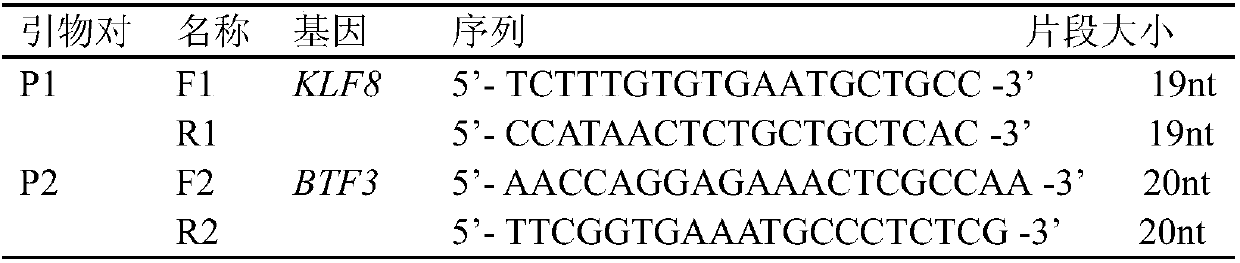
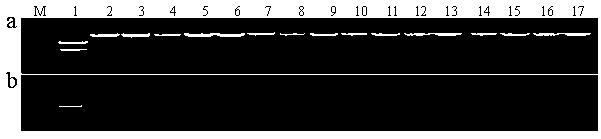Patents
Literature
773 results about "Genetic resources" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Genetic Resources Genetic resources (GRs) refer to genetic material of actual or potential value. Genetic material is any material of plant, animal, microbial or other origin containing functional units of heredity.
Salt-tolerance determining method for barley at seedling stage
InactiveCN102860159AReduce the impactSimple methodSeed and root treatmentHorticulture methodsAgricultural scienceQuantitative trait locus
The invention relates to a determining method for indicating salt tolerance of different varieties of barleys at seedling stages and belongs to the field of agriculture. The determining method includes adopting a water culturing manner to simulate salt environment artificially, investigating salt damage degree of samples to be tested under the condition of salt stress compared with the blank control condition by measuring seedling height, root length and fresh weight of each seedling of different treatment, and finally determining salt tolerance of the variety. The determining method can be widely applied to screening and evaluation of plant stress resistance genetic resources, particularly used for screening of barley salt-tolerance variety resources, salt-tolerance QTL (quantitative trait locus) genetic analysis, salt-tolerance gene positioning and seed selection of salt-tolerance barley varieties. The determining method has the advantages of simplicity, easiness in mastering and reliable results, the whole salt-tolerance determining process is under control and is slightly affected by the environment, requirements for equipment are low so that only one common illumination culturing box is required.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Corn transcription factor ZmbHLH167 and application thereof
The invention relates to a corn transcription factor ZmbHLH167 and an application of the corn transcription factor ZmbHLH167. A base sequence of the gene is shown as SEQ ID NO (sequence identifier number): 1. A corn immature embryo is transformed by taking a gene segment SEQ ID NO: 2 of the sequential coding protein ZmbHLH167 as guide RNA (ribonucleic acid) by use of a CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats)-Cas9 technology, and a plant of a gene deletion mutant is obtained. Compared with a wild seed, a corn seed of the genetically modified mutant is smaller significantly, but a germination rate is not influenced. Biochemical analysis shows that a starch content of the corn seed of the genetically modified mutant is decreased obviously, a content of protein and total oil and fat is significantly increased, and a genetic resource is provided for creating high quality corn.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Spruce somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration method
ActiveCN101983556AImprove efficiencyEasy to storePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsSomatic embryogenesisGenetic resources
The invention discloses a spruce somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration method, which comprises preparation of immature seed embryo of spruce, initial induction of embryonal suspensor mass (ESM), maintenance and proliferation of the ESM, prophase maturation culture of the somatic embryo, maturation culture of the somatic embryo and germination of the somatic. The spruce plant regeneration method has the advantages of high propagation coefficient and no limitation on the propagation season and provides an efficient means for the rapid propagation of the genetically improved materials of spruce, which not only is conducive to the storage of genetic resources of spruce, but also provides a large number of genetically improved plant materials for accelerating the cultivation of the improved materials of spruce, eases urgent requirements of the society on the genetically improved nursery stock of spruce, and provides a technology for producing an improved variety of nursery stock with short period, high efficiency and low cost.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Method for screening HRDs disease-causing mutation and gene chip hybridization probe designing method involved in same
ActiveCN103667438AClear relationshipScreening benefits are highMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationDiseaseHybridization probe
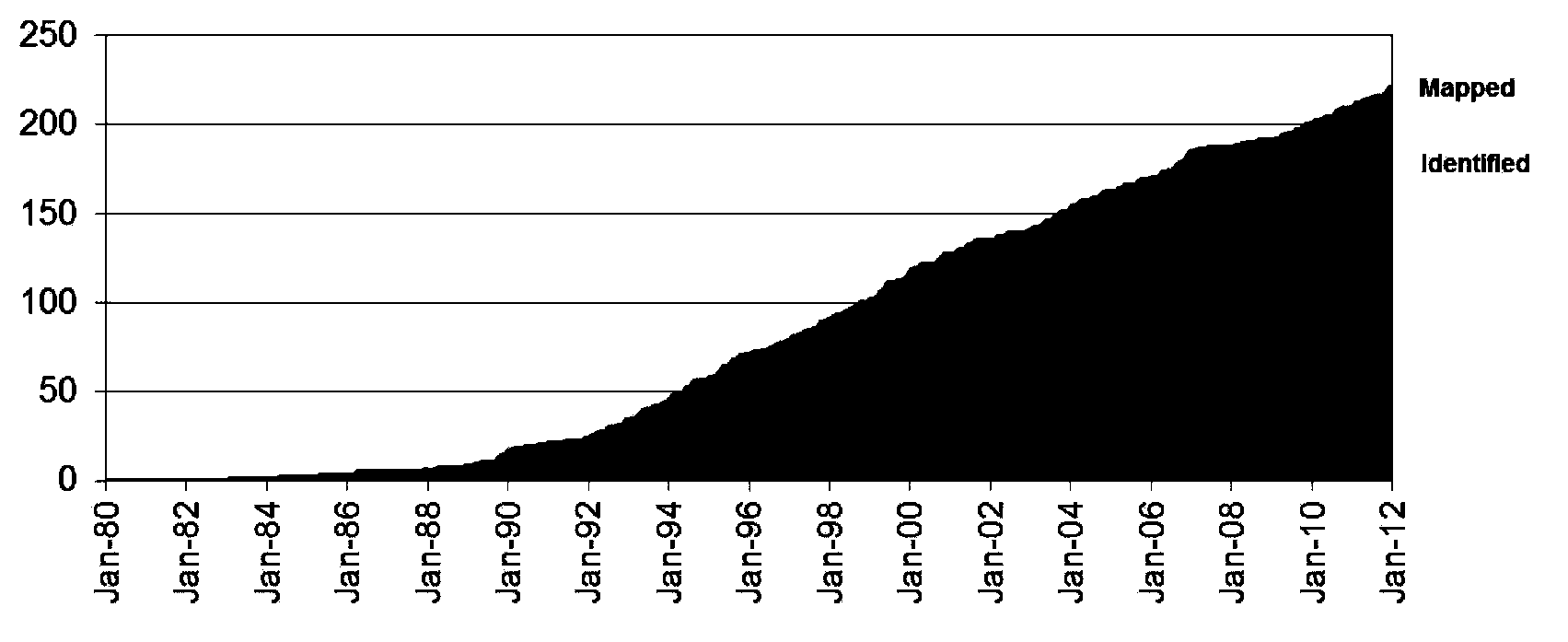
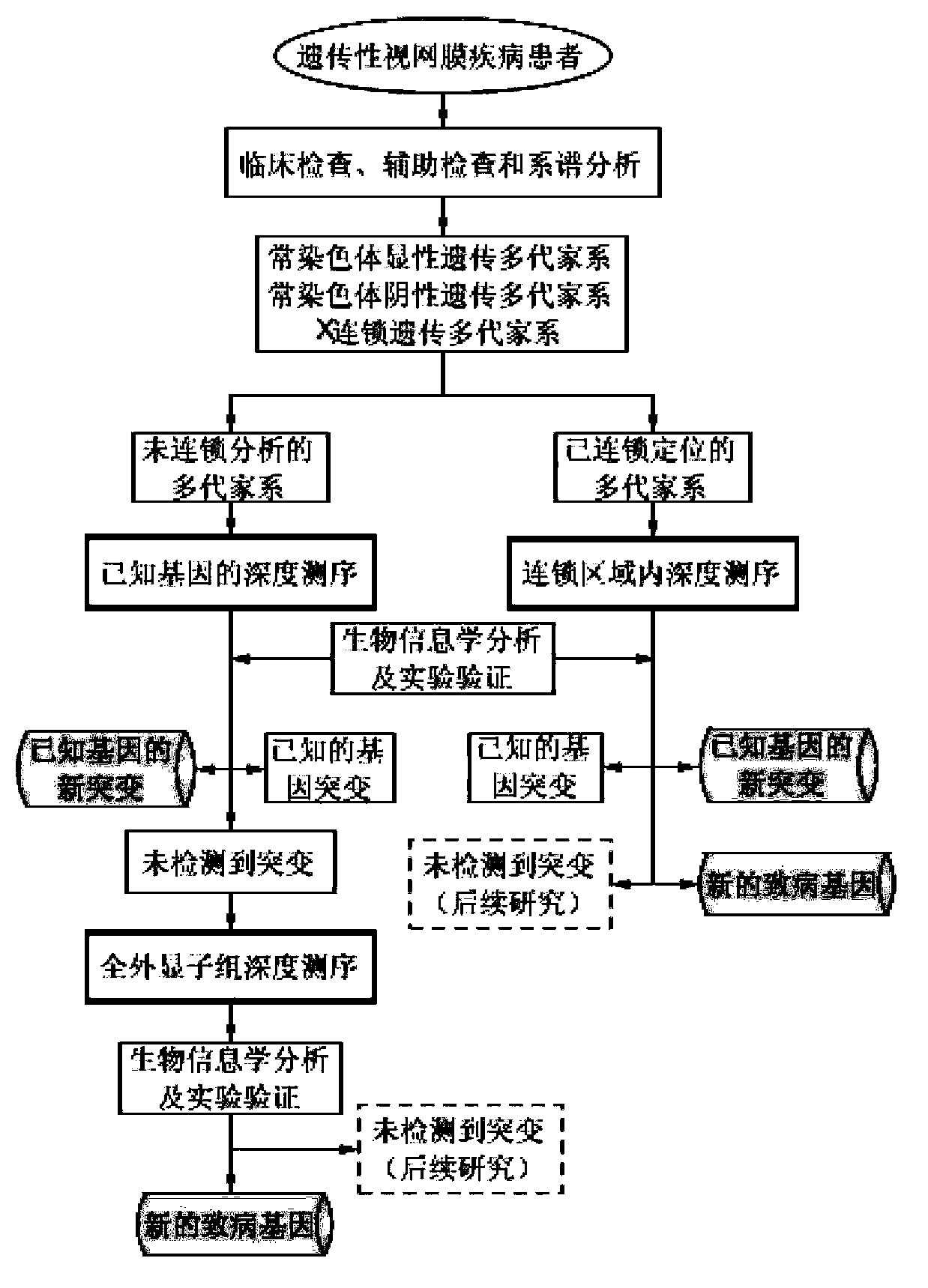
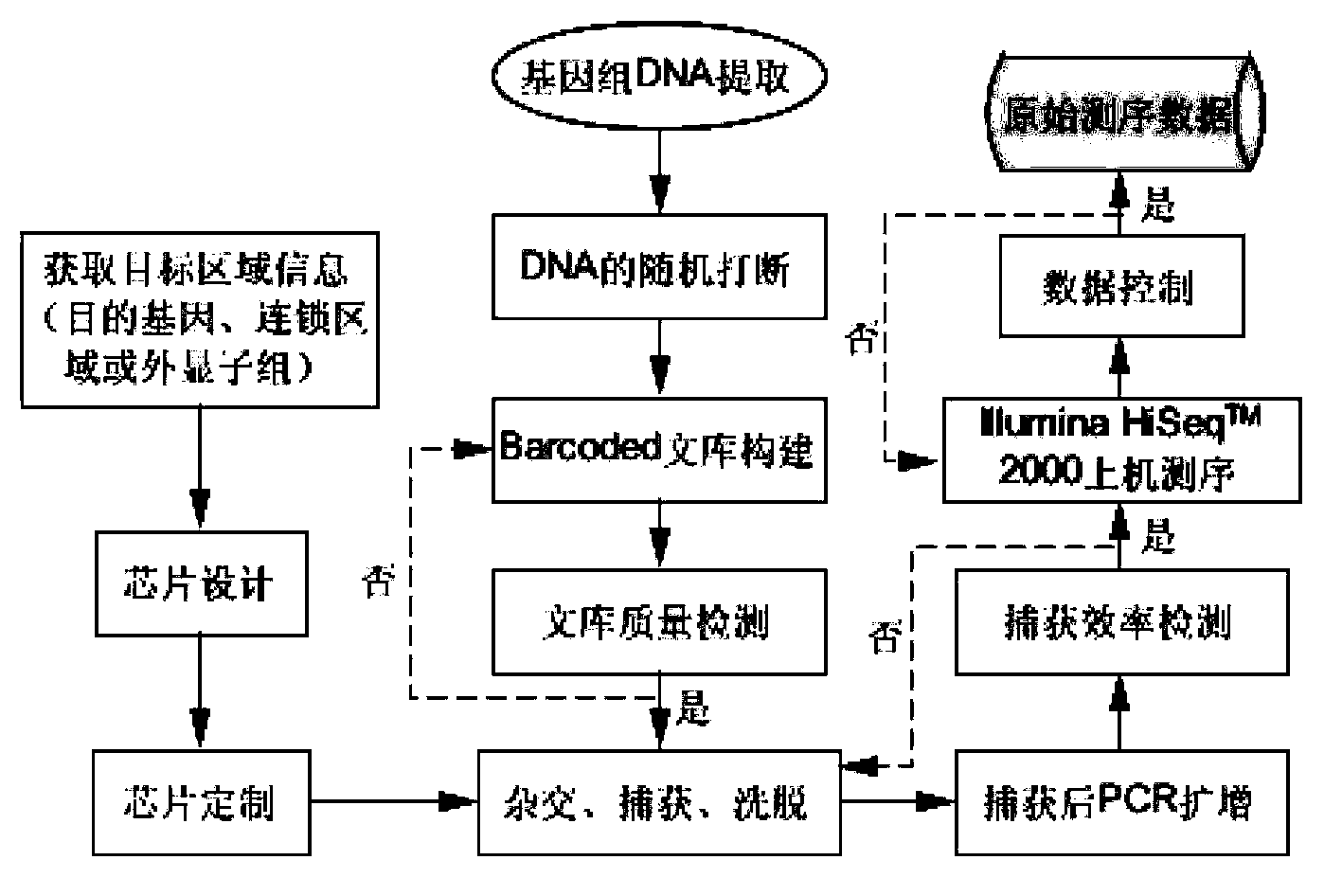
