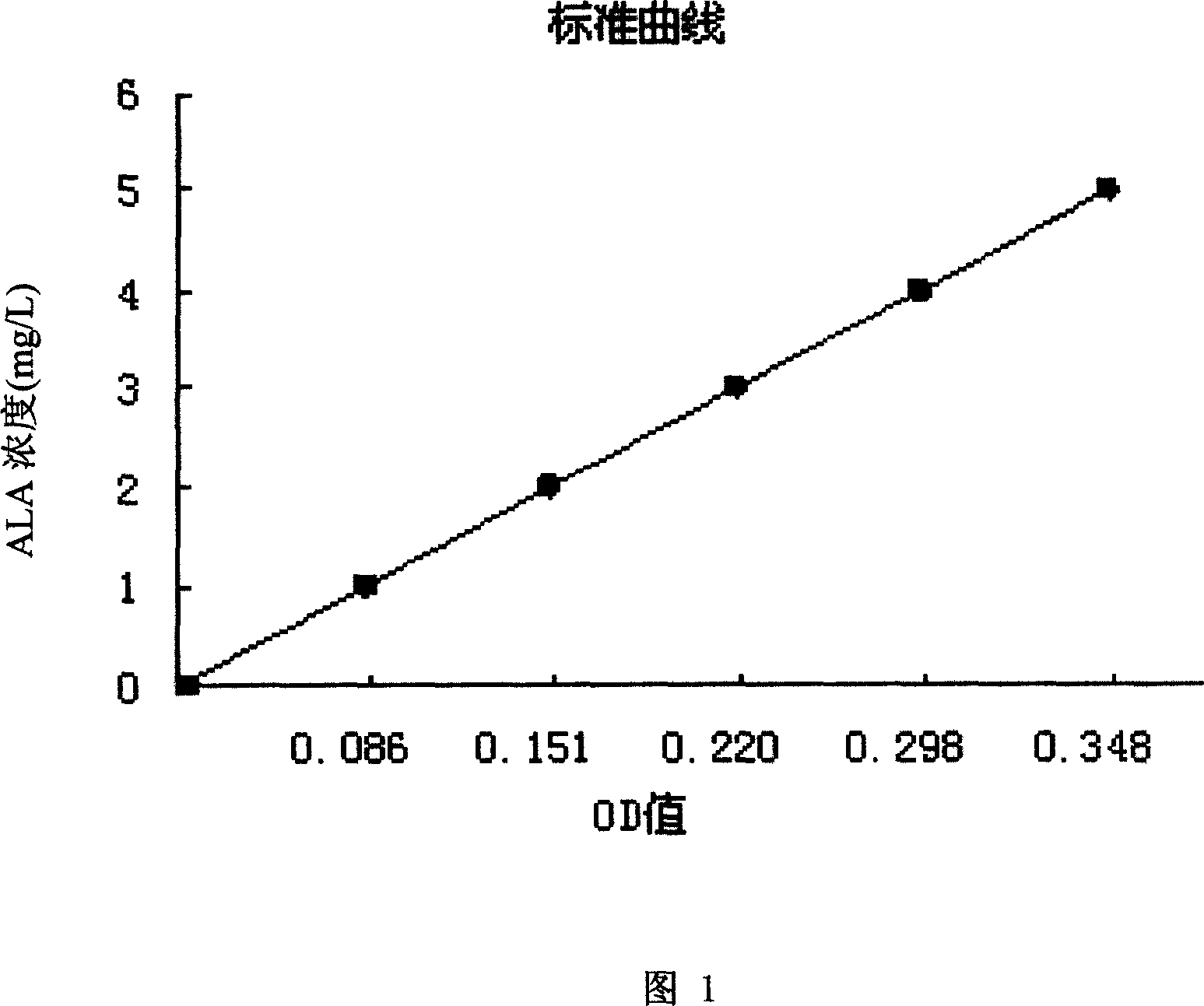
The invention relates to a microbe nematization killing agent, which is the ferment product of photosynthetic bacterium acidophilic PSB-1 Rhodoblastus acidophilus CCTCC M 206124. Said ferment product contains the nematization killing active component as 5-Aminolevulinic acid or delta-Aminolevulinic acid whose simplified name is ALA. The inventive agent is pure biological agent, which can be used to treat rootworm, or the like, without pollution but low cost. The inventive agent will not hurt the tobacco, hot pepper, or the like, while it can accelerate and excite the growth of crops.
Owner:HUNAN PLANT PROTECTION INST
Modified Bacillus Thuringiensis Cry6 Proteins For Nematode Control
The subject invention concerns plants protected from nematode feeding damage and improved versions of Cry proteins. The subject invention also concerns improved versions of Cry6A proteins. Synthetic genes encoding these modified proteins are also part of the subject invention. Another embodiment of the subject invention includes plants transformed with the genes of the subject invention. In yet another embodiment the subject invention concerns Bt proteins for in-plant protection against crop damage by root knot nematode (RKN; Meloidogyne incognita) and soybean cyst nematode (SCN; Heterodera glycines).
