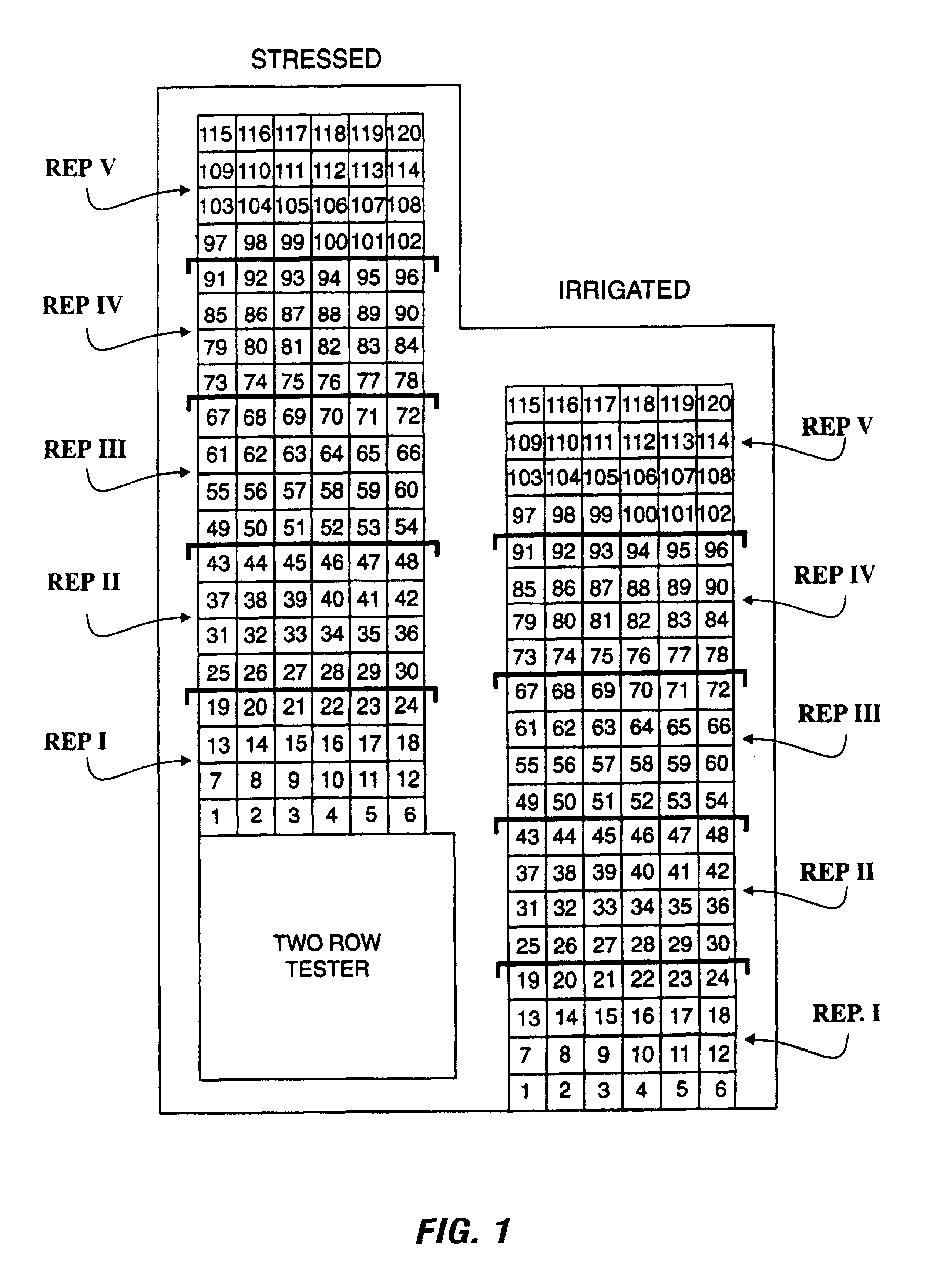
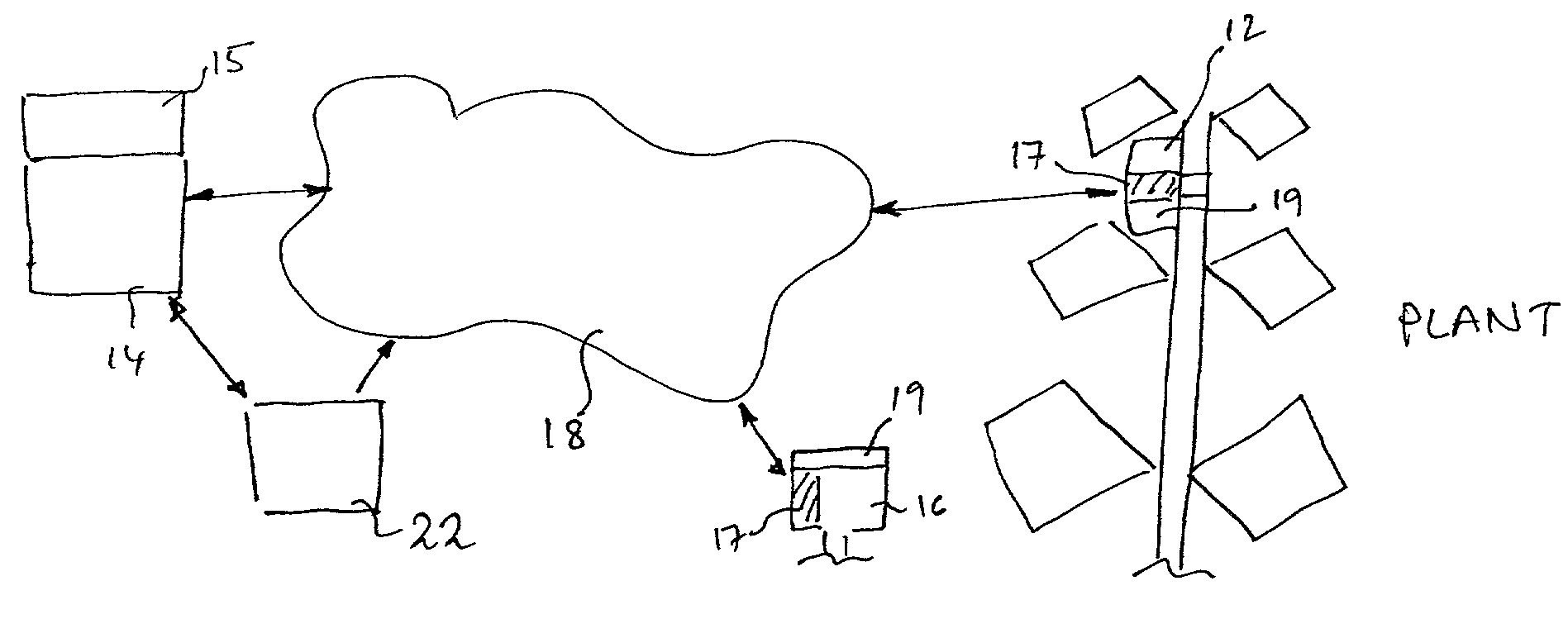
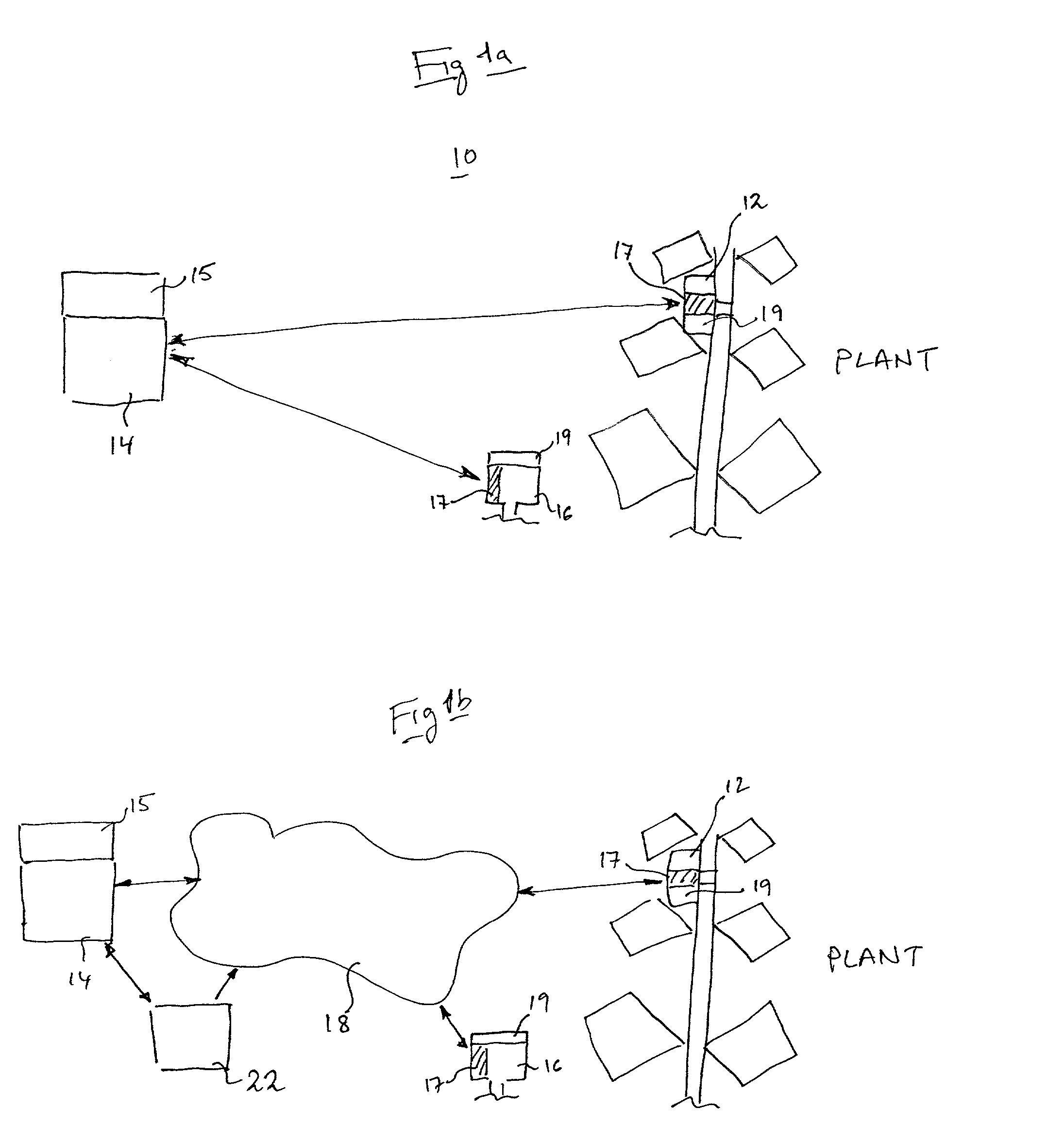
Patents
Literature
9039results about "Seed and root treatment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Herbicide resistance in plants
InactiveUS6222100B1Confers resistanceEffectively combat weed problemBiocideSeed and root treatmentPlant tissueNovel gene
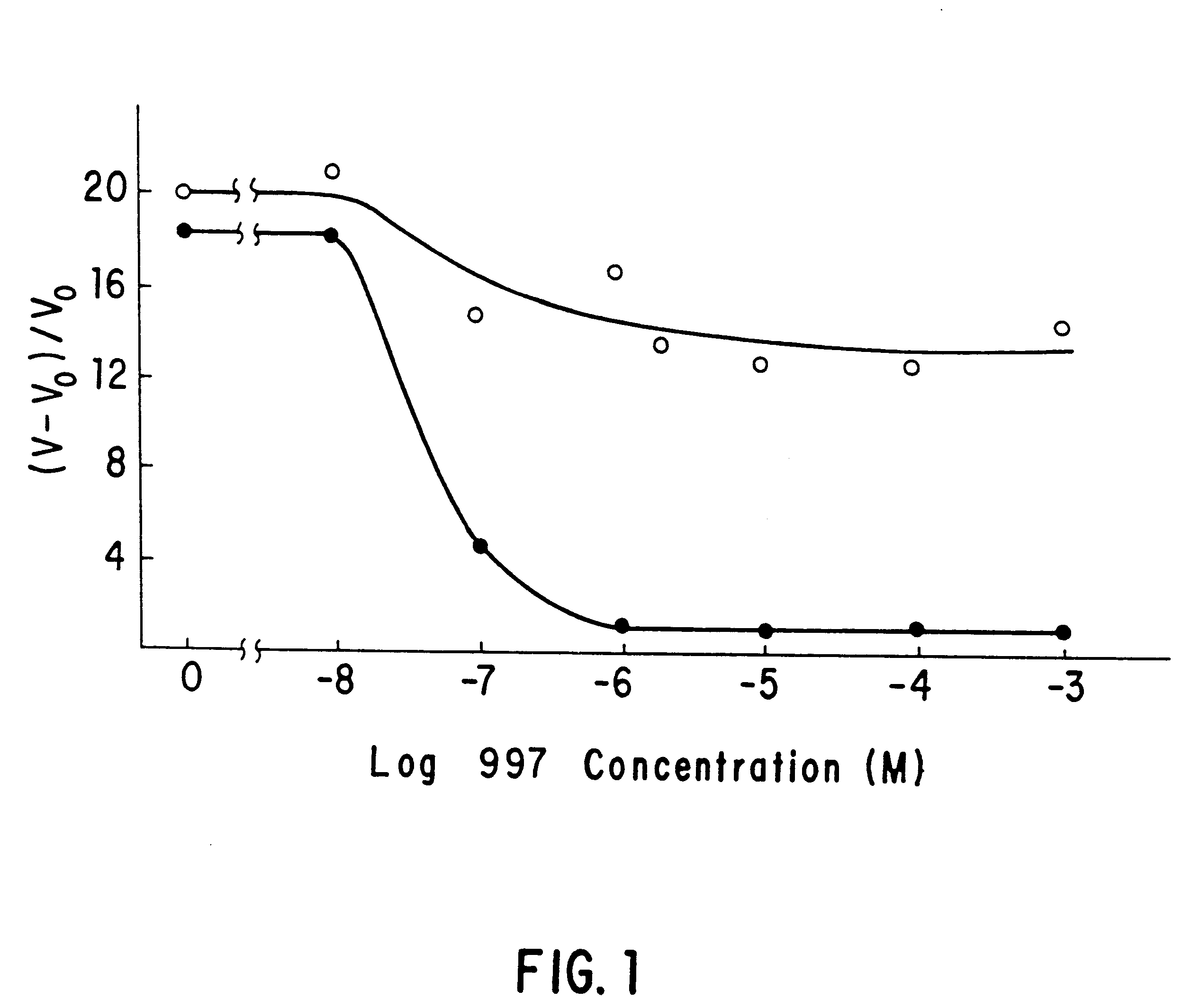
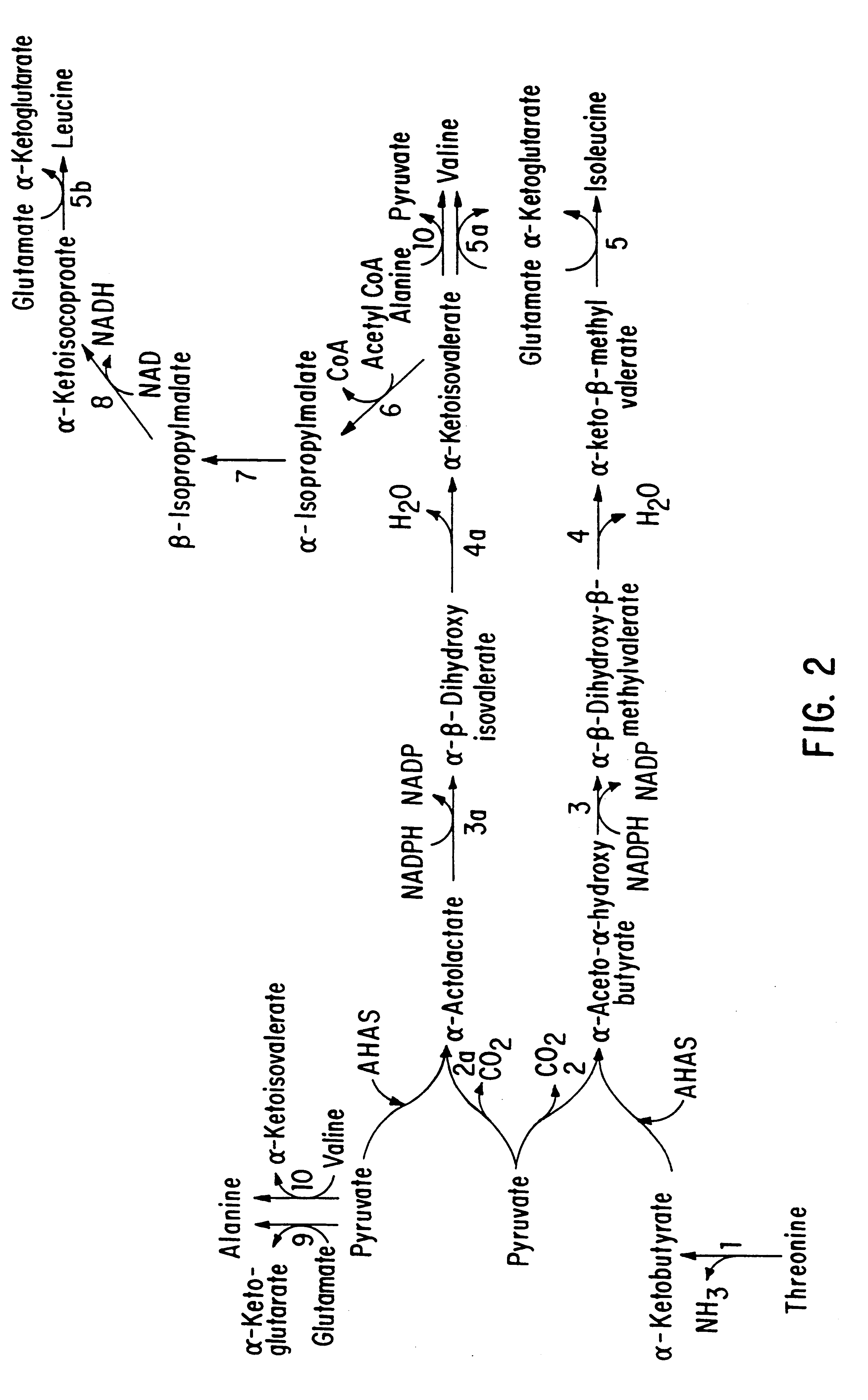
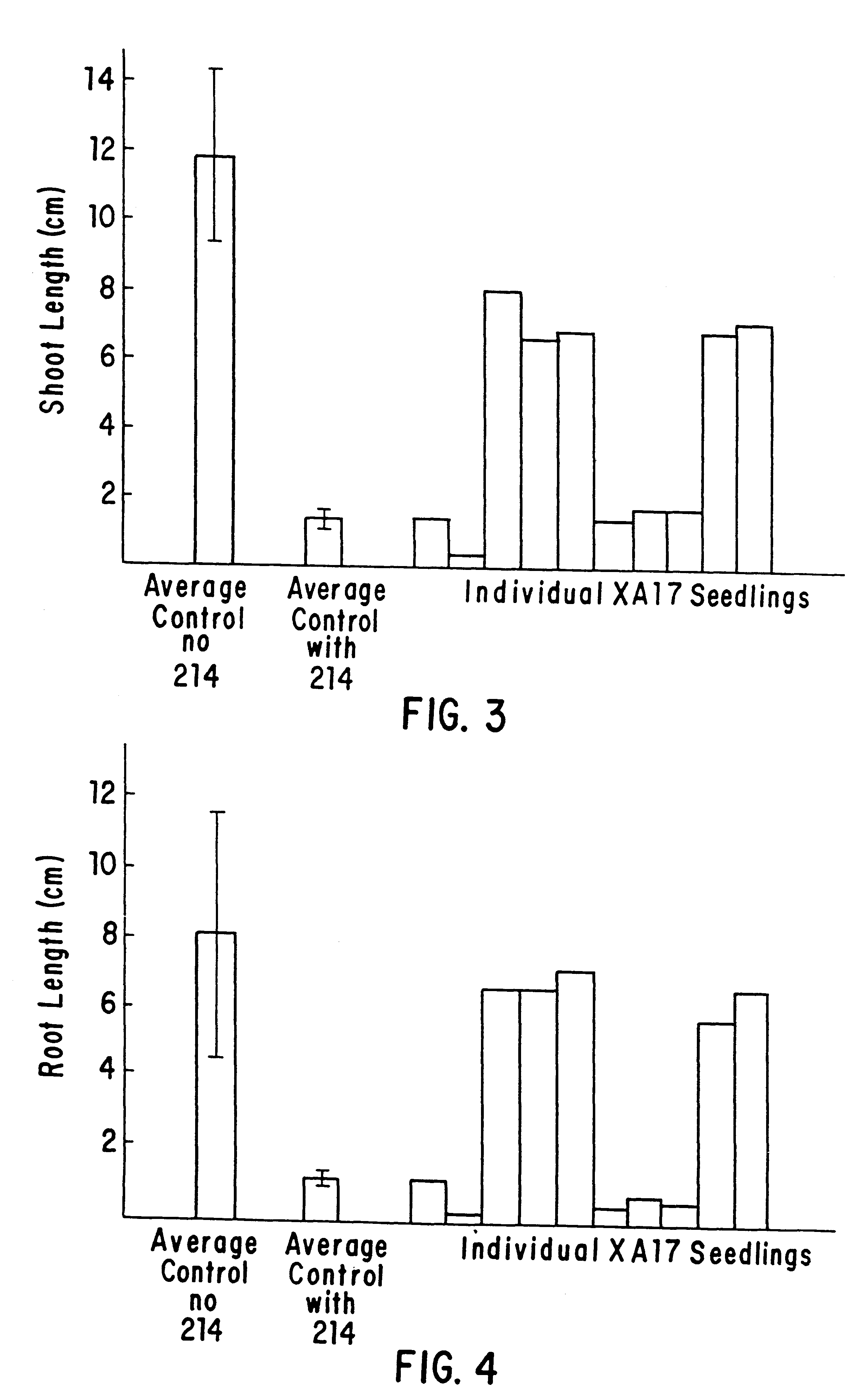
This invention is directed to the production of plants, plant tissues and seeds which are resistant to inhibition by an herbicide which normally inhibits the growth and development of those plants, plant tissues and plant seeds. In particular this invention is directed to altered acetohydroxyacid synthase enzymes which are resistant to inhibition by herbicides which normally inhibit the activity of the synthase before such alteration. This invention further relates to genes encoding such enzymes, and to processes for utilizing these novel genes and enzymes. Further products of the invention include plants, plant tissues and seeds which exhibit resistance to such herbicides resulting from expression of genes encoding herbicide resistant acetohydroxyacid synthase enzyme.