The invention belongs to the field of biological medicines, and relates to a method for screening HRDs disease-causing mutation and a gene chip hybridization probe designing method involved in the same. The method for screening the HRDs disease-causing mutation comprises the steps of (1) establishing an HRDs genetic resource repository; (2) designing and synthesizing a gene chip hybridization probe of an HRDs disease-causing gene, and integrating the gene chip hybridization probe onto a gene chip; (3) capturing a target area by utilizing the prepared gene chip and executing the depth sequencing; (4) analyzing the sequencing data on the aspect of bioinformatics, and screening the candidate disease-causing gene; (5) functionally predicting a newly-discovered splicing gene mutation site. By establishing the high-efficient HRDs target gene capturing technology, adopting the depth sequencing as a means and confirming the efficiency of the HRDs capturing chip, a high-efficient credible biological information analysis model is established.
Owner:赵晨
Method for inducing embryonal-suspensor mass (ESM) regeneration plant from immature seed of pinus massoniana
ActiveCN101849505AImprove efficiencyEasy to storeHorticulture methodsPlant tissue culturePhacusEmbryo
The invention relates to a method for inducing an embryonal-suspensor mass (ESM) regeneration plant from an immature seed of pinus massoniana. By using the characteristic of continuous schizogenesis capability of the ESM in the immature seed of the pinus massoniana, solid culture and liquid culture are performed alternatively and ESM forms a completely-grown embryo with a normal structure after a maintaining stage, a multiplication stage, an embryo pre-mature stage and a maturation culture stage, so that a pinus massoniana plant is obtained by germinating and culturing the embryo. Due to the adoption of the method, a large number of regeneration plants of a pinus massoniana embryo of which the hereditary basis is accordant can be obtained and new technology with a short period and high occurring efficiency is provided for the storage of pinus massoniana rare generic resource and the mass production of excellent-gene nursery-grown plants.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
A wheat heat resistance identification method
ActiveCN106526083AIncrease productionEasy to measurePlant cultivationCultivating equipmentsAgricultural scienceHeat resistance
A wheat heat resistance identification method is provided. The method includes identifying heat resistance in an intelligent greenhouse, identifying heat resistance in a greenhouse built in land for growing field crops, recording heat resistance identification indexes, calculating a thermal inductance index, determining variety heat resistance, determining a stable heat resistant variety, and other steps. Identification results of the method are accurate and reliable. According to the method, heat resistance identification in the intelligent greenhouse and heat resistance identification in the greenhouse built in land for growing field crops are combined, and interannual heat resistance identification results and heat resistance identification results of different ecoregions are compared and combined, and therefore the method is of great significance for heat resistance identification of wheat genetic resources and breeding parents, for screening of proper heat resistant wheat varieties suitable for plantation in Huanghuaihai zones and for grain safety in China. The identification indexes are easy to measure, and through mutual corroboration of indoor identification and land identification, heat resistance of a wheat variety can be truly reflected.
Owner:CROP RES INST SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Encapsulation-vitrification ultra-low temperature preservation method for dendrobium protocorm
InactiveCN102696579AReduce poisonConservation of germplasmDead plant preservationVitrificationPreservation methods
The invention discloses an encapsulation-vitrification ultra-low temperature preservation method for dendrobium protocorm. The encapsulation-vitrification ultra-low temperature preservation method comprises the following steps of: taking and placing young and tender the dendrobium protocorm in a pre-culture medium, respectively carrying out encapsulation by using a sodium alginate encapsulation liquid and a calcium ion encapsulation liquid after culturing for 7 days in the darkness at the temperature of 4 DEG C, placing the embedding particles of the dendrobium protocorm in a PVS2 mixed solution with 60% of mass concentration, processing for 30-60min at the temperature of 0 DEG C, removing the PVS2 mixed solution, adding a PVS2 solution, balancing for 2-3h at the temperature of 0 DEG C, rapidly placing the