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
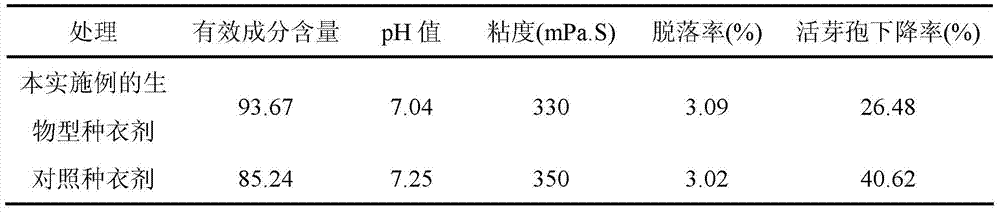
Bio-seed coating agent for preventing and treating soil-borne diseases of soybeans and preparation method of bio-seed coating agent
The invention relates to a bio-seed coating agent for preventing and treating soil-borne diseases of soybeans and a preparation method of the bio-seed coating agent, and solves the problems of toxicity, unsafety and environmental pollution of pesticides for treating the soil-borne diseases in an existing method. The bio-seed coating agent is prepared from the following components: a fermenting solution, 10g / L-50g / L of a dispersing agent, 9g / L-29g / L of a carrier and 9g / L-19g / L of a film-forming agent, wherein the fermenting solution comprises a brevibacillus laterosporus fermenting solution and a bacillus subtilis fermenting solution which are the same in volume. The method comprises the following steps: 1, preparing the brevibacillus laterosporus