Owner:MGI PHARMA
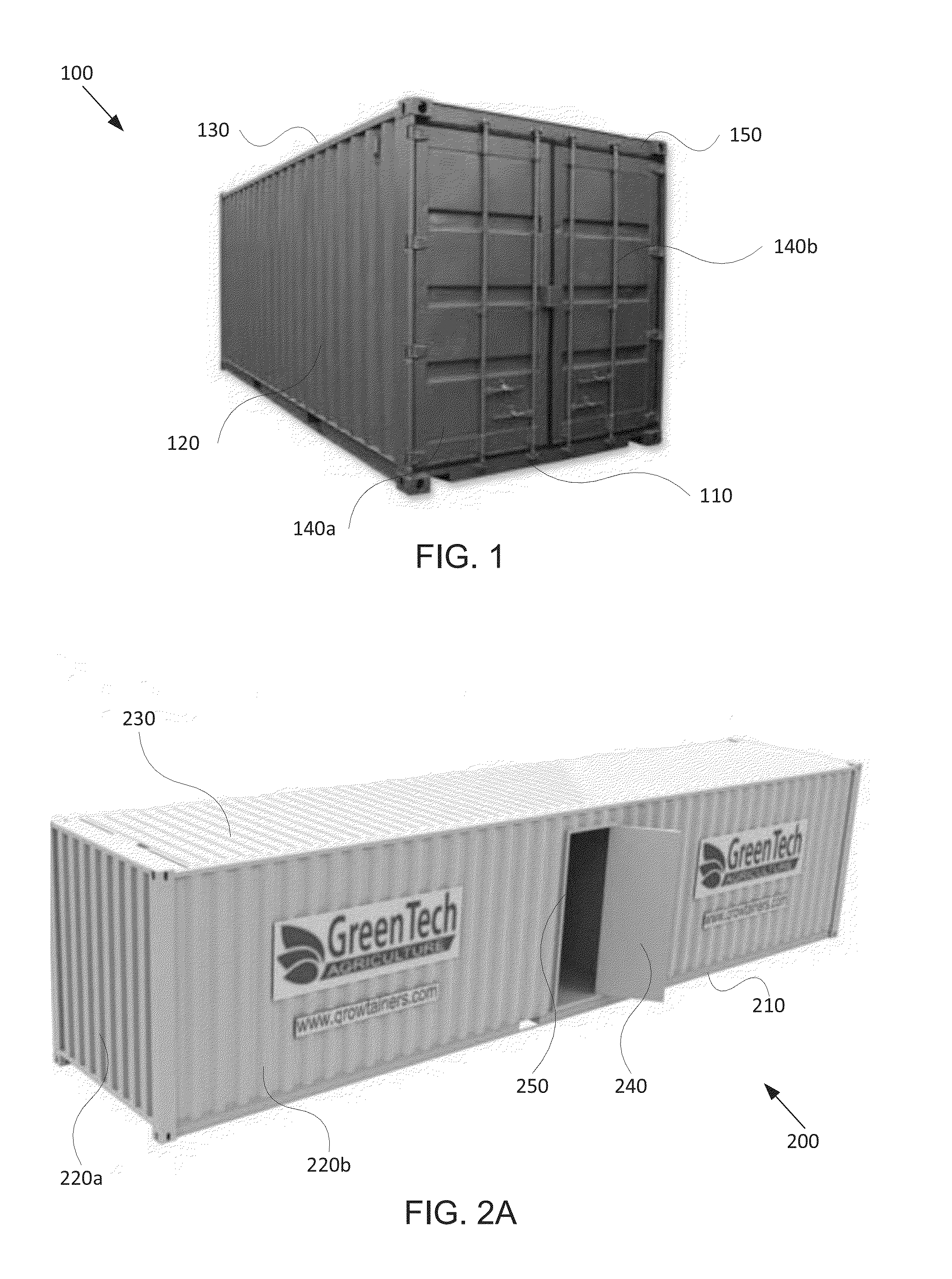
Self-sustaining artificially controllable environment within a storage container or other enclosed space
InactiveUS20140115958A1Readily apparentSeed and root treatmentClimate change adaptationEngineeringActuator
A system includes an enclosed space defining a controllable environment chamber. The system also includes at least one monitoring device configured to measure multiple characteristics of an environment within the chamber. The system further includes multiple actuators configured to alter the characteristics of the environment within the chamber. The enclosed space includes at least one rack system configured to be placed within the enclosed space. Each rack system includes multiple layers configured to receive multiple plants to be grown in the chamber. The actuators are configured to adjust the characteristics of the environment within the chamber to condition the environment based on the plants to be grown in the chamber.
Owner:GREENTECH AGRO
Pesticidal Nucleic Acids and Proteins and Uses Thereof
ActiveUS20120278954A1Improve insect resistanceBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsProtein compositionNucleotide
The invention provides compositions comprising polynucleotide molecules encoding certain pesticidal polypeptides which exhibit plant parasitic nematode and / or insect control properties, and are particularly directed to controlling plant parasitic pest species of nematodes and insects known to infest crop plant species. Methods for controlling pests are disclosed in which the toxic proteins are provided in the diet of the targeted plant pests. The invention also provides compositions such as nucleic acids, proteins, and plant and bacterial cells, plants, and seeds containing the nucleic acid and protein compositions, as well as methods and kits for identifying, detecting, and isolating the compositions of the present invention. The invention further provides a method of producing crops from recombinant seeds which contain the polynucleotide molecules encoding the pesticidal polypeptides of the present invention.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Insect resistance management with combinations of cry1be and cry1f proteins
The subject invention relates in part to stacking Cry1Be toxins along with Cry1Fa toxins to prevent insects from developing resistance towards either toxin by itself. As discussed in more detail herein, the subject pair of proteins is a particularly advantageous combination, as no other pair of proteins is known to provide high levels of control and non-cross-resistant activity against both Spodoptera frugiperda (FAW) and Ostrinia nubilalis (ECB) insects. This dual, non-cross-resistant activity is also advantageous because it can reduce the number of proteins / genes needed to target these insects with multiple, non-cross-resistant proteins. This can reduce or eliminate the need for refuge acreage. Accordingly, the subject invention also relates generally to using four genes to provide three proteins for non-cross-resistant control of a first insect, and three proteins for non-cross-resistant control of a second insect. In preferred embodiments, the targeted insects are FAW and ECB.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
COMBINED USE OF CRY1Da AND CRY1Fa PROTEINS FOR INSECT RESISTANCE MANAGEMENT
InactiveUS20120331589A1Reduce and eliminate requirementReduce selection pressureBiocideFungiCombined useToxin
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
COMBINED USE OF CRY1Ca AND CRY1Fa PROTEINS FOR INSECT RESISTANCE MANAGEMENT
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Combined use of cry1ca and cry1ab proteins for insect resistance management
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Combined use of vip3ab and cry1fa for management of resistant insects
InactiveUS20120317682A1Reduce and eliminate requirementNon-cross-resistantBiocideFungiCombined useDrug resistance
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
Insectcidal protein combinations for controlling fall armyworm and european corn borer, and methods for insect resistance management
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
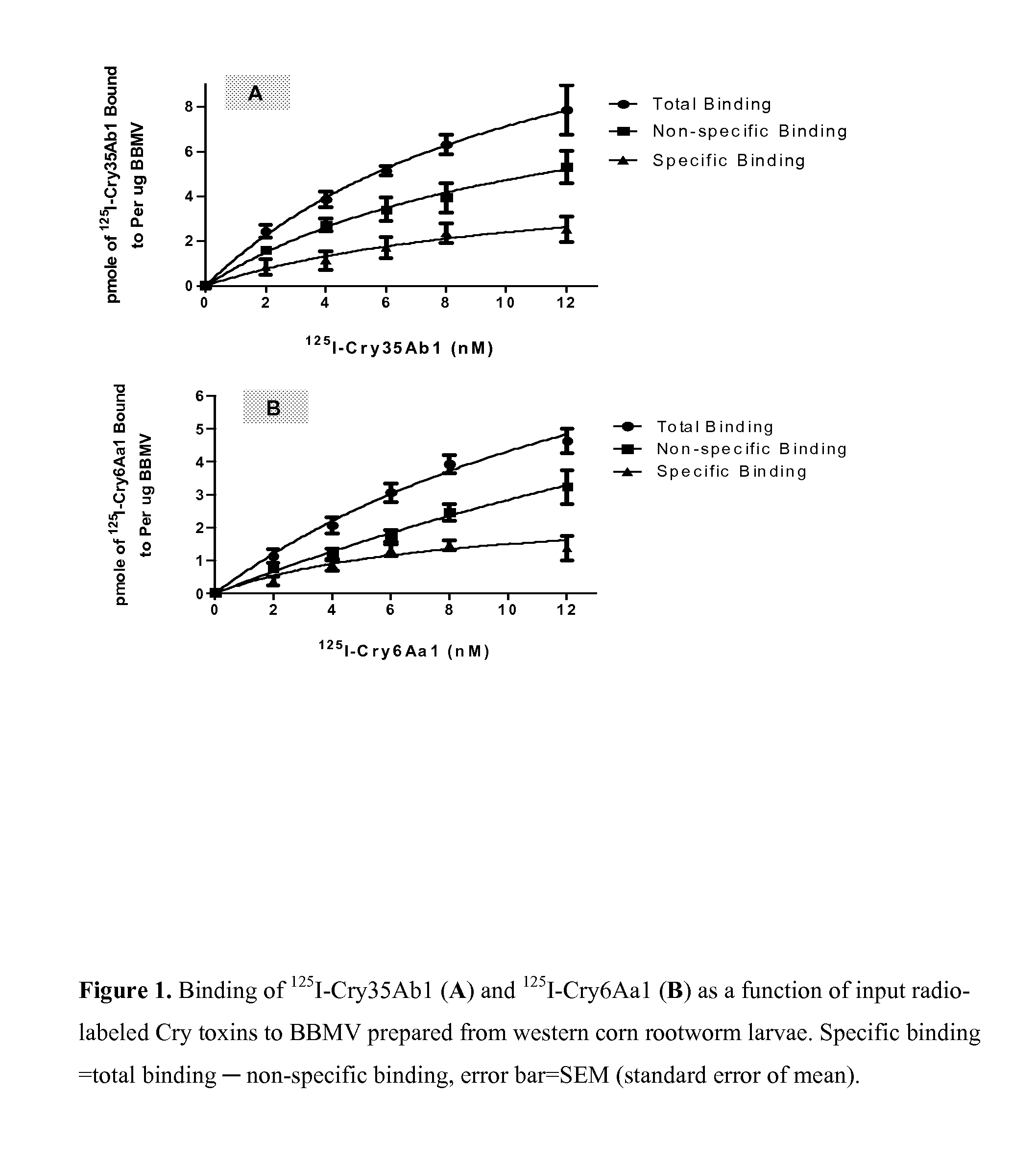
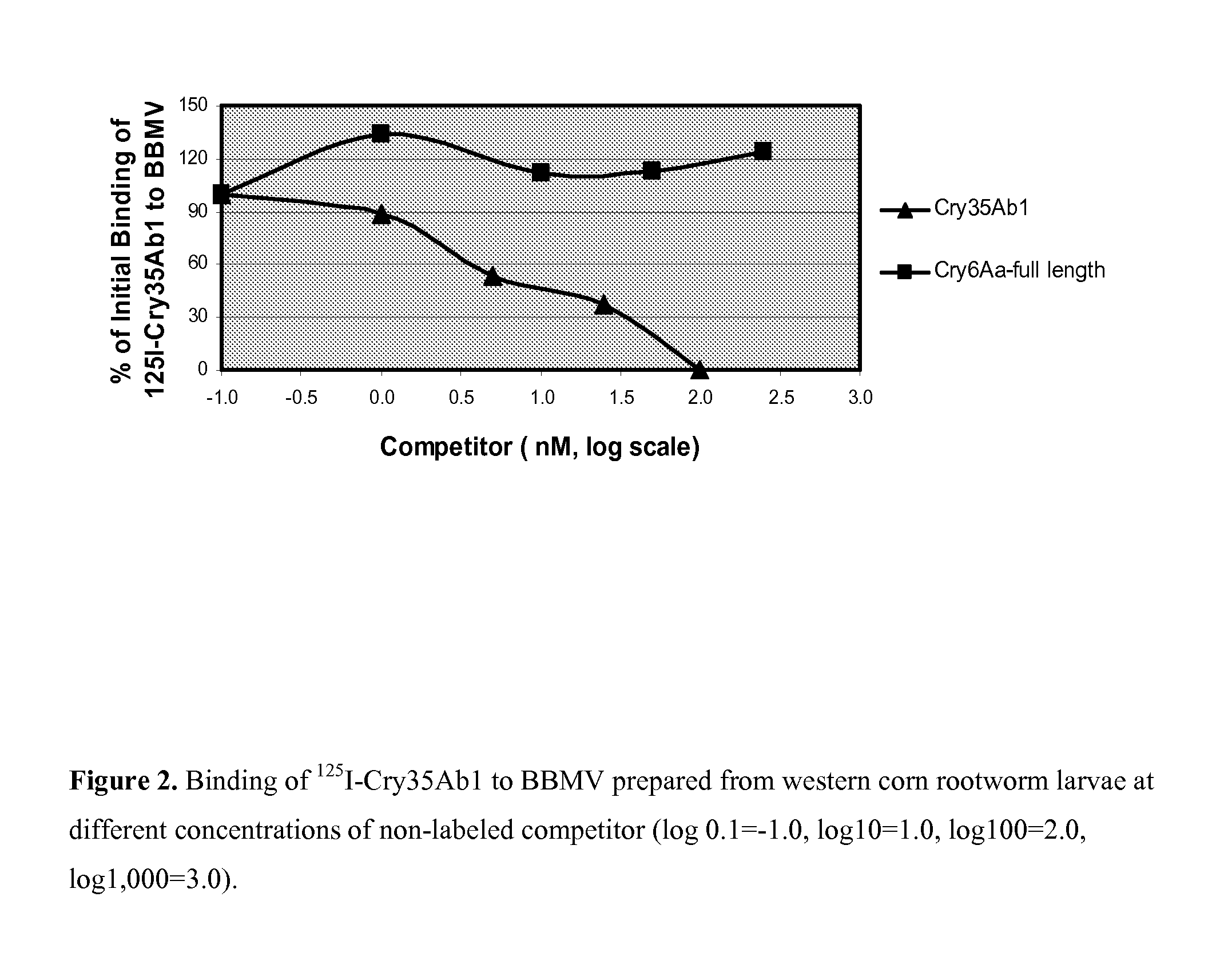
COMBINATIONS INCLUDING Cry34Ab/35Ab AND Cry6Aa PROTEINS TO PREVENT DEVELOPMENT OF RESISTANCE IN CORN ROOTWORMS (DIABROTICA SPP.)
