Patents
Literature
713results about How to "Small sample size" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Coded Molecules for Detecting Target Analytes
InactiveUS20070190543A1Easy to detectHigh sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalytePhysics
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
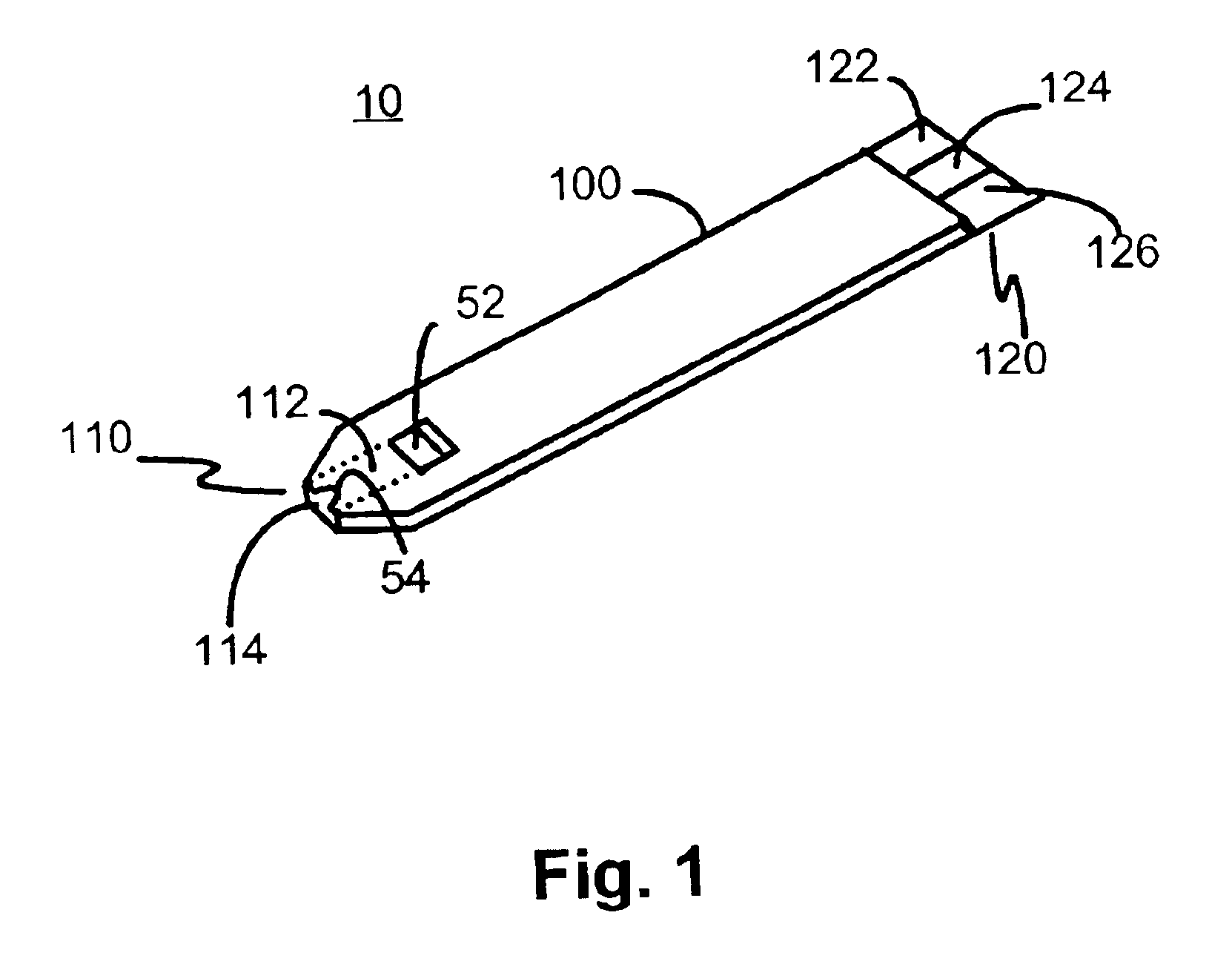
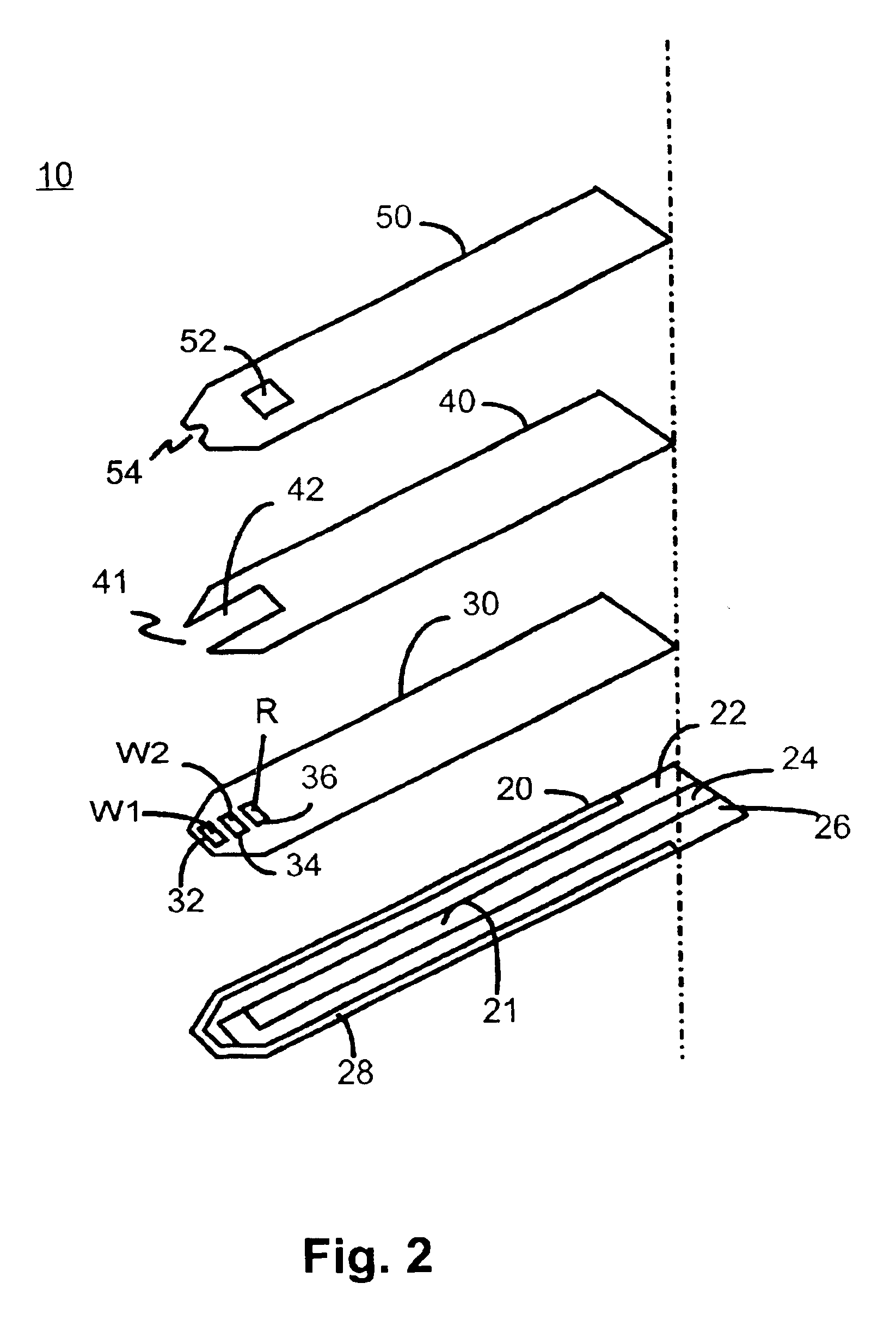
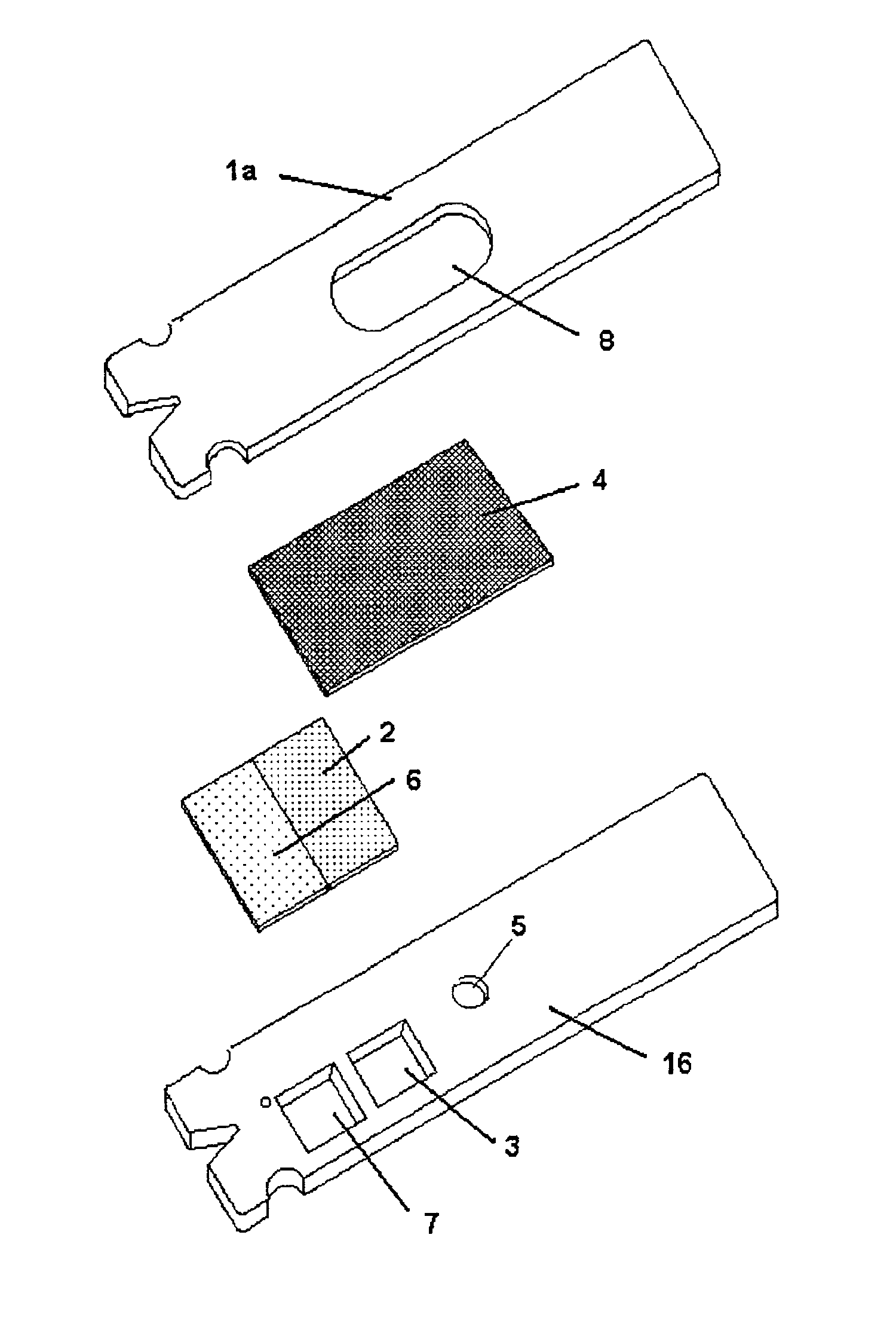
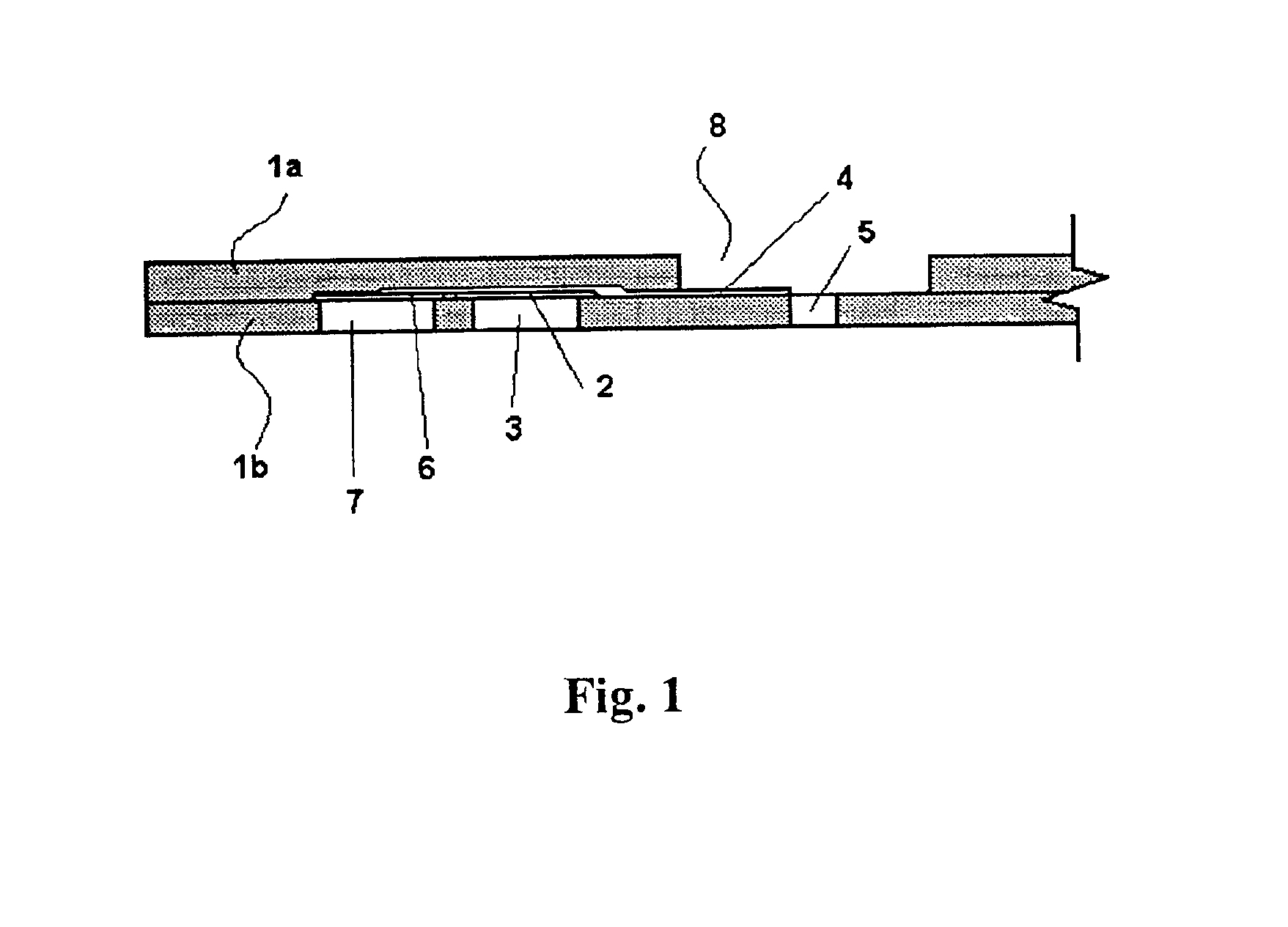
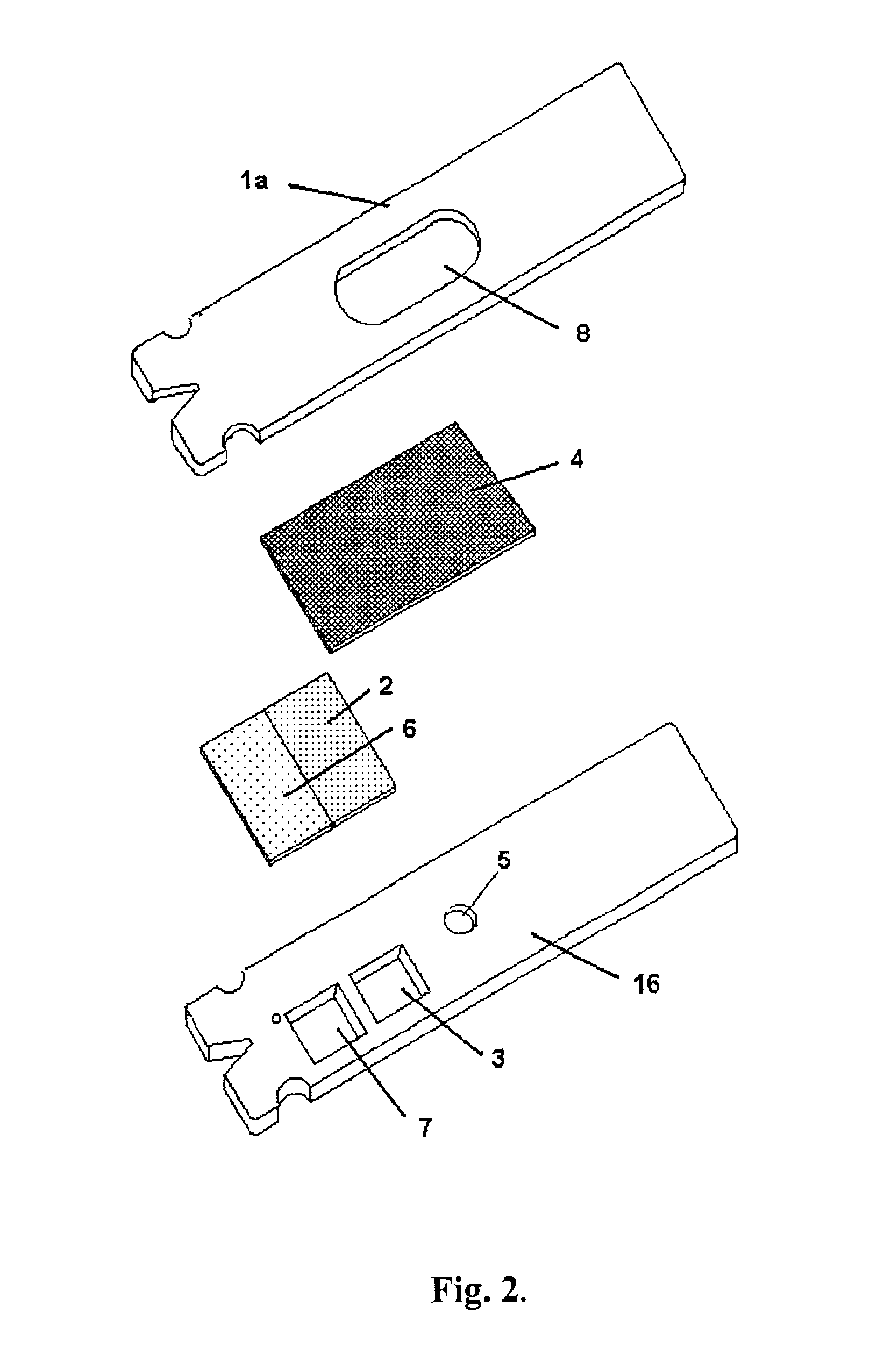
Disposable sensor with enhanced sample port inlet
InactiveUS6837976B2Interference minimizationWide linear measurement rangeImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsProximateConductive coating
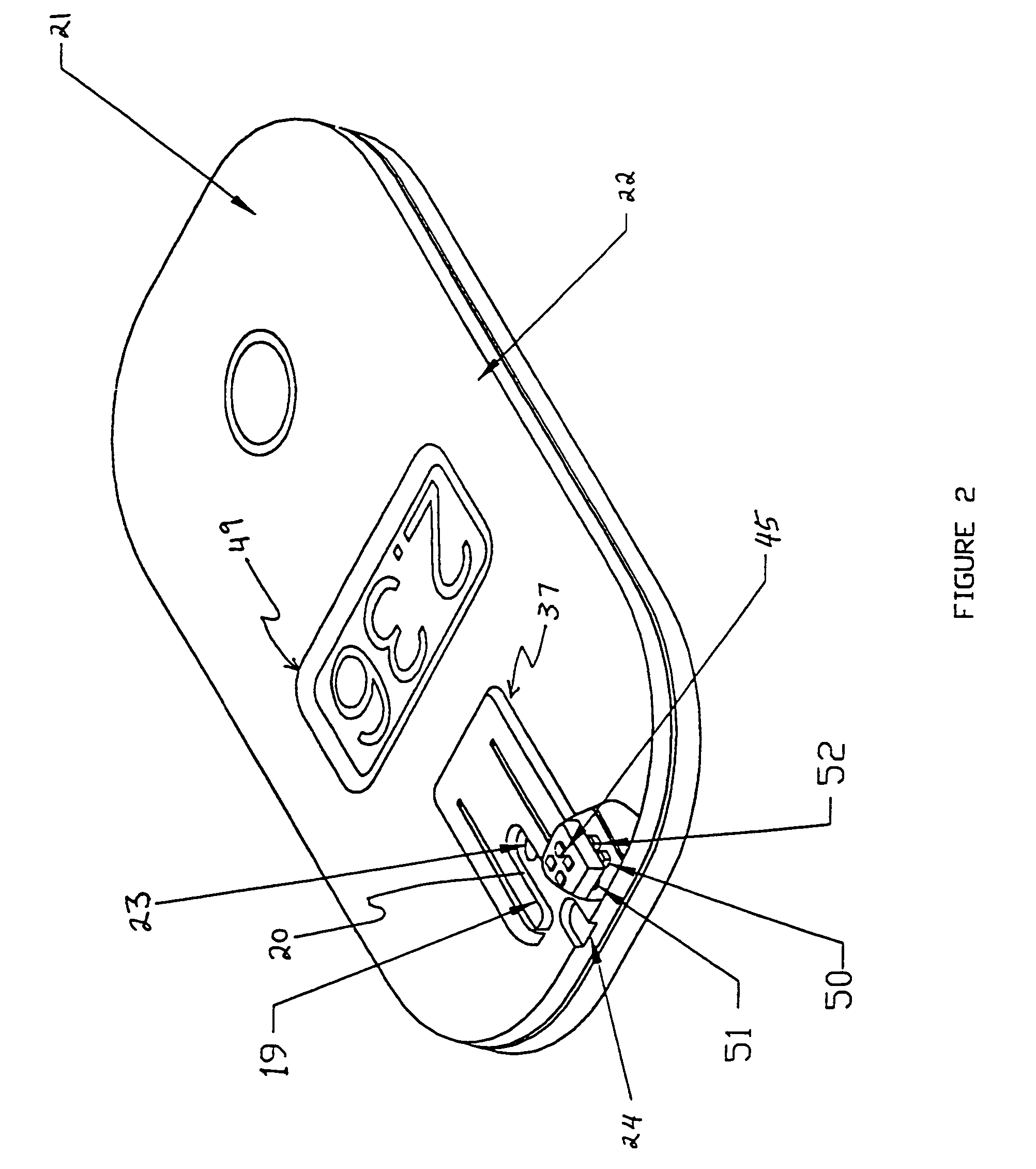
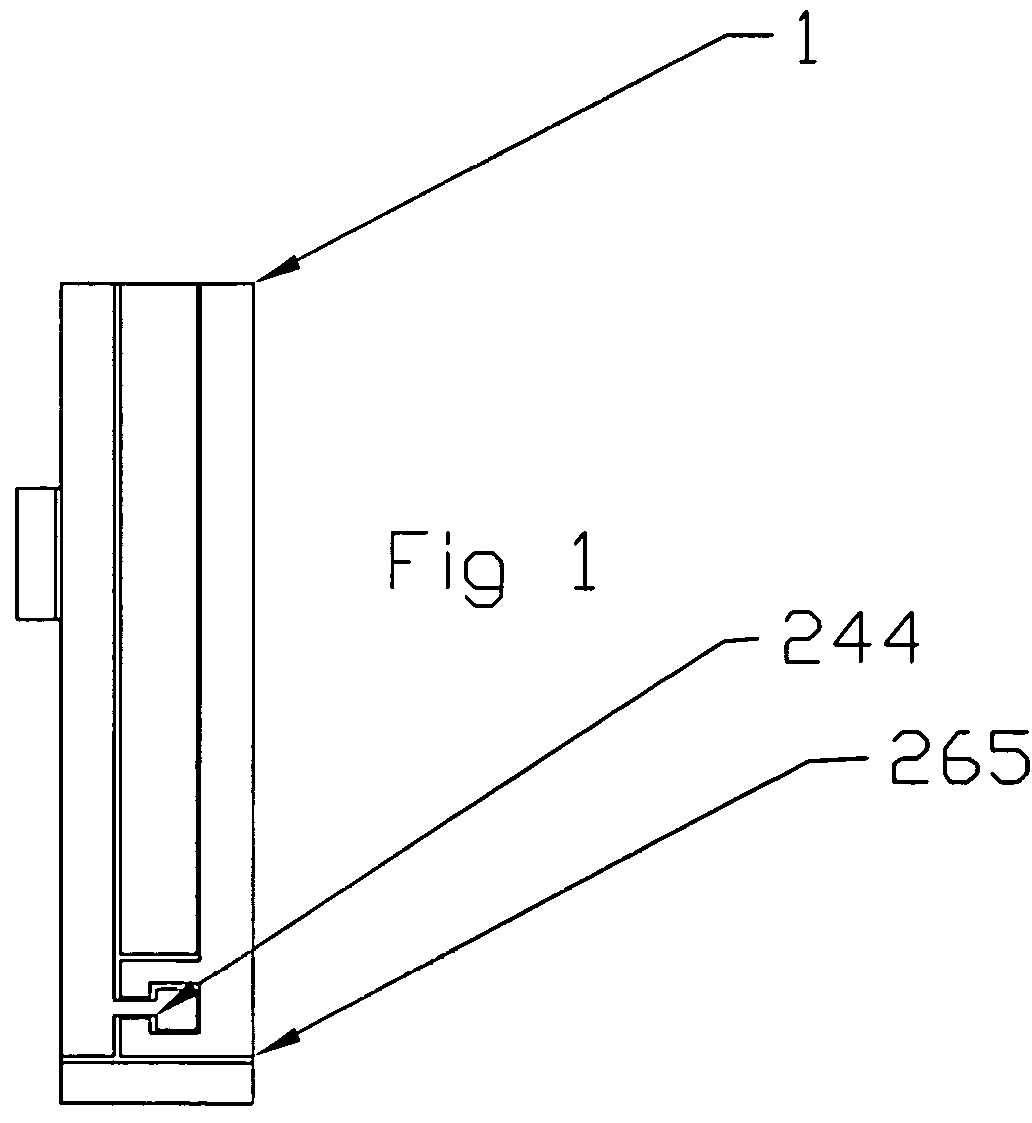
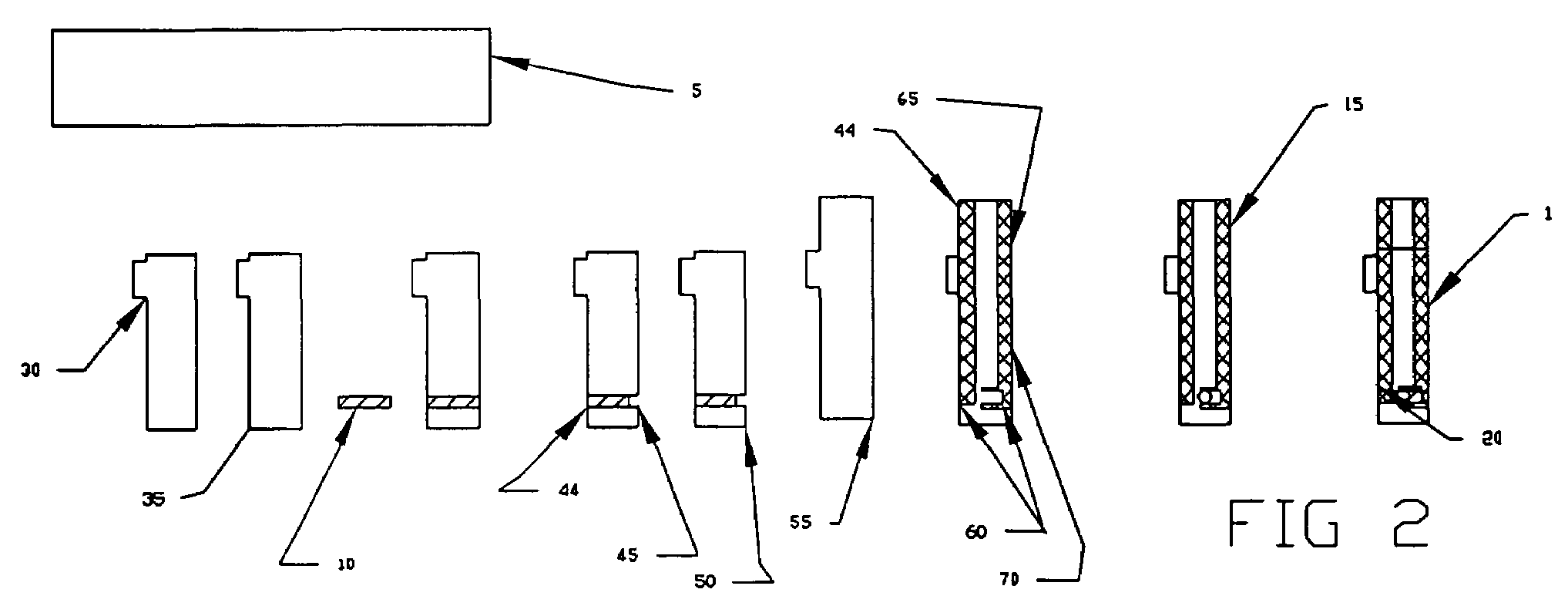
A disposable biosensor for testing a fluid sample including a laminated strip with a first and second end, a reference electrode embedded in the laminated strip proximate to the first end, at least one working electrode embedded in the laminated strip proximate to the first end and the reference electrode, an open path for receiving a fluid sample beginning from the first end and connecting to a vent spaced from the first end, the open path being sufficiently long to expose the reference electrode and the working electrode to the fluid sample, and conductive contacts located at the second end of the laminated strip. The laminated strip has a base layer with a conductive coating, a reagent holding layer, a channel forming layer and a cover having an inlet notch at the first end. The working electrode contains a reagent having an enzyme.
Owner:NOVA BIOMEDICAL
Synchronized analyte testing system
InactiveUS7347973B2Low costMinimizing upkeepMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorEnzymologyComputer hardwareAnalyte
An analyte detection system is provided with calibration information uniquely specific to the set of test strips to which the sample is to be applied. The calibration information may be stored in permanent memory of the testing device, such that the device is discarded after use of all the test strips in a kit, or it may be stored in a calibration chip accompanying the set of test strips and distributed therewith, thereby enabling re-use of the testing device with a different set of test strips and associated calibration chip.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
Disposable sub-microliter volume biosensor with enhanced sample inlet
InactiveUS6942770B2Wide linear measurement rangeReduce waiting timeImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsEngineeringOpen path
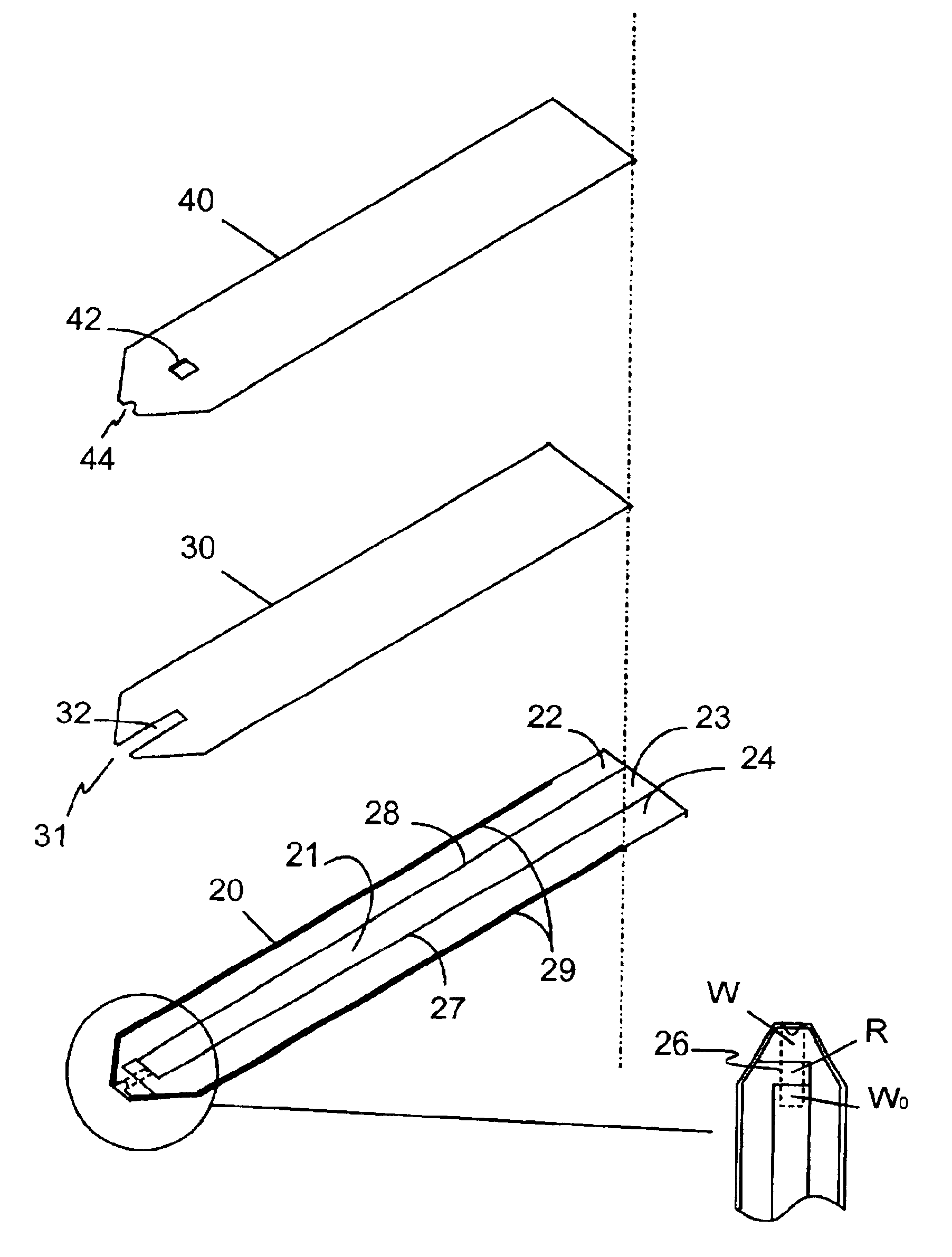
A disposable electrode strip for testing a fluid sample including a laminated strip with a first and second end, a vent, an open path for receiving a fluid sample of less than one microliter beginning from the first end and connecting to the vent, a working electrode, a reference electrode and a pseudo-working electrode embedded in the laminated strip within the open path and proximate to the first end, a reagent matrix coextensive within the open path and covering the three electrodes, and conductive contacts located at the second end of the laminated strip.