fermenting solution; 2, preparing the bacillus subtilis fermenting solution; 3, adding the dispersing agent, the carrier and the film-forming agent, and uniformly mixing. The bio-seed coating agent does not contain any high-toxicity ingredients, is safe and environmentally friendly, and is used for preventing and treating soybean root rot and soybean cyst nematode. The method is used for preparing the bio-seed coating agent.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIV
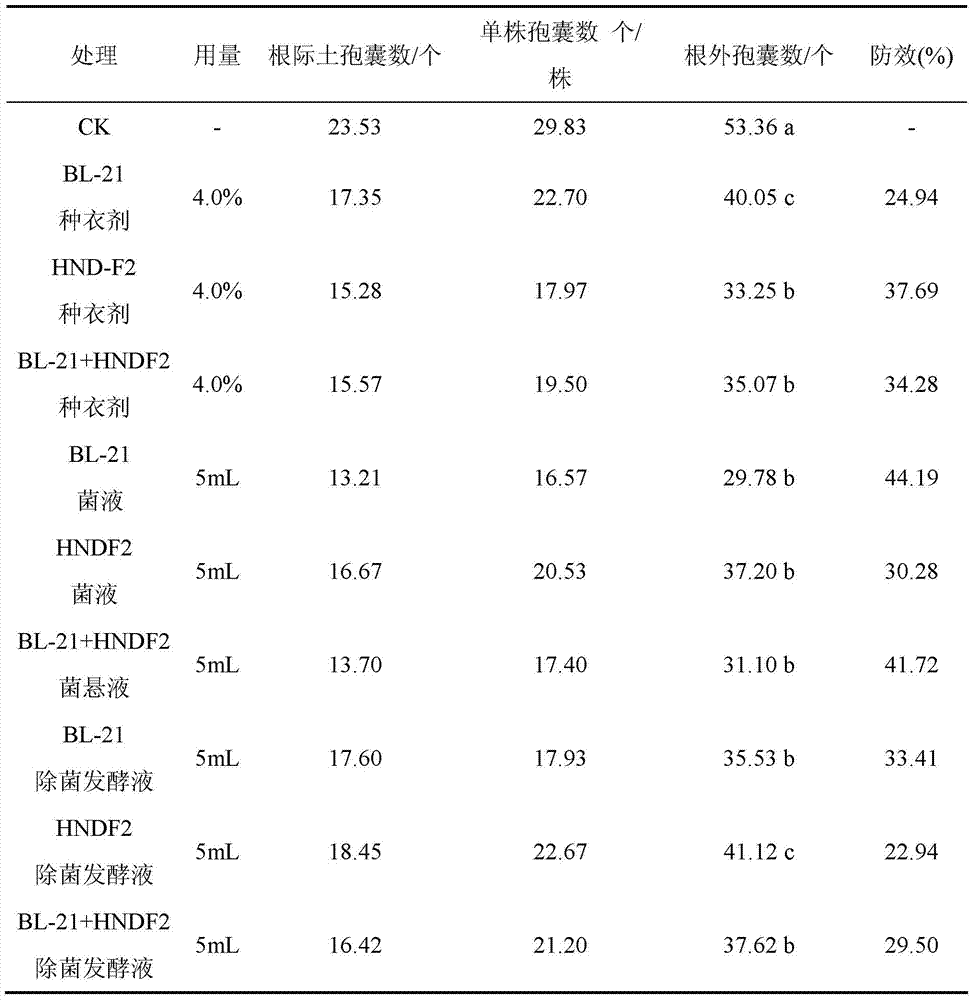
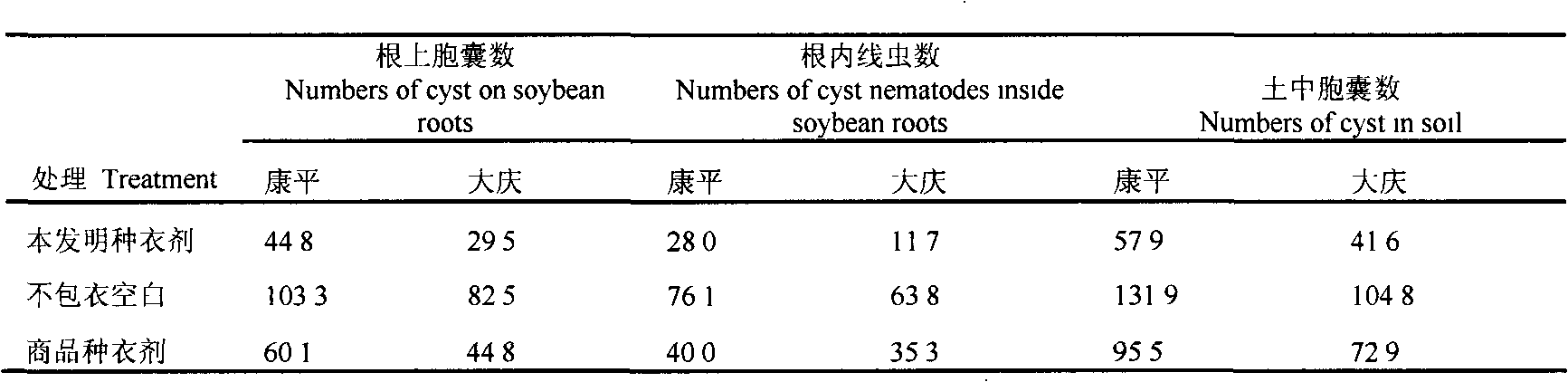
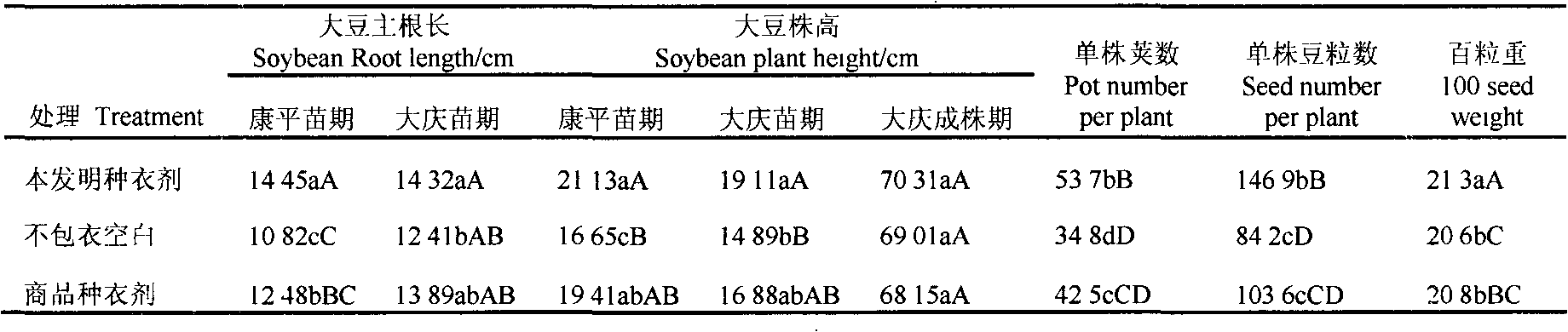
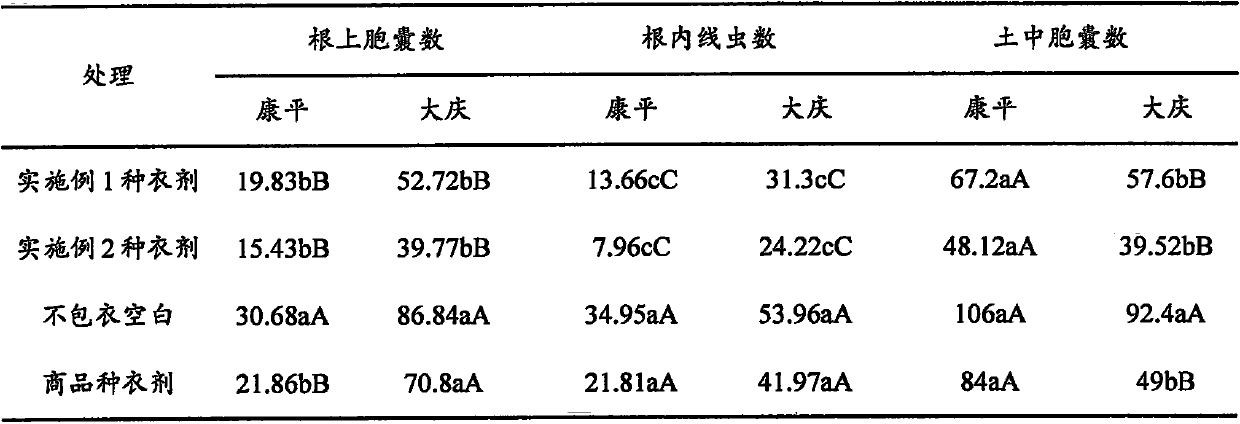
Biological seed coating for controlling soybean cyst nematodes
The invention relates to a biological seed coating for controlling soybean cyst nematodes. The biological seed coating comprises nematicidal activity substances from two kinds of bio-control agents, elements which are prepared by mixing according to a certain proportion and