InactiveUS20130167269A1Prevent development of resistanceAvoid developmentBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsMode of actionDiabrotica
The subject invention relates in part to Cry34Ab / 35Ab in combination with Cry6Aa. The subject invention relates in part to the surprising discovery that combinations of Cry34Ab / Cry35Ab and Cry6Aa are useful for preventing development of resistance (to either insecticidal protein system alone) by a corn rootworm (Diabrotica spp.) population. Included within the subject invention are plants producing these insecticidal Cry proteins, which are useful to mitigate concern that a corn rootworm population could develop that would be resistant to either of these insecticidal protein systems alone. Plants (and acreage planted with such plants) that produce these two insecticidal protein systems are included within the scope of the subject invention. The subject invention also relates in part to combinations of Cry34Ab / 35Ab and Cry3Aa proteins “triple stacked” with a Cry6Aa protein. Transgenic plants, including corn, comprising a cry6Aa gene, cry34Ab / 35Ab genes, and a cry3Aa gene are included within the scope of the subject invention. Thus, such embodiments target rootworms with three modes of action.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
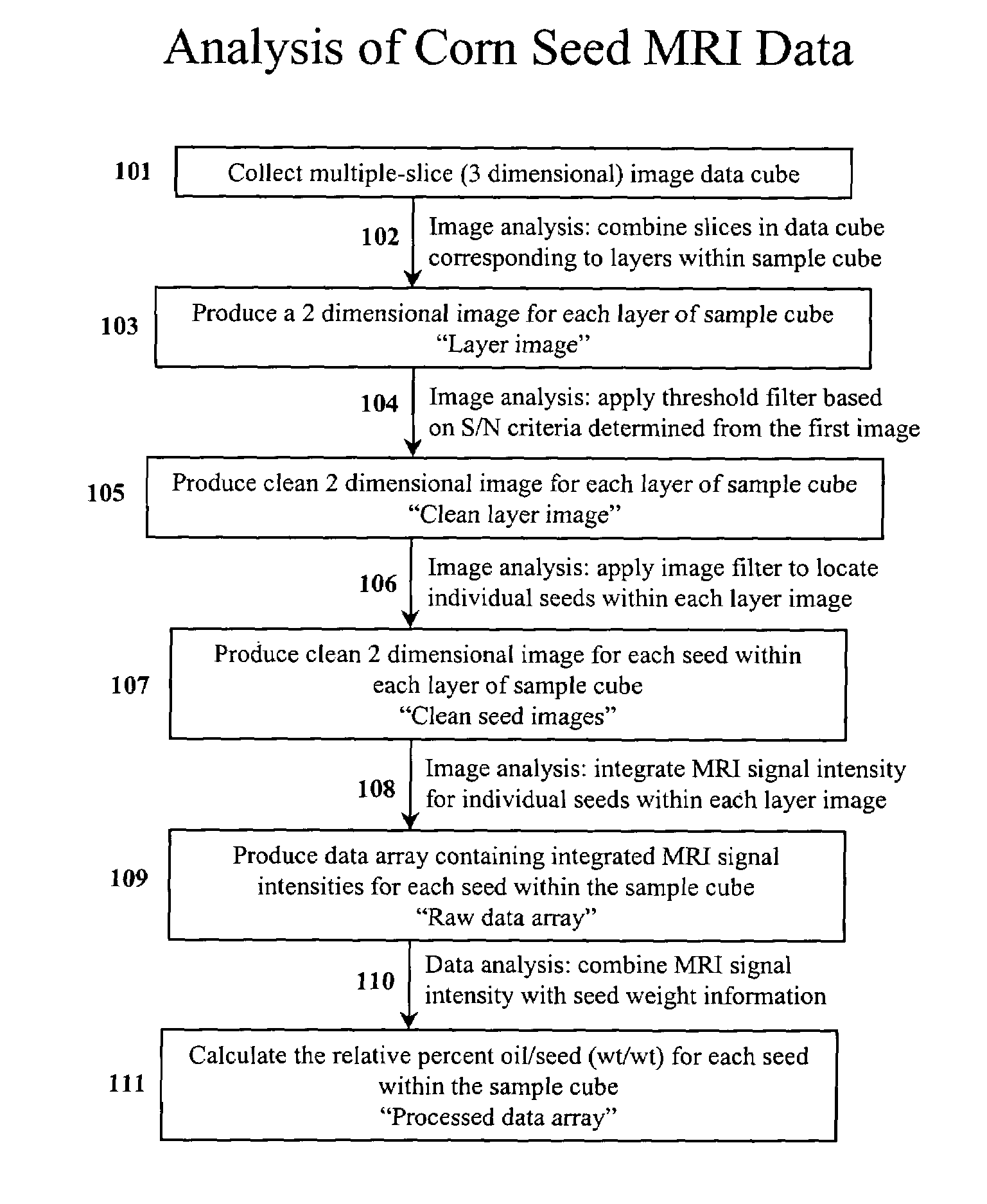
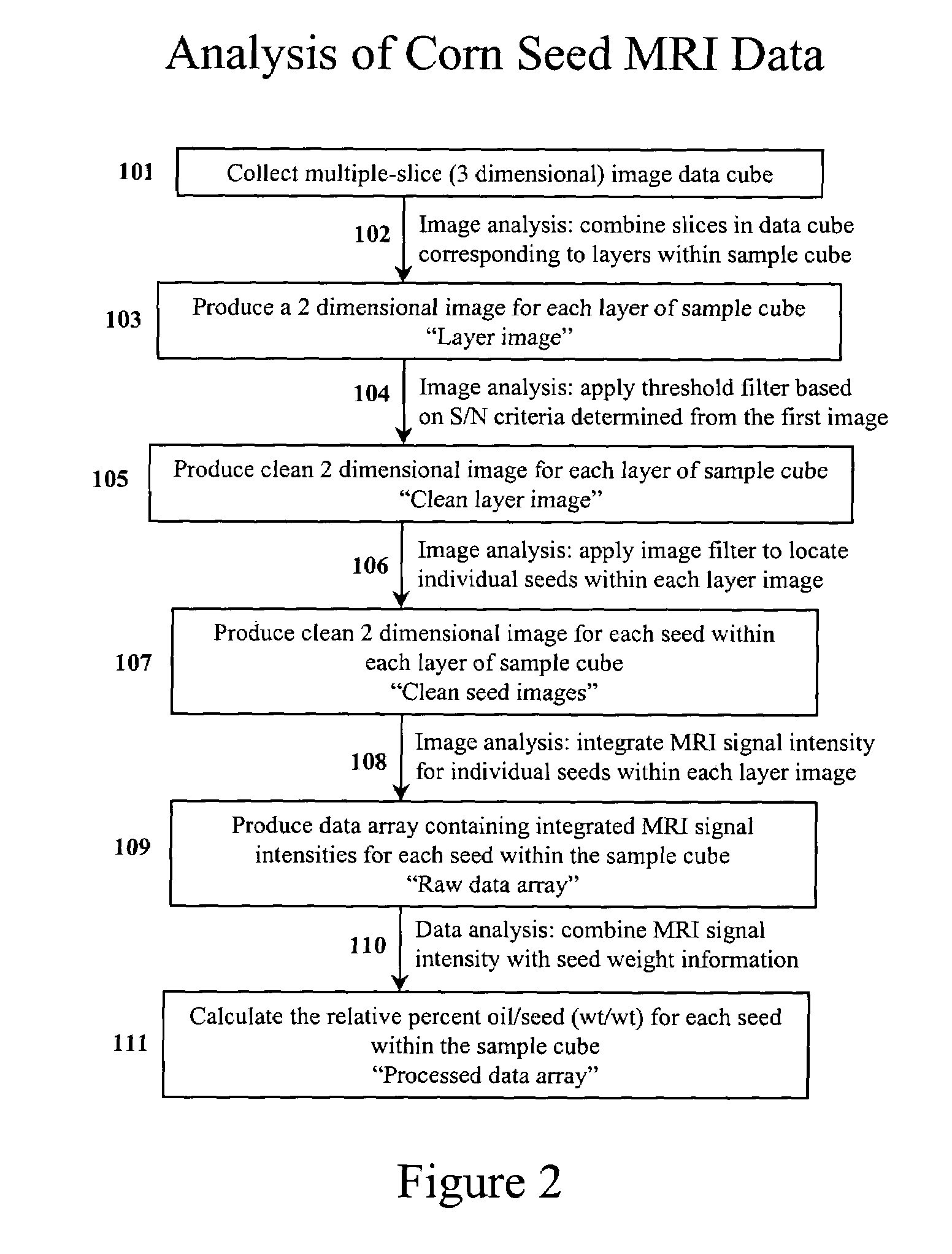
Apparatus and methods for analyzing and improving agricultural products
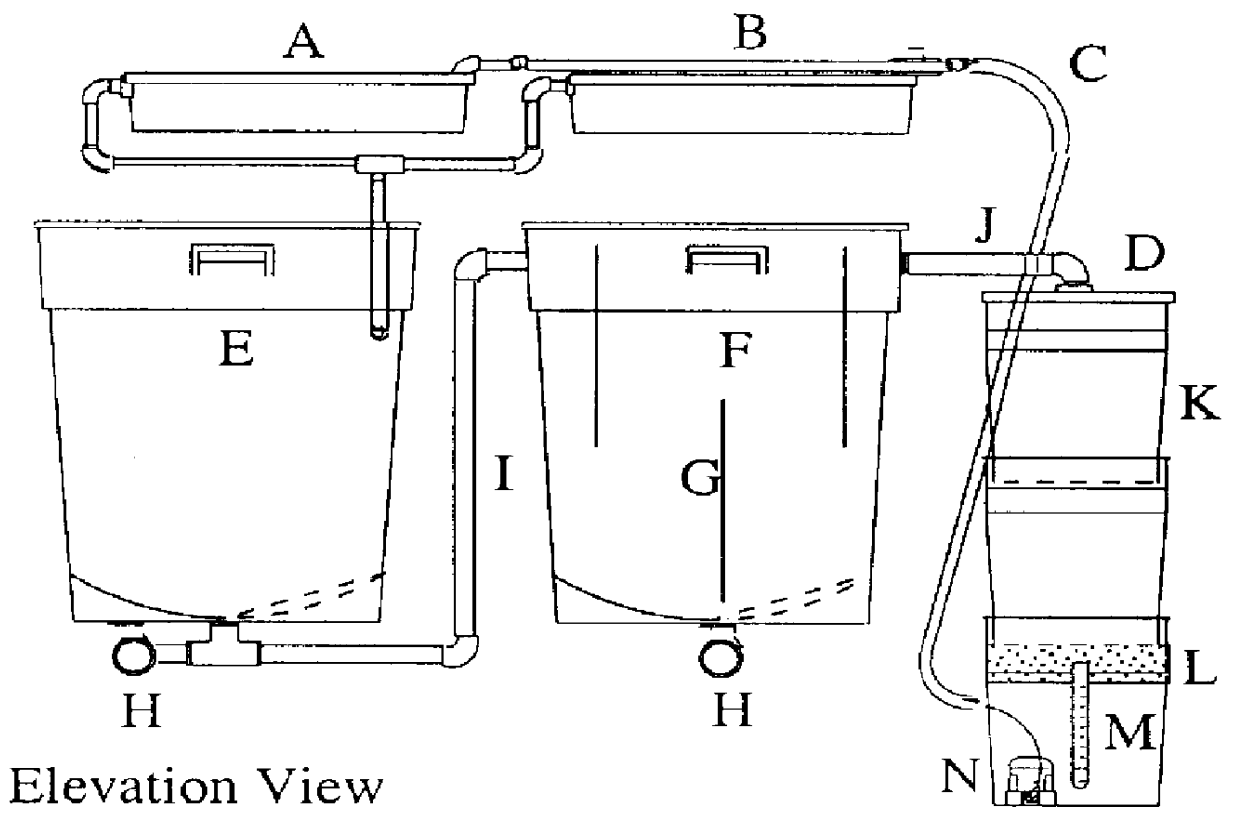
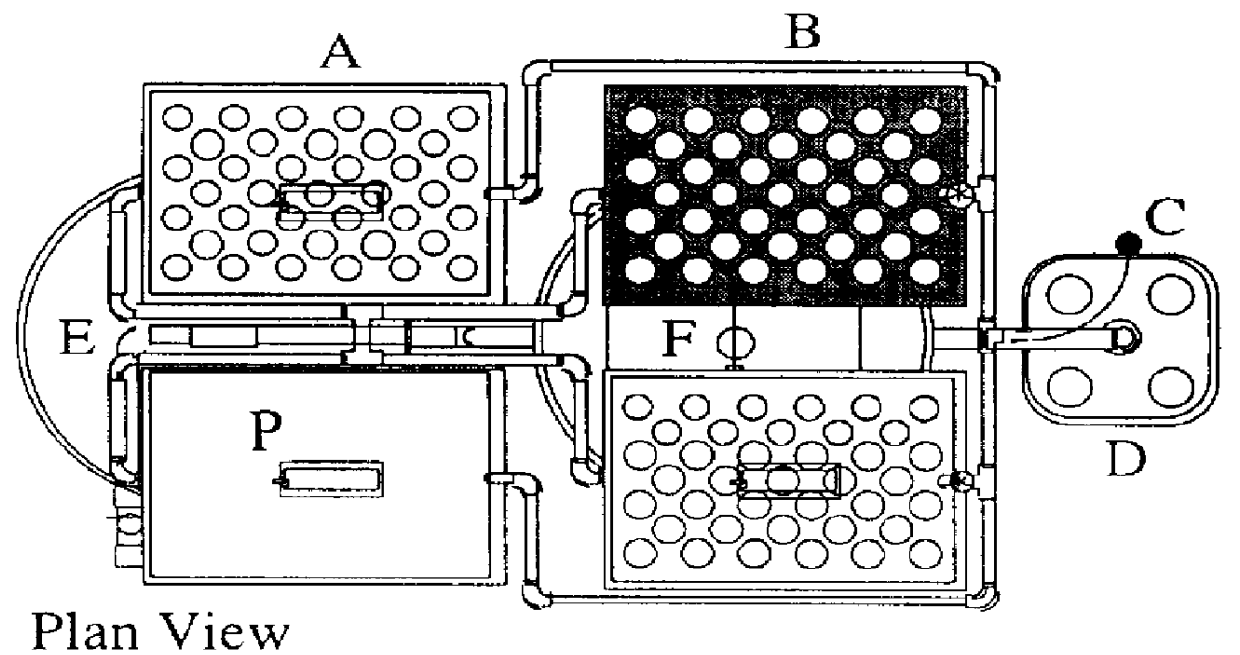
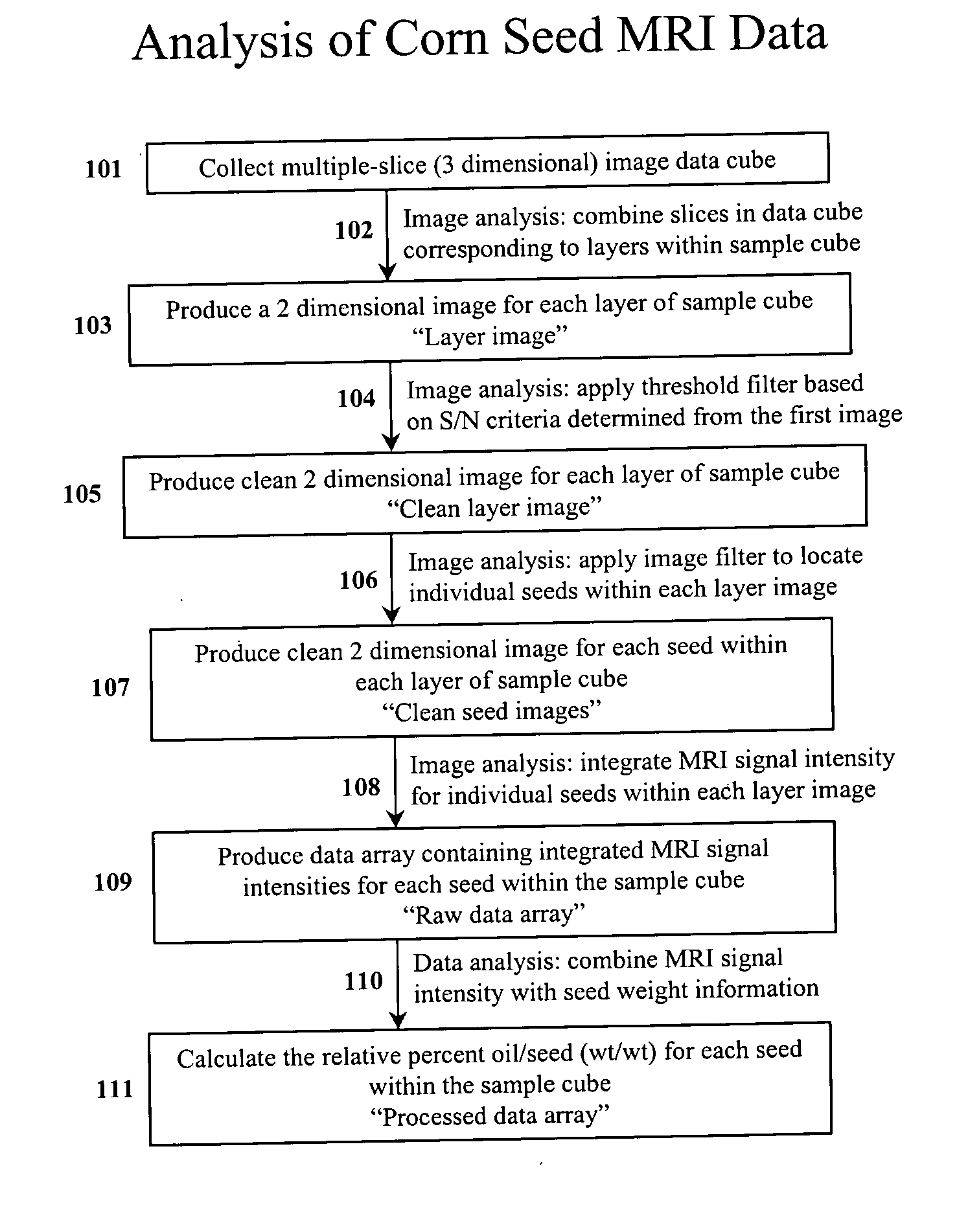
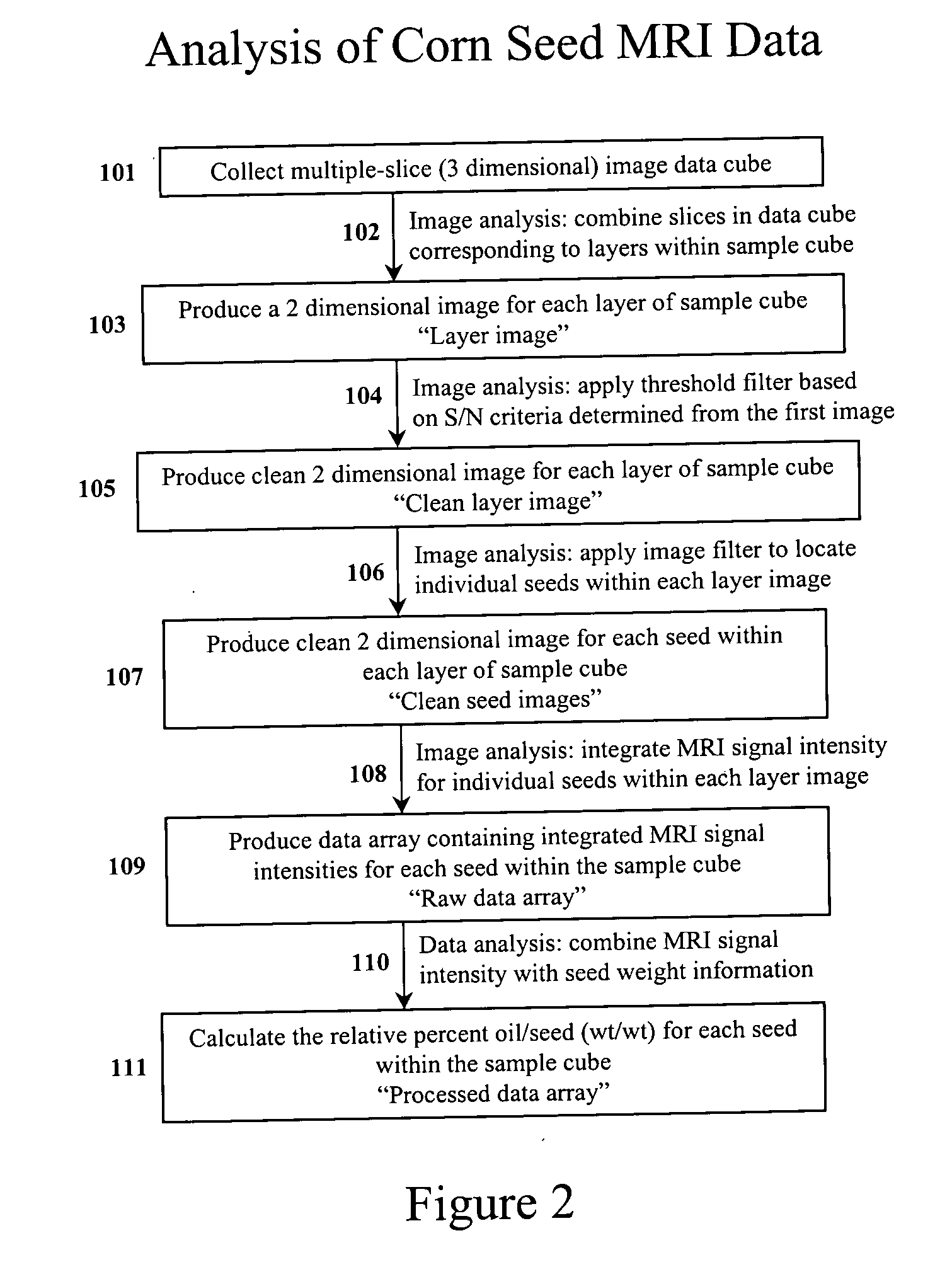
InactiveUS7367155B2Prevent inter-pixel crosstalkSeed and root treatmentLaboratory glasswaresPattern recognitionPlant tissue
A trait of interest is detected as being present within individual ones of a plurality of agricultural samples (such as seeds or plant tissues) by imaging the plurality of samples to form a magnetic resonance image. The image of the plurality of samples is then analyzed to detect image information indicative of the presence of the trait within one or more of the imaged samples. A determination is then made as to whether the trait is exhibited in individual ones of the samples based upon the foregoing analysis. As an example, the samples may be a plurality of seeds, and the detected trait may be oil. A determination is made, based on the image analysis, as to whether each individual seed in the multi-seed image contains oil. A further examination may be made to determine a relative content of oil in each seed as well as a content by weight.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Methods for classifying plants for evaluation and breeding programs by use of remote sensing and image analysis technology
InactiveUS6212824B1Improve performanceLow costSeed and root treatmentPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryImaging analysisBreeding program
Methods for classifying plants by remote sensing and image analysis technology are presented. These methods are useful for evaluating plants and for selecting plants for a plant breeding program which has as its goal to selectively alter phenotype. The methods combine the newer techniques of remote sensing technology to obtain indirect correlates of the traits of interest, with classical pedigree breeding strategies. Thermal and infrared reflectance measures of plant canopies are examples of energy values measured by remote sensing, used to indirectly predict the selected traits.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
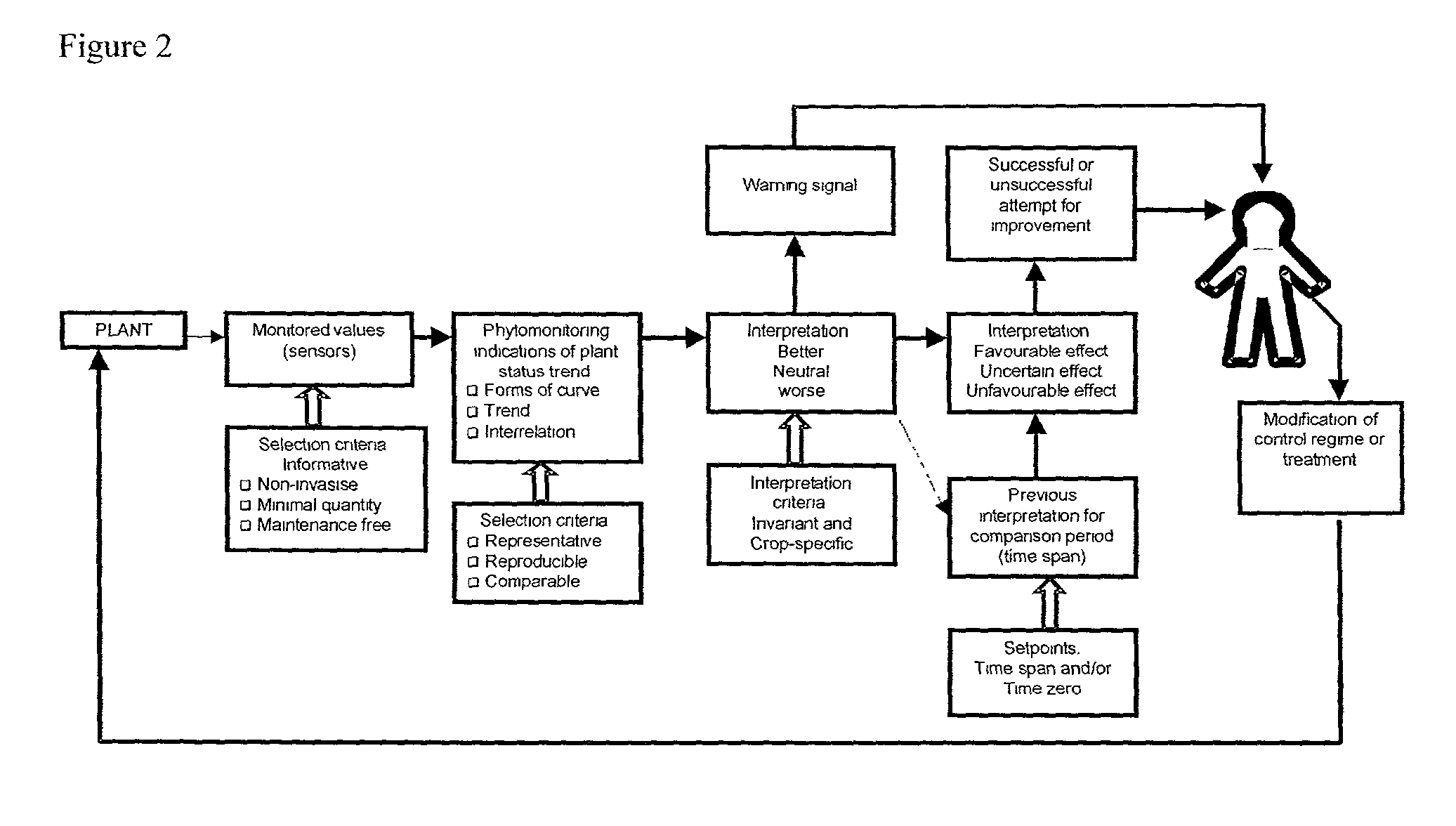
System and method for phytomonitoring
A method of assessing a state of a plant is provided. The method includes: (a) collecting data pertaining to at least one plant related parameter over a predetermined time period; and (b) analyzing the data collected over the predetermined time period to thereby identify a trend in the data over at least a portion of the predetermined time period, the trend being indicative of the state of the plant.