Owner:NOVA BIOMEDICAL
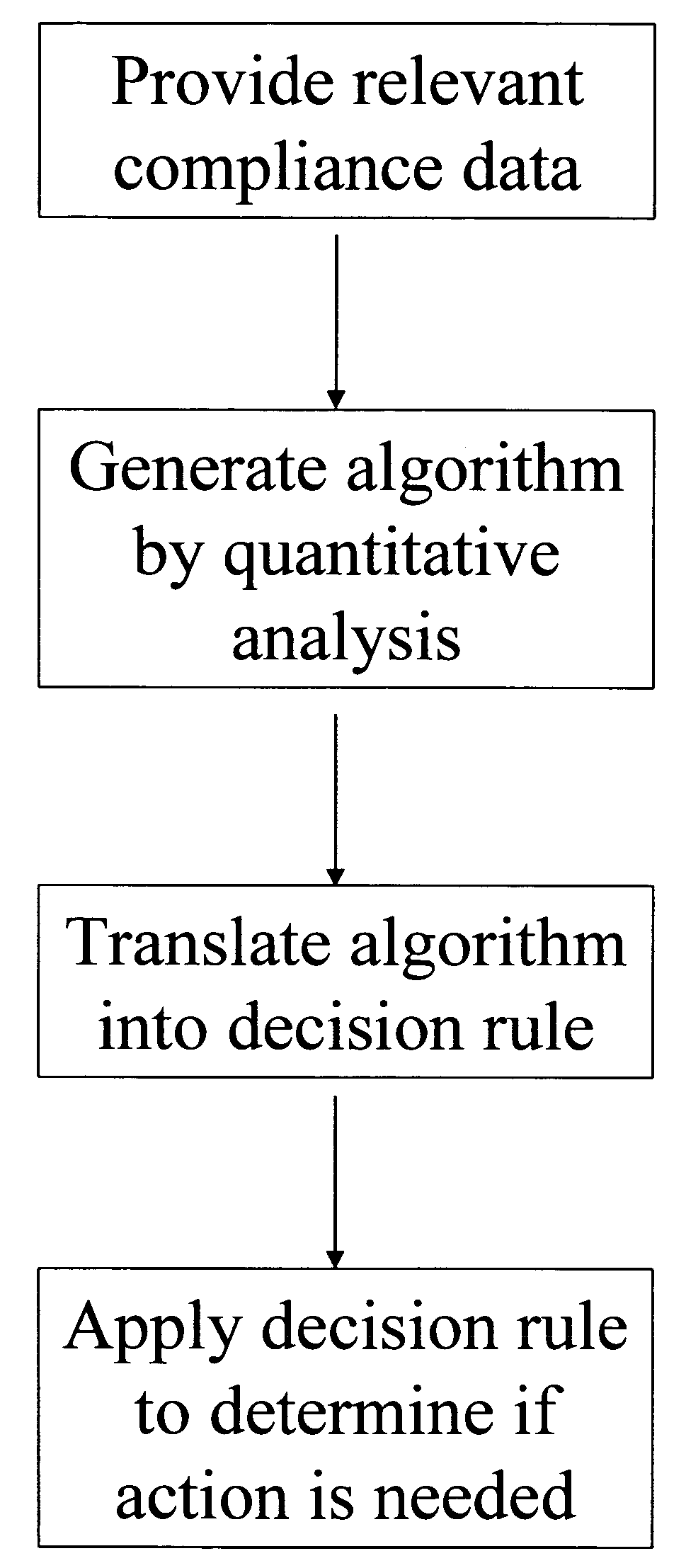
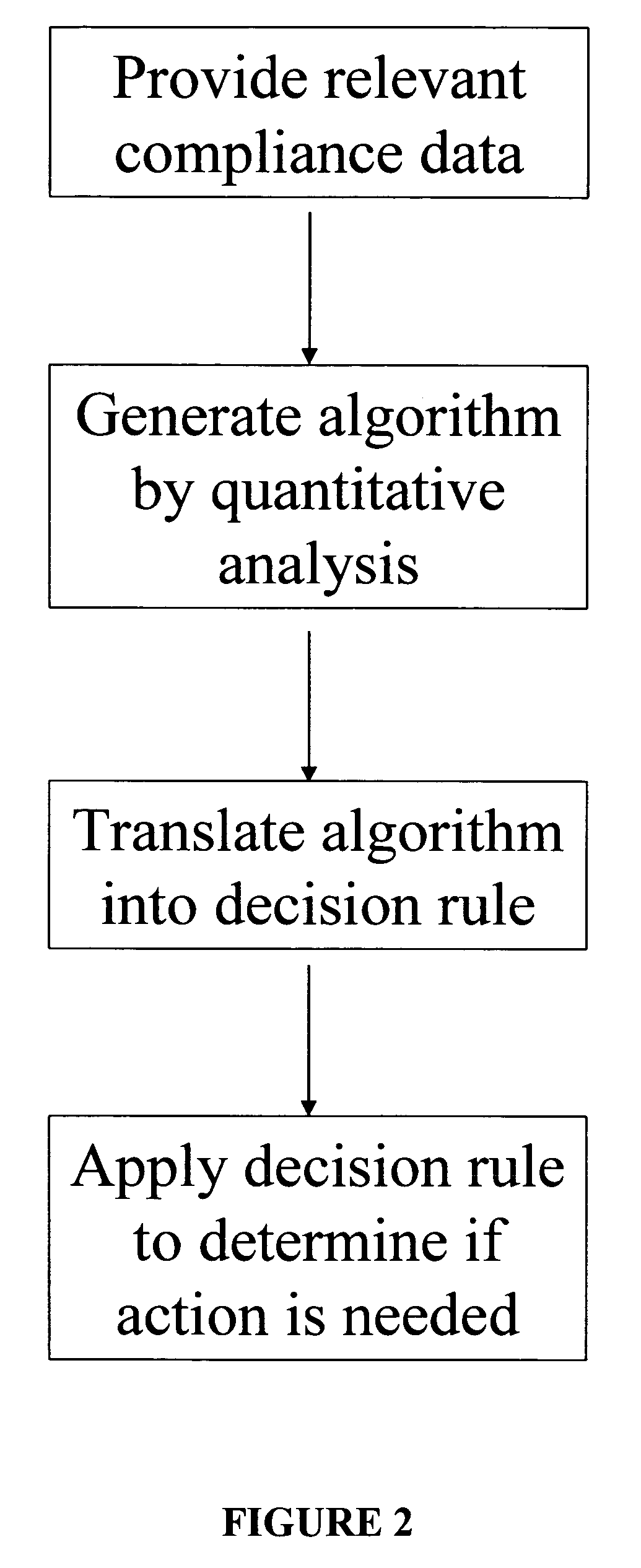
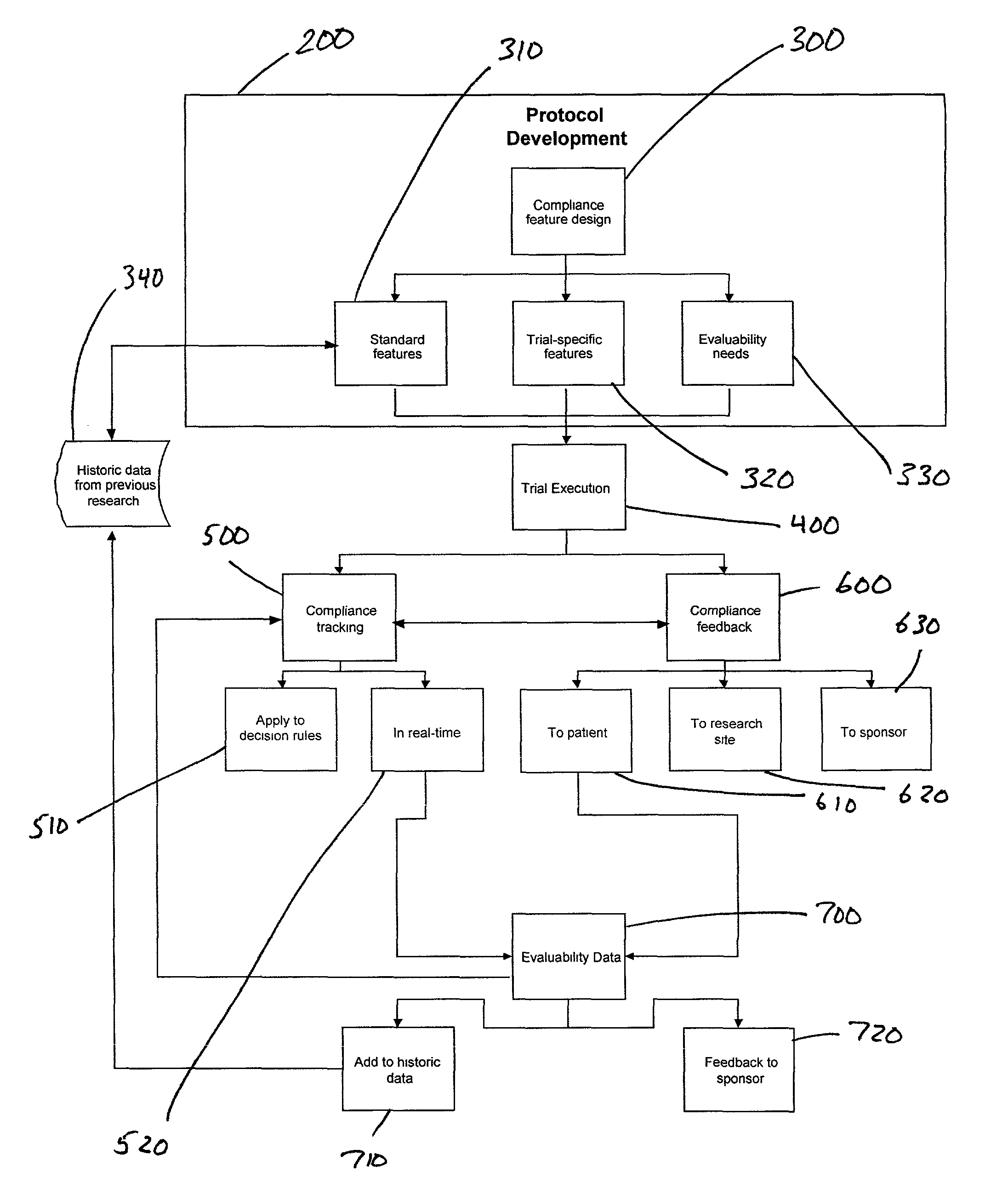
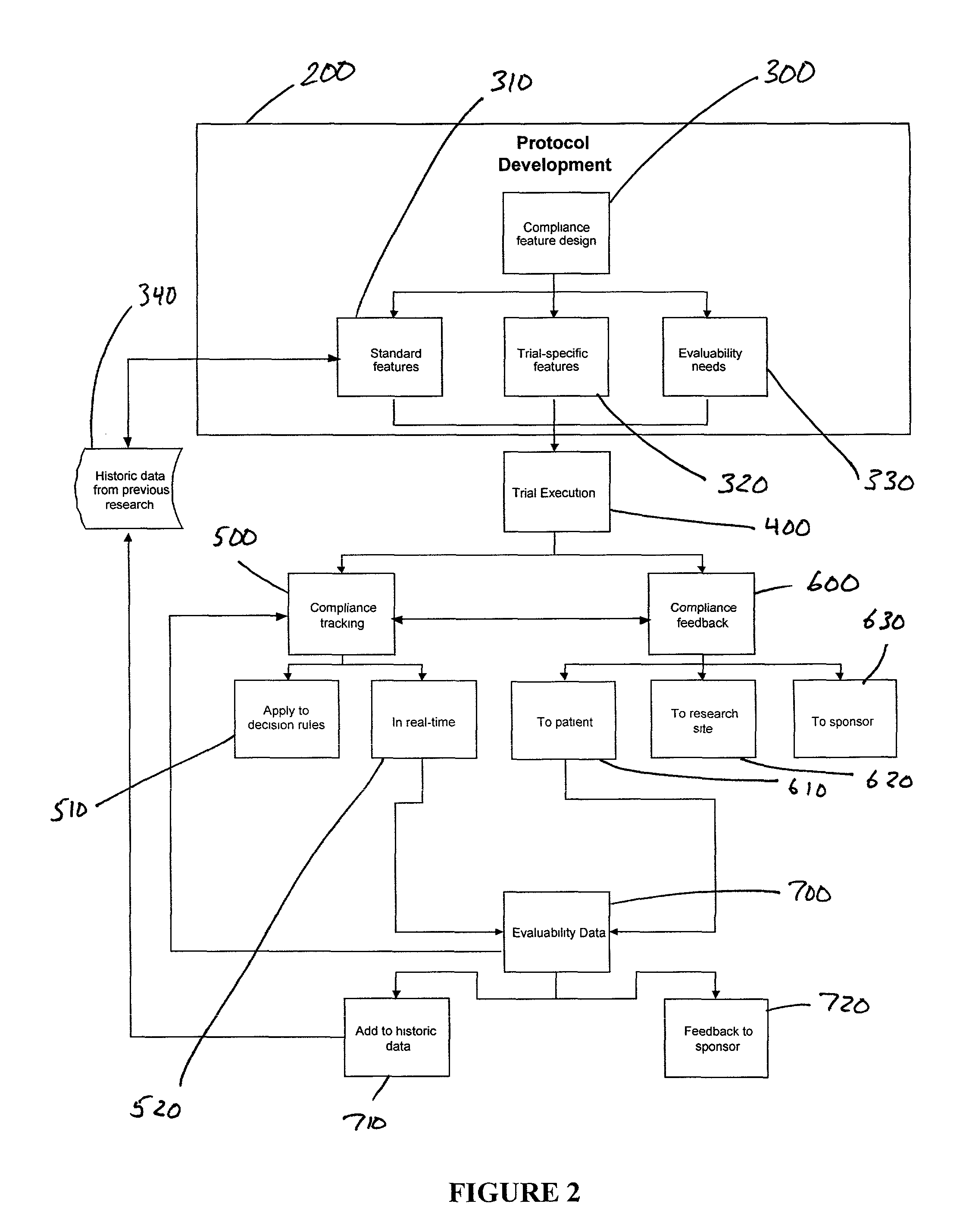
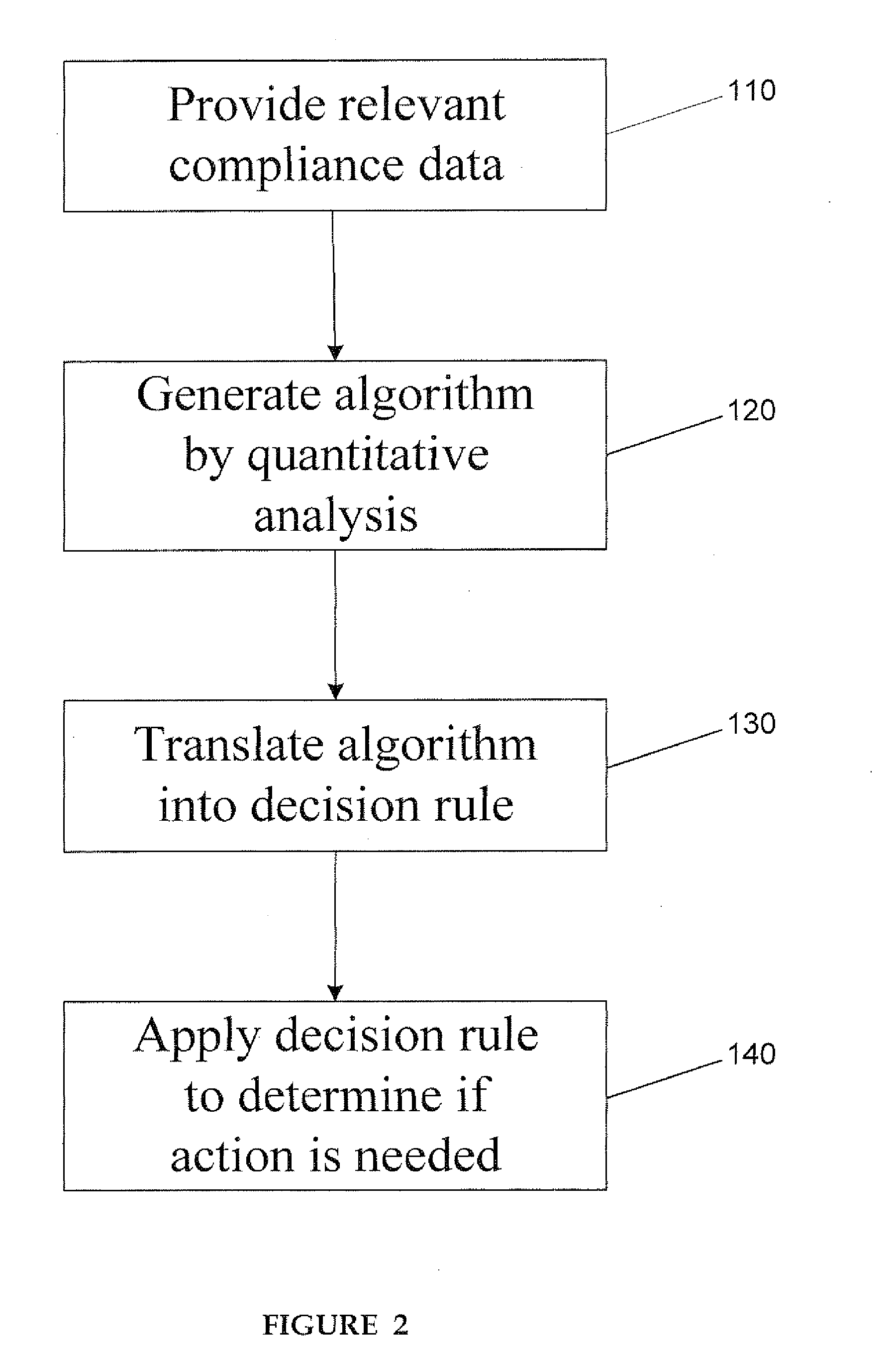
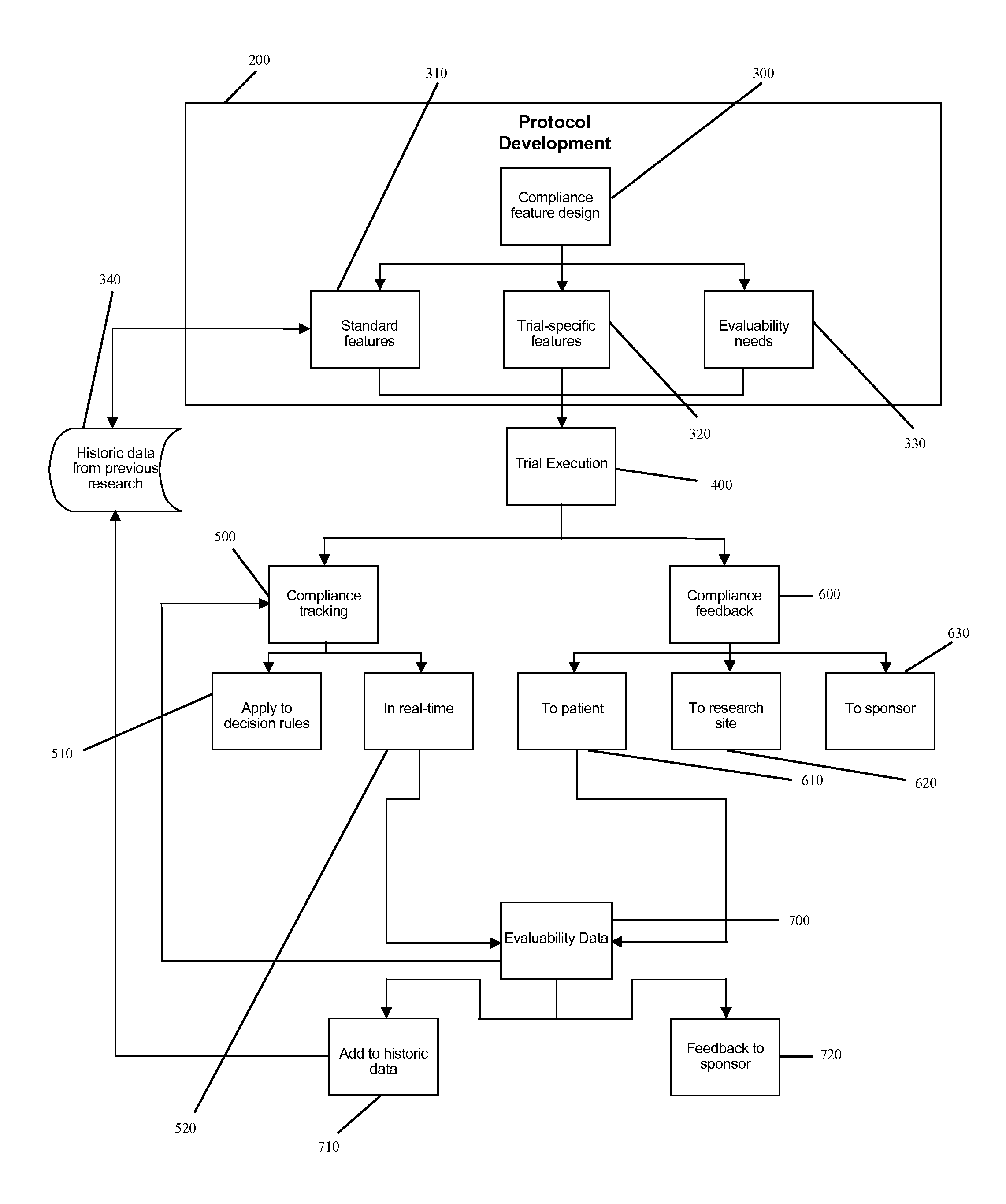
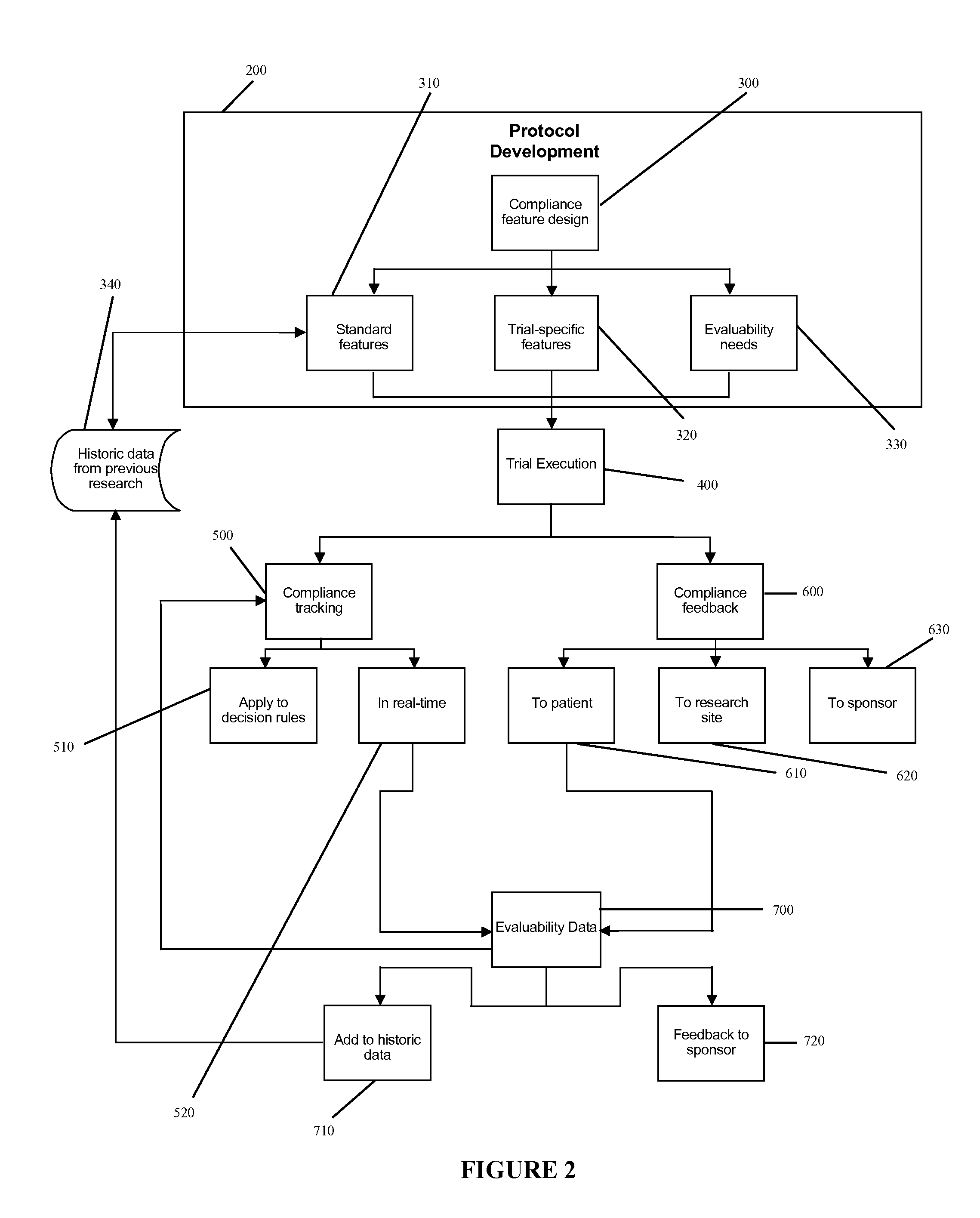
Apparatus and method for prediction and management of participant compliance in clinical research
InactiveUS7415447B2Reduce testing costsImprove statistics performanceDigital computer detailsForecastingNon complianceClinical trial
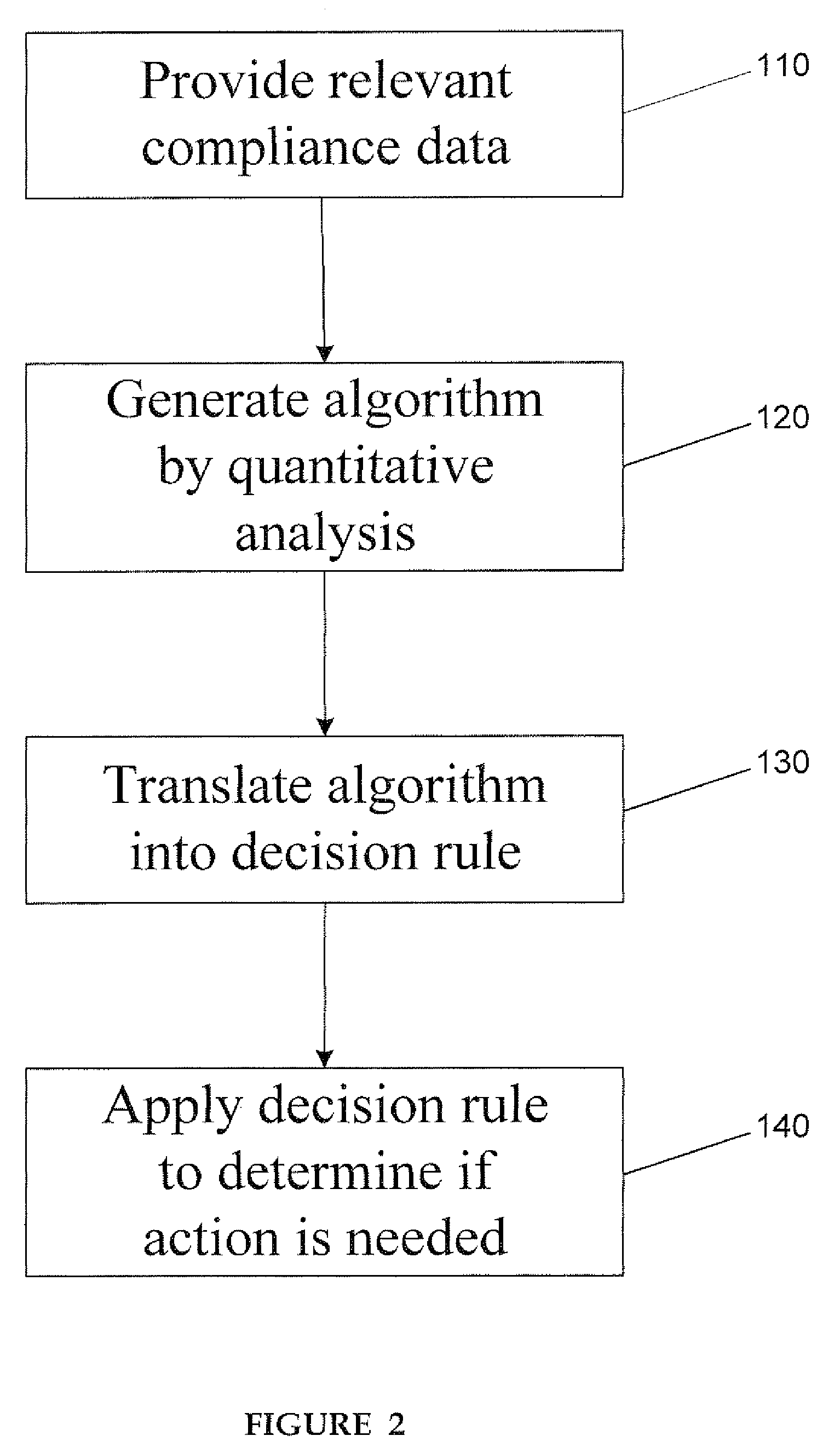
A system for developing and implementing empirically derived algorithms to generate decision rules to determine participant noncompliance and fraud with research protocols in clinical trials allows for the identification of complex patterns of variables that detect or predict participant noncompliance and fraud with research protocol, including performance and enrollment goals, in the clinical trial. The data may be used to overall predict the performance of any participant in a clinical trial, allowing selection of participants that tend to produce useful, high-quality results. The present invention can also be used to monitor participant compliance with the research protocol and goals to determine preferred actions to be performed. Optionally, the invention may provide a spectrum of noncompliance, from minor noncompliance needing only corrective feedback, to significant noncompliance requiring participant removal from the clinical trial or from future clinical trials. The algorithms and decision rules can also be domain-specific, such as detecting non-compliance or fraud among subjects in a cardiovascular drug trial, or demographically specific, such as taking into account gender, age or location, which provides for algorithms and decision rules to be optimized for the specific sample of participants being studied.
Owner:ERESTECH
Microcolumn-based, high-throughput microfluidic device
InactiveUS7390463B2Easy to superviseEasy to createBioreactor/fermenter combinationsPeptide librariesEngineeringBiological organism
A biological assay device for use in molecular biology, pharmaceutical research, genomic analysis, combinatorial chemistry, and in the general field of the analysis of molecules that may be deposited on supports of various kinds is provided. Specifically, the present invention includes a fluidic or microfluidic device, which integrates fluidic capability into existing multi-well plates of standard configuration, for performing either single or continuous fluidic manipulations in a high-throughout format. Methods for the use and manufacture of these devices are also provided.