various aids. As proved by a large quantity of tests, the biological seed coating meets the requirements of a coating on physical and chemical properties; and after coating, the growth of soybeans at a seedling stage is promoted remarkably, the yield of soybeans is increased, and the control effect on soybean cyst nematode disease at the seeding stage is remarkable.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
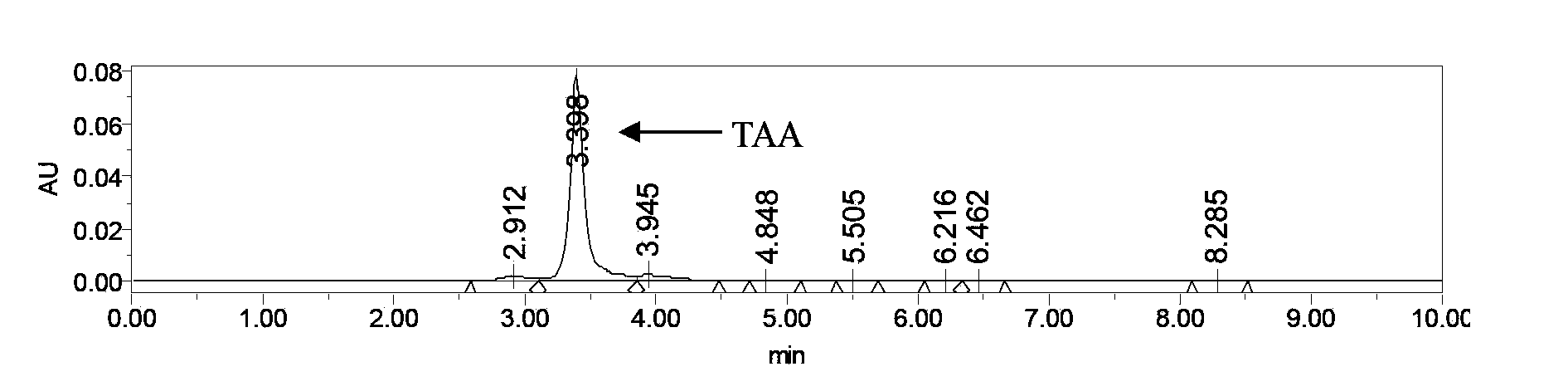
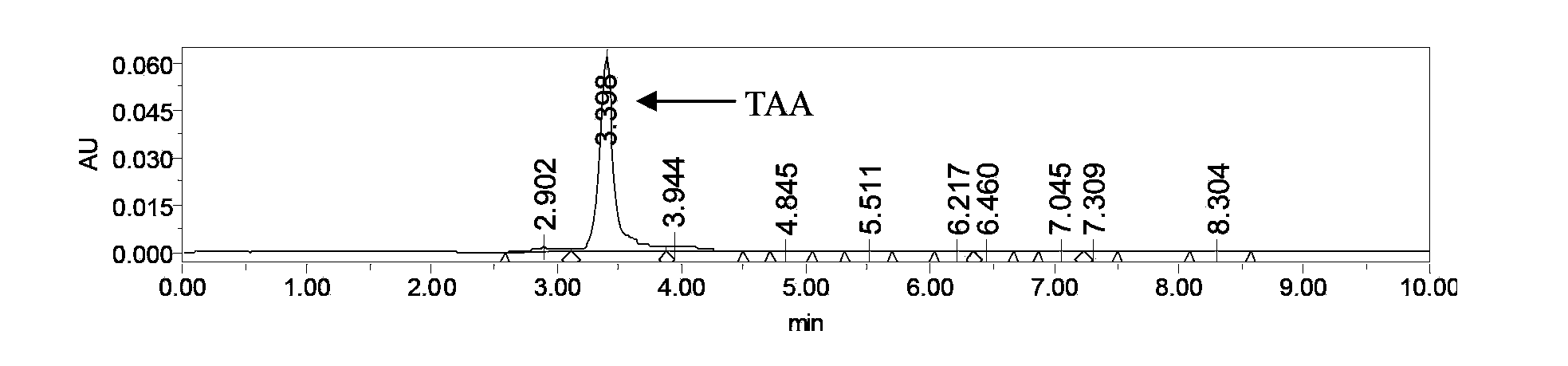
Trans-aconitic acid producing bacteria and application thereof
The invention belongs to the field of microbe biotechnology and relates to the field of biological pesticides. Two trans-aconitic acid producing bacteria, that is, bacillus thuringiensis YBT-1501 and bacillus thuringiensis YBT-1520 are obtained from bacillus thuringiensis through screening; through utilizing the fermentation products of the two strains, the coarse and refine product of the trans-aconitic acid can be