Owner:PHYTECH
System, apparatus and method for marking and tracking bulk flowable material
InactiveUS20010029996A1Seed and root treatmentSausage casingsComputer scienceGenetically modified organism
A method and apparatus are disclosed for identifying a characteristic of a bulk flowable material. An identification marker is inserted into a bulk flowable material. The identification marker carries information identifying a specified property or properties of the material. A marker dispenser can be located at one or more handling sites of the bulk flowable material. The identification markers can be pre-prepared or property-related information can be added to the marker prior to or subsequent to dispensing. The identification markers can be paper-like labels, for example, or more complex devices. The system can be used to track the lifespan of a material or to indicate a property of the material to others, such as whether the material is a genetically modified organism (GMO). A pre-printed marker source containing a single continuous bar code is also disclosed.
Owner:ROBINSON MARTIN C
Devices and methods for generation of subsurface microdisruptions for biomedical applications
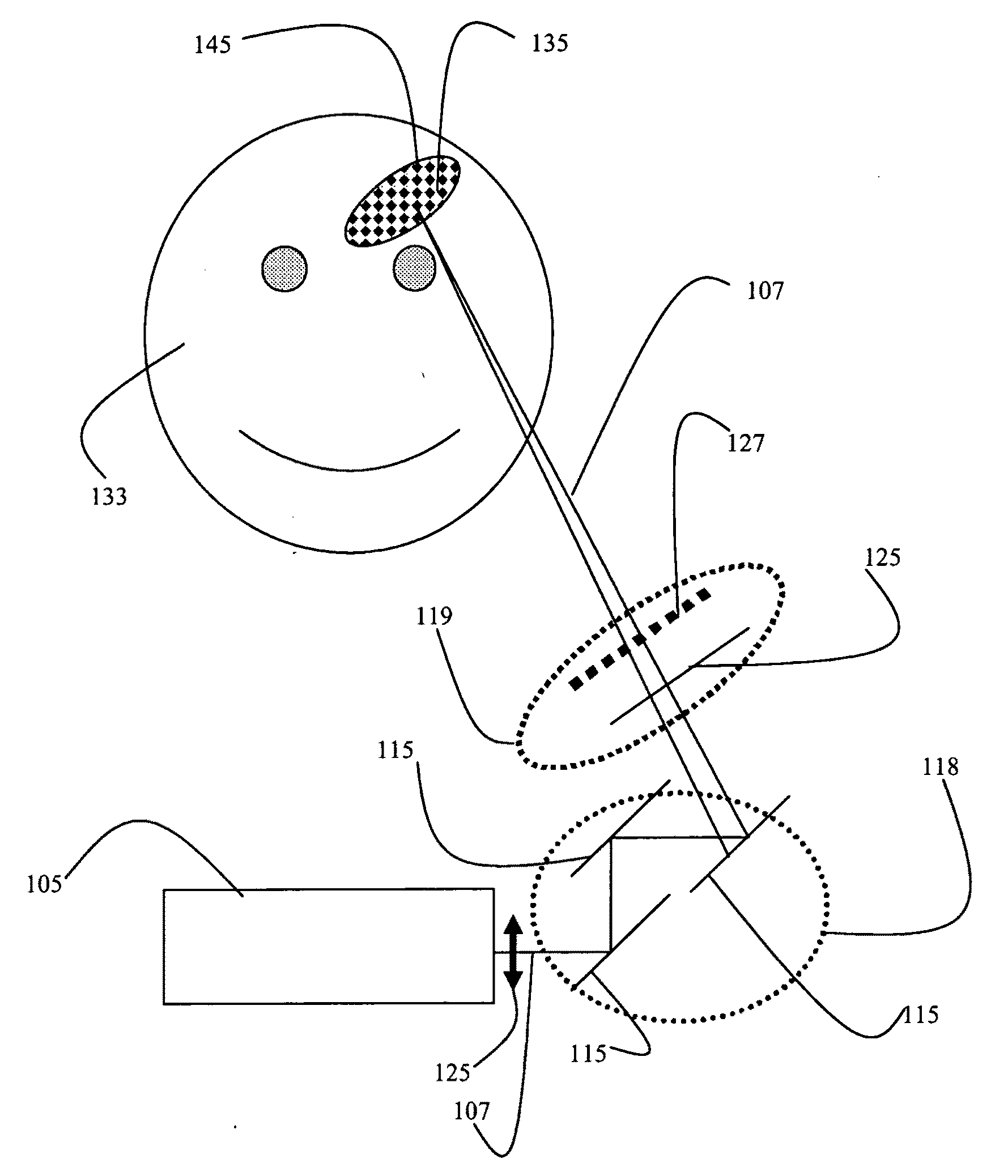
InactiveUS20100082019A1Minimizing collateral damageMinimize damageSeed and root treatmentMedical devicesPhysicsEnergy source
A device comprises an energy source capable of generating short bursts of energy at a variable pulse repetition rates. The repetition rates range from a single shot to several hundreds Mega-Hertz so that selective, three dimensional interactions with a volumetric zone of skin or issue can be created substantially without damage or substantial changes to overlying or underlying or surrounding tissue or skin.
Owner:NEEV JOSEPH
System, apparatus and method for marking and tracking bulk flowable material
A method and apparatus for identifying a characteristic of a bulk flowable material. A marker system for a bulk flowable material including a marker containing information related to the bulk flowable material. The marker being coupled with one or more granules or elements of the bulk flowable material so that the marker will migrate with surrounding granules.
Owner:ROBINSON MARTIN C
Methods of seed breeding using high throughput nondestructive seed sampling
ActiveUS7703238B2High activityExpand the populationSeed and root treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementNon destructiveGermplasm
The present invention provides for novel methods to facilitate germplasm improvement activities through the use of high throughput, nondestructive sampling of seeds. In one embodiment, a high-throughput, non-destructive method for analyzing individual seeds in a population of seeds comprises removing a sample from a plurality of seeds in the population while preserving the germination viability of the seed and analyzing the sample for the presence or absence of one or more characteristics of at least one genetic or chemical trait.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
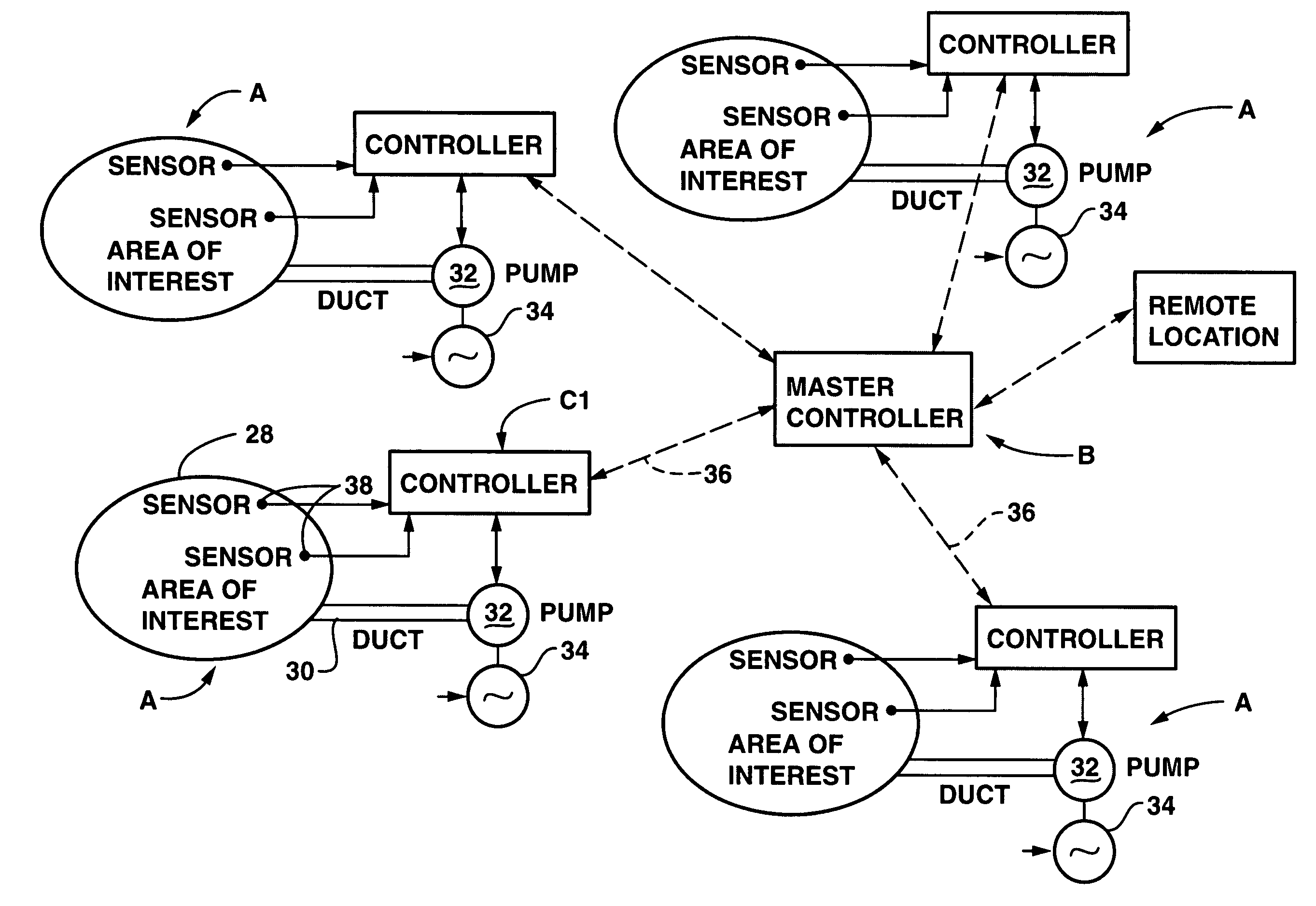
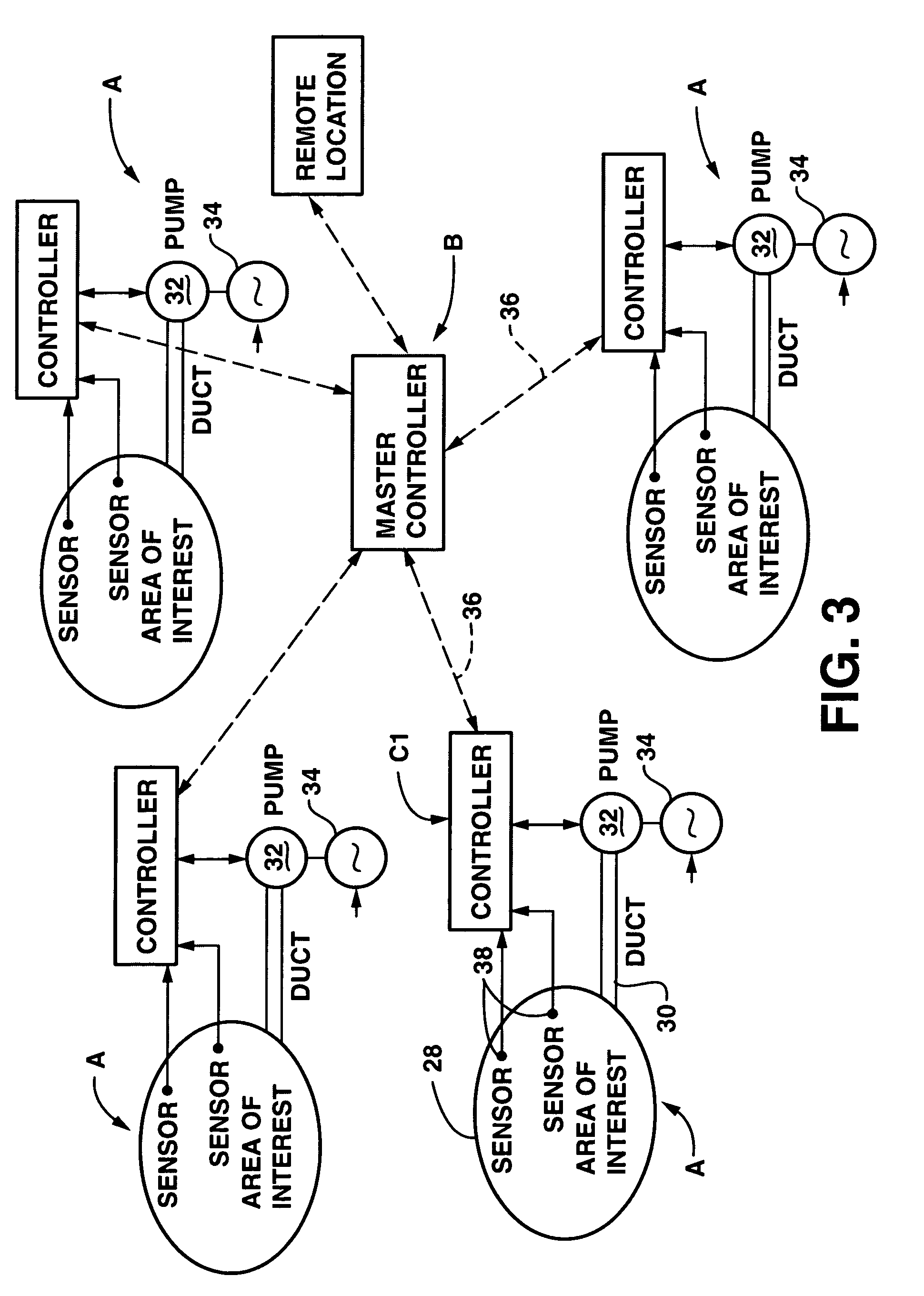
Golf course environmental management system and method
The invention is a system and method for managing a plurality of areas of interest of a golf course. The system comprises a plurality of subsurface aeration subsystems and a programmable master control module. Each subsystem provides to a specific area at least one of air under pressure and a partial vacuum. In each area of interest, a local control module is responsive to a directive and to a datum (environmental or operational parameter). The local control module is configured to operate the subsystem and is in communication with the programmable master control module. The programmable master control module receives from the local control modules area information representing a status of the respective specific area to which the local control module is dedicated, and in response to the area information and to a command, the programmable master control module issues a directive to the local control module to operate the subsurface aeration subsystem.