Owner:CORNING INC
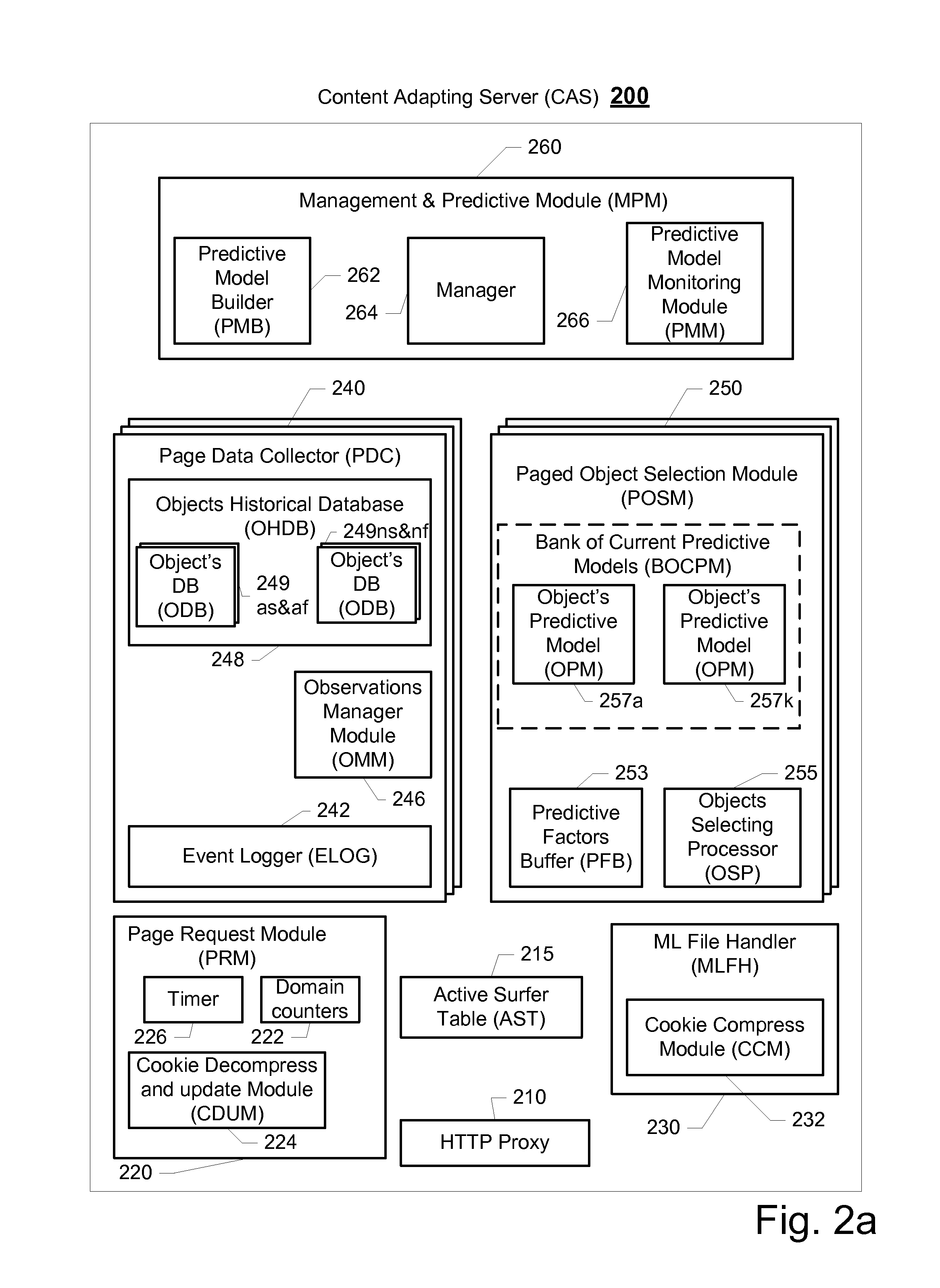
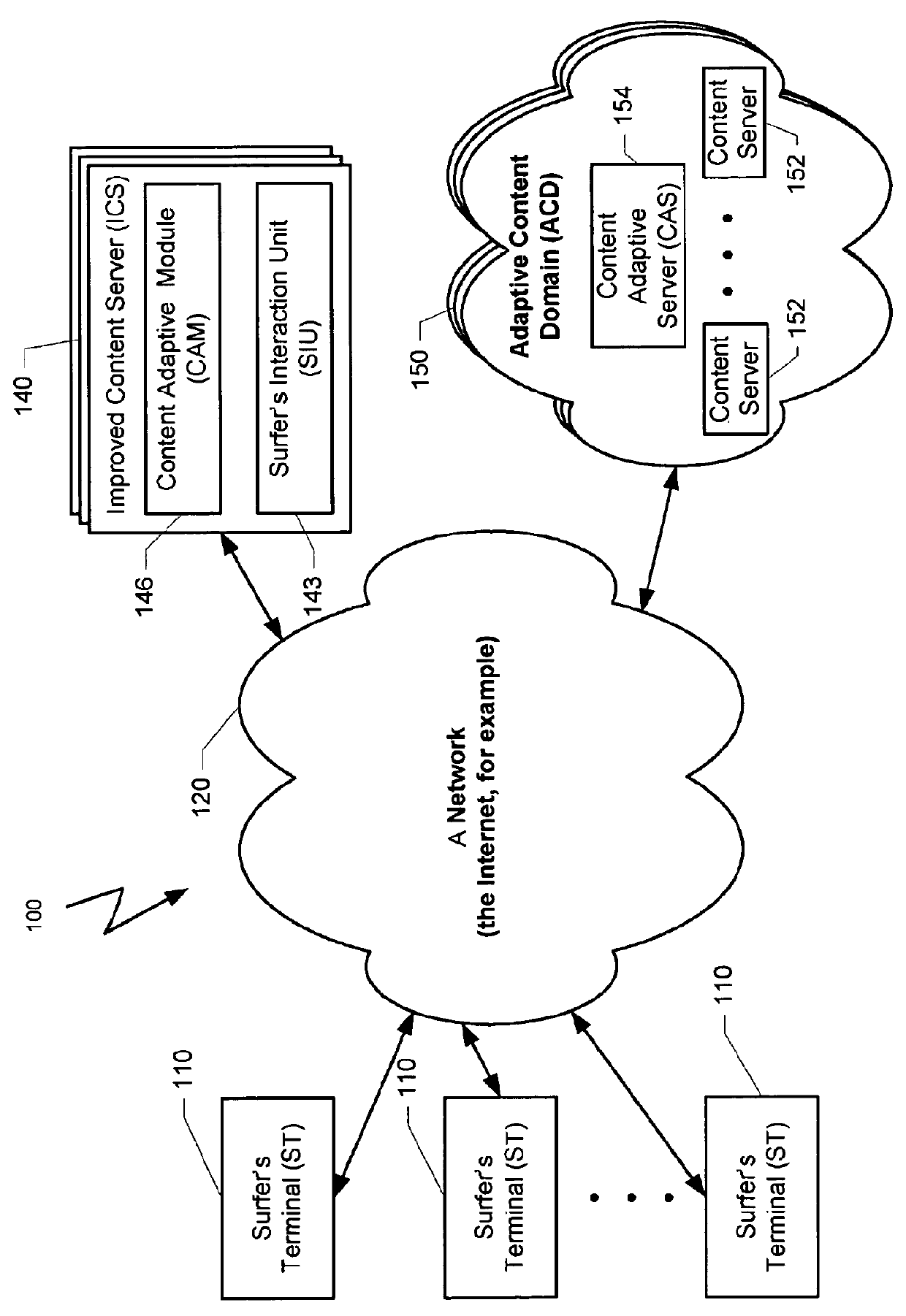
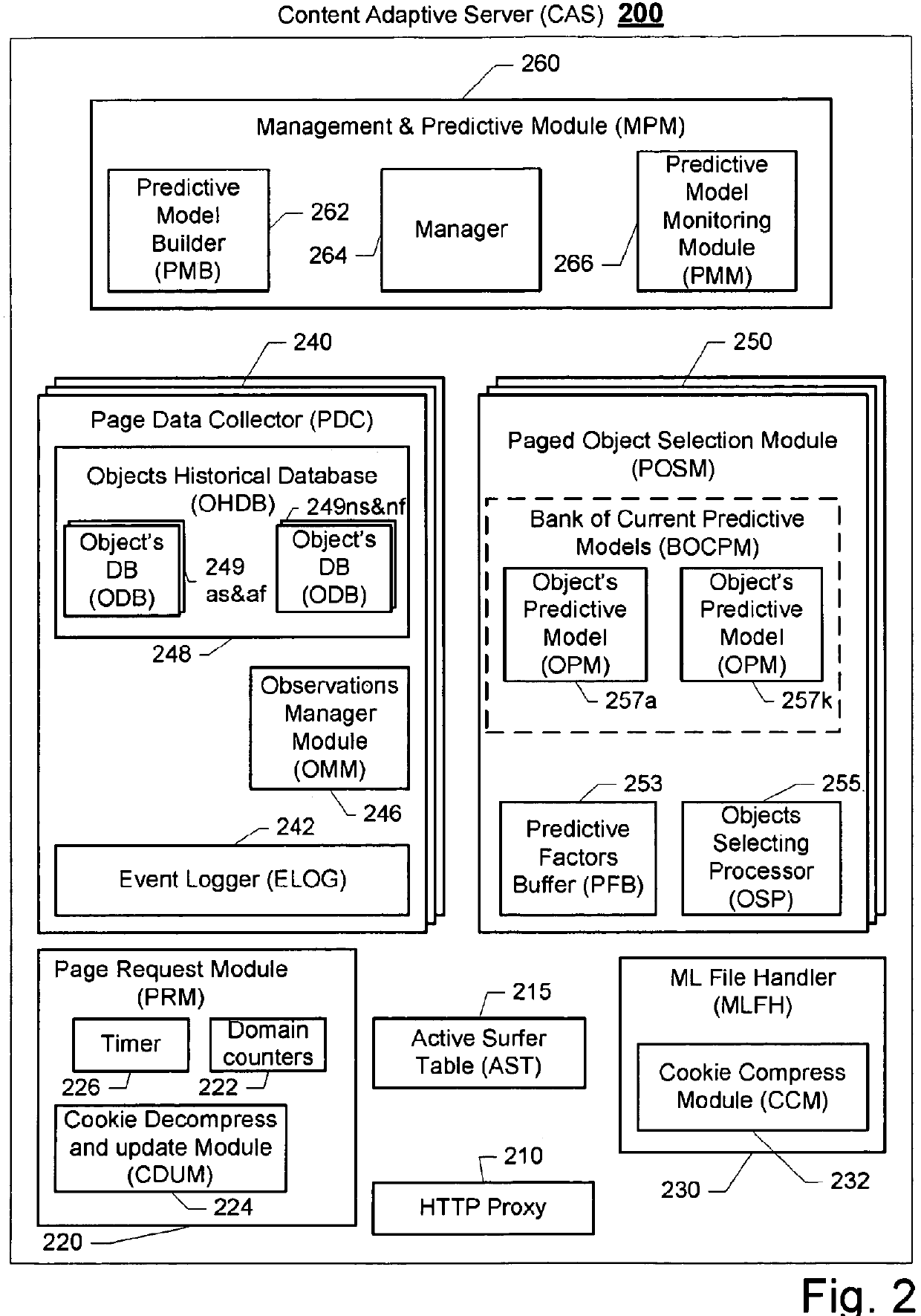
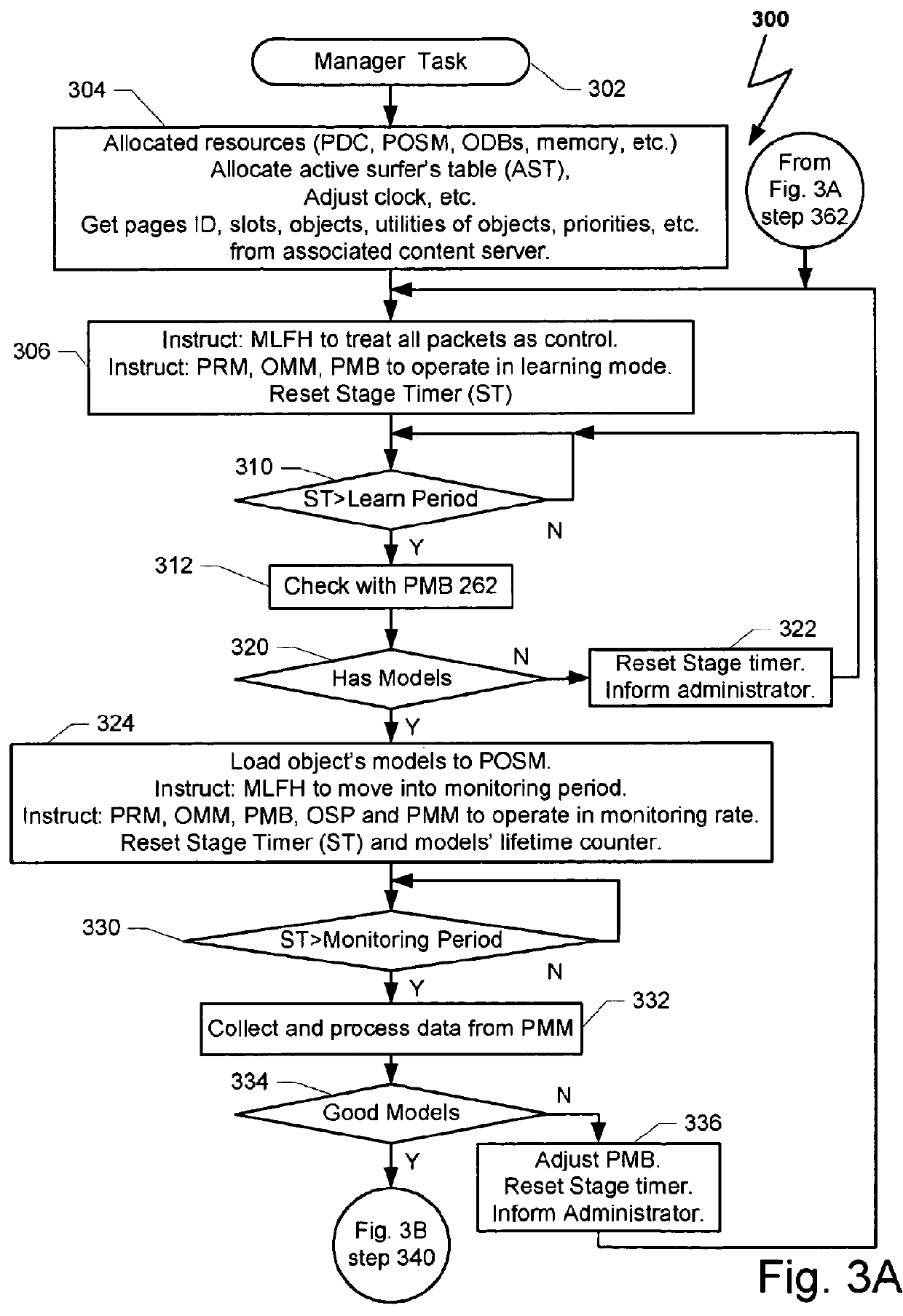
Method and system for creating a predictive model for targeting web-page to a surfer
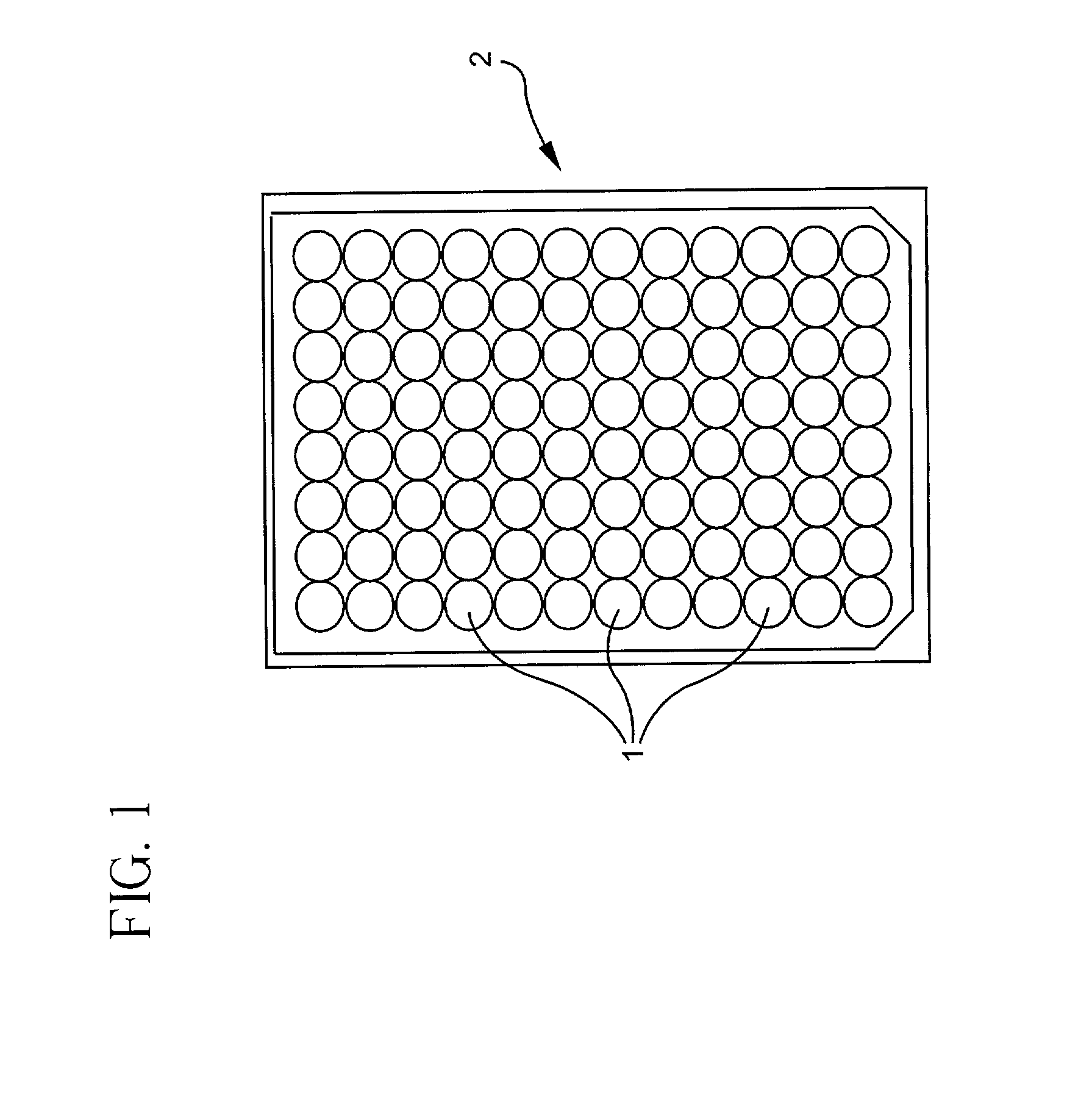
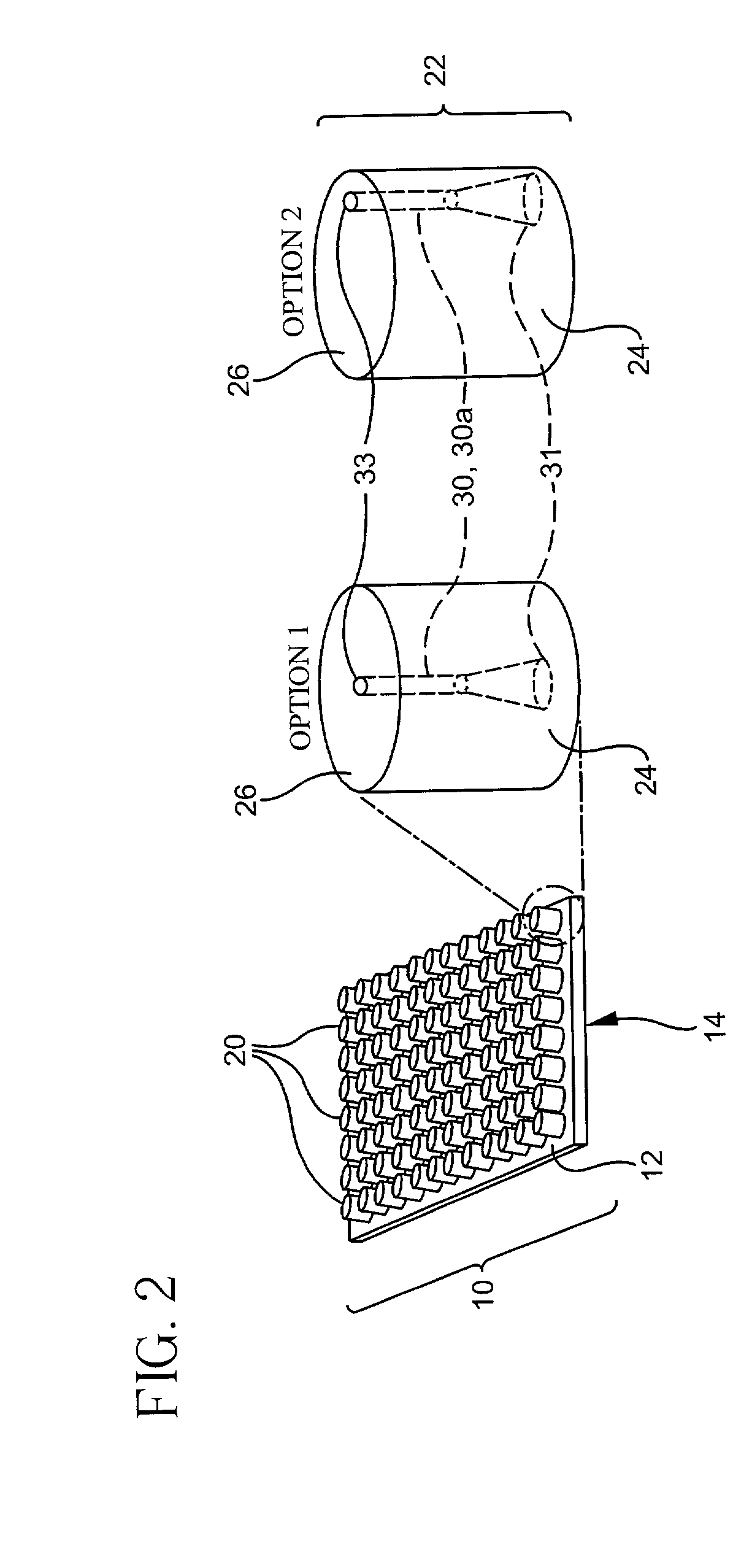
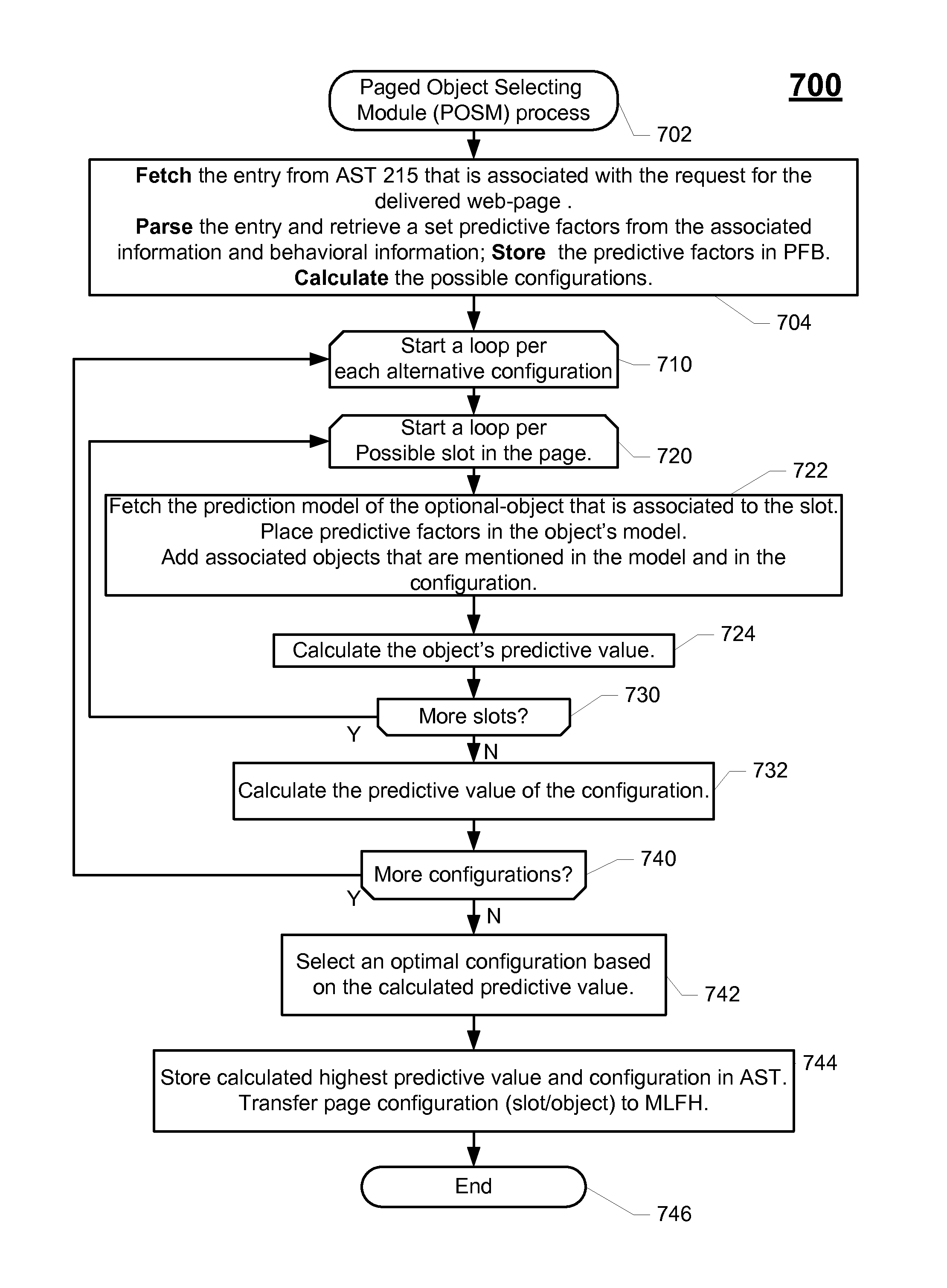
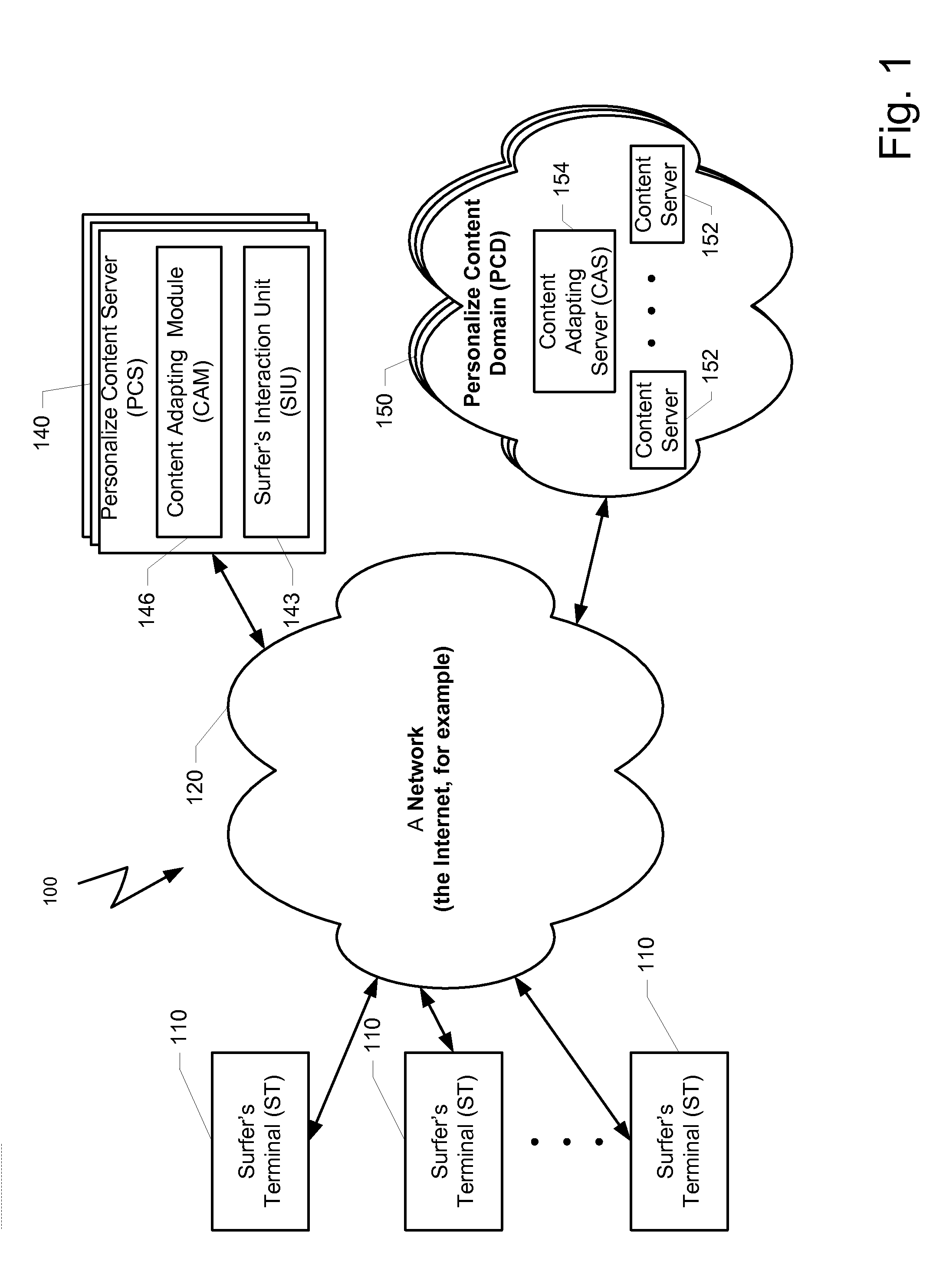
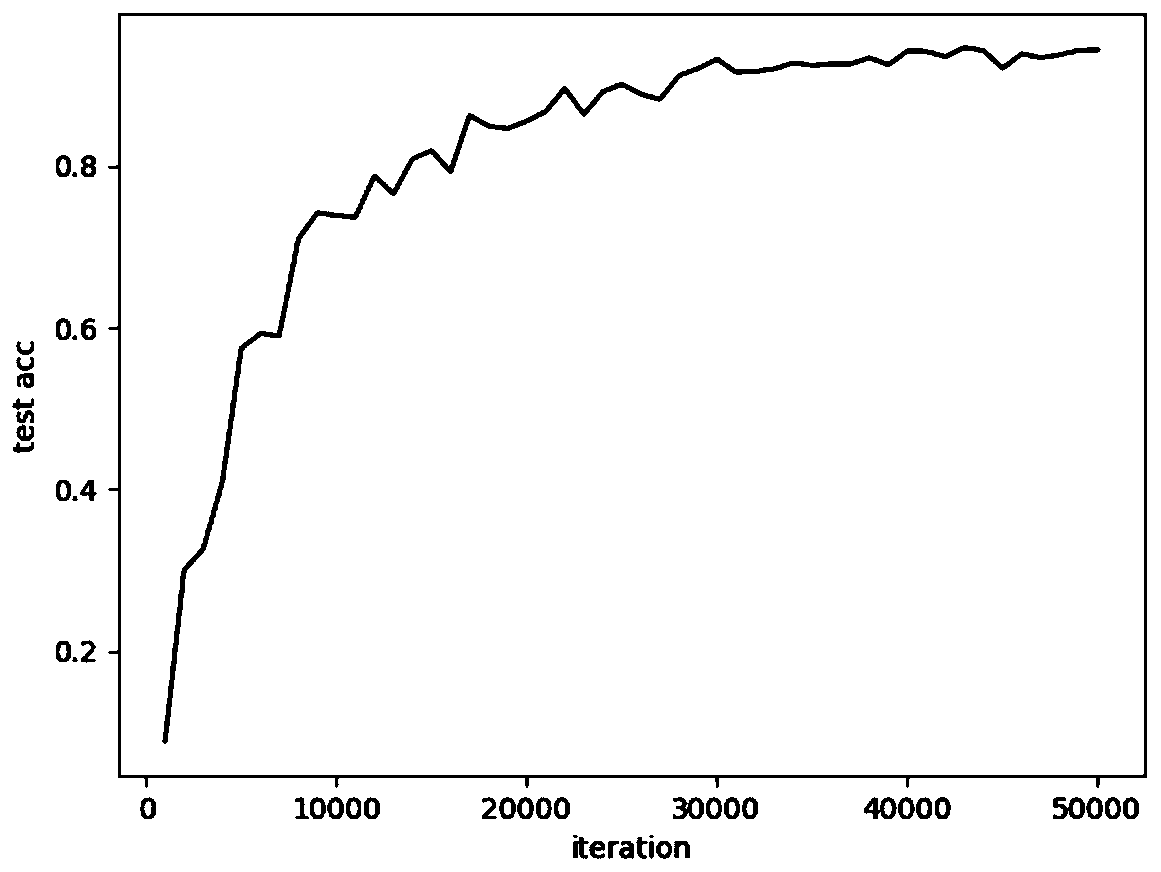
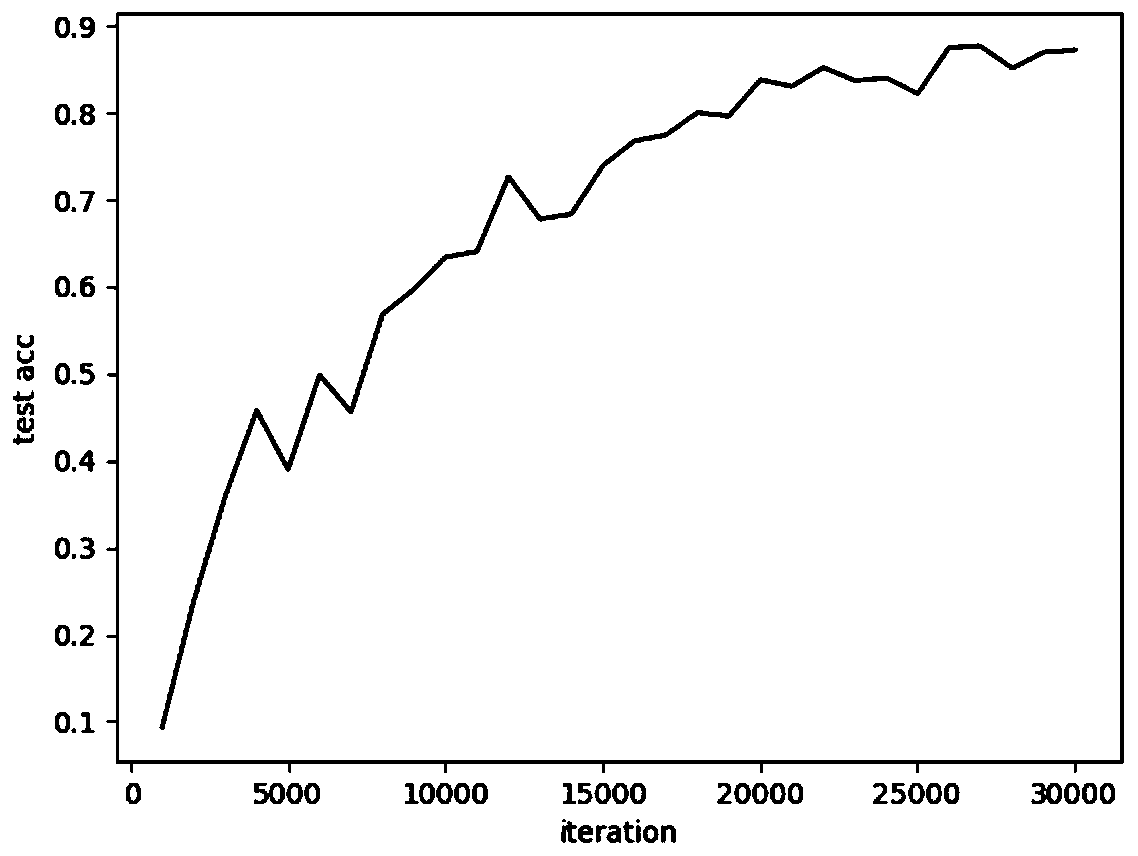
ActiveUS8762313B2Small sample sizeSmall sizeDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsAlgorithmWeb page
A system and a method for creating a predictive model to select an object from a group of objects that can be associated with a requested web-page, wherein a configuration of the requested web-page defines a subgroup of one or more selected objects from the group of objects. Each web-page can include one or more links to be associated with content objects from the group. For each content object presented over a requested web-page, one or more predictive model with relevant predictive factors is processed such that the predicted objective, the probability of success for example, is calculated. A success is defined as a surfer responding to the presented content according to the preferences of the site owner. Each predicted model can be associated with a key-performance indicator (KPI). Further, a predictive model can reflect the number of times the surfer requested the web page during the surfer's visit.