loaded encapsulated particles in cryovials and preserving the cryovials in liquid nitrogen; and when the particles are used, taking out the cryovials preserved in the liquid nitrogen, placing the unfrozen encapsulated particles in the MS basic media to restore the culturing of the particles, and realizing the ultra-low temperature preservation of dendrobium protocorm seeds. The encapsulation-vitrification ultra-low temperature preservation method has the advantages of being capable of effectively reducing the poison of dimethyl sulfoxide caused by a vitrification method to tissues, better preserving the dendrobium protocorm genetic resources and solving the problems of mutation, reduction of growth vigor and the like generated in the repeated subculture process.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Identification method of salt tolerance of barley
InactiveCN102835297AGuaranteed normal growthAvoid influenceSeed and root treatmentCultivating equipmentsBiotechnologyHordeum vulgare
The invention relates to identification, screening and variety breeding of crop genetic resources, and particularly relates to an identification method of salt tolerance of barley. The method comprises the steps of preparing a barley nutrient solution, preparing a barley germination substratum, germinating barley and identifying salt tolerance of barley. The method provided by the invention can ensure normal growth of barley during a growth period, avoid influence of environment difference for test results, reduce test errors and drastically improve screening efficiency of barley genetic resources.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Four-primer molecular marking method for identifying different genotypes of rice grain length gene GS3
ActiveCN103882146ANo errors leading to genotypingThere is no error that caused the identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceGenotype
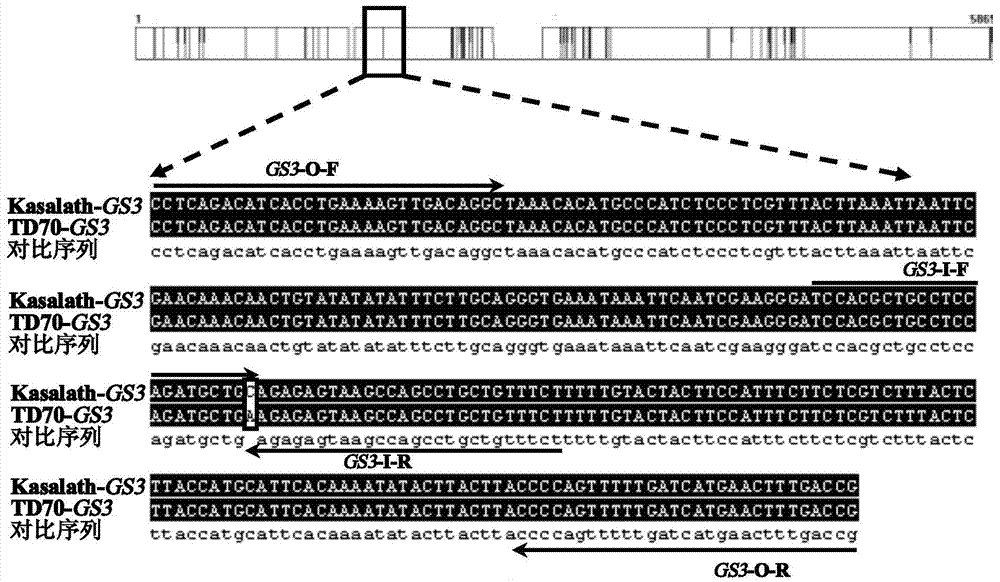
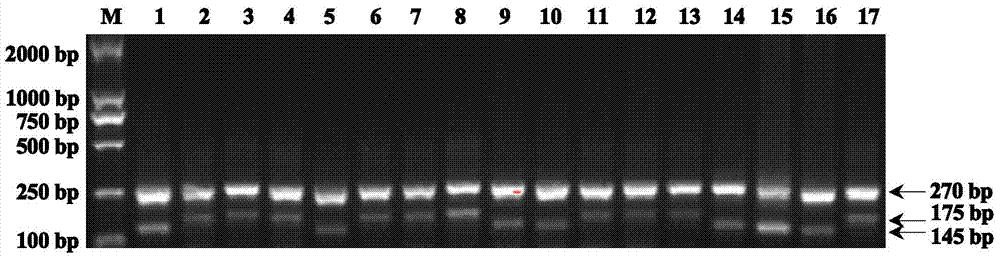
The invention relates to a four-primer molecular marking method for identifying different genotypes of a rice grain length gene GS3, belonging to the technical field of agricultural bioengineering. Four marking primers are designed and synthesized according to differences of a long and large-grain variety TD70 and a short and small-grain variety Kasalath in the nucleotide base sequence of the grain length gene GS3, and are added into the same PCR system for amplifying different rice DNA so as to distinguish different genotypes of homozygotes and heterozygotes of the GS3. The method disclosed by the invention not only can be used for rapidly and accurately identifying the different genotypes of the grain length gene GS3 in a rice genetic resource or a breeding population but also can be used for improving the selection efficiency on a long-grain genotype GS3-TGS3-T and speeding up the breeding progress of a new long-grain, high-quality and high-yield rice variety.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
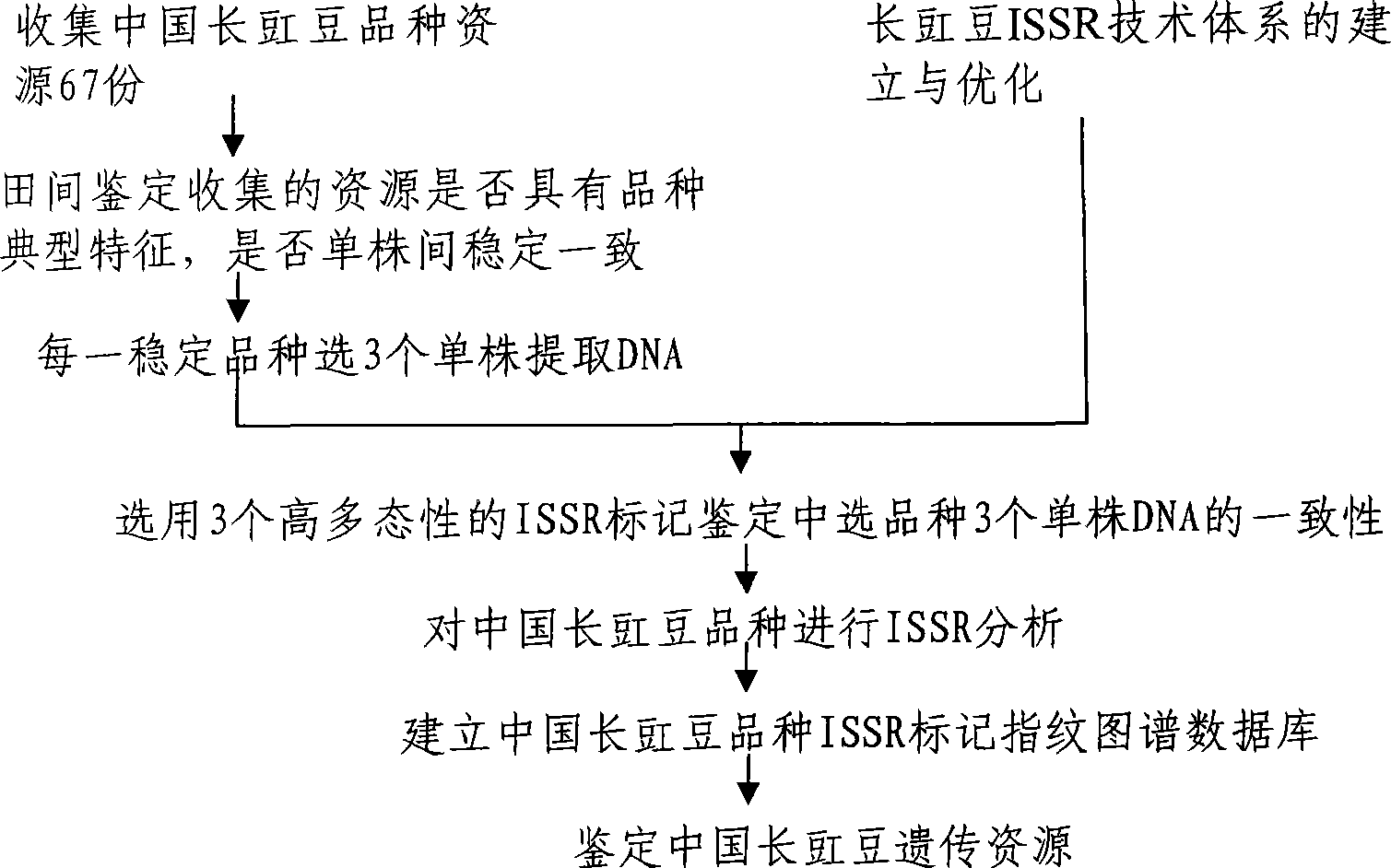
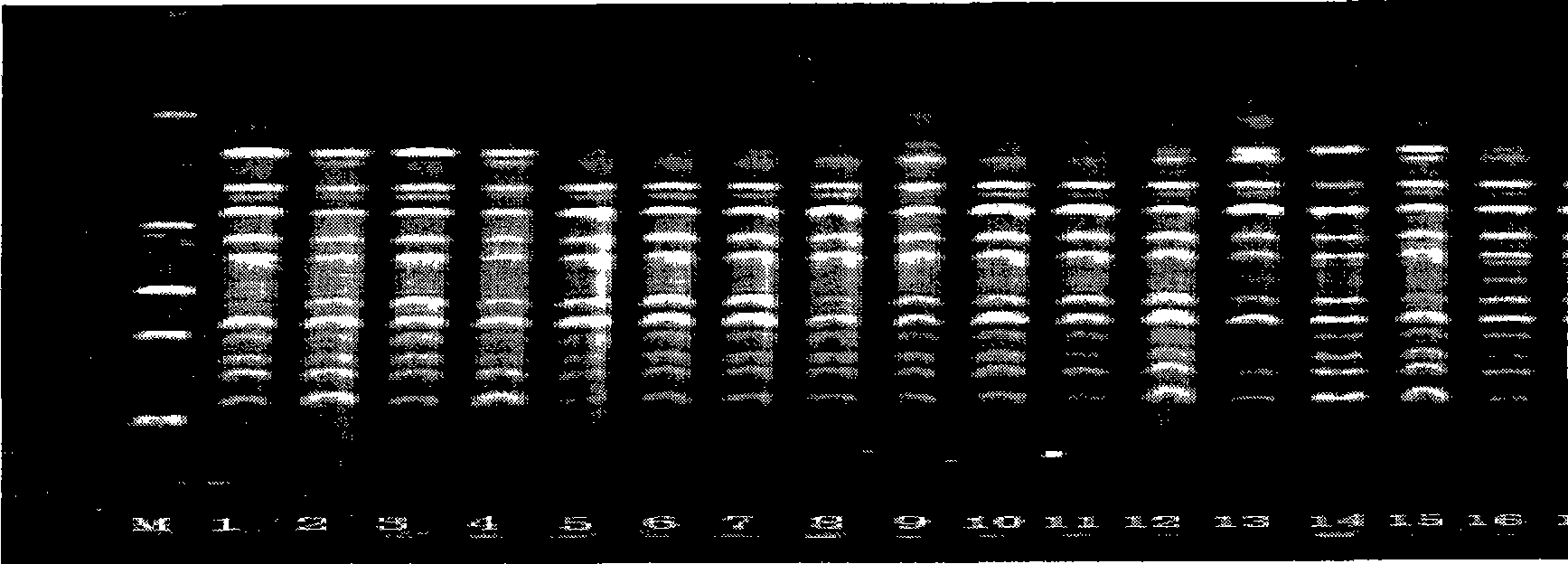
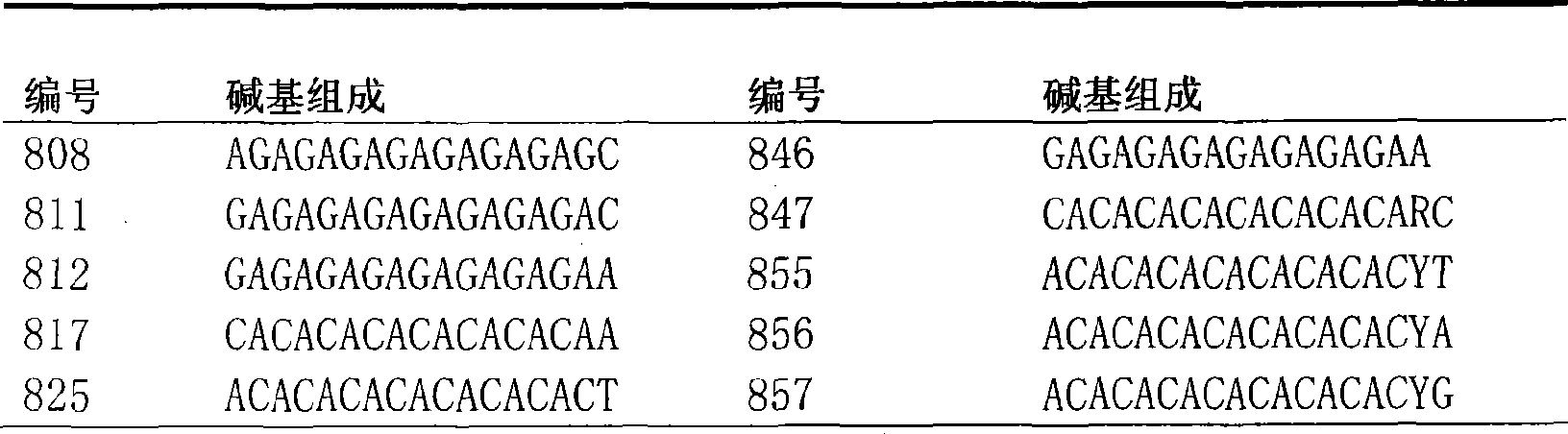
Method for constructing China asparagus bean genetic resource database based on ISSR molecular marker and uses thereof
InactiveCN101436229AValid identificationRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsDependabilityBiology
The invention discloses an ISSR molecular marking based method for constructing a Chinese asparagus bean generic resource database and application thereof. The invention also utilizes the data base to identify the trueness of a variety; according to field forms, the consistency and typicality among individual plants of the variety are identified, separated and atypical materials are given up, and DNA of the individual plant of the consistent and typical variety is picked up; by utilizing three ISSR markings with high polymorphism, the consistency of DNA level among the individual plants is primarily selected, and the variety and individual plant constructing a fingerprint are finally determined; and by utilizing the finally selected variety and individual plant, the ISSR analysis of the Chinese asparagus bean is made to construct a fingerprint database. The invention overcomes the defects existing in the construction of the prior generic resource database, such as separation among different individual plants of the variety and impurity on the DNA level, the reliability and accuracy of the Chinese asparagus bean ISSR fingerprint data base constructed by the method are greatly improved, and the planting varieties of the Chinese asparagus bean can be effectively and conveniently identified and distinguished.