obtained; according to bioassay, the trans-aconitic acid has the activity of poisoning and killing meloidogyne incognita, heterodera glycine ichinohe and ditylenchus destructor, and the activity of suppressing the growth of cotton bollworm and housefly. The trans-aconitic acid producing bacteria are novel biological disinsection pesticides and a novel prevention and cure way for the current prevention and cure strategy is provided. The bacillus thuringiensis YBT-1501 which is used for preparing the trans-aconitic acid is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection, with the serial number of CCTCC NO: M2012236.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Methods and Compositions Using Small Interfering RNA (SIRNA) for Nematode Control in Plants
InactiveUS20140007296A1Increase crop yieldImprove the immunitySugar derivativesClimate change adaptationNucleotidePlant cell
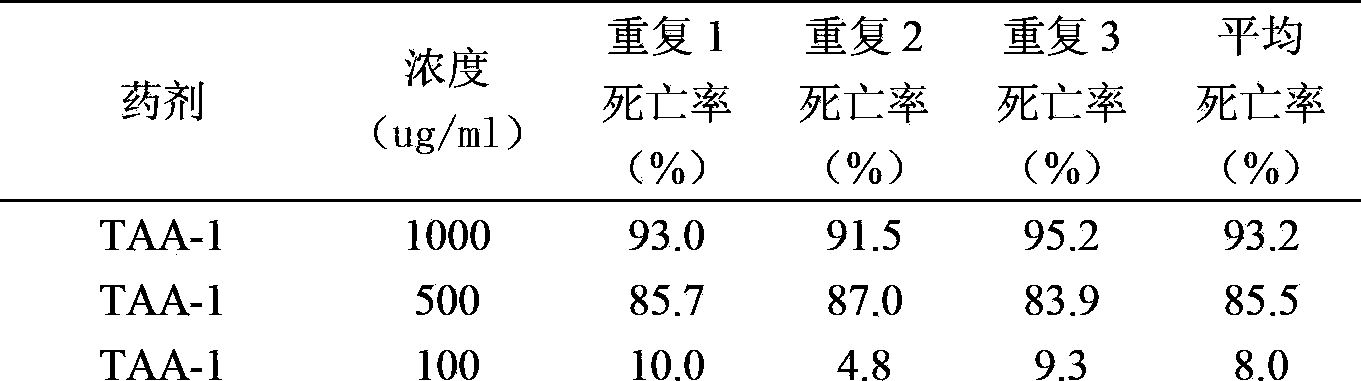
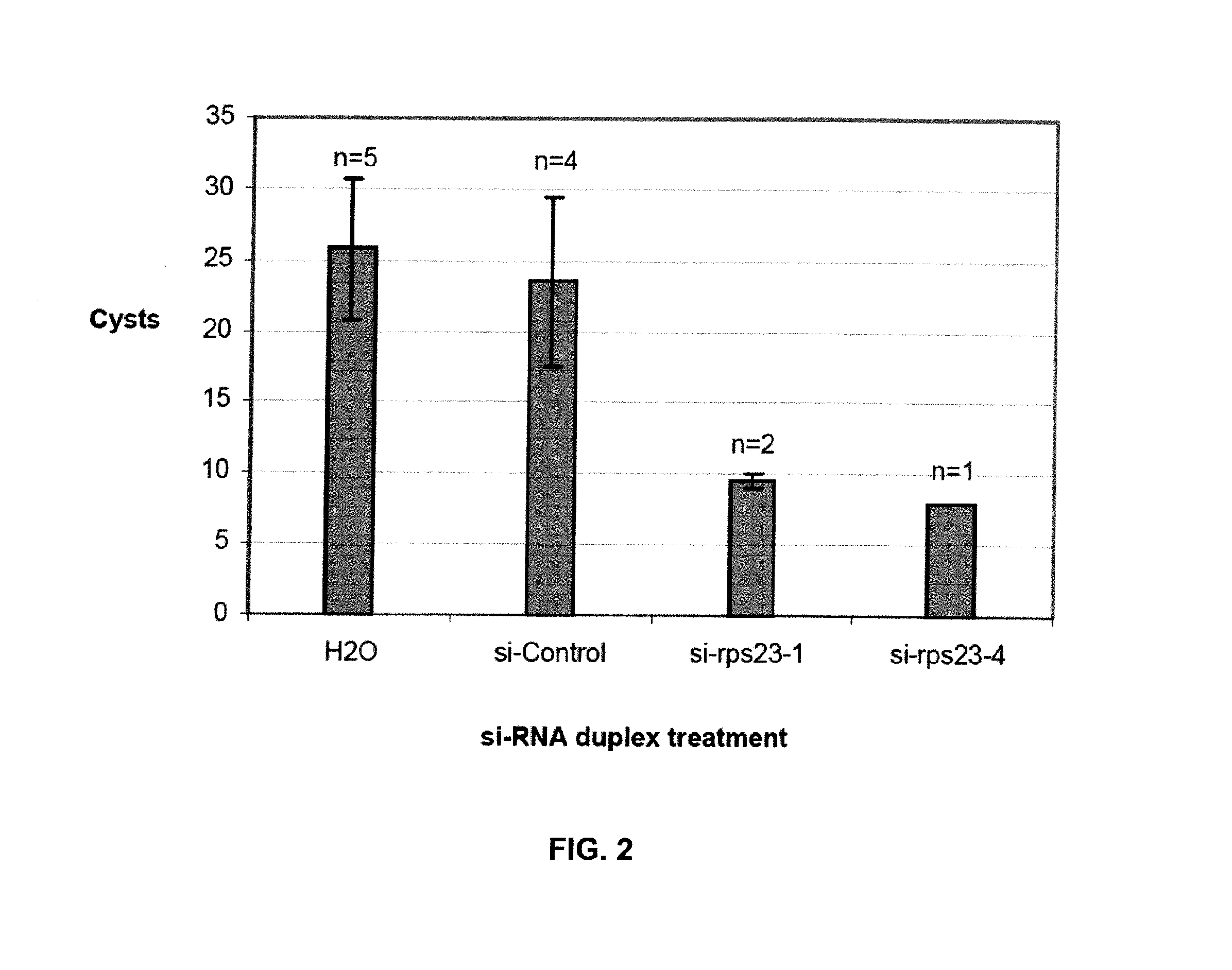