Owner:SUBAIR SYST
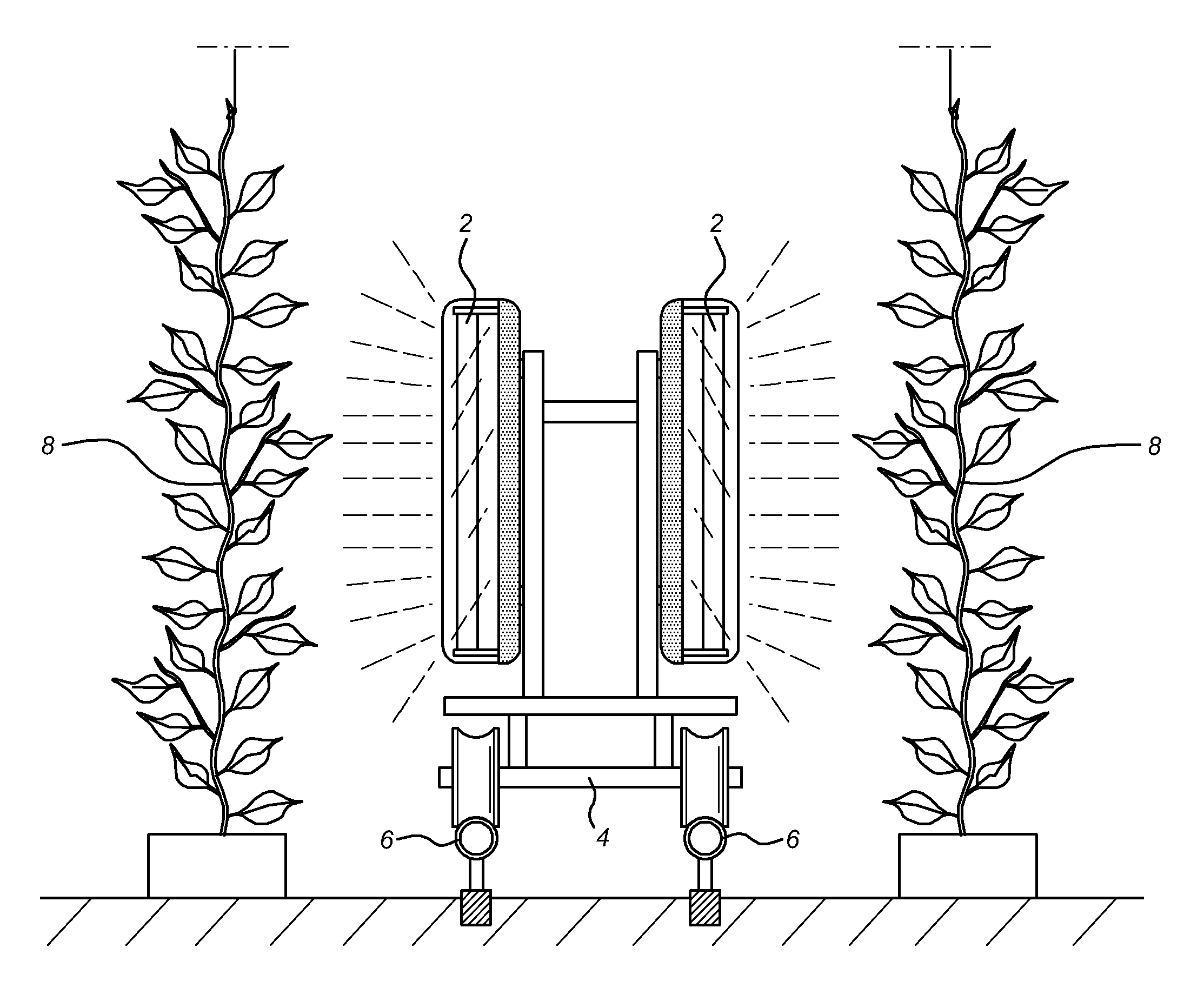
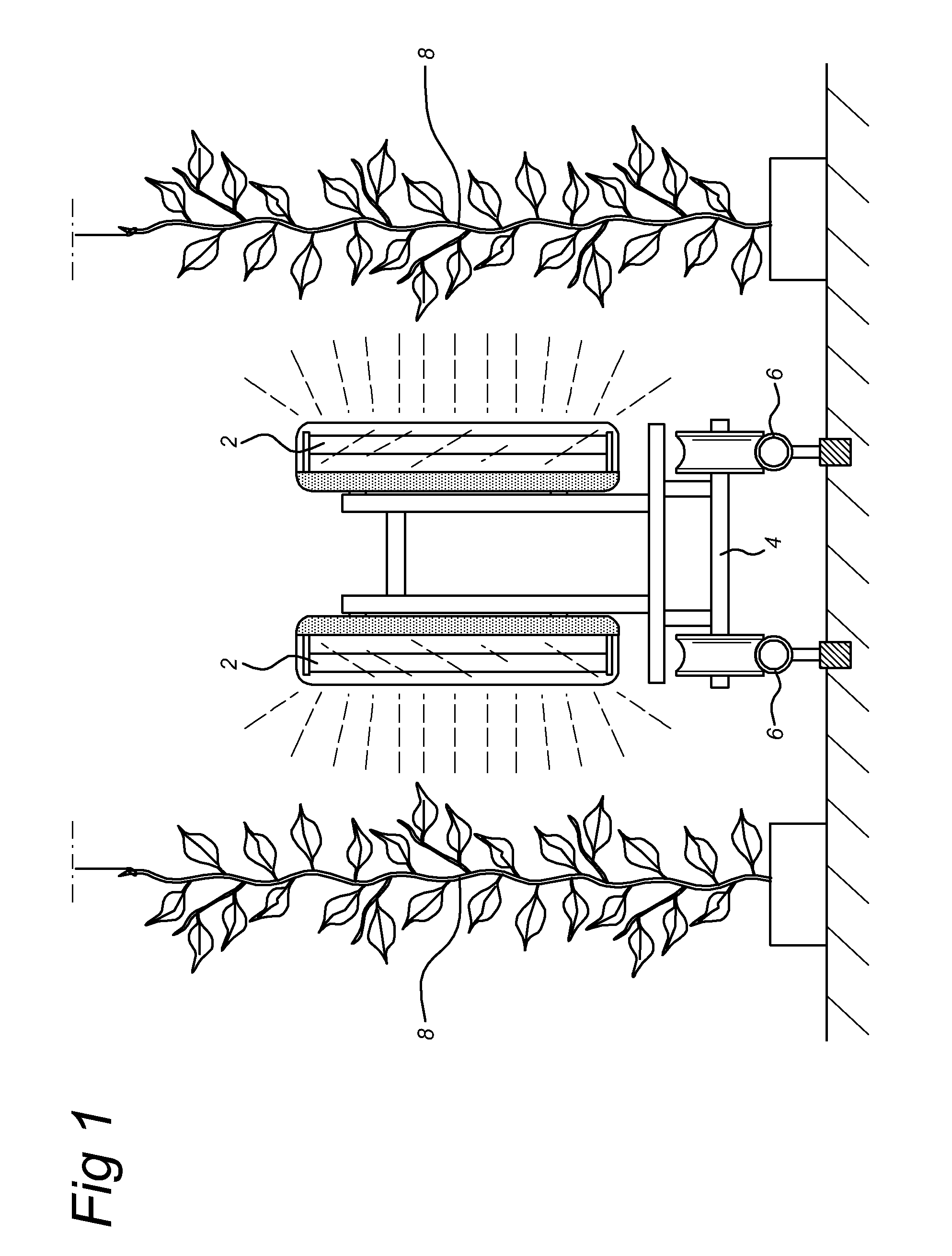
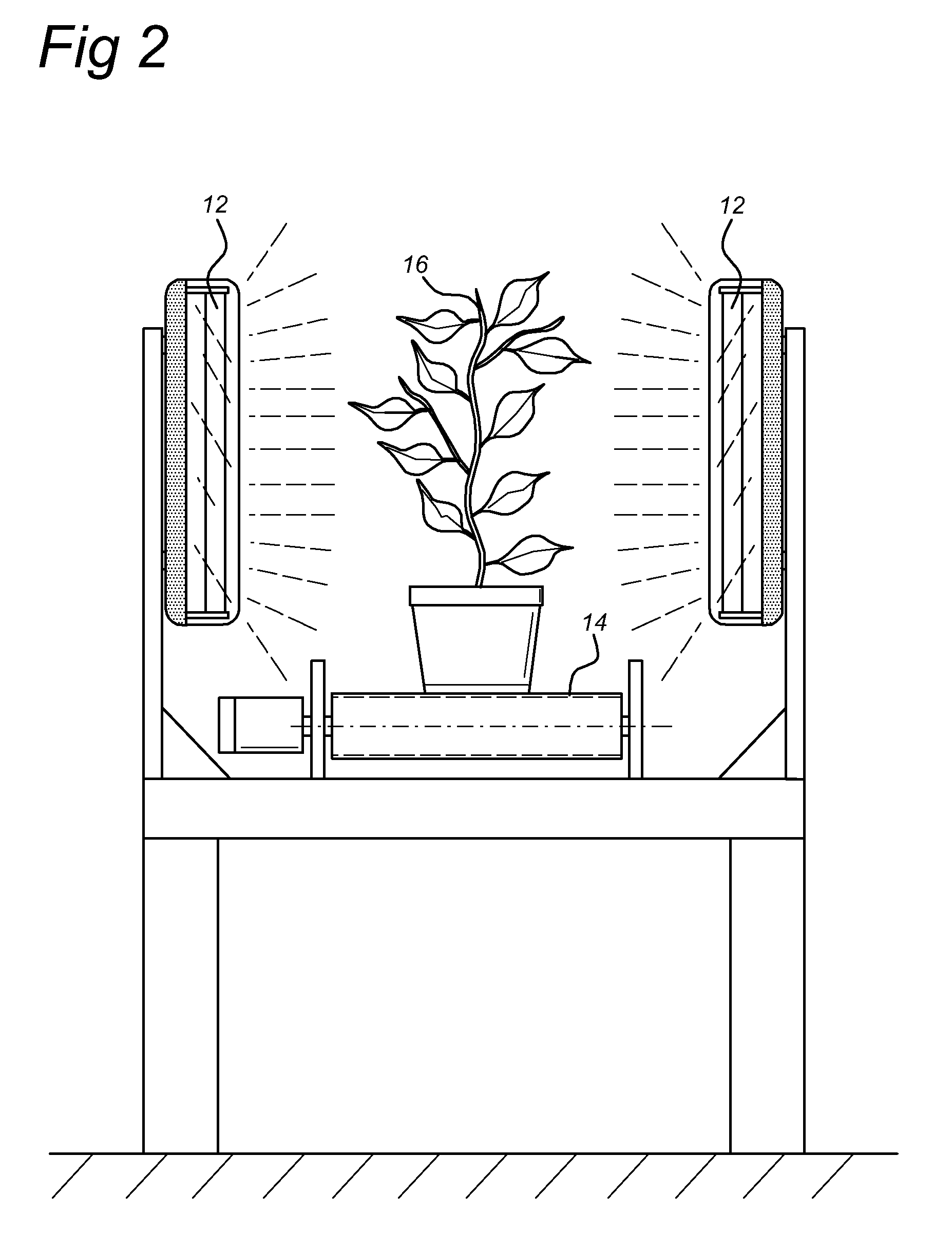
Methods for Treating Live Plants or Live Plant Parts or Mushrooms with UV-C Light
InactiveUS20090272029A1Increase humidityIncrease crop yieldDead plant preservationAgricultural machinesPlant TubersMushroom
The present invention relates to a method for controlling pathogen growth on live plants and mushrooms using UV-C light and an apparatus for use in the method. Also provided are methods for removing surplus leaves and methods for destroying aerial plant parts prior to harvest of underground roots, tubers or bulbs.
Owner:CLEAN LIGHT
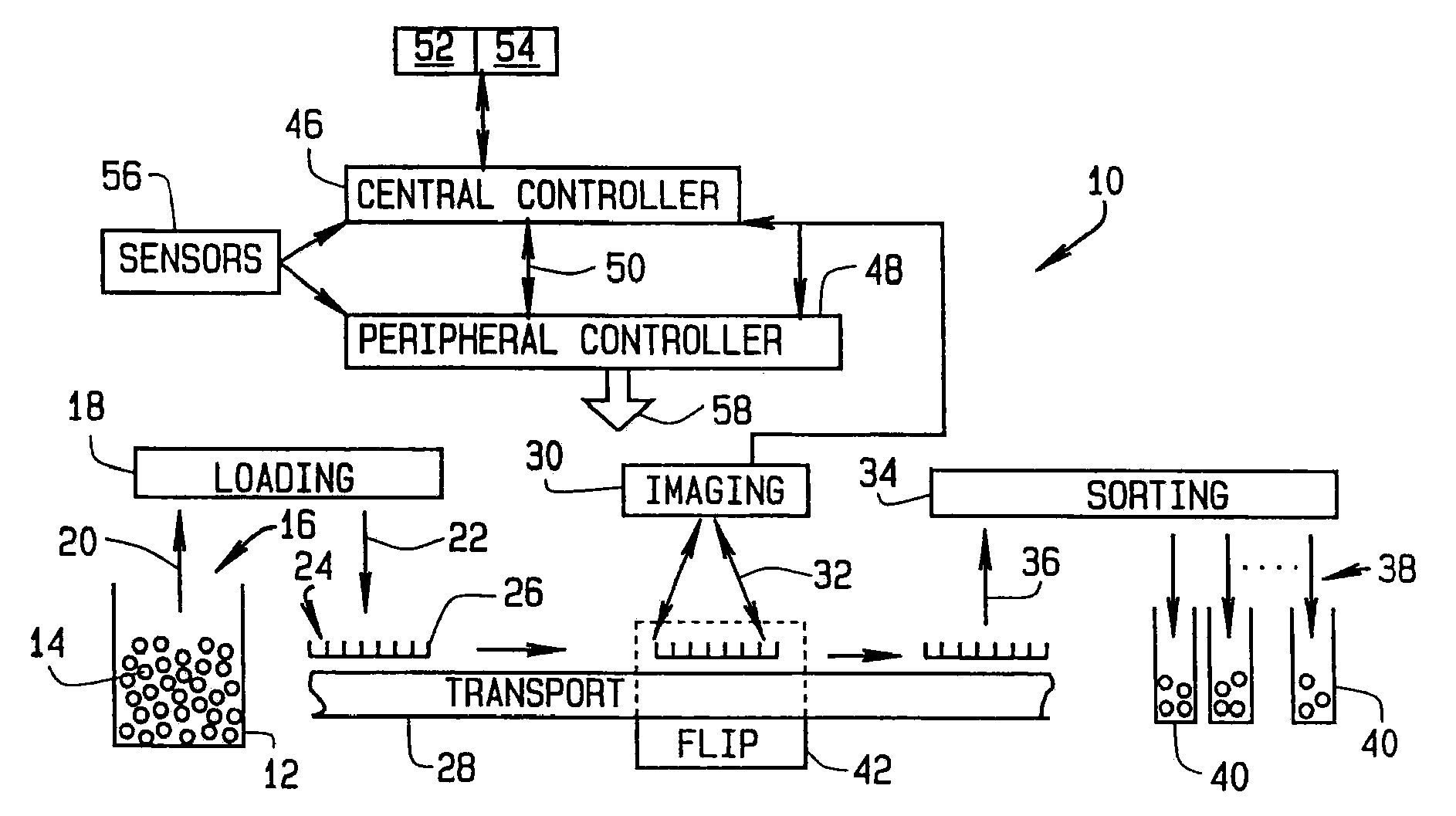
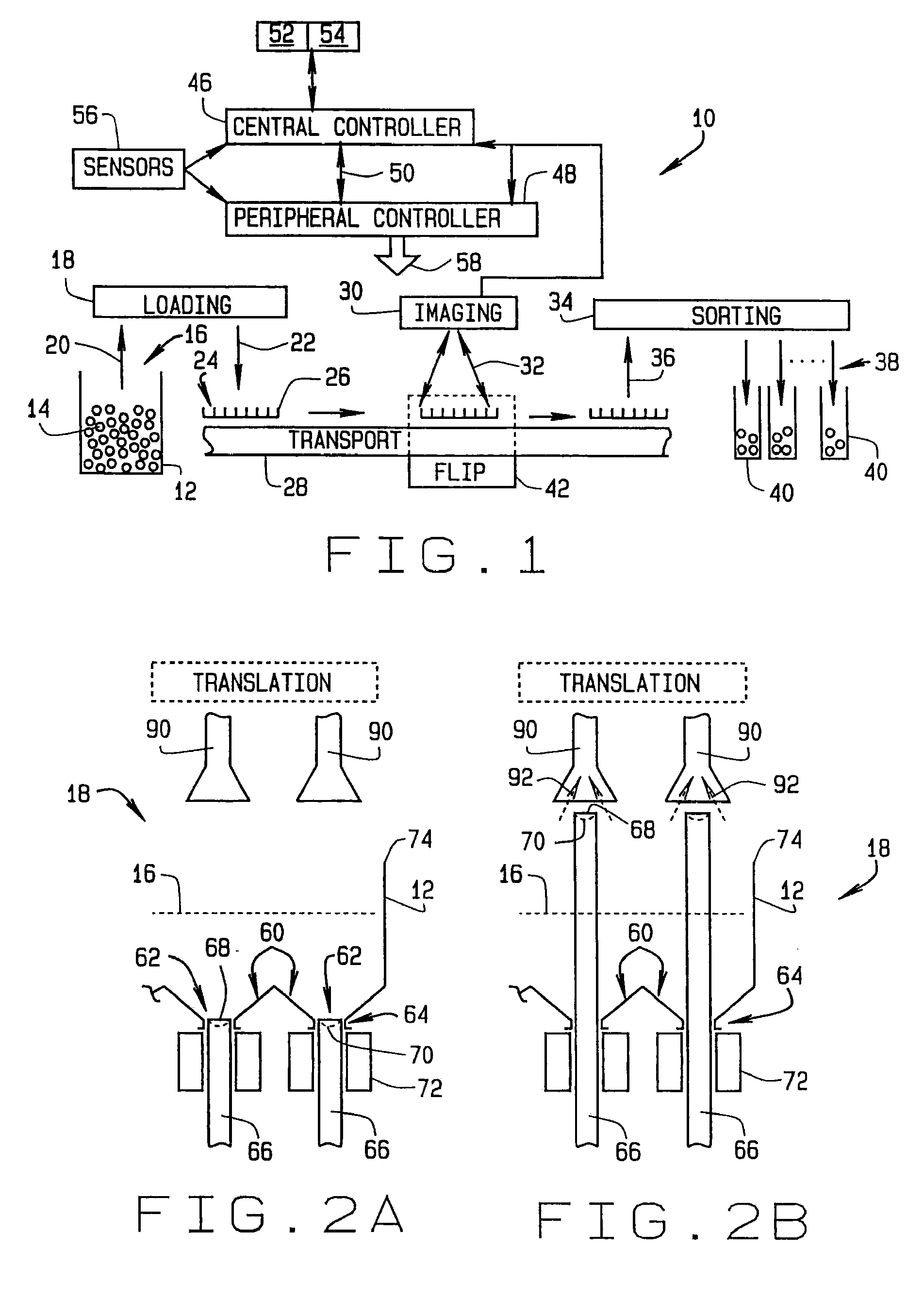
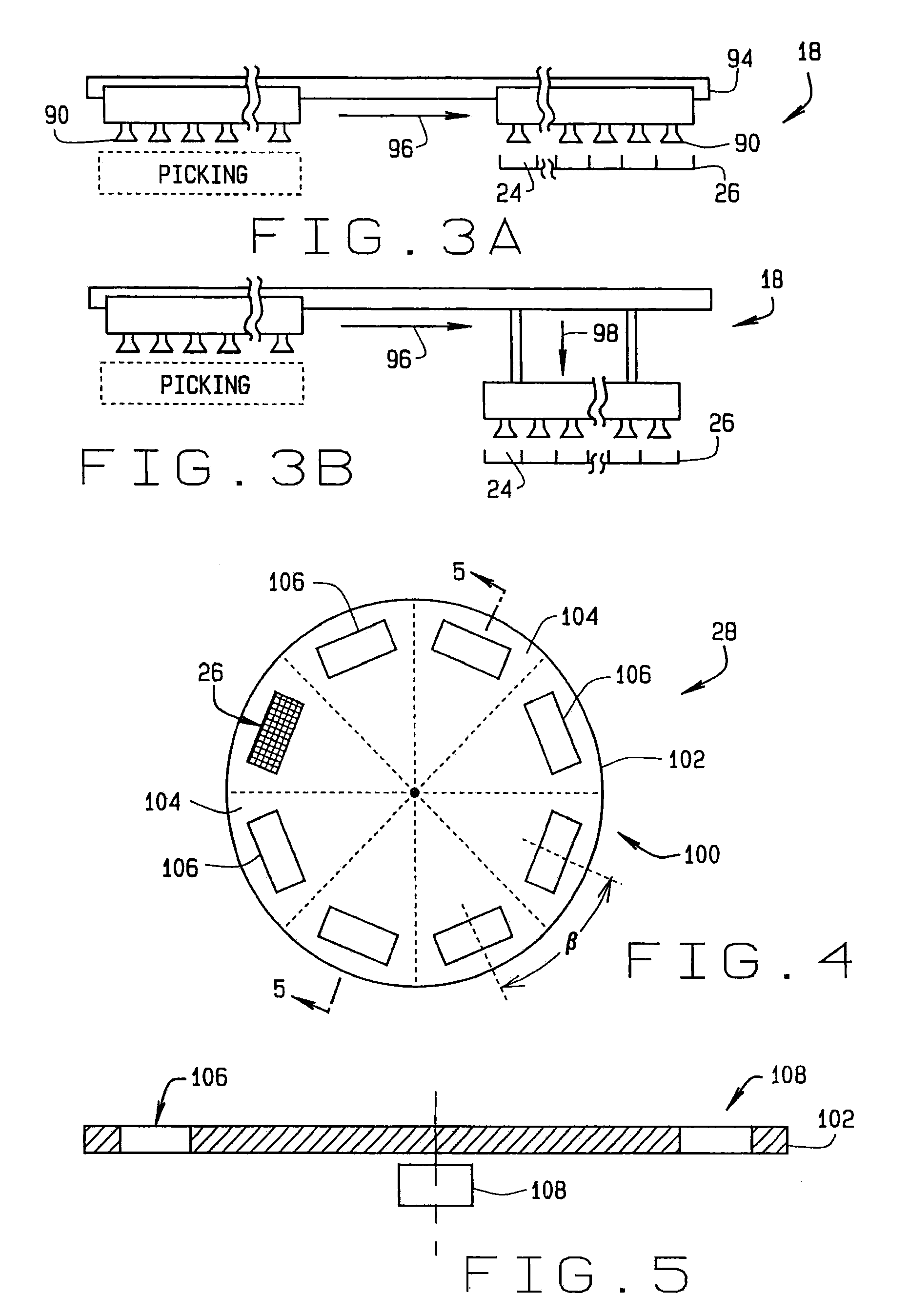
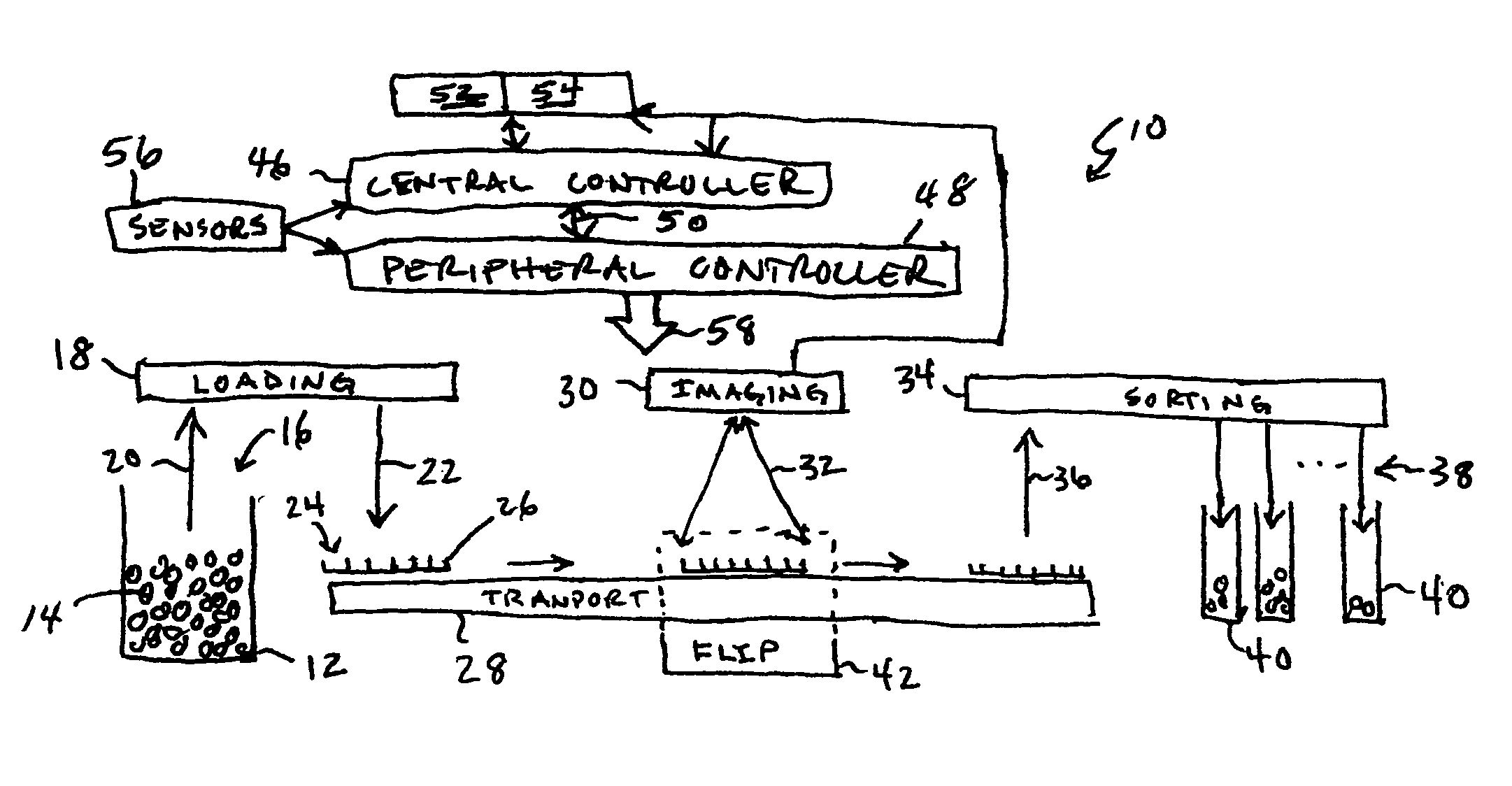
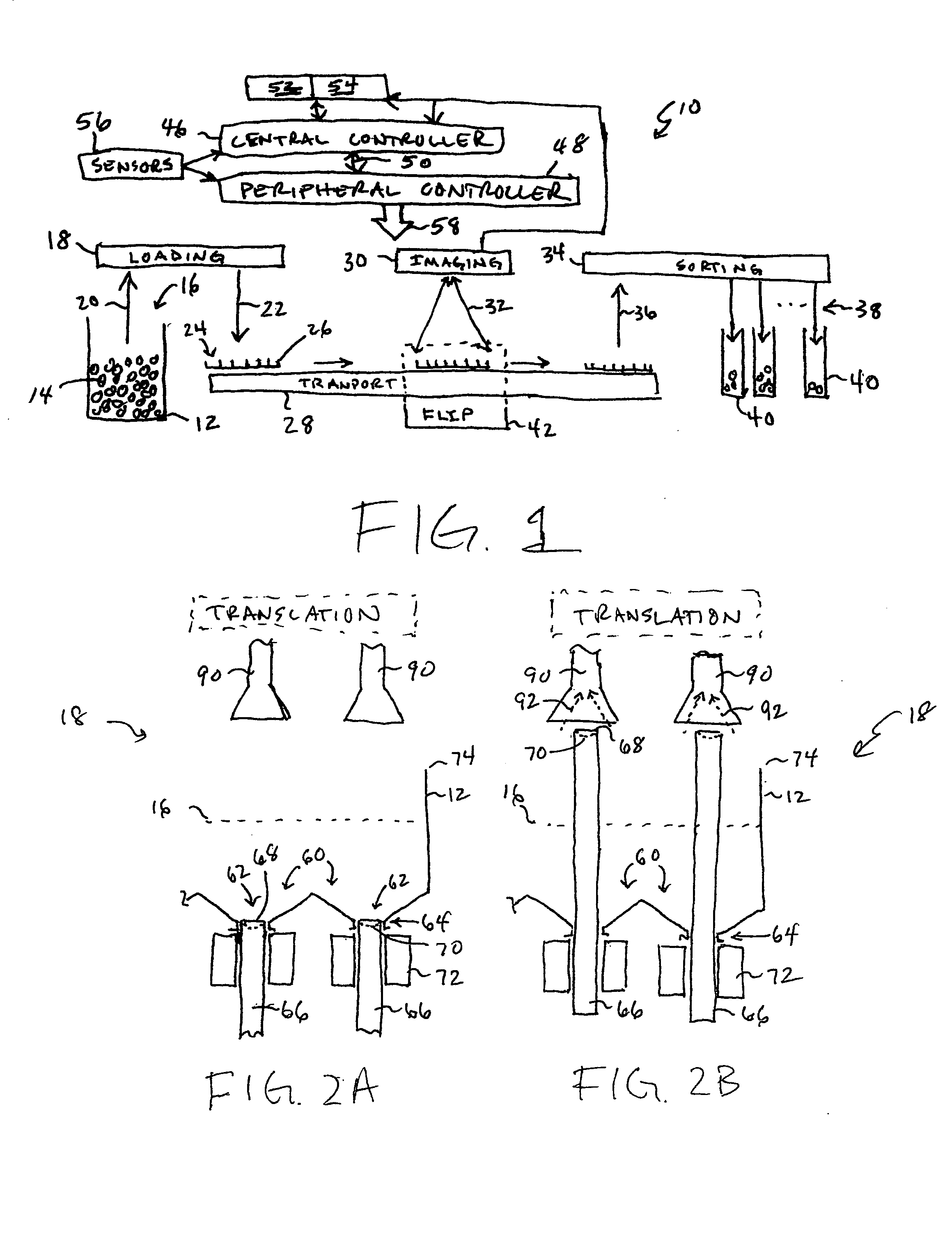
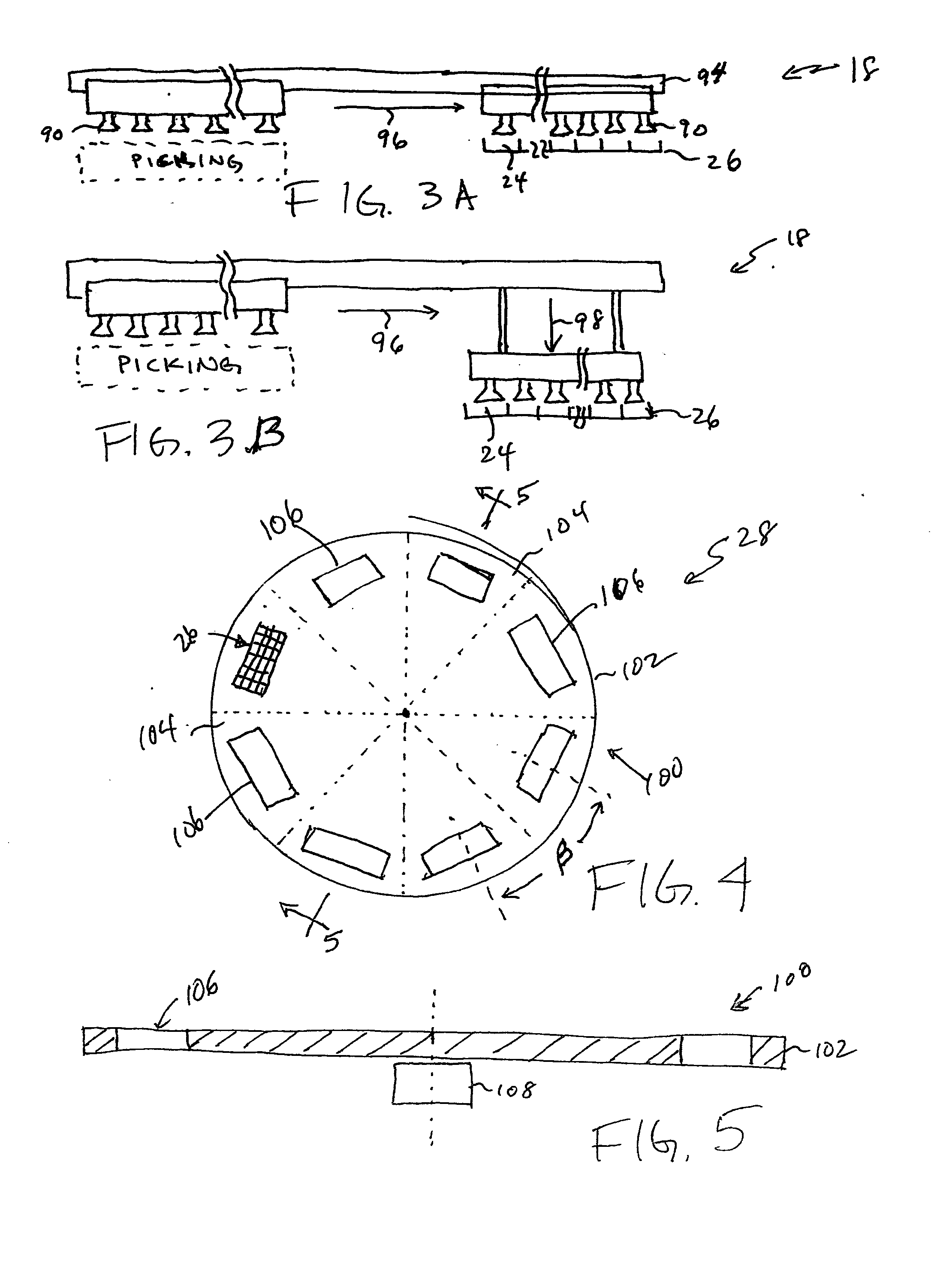
High throughput automated seed analysis system
A transport subsystem conveys seed holding well trays between a plurality of stations. A loading subsystem is positioned at a first station and is operable to load seeds into individual wells of the conveyed tray. An imaging subsystem is positioned at a second station and is operable to image the seeds contained within the tray wells. A mechanism is provided for flipping the seeds so as to enable the imaging subsystem to obtain multi-side seed images. A sorting subsystem is positioned at a third station and is operable to remove the seeds from the tray wells and sort the removed seeds into a plurality of sort bins. The sorting determination may be made based on an analysis of the seed images obtained by the imaging subsystem.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Combined intercropping and mulching method
InactiveUS7634869B1Reduce needIncrease surface moistureSeed and root treatmentFabaceae cultivationPolygonum fagopyrumMyriophyllum
A method of combined intercropping and mulching of commercial crops is described herein. Suitable annuals such as young wheat and / or buckwheat plants are planted in soil in which legumes were originally planted. A portion of the resulting upper portions of young wheat and / or buckwheat plants is mowed and blended with organic debris to provide nutrients for intercropped commercial plants such as corn and soybeans. The remaining portion is chopped blended with organic debris and sprayed onto the top layer of seeded soil as combination mulch. For larger commercial applications, conventional agricultural machines are described herein, and are modified for the most efficient intercropping. For best results, at least one intercropped commercial plant should be a legume.