Owner:JIANGHAN UNIVERSITY
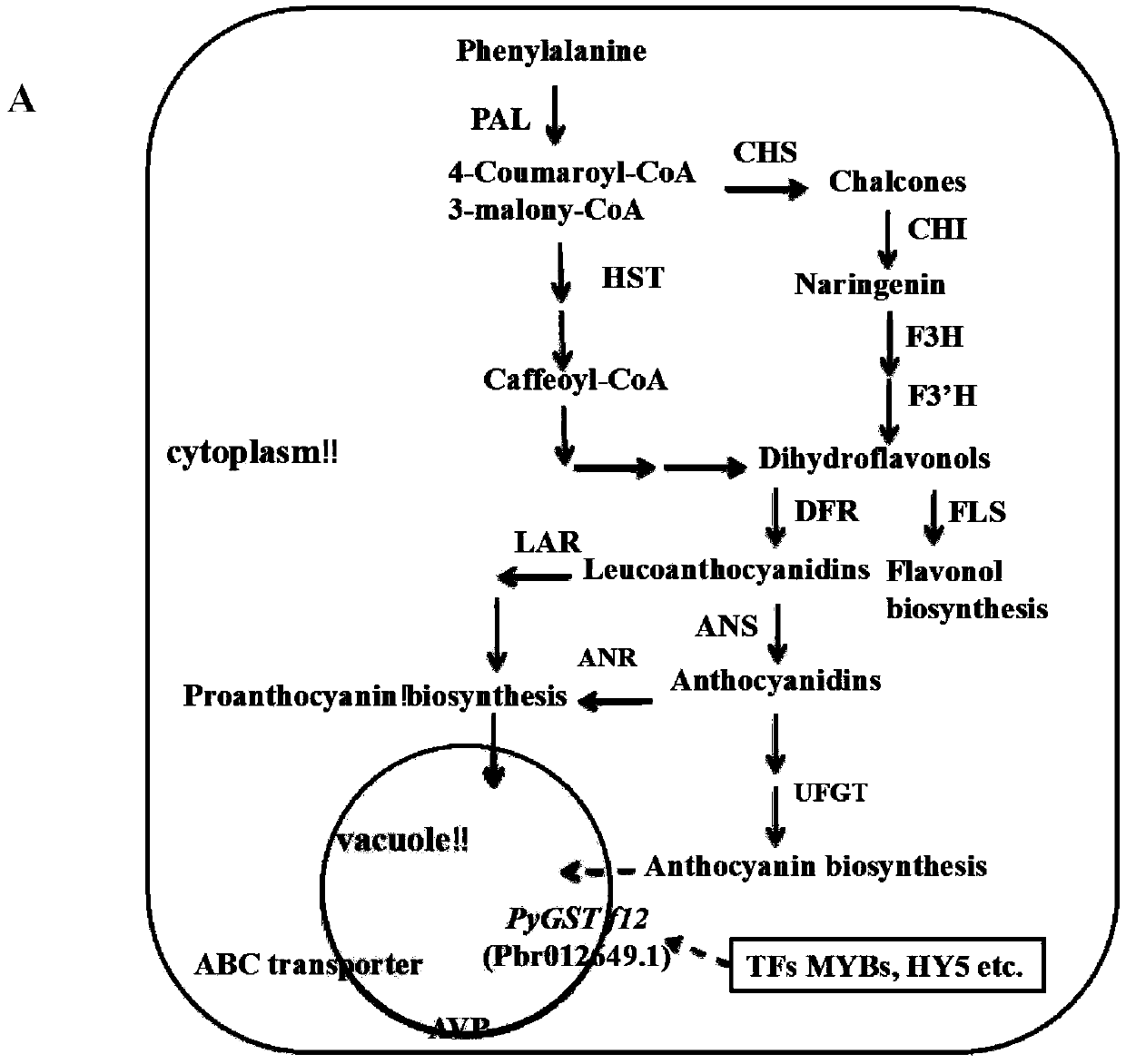
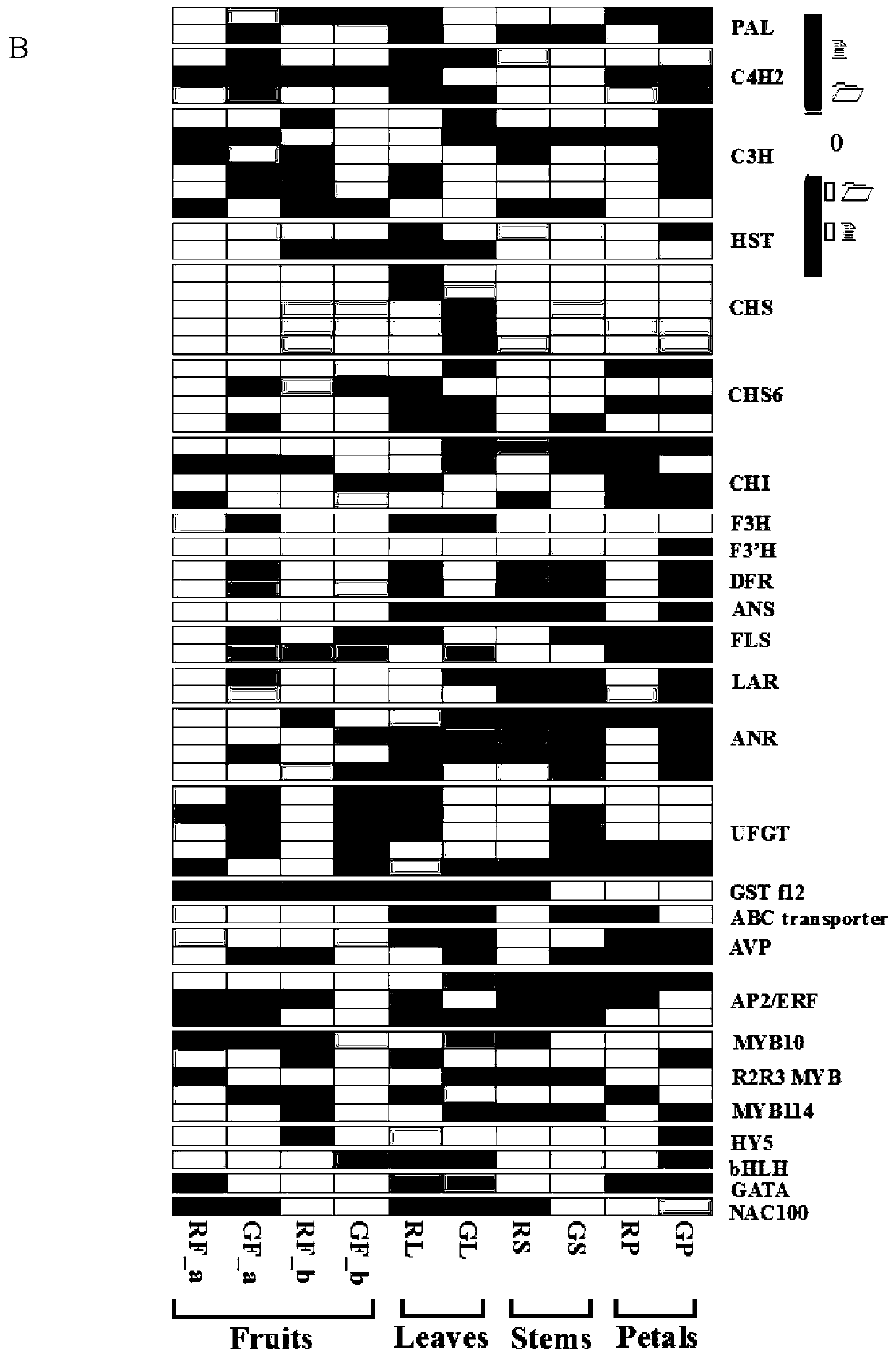
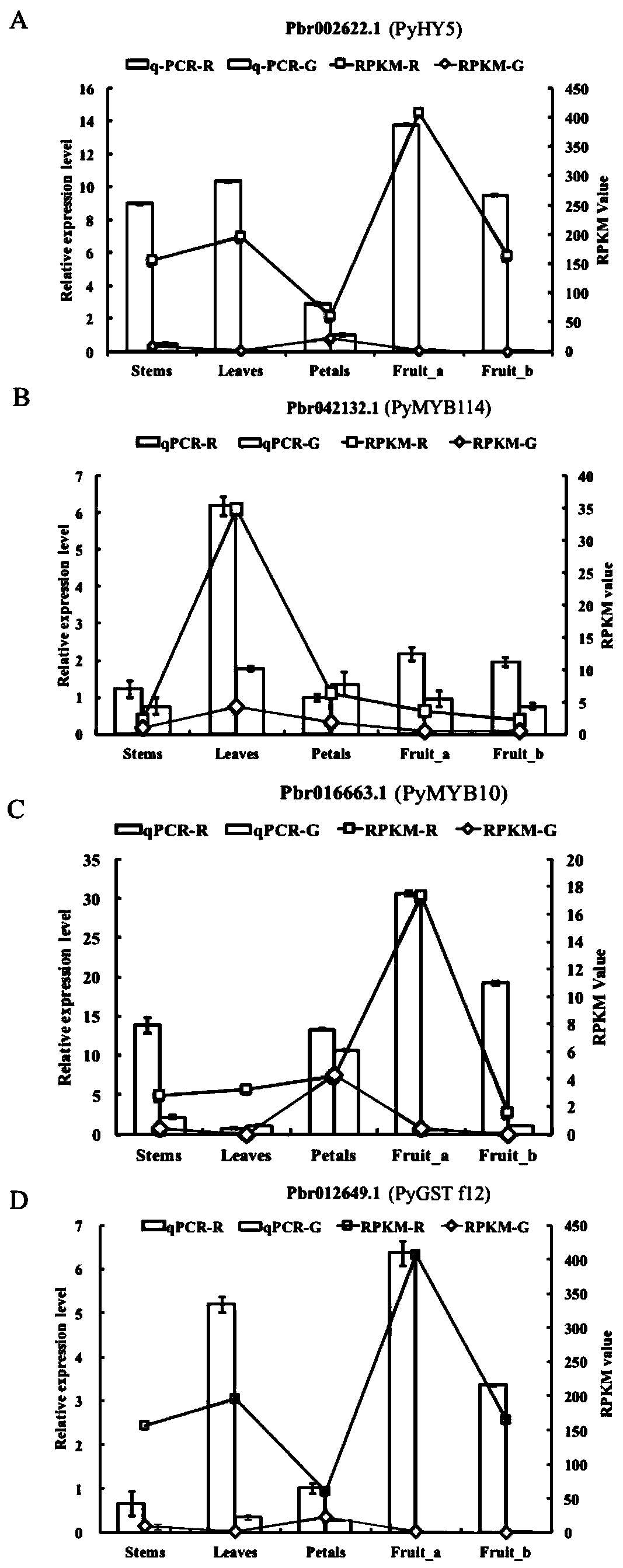
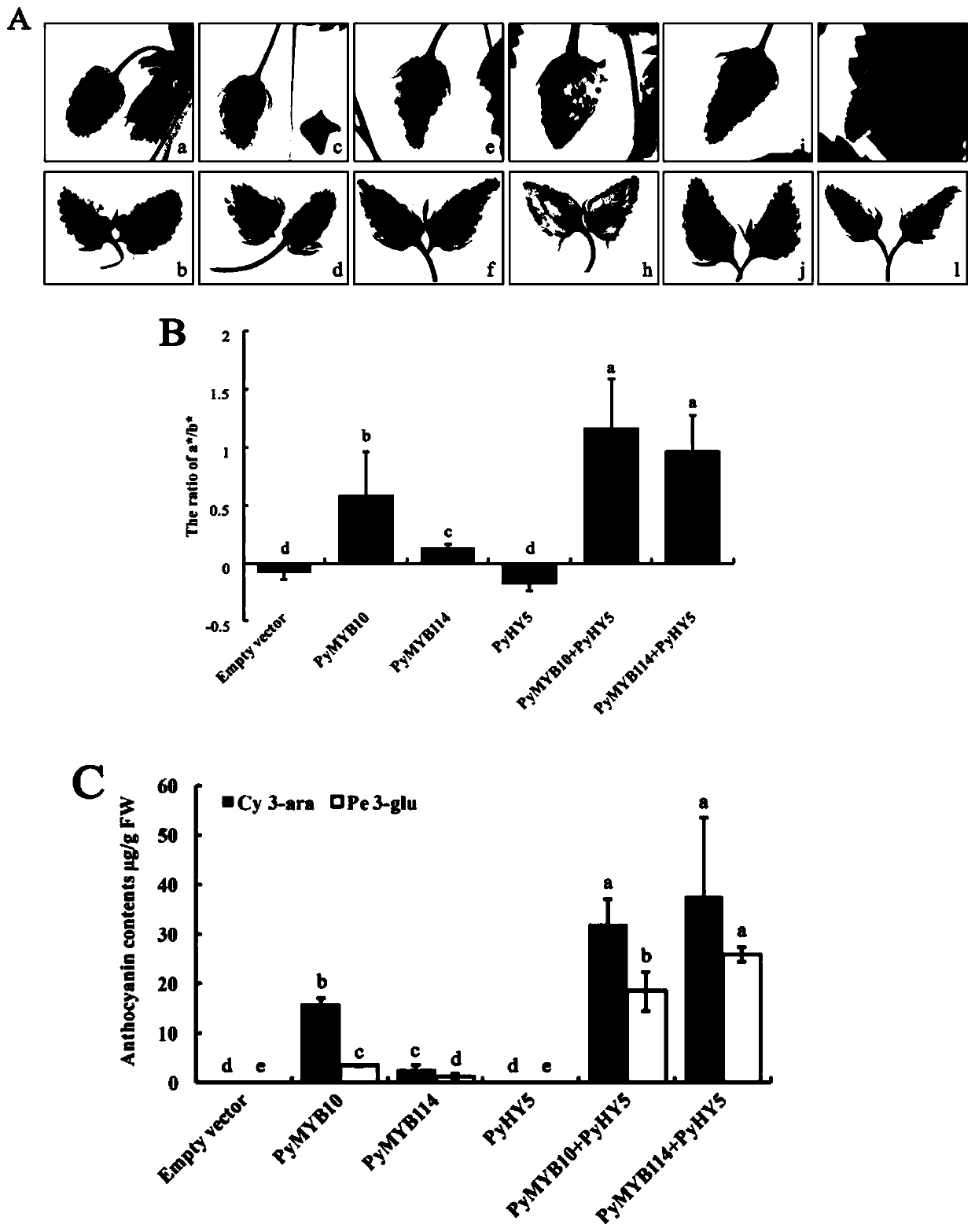
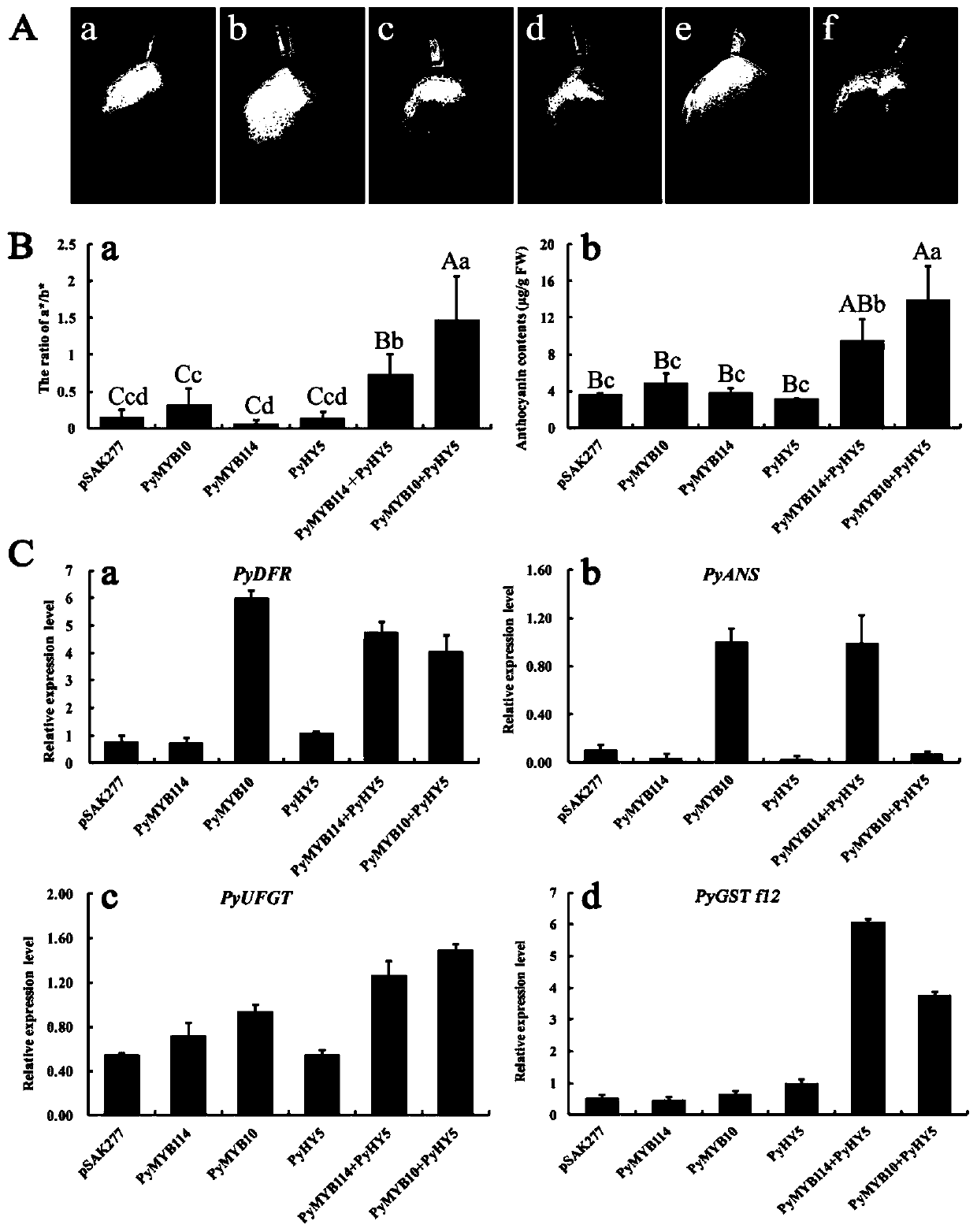
PyGSTf12 gene related to transport of anthocyanin in pear fruits, and recombinant expression vector and application of PyGSTf12 gene
InactiveCN109810990AAchieve friendlyReduce the cost of farmingBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementFragariaAgricultural science
The invention discloses a pear transcription factor PyGSTf12, and a recombinant expression vector and application thereof. The sequence difference between the PyGSTf12 and a promoter thereof is used as a molecular marker for identifying red and green peels, wherein the PyGSTf12 and the promoter are respectively separated from 'Red Zaosu' pears and yellow bud mutated fruits thereof, and the nucleotide sequences of the PyGSTf12 and the promoter are respectively as shown in SEQ ID No. 31 and SEQ ID No. 32. By a dual-luciferase report system, an agrobacterium-mediated instant genetic transformation method proves that the PyGSTf12 co-transformed by transcription factors PyHY5 and PyMYB114 promotes accumulation of anthocyanin in strawberry and pear fruits, and the PyGSTf12 promoter promotes thetransport function of the anthocyanin; through discovery of the PyGSTf12 gene, new genetic resources are provided for molecular breeding that promotes synthesis of the anthocyanin in pear peels, and new genetic resources are provided for the implementation of green agriculture; the development and utilization of the genetic resources is beneficial to agricultural cost reduction and environmental friendliness.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Pear transcription factor PyHY5, and recombinant expression vector and application thereof
The invention discloses a pear transcription factor PyHY5 and application of a recombinant expression vector of the pear transcription factor PyHY5. The nucleotide sequence of a transcription factor PyHY5 gene which is separated from 'Red Zaosu' pears and has a function of promoting anthocyanin biosynthesis of pear peels is as shown in SEQ ID No. 1, and the encoded amino acid sequence of the transcription factor PyHY5 gene is as shown in SEQ ID No. 2. Transcription factors PyHY5 and PyMYB114 are co-transformed into strawberry and pear fruits by an agrobacterium-mediated transformation method;according to biological function verification, the cloned PyHY5 gene and a cofactor PyMYB114 thereof interact to promote the transport function of anthocyanin in the pear peels; through discovery of new functions of the PyHY5, new genetic resources are provided for molecular breeding that promotes accumulation of the anthocyanin in the pear peels, and new genetic resources are provided for the implementation of green agriculture; the development and utilization of the genetic resources is beneficial to agricultural cost reduction and environmental friendliness.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Phosphate dissolving bacterium and acquisition method thereof
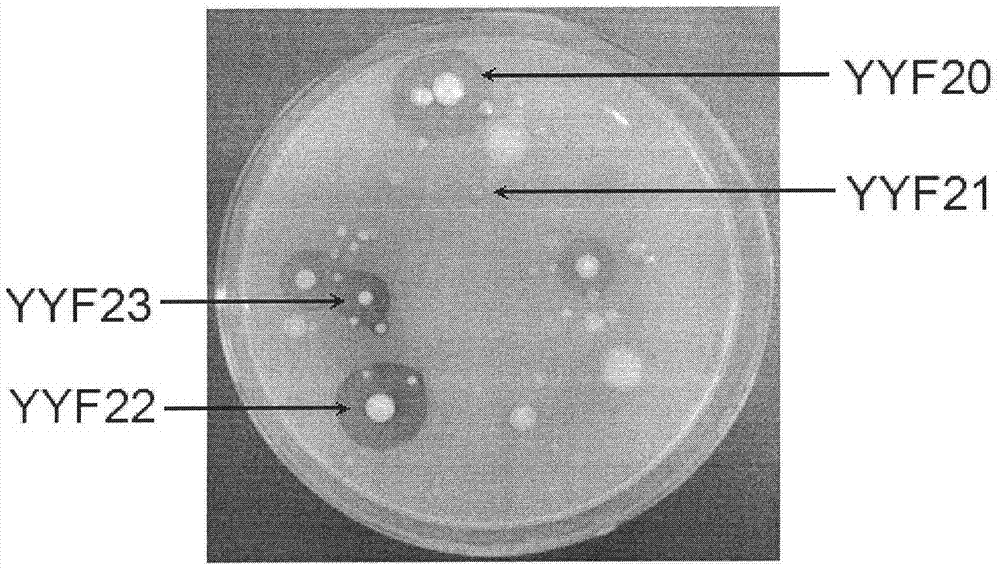
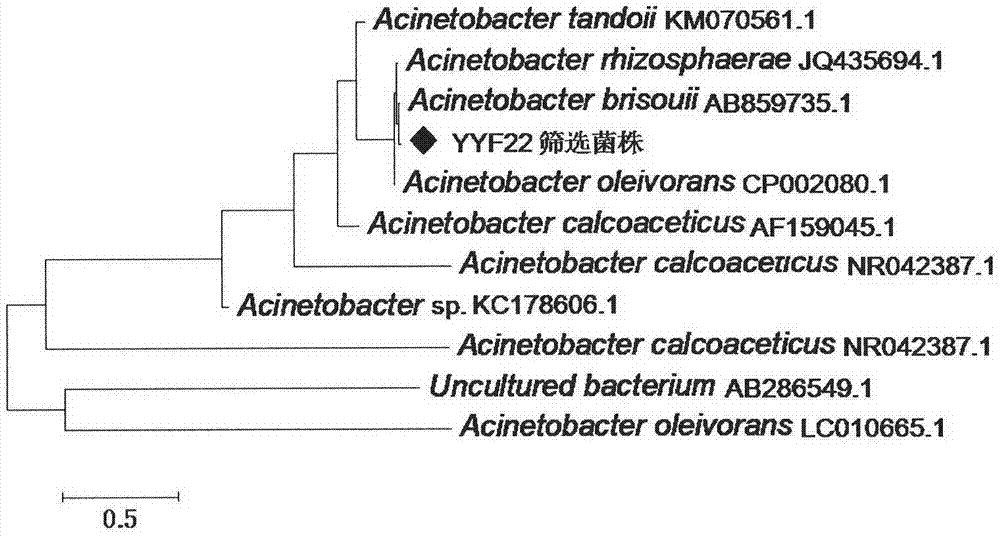
InactiveCN104774784AExtended backendRich genetic resourcesBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementPhosphateBiological organism