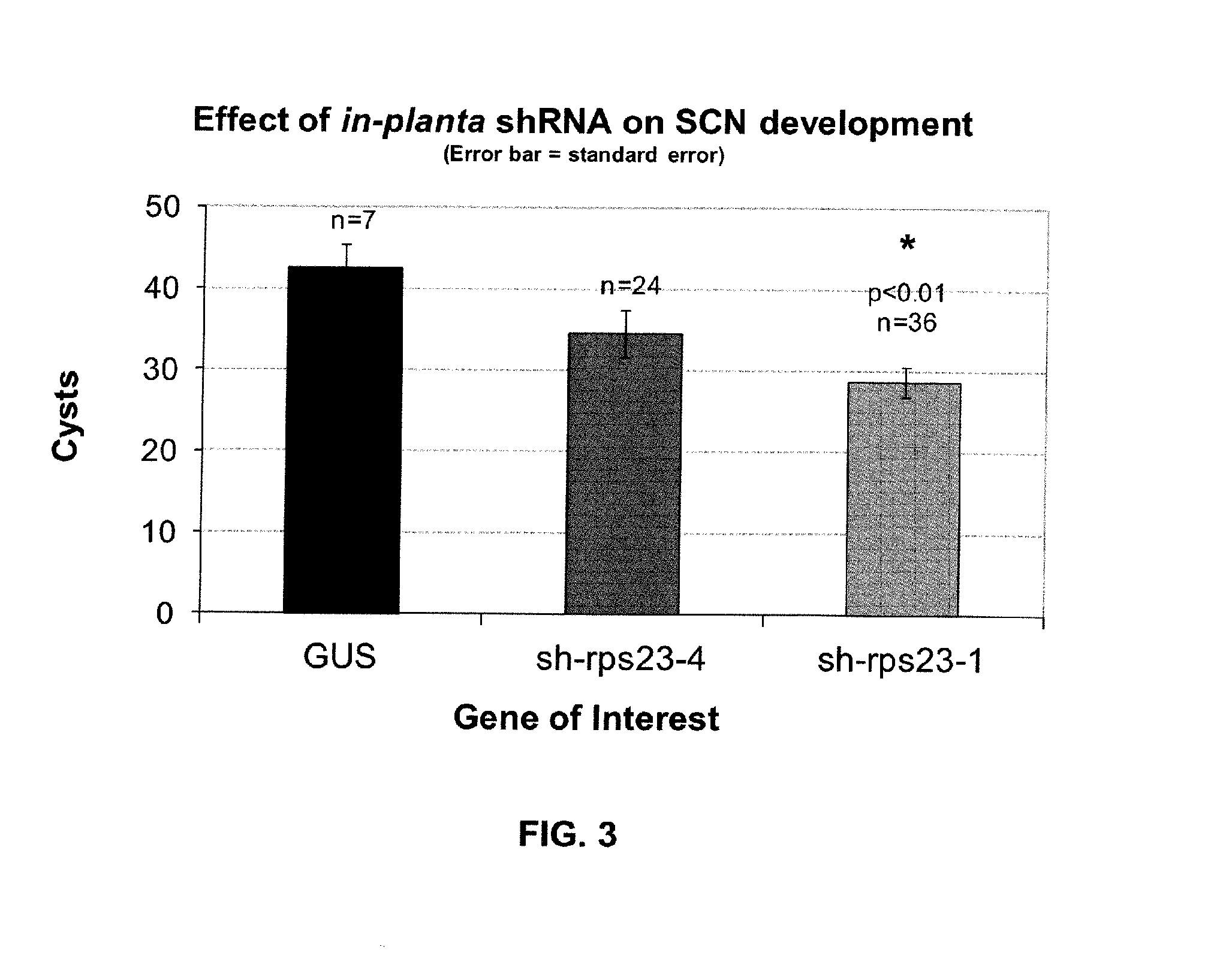
The present invention provides a double stranded RNA molecule comprising an antisense strand and a sense strand, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the antisense strand is complementary to a portion of the nucleotide sequence of a Hg-rps-23 gene of a soybean cyst nematode, nucleic acid molecules encoding the RNA molecules and compositions comprising the nucleic acid molecules and RNA molecules of this invention, as well as methods of their use in enhancing resistance of a plant or plant cell to nematode infestation and infection.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Isolated polynucleotides and polypeptides relating to loci underlying resistance to soybean cyst nematode and soybean sudden death syndrome and methods employing same
Soybean cyst nematode and soybean sudden death syndrome resistance genes, soybean cyst nematode and soybean sudden death syndrome resistant plant lines, and methods of breeding and engineering same.