Owner:WILLIAMS JR MARVIN J
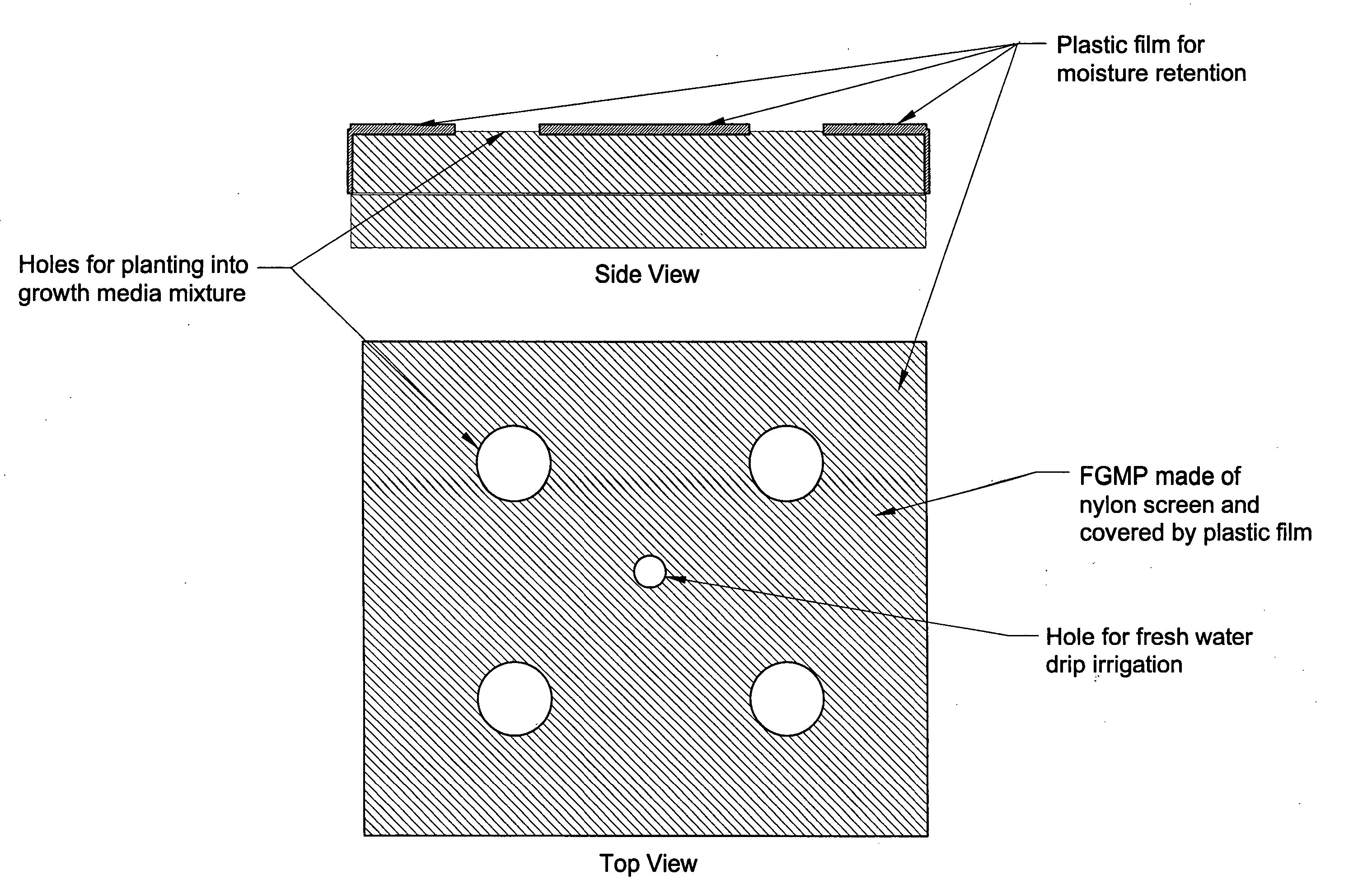
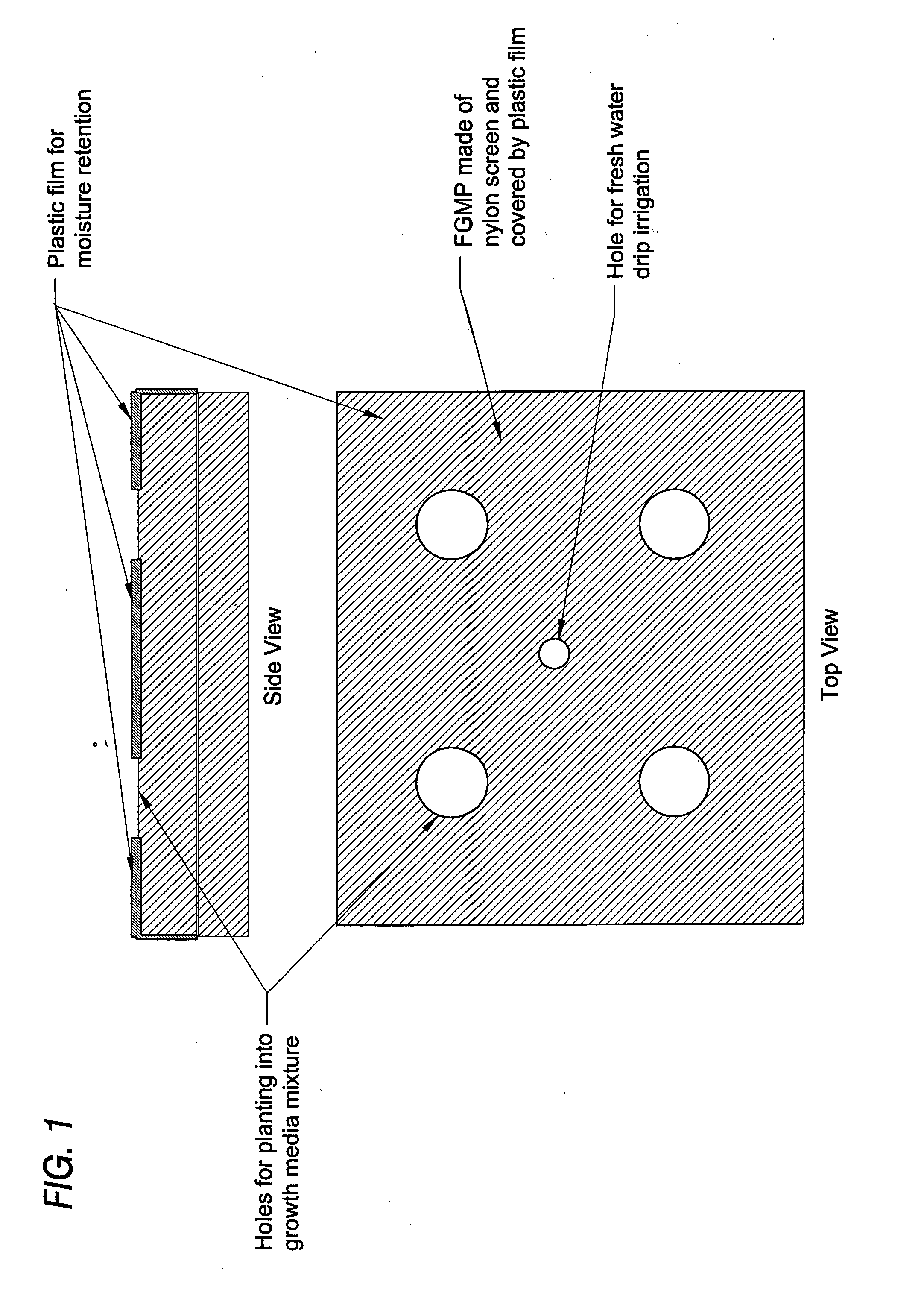
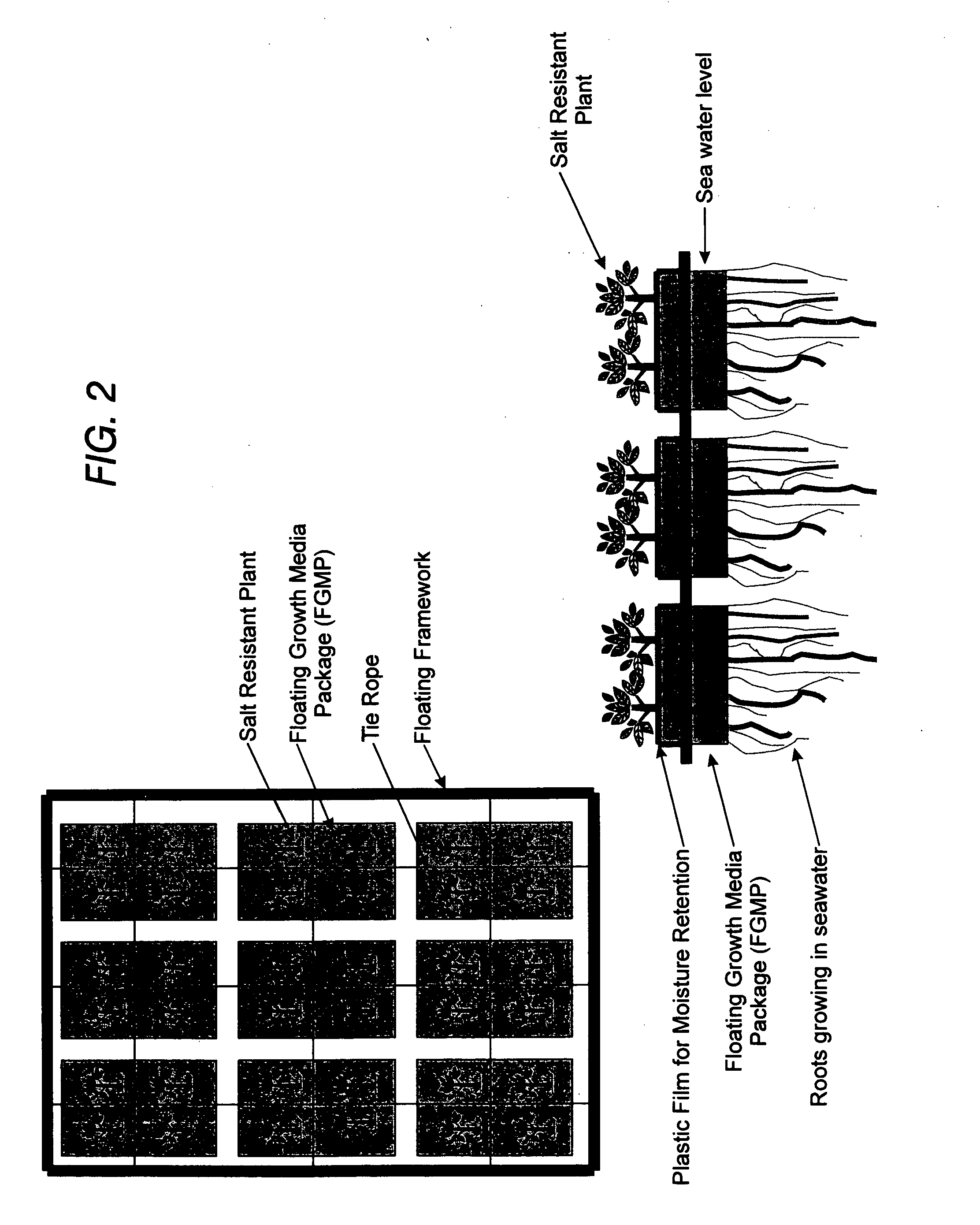
Floating plant cultivation platform and method for growing terrestrial plants in saline water of various salinities for multiple purposes
InactiveUS20050044788A1Efficient managementMinimal requirementSeed and root treatmentClimate change adaptationShootCell culture media
The cultivation of terrestrial plants in brackish water or seawater is carried out with this invention. A light-weight, floating growth medium package (FGMP) or, alternatively, a sheet of suitable material is used to support the growth of terrestrial plants floating on water bodies of various salinity, including 100% seawater in marine environments. The FGMP units can be linked together and confined in a floating, rigid or flexible framework to form a floating seawater cultivation platform (FSCP). Using the method, plants were able to grow and thrive on the FSCP floating on 100% seawater in a sustainable manner. Halophytic akulikuli (Sesuvium portulacastrum L.) can regenerate its shoot and root in seawater. Thus, the discovery will enable us to practice marine agriculture, or agriculture on the sea. The FSCP can be used for wide range of purposes, from environmental protection to landscaping to crop production.
Owner:UNIV OF HAWAII
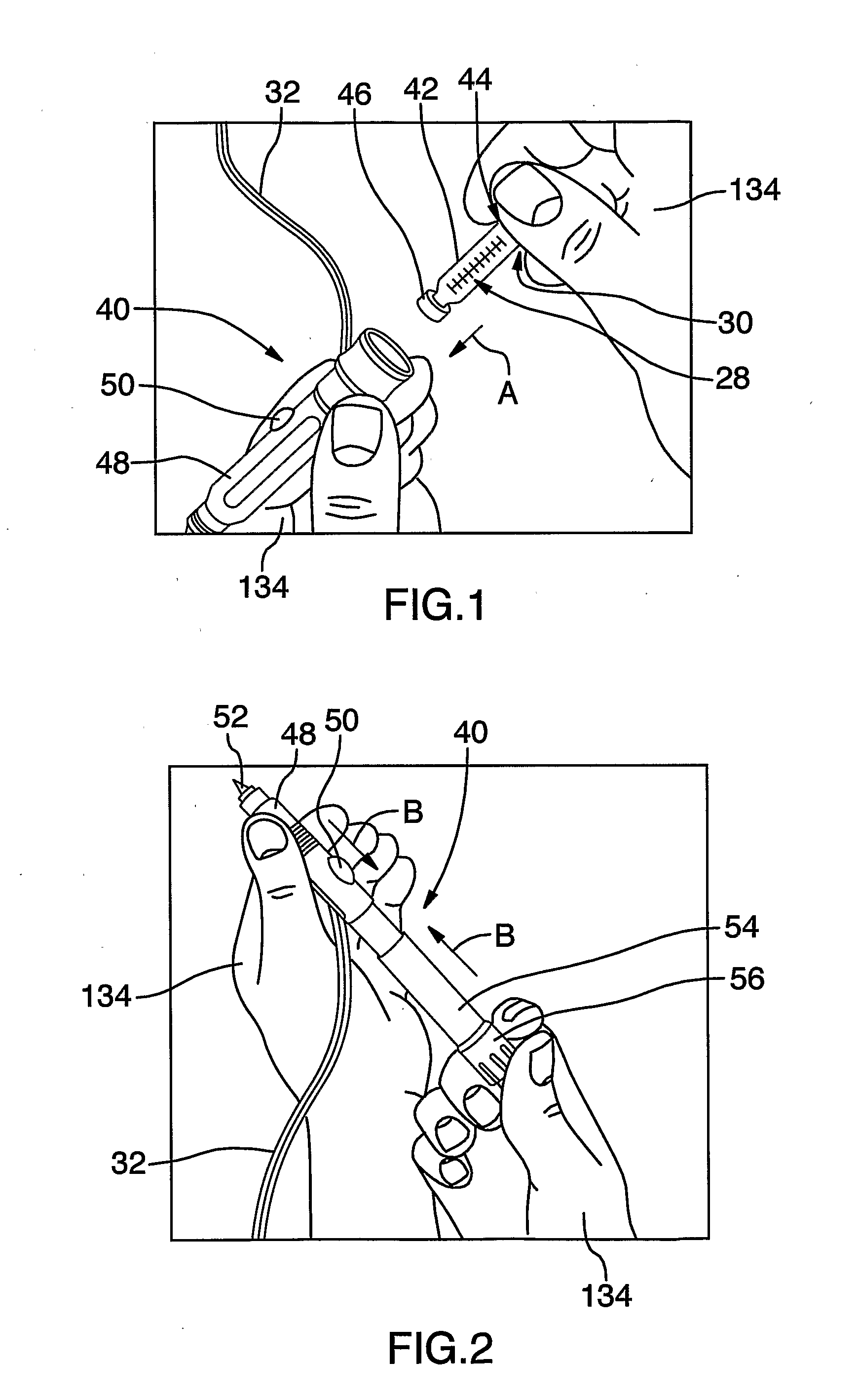
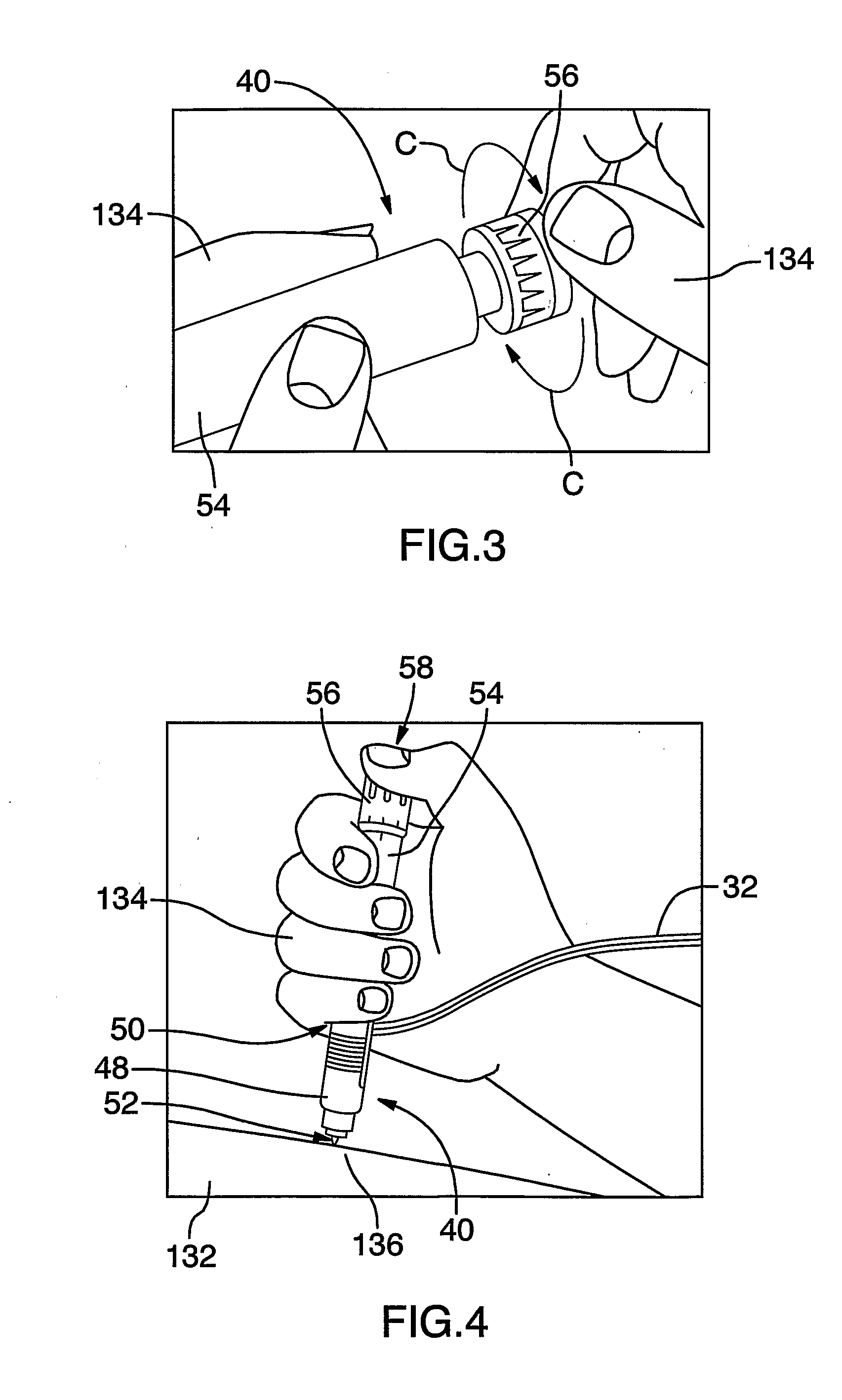
Method of Delivery of Therapeutic Metal Ions, Alloys and Salts
A method for treating a bacterial, viral, fungal, or vector-induced disease state. A therapeutically effective dose of a metal substance is delivered to the body of a potentially infected organism using a delivery methodology selected from the group consisting of syringes, auto-injectors, pricking devices, buccal embedding, transdermal patches, needle transdermal patches, aerosol inhalers, ingestible dissolvable capsules, encapsulated boluses, needle encapsulated boluses, and electrode catheterization methodologies. The metal substance is selected from the group consisting of silver, gold, copper, zinc, selenium, platinum, and their ions, alloys, salts, and combinations thereof. Preferably, an electrical current is introduced substantially in the course of utilizing the delivery methodology. The electrical current is preferably substantially varied over time, and is still more preferably a reversing electrical current.