Owner:LIVEPERSON
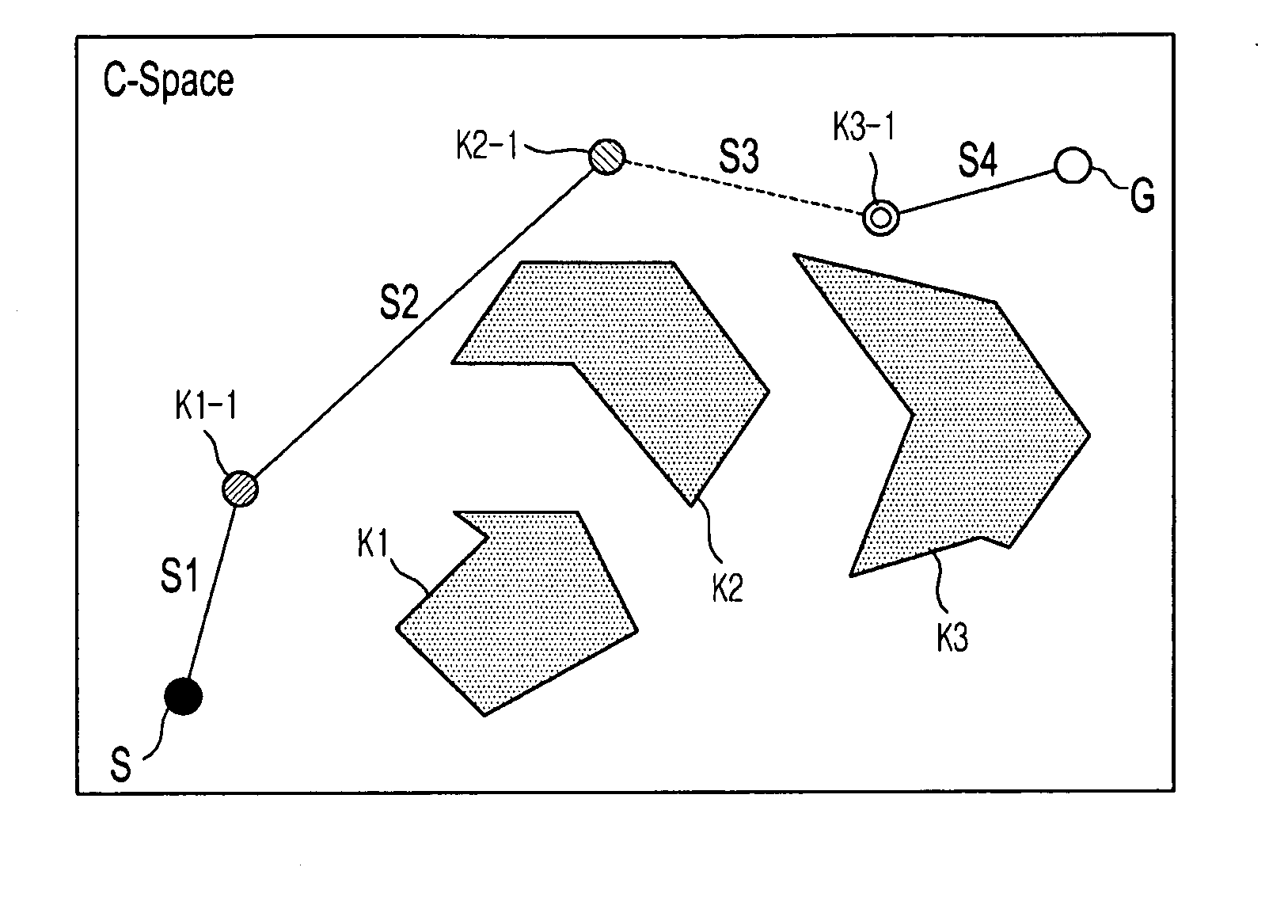
Method and apparatus to plan motion path of robot
ActiveUS20110035087A1Reduce probabilitySolution can be rapidly obtainedProgramme-controlled manipulatorInstruments for road network navigationAlgorithmRandom tree
A suitable waypoint is selected using a goal score, a section from a start point to a goal point through the waypoint is divided into a plurality of sections based on the waypoint with a solution of inverse kinematics, and trees are simultaneously expanded in the sections using a Best First Search & Rapidly Random Tree (BF-RRT) algorithm so as to generate a path. By this configuration, a probability of local minima occurring is decreased compared with the case where the waypoint is randomly selected. In addition, since the trees are simultaneously expanded in the sections each having the waypoint with a solution of inverse kinematics, the solution may be rapidly obtained. A time consumed to search for an optimal motion path may be shortened and path plan performance may be improved.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
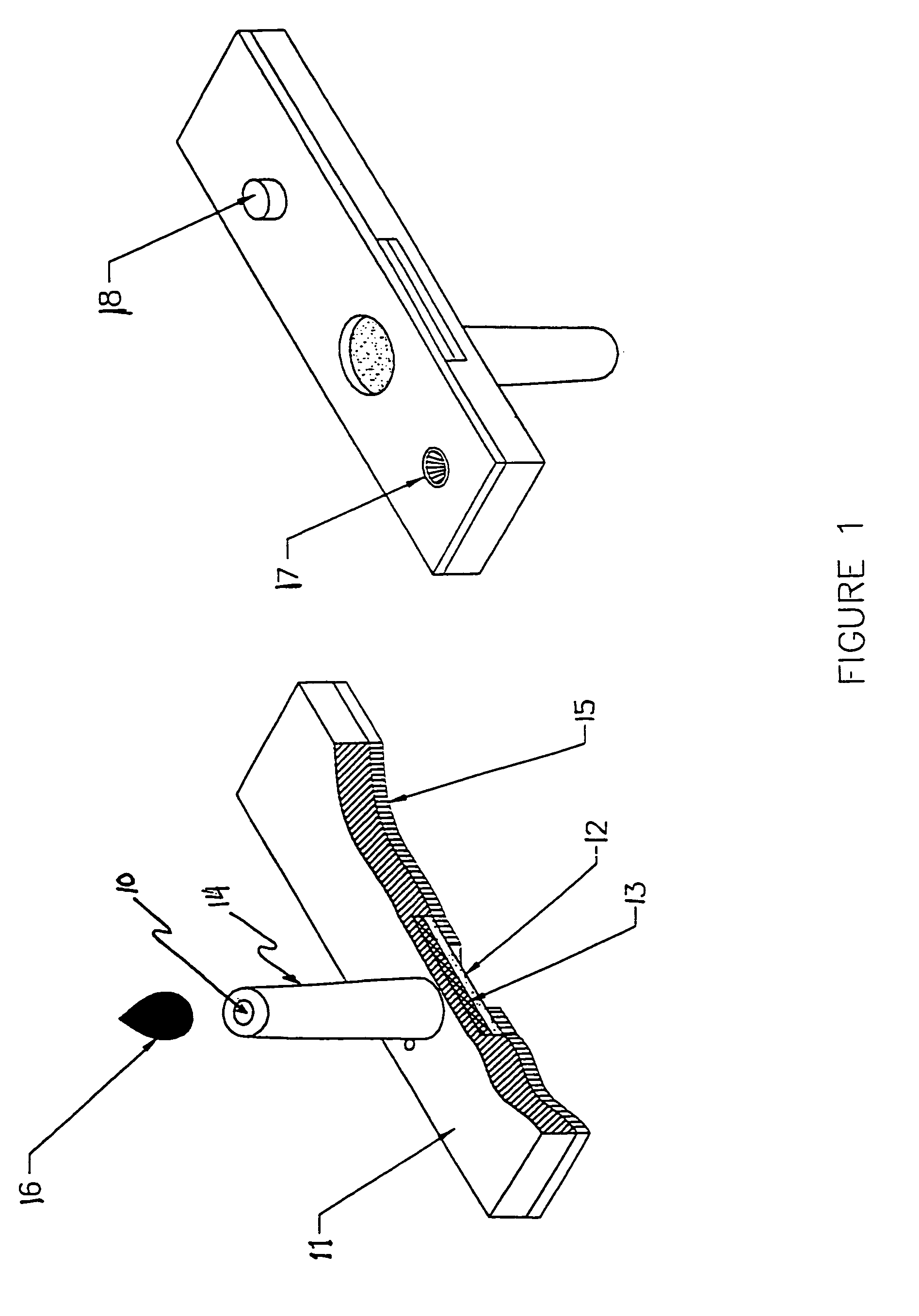
Surface-modified wick for diagnostic test strip
InactiveUS6967105B2Improve accuracyGood precisionAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorAlkaneBlood sugar
A wicking material is disclosed that exhibits a horizontal wicking velocity of at least about 1.0 millimeter per second when contacted with a physiological fluid such as blood, lymph or cellular interstitial fluid. This high wicking rate is achieved by means of treatment of a fibrous wicking material candidate with a low temperature gas plasma, particularly a glow discharge gas plasma formed in a gaseous blend made up predominantly of a mixture of oxygen with a saturated alkane chosen from the group consisting of methane, ethane and propane. Diagnostic test strips made with the surface-modified wicking material, and containing an immobilized reagent means for analysis of an analyte in a physiological fluid, show improved performance in terms of increased accuracy, finer precision of analyses, reduced time of analysis, a smaller fluid sample size requirement, and improved compliance with manufacturing standards resulting in lower manufacturing costs blood sugar determinations.
Owner:QUESTSTAR MEDICAL
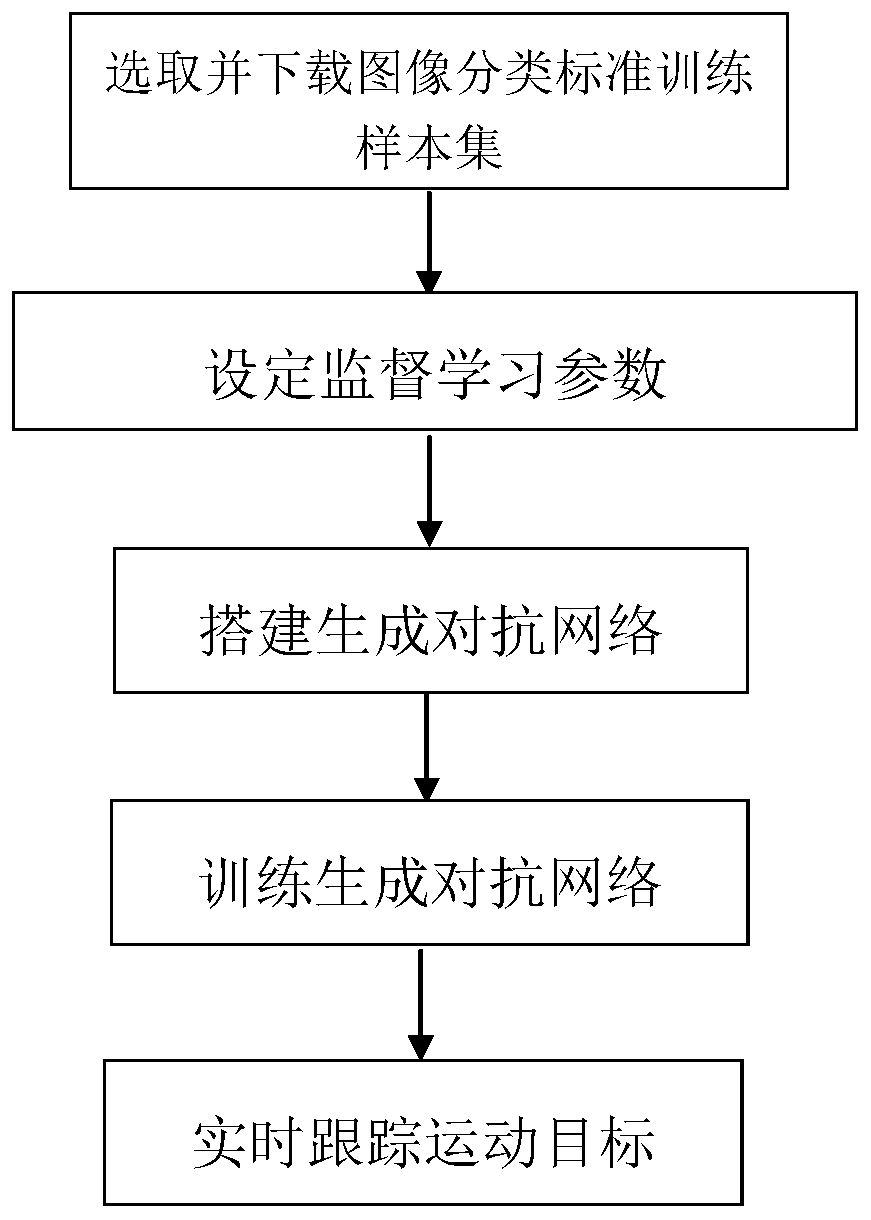
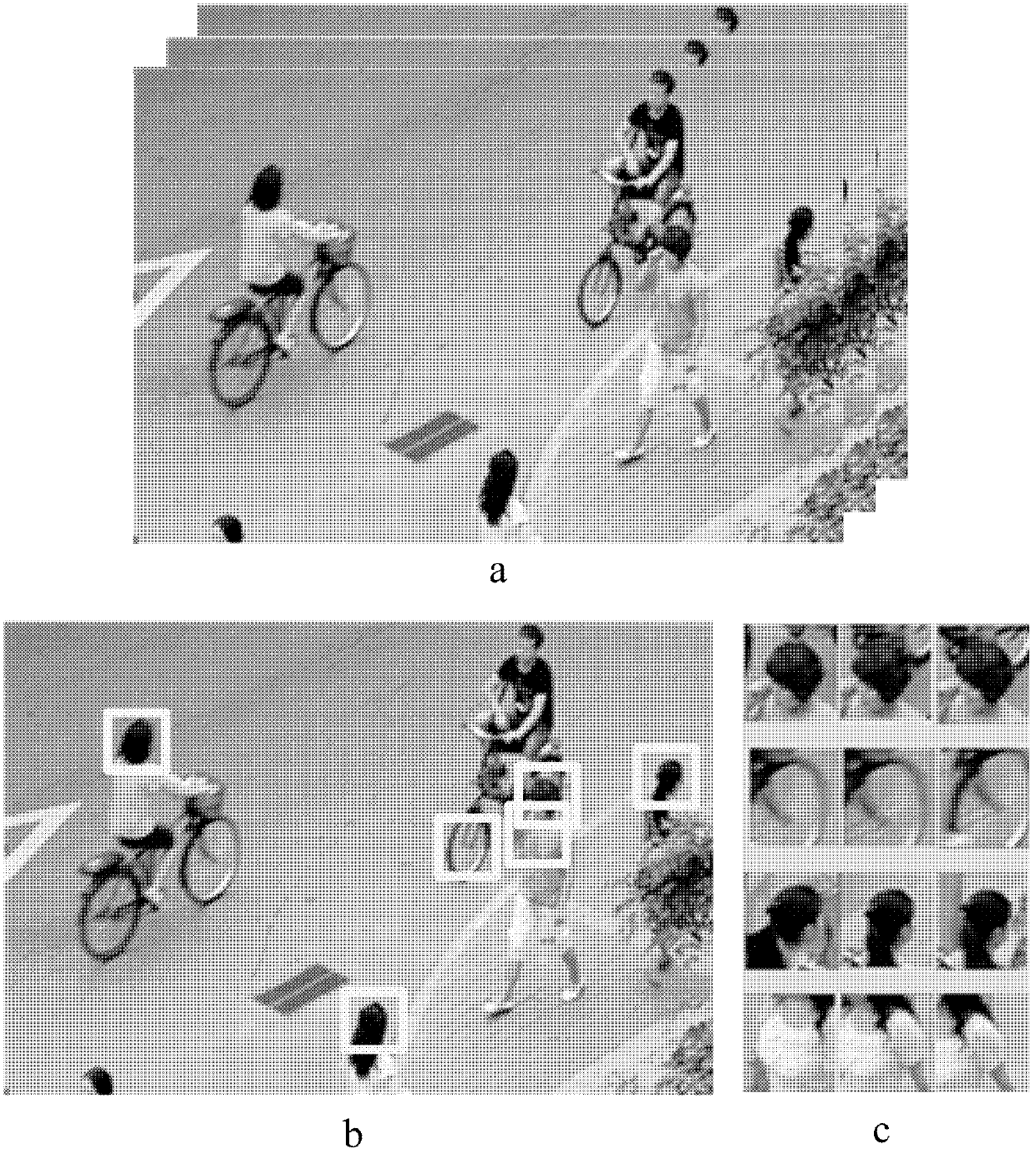
Semi-supervised image classification method based on generative adversarial network
InactiveCN110097103AImprove accuracyAccurate Classification AccuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionDiscriminatorStochastic gradient descent
The invention discloses a semi-supervised image classification method based on a generative adversarial network, which mainly solves the problems that the existing unsupervised learning classificationprecision is low and semi-supervised learning needs a large number of accurate labels, and comprises the following implementation steps of: 1) selecting and downloading a standard image training sample and a test sample; 2) setting relevant parameters of network supervised learning, and establishing a generative adversarial network consisting of a generator network, a discriminator network and anauxiliary classifier in parallel; 3) training the generative adversarial network by using a random gradient descent method; and 4) inputting the test sample to be classified into the trained generative adversarial network model, and outputting the category of the image to be detected. The method improves the image classification precision of unsupervised learning, can obtain a very good image classification effect on a sample set only containing a small amount of accurate annotation samples, and can be used for target classification in an actual scene.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method and system for providing targeted content to a surfer
ActiveUS8260846B2Small sample sizeSmall sizeMultiple digital computer combinationsProbabilistic networksIp addressUniform resource locator
Owner:LIVEPERSON
Strip electrode with conductive nano tube printing
InactiveUS20050186333A1Accurate electronic readoutMinimizing strip to strip variationImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSilver inkCarbon nanotube
A sensor system that detects a current representative of a compound in a liquid mixture features a multi or three electrode strip adapted for releasable attachment to signal readout circuitry. The strip comprises an elongated support which is preferably flat adapted for releasable attachment to the readout circuitry; a first conductor and a second and a third conductor each extend along the support and comprise means for connection to the circuitry. The circuit is formed with single-walled or multi walled nanotubes conductive traces and may be formed from multiple layers or dispersions containing, carbon nanotubes, carbon nanotubes / antimony tin oxide, carbon nanotubes / platinum, or carbon nanotubes / silver or carbon nanotubes / silver-cloride. An active electrode formed from a separate conductive carbon nanotubes layer or suitable dispersion, positioned to contact the liquid mixture and the first conductor, comprises a deposit of an enzyme capable of catalyzing a reaction involving the compound and preferably an electron mediator, capable of transferring electrons between the enzyme-catalyzed reaction and the first conductor. A reference electrode also formed from a conductive carbon nanotube layer or suitable dispersion is positioned to contact the mixture and the second conductor. The system includes circuitry adapted to provide an electrical signal representative of the current which is formed from printing conductive inks made with nano size particles such as conductive carbon or carbon / platinum or carbon / silver, or carbon nanotubes / antimony tin oxide to form a conductive carbon nanotube layers. The multiple-electrode strip is manufactured, by then applying the enzyme and preferably the mediator onto the electrode. Alternatively the electrode can have a carbon nanotubes / antimony tin oxide, carbon nanotubes / platinum, or carbon nanotubes / silver or carbon nanotubes / silver-cloride surface and or a conductive carbon or silver ink surface connecting leg. The carbon nanotube solution is first coated and patterned into electro shapes and the conductive carbon nanotubes, carbon or silver ink can be attached by printing the ink to interface with the carbon nanotube electro surface. A platinum electrode test strip is also disclosed that is formed from either nano platinum distributed in the carbon nanotube layer or by application or incorporation of platinum to the carbon nanotube conductive ink.
Owner:DOUGLAS JOEL S MR
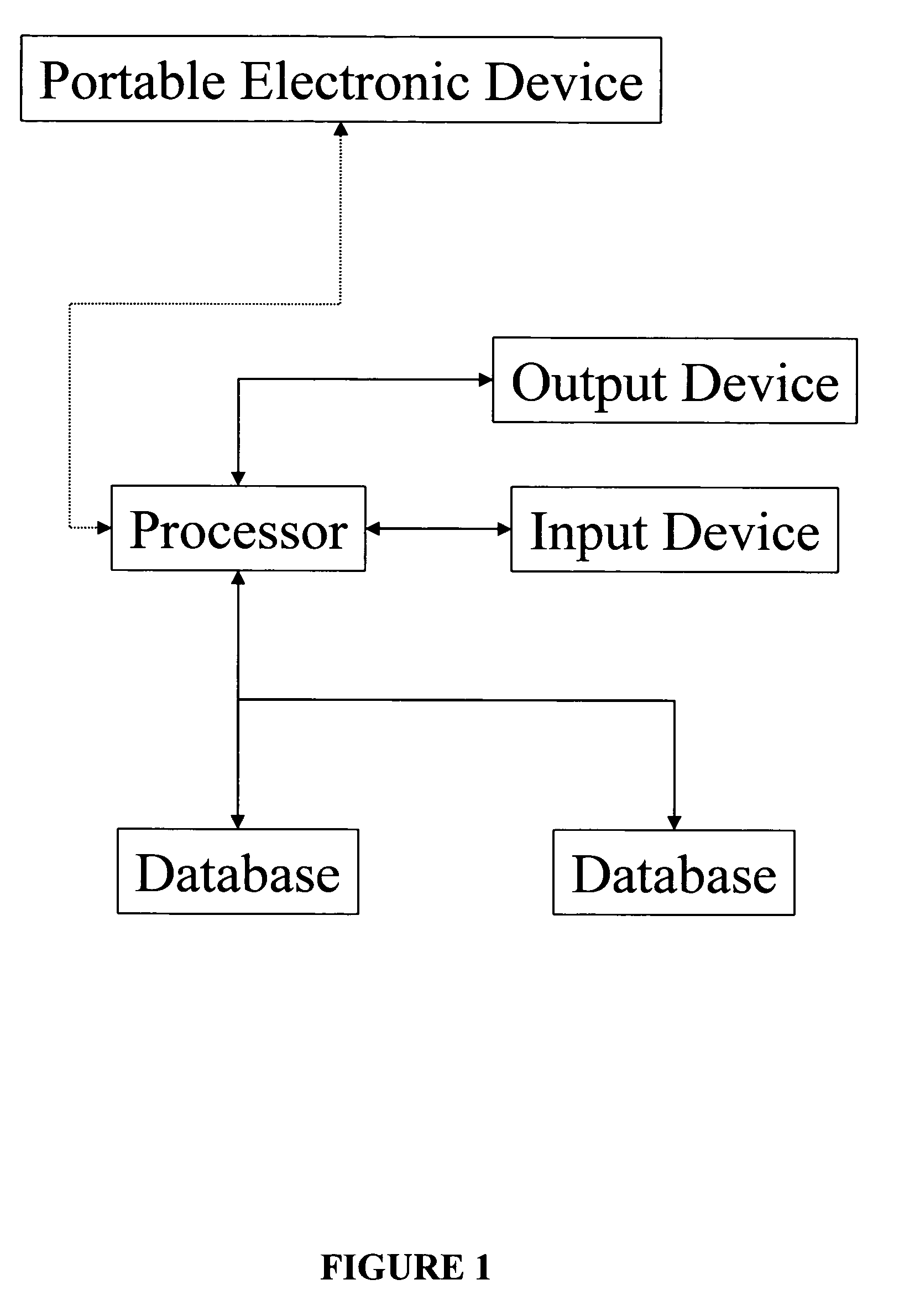
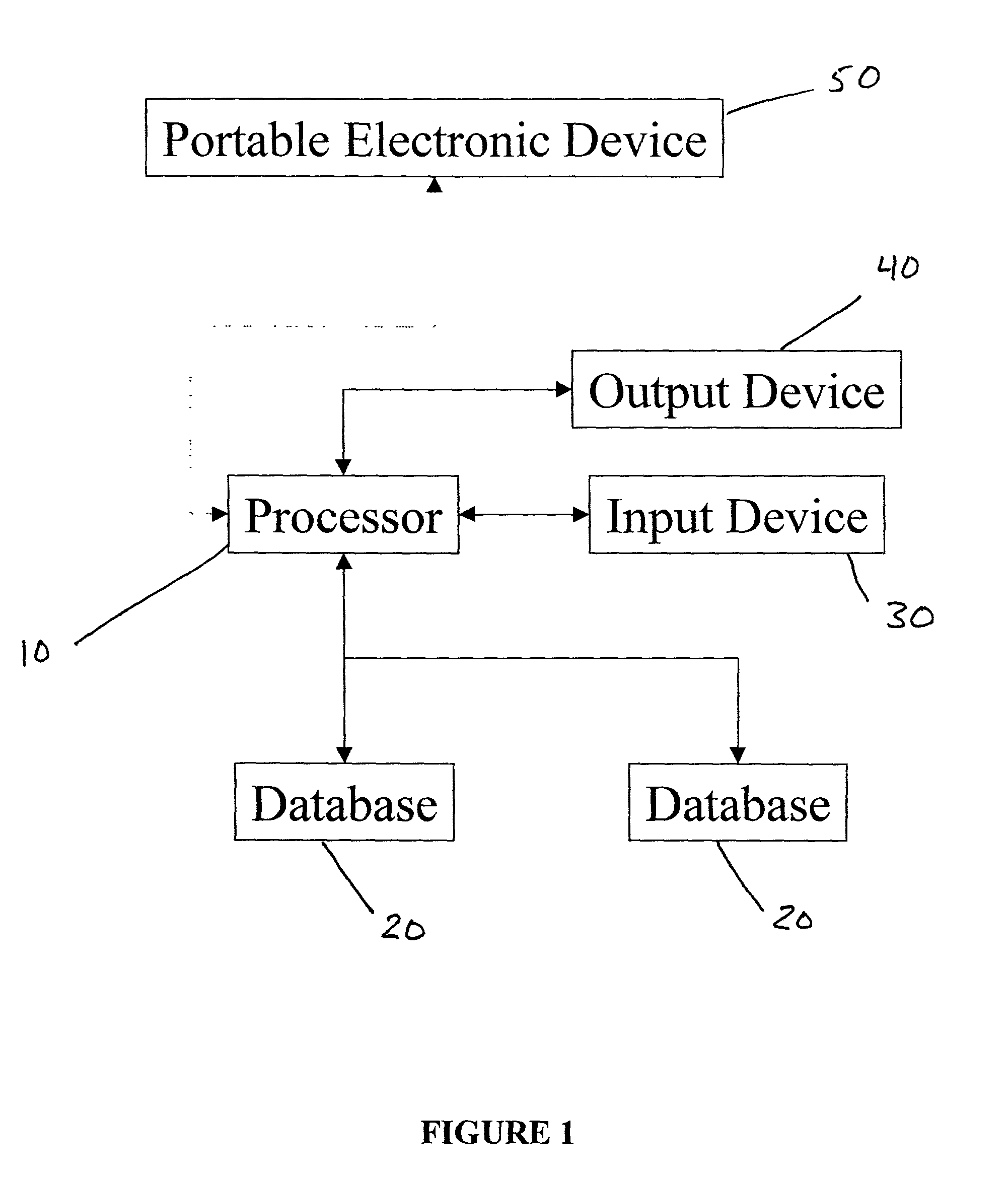
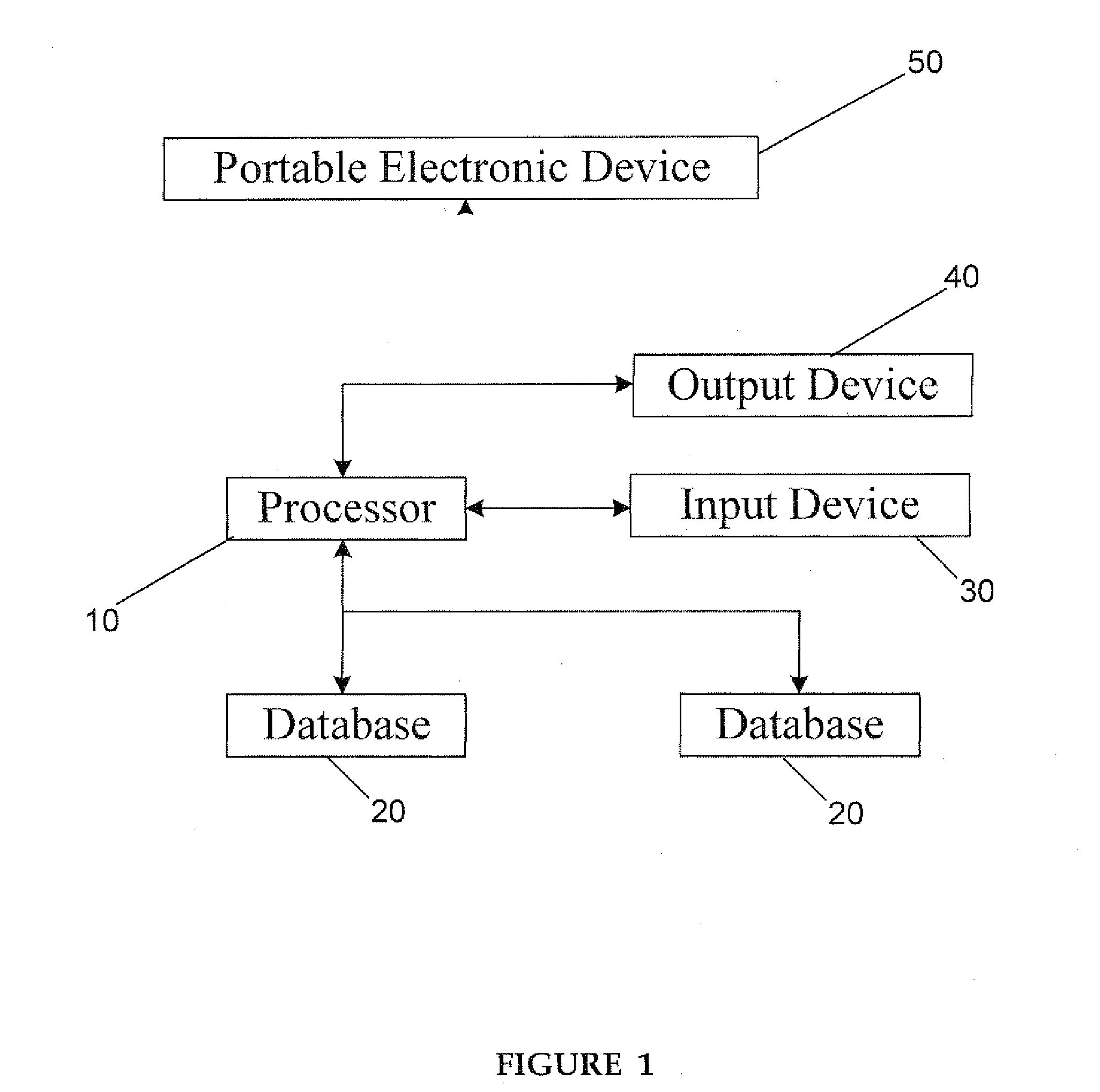
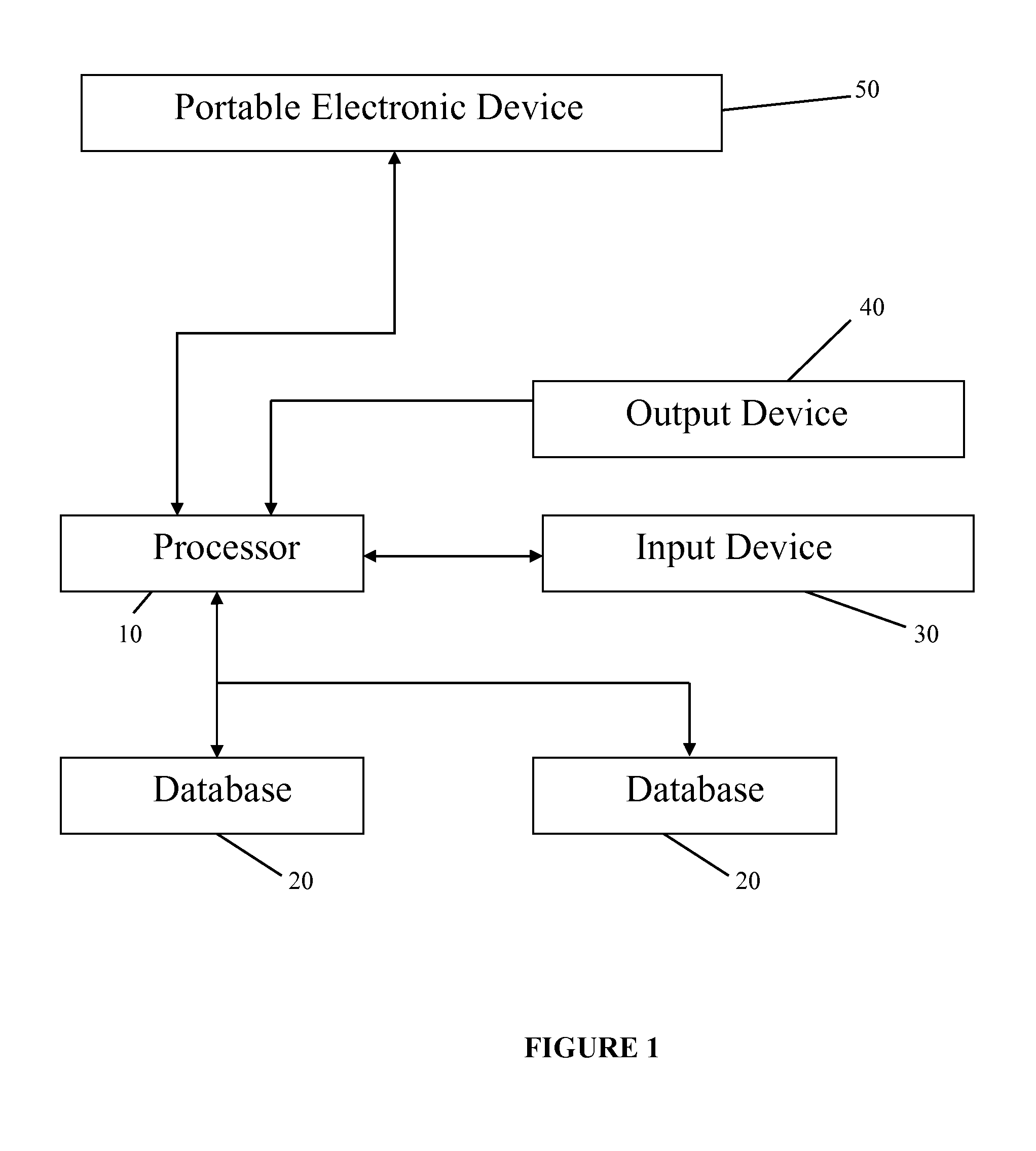
System for clinical trial subject compliance
InactiveUS8065180B2Improve statistics performanceReduce testing costsComputer-assisted medical data acquisitionMedical automated diagnosisClinical trialMedical education
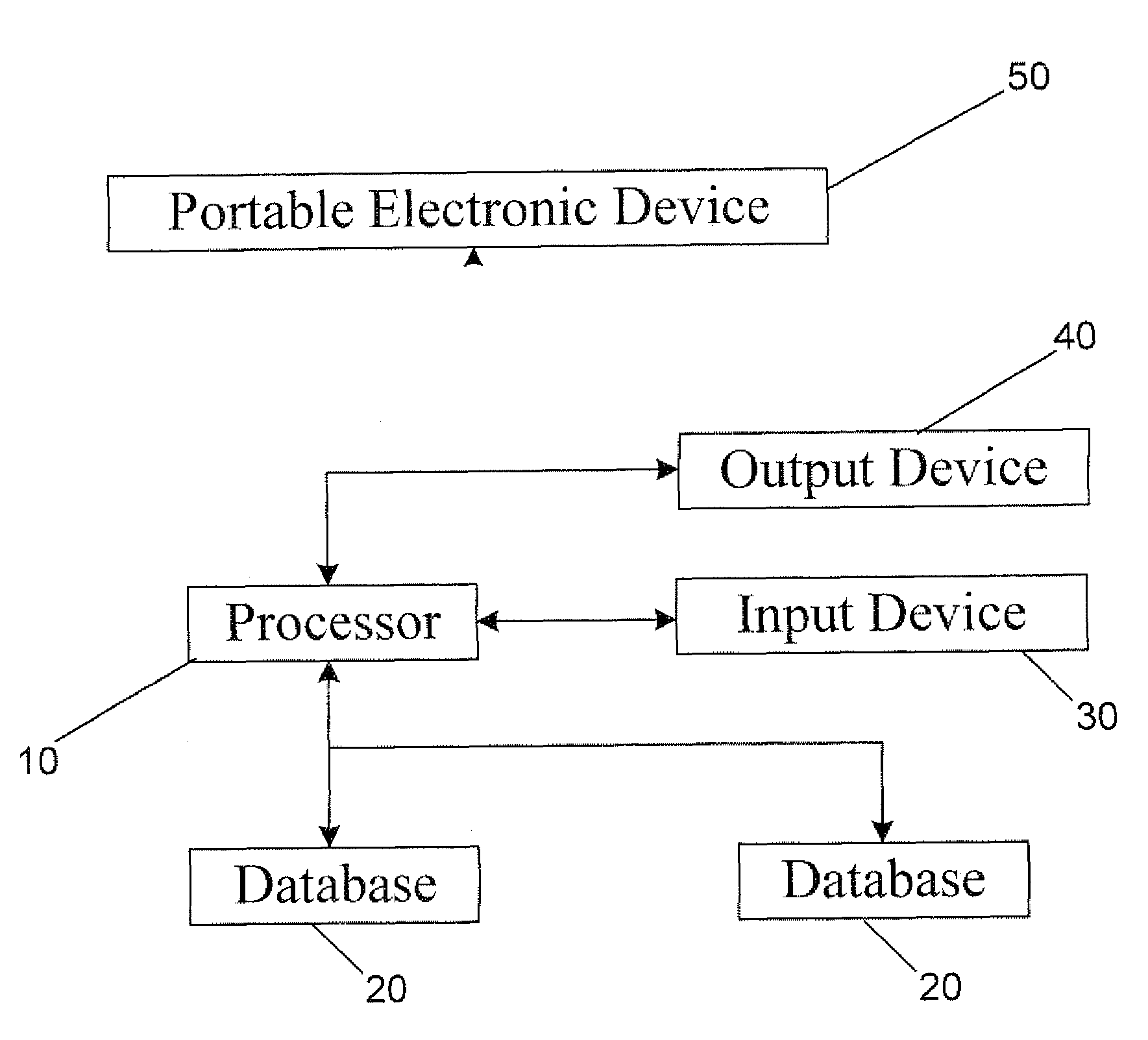
The present invention is designed to develop research protocols for clinical trials. The invention also can track and enhance subject compliance with a research protocol. The invention further provides evaluability data related to subject performance in the clinical trial. According to an alternative embodiment of the invention, a portable electronic device is used to query and collect data from the subject.