The invention provides a phosphate dissolving bacterium and an acquisition method thereof, belonging to the field of agricultural biotechnology. The phosphate dissolving bacterium and the acquisition method thereof can enrich the genetic resource of wild phosphate dissolving bacteria and enlarge a backup library for whole-genome breeding of phosphate dissolving bacteria. The phosphate dissolving bacterium provided by the invention is named as YYF22 and is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection with an accession number of CCTCC No: M2015043. The colony characteristics of the phosphate dissolving bacterium are as follows: the YYF22 strain is coccobacillus with a length of 1.2 to 2.9 [mu]m and a width of 0.4 to 1.5 [mu]m; the phosphate dissolving bacterium is normally arrayed in pairs and may independently exist; the phosphate dissolving bacteria sometimes adhere to from a filose shape or chain shape; the phosphate dissolving bacterium is free of flagellum, has a capsule, and cannot move; and on an LB flat, the colony of the bacterium has a neat edge, a moist surface and low bulges, and is glossy and cream yellow.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Establishment method of goat resource population
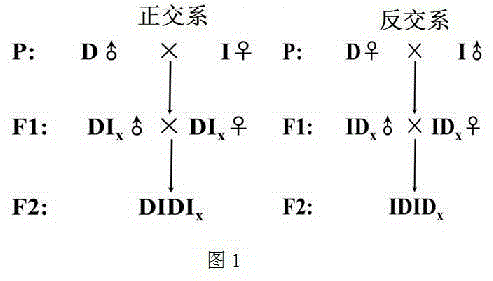
InactiveCN105123621AImprove economyImprove international competitivenessAnimal husbandryNational levelReciprocal cross
The invention belongs to the field of establishment of a population genetic resource bank, and provides a scientific establishment method of a goat resource population bank, and provides a goat reference family system establishment case, and relates to two national-level genetic resource varieties, namely, a Dazu black goat and an Inner Mongolia Cashmere goat (Alxa type). According to the resource population establishment method, forward cross and reciprocal cross of Dazu black goat and Inner Mongolia Cashmere goat (Alxa type) are utilized, random mating of genetic relationship is avoided for F1, so that Mendel genetic characters are separated, a goat economic character QTL or a functional gene is located by virtue of a genome means, and a relatively-precise genetic mark is provided for the goat breeding. The genetic resource bank comprises goat population, a genealogy inforamtion database, a phenotypic character database, a DNA sample library, an RNA sample library and a genetic variation information database.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Method for detecting goat TMEM95 gene subtle copy number variation through PCR technology and application thereof
InactiveCN105624314AImproved production traitsMicrobiological testing/measurementMarker-assisted selectionPcr ctpp
The invention discloses a method for detecting goat TMEM95 gene subtle copy number variation through the PCR technology and application thereof. According to the method, goat whole genome DNA, containing the TMEM 95 gene, in a Chinese region serves as a template, a primer pair P1 serves as a primer, part of a sequence of the goat TMEM 95 gene is amplified through PCR, and then a PCR amplification segment is subjected to agarose gel electrophoresis; according to an agarose gel electrophoresis result, non-coding region 58bp subtle copy number variation of the goat TMEM 95 gene is identified; because the TMEM 95 gene has an important regulation function on growth traits and milk production traits, the detection method lays a foundation for building of the relation between the TMEM95 gene subtle copy number variation and production traits, therefore the method can be conveniently used for assisted selection of markers of production traits of goats in China, and goat species with good genetic resources are built easily.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Indel mark of powdery mildew resistance allele er1-7 of peas and application thereof
InactiveCN105154442AOvercoming shortcomings such as long time periodImprove breeding efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural sciencePlant pathology
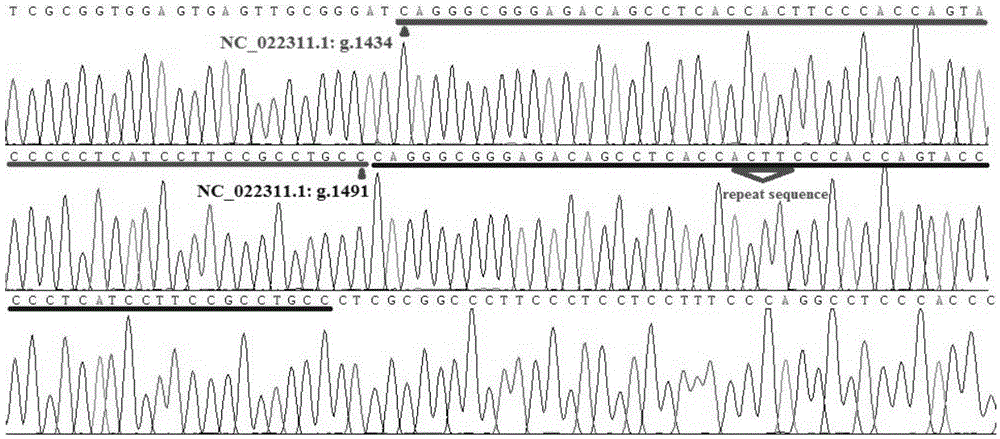
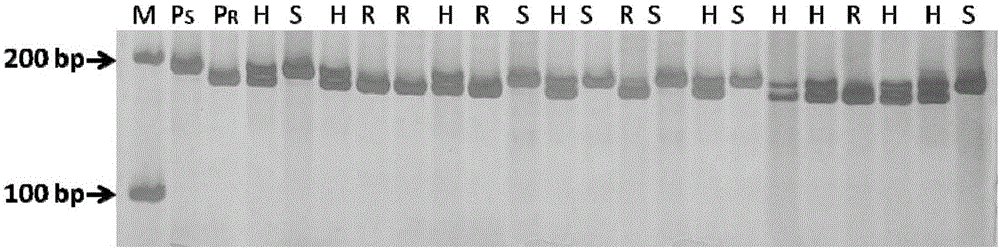
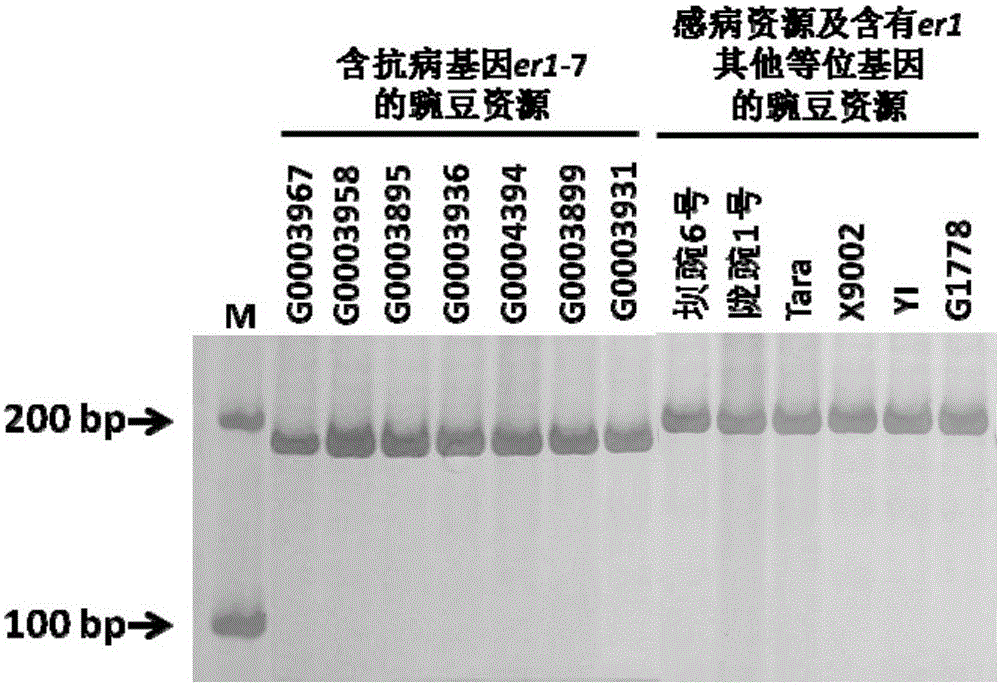
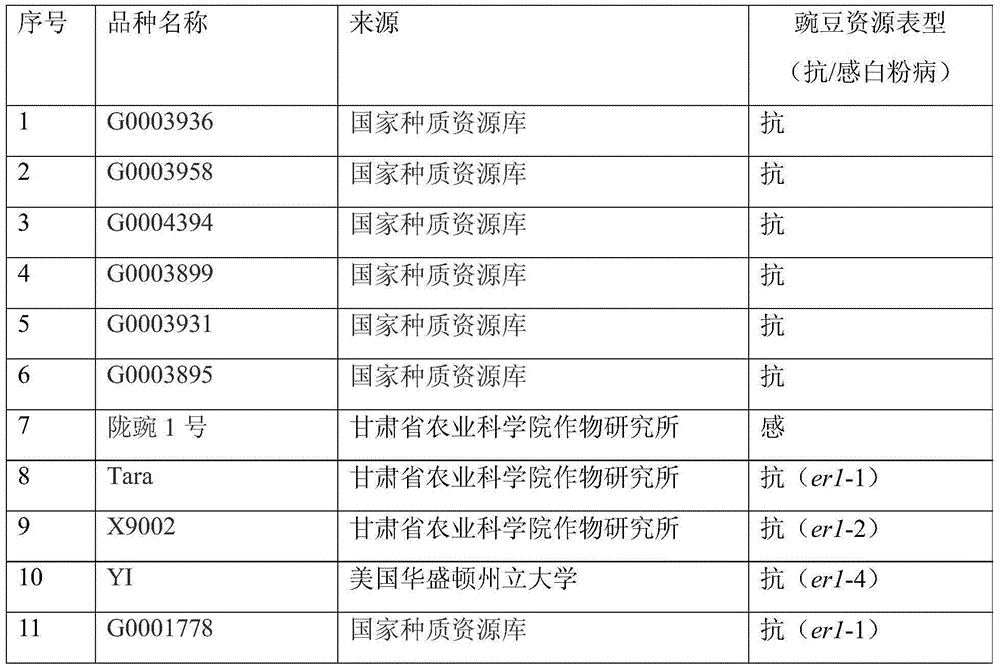