Owner:SOUTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY
Plant biochemical systems and uses thereof
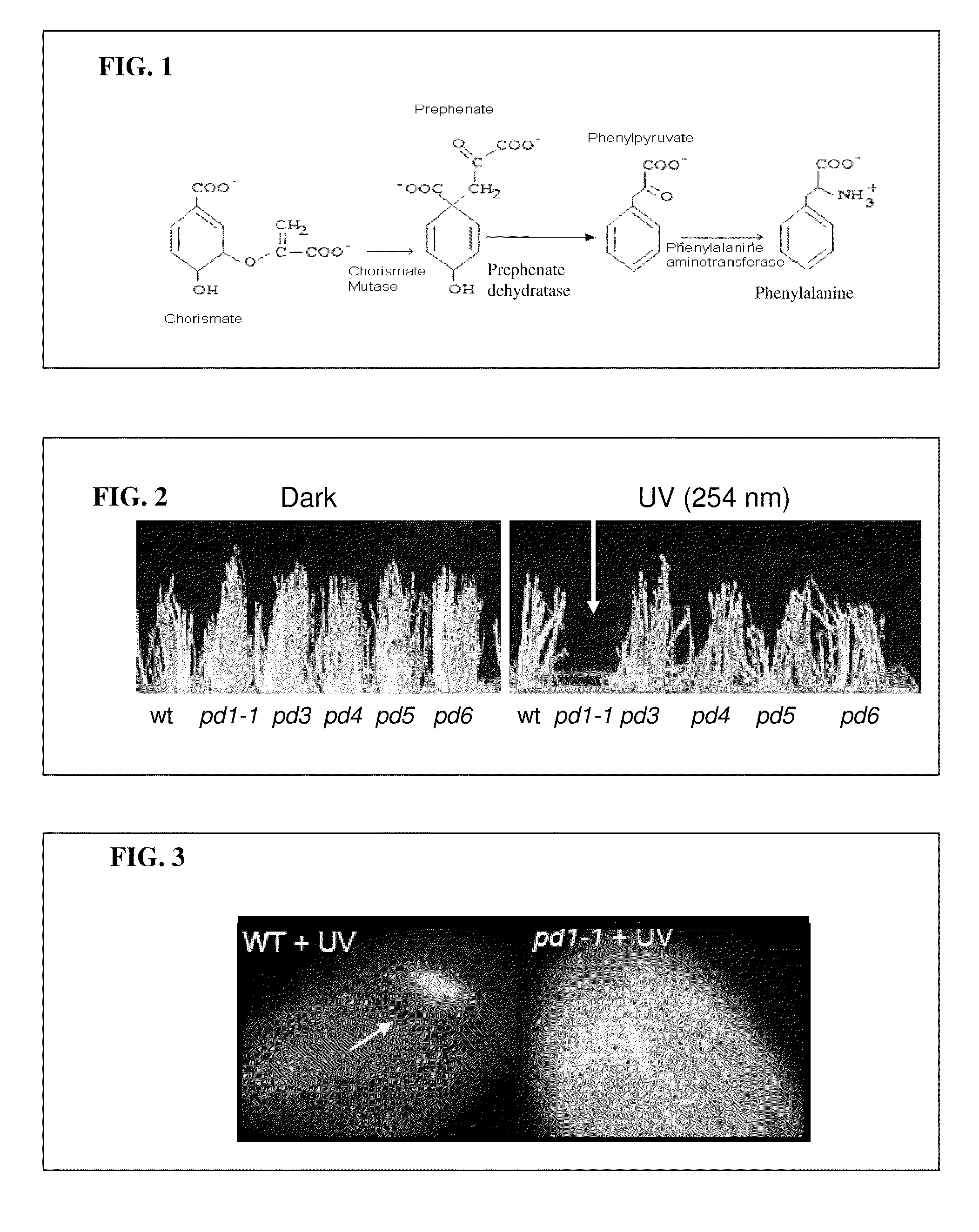
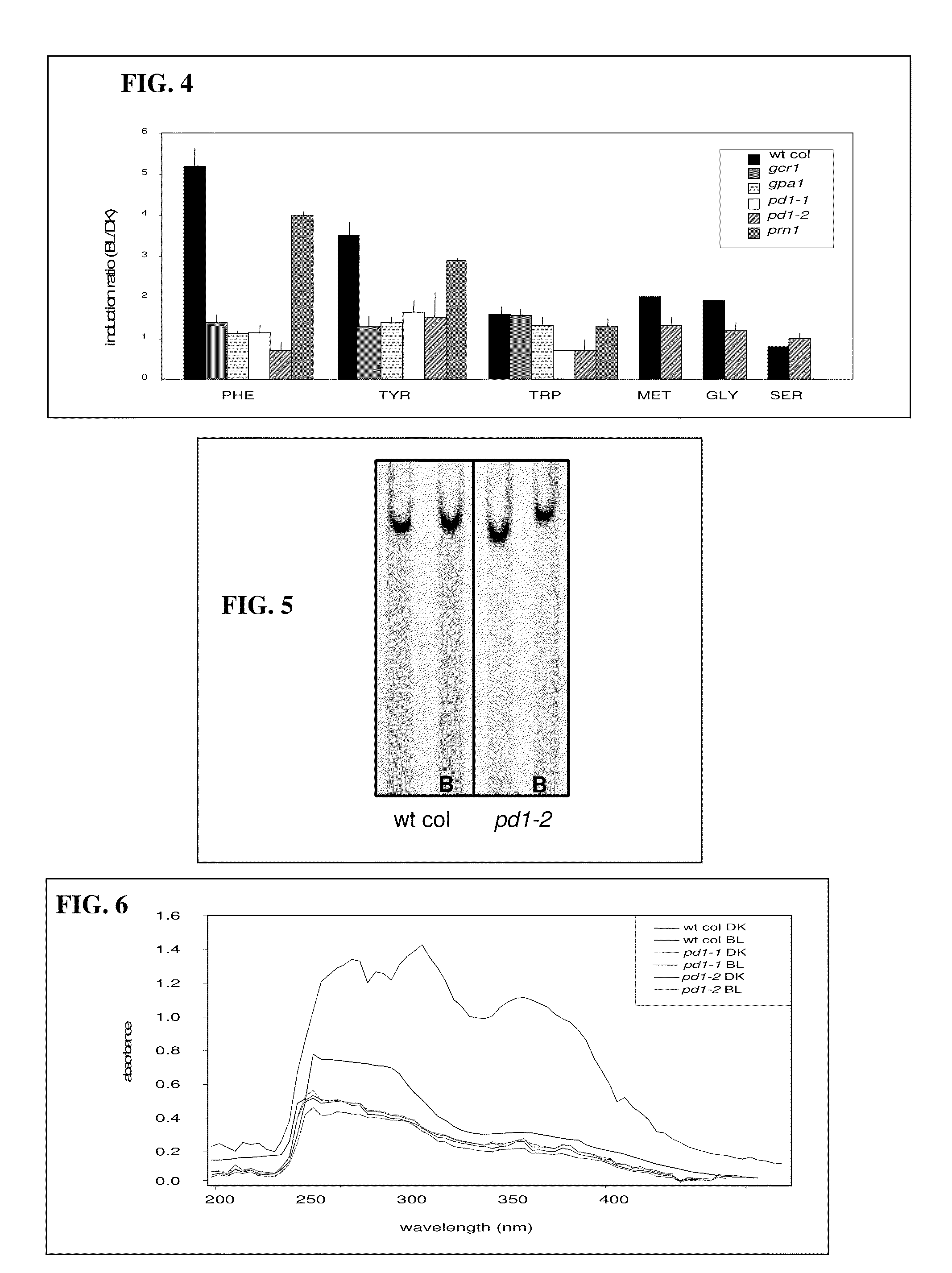
Compositions including phenylalanine, analogues, and phenylalanine precursors protect plants against environmental stressors. Delivery systems and methods of treating are provided. A method of protecting plants against environmental and / or biological stressors includes administering a composition including phenylalanine, a phenylalanine precursor or other skikimate pathway or phenylpropanoid pathway compound, or an amino acid that can be converted to phenylalanine to at least one root, at least one germinating seed, or at least one epidermal surface of a plant. Administration of the composition to the root, seed, or plant improves or restores at least one growth characteristic of the plant when the plant is exposed to an environmental stressor such as ultra-violet radiation, cold, drought, salt, heat, fungus, beetles (e.g., Japanese beetles), hormones, bacteria, arthropods, and worms (e.g., soybean cyst nematode) or products of biotic organisms. Another method of protecting plants against environmental and / or biological stressors includes coating a plant (e.g., soybean) seed with a composition including phenylalanine, a phenylalanine precursor or other skikimate pathway or phenylpropanoid pathway compound, or an amino acid that can be converted to phenylalanine such that the composition protects the seed and a plant that grows from the seed from ultra-violet