Owner:ERESTECH
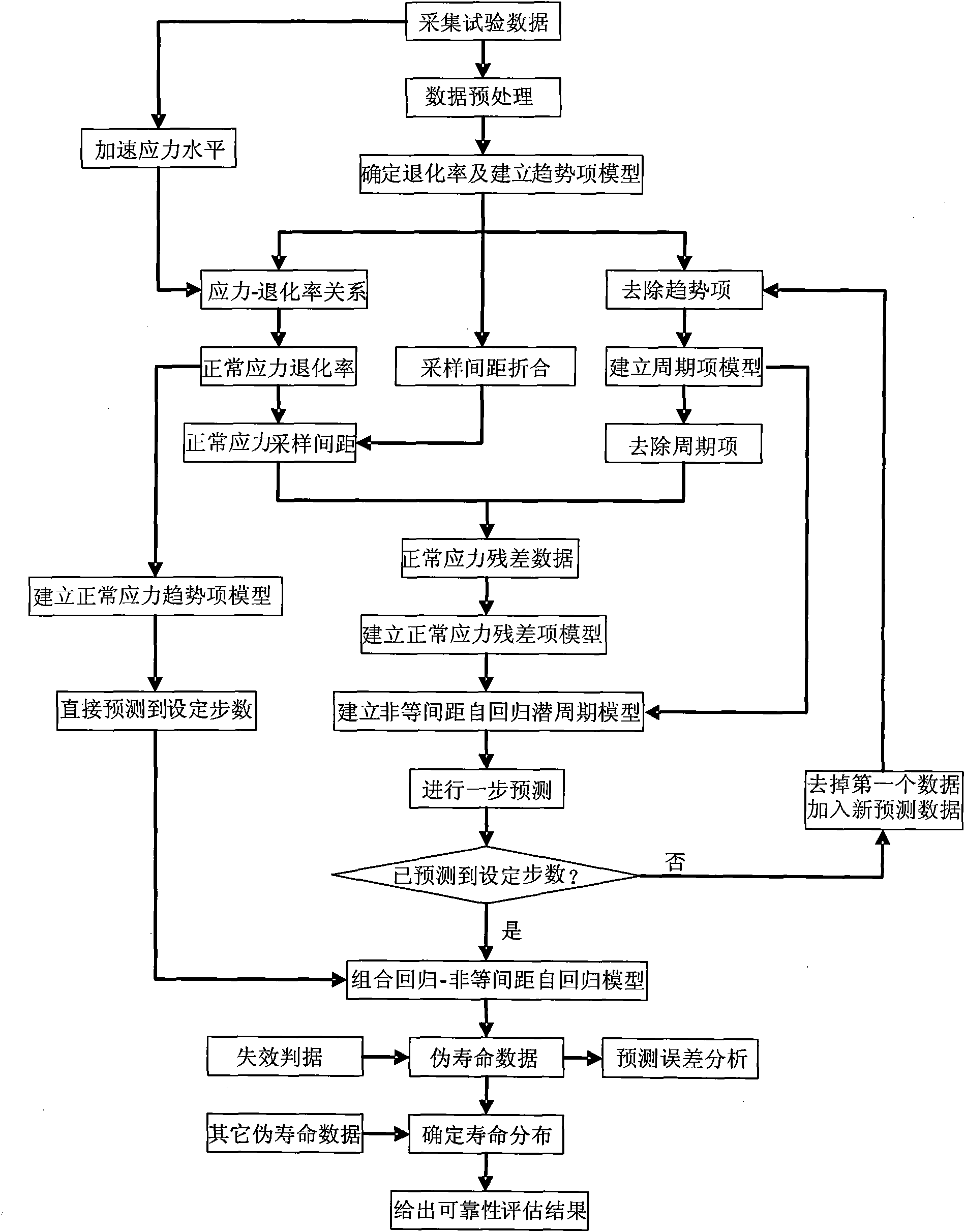
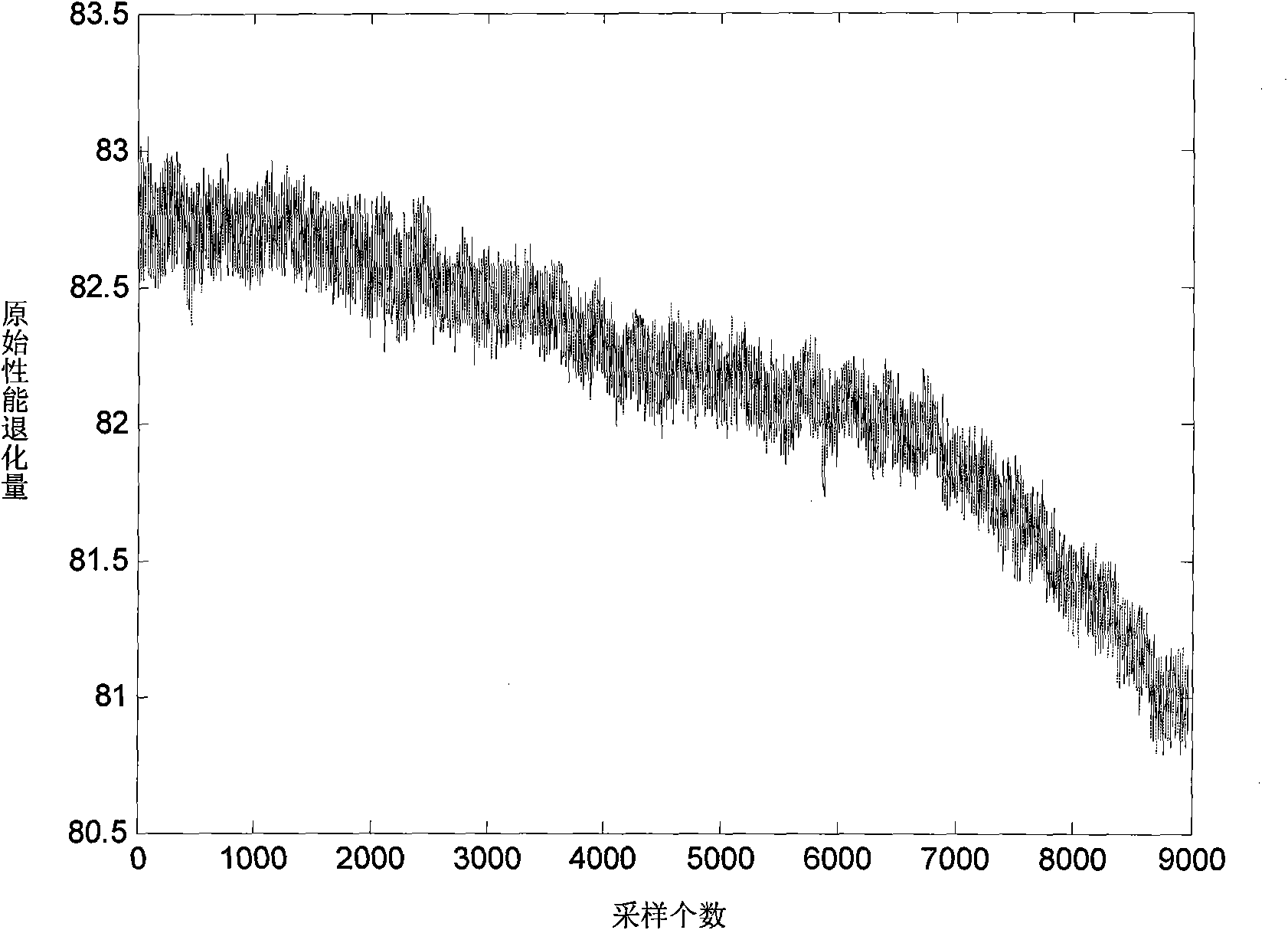
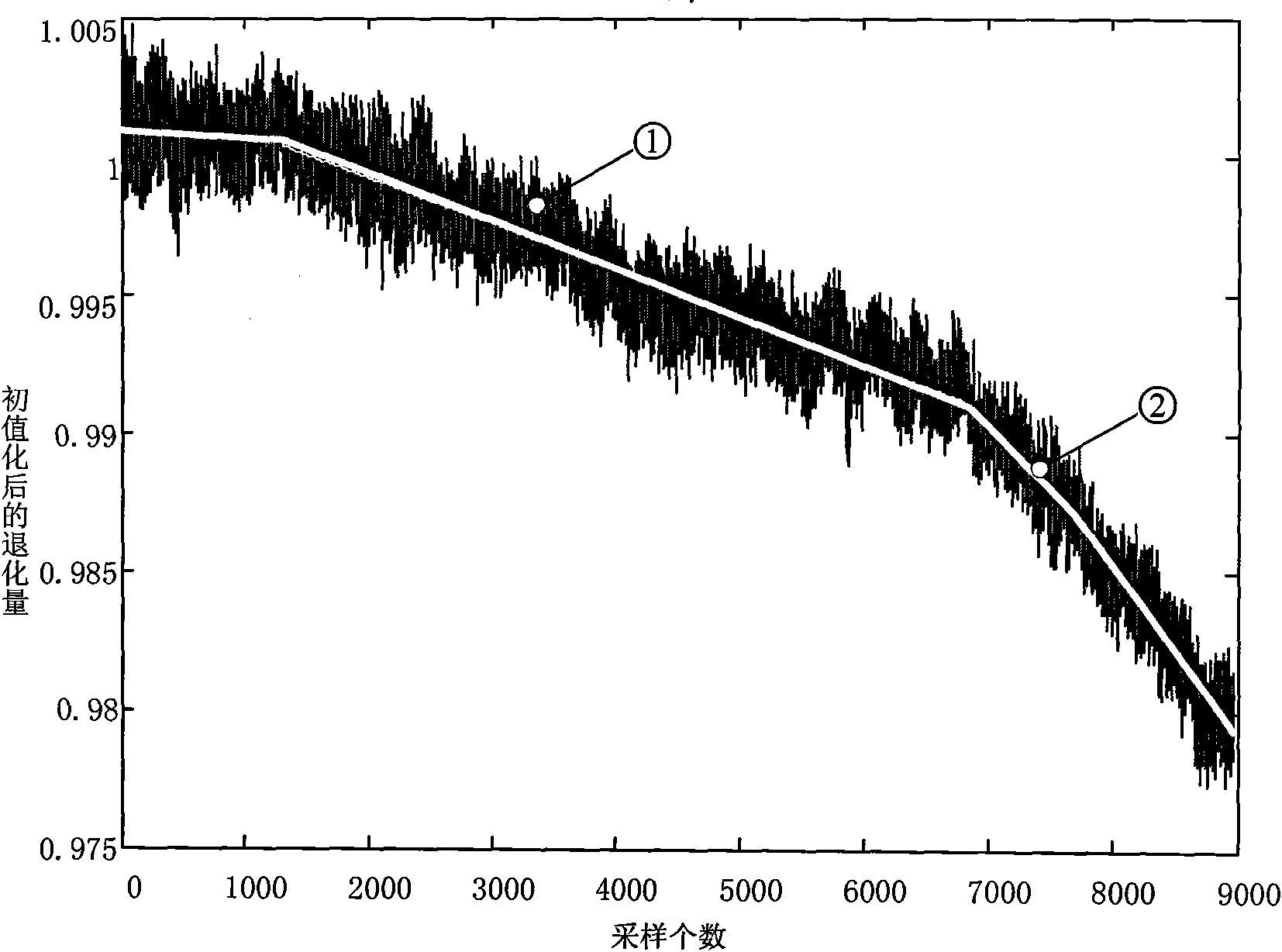
Method for evaluating reliability of stepping stress quickened degradation experiment based on time sequence
InactiveCN101620045AShorten the timeRealize Reliability AssessmentStrength propertiesCorrelation coefficientSequence analysis
The invention discloses a method for evaluating the reliability of a stepping stress quickened degradation experiment based on a time sequence. The method utilizes a correlation coefficient stationary sequence analytical method to describe non-equidistant stochastic information in stepping stress quickened degradation experiment data, establishes a regressive-non-equidistant autoregression degradation model on the basis of obtaining the respective advantages of a deterministic regression model and a stochastic correlation coefficient stationary sequence autoregression model, combines a grey theory to predict a product degradation trend and forms a function and a curve for predicting the life and evaluating the reliability of the stepping stress quickened degradation experiment based on the time sequence. The method obviously decreases the sample quantity of a product and shortens the time of the degradation experiment, thereby saving a large amount of expenses and resources, enhancing the fitting accuracy of the degradation model and enhancing the reliability of a reliability evaluating result.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
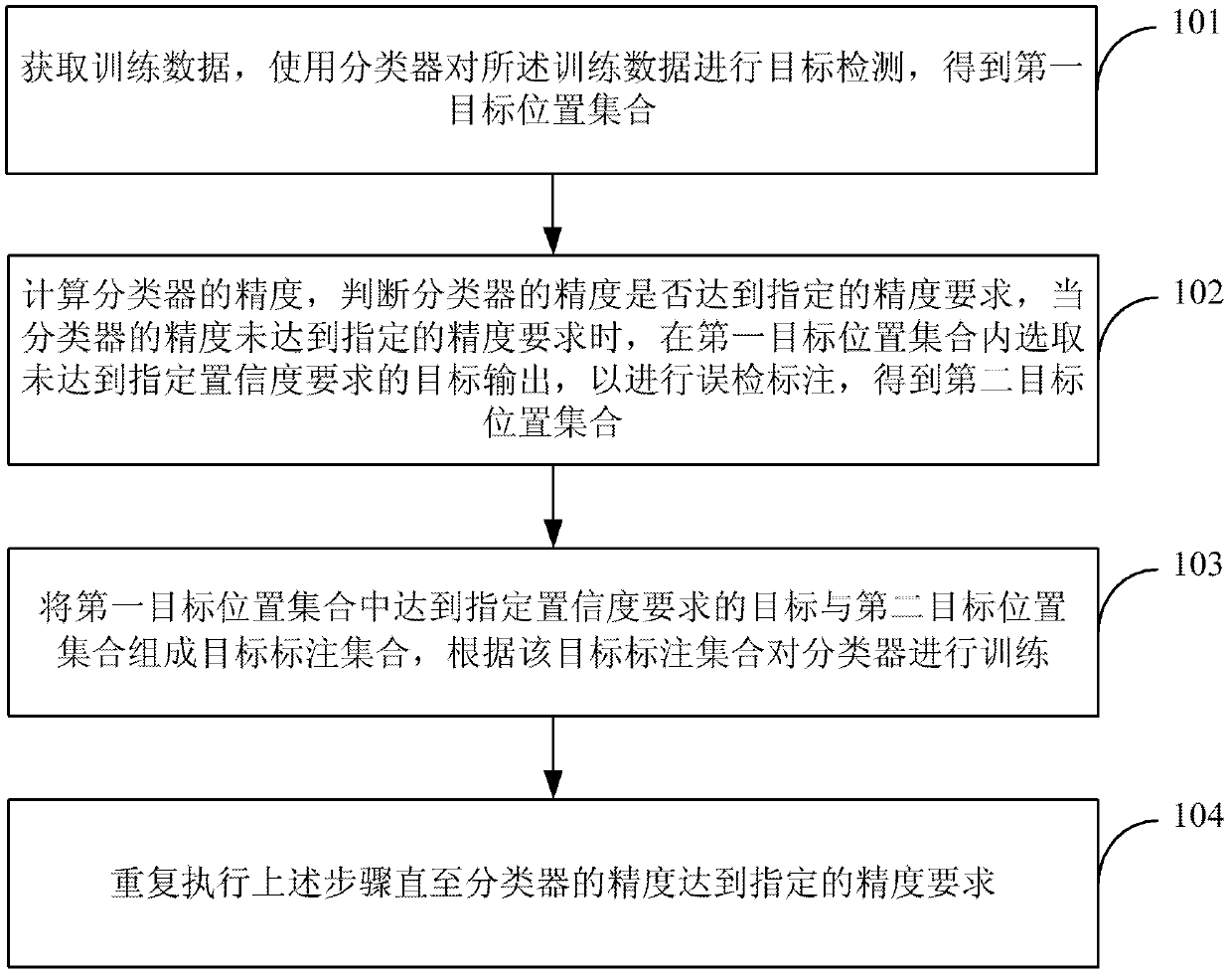
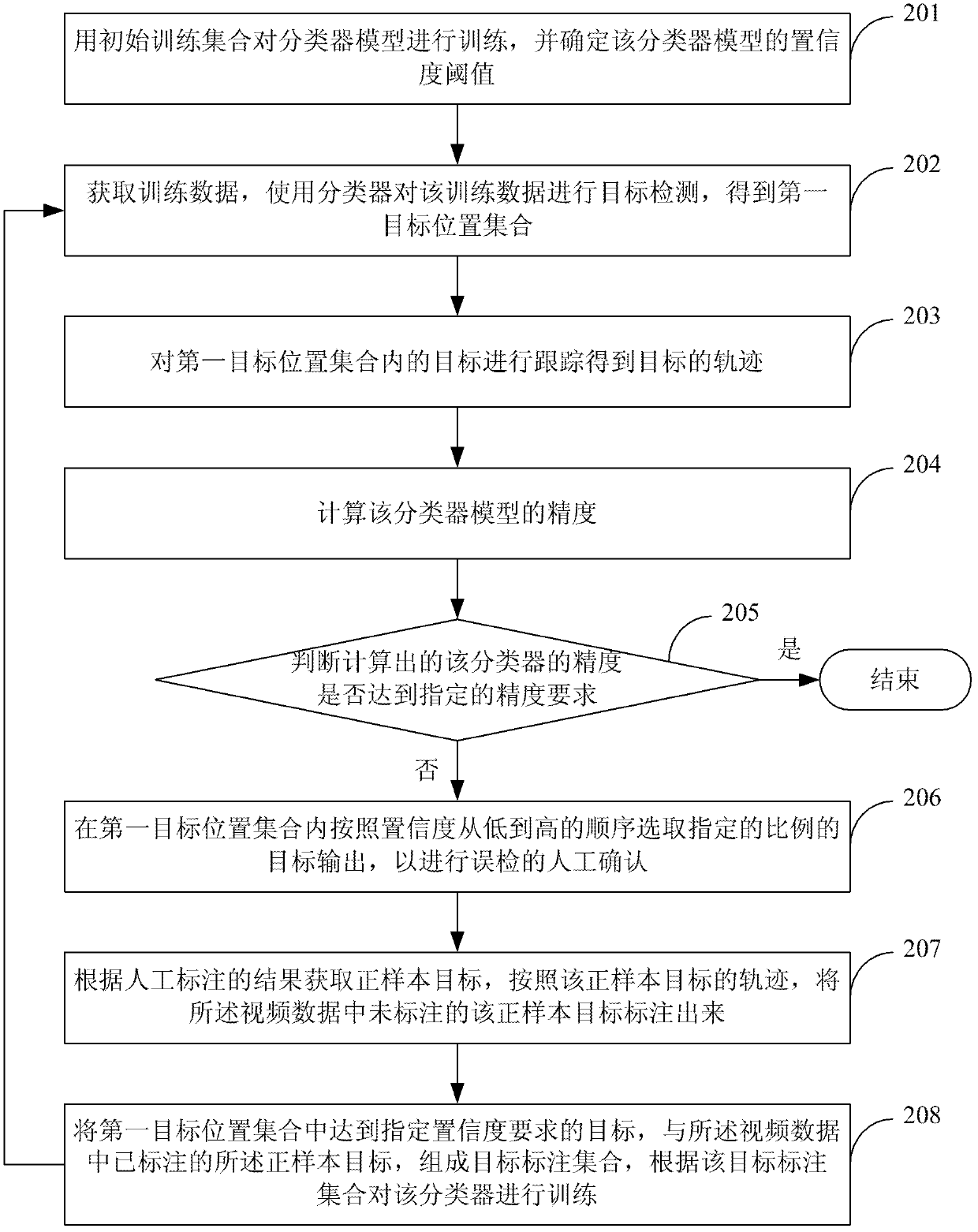
Method and device for labeling targets
ActiveCN103324937AHigh precisionReduce workloadCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmImage processing
The invention discloses a method and device for labeling targets, and belongs to the technical field of picture processing. The labeling result of the targets can be used for training a target detector. The method comprises obtaining training data, using a classifier for carrying out target detection on the training data to obtain a first target position collection, calculating the precision of the classifier, selecting the targets not meeting assigned confidence coefficient requirements from the first target position collection and output the targets to carry out false drop labeling when the precision of the classifier does not meet an assigned precision requirement, obtaining a second target position collection, combining the targets meeting the assigned confidence coefficient requirements in the first target position collection and the second target position collection to form a target labeling collection, carrying out training on the classifier according to the target labeling collection, and executing the mentioned steps repeatedly until the precision of the classifier meets the assigned precision requirement. The device comprises a target detection module, a performance testing module, a learning module, a training module and an iteration module. The method and device for labeling the targets greatly reduces the cost of manually labeling, and improves efficiency of target labeling.
Owner:NEC (CHINA) CO LTD
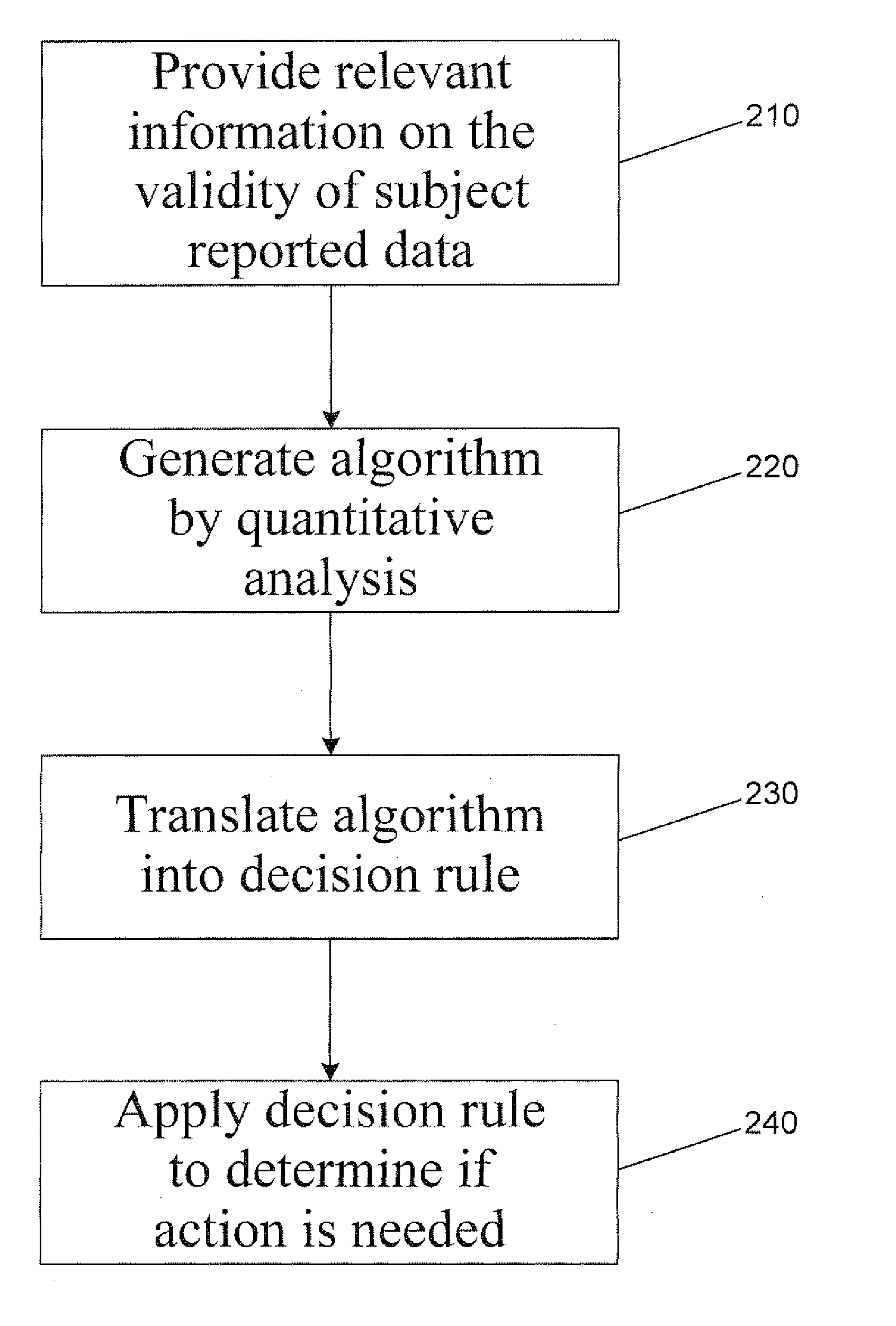
Operation and method for prediction and management of the validity of subject reported data
InactiveUS20080052259A1Improve consistencyGood reproducibilityDigital computer detailsComputation using non-denominational number representationPattern detectionSatisfaction rate
A system for developing and implementing empirically derived algorithms to generate decision rules to predict invalidity of subject reported data and fraud with research protocols in surveys allows for the identification of complex patterns of variables that detect or predict subject invalidity of subject reported data and fraud with the research protocol in the survey. The present invention may also be used to monitor invalidity of subject reported data within a research protocol to determine preferred actions to be performed. Optionally, the invention may provide a spectrum of invalidity, from minor invalidity needing only corrective feedback, to significant invalidity requiring subject removal from the survey. The algorithms and decision rules can also be domain-specific, such as detecting invalidity or fraud among subjects in a workplace satisfaction survey, or demographically specific, such as taking into account gender or age. The algorithms and decision rules may be optimized for the specific sample of subjects being studied.