Owner:INT BIO THERAPEUTIC RES
High throughput automated seed analysis system
ActiveUS20050082207A1Easy to recycleSeed and root treatmentColor/spectral properties measurementsEngineeringAdemetionine
A transport subsystem conveys seed holding well trays between a plurality of stations. A loading subsystem is positioned at a first station and is operable to load seeds into individual wells of the conveyed tray. An imaging subsystem is positioned at a second station and is operable to image the seeds contained within the tray wells. A mechanism is provided for flipping the seeds so as to enable the imaging subsystem to obtain multi-side seed images. A sorting subsystem is positioned at a third station and is operable to remove the seeds from the tray wells and sort the removed seeds into a plurality of sort bins. The sorting determination may be made based on an analysis of the seed images obtained by the imaging subsystem.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Plants and seeds of hybrid corn variety ch852179
ActiveUS20090282545A1Conferring male sterilityPreventing self-pollinationSeed and root treatmentOther foreign material introduction processesTissue cultureHybrid corn
According to the invention, there is provided seed and plants of the hybrid corn variety designated CH852179. The invention thus relates to the plants, seeds and tissue cultures of the variety CH852179, and to methods for producing a corn plant produced by crossing a corn plant of variety CH852179 with itself or with another corn plant, such as a plant of another variety. The invention further relates to genetic complements of plants of variety CH852179.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
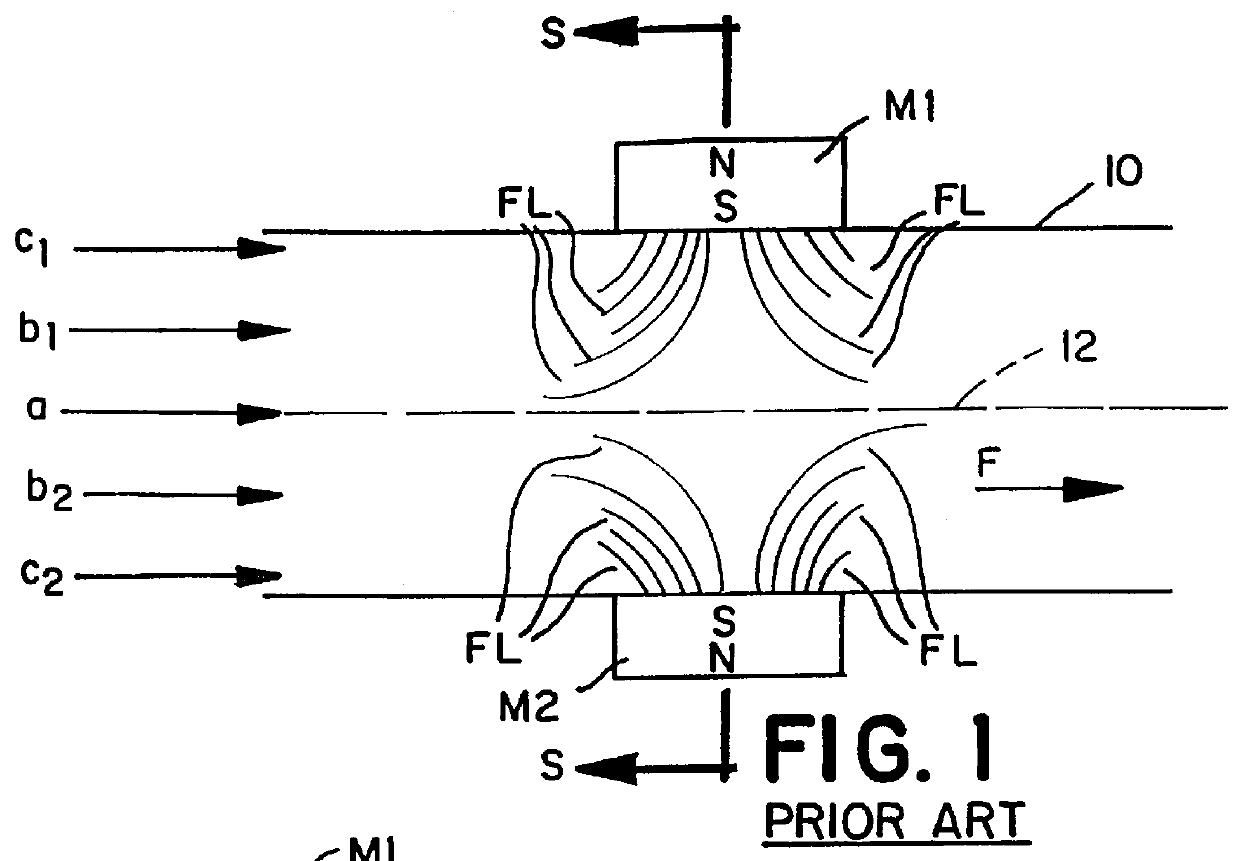
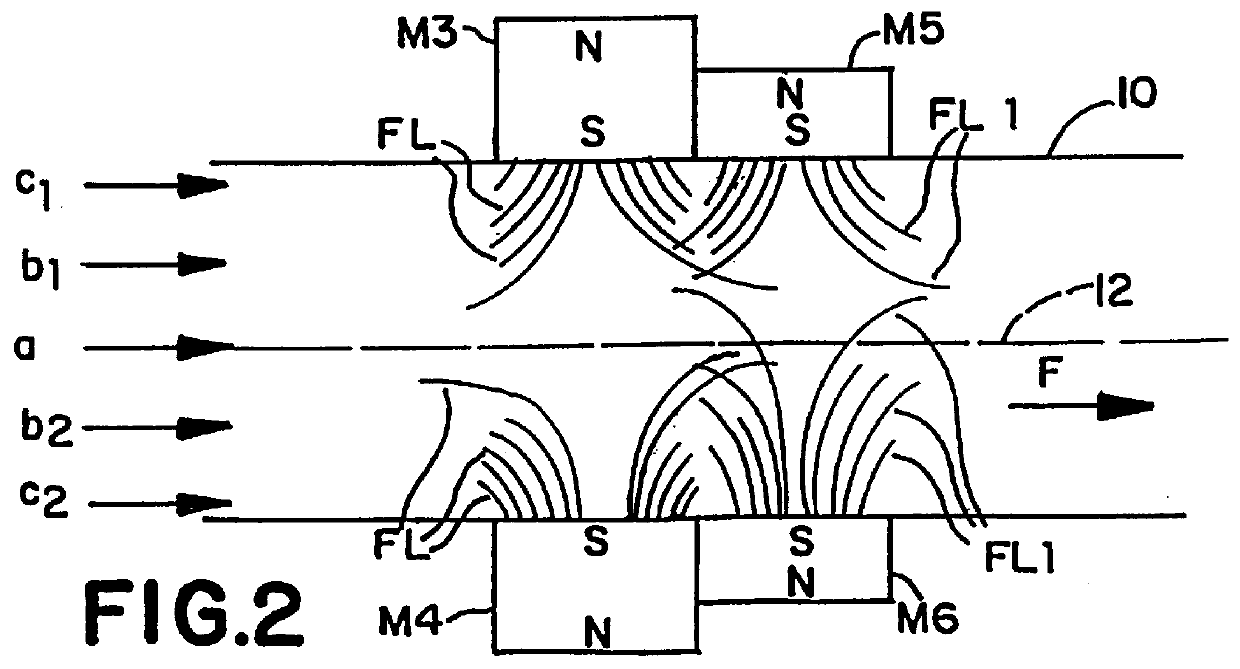
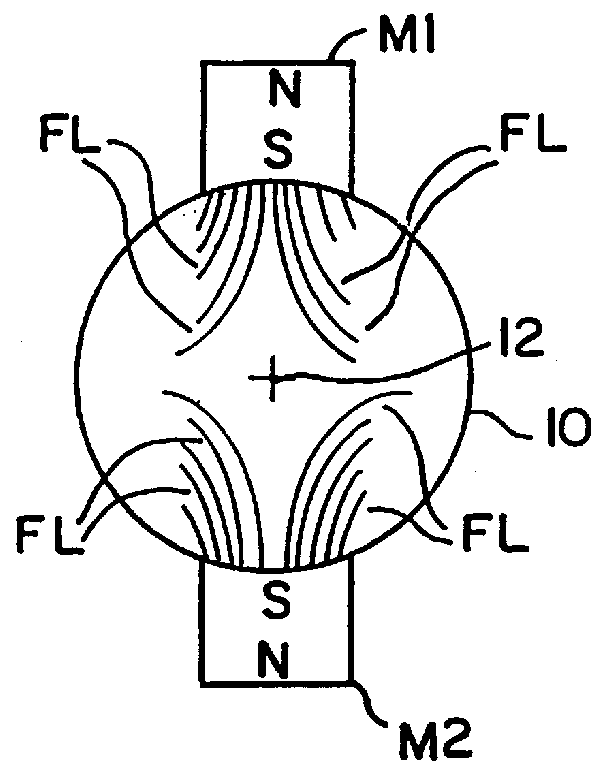
Magnetic device for the treatment of fluids
InactiveUS6056872AImproved magnetic treatmentOvercomes shortcomingSeed and root treatmentCombustion-air/fuel-air treatmentMagnetPhysics
A device for the magnetic treatment of fluids such as gases or liquids, wherein such device includes a plurality of magnets for imparting a magnetic field is arranged peripherally about a pipe or other fluid conduit within which is a flowing fluid. The device utilizes a plurality of magnets with different magnetic field strengths for varying the field flux along the length of the pipe or other fluid conduit.
Owner:KULISH PETER ANTHONY
Method for planting se-enriched rice
ActiveCN103828665AIncrease productionIncrease selenium contentSeed and root treatmentFertilising methodsBiotechnologyInsect pest
The invention discloses a method for planting se-enriched rice. The method comprises the following steps of land selection and preparation; seeding; seedling culturing; transplanting; field management: intertillage, weeding, topdressing and insect pest prevention; and harvesting. The selenium content of rice planted by using the method is high, and the yield of the rice is also high. Testing confirms that the yield of the se-enriched rice is 620-650kg per acre, and the selenium content of the rice ranges from 0.1 mg / kg to 0.3mg / kg.
Owner:和县金城米业有限责任公司
Method of producing plants, plant cultivating device, and light-emitting panel
InactiveUS20040163308A1Easy to handleEasy to manufactureSeed and root treatmentSolid-state devicesEffect lightLight-emitting diode
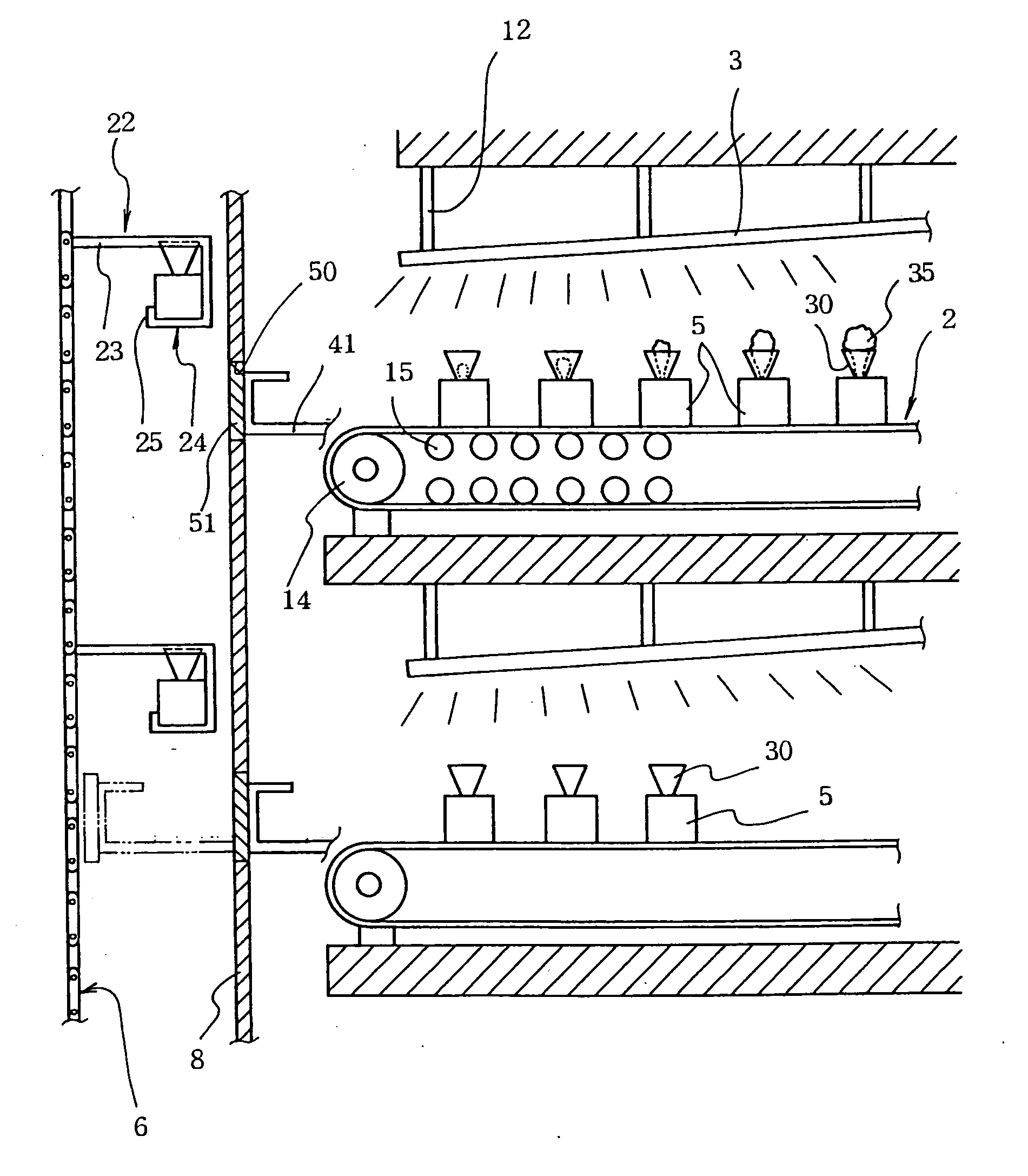
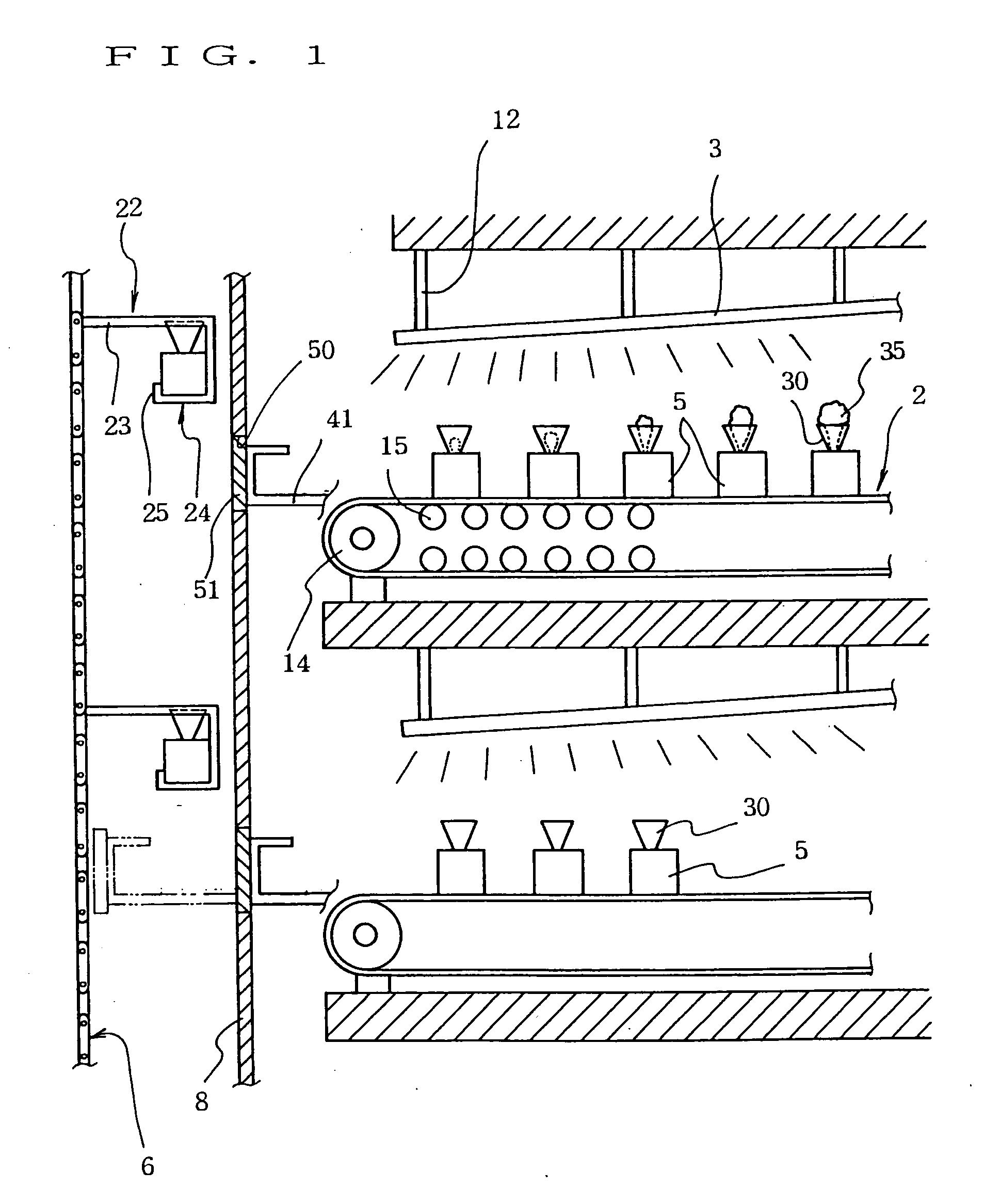
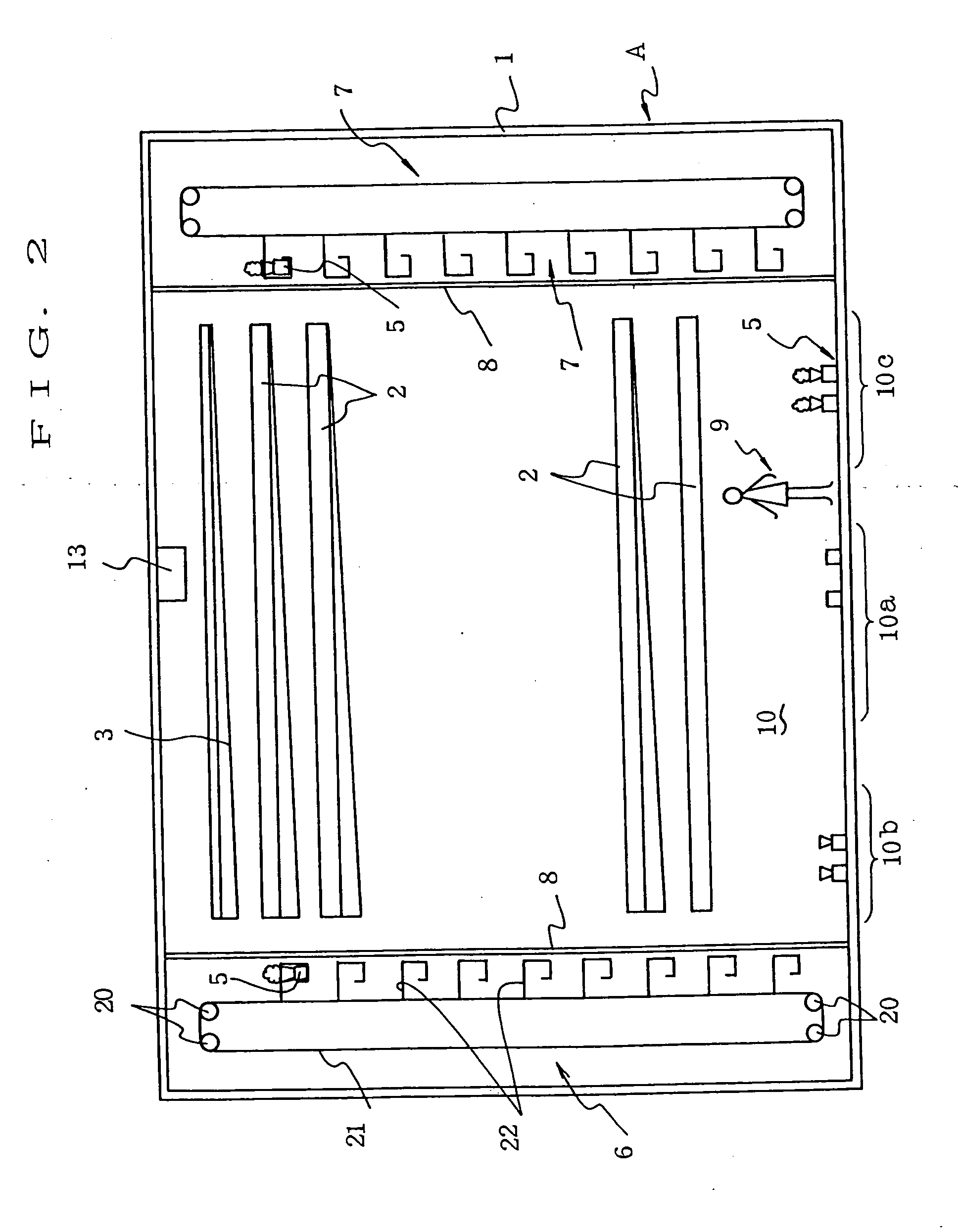
A plant cultivating device (A), comprising aluminum long square pipe trays (5) for storing plants (35) together with culture solution, a conveyor device (2) for feeding the trays (5) in order in lateral direction, and a lighting device (3), having a number of light-emitting diodes disposed thereon, located over the conveyor device (5), the lighting device (3) being disposed so as to be higher gradually from the upstream side to the downstream side of the conveyor device (2), wherein a funnel-shaped holder (30) holding the upper part of the plant (35) is provided on the upper surface of the tray (5), and a planting conveyor (6) and a harvesting conveyor (7) for supply and retrieval, a reflecting wall (8) provided between these conveyors and the conveyor device (2), and transfer bars (41) for transferring the trays (5) between the conveyor device (2) and the planting and harvesting conveyors (6,7) are installed on the upstream and downstream sides of the conveyor device (2).
Owner:KINPARA SHIRO
Integrated aquaculture-hydroponics systems: nutrient dynamics and designer diet development
InactiveUS6065245AReduced availabilityReduced bioavailabilitySeed and root treatmentEnergy based wastewater treatmentFish dietFresh water organism
Owner:SEAWRIGHT DAMON E
Apparatus and methods for analyzing and improving agricultural products
InactiveUS20060112628A1Long collection timeSmall sample sizeSeed and root treatmentLaboratory glasswaresNon destructiveComputer science
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com