radiation, cold, drought, salt, heat, fungus, beetles (e.g., Japanese beetles), hormones, bacteria, arthropods, and worms (e.g., soybean cyst nematode) or products of biotic organisms. Plants and plant cells including an isolated nucleic acid encoding at least one prephenate dehydratase operably linked to a promoter are described herein.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Biological seed coating agent for controlling soybean root disease and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105494447APromote growthEffective controlBiocideDead animal preservationBiotechnologyGrowth plant
The invention provides a biological seed coating agent for controlling a soybean root disease. The biological seed coating agent is prepared from the following components in percentage by mass: 0.02-0.15 percent of CuSO4, 0.05-0.26 percent of (NH4)6Mo7O24.4H2O, 0.01-0.05 percent of H3BO3, 0.1-0.5 percent of MnSO4, 0.04-0.25 percent of FeSO4, 1.5-6 percent of KH2PO4, 0.02-1 percent of K2SO4, 2-8 percent of dispersing agent, 2-5 percent of film-forming agent, 0.1-1.2 percent of warning color, 0.95-2.65 percent of binder and the balance of biocontrol strain fermentation solution. The biological seed coating agent provided by the invention is used for coating soybean seeds, and can achieve the effects of restraining soybean cyst nematode and soybean root rot, so that the soybean root disease is prevented and controlled effectively, soybean plant growth can be promoted, and the yield is increased.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com