Owner:ERESTECH
Clinical monitoring device with time shifting capability
InactiveUS8533029B2Reduce testing costsImprove complianceTherapiesLocal control/monitoringClinical trialTime shifting
Owner:ERESTECH
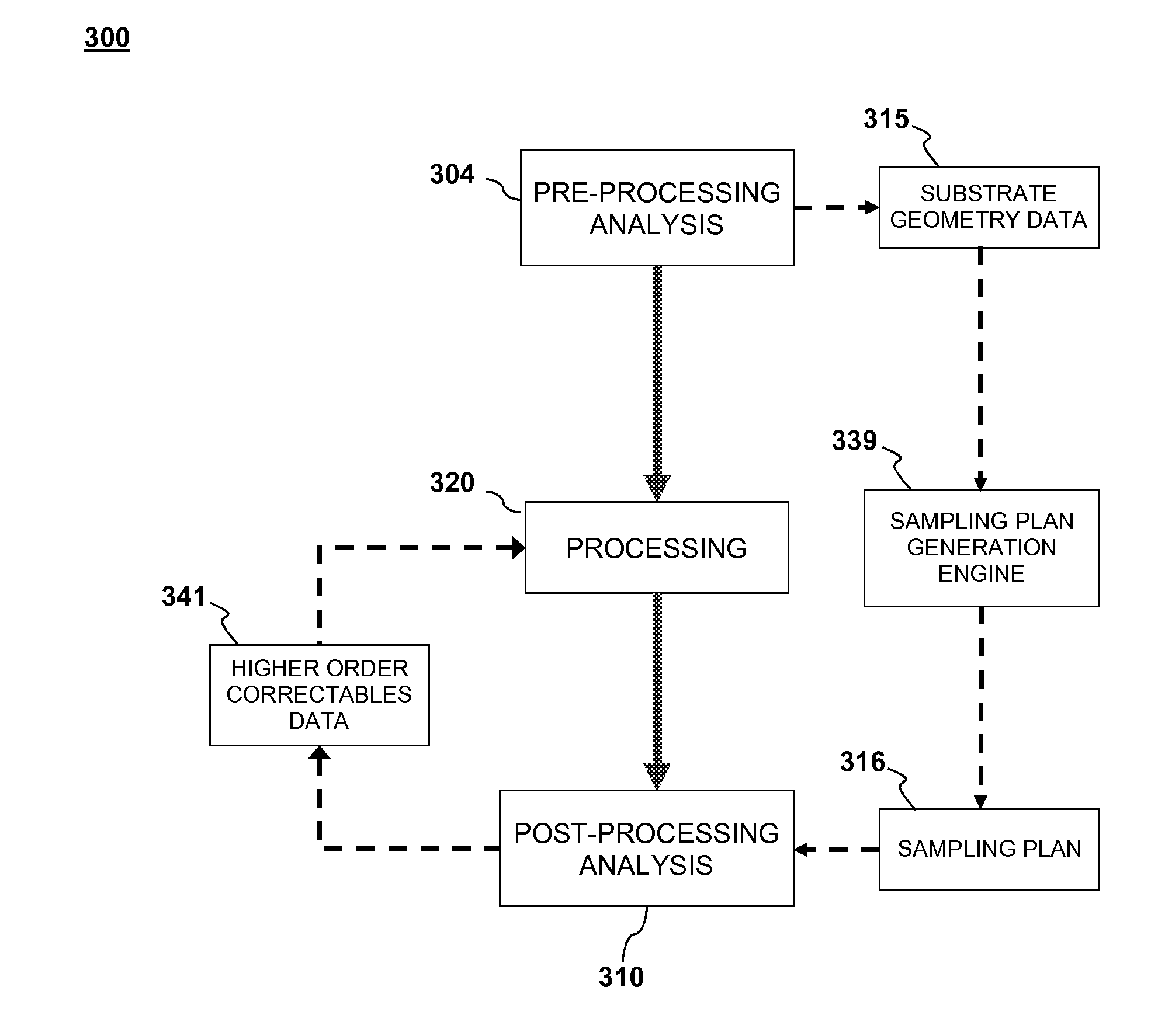
Method and device for using substrate geometry to determine optimum substrate analysis sampling
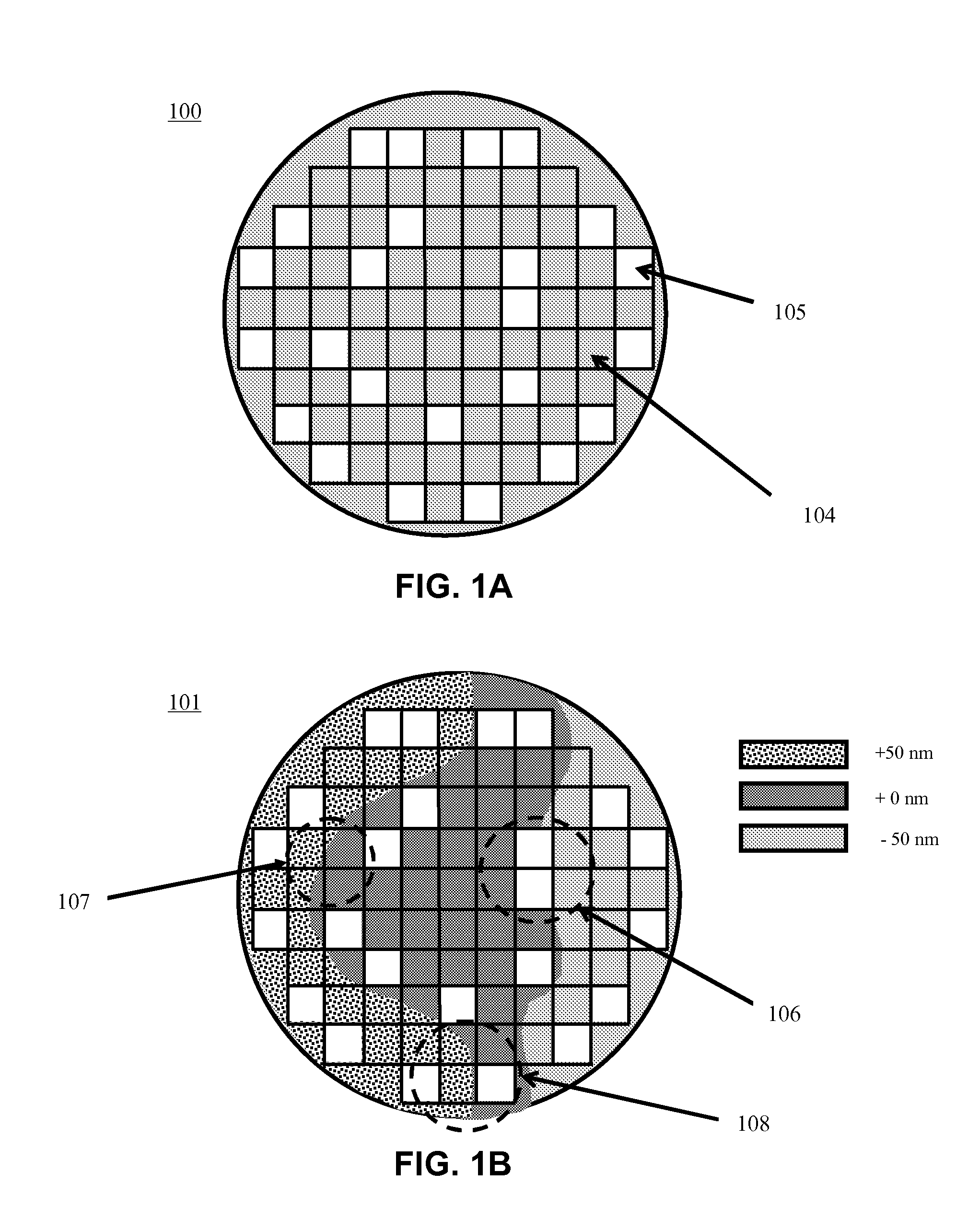
ActiveUS20130310966A1Improve chip yieldHigh yieldProgramme controlPhotomechanical apparatusEngineeringProcess control
A method and apparatus for process control in the processing of a substrate is disclosed in the present invention. Embodiments of the present invention utilize a first analysis tool to determine changes in a substrate's geometry. The substrate geometry data is used to generate sampling plan that will be used to check areas of the substrate that are likely to have errors after processing. The sampling plan is fed forwards to a second analysis tool that samples the substrate after it has been processed. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract that will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims.
Owner:KLA TENCOR CORP
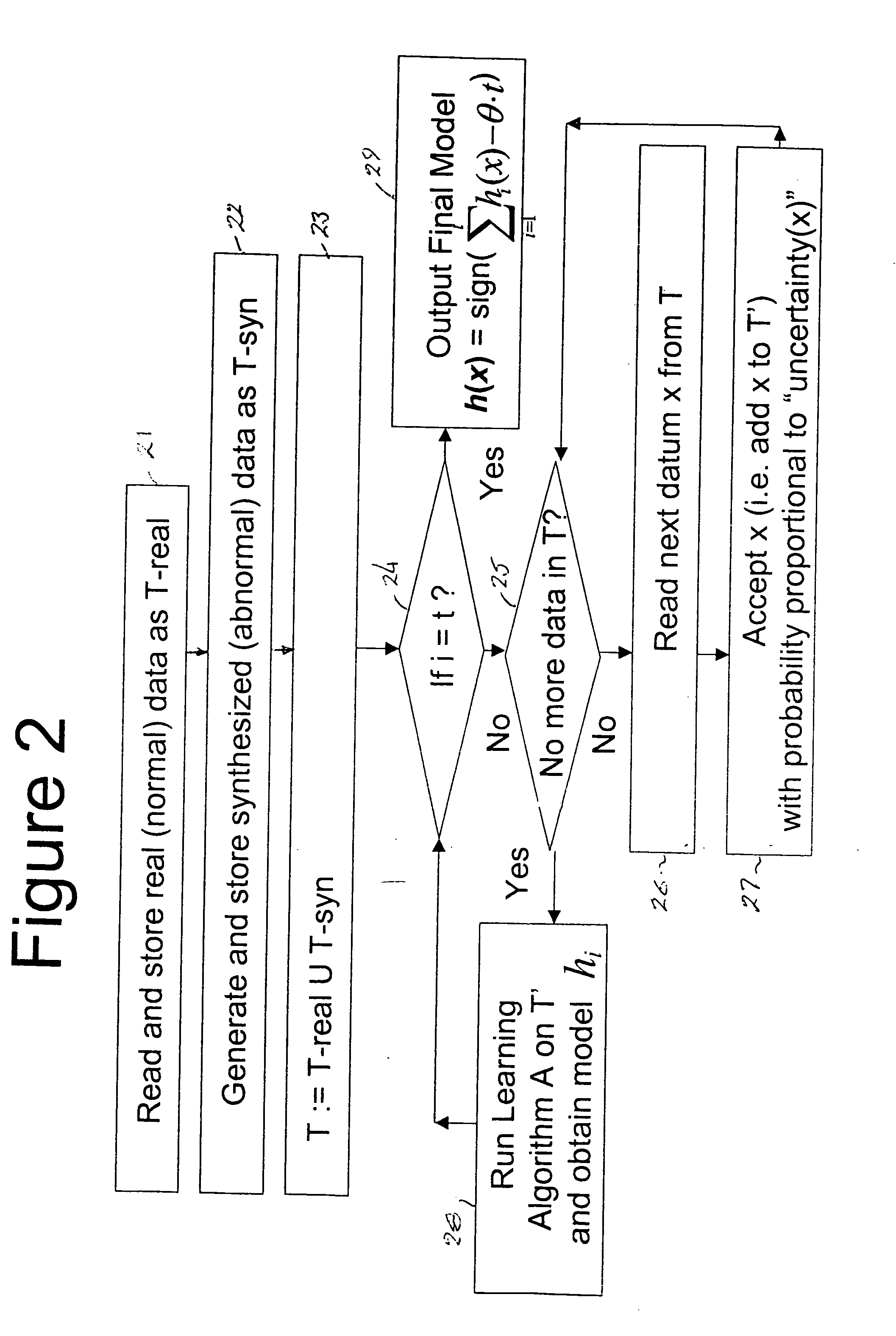
Resource-light method and apparatus for outlier detection
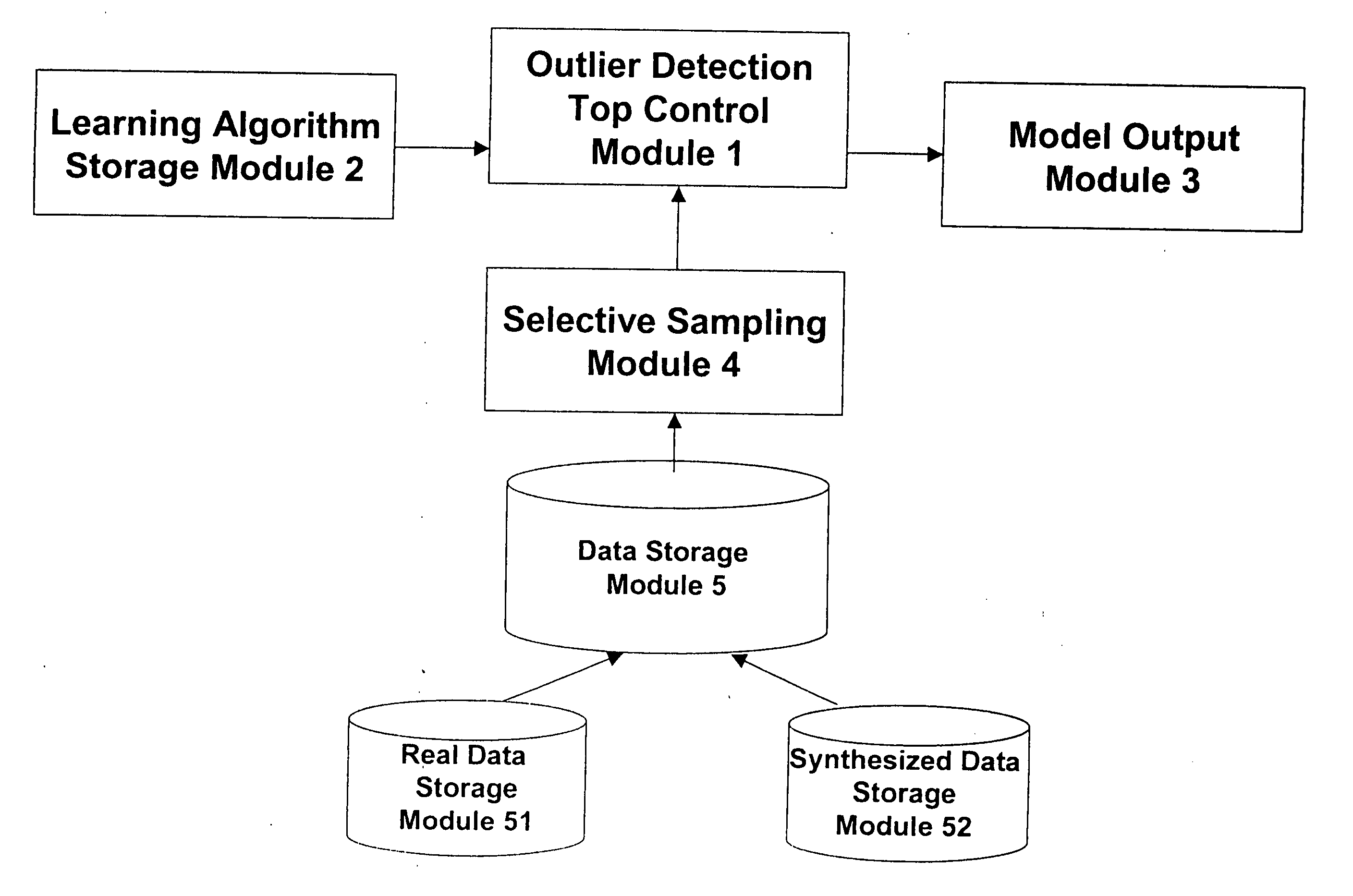
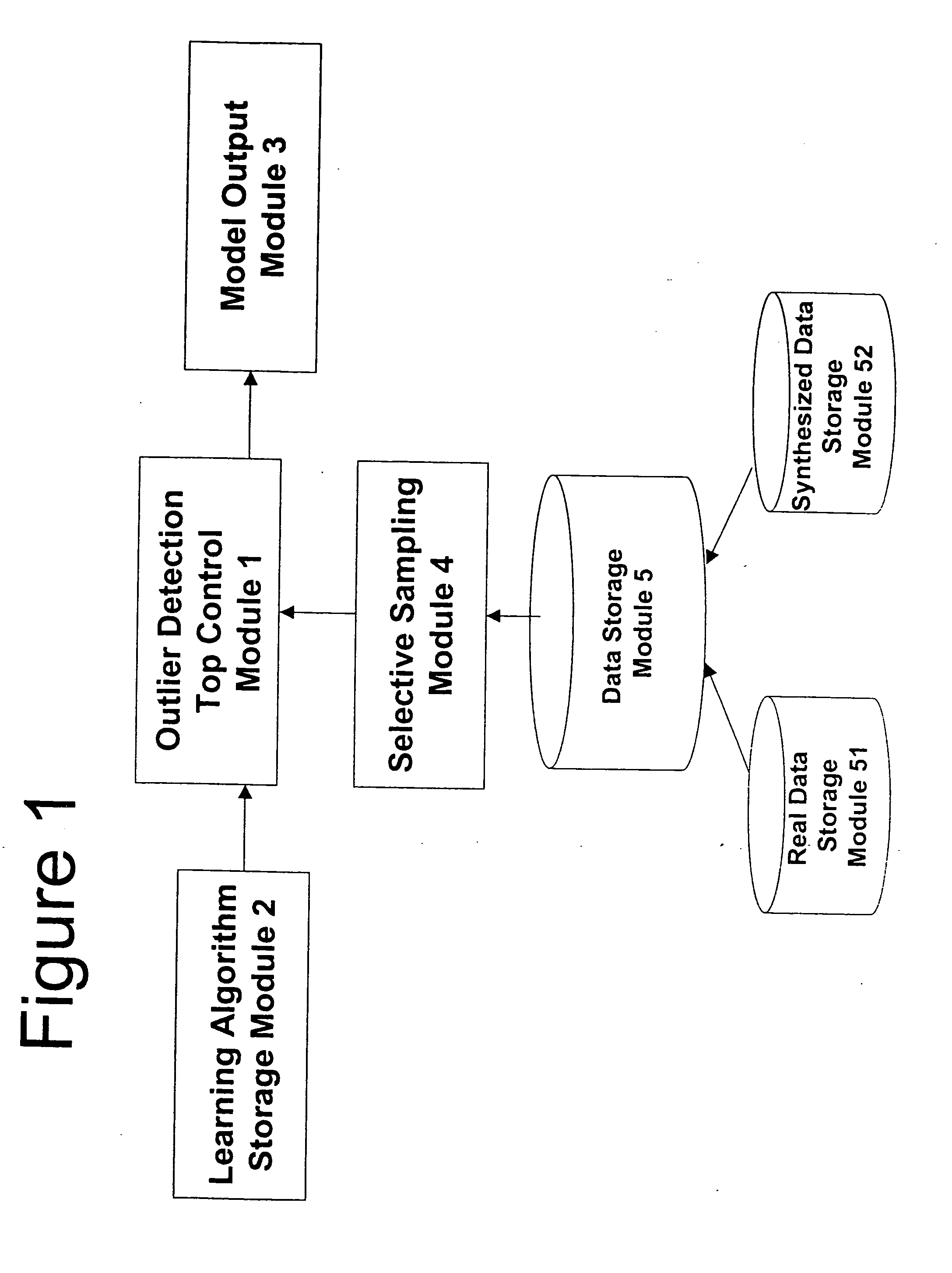
ActiveUS20050160340A1Improve predictive performanceImprove forecast accuracyData processing applicationsError preventionHypothesisAlgorithm
Outlier detection methods and apparatus have light computational resources requirement, especially on the storage requirement, and yet achieve a state-of-the-art predictive performance. The outlier detection problem is first reduced to that of a classification learning problem, and then selective sampling based on uncertainty of prediction is applied to further reduce the amount of data required for data analysis, resulting in enhanced predictive performance. The reduction to classification essentially consists in using the unlabeled normal data as positive examples, and randomly generated synthesized examples as negative examples. Application of selective sampling makes use of an underlying, arbitrary classification learning algorithm, the data labeled by the above procedure, and proceeds iteratively. Each iteration consisting of selection of a smaller sub-sample from the input data, training of the underlying classification algorithm with the selected data, and storing the classifier output by the classification algorithm. The selection is done by essentially choosing examples that are harder to classify with the classifiers obtained in the preceding iterations. The final output hypothesis is a voting function of the classifiers obtained in the iterations of the above procedure.
Owner:TREND MICRO INC
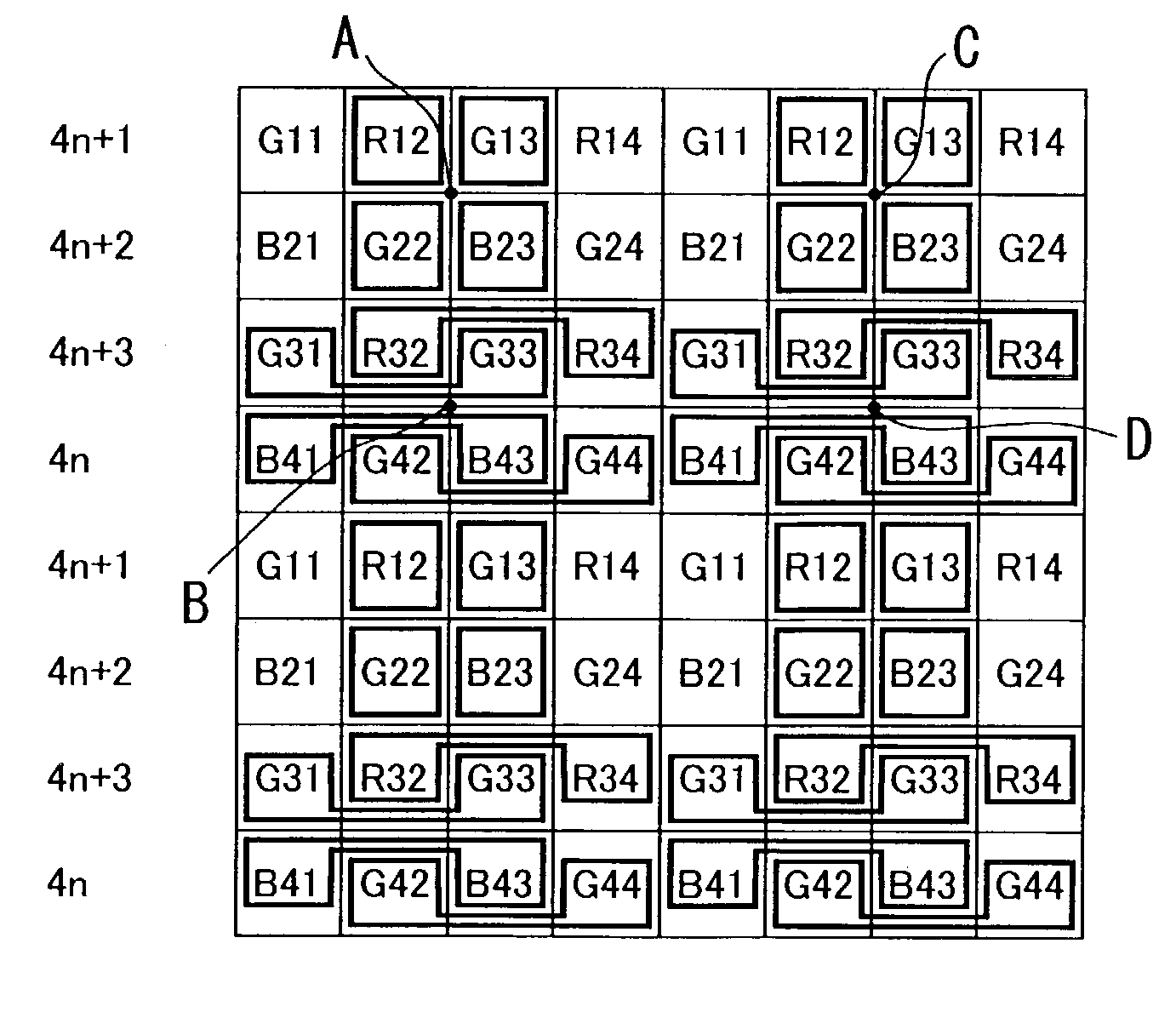
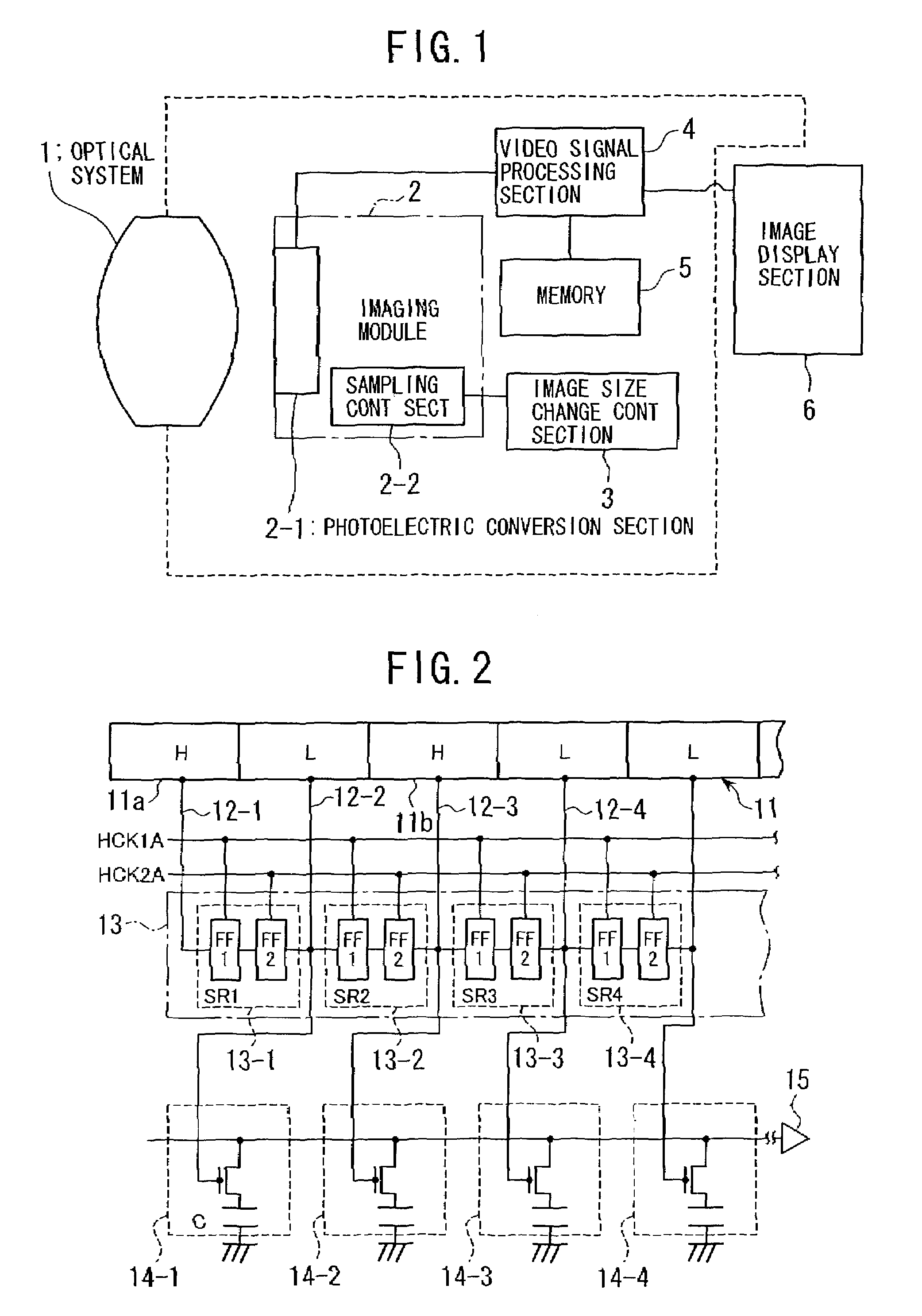
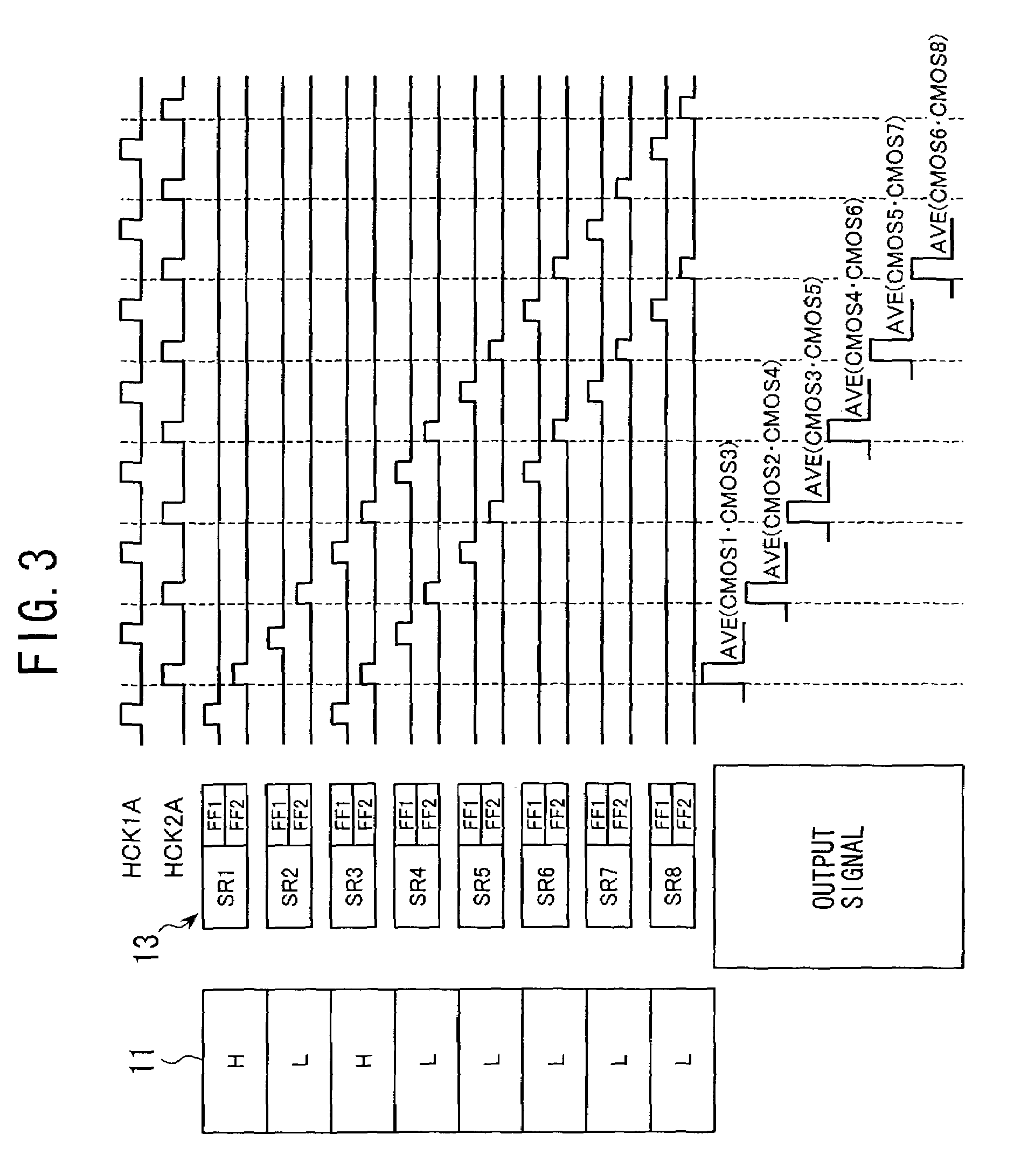
Imaging apparatus suppressing an occurrence of color moire
InactiveUS7242432B2Avoid it happening againSmall sample sizeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsSpectral transmittanceImaging equipment
An imaging apparatus for outputting image signals by photoelectrically converting an image formed at an optical system by an image sensor array having a color filter array having several spectral transmittance disposed in front thereof, including: mode setting means capable of setting at least one mode among an all-pixel read mode for effecting readout of all the pixels of at least one horizontal line, an intermittent read mode for effecting readout in a thinned-out manner of pixels to be read out from at least one horizontal line, and an averaging read mode for effecting readout by averaging a plurality of pixels as the mode for reading out image signals from the image sensor array; and readout rule control means for controlling and determining pixel locations for reading out the image signals: when the intermittent read mode and / or the averaging read mode have been set by the mode setting means, the readout pixel locations to be determined by the readout rule control means are caused to vary frame by frame in the image signals to be read out.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Coding of an information signal
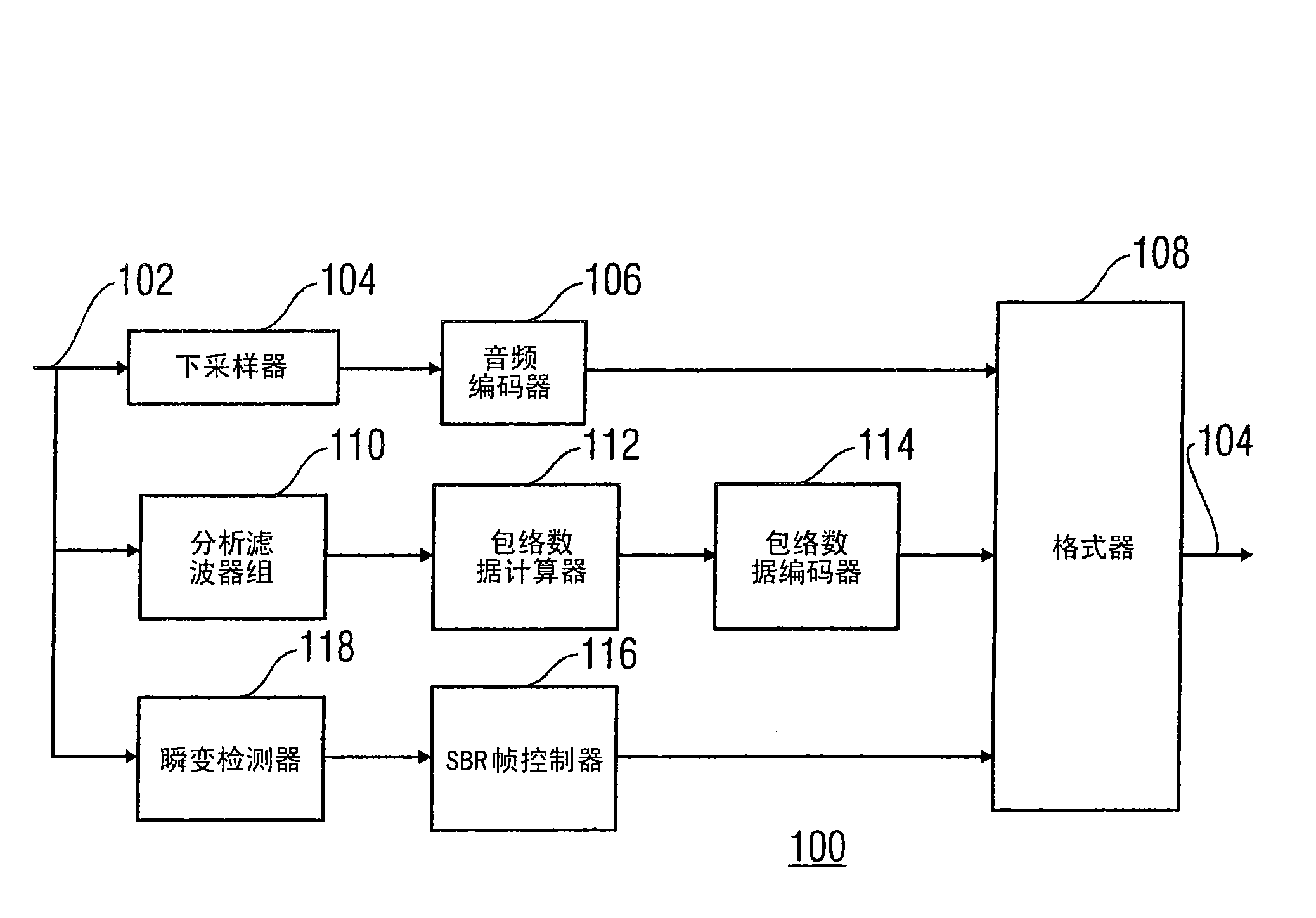
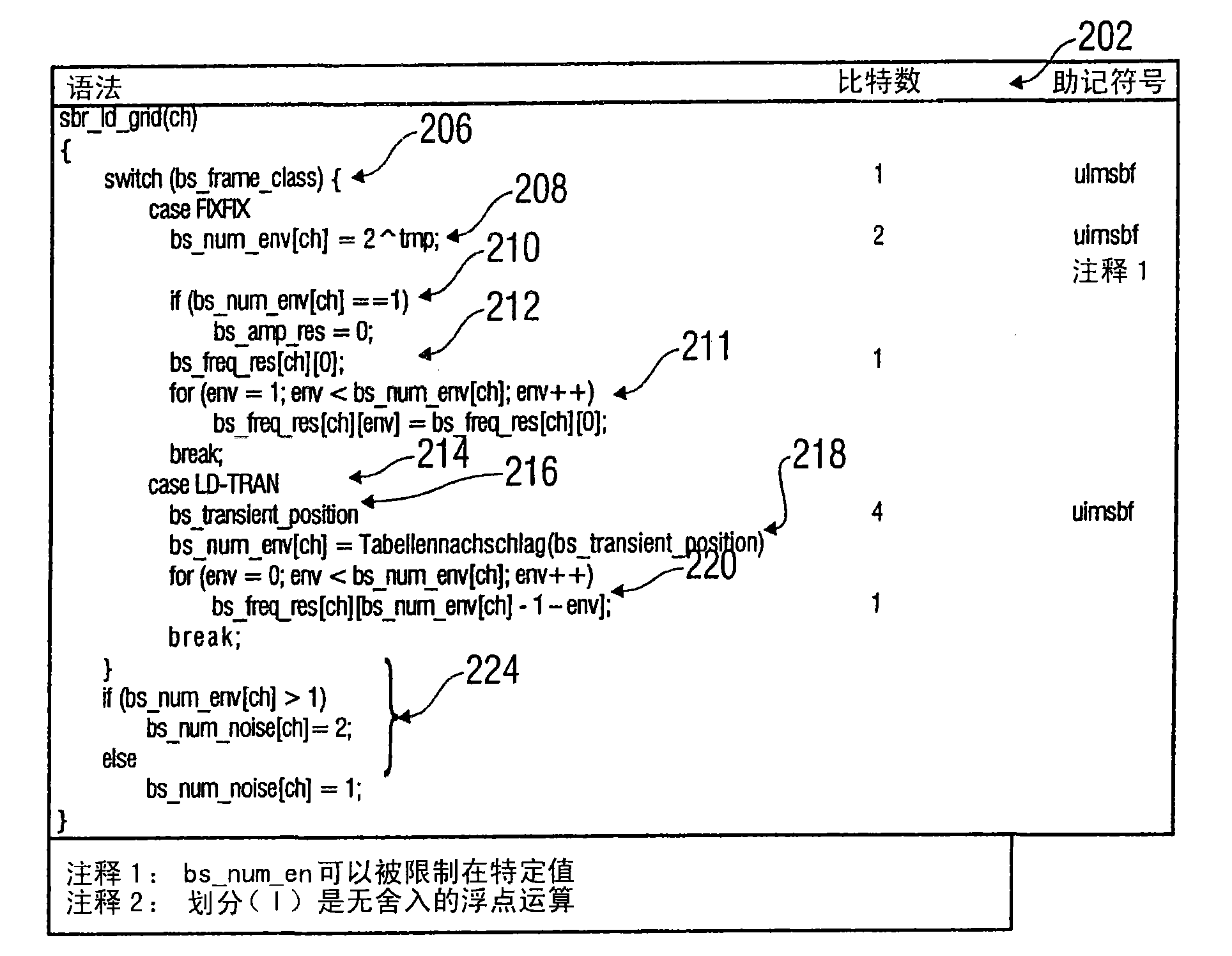
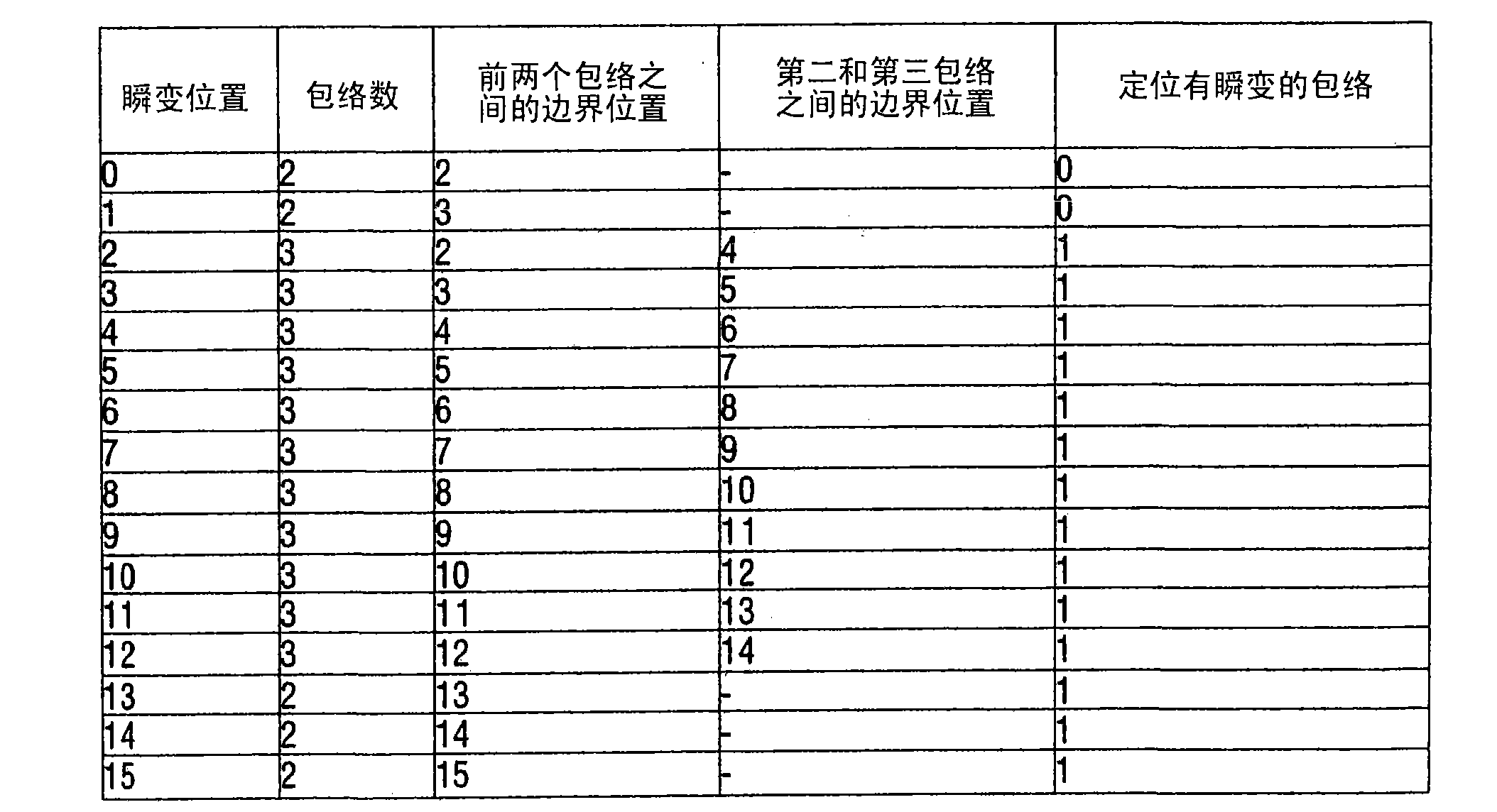
ActiveCN101529503AResolve transientsFix/or pre-echo issueSpeech analysisCode conversionSyntaxComputer science
The problem of transients can be addressed satisfactorily and a further decoding delay can be reduced for this if use is made of a new SBR frame class in which the frame limits (902a, 902b) are not shifted, that is to say the grid limits are still synchronized with the frame limits (902a, 902b), but in which a statement of the transient position is also used as a syntax element in order to be used, within the frames of this new frame class, to determine the grid limits within these frames at the coder and / or decoder end.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Strip electrode with conductive nano tube printing