The invention relates to an Indel mark InDel111-120 co-separated with a powdery mildew resistance allele er1-7 of peas and application thereof, and belongs to the field of plant pathology and crop disease resistance genetics and breeding. A primer for amplifying the Indel mark has the following nucleotide sequence of InDe1111-120-F:GGAGTTAAGGAACGAACTTTGG, InDel111-120-R:CCATGTCTGCGTCTGTATCTTT; a characteristic strip of the Indel mark which is amplified by the primer and co-separated with the powdery mildew resistance allele erl-7 adopts 183bp, and the nucleotide sequence is shown as Seq ID No.3. The invention further provides a kit for screening a pea genetic resource containing the er1-7 gene on the basis of the Indel mark. By adopting the Indel mark or the kit, the pea resource containing the resistance allete er1-7 can be rapidly and precisely distinguished out, so that the mark or the kit can be effectively applied to molecular assisted selection of the powdery mildew resistance of the peas, high efficiency, precision, convenience and rapidness are achieved, the breeding cycle is greatly shortened, and the breeding process is sped up.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Vitrification ultralow-temperature preserving method for agapanthus embryogenic callus
InactiveCN102823582AAchieve preservationPlay a guiding roleDead plant preservationHorticulture methodsGermplasmHigh water content
The invention relates to the field of ultralow-temperature preservation, and in particular relates to a vitrification ultralow-temperature preserving method for agapanthus embryogenic callus, after low temperature-hypertonic pretreatment, the agapanthus embryogenic callus is sequentially dehydrated in loading solution and vitrification solution; and finally, the dehydrated agapanthus embryogenic callus is added with the vitrification solution again, and then quickly put in liquid nitrogen to be preserved. The agapanthus embryogenic callus is preserved at ultralow temperature through specially designing the treatment methods, conditions and reagents of a vitrification ultralow temperature preserving process, so a technical guarantee is provided for preserving agapanthus genetic resources, a new effective method is provided for somatic embryogenetic seedlings and new product cultivating materials, and a guiding function is achieved for preserving plant resources which grow in tropical zones or contain high water contents and for completing an asexual propagation technical system.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Taxus chinensis propagating method
InactiveCN105309141AEffects of reduced reproductive rateNormal growth characteristicsHorticulture methodsFertilizer mixturesWater qualityCallus formation
The invention provides a taxus chinensis propagating method. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps that 1, taxus chinensis branches are selected; 2, bactericide is used for treating the branches; 3, a plant growth regulator is used for treating the branches; 4, water culture is adopted for inducing the branches to take root; 5, a nutrient solution is added for curing. By the adoption of the method for propagating taxus chinensis, restriction of cultivated land resources can be gotten rid of, and the propagation area is increased; meanwhile, the influence on the survival rate from external environment is reduced to the maximum, time for callus forming and rooting is shortened, the stem cutting survival rate is remarkably increased, the restriction that due to poor environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, soil and water quality, the stem cutting survival rate is influenced by an original propagation means is broken through, the current situation that taxus chinensis genetic resources are scanty can be relieved, and great economic value can be created.