InactiveUS7285198B2Flat surfaceImprove consistencyImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsContact padAnalyte
An electrochemical test device for determining the presence or concentration of an analyte in an aqueous fluid sample comprises a substrate comprising a non-conductive material; a working electrode comprising a conductive film formed at least with carbon nanotubes, the working electrode having a first electrode area, a first lead and a first contact pad; a counter electrode comprising a conductive film formed at least with carbon nanotubes; a reagent capable of reacting with the analyte to produce a measurable change in potential which can be correlated to the presence or concentration of the analyte in the fluid sample, the reagent overlaying at least a portion of the first electrode area of the working electrode; and a reference electrode comprising a conductive coating formed at least with carbon nanotubes, the reference electrode having a third electrode area at least a portion of which is overlaid with a reference material.
Owner:DOUGLAS JOEL S MR
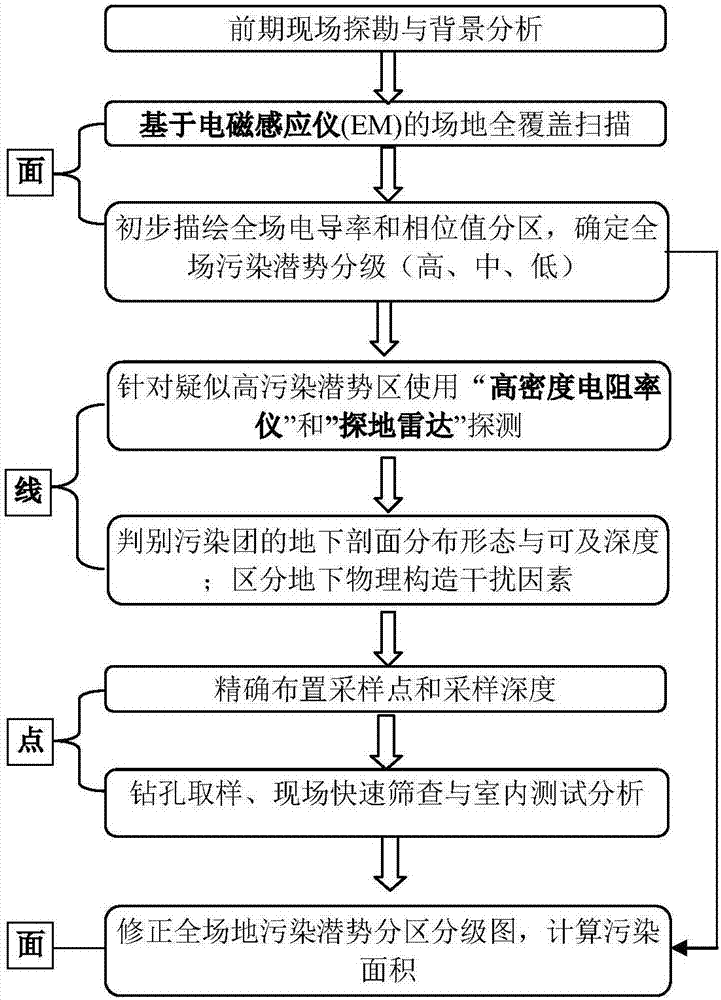
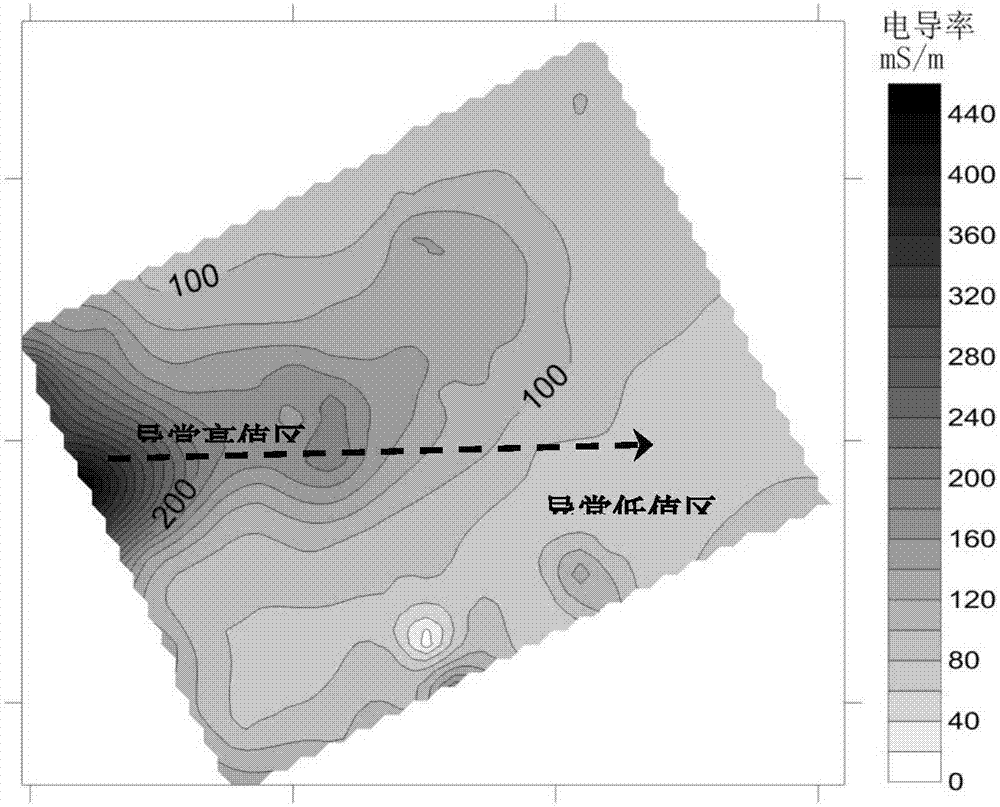
Method for accurately positioning soil contamination based on geophysical exploration and accurate estimation method
ActiveCN107544097APrecise positioningArrange sampling points reasonablyGeological measurementsHigh densitySoil science
The invention discloses a method for accurately positioning soil contamination based on geophysical exploration and an accurate estimation method. The method for accurately positioning soil contamination includes the following steps: on-site surveying, rapid exploration which covers entire site from the width perspective, further contamination body and availability positioning from the depth perspective, drilling sampling and analysis verification from specific point perspective, and accurate contamination level evaluation from the width perspective. In specific target sites or regions, the method herein adopts geophysical exploration technology which combines electromagnetic instruments, high density resistivity meters and ground penetrating radars in a step-by-step and targeted manner, can accurately position areas or points that are suspected to have soil contamination, arranges sapling points in a scientific manner, combines rapid site contamination pollution screening as well as drilling sampling, test and analysis, and establishes an entire set of soil pollution investigation procedures from the width perspective, the depth perspective and the specified point perspective. Themethod herein can rapidly and accurately position soil contamination, scientifically arrange sampling points, conducts soil contamination investigation that cover an entire region, and increases theprecision in estimating the contamination area.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACADEMY OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES
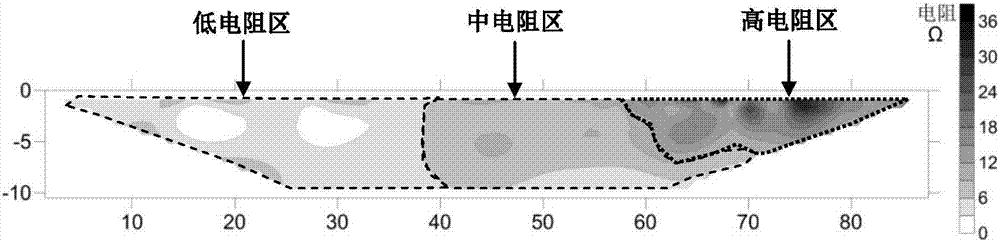
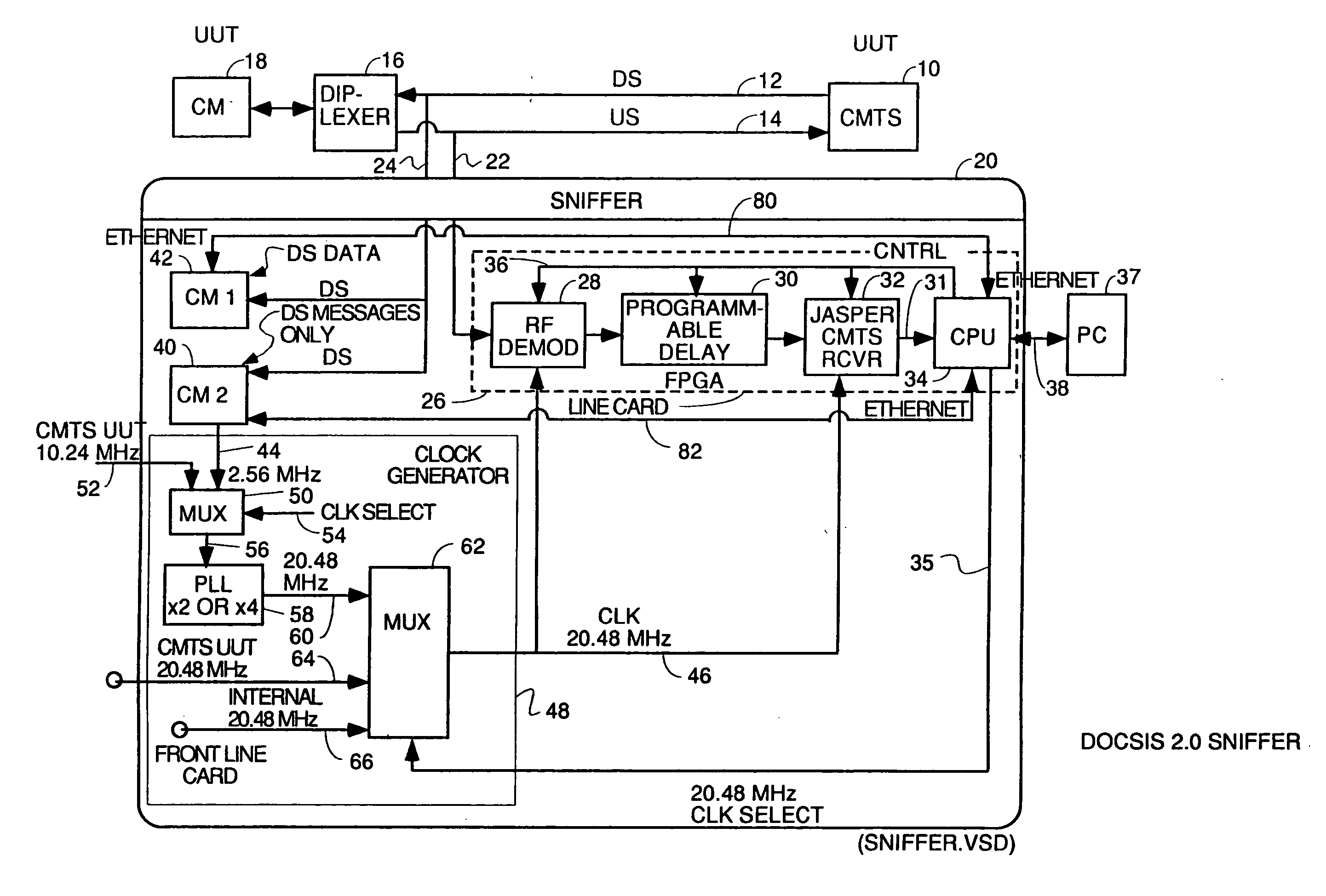
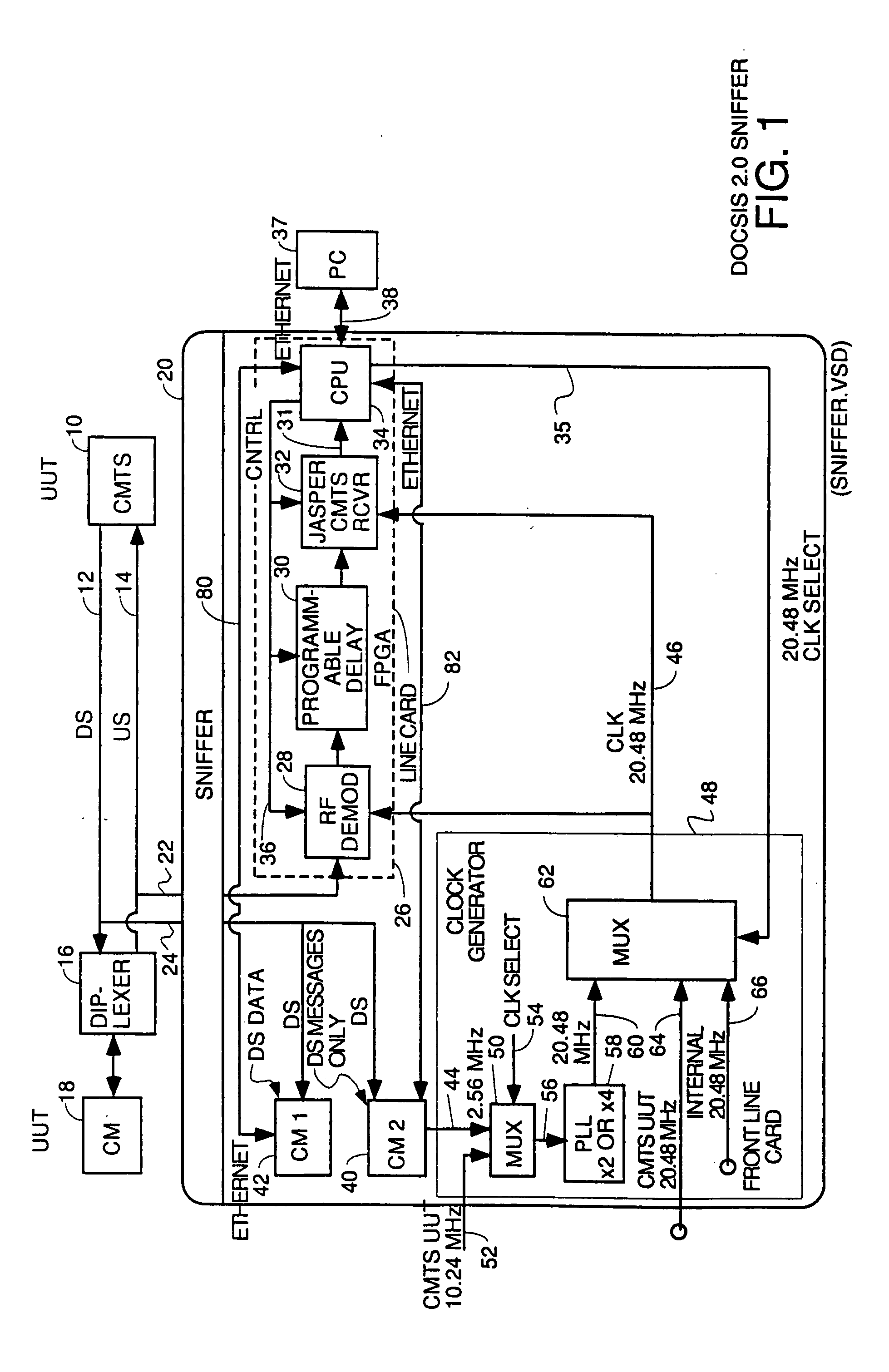
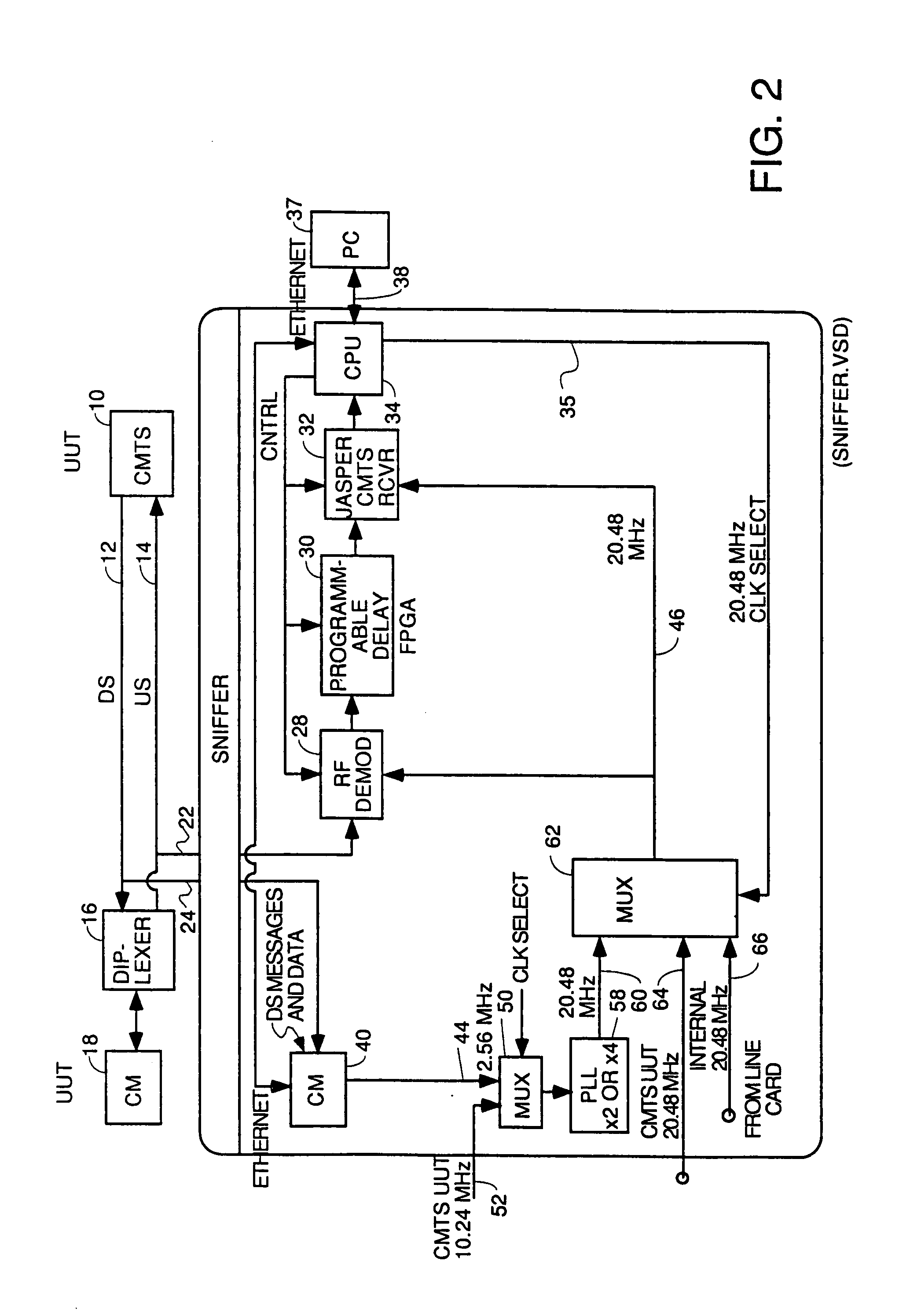
DOCSIS 2.0 SCDMA capable sniffers which can capture legacy DOCSIS bursts as well
InactiveUS20080089399A1Small sample sizeLow symbol rateBroadband local area networksDuplex signal operationModem deviceControl signal
A DOCSIS 2.0 compatible sniffer which can receive legacy DOCSIS 1.x TDMA bursts as well as DOCSIS 2.0 SCDMA bursts. One embodiment uses two cable modems in the sniffer, one to capture downstream data bursts and the other to capture downstream messages and to recover the downstream symbol clock and generate an upstream reference clock which is phase coherent with the recovered downstream symbol clock. The reference clock is used by a cable modem termination system to capture upstream SCDMA DOCSIS 2.0 bursts. DOCSIS 1.x TDMA bursts may also be captured. Other embodiments use a DOCSIS 2.0 compatible modem in the sniffer to lock onto a downstream, register as a cable modem in the system and capture downstream messages in order to derive the correct timing to generate control signals to control burst capture circuitry in the sniffer to capture DOCSIS 1.x and 2.0 upstream bursts. The digital samples of each burst can be sent digitally to the CMTS under test after some fixed delay or can be sent to the CMTS under test as an analog RF signal in repeater embodiments. This allows the CMTS under test to be simplified by pushing the burst capture circuitry out to the optical node.