Owner:苏州梵时轮园艺科技有限公司
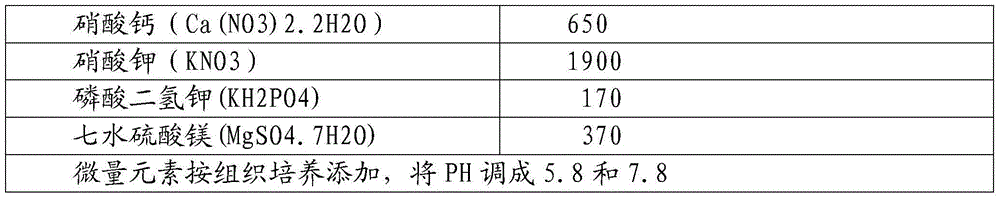
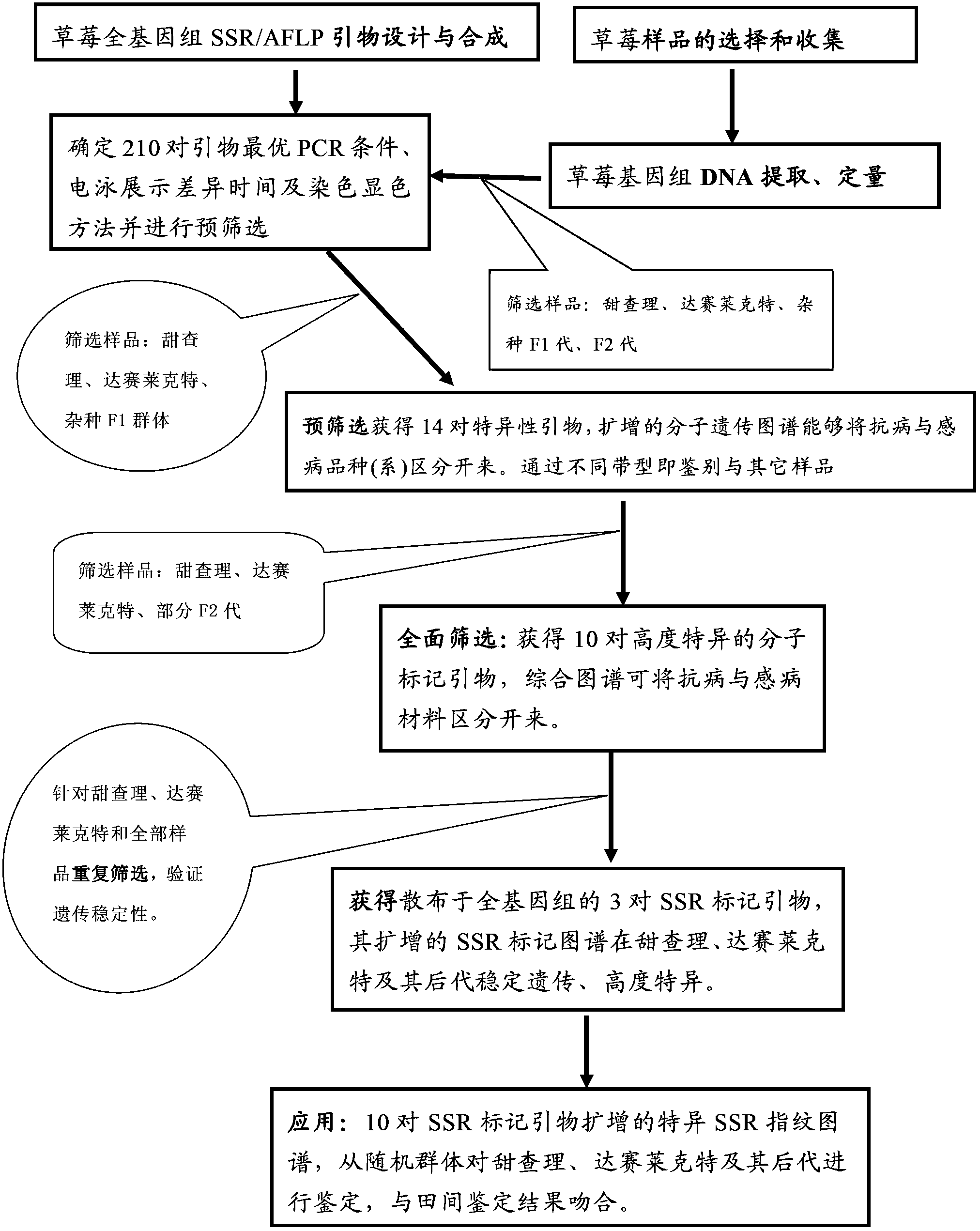
Primer sequence for authenticating resistance of strawberry genetic resource anthracnose and authentication method thereof
ActiveCN103667427AGenetic stabilitySimple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceGermplasm
The invention discloses a primer sequence for authenticating resistance of strawberry genetic resource anthracnose and an authentication method thereof. The method is characterized in that the genome DNA of 250 parts of filial generation materials obtained through the conventional cross breeding by adopting sweet Charlie and Darselect as cross parents as a template, the PCR amplification is executed for 146 pairs of SSR primers and 64 pairs of AFLP primers covering the complete genome, the specificity genetic map of the resistance of strawberry anthracnose is established through the PAGE microgel electrophoresis analysis, 10 pairs of SSR primers with high specificity and strong dominance of the filial generation are successfully obtained, and the nucleotide sequence of the SSR primer is indicated as SEQ ID No.1 to 20. When the primer sequence obtained through the method is used for authenticating the resistance of the strawberry genetic resource anthracnose, the matching rate of an authentication result and the field resistance can reach 88.4 percent. The method has the advantages of simplicity, rapidness, high efficiency, high breeding efficiency, short breeding period and the like and has high application value on the authentication of the resistance of the strawberry genetic resource anthracnose.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for quickly and preliminarily screening excellent tea tree resource based on contained contents
InactiveCN103033578AReduce dosageDoes not affect normal growthComponent separationAdditive ingredientGermplasm
The invention discloses a method for quickly and preliminarily screening excellent tea tree resources based on contained contents. The method comprises the following steps: taking first expanded leaves of tea tree buds with consistent growth conditions and growth vigor, performing freezing treatment to the leaves by liquid nitrogen, crushing the leaves, using methanol to quickly and directly extract the leaves, centrifuging the leaves, taking supernatant, utilizing a high performance liquid chromatography device to detect the contained contents in the tea leaves, comparing the contents of the contained ingredients, preliminarily screening the excellent tea tree genetic resources, and based on the preliminary screening, adopting the known method to further screen the preliminarily screened excellent tea tree genetic resources. The method is simple and convenient, low in the device requirements, low in the reagent dosage, simplifies the pretreatment procedures of the test materials, greatly reduces the labor intensity, reduces the determination cost and time, and can be used for high throughput analysis.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Detection method for insertion/deletion marker of goat gene IGF2BP1
ActiveCN110468218AAccurate detectionLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenotypeBiology
The invention discloses a detection method for an insertion / deletion marker of a goat gene IGF2BP1. The detection method comprises the following steps: with to-be-detected goat whole-genome DNA as a template, applying a part of fragments of the goat gene IGF2BP1 by PCR, then carrying out agarose gel electrophoresis, and identifying the genotypes of the 15-bp insertion / deletion polymorphic site andthe 5-bp insertion / deletion polymorphic site of the goat gene IGF2BP1 according to electrophoresis results. According to the invention, different genotypes and a combined genotype of 15-bp and 5-bp insertion / deletion polymorphic sites of the goat gene IGF2BP1 have significant correlational relationship with the litter size character of Shaanbei white-cashmere goat, so the 15-bp and 5-bp insertion / deletion polymorphic sites can be used as DNA markers to improve the litter size character of the goat. The detection method for the insertion / deletion marker of the goat gene IGF2BP1 provided by theinvention can be applied to goat molecular marker-assisted selective breeding, and accelerates establishment of an excellent goat genetic resource population.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Method for detecting CNV (copy number variation) marker of KLF8 gene of beef and application thereof
InactiveCN107619857AExcellent genetic resourcesExcellent chest widthMicrobiological testing/measurementReference genesMarker-assisted selection
The invention discloses a method for detecting a CNV (copy number variation) marker of a KLF8 gene of beef and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps of using DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of a blood whole genome of Jiaxian beef as a template; respectively amplifying the CNV area of the KLF8 gene and a reference gene BTF3 by a real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR (polymerasechain reaction) method; according to a formula of 2*log2 2<-delta delta Ct>, dividing results into an insertion type, a deletion type and a normal type, and identifying the CNV of the KLF8 gene. Displayed by the correlation analysis of production data of Jiaxian beef, the different copy numbers of the KLF8 gene have obvious influence to the growth and development of the Jiaxian beef, and the chest width of the deletion type individual is obviously higher than the chest widths of the insertion type and normal type individuals. The method has the advantages that the CNV closely related with production character of the beef is detected at the DNA level, and can be used as the important candidate molecular marker for assisted selection of the marker of growth character of beef, and the beef group with good genetic resources is quickly established.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Triple cross wheat breeding technical method
The invention discloses a triple cross wheat breeding technical method which is a cross wheat breeding technical method tightly combining a conventional cross breeding technology and a hybrid vigor breeding technology. Specifically, the technical method is organically composed of six modules, namely a genetic resource and parent garden module, a cross breed parent breeding module, a hybrid vigor testing and selecting module, a cross breed breeding module, a conventional cross breeding module and a production performance comparison test module. The relations among the modules and the relations of the working procedures in the modules are clear. The triple cross wheat breeding technical method solves the problem that due to the fact that breeding resources and information between two breeding methods cannot be effectively shared, the hybrid vigor breeding efficiency is not high.