Owner:TERAYON COMM SYST +1
Real time calibration for time-of-flight depth measurement
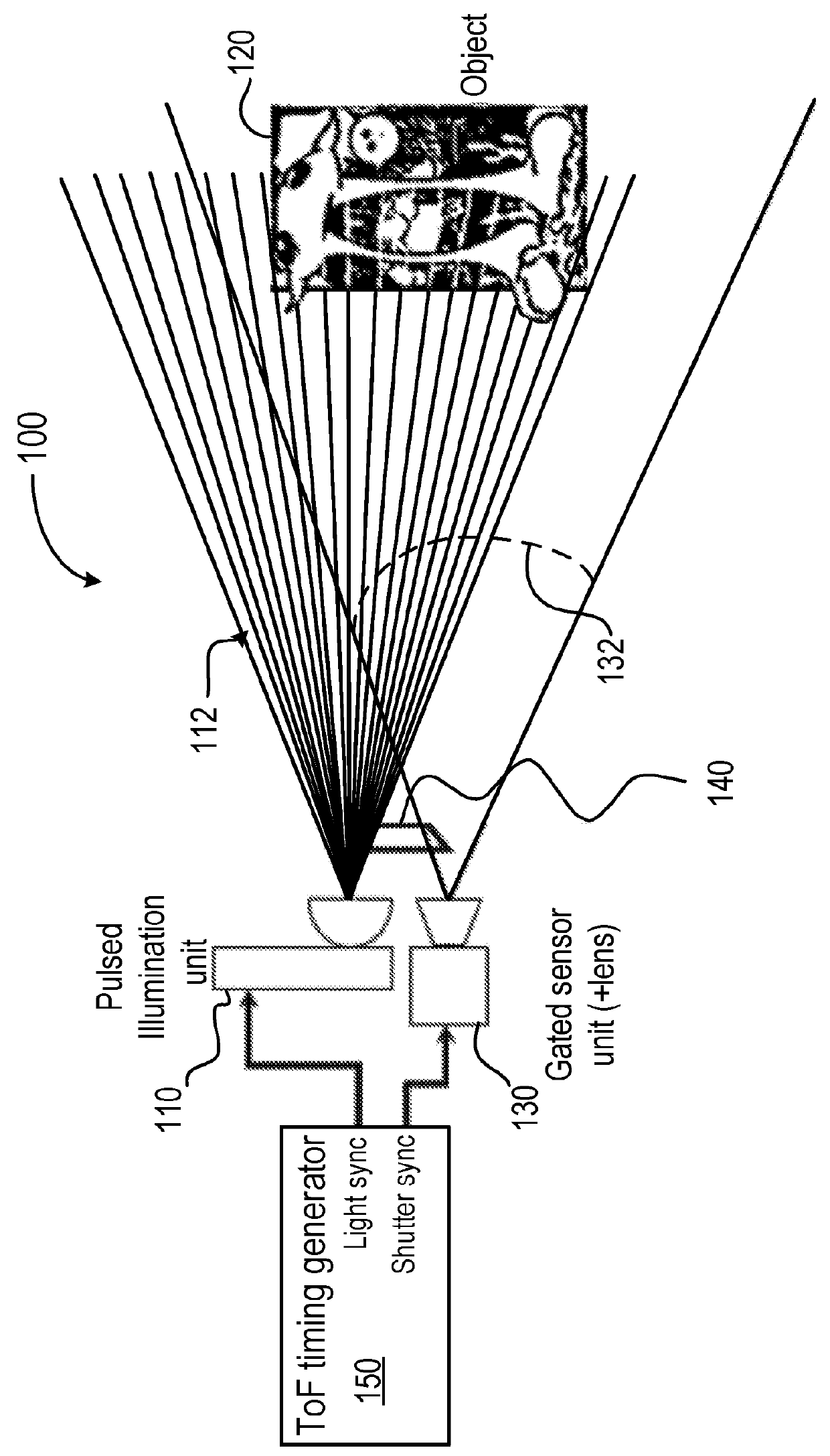
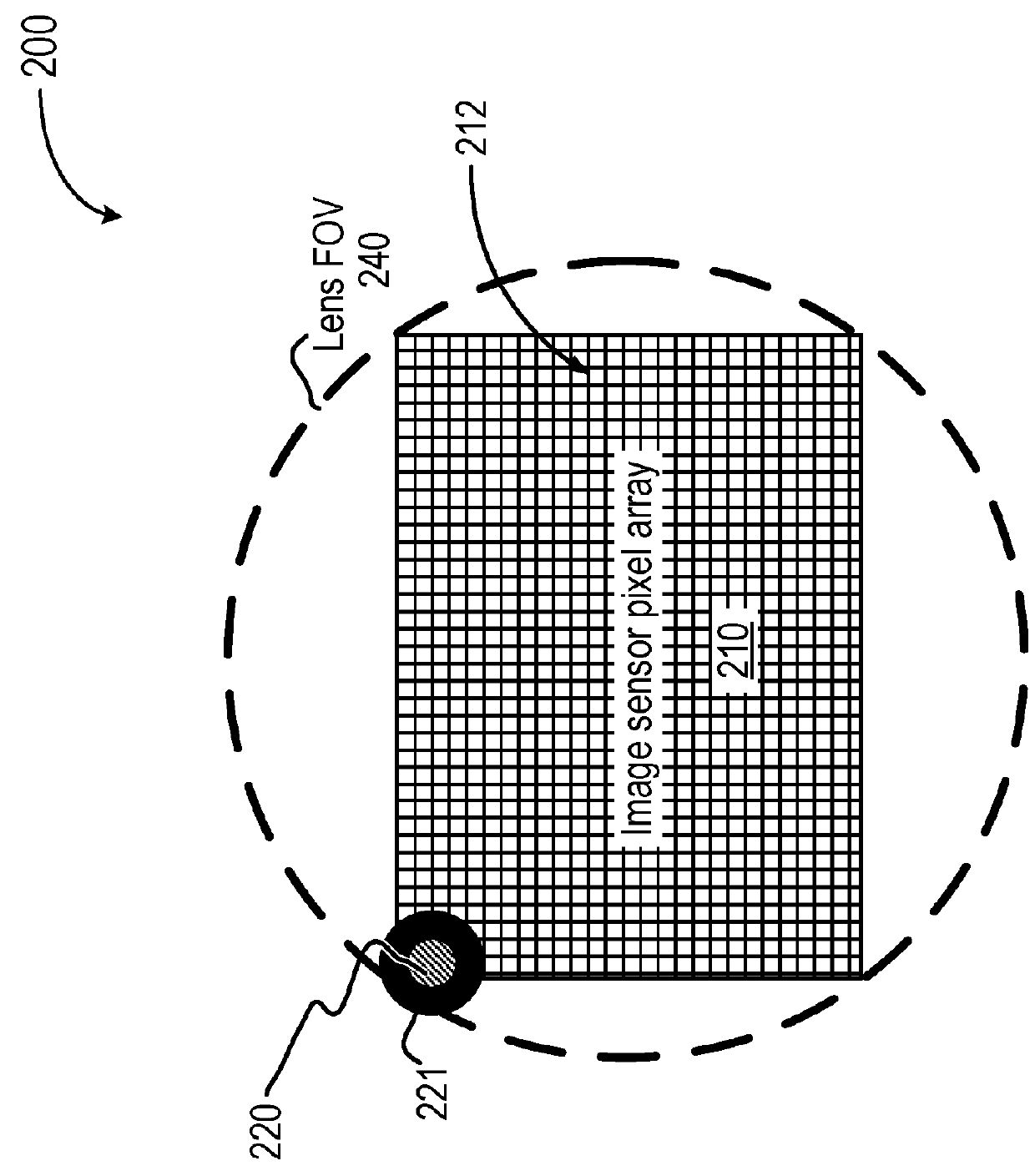
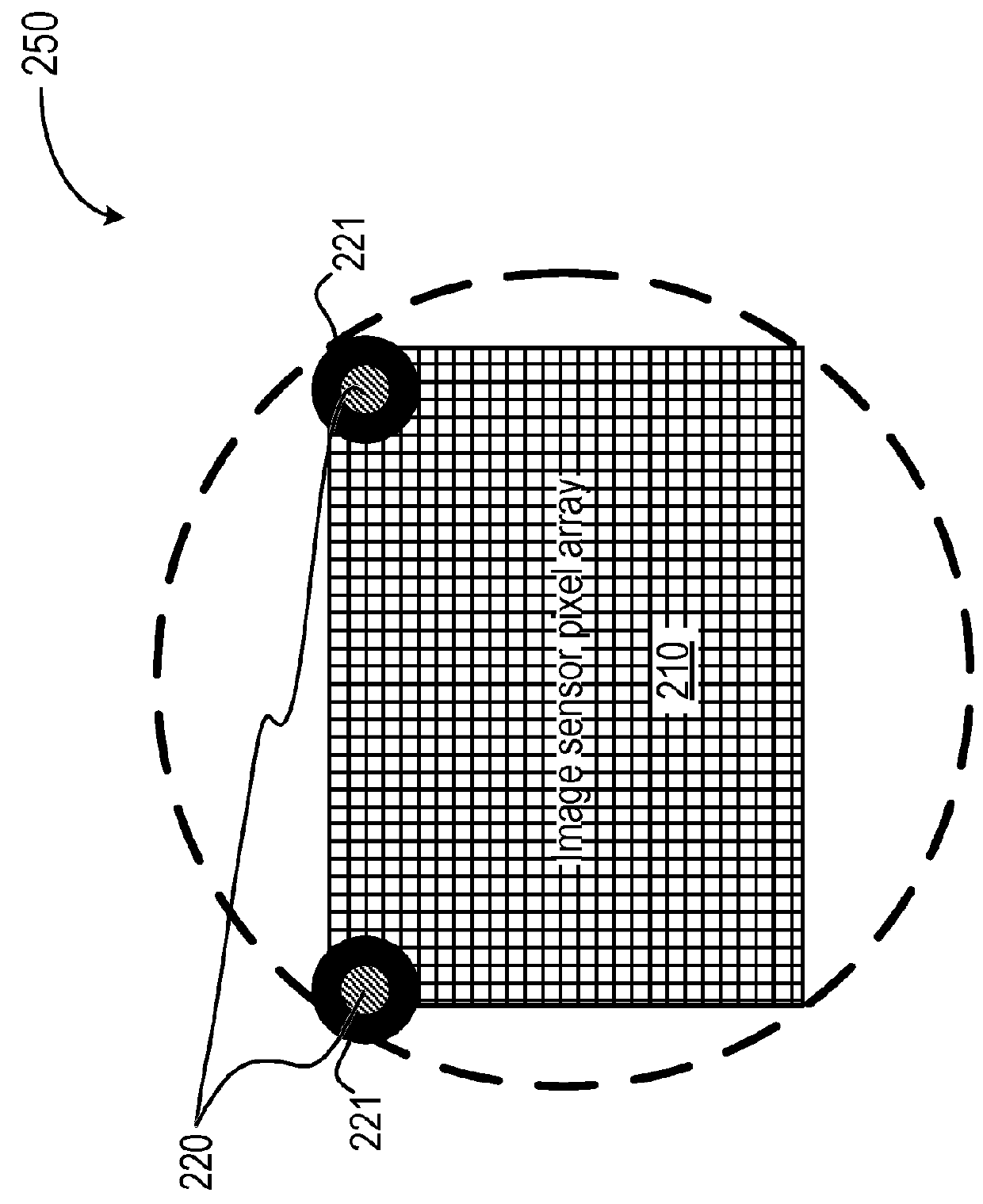
ActiveUS20180096489A1Additional operational overheadReduce impactImage enhancementImage analysisTime of flightTransmitted light
A method for determining a distance to a target object includes transmitting light pulses to illuminate the target object and sensing, in a first region of a light-sensitive pixel array, light provided from an optical feedback device that receives a portion of the transmitted light pulses. The feedback optical device includes a preset reference depth. The method includes calibrating time-of-flight (TOF) depth measurement reference information based on the sensed light in the first region of the pixel array. The method further includes sensing, in a second region of the light-sensitive pixel array, light reflected from the target object from the transmitted light pulses. The distance of the target object is determined based on the sensed reflected light and the calibrated TOF measurement reference information.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP
Evaluation method and system for accelerator transient condition driveability
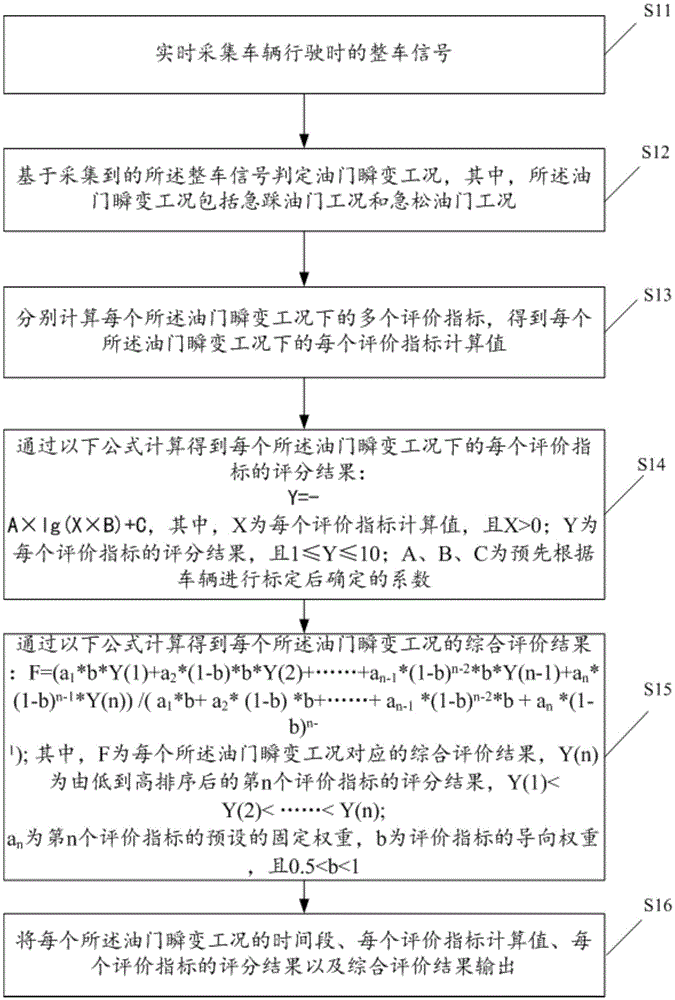
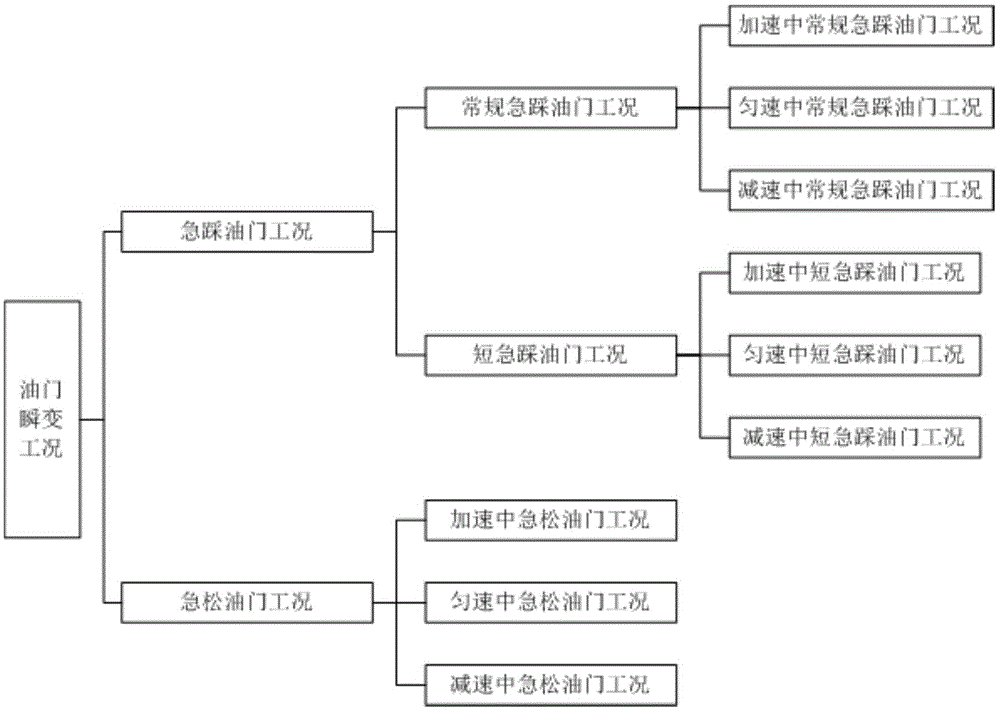
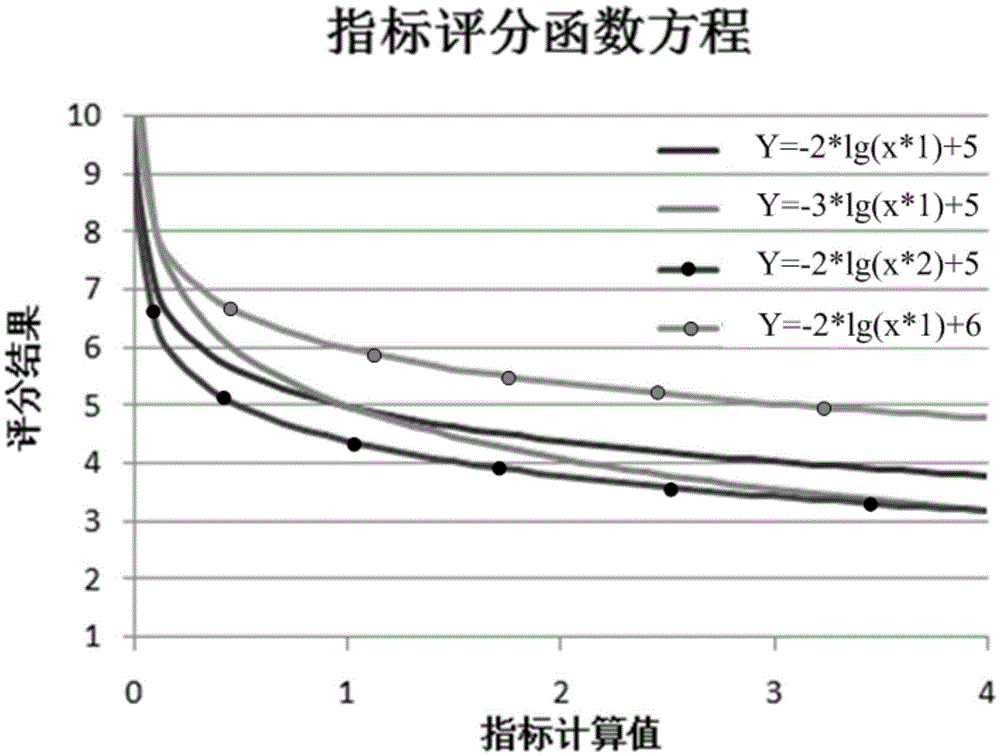
ActiveCN105644563ADrivability evaluation results are objectiveSmall sample sizeDriver input parametersEvaluation resultReliability engineering
The invention discloses an evaluation method for accelerator transient condition driveability. The method includes the steps of collecting vehicle signals in real time when a vehicle runs; judging accelerator transient conditions on the basis of the collected vehicle signals; calculating multiple evaluation indexes under each accelerator transient condition to obtain a calculated value of each evaluation index under each accelerator transient condition; conducting calculation to obtain a grading result of each evaluation index under each accelerator transient condition through a preset formula; conducting calculation to obtain a comprehensive evaluation result of each accelerator transient condition through another preset formula; and outputting the time period of each accelerator transient condition, the calculated value of each evaluation index, the grading result of each evaluation index and the comprehensive evaluation results.
Owner:GUANGZHOU AUTOMOBILE GROUP CO LTD
Operation and method for prediction and management of the validity of subject reported data
InactiveUS7873589B2Improve consistencyIncrease powerDigital computer detailsComputation using non-denominational number representationComputer scienceData science
Owner:ERESTECH
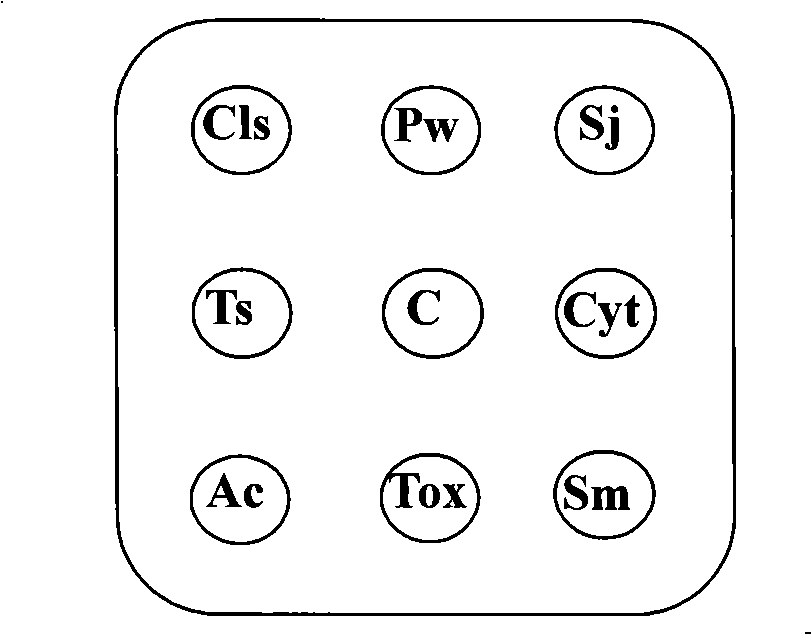
Human body important parasite antigen chip and method for making same
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, in particular to an antigen chip used for detecting human parasites antigens in serum and a preparation method thereof. The invention spots antigen array of parasites which are seriously harmful to human body, Schistosoma, Lung fluke, Clonorchis sinensis, Cysticercosis, Sparganum mansoni, Trichina, Angiostrongylus cantonensis, Toxoplasma gondii, and the like, on a solid phase membrane carrier, and specific gamma immunoglobulin (IgG) of human parasites in serum is detected by a specially made vertical flow chip detect device, and the detecting marker is colloid gold second antibody conjugate or colloid gold protein A conjugate of fresh color. IgG antibodies in serum specially bind with the antigens on the membrane in percolation process layer upon layer, and human IgG which specially binds with the antigens is detected by the colloid gold marker. Detecting of a plurality of parasites antigen indexes in serum sample can be finished within several minutes. The device and the method have the advantages of high throughput, simple operation, convenient use and being suitable for parasitic diseases clinical test and serum-epidemiological investigation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
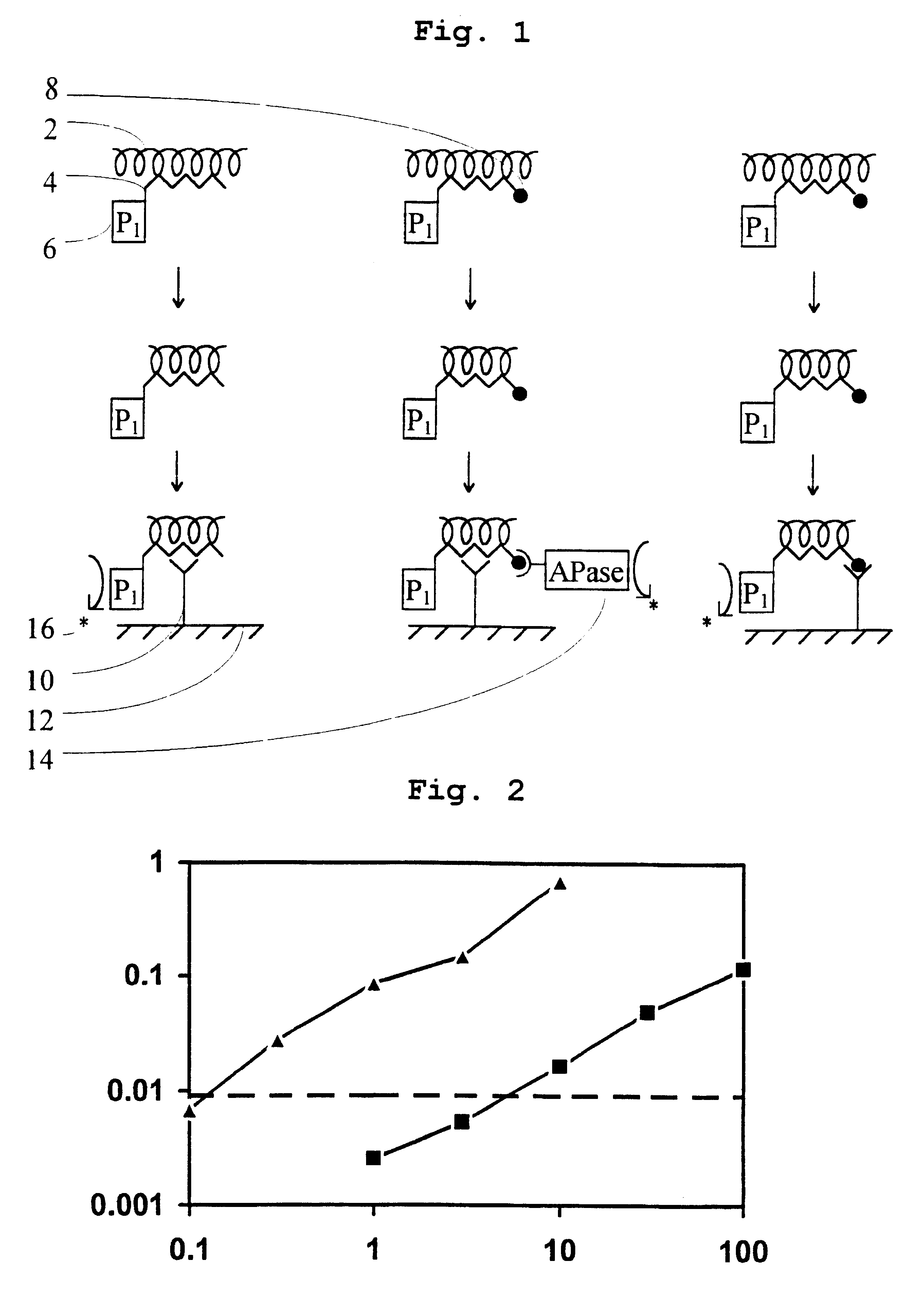
Hybridization assay for detecting a single-stranded target nucleic acid in which excess probe is destroyed
A method is disclosed for detecting single-stranded target nucleic acid (2) which comprises the steps of forming a hybrid between said target nucleic acid and a nucleic acid probe (4), said nucleic acid probe labelled with an enzyme reagent (6) which hydrolyses single-stranded nucleic acid but is substantially without effect on double-stranded nucleic acid, said hybrid formed under conditions of pH which are outside the activity range of said enzyme reagent, adjusting said pH to a value within the activity range of said enzyme reagent allowing said enzyme reagent substantially to hydrolyse any single-stranded nucleic acid present, and detecting said hybrid.
Owner:ZETATRONICS
Remote NMR/MRI detection of laser polarized gases
InactiveUS7061237B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioHigh spin densityDispersion deliveryMeasurements using NMR spectroscopySpectroscopyPulse sequence
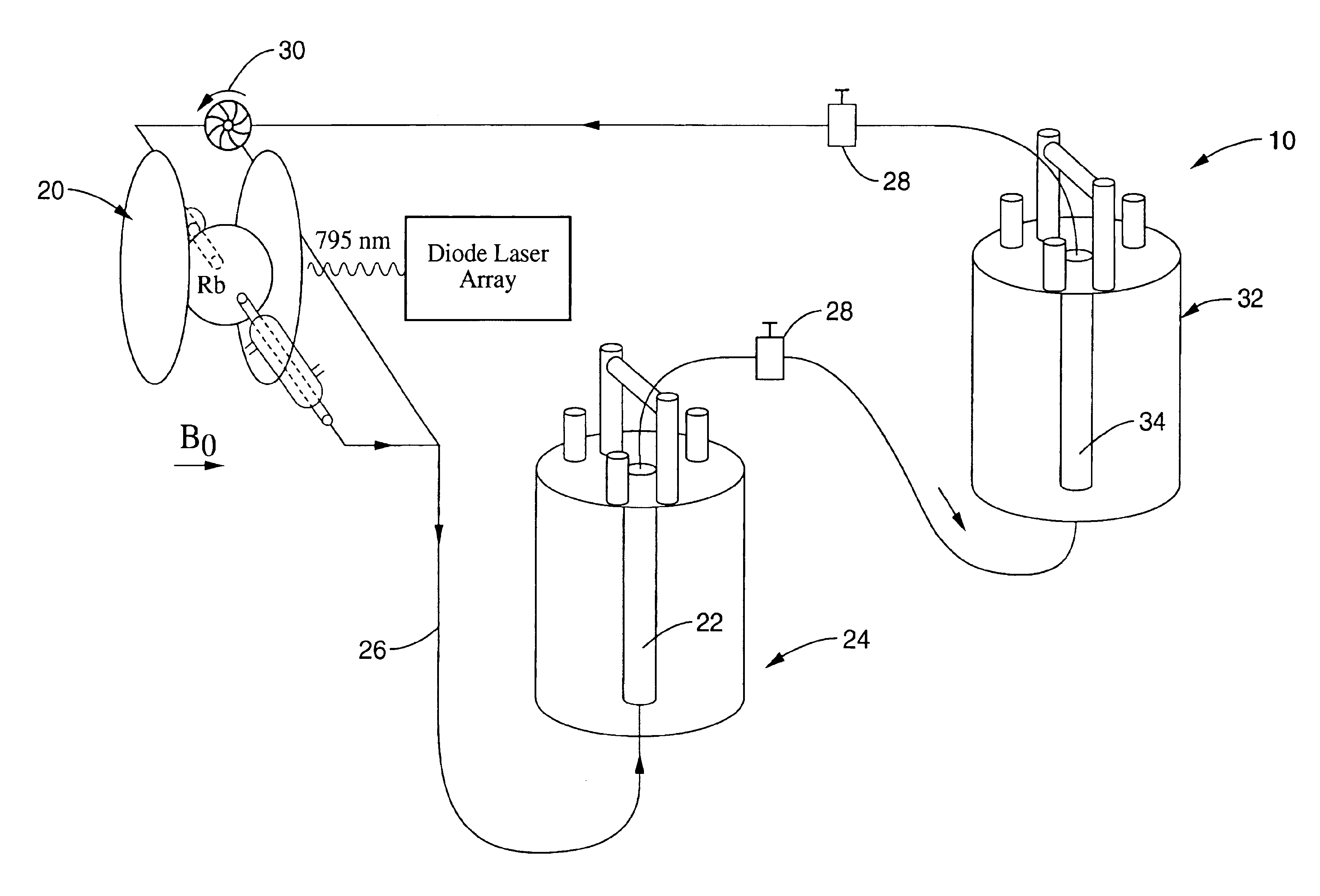
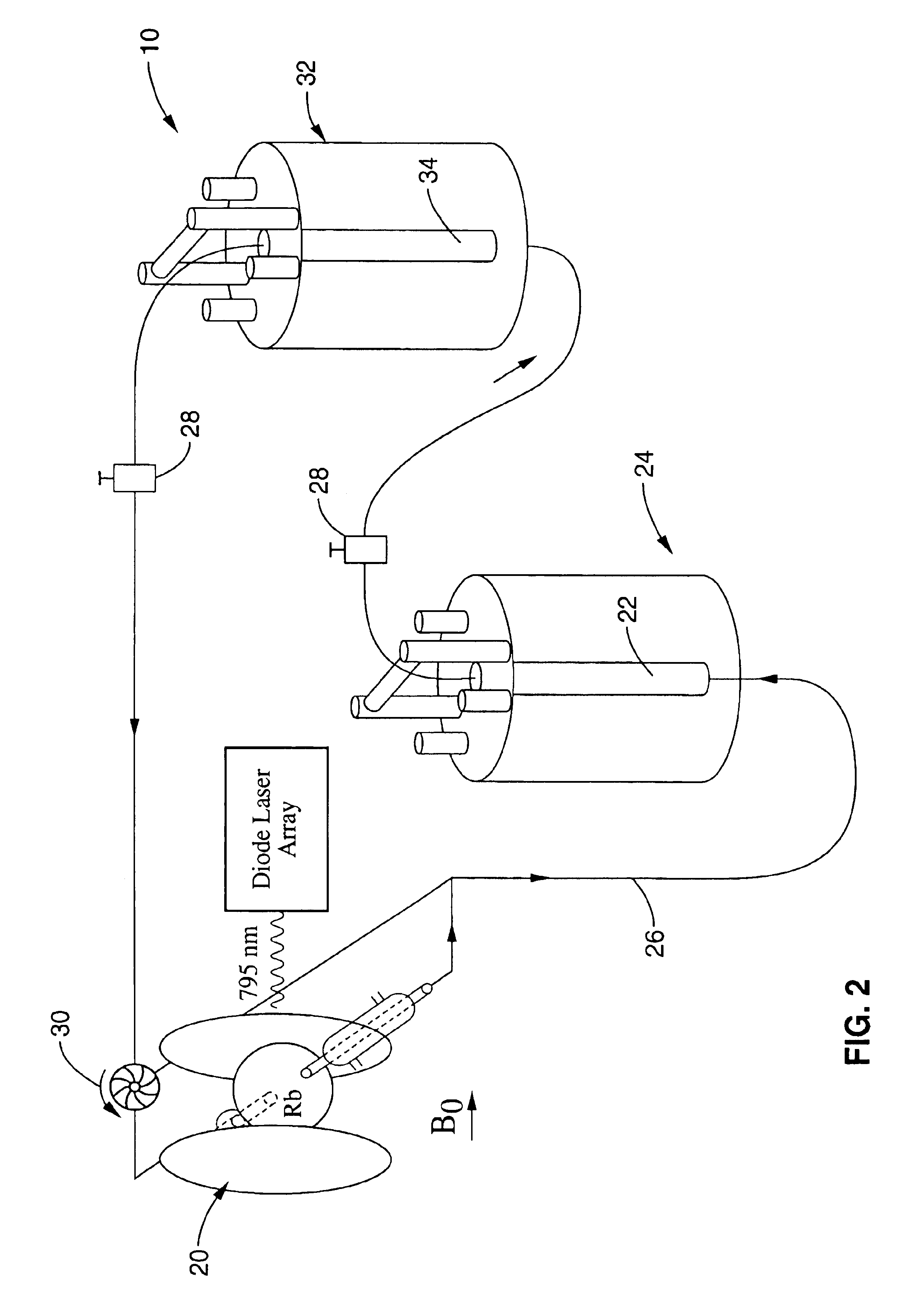
An apparatus and method for remote NMR / MRI spectroscopy having an encoding coil with a sample chamber, a supply of signal carriers, preferably hyperpolarized xenon and a detector allowing the spatial and temporal separation of signal preparation and signal detection steps. This separation allows the physical conditions and methods of the encoding and detection steps to be optimized independently. The encoding of the carrier molecules may take place in a high or a low magnetic field and conventional NMR pulse sequences can be split between encoding and detection steps. In one embodiment, the detector is a high magnetic field NMR apparatus. In another embodiment, the detector is a superconducting quantum interference device. A further embodiment uses optical detection of Rb—Xe spin exchange. Another embodiment uses an optical magnetometer using non-linear Faraday rotation. Concentration of the signal carriers in the detector can greatly improve the signal to noise ratio.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com