Owner:XINJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI & RECLAMATION SCI
Soybean cyst nematode resistance gene and application thereof
InactiveCN102206651AEffective guidanceEffectively guide conventional breedingFungiBacteriaGlycineAgricultural science
The invention relates to a soybean cyst nematode resistance gene and application thereof. The cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) fragment (SRC-J-6) provided by the invention is derived from soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merrill.) variety L-10, and has a nucleotide sequence shown in 1) a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO. 1; 2) a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) molecule capable of hybridizingwith the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO. 1 and being expressed under strict conditions; 3) an mRNA (messenger ribonucleic acid) molecule, which has homology of more than 90% with the nucleotide sequence shown in 1) and can be expressed; or 4) a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) molecule, which has homology of more than 90% with the nucleotide sequence shown in 1) and can be expressed. After theplant tissues are transformed by the gene disclosed by the invention, the resistance to cyst nematode of the transgenic soybean is significantly improved. The soybean cyst nematode resistance gene provided by the invention has important significance, not only can effectively guide conventional breeding, can also provide excellent genetic resources for the transgenic breeding of soybean and has broad application prospects in the soybean production.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Rice-shrimp intercropping symbiotic method of single-season rice and three-season shrimps
InactiveCN107494100AMaintain ecological balanceImprove the efficiency of farmingClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaOverfishingOryza
The invention relates to a rice-shrimp intercropping symbiotic method of single-season rice and three-season shrimps, and belongs to the technical field of ecological planting and breeding. The method comprises the steps of digging a circular furrow at the periphery of a farmland with the area of 50-60 mu, and then planting rice and water weeds in the farmland in the water weeds in an interval manner. Through building a rice field comprehensive planting and breeding ecological system, biological bait resources in the rice field can be fully utilized, the rice and the shrimps grow together, and the problems that a lot of pesticide is used for rice planting, environment is polluted by fertilizer, people health is also influenced, genetic resources are degenerated and yield is decreased due to overfishing of wild crayfish resources and backward artificial breeding technology are solved. The purposes of keeping ecological balance and increasing planting and breeding benefits are achieved.
Owner:FUWA GROUP
Rive CYP704B2 gene mutant, and molecular identification method and applications thereof
ActiveCN105002191ABreeding benefitsFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionMolecular identificationGenetically modified rice
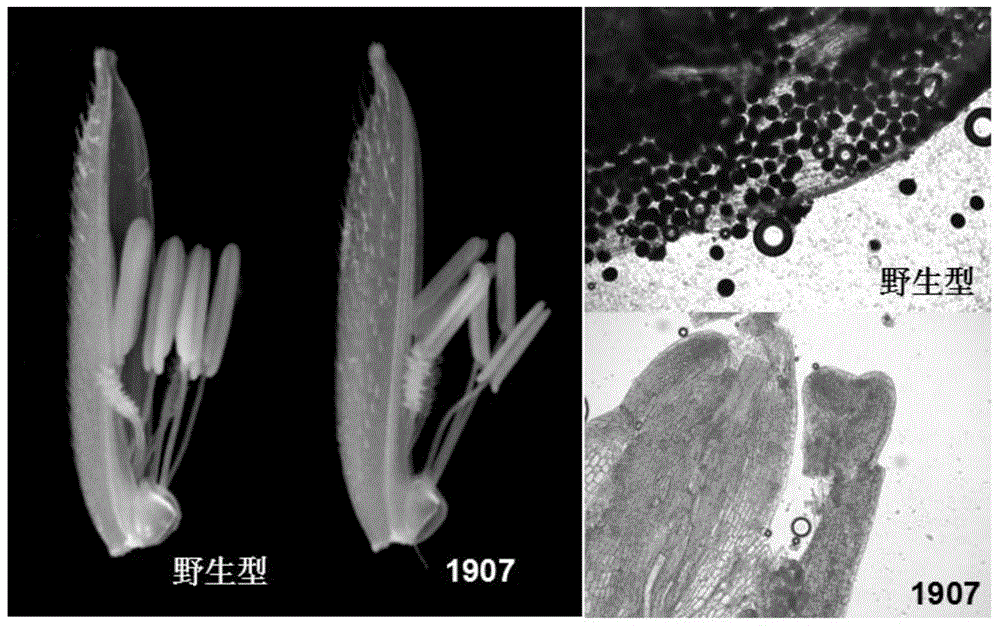
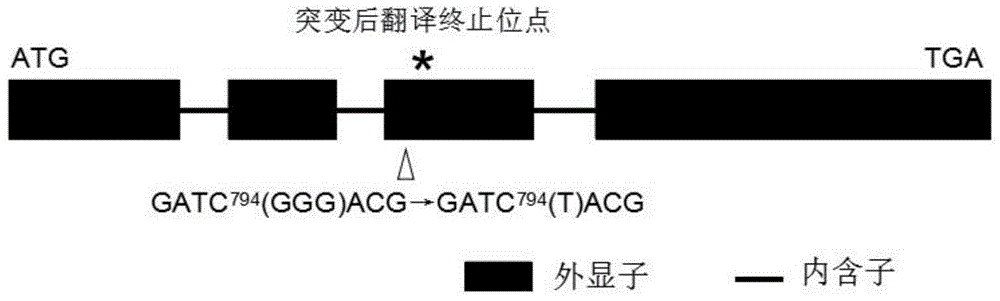
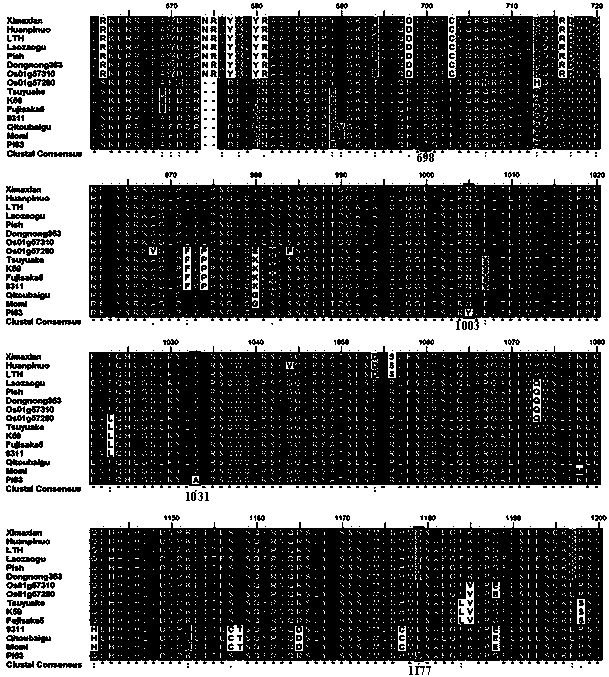
The invention provides a rive CYP704B2 gene mutant, and applications thereof, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. According to the rive CYP704B2 gene mutant, indica rice 93-11 is subjected to cobalt 60 radiation-induced mutation so as to replace three G bases after the 794th base of rice CYP704B2 gene with one T base; the CYP704B2 gene mutant is named as cyp704B2-3; the nucleotide sequence of the CYP704B2 gene mutant is represented by SEQ ID No.1; it is further confirmed that rice recessive genic male sterility is induced by the CYP704B2 gene mutant; the CYP704B2 gene mutant can be used for culturing transgenic rice with recessive genic male sterility, and possesses great importance in rice genetic resource genetic improvement-breeding. The invention also provides a molecular marked identification method and applications of the rive CYP704B2 gene mutant in breeding.
Owner:HAINAN BOLIAN RICE GENE TECH CO LTD
Function specific molecular markers of rice blast resistance gene Pi63 as well as method and application of function specific molecular markers
ActiveCN103642803ABroad-spectrum high resistanceImprove breeding efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyResistant genes
The invention discloses two pairs of function specific molecular markers YRT3 and YRT4 of a rice blast resistance gene Pi63 as well as a method and application of the function specific molecular markers. The Pi63 function specific molecular markers YRT3 and YRT4 are obtained by comparing and analyzing Pi63 allelic genes in a plurality of rice varieties and upstream sequences in coding regions thereof to obtain two Pi63 function specific loci different from an infected allelic gene and other rice blast resistance genes; designing a primer to obtain SEQ ID NO.1, SEQ ID NO.2, SEQ ID NO.3 and SEQ ID NO.4; and amplifying total DNA of rice through the primer to obtain Pi63 function specific molecular markers YRT3 and YRT4. The function resistance gene can be screened and identified in a great amount of rice genetic resources, and can be applied to molecular marker assisted selection, genetic pyramiding breeding and transgenic breeding.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Tissue culture rapid propagation method of Guangdong anoectochilus roxburghii
InactiveCN101773069AIncrease the number of seedlingsImprove qualityPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsAxillary budBud
The invention discloses a tissue culture rapid propagation method of Guangdong anoectochilus roxburghii, which selects an axillary bud or a terminal bud of anoectochilus roxburghii in the Guangdong area in China as an explant and obtains a mass of vegetative propagated progeny plants by inducing the adventitious buds, carrying out proliferation and carrying out rooting cultivation. By adopting the method of the invention, one axillary bud can be induced to generate about 2 to 4 sprouts, after two months, the proliferation coefficient is between 3 and 4, and the rooting rate can reach over 90 percent. Therefore, the method greatly improves the seedling production capacity of Guangdong anoectochilus roxburghii, shortens the seedling culture time, saves the planting cost and provides the technical guarantee for the storage of the genetic resources of Guangdong anoectochilus roxburghii.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for detecting cattle ANGPTL4 gene single nucleotide polymorphism
InactiveCN101921856AAccurate detectionQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementMarker-assisted selectionSpecies groups
The invention discloses a method for detecting cattle ANGPTL4 gene single nucleotide polymorphism, comprising the following steps of: carrying out PCR proliferation on a cattle ANGPTL4 gene by using a cattle whole-genome DNA to be detected as a template and using a primer pair P as a primer, wherein the cattle whole-genome DNA to be detected includes an ANGPTL4 gene; digesting a product subjected to PCR proliferation by using restriction enzyme MspI, and carrying out polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis on a proliferated segment subjected to enzyme cutting; and authenticating the polymorphism of the single nucleotide in the 1422nd position of the cattle ANGPTL4 gene according to the result of the polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Because the ANGPTL4 gene function relates to four important growth characteristics of weight, daily gain, body slanting length and chest circumference, the method provided by the invention lays the foundation for establishing the relation of SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) of ANGPTL4 gene and the growth characteristics so as to be convenient for mark assisted selection (MAS) of the growth characteristic for Chinese cattle meat and rapidly establishes cattle species groups with excellent genetic resources.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Method for identifying hybrid germplasm of actinidia based on genome heterozygosity
InactiveCN104630382AShorten the timeLower Sequencing CostsMicrobiological testing/measurementActinidiaGermplasm
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com